What can Single-Well Constant-Rate Pump Tests really tell about Fractured Rocks?
|
|
|
- George Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 What can Single-Well Constant-Rate Pump Tests really tell about Fractured Rocks? Stephan K. Matthäi, Sebastian Geiger, Centre for Petroleum Studies, Department of Earth Science and Engineering at Imperial Workshop on Model Concepts for Fluid-Fluid and Fluid-Solid Interactions Freudenstadt-Lauterbad, 20-22/3/2006 Imperial College London
2 Background Dynamic data from well tests often provide the only clues about the large-scale permeability and-or storativity of fractured reservoirs Rock matrix properties tend to be relatively well constrained by special core analysis (SCAL) The assumption that the permeability of the rock matrix is relatively uniform as compared with the fractures is often reasonable Single-well, constant-rate tests are the only ones which are carried out on fractured reservoirs on a routine basis Although common, shut-in tests are useless for fractured reservoirs because they only sample the fracture system Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 2
3 Outline 1. Rationale 1. ABC of well testing 2. Flow velocity spectra and the fracture-matrix flux ratio 2. Utility of fracture-matrix flux ratio for upscaling 2-phase flow 3. Estimation of fracture-matrix flux ratio in well tests Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 3
4 Well testing = transient fluid pressure diffusion p k = 2 t φµ c t p + fluid Standard plots employ dimensionless variables: Dimensionless time, t D : q where c t is the total-system compressibility and r w is the well bore radius. k h 2 Dimensionless pressure, p D : p D = q B where h is the height of the reservoir layer and B is the formation factor. t D = c t = V k t φµ c v p t r π µ w f Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 4
5 Theory (A. Gringarten, 1973) well (planview) Dimensionless time vs. pressure, log-log plot p isobars pd pd radial drawdown 0.5 infinite acting The fluid pressure-time derivative, dp/dt, at the well head is indicative of the flow regime dp/dt decreases when drawdown spreads into high permeability regions which discharge fluid more rapidly to the well dp/dt increases when internal of external impermeable boundaries get within the radius of drawdown dp/dt is constant while drawdown spreads across regions in which the bulk properties are uniform; in this infinite-acting case k can be inferred from dp/dt and the pumping rate Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 5
6 Previous work: transient response of faults Fault Properties from Outcrop Synthetic Well Test (2D) Matthäi et al., 1998 (SPE J ) Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 6
7 Simulated deviations from radial drawdown (Arches model) Topview of reservoir t = 8 hrs Def. Band Fault Joint 3 wells Matthäi et al., 1998 (Royal Soc. London, Special Publication 147, ) Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 7
8 Outline 1. Rationale 1. ABC of well testing 2. Flow velocity spectra and the fracture-matrix flux ratio 2. Utility of fracture-matrix flux ratio for upscaling 2-phase flow 3. Estimation of fracture-matrix flux ratio from well tests Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 8
9 Stochastic model with 2000 disc-shaped fractures generated using field data from San Andreas formation 1000 m 3.5 mm Fracture Aperture (m) 1 mm 1000 m Model built with FRED (Golder Associates) Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 9
10 Geometric and material properties Parameter Dimensions Porosity, Φ Φ f V f A, fracture-matrix interface Specific A f (P32) Units km - - m 3 km 2 m 2 m -3 FRACS x 1 x log k m md 10 1,468 k eff in flow direction q f /q m in x-direction log c t D - m 3 m -3 Pa Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 10
11 Single-phase flow velocity spectrum k eff = 1,468 D q f /q m (x) = 150 analysis method described in Matthäi & Belayneh, 2004, GRL 31:7, Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 11
12 Ratio q f / q m is determined together with effective permeability Single-phase flow analysis: MODEL k eff = qµ L w ( ( ) ( )) A p u p d f f q in A q out p f (u) p f (d) NB: k eff value will be different to that determined by ODA (1984) method Results depend on boundary setup (Flodin et al. 2004) L Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 12
13 Geologically conditioned, simulation-assisted upscaling From core plug to grid block scale Larger features must have a discrete model representation We have a new comprehensive strategy but it requires the fracture-matrix flux ratio to upscale relative permeability / fractional flow, water cut at breakthrough, rate of countercurrent imbibition Subseismic (mm-hm)-scale Seismic (hm-hm)-scale Oman reservoir model, p f contours 2 km Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 13
14 Outline 1. Rationale 2. Utility of fracture-matrix flux ratio for upscaling 2-phase flow 3. Estimation of fracture-matrix flux ratio from well tests Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 14
15 Numerically predicted kr i erratic? IRREGULAR-x200y20z50 mobility ratio, m =2 krw krn kri Saturation water Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 15
16 Prediction of relative permeability at ( s w(avg) ) Numerically determined total mobility, λ t is related to relative permeability λ t kr o = = kr µ k w w r t + λ µ µ o kr µ w + o o µ o µ ; w ; k kr r w = = kr kr k k r r w o λ µ µ t o w + µ µ o w Our experiments show that during water flooding, the kr w / kr o ratio is approximated closely by the q f / q m ratio Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 16
17 krw q f kr o q m Makes sense because the water immediately imbibes the fractures in a model it flows at the rate reflecting their contribution to the total flux Oil flows at the matrix rate Is determined by cheap single phase steady-state experiments Tensor property, range: 0 to ~10 4 in experiments conducted so far, anisotropy 100. Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 17
18 Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 18 Predicted grid-block scale relative permeability Example, using error functions: ( ) ( ) = + = m f w f w w w m f w f w w o q q s s s kr q q s s s kr 1 erf, 1 erfc φ φ
19 Implications of up-scaled relative permeability Derivative of fractional flow function no longer switches sign with increasing saturation but becomes monotonously increasing There is no shock in the volume integrated saturation but a long leading edge: f w f w, upscaled s w integrated over grid block s w water flood Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 19
20 Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 20
21 Summary, Utility of q f /q m Ratio for Upscaling The fracture-matrix flux ratio found by steadystate single phase analysis helps to predict gridblock scale relative permeability, fractional flow, and water cut at breakthrough Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 21
22 Outline 1. Rationale 2. Utility of fracture-matrix flux ratio for upscaling 2-phase flow 3. Estimation of fracture-matrix flux ratio from well tests Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 22
23 Well testing of fractured reservoirs Common wisdom Radial drawdown leads to a constant derivative of ½ Presence of finite length fractures is indicated by ¼ slope Presence of infinite length fractures is indicated by ½ slope Complications Real fractures have a diameter spectrum Heterogeneous rock matrix Anisotropy Storage capacity contrast between fractures and matrix Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 23
