Centripetal Propeller - Propulsion - Orbital Propeller. Swedish filing reference: Stefan Tubman PRV
|
|
|
- Baldric Stevenson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Centripetal Propeller - Propulsion - Orbital Propeller Swedish filing reference: Stefan Tubman PRV Brief : This document is a patent application by and covers a overview of Orbital Propeller which is a overview of a previously unknown and undocumented functional acceleration manipulation device which is a new concept. After reading this document you will basically understand mechanism of how to build a functional modeled propulsion device and have a understanding of functionality. Centripetal Propeller is entirely an innovation invention. This device is a rational functional aerospace propulsion chassis concept which introduces a new innovation in methodology unexpressed prior to this application to the Swedish patent authority body PRV. This innovation is not a gift or token purchase; nor collaboration from any collective with which I have collaborated; data was subsequently collected and interpreted. The resulting device is a electromagnetic acceleration manipulation device and is a new innovation. I present here manipulation which covers its capability in manipulation of acceleration as well as elaborated proposal of use as a propulsion device. This document should be reviewed by a qualified applied physicist and engineer for interpolation assessment. 1
2 Acceleration shield Prototype example In the photo picture of mono model above you will find that this idea is to build a acceleration propulsion gyro inducer like the one in the picture. This should be perhaps 2 meters in diameter weighing 40 Kilos The result is an acceleration device with a rotation disk weighted at outer edge and having a magnetic positive property for repelling.. N (+) N (+) 1kg 2
3 Propulsion disk: A dual direction Magnetic disjunction drive is stressed by placing a great force repelling magnetic field below and above covering a quarter hemisphere of the device deflecting it apart in that hemisphere to facilitate acceleration by momentum transition to the vehicle in orientation. N (+) N (+) Alice N (+) N (+) The magnet (magnetic) component deflects the rotor component with lift and release of the spokes Alice ensuring minimal spin resist. Possibly this hinder can be minimized by placing the spokes closer to one another to form a more or less flexible disk. 3
4 Overview: 4
5 Orbital operating disk logic reference frame: 270 Alice This acceleration propulsion concept Orbital disjunction above can be reasoned with the following argumentation: Alice Rotation has the potential to accelerate and given torque / coreolis / centripetal and Lorentz force properties the tensile structure of structural composition will use energy to compete for and maximize space available to it at zero degrees (y). When spun into a curved space rotation at a high state of torque acceleration the disks will occupy and attempt to own the path of least resistance affording maximum space this is to say that it will occupy with great force the available space at zero degrees of spin (y) along the equatorial of the axis of the spoke disk component. We can then say that with induction application of a opposition force the electro magnets will cause a distension zone in 5
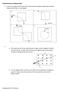
6 opposition to the 180 degree spin of the axis of the disks causing it to consummate that state of acceleration to spin at off axis of equatorial positively or negatively so that the Alice side of the disk is angularly spun off axis away from equatorial where it would afford path of least resistance and where it occupies and consummates occupancy of greatest geometric space in that by owning this path it spins with the greatest afforded space by the energy it has by torque state of acceleration. Detracting from this by opposition with great magnetic force either side of the zero or 180 degrees of axis spin the device affords less space along a restricted path of spin so it can be inferred and asserted that the Alice side of spin occupies less space by angular force acting against path of least resistance when deflected and compared to the side 0 of the device which is allowed to take the path of greatest geometric volume unhindered in unison with the Alice side. Potentially the side of the device occupies greater space geometrically with greater collective force and is in fact spinning unimpeded with greater force of acceleration than the Alice side. It can be by logic said that the side of the rim is metrically rotating faster over distance than the Alice side so that the state of acceleration torque at the side of this rim is greater than the Alice side such that the direction of drive of this device will be in the direction of the side of the device ( to the right ) allowing transference from null rotation momentum to disjunctured acceleration. b a c d In this figure above we see an illustration overview of rotation of the device where we can note rotation from a..b at the left of the device and rotation from c..d on the right side of the rotation for a coupled spoke respective fulcrum in it's middle. It takes the same time for arc rotation rpm consuming an equal degree of rotation for both the left and right side components of the device irrespective of deflection. 6
7 Alice In this figure above we see a cross section illustration of rotation from a side view of the device ( a and c ) where we can compare the solid line (c) illustration as start rotating through to the dashed line as with a..b on the left side and c..d on the right side. We can make note that at a deflected angle of 45 degrees the distance travelled by the left side is less that the distance travelled had it been at a straight line undeflected as with the right side (). The centripital force produced by the device on the left side of the device is less than the right because the radius distance of the weight ( one kilo ) on the left side is reduced. Alice 100cm 70cm We can see in this illustration of a two meter drive above that upon deflection the radius for calculating centripetal acceleration having rotated from a..b (Alice) becomes a radius of 70cm versus 100cm using a two meter drive template. 7
8 Should one then have a two meter drive with radius of one meter where the angular to linear velocity formula is : v = r ω results in a linear velocity of m/s for 70cm deflected at 100 rpm. This is a difference from the other side's counterbalance of the same weight at 100cm unhindered resulting in a velocity of m/s a difference of 3,1416m/s. 1 f = mv 2 / r is the formula for centripetal acceleration and results in centripetal force for the 70cm (Alice) side counterbalanced by of centripetal force () side spinning at 100rpm. This is a propulsive difference resulting of thrust produced by the device's component of two counter balanced spokes. 2 spanning two meters having a radius of one meter and a one kilo weight at the end of each spoke Recursive argument: A one kilogram weight at the end of a disc spoke on the Alice side of the disc when deflected at a vertical 45 degree angle from equatorial travels a shorter orbital distance in it s hemisphere than a opposing matching weight on the side of the disks; this results in disjunction where the centripetal force produced by the weight at the deflected Alice side is less than it s counter weight on the side of the device. The Alice side of the device is slower than the side in sum total producing acceleration of the rim in the direction of the side of the device. This lesser distance as stated is respective of the X / Y axis depicted in the diagram which results in and is proportional of the centripetal force produced along this plane determining the net resulting force to produce acceleration
