MTH 60 Supplemental Problem Sets SUPPLEMENT TO and 2, the y -value is 1 on the. . (At the x -value 4, the y -value is 1 on the graph.
|
|
|
- Arthur Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENT TO 106 We can use function notation to communicate the information contained in the graph of a function For example, if the point (5,) is on the graph of a function called f, we can write " f (5) " This means that if we are asked to find f (5) using the graph of the function f, we would need to search for the y -value that is associated with the x -value 5 Similarly, if we are asked to solve an equation like f( x) 4 using a graph, we would need to search for the x - value(s) associated with the y -value 4 EXAMPLE: The graph of y gx ( ) is given at the right a Find g( ) b Find g( ) c Solve gx ( ) 1 (Express your answer in a solution set) d Solve gx ( ) 1 (Express your answer in a solution set) The graph of y gx ( ) Solutions a g( ) (At the x -value, the y -value is on the graph) b g( ) 1 (At the x -value, the y -value is 1 on the graph) c The solution set is 4 (At the x -value 4, the y -value is 1 on the graph) d The solution set is, (At the x -values graph) and, the y -value is 1 on the Page
2 EXERCISES: 1 The graph of y Gx ( ) is given at the right a On the graph, if x 0, then y b Find G( ) c Find G(4) d If Gx ( ), then x e Solve Gx ( ) 4 f Find a formula for y Gx ( ) [ 44 review] g Use the formula you found in part f to find the exact coordinates of the horizontal intercept of the line [ 44 review] The graph of y Gx ( ) The graph of y f( x) is given at the right a On the graph, if x 1, then b Find f (0) c Find f ( 4) y d From the graph we can see that f ( ) 1 What point on the graph is this statement describing? e From the graph we can see that f () 4 What point on the graph is this statement describing? f If f ( x) 4, then g Solve f( x) 1 x The graph of y f( x) Find the following function values if the function H is defined by the set of ordered pairs (, 5), (7, 10), ( 4, ), ( 1, ), (5, ) a H ( 4) b H () Page 4
3 4 Billy Jean is driving home from a business meeting Shown is the graph y dt () where d represents her remaining distance (in miles) to home as a function of time, t, (in hours) since she left her meeting a Find and interpret d(1) in the context of the real-world situation Write in a complete sentence b Find and interpret d(5) in the context of the real-world situation Write in a complete sentence c Find a formula for y d() t [ 45 review] d Using your formula from part c, find and interpret the exact value of d(0) in the context of the real-world situation Write in a complete sentence [ 45 review] The graph of y d() t 5 Instead of using graphs, we can use a table to define a function For example the table below defines the function j (The top row represents the input values and the bottom row represents the output values, and each column represents an ordered pair that satisfies the function, eg, the last column implies that the ordered pair (6, 100) satisfies the function) a Find j() x 1 6 jx ( ) b When jx ( ) 170, then x c Is j a linear function? Defend your answer with a strong argument [ 4 review] d Find a formula for y jx ( ) in slope intercept form [ 44 review] e Use your answer to part d to find j( 8) f Make a graph of y jx ( ) on graph paper to verify that the formula found corresponds to the data in the table [ 44 review] Page 5
4 6 An independent tester examined several modern wind turbines (that generate power) to check if they met factory specifications The Air 40 Wind Turbine came close to its expectations The amount of power Px ( ) (in Watts) generated by a wind-speed of x miles per hour blowing on the turbine can be approximated by the formula Px ( ) 08x 6 a Evaluate P(5) Interpret your answer in a complete sentence in the context of the problem b Solve Px ( ) 450 (Round to the nearest integer) Interpret your answer in a complete sentence in the context of the problem c If you need about 00 Watts to run the power to your heated shed, at what speed does the wind have to be blowing? (Round to the nearest integer) To get the turbine to turn at all (and thus generate power), the wind has to be more than just a light breeze In parts d and e, we will investigate this fact d Evaluate P(10) Interpret your answer in a complete sentence in the context of the problem e At what speed will the power production be 0 Watts? (Round to the nearest integer) This speed is called the cut-in speed: if the wind blows even just a tiny amount faster, the turbine will start generating power Page 6
5 ANSWERS TO THE SUPPLEMENT TO 106: 1 a y 1 b G( ) 4 c G(4) 5 d x e The solution set is f Since this is a graph of a line with slope formula for the graph in slope intercept form is function is y G( x) x 1 g The horizontal intercept is the point where y 0 Thus, So the horizontal intercept is,0 0 x 1 1 x x m and vertical intercept 0, 1, the y x 1, and the formula for the a y b f (0) 1 c f ( 4) d the point, 1 e the point, 4 f x g The solution set is 1, Page 8
6 a H ( 4) b H () 5 4 a d(1) 180 This means that one hour after Billy Jean left her meeting, she still had 180 miles left to travel b d(5) 0 This means that 5 hours after Billy Jean left her meeting, she had 0 miles left to travel which implies that she must have arrived at her home c This is a linear graph, so we need to find the slope first Two points on the graph are 1, 180 and 5, 0 We can use these points to find the slope of the line" y y m x x Now we can plug this slope and the point 5, 0 into the point-slope formula to find the formula for the line: 5, 0 y 45x b 0 45(5) b 0 5 b b 5 Thus, the formula for the line is y 45x 5 but the question asks for " dt ()" so is where the x usually is! This means that we should use t instead of x in our final formula: y d() t 45t 5 t d d(0) This means that just as Billy Jean was leaving her meeting (ie, after driving for 0 hours), she had 5 miles left to drive to get home Page 9
7 5 a j() 10 b x c If a function is linear, it must have constant slope; thus, we can determine if j is linear by finding the slope between each pair of points and see if the slope is constant Recall that the slope of the line passing through two points is the ratio of the rise to the run between the points run 4 x 1 6 jx ( ) rise slope between first pair of points : 10 m 4 0 slope between second pair of points : 60 m 0 slope between third pair of points : 90 m 0 Since all the slopes are identical, j is a linear function with slope 0 d Since we know that the slope is 0, we know that the formula for the function must look like y 0x b Now we have to find b by using one of the points given in the table Let's use 1, 50 : 1, 50 y 0x b 50 0(1) b 50 0 b b 80 So, the formula must be y j( x) 0x 80 Page 10
8 e j( 8) 0( 8) f Below is the graph of y jx ( ) Points from the table are plotted and labeled for clarity (,170) (1, 50) (, 10) The graph of y j( x) (6, 100) Page 11
9 6 a P This means that when the wind blows at 5 miles per hour, the turbine generates 58 Watts of power b Watts of power, there needs to be a wind- Px ( ) x x 71 x 4 This means that in order to generate speed of about 4 miles per hour 450 c Px ( ) 00 08x x 56 x 7 So the wind needs to blow at about generate 00 Watts of power 7 miles per hour in order for the turbine to d P(10) 08(10) 6 54 A wind-speed of 10 miles per hour must not be fast enough to make the turbine spin because we cannot generate a negative quantity of power e Px ( ) 0 08x x 6 x 1 This means that when the wind blows at about 1 miles per hour, the turbine just barely starts to spin fast enough to generate power Thus, the cut-in speed for this turbine is about 1 miles per hour Page 1
Linear Function. Work through the steps below to create a linear function and use it to predict behavior.
