Abdessalem Kaddouri, Bilel Hamdi, Mourad Aidi and Taoufik Aguili
|
|
|
- Vivien Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Global Method Combined with Floquet Modal Analysis to Model an Antenna Based on Rectangular Waveguide Array Abdessalem Kaddouri, Bilel Hamdi, Mourad Aidi and Taoufik Aguili Syscom Laboratory, National Engineering School of Tunis, Tunis El Manar university BP 37, le Belvédère, Tunisia Abdessalem Kaddouri received the PhD degree in Telecommunications from the National Engineering School of Tunis. Holds a Master degree in Telecommunications from the same institution. He received his Engineering degree from The Higher School of Communication of Tunis. His research interest include numerical methods in electromagnetics, electromagnetic modeling of complex structures for microwave and antenna applications, physics quantic, cryptography, Cloud Computing, IoT, Big Data and Security. ( kaddouri.abdessalam@sotetel.tn). Bilel Hamdi received his Diploma in science physics in 2008 from the Faculty of Sciences of Bizerte (FSB)- University of Carthage and his Master degree ( M.S.) in Telecommunications in 2010 from the National Engineering School of Tunis (ENIT)- University of Tunis El Manar and the Ph.D. degree in Telecommunications from the National Engineering School of Tunis (ENIT) in collaboration with ENSEEIHT, INP de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, in He is working as Assistant at the National Engineering School of Tunis (ENIT). His main research interests are the design and optimization of periodic array antennas, almost periodic antennas modeling and electromagnetic microwave circuits analysis. ( hamdibilel1985@gmail.com). Mourad Aidi received the Master degree in Applied Physics from Higher School of Sciences and Techniques of Tunis and the MSc degree in energetic physics from National Institute of Applied Science and Technology (INSAT). In 2011, he received the PhD degree in Telecommunications from the National Engineering School of Tunis. His research interest is in the electromagnetic modeling of the nano-devices based on carbon nanotubes and graphene layers for telecommunication applications. ( mourad.aidi@enit.utm.tn). Taoufik Aguili is currently a Professor in the National Engineering School of Tunis (ENIT), Tunis El Manar University. He is also the director of Communications Systems Laboratory (Syscom) and he is the responsible of research and the master degree in the communications and information's technology Department. His research interests include modeling of microwave systems and nano-devices, numerical methods in electromagnetics, electromagnetic wave phenomena in layered media, integrated transmission lines, waveguides and antennas, and leaky wave phenomena. ( taoufik.aguili@enit.rnu.tn).
2 Global Method Combined with Floquet Modal Analysis to Model an Antenna Based on Rectangular Waveguide Array In this study, we propose a new formulation based on a global method to model a rectangular waveguide array as antenna. Our method consists to combine the method of moment (MoM), the generalized equivalent circuit method (GECM) and Floquet modal analysis. Looking for rigor, simplicity and rapidity, we repose always on the simple discontinuity in an open rectangular waveguide. So, we extended our pervious works to study in first step an infinite rectangular waveguides array and we achieve with a finite one. For validation purpose, we consider two rectangular waveguides and we compered it whit the same structure studied by direct method in our previous study. Obtained numerical results are presented and discussed. A good agreement is shown and the boundary conditions are verified. Keywords: Modeling, Antenna, Array, waveguide, Global Method, Floquet, GECM 1. Introduction The radiating characteristics of a single antenna are insufficient for wireless telecommunications and radar applications. For this purpose, antenna arrays are generally used to customize the radiation patterns by acting on the phases or modules relating to the elementary antennas by using beam-forming networks [1,2]. In satellite and radar applications, waveguide array is usually used as antennas [3,4]. Rectangular waveguides are widely used than circular waveguides because they are easier to manipulate and they offer a lower cross polarization component [5]. In our previous works, we have proposed a new rigorous approach to model a finite open ended waveguide array radiating in free space [6,7]. This formulation allows to use the MoM-GEC method to model a single waveguide and we extend this formulation to study a twice waveguides radiating in free space. The study of finite waveguides array is useful both for studying its characteristics and for determining the edge effects for nearest elements or at the edges of very wide array. In [8], the mutual coupling problem in a waveguide array radiating in the free space is expressed in terms of an aperture half-space admittance matrix and scattering parameters between the array elements. An important characteristic of antenna array is to manipulate the antenna radiation pattern by acting on the array element excitation s [9]. In many previous works, rectangular waveguide arrays are used to enhance radiation properties. For this, some amplitude distribution techniques are used, such as
3 uniform amplitude distribution [10], parabolic amplitude distribution, circular amplitude distribution [11]. These three distributions are used to generate the array pattern needed for wireless and radar communications. The radiated far field at a point in the space is the sum of the contribution of each array element's. In the case of identical array elements, the antenna array radiation pattern is calculated by multiplying the radiation pattern of single antenna by the array factor. This concept is called pattern multiplication [12,13]. The main objective is to find the appropriate antennas configuration, the antenna dimensions and the excitation distribution to produce a radiation pattern with low side lobes and narrow beam width. [14] However, the main problem of the direct method is the complexity of the computation which increases with the array elements number. In fact, the needed test function number increase quickly with the array elements number. In this paper, we propose a rigorous formulation based on MoM-GEC method combined to Floquet s modal analysis to model a rectangular open ended waveguide array radiating in free space. For a validation purpose, the proposed formulation is applied to a simple waveguide array formed by two rectangular waveguides. Obtained results show a good agreement with the direct method. 2. An infinite rectangular waveguides array radiating in free space As shown in figure 1(a), we consider the same structure studied in our previous work [7]. A real waveguide (RG) with electric wall (EW) opened in another waveguide (SG) aims to simulate the free space. But in this study, the SG is composed by periodic wall (PW). The two waveguides are tied by a transversal metallic wall. In figure 1(b), we present the relative equivalent circuit model. Figure 1. (a) An infinite rectangular waveguides array; (b) the relative equivalent circuit. The excitation is brought back to discontinuity plan as a modal source of current. Its value is the current density of the fundamental mode I f, and its internal admittance is 0 0 Ŷ1 which represents the evanescent modes' contribution of RG. Ŷ1 is given by the formula: Ŷ 1= fpq y pq f pq (1) where f pq is the RG modal basis without the fundamental f, and y 0 pq is the mode admittance of each f pq. The voltage at terminals of this source ise 1, which is its dual greatness. e E is the virtual voltage source defined in discontinuity plan, and j 1 is the current SG: PW flowing it. E e is the unknown problem, and it is expressed as a serial of test functions (a) RG : EW EW g p weighted by unknown modal amplitudes x p : (b)
4 Ee xp g p (2) p Next, we apply the Galerkin method wherein the test functions are same as modal basis functions. The modes contribution of SG is expressed in the discontinuity plane by the -1 admittance operator Ẑ which is given by the following formula. -1 Ẑ = Fmn ymn F mn (3) where F mn is the SG modal basis and y mn is the relative mode admittance. Based on the equivalent circuit shown in Figure (1), the integral equations associated with the problem can be easily derived by applying generalized Kirchhoff laws: 1 J Z E e (4) J Y 1E e I0 f0 j1 Using the equations system (4), we can write: 1 Z E e Y1 Ee I0 f0 j 1 (5) Then, we can deduce the current j 1 : j ( Y Z 1 ) E 1 1 e I f (6) 0 0 Taking into account the expression e 1 E e, we can find the relation between source variables and their duals: e1 1 0 E e (7) j Z Y I0 f0 Applying the Galerkin's method leads to the following system of equations: t V f E 0 0 x f g A X e q 0 q q (8) 1 I g f ( 0 0 g Y 1 Z ) g x 0 p p q q q This system can be rewritten as: t A X V 0 0 (9) AI y X 0 where A is the excitation vector, and y is the admittance matrix: A f0 g p (10) 1 1 g ( Y Z ) g g ( Y Z ) g pq y (11) 1 1 g ( Y Z ) g g ( Y Z ) g pq 1 10 pq 1 pq Solving the above system (9) we get: X y 1 AI (12) 0 Taking into account relations (8) and (12), we deduce the impedance matrix Z : Z A t y 1 A (13) The scattering matrix S can therefore be expressed using the reduced impedance z and the identity matrix: S 1 ( z I )( z I (14) )