9 Requirement: There is no proven technology existing for acceleration magnetic disjuncture propulsion. This is a unique breakthrough of process and methodology as well as state of acceleration component potential for logistical propulsion complementary. This employ also implies a stretch property to the E. Podkletnov predictive models and an M. Alcubierre predictive propulsion can be overlaid to fit it's design. The technologies employed exist where the practice, usage and conception did not; I claim ownership as proponent and originator of this concept step towards propulsion methodology having researched solutions. This type of acceleration device does not exist and I am the originator of this concept which is in part theoretical and unproven. This anomaly is available and justified in what can be called an anomaly of the laws of motion. Stefan Tubman 9
Chapter 9-10 Test Review
 Chapter 9-10 Test Review Chapter Summary 9.2. The Second Condition for Equilibrium Explain torque and the factors on which it depends. Describe the role of torque in rotational mechanics. 10.1. Angular
Chapter 9-10 Test Review Chapter Summary 9.2. The Second Condition for Equilibrium Explain torque and the factors on which it depends. Describe the role of torque in rotational mechanics. 10.1. Angular
Thereby: Force, average = mass * Velocity, gain / Time, duration
 Proofs Next two pictures, Picture #6 and #7 presents the Proof of the natural depletion of kinetic energy in a rotational to straight line coupled motion pertaining to the principles set out in picture
Proofs Next two pictures, Picture #6 and #7 presents the Proof of the natural depletion of kinetic energy in a rotational to straight line coupled motion pertaining to the principles set out in picture
Chapter 8: Rotational Motion
 Lecture Outline Chapter 8: Rotational Motion This lecture will help you understand: Circular Motion Rotational Inertia Torque Center of Mass and Center of Gravity Centripetal Force Centrifugal Force Rotating
Lecture Outline Chapter 8: Rotational Motion This lecture will help you understand: Circular Motion Rotational Inertia Torque Center of Mass and Center of Gravity Centripetal Force Centrifugal Force Rotating
 Question 6.1: Predict the direction of induced current in the situations described by the following Figs. 6.18(a) to (f ). (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) The direction of the induced current in a closed loop
Question 6.1: Predict the direction of induced current in the situations described by the following Figs. 6.18(a) to (f ). (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) The direction of the induced current in a closed loop
 1. Write the relation for the force acting on a charge carrier q moving with velocity through a magnetic field in vector notation. Using this relation, deduce the conditions under which this force will
1. Write the relation for the force acting on a charge carrier q moving with velocity through a magnetic field in vector notation. Using this relation, deduce the conditions under which this force will
SEMESTER REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
 SEMESTER REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM ACCELERATION When is an object s acceleration not equal to zero? What is the equation for acceleration? ANGULAR SPEED AND MOMENTUM Does an object on the outside of a spinning
SEMESTER REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM ACCELERATION When is an object s acceleration not equal to zero? What is the equation for acceleration? ANGULAR SPEED AND MOMENTUM Does an object on the outside of a spinning
Center of Gravity Pearson Education, Inc.
 Center of Gravity = The center of gravity position is at a place where the torque from one end of the object is balanced by the torque of the other end and therefore there is NO rotation. Fulcrum Point
Center of Gravity = The center of gravity position is at a place where the torque from one end of the object is balanced by the torque of the other end and therefore there is NO rotation. Fulcrum Point
Circular Motion Tangential Speed. Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition. Circular Motion Rotational Speed. Circular Motion
 Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Circular Motion Tangential Speed The distance traveled by a point on the rotating object divided by the time taken to travel that distance is called its tangential speed
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Circular Motion Tangential Speed The distance traveled by a point on the rotating object divided by the time taken to travel that distance is called its tangential speed
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes. Name
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes Name Date 1. Define uniform circular motion. 2. Determine the tangential velocity of an object moving with uniform circular motion. 3. Determine the centripetal
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9 Homework Outcomes Name Date 1. Define uniform circular motion. 2. Determine the tangential velocity of an object moving with uniform circular motion. 3. Determine the centripetal
Grade 7 Science. Enduring Understanding and Essential Questions Competencies Concepts Key Vocabulary
 Unit: The Scientific Method Length: 3 WEEKS Grade 7 Science Enduring Understanding and Essential Questions Competencies Concepts Key Vocabulary The scientific method is problem solving guide based on identification
Unit: The Scientific Method Length: 3 WEEKS Grade 7 Science Enduring Understanding and Essential Questions Competencies Concepts Key Vocabulary The scientific method is problem solving guide based on identification
Axis Balanced Forces Centripetal force. Change in velocity Circular Motion Circular orbit Collision. Conservation of Energy
 When something changes its velocity The rate of change of velocity of a moving object. Can result from a change in speed and/or a change in direction On surface of earth, value is 9.8 ms-²; increases nearer
When something changes its velocity The rate of change of velocity of a moving object. Can result from a change in speed and/or a change in direction On surface of earth, value is 9.8 ms-²; increases nearer
Magnetic field and magnetic poles
 Magnetic field and magnetic poles Magnetic Field B is analogically similar to Electric Field E Electric charges (+ and -)are in analogy to magnetic poles(north:n and South:S). Paramagnetism, Diamagnetism,
Magnetic field and magnetic poles Magnetic Field B is analogically similar to Electric Field E Electric charges (+ and -)are in analogy to magnetic poles(north:n and South:S). Paramagnetism, Diamagnetism,
AP Physics 1 Second Semester Final Exam Review
 AP Physics 1 Second Semester Final Exam Review Chapter 7: Circular Motion 1. What does centripetal mean? What direction does it indicate?. Does the centripetal force do work on the object it is rotating?
