A physical model for efficient rankings in networks
|
|
|
- Nora Beverley Robbins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A physical model for efficient rankings in networks Daniel Larremore Assistant Professor Dept. of Computer Science & BioFrontiers Institute March 5, 2018 CompleNet
2 The idea of rankings pervasive! Assumptions: 1. Competitors have some intrinsic quality (or vector of qualities). 2. Interactions can (stochastically) reveal differences in qualities. 3. Competitions or endorsements are pair-wise. (e.g. Lee Sedol vs. AlphaGo) In other words: outcomes are generated by a stochastic process, which is some function of the positions of the competitors. Cornell MIT Caltech Harvard UC Berkeley Stanford Washington Princeton Yale Carnegie Mellon Hobson & DeDeo. PLOS Computational Biology 11(9), e (2015). Clauset, Arbesman, Larremore. Science Advances 1, e (2015).
3 The idea of rankings pervasive! Assumptions: 1. Competitors have some intrinsic quality (or vector of qualities). 2. Interactions can (stochastically) reveal differences in qualities. 3. Competitions or endorsements are pair-wise. (e.g. Lee Sedol vs. AlphaGo) In other words: outcomes are generated by a stochastic process, which is some function of the positions Latent position of the competitors. can be revealed by pair-wise dominance or endorsement interactions. Cornell MIT Caltech Harvard UC Berkeley Stanford Washington Princeton Yale Carnegie Mellon Hobson & DeDeo. PLOS Computational Biology 11(9), e (2015). Clauset, Arbesman, Larremore. Science Advances 1, e (2015).
4 Ranking methods: many competing ideas! Minimum Violations Rank finds an order of nodes to minimize upsets : No ties (but see Agony methods), many minima, and provably NP hard. PageRank defines scalar rank recursively: important pages are those that are linked to by important pages. Great at finding the top 3 but low interpretability of the PageRank scores. Ball & Newman inferred ordinal rank via random graph + ranks model: infer parameters of people s attachment preferences & ranks. Found that in AddHealth data, teens link to others of nearby social status. Niche Models embed species in a latent space based on feeding preferences: most species feed from narrow range in a 1-dim. space (~body size). Great for food webs. Inference models v slow for all but small networks. Bradley-Terry-Luce embed products in a 1D space. Outcome direction is simply: Provably avoids non-transitive properties. Great when lots of data per interaction. The rest of this talk: SpringRank fast, interpretable, predictive. Honestly? Best to google BTL model. Williams & Martinez. Nature (2000). Ball, Newman. Network Science 1, (2013)
5 SpringRank: each directed edge = directed spring 4 3 energy ` =1! µ =
6 Relax and let the springs decide the ranks NX H(s) = 1 2 A ij (s i s j 1) 2 i,j=1 SpringRank Hamiltonian = energy of the system, given the node positions s. Because the springs are linear, the potential is quadratic. The SR Hamiltonian is convex in s. The solution is unique up to an additive constant (why?)
7 Derivatives work out i = X j A ij (s i s j 1) A ji (s j s i 1) Rewrite as a linear algebra problem. D out + D in A + A T s = D out D in 1 We know a priori that the matrix on the left is singular: translational invariance of H(s). [if s is a solution, then s + k is a solution for any constant k; eigenvalue 0, eigenvector 1] Uniqueness: Set s1=0, min(s)=0, or mean(s)=0. Or use a pseudoinverse. Or regularize.
8 It works! Real networks tend to be sparse our linear algebra problem is sparse we can use sparse iterative solvers millions of edges in seconds. computer science faculty hiring network Note that node positions can be clumpy.
9 rural social support parakeets CS hiring risk: stopping at ours is faster + pretty pictures
10 Generative models: create synthetic data We like generative models because they open the door to inference: GM + parameters + ranks GM + parameters + ranks stochastic draw inference Data Data Define a model: Let the expected number of edges from i to j be: And let the actual number of edges be drawn from a Poisson distribution with that mean.
11 Maximize the likelihood to find the ranks! the usual tricks: maximize the log; take derivatives & set to zero; chuck out additive constants. For low temperature ( large) or a sparse network (M small), the ML ranks are equal to the ranks minimizing the SR Hamiltonian! In other words: solving SpringRank is asymptotically equivalent to inferring s using the GM.