 Name Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS: Work these problems in the space provided and turn in these pages along with your solutions to the section review problems. Check your answers using the key provided in the
Name Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS: Work these problems in the space provided and turn in these pages along with your solutions to the section review problems. Check your answers using the key provided in the
1. The graph of a quadratic function is shown. Each square is one unit.
 1. The graph of a quadratic function is shown. Each square is one unit. a. What is the vertex of the function? b. If the lead coefficient (the value of a) is 1, write the formula for the function in vertex
1. The graph of a quadratic function is shown. Each square is one unit. a. What is the vertex of the function? b. If the lead coefficient (the value of a) is 1, write the formula for the function in vertex
MTH 103 Group Activity Problems (W1B) Name: Types of Functions and Their Rates of Change Section 1.4 part 1 (due April 6)
 MTH 103 Group Activity Problems (W1B) Name: Types of Functions and Their Rates of Change Section 1.4 part 1 (due April 6) Learning Objectives Identify linear and nonlinear functions Interpret slope as
MTH 103 Group Activity Problems (W1B) Name: Types of Functions and Their Rates of Change Section 1.4 part 1 (due April 6) Learning Objectives Identify linear and nonlinear functions Interpret slope as
GRADE 8 WINTER REVIEW MATH PACKET
 Student Name: Date: Math Teacher: Period: GRADE 8 WINTER REVIEW MATH PACKET 2014-2015 1. What is the solution to the system of equations below? a. (3, 1) b. (0, 1) c. (5, 4) d. no solution 2. Which equation
Student Name: Date: Math Teacher: Period: GRADE 8 WINTER REVIEW MATH PACKET 2014-2015 1. What is the solution to the system of equations below? a. (3, 1) b. (0, 1) c. (5, 4) d. no solution 2. Which equation
Sect The Slope-Intercept Form
 0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
Re: January 27, 2015 Math 080: Final Exam Review Page 1 of 6
 Re: January 7, 015 Math 080: Final Exam Review Page 1 of 6 Note: If you have difficulty with any of these problems, get help, then go back to the appropriate sections and work more problems! 1. Solve for
Re: January 7, 015 Math 080: Final Exam Review Page 1 of 6 Note: If you have difficulty with any of these problems, get help, then go back to the appropriate sections and work more problems! 1. Solve for
Chapter 3: Linear Functions & Their Algebra
 Chapter 3: Linear Functions & Their Algebra Lesson 1: Direct Variation Lesson 2: Average Rate of Change Lesson 3: Forms of a Line Lesson 4: Linear Modeling Lesson 5: Inverse of Linear Functions Lesson
Chapter 3: Linear Functions & Their Algebra Lesson 1: Direct Variation Lesson 2: Average Rate of Change Lesson 3: Forms of a Line Lesson 4: Linear Modeling Lesson 5: Inverse of Linear Functions Lesson
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 8x 9x 2. 25r 5 7r r + 3. 3 ( 3x 5) + + x. 3y ( 2y 5) + 11 5. 3( h 7) 7( 10 h) 2 2 +. 5 8x + 5x + 8x Find the volume or surface area
Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 8x 9x 2. 25r 5 7r r + 3. 3 ( 3x 5) + + x. 3y ( 2y 5) + 11 5. 3( h 7) 7( 10 h) 2 2 +. 5 8x + 5x + 8x Find the volume or surface area
12 Rates of Change Average Rates of Change. Concepts: Average Rates of Change
 12 Rates of Change Concepts: Average Rates of Change Calculating the Average Rate of Change of a Function on an Interval Secant Lines Difference Quotients Approximating Instantaneous Rates of Change (Section
12 Rates of Change Concepts: Average Rates of Change Calculating the Average Rate of Change of a Function on an Interval Secant Lines Difference Quotients Approximating Instantaneous Rates of Change (Section
Conceptual Explanations: Simultaneous Equations Distance, rate, and time
 Conceptual Explanations: Simultaneous Equations Distance, rate, and time If you travel 30 miles per hour for 4 hours, how far do you go? A little common sense will tell you that the answer is 120 miles.
Conceptual Explanations: Simultaneous Equations Distance, rate, and time If you travel 30 miles per hour for 4 hours, how far do you go? A little common sense will tell you that the answer is 120 miles.
Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part II
 Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part II This is an overview of the key ideas we have discussed during the middle part of this course. You may find this summary useful as a study aid, but remember that the
Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part II This is an overview of the key ideas we have discussed during the middle part of this course. You may find this summary useful as a study aid, but remember that the
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
Section 1.6 Inverse Functions
 0 Chapter 1 Section 1.6 Inverse Functions A fashion designer is travelling to Milan for a fashion show. He asks his assistant, Betty, what 7 degrees Fahrenheit is in Celsius, and after a quick search on
0 Chapter 1 Section 1.6 Inverse Functions A fashion designer is travelling to Milan for a fashion show. He asks his assistant, Betty, what 7 degrees Fahrenheit is in Celsius, and after a quick search on
Course 3 Benchmark Test Bank First Semester
 NAME DATE PERIOD Course 3 Benchmark Test Bank First Semester 1. The average distance from the Earth to the moon is about 384,000 kilometers. What is this number written in scientific notation? A. 384 10
NAME DATE PERIOD Course 3 Benchmark Test Bank First Semester 1. The average distance from the Earth to the moon is about 384,000 kilometers. What is this number written in scientific notation? A. 384 10
Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8)
 Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8) Algebra 2 Parent Function Table Linear Parent Function: x y y = Domain: Range: What patterns do you observe in the table and graph of the linear parent
Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8) Algebra 2 Parent Function Table Linear Parent Function: x y y = Domain: Range: What patterns do you observe in the table and graph of the linear parent
Name: Class: Date: Describe a pattern in each sequence. What are the next two terms of each sequence?
 Class: Date: Unit 3 Practice Test Describe a pattern in each sequence. What are the next two terms of each sequence? 1. 24, 22, 20, 18,... Tell whether the sequence is arithmetic. If it is, what is the
Class: Date: Unit 3 Practice Test Describe a pattern in each sequence. What are the next two terms of each sequence? 1. 24, 22, 20, 18,... Tell whether the sequence is arithmetic. If it is, what is the
HS Mathematics Item Specification C1 TL Task Model 1
 Task Model 1 Matching Table DOK Level 1 F-IF.B.4 models a relationship quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities, and sketch graphs showing key features given a
Task Model 1 Matching Table DOK Level 1 F-IF.B.4 models a relationship quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities, and sketch graphs showing key features given a
UNIT 8: LINEAR FUNCTIONS WEEK 31: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 8: LINEAR FUNCTIONS WEEK 31: Student Packet 31.1 Introduction to Systems of Equations Use variables to write equations and systems of equations. Solve problems involving rate, distance,
Name Period Date UNIT 8: LINEAR FUNCTIONS WEEK 31: Student Packet 31.1 Introduction to Systems of Equations Use variables to write equations and systems of equations. Solve problems involving rate, distance,
average rate of change
 average rate of change Module 2 : Investigation 5 MAT 170 Precalculus August 31, 2016 question 1 A car is driving away from a crosswalk. The distance d (in feet) of the car from the crosswalk t seconds
average rate of change Module 2 : Investigation 5 MAT 170 Precalculus August 31, 2016 question 1 A car is driving away from a crosswalk. The distance d (in feet) of the car from the crosswalk t seconds
6.1 Polynomial Functions
 6.1 Polynomial Functions Definition. A polynomial function is any function p(x) of the form p(x) = p n x n + p n 1 x n 1 + + p 2 x 2 + p 1 x + p 0 where all of the exponents are non-negative integers and
6.1 Polynomial Functions Definition. A polynomial function is any function p(x) of the form p(x) = p n x n + p n 1 x n 1 + + p 2 x 2 + p 1 x + p 0 where all of the exponents are non-negative integers and
Name Date Class. Standardized test prep Review of Linear Equations 8 Blue/Green
 Standardized test prep Review of Linear Equations 8 Blue/Green 2013-2014 Name _ Date Class Complete questions at least 1-8. 1. Which point is a solution to the system of equations shown below? a. ( 39,
Standardized test prep Review of Linear Equations 8 Blue/Green 2013-2014 Name _ Date Class Complete questions at least 1-8. 1. Which point is a solution to the system of equations shown below? a. ( 39,
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7)
 Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Exponential Functions Dr. Laura J. Pyzdrowski
 1 Names: (4 communication points) About this Laboratory An exponential function is an example of a function that is not an algebraic combination of polynomials. Such functions are called trancendental
1 Names: (4 communication points) About this Laboratory An exponential function is an example of a function that is not an algebraic combination of polynomials. Such functions are called trancendental
Solving a Linear-Quadratic System
 CC-18 Solving LinearQuadratic Systems Objective Content Standards A.REI.7 Solve a simple system consisting of a linear equation and a quadratic equation in two variables... A.REI.11 Explain why the x-coordinates
CC-18 Solving LinearQuadratic Systems Objective Content Standards A.REI.7 Solve a simple system consisting of a linear equation and a quadratic equation in two variables... A.REI.11 Explain why the x-coordinates
Portland Community College MTH 95. and MTH 91/92 SUPPLEMENTAL PROBLEM SETS ( ) 2 2 2
 Portland Community College MTH 95 and MTH 91/9 SUPPLEMENTAL PROBLEM SETS h x + h x x h x + h ( ) x + h x + xh + xh + h x + xh + h SUPPLEMENT TO 1 EXERCISES: 1 Determine whether one quantity is a function
Portland Community College MTH 95 and MTH 91/9 SUPPLEMENTAL PROBLEM SETS h x + h x x h x + h ( ) x + h x + xh + xh + h x + xh + h SUPPLEMENT TO 1 EXERCISES: 1 Determine whether one quantity is a function
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
Determine the line of best fit for this data. Write an equation to represent the line of best fit.
 Integrated Math I, Subpart 3 Calculator Allowed TN0030684 21 Samatha owns a local ice cream stand. She recorded the high temperatures, in degrees Fahrenheit, and her ice cream sales, in dollars, for eight
Integrated Math I, Subpart 3 Calculator Allowed TN0030684 21 Samatha owns a local ice cream stand. She recorded the high temperatures, in degrees Fahrenheit, and her ice cream sales, in dollars, for eight
Chapter 3. Graphing Linear Equations and Functions
 Chapter 3 Graphing Linear Equations and Functions 3.1 Plot Points in a Coordinate Plane Coordinate Plane- Two intersecting at a angle. x-axis the axis y-axis the axis The coordinate plane is divided into.
Chapter 3 Graphing Linear Equations and Functions 3.1 Plot Points in a Coordinate Plane Coordinate Plane- Two intersecting at a angle. x-axis the axis y-axis the axis The coordinate plane is divided into.
