TU/e University of Technology Eindhoven Mechanical Engineering
|
|
|
- Denis Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TU/ Unvrsty of Tcnology Endovn Mcancal Engnrng Stablty of Ntword Control Systms: Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Rolf Gaasb D&C.5 Fnal Baclor Projct (4W) Projct suprvsor: Projct coac: Dr. r. N. van d Wouw M.Sc. N.W. Baur R.I. Gaasb Fbruary
2 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag I bstract In ts rport w study stablty of a control systm wc communcats masurmnt data ovr a ntwor. T prsnc of t ntwor causs nformaton on sampld masurmnts to b snt n dgtal pacts; owvr all practcal actuators rqur a contnuous-tm nput sgnal. It s wdly accptd to apply a zro-ordr-old to convrt t dscrt-tm control sgnal to a contnuous on. Our contrbuton s a comparson btwn t zro-ordr-old (ZOH) a convntonal old wc olds ac sampld valu for on samplng ntrval to t systm-matcd-old (SMH) a spcfc typ of old wc mploys prdcton of t contnuous-tm closd-loop systm. T goal s to dtrmn wtr t systm-matcd-old mprovs robustnss for ntwor dlays and tm-varyng samplng ntrvals and trby gvs t NCS a largr stablty rgon. In ts rport w consdr tat t ntwor ntroducs two ffcts: varyng samplng ntvals and varyng dlays. W dstngus two cass: constant samplng ntrvals and transmsson dlays and t cas of on or bot of tm varyng. In t constant cas stablty analyss as bn don usng t gnvalu-basd stablty cc and by usng Lyapunov stablty tory. In t varyng cas a polytopc ovrapproxmaton of t uncrtan dscrt-tm NCS modl s mad wc nabls to formulat Lnar Matrx Inqualty (LMI) condtons guarantng (robust) asymptotc stablty. W compar t two olds by a numrcal xampl. W can conclud tat for constant ntwor dlays and samplng ntrvals a systm quppd wt t SMH (a smart old) as a sgnfcantly largr stabl ara. For varyng ntwor dlays and samplng ntrvals w also xpct a largr stabl ara wc w can prov for most cass. Howvr for t cas of small varyng ntwor dlays and samplng ntrvals mor systm stablty for t SMH s xpctd but cannot b provd.
3 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag II Tabl of Contnts bstract... I Tabl of Contnts... II. Introducton... Motvaton... B m for ts projct... C Structur of t rport.... Ntwor Control Systm modl... 3 Dscrpton of t Ntwor Control Systm... 3 B T zro-ordr old (ZOH)... 4 C Systm matcd old (SMH)... 4 D Closd-Loop Modl Stablty analyss for constant samplng ntrvals and dlays... 6 Prov stablty usng an gnvalu-basd stablty tst... 6 B Prov stablty usng Lyapunov tory... 7 C Illustratv Exampl Stablty analyss for tm varyng samplng ntrvals and dlays... 9 Polytopc ovrapproxmaton... 9 B Prov stablty for t varyng cas usng Lyapunov tory... C Illustratv xampl... D T study of stablty by smulaton Rsults... 6 Rsults for constant samplng ntrvals and transmsson dlays... 6 C Varyng cas smulaton-stablty-mtod Dscusson Concluson and Rcommndatons Rfrncs Dscrtsaton of t NCS... 4 Dtrmn... 4 B Dtrmn Rwrtng... 7 Rwrtng for t SMH... 7 B Rwrtng for t ZOH Matlab fls... 3
4 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag. Introducton Motvaton Ntword control systms (NCS) ar convnnt to us du to many advantags: as of nstallaton low mantnanc and modularty to nam a fw. Howvr t stablty of t systm can b lost by t prsnc of a wrd or wrlss ntwor n t control loop. Tr ar many communcaton ffcts wn consdrng a ntwor; n ts wor w consdr tat ts communcaton nducs varyng samplng ntrvals and transmsson dlays []. NCS ar sampld-data control systms. Wn dalng wt a sampld-data systm t dscrt-tm sgnal basd on t sampld masurmnt data s not an accptabl sgnal for t actuator and trfor nds to b convrtd to a contnuous-tm control sgnal. T convrson stp s don n t old; typcally a zro-ordr-old s usd wc olds t masurd sgnal at a constant valu for on samplng ntrval. Wat t controllr rcvs s vry dffrnt from t contnuous-tm output of t plant; t output s constant for a samplng ntrval and ts sampld valus ar rcvd by t controllr only aftr t transmsson dlay. To possbly mprov t contnuous-tm sgnal fd to t controllr a dffrnt typ of old could b usd wc s tund to t dynamcs of t plant. T da s to us a modl of t closd loop systm to mprov t nput sgnal to t controllr. Snc n practc a NCS always as varyng samplng ntrvals and transmsson dlays t s vry rasonabl to mnmz mpact of ts two uncrtan paramtrs by modfyng t nput sgnal of t controllr and trby ncras stablty of t NCS. In sort a smartr old could b abl to mnmz t nflunc of samplng ntrvals and transmsson dlays on t dffrnc btwn output sgnal of t plant and nput sgnal of t controllr. smartr old s trfor xpctd to gv t NCS mor robustnss aganst tm-varyng and uncrtan samplng ntrvals and transmsson dlay wc wll rsult n mor stablty. B m for ts projct In ts projct w wll focus on t mpact of t ntwor n t control loop usng a zroordr-old and a systm-matcd-old []. W wll loo at dffrnc btwn ts two typs of olds. T man part of our comparson wll b a stablty analyss comparson btwn t cas of constant samplng ntrvals and transmsson dlays and t cas wn samplng ntrvals and/or transmsson dlays vary. C Structur of t rport T outln of t rport s as follows. In Captr a dscrpton of t NCS a dscrpton of t olds and t closd-loop modl s prsntd. In Captr 3 t cas of constant samplng ntrvals and dlays s consdrd; ccng stablty for constant samplng ntrvals
5 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag and transmsson dlays usng t gnvalu stablty tory and t Lyapunov tory [3]. lso an llustratv xampl s consdrd. Captr 4 dals wt varyng samplng ntrvals and/or transmsson dlays. To prov stablty frst a polytopc ovrapproxmaton of an uncrtan dscrt-tm NCS modl s ntroducd and tn stablty analyss for t varyng cas s consdrd usng Lyapunov tory. Ts agan s word out n an llustratv xampl followd by smulatons. In Captr 5 t rsults of all stablty analyss ar gvn and compard. Captr 6 wll dscuss ts rsults and Captr 7 wll gv a concluson and rcommndatons. ll scrpts usd to ma stablty plots can b found as dgtal attacmnts.
6 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 3. Ntwor Control Systm modl In a classc control stup t controllr s consdrd to b drctly wrd to t plant. T output data of t plant and controllr s snt xactly at a spcfc constant samplngntrval wt no dlay. Howvr wn a controllr s mplmntd va a sard communcaton ntwor ts condtons ar not ralstc. In t control stup n ts projct varyng samplng-ntrvals and varyng dlays ar consdrd. Dscrpton of t Ntwor Control Systm For ts projct w consdr a closd-loop systm as dpctd n Fgur wr t plant dynamcs ar gvn by x x Bu() t () and t contnuous-tm stat-fdbac of t controllr s gvn by u( t) Kx ( t ). () T stat of t plant s assumd to b masurd at tm nstant s wc ylds t sampld masurmnt data x : x( s ). Ts sampld masurmnt data ar snt ovr t ntwor and consquntly dlayd by a dlay. T old mcansm convrts t sampld data x to a contnuous-tm functon x () t wc s t nput of t contnuous-tm controllr; f a nw sampl s rcvd x s rst to tat nw valu: x x t for t [ s s ) () x ( s ) x (3) wr x ( s ) dnots a stat rst at tm s. W consdr a cas n wc t samplng ntrval dfnd by s s satsfs and t sampld output arrvs at t old mcansm aftr a dlay τ wc s allowd to ta a valu n t rang. W spcfcally consdr t cas wn t dlay s assumd to always b smallr tan t samplng ntrval for all (.. ).
7 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 4 Fgur : Scmatc ovrvw of t NCS. Ts spcfc stup wc s scmatcally dpctd n Fgur s most valuabl wn snsors and actuators ar far apart. Ts s.g. t cas n watr dstrbuton ntwors. B T zro-ordr old (ZOH) Nowadays t most commonly usd typ of old s t zro-ordr old (ZOH). T zroordr old convrts a dscrt tm sgnal to a contnuous tm sgnal by oldng ac sampl valu for on samplng ntrval. Kpng (3) n mnd ts bavor can b modld wn x wc mans :. (4) C Systm matcd old (SMH) T systm matcd old (SMH) s a spcfc old tund to t dynamcs of t closd-loop systm mor spcfcally w wll dfn : BK. (5) W wll nvstgat n ts rport wtr ts spcfc old producs a systm wt mor robustnss n t prsnc of varyng samplng ntrvals and dlays. D Closd-Loop Modl Lt us dfn x x x as t stat of t closd-loop systm. Tang () () and (3) nto account t closd-loop dynamcs can b dscrbd as x BK x x for t [ s s ) x x (6) and xprncs a rst at tm s accordng to
8 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 5 x ( s ) xs ( ) x. (7) In ordr to analyz robust stablty of t systm gvn n (6) (7) w wll us tcnqus dvlopd for dscrt-tm paramtr varyng systms. Usng (6) (7) a dscrtsaton can b don. T dscrtsaton rsults n a dscrt-tm systm of t form x ( ) x (8) wr ( ) s t dscrt tm matrx. By tang two dffrnt approacs of dscrtsaton two ( ) matrcs ar drvd and usd for stablty analyss. To dstngus btwn tm ty ar dnotd ( ) and ( ). ( ) cl ( ) I I cl (9) ( ) ( ) r ( r) r ( r) BK dr BK dr ( ) () wr cl s gvn by cl BK. () T drvaton of ts two modls s ncludd n ppndx.. Of cours snc ( ) and ( ) dscrb t sam dynamcs w av tat ( ) ( ) ( ). ()
9 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 6 3. Stablty analyss for constant samplng ntrvals and dlays In ts captr w consdr t cas tat and () s a constant matrx wc w dnot by ( ) ar constant. Trfor ( ) n and t NCS s dscrbd by t dscrt-tm LTI systm x ( ) x. W can now xplot two tools for t purpos of stablty analyss; gnvalu-basd stablty tory and Lyapunov stablty tory. Prov stablty usng an gnvalu-basd stablty tst s dscrbd n Captr x ( ) x dscrbs t total modl. Snc ts s a dscrt-tm LTI systm t gnvalus of t matrx can dtrmn wtr t stats of t systm x wll convrg to t qulbrum x or not as gos to nfnty. T gnvalus of can b calculatd by solvng dt( I ). (3) If all gnvalus of av a modulus smallr tan.. t systm s asymptotcally stabl. In otr words f t gnvalus ar wtn t unt crcl as dsplayd n Fgur t NCS s asymptotcally stabl. s can b sn n () as svral ntgral componnts. To calculat t gnvalus of ts ntgrals nd to b solvd. Trfor w cc t gnvalus of snc ts form of t matrx dos not contan ntgral componnts. Fgur : Stabl gnvalus ar wtn t dpctd unt crcl.