12 Consistency: Test SpringRank using GM synthetic data A B Easy: 1. Plant s from standard normal. 2. Infer ranks. 3. Compare to s. =0.3 =2.1 Spearman correlation Spring Rank BTL Colley David`s Score Min. Viol. Page Rank Eigen. Centr inverse temperature
13 Consistency: Test SpringRank using GM synthetic data C D Hard: 1. Plant s from three normals. 2. Infer ranks. 3. Compare to s. =0.3 =2.1 Spearman correlation Spring Rank BTL Colley David`s Score Min. Viol. Page Rank Eigen. Centr inverse temperature
14 How can we validate models using empirical data? [jokes]
15 Cross validation: train on 80%, predict 20% In a linear hierarchy the key quantity to predict is edge direction, given edge existence. If i and j were to face off, who would win? I ll give you undirected(a), and you predict directed(a). Setup: learn s from 80% of A. Then predict edge directions for remaining 20% of A. SpringRank predicts edge direction based on the relative direction probabilities:
16 50 independent trials of 5-fold cross validation (250 folds) Cross validation results: SR makes better predictions Accuracy: Goal: maximize the number of correctly predicted edge directions. a SpringRank prediction accuracy Alakapurum SR 0.99 BTL Business SR 0.67 BTL Parakeet G1 SR 0.71 BTL History BTL prediction accuracy a SR 0.98 BTL 0.02
17 Cross validation results: SR makes better predictions Accuracy: Goal: maximize the number of correctly predicted edge directions. A Accuracy improvement over BTL SpringRank SpringRank (Regularized) Alakapurum Tenpatti Parakeet G1 Parakeet G2 Business Comp. Sci. History Synthetic =1 Synthetic =5 medians & quartiles; 50 independent trials of 5-fold cross validation (250 folds)
18 Conclusions and extensions 1. SpringRank is a fast, scalable, predictive approach to ranking in directed networks. Works for Dominance or Endorsement. 2. It formalizes the idea that we can learn from not just the direction of edges, but the existence of edges as well. 3. There is a corresponding generative model whose ML solution is asymptotically equivalent. SpringRank approximates this ML solution with a convex Hamiltonian. a. What if the hierarchy branches, like a Y? b. What about other convex spring potential functions? c. When might the spring constants depend on i or j?
19 Caterina De Bacco Cris Moore A physical model for efficient ranking in networks De Bacco*, Larremore*, and Moore. In Revision. {preprint, python, matlab, viz} danlarremore.com
20 Thank
Locally-biased analytics
 Locally-biased analytics You have BIG data and want to analyze a small part of it: Solution 1: Cut out small part and use traditional methods Challenge: cutting out may be difficult a priori Solution 2:
Locally-biased analytics You have BIG data and want to analyze a small part of it: Solution 1: Cut out small part and use traditional methods Challenge: cutting out may be difficult a priori Solution 2:
0.1 Naive formulation of PageRank
 PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper)
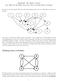 PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4)
 Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Mini-project in scientific computing
 Mini-project in scientific computing Eran Treister Computer Science Department, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Israel. March 7, 2018 1 / 30 Scientific computing Involves the solution of large computational
Mini-project in scientific computing Eran Treister Computer Science Department, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Israel. March 7, 2018 1 / 30 Scientific computing Involves the solution of large computational
Link Mining PageRank. From Stanford C246
 Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012
 Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval
 Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Introduction to Machine Learning. PCA and Spectral Clustering. Introduction to Machine Learning, Slides: Eran Halperin
 1 Introduction to Machine Learning PCA and Spectral Clustering Introduction to Machine Learning, 2013-14 Slides: Eran Halperin Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) The singular value decomposition (SVD)
1 Introduction to Machine Learning PCA and Spectral Clustering Introduction to Machine Learning, 2013-14 Slides: Eran Halperin Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) The singular value decomposition (SVD)
CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68
 CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68 References 1 L. Freeman, Centrality in Social Networks: Conceptual Clarification, Social Networks, Vol. 1, 1978/1979, pp. 215 239. 2 S. Wasserman
CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68 References 1 L. Freeman, Centrality in Social Networks: Conceptual Clarification, Social Networks, Vol. 1, 1978/1979, pp. 215 239. 2 S. Wasserman
Lecture 9 Tuesday, 4/20/10. Linear Programming
 UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Karen Daniels Spring, 2010 Lecture 9 Tuesday, 4/20/10 Linear Programming 1 Overview Motivation & Basics Standard & Slack Forms Formulating
UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Karen Daniels Spring, 2010 Lecture 9 Tuesday, 4/20/10 Linear Programming 1 Overview Motivation & Basics Standard & Slack Forms Formulating
Link Analysis and Web Search
 Link Analysis and Web Search Episode 11 Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Link Analysis and Web Search (Chapter 13, 14) Information networks and
Link Analysis and Web Search Episode 11 Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Link Analysis and Web Search (Chapter 13, 14) Information networks and
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity. Due July 18, 2014
 Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence
 Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Data and Algorithms of the Web
 Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Quilting Stochastic Kronecker Graphs to Generate Multiplicative Attribute Graphs
 Quilting Stochastic Kronecker Graphs to Generate Multiplicative Attribute Graphs Hyokun Yun (work with S.V.N. Vishwanathan) Department of Statistics Purdue Machine Learning Seminar November 9, 2011 Overview