Unit 4 Study Guide Part I: Equations of Lines
 Unit 4 Study Guide Part I: Equations of Lines Write out the general equations for: Point Slope Form: Slope-Intercept Form: Standard Form: 1. Given the points: (3, -7) and (-2, 8) a. Write an equation in
Unit 4 Study Guide Part I: Equations of Lines Write out the general equations for: Point Slope Form: Slope-Intercept Form: Standard Form: 1. Given the points: (3, -7) and (-2, 8) a. Write an equation in
Unit 3 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey
 HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
 590 Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions In this section, you will: Learning Objectives 4.4.1 Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. 4.4.2 Graph logarithmic
590 Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions In this section, you will: Learning Objectives 4.4.1 Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. 4.4.2 Graph logarithmic
Unit 2 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey
 HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit 2 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) Determine for each of the following graphed relationships whether y is a function of x using the Vertical Line Test. 2) What are the outputs for
HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit 2 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) Determine for each of the following graphed relationships whether y is a function of x using the Vertical Line Test. 2) What are the outputs for
Name Date. Answers 1.
 Name Date Honors Algebra 2 Summer Work Due at Meet the Teacher Night Show all work. You will be graded on accuracy and completion. Partial credit will be given on problems where work is not shown. 1. Plot
Name Date Honors Algebra 2 Summer Work Due at Meet the Teacher Night Show all work. You will be graded on accuracy and completion. Partial credit will be given on problems where work is not shown. 1. Plot
Unit 5 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS. A function with a variable in the denominator Parent function 1 x Graph is a hyperbola
 Unit 5 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS A function with a variable in the denominator Parent function 1 x Graph is a hyperbola A direct variation is a relationship between two variables x and y that can be written in
Unit 5 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS A function with a variable in the denominator Parent function 1 x Graph is a hyperbola A direct variation is a relationship between two variables x and y that can be written in
Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review #2
 Lesson 1 1. Simplify the expression. (r 6) +10r A1.1.3.1 Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review # Lesson. Solve the equation. 5x + 4x = 10 +6x + x A1..1 Lesson 3. Solve the equation. 1 +
Lesson 1 1. Simplify the expression. (r 6) +10r A1.1.3.1 Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review # Lesson. Solve the equation. 5x + 4x = 10 +6x + x A1..1 Lesson 3. Solve the equation. 1 +
Algebra II. Note workbook. Chapter 2. Name
 Algebra II Note workbook Chapter 2 Name Algebra II: 2-1 Relations and Functions The table shows the average lifetime and maximum lifetime for some animals. This data can be written as. The ordered pairs
Algebra II Note workbook Chapter 2 Name Algebra II: 2-1 Relations and Functions The table shows the average lifetime and maximum lifetime for some animals. This data can be written as. The ordered pairs
Chapter 7. Linear Regression (Pt. 1) 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 The Least-Squares Regression Line
 Chapter 7 Linear Regression (Pt. 1) 7.1 Introduction Recall that r, the correlation coefficient, measures the linear association between two quantitative variables. Linear regression is the method of fitting
Chapter 7 Linear Regression (Pt. 1) 7.1 Introduction Recall that r, the correlation coefficient, measures the linear association between two quantitative variables. Linear regression is the method of fitting
Properties of Radicals
 9. Properties of Radicals Essential Question How can you multiply and divide square roots? Operations with Square Roots Work with a partner. For each operation with square roots, compare the results obtained
9. Properties of Radicals Essential Question How can you multiply and divide square roots? Operations with Square Roots Work with a partner. For each operation with square roots, compare the results obtained
9-3 Constant Rate of Change and Slope
 Find the constant rate of change between the quantities in each table. Find the constant rate of change for each linear function and interpret its meaning. 1. The cost increases by $12 for every 5 items.
Find the constant rate of change between the quantities in each table. Find the constant rate of change for each linear function and interpret its meaning. 1. The cost increases by $12 for every 5 items.
Summer Assignment for Students Entering Algebra 1 Level 3
 Summer Assignment for Students Entering Algebra 1 Level 3 The following packet of material contains prerequisite skills and concepts that will be drawn upon from the middle school mathematics courses which
Summer Assignment for Students Entering Algebra 1 Level 3 The following packet of material contains prerequisite skills and concepts that will be drawn upon from the middle school mathematics courses which
MAT 145: Test #3 (50 points)
 MAT 145: Test #3 (50 points) Part 2: Calculator OK! Name Calculator Used Score 21. For f (x) = 8x 3 +81x 2 42x 8, defined for all real numbers, use calculus techniques to determine all intervals on which
MAT 145: Test #3 (50 points) Part 2: Calculator OK! Name Calculator Used Score 21. For f (x) = 8x 3 +81x 2 42x 8, defined for all real numbers, use calculus techniques to determine all intervals on which
My Math Plan Assessment #3 Study Guide
 My Math Plan Assessment # Study Guide 1. Identify the vertex of the parabola with the given equation. f(x) = (x 5) 2 7 2. Find the value of the function. Find f( 6) for f(x) = 2x + 11. Graph the linear
My Math Plan Assessment # Study Guide 1. Identify the vertex of the parabola with the given equation. f(x) = (x 5) 2 7 2. Find the value of the function. Find f( 6) for f(x) = 2x + 11. Graph the linear
0815AI Common Core State Standards
 0815AI Common Core State Standards 1 Given the graph of the line represented by the equation f(x) = 2x + b, if b is increased by 4 units, the graph of the new line would be shifted 4 units 1) right 2)
0815AI Common Core State Standards 1 Given the graph of the line represented by the equation f(x) = 2x + b, if b is increased by 4 units, the graph of the new line would be shifted 4 units 1) right 2)
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. x )
 Midterm Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the arrow diagram defines a function. 1) Domain Range 1) Determine
Midterm Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the arrow diagram defines a function. 1) Domain Range 1) Determine
GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS
 GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Evaluate exponential functions. Find the equation of an exponential function. Use compound interest formulas. Evaluate
GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Evaluate exponential functions. Find the equation of an exponential function. Use compound interest formulas. Evaluate
Unit 5 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS. A function with a variable in the denominator Parent function 1 x Graph is a hyperbola
 Unit 5 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS A function with a variable in the denominator Parent function 1 x Graph is a hyperbola I will be following the Alg 2 book in this Unit Ch 5 Sections 1-5 Use the Practice Packet
Unit 5 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS A function with a variable in the denominator Parent function 1 x Graph is a hyperbola I will be following the Alg 2 book in this Unit Ch 5 Sections 1-5 Use the Practice Packet
Chapter Product Rule and Quotient Rule for Derivatives
 Chapter 3.3 - Product Rule and Quotient Rule for Derivatives Theorem 3.6: The Product Rule If f(x) and g(x) are differentiable at any x then Example: The Product Rule. Find the derivatives: Example: The
Chapter 3.3 - Product Rule and Quotient Rule for Derivatives Theorem 3.6: The Product Rule If f(x) and g(x) are differentiable at any x then Example: The Product Rule. Find the derivatives: Example: The
Section 3.4 Writing the Equation of a Line
 Chapter Linear Equations and Functions Section.4 Writing the Equation of a Line Writing Equations of Lines Critical to a thorough understanding of linear equations and functions is the ability to write
Chapter Linear Equations and Functions Section.4 Writing the Equation of a Line Writing Equations of Lines Critical to a thorough understanding of linear equations and functions is the ability to write
Science 1206 Unit2 -Physics Test 04
 Science 1206 Unit2 -Physics Test 04 1. The correct way to write 32 000 000 in scientific notation with 2 significant digits is: a. 32.000 000 x 10 6 b. 3.2 x 10 7 c. 0.32 x 10 8 d. 3.2 x 10-7 2. How many
Science 1206 Unit2 -Physics Test 04 1. The correct way to write 32 000 000 in scientific notation with 2 significant digits is: a. 32.000 000 x 10 6 b. 3.2 x 10 7 c. 0.32 x 10 8 d. 3.2 x 10-7 2. How many
= 9 = x + 8 = = -5x 19. For today: 2.5 (Review) and. 4.4a (also review) Objectives:
 Math 65 / Notes & Practice #1 / 20 points / Due. / Name: Home Work Practice: Simplify the following expressions by reducing the fractions: 16 = 4 = 8xy =? = 9 40 32 38x 64 16 Solve the following equations
Math 65 / Notes & Practice #1 / 20 points / Due. / Name: Home Work Practice: Simplify the following expressions by reducing the fractions: 16 = 4 = 8xy =? = 9 40 32 38x 64 16 Solve the following equations
In order to prepare for the final exam, you need to understand and be able to work problems involving the following topics:
 MATH 080: Review for the Final Exam In order to prepare for the final exam, you need to understand and be able to work problems involving the following topics: I. Simplifying Expressions: Do you know how
MATH 080: Review for the Final Exam In order to prepare for the final exam, you need to understand and be able to work problems involving the following topics: I. Simplifying Expressions: Do you know how
********************************************************************************************************
 QUESTION # 1 1. Let the random variable X represent the number of telephone lines in use by the technical support center of a software manufacturer at noon each day. The probability distribution of X is
QUESTION # 1 1. Let the random variable X represent the number of telephone lines in use by the technical support center of a software manufacturer at noon each day. The probability distribution of X is
LESSON #12 - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
RELATING GRAPHS TO EVENTS
 RELATING GRAPHS TO EVENTS Independent Variable: The cause variable (the tested variable or input). Always labeled on the x axis of graph. Dependent Variable: The effect variable (output). Always labeled
RELATING GRAPHS TO EVENTS Independent Variable: The cause variable (the tested variable or input). Always labeled on the x axis of graph. Dependent Variable: The effect variable (output). Always labeled
Name Period. Algebra 2 Agenda. Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade
 Name Period Algebra Agenda Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade Monday January 3, 07 Tuesday January 4, 07 Wednesday January 5, 07 Thursday January 6, 07 Friday January 7, 07 Solving Equations with Radicals
Name Period Algebra Agenda Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade Monday January 3, 07 Tuesday January 4, 07 Wednesday January 5, 07 Thursday January 6, 07 Friday January 7, 07 Solving Equations with Radicals
Eureka Math. Grade, Module 4. Student File_B Contains Sprint and Fluency, Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials
 A Story of Eureka Math Grade, Module 4 Student File_B Contains Sprint and Fluency,, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may
A Story of Eureka Math Grade, Module 4 Student File_B Contains Sprint and Fluency,, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Calculus I - Homework Chapter 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the graph is the graph of a function. 1) 1)
Calculus I - Homework Chapter 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the graph is the graph of a function. 1) 1)
STUDY GUIDE FOR TEST 2. Project 3: Fill in the blanks and do the assigned questions. 11/6/07
 STUDY GUIDE FOR TEST 2 Name: Project 3: Fill in the blanks and do the assigned questions. 11/6/07 Quadrant II Quadrant I ORDERED PAIR: The first number in the ordered pair is the -coordinate and the second
STUDY GUIDE FOR TEST 2 Name: Project 3: Fill in the blanks and do the assigned questions. 11/6/07 Quadrant II Quadrant I ORDERED PAIR: The first number in the ordered pair is the -coordinate and the second
NTI Work Day #1 Math. 4. What is the slope of the line that passes through the origin and (-3, -2)? a. 3 2 b. 2 3 c. 0 d. 2 3 e.
 NTI Work Day #1 Math 1. 2 0 + 2 3 2 2 =? a. 4 b. 6 1 4 c. 7 d. 8 3 4 e. 9 3 4 2. The figure below is a graph of which of the following equations? a. y = -3x + 5 b. y = -2x + 2 c. y = 3 2 x 2 d. y = 2 3
NTI Work Day #1 Math 1. 2 0 + 2 3 2 2 =? a. 4 b. 6 1 4 c. 7 d. 8 3 4 e. 9 3 4 2. The figure below is a graph of which of the following equations? a. y = -3x + 5 b. y = -2x + 2 c. y = 3 2 x 2 d. y = 2 3
A. 16 B. 16 C. 4 D What is the solution set of 4x + 8 > 16?
 Algebra II Honors Summer Math Packet 2017 Name: Date: 1. Solve for x: x + 6 = 5x + 12 2. What is the value of p in the equation 8p + 2 = p 10? F. 1 G. 1 H. J.. Solve for x: 15x (x + ) = 6 11. Solve for
Algebra II Honors Summer Math Packet 2017 Name: Date: 1. Solve for x: x + 6 = 5x + 12 2. What is the value of p in the equation 8p + 2 = p 10? F. 1 G. 1 H. J.. Solve for x: 15x (x + ) = 6 11. Solve for
UNIT 5: DERIVATIVES OF EXPONENTIAL AND TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS. Qu: What do you remember about exponential and logarithmic functions?