10 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 7 B Prov stablty usng Lyapunov tory Provng stablty usng Lyapunov tory s t asst to undrstand by tnng of a pyscal systm and consdrng t Lyapunov functon to dscrb t stord nrgy of suc a systm. If t nrgy (Lyapunov functon) dcrass ovr tm t systm wll nd up n t qulbrum pont. T stat x of a systm s usd n a functon V x wc s postv dfnt and V. T functons V w consdr ar all of t followng quadratc form T T V x x Px wt P P. (4) If V x always dcrass tn w now x convrgs towards as gos to nfnty and t systm (8) wt s asymptotcally stabl. To cc f V s always dcrasng w can comput t ncrmnt V of t Lyapunov functon along solutons of t dscrt-tm systm and s wat t condtons ar to nsur tat t s ngatv. T condton w want to satsfy for stablty s trfor T T V V V x Px x Px. Substtutng (8) (wt ) for x V s qual to V V V x ( ) P ( ) x x Px T T T V V V x ( ) P ( ) P x. T T T abov nqualty s satsfd wn t followng lnar matrx nqualty (LMI) olds: T T ( ) P ( ) P wt P P. (5) W can now mploy an LMI solvr to sarc for a matrx P satsfyng (5). If t LMI-solvr fnds suc a P for wc (5) s vald stablty of t NCS s provd. For constant samplng ntrvals and dlays a good LMI solvr s always abl to fnd a vald P f t systm s stabl. Trfor wn usng a quadratc Lyapunov functon systm nstablty can also b provd. C Illustratv Exampl T tors xpland n scton 3. and 3.B bot us matrcs ar formd usng B to dtrmn stablty. Frst t and K 8 6 wc s a NCS wc uss t ZOH. By coosng dffrnt combnatons of and can b dtrmnd
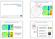
11 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 8 for all combnatons. T sam can b don for a NCS wc uss t SMH tn B and K 8 6. s can b sn n bot cass t sam valus of 8 6 B and K ar usd. By mang plots of provd stablty for t dffrnt combnatons of constant and w can compar t ZOH and t SMH and a gnral da of t stablty nflunc of t old can b gand. T plots ar dsplayd n Fgurs and 6. It can b sn tat t gnvalu cc xactly matcs t rsults of t Lyapunov functon cc. Blu = stablty Rd = nstablty Blu = stablty Rd = nstablty Fgur 3: Stablty cc usng gnvalu stablty tory for ZOH. Fgur 4: Stablty cc usng Lyapunov tory for ZOH. Blu = stablty Rd = nstablty Blu = stablty Rd = nstablty Fgur 5: Stablty cc usng gnvalu stablty tory for SMH. Fgur 6: Stablty cc usng Lyapunov tory for SMH. Fgurs and 6 gv a good comparson of t systm usng t SMH and t systm usng t ZOH. T rsults of t SMH ar mprssv; t actuator s fd wt a bttr nput sgnal wc translats nto a sgnfcantly largr stablty ara. Not only t systm wt t SMH s bttr capabl of dalng wt larg samplng ntrvals t also gvs mor robustnss aganst ntwor dlays. Howvr w nd to ta n mnd tat ts stablty analyss s only vald for constant and. In Fgur 5 and 6 w can also spot tat t systm usng t SMH sms to b stabl for arbtrarly larg samplng ntrvals n cas of no ntwor dlays. Snc t SMH s tund to t dynamcs of t closd-loop systm wc w av a prfct dscrpton of ts could b suspctd. It can also b provn usng t gnvalu stablty tory for t SMH. Wn w ta t xampl systm usng t SMH w fnd t followng gnvalus for ( ) : Snc t gnvalus ar always btwn and so n cas of no ntwor dlays t systm wt t SMH s always stabl. 4
12 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 9 4. Stablty analyss for tm varyng samplng ntrvals and dlays For t cas tat and ar tm-varyng and uncrtan s not a constant matrx. Snc and l n a compact st ( ) also ls n a compact matrx st. Trfor t gnvalu stablty tory of scton 3. cannot b usd. lso Lyapunov tory as sown n scton 3.B cannot b usd drctly bcaus of t uncrtants causd by t varyng and. Howvr t s possbl to ma a polytopc ovrapproxmaton of t uncrtan dscrt-tm NCS modl wc tn allows for LMI basd ccs to prov stablty. Polytopc ovrapproxmaton Lt us construct a polytopc ovrapproxmaton of systm (8). T polytopc ovrapproxmaton can b don n a fw stps. Frst w rwrt ( ) n t followng form: n ( ) ( ) S (6) wr ( ) ar scalar functons and S ar constant matrcs for... n. T systm matrx as dtrmnd n Scton.D: ( ) ( ) r ( r) r ( r) BK dr BK dr ( ). Tr ar two componnts n ts matrx wc contan or trms. Ts componnts ar s s and... ds. W can us t Jordan form of t contnuous-tm systm matrcs and (.g. QJQ wt J J J n ) to rwrt t s trms as follows Js s Q Q () s R J ns. (7)
13 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag T ntgrals can b rwrttn usng (7): b a b a s ( s) BK ds ( s) W BK ( s) T ds j j j b j a ( s) ( s) ds W BKT. (8) j j T rprsntaton of ( ) as n (6) can now b constructd by xplotng (7) (8). Ts as bn don compltly for an xampl cas s Scton.. W now av a systm dscrbd by (6) wc s not yt an ovrapproxmaton. T ovrapproxmaton of t uncrtan matrx ( ) for all and to b of t followng form: as ( ) co (9) N n wc co stands for convx ull. convx ull s dfnd by ts vrtcs N ; ts vrtcs ar t cornr ponts of a polytopc ovrapproxmaton as vsualzd n Fgur 7. ( ) as wrttn n (9) and vry otr matrx n t ara contand n t convx ull can b wrttn as convx combnatons of t vrtcs as follows: N ( ) for any and. N and () Fgur 7: Vsualzaton polytopc st wt 5 vrtcs. Consdrng (6) t mnmal and maxmal valus of ( ) can b calculatd by
14 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag mn : ( ) max ( ). () Usng ts mnmal and maxmal valus t vrtcs can b cratd. T vrtcs concrn all combnatons of mnmal and maxmal valus of t functons so n total n N vrtcs rsult wc can b dscrbd as follows: V V V V V V n n n n () V V V N n n Ts matrcs N ar calld t ovrapproxmaton vrtcs wc dfn t polytopc st as formulatd n (9) and (). Ts polytopc st s also calld t ovrapproxmaton systm snc all t dynamc bavors of t orgnal systm (8) ar dscrbd by t ovrapproxmatd systm. B Prov stablty for t varyng cas usng Lyapunov tory s can b rcalld from (5) of scton 3.B stablty can b provd wt t Lyapunov tory T by provng tat tr xsts a P P suc tat t followng LMI s satsfd T ( ) P ( ) P. s mntond bfor w cannot drctly us ts formula n t varyng cas snc s not constant. Howvr rcallng() all ar unnown constants but all ar constant matrcs wc ar nown. Wn w substtut () nto (5) w obtan N N N T P P wr and. (3) T nqualts n (3) can also b wrttn as N N T P P wr and. (4) Snc (4) s satsfd f t followng LMIs ar satsfd T P P N. (5)
15 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag T Ts mans tat w can us a LMI-solvr to fnd a matrx P P for wc (5) s vald and trfor prov stablty of our NCS wt varyng and varyng. If suc a matrx can b found for all t ovrapproxmaton vrtcs stablty s provd for t wol polytopc ovrapproxmaton (wc of cours contans ). Provng stablty of by mang a polytopc ovrapproxmaton and us t Lyapunov tory to prov stablty of t ovrapproxmaton vrtcs s furtr rfrrd to as LMI- OvrprxVrt-mtod. downsd of ts mtod s tat f t ovrapproxmaton s too larg muc consrvatsm could b addd and t may appn tat t uncrtan dscrt-tm NCS modl s stabl wl t cannot b provd du to t consrvatsm n t ovrapproxmaton. C Illustratv xampl Provng stablty for t cas of tm-varyng and can b don as dscrbd n scton 4.B. In ts scton t llustratv xampl of scton 3.C s laboratd for t varyng cas. Rcall for t NCS wt t ZOH t followng systm matrcs ar vald B B and K 8 6. For t NCS wt t SMH w av tat and K T frst stp of mang t polytopc ovrapproxmaton s rwrtng from () n a form of a product of constant matrcs and tm-varyng functons wc dpnd on and. Rcall tat: ( ) r ( r) r ( r) n BK dr BK dr ( ) ( ) S. ( ) W start by rwrtng t ( ) trm usng t Jordan form dcomposton of t matrx : s s S () s S s. (6) s Ts mtod can b usd for t otr trms nvolvng. W can also us t mtod as gvn n (8) to rwrt t ntgral trms ts s compltly word out n Scton.. Ts gvs us for t ZOH:
16 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag ZOH ( ) V ( ) ( ) (7) and for t SMH can b rwrttn as ( ) 4( ) SMH ( ) V ( ) ( ) 4 ( ) 4 4 (8) s word out n (9) () t polytopc st wc mbds t uncrtan matrx st ( ) s caractrzd by vrtcs wr ac vrtx s a
17 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 4 combnaton of mnmal and maxmal valus of s (so n total n N vrtcs s (9)). If tn and all vrtcs ar qual (.. tr s only on vrtx). If and ZOH (ts bcaus n bot cass ts rsults n 8 = 56 vrtcs for t SMH and 4 = 6 vrtcs for t s constant). Basd on t LMI cc (5) stablty plots can b mad; ts can b found n t rsults n scton 5.B. D T study of stablty by smulaton s alrady pontd out n Scton 4.B a downsd of t LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod s tat tr ar som scnaros n wc t NCS s stabl but stablty cannot b provd usng t LMI-basd mtod dscussd abov. For nstanc f w us t NCS wt t paramtrs of t llustratv xampl for t SMH: B and K 8 6 ; and us and. tn t LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod cannot prov stablty. Howvr ts pont can also b smulatd usng t dscrt-tm NCS modl x ( ) x. (9) By startng wt a crtan ntal condton x w can smulat t valu of x on stp furtr n tm. By calculat ac tmstp by tang a random.. and.... T componnts of x can b plottd aganst t tm. Fgur 8 s suc a plot for t dscussd cas of.. and.... Dspt t lac of proof of stablty va t LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod Fgur 8 s a plot of a stabl systm. Fgur 8: Smulatd componnts of systm output n tm.
18 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 5 Of cours for t sam ntal condton x ts plot s dffrnt vry run snc t valus of and ar cosn randomly vry run. To gv suc smulatons somwat mor rlablty ty can b rpatd (ac tm wt nwly gnratd random and ). Howvr t s mpossbl to dtrmn t 'worst cas' squnc of and trfor dtrmnng stablty by smulaton s xtrmly unrlabl. ltoug suc a smulaton s not a good way to vrfy stablty t s an accptabl way to dsprov stablty. In t sns tat f t LMI ccs say t systm s stabl t only tas on unstabl smulaton to say tat t systm s n fact not guarantd to b stabl. To cc for stablty by smulaton n smulaton runs ar don. Evry run s as long as tm stps. If for all n smulaton runs at tm stp t absolut valu of vry componnt of x s smallr tan t maxmum absolut valu m t combnaton of and s suggstd to b stabl. Stablty of cours can nvr b rlabl provd n ts way snc t n smulaton could av dvrgd from zro. lso an nstablty suggston sn t rlabl; bcaus f m s tan too strct (or to small) nstablty could b suggstd wn t systm s stabl. Ts smulaton basd mtod of vrfyng stablty wc of cours s not a rlabl way to prov stablty can also b usd as a 'santy cc' to ma stablty plots. Ts can b found n t Rsults (Captr 5). T mtod wll b rfrrd to as smulaton-stabltymtod and can gv an ndcaton of stablty.
19 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 6 5. Rsults W want to dtrmn wtr for a crtan NCS t SMH as a bttr robustnss for varyng ntwor dlays and varyng samplng ntrvals tan t ZOH. To b abl to compar t two olds stablty plots nd to b mad on ntwor dlays bot for varyng and nonvaryng samplng ntrvals and transmsson dlays. Trfor mtods of Captr 3 and 4 can b usd. ltoug all mtods ar not lmtd to on systm t rsults ar gnratd usng a spcfc NCS wt t followng paramtrs for t ZOH: B and K 8 6. nd for t SMH t paramtrs: B and K By usng t sam systm mtods can b compard. Rsults for constant samplng ntrvals and transmsson dlays For constant and LTI systm x ( ) x dscrbs t dynamcs of t total modl. Snc ts s a dscrt-tm LTI systm t gnvalu-basd stablty cc as dscrbd n scton 3. gvs us t stablty plots as gvn n Fgur 9 and. Blu = stablty provd Rd = nstablty provd Blu = stablty provd Rd = nstablty can t provd b provd Fgur 9: Stablty cc ZOH. Fgur : Stablty cc SMH. Snc t SMH s tund to t dynamcs of t closd-loop systm t as a sgnfcant largr stabl ara. Not only t systm wt t SMH s bttr capabl of dalng wt larg samplng ntrvals t also gvs mor robustnss aganst ntwor dlays. lso t systm usng t SMH sms to b stabl for arbtrarly larg samplng ntrvals n cas of no ntwor dlays ; proof can b found n Scton 3.C. Howvr w nd to ta n mnd tat ts stablty analyss s only vald for constant and.
20 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 7 B Cas tm-varyng dlays and samplng ntrvals LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod Wn and/or ar not constant s not a constant matrx. By mang a polytopc ovrapproxmaton as dscussd n Scton 4. systm stablty can b provn for crtan bounds and on t tm-varyng dlays and samplng ntrvals. If w substtut t ovrapproxmaton vrtcs nto t ncrmnt of a Lyapunov functon (as xpland n Scton 4.B) w can prov stablty by solvng an LMI. Trfor stablty of t ovrapproxmaton systm can b provd wt usng a LMI-solvr. Stablty plots mad wt t LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod ar gvn n Fgur 3 and 4. Ts ar gnratd wt a Matlab scrpt gvn n.3. Dpctd n Fgur and ar t stablty plots wt.3. Wn w loo at Fgur 9 and t can b spottd tat for.3 and constant dlays w av bot a stabl and an unstabl ara for bot of t olds. Trfor ts cas s ntrstng snc w can spot robustnss and stablty around t boundary of t stabl ara. Fgur and 3 ar t stablty plots wt.. Wn w loo at Fgur 9 and for. t SMH s always stabl. Howvr w don t now anytng about t robustnss aganst varyng samplng ntrvals wc w can plot usng t LMI-OvrprxVrtmtod. Blu = stablty provd Rd = stablty can t b provd Blu = stablty provd Rd = stablty can t b provd Fgur : Stablty cc ZOH =.3. Fgur : Stablty cc SMH =.3. Blu = stablty provd Rd = stablty can t b provd Blu = stablty provd Rd = stablty can t b provd Fgur 3: Stablty cc ZOH τ =.. Fgur 4: Stablty cc SMH τ =..