Quilting Stochastic Kronecker Graphs to Generate Multiplicative Attribute Graphs Hyokun Yun (work with S.V.N. Vishwanathan) Department of Statistics Purdue Machine Learning Seminar November 9, 2011 Overview
CS 277: Data Mining. Mining Web Link Structure. CS 277: Data Mining Lectures Analyzing Web Link Structure Padhraic Smyth, UC Irvine
 CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
RaRE: Social Rank Regulated Large-scale Network Embedding
 RaRE: Social Rank Regulated Large-scale Network Embedding Authors: Yupeng Gu 1, Yizhou Sun 1, Yanen Li 2, Yang Yang 3 04/26/2018 The Web Conference, 2018 1 University of California, Los Angeles 2 Snapchat
RaRE: Social Rank Regulated Large-scale Network Embedding Authors: Yupeng Gu 1, Yizhou Sun 1, Yanen Li 2, Yang Yang 3 04/26/2018 The Web Conference, 2018 1 University of California, Los Angeles 2 Snapchat
November 28 th, Carlos Guestrin 1. Lower dimensional projections
 PCA Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University November 28 th, 2007 1 Lower dimensional projections Rather than picking a subset of the features, we can new features that are
PCA Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University November 28 th, 2007 1 Lower dimensional projections Rather than picking a subset of the features, we can new features that are
o A set of very exciting (to me, may be others) questions at the interface of all of the above and more
 Devavrat Shah Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems Department of EECS Massachusetts Institute of Technology http://web.mit.edu/devavrat/www (list of relevant references in the last set of slides)
Devavrat Shah Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems Department of EECS Massachusetts Institute of Technology http://web.mit.edu/devavrat/www (list of relevant references in the last set of slides)
Link Prediction. Eman Badr Mohammed Saquib Akmal Khan
 Link Prediction Eman Badr Mohammed Saquib Akmal Khan 11-06-2013 Link Prediction Which pair of nodes should be connected? Applications Facebook friend suggestion Recommendation systems Monitoring and controlling
Link Prediction Eman Badr Mohammed Saquib Akmal Khan 11-06-2013 Link Prediction Which pair of nodes should be connected? Applications Facebook friend suggestion Recommendation systems Monitoring and controlling
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank. Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018
 Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
The non-backtracking operator
 The non-backtracking operator Florent Krzakala LPS, Ecole Normale Supérieure in collaboration with Paris: L. Zdeborova, A. Saade Rome: A. Decelle Würzburg: J. Reichardt Santa Fe: C. Moore, P. Zhang Berkeley:
The non-backtracking operator Florent Krzakala LPS, Ecole Normale Supérieure in collaboration with Paris: L. Zdeborova, A. Saade Rome: A. Decelle Würzburg: J. Reichardt Santa Fe: C. Moore, P. Zhang Berkeley:
Facebook Friends! and Matrix Functions
 Facebook Friends! and Matrix Functions! Graduate Research Day Joint with David F. Gleich, (Purdue), supported by" NSF CAREER 1149756-CCF Kyle Kloster! Purdue University! Network Analysis Use linear algebra
Facebook Friends! and Matrix Functions! Graduate Research Day Joint with David F. Gleich, (Purdue), supported by" NSF CAREER 1149756-CCF Kyle Kloster! Purdue University! Network Analysis Use linear algebra
CS885 Reinforcement Learning Lecture 7a: May 23, 2018
 CS885 Reinforcement Learning Lecture 7a: May 23, 2018 Policy Gradient Methods [SutBar] Sec. 13.1-13.3, 13.7 [SigBuf] Sec. 5.1-5.2, [RusNor] Sec. 21.5 CS885 Spring 2018 Pascal Poupart 1 Outline Stochastic
CS885 Reinforcement Learning Lecture 7a: May 23, 2018 Policy Gradient Methods [SutBar] Sec. 13.1-13.3, 13.7 [SigBuf] Sec. 5.1-5.2, [RusNor] Sec. 21.5 CS885 Spring 2018 Pascal Poupart 1 Outline Stochastic
Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications
 Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications CDSE Days University at Buffalo, State University of New York Monday April 9, 2018 Dane Taylor Assistant Professor of Mathematics
Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications CDSE Days University at Buffalo, State University of New York Monday April 9, 2018 Dane Taylor Assistant Professor of Mathematics
26 : Spectral GMs. Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Guillermo A Cidre, Abelino Jimenez G.
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 26 : Spectral GMs Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Guillermo A Cidre, Abelino Jimenez G. 1 Introduction A common task in machine learning is to work with
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 26 : Spectral GMs Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Guillermo A Cidre, Abelino Jimenez G. 1 Introduction A common task in machine learning is to work with
ELE 538B: Mathematics of High-Dimensional Data. Spectral methods. Yuxin Chen Princeton University, Fall 2018
 ELE 538B: Mathematics of High-Dimensional Data Spectral methods Yuxin Chen Princeton University, Fall 2018 Outline A motivating application: graph clustering Distance and angles between two subspaces Eigen-space
ELE 538B: Mathematics of High-Dimensional Data Spectral methods Yuxin Chen Princeton University, Fall 2018 Outline A motivating application: graph clustering Distance and angles between two subspaces Eigen-space
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
 STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
Sparse PCA in High Dimensions
 Sparse PCA in High Dimensions Jing Lei, Department of Statistics, Carnegie Mellon Workshop on Big Data and Differential Privacy Simons Institute, Dec, 2013 (Based on joint work with V. Q. Vu, J. Cho, and
Sparse PCA in High Dimensions Jing Lei, Department of Statistics, Carnegie Mellon Workshop on Big Data and Differential Privacy Simons Institute, Dec, 2013 (Based on joint work with V. Q. Vu, J. Cho, and
If Mathematical Proof is a Game, What are the States and Moves? David McAllester
 If Mathematical Proof is a Game, What are the States and Moves? David McAllester 1 AlphaGo Fan (October 2015) AlphaGo Defeats Fan Hui, European Go Champion. 2 AlphaGo Lee (March 2016) 3 AlphaGo Zero vs.
