Intro. To Graphing Linear. Equations
|
|
|
- Kathlyn Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Coordinate Plane Intro. To Graphing Linear A. The coordinate plane has 4 quadrants. Equations B. Each point in the coordinate plain has an x-coordinate (the abscissa) and a y-coordinate (the ordinate). The point is stated as an ordered pair (x,y). C. Horizontal Axis is the X Axis. (y = 0) D. Vertical Axis is the Y- Axis (x = 0) Plot the following points: a) (3,7) b) (-4,5) c) (-6,-1) d) (6,-7) e) (5,0) f) (0,5) g) (-5,0) f) (0, -5) y-axis x-axis 1
2 Slope Intercept Form Before graphing linear equations, we need to be familiar with slope intercept form. To understand slope intercept form, we need to understand two major terms: The slope and the y-intercept. Slope (m): The slope measures the steepness of a non-vertical line. It is sometimes referred to as the rise over run. It s how fast and in what direction y changes compared to x. y-intercept: The y-intercept is where a line passes through the y axis. It is always stated as an ordered pair (x,y). The x coordinate is always zero. The y coordinate can be found by plugging in 0 for the X in the equation or by finding exactly where the line crosses the y-axis. What are the coordinates of the y-intercept line pictured in the diagram above? : Some of you have worked with slope intercept form of a linear equation before. You may remember: y = mx + b Using y = mx + b, can you figure out the equation of the line pictured above?: 2
3 Graphing Linear Equations Graphing The Linear Equation: y = 3x - 5 1) Find the slope: m = 3 m = 3. = y. 1 x 2) Find the y-intercept: x = 0, b = -5 (0, -5) 3) Plot the y-intercept 4) Use slope to find the next point: Start at (0,-5) m = 3. = y. up 3 on the y-axis 1 x right 1 on the x-axis (1,-2) Repeat: (2,1) (3,4) (4,7) 5) To plot to the left side of the y-axis, go to y-int. and do the opposite. (Down 3 on the y, left 1 on the x) (-1,-8) 6) Connect the dots. 1) y = 2x + 1 2) y = -4x + 5 3
4 3) y = ½ x 3 4) y= - ⅔x + 2 5) y = -x 3 6) y= 5x 4
5 Q3 Quiz 1 Review 1) y = 4x - 6 Graphing and Systems of Equations Packet 2) y = -2x + 7 5
6 3) y = -x - 5 4) y = 5x + 5 6
7 5) y = - ½ x - 7 6) y = ⅗x - 4 7
8 7) y = ⅔x 8) y = - ⅓x + 4 8
9 Finding the equation of a line in slope intercept form (y=mx + b) Example: Using slope intercept form [y = mx + b] Find the equation in slope intercept form of the line formed by (1,2) and (-2, -7). A. Find the slope (m): B. Use m and one point to find b: m = y 2 y 1 y = mx + b x 2 x 1 m= 3 x= 1 y= 2 m = (-7) (2). 2 = 3(1) + b (-2) (1) 2 = 3 + b -3-3 m = = b -3 m= 3 y = 3x 1 Example: Using point slope form [ y y 1 = m(x x 1 ) ] Find the equation in slope intercept form of the line formed by (1,2) and (-2, -7). A. Find the slope (m): B. Use m and one point to find b: m = y 2 y 1 y y 1 = m(x x 1 ) x 2 x 1 m= 3 x= 1 y= 2 y (2) = 3(x (1)) m = (-7) (2). y 2 = 3x - 3 (-2) (1) m = -9. y = 3x 1-3 m= 3 9
10 Find the equation in slope intercept form of the line formed by the given points. When you re finished, graph the equation on the given graph. 1) (4,-6) and (-8, 3) 10
11 2) (4,-3) and (9,-3) 3) (7,-2) and (7, 4) III. Special Slopes A. Zero Slope B. No Slope (undefined slope) * No change in Y * No change in X * Equation will be Y = * Equation will be X = * Horizontal Line * Vertical Line 11
12 Q3 Quiz 2 Review 1) (7,-10) (-2,8) Graphing and Systems of Equations Packet 2) m = - ¾ (-8,6) 12
13 3) (-4,9)(-4,-2) 4) m = - ½ ;(-6, 5). 13
14 5) (-5,6)(2,6) 6) (-4,7)(4,-1) 14
15 7) m = undefined (8,-1) 8) m = 0 (6,-5) Answers: 1) y = -2x + 4 2) y = - ¾ x 3) x = -4 4) y = - ½x + 2 5) y = 6 6) y = - x + 3 7) x = 8 8) y = -5 15
16 Point-Slope Form y y 1 = m(x x 1 ) Graphing and Systems of Equations Packet Slope Intercept Form y = mx + b y is by itself Standard Form: Ax + By = C Constant (number) is by itself Given the slope and 1 point, write the equation of the line in: (a) point-slope form, (b) slope intercept form, and (c) standard form: Example: m = ½ ; (-6,-1) a) Point-Slope Form b) Slope intercept form c) Standard Form 16
17 1) m = -2; (-3,1) a) Point-Slope Form b) Slope intercept form c) Standard Form 2) m = - ¾ ; (-8, 5) Point-Slope Form b) Slope intercept form c) Standard Form 3) m = ⅔; (-6, -4) Point-Slope Form b) Slope intercept form c) Standard Form 4) m = -1 (5, -1) Point-Slope Form b) Slope intercept form c) Standard Form 17
18 Find equation in slope intercept form and graph: 1) (3,-2)(-6,-8) 2) (-6,10) (9,-10) 3) (3,7) (3,-7) 4) (7,-6)(-3,4) 18
19 5) (5,-9)(-5,-9) 6) m= 4 (-2,-5) 7) m= ⅔ (-6,-7) 8) m= - (8,-4) 19
20 9) m = 0 (4,3) 10) m = undefined (-6, 5) 11) 16x -4y =36 12) 8x+24y = 96 20
21 13) y+7=2(x+1) 14) y+5=(2/5)(x+10) 15) y-7= ¾ (x-12) 16) y-2=-3(x-2) 21
22 Q3 Quiz 3 Review 1) y - 2 = -3(x 1) Graphing and Systems of Equations Packet 2) 14x + 21y =
23 . 3) y + 10 = 5(x + 2) 4) y 7 = ¼ (x 20) 23
24 5) 8x 8y = 56 6) y + 6 = -1(x 3) 24
25 7) 18x 12y = -12 8) y 15 = (-5/3)(x + 9) Answers: 1) y = -3x + 5 2) y = - ⅔ x - 4 3) y = 5x 4) y = ¼ x + 2 5) y = x - 7 6) y = - x 3 7) y = (3/2)x + 1 8) y = -(5/3)x 25
26 Graph both of the lines on the same set of axis: y = -2x + 6 y = -2x 5 IV. Parallel and Perpendicular Lines: A. Parallel Lines * Do not intersect * Have same slopes For the given line, find a line that is parallel and passes through the given point and graph Given Line: Parallel: Given Line: Parallel: 7) y = ⅓ x + 4 (6,1) 8) y = 4x 5 (2,13) Given Line: Parallel: Given Line: Parallel: 9) y = -⅔ x + 2 (-9,2) 10) y = 5x + 6 (4,-27) 26
27 Practice Problems: a) Use the two points to find the equation of the line. b) For the line found in part a, find a line that is parallel and passes through the given point. c) Graph both lines on the same set of axis. Given Line: Parallel: 1) (-5, 13) (3, -3) (4,-10) Given Line: Parallel: 2) (-6,0) (3,6) (6,3) 27
28 Given Line: Parallel: 3) (2,6)(-3,-19) (5,30) Given Line: Parallel: 4) (-4,3) (-8,6) (-4, 10) 28
29 Given Line: Parallel: 5) (2,-5) (-2, -5) (8,-2) Given Line: Parallel: 6) (-9,-11)(6,9) (-3,-9) 29
30 Given Line: Parallel: 7) (8,-3) (-4,9) (-2, 1) Given Line: Parallel: 8) (3,6)(3,-6) (7,-3) 30
31 Given Line: Parallel: 9) (4,-3)(-6,-8) (6,7) Given Line: Parallel: 10) (2,4)(-6,-12) (-3,-5) 31
32 11) Find the equation of the line parallel to y = 3x 2, passing through (-2, 1). 12) Find the equation of the line parallel to y = -½x 5, passing through (-2, 7) 13) Find the equation of the line parallel to y = -¼ x + 2, passing through (-8, 4) 14) Find the equation of the line parallel to y = (3/2)x + 6, passing through (-6, -11) 15) Find the equation of the line parallel to y = -5, passing through (2,7) 16) Find the equation of the line parallel to x = 5, passing through (6, -4). 32
33 Q3 Quiz 4 Review Graphing and Systems of Equations Packet FOLLOW REQUIRED FORMAT AND SHOW ALL PROPER WORK! a) Use the two points to find the equation of the line. b) For the line found in part a, find a line that is parallel and passes through the given point. c) Graph both lines on the same set of axis. Given Line: Parallel: 1) (-4, 13) (3, -8) (4,-17) Given Line: Parallel: 2) (8,1) (-4,-5) (-6,2) 33
34 Given Line: Parallel: 3) (5,4) (-4,4) (-6,-7) Graphing and Systems of Equations Packet For # s 4-7, just find the equation. You do not have to graph. 4) Find the equation of the line parallel to y = -⅗x 2, passing through (-5, 7). 5) Find the equation of the line parallel to y = 4x 5, passing through (-4, 9) 6) Find the equation of the line parallel to y = 2, passing through (-8, -9) 7) Find the equation of the line parallel to x = 5, passing through (-6, -11) 34