24 Closer to reality (horizontal well in Kilve a.r.) p f contours p f drop blue=5 x 10-6 ms -1 red= 0.1 ms -1 L = 2.32 κt well Belayneh, Geiger, Matthai, AAPG Bulletin, in press Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 24
25 Matrix and fracture storativity Hydraulic diffusivity Matrix storativity S κ = k φµ c t = αφ + β 1 k S µ ( φ ) Fracture storativity derived from toughness of mode I joint: S f = V f a 3 π µ ( ν 1) V f = 2 x x = = d 0 a ( x ) dx Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 25
26 Relative importance of fracture vs. matrix storativity Storativity light oil (API=45) saturated Troll sandstone with single fracture of variable length α = 3.1 x β = 2.6 x µ = 15 GPa ν = 0.25 Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 26
27 A fresh look at well tests We perform numerical well-test experiments on fracture models with known effective permeability and fracture-matrix flux ratio Key question: can we determine k eff and q f / q m in constant-rate, single-well pump tests? We will assume that the permeability of the rock matrix is known from core plug testing (SCAL), is isotropic, and lacks a correlation structure on the grid-block scale Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 27
28 Governing equations p = κ 2 t p Time discretization: + q Backward Euler, finite difference, progressive t: ([ φ S t ] + [ K ]){ p } = {[ S t ]} p q Spatial discretization: t + t φ t + Linear finite-element basis, adaptively refined hybrid element mesh, variable representations of wells Solution method: Algebraic Multigrid (SAMG, SCAI Fraunhofer), grid-reuse + p t as initial guess Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 28
29 Benchmarks uniform 3D model For different well shapes and hybrid element meshes our numerical method tracks the expected properties of homogeneos models closely 0.5 plot normalized by well rate and permeability assigned to grid Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 29
30 Benchmarks (continued) 3D experiments with triangular well Well intersects the fracture finite-length fractures infinite fractures Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 30
31 benchmark case well next to fracture Spatial drawdown patterns in the presence of fractures finite length fracture Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 31
32 Model FRACS2000 revisited well does not intersect fracture drawdown is not radial k m =1 x m 2 k f = 1 x to 4 x m 2 q f /q m =~150, anisotropy=1.3 Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 32
33 Derivative plot, normalized using matrix permeability FRACS2000? drawdown begins to affect model boundary Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 33
34 Single set of fractures with powerlaw diameter distribution Model POWERLAW200 a( x,..) = 2 ( ) ( 1 ν σ ) d yy p f µ Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 34 2 x 2
35 How should one interpret this test? Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 35
36 Summary 3, Well Test Experiments So far we have not found a way to deduce the q f /q m ratio from the results of a single-well constant rate test Radial drawdown needed to measure k eff may occur in the presence of fractures but only if the nature and abundance of fracture heterogeneities near the well does not change in a sufficiently large area around the well the effective permeability of this region is close to isotropic therefore - a separation of scales is possible Provided that a sufficiently long period of radial flow occurs once the effects of well-bore storage have ceased, q f / q m may determined in this largely hypothetical case but only if the permeability of the host rock is known Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 36
37 Mandefro Belayneh, Paul LaPointe, Miguel Gomez, Tanja Clees, Klaus Stüben, Alain Gringarten, Thomas von Schröter, Mike Homeyer Thank You FRED Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 37
38 CSP Complex Systems Platform API by Stephan K Matthäi (IC), Stephen G. Roberts (ANU), Sebastian Geiger (ETH), + contributions from: Thomas Driesner, Chris Pain, Andrey Mezentsev, Dim Coumou, Adriana Paluszny 1994: Idea of CSP at Cornell University, NY Spring 1995: SKM s first implementation of CSP Autumn 1995: Sabbatical of S.G. Roberts at Stanford University, CA, CSP with Meschach & AMG solver 1996: Review of CSP and suggestions by Bruce Eckel : SKM s main development and implementation of CSP : S. Geiger develops FV capabilities 2001: CSP3D 4.0 in Std C++ using meta-template programming techniques 2001: ICEM CSP interface 2002: Design of IMP-IMPS capabilities in collaboration with C. Pain, integration and interfacing with CFD tools 2003: SAMG-based large-scale mechanical calculations 2003: Interface to anisotropic adaptivity module 2003: SAMG-based large-scale mechanical calculations 2003: Interface to anisotropic adaptivity module 2003: Generalized 3D IMP-IMPS multiphase flow capabilities including gravity drainage and capillary driven flow 2004: Introduction of DFEM methods to deal with discontinua, EOS for H20-NaCl mixtures 2005: Parallelisation including SAMGp, work on advanced graphical user-interface, Navier-Stokes compressible flows Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 38
39 At beginning of water flood fractures are not water saturated Is this a problem? Case 1: well interconnected fractures q f >> q m, but fracture contribution to total porosity is only % (FRACS2000) At a high q f / q m, water breaks through the fractures instantaneously (compare slide 15). In this case the approximation applies Case 2: poorly interconnected fractures As q f approaches a fraction of q m, flow is controlled by the relative permeability-saturation curve of the rock matrix Matthäi/Geiger-Lauterbad 21/3/06, slide 39
Cracks, Fractures and Faults Fluid Flow Through Fractured Rock. Stephan K. Matthäi, 18 to June, 2008 Avon Gorge Hotel, Bristol
 Cracks, Fractures and Faults Fluid Flow Through Fractured Rock Stephan K. Matthäi, Department of Earth Science & Engineering, Imperial College London s.matthai@ic.ac.uk 18 to June, 2008 Avon Gorge Hotel,
Cracks, Fractures and Faults Fluid Flow Through Fractured Rock Stephan K. Matthäi, Department of Earth Science & Engineering, Imperial College London s.matthai@ic.ac.uk 18 to June, 2008 Avon Gorge Hotel,
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS
 THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals COPYRIGHT. Introduction
 Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals Why This Module is Important Introduction Fundamental understanding of the flow through rocks is extremely important to understand the behavior of the reservoir Permeability
Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals Why This Module is Important Introduction Fundamental understanding of the flow through rocks is extremely important to understand the behavior of the reservoir Permeability
18 Single vertical fractures
 18 Single vertical fractures 18.1 Introduction If a well intersects a single vertical fracture, the aquifer s unsteady drawdown response to pumping differs significantly from that predicted by the Theis