If Mathematical Proof is a Game, What are the States and Moves? David McAllester 1 AlphaGo Fan (October 2015) AlphaGo Defeats Fan Hui, European Go Champion. 2 AlphaGo Lee (March 2016) 3 AlphaGo Zero vs.
Calculating Web Page Authority Using the PageRank Algorithm
 Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Data Mining Techniques
 Data Mining Techniques CS 622 - Section 2 - Spring 27 Pre-final Review Jan-Willem van de Meent Feedback Feedback https://goo.gl/er7eo8 (also posted on Piazza) Also, please fill out your TRACE evaluations!
Data Mining Techniques CS 622 - Section 2 - Spring 27 Pre-final Review Jan-Willem van de Meent Feedback Feedback https://goo.gl/er7eo8 (also posted on Piazza) Also, please fill out your TRACE evaluations!
Communities, Spectral Clustering, and Random Walks
 Communities, Spectral Clustering, and Random Walks David Bindel Department of Computer Science Cornell University 26 Sep 2011 20 21 19 16 22 28 17 18 29 26 27 30 23 1 25 5 8 24 2 4 14 3 9 13 15 11 10 12
Communities, Spectral Clustering, and Random Walks David Bindel Department of Computer Science Cornell University 26 Sep 2011 20 21 19 16 22 28 17 18 29 26 27 30 23 1 25 5 8 24 2 4 14 3 9 13 15 11 10 12
CS 6375 Machine Learning
 CS 6375 Machine Learning Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Course Info. Instructor: Nicholas Ruozzi Office: ECSS 3.409 Office hours: Tues.
CS 6375 Machine Learning Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Course Info. Instructor: Nicholas Ruozzi Office: ECSS 3.409 Office hours: Tues.
Eigenvalue Problems Computation and Applications
 Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and Applications p. 1/36 Eigenvalue Problems Computation and Applications Che-Rung Lee cherung@gmail.com National Tsing Hua University Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and
Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and Applications p. 1/36 Eigenvalue Problems Computation and Applications Che-Rung Lee cherung@gmail.com National Tsing Hua University Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and
Communities, Spectral Clustering, and Random Walks
 Communities, Spectral Clustering, and Random Walks David Bindel Department of Computer Science Cornell University 3 Jul 202 Spectral clustering recipe Ingredients:. A subspace basis with useful information
Communities, Spectral Clustering, and Random Walks David Bindel Department of Computer Science Cornell University 3 Jul 202 Spectral clustering recipe Ingredients:. A subspace basis with useful information
CS60021: Scalable Data Mining. Large Scale Machine Learning
 J. Leskovec, A. Rajaraman, J. Ullman: Mining of Massive Datasets, http://www.mmds.org 1 CS60021: Scalable Data Mining Large Scale Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Example: Spam filtering Instance
J. Leskovec, A. Rajaraman, J. Ullman: Mining of Massive Datasets, http://www.mmds.org 1 CS60021: Scalable Data Mining Large Scale Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Example: Spam filtering Instance
Using R for Iterative and Incremental Processing
 Using R for Iterative and Incremental Processing Shivaram Venkataraman, Indrajit Roy, Alvin AuYoung, Robert Schreiber UC Berkeley and HP Labs UC BERKELEY Big Data, Complex Algorithms PageRank (Dominant
Using R for Iterative and Incremental Processing Shivaram Venkataraman, Indrajit Roy, Alvin AuYoung, Robert Schreiber UC Berkeley and HP Labs UC BERKELEY Big Data, Complex Algorithms PageRank (Dominant
A Note on Google s PageRank
 A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
Spectral Method and Regularized MLE Are Both Optimal for Top-K Ranking
 Spectral Method and Regularized MLE Are Both Optimal for Top-K Ranking Yuxin Chen Electrical Engineering, Princeton University Joint work with Jianqing Fan, Cong Ma and Kaizheng Wang Ranking A fundamental
Spectral Method and Regularized MLE Are Both Optimal for Top-K Ranking Yuxin Chen Electrical Engineering, Princeton University Joint work with Jianqing Fan, Cong Ma and Kaizheng Wang Ranking A fundamental
CS281 Section 4: Factor Analysis and PCA
 CS81 Section 4: Factor Analysis and PCA Scott Linderman At this point we have seen a variety of machine learning models, with a particular emphasis on models for supervised learning. In particular, we
CS81 Section 4: Factor Analysis and PCA Scott Linderman At this point we have seen a variety of machine learning models, with a particular emphasis on models for supervised learning. In particular, we
Lecture 4: January 26
 10-725/36-725: Conve Optimization Spring 2015 Lecturer: Javier Pena Lecture 4: January 26 Scribes: Vipul Singh, Shinjini Kundu, Chia-Yin Tsai Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer:
10-725/36-725: Conve Optimization Spring 2015 Lecturer: Javier Pena Lecture 4: January 26 Scribes: Vipul Singh, Shinjini Kundu, Chia-Yin Tsai Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer:
Neural Network Training
 Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
Background Mathematics (2/2) 1. David Barber
 Background Mathematics (2/2) 1 David Barber University College London Modified by Samson Cheung (sccheung@ieee.org) 1 These slides accompany the book Bayesian Reasoning and Machine Learning. The book and