35 Solving Systems of Equations Graphically A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations with a same set of unknowns. In solving a system of equations, we try to find values for each of the unknowns that will satisfy every equation in the system. When solving a system containing two linear equations there will be one ordered pair (x,y) that will work in both equations. To solve such a system graphically, we will graph both lines on the same set of axis and look for the point of intersection. The point of intersection will be the one ordered pair that works in both equations. We must then CHECK the solution by substituting the x and y coordinates in BOTH ORIGINAL EQUATIONS. 1) Solve the following system graphically: y = 2x 5 y = - ⅓x
36 Solve each of the systems of equations graphically: 2) y + 1 = -3(x 1) 7x + 7y = 42 3) y 9 = ¾ (x 12) 6x + 12y =
37 4) 12x 8y = 48 y 4 = -2(x 2) 5) y + 5 = 2(x + 4) y 10 = - ½ (x + 4) 37
38 Solve each system graphically and check: 6) y = -4x -5 y = 2x -7 7) 6x + 3y =21 12x + 16y =
39 8) 12x 6y = -6 16x -8y = 40 9) y= -4 x = 7 39
40 10) y-2= (3/5)(x-10) y+11 =2(x+7) 11) 6x + 9y = 45 9x +15y = 75 40
41 12) x = 5 y-12 = -3(x+2) 13) 9x 18y = 126 y = -4 41
42 Q3 Quiz 5 Review 1) y = 2x + 6 y = - ½x - 4 Graphing and Systems of Equations Packet 2) 15x - 15y = -45 y - 2 = -3(x + 1) 42
43 3) y + 3 = (-2/3)(x - 3) y + 1 = -1(x + 2) 4) 24x - 18y = -18 y = -7 43
44 5) y + 2 = (-3/4)(x - 8) 17x - 34y = 204 6) x = -6 y + 15 = (5/3)(x + 9) 44
45 7) y - 5 = ¼(x - 4) 45x - 15y = 105 8) 24x - 12y = -72 y 2 = 2(x + 2) 45
46 9) 11x + 44y = -176 y - 3 = - ¼ (x + 4) 10) y + 4 = (2/3)(x + 12) 25x + 50y = -150 Answer Key: 1) (-4,-2) 2) (-1,2) 3) (-6,3) 4) (-6, -7) 5) (8,-2) 6) (-6,-10) 7) (4,5) 8) Many Solutions 9) No Solution 10) (-6,0) 46
47 Find x if y = -12: y = -12 7x + 5y = 31 Solve graphically: 1) 16x - 32y = 224 y = 2x 1 47
48 Solve the system algebraically: 2) 16x - 32y = 224 y = 2x 1 Solving Systems of Equations Algebraically In order to solve for two variables, you need to have two equations. If you only have one equation there are an infinite amount of ordered pairs (x,y) that will work. For example: 4x 2y = 16 you can have x = 4 and y = 0 (4,0) and (2, -2) and (0, -4) and an infinite amount of others. To be able to solve for a single ordered pair, you need a second equation. When we introduce the second equation, we will be able to solve for a single ordered pair that will work in both equations. There are two ways to solve a system of equations (algebraically and graphically). We will focus on solving algebraically. There are two methods of solving algebraically (substitution and elimination). The key to both of them is changing one (or both) equations so there is only one variable to solve for. Then you follow all the rules of solving for the one variable. Then plug the value back into one of the original equations to find the value of the second variable. Always state your answer as an ordered pair. SUBSTITUTION Example: x = 3y + 8 5x + 2y = 6 Substitute 3y +8 for substitute the value Check in BOTH the x in the 2nd equation for y back in to find x. ORIGINAL EQUATIONS! 5(3y + 8) + 2y = 6 y = -2 x = 3y + 8 Distribute and solve: x = 3(-2) + 8 (2) = 3(-2) y y = 6 x= = y + 40 = 6 x = 2 2 = 2 17y = -34 5x + 2y = (2, -2) State answer as an 5(2) + 2(-2) = 6 y = -2 ordered pair (x,y) 10 6 = 4 4 = 4 48
49 Solve each system and check (in both equations): a) x = 2y + 1 5x 6y = 13 Graphing and Systems of Equations Packet b) y = 3x + 4 9x + 2y = -37 c) 4x + 2y = 24 10x + y = 8 49
50 d) 6x 5y = 20 x + 3y = 11 e) 7x + 9y = -74 4x + y = -5 f) 8x + 3y = 35 10x y = 1 50
51 Q3 Quiz 6 Review 1) y = 3x 8 6x 5y = 31 2) x = 2y + 9 5x + 8y =
52 3) y = 2x 3 6x 5y = 31 4) 4x + y = -9 12x 7y =
53 5) x 7y = 19 6x + 11y = 61 6) 3y 2 = x 3x 7y = -16 Answer Key: (1,-5) 2) (17,4) 3) -4,-11) 4) (1.5, -15) 5) (12,-1) 6) (-17,-5) 53
54 Solving Systems with Linear Combinations ( Elimination ): Sometimes solving a system of equations using substitution can be very difficult. For these problems we solve using Linear Combinations (or Elimination). With elimination you solve by eliminating one of the variables. This is accomplished by adding the 2 equations together. Before you can add the equations together, you need one of the two variables to have two things: 1) Same Coefficient 2) Different Signs (one positive and one negative) When you add terms with the same coefficient and different signs, the term drops out. You then solve for the variable that is left. After you have solved for one variable, you plug the value into one of the original equations and solve for the 2 nd variable (just like Substitution). Then, you check the solution in both original equations. The only difference between Substitution and Elimination is how you solve for the 1 st variable. After that they are the same. Examples: A) Sometimes it works out that the 2 equations already have a variable with the same coefficient and different signs. You can then just add the equations: 3x + 4y = 10 (The +4y and -4y cancel out Plug x = -6 in: 3x+4y = 10 5x 4y = -58 leaving you with just 8x.) 3(-6) + 4y = 10 3(-6) + 4(7) = 10 8x = y = = = 10(check) 4y = 28 5x 4y = -58 x = (-6) 4(7) = -58 y = = = -58(check) Final Solution: (-6, 7) CHECK IN BOTH!!!! B) Sometimes (usually) the equations do not have same coefficient and different signs, so we have a little bit of manipulating to do. 3x + 8y = 25 With this system, nothing will drop out if we just add the 5x + 4y = 23 equations. So we will multiply the bottom one by (-2). -2(5x + 4y = 23) Now the y s have the same coefficient with different signs. - 10x -8y = -46 3x + 8y = 25 3x + 8y = 25 Now plug x = 3 in: 3(3)+8(2) = 25-10x -8y = -46 3(3) + 8y = = 25-7x = y = = 25 (check) x + 4y = 23 8y = 16 5(3) + 4(2) = 23 x = = 23 y = 2 23 = 23 (check) Final Solution: (3,2) CHECK IN BOTH!!!! 54
55 C. Sometimes we need to manipulate both equations. We can do this by criss crossing the coefficients. 6x + 7y = 11 This is different than Example B, because no coeffcient 5x 6y = -50 goes into another evenly. You need the negative sign to change the 6x to negative -5(6x + 7y = 11) so the signs will be different. 6(5x 6y = -50) You can also use 5 and -6. You can also criss cross the y coefficients. -30x 35y = -55 Plug in y = 5 6x + 7y = 11 30x 36y = x 6(5) = -50 6(-4) + 7(5) = 11-71y = x 30 = = = 11 (check) 5x = -20 5x 6y = -50 y = (-4) 6(5) = = -50 x = = -50 (check) Practice: 1) 7x + 3y = 10 5x 6y = 56 Final Solution: (-4, 5) CHECK IN BOTH!!!! 55
56 2) 11x + 5y = 27 4x + 6y = 60 3) 9x + 7y = 126 7x 9y =
57 4) 12x 5y = 63 8x + 3y = 23 5) 5x + 9y = 14 6x + 11y = 18 57
58 6) 10x 9y = 36 4x + 3y = -12 7) 5x + 6y = 42 3x + 14y = 20 58
59 8) 7x 5y = -42 8x + 3y = -48 9) 4x 3y = 19 8x + 5y =
60 Mixed Substitution and Elimination: Solve each system algebraically: 1) 5x - 2y = -9 7x + 2y = -27 Graphing and Systems of Equations Packet 2) -4x + 2y = -16 5x 3y = 19 60
61 3) x = 2y -6 5y 3x = 11 4) 5x 6y = -74 7x + 5y = 17 61
62 5) 4x 5 = y 7x + 5y = 83 6) 7x + 4y = -11 5x + 2y =
63 7) 5x 6y = -17 3x + 8y = -16 8) x = 6 + 2y 6x 5y = 15 63
64 9) 6x + 5y = 23 11x + 4y = 6 10) y = 3x + 4 8x 9y = 59 64
65 11) 12x 7y = 46 4x + 3y = -6 12) 9x 4y = -88 2x + 5y = 4 65
66 13) 24x 6y = x 3y = ) 5x 6y = 42 15x 18y = 54 66
67 15) 7x + 6y = -12 5x + 2y = ) 13x 3y = 78 4x + 6y =
68 17) 2y 5 = x 4x 11y = ) 3x 7y = -10 5x + 12y =
69 19) 6x 17y = x 7y = ) 9x 5y = -43 3x + 11y = 87 69
70 21) 9x = 11y x 12y = 8 22) 6y = 5x x + 9y = 1 70
71 23) 6x + 5y = 33 5x + 37 = 3y 24) y = 3x x 7y = 1 Answer Key to Algebraic Systems: 1) (-3,-3) 7) (-4, -.5) 13) many sol. 19) (2.5, 7) 2) (5,2) 8) (0,-3) 14) no sol. 20) (-1/3, 8) 3) (8,7) 9) (-2,7) 15) (-6,5) 21) (4,1) 4) (-4,9) 10) (-5,-11) 16) (3,-13) 22) (4,-3) 5) (4,11) 11) (1.5, -4) 17) (7,6) 23) (-2,9) 6) (-5,6) 12)(-8, 4) 18) (-8, -2) 24) (-4,-7) 71
