Differential Equations
|
|
|
- Blake Rodgers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Differential Equations Big Ideas Slope fields draw a slope field, sketch a particular solution Separation of variables separable differential equations General solution Particular solution Growth decay problems Antidifferentiation by substitution Antidifferentiation by parts Winplot graphing program is very good for drawing slope fields. Domain Issues The Domain of Solutions to Differential Equations by Larry Riddle (AP Central) Definition: The solution of a differential equation is a differentiable function on an open interval that contains the initial -value. For all parts of the domain, the derivative of the eplicit solution does not contradict the original differential equation The derivative eists for all values in its domain Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
2 Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
3 Remember the Domain!. Find a solution y = f( ) to the differential equation d = satisfying y( ) =.. Find a solution y = f( ) to the differential equation = y satisfying () d y =.. Find a solution y = f( ) to the differential equation = y satisfying () 0 d y =.. Find a solution y f( ) = to the differential equation = ( y + ) satisfying (0) d y =. Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
4 Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
5 AP Multiple Choice Questions 008 AB Multiple Choice BC Multiple Choice 7 00 AB Multiple Choice. The rate of change of the volume,v, of water in a tank with respect to time, t, is directly proportional to the square root of the volume. Which of the following is a differential equation that describes this relationship? A) Vt () = k t B) Vt () = k V C) dv dv k = k t D) = dt dt V E) dv = k V dt 9. A curve has slope + at each point (, ) curve if it passes through the point (, )? A) y = 5 B) D) y = + E) y on the curve. Which of the following is an equation for this y y = + = + C) y = + 00 BC Multiple Choice. Shown to the right is a slope field for which of the following differential equations? A) = B) d y = C) d y = d y D) = E) d y = d y Mike Koehler 6-5 Differential Equations
6 998 AB Multiple Choice. If ky and k dt = is a nonzero constant, then y could be A) e kty B) e kt kt C) e + D) kty + 5 E) ky + 8. Population y grows according to the equation ky d =, where k is a constant and t is measured in years. If the population doubles every 0 years, then the value of k is A) B).000 C) 0.0 D). E) BC Multiple Choice 8. If sin( )cos ( ) d = and if 0 when π y = =, what is the value of y when = 0? A) - B) C) 0 D) E) 99 AB Multiple Choice. If y and if y when, then when, y d = = = = = A) B) C) 0 D) E). A puppy weighs.0 pounds at birth and.5 pounds two months later. If the weight of the puppy during its first 6 months is increasing at a rate proportional to its weight, then how much will the puppy weigh when it is months old? A). pounds B).6 pounds C).8 pounds D) 5.6 pounds E) 6.5 pounds 99 BC Multiple Choice. If y, then ycould be d = A) ln B) 7 e + C) e D) e E) + 8. During a certain epidemic, the number of people that are infected at any time increases at a rate proportional to the number of people that are infected at that time. If,000 people are infected when the epidemic is first discovered, and,00 are infected 7 days later, how many people are infected days after the epidemic is first discovered? A) B), C),67 D),00 E),057 Mike Koehler 6-6 Differential Equations
7 988 BC Multiple Choice 9. If ysec and y 5 when 0, then y d = = = = tan( ) A) tan( ) tan( ) e + B) e + 5 C) 5e D) tan( ) + 5 E) tan( ) + 5e. Bacteria in a certain culture increase at a rate proportional to the number present. If the number of bacteria doubles in three hours, in how many hours will the number of bacteria triple? ln ln ln 7 A) B) C) D) ln ln ln ln 9 E) ln 985 BC Multiple Choice. At each point ( y, ) on a certain curve, the slope of the curve is y. If the curve contains the point ( 0,8 ), then its equation is A) y = 8e B) y = + 8 C) y = e + 7 D) y ln ( ) 8 y = + 8 = + + E) Integration by substitution Multiple Choice 00 ab 0 A) e d = e B) e C) e D) e E) e 00 ab Using the substitution u = +, + d is equivalent to A) D) u du B) u du E) 0 0 u du C) 0 5 u du 5 u du 998 7ab What is the average value of A) 6 9 B) 5 9 = + on the interval [ ] y C) 6 0,? D) 5 E) Mike Koehler 6-7 Differential Equations