Background Mathematics (2/2) 1 David Barber University College London Modified by Samson Cheung (sccheung@ieee.org) 1 These slides accompany the book Bayesian Reasoning and Machine Learning. The book and
Managing Uncertainty
 Managing Uncertainty Bayesian Linear Regression and Kalman Filter December 4, 2017 Objectives The goal of this lab is multiple: 1. First it is a reminder of some central elementary notions of Bayesian
Managing Uncertainty Bayesian Linear Regression and Kalman Filter December 4, 2017 Objectives The goal of this lab is multiple: 1. First it is a reminder of some central elementary notions of Bayesian
Lecture 21: Spectral Learning for Graphical Models
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2016 Lecture 21: Spectral Learning for Graphical Models Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Maruan Al-Shedivat, Wei-Cheng Chang, Frederick Liu 1 Motivation
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2016 Lecture 21: Spectral Learning for Graphical Models Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Maruan Al-Shedivat, Wei-Cheng Chang, Frederick Liu 1 Motivation
 https://goo.gl/kfxweg KYOTO UNIVERSITY Statistical Machine Learning Theory Sparsity Hisashi Kashima kashima@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp DEPARTMENT OF INTELLIGENCE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 1 KYOTO UNIVERSITY Topics:
https://goo.gl/kfxweg KYOTO UNIVERSITY Statistical Machine Learning Theory Sparsity Hisashi Kashima kashima@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp DEPARTMENT OF INTELLIGENCE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 1 KYOTO UNIVERSITY Topics:
Math 307 Learning Goals. March 23, 2010
 Math 307 Learning Goals March 23, 2010 Course Description The course presents core concepts of linear algebra by focusing on applications in Science and Engineering. Examples of applications from recent
Math 307 Learning Goals March 23, 2010 Course Description The course presents core concepts of linear algebra by focusing on applications in Science and Engineering. Examples of applications from recent
Mathematical Formulation of Our Example
 Mathematical Formulation of Our Example We define two binary random variables: open and, where is light on or light off. Our question is: What is? Computer Vision 1 Combining Evidence Suppose our robot
Mathematical Formulation of Our Example We define two binary random variables: open and, where is light on or light off. Our question is: What is? Computer Vision 1 Combining Evidence Suppose our robot
INTRODUCTION TO DATA SCIENCE
 INTRODUCTION TO DATA SCIENCE JOHN P DICKERSON Lecture #13 3/9/2017 CMSC320 Tuesdays & Thursdays 3:30pm 4:45pm ANNOUNCEMENTS Mini-Project #1 is due Saturday night (3/11): Seems like people are able to do
INTRODUCTION TO DATA SCIENCE JOHN P DICKERSON Lecture #13 3/9/2017 CMSC320 Tuesdays & Thursdays 3:30pm 4:45pm ANNOUNCEMENTS Mini-Project #1 is due Saturday night (3/11): Seems like people are able to do
Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search
 CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
COMP538: Introduction to Bayesian Networks
 COMP538: Introduction to Bayesian Networks Lecture 9: Optimal Structure Learning Nevin L. Zhang lzhang@cse.ust.hk Department of Computer Science and Engineering Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
COMP538: Introduction to Bayesian Networks Lecture 9: Optimal Structure Learning Nevin L. Zhang lzhang@cse.ust.hk Department of Computer Science and Engineering Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
Supporting Statistical Hypothesis Testing Over Graphs
 Supporting Statistical Hypothesis Testing Over Graphs Jennifer Neville Departments of Computer Science and Statistics Purdue University (joint work with Tina Eliassi-Rad, Brian Gallagher, Sergey Kirshner,
Supporting Statistical Hypothesis Testing Over Graphs Jennifer Neville Departments of Computer Science and Statistics Purdue University (joint work with Tina Eliassi-Rad, Brian Gallagher, Sergey Kirshner,
APPENDIX A. Background Mathematics. A.1 Linear Algebra. Vector algebra. Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components x 1 x 2.
 APPENDIX A Background Mathematics A. Linear Algebra A.. Vector algebra Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components 0 x x 2 B C @. A x n Definition 6 (scalar product). The scalar product
APPENDIX A Background Mathematics A. Linear Algebra A.. Vector algebra Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components 0 x x 2 B C @. A x n Definition 6 (scalar product). The scalar product
A New Method to Find the Eigenvalues of Convex. Matrices with Application in Web Page Rating
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 4, 200, no. 9, 905-9 A New Method to Find the Eigenvalues of Convex Matrices with Application in Web Page Rating F. Soleymani Department of Mathematics, Islamic Azad
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 4, 200, no. 9, 905-9 A New Method to Find the Eigenvalues of Convex Matrices with Application in Web Page Rating F. Soleymani Department of Mathematics, Islamic Azad
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Some material on these is slides borrowed from Andrew Moore's excellent machine learning tutorials located at: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~awm/tutorials/ Where Should We Draw the Line????