72 Extra Practice (do in NB) 1) 6x 5y = -7 2) 5x + 4y = x + 5y = 58 5x -7y = 52 3) 6x + 7y = -28 4) 11x 4y = 53 5x 14y = x 8y = 1 5) 3x 7y = 42 6) 9x 4y = 177 2x + 5y = 57 6x 5y = 111 7) 8x 11y = 77 8) 13x 2y = 72 6x + 4y = -28 9x + 5y = -14 9) 12x = 20-8y 10) 5y = 8x x 6y = x + 7y = 51 Answer Key: 1) (3, 5) 2) (-5, -11) 3) (-14, 8) 4) (7,6) 5) (21,3) 6) (21, 3) 7) (0, -7) 8) (4, -10) 9) (-3,7) 10) (-4, 13) 72
73 Q3 Quiz 7 Review 1) 7x 4y = -86 9x 4y = -98 Graphing and Systems of Equations Packet 2) 3x 10y = -18 9x + 8y = ) 5x + 8y = 70-4x - 5y =
74 4) 10x + 11y = 37 8x 7y = ) 6x + 13y = -66 4x + 7y = -34 6) 5x - 9y = 22 8x 5y = 101 Answer Key: 1) (-6,11) 2) (-16,-3) 3) (14,0) 4) (-9.5, 12) 5) (2,-6) 6) (17,7) 74
75 Word Problems Involving Systems A Day With Boohbah!! 1) Boohbah went into Dunkin Donuts for breakfast. Boohbah bought 5 donuts and 2 muffins for $5.10. Boohbah went to order some more and the guy behind the counter made fun of him for eating so much. He smacked around the guy behind the counter and bought 2 donuts and 7 muffins for $8.55. Find the price of 1 donut and 1 muffin. 2) Boohbah was still angered by the guy behind the counter. So, he went and beat up some of his family members. This made Boohbah hungry again. At Cherry Valley deli, Boohbah went in and bought 7 TCS s and 3 sodas for $ This didn t fill him up, so he went back in and bought 2 more TCS s and 2 more sodas for $ What would the price of 4 TCS s and 3 sodas be? 75
76 3) Boohbah finished off the clown from Dunkin Donuts, hid the body, and was then ready for dessert, so he hit Maggie Moos!! He bought 2 cones and a sundae for $9.70. Again, Boohbah wanted more. Much more. So he bought 4 more cones and 5 more sundaes for $ Find the price of each item. 4) Boohbah went home and found his jar of change. Boohbah hates pennies and nickels. So there are only dimes and quarters in his jar. If there are 400 coins in the jar and the total amount of money is $79.45, how many of each coin are in the jar? 76
77 Mixed Problems: 1) After a big Yankee win, Didi bought 4 slices of pizza and 2 cokes for $10.20 and Giancarlo bought 3 slices of pizza and 3 cokes for $9.90. Find the price of one coke. Find the price of 1 slice of pizza. 2) Brett went to the donut shop and bought 6 donuts and 4 large coffees for $8.92. Chase went in right after Brett and bought 5 doughnuts and 6 large coffees for $ Find the price of 1 large coffee. Find the price of 1 donut. Gary went in and bought 3 donuts and 2 large coffees. How much did he pay? 77
78 3) Greg and CC went to the burger stand and bought dinner. Greg had 2 cheeseburgers and 3 fries. CC bought 3 cheeseburgers and 2 fries. Greg paid $ CC paid $ How much would 2 cheeseburgers and 1 fries cost? 4) Aaron and Masahiro went shopping for some new Yankee gear. Aaron bought 4 sweatshirts and 5 t-shirts for $254. Masahiro bought 2 sweatshirts and 4 t-shirts for $154. How much would 2 sweatshirts and 3 t-shirts cost? 78
79 5) Maggie and Erin went to see Frozen and went to the snack bar before finding their seats. Maggie paid $11.05 for 2 candy bars and 3 sodas. Erin paid $17.55 for 3 candy bars and 5 sodas. Find the total cost of 4 candy bars and 1 soda. 6) Sam and Peter went to the pizzeria and ordered some slices. Sam bought 2 slices of Sicilian and 2 regular and his bill was $10. Peter bought 3 slices of Sicilian and 1 regular for $ How much would 4 Sicilian and 5 slices of regular cost? 79
80 Alg1 Q3 Quiz 8 Review 7) Solid ties cost $21 and striped ties cost $24. The store sold 200 ties and made $4,413. How many of each were sold? 8) At a movie theater adult tickets cost $9.00 and child tickets cost $ people attended the last showing of Silver Linings Playbook and $720 was collected at the ticket booth. How many of each ticket was sold? 80
81 9) A jar of change was filled with only quarters and dimes. If there were 600 coins in the jar and there was $ in the jar, how many of each coin were there? 10) A 35-minute phone call cost $4.95. Introductory minutes cost $.16/min and additional minutes are $.11/min. How many minutes were billed at each rate? 81
82 11) A 32-minute phone call cost $3.01. Introductory minutes cost $.17/min and additional minutes are $.08/min. How many minutes were billed at each rate? 12) There was a jar of coins filled only with nickels and quarters. If there is $53.00 in the jar and there is a total of 300 coins, how many of each coin are in the jar? 82
83 Answer Key 1) 1 coke cost $1.50, 1 slice cost $ ) 1 large coffee cost $1.15, 1 donut cost $.72. Gary paid $4.46 3) 2 Cheeseburgers and 1 Fries cost $9.45. (CB cost $2.95 and fries cost $3.85) 4) 2 sweatshirts and 3 t-shirts cost $136. (Sweatshirts cost $41 and t-shirts cost $18) 5) 4 candy bars and 1 soda costs $12.35 (candy bars are $2.60 and sodas are $1.95) 6) 4 Sicilian and5 regular slices would cost $22.25 (Sicilian slice cost $2.75 and the regular slice cost $2.25) Alg1 Q3 Quiz 8 Review 7) 129 solid and 71 striped. 8) 48 adults and 72 child tickets 9) 407 quarters and 193 dimes 10) 22 introductory minutes and 13 additional minutes 11) 5 introductory minutes and 27 additional minutes 12) 190 quarters and 110 nickels 83
Systems of Equations Algebraically
 Find x if y = -12: y = -12 7x + 5y = 31 Solve graphically: 1) 16x - 32y = 224 y = 2x 1 Solve the system algebraically: 2) 16x - 32y = 224 y = 2x 1 1 Solving Systems of Equations In order to solve for two
Find x if y = -12: y = -12 7x + 5y = 31 Solve graphically: 1) 16x - 32y = 224 y = 2x 1 Solve the system algebraically: 2) 16x - 32y = 224 y = 2x 1 1 Solving Systems of Equations In order to solve for two
Foundations of Math. Chapter 3 Packet. Table of Contents
 Foundations of Math Chapter 3 Packet Name: Table of Contents Notes #43 Solving Systems by Graphing Pg. 1-4 Notes #44 Solving Systems by Substitution Pg. 5-6 Notes #45 Solving by Graphing & Substitution
Foundations of Math Chapter 3 Packet Name: Table of Contents Notes #43 Solving Systems by Graphing Pg. 1-4 Notes #44 Solving Systems by Substitution Pg. 5-6 Notes #45 Solving by Graphing & Substitution
Lesson 12: Systems of Linear Equations
 Our final lesson involves the study of systems of linear equations. In this lesson, we examine the relationship between two distinct linear equations. Specifically, we are looking for the point where the
Our final lesson involves the study of systems of linear equations. In this lesson, we examine the relationship between two distinct linear equations. Specifically, we are looking for the point where the
Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers
 Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers Absolute Value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line. 5 = 5 and 5 = 5 Adding Numbers with the Same Sign: Add the absolute values and use the sign
Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers Absolute Value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line. 5 = 5 and 5 = 5 Adding Numbers with the Same Sign: Add the absolute values and use the sign
Oregon Focus on Linear Equations Lesson 1 Answers
 Lesson 1 Answers 1. a. Nathan; multiplication b. Subtraction 2. 30 3. 28 4. 40 5. 17 6. 29 7. 21 8. 7 9. 4 10. 33 11. 8 12. 1 13. 5 14. 19 15. 12 16. 15 17. a. 130 5 + 40 8 b. $970 18. a. (11 + 8 + 13)
Lesson 1 Answers 1. a. Nathan; multiplication b. Subtraction 2. 30 3. 28 4. 40 5. 17 6. 29 7. 21 8. 7 9. 4 10. 33 11. 8 12. 1 13. 5 14. 19 15. 12 16. 15 17. a. 130 5 + 40 8 b. $970 18. a. (11 + 8 + 13)
ANSWER KEY. Checklist Do I understand? Test Date: A-Day 2/7. Algebra 1 Benchmark Review study guide is due on test day!