5 3. A finite rectangular waveguides array radiating in free space Our study structure is a periodic array composed by nine rectangular waveguides, called NG (Network-Guide), radiating in free space. This latter is simulated by another rectangular waveguide, called SG (Space-Guide), with large dimensions. All structure is linked by a transversal electrical wall and (Figure2). EW (a) NG SG Figure 2. (a) A finite rectangular waveguides array; (b) the relative equivalent circuit. This formulation is very different of a unit cell in terms of complexity. Indeed, increasing the number of array antennas will made the direct approach is difficult to contemplate. For this, we propose to consider a structure studied in Figure (1) as a unit cell and we introduce the Floquet modal analysis to apply it on this cell. The Floquet method permit to duplicate several times a unit cell on the x and y axes to form an array as desired. Then, the cell (i,s), in Figure (3), is considered as a translation of the cell (0,0) in space domain followed by another in the modal domain and expressed in dependence of the Floquet modes phases (α, β). So, if we assume that: 2 N x N x ( i, p) and comprised within the range, ( s, q ) 2 N y N y and comprised within the range, N x and N y are the numbers of array elements in the x and y directions respectively. Lx and L y are the lengths of the array respectively according to the axes x and y. (b)
6 p, q will have the following forms: 2 p p (15) Lx 2 q q (16) L y Where Lx and L y are given by: Lx Nxd x (17) Ly N yd y (18) Figure 3. A finite rectangular waveguide array. So, the electric field at the position of cell (i, s) can be written as the superposition of the fields associated with the Floquet modes (spectral domain). And we can consider this decomposition as the transformation of the electric field of the space domain to modal domain (Figure 3). Mathematically this transformation is the inverse Fourier transform (19). Similarly, the radiating field of phase shift (, ) can be written as a sum of the radiated energy of this field on all cells. This summation can be seen as the Fourier transform of the electric field of the modal domain in space domain (20). 1 ( ) ( ) (, ) j p idx jq sdy E i s E, x y p e e (19) N N q p, q 1 j p( id ) ( ), (, ) x jq sd E y p E id q x sd y e e (20) NxN y i, s It has been demonstrated [15,16] that these transformations lead to other expressions emphasizing the coupling terms established between array elements such as the Z, Y and S parameters. 1 Z, i s TF Z p, TF (21) q 1 Y, i s TF Y p, TF (22) q
7 1 S, i s TF S p, TF (23) q Here, Z p, q is a spectral representation of the diagonal matrix that concatenates the intrinsic input impedance associated with a cell Floquet modes of the array. In our case, it is written as follows: Z , 1 0 Z.. 1, 0.. Z.. 1, 1.. Z.. 0, 1 Z...., Z 0, p q (24) 0.. Z.. 0, 1.. Z.. 1, 1.. Z 0 1, Z 1, 1 4. Numerical Results 4.1. An infinite rectangular waveguides array We determine in this case the reflexing parameter and the normalized electric field for d 2. S (27) In Figure 4, we present the normalized electric field distribution on discontinuity plan, and we can verify that the coupling is very low especially on the x axis. This can be explained by the fact that the fundamental mode TE10 which represents the source of the electric field discontinuity has no component along the x axis. The allure of the electric field was not affected by the periodic walls, and the boundary conditions are verified; the field is maximum at the center of the opening and it vanishes on the metal part. Figure 4. Normalized electric Field distribution on discontinuity, d = 2λ, f = 9.33GHz
8 4.2. A finite rectangular waveguides array For the finite network, we propose to make a parametric study based on coupling distances. So, we choose three distances: lower than wavelength λ, in the order of λ and upper than λ Scattering parameters When we determine the S parameters matrix for the different coupling distances, we remark that there are values that are repeated, and their positions in matrix do not change regardless of the coupling distance. Then, to better understand the meaning of this, we stained in this usual matrix (Figure 5. (a)) each set of these values in the same color. So, if we consider the initial cell, we can represent the diffraction parameters as follows (Figure 5. (b)), all the others are similar. (a) S S11 S12 S13 S14 S15 S 16 S17 S18 S19 S21 S22 S23 S 24 S25 S26 S27 S28 S 29 S31 S32 S3 3 S34 S 35 S36 S37 S38 S 39 S41 S42 S43 S44 S45 S46 S47 S48 S49 S51 S5 2 S53 S54 S 55 S56 S57 S58 S 59 S61 S62 S63 S64 S65 S66 S67 S 68 S69 S7 1 S72 S73 S74 S75 S76 S77 S78 S 79 S 81 S82 S83 S84 S85 S86 S87 S88 S 89 S 91 S 92 S9 3 S94 S9 5 S96 S9 7 S98 S99 Figure 5. (a) Usual Scattering matrix; (b) Schematic representation of S parameters. In the Table 1, we represent the squares of values of nine sets of diffraction parameter as a function of the coupling distance d. These physical magnitudes present the percentages of powers relating to these parameters with respect to the power initially issued. Table 1. Scattering parameters as a function of coupling distance d. 2 d (λ) S55 S45 2 S65 2 S25 2 S85 2 S75 2 S35 2 S95 2 S ,0661 0,0801 0,0546 0,1285 0,0306 0,0058 0,0135 0,0523 0, ,0780 0,1000 0,0969 0,1526 0,0938 0,0101 0,0260 0,0541 0, ,1418 0,1054 0,1000 0,1643 0,1095 0,0181 0,0370 0,0587 0,0324 To understand the physical meaning of these parameters we define three follow types of power: 2 - Self-reflected Power: SP S ii 2 - Coupling Power: CP S ij i j (b)
9 EPH - International Journal of Science And Engineering ISSN: Radiated power: RP 1 (SP CP) And we set forth these powers in Table 2. We can notice that the self-reflective powers and coupled powers are inversely proportional to the coupling distance d, rather radiated powers which are proportional to the distance. Table 2. Comparison of self-reflected power, radiated power and coupled power, according to the coupling distance d. d(λ) 2 1 SP CP RP Electric field distribution We represent the electric field distribution on the discontinuity surface for the three cases respectively. And we can notice that the conditions to limit its verified except for low coupling distance, where the coupling is so intense that the fields overflow the openings. (b) Normalized electric field in discontinuity plan, d = λ, f = 9.33GHz Volume-4 Issue-4 April,
10 EPH - International Journal of Science And Engineering (c) ISSN: Normalized electric field in discontinuity plan, d = 0.1λ, f = 9.33GHz Figure 6. Normalized electric Field distribution on discontinuity plan for f=9.33ghz (a) d=2λ; (b) d=λ; (c) d=0.1λ 4.3. Validation To validate this new formulation based on Floquet modal analysis, its proposed to apply it into a a dual waveguide network in order to compare it with the direct method used in previous work [6]. As shown in Figure 8, first, we can confirm that there is a good agreement in term of the boundary conditions. Second, we can verify the presence of the same behaviors of electric field in waveguides modeling the free space for the two methods. Third, we can validate that the maximum of electric field distribution is concentrated in the network waveguides as it should be. However, we can remark that the distributions of electric fields in the network waveguides have not a same appearance. Indeed, it s due to the use of different methods. Other works should be held in order to remedy to this result. Volume-4 Issue-4 April,
11 Figure 7. Normalized electric Field distribution d=2λ and on discontinuity plan for a network of two waveguides for a coupling distance operational frequency f 9.33GHz (a) Method based on Floquet modal analysis; (b) Direct Method. 5. Conclusion In this work, we proposed a new formulation based on the combination of MoM-GEC method and Floquet modal analysis to model a finite network of rectangular waveguide radiating in free space. We conceive an infinite array by using the property of periodic walls with a single waveguide. Then, we consider this structure as a unit cell, and we applying the Floquet modal analysis in order to model the finite array. Later, we apply a parametric study to understand how the electric field and coupling behaves based on coupling distance. For validation purpose, first, we compared the scattering parameters with the results published in previous work, and verified the boundary conditions and good agreement is shown. Secondly, we compared the distribution of electric field in the discontinuity plane for a two waveguides array by two formulations, a direct one and Floquet modal analysis one, and good agreement is shown. References [1] G. Ram, D. Mandal, R. Kar and S. Ghoshal, "Optimized Hyper Beamforming of Linear Antenna Arrays Using Collective Animal Behaviour", The Scientific World Journal, vol. 2013, pp. 1-13, [2] K. Ghatak, A. Senapati and J. Sekhar Roy, "Investigations on Adaptive Beamforming for Linear and Planar Smart Antenna Arrays using Sample Matrix Inversion Algorithm", International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 117, no. 8, pp , [3] D. Hotte, Y. Duroc, S. Tedjini and R. Siragusa, "Directive and high-efficiency slotted waveguide antenna array for V-band made by wire electrical discharge machining", Electronics Letters, vol. 51, no. 5, pp , 2015.