8 998 8ab If f is a continuous function and if F'( ) = f( ) for all real numbers, then A) F() F() B) F() F() C) F(6) F() D) F(6) F() E) F(6) F() f ( ) d = 997 6ab t e dt = t A) e B) e t t C) e D) e t t E) e 997 8ab π tan e d = 0 cos A) 0 B) C) e D) e E) e bc 0 e d = A) ( ) e B) e C) e D) e E) ( e ) 988 7ab d = A) ( ) + B) ( ) + 5 C) ( ) 5 D) ( ) + E) ( ) ab tan ( ) d = ln cos A) ln cos( ) B) ( ) C) ( ) D) ln cos( ) ln cos E) sec ( ) tan ( ) 985 ab π 0 ( ) sin d = A) - B) C) 0 D) E) Mike Koehler 6-8 Differential Equations
9 985 bc + d = + A) ln 8 ln B) ln 8 ln C) ln 8 D) ln E) ln bc If the substitution u = is made, the integral d = A) u u du B) du u u C) D) u u du E) u du u u u du 97 ab 0 ( ) + + e d = e A) B) e C) e e D) e E) e e 97 7ab 0 d = A) B) ln C) π 6 π D) E) bc 969 ab d = A) ( ) B) ( ) C) ( ) D) ( ) E) ( ) ( ) sin + d = cos cos A) ( + ) B) cos( + ) C) cos( ) cos + 5 D) ( + ) E) ( ) + Mike Koehler 6-9 Differential Equations
10 Integration by parts Multiple Choice 00 bc sin(6 ) d = A) cos(6 ) + sin(6 ) B) C) cos(6 ) + sin(6 ) 6 6 D) E) 6cos(6 ) sin(6 ) cos(6 ) + sin(6 ) 6 6 cos(6 ) + sin(6 ) ab f ( ) d = A) f( ) f ( ) d B) D) f ( ) f ( ) d E) f ( ) f ( ) d C) f ( ) d = f( ) f( ) 997 5ab sin ( ) d = cos sin C cos sin A) cos( ) + sin ( ) B) cos( ) sin ( ) C) ( ) ( ) + D) cos( ) sin ( ) E) ( ) ( ) bc sin d = A) cos sin cos B) cos + sin cos + C C) cos + sin + cos D) E) cos + C cos + C 988 6bc e d = A) D) e e B) e e + E) e e C) e e e bc If f ( )sin d = f ( )cos + cos d, then f ( ) could be A) B) C) D) sin E) cos (insightful) Mike Koehler 6-0 Differential Equations
11 AP Free Response Questions 0 AB5 The rate at which a baby bird gains weight is proportional to the difference between its adult weight and its current weight. At time t = 0, when the bird is first weighed, its weight is 0 grams. If Bt () is the weight of the bird, in grams, at time t days after it is first weighed, then db ( 00 B) dt = 5. Let y= Bt () be the solution to the differential equation above with initial condition B (0) = 0. a) Is the bird gaining weight faster when it weighs 0 grams or when it weighs 70 grams? Eplain your reasoning. b) d B d B Find in terms of B. Use to eplain why the graph of B cannot resemble the graph above. dt dt c) Use separation of variables to find y= Bt (), the particular solution to the differential equation with initial condition B (0) = 0. 0 AB5 At the beginning of 00, a landfill contained 00 tons of solid waste. The increasing function W models the total amount of solid waste stored at the landfill. Planners estimate that W will satisfy the differential equation dw = ( W 00) for the net 0 years. W is measured in tons, and t is measured in years from the start of 00. dt 5 a) Use the line tangent to the graph of W at t = 0 to approimate the amount of solid waste that the landfill contains at the end of the first months of 00 time t =. b) dw dw Find in terms of W. Use to determine whether your answer in part (a) is an underestimate or dt dt an overestimate of the amount of solid waste that the landfill contains at time t =. c) dw Find the particular solution W= Wt () to the differential equation = ( W 00) with initial condition dt 5 W (0) = 00. Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
12 00 AB6 d y Solutions to the differential equation = y also satisfy = y ( + y ). Let y = f( ) be a particular d d solution to the differential equation = y with () d f =. a) Write an equation for the line tangent to the graph of y = f( ) at =. b) Use the tangent line equation from part (a) to approimate f (.). Given that f( ) > 0 for < <., is the approimation for f (.) greater than or less than f (.)? Eplain your reasoning. c) Find the particular solution y = f( ) with initial condition f () =. 008 AB5 y Consider the differential equation =, where 0. d a) On the aes provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation at the nine points indicated. b) Find the particular solution y = f( ) to the differential equation with the initial condition f () = 0. c) For the particular solution y = f( ) described in part (b), find lim f( ) 006 AB 5 Consider the differential equation + y =, where 0. d a) On the ais provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation at the eight points indicated. b) Find the particular solution y = f( ) to the differential equation with the initial condition f ( ) = and state its domain. Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