21 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 8 In gnral t SMH as a bggr stablty rgon for constant and and gvs bttr robustnss aganst tr of tm varyng. Ts s as xpctd and t LMI-OvrprxVrtmtod gvs proof for tat owvr wn and ar small and trfor t varyng n t dlays rlatvly small t ZOH sms to b mor robust aganst dlays. Ts mans tat t LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod s unabl to fnd a proof for stablty wt t SMH wn and ar small. T systm could tn tr b unstabl or t s stabl but t LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod cannot prov stablty. Ts could b causd by varous rasons furtr xpland n Captr 6. C Varyng cas smulaton-stablty-mtod Snc t LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod gvs som unxpctd stablty plots for small and t smulaton-stablty-mtod as dscrbd n scton 6.D can tr partly confrm or rjct ts rsults. Of cours snc t smulaton-stablty-mtod as no provng caractr ts plots wll not provd proof for anytng. Fgur 5- gv stablty plots wc ar mad usng t smulaton-stablty-mtod. Wn t ttl ndcats unform a unform dstrbuton s usd for cratng t random and for ac stp. Evn so normal ndcats a normal dstrbuton. Wn comparng Fgur 5- wt Fgur -4 som ponts ar mard unstabl wn usng t smulaton-stablty-mtod but ar provd to b stabl by t LMI-OvrprxVrtmtod. Ts s du to t paramtrs of t smulaton-basd stablty cc. s xpland n scton 6.D a smulaton s tm stps long and wll b rpatd n tms. If for all n smulaton runs at tm stp t absolut valu of vry componnt of x s smallr tan maxmum absolut valu m t combnaton of and s suggstd to b stabl. In Fgur 5- t xampl systm s bng analyzd usng t smulaton-stablty-mtod usng t paramtrs m.and n 5. Blu = stablty suggstd Rd = nstablty suggstd Blu = stablty suggstd Rd = nstablty suggstd Fgur 5: Stablty cc ZOH =.3. Fgur 6: Stablty cc SMH =.3.
22 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 9 Blu = stablty suggstd Rd = nstablty suggstd Blu = stablty suggstd Rd = nstablty suggstd Fgur 7: Stablty cc ZOH =.3. Fgur 8: Stablty cc SMH =.3. Blu = stablty suggstd Rd = nstablty suggstd Blu = stablty suggstd Rd = nstablty suggstd Fgur 9: Stablty cc ZOH τ =.. Fgur : Stablty cc SMH τ =.. Blu = stablty suggstd Rd = nstablty suggstd Blu = stablty suggstd Rd = nstablty suggstd Fgur : Stablty cc ZOH τ =.. Fgur : Stablty cc SMH τ =.. In som cass at tm stp t absolut valu s bggr tan maxmum absolut valu m altoug t valus do slowly convrg to. Du to ts fact som ponts ar mard unstabl wl n ralty ty ar not. Ts can b sn n Fgur 9 and for larg tr stablty as alrady bn provd usng t LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod but t spcfc run of smulaton-stablty-mtod gvs an nstablty suggston. Of cours t s also possbl tat at tm stp t absolut valu s smallr tan m but t systm s unstabl. Trfor t smulaton-stablty-mtod as no provng caractr.
23 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag Howvr t smulaton-stablty-mtod dos ndcat a sgnfcantly largr stablty ara for t SMH. Trfor t s xpctd tat t SMH s also mor robust aganst small ntwor dlays and samplng ntrvals but t LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod s unabl to prov tat.
24 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 6. Dscusson s rportd n Captr 5 som of t rsults wr unxpctd or can t b provn. Ts captr wll gv som ntrprtaton to ts cass by suggstng crtan tors. lso t probablty of ts tors s xamnd. Wn loong at t constant cas (Captr 3) wr ( ) s constant t gnvalu-basd stablty tory gvs t sam stablty ara as t Lyapunov tory. In t cas tat and as dscussd n captr 4 t LMI- OvrprxVrt-mtod provs tat t SMH also as a bttr robustnss. Howvr on low valus of dlays t ZOH sms to av bttr robustnss for varyng dlays. T smulaton-stablty-mtod on t otr and dos suggst a bttr robustnss for t SMH also n cas of small varyng dlays. Howvr snc t only smulats t dscrt-tm NCS modl usng matrcs ( ) wr and ta random valus for ac ts can nvr guarant stablty for vry squnc of and. Tr ar tr tngs wc could b causng ts rsults. T frst s tat t LMI-solvr dos not succd n fndng t propr Lyapunov functon and trfor can t prov stablty wn tr rally s stablty. Possbly a paramtrdpndant Lyapunov functon [4] would b mor ffctv n provng stablty. scond suspcon s tat t rsults of t smulaton-stablty-mtod ar unrlabl. Dspt t fact tat t can nvr b provd tat t stablty suggstons of t smulatonstablty-mtod ar corrct t paramtrs for t m and n usd n mang t plots ar vry strct (a larg numbr of runs for low tm stps and a strct margn) wc ncrass t valu of ts mtod. Lastly t s possbl tat t polytopc ovrapproxmaton s too larg. Wn tr s unstabl ara n t polytopc ovrapproxmaton but t systm tslf s stabl stablty can t b provd by t LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod. s xpland n Scton 4. all matrcs wtn t ovrapproxmaton systm can b wrttn as lnar combnatons of t vrtcs n t convx ull. In cas of t SMH t convx ull xsts of 56 unqu vrtcs. In cas of t ZOH t convx ull xsts of only 6 vrtcs. T larg amount of vrtcs for t SMH may ndcat a poor ovrapproxmaton. If ndd t ovrapproxmaton s poor ts could b t rason for an nfasbl soluton. ltoug tr s no guarant tat a tgt ovrapproxmaton rsults n fasblty of t LMI condtons a tgtr ovrapproxmaton wll provd a bttr rprsntaton of t NCS and tus mor accurat LMI-basd stablty rsults. Futur wor could focus on loong nto ow to tgtn t ovrapproxmaton.
25 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 7. Concluson and Rcommndatons In stablty analyss of a ntword control systm (NCS) wt tm-varyng samplng ntrvals and transmsson dlays t old s oftn assumd as gvn; typcally bng a zro-ordr old. Howvr t can b dsgnd n dffrnt ways and t plays an mportant rol n t stablty of t NCS. In ts rport w compar t zro-ordr-old (ZOH) a convntonal old wc olds ac sampld valu for on samplng ntrval and t systm-matcd-old (SMH) a spcfc old tund to t dynamcs of t closd-loop systm. Wn and ar constant. T stablty ara of t SMH s sgnfcantly largr tan t stablty ara of t ZOH. Ts as bn provd usng t gnvalu-stablty-cc. Wn and/or ar not constant t systm matrx of t uncrtan dscrt-tm NCS modl contans trms wc dpnd nonlnarly on t uncrtanty paramtrs and. Howvr a polytopc ovrapproxmaton systm can b constructd and t stablty of t systm can b analyzd basd on t ovrapproxmaton vrtcs. T stablty of ts vrtcs can b vrfd by a LMI cc snc t ovrapproxmatd systm contans t dynamcs of t orgnal NCS. Trfor stablty of t NCS can b provd wt Lyapunov tory usng an LMI-basd tcnqu. s xpctd t SMH as a bggr stablty ara tan t ZOH. Howvr wn t varyng ntrval of and ar rlatvly small t ZOH sms to b mor robust aganst varyng and. W can also do ts cc smulatng t systm x ( ) x wr w calculat ac tmstp by tang a random and. T stablty plots rsultng from ts smulaton basd approac ndcat tat t SMH not only as a bggr ara but s also mor robust aganst varyng and wn t varyng ntrval s rlatvly small. T rason w suspct tat t smulaton basd stablty tst sows a largr stablty rgon for t SMH tan t ovrapproxmaton stablty tst s tat t polytopc ovrapproxmaton for t SMH s too larg. Wn t polytopc ovrapproxmaton s too larg n spt of t fact tat t NCS s stabl t polytopc ovrapproxmaton also contans an unstabl ara; tn stablty cannot b provd by t LMI-OvrprxVrt-mtod. In furtr rsarc on ts mattr t cas of varyng and sould b furtr studd. Ts can b don by usng anotr stablty cc or by optmzng t LMI-OvrprxVrtmtod. Possbly a paramtr-dpndant Lyapunov functon [5] would b mor ffctv n provng stablty. lso a tgtr polytopc ovrapproxmaton can mprov t mtod. Hopfully wt ts masurs bttr robustnss aganst varyng dlays can also b provd for rlatvly small varyng ntrvals.
26 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 3 8. Rfrncs [] W Zang Mcal S. Brancy and Stpn M. Pllps () Stablty of Ntword Control Systms IEEE Control Systms Magazn. [] Gawtrop Ptr J. and Wang Lupng (9) Constrand ntrmttnt modl prdctv control Intrnatonal Journal of Control 8: [3] João P. Hspana (7) Cours n Lnar Systms Tory [4] M.B.G. Cloostrman L. Htl N. van d Wouwa W.P.M.H. Hmlsa J. Daafouz H. Njmjr () Controllr syntss for ntword control systms utomatca
27 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 4. Dscrtsaton of t NCS To b abl to dtrmn stablty of t NCS a dscrtsaton of t sampld-data NCS dynamcs nds to b don. Tang nto account () () and (3) t closd-loop dynamcs of t NCS can b dscrbd wt t stat x x x. W rcall tat t sampld-data NCS dynamcs s dscrbd as follows: x BK x x for t s s x x x ( s ) xs ( ) x. (3) Usng (3) a dscrtsaton can b don n two ways ladng n a dscrt-tm NCS modl of t form: x ( ) x T two ways dffr n t matrx ( ). Trfor t matrx can b wrttn n two ways wc wll b rfrrd to as and. Dtrmn Frst w loo at. From (3) w can conclud tat: x s x s x cl ( ) ( ) ( ) and ( s ) I x s cl ( ) ( ) cl ( ) ( ) x I x( s ) I x s (3) x s x s (3) ( ) ( ) cl ( ) wr cl s gvn by
28 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 5 cl BK. Combnng (3) and (3) gvs us t followng xprsson: x x s x ( ) cl ( ) cl ( ) x x I I n wc w rcognz t dscrt-tm NCS modl x ( ) x wt I cl ( ) cl ( ) I. B Dtrmn Frst lt us valuat t soluton of t old n on samplng ntrval. x t x s for t s s ( t s) ( ) ( ) x ( s ) x x t x for t s s ( t s ) ( ) x ( s ) x ( ) Now w can dtrmn voluton of t plant stat xt () at t s by s ( s s ) ( s ) s x( s ) x BKx ( ) d s ( ) ( s ) ( s ) s x BK x ( s ) d s s ( s ) ( s ) BK xd. To solv t ntgrals w cang t boundars by coosng r s :
29 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 6 ( ) ( ) ( ) r r ( ) x s x BK x s dr r ( r) BK xdr wc can b wrttn n matrx form as: x ( ) r ( r) r ( r) BK dr BK dr ( ) x Wn w rwrt ts n t convoluton x x( s ) x w can also fnd ( ) r ( r) r ( r) BK dr BK dr ( ).
30 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 7 In ts attacmnt. Rwrtng s rwrttn nto a form of ( ) V. Ts only for t spcfc llustratv xampl as dscussd n t rport. T llustratv xampl for t ZOH s: B and K 8 6 nd for t NSC wt t SMH: B and K s provd bfor ( ) r ( r) r ( r) BK dr BK dr ( ). (33) Rwrtng for t SMH ll functons wtn can b rwrttn n t form ( ) V. Startng wt t trm ( ) w av tat: s s S () s S wr S I S and () s s. ( ) Ts can also b don for : s ( s) T ( s) T wr s T 4 () s s and T. 4 () 4s T trm n t ntgral can b rwrttn as follows:
31 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 8 r BK ( r) S ( r) S BK ( r) T ( r) T S BKT ( r) S BKT ( r) S BKT ( r) ( r) S BKT ( r) ( r). Ts can b substtutd n t frst ntgral n (33): r ( r) BK dr S BKT ( r) dr S BKT ( r) dr S BKT ( r) ( r) dr S BKT ( r) ( r) dr ( r ( r ) ) 8 r ( r ) 4( r ) ( ) r ( ) ( ) 4( ) 4( ). T scond ntgral can b rwrttn nto: r ( r) ( r) BK dr S BKT dr 4( r) ( r) S BKT dr S BKT r dr S BKT r dr 8 4( r) ( r )
32 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 9 4( r ) r ( r ) ( r ) 6 8 4r ( ) ( ) Snc now all trms ar word out ty can b flld nto t total dscrt-tm matrx as follows: ( ) r ( r) r ( r) BK dr BK dr ( ) () () () (). (34) T sparat trms n (34) can b wrttn as: 4 4 ( ) 4( ) () ( ) () ( ) 4 4 () 4 4 () 4 ( ) 4 wc gvs for t SMH: 4 V ( ) ( ) SMH 4( ) 4 ( ) 4 4 4
33 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag ( ) ( ). B Rwrtng for t ZOH Wn w ta t sam approac as wt t SMH as dscussd n t prvous scton; w can also us t systm wt t ZOH: B and K 8 6. Tn w obtan t followng matrx for : ZOH ( ) V ( ) ( ).