 UNIT 5: DERIVATIVES OF EXPONENTIAL AND TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS 5.1 DERIVATIVES OF EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS, y = e X Qu: What do you remember about exponential and logarithmic functions? e, called Euler s
UNIT 5: DERIVATIVES OF EXPONENTIAL AND TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS 5.1 DERIVATIVES OF EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS, y = e X Qu: What do you remember about exponential and logarithmic functions? e, called Euler s
November 30, direct variation ink.notebook. page 162. page Direct Variation. page 163. page 164 page 165
 4.6 direct variation ink.notebook page 161 page 162 4.6 Direct Variation page 163 page 164 page 165 1 Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes 4.6 Direct Variation
4.6 direct variation ink.notebook page 161 page 162 4.6 Direct Variation page 163 page 164 page 165 1 Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes 4.6 Direct Variation
Math Review Problems Exam 2
 14.1 The graph shows distance from home as a function of time for Laura s trip to the mall. Write a brief description of her trip that explains all features of the graph. A. distance from home A B C D
14.1 The graph shows distance from home as a function of time for Laura s trip to the mall. Write a brief description of her trip that explains all features of the graph. A. distance from home A B C D
For problems 1 4, evaluate each expression, if possible. Write answers as integers or simplified fractions
 / MATH 05 TEST REVIEW SHEET TO THE STUDENT: This Review Sheet gives you an outline of the topics covered on Test as well as practice problems. Answers are at the end of the Review Sheet. I. EXPRESSIONS
/ MATH 05 TEST REVIEW SHEET TO THE STUDENT: This Review Sheet gives you an outline of the topics covered on Test as well as practice problems. Answers are at the end of the Review Sheet. I. EXPRESSIONS
CHAPTER 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS Systems of Linear equations have either one solution (independent), no solutions (inconsistent), or infinitely many solutions (dependent). An independent system is the case when
CHAPTER 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS Systems of Linear equations have either one solution (independent), no solutions (inconsistent), or infinitely many solutions (dependent). An independent system is the case when
MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM
 MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM March 31, 2009 NAME: SOLUTIONS INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has 9 pages including this cover. There are 9 questions.
MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM March 31, 2009 NAME: SOLUTIONS INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has 9 pages including this cover. There are 9 questions.
GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS
 GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Evaluate exponential functions. Find the equation of an exponential function. Use compound interest formulas. Evaluate
GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Evaluate exponential functions. Find the equation of an exponential function. Use compound interest formulas. Evaluate
Name: 2 NO PARTIAL CREDIT SECTION. (Problems 1{6.) No eplanation necessar; no need to show work. 1. (9 points) The graph below describes f 0 () (NOT f
 Math 115 Calculus Eam II 29 October 1997 Department of Mathematics Universit of Michigan Name: Signature: Instructor: Section: General instructions: Please read the instructions on each individual problem
Math 115 Calculus Eam II 29 October 1997 Department of Mathematics Universit of Michigan Name: Signature: Instructor: Section: General instructions: Please read the instructions on each individual problem
Practice Test Chapter 6 Polynomial Functions
 FOM 12 Practice Test Chapter 6 Polnomial Functions Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Name: Block: _ 1. Determine the degree of this polnomial
FOM 12 Practice Test Chapter 6 Polnomial Functions Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Name: Block: _ 1. Determine the degree of this polnomial
My Math Plan Assessment #2 Study Guide
 My Math Plan Assessment #2 Study Guide 1. Find the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the linear equation. 8x y = 4 2. Use factoring to solve the quadratic equation. x 2 + 9x + 1 = 17. Multiply and simplify
My Math Plan Assessment #2 Study Guide 1. Find the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the linear equation. 8x y = 4 2. Use factoring to solve the quadratic equation. x 2 + 9x + 1 = 17. Multiply and simplify
Algebra 1: Chapter 4 Notes
 Algebra : Chapter Notes Notes #: Sections. and. Section.: Graphing on the Coordinate Plane A written as (, ) represents a dot on the coordinate plane; ou just need to find where the point goes. The first
Algebra : Chapter Notes Notes #: Sections. and. Section.: Graphing on the Coordinate Plane A written as (, ) represents a dot on the coordinate plane; ou just need to find where the point goes. The first
Classwork. Exercises. hours, and 2 hours. Note that the units are in minutes and hours.
 Classwork Exercises 1. Peter paints a wall at a constant rate of 2 square feet per minute. Assume he paints an area, in square feet after minutes. a. Express this situation as a linear equation in two
Classwork Exercises 1. Peter paints a wall at a constant rate of 2 square feet per minute. Assume he paints an area, in square feet after minutes. a. Express this situation as a linear equation in two
Franklin Math Bowl 2010 Group Problem Solving Test Grade 6
 Group Problem Solving Test Grade 6 1. Carrie lives 10 miles from work. She leaves in the morning before traffic is heavy and averages 30 miles per hour. When she goes home at the end of the day, traffic
Group Problem Solving Test Grade 6 1. Carrie lives 10 miles from work. She leaves in the morning before traffic is heavy and averages 30 miles per hour. When she goes home at the end of the day, traffic
6-1 Using Graphs to Solve a System of Equations., together form a system of linear equations.