13 005 AB 6 Consider the differential equation =. d y a) On the ais provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation at the twelve points indicated. b) Let y = f( ) be the particular solution to the differential equation with the initial condition f () =. Write an equation for the line tangent to the graph of f at (, ) and use it to approimate f (.). c) Find the particular solution y = f( ) to the given differential equation with the initial condition f () =. 00 AB6 Consider the differential equation ( y ) d =. a) On the ais provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation at the twelve points indicated. b) While the slope field in part (a) is drawn for only twelve points, it is defined at every point in the y-plane. Describe all points in the y-plane for which the slopes are positive. c) Find the particular solution y = f( ) to the given differential equation with the initial condition f (0) =. Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
14 00 AB5 A coffeepot has the shape of a cylinder with radius 5 inches. Let h be the depth of the coffee in the pot, measured in inches, where h is a function of time t, measured in seconds. The volume V of coffee in the pot is changing at the rate of 5π h cubic inches per second. (The volume V of a cylinder with radius r and height h is V= π rh.) a) dh h Show that dt = 5. b) dh h Given that h = 7 at time t = 0 solve the differential equation = for h as a function of t. dt 5 c) At what time t is the coffeepot empty? 000 AB6 Consider the differential equation =. y d e a) Find a solution y = f( ) to the differential equation satisfying f (0) =. b) Find the domain and range of the function f found in part (a). 998 AB Let f be a function with f () = such that for all points ( yon, ) the graph of f the slope is given by a) Find the slope of the graph of f at the point where =. b) Write an equation for the line tangent to the graph of f at = and use it to approimate f (.). c) Find f( ) by solving the separable differential equation d) Use your solution from part c to find f (.). + = with initial condition f () = d y +. y 99 AB 6 Let Pt () represent the number of wolves in a population at time t years, when t 0. The population Pt () is increasing at a rate directly proportional to 800 Pt ( ), where the constant of proportionality is k. a) If P(0) = 500, find Pt ( ) in term of tand k. b) If P() = 700, find k. c) Find lim Pt ( ). t Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
15 989 AB6 Oil is being pumped continuously from a certain oil well at a rate proportional to the amount of oil left in the well; that is, ky dt =, where y is the amount of oil left in the well at any time t. Initially there were,000,000 gallons of oil in the well, and 6 years later there were 500,000 gallons remaining. It will no longer be profitable to pump oil when there are fewer than 50,000 gallons remaining. a) Write an equation for y, the amount of oil remaining in the well at any time t. b) At what rate is the amount of oil in the well decreasing when there are 600,000 gallons of oil remaining? c) In order not to lose money, at what time t should oil no longer be pumped from the well? 000 BC6 y d =. Consider the differential equation given by ( ) a) On the ais provided, sketch a slope field for the differential equation at the eleven points indicated. b) Use the slope field for the given differential equation to eplain why a solution could not have the graph shown in the figure on the right above. c) Find the particular solution y = f( ) to the given differential equation with the initial condition f (0) =. d) Find the range of the solution fount in part (c). Mike Koehler 6-5 Differential Equations
16 Mike Koehler 6-6 Differential Equations
17 Tetbook Problems Calculus, Finney, Demanna, Waits, Kenne; Prentice Hal, l0 Section Questions QQ p QQ p76 7.R 9-60 Handout Problems Mike Koehler 6-7 Differential Equations
18 Mike Koehler 6-8 Differential Equations
19 AP Calculus Chapter 6 Section Slope Fields A slope field is a plot of short line segments with slope f( y, ) for a lattice of points in the plane. Slope fields enable us to graph solution curves without solving the differential equation. Let = f (, y) = y + y. Sketch the slope field at the points indicated on the ais provided. d For the point (,), the slope is equal to + =. Draw a short line segment with slope through the point (,). Repeat for each of the lattice points in the graph below. Draw a possible graph for the function f with the given slope field that goes through the point (0,). Mike Koehler 6-9 Differential Equations