 ANSWER KEY Name: Algebra 1 Benchmark Review study guide is due on test day! Test Date: A-Day 2/7 Checklist Do I understand? Unit 1 Solving Equations and Inequalities Two Step Equations Properties of Real
ANSWER KEY Name: Algebra 1 Benchmark Review study guide is due on test day! Test Date: A-Day 2/7 Checklist Do I understand? Unit 1 Solving Equations and Inequalities Two Step Equations Properties of Real
Unit 12: Systems of Equations
 Section 12.1: Systems of Linear Equations Section 12.2: The Substitution Method Section 12.3: The Addition (Elimination) Method Section 12.4: Applications KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS Look for the following
Section 12.1: Systems of Linear Equations Section 12.2: The Substitution Method Section 12.3: The Addition (Elimination) Method Section 12.4: Applications KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS Look for the following
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1)
 ALGEBRA UNIT 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent
October 5 th October 9 th. Unit 2: Equations & Inequalities
 Algebra I: Week 6 Math Packet October 5 th October 9 th Unit 2: Equations & Inequalities Jump Start Directions: Answer the Regents question below to the best of your ability. Solve the inequality below
Algebra I: Week 6 Math Packet October 5 th October 9 th Unit 2: Equations & Inequalities Jump Start Directions: Answer the Regents question below to the best of your ability. Solve the inequality below
Algebra I. Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities. Slide 1 / 179. Slide 2 / 179. Slide 3 / 179. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 179 Algebra I Slide 2 / 179 Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities 2015-04-23 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 179 Click on the topic to go to that section 8th Grade Review of
Slide 1 / 179 Algebra I Slide 2 / 179 Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities 2015-04-23 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 179 Click on the topic to go to that section 8th Grade Review of
Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation
 Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation Algebraically 2( x 3) = 12 Graphically 2( x 3) = 12 2. Solve the following equations algebraically a. 5w 15 2w = 2(w 5) b. 1
Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation Algebraically 2( x 3) = 12 Graphically 2( x 3) = 12 2. Solve the following equations algebraically a. 5w 15 2w = 2(w 5) b. 1
Algebra. Chapter 6: Systems of Equations and Inequalities. Name: Teacher: Pd:
 Algebra Chapter 6: Systems of Equations and Inequalities Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents Chapter 6-1: SWBAT: Identify solutions of systems of linear equations in two variables; Solve systems of linear
Algebra Chapter 6: Systems of Equations and Inequalities Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents Chapter 6-1: SWBAT: Identify solutions of systems of linear equations in two variables; Solve systems of linear
Unit 5 Review Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities
 Unit 5 Review Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities Name: Algebra 1B Day 1: Solutions to Systems and Solving by Graphing Warm Up: Determine if the point (2,5) is a solution to each of the systems
Unit 5 Review Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities Name: Algebra 1B Day 1: Solutions to Systems and Solving by Graphing Warm Up: Determine if the point (2,5) is a solution to each of the systems
1. Graph the system of equations and tell the solution. 1. Solution
 Algebra Reporting Strand 4: Systems of Equations & Inequalities Subunit 4a: Solving Systems of Equations Review Name: Period: Date: Read all the directions carefully, put your answers in the blanks provided,
Algebra Reporting Strand 4: Systems of Equations & Inequalities Subunit 4a: Solving Systems of Equations Review Name: Period: Date: Read all the directions carefully, put your answers in the blanks provided,
WRITING EQUATIONS through 6.1.3
 WRITING EQUATIONS 6.1.1 through 6.1.3 An equation is a mathematical sentence that conveys information to the reader. It uses variables and operation symbols (like +, -, /, =) to represent relationships
WRITING EQUATIONS 6.1.1 through 6.1.3 An equation is a mathematical sentence that conveys information to the reader. It uses variables and operation symbols (like +, -, /, =) to represent relationships
NOTES. [Type the document subtitle] Math 0310
![NOTES. [Type the document subtitle] Math 0310 NOTES. [Type the document subtitle] Math 0310](/thumbs/79/79061464.jpg) NOTES [Type the document subtitle] Math 010 Cartesian Coordinate System We use a rectangular coordinate system to help us map out relations. The coordinate grid has a horizontal axis and a vertical axis.
NOTES [Type the document subtitle] Math 010 Cartesian Coordinate System We use a rectangular coordinate system to help us map out relations. The coordinate grid has a horizontal axis and a vertical axis.
Math 1 Unit 7 Review
 Name: ate: 1. Which ordered pair is the solution to this system of equations? 5. system of equations is graphed on the set of axes below. y = x + 4 x + y = 2. (1, 5). (0, 2). ( 1, 3). ( 4, 0) 2. Which
Name: ate: 1. Which ordered pair is the solution to this system of equations? 5. system of equations is graphed on the set of axes below. y = x + 4 x + y = 2. (1, 5). (0, 2). ( 1, 3). ( 4, 0) 2. Which
Warm Up. Unit #1: Basics of Algebra
 1) Write an equation of the given points ( 3, 4) & (5, 6) Warm Up 2) Which of the following choices is the Associative Property 1) 4(x + 2) = 4x + 8 2) 4 + 5 = 5 + 4 3) 5 + ( 5) = 0 4) 4 + (3 + 1) = (4
1) Write an equation of the given points ( 3, 4) & (5, 6) Warm Up 2) Which of the following choices is the Associative Property 1) 4(x + 2) = 4x + 8 2) 4 + 5 = 5 + 4 3) 5 + ( 5) = 0 4) 4 + (3 + 1) = (4
Algebra I System of Linear Equations
 1 Algebra I System of Linear Equations 2015-11-12 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section Solving Systems by Graphing Solving Systems by Substitution Solving Systems
1 Algebra I System of Linear Equations 2015-11-12 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section Solving Systems by Graphing Solving Systems by Substitution Solving Systems
Chapter Systems of Equations
 SM-1 Name: 011314 Date: Hour: Chapter 6.1-6.4 Systems of Equations 6.1- Solving Systems by Graphing CCS A.REI.6: Solve systems of equations exactly and approximately (e.g. with graphs), focusing on pairs
SM-1 Name: 011314 Date: Hour: Chapter 6.1-6.4 Systems of Equations 6.1- Solving Systems by Graphing CCS A.REI.6: Solve systems of equations exactly and approximately (e.g. with graphs), focusing on pairs
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES. ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra I Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra I Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
Unit 5 SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS
 MATH 8 Unit 5 SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS By the end of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Solve simultaneous linear equations by graphing. 2. Understand what it means to solve a system of equations.
MATH 8 Unit 5 SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS By the end of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Solve simultaneous linear equations by graphing. 2. Understand what it means to solve a system of equations.
REVIEW Algebra 1 Fall Final
 1. (A.5A) Solve: 4(x 8) = 4x (7x 3) A. x = 29/7 B. x = 5 C. x = no solution D. x = 5 Use the graph below to answer questions #2-3 6. (A.2E) Write the equation of a line passing through ( 5, 7)that is parallel
1. (A.5A) Solve: 4(x 8) = 4x (7x 3) A. x = 29/7 B. x = 5 C. x = no solution D. x = 5 Use the graph below to answer questions #2-3 6. (A.2E) Write the equation of a line passing through ( 5, 7)that is parallel
Algebra I. Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities. 8th Grade Review. Slide 1 / 179 Slide 2 / 179. Slide 4 / 179. Slide 3 / 179.