Support Vector Machines Some material on these is slides borrowed from Andrew Moore's excellent machine learning tutorials located at: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~awm/tutorials/ Where Should We Draw the Line????
A New Space for Comparing Graphs
 A New Space for Comparing Graphs Anshumali Shrivastava and Ping Li Cornell University and Rutgers University August 18th 2014 Anshumali Shrivastava and Ping Li ASONAM 2014 August 18th 2014 1 / 38 Main
A New Space for Comparing Graphs Anshumali Shrivastava and Ping Li Cornell University and Rutgers University August 18th 2014 Anshumali Shrivastava and Ping Li ASONAM 2014 August 18th 2014 1 / 38 Main
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701
 Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Barnabás Póczos Contents Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Sampling Rejection Importance Hastings-Metropolis Gibbs Markov Chains
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Barnabás Póczos Contents Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Sampling Rejection Importance Hastings-Metropolis Gibbs Markov Chains
Linear Regression. CSL603 - Fall 2017 Narayanan C Krishnan
 Linear Regression CSL603 - Fall 2017 Narayanan C Krishnan ckn@iitrpr.ac.in Outline Univariate regression Multivariate regression Probabilistic view of regression Loss functions Bias-Variance analysis Regularization
Linear Regression CSL603 - Fall 2017 Narayanan C Krishnan ckn@iitrpr.ac.in Outline Univariate regression Multivariate regression Probabilistic view of regression Loss functions Bias-Variance analysis Regularization
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University
 Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University We ve had our first HC cases. Please, please, please, before you do anything that might violate the HC, talk to me or a TA to make sure it is legitimate. It is much
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University We ve had our first HC cases. Please, please, please, before you do anything that might violate the HC, talk to me or a TA to make sure it is legitimate. It is much
Machine Learning and Computational Statistics, Spring 2017 Homework 2: Lasso Regression
 Machine Learning and Computational Statistics, Spring 2017 Homework 2: Lasso Regression Due: Monday, February 13, 2017, at 10pm (Submit via Gradescope) Instructions: Your answers to the questions below,
Machine Learning and Computational Statistics, Spring 2017 Homework 2: Lasso Regression Due: Monday, February 13, 2017, at 10pm (Submit via Gradescope) Instructions: Your answers to the questions below,
Linear Regression. CSL465/603 - Fall 2016 Narayanan C Krishnan
 Linear Regression CSL465/603 - Fall 2016 Narayanan C Krishnan ckn@iitrpr.ac.in Outline Univariate regression Multivariate regression Probabilistic view of regression Loss functions Bias-Variance analysis
Linear Regression CSL465/603 - Fall 2016 Narayanan C Krishnan ckn@iitrpr.ac.in Outline Univariate regression Multivariate regression Probabilistic view of regression Loss functions Bias-Variance analysis
The Trouble with Community Detection
 The Trouble with Community Detection Aaron Clauset Santa Fe Institute 7 April 2010 Nonlinear Dynamics of Networks Workshop U. Maryland, College Park Thanks to National Science Foundation REU Program James
The Trouble with Community Detection Aaron Clauset Santa Fe Institute 7 April 2010 Nonlinear Dynamics of Networks Workshop U. Maryland, College Park Thanks to National Science Foundation REU Program James
Multiclass Classification-1
 CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
Link Analysis Ranking
 Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Expectation Maximization
 Expectation Maximization Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington November 13, 2014 1 E.M.: The General Case E.M. widely used beyond mixtures of Gaussians The recipe is the same
Expectation Maximization Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington November 13, 2014 1 E.M.: The General Case E.M. widely used beyond mixtures of Gaussians The recipe is the same
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3
 Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
Mixed Membership Stochastic Blockmodels
 Mixed Membership Stochastic Blockmodels (2008) Edoardo M. Airoldi, David M. Blei, Stephen E. Fienberg and Eric P. Xing Herrissa Lamothe Princeton University Herrissa Lamothe (Princeton University) Mixed
Mixed Membership Stochastic Blockmodels (2008) Edoardo M. Airoldi, David M. Blei, Stephen E. Fienberg and Eric P. Xing Herrissa Lamothe Princeton University Herrissa Lamothe (Princeton University) Mixed
STA 414/2104: Lecture 8
 STA 414/2104: Lecture 8 6-7 March 2017: Continuous Latent Variable Models, Neural networks With thanks to Russ Salakhutdinov, Jimmy Ba and others Outline Continuous latent variable models Background PCA
STA 414/2104: Lecture 8 6-7 March 2017: Continuous Latent Variable Models, Neural networks With thanks to Russ Salakhutdinov, Jimmy Ba and others Outline Continuous latent variable models Background PCA
Final. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence. CS 188 Spring You have approximately 2 hours and 50 minutes.