20 Mike Koehler 6-0 Differential Equations
21 AP Calculus Chapter 6 Section Slope Fields Draw the slope field for each of the following differential equations.. d = +. y d =. y d = +. d = 5. y d = 6. y = d Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
22 Match the following differential equations to their slope fields. i..5y d = + ii. = d y iii. d = iv. y d = v..5y d = A. B C. D E. - Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
23 AP Calculus Chapter 6 Section Match the following integrals to one of the following types: A) Identify u for each integral. du B) u n u du C) u e du D) Other. e d u =. d u = + d. u =. ln ln d u = ln d u = 6. d u = + d u = 8. d u = + 5 e 9. tan sec d u = 0. e d u = + e. ( + ) d u =. d u =. 5. e d u =. d u = 6. + e e + e e d u = sin cos ( e ) d u = tan 7. d u = 8. cos sin cos d u = 9. sin d u = 0. + cos 6 ln d u =. cos( ) d u =. + d u =. sin d u =. ln(cos ) tan d u = e 5. d u = 6. (e 5) e d u = ( e + ) Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
24 AP Calculus Chapter 6 Section Answers Match the following integrals to one of the following types: A) Identify u for each integral. du B) u n u du C) u e du D) Other.C e d u =.A d u = + +.A d ln u = ln.b ln d u = ln 5.B ln d u ln = 6.B d u = 7.B d u = C d e u = 9.B tan sec d u tan = 0.A e d u = + e + e.b ( + ) d u = +.A d u =.B e d u =.A e e + e e d u = e e 5.B d u = + 6.C + sin cos ( e ) d u = sin tan 7.B d u = tan 8.B cos sin cos d u = cos 9.A sin d u = + cos 0.B + cos 6 ln d u = ln.d cos( ) d u =.B + d u = +.B sin d u sin =.B ln(cos ) tan d u = ln(cos ) e 5.B d u = e 5 6.A (e 5) e d u = e + ( e + ) Mike Koehler 6 - Differential Equations
25 AP Calculus Chapter 6 Section Part : Calculate du for the given function.. u =. u = sin. u = cos( ) 6. tan u = + u = u = Part : Write the integral in terms of u and du. Then evaluate the integrals. Final answer should be in terms of.. ( 7) d u = 7. + d u = +. ( + ) d u = +. ( + ) d u = + 5. sin( ) d u = 6. d u = + 9 ( + ) + 7. d u = + 8. d u = sin d u = ( + ) ( 8 + 5) ( ) ( ) 0. d u =. d u =. + sin 9 cos d u = + sin. cos( ) d u =. sin ( )cos( ) d u = sin( ) 5. sec ( ) tan( ) d u = tan( ) Part : Evaluate the indefinite integrals.. ( + ) d. ( + ) d. d 7 ( ) ( + )( + ). sin 7 d 5. d 6. d + 7. d 8. d 9. d ( ) ( + ) d. d. + d ( )( ) 5 ( + ) ( ) ( + ) ( + ) ( + ) d. 9 d 5. d 5 ( ) d 7. sin ( ) cos( ) 8. sin ( + ) 6. sin d d ( ) ( ) ( ) 9. sec + 9 d 0. sec tan d. sin cos + d cos( ) ( ) ( + sin ) cos. d. cos sin d. d Mike Koehler 6-5 Differential Equations
26 AP Calculus Chapter 6 Section Answers Part :. du = d. du = cosd. du = d ( ) sin( ) 6. sec du = + d du = d du = d Part :. u du = ( 7 ). u du = ( + ). u du = ( u ) u du = u u du = ( + ) ( + ) 0 5. sin udu = cos( ) 6. u du ( ) C = + + u C du = du u u du u = = ( + ) u ( 8 5) ( 8 5) 9. sin udu = cos u 5 0. ( ). ( ) ( ) u du = 6 u du = 6 u u du = + C u du = ( + sin ) 0. cos( u) du = sin ( ). u du = sin ( ) 5. u d tan u = + C Part : 5. ( + ). ( + ) cos( 7) 5. ( ) 6. ( + ) ( + ) ( ) 5 0. ( + ).. ( + ) 5 5 ( + ). 5. ( + 9). ( + 9) ( + 9) ( + ) + ( + ) + ( + ) cos( ) 7. sin ( ) 8. cos( + ) tan ( + 9) 0. tan ( ). ( cos + ) 5 6. ( + sin ). ( sin ) 6. sin Mike Koehler 6-6 Differential Equations
27 AP Calculus Chapter 6 Section. Consider the differential equation =. d y a. Let y = f( ) be the particular solution to the given differential equation for < < 5such that the line y = is tangent to the graph of f. Find the -coordinate of the point of tangency, and determine whether f has a local maimum, local minimum, or neither at this point. Justify your answer. b. Let y= g ( ) be the particular solution to the given differential equation for < < 8, with the initial condition g (6) =. Find y= g ( ).. Let f be the function satisfying f ( ) = f( ) for all real numbers, where f () = 5. a. Find f (). b. Write an epression for y = f( ) by solving the differential equation y d = with the initial condition f () = 5 =. d. Consider the differential equation ( y ) cos( π ) a. On the aes provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation at the nine points indicated. b. There is a horizontal line with equation y = c that satisfies this differential equation. Find the value of c. c. Find the particular solution y = f( ) to the differential equation with the initial condition f () = 0. Show the work that leads to your answer. Mike Koehler 6-7 Differential Equations