18 Single vertical fractures 18.1 Introduction If a well intersects a single vertical fracture, the aquifer s unsteady drawdown response to pumping differs significantly from that predicted by the Theis
Pressure Transient Analysis COPYRIGHT. Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Pressure Transient Analysis Core Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives
Pressure Transient Analysis Core Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives
Mathematics Research Report No. MRR 003{96, HIGH RESOLUTION POTENTIAL FLOW METHODS IN OIL EXPLORATION Stephen Roberts 1 and Stephan Matthai 2 3rd Febr
 HIGH RESOLUTION POTENTIAL FLOW METHODS IN OIL EXPLORATION Stephen Roberts and Stephan Matthai Mathematics Research Report No. MRR 003{96, Mathematics Research Report No. MRR 003{96, HIGH RESOLUTION POTENTIAL
HIGH RESOLUTION POTENTIAL FLOW METHODS IN OIL EXPLORATION Stephen Roberts and Stephan Matthai Mathematics Research Report No. MRR 003{96, Mathematics Research Report No. MRR 003{96, HIGH RESOLUTION POTENTIAL
The Challenge of Estimating Recovery from Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. Dr Shane Hattingh Principal Reservoir Engineer, ERC Equipoise
 The Challenge of Estimating Recovery from Naturally Fractured Reservoirs Dr Shane Hattingh Principal Reservoir Engineer, ERC Equipoise 1 Disclaimer Disclaimer ERC Equipoise Ltd ( ERC Equipoise or ERCE
The Challenge of Estimating Recovery from Naturally Fractured Reservoirs Dr Shane Hattingh Principal Reservoir Engineer, ERC Equipoise 1 Disclaimer Disclaimer ERC Equipoise Ltd ( ERC Equipoise or ERCE
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS USING RESISTIVITY
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 01 SGP-TR-194 CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 01 SGP-TR-194 CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS
Partial Saturation Fluid Substitution with Partial Saturation
 Fluid Substitution with 261 5 4.5 ρ fluid S w ρ w + S o ρ o + S g ρ g Vp (km/s) 4 3.5 K fluid S w K w + S o K o + S g K g Patchy Saturation Drainage 3 2.5 2 Fine-scale mixing 1 = S w + S o + S g K fluid
Fluid Substitution with 261 5 4.5 ρ fluid S w ρ w + S o ρ o + S g ρ g Vp (km/s) 4 3.5 K fluid S w K w + S o K o + S g K g Patchy Saturation Drainage 3 2.5 2 Fine-scale mixing 1 = S w + S o + S g K fluid
Rate Transient Analysis COPYRIGHT. Introduction. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Learning Objectives Rate Transient Analysis Core Introduction This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define the rate time analysis Distinguish between traditional pressure transient
Learning Objectives Rate Transient Analysis Core Introduction This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define the rate time analysis Distinguish between traditional pressure transient
XYZ COMPANY LTD. Prepared For: JOHN DOE. XYZ et al Knopcik 100/ W5/06 PAS-TRG. Dinosaur Park Formation
 All depths reported in mkb TVD per EUB requirements. All pressures reported in (a) per EUB requirements. 9.01 used as atmospheric pressure adjustment to convert from gauge to absolute pressure. XYZ COMPANY
All depths reported in mkb TVD per EUB requirements. All pressures reported in (a) per EUB requirements. 9.01 used as atmospheric pressure adjustment to convert from gauge to absolute pressure. XYZ COMPANY
Presentation of MSc s Thesis
 Presentation of MSc s Thesis A Framework for Building Transient Well Testing Numerical Models Using Unstructured Grids Mohammed H. Sayyouh Professor in Petroleum Engineering Department FECU Khaled A. Abdel-Fattah
Presentation of MSc s Thesis A Framework for Building Transient Well Testing Numerical Models Using Unstructured Grids Mohammed H. Sayyouh Professor in Petroleum Engineering Department FECU Khaled A. Abdel-Fattah
Fracture-matrix transfer function in fractured porous media
 Fluid Structure Interaction VII 109 Fracture-matrix transfer function in fractured porous media A. J. Mahmood Department of Chemical Industries, Al-Anbar Technical Institute, Iraq Abstract One of the mathematical
Fluid Structure Interaction VII 109 Fracture-matrix transfer function in fractured porous media A. J. Mahmood Department of Chemical Industries, Al-Anbar Technical Institute, Iraq Abstract One of the mathematical
R.M. Manasipov and J.E. Mindel. Montanuniversitaet Leoben. October 3, 2014
 Comparative Analysis of Compositional Two-Phase Flow Modeling in Heterogeneous Media Between the Discrete Event Simulation Method Coupled to a Split Node Formulation and Classical Timestep-Driven Approaches
Comparative Analysis of Compositional Two-Phase Flow Modeling in Heterogeneous Media Between the Discrete Event Simulation Method Coupled to a Split Node Formulation and Classical Timestep-Driven Approaches
Chapter Seven. For ideal gases, the ideal gas law provides a precise relationship between density and pressure:
 Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF BOILING HEAT CONVECTION WITH RADIAL FLOW IN A FRACTURE
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 25-27, 1999 SGP-TR-162 AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF BOILING HEAT CONVECTION
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 25-27, 1999 SGP-TR-162 AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF BOILING HEAT CONVECTION
Numerical Simulation and Multiple Realizations for Sensitivity Study of Shale Gas Reservoir
 SPE 141058 Numerical Simulation and Multiple Realizations for Sensitivity Study of Shale Gas Reservoir A.Kalantari-Dahaghi, S.D.Mohaghegh,SPE, Petroleum Engineering and Analytic Research Laboratory(PEARL)
SPE 141058 Numerical Simulation and Multiple Realizations for Sensitivity Study of Shale Gas Reservoir A.Kalantari-Dahaghi, S.D.Mohaghegh,SPE, Petroleum Engineering and Analytic Research Laboratory(PEARL)
TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL. A Thesis ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL
 TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL A Thesis by ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL A Thesis by ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
NEW DEMANDS FOR APPLICATION OF NUMERICAL SIMULATION TO IMPROVE RESERVOIR STUDIES IN CHINA
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 148 152 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information NEW DEMANDS FOR APPLICATION OF NUMERICAL SIMULATION TO IMPROVE
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 148 152 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information NEW DEMANDS FOR APPLICATION OF NUMERICAL SIMULATION TO IMPROVE
dynamics of f luids in porous media
 dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
A Physics-Based Data-Driven Model for History Matching, Prediction and Characterization of Unconventional Reservoirs*
 A Physics-Based Data-Driven Model for History Matching, Prediction and Characterization of Unconventional Reservoirs* Yanbin Zhang *This work has been submitted to SPEJ and under review for publication
A Physics-Based Data-Driven Model for History Matching, Prediction and Characterization of Unconventional Reservoirs* Yanbin Zhang *This work has been submitted to SPEJ and under review for publication
Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured Reservoirs
 Transport in Porous Media 49: 209 240, 2002. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 209 Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured
Transport in Porous Media 49: 209 240, 2002. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 209 Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured
Fracture-Matrix Flow Partitioning and Cross Flow: Numerical Modeling of Laboratory Fractured Core Flood
 Fracture-Matrix Flow Partitioning and Cross Flow: Numerical Modeling of Laboratory Fractured Core Flood R. Sanaee *, G. F. Oluyemi, M. Hossain, and M. B. Oyeneyin Robert Gordon University *Corresponding
Fracture-Matrix Flow Partitioning and Cross Flow: Numerical Modeling of Laboratory Fractured Core Flood R. Sanaee *, G. F. Oluyemi, M. Hossain, and M. B. Oyeneyin Robert Gordon University *Corresponding
2. Governing Equations. 1. Introduction
 Multiphysics Between Deep Geothermal Water Cycle, Surface Heat Exchanger Cycle and Geothermal Power Plant Cycle Li Wah Wong *,1, Guido Blöcher 1, Oliver Kastner 1, Günter Zimmermann 1 1 International Centre
Multiphysics Between Deep Geothermal Water Cycle, Surface Heat Exchanger Cycle and Geothermal Power Plant Cycle Li Wah Wong *,1, Guido Blöcher 1, Oliver Kastner 1, Günter Zimmermann 1 1 International Centre
Complexity of Two-Phase Flow in Porous Media
 1 Complexity of Two-Phase Flow in Porous Media Rennes September 16, 2009 Eyvind Aker Morten Grøva Henning Arendt Knudsen Thomas Ramstad Bo-Sture Skagerstam Glenn Tørå Alex Hansen 2 Declining oil production,
1 Complexity of Two-Phase Flow in Porous Media Rennes September 16, 2009 Eyvind Aker Morten Grøva Henning Arendt Knudsen Thomas Ramstad Bo-Sture Skagerstam Glenn Tørå Alex Hansen 2 Declining oil production,
Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions
 SPE-185479-MS Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions J. R. Garcia-Pastrana, A. R. Valdes-Perez, and T. A. Blasingame,
SPE-185479-MS Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions J. R. Garcia-Pastrana, A. R. Valdes-Perez, and T. A. Blasingame,
Reservoir Simulator Practical
 Reservoir Simulator Practical Course Notes 2012 Philipp Lang IZR Room 403 Tel 3004 philipp.lang@unileoben.ac.at for further information please refer to the accompanying document Info Sheet & Course Logistics
Reservoir Simulator Practical Course Notes 2012 Philipp Lang IZR Room 403 Tel 3004 philipp.lang@unileoben.ac.at for further information please refer to the accompanying document Info Sheet & Course Logistics
Training Venue and Dates Ref # Reservoir Geophysics October, 2019 $ 6,500 London
 Training Title RESERVOIR GEOPHYSICS Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates Ref # Reservoir Geophysics DE035 5 07 11 October, 2019 $ 6,500 London In any of the 5 star hotels. The exact venue
Training Title RESERVOIR GEOPHYSICS Training Duration 5 days Training Venue and Dates Ref # Reservoir Geophysics DE035 5 07 11 October, 2019 $ 6,500 London In any of the 5 star hotels. The exact venue
GG655/CEE623 Groundwater Modeling. Aly I. El-Kadi
 GG655/CEE63 Groundwater Modeling Model Theory Water Flow Aly I. El-Kadi Hydrogeology 1 Saline water in oceans = 97.% Ice caps and glaciers =.14% Groundwater = 0.61% Surface water = 0.009% Soil moisture
GG655/CEE63 Groundwater Modeling Model Theory Water Flow Aly I. El-Kadi Hydrogeology 1 Saline water in oceans = 97.% Ice caps and glaciers =.14% Groundwater = 0.61% Surface water = 0.009% Soil moisture
Quarterly Report for January March 1998 Stanford Geothermal Program DE-FG07-95ID13370
 Quarterly Report for January 1998 - March 1998 Stanford Geothermal Program DE-FG7-95ID1337 Table of Contents 1. MEASUREMENTS OF STEAM-WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITY 1 1.1 SUMMARY 1 1.2 INTRODUCTION 1 1.3
Quarterly Report for January 1998 - March 1998 Stanford Geothermal Program DE-FG7-95ID1337 Table of Contents 1. MEASUREMENTS OF STEAM-WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITY 1 1.1 SUMMARY 1 1.2 INTRODUCTION 1 1.3
In all of the following equations, is the coefficient of permeability in the x direction, and is the hydraulic head.
 Groundwater Seepage 1 Groundwater Seepage Simplified Steady State Fluid Flow The finite element method can be used to model both steady state and transient groundwater flow, and it has been used to incorporate
Groundwater Seepage 1 Groundwater Seepage Simplified Steady State Fluid Flow The finite element method can be used to model both steady state and transient groundwater flow, and it has been used to incorporate
DETERMINING WETTABILITY FROM IN SITU PRESSURE AND SATURATION MEASUREMENTS
 SCA2010-44 1/6 DETERMINING WETTABILITY FROM IN SITU PRESSURE AND SATURATION MEASUREMENTS Brautaset, A.*, Ersland, G., Graue, A. Department of Physics and Technology, University of Bergen, Norway * Now
SCA2010-44 1/6 DETERMINING WETTABILITY FROM IN SITU PRESSURE AND SATURATION MEASUREMENTS Brautaset, A.*, Ersland, G., Graue, A. Department of Physics and Technology, University of Bergen, Norway * Now
Computing permeability of fault zones in eolian sandstone from outcrop measurements
 Computing permeability of fault zones in eolian sandstone from outcrop measurements Hervé Jourde, Eric A. Flodin, Atilla Aydin, Louis J. Durlofsky, and Xian-Huan Wen ABSTRACT The large-scale equivalent
Computing permeability of fault zones in eolian sandstone from outcrop measurements Hervé Jourde, Eric A. Flodin, Atilla Aydin, Louis J. Durlofsky, and Xian-Huan Wen ABSTRACT The large-scale equivalent
A BOOKLET ON. T Rangasamy, A R Leach and A P Cook. Facilitating safety and health research in the South African mining industry
 A BOOKLET ON THE HYDRAULIC DESIGN OF COAL BARRIER PILLARS T Rangasamy, A R Leach and A P Cook Facilitating safety and health research in the South African mining industry A BOOKLET ON THE HYDRAULIC DESIGN
A BOOKLET ON THE HYDRAULIC DESIGN OF COAL BARRIER PILLARS T Rangasamy, A R Leach and A P Cook Facilitating safety and health research in the South African mining industry A BOOKLET ON THE HYDRAULIC DESIGN
Pengcheng Fu, Yue Hao, and Charles R. Carrigan
 Pengcheng Fu, Yue Hao, and Charles R. Carrigan Math, Science and Computation of Hydraulic Fracturing Workshop Stanford, March 21, 2013 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department
Pengcheng Fu, Yue Hao, and Charles R. Carrigan Math, Science and Computation of Hydraulic Fracturing Workshop Stanford, March 21, 2013 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department
Comparison of Heat and Mass Transport at the Micro-Scale
 Comparison of Heat and Mass Transport at the Micro-Scale E. Holzbecher, S. Oehlmann Georg-August Univ. Göttingen *Goldschmidtstr. 3, 37077 Göttingen, GERMANY, eholzbe@gwdg.de Abstract: Phenomena of heat
Comparison of Heat and Mass Transport at the Micro-Scale E. Holzbecher, S. Oehlmann Georg-August Univ. Göttingen *Goldschmidtstr. 3, 37077 Göttingen, GERMANY, eholzbe@gwdg.de Abstract: Phenomena of heat
Fundamentals of Basin and Petroleum Systems Modeling
 Thomas Hantschel Armin I. Kauerauf Fundamentals of Basin and Petroleum Systems Modeling 4ü Springer Contents Introduction to Basin Modeling 1 1.1 History 1 1.2 Geologien! Processes 3 1.3 Structure of a
Thomas Hantschel Armin I. Kauerauf Fundamentals of Basin and Petroleum Systems Modeling 4ü Springer Contents Introduction to Basin Modeling 1 1.1 History 1 1.2 Geologien! Processes 3 1.3 Structure of a
Opportunities in Oil and Gas Fields Questions TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS A. Asset... 3 1. What is the size of the opportunity (size the prize)?... 3 2. Volumetric Evaluation... 3 3. Probabilistic Volume Estimates... 3 4. Material Balance Application... 3 5.