12 [4] T. Bird and C. Granet, "Optimization of Profiles of Rectangular Horns for High Efficiency",IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 55, no. 9, pp , [5] K. Yeap, E. Wong, H. Nisar, K. Lai and C. Ng, "Attenuation in Circular and Rectangular Waveguides", Electromagnetics, vol. 37, no. 3, pp , [6] A. Kaddouri, M. Aidi and T. Aguili, "A New Approach Based on MoM-GEC Method to Mutual Coupling Analysis of Symmetric Twin Waveguides for Antenna Applications", Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis and Applications, vol. 07, no. 12, pp , [7] A. Kaddouri, M. Aidi and T. Aguili, "New Formulation of Open Ended Waveguide Radiating in Free Space Based on MoM-GEC Method", International Journal of Microwave and Optical Technology, vol. 11, no. 2, [8] J. Luzwick and R. Harrington, "MUTUAL COUPLING ANALYSIS IN A FINITE PLANAR RECTANGULAR WAVEGUIDE ANTENNA ARRAY", Electromagnetics, vol. 2, no. 1, pp , [9] J. Hirokawa, "Plate-laminated Waveguide Slot Array Antennas and its Polarization Conversion Layers",Automatika Journal for Control, Measurement, Electronics, Computing and Communications, vol. 53, no 1, [10] A. Abed, "Study of Radiation Properties in Taylor Distribution Uniform Spaced Backfire Antenna Arrays", American Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications, vol. 2, no. 3, p. 23, [11] C. Balanis, "Modern Antenna Handbook". Somerset: Wiley, [12] M. Aidi and T. Aguili, "ELECTROMAGNETIC MODELING OF COUPLED CARBON NANOTUBE DIPOLE ANTENNAS BASED ON INTEGRAL EQUATIONS SYSTEM", Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, vol. 40, pp , [13] R. L. Haupt, "Antenna Arrays: A Computational Approach", Wiley, 2010, ISBN: [14] P. Rajyalaxmi, M. Surendra Kumar, "Design of Rectangular Waveguide Arrays for Generating Low Side Lobes", International Journal of Electronics, Communication & Instrumentation Engineering Research and Development, Vol. 5, Issue 5, pp , 2015, [15] BHATTACHARYYA, Arun K. Phased array antennas: Floquet analysis, synthesis, BFNs and active array systems. John Wiley & Sons, [16] Hamdi, B., Aguili, T., & Baudrand, H. (2015). Floquet modal analysis to modelize and study 2-D planar almost periodic structures in finite and infinite extent with coupled motifs. Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, 62,
Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines
 Mikrotalasna revija Novembar 4. Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines Ján Zehentner, Jan Mrkvica, Jan Macháč Abstract The paper presents a new code calculating the basic characteristics
Mikrotalasna revija Novembar 4. Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines Ján Zehentner, Jan Mrkvica, Jan Macháč Abstract The paper presents a new code calculating the basic characteristics
Calculation of the Mutual Coupling Parameters and Their Effects in 1-D Planar Almost Periodic Structures
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 59, 269 289, 214 Calculation of the Mutual Coupling Parameters and Their Effects in 1-D Planar Almost Periodic Structures Bilel Hamdi 1, 2, *, Taoufik Aguili
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 59, 269 289, 214 Calculation of the Mutual Coupling Parameters and Their Effects in 1-D Planar Almost Periodic Structures Bilel Hamdi 1, 2, *, Taoufik Aguili
Contribution of Feed Waveguide on the Admittance Characteristics Of Coplanar Slot Coupled E-H Tee Junction
 ISSN(Online): 30-9801 Contribution of Feed Waveguide on the Admittance Characteristics Of Coplanar Slot Coupled E-H Tee Junction M.Murali, Prof. G.S.N Raju Research Scholar, Dept.of ECE, Andhra University,
ISSN(Online): 30-9801 Contribution of Feed Waveguide on the Admittance Characteristics Of Coplanar Slot Coupled E-H Tee Junction M.Murali, Prof. G.S.N Raju Research Scholar, Dept.of ECE, Andhra University,
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS
 UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
A MATLAB GUI FOR SIMULATING THE PROPAGATION OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD IN A 2-D INFINITE SPACE
 A MATLAB GUI FOR SIMULATING THE PROPAGATION OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD IN A 2-D INFINITE SPACE Ioana SĂRĂCUŢ Victor POPESCU Marina Dana ŢOPA Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, G. Bariţiu Street 26-28,
A MATLAB GUI FOR SIMULATING THE PROPAGATION OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD IN A 2-D INFINITE SPACE Ioana SĂRĂCUŢ Victor POPESCU Marina Dana ŢOPA Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, G. Bariţiu Street 26-28,
Microwave Network Analysis
 Prof. Dr. Mohammad Tariqul Islam titareq@gmail.my tariqul@ukm.edu.my Microwave Network Analysis 1 Text Book D.M. Pozar, Microwave engineering, 3 rd edition, 2005 by John-Wiley & Sons. Fawwaz T. ILABY,
Prof. Dr. Mohammad Tariqul Islam titareq@gmail.my tariqul@ukm.edu.my Microwave Network Analysis 1 Text Book D.M. Pozar, Microwave engineering, 3 rd edition, 2005 by John-Wiley & Sons. Fawwaz T. ILABY,
COMPLEX RECTANGULAR FILTER DESIGN USING HYBRID FINITE ELEMENT METHOD AND MODIFIED MULTIMODAL VARIATIONAL FORMULATION
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 44, 55 66, 2013 COMPLEX RECTANGULAR FILTER DESIGN USING HYBRID FINITE ELEMENT METHOD AND MODIFIED MULTIMODAL VARIATIONAL FORMULATION Mohamed Yahia 1, *, Jun
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 44, 55 66, 2013 COMPLEX RECTANGULAR FILTER DESIGN USING HYBRID FINITE ELEMENT METHOD AND MODIFIED MULTIMODAL VARIATIONAL FORMULATION Mohamed Yahia 1, *, Jun
feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field matching
 CHAPTER-2 MATCHED FEED FOR OFFSET REFLECTOR ANTENNA The primary objective of this chapter is to discuss the basic concept of matched feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field
CHAPTER-2 MATCHED FEED FOR OFFSET REFLECTOR ANTENNA The primary objective of this chapter is to discuss the basic concept of matched feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field
A Plane Wave Expansion of Spherical Wave Functions for Modal Analysis of Guided Wave Structures and Scatterers
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 51, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2003 2801 A Plane Wave Expansion of Spherical Wave Functions for Modal Analysis of Guided Wave Structures and Scatterers Robert H.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 51, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2003 2801 A Plane Wave Expansion of Spherical Wave Functions for Modal Analysis of Guided Wave Structures and Scatterers Robert H.