28 AP Calculus Chapter 6 Section Answers. a. 0 when. d = = Use second derivative test or first derivative test to justify that the function has a minimum at =. b. y = a. f ( ) = f( ) +. Show the work that leads to this answer. 9 f () =. b. y = + = ( + ) 6. a. b. The line y = satisfies the differential equation so c =. c. y = π sin for - + π < < ( π) Mike Koehler 6-8 Differential Equations
29 AP Calculus Chapter 6. Shown on the right is a slope field for which of the following differential equations? A) D) y d = B) y y d = C) y y d = + = y + E) ( ) d d = +. d =. cos( ) d =. e d = 5. Let R be the region between y = e and the -ais for. Find the area of R. Solve analytically. 6. Solve the differential equation = with initial condition y () =. d y 7. The rate of change of the volume, V, of water in a tank with respect to time, t, is directly proportional to the square root of the volume. Write a differential equation that describes this relationship. 8. The slope of the line tangent to the curve y = f( ) is given by point (, ), find the positive value of when y =. y d =. If the curve passes through the 9. Solve the differential equation = y and () d y =. Mike Koehler 6-9 Differential Equations
30 0. At any time t 0, in days, the rate of growth of a bacteria population is given by ky dt =, where k is a constant and y is the number of bacteria present. The initial population is 000 and the population triples during the first 5 days. a. Write an epression for y at any time t 0. b. What will the population of bacteria be in days? c. When will there be 6000 bacteria?. Consider the differential equation ( y ) d = a. On the aes provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation. b. While the slope field in part (a) is drawn at only twelve points, it is defined at every point in the y-plane. Describe all points in the y-plane for which the slopes are negative. c. Find the particular solution y = f( ) to the given differential equation with the initial condition f (0) = 0. Answers. C. ln. sin ( ). e 6 8 e 5. ( e e ) = 8 e y = dv = k V dt 8. 8 = 9. y = e ln t t 0. a. y = 000e = 000e b. 967 bacteria 5ln(6) c. t = = 8.56 days ln(). a. Slope field. b. Slopes are negative at points ( y, ) where 0 and y<. c. 5 5 y = e Mike Koehler 6-0 Differential Equations
( + ) 3. AP Calculus BC Chapter 6 AP Exam Problems. Antiderivatives. + + x + C. 2. If the second derivative of f is given by f ( x) = 2x cosx
 Chapter 6 AP Eam Problems Antiderivatives. ( ) + d = ( + ) + 5 + + 5 ( + ) 6 ( + ). If the second derivative of f is given by f ( ) = cos, which of the following could be f( )? + cos + cos + + cos + sin
Chapter 6 AP Eam Problems Antiderivatives. ( ) + d = ( + ) + 5 + + 5 ( + ) 6 ( + ). If the second derivative of f is given by f ( ) = cos, which of the following could be f( )? + cos + cos + + cos + sin
AP CALCULUS AB 2017 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP CALCULUS AB 07 SCORING GUIDELINES Consider the differential equation AP CALCULUS AB 06 SCORING GUIDELINES y =. Question 4 On the aes provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation
AP CALCULUS AB 07 SCORING GUIDELINES Consider the differential equation AP CALCULUS AB 06 SCORING GUIDELINES y =. Question 4 On the aes provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation
Houston Area Calculus Teacher 1/30/2016. Card sort for f, f and f. Ambiguity in understanding decreasing at a increasing rate
 Houston Area Calculus Teacher /30/06 Experiments, Mishaps and Mistakes in AP Calculus. Card sort for f, f and f. Ambiguity in understanding decreasing at a increasing rate Developing of an understanding
Houston Area Calculus Teacher /30/06 Experiments, Mishaps and Mistakes in AP Calculus. Card sort for f, f and f. Ambiguity in understanding decreasing at a increasing rate Developing of an understanding
4.3 Worksheet - Derivatives of Inverse Functions
 AP Calculus 3.8 Worksheet 4.3 Worksheet - Derivatives of Inverse Functions All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers ma receive NO credit.. What are the following derivatives