 Slide 1 / 179 Slide 2 / 179 lgebra I Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities 2015-04-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 179 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section 8th Grade Review of Systems
Slide 1 / 179 Slide 2 / 179 lgebra I Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities 2015-04-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 179 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section 8th Grade Review of Systems
1 Numbers, Sets, Algebraic Expressions
 AAU - Business Mathematics I Lecture #1, February 27, 2010 1 Numbers, Sets, Algebraic Expressions 1.1 Constants, Variables, and Sets A constant is something that does not change, over time or otherwise:
AAU - Business Mathematics I Lecture #1, February 27, 2010 1 Numbers, Sets, Algebraic Expressions 1.1 Constants, Variables, and Sets A constant is something that does not change, over time or otherwise:
Unit 2 Day 3 MATRICES. MATRIX Applications Quiz 1
 Unit 2 Day 3 MATRICES MATRIX Applications Quiz 1 Remember: Phones OFF Warm-Up and in Blue Pockets! Check the list. Tracey, Danica, and Sherri bought snacks for a girls sleepover. They each bought the items
Unit 2 Day 3 MATRICES MATRIX Applications Quiz 1 Remember: Phones OFF Warm-Up and in Blue Pockets! Check the list. Tracey, Danica, and Sherri bought snacks for a girls sleepover. They each bought the items
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 -SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1)
 ALGEBRA UNIT 5 -SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent independent
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 -SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent independent
Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review #1
 Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review #1 Lesson 1 1. Simplify the expression. 8 5(7 r) A1.1.3.1 Lesson. Solve the equation. 4x 1 = 9 x A1..1 Lesson 3. Solve the equation. 1.6n 5.95 = 11.7
Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review #1 Lesson 1 1. Simplify the expression. 8 5(7 r) A1.1.3.1 Lesson. Solve the equation. 4x 1 = 9 x A1..1 Lesson 3. Solve the equation. 1.6n 5.95 = 11.7
Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review #2
 Lesson 1 1. Simplify the expression. (r 6) +10r A1.1.3.1 Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review # Lesson. Solve the equation. 5x + 4x = 10 +6x + x A1..1 Lesson 3. Solve the equation. 1 +
Lesson 1 1. Simplify the expression. (r 6) +10r A1.1.3.1 Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review # Lesson. Solve the equation. 5x + 4x = 10 +6x + x A1..1 Lesson 3. Solve the equation. 1 +
UNIT 5: Systems of Equations
 Algebra 2 Trig UNIT 5: Systems of Equations Name: Teacher: Pd: 1 Table of Contents Day 1: Review Solving Linear Systems SWBAT: Solve linear systems algebraically and graphically. Homework: Page 7 Day 2:
Algebra 2 Trig UNIT 5: Systems of Equations Name: Teacher: Pd: 1 Table of Contents Day 1: Review Solving Linear Systems SWBAT: Solve linear systems algebraically and graphically. Homework: Page 7 Day 2:
Semester One Review. FORMULAS Given on Exam! 3. What is the value of f(5), given the equation f(x) = x 2 4x + 1? Slope:
 FORMULAS Given on Exam!. What is equivalent to A. -(x )? B. (x + ) (x + ). Evaluate: A. + 7 B. C.. D.. = i. 6.6 ii. 6.6 iii. 6 iv. 6 E. + F. 0 + G. 9. ( ) H. ( + ) + ( + ) I. ( ) + = J. 9x 0 + y (when
FORMULAS Given on Exam!. What is equivalent to A. -(x )? B. (x + ) (x + ). Evaluate: A. + 7 B. C.. D.. = i. 6.6 ii. 6.6 iii. 6 iv. 6 E. + F. 0 + G. 9. ( ) H. ( + ) + ( + ) I. ( ) + = J. 9x 0 + y (when
Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming
 Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to solve linear equations students should be able to graph linear equations students should be able to create linear equations
Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to solve linear equations students should be able to graph linear equations students should be able to create linear equations
Consistent and Dependent
 Graphing a System of Equations System of Equations: Consists of two equations. The solution to the system is an ordered pair that satisfies both equations. There are three methods to solving a system;
Graphing a System of Equations System of Equations: Consists of two equations. The solution to the system is an ordered pair that satisfies both equations. There are three methods to solving a system;
ALGEBRA 1 FINAL EXAM TOPICS
 ALGEBRA 1 FINAL EXAM TOPICS Chapter 2 2-1 Writing Equations 2-2 Solving One Step Equations 2-3 Solving Multi-Step Equations 2-4 Solving Equations with the Variable on Each Side 2-5 Solving Equations Involving
ALGEBRA 1 FINAL EXAM TOPICS Chapter 2 2-1 Writing Equations 2-2 Solving One Step Equations 2-3 Solving Multi-Step Equations 2-4 Solving Equations with the Variable on Each Side 2-5 Solving Equations Involving
Pre-AP Algebra II Summer Packet 2014
 Pre-AP Algebra II Summer Packet 014 Name: Period: PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING!!!!!!! Wait until a few weeks before school starts to work through this packet so that the material will be fresh when you begin
Pre-AP Algebra II Summer Packet 014 Name: Period: PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING!!!!!!! Wait until a few weeks before school starts to work through this packet so that the material will be fresh when you begin
Sample: Do Not Reproduce LF6 STUDENT PAGES LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS. Name Period Date
 Name Period Date LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LF6.1 LF6.2 LF6.3 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Understand the definition of a system of linear equations Understand
Name Period Date LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LF6.1 LF6.2 LF6.3 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Understand the definition of a system of linear equations Understand
Addition and Subtraction of real numbers (1.3 & 1.4)
 Math 051 lecture notes Professor Jason Samuels Addition and Subtraction of real numbers (1.3 & 1.4) ex) 3 + 5 = ex) 42 + 29 = ex) 12-4 = ex) 7-9 = ex) -3-4 = ex) 6 - (-2) = ex) -5 - (-3) = ex) 7 + (-2)
Math 051 lecture notes Professor Jason Samuels Addition and Subtraction of real numbers (1.3 & 1.4) ex) 3 + 5 = ex) 42 + 29 = ex) 12-4 = ex) 7-9 = ex) -3-4 = ex) 6 - (-2) = ex) -5 - (-3) = ex) 7 + (-2)
Chapter 9 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Algebraically
 Name: Chapter 9 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Algebraically 9.1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution Outcomes: 1. Interpret algebraic reasoning through the study of relations 9. Solve
Name: Chapter 9 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Algebraically 9.1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution Outcomes: 1. Interpret algebraic reasoning through the study of relations 9. Solve
Name Class Date. What is the solution to the system? Solve by graphing. Check. x + y = 4. You have a second point (4, 0), which is the x-intercept.
 6-1 Reteaching Graphing is useful for solving a system of equations. Graph both equations and look for a point of intersection, which is the solution of that system. If there is no point of intersection,
6-1 Reteaching Graphing is useful for solving a system of equations. Graph both equations and look for a point of intersection, which is the solution of that system. If there is no point of intersection,
5-3B Systems Review Puzzle
 5-3B Systems Review Puzzle x + y = 4 x y = -2 2x + y = -4 2x + 3y = 4 2x + y = 1 4x 2y = 6 2x + y = 1 x + y = 1 3x 2y = 4-2x + 2y = -1 x = -2y + 1 4 = x + y y = 2 2x x = y 5 y = 4 + 3x 2x + 1 = y x y =
5-3B Systems Review Puzzle x + y = 4 x y = -2 2x + y = -4 2x + 3y = 4 2x + y = 1 4x 2y = 6 2x + y = 1 x + y = 1 3x 2y = 4-2x + 2y = -1 x = -2y + 1 4 = x + y y = 2 2x x = y 5 y = 4 + 3x 2x + 1 = y x y =
Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 1 Systems of Equations and Inequalities 2015 03 24 2 Table of Contents Solving Systems by Graphing Solving Systems by Substitution Solve Systems by Elimination Choosing your Strategy Solving Systems of
1 Systems of Equations and Inequalities 2015 03 24 2 Table of Contents Solving Systems by Graphing Solving Systems by Substitution Solve Systems by Elimination Choosing your Strategy Solving Systems of
Geometry Summer Assignment 2018
 Geometry Summer Assignment 2018 The following packet contains topics and definitions that you will be required to know in order to succeed in Geometry this year. You are advised to be familiar with each
Geometry Summer Assignment 2018 The following packet contains topics and definitions that you will be required to know in order to succeed in Geometry this year. You are advised to be familiar with each
Gearing Up for Geometry!