34 Do smart olds mprov robustnss for ntwor dlays? Pag 3.3 Matlab fls Ts CD contans all Matlab fls usd to ma t plots wc ar dsplayd n ts rport. Tabl gvs an ovrvw of t fls and tr dscrpton. Tabl Matlab fls gn.m systm_on_zoh.m systm_on_smh.m smulat_plot.m smu.m stab_cc.m runnr_const.m runnr_tauconst.m runnr_mnmn.m % Ts functon gnrats t matrx dt wc dscrbs % t systm. T gnvalus of ts matrx ar ccd % f t modulus of t gnvalus ar all smallr tan %. Stablty valus ar. Ts s don for bot t % ZOH (mard n t scrpt) and t SMH (mard ). % Ts functon crats an OvrprxVrt (a st % of vrtcs wc s gratr tan t stuat- % onmatrx w want to cc for stablty). T % functon s only usabl n t cas of systm % wt t zro-ordr old: % = [ ; ]; B = [ ; ]; K = [8 6]; = [ ; ]; % Ts functon crats an OvrprxVrt (a st % of vrtcs wc s gratr tan t stuat- % onmatrx w want to cc for stablty). T % functon s only usabl n t cas of systm % wt t systm matcd old: % = [ ; ]; B = [ ; ]; K = [8 6]; = [ - B* ] % Ts functon gvs out n plots smulatng X for ZOH % and SMH. It smulats X X... Xstps_. Plots ar % savd n worspac. Bcaus of random varyng dlays % vry plot sould b dffrnt. If output == _ % and tau_ ar dsplayd. If lgnds == t lgnds % ar dsplayd. % Ts functon smulats valus of x n tm usng t % convoluton X+=dtX. Usng a dt formd of random % componnts and tau. Smulaton s don for as long as % tmstps and rpat t n tms. If t absolut valu % of vry componnt of x s smallr tan x for tmstp % for ac of t n tms. Stablty s suggstd and % stablty output of ts functon s otrws t % output s. Stablty s onc ccd usng unform % dstrbuton for tang random valus and onc for usng % normal dstrbuton. % Stab_cc uss and tau (wc conssts of mnmal and % maxmal and tau). nd for tat spcfc combnaton of % _mn _max tau_mn tau_max t calculats stablty % usng svral dffrnt mtods. ll mtods ar addd to a % -cll. % Ts functon gnrats stablty plots for % fxd and varyng tau_mn and tau_max. % It uss t functon stabl_cc to gt all % stablty data for svral stablty-dtr- % mnaton mtods. Ts data s usd to ma % t plots plots ar also savd as *.png. % Ts functon gnrats stablty plots for % fxd tau and varyng _mn and _max. % It uss t functon stabl_cc to gt all % stablty data for svral stablty-dtr- % mnaton mtods. Ts data s usd to ma % t plots plots ar also savd as *.png. % Ts functon gnrats stablty plots for % fxd _mn and tau_mn and varyng maxmals. % It uss t functon stabl_cc to gt all % stablty data for svral stablty-dtr- % mnaton mtods. Ts data s usd to ma % t plots plots ar also savd as *.png.
167 T componnt oftforc on atom B can b drvd as: F B =, E =,K (, ) (.2) wr w av usd 2 = ( ) =2 (.3) T scond drvatv: 2 E = K (, ) = K (1, ) + 3 (.4).2.2
 166 ppnd Valnc Forc Flds.1 Introducton Valnc forc lds ar usd to dscrb ntra-molcular ntractons n trms of 2-body, 3-body, and 4-body (and gr) ntractons. W mplmntd many popular functonal forms n our program..2
166 ppnd Valnc Forc Flds.1 Introducton Valnc forc lds ar usd to dscrb ntra-molcular ntractons n trms of 2-body, 3-body, and 4-body (and gr) ntractons. W mplmntd many popular functonal forms n our program..2
Economics 600: August, 2007 Dynamic Part: Problem Set 5. Problems on Differential Equations and Continuous Time Optimization
 THE UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND COLLEGE PARK, MARYLAND Economcs 600: August, 007 Dynamc Part: Problm St 5 Problms on Dffrntal Equatons and Contnuous Tm Optmzaton Quston Solv th followng two dffrntal quatons.
THE UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND COLLEGE PARK, MARYLAND Economcs 600: August, 007 Dynamc Part: Problm St 5 Problms on Dffrntal Equatons and Contnuous Tm Optmzaton Quston Solv th followng two dffrntal quatons.
A Note on Estimability in Linear Models
 Intrnatonal Journal of Statstcs and Applcatons 2014, 4(4): 212-216 DOI: 10.5923/j.statstcs.20140404.06 A Not on Estmablty n Lnar Modls S. O. Adymo 1,*, F. N. Nwob 2 1 Dpartmnt of Mathmatcs and Statstcs,
Intrnatonal Journal of Statstcs and Applcatons 2014, 4(4): 212-216 DOI: 10.5923/j.statstcs.20140404.06 A Not on Estmablty n Lnar Modls S. O. Adymo 1,*, F. N. Nwob 2 1 Dpartmnt of Mathmatcs and Statstcs,
The Hyperelastic material is examined in this section.
 4. Hyprlastcty h Hyprlastc matral s xad n ths scton. 4..1 Consttutv Equatons h rat of chang of ntrnal nrgy W pr unt rfrnc volum s gvn by th strss powr, whch can b xprssd n a numbr of dffrnt ways (s 3.7.6):
4. Hyprlastcty h Hyprlastc matral s xad n ths scton. 4..1 Consttutv Equatons h rat of chang of ntrnal nrgy W pr unt rfrnc volum s gvn by th strss powr, whch can b xprssd n a numbr of dffrnt ways (s 3.7.6):
1) They represent a continuum of energies (there is no energy quantization). where all values of p are allowed so there is a continuum of energies.
 Unbound Stats OK, u untl now, w a dalt solly wt stats tat ar bound nsd a otntal wll. [Wll, ct for our tratnt of t fr artcl and w want to tat n nd r.] W want to now consdr wat ans f t artcl s unbound. Rbr
Unbound Stats OK, u untl now, w a dalt solly wt stats tat ar bound nsd a otntal wll. [Wll, ct for our tratnt of t fr artcl and w want to tat n nd r.] W want to now consdr wat ans f t artcl s unbound. Rbr
Grand Canonical Ensemble
 Th nsmbl of systms mmrsd n a partcl-hat rsrvor at constant tmpratur T, prssur P, and chmcal potntal. Consdr an nsmbl of M dntcal systms (M =,, 3,...M).. Thy ar mutually sharng th total numbr of partcls
Th nsmbl of systms mmrsd n a partcl-hat rsrvor at constant tmpratur T, prssur P, and chmcal potntal. Consdr an nsmbl of M dntcal systms (M =,, 3,...M).. Thy ar mutually sharng th total numbr of partcls
COMPLEX NUMBER PAIRWISE COMPARISON AND COMPLEX NUMBER AHP
 ISAHP 00, Bal, Indonsa, August -9, 00 COMPLEX NUMBER PAIRWISE COMPARISON AND COMPLEX NUMBER AHP Chkako MIYAKE, Kkch OHSAWA, Masahro KITO, and Masaak SHINOHARA Dpartmnt of Mathmatcal Informaton Engnrng
ISAHP 00, Bal, Indonsa, August -9, 00 COMPLEX NUMBER PAIRWISE COMPARISON AND COMPLEX NUMBER AHP Chkako MIYAKE, Kkch OHSAWA, Masahro KITO, and Masaak SHINOHARA Dpartmnt of Mathmatcal Informaton Engnrng
Analyzing Frequencies
 Frquncy (# ndvduals) Frquncy (# ndvduals) /3/16 H o : No dffrnc n obsrvd sz frquncs and that prdctd by growth modl How would you analyz ths data? 15 Obsrvd Numbr 15 Expctd Numbr from growth modl 1 1 5
Frquncy (# ndvduals) Frquncy (# ndvduals) /3/16 H o : No dffrnc n obsrvd sz frquncs and that prdctd by growth modl How would you analyz ths data? 15 Obsrvd Numbr 15 Expctd Numbr from growth modl 1 1 5
Review - Probabilistic Classification
 Mmoral Unvrsty of wfoundland Pattrn Rcognton Lctur 8 May 5, 6 http://www.ngr.mun.ca/~charlsr Offc Hours: Tusdays Thursdays 8:3-9:3 PM E- (untl furthr notc) Gvn lablld sampls { ɛc,,,..., } {. Estmat Rvw
Mmoral Unvrsty of wfoundland Pattrn Rcognton Lctur 8 May 5, 6 http://www.ngr.mun.ca/~charlsr Offc Hours: Tusdays Thursdays 8:3-9:3 PM E- (untl furthr notc) Gvn lablld sampls { ɛc,,,..., } {. Estmat Rvw
CHAPTER 33: PARTICLE PHYSICS
 Collg Physcs Studnt s Manual Chaptr 33 CHAPTER 33: PARTICLE PHYSICS 33. THE FOUR BASIC FORCES 4. (a) Fnd th rato of th strngths of th wak and lctromagntc forcs undr ordnary crcumstancs. (b) What dos that
Collg Physcs Studnt s Manual Chaptr 33 CHAPTER 33: PARTICLE PHYSICS 33. THE FOUR BASIC FORCES 4. (a) Fnd th rato of th strngths of th wak and lctromagntc forcs undr ordnary crcumstancs. (b) What dos that
CHAPTER 7d. DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION
 CHAPTER 7d. DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION A. J. Clark School o Engnrng Dpartmnt o Cvl and Envronmntal Engnrng by Dr. Ibrahm A. Assakka Sprng ENCE - Computaton Mthods n Cvl Engnrng II Dpartmnt o Cvl and
CHAPTER 7d. DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION A. J. Clark School o Engnrng Dpartmnt o Cvl and Envronmntal Engnrng by Dr. Ibrahm A. Assakka Sprng ENCE - Computaton Mthods n Cvl Engnrng II Dpartmnt o Cvl and
10/7/14. Mixture Models. Comp 135 Introduction to Machine Learning and Data Mining. Maximum likelihood estimation. Mixture of Normals in 1D
 Comp 35 Introducton to Machn Larnng and Data Mnng Fall 204 rofssor: Ron Khardon Mxtur Modls Motvatd by soft k-mans w dvlopd a gnratv modl for clustrng. Assum thr ar k clustrs Clustrs ar not rqurd to hav
Comp 35 Introducton to Machn Larnng and Data Mnng Fall 204 rofssor: Ron Khardon Mxtur Modls Motvatd by soft k-mans w dvlopd a gnratv modl for clustrng. Assum thr ar k clustrs Clustrs ar not rqurd to hav
Heisenberg Model. Sayed Mohammad Mahdi Sadrnezhaad. Supervisor: Prof. Abdollah Langari
 snbrg Modl Sad Mohammad Mahd Sadrnhaad Survsor: Prof. bdollah Langar bstract: n ths rsarch w tr to calculat analtcall gnvalus and gnvctors of fnt chan wth ½-sn artcls snbrg modl. W drov gnfuctons for closd
snbrg Modl Sad Mohammad Mahd Sadrnhaad Survsor: Prof. bdollah Langar bstract: n ths rsarch w tr to calculat analtcall gnvalus and gnvctors of fnt chan wth ½-sn artcls snbrg modl. W drov gnfuctons for closd
GPC From PeakSimple Data Acquisition
 GPC From PakSmpl Data Acquston Introducton Th follong s an outln of ho PakSmpl data acquston softar/hardar can b usd to acqur and analyz (n conjuncton th an approprat spradsht) gl prmaton chromatography
GPC From PakSmpl Data Acquston Introducton Th follong s an outln of ho PakSmpl data acquston softar/hardar can b usd to acqur and analyz (n conjuncton th an approprat spradsht) gl prmaton chromatography
CHAPTER 4. The First Law of Thermodynamics for Control Volumes
 CHAPTER 4 T Frst Law of Trodynacs for Control olus CONSERATION OF MASS Consrvaton of ass: Mass, lk nrgy, s a consrvd proprty, and t cannot b cratd or dstroyd durng a procss. Closd systs: T ass of t syst
CHAPTER 4 T Frst Law of Trodynacs for Control olus CONSERATION OF MASS Consrvaton of ass: Mass, lk nrgy, s a consrvd proprty, and t cannot b cratd or dstroyd durng a procss. Closd systs: T ass of t syst
September 27, Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations. ME 501A Seminar in Engineering Analysis Page 1. Outline
 Introucton to Ornar Dffrntal Equatons Sptmbr 7, 7 Introucton to Ornar Dffrntal Equatons Larr artto Mchancal Engnrng AB Smnar n Engnrng Analss Sptmbr 7, 7 Outln Rvw numrcal solutons Bascs of ffrntal quatons
Introucton to Ornar Dffrntal Equatons Sptmbr 7, 7 Introucton to Ornar Dffrntal Equatons Larr artto Mchancal Engnrng AB Smnar n Engnrng Analss Sptmbr 7, 7 Outln Rvw numrcal solutons Bascs of ffrntal quatons
Discrete Shells Simulation
 Dscrt Shlls Smulaton Xaofng M hs proct s an mplmntaton of Grnspun s dscrt shlls, th modl of whch s govrnd by nonlnar mmbran and flxural nrgs. hs nrgs masur dffrncs btwns th undformd confguraton and th
Dscrt Shlls Smulaton Xaofng M hs proct s an mplmntaton of Grnspun s dscrt shlls, th modl of whch s govrnd by nonlnar mmbran and flxural nrgs. hs nrgs masur dffrncs btwns th undformd confguraton and th
Outlier-tolerant parameter estimation
 Outlr-tolrant paramtr stmaton Baysan thods n physcs statstcs machn larnng and sgnal procssng (SS 003 Frdrch Fraundorfr fraunfr@cg.tu-graz.ac.at Computr Graphcs and Vson Graz Unvrsty of Tchnology Outln
Outlr-tolrant paramtr stmaton Baysan thods n physcs statstcs machn larnng and sgnal procssng (SS 003 Frdrch Fraundorfr fraunfr@cg.tu-graz.ac.at Computr Graphcs and Vson Graz Unvrsty of Tchnology Outln
8-node quadrilateral element. Numerical integration
 Fnt Elmnt Mthod lctur nots _nod quadrlatral lmnt Pag of 0 -nod quadrlatral lmnt. Numrcal ntgraton h tchnqu usd for th formulaton of th lnar trangl can b formall tndd to construct quadrlatral lmnts as wll
Fnt Elmnt Mthod lctur nots _nod quadrlatral lmnt Pag of 0 -nod quadrlatral lmnt. Numrcal ntgraton h tchnqu usd for th formulaton of th lnar trangl can b formall tndd to construct quadrlatral lmnts as wll
Maximum Matching Width: new characterizations and a fast algorithm for dominating set
 Maxmum Matcn Wdt: nw caractrzatons and a ast alortm or domnatn st 정지수 (KAIST) jont work wt Sv Hortmo Sætr and Jan Arn Tll (Unvrsty o Brn) 1st Koran Worksop on Grap Tory 2015.8.27. KAIST Grap wdt paramtrs
Maxmum Matcn Wdt: nw caractrzatons and a ast alortm or domnatn st 정지수 (KAIST) jont work wt Sv Hortmo Sætr and Jan Arn Tll (Unvrsty o Brn) 1st Koran Worksop on Grap Tory 2015.8.27. KAIST Grap wdt paramtrs
ACOUSTIC WAVE EQUATION. Contents INTRODUCTION BULK MODULUS AND LAMÉ S PARAMETERS
 ACOUSTIC WAE EQUATION Contnts INTRODUCTION BULK MODULUS AND LAMÉ S PARAMETERS INTRODUCTION As w try to vsualz th arth ssmcally w mak crtan physcal smplfcatons that mak t asr to mak and xplan our obsrvatons.