TABLE OF CONTENTS A. Asset... 3 1. What is the size of the opportunity (size the prize)?... 3 2. Volumetric Evaluation... 3 3. Probabilistic Volume Estimates... 3 4. Material Balance Application... 3 5.
Storage 6 - Modeling for CO 2 Storage. Professor John Kaldi Chief Scientist, CO2CRC Australian School of Petroleum, University of Adelaide, Australia
 Storage 6 - Modeling for CO 2 Storage Professor John Kaldi Chief Scientist, CO2CRC Australian School of Petroleum, University of Adelaide, Australia Regina, Sask., Canada, 17-22 July, 2016 Modeling 2 What
Storage 6 - Modeling for CO 2 Storage Professor John Kaldi Chief Scientist, CO2CRC Australian School of Petroleum, University of Adelaide, Australia Regina, Sask., Canada, 17-22 July, 2016 Modeling 2 What
Coalbed Methane Properties
 Coalbed Methane Properties Subtopics: Permeability-Pressure Relationship Coal Compressibility Matrix Shrinkage Seidle and Huitt Palmer and Mansoori Shi and Durucan Constant Exponent Permeability Incline
Coalbed Methane Properties Subtopics: Permeability-Pressure Relationship Coal Compressibility Matrix Shrinkage Seidle and Huitt Palmer and Mansoori Shi and Durucan Constant Exponent Permeability Incline
CO 2 storage capacity and injectivity analysis through the integrated reservoir modelling
 CO 2 storage capacity and injectivity analysis through the integrated reservoir modelling Dr. Liuqi Wang Geoscience Australia CO 2 Geological Storage and Technology Training School of CAGS Beijing, P.
CO 2 storage capacity and injectivity analysis through the integrated reservoir modelling Dr. Liuqi Wang Geoscience Australia CO 2 Geological Storage and Technology Training School of CAGS Beijing, P.
q v = - K h = kg/ν units of velocity Darcy's Law: K = kρg/µ HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY, K Proportionality constant in Darcy's Law
 Darcy's Law: q v - K h HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY, K m/s K kρg/µ kg/ν units of velocity Proportionality constant in Darcy's Law Property of both fluid and medium see D&S, p. 62 HYDRAULIC POTENTIAL (Φ): Φ g
Darcy's Law: q v - K h HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY, K m/s K kρg/µ kg/ν units of velocity Proportionality constant in Darcy's Law Property of both fluid and medium see D&S, p. 62 HYDRAULIC POTENTIAL (Φ): Φ g
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock
 Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
If your model can t do this, why run it?
 FRACTURE MODEL DESIGN MODEL REQUIREMENTS Describe/Include the basic physics of all important processes Ability to predict (not just mimic) job results Provide decision making capability Understand what
FRACTURE MODEL DESIGN MODEL REQUIREMENTS Describe/Include the basic physics of all important processes Ability to predict (not just mimic) job results Provide decision making capability Understand what
DFNModeler: AN EFFICIENT DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODELER
 1 DFNModeler: AN EFFICIENT DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODELER 0709 Guohai Jin and Jack C. Pashin Geological Survey of Alabama, P. O. Box 869999, Tuscaloosa, AL 35486 ABSTRACT DFNModeler is a Windows application
1 DFNModeler: AN EFFICIENT DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODELER 0709 Guohai Jin and Jack C. Pashin Geological Survey of Alabama, P. O. Box 869999, Tuscaloosa, AL 35486 ABSTRACT DFNModeler is a Windows application
Earth dam steady state seepage analysis
 Engineering manual No. 32 Updated 3/2018 Earth dam steady state seepage analysis Program: FEM Water Flow File: Demo_manual_32.gmk Introduction This example illustrates an application of the GEO5 FEM module
Engineering manual No. 32 Updated 3/2018 Earth dam steady state seepage analysis Program: FEM Water Flow File: Demo_manual_32.gmk Introduction This example illustrates an application of the GEO5 FEM module
Derivation of the fractional flow equation for a one-dimensional oil-water system. Consider displacement of oil by water in a system of dip angle α
 TPG45 Reservoir Recovery Techniques 27 /9 BUCKLEY-LEVERETT ANALYSIS Derivation of the fractional flow equation for a one-dimensional oil-water system Consider displacement of oil by water in a system of
TPG45 Reservoir Recovery Techniques 27 /9 BUCKLEY-LEVERETT ANALYSIS Derivation of the fractional flow equation for a one-dimensional oil-water system Consider displacement of oil by water in a system of
Simplified In-Situ Stress Properties in Fractured Reservoir Models. Tim Wynn AGR-TRACS
 Simplified In-Situ Stress Properties in Fractured Reservoir Models Tim Wynn AGR-TRACS Before the What and the How is Why Potential decrease in fault seal capacity Potential increase in natural fracture
Simplified In-Situ Stress Properties in Fractured Reservoir Models Tim Wynn AGR-TRACS Before the What and the How is Why Potential decrease in fault seal capacity Potential increase in natural fracture
Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks
 Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks RPSEA Piceance Basin Tight Gas Research Review Xiaolong Yin, Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering, Colorado School
Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks RPSEA Piceance Basin Tight Gas Research Review Xiaolong Yin, Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering, Colorado School
Local Time Step for a Finite Volume Scheme I.Faille F.Nataf*, F.Willien, S.Wolf**
 Controlled CO 2 Diversified fuels Fuel-efficient vehicles Clean refining Extended reserves Local Time Step for a Finite Volume Scheme I.Faille F.Nataf*, F.Willien, S.Wolf** *: Laboratoire J.L.Lions **:Université
Controlled CO 2 Diversified fuels Fuel-efficient vehicles Clean refining Extended reserves Local Time Step for a Finite Volume Scheme I.Faille F.Nataf*, F.Willien, S.Wolf** *: Laboratoire J.L.Lions **:Université
Hydraulic properties of porous media
 PART 5 Hydraulic properties of porous media Porosity Definition: Void space: n V void /V total total porosity e V void /V solid Primary porosity - between grains Secondary porosity - fracture or solution
PART 5 Hydraulic properties of porous media Porosity Definition: Void space: n V void /V total total porosity e V void /V solid Primary porosity - between grains Secondary porosity - fracture or solution
A Multi-Continuum Multi-Component Model for Simultaneous Enhanced Gas Recovery and CO 2 Storage in Stimulated Fractured Shale Gas Reservoirs Jiamin
 A Multi-Continuum Multi-Component Model for Simultaneous Enhanced Gas Recovery and CO 2 Storage in Stimulated Fractured Shale Gas Reservoirs Jiamin Jiang M.S. Candidate Joined Fall 2013 1 Main Points Advanced
A Multi-Continuum Multi-Component Model for Simultaneous Enhanced Gas Recovery and CO 2 Storage in Stimulated Fractured Shale Gas Reservoirs Jiamin Jiang M.S. Candidate Joined Fall 2013 1 Main Points Advanced
Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot
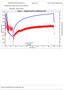 BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON. Department of Earth Science and Engineering. Centre for Petroleum Studies
 IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies Upscaling of Relative Permeability to Minimise Numerical Dispersion By Anthony Tobechukwu Afoaku A report
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies Upscaling of Relative Permeability to Minimise Numerical Dispersion By Anthony Tobechukwu Afoaku A report
Modeling seismic wave propagation during fluid injection in a fractured network: Effects of pore fluid pressure on time-lapse seismic signatures
 Modeling seismic wave propagation during fluid injection in a fractured network: Effects of pore fluid pressure on time-lapse seismic signatures ENRU LIU, SERAFEIM VLASTOS, and XIANG-YANG LI, Edinburgh
Modeling seismic wave propagation during fluid injection in a fractured network: Effects of pore fluid pressure on time-lapse seismic signatures ENRU LIU, SERAFEIM VLASTOS, and XIANG-YANG LI, Edinburgh
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
HEAT TRANSFER IN A LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL WELL
 HEAT TRANSFER IN A LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL WELL Marcel Rosca University of Oradea, Armata Romana 5, RO-37 Oradea, Romania Key Words: low enthalpy, numerical modeling, wellbore heat transfer, Oradea reservoir,
HEAT TRANSFER IN A LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL WELL Marcel Rosca University of Oradea, Armata Romana 5, RO-37 Oradea, Romania Key Words: low enthalpy, numerical modeling, wellbore heat transfer, Oradea reservoir,
Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN
 Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN Introduction Early days: Microseismic monitoring has been around since the early
Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN Introduction Early days: Microseismic monitoring has been around since the early
PROCEEDINGS THIRD WORKSHOP GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ENGINEERING. December 14-15,1977
 SGPTR258 PROCEEDINGS THIRD WORKSHOP GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ENGINEERING December 1415,1977 *Conducted under Subcontract No. 16735 with Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, Universityof California, sponsored by the
SGPTR258 PROCEEDINGS THIRD WORKSHOP GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ENGINEERING December 1415,1977 *Conducted under Subcontract No. 16735 with Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, Universityof California, sponsored by the
Imperial College London
 Imperial College London Title Page IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies PREDICTING WHEN CONDENSATE BANKING BECOMES VISIBLE ON BUILD-UP DERIVATIVES
Imperial College London Title Page IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies PREDICTING WHEN CONDENSATE BANKING BECOMES VISIBLE ON BUILD-UP DERIVATIVES
Homogenization and numerical Upscaling. Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow
 Homogenization and numerical Upscaling Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow Insa Neuweiler Institute of Hydromechanics, University of Stuttgart Outline Block 1: Introduction and Repetition Homogenization
Homogenization and numerical Upscaling Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow Insa Neuweiler Institute of Hydromechanics, University of Stuttgart Outline Block 1: Introduction and Repetition Homogenization
Reservoir Simulator Compaction Modelling: A Predictor for Accelerated Coupled Rock Mechanics -- Reservoir Simulation
 Reservoir Simulator Compaction Modelling: A Predictor for Accelerated Coupled Rock Mechanics -- Reservoir Simulation by Øystein Pettersen Centre for Integrated Petroleum Research, Bergen, Norway ECMOR
Reservoir Simulator Compaction Modelling: A Predictor for Accelerated Coupled Rock Mechanics -- Reservoir Simulation by Øystein Pettersen Centre for Integrated Petroleum Research, Bergen, Norway ECMOR
TOUGH2 Flow Simulator Used to Simulate an Electric Field of a Reservoir With a Conductive Tracer for Fracture Characterization
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 36, 2012 TOUGH2 Flow Simulator Used to Simulate an Electric Field of a Reservoir With a Conductive Tracer for Fracture Characterization Lilja Magnusdottir and Roland N. Horne Stanford
GRC Transactions, Vol. 36, 2012 TOUGH2 Flow Simulator Used to Simulate an Electric Field of a Reservoir With a Conductive Tracer for Fracture Characterization Lilja Magnusdottir and Roland N. Horne Stanford
Storage 4 - Modeling for CO 2 Storage. Professor John Kaldi Chief Scientist, CO2CRC Australian School of Petroleum, University of Adelaide, Australia
 Storage 4 - Modeling for CO 2 Storage Professor John Kaldi Chief Scientist, CO2CRC Australian School of Petroleum, University of Adelaide, Australia 1 Modelling 2 On Models. All models are wrong. some
Storage 4 - Modeling for CO 2 Storage Professor John Kaldi Chief Scientist, CO2CRC Australian School of Petroleum, University of Adelaide, Australia 1 Modelling 2 On Models. All models are wrong. some
Determination of Capillary pressure & relative permeability curves
 Determination of Capillary pressure & relative permeability curves With Refrigerated Centrifuge Multi speed centrifuge experiments Introduction As the porous diaphragm method see Vinci s CAPRI, the centrifuge
Determination of Capillary pressure & relative permeability curves With Refrigerated Centrifuge Multi speed centrifuge experiments Introduction As the porous diaphragm method see Vinci s CAPRI, the centrifuge
Prediction of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Performance using Novel Integrated Workflow
 Prediction of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Performance using Novel Integrated Workflow Reda Abdel Azim Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Department American University of Ras Al Khaimah Ras Al Khaimah,
Prediction of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Performance using Novel Integrated Workflow Reda Abdel Azim Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Department American University of Ras Al Khaimah Ras Al Khaimah,
WP 4.1. Site selection criteria and ranking methodology. Karen Kirk
 WP 4.1 Site selection criteria and ranking methodology Karen Kirk 1 Basic site selection criteria Sufficient depth and storage capacity supercritical CO 2 below 700-800 m (rule of thumb) 2 Variation of
WP 4.1 Site selection criteria and ranking methodology Karen Kirk 1 Basic site selection criteria Sufficient depth and storage capacity supercritical CO 2 below 700-800 m (rule of thumb) 2 Variation of
FRACTURE REORIENTATION IN HORIZONTAL WELL WITH MULTISTAGE HYDRAULIC FRACTURING