 Gearing Up for Geometry! Geometry is right around the corner and you need to make sure you are ready! Many of the concepts you learned in Algebra I will be used in Geometry and you will be epected to remember
Gearing Up for Geometry! Geometry is right around the corner and you need to make sure you are ready! Many of the concepts you learned in Algebra I will be used in Geometry and you will be epected to remember
ALGEBRA 1 Semester 2 Final Exam Review #1 Name Date: Semester 2 Exam will cover the following:
 ALGEBRA 1 Semester Final Exam Review #1 Name Date: Semester Exam will cover the following: Unit 4 Linear Functions Slope, slope intercept form, standard form Write equations of linear functions given different
ALGEBRA 1 Semester Final Exam Review #1 Name Date: Semester Exam will cover the following: Unit 4 Linear Functions Slope, slope intercept form, standard form Write equations of linear functions given different
How can you use linear functions of two independent variables to represent problem situations?
 Problems that occur in business situations often require expressing income as a linear function of one variable like time worked or number of sales. For example, if an employee earns $7.25 per hour, then
Problems that occur in business situations often require expressing income as a linear function of one variable like time worked or number of sales. For example, if an employee earns $7.25 per hour, then
Inequalities Chapter Test
 Inequalities Chapter Test Part 1: For questions 1-9, circle the answer that best answers the question. 1. Which graph best represents the solution of 8 4x < 4 A. B. C. D. 2. Which of the following inequalities
Inequalities Chapter Test Part 1: For questions 1-9, circle the answer that best answers the question. 1. Which graph best represents the solution of 8 4x < 4 A. B. C. D. 2. Which of the following inequalities
FOR STUDENTS WHO HAVE COMPLETED ALGEBRA 1 (Students entering Geometry)
 FOR STUDENTS WHO HAVE COMPLETED ALGEBRA (Students entering Geometry) Dear Parent/Guardian and Student, Name: Date: Period: Attached you will find a review packet of skills which each student is expected
FOR STUDENTS WHO HAVE COMPLETED ALGEBRA (Students entering Geometry) Dear Parent/Guardian and Student, Name: Date: Period: Attached you will find a review packet of skills which each student is expected
Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations. Unit Calendar
 Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations Unit Calendar Date Topic Homework Nov 5 (A ) 6.1 Solving Linear Inequalities +/- 6.2 Solving Linear Inequalities x/ 6.3 Solving
Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations Unit Calendar Date Topic Homework Nov 5 (A ) 6.1 Solving Linear Inequalities +/- 6.2 Solving Linear Inequalities x/ 6.3 Solving
4) Solve for this system using your graphing
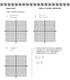 Algebra Unit 5 HW Day 1 SOLVING GRAPHICALLY Graph the following systems: 1) x 2y 12 y 2x 6 2) y x 2 6x 2y 10 ) x y 9 4) Solve for this system using your graphing x calculator. [You will still need to put
Algebra Unit 5 HW Day 1 SOLVING GRAPHICALLY Graph the following systems: 1) x 2y 12 y 2x 6 2) y x 2 6x 2y 10 ) x y 9 4) Solve for this system using your graphing x calculator. [You will still need to put
MTH 111 Fall 2017 Mathematics Department Missouri State University-West Plains
 MTH 111 Fall 2017 Mathematics Department Missouri State University-West Plains 2 MTH 111 Unit Objectives Unit 1: 1. Simplify numeric expressions using the Order of Operations. 2. Simplify variable expressions
MTH 111 Fall 2017 Mathematics Department Missouri State University-West Plains 2 MTH 111 Unit Objectives Unit 1: 1. Simplify numeric expressions using the Order of Operations. 2. Simplify variable expressions
June If you want, you may scan your assignment and convert it to a.pdf file and it to me.
 Summer Assignment Pre-Calculus Honors June 2016 Dear Student: This assignment is a mandatory part of the Pre-Calculus Honors course. Students who do not complete the assignment will be placed in the regular
Summer Assignment Pre-Calculus Honors June 2016 Dear Student: This assignment is a mandatory part of the Pre-Calculus Honors course. Students who do not complete the assignment will be placed in the regular
Name Class Date. 3. Write an equation for the following description: y is three times the value of x.
 Name Class Date Practice 5-2 Linear Equations: y = mx 5-2 Linear Equations: y = mx 1. The variable y has a proportional relationship with x as suggested by the graph. Use the graph to write an equation
Name Class Date Practice 5-2 Linear Equations: y = mx 5-2 Linear Equations: y = mx 1. The variable y has a proportional relationship with x as suggested by the graph. Use the graph to write an equation
1. What are the various types of information you can be given to graph a line? 2. What is slope? How is it determined?
 Graphing Linear Equations Chapter Questions 1. What are the various types of information you can be given to graph a line? 2. What is slope? How is it determined? 3. Why do we need to be careful about
Graphing Linear Equations Chapter Questions 1. What are the various types of information you can be given to graph a line? 2. What is slope? How is it determined? 3. Why do we need to be careful about
Chapter 7 Quadratic Equations
 Chapter 7 Quadratic Equations We have worked with trinomials of the form ax 2 + bx + c. Now we are going to work with equations of this form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 quadratic equations. When we write a quadratic
Chapter 7 Quadratic Equations We have worked with trinomials of the form ax 2 + bx + c. Now we are going to work with equations of this form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 quadratic equations. When we write a quadratic
Basic ALGEBRA 2 SUMMER PACKET
 Name Basic ALGEBRA SUMMER PACKET This packet contains Algebra I topics that you have learned before and should be familiar with coming into Algebra II. We will use these concepts on a regular basis throughout
Name Basic ALGEBRA SUMMER PACKET This packet contains Algebra I topics that you have learned before and should be familiar with coming into Algebra II. We will use these concepts on a regular basis throughout
Lesson: Slope. Warm Up. Unit #2: Linear Equations. 2) If f(x) = 7x 5, find the value of the following: f( 2) f(3) f(0)
 Warm Up 1) 2) If f(x) = 7x 5, find the value of the following: f( 2) f(3) f(0) Oct 15 10:21 AM Unit #2: Linear Equations Lesson: Slope Oct 15 10:05 AM 1 Students will be able to find the slope Oct 16 12:19
Warm Up 1) 2) If f(x) = 7x 5, find the value of the following: f( 2) f(3) f(0) Oct 15 10:21 AM Unit #2: Linear Equations Lesson: Slope Oct 15 10:05 AM 1 Students will be able to find the slope Oct 16 12:19
Chapter 5: Writing Linear Equations Study Guide (REG)
 Chapter 5: Writing Linear Equations Study Guide (REG) 5.1: Write equations of lines given slope and y intercept or two points Write the equation of the line with the given information: Ex: Slope: 0, y
Chapter 5: Writing Linear Equations Study Guide (REG) 5.1: Write equations of lines given slope and y intercept or two points Write the equation of the line with the given information: Ex: Slope: 0, y
Grade 8 Systems of Linear Equations 8.EE.8a-c
 THE NEWARK PUBLIC SCHOOLS THE OFFICE OF MATHEMATICS Grade 8 Systems of Linear Equations 8.EE.8a-c 2012 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS ALIGNED MODULES 2012 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS ALIGNED MODULES THE NEWARK
THE NEWARK PUBLIC SCHOOLS THE OFFICE OF MATHEMATICS Grade 8 Systems of Linear Equations 8.EE.8a-c 2012 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS ALIGNED MODULES 2012 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS ALIGNED MODULES THE NEWARK
Addition and Subtraction of real numbers (1.3 & 1.4)
 Math 051 lecture notes Professor Jason Samuels Addition and Subtraction of real numbers (1.3 & 1.4) ex) 3 + 5 = ex) 42 + 29 = ex) 12-4 = ex) 7-9 = ex) -3-4 = ex) 6 - (-2) = ** CHECK YOUR SIGNS ** IDENTIFY
Math 051 lecture notes Professor Jason Samuels Addition and Subtraction of real numbers (1.3 & 1.4) ex) 3 + 5 = ex) 42 + 29 = ex) 12-4 = ex) 7-9 = ex) -3-4 = ex) 6 - (-2) = ** CHECK YOUR SIGNS ** IDENTIFY
MATHEMATICS. Perform a series of transformations and/or dilations to a figure. A FAMILY GUIDE FOR STUDENT SUCCESS 17
 MATHEMATICS In grade 8, your child will focus on three critical areas. The first is formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a
MATHEMATICS In grade 8, your child will focus on three critical areas. The first is formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a
Cartesian Plane. Analytic Geometry. Unit Name
 3.1cartesian Unit Name Analytic Geometry Unit Goals 1. Create table of values in order to graph &/or determine if a relation is linear. Determine slope 3. Calculate missing information for linearelationships.
3.1cartesian Unit Name Analytic Geometry Unit Goals 1. Create table of values in order to graph &/or determine if a relation is linear. Determine slope 3. Calculate missing information for linearelationships.
Here are the exams I wrote when teaching Math 115 in Fall 2018 at Ferris State University. Each exam is followed by its solutions.