 AH Notes# 6-1 Using Graphs to Solve a System of Equations Two or more linear equations in the same variables, such as, together form a system of linear equations. The solution to the system is any/all
AH Notes# 6-1 Using Graphs to Solve a System of Equations Two or more linear equations in the same variables, such as, together form a system of linear equations. The solution to the system is any/all
0817AI Common Core State Standards
 0817AI Common Core State Standards 1 A part of Jennifer's work to solve the equation 2(6x 2 3) = 11x 2 x is shown below. Given: 2(6x 2 3) = 11x 2 x Step 1: 12x 2 6 = 11x 2 x Which property justifies her
0817AI Common Core State Standards 1 A part of Jennifer's work to solve the equation 2(6x 2 3) = 11x 2 x is shown below. Given: 2(6x 2 3) = 11x 2 x Step 1: 12x 2 6 = 11x 2 x Which property justifies her
FUNCTIONS. Algebra 2 & Trigonometry Mrs. Martin Room 227. Name:
 FUNCTIONS Algebra & Trigonometry Mrs. Martin Room 7 Name: Functions Topic Pages Day 1 Relations & Functions / Domain & Range Graphically 3 9 Day One-to-One and Onto Functions / Applications of Functions
FUNCTIONS Algebra & Trigonometry Mrs. Martin Room 7 Name: Functions Topic Pages Day 1 Relations & Functions / Domain & Range Graphically 3 9 Day One-to-One and Onto Functions / Applications of Functions
8-2 Vectors in the Coordinate Plane
 37. ROWING Nadia is rowing across a river at a speed of 5 miles per hour perpendicular to the shore. The river has a current of 3 miles per hour heading downstream. a. At what speed is she traveling? b.
37. ROWING Nadia is rowing across a river at a speed of 5 miles per hour perpendicular to the shore. The river has a current of 3 miles per hour heading downstream. a. At what speed is she traveling? b.
Pre-Algebra Chapter 8 Linear Functions and Graphing
 Pre-Algebra Chapter 8 Linear Functions and Graphing SOME NUMBERED QUESTIONS HAVE BEEN DELETED OR REMOVED. YOU WILL NOT BE USING A CALCULATOR FOR PART I MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS, AND THEREFORE YOU SHOULD
Pre-Algebra Chapter 8 Linear Functions and Graphing SOME NUMBERED QUESTIONS HAVE BEEN DELETED OR REMOVED. YOU WILL NOT BE USING A CALCULATOR FOR PART I MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS, AND THEREFORE YOU SHOULD
Chapter 5B - Rational Functions
 Fry Texas A&M University Math 150 Chapter 5B Fall 2015 143 Chapter 5B - Rational Functions Definition: A rational function is The domain of a rational function is all real numbers, except those values
Fry Texas A&M University Math 150 Chapter 5B Fall 2015 143 Chapter 5B - Rational Functions Definition: A rational function is The domain of a rational function is all real numbers, except those values
Algebra 2 Honors. Unit 4, Day 1 Period: Date: Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form. (Three more problems on the back )
 Algebra Honors Name: Unit 4, Day 1 Period: Date: Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form 1. y = 3x. y = 5x + 1 3. y = x 5 4. y = 1 5 x 6. y = x + x + 1 7. f(x) = 6x 4x 5 (Three more problems on the
Algebra Honors Name: Unit 4, Day 1 Period: Date: Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form 1. y = 3x. y = 5x + 1 3. y = x 5 4. y = 1 5 x 6. y = x + x + 1 7. f(x) = 6x 4x 5 (Three more problems on the
COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
 COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 8 4 Lesson 1: Writing Equations Using Symbols Write each of the following statements using symbolic language. 1. When you square five times a number you get
COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 8 4 Lesson 1: Writing Equations Using Symbols Write each of the following statements using symbolic language. 1. When you square five times a number you get
9-3 Constant Rate of Change and Slope
 Find the constant rate of change between the quantities in each table. 5. Find the slope of the line in the graph below. 1. $2.40 per item 2. 20 ft per min Find the constant rate of change for each linear
Find the constant rate of change between the quantities in each table. 5. Find the slope of the line in the graph below. 1. $2.40 per item 2. 20 ft per min Find the constant rate of change for each linear
UNIT #3 LINEAR FUNCTIONS, EQUATIONS, AND THEIR ALGEBRA COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 Name: Date: Part I Questions UNIT #3 LINEAR FUNCTIONS, EQUATIONS, AND THEIR ALGEBRA COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II. The distance that a person drives at a constant speed varies directly with the amount of time
Name: Date: Part I Questions UNIT #3 LINEAR FUNCTIONS, EQUATIONS, AND THEIR ALGEBRA COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II. The distance that a person drives at a constant speed varies directly with the amount of time
Ordered pair: Domain: Range:
 Sec 2.1 Relations Learning Objectives: 1. Understand relations. 2. Find the domain and the range of a relation. 3. Graph a relation defined b an equation. 1. Understand relations Relation eists when the
Sec 2.1 Relations Learning Objectives: 1. Understand relations. 2. Find the domain and the range of a relation. 3. Graph a relation defined b an equation. 1. Understand relations Relation eists when the
Equations and Inequalities in One Variable
 Name Date lass Equations and Inequalities in One Variable. Which of the following is ( r ) 5 + + s evaluated for r = 8 and s =? A 3 B 50 58. Solve 3x 9= for x. A B 7 3. What is the best first step for
Name Date lass Equations and Inequalities in One Variable. Which of the following is ( r ) 5 + + s evaluated for r = 8 and s =? A 3 B 50 58. Solve 3x 9= for x. A B 7 3. What is the best first step for
MAT Polynomial and Rational Inequalities
 MAT 171 3.7 Polynomial and Rational Inequalities A. Quadratic Inequalities Mar 15 10:35 AM B. Polynomial Inequalities Solving Polynomial Inequalities Given f (x) is a polynomial in standard form, 1. Write
MAT 171 3.7 Polynomial and Rational Inequalities A. Quadratic Inequalities Mar 15 10:35 AM B. Polynomial Inequalities Solving Polynomial Inequalities Given f (x) is a polynomial in standard form, 1. Write
1) Solve the formula for the indicated variable. P = 2L + 2W for W. 2) Solve the formula for the variable y. 5 = 7x - 8y
 Math120 Cumulative Review This is to help prepare you for the 40 question final exam. It is not all inclusive of the material covered in your course. Therefore items not on this review may appear on the