So far, we have considered three basic classes of antennas electrically small, resonant
 Unit 5 Aperture Antennas So far, we have considered three basic classes of antennas electrically small, resonant (narrowband) and broadband (the travelling wave antenna). There are amny other types of
Unit 5 Aperture Antennas So far, we have considered three basic classes of antennas electrically small, resonant (narrowband) and broadband (the travelling wave antenna). There are amny other types of
Engineering Electromagnetics
 Nathan Ida Engineering Electromagnetics With 821 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vu Vector Algebra 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Scalars and Vectors 2 1.3 Products of Vectors 13 1.4 Definition of Fields
Nathan Ida Engineering Electromagnetics With 821 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vu Vector Algebra 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Scalars and Vectors 2 1.3 Products of Vectors 13 1.4 Definition of Fields
J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian University Xi an, Shaanxi , P. R.
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 55 60, 2009 MULTIFUNCTIONAL MEANDER LINE POLARIZER J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 55 60, 2009 MULTIFUNCTIONAL MEANDER LINE POLARIZER J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian
New Formulation of the Mulilayer Iterative Method: Application to Coplanar Lines with Thick Conductor
 Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis and Applications, 2016, 8, 197-218 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa ISSN Online: 1942-0749 ISSN Print: 1942-0730 New Formulation of the Mulilayer Iterative Method:
Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis and Applications, 2016, 8, 197-218 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa ISSN Online: 1942-0749 ISSN Print: 1942-0730 New Formulation of the Mulilayer Iterative Method:
ANALYSIS OF LINEAR TAPERED WAVEGUIDE BY TWO APPROACHES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 64, 19 38, 006 ANALYSIS OF LINEAR TAPERED WAVEGUIDE BY TWO APPROACHES S. Dwari, A. Chakraborty, and S. Sanyal Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 64, 19 38, 006 ANALYSIS OF LINEAR TAPERED WAVEGUIDE BY TWO APPROACHES S. Dwari, A. Chakraborty, and S. Sanyal Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication
TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide
 1534 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 50, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2002 TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide Jae Yong Kwon, Member, IEEE, Jae Wook Lee, Associate Member,
1534 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 50, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2002 TM-Radiation From an Obliquely Flanged Parallel-Plate Waveguide Jae Yong Kwon, Member, IEEE, Jae Wook Lee, Associate Member,
USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION
 October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
Generalized network formulation for symmetric double-step waveguide discontinuities
 INT. J. ELECTRONICS, 1989, VOL. 67, NO. 3, 427-435 Generalized network formulation for symmetric double-step waveguide discontinuities A. K. HAMIDt, I. R. CIRICt and M. HAMIDH The equivalence principle
INT. J. ELECTRONICS, 1989, VOL. 67, NO. 3, 427-435 Generalized network formulation for symmetric double-step waveguide discontinuities A. K. HAMIDt, I. R. CIRICt and M. HAMIDH The equivalence principle
4.4 Microstrip dipole
 4.4 Microstrip dipole Basic theory Microstrip antennas are frequently used in today's wireless communication systems. Thanks to their low profile, they can be mounted to the walls of buildings, to the
4.4 Microstrip dipole Basic theory Microstrip antennas are frequently used in today's wireless communication systems. Thanks to their low profile, they can be mounted to the walls of buildings, to the
Finitely Large Phased Arrays of Microstrip Antennas Analysis and Design
 I Preface The paper in this RN report has been submitted to the proceedings of the 4th International Workshop Scientific Computing in Electrical Engineering (SCEE). This workshop was organized by the Eindhoven
I Preface The paper in this RN report has been submitted to the proceedings of the 4th International Workshop Scientific Computing in Electrical Engineering (SCEE). This workshop was organized by the Eindhoven
1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides
 1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides 1.1 Introduction to optical waveguides Optical waveguides are made from material structures that have a core region which has a higher index of refraction
1 The formation and analysis of optical waveguides 1.1 Introduction to optical waveguides Optical waveguides are made from material structures that have a core region which has a higher index of refraction
Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts
 NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES MAGDY F. ISKANDER Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS PREFACE VECTOR ANALYSIS AND MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND WAVES MAGDY F. ISKANDER Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Utah Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 CONTENTS PREFACE VECTOR ANALYSIS AND MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN
New Formula for Evaluating the Number of Unit Cell of a Finite Periodic Structure Considered as Infinite Periodic One
 Journal of Electromagnetic nalysis and pplications, 11, 3, 343-35 doi:1.436/jemaa.11.3955 ublished Online September 11 (http://www.scir.org/journal/jemaa) 343 ew Formula for Evaluating the umber of Unit
Journal of Electromagnetic nalysis and pplications, 11, 3, 343-35 doi:1.436/jemaa.11.3955 ublished Online September 11 (http://www.scir.org/journal/jemaa) 343 ew Formula for Evaluating the umber of Unit
Network Theory and the Array Overlap Integral Formulation
 Chapter 7 Network Theory and the Array Overlap Integral Formulation Classical array antenna theory focuses on the problem of pattern synthesis. There is a vast body of work in the literature on methods
Chapter 7 Network Theory and the Array Overlap Integral Formulation Classical array antenna theory focuses on the problem of pattern synthesis. There is a vast body of work in the literature on methods
Modeling of Multiconductor Microstrip Systems on Microwave Integrated Circuits
 Modeling of Multiconductor Microstrip Systems on Microwave Integrated Circuits S. M. Musa, M. N. O. Sadiku, and K. T. Harris Roy G. Perry College of Engineering, Prairie View A&M University Prairie View,
Modeling of Multiconductor Microstrip Systems on Microwave Integrated Circuits S. M. Musa, M. N. O. Sadiku, and K. T. Harris Roy G. Perry College of Engineering, Prairie View A&M University Prairie View,
New 3D Aware Formulation of MoM-GEC Method for Studying Planar Structures with Vertical Sources
 Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis and Applications, 06, 8, 79-94 Published Online April 06 in SciRes http://wwwscirporg/journal/jemaa http://dxdoiorg/0436/jemaa0684009 New 3D Aware Formulation of MoM-GEC
Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis and Applications, 06, 8, 79-94 Published Online April 06 in SciRes http://wwwscirporg/journal/jemaa http://dxdoiorg/0436/jemaa0684009 New 3D Aware Formulation of MoM-GEC
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Our discussion on dynamic electromagnetic field is incomplete. I H E An AC current induces a magnetic field, which is also AC and thus induces an AC electric field. H dl Edl J ds
Electromagnetic Waves Our discussion on dynamic electromagnetic field is incomplete. I H E An AC current induces a magnetic field, which is also AC and thus induces an AC electric field. H dl Edl J ds
On the Modal Superposition Lying under the MoM Matrix Equations
 42 P. HAZDRA, P. HAMOUZ, ON THE MODAL SUPERPOSITION LYING UNDER THE MOM MATRIX EQUATIONS On the Modal Superposition Lying under the MoM Matrix Equations Pavel HAZDRA 1, Pavel HAMOUZ 1 Dept. of Electromagnetic
42 P. HAZDRA, P. HAMOUZ, ON THE MODAL SUPERPOSITION LYING UNDER THE MOM MATRIX EQUATIONS On the Modal Superposition Lying under the MoM Matrix Equations Pavel HAZDRA 1, Pavel HAMOUZ 1 Dept. of Electromagnetic
Module 6 : Wave Guides. Lecture 40 : Introduction of Parallel Waveguide. Objectives. In this course you will learn the following
 Objectives In this course you will learn the following Introduction of Parallel Plane Waveguide. Introduction of Parallel Plane Waveguide Wave Guide is a structure which can guide Electro Magnetic Energy.