AP Calculus 3.8 Worksheet 4.3 Worksheet - Derivatives of Inverse Functions All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers ma receive NO credit.. What are the following derivatives
Slope Fields and Differential Equations
 Student Stud Session Slope Fields and Differential Equations Students should be able to: Draw a slope field at a specified number of points b hand. Sketch a solution that passes through a given point on
Student Stud Session Slope Fields and Differential Equations Students should be able to: Draw a slope field at a specified number of points b hand. Sketch a solution that passes through a given point on
Slope Fields and Differential Equations
 Student Stud Session Slope Fields and Differential Equations Students should be able to: Draw a slope field at a specified number of points b hand. Sketch a solution that passes through a given point on
Student Stud Session Slope Fields and Differential Equations Students should be able to: Draw a slope field at a specified number of points b hand. Sketch a solution that passes through a given point on
AP CALCULUS BC 2016 SCORING GUIDELINES
 Consider the differential equation (a) Find in terms of x an. AP CALCULUS BC 06 SCORING GUIDELINES x y. = Question 4 (b) Let y = f ( x) be the particular solution to the given differential equation whose
Consider the differential equation (a) Find in terms of x an. AP CALCULUS BC 06 SCORING GUIDELINES x y. = Question 4 (b) Let y = f ( x) be the particular solution to the given differential equation whose
6.1 Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus
 6. Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus 6. ANTIDERIVATIVES AND SLOPE FIELDS Indefinite Integrals In the previous chapter we dealt with definite integrals. Definite integrals had limits of integration.
6. Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus 6. ANTIDERIVATIVES AND SLOPE FIELDS Indefinite Integrals In the previous chapter we dealt with definite integrals. Definite integrals had limits of integration.
All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.
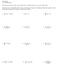 AP Calculus 6. Worksheet Da All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers ma receive NO credit. Indefinite Integrals: Remember the first step to evaluating an integral is to
AP Calculus 6. Worksheet Da All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers ma receive NO credit. Indefinite Integrals: Remember the first step to evaluating an integral is to
5.1 Separable Differential Equations
 5.1 Separable Differential Equations A differential equation is an equation that has one or more derivatives in it. The order of a differential equation is the highest derivative present in the equation.
5.1 Separable Differential Equations A differential equation is an equation that has one or more derivatives in it. The order of a differential equation is the highest derivative present in the equation.
CALCULUS AB SECTION II, Part A
 CALCULUS AB SECTION II, Part A Time 45 minutes Number of problems 3 A graphing calculator is required for some problems or parts of problems. pt 1. The rate at which raw sewage enters a treatment tank
CALCULUS AB SECTION II, Part A Time 45 minutes Number of problems 3 A graphing calculator is required for some problems or parts of problems. pt 1. The rate at which raw sewage enters a treatment tank
AP Calculus AB Free-Response Scoring Guidelines
 Question pt The rate at which raw sewage enters a treatment tank is given by Et 85 75cos 9 gallons per hour for t 4 hours. Treated sewage is removed from the tank at the constant rate of 645 gallons per
Question pt The rate at which raw sewage enters a treatment tank is given by Et 85 75cos 9 gallons per hour for t 4 hours. Treated sewage is removed from the tank at the constant rate of 645 gallons per
Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 584 Mark Sparks 2012
 The Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Functions Defined by Integrals Given the functions, f(t), below, use F( ) f ( t) dt to find F() and F () in terms of.. f(t) = 4t t. f(t) = cos t Given the functions,
The Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Functions Defined by Integrals Given the functions, f(t), below, use F( ) f ( t) dt to find F() and F () in terms of.. f(t) = 4t t. f(t) = cos t Given the functions,