 Here are the exams I wrote when teaching Math 5 in Fall 208 at Ferris State University. Each exam is followed by its solutions. Fall 208 Exam. (a) Find the slope of the line passing through the points
Here are the exams I wrote when teaching Math 5 in Fall 208 at Ferris State University. Each exam is followed by its solutions. Fall 208 Exam. (a) Find the slope of the line passing through the points
Chapter 7: Systems of Linear Equations
 Chapter 7: Systems of Linear Equations Section 7.1 Chapter 7: Systems of Linear Equations Section 7.1: Developing Systems of Linear Equations Terminology: System of Linear Equations: A grouping of two
Chapter 7: Systems of Linear Equations Section 7.1 Chapter 7: Systems of Linear Equations Section 7.1: Developing Systems of Linear Equations Terminology: System of Linear Equations: A grouping of two
0-2. 2) Plot the points and connect them. X
 1) Pam s Pie Pantry had 2 backorders for cherry pies. Pam can bake 3 pies every hour. Fill in the blanks. Hours 0-2 Pies Practice 6C 2) Plot the points and connect them. 3) Write an equation for the line.
1) Pam s Pie Pantry had 2 backorders for cherry pies. Pam can bake 3 pies every hour. Fill in the blanks. Hours 0-2 Pies Practice 6C 2) Plot the points and connect them. 3) Write an equation for the line.
Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie. Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks
 Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by
Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by
Introduction to Systems of Equations
 Systems of Equations 1 Introduction to Systems of Equations Remember, we are finding a point of intersection x 2y 5 2x y 4 1. A golfer scored only 4 s and 5 s in a round of 18 holes. His score was 80.
Systems of Equations 1 Introduction to Systems of Equations Remember, we are finding a point of intersection x 2y 5 2x y 4 1. A golfer scored only 4 s and 5 s in a round of 18 holes. His score was 80.
One solution No solutions Infinite solutions
 6.5 Solving Systems by Inspection What makes a system of linear equations have a single solution, no solutions, or infinite solutions? One of the first representations we looked at for systems was the
6.5 Solving Systems by Inspection What makes a system of linear equations have a single solution, no solutions, or infinite solutions? One of the first representations we looked at for systems was the
Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Adding
 8.2 Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Adding 8.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve systems using the addition method 2. Solve applications of systems of equations The graphical method of solving equations, shown
8.2 Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Adding 8.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve systems using the addition method 2. Solve applications of systems of equations The graphical method of solving equations, shown
Unit 2 Solving Equations & Inequalities
 Coordinate Algebra Unit Solving Equations & Inequalities Name: Date: Unit Review Solve each system of linear equations by the given method. 1. Solve by Substitution: 5y 9 x y. Solve by Substitution: 15y
Coordinate Algebra Unit Solving Equations & Inequalities Name: Date: Unit Review Solve each system of linear equations by the given method. 1. Solve by Substitution: 5y 9 x y. Solve by Substitution: 15y
Algebra Unit 6 Test review white boards notea.notebook. February 02, y = y = a) (-3, -2) b) (1, -3) c) (0, -1) c) (2, 3) a) ( 1, 3) d) ( 3, 1)
 Unit 6 white board review 1. Find the solution to the graph on the right. ( 1, 3) (3, 1) c) (2, 3) d) ( 3, 1) Graph and find the point of intersection for each. 2. (-3, -2) (1, -3) c) (0, -1) 3. Graph
Unit 6 white board review 1. Find the solution to the graph on the right. ( 1, 3) (3, 1) c) (2, 3) d) ( 3, 1) Graph and find the point of intersection for each. 2. (-3, -2) (1, -3) c) (0, -1) 3. Graph
CC Math I UNIT 7 Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 CC Math I UNIT 7 Systems of Equations and Inequalities Name Teacher Estimated Test Date MAIN CONCEPTS Page(s) Study Guide 1 2 Equations of Circles & Midpoint 3 5 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 6 8 Systems
CC Math I UNIT 7 Systems of Equations and Inequalities Name Teacher Estimated Test Date MAIN CONCEPTS Page(s) Study Guide 1 2 Equations of Circles & Midpoint 3 5 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 6 8 Systems
Finite Math - Fall Section Present Value of an Annuity; Amortization
 Finite Math - Fall 016 Lecture Notes - 9/1/016 Section 3. - Present Value of an Annuity; Amortization Amortization Schedules. Suppose you are amortizing a debt by making equal payments, but then decided
Finite Math - Fall 016 Lecture Notes - 9/1/016 Section 3. - Present Value of an Annuity; Amortization Amortization Schedules. Suppose you are amortizing a debt by making equal payments, but then decided
Chapter 1: Precalculus Review
 : Precalculus Review Math 115 17 January 2018 Overview 1 Important Notation 2 Exponents 3 Polynomials 4 Rational Functions 5 Cartesian Coordinates 6 Lines Notation Intervals: Interval Notation (a, b) (a,
: Precalculus Review Math 115 17 January 2018 Overview 1 Important Notation 2 Exponents 3 Polynomials 4 Rational Functions 5 Cartesian Coordinates 6 Lines Notation Intervals: Interval Notation (a, b) (a,
6 which of the following equations would give you a system of equations with the same line and infinitely many solutions?
 Algebra 1 4 1 Worksheet Name: Per: Part I: Solve each system of equations using the graphing method. 1) y = x 5 ) -x + y = 6 y = x + 1 y = -x 3) y = 1 x 3 4) 4x y = 8 y = 1 x + 1 y = x + 3 5) x + y = 6
Algebra 1 4 1 Worksheet Name: Per: Part I: Solve each system of equations using the graphing method. 1) y = x 5 ) -x + y = 6 y = x + 1 y = -x 3) y = 1 x 3 4) 4x y = 8 y = 1 x + 1 y = x + 3 5) x + y = 6
Intermediate Algebra Semester Summary Exercises. 1 Ah C. b = h
 . Solve: 3x + 8 = 3 + 8x + 3x A. x = B. x = 4 C. x = 8 8 D. x =. Solve: w 3 w 5 6 8 A. w = 4 B. w = C. w = 4 D. w = 60 3. Solve: 3(x ) + 4 = 4(x + ) A. x = 7 B. x = 5 C. x = D. x = 4. The perimeter of
. Solve: 3x + 8 = 3 + 8x + 3x A. x = B. x = 4 C. x = 8 8 D. x =. Solve: w 3 w 5 6 8 A. w = 4 B. w = C. w = 4 D. w = 60 3. Solve: 3(x ) + 4 = 4(x + ) A. x = 7 B. x = 5 C. x = D. x = 4. The perimeter of
For the given equation, first find the x-intercept by setting y = 0: Next, find the y-intercept by setting x = 0:
 1. Find the x- and y-intercepts and graph the equation. 5x + 6y = 30 To find the x- and y-intercepts, set one variable equal to 0, and solve for the other variable. To find the x-intercept, set y = 0 and
1. Find the x- and y-intercepts and graph the equation. 5x + 6y = 30 To find the x- and y-intercepts, set one variable equal to 0, and solve for the other variable. To find the x-intercept, set y = 0 and
Strategic Math. General Review of Algebra I. With Answers. By: Shirly Boots
 Strategic Math General Review of Algebra I With Answers By: Shirly Boots 1/6 Add/Subtract/Multiply/Divide Addmoves to the right -3-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Subtract moves to the left Ex: -2 + 8 = 6 Ex: -2 8 = - 10
Strategic Math General Review of Algebra I With Answers By: Shirly Boots 1/6 Add/Subtract/Multiply/Divide Addmoves to the right -3-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Subtract moves to the left Ex: -2 + 8 = 6 Ex: -2 8 = - 10
Name Vetter Midterm REVIEW January 2019
 Name Vetter Midterm REVIEW January 2019 1. Name the property that justifies each step in the following equation: 3x + 1+ 2x 7 = x + 22 ( 3x + 2x + 1 7 = x + 22 ( (2) x(3 + 2) 6 = x+ 22 5x 6 = x+ 22 (3)
Name Vetter Midterm REVIEW January 2019 1. Name the property that justifies each step in the following equation: 3x + 1+ 2x 7 = x + 22 ( 3x + 2x + 1 7 = x + 22 ( (2) x(3 + 2) 6 = x+ 22 5x 6 = x+ 22 (3)
Algebra I Solving & Graphing Inequalities
 Slide 1 / 182 Slide 2 / 182 Algebra I Solving & Graphing Inequalities 2016-01-11 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 182 Table of Contents Simple Inequalities Addition/Subtraction click on the topic to go to that
Slide 1 / 182 Slide 2 / 182 Algebra I Solving & Graphing Inequalities 2016-01-11 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 182 Table of Contents Simple Inequalities Addition/Subtraction click on the topic to go to that
7.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 7.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Learn how to solve a sstem of linear equations b graphing Learn how to model a real-life situation using a sstem of linear equations With an equation, an
7.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Learn how to solve a sstem of linear equations b graphing Learn how to model a real-life situation using a sstem of linear equations With an equation, an
LESSON 2 ALGEBRA & FUNCTIONS
 LESSON ALGEBRA & FUNCTIONS A) SIMPLIFYING EXPRESSIONS An expression does not have an equal sign with a left side and a right side. In an expression we can only simplify rather than solve. Simplify each
LESSON ALGEBRA & FUNCTIONS A) SIMPLIFYING EXPRESSIONS An expression does not have an equal sign with a left side and a right side. In an expression we can only simplify rather than solve. Simplify each
WRITING EQUATIONS 4.1.1
 WRITING EQUATIONS 4.1.1 In this lesson, students translate written information, often modeling everyday situations, into algebraic symbols and linear equations. Students use let statements to specifically
WRITING EQUATIONS 4.1.1 In this lesson, students translate written information, often modeling everyday situations, into algebraic symbols and linear equations. Students use let statements to specifically
1. Write an expression of the third degree that is written with a leading coefficient of five and a constant of ten., find C D.