 CS 188 Spring 2014 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Final You have approximately 2 hours and 50 minutes. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your two-page crib sheet. Mark your answers
CS 188 Spring 2014 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Final You have approximately 2 hours and 50 minutes. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your two-page crib sheet. Mark your answers
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
Graph Detection and Estimation Theory
 Introduction Detection Estimation Graph Detection and Estimation Theory (and algorithms, and applications) Patrick J. Wolfe Statistics and Information Sciences Laboratory (SISL) School of Engineering and
Introduction Detection Estimation Graph Detection and Estimation Theory (and algorithms, and applications) Patrick J. Wolfe Statistics and Information Sciences Laboratory (SISL) School of Engineering and
Simple Techniques for Improving SGD. CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017
 Simple Techniques for Improving SGD CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017 Step Sizes and Convergence Where we left off Stochastic gradient descent x t+1 = x t rf(x t ; yĩt ) Much faster per iteration than gradient
Simple Techniques for Improving SGD CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017 Step Sizes and Convergence Where we left off Stochastic gradient descent x t+1 = x t rf(x t ; yĩt ) Much faster per iteration than gradient
Ordinary Least Squares Linear Regression
 Ordinary Least Squares Linear Regression Ryan P. Adams COS 324 Elements of Machine Learning Princeton University Linear regression is one of the simplest and most fundamental modeling ideas in statistics
Ordinary Least Squares Linear Regression Ryan P. Adams COS 324 Elements of Machine Learning Princeton University Linear regression is one of the simplest and most fundamental modeling ideas in statistics
Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming
 CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Winter 2017 Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan 3/01/17 Scribe: Laura Vonessen Disclaimer: These
CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Winter 2017 Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan 3/01/17 Scribe: Laura Vonessen Disclaimer: These
Learning Gaussian Graphical Models with Unknown Group Sparsity
 Learning Gaussian Graphical Models with Unknown Group Sparsity Kevin Murphy Ben Marlin Depts. of Statistics & Computer Science Univ. British Columbia Canada Connections Graphical models Density estimation
Learning Gaussian Graphical Models with Unknown Group Sparsity Kevin Murphy Ben Marlin Depts. of Statistics & Computer Science Univ. British Columbia Canada Connections Graphical models Density estimation
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
Multivariate Normal Models
 Case Study 3: fmri Prediction Graphical LASSO Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Emily Fox February 26 th, 2013 Emily Fox 2013 1 Multivariate Normal Models
Case Study 3: fmri Prediction Graphical LASSO Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Emily Fox February 26 th, 2013 Emily Fox 2013 1 Multivariate Normal Models
Lecture 25: November 27
 10-725: Optimization Fall 2012 Lecture 25: November 27 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Scribes: Matt Wytock, Supreeth Achar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have
10-725: Optimization Fall 2012 Lecture 25: November 27 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Scribes: Matt Wytock, Supreeth Achar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have
Announcements: Warm-up Exercise:
 Fri Mar 30 5.6 Discrete dynamical systems: Google page rank, using some notes I wrote a while ago. I'll probably also bring a handout to class. There are other documents on the internet about this subject.
Fri Mar 30 5.6 Discrete dynamical systems: Google page rank, using some notes I wrote a while ago. I'll probably also bring a handout to class. There are other documents on the internet about this subject.
Empirical Risk Minimization, Model Selection, and Model Assessment
 Empirical Risk Minimization, Model Selection, and Model Assessment CS6780 Advanced Machine Learning Spring 2015 Thorsten Joachims Cornell University Reading: Murphy 5.7-5.7.2.4, 6.5-6.5.3.1 Dietterich,
Empirical Risk Minimization, Model Selection, and Model Assessment CS6780 Advanced Machine Learning Spring 2015 Thorsten Joachims Cornell University Reading: Murphy 5.7-5.7.2.4, 6.5-6.5.3.1 Dietterich,
Spectral Graph Theory
 Spectral Graph Theory Aaron Mishtal April 27, 2016 1 / 36 Outline Overview Linear Algebra Primer History Theory Applications Open Problems Homework Problems References 2 / 36 Outline Overview Linear Algebra
Spectral Graph Theory Aaron Mishtal April 27, 2016 1 / 36 Outline Overview Linear Algebra Primer History Theory Applications Open Problems Homework Problems References 2 / 36 Outline Overview Linear Algebra
Sparse Stochastic Inference for Latent Dirichlet Allocation
 Sparse Stochastic Inference for Latent Dirichlet Allocation David Mimno 1, Matthew D. Hoffman 2, David M. Blei 1 1 Dept. of Computer Science, Princeton U. 2 Dept. of Statistics, Columbia U. Presentation
Sparse Stochastic Inference for Latent Dirichlet Allocation David Mimno 1, Matthew D. Hoffman 2, David M. Blei 1 1 Dept. of Computer Science, Princeton U. 2 Dept. of Statistics, Columbia U. Presentation
Data Mining Techniques
 Data Mining Techniques CS 6220 - Section 3 - Fall 2016 Lecture 12 Jan-Willem van de Meent (credit: Yijun Zhao, Percy Liang) DIMENSIONALITY REDUCTION Borrowing from: Percy Liang (Stanford) Linear Dimensionality
Data Mining Techniques CS 6220 - Section 3 - Fall 2016 Lecture 12 Jan-Willem van de Meent (credit: Yijun Zhao, Percy Liang) DIMENSIONALITY REDUCTION Borrowing from: Percy Liang (Stanford) Linear Dimensionality
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017
 ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks
 ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
Introduction Eigen Values and Eigen Vectors An Application Matrix Calculus Optimal Portfolio. Portfolios. Christopher Ting.