 SPE Workshop OILFIELD GEOMECHANICS Slide 1 FRACTURE REORIENTATION IN HORIZONTAL WELL WITH MULTISTAGE HYDRAULIC FRACTURING A. Pimenov, R. Kanevskaya Ltd. BashNIPIneft March 27-28, 2017 Moscow, Russia Slide
SPE Workshop OILFIELD GEOMECHANICS Slide 1 FRACTURE REORIENTATION IN HORIZONTAL WELL WITH MULTISTAGE HYDRAULIC FRACTURING A. Pimenov, R. Kanevskaya Ltd. BashNIPIneft March 27-28, 2017 Moscow, Russia Slide
Characterization and Modeling of Naturally Fractured Tensleep Reservoirs
 Characterization and Modeling of Naturally Fractured Tensleep Reservoirs Shaochang Wo, Peigui Yin, Scott Cooper, John Lorenz J A N U A R Y 1 8, 2 0 1 1, D E N V E R A Brief Overview of the Tensleep Reservoirs
Characterization and Modeling of Naturally Fractured Tensleep Reservoirs Shaochang Wo, Peigui Yin, Scott Cooper, John Lorenz J A N U A R Y 1 8, 2 0 1 1, D E N V E R A Brief Overview of the Tensleep Reservoirs
STUDY AND SIMULATION OF TRACER AND THERMAL TRANSPORT IN FRACTURED RESERVOIRS
 Equation Chapter 1 Section 1PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Fifth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 1-3, 2010 SGP-TR-188 STUDY AND SIMULATION OF TRACER
Equation Chapter 1 Section 1PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Fifth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 1-3, 2010 SGP-TR-188 STUDY AND SIMULATION OF TRACER
PETROPHYSICAL WELLBORE INVERSION. TOTAL Emmanuel CAROLI, Peppino TERPOLILLI
 PETROPHYSICAL WELLBORE INVERSION A NEW VALUE TO LOG DATA TOTAL Emmanuel CAROLI, Peppino TERPOLILLI ENSEEIHT/CERFACS Serge GRATTON, Thibaud VANDAMME EXPLORATION-DEVELOPMENT IN ONE SLIDE How to convert a
PETROPHYSICAL WELLBORE INVERSION A NEW VALUE TO LOG DATA TOTAL Emmanuel CAROLI, Peppino TERPOLILLI ENSEEIHT/CERFACS Serge GRATTON, Thibaud VANDAMME EXPLORATION-DEVELOPMENT IN ONE SLIDE How to convert a
Oil and Gas Well Performance
 Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
Hydraulic fracturing in unconventional shale gas reservoirs. Dr.-Ing. Johannes Will, Dynardo GmbH, Weimar, Germany
 Hydraulic fracturing in unconventional shale gas reservoirs Dr.-Ing. Johannes Will, Dynardo GmbH, Weimar, Germany Founded: 2001 (Will, Bucher, CADFEM International) More than 35 employees, offices at Weimar
Hydraulic fracturing in unconventional shale gas reservoirs Dr.-Ing. Johannes Will, Dynardo GmbH, Weimar, Germany Founded: 2001 (Will, Bucher, CADFEM International) More than 35 employees, offices at Weimar
Numerical modelling of coupled TH processes to facilitate analysis of geothermal reservoirs - Groß Schönebeck as an example-
 Numerical modelling of coupled TH processes to facilitate analysis of geothermal reservoirs - Groß Schönebeck as an example- N Watanabe 1, G Blöcher 2, M Cacace 2, H Shao 1, O Kolditz 1 1 Helmholtz Centre
Numerical modelling of coupled TH processes to facilitate analysis of geothermal reservoirs - Groß Schönebeck as an example- N Watanabe 1, G Blöcher 2, M Cacace 2, H Shao 1, O Kolditz 1 1 Helmholtz Centre
Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/559655 Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests Article
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/559655 Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests Article
Before beginning, I would like to acknowledge the amazing contributions of Ken Nolte. I suspect that the origins of most of our discussion during
 1 Before beginning, I would like to acknowledge the amazing contributions of Ken Nolte. I suspect that the origins of most of our discussion during this workshop can be traced to Dr. Nolte. He was a true
1 Before beginning, I would like to acknowledge the amazing contributions of Ken Nolte. I suspect that the origins of most of our discussion during this workshop can be traced to Dr. Nolte. He was a true
Analytical and Numerical Modeling of Heat Transport in Fractured Reservoirs
 PROCEEDINGS, 43rd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 12-14, 218 SGP-TR-213 Analytical and Numerical Modeling of Heat Transport in Fractured
PROCEEDINGS, 43rd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 12-14, 218 SGP-TR-213 Analytical and Numerical Modeling of Heat Transport in Fractured
American University of Ras Al Khaimah, United Arab Emirates, Ras Al Khaimah
 Article Open Access DETERMINATION OF INFLOW PERFORMANCE RELATIONSHIP FOR A VERTICAL WELL IN NATU- RALLY FRACTURED OIL RESERVOIRS: NUMERICAL SIMULATION STUDY Reda Abdel Azim, Melissa Ramirez, and Mohammad
Article Open Access DETERMINATION OF INFLOW PERFORMANCE RELATIONSHIP FOR A VERTICAL WELL IN NATU- RALLY FRACTURED OIL RESERVOIRS: NUMERICAL SIMULATION STUDY Reda Abdel Azim, Melissa Ramirez, and Mohammad
Integration of seismic and fluid-flow data: a two-way road linked by rock physics
 Integration of seismic and fluid-flow data: a two-way road linked by rock physics Abstract Yunyue (Elita) Li, Yi Shen, and Peter K. Kang Geologic model building of the subsurface is a complicated and lengthy
Integration of seismic and fluid-flow data: a two-way road linked by rock physics Abstract Yunyue (Elita) Li, Yi Shen, and Peter K. Kang Geologic model building of the subsurface is a complicated and lengthy
Simulation of Naturally Fractured Reservoirs with Dual Porosity Models
 Simulation of Naturally Fractured Reservoirs ith Dual Porosity Models Pallav Sarma Prof. Khalid Aziz Stanford University SUPRI-HW Motivations! NFRs represent at least 0%of orld reserves, but difficult
Simulation of Naturally Fractured Reservoirs ith Dual Porosity Models Pallav Sarma Prof. Khalid Aziz Stanford University SUPRI-HW Motivations! NFRs represent at least 0%of orld reserves, but difficult
Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS
 Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization
 P-408 Summary Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization Asha S. Mishra* and S. K. Mishra 1 The present paper describes the pressure transient
P-408 Summary Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization Asha S. Mishra* and S. K. Mishra 1 The present paper describes the pressure transient
Multi-scale multi-phase flow upscaling
 Multi-scale multi-phase flow upscaling Philip Ringrose Statoil ASA & NTNU, Norway IEAGHG Modelling and Monitoring Network Meeting, 6-8 th July 2016 Edinburgh, Scotland Full-field simulation grids Geological
Multi-scale multi-phase flow upscaling Philip Ringrose Statoil ASA & NTNU, Norway IEAGHG Modelling and Monitoring Network Meeting, 6-8 th July 2016 Edinburgh, Scotland Full-field simulation grids Geological
Grimsel In-situ Stimulation and Circulation experiment: First results SCCER Annual meeting , Birmensdorf, Switzerland
 Grimsel In-situ Stimulation and Circulation experiment: First results SCCER Annual meeting 14 15.09.2017, Birmensdorf, Switzerland J. Doetsch, F. Amann, V. Gischig, M. Jalali, H. Krietsch, B. Valley, C.
Grimsel In-situ Stimulation and Circulation experiment: First results SCCER Annual meeting 14 15.09.2017, Birmensdorf, Switzerland J. Doetsch, F. Amann, V. Gischig, M. Jalali, H. Krietsch, B. Valley, C.
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Two-phase flow in a fissurized-porous media
 Two-phase low in a issurized-porous media P. Ø. Andersen and S. Evje Citation: AIP Con. Proc. 479, 234 (22); doi:.63/.4756663 View online: http://dx.doi.org/.63/.4756663 View Table o Contents: http://proceedings.aip.org/dbt/dbt.jsp?key=apcpcs&volume=479&issue=
Two-phase low in a issurized-porous media P. Ø. Andersen and S. Evje Citation: AIP Con. Proc. 479, 234 (22); doi:.63/.4756663 View online: http://dx.doi.org/.63/.4756663 View Table o Contents: http://proceedings.aip.org/dbt/dbt.jsp?key=apcpcs&volume=479&issue=
THE INVESTIGATION OF NUMERICAL SIMULATION SOFTWARE FOR FRACTURED RESERVOIRS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 161 168 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information THE INVESTIGATION OF NUMERICAL SIMULATION SOFTWARE FOR FRACTURED
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 161 168 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information THE INVESTIGATION OF NUMERICAL SIMULATION SOFTWARE FOR FRACTURED
The Interaction of Reservoir Engineering and Geomechanics (a story)
 The Interaction of Reservoir Engineering and Geomechanics (a story) Brian G D Smart FREng, FRSE, FIMMM, CEng Petromall Ltd Why is the interaction a good thing? Assertion - Reservoir Geomechanics enables
The Interaction of Reservoir Engineering and Geomechanics (a story) Brian G D Smart FREng, FRSE, FIMMM, CEng Petromall Ltd Why is the interaction a good thing? Assertion - Reservoir Geomechanics enables
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF THE PETROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES VARIATIONS ON THE SEISMIC RESPONSE OF A CO2 STORAGE SITE. Juan E. Santos
 SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF THE PETROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES VARIATIONS ON THE SEISMIC RESPONSE OF A CO2 STORAGE SITE Juan E. Santos Instituto del Gas y del Petróleo, Facultad de Ingeniería UBA and Department
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF THE PETROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES VARIATIONS ON THE SEISMIC RESPONSE OF A CO2 STORAGE SITE Juan E. Santos Instituto del Gas y del Petróleo, Facultad de Ingeniería UBA and Department
A PSEUDO FUNCTION APPROACH IN RESERVOIR SIMULATION
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 58 67 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information A PSEUDO FUNCTION APPROACH IN RESERVOIR SIMULATION ZHANGXIN
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 58 67 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information A PSEUDO FUNCTION APPROACH IN RESERVOIR SIMULATION ZHANGXIN
Gas Shale Hydraulic Fracturing, Enhancement. Ahmad Ghassemi
 Gas Shale Hydraulic Fracturing, Stimulated Volume and Permeability Enhancement Ahmad Ghassemi Tight Gas A reservoir that cannot produce gas in economic quantities without massive fracture stimulation treatments
Gas Shale Hydraulic Fracturing, Stimulated Volume and Permeability Enhancement Ahmad Ghassemi Tight Gas A reservoir that cannot produce gas in economic quantities without massive fracture stimulation treatments
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Groundwater Chapter 10 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois Co Jennifer Cole Northeastern University
Essentials of Geology, 11e Groundwater Chapter 10 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois Co Jennifer Cole Northeastern University
Thermal Modeling of the Mountain Home Geothermal Area
 PROCEEDINGS, 41st Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 22-24, 2016 SGP-TR-209 Thermal Modeling of the Mountain Home Geothermal Area Sabodh K.
PROCEEDINGS, 41st Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 22-24, 2016 SGP-TR-209 Thermal Modeling of the Mountain Home Geothermal Area Sabodh K.
MODELING OF GAS MIGRATION THROUGH LOW-PERMEABILITY CLAY USING INFORMATION ON PRESSURE AND DEFORMATION FROM FAST AIR INJECTION TESTS
 PROCEEDINGS, TOUGH Symposium 2015 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California, September 28-30, 2015 MODELING OF GAS MIGRATION THROUGH LOW-PERMEABILITY CLAY USING INFORMATION ON PRESSURE
PROCEEDINGS, TOUGH Symposium 2015 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California, September 28-30, 2015 MODELING OF GAS MIGRATION THROUGH LOW-PERMEABILITY CLAY USING INFORMATION ON PRESSURE
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON
 IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies Skin Uncertainty in Multi-Layered Commingled Reservoirs with Non- Uniform Formation Damage By Sudhakar Mishra
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies Skin Uncertainty in Multi-Layered Commingled Reservoirs with Non- Uniform Formation Damage By Sudhakar Mishra
Enabling Technologies
 Enabling Technologies Mechanical Modelling 1 Key Parameter Mineral System Exploration is reflected in scale-dependent translation A. Gradient in hydraulic potential B. Permeability C. Solubility sensitivity
Enabling Technologies Mechanical Modelling 1 Key Parameter Mineral System Exploration is reflected in scale-dependent translation A. Gradient in hydraulic potential B. Permeability C. Solubility sensitivity
Darcy's Law. Laboratory 2 HWR 531/431
 Darcy's Law Laboratory HWR 531/431-1 Introduction In 1856, Henry Darcy, a French hydraulic engineer, published a report in which he described a series of experiments he had performed in an attempt to quantify
Darcy's Law Laboratory HWR 531/431-1 Introduction In 1856, Henry Darcy, a French hydraulic engineer, published a report in which he described a series of experiments he had performed in an attempt to quantify
BOILING IN A VERTICAL FRACTURE
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Third Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford. California. January 26-28. 1998 SGP-TR-158 BOILING IN A VERTICAL FRACTURE Robert J. DuTeaux Stanford
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Third Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford. California. January 26-28. 1998 SGP-TR-158 BOILING IN A VERTICAL FRACTURE Robert J. DuTeaux Stanford
Fracture relative permeability revisited
 Fracture relative permeability revisited NOROLLAH KASIRI and GHASEM BASHIRI, Iran University of Science and Technology Relative permeability is one of the most uncertain terms in multiphase flow through
Fracture relative permeability revisited NOROLLAH KASIRI and GHASEM BASHIRI, Iran University of Science and Technology Relative permeability is one of the most uncertain terms in multiphase flow through