ACOUSTIC WAE EQUATION Contnts INTRODUCTION BULK MODULUS AND LAMÉ S PARAMETERS INTRODUCTION As w try to vsualz th arth ssmcally w mak crtan physcal smplfcatons that mak t asr to mak and xplan our obsrvatons.
Electrochemical Equilibrium Electromotive Force. Relation between chemical and electric driving forces
 C465/865, 26-3, Lctur 7, 2 th Sp., 26 lctrochmcal qulbrum lctromotv Forc Rlaton btwn chmcal and lctrc drvng forcs lctrochmcal systm at constant T and p: consdr G Consdr lctrochmcal racton (nvolvng transfr
C465/865, 26-3, Lctur 7, 2 th Sp., 26 lctrochmcal qulbrum lctromotv Forc Rlaton btwn chmcal and lctrc drvng forcs lctrochmcal systm at constant T and p: consdr G Consdr lctrochmcal racton (nvolvng transfr
Soft k-means Clustering. Comp 135 Machine Learning Computer Science Tufts University. Mixture Models. Mixture of Normals in 1D
 Comp 35 Machn Larnng Computr Scnc Tufts Unvrsty Fall 207 Ron Khardon Th EM Algorthm Mxtur Modls Sm-Suprvsd Larnng Soft k-mans Clustrng ck k clustr cntrs : Assocat xampls wth cntrs p,j ~~ smlarty b/w cntr
Comp 35 Machn Larnng Computr Scnc Tufts Unvrsty Fall 207 Ron Khardon Th EM Algorthm Mxtur Modls Sm-Suprvsd Larnng Soft k-mans Clustrng ck k clustr cntrs : Assocat xampls wth cntrs p,j ~~ smlarty b/w cntr
Lecture 14. Relic neutrinos Temperature at neutrino decoupling and today Effective degeneracy factor Neutrino mass limits Saha equation
 Lctur Rlc nutrnos mpratur at nutrno dcoupln and today Effctv dnracy factor Nutrno mass lmts Saha quaton Physcal Cosmoloy Lnt 005 Rlc Nutrnos Nutrnos ar wakly ntractn partcls (lptons),,,,,,, typcal ractons
Lctur Rlc nutrnos mpratur at nutrno dcoupln and today Effctv dnracy factor Nutrno mass lmts Saha quaton Physcal Cosmoloy Lnt 005 Rlc Nutrnos Nutrnos ar wakly ntractn partcls (lptons),,,,,,, typcal ractons
Optimal Ordering Policy in a Two-Level Supply Chain with Budget Constraint
 Optmal Ordrng Polcy n a Two-Lvl Supply Chan wth Budgt Constrant Rasoul aj Alrza aj Babak aj ABSTRACT Ths papr consdrs a two- lvl supply chan whch consst of a vndor and svral rtalrs. Unsatsfd dmands n rtalrs
Optmal Ordrng Polcy n a Two-Lvl Supply Chan wth Budgt Constrant Rasoul aj Alrza aj Babak aj ABSTRACT Ths papr consdrs a two- lvl supply chan whch consst of a vndor and svral rtalrs. Unsatsfd dmands n rtalrs
The Fourier Transform
 /9/ Th ourr Transform Jan Baptst Josph ourr 768-83 Effcnt Data Rprsntaton Data can b rprsntd n many ways. Advantag usng an approprat rprsntaton. Eampls: osy ponts along a ln Color spac rd/grn/blu v.s.
/9/ Th ourr Transform Jan Baptst Josph ourr 768-83 Effcnt Data Rprsntaton Data can b rprsntd n many ways. Advantag usng an approprat rprsntaton. Eampls: osy ponts along a ln Color spac rd/grn/blu v.s.
2. Grundlegende Verfahren zur Übertragung digitaler Signale (Zusammenfassung) Informationstechnik Universität Ulm
 . Grundlgnd Vrfahrn zur Übrtragung dgtalr Sgnal (Zusammnfassung) wt Dc. 5 Transmsson of Dgtal Sourc Sgnals Sourc COD SC COD MOD MOD CC dg RF s rado transmsson mdum Snk DC SC DC CC DM dg DM RF g physcal
. Grundlgnd Vrfahrn zur Übrtragung dgtalr Sgnal (Zusammnfassung) wt Dc. 5 Transmsson of Dgtal Sourc Sgnals Sourc COD SC COD MOD MOD CC dg RF s rado transmsson mdum Snk DC SC DC CC DM dg DM RF g physcal
External Equivalent. EE 521 Analysis of Power Systems. Chen-Ching Liu, Boeing Distinguished Professor Washington State University
 xtrnal quvalnt 5 Analyss of Powr Systms Chn-Chng Lu, ong Dstngushd Profssor Washngton Stat Unvrsty XTRNAL UALNT ach powr systm (ara) s part of an ntrconnctd systm. Montorng dvcs ar nstalld and data ar
xtrnal quvalnt 5 Analyss of Powr Systms Chn-Chng Lu, ong Dstngushd Profssor Washngton Stat Unvrsty XTRNAL UALNT ach powr systm (ara) s part of an ntrconnctd systm. Montorng dvcs ar nstalld and data ar
Decentralized Adaptive Control and the Possibility of Utilization of Networked Control System
 Dcntralzd Adaptv Control and th Possblty of Utlzaton of Ntworkd Control Systm MARIÁN ÁRNÍK, JÁN MURGAŠ Slovak Unvrsty of chnology n Bratslava Faculty of Elctrcal Engnrng and Informaton chnology Insttut
Dcntralzd Adaptv Control and th Possblty of Utlzaton of Ntworkd Control Systm MARIÁN ÁRNÍK, JÁN MURGAŠ Slovak Unvrsty of chnology n Bratslava Faculty of Elctrcal Engnrng and Informaton chnology Insttut
Relate p and T at equilibrium between two phases. An open system where a new phase may form or a new component can be added
 4.3, 4.4 Phas Equlbrum Dtrmn th slops of th f lns Rlat p and at qulbrum btwn two phass ts consdr th Gbbs functon dg η + V Appls to a homognous systm An opn systm whr a nw phas may form or a nw componnt
4.3, 4.4 Phas Equlbrum Dtrmn th slops of th f lns Rlat p and at qulbrum btwn two phass ts consdr th Gbbs functon dg η + V Appls to a homognous systm An opn systm whr a nw phas may form or a nw componnt
te Finance (4th Edition), July 2017.
 Appndx Chaptr. Tchncal Background Gnral Mathmatcal and Statstcal Background Fndng a bas: 3 2 = 9 3 = 9 1 /2 x a = b x = b 1/a A powr of 1 / 2 s also quvalnt to th squar root opraton. Fndng an xponnt: 3
Appndx Chaptr. Tchncal Background Gnral Mathmatcal and Statstcal Background Fndng a bas: 3 2 = 9 3 = 9 1 /2 x a = b x = b 1/a A powr of 1 / 2 s also quvalnt to th squar root opraton. Fndng an xponnt: 3
ST 524 NCSU - Fall 2008 One way Analysis of variance Variances not homogeneous
 ST 54 NCSU - Fall 008 On way Analyss of varanc Varancs not homognous On way Analyss of varanc Exampl (Yandll, 997) A plant scntst masurd th concntraton of a partcular vrus n plant sap usng ELISA (nzym-lnkd
ST 54 NCSU - Fall 008 On way Analyss of varanc Varancs not homognous On way Analyss of varanc Exampl (Yandll, 997) A plant scntst masurd th concntraton of a partcular vrus n plant sap usng ELISA (nzym-lnkd
Polytropic Process. A polytropic process is a quasiequilibrium process described by
 Polytropc Procss A polytropc procss s a quasqulbrum procss dscrbd by pv n = constant (Eq. 3.5 Th xponnt, n, may tak on any valu from to dpndng on th partcular procss. For any gas (or lqud, whn n = 0, th
Polytropc Procss A polytropc procss s a quasqulbrum procss dscrbd by pv n = constant (Eq. 3.5 Th xponnt, n, may tak on any valu from to dpndng on th partcular procss. For any gas (or lqud, whn n = 0, th
5- Scattering Stationary States
 Lctu 19 Pyscs Dpatmnt Yamou Unvsty 1163 Ibd Jodan Pys. 441: Nucla Pyscs 1 Pobablty Cunts D. Ndal Esadat ttp://ctaps.yu.du.jo/pyscs/couss/pys641/lc5-3 5- Scattng Statonay Stats Rfnc: Paagaps B and C Quantum
Lctu 19 Pyscs Dpatmnt Yamou Unvsty 1163 Ibd Jodan Pys. 441: Nucla Pyscs 1 Pobablty Cunts D. Ndal Esadat ttp://ctaps.yu.du.jo/pyscs/couss/pys641/lc5-3 5- Scattng Statonay Stats Rfnc: Paagaps B and C Quantum
Group Codes Define Over Dihedral Groups of Small Order
 Malaysan Journal of Mathmatcal Scncs 7(S): 0- (0) Spcal Issu: Th rd Intrnatonal Confrnc on Cryptology & Computr Scurty 0 (CRYPTOLOGY0) MALAYSIA JOURAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIECES Journal hompag: http://nspm.upm.du.my/ournal
Malaysan Journal of Mathmatcal Scncs 7(S): 0- (0) Spcal Issu: Th rd Intrnatonal Confrnc on Cryptology & Computr Scurty 0 (CRYPTOLOGY0) MALAYSIA JOURAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIECES Journal hompag: http://nspm.upm.du.my/ournal
Lucas Test is based on Euler s theorem which states that if n is any integer and a is coprime to n, then a φ(n) 1modn.