AP Physics 1 Second Semester Final Exam Review Chapter 7: Circular Motion 1. What does centripetal mean? What direction does it indicate?. Does the centripetal force do work on the object it is rotating?
Maximum stress location. For visualization purposes this is illustrated with a differential element shown to be in tension
 Can a standard CD-OM drive shatter a CD? A CD can be treated as an annular disk with inner hole radius a and outer radius b. The maximum stress occurs at the inner hole location at radius a. This is the
Can a standard CD-OM drive shatter a CD? A CD can be treated as an annular disk with inner hole radius a and outer radius b. The maximum stress occurs at the inner hole location at radius a. This is the
Acceleration in Uniform Circular Motion
 Acceleration in Uniform Circular Motion The object in uniform circular motion has a constant speed, but its velocity is constantly changing directions, generating a centripetal acceleration: a c v r 2
Acceleration in Uniform Circular Motion The object in uniform circular motion has a constant speed, but its velocity is constantly changing directions, generating a centripetal acceleration: a c v r 2
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
Centripetal force keeps an Rotation and Revolution
 Centripetal force keeps an object in circular motion. Which moves faster on a merry-go-round, a horse near the outside rail or one near the inside rail? While a hamster rotates its cage about an axis,
Centripetal force keeps an object in circular motion. Which moves faster on a merry-go-round, a horse near the outside rail or one near the inside rail? While a hamster rotates its cage about an axis,
We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω. What's a radian?
 We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω Units: θ = rad ω = rad/s What's a radian? Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius note: counterclockwise is + clockwise
We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω Units: θ = rad ω = rad/s What's a radian? Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius note: counterclockwise is + clockwise
PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences
 PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences ROTATIONAL MOTION D R. B E N J A M I N C H A N A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R P H Y S I C S D E P A R T M E N T F E B R U A R Y 0 1 4 Questions and Problems
PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences ROTATIONAL MOTION D R. B E N J A M I N C H A N A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R P H Y S I C S D E P A R T M E N T F E B R U A R Y 0 1 4 Questions and Problems
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics. UCVTS AIT Physics
 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
= o + t = ot + ½ t 2 = o + 2
 Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
Magnets and Electromagnetism
 Review 9 Magnets and Electromagnetism 1. A 1.2 cm wire carrying a current of 0.8 A is perpendicular to a 2.4 T magnetic field. What is the magnitude of the force on the wire? 2. A 24 cm length of wire
Review 9 Magnets and Electromagnetism 1. A 1.2 cm wire carrying a current of 0.8 A is perpendicular to a 2.4 T magnetic field. What is the magnitude of the force on the wire? 2. A 24 cm length of wire
Proficient. a. The gravitational field caused by a. The student is able to approximate a numerical value of the
 Unit 6. Circular Motion and Gravitation Name: I have not failed. I've just found 10,000 ways that won't work.-- Thomas Edison Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems
Unit 6. Circular Motion and Gravitation Name: I have not failed. I've just found 10,000 ways that won't work.-- Thomas Edison Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems
Chapter 12. Magnetism and Electromagnetism
 Chapter 12 Magnetism and Electromagnetism 167 168 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Magnetism and Electromagnetism SECTION A Magnetostatics 1. Four infinitely long wires are arranged as shown in the
Chapter 12 Magnetism and Electromagnetism 167 168 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Magnetism and Electromagnetism SECTION A Magnetostatics 1. Four infinitely long wires are arranged as shown in the
Chapter 12 Study Guide
 Chapter 12 Study Guide Key Concepts 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 A force can cause a resting object to move, or it can accelerate a moving object by changing the object s speed or direction. When the forces on
Chapter 12 Study Guide Key Concepts 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 A force can cause a resting object to move, or it can accelerate a moving object by changing the object s speed or direction. When the forces on
Rotation. PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
Chapter test: Probing the Heart of Matter
 PRO dditional sheet 5 Chapter test: Probing the Heart of Matter 40 marks total nswer LL the questions. Write your answers in the spaces provided in this question paper. The marks for individual questions
PRO dditional sheet 5 Chapter test: Probing the Heart of Matter 40 marks total nswer LL the questions. Write your answers in the spaces provided in this question paper. The marks for individual questions
Downloaded from
 Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields
 Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields Magnets can or other magnets. They are able to exert forces on each other without touching because they are surrounded by. Magnetic Flux refers to Areas with many
Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields Magnets can or other magnets. They are able to exert forces on each other without touching because they are surrounded by. Magnetic Flux refers to Areas with many
General Physical Science
 General Physical Science Chapter 3 Force and Motion Force and Net Force Quantity capable of producing a change in motion (acceleration). Key word = capable Tug of War Balanced forces Unbalanced forces
General Physical Science Chapter 3 Force and Motion Force and Net Force Quantity capable of producing a change in motion (acceleration). Key word = capable Tug of War Balanced forces Unbalanced forces
SEE the list given for chapter 04 where Newton s laws were introduced.