Objectives In this course you will learn the following Introduction of Parallel Plane Waveguide. Introduction of Parallel Plane Waveguide Wave Guide is a structure which can guide Electro Magnetic Energy.
AXIALLY SLOTTED ANTENNA ON A CIRCULAR OR ELLIPTIC CYLINDER COATED WITH METAMATERIALS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 1, 329 341, 2 AXIALLY SLOTTED ANTENNA ON A CIRCULAR OR ELLIPTIC CYLINDER COATED WITH METAMATERIALS A-K. Hamid Department of Electrical/Electronics and Computer
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 1, 329 341, 2 AXIALLY SLOTTED ANTENNA ON A CIRCULAR OR ELLIPTIC CYLINDER COATED WITH METAMATERIALS A-K. Hamid Department of Electrical/Electronics and Computer
Improvement of the Reflection Coefficient of Waveguide-Fed Phased-Array Antenna Using Liquid Crystal
 Journal of Communication Engineering, Vol. 4, No. 1, Jan.-June 2015 41 Improvement of the Reflection Coefficient of Waveguide-Fed Phased-Array Antenna Using Liquid Crystal S. Barzegari, G. R. Dadashzadeh
Journal of Communication Engineering, Vol. 4, No. 1, Jan.-June 2015 41 Improvement of the Reflection Coefficient of Waveguide-Fed Phased-Array Antenna Using Liquid Crystal S. Barzegari, G. R. Dadashzadeh
Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff
 Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff CHARLES R. BOYD, JR. Microwave Applications Group, Santa Maria, California, U. S. A. ABSTRACT Unlike conventional waveguides, lossless
Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff CHARLES R. BOYD, JR. Microwave Applications Group, Santa Maria, California, U. S. A. ABSTRACT Unlike conventional waveguides, lossless
International Distinguished Lecturer Program
 U 005-006 International Distinguished Lecturer Program Ken-ya Hashimoto Chiba University Sponsored by The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics and Frequency
U 005-006 International Distinguished Lecturer Program Ken-ya Hashimoto Chiba University Sponsored by The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics and Frequency
A COMPACT PI-STRUCTURE DUAL BAND TRANSFORMER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 88, 121 134, 2008 A COMPACT PI-STRUCTURE DUAL BAND TRANSFORMER Y. Wu, Y. Liu, and S. Li School of Electronic Engineering Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 88, 121 134, 2008 A COMPACT PI-STRUCTURE DUAL BAND TRANSFORMER Y. Wu, Y. Liu, and S. Li School of Electronic Engineering Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
Module 13: Network Analysis and Directional Couplers
 Module 13: Network Analysis and Directional Couplers 13.2 Network theory two port networks, S-parameters, Z-parameters, Y-parameters The study of two port networks is important in the field of electrical
Module 13: Network Analysis and Directional Couplers 13.2 Network theory two port networks, S-parameters, Z-parameters, Y-parameters The study of two port networks is important in the field of electrical
5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves
 5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves 5.1 Introduction Radar absorbing materials (RAM s) applied as a coating on the surface of an object, partially transform the energy of an incident radar beam into
5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves 5.1 Introduction Radar absorbing materials (RAM s) applied as a coating on the surface of an object, partially transform the energy of an incident radar beam into
ELECTROMAGNETIC band-gap (EBG) materials are. Analysis of Directive Radiation From a Line Source in a Metamaterial Slab With Low Permittivity
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 54, NO. 3, MARCH 2006 1017 Analysis of Directive Radiation From a Line Source in a Metamaterial Slab With Low Permittivity Giampiero Lovat, Member, IEEE,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 54, NO. 3, MARCH 2006 1017 Analysis of Directive Radiation From a Line Source in a Metamaterial Slab With Low Permittivity Giampiero Lovat, Member, IEEE,
ANALYTICAL POLE RESIDUE CALCULATION IN SPECTRAL METHOD OF MOMENTS FORMULATIONS FOR PERIODIC STRUCTURES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 13, 83 94, 2010 ANALYTICAL POLE RESIDUE CALCULATION IN SPECTRAL METHOD OF MOMENTS FORMULATIONS FOR PERIODIC STRUCTURES Y. Kaganovsky Department of Physical
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 13, 83 94, 2010 ANALYTICAL POLE RESIDUE CALCULATION IN SPECTRAL METHOD OF MOMENTS FORMULATIONS FOR PERIODIC STRUCTURES Y. Kaganovsky Department of Physical
A. Bouzidi * and T. Aguili Syscom Laboratory, Engineer National School, B.P. 37, Le Belvedere 1002, Tunis, Tunisia
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol., 41 55, 01 RCS PREDICTION FROM PLANAR NEAR-FIELD MEASUREMENTS A. Bouzidi * and T. Aguili Syscom Laboratory, Engineer National School, B.P. 37, Le Belvedere
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol., 41 55, 01 RCS PREDICTION FROM PLANAR NEAR-FIELD MEASUREMENTS A. Bouzidi * and T. Aguili Syscom Laboratory, Engineer National School, B.P. 37, Le Belvedere
ONEMAG - Electromagnetic Waves
 Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 739 - TSC - Department of Signal Theory and Communications Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE
Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 739 - TSC - Department of Signal Theory and Communications Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE
Closed-Form Evaluation of Mutual Coupling in a Planar Array of Circular Apertures
 NASA Technical Paper 3552 Closed-Form Evaluation of Mutual Coupling in a Planar Array of Circular Apertures M. C. Bailey Langley Research Center Hampton, Virginia National Aeronautics and Space Administration
NASA Technical Paper 3552 Closed-Form Evaluation of Mutual Coupling in a Planar Array of Circular Apertures M. C. Bailey Langley Research Center Hampton, Virginia National Aeronautics and Space Administration
Comparative Analysis of Techniques for Source Radiation in Cylindrical EBG with and without Periodic Discontinuities
 1398 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Abstracts, St Petersburg, Russia, 22 25 May 2017 Comparative Analysis of Techniques for Source Radiation in Cylindrical EBG with and without Periodic
1398 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Abstracts, St Petersburg, Russia, 22 25 May 2017 Comparative Analysis of Techniques for Source Radiation in Cylindrical EBG with and without Periodic
Design of a Non-uniform High Impedance Surface for a Low Profile Antenna
 352 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 Design of a Non-uniform High Impedance Surface for a Low Profile Antenna M. Hosseini 2, A. Pirhadi 1,2, and M. Hakkak
352 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 Design of a Non-uniform High Impedance Surface for a Low Profile Antenna M. Hosseini 2, A. Pirhadi 1,2, and M. Hakkak
Physics of Classical Electromagnetism
 Physics of Classical Electromagnetism Minoru Fujimoto Physics of Classical Electromagnetism Minoru Fujimoto Department of Physics University of Guelph Guelph, Ontario Canada, N1G 2W1 Library of Congress
Physics of Classical Electromagnetism Minoru Fujimoto Physics of Classical Electromagnetism Minoru Fujimoto Department of Physics University of Guelph Guelph, Ontario Canada, N1G 2W1 Library of Congress
REALIZATION OF A MATCHING REGION BETWEEN A RADOME AND A GROUND PLANE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 17, 1 1, 21 REALIZATION OF A MATCHING REGION BETWEEN A RADOME AND A GROUND PLANE D. Sjöberg and M. Gustafsson Department of Electrical and Information
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 17, 1 1, 21 REALIZATION OF A MATCHING REGION BETWEEN A RADOME AND A GROUND PLANE D. Sjöberg and M. Gustafsson Department of Electrical and Information
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE. Scaling rules for the design of a narrow-band grating filter at the focus of a free-space beam
 PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Scaling rules for the design of a narrow-band grating filter at the focus of a free-space beam Eanuel Bonnet, Alain Cachard, Alexandre
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Scaling rules for the design of a narrow-band grating filter at the focus of a free-space beam Eanuel Bonnet, Alain Cachard, Alexandre
Metamaterial-Based Flat Lens: Wave Concept Iterative Process Approach
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 75, 13 21, 2017 Metamaterial-Based Flat Lens: Wave Concept Iterative Process Approach Mohamed K. Azizi 1, *, Henri Baudrand 2, Lassaad Latrach 1, and Ali Gharsallah
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 75, 13 21, 2017 Metamaterial-Based Flat Lens: Wave Concept Iterative Process Approach Mohamed K. Azizi 1, *, Henri Baudrand 2, Lassaad Latrach 1, and Ali Gharsallah
MODAL ANALYSIS OF EXTRAORDINARY TRANSMISSION THROUGH AN ARRAY OF SUBWAVELENGTH SLITS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 79, 59 74, 008 MODAL ANALYSIS OF EXTRAORDINARY TRANSMISSION THROUGH AN ARRAY OF SUBWAVELENGTH SLITS G. Ghazi and M. Shahabadi Center of Excellence for Applied
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 79, 59 74, 008 MODAL ANALYSIS OF EXTRAORDINARY TRANSMISSION THROUGH AN ARRAY OF SUBWAVELENGTH SLITS G. Ghazi and M. Shahabadi Center of Excellence for Applied
FDTD implementations for electromagnetic shields
 FDTD implementations for electromagnetic shields S.Ursache 1, M. Branzila 1, C. Bratescu 1, R. Burlacu 1 1 Technical University of Iasi, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Bd. Profesor Dimitrie Mangeron,
FDTD implementations for electromagnetic shields S.Ursache 1, M. Branzila 1, C. Bratescu 1, R. Burlacu 1 1 Technical University of Iasi, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Bd. Profesor Dimitrie Mangeron,
Author(s) Tamayama, Y; Nakanishi, T; Sugiyama. Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW B (2006), 73(19)
 Observation of Brewster's effect fo Titleelectromagnetic waves in metamateri theory Author(s) Tamayama, Y; Nakanishi, T; Sugiyama Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW B (2006), 73(19) Issue Date 2006-05 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/39884
Observation of Brewster's effect fo Titleelectromagnetic waves in metamateri theory Author(s) Tamayama, Y; Nakanishi, T; Sugiyama Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW B (2006), 73(19) Issue Date 2006-05 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/39884
Transmission Lines. Plane wave propagating in air Y unguided wave propagation. Transmission lines / waveguides Y. guided wave propagation
 Transmission Lines Transmission lines and waveguides may be defined as devices used to guide energy from one point to another (from a source to a load). Transmission lines can consist of a set of conductors,
Transmission Lines Transmission lines and waveguides may be defined as devices used to guide energy from one point to another (from a source to a load). Transmission lines can consist of a set of conductors,
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) Equation Section 18
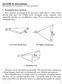 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
AC : INDIVIDUALIZED MATLAB PROJECTS IN UNDERGRADUATE ELECTROMAGNETICS
 AC 2010-36: INDIVIDUALIZED MATLAB PROJECTS IN UNDERGRADUATE ELECTROMAGNETICS Stuart Wentworth, Auburn University Stu Wentworth received his Electrical Engineering doctorate from the University of Texas,
AC 2010-36: INDIVIDUALIZED MATLAB PROJECTS IN UNDERGRADUATE ELECTROMAGNETICS Stuart Wentworth, Auburn University Stu Wentworth received his Electrical Engineering doctorate from the University of Texas,
COMSOL Design Tool: Simulations of Optical Components Week 6: Waveguides and propagation S matrix
 COMSOL Design Tool: Simulations of Optical Components Week 6: Waveguides and propagation S matrix Nikola Dordevic and Yannick Salamin 30.10.2017 1 Content Revision Wave Propagation Losses Wave Propagation
COMSOL Design Tool: Simulations of Optical Components Week 6: Waveguides and propagation S matrix Nikola Dordevic and Yannick Salamin 30.10.2017 1 Content Revision Wave Propagation Losses Wave Propagation
NASA Contractor Report. Application of FEM to Estimate Complex Permittivity of Dielectric Material at Microwave Frequency Using Waveguide Measurements
 NASA Contractor Report Application of FEM to Estimate Complex Permittivity of Dielectric Material at Microwave Frequency Using Waveguide Measurements M. D.Deshpande VIGYAN Inc., Hampton, VA C. J. Reddy
NASA Contractor Report Application of FEM to Estimate Complex Permittivity of Dielectric Material at Microwave Frequency Using Waveguide Measurements M. D.Deshpande VIGYAN Inc., Hampton, VA C. J. Reddy
MSc Physics - SC530 (Under Review)
 MSc Physics - SC530 (Under Review) 1. Specific Titles 1) MSc Physics 2) Postgraduate Diploma in Physics 3) Postgraduate Certificate in Physics 2. Objectives This Programme aims at enhancing the knowledge
MSc Physics - SC530 (Under Review) 1. Specific Titles 1) MSc Physics 2) Postgraduate Diploma in Physics 3) Postgraduate Certificate in Physics 2. Objectives This Programme aims at enhancing the knowledge
METHODS OF THEORETICAL PHYSICS
 METHODS OF THEORETICAL PHYSICS Philip M. Morse PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Herman Feshbach PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PART II: CHAPTERS 9
METHODS OF THEORETICAL PHYSICS Philip M. Morse PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Herman Feshbach PROFESSOR OF PHYSICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PART II: CHAPTERS 9
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Schematic defining the relevant physical parameters in our grating coupler model. The schematic shows a normally-incident light
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Schematic defining the relevant physical parameters in our grating coupler model. The schematic shows a normally-incident light
Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, ISBN:
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989. ISBN: 9780132490207. Please use the following
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989. ISBN: 9780132490207. Please use the following
SCATTERING BY DIELECTRIC ARRAYS ANALYSIS USING THE EXTENDED METHOD OF AUXILIARY SOURCES EMAS IN CONJUNCTION WITH GLOBAL AND PARTIAL COUPLING
 IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues Vol. 10 Issue 6 No 2 November 2013 ISSN Print: 16940814 ISSN Online: 16940784 www.ijcsi.org 244 SCATTERING BY DIELECTRIC ARRAYS ANALYSIS USING THE
IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues Vol. 10 Issue 6 No 2 November 2013 ISSN Print: 16940814 ISSN Online: 16940784 www.ijcsi.org 244 SCATTERING BY DIELECTRIC ARRAYS ANALYSIS USING THE
FINAL EXAM IN FYS-3007
 Page 1 of 4 pages + chart FINAL EXAM IN FYS-007 Exam in : Fys-007 Microwave Techniques Date : Tuesday, May 1, 2011 Time : 09.00 1.00 Place : Åsgårdveien 9 Approved remedies : All non-living and non-communicating
Page 1 of 4 pages + chart FINAL EXAM IN FYS-007 Exam in : Fys-007 Microwave Techniques Date : Tuesday, May 1, 2011 Time : 09.00 1.00 Place : Åsgårdveien 9 Approved remedies : All non-living and non-communicating
THEORETICAL ANALYSIS OF A DIPOLE-FED HORN ANTENNA
 First International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 187 THEORETICAL ANALYSIS OF A DIPOLE-FED HORN ANTENNA G.V. Eleftheriades, Walid Ali-Ahmad, L.P.B. Katehi, G.M Rebeiz Center for Space Terahertz
First International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 187 THEORETICAL ANALYSIS OF A DIPOLE-FED HORN ANTENNA G.V. Eleftheriades, Walid Ali-Ahmad, L.P.B. Katehi, G.M Rebeiz Center for Space Terahertz
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan. Analysis of Electromagnetic Propagation for Evaluating the
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Analysis of Electromagnetic Propagation for Evaluating the Dimensions of a Large Lossy Medium A. Pellegrini, FCosta F. 14-16 October 2009 Outline Introduction
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Analysis of Electromagnetic Propagation for Evaluating the Dimensions of a Large Lossy Medium A. Pellegrini, FCosta F. 14-16 October 2009 Outline Introduction
Periodic FDTD Characterization of Guiding and Radiation Properties of Negative Refractive Index Transmission Line Metamaterials
 Periodic FDTD Characterization of Guiding and Radiation Properties of Negative Refractive Index Transmission Line Metamaterials Costas D. Sarris The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer
Periodic FDTD Characterization of Guiding and Radiation Properties of Negative Refractive Index Transmission Line Metamaterials Costas D. Sarris The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer
Evanescent modes stored in cavity resonators with backward-wave slabs
 arxiv:cond-mat/0212392v1 17 Dec 2002 Evanescent modes stored in cavity resonators with backward-wave slabs S.A. Tretyakov, S.I. Maslovski, I.S. Nefedov, M.K. Kärkkäinen Radio Laboratory, Helsinki University
arxiv:cond-mat/0212392v1 17 Dec 2002 Evanescent modes stored in cavity resonators with backward-wave slabs S.A. Tretyakov, S.I. Maslovski, I.S. Nefedov, M.K. Kärkkäinen Radio Laboratory, Helsinki University