Math120 Cumulative Review This is to help prepare you for the 40 question final exam. It is not all inclusive of the material covered in your course. Therefore items not on this review may appear on the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. B) 6x + 4
 Math1420 Review Comprehesive Final Assessment Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Add or subtract as indicated. x + 5 1) x2
Math1420 Review Comprehesive Final Assessment Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Add or subtract as indicated. x + 5 1) x2
G.3 Forms of Linear Equations in Two Variables
 section G 2 G. Forms of Linear Equations in Two Variables Forms of Linear Equations Linear equations in two variables can take different forms. Some forms are easier to use for graphing, while others are
section G 2 G. Forms of Linear Equations in Two Variables Forms of Linear Equations Linear equations in two variables can take different forms. Some forms are easier to use for graphing, while others are
Graphing Equations Chapter Test
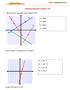 1. Which line on the graph has a slope of 2/3? Graphing Equations Chapter Test A. Line A B. Line B C. Line C D. Line D 2. Which equation is represented on the graph? A. y = 4x 6 B. y = -4x 6 C. y = 4x
1. Which line on the graph has a slope of 2/3? Graphing Equations Chapter Test A. Line A B. Line B C. Line C D. Line D 2. Which equation is represented on the graph? A. y = 4x 6 B. y = -4x 6 C. y = 4x
Name Date Class. Original content Copyright by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
 Name Date Class 1-1 Graphing Linear Equations Write the correct answer. 1. The distance in feet traveled by a falling object is found by the formula d = 16t where d is the distance in feet and t is the
Name Date Class 1-1 Graphing Linear Equations Write the correct answer. 1. The distance in feet traveled by a falling object is found by the formula d = 16t where d is the distance in feet and t is the
MLK Day!!! Solving Equations with Radicals Day 1. Practice. Solving Equations with Radicals Day 2. Practice. Applications of Radicals.
 Name Algebra 2 Agenda Period Week.3 Objective Stamp Grade Monday January 8, 206 MLK Day!!! Tuesday January 9, 206 Solving Equations with Radicals Day Practice Wednesday January 20, 206 Solving Equations
Name Algebra 2 Agenda Period Week.3 Objective Stamp Grade Monday January 8, 206 MLK Day!!! Tuesday January 9, 206 Solving Equations with Radicals Day Practice Wednesday January 20, 206 Solving Equations
CHANCE Program. Admissions Mathematics Practice Test. Part One will test your background in basic arithmetic, while Part Two will cover basic algebra.
 CHANCE Program Admissions Mathematics Practice Test Part One will test your background in basic arithmetic, while Part Two will cover basic algebra. Each part of the test has 30 questions and has been
CHANCE Program Admissions Mathematics Practice Test Part One will test your background in basic arithmetic, while Part Two will cover basic algebra. Each part of the test has 30 questions and has been
Section 4.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree
 Section 4.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Polynomial Function P(x) P(x) = a degree 0 P(x) = ax +b (degree 1) Graph Horizontal line through (0,a) line with y intercept (0,b) and slope a P(x) = ax
Section 4.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Polynomial Function P(x) P(x) = a degree 0 P(x) = ax +b (degree 1) Graph Horizontal line through (0,a) line with y intercept (0,b) and slope a P(x) = ax
2. (10 points) Find an equation for the line tangent to the graph of y = e 2x 3 at the point (3/2, 1). Solution: y = 2(e 2x 3 so m = 2e 2 3
 November 24, 2009 Name The total number of points available is 145 work Throughout this test, show your 1 (10 points) Find an equation for the line tangent to the graph of y = ln(x 2 +1) at the point (1,
November 24, 2009 Name The total number of points available is 145 work Throughout this test, show your 1 (10 points) Find an equation for the line tangent to the graph of y = ln(x 2 +1) at the point (1,
QUESTIONS 1-46 REVIEW THE OBJECTIVES OF CHAPTER 2.
 MAT 101 Course Review Questions Valid for Fall 2014, Spring 2015 and Summer 2015 MIDTERM EXAM FINAL EXAM Questions 1-86 are covered on the Midterm. There are 25 questions on the midterm, all multiple choice,
MAT 101 Course Review Questions Valid for Fall 2014, Spring 2015 and Summer 2015 MIDTERM EXAM FINAL EXAM Questions 1-86 are covered on the Midterm. There are 25 questions on the midterm, all multiple choice,
Algebra I Midterm Exam Review
 Chapter 1: Expressions, Equations, and Functions Lesson 1.1 Variables and Expressions Write a verbal expression for each algebraic expression. 23f 5m 2 + 2c 3 4n 1 7 Write an algebraic expression for each
Chapter 1: Expressions, Equations, and Functions Lesson 1.1 Variables and Expressions Write a verbal expression for each algebraic expression. 23f 5m 2 + 2c 3 4n 1 7 Write an algebraic expression for each
Free Response Questions Included in Training Module
 Free Response Questions Included in Training Module Copyright 2011 Laying the Foundation, Inc. All right reserved. The materials included in these files are intended for noncommercial use by educators
Free Response Questions Included in Training Module Copyright 2011 Laying the Foundation, Inc. All right reserved. The materials included in these files are intended for noncommercial use by educators
Tips for doing well on the final exam
 Algebra I Final Exam 01 Study Guide Name Date Block The final exam for Algebra 1 will take place on May 1 and June 1. The following study guide will help you prepare for the exam. Tips for doing well on
Algebra I Final Exam 01 Study Guide Name Date Block The final exam for Algebra 1 will take place on May 1 and June 1. The following study guide will help you prepare for the exam. Tips for doing well on
Limits at Infinity. Horizontal Asymptotes. Definition (Limits at Infinity) Horizontal Asymptotes
 Limits at Infinity If a function f has a domain that is unbounded, that is, one of the endpoints of its domain is ±, we can determine the long term behavior of the function using a it at infinity. Definition
Limits at Infinity If a function f has a domain that is unbounded, that is, one of the endpoints of its domain is ±, we can determine the long term behavior of the function using a it at infinity. Definition