 PH2213 : Examples from Chapter 5 : Applying Newton s Laws Key Concepts Newton s Laws (basically Σ F = m a ) allow us to relate the forces acting on an object (left-hand side) to the motion of the object,
PH2213 : Examples from Chapter 5 : Applying Newton s Laws Key Concepts Newton s Laws (basically Σ F = m a ) allow us to relate the forces acting on an object (left-hand side) to the motion of the object,
ΣF = ma Στ = Iα ½mv 2 ½Iω 2. mv Iω
 Thur Oct 22 Assign 9 Friday Today: Torques Angular Momentum x θ v ω a α F τ m I Roll without slipping: x = r Δθ v LINEAR = r ω a LINEAR = r α ΣF = ma Στ = Iα ½mv 2 ½Iω 2 I POINT = MR 2 I HOOP = MR 2 I
Thur Oct 22 Assign 9 Friday Today: Torques Angular Momentum x θ v ω a α F τ m I Roll without slipping: x = r Δθ v LINEAR = r ω a LINEAR = r α ΣF = ma Στ = Iα ½mv 2 ½Iω 2 I POINT = MR 2 I HOOP = MR 2 I
Ch 17 Problem Set 31. A toaster is rated at 600 W when connected to a 120-V source. What current does the toaster carry, and what is its resistance?
 Ch 17 Problem Set 31. A toaster is rated at 600 W when connected to a 120-V source. What current does the toaster carry, and what is its resistance? 33. How many 100-W lightbulbs can you use in a 120-V
Ch 17 Problem Set 31. A toaster is rated at 600 W when connected to a 120-V source. What current does the toaster carry, and what is its resistance? 33. How many 100-W lightbulbs can you use in a 120-V
Electromagnetic Propulsion using the Concepts of a Homopolar Motor
 Long Beach 2010 PROCEEDINGS of the NPA 1 Electromagnetic Propulsion using the Concepts of a Homopolar Motor John R. Warfield 8250 N via Paseo Del Norte, Apt. E 102, Scottsdale, AZ 85258 e-mail: warf1002@aol.com
Long Beach 2010 PROCEEDINGS of the NPA 1 Electromagnetic Propulsion using the Concepts of a Homopolar Motor John R. Warfield 8250 N via Paseo Del Norte, Apt. E 102, Scottsdale, AZ 85258 e-mail: warf1002@aol.com
1. Draw in the magnetic field inside each box that would be capable of deflecting the particle along the path shown in each diagram.
 Charged Particles in Magnetic Fields 1. Draw in the magnetic field inside each box that would be capable of deflecting the particle along the path shown in each diagram. a b c d 2. a. Three particles with
Charged Particles in Magnetic Fields 1. Draw in the magnetic field inside each box that would be capable of deflecting the particle along the path shown in each diagram. a b c d 2. a. Three particles with
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are primarily conceptual questions, designed to see whether you understand the main concepts of the chapter. 1. A charged particle is moving with a constant velocity
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are primarily conceptual questions, designed to see whether you understand the main concepts of the chapter. 1. A charged particle is moving with a constant velocity
Chapter 7 Magnetism 7.1 Introduction Magnetism has been known thousands of years dating back to the discovery recorded by the ancient Greek.
 Chapter 7 Magnetism 7.1 Introduction Magnetism has been known thousands of years dating back to the discovery recorded by the ancient Greek. 1900 Maxwell combine the theory of electric and magnetic to
Chapter 7 Magnetism 7.1 Introduction Magnetism has been known thousands of years dating back to the discovery recorded by the ancient Greek. 1900 Maxwell combine the theory of electric and magnetic to
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Physics 2414 - Strauss Formulas: v = l / t = r θ / t = rω a T = v / t = r ω / t =rα a C = v 2 /r = ω 2 r ω = ω 0 + αt θ = ω 0 t +(1/2)αt 2 θ = (1/2)(ω 0 +ω)t ω 2 = ω 0 2 +2αθ τ
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Physics 2414 - Strauss Formulas: v = l / t = r θ / t = rω a T = v / t = r ω / t =rα a C = v 2 /r = ω 2 r ω = ω 0 + αt θ = ω 0 t +(1/2)αt 2 θ = (1/2)(ω 0 +ω)t ω 2 = ω 0 2 +2αθ τ
Solutions to Exam #1
 SBCC 2017Summer2 P 101 Solutions to Exam 01 2017Jul11A Page 1 of 9 Solutions to Exam #1 1. Which of the following natural sciences most directly involves and applies physics? a) Botany (plant biology)
SBCC 2017Summer2 P 101 Solutions to Exam 01 2017Jul11A Page 1 of 9 Solutions to Exam #1 1. Which of the following natural sciences most directly involves and applies physics? a) Botany (plant biology)
Chapter: The Laws of Motion
 Table of Contents Chapter: The Laws of Motion Section 1: Newton s Second Law Section 2: Gravity Section 3: The Third Law of Motion 1 Newton s Second Law Force, Mass, and Acceleration Newton s first law
Table of Contents Chapter: The Laws of Motion Section 1: Newton s Second Law Section 2: Gravity Section 3: The Third Law of Motion 1 Newton s Second Law Force, Mass, and Acceleration Newton s first law
Today s lecture: Motion in a Uniform Magnetic Field continued Force on a Current Carrying Conductor Introduction to the Biot-Savart Law
 PHYSICS 1B Today s lecture: Motion in a Uniform Magnetic Field continued Force on a Current Carrying Conductor Introduction to the Biot-Savart Law Electricity & Magnetism A Charged Particle in a Magnetic
PHYSICS 1B Today s lecture: Motion in a Uniform Magnetic Field continued Force on a Current Carrying Conductor Introduction to the Biot-Savart Law Electricity & Magnetism A Charged Particle in a Magnetic
7.1 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion.notebook November 03, 2017
 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion Rotational motion is the motion of objects that spin about an axis. Section 7.1 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion We use the angle θ from the positive
Describing Circular and Rotational Motion Rotational motion is the motion of objects that spin about an axis. Section 7.1 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion We use the angle θ from the positive
Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006
 Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006 1. A figure skater is spinning with arms stretched out. A moment later she rapidly brings her arms close to her body, but maintains her dynamic equilibrium.
Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006 1. A figure skater is spinning with arms stretched out. A moment later she rapidly brings her arms close to her body, but maintains her dynamic equilibrium.
Physics General Physics. Lecture 14 Rotational Motion. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 14 Rotational Motion Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 Static Equilibrium In the last lecture, we learned about the torque that a force can exert on a rigid
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 14 Rotational Motion Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 Static Equilibrium In the last lecture, we learned about the torque that a force can exert on a rigid
l Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an
 Motion and Machine Unit Notes DO NOT LOSE! Name: Energy Ability to do work To cause something to change move or directions Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but transferred from one form to another.
Motion and Machine Unit Notes DO NOT LOSE! Name: Energy Ability to do work To cause something to change move or directions Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but transferred from one form to another.
Chapter 4 - Moving Charges and Magnetism. Magnitude of the magnetic field at the centre of the coil is given by the relation,
 Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead. Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity
 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity Text: p. 160 Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Back: Centripetal Acceleration In Section 3.8, you learned
Chapter 6 Preview Looking Ahead Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity Text: p. 160 Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Preview Looking Back: Centripetal Acceleration In Section 3.8, you learned
AP Physics C - Problem Drill 18: Gravitation and Circular Motion
 AP Physics C - Problem Drill 18: Gravitation and Circular Motion Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully () Work the problems on paper as 1. Two objects some
AP Physics C - Problem Drill 18: Gravitation and Circular Motion Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully () Work the problems on paper as 1. Two objects some
CIRCULAR MOTION AND UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION
 CIRCULAR MOTION AND UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION Uniform Circular Motion What holds an object in a circular path? A force. String Friction Gravity What happens when the force is diminished? Object flies off in
CIRCULAR MOTION AND UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION Uniform Circular Motion What holds an object in a circular path? A force. String Friction Gravity What happens when the force is diminished? Object flies off in
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 19, 2015 NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 3 hours STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 19, 2015 NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 3 hours STUDENT
21 MAGNETIC FORCES AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
 CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC FORCES AND MAGNETIC FIELDS ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1 (d) Right-Hand Rule No 1 gives the direction of the magnetic force as x for both drawings A and B In drawing C, the
CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC FORCES AND MAGNETIC FIELDS ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1 (d) Right-Hand Rule No 1 gives the direction of the magnetic force as x for both drawings A and B In drawing C, the
Electric Sail Propulsion Modeling and Mission Analysis
 Electric Sail Propulsion Modeling and Mission Analysis IEPC-007-35 Presented at the 30 th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Florence, Italy Pekka Janhunen Finnish Meteorological Institute,
Electric Sail Propulsion Modeling and Mission Analysis IEPC-007-35 Presented at the 30 th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Florence, Italy Pekka Janhunen Finnish Meteorological Institute,
Cp physics web review chapter 7 gravitation and circular motion
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Cp physics web review chapter 7 gravitation and circular motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What is the
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Cp physics web review chapter 7 gravitation and circular motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What is the
Rotational kinematics
 Rotational kinematics Suppose you cut a circle out of a piece of paper and then several pieces of string which are just as long as the radius of the paper circle. If you then begin to lay these pieces
Rotational kinematics Suppose you cut a circle out of a piece of paper and then several pieces of string which are just as long as the radius of the paper circle. If you then begin to lay these pieces
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
CHAPTER 5 FUZZY LOGIC FOR ATTITUDE CONTROL
 104 CHAPTER 5 FUZZY LOGIC FOR ATTITUDE CONTROL 5.1 INTRODUCTION Fuzzy control is one of the most active areas of research in the application of fuzzy set theory, especially in complex control tasks, which
104 CHAPTER 5 FUZZY LOGIC FOR ATTITUDE CONTROL 5.1 INTRODUCTION Fuzzy control is one of the most active areas of research in the application of fuzzy set theory, especially in complex control tasks, which
Dynamics of Rotational Motion: Rotational Inertia
 Dynamics of Rotational Motion: Rotational Inertia Bởi: OpenStaxCollege If you have ever spun a bike wheel or pushed a merry-go-round, you know that force is needed to change angular velocity as seen in
Dynamics of Rotational Motion: Rotational Inertia Bởi: OpenStaxCollege If you have ever spun a bike wheel or pushed a merry-go-round, you know that force is needed to change angular velocity as seen in
Physics 53 Exam 3 November 3, 2010 Dr. Alward
 1. When the speed of a rear-drive car (a car that's driven forward by the rear wheels alone) is increasing on a horizontal road the direction of the frictional force on the tires is: A) forward for all
1. When the speed of a rear-drive car (a car that's driven forward by the rear wheels alone) is increasing on a horizontal road the direction of the frictional force on the tires is: A) forward for all
Physics Christmas Break Packet w/ Answers Which vector below represents the resultant of the two displacement vectors shown?