 Modul 10 Addtonal Topcs 10.1 Lctur 1 Prambl: Dtrmnng whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or compost s known as prmalty tstng. Thr ar prmalty tsts whch mrly tll us whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or not, wthout gvng us th factors
Modul 10 Addtonal Topcs 10.1 Lctur 1 Prambl: Dtrmnng whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or compost s known as prmalty tstng. Thr ar prmalty tsts whch mrly tll us whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or not, wthout gvng us th factors
Trigonometric functions
 Robrto s Nots on Diffrntial Calculus Captr 5: Drivativs of transcndntal functions Sction 5 Drivativs of Trigonomtric functions Wat you nd to know alrady: Basic trigonomtric limits, t dfinition of drivativ,
Robrto s Nots on Diffrntial Calculus Captr 5: Drivativs of transcndntal functions Sction 5 Drivativs of Trigonomtric functions Wat you nd to know alrady: Basic trigonomtric limits, t dfinition of drivativ,
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 453 Winter Quarter 2014 Lecture 20: Transition State Theory. ERD: 25.14
 Univrsity of Wasinton Dpartmnt of Cmistry Cmistry 453 Wintr Quartr 04 Lctur 0: Transition Stat Tory. ERD: 5.4. Transition Stat Tory Transition Stat Tory (TST) or ctivatd Complx Tory (CT) is a raction mcanism
Univrsity of Wasinton Dpartmnt of Cmistry Cmistry 453 Wintr Quartr 04 Lctur 0: Transition Stat Tory. ERD: 5.4. Transition Stat Tory Transition Stat Tory (TST) or ctivatd Complx Tory (CT) is a raction mcanism
3-2-1 ANN Architecture
 ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS (ANNs) Profssor Tom Fomby Dpartmnt of Economics Soutrn Mtodist Univrsity Marc 008 Artificial Nural Ntworks (raftr ANNs) can b usd for itr prdiction or classification problms.
ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS (ANNs) Profssor Tom Fomby Dpartmnt of Economics Soutrn Mtodist Univrsity Marc 008 Artificial Nural Ntworks (raftr ANNs) can b usd for itr prdiction or classification problms.
Chapter 6 Student Lecture Notes 6-1
 Chaptr 6 Studnt Lctur Nots 6-1 Chaptr Goals QM353: Busnss Statstcs Chaptr 6 Goodnss-of-Ft Tsts and Contngncy Analyss Aftr compltng ths chaptr, you should b abl to: Us th ch-squar goodnss-of-ft tst to dtrmn
Chaptr 6 Studnt Lctur Nots 6-1 Chaptr Goals QM353: Busnss Statstcs Chaptr 6 Goodnss-of-Ft Tsts and Contngncy Analyss Aftr compltng ths chaptr, you should b abl to: Us th ch-squar goodnss-of-ft tst to dtrmn
Strategies evaluation on the attempts to gain access to a service system (the second problem of an impatient customer)
 h ublcaton aard n Sostk R.: Stratgs valuaton on th attmts to gan accss to a vc systm th scond roblm of an matnt customr, Intrnatonal Journal of Elctroncs and lcommuncatons Quartrly 54, no, PN, Warsa 8,.
h ublcaton aard n Sostk R.: Stratgs valuaton on th attmts to gan accss to a vc systm th scond roblm of an matnt customr, Intrnatonal Journal of Elctroncs and lcommuncatons Quartrly 54, no, PN, Warsa 8,.
Two-Temperature Plasma Modeling of Argon Gas Tungsten Arcs.
 Ttl Autor(s) Two-Tmpratur Plasma Modlng of Argon Gas Tungstn Arcs Tasro, Snc; Tanaa, Manabu Ctaton Transactons of JWRI. 37(1) P.7-P.11 Issu Dat 2008-07 Txt Vrson publsr URL ttp://dl.andl.nt/11094/8887
Ttl Autor(s) Two-Tmpratur Plasma Modlng of Argon Gas Tungstn Arcs Tasro, Snc; Tanaa, Manabu Ctaton Transactons of JWRI. 37(1) P.7-P.11 Issu Dat 2008-07 Txt Vrson publsr URL ttp://dl.andl.nt/11094/8887
Jones vector & matrices
 Jons vctor & matrcs PY3 Colást na hollscol Corcagh, Ér Unvrst Collg Cork, Irland Dpartmnt of Phscs Matr tratmnt of polarzaton Consdr a lght ra wth an nstantanous -vctor as shown k, t ˆ k, t ˆ k t, o o
Jons vctor & matrcs PY3 Colást na hollscol Corcagh, Ér Unvrst Collg Cork, Irland Dpartmnt of Phscs Matr tratmnt of polarzaton Consdr a lght ra wth an nstantanous -vctor as shown k, t ˆ k, t ˆ k t, o o
Heating of a solid cylinder immersed in an insulated bath. Thermal diffusivity and heat capacity experimental evaluation.
 Hatng of a sold cylndr mmrsd n an nsulatd bath. Thrmal dffusvty and hat capacty xprmntal valuaton. Žtný R., CTU FE Dpartmnt of Procss Engnrng, arch. Introducton Th problm as ntatd by th follong E-mal from
Hatng of a sold cylndr mmrsd n an nsulatd bath. Thrmal dffusvty and hat capacty xprmntal valuaton. Žtný R., CTU FE Dpartmnt of Procss Engnrng, arch. Introducton Th problm as ntatd by th follong E-mal from
Physics of Very High Frequency (VHF) Capacitively Coupled Plasma Discharges
 Physcs of Vry Hgh Frquncy (VHF) Capactvly Coupld Plasma Dschargs Shahd Rauf, Kallol Bra, Stv Shannon, and Kn Collns Appld Matrals, Inc., Sunnyval, CA AVS 54 th Intrnatonal Symposum Sattl, WA Octobr 15-19,
Physcs of Vry Hgh Frquncy (VHF) Capactvly Coupld Plasma Dschargs Shahd Rauf, Kallol Bra, Stv Shannon, and Kn Collns Appld Matrals, Inc., Sunnyval, CA AVS 54 th Intrnatonal Symposum Sattl, WA Octobr 15-19,
Stress-Based Finite Element Methods for Dynamics Analysis of Euler-Bernoulli Beams with Various Boundary Conditions
 9 Strss-Basd Fnt Elmnt Mthods for Dynamcs Analyss of Eulr-Brnoull Bams wth Varous Boundary Condtons Abstract In ths rsarch, two strss-basd fnt lmnt mthods ncludng th curvatur-basd fnt lmnt mthod (CFE)
9 Strss-Basd Fnt Elmnt Mthods for Dynamcs Analyss of Eulr-Brnoull Bams wth Varous Boundary Condtons Abstract In ths rsarch, two strss-basd fnt lmnt mthods ncludng th curvatur-basd fnt lmnt mthod (CFE)
A Probabilistic Characterization of Simulation Model Uncertainties
 A Proalstc Charactrzaton of Sulaton Modl Uncrtants Vctor Ontvros Mohaad Modarrs Cntr for Rsk and Rlalty Unvrsty of Maryland 1 Introducton Thr s uncrtanty n odl prdctons as wll as uncrtanty n xprnts Th
A Proalstc Charactrzaton of Sulaton Modl Uncrtants Vctor Ontvros Mohaad Modarrs Cntr for Rsk and Rlalty Unvrsty of Maryland 1 Introducton Thr s uncrtanty n odl prdctons as wll as uncrtanty n xprnts Th
An Overview of Markov Random Field and Application to Texture Segmentation
 An Ovrvw o Markov Random Fld and Applcaton to Txtur Sgmntaton Song-Wook Joo Octobr 003. What s MRF? MRF s an xtnson o Markov Procss MP (D squnc o r.v. s unlatral (causal: p(x t x,
An Ovrvw o Markov Random Fld and Applcaton to Txtur Sgmntaton Song-Wook Joo Octobr 003. What s MRF? MRF s an xtnson o Markov Procss MP (D squnc o r.v. s unlatral (causal: p(x t x,
Estimation Theory. Chapter 4
 Estmato ory aptr 4 LIEAR MOELS W - I matrx form Estmat slop B ad trcpt A,,.. - WG W B A l fttg Rcall W W W B A W ~ calld vctor I gral, ormal or Gaussa ata obsrvato paramtr Ma, ovarac KOW p matrx to b stmatd,
Estmato ory aptr 4 LIEAR MOELS W - I matrx form Estmat slop B ad trcpt A,,.. - WG W B A l fttg Rcall W W W B A W ~ calld vctor I gral, ormal or Gaussa ata obsrvato paramtr Ma, ovarac KOW p matrx to b stmatd,
Lecture 23 APPLICATIONS OF FINITE ELEMENT METHOD TO SCALAR TRANSPORT PROBLEMS
 COMPUTTION FUID DYNMICS: FVM: pplcatons to Scalar Transport Prolms ctur 3 PPICTIONS OF FINITE EEMENT METHOD TO SCR TRNSPORT PROBEMS 3. PPICTION OF FEM TO -D DIFFUSION PROBEM Consdr th stady stat dffuson
COMPUTTION FUID DYNMICS: FVM: pplcatons to Scalar Transport Prolms ctur 3 PPICTIONS OF FINITE EEMENT METHOD TO SCR TRNSPORT PROBEMS 3. PPICTION OF FEM TO -D DIFFUSION PROBEM Consdr th stady stat dffuson
Decision-making with Distance-based Operators in Fuzzy Logic Control
 Dcson-makng wth Dstanc-basd Oprators n Fuzzy Logc Control Márta Takács Polytchncal Engnrng Collg, Subotca 24000 Subotca, Marka Orškovća 16., Yugoslava marta@vts.su.ac.yu Abstract: Th norms and conorms
Dcson-makng wth Dstanc-basd Oprators n Fuzzy Logc Control Márta Takács Polytchncal Engnrng Collg, Subotca 24000 Subotca, Marka Orškovća 16., Yugoslava marta@vts.su.ac.yu Abstract: Th norms and conorms
HORIZONTAL IMPEDANCE FUNCTION OF SINGLE PILE IN SOIL LAYER WITH VARIABLE PROPERTIES
 13 th World Confrnc on Earthquak Engnrng Vancouvr, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 4 Papr No. 485 ORIZONTAL IMPEDANCE FUNCTION OF SINGLE PILE IN SOIL LAYER WIT VARIABLE PROPERTIES Mngln Lou 1 and Wnan Wang Abstract:
13 th World Confrnc on Earthquak Engnrng Vancouvr, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 4 Papr No. 485 ORIZONTAL IMPEDANCE FUNCTION OF SINGLE PILE IN SOIL LAYER WIT VARIABLE PROPERTIES Mngln Lou 1 and Wnan Wang Abstract:
MCB137: Physical Biology of the Cell Spring 2017 Homework 6: Ligand binding and the MWC model of allostery (Due 3/23/17)
 MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
A NEW GENERALISATION OF SAM-SOLAI S MULTIVARIATE ADDITIVE GAMMA DISTRIBUTION*
 A NEW GENERALISATION OF SAM-SOLAI S MULTIVARIATE ADDITIVE GAMMA DISTRIBUTION* Dr. G.S. Davd Sam Jayakumar, Assstant Profssor, Jamal Insttut of Managmnt, Jamal Mohamd Collg, Truchraall 620 020, South Inda,
A NEW GENERALISATION OF SAM-SOLAI S MULTIVARIATE ADDITIVE GAMMA DISTRIBUTION* Dr. G.S. Davd Sam Jayakumar, Assstant Profssor, Jamal Insttut of Managmnt, Jamal Mohamd Collg, Truchraall 620 020, South Inda,
STEP-INVARIANT TRANSFORM FROM Z- TO S-DOMAIN A General Framework
 IEEE Instrumntaton and Masurmnt Tchnology Confrnc, IMTC/ May -4,, Baltmor, MD, USA STEP-IVARIAT TRASFORM FROM Z- TO S-DOMAI A Gnral Framwork JÓZSEF G. ÉMET and ISTVÁ KOLLÁR DEPARTMET OF MEASUREMET AD IFORMATIO
IEEE Instrumntaton and Masurmnt Tchnology Confrnc, IMTC/ May -4,, Baltmor, MD, USA STEP-IVARIAT TRASFORM FROM Z- TO S-DOMAI A Gnral Framwork JÓZSEF G. ÉMET and ISTVÁ KOLLÁR DEPARTMET OF MEASUREMET AD IFORMATIO
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Yufi Tao ITEE Univrsity of Qunslan In tis lctur, w will stuy anotr classic prolm: finin a minimum spannin tr of an unirct wit rap. Intrstinly, vn tou t prolm appars ratr iffrnt from SSSP (sinl sourc sortst
Yufi Tao ITEE Univrsity of Qunslan In tis lctur, w will stuy anotr classic prolm: finin a minimum spannin tr of an unirct wit rap. Intrstinly, vn tou t prolm appars ratr iffrnt from SSSP (sinl sourc sortst
ANALYSIS: The mass rate balance for the one-inlet, one-exit control volume at steady state is
 Problm 4.47 Fgur P4.47 provds stady stat opratng data for a pump drawng watr from a rsrvor and dlvrng t at a prssur of 3 bar to a storag tank prchd 5 m abov th rsrvor. Th powr nput to th pump s 0.5 kw.
Problm 4.47 Fgur P4.47 provds stady stat opratng data for a pump drawng watr from a rsrvor and dlvrng t at a prssur of 3 bar to a storag tank prchd 5 m abov th rsrvor. Th powr nput to th pump s 0.5 kw.