 Portfolios Christopher Ting Christopher Ting http://www.mysmu.edu/faculty/christophert/ : christopherting@smu.edu.sg : 6828 0364 : LKCSB 5036 November 4, 2016 Christopher Ting QF 101 Week 12 November 4,
Portfolios Christopher Ting Christopher Ting http://www.mysmu.edu/faculty/christophert/ : christopherting@smu.edu.sg : 6828 0364 : LKCSB 5036 November 4, 2016 Christopher Ting QF 101 Week 12 November 4,
Simon Trebst. Quantitative Modeling of Complex Systems
 Quantitative Modeling of Complex Systems Machine learning In computer science, machine learning is concerned with algorithms that allow for data analytics, most prominently dimensional reduction and feature
Quantitative Modeling of Complex Systems Machine learning In computer science, machine learning is concerned with algorithms that allow for data analytics, most prominently dimensional reduction and feature
a table or a graph or an equation.
 Topic (8) POPULATION DISTRIBUTIONS 8-1 So far: Topic (8) POPULATION DISTRIBUTIONS We ve seen some ways to summarize a set of data, including numerical summaries. We ve heard a little about how to sample
Topic (8) POPULATION DISTRIBUTIONS 8-1 So far: Topic (8) POPULATION DISTRIBUTIONS We ve seen some ways to summarize a set of data, including numerical summaries. We ve heard a little about how to sample
Final Report on the Newton Institute Programme Polynomial Optimisation
 Final Report on the Newton Institute Programme Polynomial Optimisation July 15th to August 19th 2013 1 Committees The organising committee consisted of: Adam N. Letchford (Department of Management Science,
Final Report on the Newton Institute Programme Polynomial Optimisation July 15th to August 19th 2013 1 Committees The organising committee consisted of: Adam N. Letchford (Department of Management Science,
Multivariate Normal Models
 Case Study 3: fmri Prediction Coping with Large Covariances: Latent Factor Models, Graphical Models, Graphical LASSO Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Emily Fox February
Case Study 3: fmri Prediction Coping with Large Covariances: Latent Factor Models, Graphical Models, Graphical LASSO Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Emily Fox February
The Deep Ritz method: A deep learning-based numerical algorithm for solving variational problems
 The Deep Ritz method: A deep learning-based numerical algorithm for solving variational problems Weinan E 1 and Bing Yu 2 arxiv:1710.00211v1 [cs.lg] 30 Sep 2017 1 The Beijing Institute of Big Data Research,
The Deep Ritz method: A deep learning-based numerical algorithm for solving variational problems Weinan E 1 and Bing Yu 2 arxiv:1710.00211v1 [cs.lg] 30 Sep 2017 1 The Beijing Institute of Big Data Research,
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701
 Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Goal & Motivation Sampling Rejection Importance Markov
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Goal & Motivation Sampling Rejection Importance Markov
Statistical Problem. . We may have an underlying evolving system. (new state) = f(old state, noise) Input data: series of observations X 1, X 2 X t
 Markov Chains. Statistical Problem. We may have an underlying evolving system (new state) = f(old state, noise) Input data: series of observations X 1, X 2 X t Consecutive speech feature vectors are related
Markov Chains. Statistical Problem. We may have an underlying evolving system (new state) = f(old state, noise) Input data: series of observations X 1, X 2 X t Consecutive speech feature vectors are related
CS340 Winter 2010: HW3 Out Wed. 2nd February, due Friday 11th February
 CS340 Winter 2010: HW3 Out Wed. 2nd February, due Friday 11th February 1 PageRank You are given in the file adjency.mat a matrix G of size n n where n = 1000 such that { 1 if outbound link from i to j,
CS340 Winter 2010: HW3 Out Wed. 2nd February, due Friday 11th February 1 PageRank You are given in the file adjency.mat a matrix G of size n n where n = 1000 such that { 1 if outbound link from i to j,
10725/36725 Optimization Homework 4
 10725/36725 Optimization Homework 4 Due November 27, 2012 at beginning of class Instructions: There are four questions in this assignment. Please submit your homework as (up to) 4 separate sets of pages
10725/36725 Optimization Homework 4 Due November 27, 2012 at beginning of class Instructions: There are four questions in this assignment. Please submit your homework as (up to) 4 separate sets of pages
Reconstruction in the Generalized Stochastic Block Model
 Reconstruction in the Generalized Stochastic Block Model Marc Lelarge 1 Laurent Massoulié 2 Jiaming Xu 3 1 INRIA-ENS 2 INRIA-Microsoft Research Joint Centre 3 University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign GDR
Reconstruction in the Generalized Stochastic Block Model Marc Lelarge 1 Laurent Massoulié 2 Jiaming Xu 3 1 INRIA-ENS 2 INRIA-Microsoft Research Joint Centre 3 University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign GDR