 Physics hristmas reak Packet w/ nswers 2018 Name: ate: 1. Which vector below represents the resultant of the two displacement vectors shown? 4. The accompanying diagram represents a block sliding down
Physics hristmas reak Packet w/ nswers 2018 Name: ate: 1. Which vector below represents the resultant of the two displacement vectors shown? 4. The accompanying diagram represents a block sliding down
UNIT HW ROTATION ANSWER KEY
 Conceptual Questions UNIT HW ROTATION ANSWER KEY 1) D_What type of linear acceleration does an object moving with constant linear speed (st) in a circular path experience? A) free fall C) linear acceleration
Conceptual Questions UNIT HW ROTATION ANSWER KEY 1) D_What type of linear acceleration does an object moving with constant linear speed (st) in a circular path experience? A) free fall C) linear acceleration
Rotational Motion. Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart
 Rotational Motion & Angular Momentum Rotational Motion Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angular Displacement
Rotational Motion & Angular Momentum Rotational Motion Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angular Displacement
Page 2 (20) Page 3 (12) Page 4 (14) Page 5 (14) Total (60) PHYSICS 11 (Fall 2003) Exam 3. Elementary Physics November 21, 2003 SCORE BOX
 INSTRUCTIONS: Except for the multiple choice questions 1 5, you must show all your work. An answer will not be enough; understanding must be demonstrated as well. This can take the form of a clear calculation,
INSTRUCTIONS: Except for the multiple choice questions 1 5, you must show all your work. An answer will not be enough; understanding must be demonstrated as well. This can take the form of a clear calculation,
(b) The period T and the angular frequency ω of uniform rotation are related to the cyclic frequency f as. , ω = 2πf =
 PHY 302 K. Solutions for problem set #9. Non-textbook problem #1: (a) Rotation frequency of 1 Hz means one revolution per second, or 60 revolutions per minute (RPM). The pre-lp vinyl disks rotated at 78
PHY 302 K. Solutions for problem set #9. Non-textbook problem #1: (a) Rotation frequency of 1 Hz means one revolution per second, or 60 revolutions per minute (RPM). The pre-lp vinyl disks rotated at 78
Einstein s silence to Hermann Oberth s principle of relativistic fuelenergy Inflation and thirteen unanswered relativity questions
 Einstein s silence to Hermann Oberth s principle of relativistic fuelenergy Inflation and thirteen unanswered relativity questions Abstract: The American Apollo Space Program Rocket Pioneer group member
Einstein s silence to Hermann Oberth s principle of relativistic fuelenergy Inflation and thirteen unanswered relativity questions Abstract: The American Apollo Space Program Rocket Pioneer group member
Chapter 27, 28 & 29: Magnetism & Electromagnetic Induction
 Chapter 27, 28 & 29: Magnetism & Electromagnetic Induction The Magnetic Field The Magnetic Force on Moving Charges The Motion of Charged Particles in a Magnetic Field The Magnetic Force Exerted on a Current-Carrying
Chapter 27, 28 & 29: Magnetism & Electromagnetic Induction The Magnetic Field The Magnetic Force on Moving Charges The Motion of Charged Particles in a Magnetic Field The Magnetic Force Exerted on a Current-Carrying
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium 8.1 Rigid Bodies, Translations, and Rotations A rigid body is an object or a system of particles in which the distances between particles are fixed (remain constant).
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium 8.1 Rigid Bodies, Translations, and Rotations A rigid body is an object or a system of particles in which the distances between particles are fixed (remain constant).
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. Figure 11.21 shows four different cases involving a
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. Figure 11.21 shows four different cases involving a
Chapter 12 Forces and Motion
 Chapter 12 Forces and Motion GOAL: Students will be able to interpret and apply Newton s three laws of motion and analyze the motion of an object in terms of its position, velocity, and acceleration. Standard:
Chapter 12 Forces and Motion GOAL: Students will be able to interpret and apply Newton s three laws of motion and analyze the motion of an object in terms of its position, velocity, and acceleration. Standard:
Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW
 Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the following situation. An object weighing 10 N swings at the end of a rope that is 0.72 m long as a simple pendulum.
Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the following situation. An object weighing 10 N swings at the end of a rope that is 0.72 m long as a simple pendulum.
Torque on a Current Loop
 Today Chapter 19 Magnetism Torque on a current loop, electrical motor Magnetic field around a current carrying wire. Ampere s law Solenoid Material magnetism Clicker 1 Which of the following is wrong?
Today Chapter 19 Magnetism Torque on a current loop, electrical motor Magnetic field around a current carrying wire. Ampere s law Solenoid Material magnetism Clicker 1 Which of the following is wrong?