Multiple-Choice Test Runge-Kutta 4 th Order Method Ordinary Differential Equations COMPLETE SOLUTION SET
 Multpl-Co Tst Rung-Kutta t Ordr Mtod Ordnar Drntal Equatons COMPLETE SOLUTION SET. To solv t ordnar drntal quaton sn ( Rung-Kutta t ordr mtod ou nd to rwrt t quaton as (A sn ( (B ( sn ( (C os ( (D sn (
Multpl-Co Tst Rung-Kutta t Ordr Mtod Ordnar Drntal Equatons COMPLETE SOLUTION SET. To solv t ordnar drntal quaton sn ( Rung-Kutta t ordr mtod ou nd to rwrt t quaton as (A sn ( (B ( sn ( (C os ( (D sn (
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 301 Signals & Systms Prof. Mark Fowlr ot St #21 D-T Signals: Rlation btwn DFT, DTFT, & CTFT 1/16 W can us th DFT to implmnt numrical FT procssing This nabls us to numrically analyz a signal to find
EECE 301 Signals & Systms Prof. Mark Fowlr ot St #21 D-T Signals: Rlation btwn DFT, DTFT, & CTFT 1/16 W can us th DFT to implmnt numrical FT procssing This nabls us to numrically analyz a signal to find
Econ107 Applied Econometrics Topic 10: Dummy Dependent Variable (Studenmund, Chapter 13)
 Pag- Econ7 Appld Economtrcs Topc : Dummy Dpndnt Varabl (Studnmund, Chaptr 3) I. Th Lnar Probablty Modl Suppos w hav a cross scton of 8-24 yar-olds. W spcfy a smpl 2-varabl rgrsson modl. Th probablty of
Pag- Econ7 Appld Economtrcs Topc : Dummy Dpndnt Varabl (Studnmund, Chaptr 3) I. Th Lnar Probablty Modl Suppos w hav a cross scton of 8-24 yar-olds. W spcfy a smpl 2-varabl rgrsson modl. Th probablty of
Lecture 3: Phasor notation, Transfer Functions. Context
 EECS 5 Fall 4, ctur 3 ctur 3: Phasor notaton, Transfr Functons EECS 5 Fall 3, ctur 3 Contxt In th last lctur, w dscussd: how to convrt a lnar crcut nto a st of dffrntal quatons, How to convrt th st of
EECS 5 Fall 4, ctur 3 ctur 3: Phasor notaton, Transfr Functons EECS 5 Fall 3, ctur 3 Contxt In th last lctur, w dscussd: how to convrt a lnar crcut nto a st of dffrntal quatons, How to convrt th st of
From Structural Analysis to FEM. Dhiman Basu
 From Structural Analyss to FEM Dhman Basu Acknowldgmnt Followng txt books wr consultd whl prparng ths lctur nots: Znkwcz, OC O.C. andtaylor Taylor, R.L. (000). Th FntElmnt Mthod, Vol. : Th Bass, Ffth dton,
From Structural Analyss to FEM Dhman Basu Acknowldgmnt Followng txt books wr consultd whl prparng ths lctur nots: Znkwcz, OC O.C. andtaylor Taylor, R.L. (000). Th FntElmnt Mthod, Vol. : Th Bass, Ffth dton,
Folding of Regular CW-Complexes
 Ald Mathmatcal Scncs, Vol. 6,, no. 83, 437-446 Foldng of Rgular CW-Comlxs E. M. El-Kholy and S N. Daoud,3. Dartmnt of Mathmatcs, Faculty of Scnc Tanta Unvrsty,Tanta,Egyt. Dartmnt of Mathmatcs, Faculty
Ald Mathmatcal Scncs, Vol. 6,, no. 83, 437-446 Foldng of Rgular CW-Comlxs E. M. El-Kholy and S N. Daoud,3. Dartmnt of Mathmatcs, Faculty of Scnc Tanta Unvrsty,Tanta,Egyt. Dartmnt of Mathmatcs, Faculty
Α complete processing methodology for 3D monitoring using GNSS receivers
 7-5-5 NATIONA TECHNICA UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS SCHOO OF RURA AND SURVEYING ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF TOPOGRAPHY AORATORY OF GENERA GEODESY Α complt procssng mthodology for D montorng usng GNSS rcvrs Gorg
7-5-5 NATIONA TECHNICA UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS SCHOO OF RURA AND SURVEYING ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF TOPOGRAPHY AORATORY OF GENERA GEODESY Α complt procssng mthodology for D montorng usng GNSS rcvrs Gorg
Copyright 2002 IFAC 15th Triennial World Congress, Barcelona, Spain
 Copyrgt IFAC 1t Trnnal World Congrss, Barclona, Span ROBUST H-INFINITY REDUCED ORDER FILTERING F OR UNCER TAIN BILINEAR SYSTEMS H Souly Al, M Zasadznsk, H Rafarala y and M Darouac CRAN, IUT d Longy, Unvrst
Copyrgt IFAC 1t Trnnal World Congrss, Barclona, Span ROBUST H-INFINITY REDUCED ORDER FILTERING F OR UNCER TAIN BILINEAR SYSTEMS H Souly Al, M Zasadznsk, H Rafarala y and M Darouac CRAN, IUT d Longy, Unvrst
Code Design for the Low SNR Noncoherent MIMO Block Rayleigh Fading Channel
 Cod Dsgn for th Low SNR Noncohrnt MIMO Block Raylgh Fadng Channl Shvratna Gr Srnvasan and Mahsh K. Varanas -mal: {srnvsg, varanas}@dsp.colorado.du Elctrcal & Computr Engnrng Dpartmnt Unvrsty of Colorado,
Cod Dsgn for th Low SNR Noncohrnt MIMO Block Raylgh Fadng Channl Shvratna Gr Srnvasan and Mahsh K. Varanas -mal: {srnvsg, varanas}@dsp.colorado.du Elctrcal & Computr Engnrng Dpartmnt Unvrsty of Colorado,
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
Optimal Data Transmission and Channel Code Rate Allocation in Multi-path Wireless Networks
 Optmal Data Transmsson and Channl Cod Rat Allocaton n Mult-path Wrlss Ntwors Kvan Ronas, Amr-Hamd Mohsnan-Rad,VncntW.S.Wong, Sathsh Gopalarshnan, and Robrt Schobr Dpartmnt of Elctrcal and Computr Engnrng
Optmal Data Transmsson and Channl Cod Rat Allocaton n Mult-path Wrlss Ntwors Kvan Ronas, Amr-Hamd Mohsnan-Rad,VncntW.S.Wong, Sathsh Gopalarshnan, and Robrt Schobr Dpartmnt of Elctrcal and Computr Engnrng
Physics 43 HW #9 Chapter 40 Key
 Pysics 43 HW #9 Captr 4 Ky Captr 4 1 Aftr many ours of dilignt rsarc, you obtain t following data on t potolctric ffct for a crtain matrial: Wavlngt of Ligt (nm) Stopping Potntial (V) 36 3 4 14 31 a) Plot
Pysics 43 HW #9 Captr 4 Ky Captr 4 1 Aftr many ours of dilignt rsarc, you obtain t following data on t potolctric ffct for a crtain matrial: Wavlngt of Ligt (nm) Stopping Potntial (V) 36 3 4 14 31 a) Plot
??? Dynamic Causal Modelling for M/EEG. Electroencephalography (EEG) Dynamic Causal Modelling. M/EEG analysis at sensor level. time.
 Elctroncphalography EEG Dynamc Causal Modllng for M/EEG ampltud μv tm ms tral typ 1 tm channls channls tral typ 2 C. Phllps, Cntr d Rchrchs du Cyclotron, ULg, Blgum Basd on slds from: S. Kbl M/EEG analyss
Elctroncphalography EEG Dynamc Causal Modllng for M/EEG ampltud μv tm ms tral typ 1 tm channls channls tral typ 2 C. Phllps, Cntr d Rchrchs du Cyclotron, ULg, Blgum Basd on slds from: S. Kbl M/EEG analyss
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 th January Vol. 47 No JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
 Journal o Thortcal and Appld Inormaton Tchnology th January 3. Vol. 47 No. 5-3 JATIT & LLS. All rghts rsrvd. ISSN: 99-8645 www.att.org E-ISSN: 87-395 RESEARCH ON PROPERTIES OF E-PARTIAL DERIVATIVE OF LOGIC
Journal o Thortcal and Appld Inormaton Tchnology th January 3. Vol. 47 No. 5-3 JATIT & LLS. All rghts rsrvd. ISSN: 99-8645 www.att.org E-ISSN: 87-395 RESEARCH ON PROPERTIES OF E-PARTIAL DERIVATIVE OF LOGIC
MTX221. Session 40 ENTROPY (CONTROL VOLUME) Sessie 40 ENTROPIE (KONTROLE VOLUME) Dr. Jaco Dirker. These slides also appear on Click-UP
 s.40-1 MTX1 ss 40 ENTROPIE (KONTROLE VOLUME) sson 40 ENTROPY (CONTROL VOLUME) Dr. Jaco Drkr Ths slds also appar on Clck-UP Hrd skyfs vrskyn ook op Clck-UP 8 th dton / 8 utgaw 7.3 7.5 Dpartmnt of Mchancal
s.40-1 MTX1 ss 40 ENTROPIE (KONTROLE VOLUME) sson 40 ENTROPY (CONTROL VOLUME) Dr. Jaco Drkr Ths slds also appar on Clck-UP Hrd skyfs vrskyn ook op Clck-UP 8 th dton / 8 utgaw 7.3 7.5 Dpartmnt of Mchancal
EEC 686/785 Modeling & Performance Evaluation of Computer Systems. Lecture 12
 EEC 686/785 Modlng & Prformanc Evaluaton of Computr Systms Lctur Dpartmnt of Elctrcal and Computr Engnrng Clvland Stat Unvrsty wnbng@.org (basd on Dr. Ra Jan s lctur nots) Outln Rvw of lctur k r Factoral
EEC 686/785 Modlng & Prformanc Evaluaton of Computr Systms Lctur Dpartmnt of Elctrcal and Computr Engnrng Clvland Stat Unvrsty wnbng@.org (basd on Dr. Ra Jan s lctur nots) Outln Rvw of lctur k r Factoral
1 Minimum Cut Problem
 CS 6 Lctur 6 Min Cut and argr s Algorithm Scribs: Png Hui How (05), Virginia Dat: May 4, 06 Minimum Cut Problm Today, w introduc th minimum cut problm. This problm has many motivations, on of which coms
CS 6 Lctur 6 Min Cut and argr s Algorithm Scribs: Png Hui How (05), Virginia Dat: May 4, 06 Minimum Cut Problm Today, w introduc th minimum cut problm. This problm has many motivations, on of which coms
Linear Algebra Provides a Basis for Elasticity without Stress or Strain
 Soft, 05, 4, 5-4 Publshd Onln Sptmbr 05 n ScRs. http://www.scrp.org/ournal/soft http://dx.do.org/0.46/soft.05.400 Lnar Algbra Provds a Bass for Elastcty wthout Strss or Stran H. H. Hardy Math/Physcs Dpartmnt,
Soft, 05, 4, 5-4 Publshd Onln Sptmbr 05 n ScRs. http://www.scrp.org/ournal/soft http://dx.do.org/0.46/soft.05.400 Lnar Algbra Provds a Bass for Elastcty wthout Strss or Stran H. H. Hardy Math/Physcs Dpartmnt,
Guo, James C.Y. (1998). "Overland Flow on a Pervious Surface," IWRA International J. of Water, Vol 23, No 2, June.
 Guo, Jams C.Y. (006). Knmatc Wav Unt Hyrograph for Storm Watr Prctons, Vol 3, No. 4, ASCE J. of Irrgaton an Dranag Engnrng, July/August. Guo, Jams C.Y. (998). "Ovrlan Flow on a Prvous Surfac," IWRA Intrnatonal
Guo, Jams C.Y. (006). Knmatc Wav Unt Hyrograph for Storm Watr Prctons, Vol 3, No. 4, ASCE J. of Irrgaton an Dranag Engnrng, July/August. Guo, Jams C.Y. (998). "Ovrlan Flow on a Prvous Surfac," IWRA Intrnatonal
EXST Regression Techniques Page 1
 EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Mnmum Spnnng Trs Spnnng Tr A tr (.., connctd, cyclc grph) whch contns ll th vrtcs of th grph Mnmum Spnnng Tr Spnnng tr wth th mnmum sum of wghts 1 1 Spnnng forst If grph s not connctd, thn thr s spnnng
Mnmum Spnnng Trs Spnnng Tr A tr (.., connctd, cyclc grph) whch contns ll th vrtcs of th grph Mnmum Spnnng Tr Spnnng tr wth th mnmum sum of wghts 1 1 Spnnng forst If grph s not connctd, thn thr s spnnng
Naresuan University Journal: Science and Technology 2018; (26)1
 Narsuan Unvrsty Journal: Scnc and Tchnology 018; (6)1 Th Dvlopmnt o a Corrcton Mthod or Ensurng a Contnuty Valu o Th Ch-squar Tst wth a Small Expctd Cll Frquncy Kajta Matchma 1 *, Jumlong Vongprasrt and
Narsuan Unvrsty Journal: Scnc and Tchnology 018; (6)1 Th Dvlopmnt o a Corrcton Mthod or Ensurng a Contnuty Valu o Th Ch-squar Tst wth a Small Expctd Cll Frquncy Kajta Matchma 1 *, Jumlong Vongprasrt and
You already learned about dummies as independent variables. But. what do you do if the dependent variable is a dummy?