Chapter 4 Layered Substrates 4.1 Introduction
 Chapter 4 Layered Substrates 4.1 Introduction The significant result of the previous chapter is that guided mode (surface wave) losses can be avoided on substrates with thicknesses of an odd integral multiple
Chapter 4 Layered Substrates 4.1 Introduction The significant result of the previous chapter is that guided mode (surface wave) losses can be avoided on substrates with thicknesses of an odd integral multiple
Network Methods for Electromagnetic Field. Multiphysics Modeling
 Network Methods for Electromagnetic Field and Multiphysics Modeling Peter Russer and Johannes Russer Institute for Nanoelectronics Technical University Munich, Germany Email: russer@tum.de #1 Introduction
Network Methods for Electromagnetic Field and Multiphysics Modeling Peter Russer and Johannes Russer Institute for Nanoelectronics Technical University Munich, Germany Email: russer@tum.de #1 Introduction
Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves
 9210-112 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler No additional data is attached
9210-112 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler No additional data is attached
DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY. Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University
 DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University 1995 ELSEVIER Amsterdam Lausanne New York Oxford Shannon Tokyo CONTENTS Preface to the first
DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University 1995 ELSEVIER Amsterdam Lausanne New York Oxford Shannon Tokyo CONTENTS Preface to the first
Characterising Properties and Loss in High Powered Metamaterials
 Characterising Properties and Loss in High Powered Metamaterials Aimée Hopper PhD Student Supervisor: R. Seviour International Institute for Accelerator Applications University of Huddersfield (UK) Email:
Characterising Properties and Loss in High Powered Metamaterials Aimée Hopper PhD Student Supervisor: R. Seviour International Institute for Accelerator Applications University of Huddersfield (UK) Email:
! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 && & 44&, &&7 4/ 00
 ! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 &&4 2 05 6. 4& 44&, &&7 4/ 00 8 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 56, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 345 Moment Method Analysis of an Archimedean Spiral Printed
! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 &&4 2 05 6. 4& 44&, &&7 4/ 00 8 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 56, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 345 Moment Method Analysis of an Archimedean Spiral Printed
Classical Electrodynamics
 Classical Electrodynamics Third Edition John David Jackson Professor Emeritus of Physics, University of California, Berkeley JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Contents Introduction and Survey 1 I.1 Maxwell Equations
Classical Electrodynamics Third Edition John David Jackson Professor Emeritus of Physics, University of California, Berkeley JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Contents Introduction and Survey 1 I.1 Maxwell Equations
AN OPEN-ENDED rectangular waveguide, which is a typical
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 53, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2005 3953 Radiation From a Flanged Rectangular Waveguide Hirohide Serizawa and Kohei Hongo Abstract The radiation from a rectangular
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 53, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2005 3953 Radiation From a Flanged Rectangular Waveguide Hirohide Serizawa and Kohei Hongo Abstract The radiation from a rectangular
Wave scattering and splitting by magnetic metamaterials
 Wave scattering and splitting by magnetic metamaterials Alexander B. Kozyrev 1, Chao Qin 1, Ilya V. Shadrivov 2, Yuri S. Kivshar 2, Isaac L. Chuang 3, and Daniel W. van der Weide 1 1 Department of Electrical
Wave scattering and splitting by magnetic metamaterials Alexander B. Kozyrev 1, Chao Qin 1, Ilya V. Shadrivov 2, Yuri S. Kivshar 2, Isaac L. Chuang 3, and Daniel W. van der Weide 1 1 Department of Electrical
Chapter 6 Shielding. Electromagnetic Compatibility Engineering. by Henry W. Ott
 Chapter 6 Shielding Electromagnetic Compatibility Engineering by Henry W. Ott 1 Forward A shield is a metallic partition placed between two regions of space. To maintain the integrity of the shielded enclosure,
Chapter 6 Shielding Electromagnetic Compatibility Engineering by Henry W. Ott 1 Forward A shield is a metallic partition placed between two regions of space. To maintain the integrity of the shielded enclosure,
Effects from the Thin Metallic Substrate Sandwiched in Planar Multilayer Microstrip Lines
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 115 Effects from the Thin Metallic Substrate Sandwiched in Planar Multilayer Microstrip Lines L. Zhang and J. M. Song Iowa
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 115 Effects from the Thin Metallic Substrate Sandwiched in Planar Multilayer Microstrip Lines L. Zhang and J. M. Song Iowa
Microstrip Antennas. Prof. Girish Kumar Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Bombay. (022)
 Microstrip Antennas Prof. Girish Kumar Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Bombay gkumar@ee.iitb.ac.in (022) 2576 7436 Rectangular Microstrip Antenna (RMSA) Y Top View W x X L Side View r Ground plane
Microstrip Antennas Prof. Girish Kumar Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Bombay gkumar@ee.iitb.ac.in (022) 2576 7436 Rectangular Microstrip Antenna (RMSA) Y Top View W x X L Side View r Ground plane
Problem Formulation CHAPTER 2 PROBLEM FORMULATION. Three broad categories of techniques are utilized for the analysis of microstrip
 CHAPTER PROBLEM FORMULATION Three broad categories of techniques are utilized for the analysis of microstrip antennas [4, 18]. The simplest of these and the relatively basic analysis approach is the transmission
CHAPTER PROBLEM FORMULATION Three broad categories of techniques are utilized for the analysis of microstrip antennas [4, 18]. The simplest of these and the relatively basic analysis approach is the transmission
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications
 Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2013 Lecture 02 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Lecture 2: outline 2 Introduction to Nanophotonics Theoretical
Nanomaterials and their Optical Applications Winter Semester 2013 Lecture 02 rachel.grange@uni-jena.de http://www.iap.uni-jena.de/multiphoton Lecture 2: outline 2 Introduction to Nanophotonics Theoretical
OKLAHOMA SUBJECT AREA TESTS (OSAT )
 CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONS FOR OKLAHOMA EDUCATORS (CEOE ) OKLAHOMA SUBJECT AREA TESTS (OSAT ) FIELD 014: PHYSICS September 2011 Subarea Range of Competencies I. Scientific and Engineering Processes 0001
CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONS FOR OKLAHOMA EDUCATORS (CEOE ) OKLAHOMA SUBJECT AREA TESTS (OSAT ) FIELD 014: PHYSICS September 2011 Subarea Range of Competencies I. Scientific and Engineering Processes 0001
SIMULATION OF ELECTROMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ORDERED CARBON NANOTUBE ARRAYS
 Materials Physics and Mechanics 27 (216) 113-117 Received: February 19, 216 SIMULATION OF ELECTROMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ORDERED CARBON NANOTUBE ARRAYS Viatcheslav Baraline *, Aliasandr Chashynsi Belarusian
Materials Physics and Mechanics 27 (216) 113-117 Received: February 19, 216 SIMULATION OF ELECTROMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ORDERED CARBON NANOTUBE ARRAYS Viatcheslav Baraline *, Aliasandr Chashynsi Belarusian
Electromagnetic scattering from multiple sub-wavelength apertures in metallic screens using the surface integral equation method
 B. Alavikia and O. M. Ramahi Vol. 27, No. 4/April 2010/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 815 Electromagnetic scattering from multiple sub-wavelength apertures in metallic screens using the surface integral equation method
B. Alavikia and O. M. Ramahi Vol. 27, No. 4/April 2010/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 815 Electromagnetic scattering from multiple sub-wavelength apertures in metallic screens using the surface integral equation method
Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials
 Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIV 41 Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials R. Kubacki,. Nowosielski & R. Przesmycki Faculty of Electronics,
Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIV 41 Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials R. Kubacki,. Nowosielski & R. Przesmycki Faculty of Electronics,
Nature of diffraction. Diffraction
 Nature of diffraction Diffraction From Grimaldi to Maxwell Definition of diffraction diffractio, Francesco Grimaldi (1665) The effect is a general characteristics of wave phenomena occurring whenever a
Nature of diffraction Diffraction From Grimaldi to Maxwell Definition of diffraction diffractio, Francesco Grimaldi (1665) The effect is a general characteristics of wave phenomena occurring whenever a
Homogenous Optic-Null Medium Performs as Optical Surface Transformation
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 151, 169 173, 2015 Homogenous Optic-Null Medium Performs as Optical Surface Transformation Fei Sun 1 and Sailing He1, 2, * Abstract An optical surface transformation
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 151, 169 173, 2015 Homogenous Optic-Null Medium Performs as Optical Surface Transformation Fei Sun 1 and Sailing He1, 2, * Abstract An optical surface transformation
An Optimized Ku-Band Corrugated Feed Horn Antenna Design for a Cassegrain Reflector Using Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization
 An Optimized Ku-Band Corrugated Feed Horn Antenna Design for a Cassegrain Reflector Using Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization MOHAMMAD ASIF ZAMAN, MD. GAFFAR, MD. ABDUL MATIN Department of Electrical
An Optimized Ku-Band Corrugated Feed Horn Antenna Design for a Cassegrain Reflector Using Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization MOHAMMAD ASIF ZAMAN, MD. GAFFAR, MD. ABDUL MATIN Department of Electrical
Omar M. Ramahi University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, Canada
 Omar M. Ramahi University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, Canada Traditional Material!! Electromagnetic Wave ε, μ r r The only properties an electromagnetic wave sees: 1. Electric permittivity, ε 2. Magnetic
Omar M. Ramahi University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, Canada Traditional Material!! Electromagnetic Wave ε, μ r r The only properties an electromagnetic wave sees: 1. Electric permittivity, ε 2. Magnetic
Sensitivity Analysis of Coupled Resonator Filters
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: ANALOG AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 47, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2000 1017 Sensitivity Analysis of Coupled Resonator Filters Smain Amari, Member, IEEE Abstract
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: ANALOG AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 47, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2000 1017 Sensitivity Analysis of Coupled Resonator Filters Smain Amari, Member, IEEE Abstract
ELECTROMAGNETISM. Second Edition. I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips. John Wiley & Sons. Department of Physics University of Manchester
 ELECTROMAGNETISM Second Edition I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips Department of Physics University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Flow diagram inside front cover
ELECTROMAGNETISM Second Edition I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips Department of Physics University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Flow diagram inside front cover
Lecture 5 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell
 Lecture 5 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Waveguides Continued - In the previous lecture we made the assumption that
Lecture 5 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory II Dr. Christopher S. Baird, faculty.uml.edu/cbaird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Waveguides Continued - In the previous lecture we made the assumption that
Nanoscale optical circuits: controlling light using localized surface plasmon resonances
 Nanoscale optical circuits: controlling light using localized surface plasmon resonances T. J. Davis, D. E. Gómez and K. C. Vernon CSIRO Materials Science and Engineering Localized surface plasmon (LSP)
Nanoscale optical circuits: controlling light using localized surface plasmon resonances T. J. Davis, D. E. Gómez and K. C. Vernon CSIRO Materials Science and Engineering Localized surface plasmon (LSP)
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. Electrical Engineering Department ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF MICROWAVE AND OPTICAL
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Electrical Engineering Department ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF MICROWAVE AND OPTICAL PLASMONIC ANTENNAS A Thesis in Electrical Engineering by Bingqian Lu
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Electrical Engineering Department ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF MICROWAVE AND OPTICAL PLASMONIC ANTENNAS A Thesis in Electrical Engineering by Bingqian Lu
Some Interesting Properties of Scattering Matrix of Passive Microwave Devices
 Forum for Electromagnetic Research Methods and Application Technologies (FERMAT) Some Interesting Properties of Scattering Matrix of Passive Microwave Devices Ramakrishna Janaswamy Professor, Department
Forum for Electromagnetic Research Methods and Application Technologies (FERMAT) Some Interesting Properties of Scattering Matrix of Passive Microwave Devices Ramakrishna Janaswamy Professor, Department
CHAPTER 4 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF THE DUAL INVERTED-F ANTENNA
 CHAPTER 4 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF THE DUAL INVERTED-F ANTENNA 4.1. Introduction The previous chapter presented the Inverted-F Antenna (IFA) and its variations as antenna designs suitable for use in hand-held
CHAPTER 4 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF THE DUAL INVERTED-F ANTENNA 4.1. Introduction The previous chapter presented the Inverted-F Antenna (IFA) and its variations as antenna designs suitable for use in hand-held
Ansoft HFSS 3D Boundary Manager Sources
 Lumped Gap Defining s Voltage and Current When you select Source, you may choose from the following source types: Incident wave Voltage drop Current Magnetic bias These sources are available only for driven
Lumped Gap Defining s Voltage and Current When you select Source, you may choose from the following source types: Incident wave Voltage drop Current Magnetic bias These sources are available only for driven
Array Antennas. Chapter 6
 Chapter 6 Array Antennas An array antenna is a group of antenna elements with excitations coordinated in some way to achieve desired properties for the combined radiation pattern. When designing an array
Chapter 6 Array Antennas An array antenna is a group of antenna elements with excitations coordinated in some way to achieve desired properties for the combined radiation pattern. When designing an array
FREQUENCY selective surfaces (FSS) are arrays of periodically
 2824 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 55, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2007 Multimode Equivalent Networks for the Design and Analysis of Frequency Selective Surfaces Stefania Monni, Member, IEEE,
2824 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 55, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2007 Multimode Equivalent Networks for the Design and Analysis of Frequency Selective Surfaces Stefania Monni, Member, IEEE,
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 6
 ECE 6341 Spring 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 6 1 Leaky Modes v TM 1 Mode SW 1 v= utan u ε R 2 R kh 0 n1 r = ( ) 1 u Splitting point ISW f = f s f > f s We will examine the solutions as the
ECE 6341 Spring 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 6 1 Leaky Modes v TM 1 Mode SW 1 v= utan u ε R 2 R kh 0 n1 r = ( ) 1 u Splitting point ISW f = f s f > f s We will examine the solutions as the
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
A DIRICHLET TO NEUMANN MAP BASED HY- BRIDIZATION OF A MODE MATCHING AND OFFSET MOMENT METHOD FOR HORN ANTENNAS ANALYSIS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 40, 101 140, 2012 A DIRICHLET TO NEUMANN MAP BASED HY- BRIDIZATION OF A MODE MATCHING AND OFFSET MOMENT METHOD FOR HORN ANTENNAS ANALYSIS S. G. Diamantis,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 40, 101 140, 2012 A DIRICHLET TO NEUMANN MAP BASED HY- BRIDIZATION OF A MODE MATCHING AND OFFSET MOMENT METHOD FOR HORN ANTENNAS ANALYSIS S. G. Diamantis,