Centripetal force keeps an object in circular motion Rotation and Revolution
 Centripetal force keeps an object in circular motion. 10.1 Rotation and Revolution Two types of circular motion are and. An is the straight line around which rotation takes place. When an object turns
Centripetal force keeps an object in circular motion. 10.1 Rotation and Revolution Two types of circular motion are and. An is the straight line around which rotation takes place. When an object turns
Physics 12. Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1
 Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. Meters B. Seconds C. Radians D. Radian per second E. Inches
 AP Physics B Practice Questions: Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. Meters B. Seconds C. Radians D. Radian per second E. Inches
AP Physics B Practice Questions: Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. Meters B. Seconds C. Radians D. Radian per second E. Inches
Control Volume. Dynamics and Kinematics. Basic Conservation Laws. Lecture 1: Introduction and Review 1/24/2017
 Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review
 Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Review of fundamental mathematical tools Fundamental and apparent forces Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Review of fundamental mathematical tools Fundamental and apparent forces Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study
Blueberry Muffin Nov. 29/30, 2016 Period: Names:
 Blueberry Muffin Nov. 9/30, 016 Period: Names: Congratulations! 1. To solve the problems, use your etextbook, physical textbooks, physics websites, your Sketchbooks.. Show your thinking through calculations,
Blueberry Muffin Nov. 9/30, 016 Period: Names: Congratulations! 1. To solve the problems, use your etextbook, physical textbooks, physics websites, your Sketchbooks.. Show your thinking through calculations,
Lecture 3. Rotational motion and Oscillation 06 September 2018
 Lecture 3. Rotational motion and Oscillation 06 September 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Angular Position, Velocity and Acceleration: Life Science applications Recall last t ime. Rigid Body - An object
Lecture 3. Rotational motion and Oscillation 06 September 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Angular Position, Velocity and Acceleration: Life Science applications Recall last t ime. Rigid Body - An object
Unit 8: Electromagnetism
 Multiple Choice Portion Unit 8: Electromagnetism 1. Four compasses are placed around a conductor carrying a current into the page, as shown below. Which compass correctly shows the direction of the magnetic
Multiple Choice Portion Unit 8: Electromagnetism 1. Four compasses are placed around a conductor carrying a current into the page, as shown below. Which compass correctly shows the direction of the magnetic
A. Incorrect! It looks like you forgot to include π in your calculation of angular velocity.
 High School Physics - Problem Drill 10: Rotational Motion and Equilbrium 1. If a bike wheel of radius 50 cm rotates at 300 rpm what is its angular velocity and what is the linear speed of a point on the
High School Physics - Problem Drill 10: Rotational Motion and Equilbrium 1. If a bike wheel of radius 50 cm rotates at 300 rpm what is its angular velocity and what is the linear speed of a point on the
Lecture: October 1, 2010
 Lecture: October 1, 2010 How long would it take to walk to Alpha Centauri? Announcements: Next Observatory Opportunity: Wednesday October 6 Phases of Matter the phases solid liquid gas plasma depend on
Lecture: October 1, 2010 How long would it take to walk to Alpha Centauri? Announcements: Next Observatory Opportunity: Wednesday October 6 Phases of Matter the phases solid liquid gas plasma depend on
Cannon Ball vs Cannon Momentum and Energy Force = mass x acceleration ma = Momentum = mv
 Measuring Inertial,, and s and Motions Many people are quite confused about the true nature and dynamics of centrifugal and centripetal forces. Some believe that centrifugal force is a fictitious radial
Measuring Inertial,, and s and Motions Many people are quite confused about the true nature and dynamics of centrifugal and centripetal forces. Some believe that centrifugal force is a fictitious radial
Forces, Momentum, & Gravity. Force and Motion Cause and Effect. Student Learning Objectives 2/16/2016
 Forces, Momentum, & Gravity (Chapter 3) Force and Motion Cause and Effect In chapter 2 we studied motion but not its cause. In this chapter we will look at both force and motion the cause and effect. We
Forces, Momentum, & Gravity (Chapter 3) Force and Motion Cause and Effect In chapter 2 we studied motion but not its cause. In this chapter we will look at both force and motion the cause and effect. We
Chapter 8. Conservation Laws. 8.3 Magnetic Forces Do No Work
 Chapter 8. Conservation Laws 8.3 Magnetic Forces Do No Work 8.2 Momentum of EM fields 8.2.1 Newton's Third Law in Electrodynamics Consider two charges, q 1 and q 2, moving with speeds v 1 and v 2 magnetic
Chapter 8. Conservation Laws 8.3 Magnetic Forces Do No Work 8.2 Momentum of EM fields 8.2.1 Newton's Third Law in Electrodynamics Consider two charges, q 1 and q 2, moving with speeds v 1 and v 2 magnetic
Circular Motion & Rotational Mechanics. Semester 2 Review Project - Sonya Kalara, Ellie Kim, and Charlotte Spry
 Circular Motion & Rotational Mechanics Semester 2 Review Project - Sonya Kalara, Ellie Kim, and Charlotte Spry Definitions II. III. IV. I. Uniform Circular Motion - an object that moves in a circle at
Circular Motion & Rotational Mechanics Semester 2 Review Project - Sonya Kalara, Ellie Kim, and Charlotte Spry Definitions II. III. IV. I. Uniform Circular Motion - an object that moves in a circle at
Electromagnetic Formation Flight Progress Report: July 2002
 Electromagnetic Formation Flight Progress Report: July 00 Submitted to: Lt. Col. John Comtois Technical Scientific Officer National Reconnaissance Office Contract Number: NRO-000-0-C0387-CLIN0001 MIT WBS
Electromagnetic Formation Flight Progress Report: July 00 Submitted to: Lt. Col. John Comtois Technical Scientific Officer National Reconnaissance Office Contract Number: NRO-000-0-C0387-CLIN0001 MIT WBS
PHYSICS - CLUTCH 1E CH 12: TORQUE & ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO TORQUE TORQUE is a twist that a Force gives an object around an axis of rotation. - For example, when you push on a door, it rotates around its hinges. - When a Force acts
!! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO TORQUE TORQUE is a twist that a Force gives an object around an axis of rotation. - For example, when you push on a door, it rotates around its hinges. - When a Force acts
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 12: TORQUE & ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com TORQUE & ACCELERATION (ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS) When a Force causes rotation, it produces a Torque. Think of TORQUE as the equivalent of FORCE! FORCE (F) TORQUE (τ) - Causes linear acceleration
!! www.clutchprep.com TORQUE & ACCELERATION (ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS) When a Force causes rotation, it produces a Torque. Think of TORQUE as the equivalent of FORCE! FORCE (F) TORQUE (τ) - Causes linear acceleration
Model of a DC Generator Driving a DC Motor (which propels a car)
 Model of a DC Generator Driving a DC Motor (which propels a car) John Hung 5 July 2011 The dc is connected to the dc as illustrated in Fig. 1. Both machines are of permanent magnet type, so their respective
Model of a DC Generator Driving a DC Motor (which propels a car) John Hung 5 July 2011 The dc is connected to the dc as illustrated in Fig. 1. Both machines are of permanent magnet type, so their respective
3. If you drag a rip-cord 2.0m across a wheel and it turns 10rad, what is the radius of the wheel? a. 0.1m b. 0.2m c. 0.4m d.
 1. Two spheres are rolled across the floor the same distance at the same speed. Which will have the greater angular velocity? a. the smaller sphere b. the larger sphere c. the angular velocities will be
1. Two spheres are rolled across the floor the same distance at the same speed. Which will have the greater angular velocity? a. the smaller sphere b. the larger sphere c. the angular velocities will be
Rotational Motion Test
 Rotational Motion Test Multiple Choice: Write the letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 2pts. 1. Angular momentum is: A.) The sum of moment of inertia and angular velocity B.) The
Rotational Motion Test Multiple Choice: Write the letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 2pts. 1. Angular momentum is: A.) The sum of moment of inertia and angular velocity B.) The
General classifications:
 General classifications: Physics is perceived as fundamental basis for study of the universe Chemistry is perceived as fundamental basis for study of life Physics consists of concepts, principles and notions,
General classifications: Physics is perceived as fundamental basis for study of the universe Chemistry is perceived as fundamental basis for study of life Physics consists of concepts, principles and notions,
Exam #1. On-line review questions for chapters 3-6 at uw.physics.wisc.edu/~rzchowski/phy107. Sep. 27, 2004 Physics 107, Lecture 10
 Exam #1 Hour Exam I, Wednesday Sep 29, in-class Material from Chapters 1,3,4,5,6 One page of notes (8.5 x 11 ) allowed. Can write on both sides Questions are multiple choice Scantron sheets will be used
Exam #1 Hour Exam I, Wednesday Sep 29, in-class Material from Chapters 1,3,4,5,6 One page of notes (8.5 x 11 ) allowed. Can write on both sides Questions are multiple choice Scantron sheets will be used
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Chapter 8 Rotational Motion In this chapter you will: Learn how to describe and measure rotational motion. Learn how torque changes rotational velocity. Explore factors that
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Chapter 8 Rotational Motion In this chapter you will: Learn how to describe and measure rotational motion. Learn how torque changes rotational velocity. Explore factors that
Gravity Propulsion in a Fluid Membrane- A New Propulsion Methodology. Paul Richard Price
 Gravity Propulsion in a Fluid Membrane- A New Propulsion Methodology Paul Richard Price Discussion Gravity is assumed to be a wave interaction with solid matter in the space time continuum. The Michealson-Morley
Gravity Propulsion in a Fluid Membrane- A New Propulsion Methodology Paul Richard Price Discussion Gravity is assumed to be a wave interaction with solid matter in the space time continuum. The Michealson-Morley
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. A grinding wheel is used to sharpen chisels in a school workshop. A chisel is forced against the edge of the grinding wheel so that the tangential force on the wheel is a
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. A grinding wheel is used to sharpen chisels in a school workshop. A chisel is forced against the edge of the grinding wheel so that the tangential force on the wheel is a
Mechanics 5 Dynamics of a rigid body. Basic phenomena
 Mechanics 5 Dynamics of a rigid body Torque Moment of Inertia Newton s laws for a rigid body Angular momentum Conservation law Basic phenomena In an empty space with no external forces acting on the body,
Mechanics 5 Dynamics of a rigid body Torque Moment of Inertia Newton s laws for a rigid body Angular momentum Conservation law Basic phenomena In an empty space with no external forces acting on the body,
Problem Set 6: Magnetism
 University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 10- / LeClair Spring 008 Problem Set 6: Magnetism 1. 10 points. A wire with a weight per unit length of 0.10 N/m is suspended directly above
University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 10- / LeClair Spring 008 Problem Set 6: Magnetism 1. 10 points. A wire with a weight per unit length of 0.10 N/m is suspended directly above
AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology
 AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology L E C T U R E 22 Part B, Lecture 22 19 April, 2017 C O N T E N T S Attitude stabilization passive and active. Actuators for three axis or active stabilization.
AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology L E C T U R E 22 Part B, Lecture 22 19 April, 2017 C O N T E N T S Attitude stabilization passive and active. Actuators for three axis or active stabilization.
Force, Motion, and Sound
 Force, Motion, and Sound Physics 160, Spring 2006 Galileo (1564-1642) 1642) Isaac Newton (1643-1727) 1727) Uniform Motion x = 1cm 2cm 3cm 4cm 5cm 6cm 7cm 8cm O t = 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s 7s 8s This picture
Force, Motion, and Sound Physics 160, Spring 2006 Galileo (1564-1642) 1642) Isaac Newton (1643-1727) 1727) Uniform Motion x = 1cm 2cm 3cm 4cm 5cm 6cm 7cm 8cm O t = 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s 7s 8s This picture