 CHATER 5: DUMMY DEENDENT VARIABLES AND NON-LINEAR REGRESSION. Th roblm of Dummy Dpndnt Varabls You alrady larnd about dumms as ndpndnt varabls. But what do you do f th dpndnt varabl s a dummy? On answr
CHATER 5: DUMMY DEENDENT VARIABLES AND NON-LINEAR REGRESSION. Th roblm of Dummy Dpndnt Varabls You alrady larnd about dumms as ndpndnt varabls. But what do you do f th dpndnt varabl s a dummy? On answr
:2;$-$(01*%<*=,-./-*=0;"%/;"-*
 !"#$%'()%"*#%*+,-./-*+01.2(.*3+456789*!"#$%"'()'*+,-."/0.%+1'23"45'46'7.89:89'/' ;8-,"$4351415,8:+#9' Dr. Ptr T. Gallaghr Astrphyscs Rsarch Grup Trnty Cllg Dubln :2;$-$(01*%
!"#$%'()%"*#%*+,-./-*+01.2(.*3+456789*!"#$%"'()'*+,-."/0.%+1'23"45'46'7.89:89'/' ;8-,"$4351415,8:+#9' Dr. Ptr T. Gallaghr Astrphyscs Rsarch Grup Trnty Cllg Dubln :2;$-$(01*%
Fakultät III Wirtschaftswissenschaften Univ.-Prof. Dr. Jan Franke-Viebach
 Unvrstät Sgn Fakultät III Wrtschaftswssnschaftn Unv.-rof. Dr. Jan Frank-Vbach Exam Intrnatonal Fnancal Markts Summr Smstr 206 (2 nd Exam rod) Avalabl tm: 45 mnuts Soluton For your attnton:. las do not
Unvrstät Sgn Fakultät III Wrtschaftswssnschaftn Unv.-rof. Dr. Jan Frank-Vbach Exam Intrnatonal Fnancal Markts Summr Smstr 206 (2 nd Exam rod) Avalabl tm: 45 mnuts Soluton For your attnton:. las do not
Maneuvering Target Tracking Using Current Statistical Model Based Adaptive UKF for Wireless Sensor Network
 Journal of Communcatons Vol. 0, No. 8, August 05 Manuvrng argt racng Usng Currnt Statstcal Modl Basd Adaptv UKF for Wrlss Snsor Ntwor Xaojun Png,, Kuntao Yang, and Chang Lu School of Optcal and Elctronc
Journal of Communcatons Vol. 0, No. 8, August 05 Manuvrng argt racng Usng Currnt Statstcal Modl Basd Adaptv UKF for Wrlss Snsor Ntwor Xaojun Png,, Kuntao Yang, and Chang Lu School of Optcal and Elctronc
Physics 256: Lecture 2. Physics
 Physcs 56: Lctur Intro to Quantum Physcs Agnda for Today Complx Numbrs Intrfrnc of lght Intrfrnc Two slt ntrfrnc Dffracton Sngl slt dffracton Physcs 01: Lctur 1, Pg 1 Constructv Intrfrnc Ths wll occur
Physcs 56: Lctur Intro to Quantum Physcs Agnda for Today Complx Numbrs Intrfrnc of lght Intrfrnc Two slt ntrfrnc Dffracton Sngl slt dffracton Physcs 01: Lctur 1, Pg 1 Constructv Intrfrnc Ths wll occur
Case Study 1 PHA 5127 Fall 2006 Revised 9/19/06
 Cas Study Qustion. A 3 yar old, 5 kg patint was brougt in for surgry and was givn a /kg iv bolus injction of a muscl rlaxant. T plasma concntrations wr masurd post injction and notd in t tabl blow: Tim
Cas Study Qustion. A 3 yar old, 5 kg patint was brougt in for surgry and was givn a /kg iv bolus injction of a muscl rlaxant. T plasma concntrations wr masurd post injction and notd in t tabl blow: Tim
Spectral stochastic finite element analysis of structures with random field parameters under bounded-but-uncertain forces
 Southrn Cross Unvrsty Publcatons@SCU 23rd Australasan Confrnc on th Mchancs of Structurs and Matrals 24 Spctral stochastc fnt lmnt analyss of structurs wth random fld paramtrs undr boundd-but-uncrtan forcs
Southrn Cross Unvrsty Publcatons@SCU 23rd Australasan Confrnc on th Mchancs of Structurs and Matrals 24 Spctral stochastc fnt lmnt analyss of structurs wth random fld paramtrs undr boundd-but-uncrtan forcs
Computation of Greeks Using Binomial Tree
 Journal of Mathmatcal Fnanc, 07, 7, 597-63 http://www.scrp.org/journal/jmf ISSN Onln: 6-44 ISSN Prnt: 6-434 Computaton of Grks Usng Bnomal Tr Yoshfum Muro, Shntaro Suda Graduat School of conomcs and Managmnt,
Journal of Mathmatcal Fnanc, 07, 7, 597-63 http://www.scrp.org/journal/jmf ISSN Onln: 6-44 ISSN Prnt: 6-434 Computaton of Grks Usng Bnomal Tr Yoshfum Muro, Shntaro Suda Graduat School of conomcs and Managmnt,
Asymptotics of the Solution of a Boundary Value. Problem for One-Characteristic Differential. Equation Degenerating into a Parabolic Equation
 Nonl. Analyss and Dfferental Equatons, ol., 4, no., 5 - HIKARI Ltd, www.m-har.com http://dx.do.org/.988/nade.4.456 Asymptotcs of the Soluton of a Boundary alue Problem for One-Characterstc Dfferental Equaton
Nonl. Analyss and Dfferental Equatons, ol., 4, no., 5 - HIKARI Ltd, www.m-har.com http://dx.do.org/.988/nade.4.456 Asymptotcs of the Soluton of a Boundary alue Problem for One-Characterstc Dfferental Equaton
( V ) 0 in the above equation, but retained to keep the complete vector identity for V in equation.
 Cuvlna Coodnats Outln:. Otogonal cuvlna coodnat systms. Dffntal opatos n otogonal cuvlna coodnat systms. Dvatvs of t unt vctos n otogonal cuvlna coodnat systms 4. Incompssbl N-S quatons n otogonal cuvlna
Cuvlna Coodnats Outln:. Otogonal cuvlna coodnat systms. Dffntal opatos n otogonal cuvlna coodnat systms. Dvatvs of t unt vctos n otogonal cuvlna coodnat systms 4. Incompssbl N-S quatons n otogonal cuvlna
Transfer Functions. Convenient representation of a linear, dynamic model. A transfer function (TF) relates one input and one output: ( ) system
 Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
EFFECTS OF INCLINED CUTOFFS AND SOIL FOUNDATION CHARACTERISTICS ON SEEPAGE BENEATH HYDRAULIC STRUCTURES
 Twlft Intrnatonal Watr Tcnology Confrnc, IWTC2 28, Alandra, Egypt 597 EFFECTS OF INCLINED CUTOFFS AND SOIL FOUNDATION CHARACTERISTICS ON SEEPAGE BENEATH HYDRAULIC STRUCTURES Kald Fadl Alsnous and Hasan
Twlft Intrnatonal Watr Tcnology Confrnc, IWTC2 28, Alandra, Egypt 597 EFFECTS OF INCLINED CUTOFFS AND SOIL FOUNDATION CHARACTERISTICS ON SEEPAGE BENEATH HYDRAULIC STRUCTURES Kald Fadl Alsnous and Hasan
UNIT 8 TWO-WAY ANOVA WITH m OBSERVATIONS PER CELL
 UNIT 8 TWO-WAY ANOVA WITH OBSERVATIONS PER CELL Two-Way Anova wth Obsrvatons Pr Cll Structur 81 Introducton Obctvs 8 ANOVA Modl for Two-way Classfd Data wth Obsrvatons r Cll 83 Basc Assutons 84 Estaton
UNIT 8 TWO-WAY ANOVA WITH OBSERVATIONS PER CELL Two-Way Anova wth Obsrvatons Pr Cll Structur 81 Introducton Obctvs 8 ANOVA Modl for Two-way Classfd Data wth Obsrvatons r Cll 83 Basc Assutons 84 Estaton
Maneuvering Target Tracking Using Current Statistical Model Based Adaptive UKF for Wireless Sensor Network
 Journal of Communcatons Vol. 0, No. 8, August 05 Manuvrng argt racng Usng Currnt Statstcal Modl Basd Adaptv UKF for Wrlss Snsor Ntwor Xaojun Png,, Kuntao Yang, and Chang Lu School of Optcal and Elctronc
Journal of Communcatons Vol. 0, No. 8, August 05 Manuvrng argt racng Usng Currnt Statstcal Modl Basd Adaptv UKF for Wrlss Snsor Ntwor Xaojun Png,, Kuntao Yang, and Chang Lu School of Optcal and Elctronc
EEO 401 Digital Signal Processing Prof. Mark Fowler
 EEO 401 Digital Signal Procssing Prof. Mark Fowlr ot St #18 Introduction to DFT (via th DTFT) Rading Assignmnt: Sct. 7.1 of Proakis & Manolakis 1/24 Discrt Fourir Transform (DFT) W v sn that th DTFT is
EEO 401 Digital Signal Procssing Prof. Mark Fowlr ot St #18 Introduction to DFT (via th DTFT) Rading Assignmnt: Sct. 7.1 of Proakis & Manolakis 1/24 Discrt Fourir Transform (DFT) W v sn that th DTFT is
u x v x dx u x v x v x u x dx d u x v x u x v x dx u x v x dx Integration by Parts Formula
 7. Intgration by Parts Each drivativ formula givs ris to a corrsponding intgral formula, as w v sn many tims. Th drivativ product rul yilds a vry usful intgration tchniqu calld intgration by parts. Starting
7. Intgration by Parts Each drivativ formula givs ris to a corrsponding intgral formula, as w v sn many tims. Th drivativ product rul yilds a vry usful intgration tchniqu calld intgration by parts. Starting
MP IN BLOCK QUASI-INCOHERENT DICTIONARIES
 CHOOL O ENGINEERING - TI IGNAL PROCEING INTITUTE Lornzo Potta and Prr Vandrghynst CH-1015 LAUANNE Tlphon: 4121 6932601 Tlfax: 4121 6937600 -mal: lornzo.potta@pfl.ch ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE ÉDÉRALE DE LAUANNE
CHOOL O ENGINEERING - TI IGNAL PROCEING INTITUTE Lornzo Potta and Prr Vandrghynst CH-1015 LAUANNE Tlphon: 4121 6932601 Tlfax: 4121 6937600 -mal: lornzo.potta@pfl.ch ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE ÉDÉRALE DE LAUANNE
a g f 8 e 11 Also: Minimum degree, maximum degree, vertex of degree d 1 adjacent to vertex of degree d 2,...
 Warmup: Lt b 2 c 3 d 1 12 6 4 5 10 9 7 a 8 11 (i) Vriy tat G is connctd by ivin an xampl o a walk rom vrtx a to ac o t vrtics b. (ii) Wat is t sortst pat rom a to c? to? (iii) Wat is t lonst pat rom a
Warmup: Lt b 2 c 3 d 1 12 6 4 5 10 9 7 a 8 11 (i) Vriy tat G is connctd by ivin an xampl o a walk rom vrtx a to ac o t vrtics b. (ii) Wat is t sortst pat rom a to c? to? (iii) Wat is t lonst pat rom a
ph People Grade Level: basic Duration: minutes Setting: classroom or field site
 ph Popl Adaptd from: Whr Ar th Frogs? in Projct WET: Curriculum & Activity Guid. Bozman: Th Watrcours and th Council for Environmntal Education, 1995. ph Grad Lvl: basic Duration: 10 15 minuts Stting:
ph Popl Adaptd from: Whr Ar th Frogs? in Projct WET: Curriculum & Activity Guid. Bozman: Th Watrcours and th Council for Environmntal Education, 1995. ph Grad Lvl: basic Duration: 10 15 minuts Stting:
ITER Performance Study with the Presence of Internal Transport Barrier
 J. Plasma Fuson Rs. SERIES, Vol. 8 (9) IER Prformanc Study wth th Prsnc of Intrnal ransport arrr hawatcha Onjun Plasma and Fuson Rsarch Unt, Srndhorn Intrnatonal Insttut of chnology, hammasat Unvrsty,
J. Plasma Fuson Rs. SERIES, Vol. 8 (9) IER Prformanc Study wth th Prsnc of Intrnal ransport arrr hawatcha Onjun Plasma and Fuson Rsarch Unt, Srndhorn Intrnatonal Insttut of chnology, hammasat Unvrsty,
Group Consensus of Multi-agent Networks With Multiple Time Delays
 Intrnatonal Confrnc on Artfcal Intllgnc: Tchnologs and Applcatons (ICAITA 06 Group Consnsus of Mult-agnt Ntworks Wth Multpl Tm Dlays Langhao J* Xnyu Zhao Qun Lu and Yong Wang Chongqng Ky Laboratory of
Intrnatonal Confrnc on Artfcal Intllgnc: Tchnologs and Applcatons (ICAITA 06 Group Consnsus of Mult-agnt Ntworks Wth Multpl Tm Dlays Langhao J* Xnyu Zhao Qun Lu and Yong Wang Chongqng Ky Laboratory of