 1. Write an expression of the third degree that is written with a leading coefficient of five and a constant of ten. 2 2 2. If C = 4x 7x 9 and D = 5x 7x 3, find C D. 3. At an ice cream shop, the profit,,
1. Write an expression of the third degree that is written with a leading coefficient of five and a constant of ten. 2 2 2. If C = 4x 7x 9 and D = 5x 7x 3, find C D. 3. At an ice cream shop, the profit,,
Rising 8th Grade Math. Algebra 1 Summer Review Packet
 Rising 8th Grade Math Algebra 1 Summer Review Packet 1. Clear parentheses using the distributive property. 2. Combine like terms within each side of the equal sign. Solving Multi-Step Equations 3. Add/subtract
Rising 8th Grade Math Algebra 1 Summer Review Packet 1. Clear parentheses using the distributive property. 2. Combine like terms within each side of the equal sign. Solving Multi-Step Equations 3. Add/subtract
MFM2P Foundations of Mathematics Unit 3 Lesson 11
 The Line Lesson MFMP Foundations of Mathematics Unit Lesson Lesson Eleven Concepts Introduction to the line Using standard form of an equation Using y-intercept form of an equation x and y intercept Recognizing
The Line Lesson MFMP Foundations of Mathematics Unit Lesson Lesson Eleven Concepts Introduction to the line Using standard form of an equation Using y-intercept form of an equation x and y intercept Recognizing
OTHER METHODS FOR SOLVING SYSTEMS
 Topic 18: Other methods for solving systems 175 OTHER METHODS FOR SOLVING SYSTEMS Lesson 18.1 The substitution method 18.1 OPENER 1. Evaluate ab + 2c when a = 2, b = 3, and c = 5. 2. Following is a set
Topic 18: Other methods for solving systems 175 OTHER METHODS FOR SOLVING SYSTEMS Lesson 18.1 The substitution method 18.1 OPENER 1. Evaluate ab + 2c when a = 2, b = 3, and c = 5. 2. Following is a set
Directions: Answers must be left in one of the following forms:
 Directions: Answers must be left in one of the following forms: 1. Integer (example: 7) 2. Reduced fraction (example: 3/4) 3. Mixed number, fraction part simplified (example: 2 1/3) 4. Money: rounded to
Directions: Answers must be left in one of the following forms: 1. Integer (example: 7) 2. Reduced fraction (example: 3/4) 3. Mixed number, fraction part simplified (example: 2 1/3) 4. Money: rounded to
Math 60 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Xtra Practice: Section 2.7, Chapters 3 and 4
 Name of Math lover: my favorite student Date: Math 60 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Xtra Practice: Section 2.7, Chapters 3 and 4 Ok to use a calculator (But don t forget to show enough work in order to receive credit)
Name of Math lover: my favorite student Date: Math 60 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Xtra Practice: Section 2.7, Chapters 3 and 4 Ok to use a calculator (But don t forget to show enough work in order to receive credit)
Midterm Review Packet
 Algebra 1 CHAPTER 1 Midterm Review Packet Name Date Match the following with the appropriate property. 1. x y y x A. Distributive Property. 6 u v 6u 1v B. Commutative Property of Multiplication. m n 5
Algebra 1 CHAPTER 1 Midterm Review Packet Name Date Match the following with the appropriate property. 1. x y y x A. Distributive Property. 6 u v 6u 1v B. Commutative Property of Multiplication. m n 5
= $ m. Telephone Company B charges $11.50 per month plus five cents per minute. Writing that mathematically, we have c B. = $
 Chapter 6 Systems of Equations Sec. 1 Systems of Equations How many times have you watched a commercial on television touting a product or services as not only the best, but the cheapest? Let s say you
Chapter 6 Systems of Equations Sec. 1 Systems of Equations How many times have you watched a commercial on television touting a product or services as not only the best, but the cheapest? Let s say you
Checkpoint 1 Simplifying Like Terms and Distributive Property
 Checkpoint 1 Simplifying Like Terms and Distributive Property Simplify the following expressions completely. 1. 3 2 2. 3 ( 2) 3. 2 5 4. 7 3 2 3 2 5. 1 6 6. (8x 5) + (4x 6) 7. (6t + 1)(t 2) 8. (2k + 11)
Checkpoint 1 Simplifying Like Terms and Distributive Property Simplify the following expressions completely. 1. 3 2 2. 3 ( 2) 3. 2 5 4. 7 3 2 3 2 5. 1 6 6. (8x 5) + (4x 6) 7. (6t + 1)(t 2) 8. (2k + 11)
Systems of Equations. Red Company. Blue Company. cost. 30 minutes. Copyright 2003 Hanlonmath 1
 Chapter 6 Systems of Equations Sec. 1 Systems of Equations How many times have you watched a commercial on television touting a product or services as not only the best, but the cheapest? Let s say you
Chapter 6 Systems of Equations Sec. 1 Systems of Equations How many times have you watched a commercial on television touting a product or services as not only the best, but the cheapest? Let s say you
a. Bob: 7, Bridget: 4, Brian 1 b. Bob: 7, Bridget: 4, Brian 3 c. Bob: 7, Bridget: 14, Brian 3 a. 100 b. 150 c c. 2 d.
 Period: Date: K. Williams 8th Grade Year Review: Chapters -4. A neighborhood pool charges $22 for a pool membership plus an additional $2 for each visit to the pool. If Elliot visited the pool 6 times,
Period: Date: K. Williams 8th Grade Year Review: Chapters -4. A neighborhood pool charges $22 for a pool membership plus an additional $2 for each visit to the pool. If Elliot visited the pool 6 times,
Unit 8 Solving System of Equations
 Unit 8 Solving System of Equations NAME: GRADE: TEACHER: Ms. Schmidt _ Solving Systems of Linear Equations Graphically Classwork Day 1 Vocabulary: System of Equations: Solutions: When you graph two lines,
Unit 8 Solving System of Equations NAME: GRADE: TEACHER: Ms. Schmidt _ Solving Systems of Linear Equations Graphically Classwork Day 1 Vocabulary: System of Equations: Solutions: When you graph two lines,
ALGEBRA MIDTERM REVIEW SHEET
 Name Date Part 1 (Multiple Choice): Please show ALL work! ALGEBRA MIDTERM REVIEW SHEET 1) The equations 5x 2y 48 and 3x 2y 32 represent the money collected from school concert ticket sales during two class
Name Date Part 1 (Multiple Choice): Please show ALL work! ALGEBRA MIDTERM REVIEW SHEET 1) The equations 5x 2y 48 and 3x 2y 32 represent the money collected from school concert ticket sales during two class
Algebra 1. Math Review Packet. Equations, Inequalities, Linear Functions, Linear Systems, Exponents, Polynomials, Factoring, Quadratics, Radicals
 Algebra 1 Math Review Packet Equations, Inequalities, Linear Functions, Linear Systems, Exponents, Polynomials, Factoring, Quadratics, Radicals 2017 Math in the Middle 1. Clear parentheses using the distributive
Algebra 1 Math Review Packet Equations, Inequalities, Linear Functions, Linear Systems, Exponents, Polynomials, Factoring, Quadratics, Radicals 2017 Math in the Middle 1. Clear parentheses using the distributive
LAKOTA WEST HIGH SCHOOL HONORS ALGEBRA II EXPECTATIONS ( )
 LAKOTA WEST HIGH SCHOOL HONORS ALGEBRA II EXPECTATIONS (07-08) Upon entering Honors Algebra II class at Lakota West HS it will be expected that you to have an excellent understanding of certain topics
LAKOTA WEST HIGH SCHOOL HONORS ALGEBRA II EXPECTATIONS (07-08) Upon entering Honors Algebra II class at Lakota West HS it will be expected that you to have an excellent understanding of certain topics
Geometry 21 Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide
 Geometry Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide This study guide is designed to accompany the Geometry Summer Work Packet. Its purpose is to offer a review of the ten specific concepts covered in the
Geometry Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide This study guide is designed to accompany the Geometry Summer Work Packet. Its purpose is to offer a review of the ten specific concepts covered in the
Sect The Slope-Intercept Form
 0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables
 Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Graphing Inequalities To graph inequalities you will get y by itself and graph the line as usual. To take care of the inequality part, you do the following:
Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Graphing Inequalities To graph inequalities you will get y by itself and graph the line as usual. To take care of the inequality part, you do the following:
