Electrostatics and cohesion: Cause or effect?
|
|
|
- Howard Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrostatics and cohesion: Cause or effect? Fernando Muzzio Rutgers University Department of Chemical and Biochemical Engineering, 98 Brett Road, Piscataway, NJ Powder Flow December ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTER FOR STRUCTURED ORGANIC PARTICULATE SYSTEMS RUTGERS UNIVERSITY PURDUE UNIVERSITY NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO AT MAYAGÜEZ 10/11/2005 1
2 Charging and Granular Flow Adhesion Grains stick to surfaces Coating Grains stick to one another Agglomeration Jamming Nonuniform/intermittent flow Unpredictable behavior Poor mixing Repulsion From charged surfaces From other grains May lead to segregation Sand adhered to a hopper Cellulose adhered to a charged rod Lemarche et al., Electrostatic instabilities, charging and agglomeration in flowing granular materials,
3 Case Study 1: Pharmaceuticals (1) Preblend 50% Avicel % Pharmatose (2) Preblend + API 9% Mic.Acetaminophen % Avicel % Pharmatose (3) Preblend + API + MgSt 9% Mic.Acetaminophen + 45% Avicel % Pharmatose + 1% MgSt (4) Preblend + API + MgSt + Talc 9% Mic.Acetaminophen % Avicel % Pharmatose + 1% MgSt + 1% talc (5) Preblend + API + MgSt + Cab-O-Sil 9% Mic.Acetaminophen % Avicel % Pharmatose + 1% MgSt + 1% Cab-O-Sil (6) Preblend + API + MgSt + Cab-O-Sil + Talc 9% Mic.Acetaminophen + 44% Avicel % Pharmatose + 1% MgSt + 1% Cab-O-Sil + 1% Talc 3
4 Equipment For Sample Preparation: Controlled Shear Environment (a) Rutgers controlled shear environment. (b) Shear compartment where the powders processed were limited to 200g per run due to the limited size. (c) The baffles provide the shear stress to the powder particles. 4
5 Measurement of Acquired Charge (a) Measurement of charge density Charge (coul) * 10^( Mass (g) (b) 5
6 Acquired Charge Charge Density Preblend Charge * 10^(-7) Coulombs Mass (grams) Drug in Non-Lubricated Blend Drug in Lubricated Blend Drug in Lubricated Blend with Talc Drug in Lubricated Blend w ith Cab-O-Sil Drug in Lubricated Blend w ith Talc and Cab-O-Sil Shear rate = 40 rpm Strain = 640 rev MgSt, Talc and Cab-O-Sil are effective in decreasing charge density. 6
7 Effect of Shear Rate, Strain, and Blend Composition on Electric Properties Monopolar Charge Density Y ijk = μ + B i +R j +BR ij +S k +BS ik +RS jk +ε ijk B i =Blend effect R j =Shear Rate effect BR ij =Blend-Shear Rate interaction S k =Strain Effect BS ik =Blend-Strain interaction RS jk =Shear Rate-Strain Interaction ε ijk = Residual Error Main ANOVA Charge Density Source of Variation SS df MS F P-value F crit blend E shear rate strain blend*shear rate Blend*strain shear rate*strain Error Total Predicted Charge Density Statistical Model, Charge Dens. R² = Measured Charge Density Comparison between predicted and observed values for charge density. The factors blend, shear rate, and strain, and their two-way interactions account for 95% of all the variability in the data set. Y (residual) Normalized residuals, Charge Dens z (normalized score) R² = Test of normality for residuals of the observed charge density measurements. Clearly, the residuals are normally distributed. 7
8 Methods: Impedance Pingali et al (2009) R = p V I s out Voltage is supplied to Faraday cup loaded with 40g sample Function generator and TREK amplifier generate output high voltage Peak-to-peak voltage at several applied frequencies is recorded Impedance is recorded as ratio of supplied voltage and output current Impedance value at lowest measured frequency (100Hz) is taken as an index value for comparison to flow measurements 8
9 Effect of Shear Rate, Strain, and Blend Composition on Electric Properties Impedance Preblend (a) Preblend + API (b) Impedance (ohms) rpm, 40 rev 20 rpm, 160 rev 20 rpm, 640 rev Frequency (Hz) Impedance (ohms) rpm, 40 rev 20 rpm, 160 rev 20 rpm, 640 rev Frequency (Hz) No MgSt Preblend + API + MgSt (c) Preblend + API + MgSt + Talc (d) Impedance (ohms) rpm, 40 rev rpm, 160 rev rpm, 640 rev Frequency (Hz) Impedance (ohms) rpm, 40 rev 20 rpm, 160 rev 20 rpm, 640 rev Frequency (Hz) With MgSt Preblend + API + MgSt + Cab-O-Sil (e) Preblend + API + MgSt + Talc + Cab-O-Sil (f) Impedance (ohms) rpm, 40 rev rpm, 160 rev rpm, 640 rev Frequency (Hz) Impedance (ohms) rpm, 40 rev 20 rpm, 160 rev 20 rpm, 640 rev Frequency (Hz) Effect of shear on impedance. - Blends without lubricants showed increased impedance. - The effect was reversed with the presence of lubricant. 9
10 Effect of Shear Rate, Strain, and Blend Composition on Electric Properties Impedance Y Statistical Model, Impedance ijk = μ + B i +R j +BR ij +S k +BS ik +RS jk +ε ijk B i =Blend effect R j =Shear Rate effect BR ij =Blend-Shear Rate interaction S k =Strain Effect BS ik =Blend-Strain interaction RS jk =Shear Rate-Strain Interaction ε ijk = Residual Error Main ANOVA Impedance Source of Variation SS df MS F P-value F crit blend E shear rate strain blend*shear rate E Blend*strain E shear rate*strain Error Predicted Impedance R² = Measured Impedance Comparison between predicted and observed values for impedance. The factors blend, shear rate, and strain, and their two-way interactions account for 98% of all the variability in the data set. Y (residual) Normalized residuals, Impedance R² = z (normalized score) Total Test of normality for residuals of the observed impedance measurements. The residuals are normally distributed, displaying a R 2 of.97 when compared to a normal distribution. 10
11 Experiments Powder Adhesion in nonuniform Electric Fields High voltage produced with Van de Graaff generator Microcrystalline Cellulose Lactose Marche et al., Electrostatic instabilities, charging and agglomeration in flowing granular materials, White Sand 150μm glass beads 11
12 Adhesion Materials adhere to a grounded rod in E-field White Sand Cellulose Glass Beads 12
13 Adhesion and E-field E Strength Adhered Mass Preblend Mass (g) Shear Stress = 40 rpm Shear Strain = 650 rev Drug in Non-Lubricated Blend Drug in Lubricated Blend Drug in Lubricated Blend w ith Talc Drug In Lubricated Blend w ith Cab-O-Sil Drug In Lubricated Blend w ith Talc and Cab-O-Sil Voltage (kv) MgSt, Talc and Cab-O-Sil are effective in decreasing adhered mass. 13
14 Effect of Shear Rate, Strain, and Blend Composition on Electric Properties Dielectrophoresis Y ijk = μ + B i +R j +BR ij +S k +BS ik +RS jk +ε ijk 0.1 Statistical Model, AMCS B i =Blend effect R j =Shear Rate effect BR ij =Blend-Shear Rate interaction S k =Strain Effect BS ik =Blend-Strain interaction RS jk =Shear Rate-Strain Interaction ε ijk = Residual Error Main ANOVA Adhered mass Source of Variation SS df MS F P-value F crit blend E shear rate strain blend*shear rate E Blend*strain shear rate*strain Error Total predicted AMCS R² = Measured AMCS Comparison between predicted and observed values for AMCS. The factors blend, shear rate, and strain, and their two-way interactions account for 92% of all the variability in the data set. Y (residual) Normalized Residuals, AMCS z (normalized score) R² = Test of normality for residuals of the observed impedance measurements. The residuals are normally distributed, displaying a R 2 of.97 when compared to a normal distribution. 14
15 Effect of Strain and Composition on Electric Properties Charge Density vs. Impedance AMCS vs. Impedance Charge Density R² = R² = R² = revs 160 revs 640 revs Added Mass R² = R² = R² = revs 160 revs 640 revs Impedance Impedance Correlation of Charge Density vs. Impedance. A high degree of correlation between charge density and impedance is observed across blends and strain levels. Correlation of AMCS vs. Impedance for the samples in Table (8). A high degree of correlation between dielectrophoresis and impedance is observed across blends and strain levels. 15
16 Flow Measurement of Powders Flow Index This program displays the changes (standard deviations) in center of mass/volume over a range of rotation rates. The protocol for powder testing includes calibration of load cell (to ensure uniformity of measurement and testing using the standard drum), selecting the powder of known bulk density, imaging set up and running test sequence. The step wise prompts guides the user to carry out a sequence of testing procedure featuring automation of measuring technique of load cell data acquisition, automatic data retrieval, report generation and printout. 16
17 Dilation Measurement Dilation assembly consists of LED backlighted GDR drum with fire wire camera (640 x 480 pixels) causing the shadow on the end of the drum. Dilation As the drum rotates, the geometric shift of the powder as a percentage of drum radius is displayed continuously. 17
18 Dilation needed to flow Slide 18 18
19 Effect of composition and strain on flow properties: an electric connection Flow Index Dilation (%) R 2 = rev 160 rev R 2 = R 2 = rev Charge Density (coul/g) rev R 2 = R 2 = R 2 = rev 640 rev Charge Density (coul/g) Flow index and dilation correlate to charge acquisition for different shear treatments. Flow index and dilation increased with charge acquisition indicating worsening of powder flow with charge accumulation. 19
20 Effect of composition and strain on flow properties: an electric connection Flow Index Dilation (%) R 2 = R 2 = R 2 = Impedance (ohms) R 2 = rev 160 rev 40 rev 160 rev R 2 = R 2 = Impedance (ohms) 640 rev 640 rev (a) Flow index and (b) dilation correlate to impedance for different strain treatments. A decrease in cohesion is observed with an increase in strain. 20
21 Case Study 2: APIs Acetaminophen LEV DDMS SiO2, MgSt, Talc High shear blending in a V-blender with IB Flow index, dilation, impedance 21
22 Cohesive powder sticking to the walls Static ball rolling over during rotation Formation of static ball Static ball breaking down with increase in shear rate Persistence of static lumps 22 22
23 Flow Properties of Acetaminophen Blends Dilation (Mic.Acetaminophen) % Increase in Volume Number of Rotations 1 - Pure ACET 2 - ACET + SiO2 3 - ACET + MgSt 4 - ACET + Talc 5 - ACET + SiO2 + MgSt 6 - ACET + SiO2 + Talc 7 - ACET + Talc + MgSt 8 - ACET + SiO2 + Talc + MgSt 23
24 Dilation (LEV) % Increase in Volum e Number of Rotations 1 - Pure LEV 2 - LEV + SiO2 3 - LEV + MgSt 4 - LEV + Talc 5 - LEV + SiO2 + MgSt 6 - LEV + SiO2 + Talc 7 - LEV + Talc + MgSt 8 - LEV + SiO2 + Talc + MgSt 24
25 % Increase in Volum e Dilation (DDMS) Number of Rotations 1 - Pure DDMS 2 - DDMS + SiO2 3 - DDMS + MgSt 4 - DDMS + Talc 5 - DDMS + SiO2 + MgSt 6 - DDMS + SiO2 + Talc 8 - DDMS + SiO2 + Talc + MgSt 25
26 Impedance Impedance (LEV) Impedance (DDMS) P ure LEV Pure DDM S LEV + SiO DDM S + SiO2 Impedance (ohms) LEV + M gst 4 - LEV + Talc 5 - LEV + SiO2 + M gst 6 - LEV + SiO2 + Talc 7 - LEV + Talc + M gst 8 - LEV + Talc + SiO2 + M gst Impedance (ohms) DDMS + MgSt 4 - DDM S + Talc 5 - DDM S + SiO2 + M gst 6 - DDM S + SiO2 + Talc 8 - D DM S + T alc + SiO2 + M gst Frequency (Hz) Frequency (Hz) Impedance (ohms) Impedance (Mic.Acet) Frequency (Hz) 1 - Pure Drug (Mic. Acet) 2 - ACET + SiO2 3 - ACET + MgSt 4 -ACET + Talc 5 - ACET + SiO2 + MgSt 6 - ACET + SiO2 + Talc 7 - ACET + Talc + MgSt 8 - ACET + Talc + SiO2 + MgSt Again, the rank-ordering of impedance results is identical to the rank-ordering of flow index and dilation results of the blends. In all the cases, combination of additives improved the powder flow and decreased impedance. 26
27 Relation Between Flow And Electrical Properties for APIs Flow Index Vs Impedance (LEV) Dilation Vs Impedance (LEV) Impedance (ohms) R 2 = Impedance (ohms) R 2 = Flow Index (Standard Deviation) Flow Index (Standard Deviation) Dilation Vs Impedance (DDMS) Flow Index Vs Impedance (ACET) Impedance (ohms) R 2 = Flow Index R 2 = Flow Index (Standard Deviation) 10 1E+07 1E+07 1E+07 2E+07 2E+07 2E+07 2E+07 2E+07 3E+07 Impedance (ohms) Impedance (ohms) Dilation Vs Impedance (ACET) R 2 = E+07 1E+07 1E+07 2E+07 2E+07 2E+07 2E+07 2E+07 3E+07 Flow Index (Standard Deviation) 27
28 Case study 3: Ceramics Three materials: Fine Boehmite (dp = 5μm) - FB Clay (dp = 22μm) - C Coarse Boehmite (dp = 60μm) - CB Blends (ranked from worst to best flow): 100% Fine Boehmite 75% Fine Boehmite and 25% Clay 50% Fine Boehmite and 50% Clay 25% Fine Boehmite and 75% Clay 100% Clay 75% Clay and 25% Coarse Boehmite 50% Clay and 50% Coarse Boehmite 25% Clay and 75% Coarse Boehmite 100% Coarse Boehmite Volume Fraction (-) 10 9 Coarse Boehmite Fine Boehmite 8 Clay Particle Diameter (μm) (PSD data courtesy AlbeMarle) JJH 28
29 GDR and Dilation Data (intermediate to best flow) The flow ranking was expected to be pure clay (worst) clay (75%) clay (50%) clay (25%) CB (best) The flow behavior of mixtures was in direct correlation with the component concentration 29
30 GDR and Dilation Data (worst to intermediate flow) In case of FB/C mixtures, the flow behavior of the blends was governed by the presence of fine boehmite. 30
31 Impedance Impedance is related to cohesion through 1) Larger capacitance = increased interparticle forces 2) Lower density = lower conductivity = higher resistance Impedance correlates well with dilation measurements, suggesting that it can be used as a flow properties measurement 31
32 Compressibility Test Measures cohesion by relating it to the amount of entrapped air Technique shows general correlation to particle size and therefore cohesion, but some exceptions exist Procedure: Powder is conditioned by a helical blade passing through Normal force is subsequently applied with a vented piston in intervals from 0.5kPa to 15kPa The change of volume upon compression is measured at each step The compressibility index (I C ) is calculated as I C ρ = ρ compr cond 100% 32
33 Density Comparisons Both, FT4 Conditioned Density and GDR Dilated Density, correlate remarkably well to the Bulk (Poured) Density measurements 33
34 Compressibility Dependence of Compressibility index on composition is very pronounced 34
35 Compressibility vs. Dilation Flow properties of worst/intermediate flow blends are greatly influenced by the presence of highly compressible component High correlation between compressibility and dilation is present 35
36 Impedance: Dependence on Density Impedance values correlated well with compressibility index Recall from previous (Reason #2), that lower density corresponds to larger voids, which results in lower conductivity and greater resistance of the powder bed To confirm this, impedance was also compared to bulk density measurements and showed good correlation 36
37 Relation Between Flow and Electrical Properties (Observations and Conclusions) Capacitance Charge Composition Impedance Cohesion Resistance Charge Shear Structure Resistance Density 37
38 Methods: Rotating Shear Cell Application: Originally developed to assist in design of hoppers and silos Subsequently used to characterize powder behavior in consolidated state Procedure: Sample is loaded into a holding cup and preconditioned by dynamic blade Sample is pre-compacted with a consolidation force S (stress σ) Sample is pre-sheared to achieve critical consolidation state (steady-state flow) Normal stress is lowered, sample is sheared further to obtain the yield point (a point of failure) FT4 Shear Cell 38
39 Methods: Rotating Shear Cell Yield Data: Procedure above is repeated several times to obtain yield locus Schwedes (1999) From yield locus, values of major principal stress (σ 1 ), unconfined yield stress (σ c ), and cohesion (the intercept) are obtained by Mohr stress circle analysis 39
40 Methods: Rotational Shear Cell Yield Data: (Schwedes,1999) σ c was plotted against σ 1 Every blend was tested at 4 different consolidation stresses to obtain a flow function σ c = f(σ 1 ) Flow factor (ff c ) was calculated for σ N = 3 kpa (the smallest consolidation load tested) Additionally, the value of cohesion parameter (value of shear stress at zero consolidation) was plotted against major principal stress (σ 1 ) Unconfined Yield Strength ff C = σ σ 1 = c 1 m Major Principal Stress 40
41 Shear Cell Data (Flow Functions) For FB/C mixtures: while the flow ranking was expected to be pure clay (best) clay (75%) clay (50%) clay (25%) FB (worst), all mixtures exhibited shear flow behavior that was worse than any of the pure components. For CB/C mixtures: shear behavior of mixtures was mostly as expected. 41
42 Shear Cell Data (Cohesion) For FB/C mixtures: the flow ranking was expected to be pure clay (best) clay (75%) clay (50%) clay (25%) FB (worst), and most mixtures exhibited expected shear flow behavior. For CB/C mixtures: shear behavior of mixtures was mostly as expected. 42
43 Shear Cell Results: Difference in Consolidation Shear Cell Flow Factor (ff c ) and Cohesion parameter (τ C ) have a non-linear relationship; Cohesion parameter measures flowability under zero consolidation, while ff c is much more consolidation-dependent 43
44 FT4 Techniques: Dependence on Consolidation Shear Cell Flow Factor (ff c ) has a non-linear correlation to the Compressibility Index (I C ) due to the presence of cohesive components The correlation between I C and cohesion is much more pronounced 44
45 GDR vs. Shear Cell Correlations Relationship between cohesion parameter (τc) and GDR Flow Index is quite more linear than for shear cell flow index (ff c ) Techniques measure flow characteristics at similar degrees of consolidation 45
46 Conclusions (???) Higher impedance blends produce more cohesive beds that flow in larger chunks (i.e. produce higher flow indices) and dilate more. For materials with larger capacitance, capacitive charge storage increases the strength of inter-particle forces, leading to increases in cohesion. For more cohesive materials, decrease in density (increases in dilation) decreases electric conductivity. The powders with the best flow characteristics exhibited the lowest electrostatics (higher rates of discharge of electric charge are associated with improved flow). Higher dilation was mitigated by the presence of MgSt, which reduced the bed conductivity and dilation, and correspondingly improved the powder flow. Observed flow and electric properties are a complex function of blend composition. 46
47 47
48 Methods: Variable Flow Rate Blade moves through the powder bed at decreasing flow rates (blade speed through the vessel) Several parameters are derived from the measurements: BFE (Basic Flowability Energy) energy measured with the blade passing downward through the bed (applying some compression) FRI (Flow Rate Index) ratio of flow energy of test 1 to flow energy of test 4 (sensitivity of powder to 10-fold decrease in flow rate) SE (Specific Energy) measures unconfined flow energy (energy on the blade moving upward) 48
49 Methods: Aeration Air is introduced through the bottom plate of the vessel at incremented intervals; Energy on the passing through blade is measured at every flow rate Measures how flow energy reduces with aeration Free Flowing Cohesive 49
50 Methods: Permeability Permeability measures how easily air passes through a powder at increasing bulk stress During the test the air is passed through the powder column base as the normal stress is applied in increments Pressure drop across the powder bed is measured, permeability constant (k) can be calculated Where, Q = air volume flow rate (cm 3 /s) k = permeability (cm 2 ) A = cross-sectional area of bed (cm 2 ) µ = air viscosity (Pa.s) Pa-Pb = pressure drop across the bed (Pa) L = length of powder bed (cm) 50
51 Aeration Results Less Cohesive Blends containing fine PSD ingredient were hardly affected by aeration, with cohesive forces resisting fluidization Blends containing coarse component became fluidized quickly due to weaker cohesive forces between the particles More Cohesive The order, in which blends became fluidizes, follows the predicted order of blends cohesion (clay (worst) 25% Coarse 50% Coarse 75% Coarse 100% Coarse (best)) 51
52 Aeration and Dilation Lower aerated ratios tend to correspond to higher dilation volumes Larger cohesive forces between the particles contribute to the formation of larger voids upon dilation; as well as, constrict the ability of air to pass through the powder bed and fluidize the powder As a result, both these indices measure the same phenomenon 52
53 Permeability Pressure drop (and permeability) showed to be a function of fines (clay) concentration Trend of decrease in permeability with fines concentration is present, however, this dependence is non-linear 53
54 Permeability: Consolidation Previous finding also explain the non-linear trend between permeability and dilation (upper graph) and permeability and compressibility index, suggesting a combination of other factors may influence the permeability results 54
Measuring the flow properties of powders. FT4 Powder Rheometer. freemantechnology
 Measuring the flow properties of powders FT4 Powder Rheometer freemantechnology Efficiency, quality and productivity Successful powder processing requires the ability to reliably and repeatably predict
Measuring the flow properties of powders FT4 Powder Rheometer freemantechnology Efficiency, quality and productivity Successful powder processing requires the ability to reliably and repeatably predict
A Digital Design Approach to Prediction of Powder Flowability
 A Digital Design Approach to Prediction of Powder Flowability James Elliott, Xizhong Chen ( 陈锡忠 ) and Chunlei Pei ( 裴春雷 ) Macromolecular Materials Laboratory University of Cambridge ADDoPT Work Package
A Digital Design Approach to Prediction of Powder Flowability James Elliott, Xizhong Chen ( 陈锡忠 ) and Chunlei Pei ( 裴春雷 ) Macromolecular Materials Laboratory University of Cambridge ADDoPT Work Package
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses.
 8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
3 Flow properties of bulk solids
 3 Flow properties of bulk solids The flow properties of bulk solids depend on many parameters, e.g.: particle size distribution, particle shape, chemical composition of the particles, moisture, temperature.
3 Flow properties of bulk solids The flow properties of bulk solids depend on many parameters, e.g.: particle size distribution, particle shape, chemical composition of the particles, moisture, temperature.
Chapter 7 Mixing and Granulation
 Chapter 7 Mixing and Granulation 7.1 Mixing and Segregation (Chapter 9) Mixing vs. segregation (1) Types of Mixture * Perfect mixing Random mixing Segregating mixing Figure 9.1 (2) Segregation 1) Causes
Chapter 7 Mixing and Granulation 7.1 Mixing and Segregation (Chapter 9) Mixing vs. segregation (1) Types of Mixture * Perfect mixing Random mixing Segregating mixing Figure 9.1 (2) Segregation 1) Causes
Laboratory Testing Total & Effective Stress Analysis
 SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Laboratory Testing Total & Effective Stress Analysis Prepared by: Dr. Hetty Mohr Coulomb failure criterion with Mohr circle of stress 2 ' 2 ' ' ' 3 ' 1 ' 3 ' 1 Cot Sin c ' ' 2
SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Laboratory Testing Total & Effective Stress Analysis Prepared by: Dr. Hetty Mohr Coulomb failure criterion with Mohr circle of stress 2 ' 2 ' ' ' 3 ' 1 ' 3 ' 1 Cot Sin c ' ' 2
QbD QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENTS OF CQAS IN SOLID DOSAGE FORM UNIT OPERATIONS
 QbD QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENTS OF CQAS IN SOLID DOSAGE FORM UNIT OPERATIONS Particle Size Material Segregation-Flow USP USP USP Ph. Eur. 2.9.31 Ph. Eur. 2.9.36 JP 1 JP 18 Light Diffraction
QbD QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENTS OF CQAS IN SOLID DOSAGE FORM UNIT OPERATIONS Particle Size Material Segregation-Flow USP USP USP Ph. Eur. 2.9.31 Ph. Eur. 2.9.36 JP 1 JP 18 Light Diffraction
D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test.
 (d) COMPRESSIBILITY AND CONSOLIDATION D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test. (a) Plot the e - σ curve. (b)
(d) COMPRESSIBILITY AND CONSOLIDATION D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test. (a) Plot the e - σ curve. (b)
Bulk Solid Handling Rodrigo Gutierrez
 Bulk Solid Handling Rodrigo Gutierrez INTRODUCCION Throughout the world, the handling and processing of powders and bulk materials are key operations in a great number and variety of industries. Such industries
Bulk Solid Handling Rodrigo Gutierrez INTRODUCCION Throughout the world, the handling and processing of powders and bulk materials are key operations in a great number and variety of industries. Such industries
Formulation of Low Dose Medicines - Theory and Practice
 Hashim Ahmed, Ph.D. and Navnit Shah, Ph.D. Pharmaceutical and Analytical R&D, Hoffmann-La Roche Inc., Nutley NJ Formulation of Low Dose Medicines - Theory and Practice Progress in pharmaceutical research
Hashim Ahmed, Ph.D. and Navnit Shah, Ph.D. Pharmaceutical and Analytical R&D, Hoffmann-La Roche Inc., Nutley NJ Formulation of Low Dose Medicines - Theory and Practice Progress in pharmaceutical research
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL
 Soil Failure Criteria SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Knowledge about the shear strength of soil important for the analysis of: Bearing capacity of foundations, Slope stability, Lateral pressure on retaining structures,
Soil Failure Criteria SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Knowledge about the shear strength of soil important for the analysis of: Bearing capacity of foundations, Slope stability, Lateral pressure on retaining structures,
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL UNCONFINED COMPRESSION TEST
 SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL DEFINITION The shear strength of the soil mass is the internal resistance per unit area that the soil mass can offer to resist failure and sliding along any plane inside it. INTRODUCTION
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL DEFINITION The shear strength of the soil mass is the internal resistance per unit area that the soil mass can offer to resist failure and sliding along any plane inside it. INTRODUCTION
Shear Strength of Soils
 Shear Strength of Soils STRESSES IN A SOIL ELEMENT t s v Analyze Effective Stresses (s ) Load carried by Soil t Where: s H t t s H s = t f = s v = s H = t = s v Stresses in a Soil Element after Figure
Shear Strength of Soils STRESSES IN A SOIL ELEMENT t s v Analyze Effective Stresses (s ) Load carried by Soil t Where: s H t t s H s = t f = s v = s H = t = s v Stresses in a Soil Element after Figure
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 56 Module 4: Lecture 7 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-Coulomb failure
56 Module 4: Lecture 7 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-Coulomb failure
The Influence of Contact Friction on the Breakage Behavior of Brittle Granular Materials using DEM
 The Influence of Contact Friction on the Breakage Behavior of Brittle Granular Materials using DEM *Yi-Ming Liu 1) and Hua-Bei Liu 2) 1), 2) School of Civil Engineering and Mechanics, Huazhong University
The Influence of Contact Friction on the Breakage Behavior of Brittle Granular Materials using DEM *Yi-Ming Liu 1) and Hua-Bei Liu 2) 1), 2) School of Civil Engineering and Mechanics, Huazhong University
Understanding segregation mechanisms Segregation can occur by several different mechanisms, depending on the particles physical characteristics and th
 Predicting, diagnosing, and solving mixture segregation problems Herman Purutyan and John W. Carson Jenike & Johanson, Inc. Keeping a dry bulk material mixture together from the blender to the final package
Predicting, diagnosing, and solving mixture segregation problems Herman Purutyan and John W. Carson Jenike & Johanson, Inc. Keeping a dry bulk material mixture together from the blender to the final package
Application of Ring Shear Testing to Optimize Pharmaceutical Formulation and Process Development of Solid Dosage Forms
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 21, 2013 Application of Ring Shear Testing to Optimize Pharmaceutical Formulation and Process Development of Solid Dosage Forms Søren V. Søgaard
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 21, 2013 Application of Ring Shear Testing to Optimize Pharmaceutical Formulation and Process Development of Solid Dosage Forms Søren V. Søgaard
1.8 Unconfined Compression Test
 1-49 1.8 Unconfined Compression Test - It gives a quick and simple measurement of the undrained strength of cohesive, undisturbed soil specimens. 1) Testing method i) Trimming a sample. Length-diameter
1-49 1.8 Unconfined Compression Test - It gives a quick and simple measurement of the undrained strength of cohesive, undisturbed soil specimens. 1) Testing method i) Trimming a sample. Length-diameter
What is segregation? Gabrie Meesters
 What is segregation? Gabrie Meesters Outline of the presentation What is segregation Types of segregation Do s and don ts with respect to segregation .so what is segregation Segregation results when particles
What is segregation? Gabrie Meesters Outline of the presentation What is segregation Types of segregation Do s and don ts with respect to segregation .so what is segregation Segregation results when particles
Limestone Powders Yielding and Steady State Resistance under Shearing with Different Testers
 1 Limestone Powders Yielding and Steady State Resistance under Shearing with Different Testers Hao Shi 1, Stefan Luding 1 and Vanessa Magnanimo 1 Multi Scale Mechanics, CTW, MESA+, University of Twente,
1 Limestone Powders Yielding and Steady State Resistance under Shearing with Different Testers Hao Shi 1, Stefan Luding 1 and Vanessa Magnanimo 1 Multi Scale Mechanics, CTW, MESA+, University of Twente,
Development of a Reproducible Powder Characterization Method Using a Powder Rheometer
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 20, 2012 Development of a Reproducible Powder Characterization Method Using a Powder Rheometer Søren Vinter Søgaard 1, Morten Allesø 2, Joergen
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 20, 2012 Development of a Reproducible Powder Characterization Method Using a Powder Rheometer Søren Vinter Søgaard 1, Morten Allesø 2, Joergen
Simulation of Particulate Solids Processing Using Discrete Element Method Oleh Baran
 Simulation of Particulate Solids Processing Using Discrete Element Method Oleh Baran Outline DEM overview DEM capabilities in STAR-CCM+ Particle types and injectors Contact physics Coupling to fluid flow
Simulation of Particulate Solids Processing Using Discrete Element Method Oleh Baran Outline DEM overview DEM capabilities in STAR-CCM+ Particle types and injectors Contact physics Coupling to fluid flow
Influence of forced material in roller compactor parameters I.
 1 Portál pre odborné publikovanie ISSN 1338-0087 Influence of forced material in roller compactor parameters I. Krok Alexander Elektrotechnika, Strojárstvo 24.08.2009 In the chemical, pharmaceutical and
1 Portál pre odborné publikovanie ISSN 1338-0087 Influence of forced material in roller compactor parameters I. Krok Alexander Elektrotechnika, Strojárstvo 24.08.2009 In the chemical, pharmaceutical and
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL
 SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Necessity of studying Shear Strength of soils : Soil failure usually occurs in the form of shearing along internal surface within the soil. Shear Strength: Thus, structural strength
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Necessity of studying Shear Strength of soils : Soil failure usually occurs in the form of shearing along internal surface within the soil. Shear Strength: Thus, structural strength
Theory of Shear Strength
 MAJ 1013 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 Strength of different materials Steel Concrete Soil Tensile strength Compressive strength Shear strength Complex behavior
MAJ 1013 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 Strength of different materials Steel Concrete Soil Tensile strength Compressive strength Shear strength Complex behavior
BIO & PHARMA ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES. Chapter 5 Particle Size Analysis
 BIO & PHARMA ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Chapter 5 by Dr Siti Umairah Mokhtar Faculty of Engineering Technology umairah@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims Discuss theory, principles and application of analytical
BIO & PHARMA ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Chapter 5 by Dr Siti Umairah Mokhtar Faculty of Engineering Technology umairah@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims Discuss theory, principles and application of analytical
Theory of Shear Strength
 SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 SOIL STRENGTH DEFINITION Shear strength of a soil is the maximum internal resistance to applied shearing forces The maximum or
SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 SOIL STRENGTH DEFINITION Shear strength of a soil is the maximum internal resistance to applied shearing forces The maximum or
9 Stresses. 9.1 Stress states in silos
 9 Stresses The knowledge of the stresses prevailing in bulk solids, especially when being stored in bins and silos, is extremely important when considering the following topics: Silo design for flow (e.g.,
9 Stresses The knowledge of the stresses prevailing in bulk solids, especially when being stored in bins and silos, is extremely important when considering the following topics: Silo design for flow (e.g.,
The Effects of Shear on the Flow Properties of Multiple Pharmaceutical Blends
 The Effects of Shear on the Flow Properties of Multiple Pharmaceutical Blends Binni Kunvarjee binnik1219@yahoo.com Amber Cox amariecox@gmail.com Diana Mak squirrelicious@gmail.com Eric Penalver ericpenalver@gmail.com
The Effects of Shear on the Flow Properties of Multiple Pharmaceutical Blends Binni Kunvarjee binnik1219@yahoo.com Amber Cox amariecox@gmail.com Diana Mak squirrelicious@gmail.com Eric Penalver ericpenalver@gmail.com
Effect of Applied Vibration on Silo Hopper Design
 Effect of Applied Vibration on Silo Hopper Design Th. Kollmann and J. Tomas Mechanical Process Engineering, Department of Process Engineering, The Otto-von-Guericke- University of Magdeburg, P.O. Box 412,
Effect of Applied Vibration on Silo Hopper Design Th. Kollmann and J. Tomas Mechanical Process Engineering, Department of Process Engineering, The Otto-von-Guericke- University of Magdeburg, P.O. Box 412,
Inter-particle force and stress models for wet and dry particulate flow at the intermediate flow regime
 Inter-particle force and stress models for wet and dry particulate flow at the intermediate flow regime Xi Yu 1, Raffaella Ocone 3, Sotos Generalis 2, Yassir Makkawi 1 1 Chemical Engineering & Applied
Inter-particle force and stress models for wet and dry particulate flow at the intermediate flow regime Xi Yu 1, Raffaella Ocone 3, Sotos Generalis 2, Yassir Makkawi 1 1 Chemical Engineering & Applied
Chapter (12) Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad
 Chapter (12) Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter Outlines Shear strength in soils Direct shear test Unconfined Compression Test Tri-axial Test Shear Strength The strength of a material is the
Chapter (12) Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter Outlines Shear strength in soils Direct shear test Unconfined Compression Test Tri-axial Test Shear Strength The strength of a material is the
Tendency of blends for segregation
 Tendency of blends for segregation How to study it? Methods for measuring the segregation potential Louk Peffer 1 Outline/Themes Blends unmix Theory or reality Visual inspection Segregation mechanisms
Tendency of blends for segregation How to study it? Methods for measuring the segregation potential Louk Peffer 1 Outline/Themes Blends unmix Theory or reality Visual inspection Segregation mechanisms
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL. Chapter 10: Sections Chapter 12: All sections except
 SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Chapter 10: Sections 10. 10.3 Chapter 1: All sections ecept 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.17 1.18 TOPICS Introduction Components of Shear Strength of Soils Normal and Shear Stresses on a Plane
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Chapter 10: Sections 10. 10.3 Chapter 1: All sections ecept 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.17 1.18 TOPICS Introduction Components of Shear Strength of Soils Normal and Shear Stresses on a Plane
Powder Technology 194 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Powder Technology. journal homepage:
 Powder Technology 194 (2009) 217 227 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Powder Technology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/powtec Effects of rotation rate, mixing angle, and cohesion in
Powder Technology 194 (2009) 217 227 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Powder Technology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/powtec Effects of rotation rate, mixing angle, and cohesion in
THE BENEFITS OF POWDER CHARACTERISATION
 SHAPA Technical Bulletin No.14 THE BENEFITS OF POWDER CHARACTERISATION Page 1 of 11 THE BENEFITS OF POWDER CHARACTERISATION Eddie McGee 1 1 Technical Director, Ajax Equipment Limited, Milton Works, Mule
SHAPA Technical Bulletin No.14 THE BENEFITS OF POWDER CHARACTERISATION Page 1 of 11 THE BENEFITS OF POWDER CHARACTERISATION Eddie McGee 1 1 Technical Director, Ajax Equipment Limited, Milton Works, Mule
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
CFD Investigations of Effects of Cohesive Particles Proportion on Fluidization of Binary Particles
 Proceedings of the 2 nd World Congress on Momentum, Heat and Mass Transfer (MHMT 17) Barcelona, Spain April 6 8, 2017 Paper No. ICMFHT 122 ISSN: 2371-5316 DOI: 10.11159/icmfht17.122 CFD Investigations
Proceedings of the 2 nd World Congress on Momentum, Heat and Mass Transfer (MHMT 17) Barcelona, Spain April 6 8, 2017 Paper No. ICMFHT 122 ISSN: 2371-5316 DOI: 10.11159/icmfht17.122 CFD Investigations
With high enough plate forces in opposite directions Bolts. How do these fail? Each pin has sheared into two pieces.
 SHEAR STRENGTH In general, the shear strength of any material is the load per unit area or pressure that it can withstand before undergoing shearing failure. Shearing When you Pins hear can Shear be used
SHEAR STRENGTH In general, the shear strength of any material is the load per unit area or pressure that it can withstand before undergoing shearing failure. Shearing When you Pins hear can Shear be used
Experimental study of sand deformations during a CPT
 3 rd International Symposium on Cone Penetration Testing, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA - 2014 Experimental study of sand deformations during a CPT A.V. Melnikov & G.G. Boldyrev Penza State University of Architecture
3 rd International Symposium on Cone Penetration Testing, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA - 2014 Experimental study of sand deformations during a CPT A.V. Melnikov & G.G. Boldyrev Penza State University of Architecture
16 Rainfall on a Slope
 Rainfall on a Slope 16-1 16 Rainfall on a Slope 16.1 Problem Statement In this example, the stability of a generic slope is analyzed for two successive rainfall events of increasing intensity and decreasing
Rainfall on a Slope 16-1 16 Rainfall on a Slope 16.1 Problem Statement In this example, the stability of a generic slope is analyzed for two successive rainfall events of increasing intensity and decreasing
Triaxial Shear Test. o The most reliable method now available for determination of shear strength parameters.
 TOPICS Introduction Components of Shear Strength of Soils Normal and Shear Stresses on a Plane Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criterion Laboratory Shear Strength Testing Direct Shear Test Triaxial Compression Test
TOPICS Introduction Components of Shear Strength of Soils Normal and Shear Stresses on a Plane Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criterion Laboratory Shear Strength Testing Direct Shear Test Triaxial Compression Test
Shear strength. Common cases of shearing In practice, the state of stress in the ground will be complex. Common cases of shearing Strength
 Shear strength Common cases of shearing Strength Near any geotechnical construction (e.g. slopes, excavations, tunnels and foundations) there will be both mean and normal stresses and shear stresses. The
Shear strength Common cases of shearing Strength Near any geotechnical construction (e.g. slopes, excavations, tunnels and foundations) there will be both mean and normal stresses and shear stresses. The
Soil strength. the strength depends on the applied stress. water pressures are required
 Soil Strength Soil strength u Soils are essentially frictional materials the strength depends on the applied stress u Strength is controlled by effective stresses water pressures are required u Soil strength
Soil Strength Soil strength u Soils are essentially frictional materials the strength depends on the applied stress u Strength is controlled by effective stresses water pressures are required u Soil strength
Mixing of powders. Wim Oostra
 Mixing of powders Wim Oostra Introduction Concepts of mixtures Statistics Mechanisms of mixing Segregation Equipment Practice Scale - up References Content Types of Mixtures Types of Mixtures Ordered Mixture
Mixing of powders Wim Oostra Introduction Concepts of mixtures Statistics Mechanisms of mixing Segregation Equipment Practice Scale - up References Content Types of Mixtures Types of Mixtures Ordered Mixture
Mechanistic Study of Nano-Particle Fluidization
 Refereed Proceedings The 1th International Conference on Fluidization - New Horizons in Fluidization Engineering Engineering Conferences International Year 007 Mechanistic Study of Nano-Particle Fluidization
Refereed Proceedings The 1th International Conference on Fluidization - New Horizons in Fluidization Engineering Engineering Conferences International Year 007 Mechanistic Study of Nano-Particle Fluidization
Micro-scale modelling of internally
 Micro-scale modelling of internally unstable soils Dr Tom Shire School of Engineering, University of Glasgow 1 st September 2017 Outline Internal instability Micro-scale modelling Hydromechanical criteria
Micro-scale modelling of internally unstable soils Dr Tom Shire School of Engineering, University of Glasgow 1 st September 2017 Outline Internal instability Micro-scale modelling Hydromechanical criteria
Yield Energy of Asphalt Binders Using the Dynamic Shear Rheometer
 Standard Method of Test for Yield Energy of Asphalt Binders Using the Dynamic Shear Rheometer AASHTO Designation: T XXX-09 1. SCOPE 1.1. This test method covers the indication of asphalt binders resistance
Standard Method of Test for Yield Energy of Asphalt Binders Using the Dynamic Shear Rheometer AASHTO Designation: T XXX-09 1. SCOPE 1.1. This test method covers the indication of asphalt binders resistance
Ch 4a Stress, Strain and Shearing
 Ch. 4a - Stress, Strain, Shearing Page 1 Ch 4a Stress, Strain and Shearing Reading Assignment Ch. 4a Lecture Notes Sections 4.1-4.3 (Salgado) Other Materials Handout 4 Homework Assignment 3 Problems 4-13,
Ch. 4a - Stress, Strain, Shearing Page 1 Ch 4a Stress, Strain and Shearing Reading Assignment Ch. 4a Lecture Notes Sections 4.1-4.3 (Salgado) Other Materials Handout 4 Homework Assignment 3 Problems 4-13,
The role of interparticle forces in the fluidization of micro and nanoparticles
 The role of interparticle forces in the fluidization of micro and nanoparticles A. Castellanos POWDER FLOW 2009 London, December 16 Acknowledgements The experimental work presented here has been done in
The role of interparticle forces in the fluidization of micro and nanoparticles A. Castellanos POWDER FLOW 2009 London, December 16 Acknowledgements The experimental work presented here has been done in
Pharmaceutical Polymers for Tablets and Capsules
 Pharmaceutical Polymers for Tablets and Capsules Edition: March 23, 2010 Wet Granulation Direct compression is not feasible for matrix formulations containing high levels of powder Carbopol polymers (>5%
Pharmaceutical Polymers for Tablets and Capsules Edition: March 23, 2010 Wet Granulation Direct compression is not feasible for matrix formulations containing high levels of powder Carbopol polymers (>5%
Fundamentals of Static Electricity
 Fundamentals of Static Electricity Basic Concepts Calculation Methods Guidelines Case Histories Fundamentals of Static Electricity How Do Charges Accumulate? How Do Accumulated Charges Discharge? How Do
Fundamentals of Static Electricity Basic Concepts Calculation Methods Guidelines Case Histories Fundamentals of Static Electricity How Do Charges Accumulate? How Do Accumulated Charges Discharge? How Do
Geomorphology 5. Stream Sediment Stream Sediment
 Geomorphology 5. Stream Sediment 1 Name 47 Points LEARNING OUTCOMES 5. Stream Sediment By the end of this assignment you should be able to: Describe the relationship between particle size and critical
Geomorphology 5. Stream Sediment 1 Name 47 Points LEARNING OUTCOMES 5. Stream Sediment By the end of this assignment you should be able to: Describe the relationship between particle size and critical
Fluid Mechanics Introduction
 Fluid Mechanics Introduction Fluid mechanics study the fluid under all conditions of rest and motion. Its approach is analytical, mathematical, and empirical (experimental and observation). Fluid can be
Fluid Mechanics Introduction Fluid mechanics study the fluid under all conditions of rest and motion. Its approach is analytical, mathematical, and empirical (experimental and observation). Fluid can be
COMPRESSIBILITY AND FLOW PROPERTIES OF A COHESIVE LIMESTONE POWDER IN A MEDIUM PRESSURE RANGE
 COMPRESSIBILITY AND FLOW PROPERTIES OF A COHESIVE LIMESTONE POWDER IN A MEDIUM PRESSURE RANGE L. Grossmann 1, J. Tomas 1 and B. Csőke 2 1. Otto-von-Guericke-University Department of Mechanical Process
COMPRESSIBILITY AND FLOW PROPERTIES OF A COHESIVE LIMESTONE POWDER IN A MEDIUM PRESSURE RANGE L. Grossmann 1, J. Tomas 1 and B. Csőke 2 1. Otto-von-Guericke-University Department of Mechanical Process
Lateral Earth Pressure
 1 of 11 6/2/2012 4:28 AM Lateral Earth Pressure The magnitude of lateral earth pressure depends on: 1. Shear strength characteristics of soil 2. Lateral strain condition 3. Pore water pressure 4. State
1 of 11 6/2/2012 4:28 AM Lateral Earth Pressure The magnitude of lateral earth pressure depends on: 1. Shear strength characteristics of soil 2. Lateral strain condition 3. Pore water pressure 4. State
Asphalt Mix Designer. Module 2 Physical Properties of Aggregate. Specification Year: July Release 4, July
 Specification Year: July 2005 Release 4, July 2005 2-1 The first step in the development of an HMA mix design is to identify the materials that will be used in the pavement. In Florida the asphalt binder
Specification Year: July 2005 Release 4, July 2005 2-1 The first step in the development of an HMA mix design is to identify the materials that will be used in the pavement. In Florida the asphalt binder
Stress and Strains in Soil and Rock. Hsin-yu Shan Dept. of Civil Engineering National Chiao Tung University
 Stress and Strains in Soil and Rock Hsin-yu Shan Dept. of Civil Engineering National Chiao Tung University Stress and Strain ε 1 1 2 ε 2 ε Dimension 1 2 0 ε ε ε 0 1 2 ε 1 1 2 ε 2 ε Plane Strain = 0 1 2
Stress and Strains in Soil and Rock Hsin-yu Shan Dept. of Civil Engineering National Chiao Tung University Stress and Strain ε 1 1 2 ε 2 ε Dimension 1 2 0 ε ε ε 0 1 2 ε 1 1 2 ε 2 ε Plane Strain = 0 1 2
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIQUEFIED SILTY SANDS FROM MEIZOSEISMAL REGION OF SHILLONG PLATEAU, ASSAM AND BHUJ IN INDIA
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 2375 CHARACTERISTICS OF LIQUEFIED SILTY SANDS FROM MEIZOSEISMAL REGION OF SHILLONG PLATEAU, ASSAM AND BHUJ
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 2375 CHARACTERISTICS OF LIQUEFIED SILTY SANDS FROM MEIZOSEISMAL REGION OF SHILLONG PLATEAU, ASSAM AND BHUJ
VŠB - Technical University of Ostrava, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Transportation,
 EFFECT OF SiO 2 NANOPARTICLES ON THE MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF SiO 2 MICROPARTICLES MIXTURES ZEGZULKA Jiří 1, 2, JEZERSKÁ Lucie 2, HLOSTA Jakub 1, 2, ŽÍDEK Martin 1, 2, NEČAS Jan 1, 2 1 VŠB - Technical
EFFECT OF SiO 2 NANOPARTICLES ON THE MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF SiO 2 MICROPARTICLES MIXTURES ZEGZULKA Jiří 1, 2, JEZERSKÁ Lucie 2, HLOSTA Jakub 1, 2, ŽÍDEK Martin 1, 2, NEČAS Jan 1, 2 1 VŠB - Technical
Mohr s Circle of Stress
 Department of Civil Engineering Mohr s Circle of Stress by David Nash Department of Civil Engineering University of Bristol David.Nash@bristol.ac.uk 1 Principal planes and principal stresses Within any
Department of Civil Engineering Mohr s Circle of Stress by David Nash Department of Civil Engineering University of Bristol David.Nash@bristol.ac.uk 1 Principal planes and principal stresses Within any
Changes in soil deformation and shear strength by internal erosion
 Changes in soil deformation and shear strength by internal erosion C. Chen & L. M. Zhang The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, China D. S. Chang AECOM Asia Company Ltd., Hong Kong,
Changes in soil deformation and shear strength by internal erosion C. Chen & L. M. Zhang The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, China D. S. Chang AECOM Asia Company Ltd., Hong Kong,
Drained Against Undrained Behaviour of Sand
 Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 54 (2007), No. 3, pp. 207 222 IBW PAN, ISSN 1231 3726 Drained Against Undrained Behaviour of Sand Andrzej Sawicki, Waldemar Świdziński Institute
Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 54 (2007), No. 3, pp. 207 222 IBW PAN, ISSN 1231 3726 Drained Against Undrained Behaviour of Sand Andrzej Sawicki, Waldemar Świdziński Institute
Jaky s formula was often used to calculate the earth pressure at-rest behind a
 Chapter 2 LITERATURE REVIEW Jaky s formula was often used to calculate the earth pressure at-rest behind a retaining wall. However, the theory to estimate the lateral earth pressure on retaining wall near
Chapter 2 LITERATURE REVIEW Jaky s formula was often used to calculate the earth pressure at-rest behind a retaining wall. However, the theory to estimate the lateral earth pressure on retaining wall near
Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
Development and validation of calibration methods for discrete element modelling
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 211 Development and validation of calibration methods for discrete element
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 211 Development and validation of calibration methods for discrete element
Mixing Process of Binary Polymer Particles in Different Type of Mixers
 Vol. 3, No. 6 Mixing Process of Binary Polymer Particles in Different Type of Mixers S.M.Tasirin, S.K.Kamarudin & A.M.A. Hweage Department of Chemical and Process Engineering, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
Vol. 3, No. 6 Mixing Process of Binary Polymer Particles in Different Type of Mixers S.M.Tasirin, S.K.Kamarudin & A.M.A. Hweage Department of Chemical and Process Engineering, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
Landslide FE Stability Analysis
 Landslide FE Stability Analysis L. Kellezi Dept. of Geotechnical Engineering, GEO-Danish Geotechnical Institute, Denmark S. Allkja Altea & Geostudio 2000, Albania P. B. Hansen Dept. of Geotechnical Engineering,
Landslide FE Stability Analysis L. Kellezi Dept. of Geotechnical Engineering, GEO-Danish Geotechnical Institute, Denmark S. Allkja Altea & Geostudio 2000, Albania P. B. Hansen Dept. of Geotechnical Engineering,
Erosion of sand under high flow velocities
 Delft University of Technology Faculty of Mechanical, Maritime and Materials Engineering Department of Offshore Engineering Erosion of sand under high flow velocities Author: Juneed Sethi MSc Thesis Thesis
Delft University of Technology Faculty of Mechanical, Maritime and Materials Engineering Department of Offshore Engineering Erosion of sand under high flow velocities Author: Juneed Sethi MSc Thesis Thesis
GEO E1050 Finite Element Method Mohr-Coulomb and other constitutive models. Wojciech Sołowski
 GEO E050 Finite Element Method Mohr-Coulomb and other constitutive models Wojciech Sołowski To learn today. Reminder elasticity 2. Elastic perfectly plastic theory: concept 3. Specific elastic-perfectly
GEO E050 Finite Element Method Mohr-Coulomb and other constitutive models Wojciech Sołowski To learn today. Reminder elasticity 2. Elastic perfectly plastic theory: concept 3. Specific elastic-perfectly
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
A Critical Review on Modeling and Analysis of Granular Matter Flows
 A Critical Review on Modeling and Analysis of Granular Matter Flows MELDA OZDINC CARPINLIOGLU Mechanical Engineering Department Universityof Gaziantep Gaziantep 27310 TURKEY melda@gantep.edu.tr http://www.gantep.edu.tr
A Critical Review on Modeling and Analysis of Granular Matter Flows MELDA OZDINC CARPINLIOGLU Mechanical Engineering Department Universityof Gaziantep Gaziantep 27310 TURKEY melda@gantep.edu.tr http://www.gantep.edu.tr
Chapter 5 Shear Strength of Soil
 Page 5 Chapter 5 Shear Strength of Soil. The internal resistance per unit area that the soil mass can offer to resist failure and sliding along any plane inside it is called (a) strength (b) shear strength
Page 5 Chapter 5 Shear Strength of Soil. The internal resistance per unit area that the soil mass can offer to resist failure and sliding along any plane inside it is called (a) strength (b) shear strength
Following are the results of four drained direct shear tests on an overconsolidated clay: Diameter of specimen 50 mm Height of specimen 25 mm
 444 Chapter : Shear Strength of Soil Example. Following are the results of four drained direct shear tests on an overconsolidated clay: Diameter of specimen 50 mm Height of specimen 5 mm Normal Shear force
444 Chapter : Shear Strength of Soil Example. Following are the results of four drained direct shear tests on an overconsolidated clay: Diameter of specimen 50 mm Height of specimen 5 mm Normal Shear force
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 1, No 4, 2011
 Undrained response of mining sand with fines contents Thian S. Y, Lee C.Y Associate Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Universiti Tenaga Nasional, Malaysia siawyin_thian@yahoo.com ABSTRACT This
Undrained response of mining sand with fines contents Thian S. Y, Lee C.Y Associate Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Universiti Tenaga Nasional, Malaysia siawyin_thian@yahoo.com ABSTRACT This
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
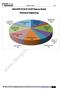 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
SOIL SHEAR STRENGTH. Prepared by: Dr. Hetty Muhammad Azril Fauziah Kassim Norafida
 SOIL SHEAR STRENGTH Prepared by: Dr. Hetty Muhammad Azril Fauziah Kassim Norafida What is shear strength Shear strength of a soil is the maximum internal resistance to applied shearing forces Why it is
SOIL SHEAR STRENGTH Prepared by: Dr. Hetty Muhammad Azril Fauziah Kassim Norafida What is shear strength Shear strength of a soil is the maximum internal resistance to applied shearing forces Why it is
Intro to Soil Mechanics: the what, why & how. José E. Andrade, Caltech
 Intro to Soil Mechanics: the what, why & how José E. Andrade, Caltech The What? What is Soil Mechanics? erdbaumechanik The application of the laws of mechanics (physics) to soils as engineering materials
Intro to Soil Mechanics: the what, why & how José E. Andrade, Caltech The What? What is Soil Mechanics? erdbaumechanik The application of the laws of mechanics (physics) to soils as engineering materials
Brittle Deformation. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
CHARACTERISING THE FAILURE AND REPOSE ANGLES OF IRREGULARLY SHAPED THREE-DIMENSIONAL PARTICLES USING DEM
 Ninth International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 10-12 December 2012 CHARACTERISING THE FAILURE AND REPOSE ANGLES OF IRREGULARLY SHAPED THREE-DIMENSIONAL
Ninth International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 10-12 December 2012 CHARACTERISING THE FAILURE AND REPOSE ANGLES OF IRREGULARLY SHAPED THREE-DIMENSIONAL
Classical fracture and failure hypotheses
 : Chapter 2 Classical fracture and failure hypotheses In this chapter, a brief outline on classical fracture and failure hypotheses for materials under static loading will be given. The word classical
: Chapter 2 Classical fracture and failure hypotheses In this chapter, a brief outline on classical fracture and failure hypotheses for materials under static loading will be given. The word classical
Geotechnical Properties of Soil
 Geotechnical Properties of Soil 1 Soil Texture Particle size, shape and size distribution Coarse-textured (Gravel, Sand) Fine-textured (Silt, Clay) Visibility by the naked eye (0.05 mm is the approximate
Geotechnical Properties of Soil 1 Soil Texture Particle size, shape and size distribution Coarse-textured (Gravel, Sand) Fine-textured (Silt, Clay) Visibility by the naked eye (0.05 mm is the approximate
Particle interactions in dry and suspension based formulations
 Finnish Society of Physical Pharmacy, 9 th Feb 2012 Particle interactions in dry and suspension based formulations Pharmaceutical Surface Science Research Group, Department of Pharmacy and Pharmacology,
Finnish Society of Physical Pharmacy, 9 th Feb 2012 Particle interactions in dry and suspension based formulations Pharmaceutical Surface Science Research Group, Department of Pharmacy and Pharmacology,
Lecture 6: Flow regimes fluid-like
 Granular Flows 1 Lecture 6: Flow regimes fluid-like Quasi-static granular flows have plasticity laws, gaseous granular flows have kinetic theory -- how to model fluid-like flows? Intermediate, dense regime:
Granular Flows 1 Lecture 6: Flow regimes fluid-like Quasi-static granular flows have plasticity laws, gaseous granular flows have kinetic theory -- how to model fluid-like flows? Intermediate, dense regime:
A Constitutive Framework for the Numerical Analysis of Organic Soils and Directionally Dependent Materials
 Dublin, October 2010 A Constitutive Framework for the Numerical Analysis of Organic Soils and Directionally Dependent Materials FracMan Technology Group Dr Mark Cottrell Presentation Outline Some Physical
Dublin, October 2010 A Constitutive Framework for the Numerical Analysis of Organic Soils and Directionally Dependent Materials FracMan Technology Group Dr Mark Cottrell Presentation Outline Some Physical
Welcome back. So, in the last lecture we were seeing or we were discussing about the CU test. (Refer Slide Time: 00:22)
 Geology and Soil Mechanics Prof. P. Ghosh Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture - 43 Shear Strength of Soils Keywords: Triaxial shear test, unconsolidated undrained
Geology and Soil Mechanics Prof. P. Ghosh Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture - 43 Shear Strength of Soils Keywords: Triaxial shear test, unconsolidated undrained
Contribution of electrostatic interactions to the dispersion of powders for inhalation
 Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics 2008, Paper M2 1 Contribution of electrostatic interactions to the dispersion of powders for inhalation M. Teresa Carvajal Department of Industrial and Physical
Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics 2008, Paper M2 1 Contribution of electrostatic interactions to the dispersion of powders for inhalation M. Teresa Carvajal Department of Industrial and Physical
Albert Alexander, Paulo Arratia, Chris Goodridge, Osama Sudah, Dean Brone, and Fernando Muzzio*
 Characterization of the Performance of Bin Blenders Part 1 of 3: Methodology Albert Alexander, Paulo Arratia, Chris Goodridge, Osama Sudah, Dean Brone, and Fernando Muzzio* In this series of articles,
Characterization of the Performance of Bin Blenders Part 1 of 3: Methodology Albert Alexander, Paulo Arratia, Chris Goodridge, Osama Sudah, Dean Brone, and Fernando Muzzio* In this series of articles,
both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the
 Quantitative Problems Problem 4-3 Figure 4-45 shows the state of stress at a point within a soil deposit. Using both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the principal
Quantitative Problems Problem 4-3 Figure 4-45 shows the state of stress at a point within a soil deposit. Using both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the principal
Particle Characterization of Pharmaceutical Products by Dynamic Image Analysis
 WHITE PAPER Particle Characterization of Pharmaceutical Products by Dynamic Image Analysis Retsch Technology GmbH Retsch-Allee 1-5 42781 Haan, Germany Phone: +49 24/2333-0 E-Mail: technology@retsch.com
WHITE PAPER Particle Characterization of Pharmaceutical Products by Dynamic Image Analysis Retsch Technology GmbH Retsch-Allee 1-5 42781 Haan, Germany Phone: +49 24/2333-0 E-Mail: technology@retsch.com
Prediction Quality Attributes For Mixtures From Single Component Data
 Prediction Quality Attributes For Mixtures From Single Component Data John Strong, PhD Sean Garner, PhD Global Pharmaceutical Sciences AbbVie, North Chicago, IL CPDG Sep 27th, 2016 AbbVie: Our reach is
Prediction Quality Attributes For Mixtures From Single Component Data John Strong, PhD Sean Garner, PhD Global Pharmaceutical Sciences AbbVie, North Chicago, IL CPDG Sep 27th, 2016 AbbVie: Our reach is
THE ONSET OF FLUIDIZATION OF FINE POWDERS IN ROTATING DRUMS
 The Mater.Phys.Mech.3 Onset of Fluidization (1) 57-6 of Fine Powders in Rotating Drums 57 THE ONSET OF FLUIDIZATION OF FINE POWDERS IN ROTATING DRUMS A. Castellanos, M.A. Sánchez and J.M. Valverde Departamento
The Mater.Phys.Mech.3 Onset of Fluidization (1) 57-6 of Fine Powders in Rotating Drums 57 THE ONSET OF FLUIDIZATION OF FINE POWDERS IN ROTATING DRUMS A. Castellanos, M.A. Sánchez and J.M. Valverde Departamento
FRICTION. Friction: FRICARE = to rub (Latin)
 FRICTION 1 Friction: FRICARE = to rub (Latin) Resisting force (F) tangential to the interface between two bodies when, under the action of an external force, one body moves or tends to move relative to
FRICTION 1 Friction: FRICARE = to rub (Latin) Resisting force (F) tangential to the interface between two bodies when, under the action of an external force, one body moves or tends to move relative to
Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1
 Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS 1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.2 Relation to Equivalent-Linear Methods... 1-2 1.2.1 Characteristics of the Equivalent-Linear Method... 1-2 1.2.2
Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS 1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.2 Relation to Equivalent-Linear Methods... 1-2 1.2.1 Characteristics of the Equivalent-Linear Method... 1-2 1.2.2
Pharmaceutics I صيدالنيات 1. Unit 6
 Pharmaceutics I صيدالنيات 1 Unit 6 1 Rheology of suspensions Rheology, the study of flow, addresses the viscosity characteristics of powders, fluids, and semisolids. Materials are divided into two general
Pharmaceutics I صيدالنيات 1 Unit 6 1 Rheology of suspensions Rheology, the study of flow, addresses the viscosity characteristics of powders, fluids, and semisolids. Materials are divided into two general
High-Precision Strength Evaluation of Rock Materials and Stability Analysis for Rockfill Dams
 1st International Symposium on Rockfill Dams High-Precision Strength Evaluation of Rock Materials and Stability Analysis for Rockfill Dams Hiroki SAKAMOTO Research Engineer Public Works Research Institute,
1st International Symposium on Rockfill Dams High-Precision Strength Evaluation of Rock Materials and Stability Analysis for Rockfill Dams Hiroki SAKAMOTO Research Engineer Public Works Research Institute,
DEM Simulation of a Screw Feeder Using the Adhesion Powder
 APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th December, 2013, Singapore Abstract DEM Simulation of a Screw Feeder Using the Adhesion Powder *M. Kimata, S. Kikai, T. Kagami and M. Hasegawa Department of Chemistry and Chemical
APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th December, 2013, Singapore Abstract DEM Simulation of a Screw Feeder Using the Adhesion Powder *M. Kimata, S. Kikai, T. Kagami and M. Hasegawa Department of Chemistry and Chemical
New Developments Of Cutting Theories With Respect To Offshore Applications
 Miedema, S.A., ew developments of cutting theories with respect to offshore applications, the cutting of sand, clay and rock. ISOPE 010, Beijing China, June 010. ew Developments Of Cutting Theories With
Miedema, S.A., ew developments of cutting theories with respect to offshore applications, the cutting of sand, clay and rock. ISOPE 010, Beijing China, June 010. ew Developments Of Cutting Theories With
Experimental Device for Measuring Sandy Soil Sinkage Parameters
 Bull. Fac. Agr., Saga Univ. No Experimental Device for Measuring Sandy Soil Sinkage Parameters Nang Nguyen Van, Takaaki MATSUO, Tatsuya KOUMOTO * and Shigeki INABA ** (Laboratory of Agricultural Machinery,
Bull. Fac. Agr., Saga Univ. No Experimental Device for Measuring Sandy Soil Sinkage Parameters Nang Nguyen Van, Takaaki MATSUO, Tatsuya KOUMOTO * and Shigeki INABA ** (Laboratory of Agricultural Machinery,