1. Find A and B so that f x Axe Bx. has a local minimum of 6 when. x 2.
 . Find A and B so that f Ae B has a local minimum of 6 when.. The graph below is the graph of f, the derivative of f; The domain of the derivative is 5 6. Note there is a cusp when =, a horizontal tangent
. Find A and B so that f Ae B has a local minimum of 6 when.. The graph below is the graph of f, the derivative of f; The domain of the derivative is 5 6. Note there is a cusp when =, a horizontal tangent
x f(x)
 CALCULATOR SECTION. For y y 8 find d point (, ) on the curve. A. D. dy at the 7 E. 6. Suppose silver is being etracted from a.t mine at a rate given by A'( t) e, A(t) is measured in tons of silver and
CALCULATOR SECTION. For y y 8 find d point (, ) on the curve. A. D. dy at the 7 E. 6. Suppose silver is being etracted from a.t mine at a rate given by A'( t) e, A(t) is measured in tons of silver and
1993 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
1993 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 90 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 90 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
Answer Key for AP Calculus AB Practice Exam, Section I
 Answer Key for AP Calculus AB Practice Exam, Section I Multiple-Choice Questions Question # Key B B 3 A 4 E C 6 D 7 E 8 C 9 E A A C 3 D 4 A A 6 B 7 A 8 B 9 C D E B 3 A 4 A E 6 A 7 A 8 A 76 E 77 A 78 D
Answer Key for AP Calculus AB Practice Exam, Section I Multiple-Choice Questions Question # Key B B 3 A 4 E C 6 D 7 E 8 C 9 E A A C 3 D 4 A A 6 B 7 A 8 B 9 C D E B 3 A 4 A E 6 A 7 A 8 A 76 E 77 A 78 D
Calculus BC AP/Dual Fall Semester Review Sheet REVISED 1 Name Date. 3) Explain why f(x) = x 2 7x 8 is a guarantee zero in between [ 3, 0] g) lim x
![Calculus BC AP/Dual Fall Semester Review Sheet REVISED 1 Name Date. 3) Explain why f(x) = x 2 7x 8 is a guarantee zero in between [ 3, 0] g) lim x Calculus BC AP/Dual Fall Semester Review Sheet REVISED 1 Name Date. 3) Explain why f(x) = x 2 7x 8 is a guarantee zero in between [ 3, 0] g) lim x](/thumbs/92/110115052.jpg) Calculus BC AP/Dual Fall Semester Review Sheet REVISED Name Date Eam Date and Time: Read and answer all questions accordingly. All work and problems must be done on your own paper and work must be shown.
Calculus BC AP/Dual Fall Semester Review Sheet REVISED Name Date Eam Date and Time: Read and answer all questions accordingly. All work and problems must be done on your own paper and work must be shown.
AP Calculus. Slope Fields and Differential Equations. Student Handout
 AP Calculus Slope Fields and Differential Equations Student Handout 016-017 EDITION Use the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Stud Session https://www.survemonke.com/r/s_sss
AP Calculus Slope Fields and Differential Equations Student Handout 016-017 EDITION Use the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Stud Session https://www.survemonke.com/r/s_sss
Average rates of change May be used to estimate the derivative at a point
 Derivatives Big Ideas Rule of Four: Numerically, Graphically, Analytically, and Verbally Average rate of Change: Difference Quotient: y x f( a+ h) f( a) f( a) f( a h) f( a+ h) f( a h) h h h Average rates
Derivatives Big Ideas Rule of Four: Numerically, Graphically, Analytically, and Verbally Average rate of Change: Difference Quotient: y x f( a+ h) f( a) f( a) f( a h) f( a+ h) f( a h) h h h Average rates
AP Calculus BC Fall Final Part IIa
 AP Calculus BC 18-19 Fall Final Part IIa Calculator Required Name: 1. At time t = 0, there are 120 gallons of oil in a tank. During the time interval 0 t 10 hours, oil flows into the tank at a rate of
AP Calculus BC 18-19 Fall Final Part IIa Calculator Required Name: 1. At time t = 0, there are 120 gallons of oil in a tank. During the time interval 0 t 10 hours, oil flows into the tank at a rate of
1998 AP Calculus AB: Section I, Part A
 998 AP Calculus AB: 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate
998 AP Calculus AB: 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate
Extra Practice Recovering C
 Etra Practice Recovering C 1 Given the second derivative of a function, integrate to get the first derivative, then again to find the equation of the original function. Use the given initial conditions
Etra Practice Recovering C 1 Given the second derivative of a function, integrate to get the first derivative, then again to find the equation of the original function. Use the given initial conditions
x f(x)
 CALCULATOR SECTION. For y + y = 8 find d point (, ) on the curve. A. B. C. D. dy at the 7 E. 6. Suppose silver is being etracted from a.t mine at a rate given by A'( t) = e, A(t) is measured in tons of
CALCULATOR SECTION. For y + y = 8 find d point (, ) on the curve. A. B. C. D. dy at the 7 E. 6. Suppose silver is being etracted from a.t mine at a rate given by A'( t) = e, A(t) is measured in tons of
ANOTHER FIVE QUESTIONS:
 No peaking!!!!! See if you can do the following: f 5 tan 6 sin 7 cos 8 sin 9 cos 5 e e ln ln @ @ Epress sin Power Series Epansion: d as a Power Series: Estimate sin Estimate MACLAURIN SERIES ANOTHER FIVE
No peaking!!!!! See if you can do the following: f 5 tan 6 sin 7 cos 8 sin 9 cos 5 e e ln ln @ @ Epress sin Power Series Epansion: d as a Power Series: Estimate sin Estimate MACLAURIN SERIES ANOTHER FIVE
1998 AP Calculus AB: Section I, Part A
 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate of the point
55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate of the point
AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (169 points)
 AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (69 points) This packet is a review of some Precalculus topics and some Calculus topics. It is to be done NEATLY and on a SEPARATE sheet of paper. Use your discretion
AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (69 points) This packet is a review of some Precalculus topics and some Calculus topics. It is to be done NEATLY and on a SEPARATE sheet of paper. Use your discretion
y=5 y=1+x 2 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions
 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
1985 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
y=5 y=1+x 2 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions
 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
AP Calculus Review Assignment Answer Sheet 1. Name: Date: Per. Harton Spring Break Packet 2015
 AP Calculus Review Assignment Answer Sheet 1 Name: Date: Per. Harton Spring Break Packet 015 This is an AP Calc Review packet. As we get closer to the eam, it is time to start reviewing old concepts. Use
AP Calculus Review Assignment Answer Sheet 1 Name: Date: Per. Harton Spring Break Packet 015 This is an AP Calc Review packet. As we get closer to the eam, it is time to start reviewing old concepts. Use
Students! (1) with calculator. (2) No calculator
 Students! (1) with calculator Let R be the region bounded by the graphs of y = sin(π x) and y = x 3 4x, as shown in the figure above. (a) Find the area of R. (b) The horizontal line y = splits the region
Students! (1) with calculator Let R be the region bounded by the graphs of y = sin(π x) and y = x 3 4x, as shown in the figure above. (a) Find the area of R. (b) The horizontal line y = splits the region
AP Calculus Prep Session Handout. Integral Defined Functions
 AP Calculus Prep Session Handout A continuous, differentiable function can be epressed as a definite integral if it is difficult or impossible to determine the antiderivative of a function using known
AP Calculus Prep Session Handout A continuous, differentiable function can be epressed as a definite integral if it is difficult or impossible to determine the antiderivative of a function using known
All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.
 AP Calculus.1 Worksheet Day 1 All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit. 1. The only way to guarantee the eistence of a it is to algebraically prove
AP Calculus.1 Worksheet Day 1 All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit. 1. The only way to guarantee the eistence of a it is to algebraically prove
Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 119 Mark Sparks 2012
 Unit # Understanding the Derivative Homework Packet f ( h) f ( Find lim for each of the functions below. Then, find the equation of the tangent line to h 0 h the graph of f( at the given value of. 1. f
Unit # Understanding the Derivative Homework Packet f ( h) f ( Find lim for each of the functions below. Then, find the equation of the tangent line to h 0 h the graph of f( at the given value of. 1. f
f x x, where f x (E) f, where ln
 AB Review 08 Calculator Permitted (unless stated otherwise) 1. h0 ln e h 1 lim is h (A) f e, where f ln (B) f e, where f (C) f 1, where ln (D) f 1, where f ln e ln 0 (E) f, where ln f f 1 1, where t is
AB Review 08 Calculator Permitted (unless stated otherwise) 1. h0 ln e h 1 lim is h (A) f e, where f ln (B) f e, where f (C) f 1, where ln (D) f 1, where f ln e ln 0 (E) f, where ln f f 1 1, where t is
Slope Fields and Differential Equations
 Slope Fields and Differential Equations Students should be able to: Draw a slope field at a specified number of points b hand. Sketch a solution that passes through a given point on a slope field. Match
Slope Fields and Differential Equations Students should be able to: Draw a slope field at a specified number of points b hand. Sketch a solution that passes through a given point on a slope field. Match
AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 (A) 12 (B) 40 (C) 46 (D) 55 (E) 66
 AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 REVIEW 4.1 4.4 Name Date Period NO CALCULATOR IS ALLOWED FOR THIS PORTION OF THE REVIEW. 1. 4 d dt (3t 2 + 2t 1) dt = 2 (A) 12 (B) 4 (C) 46 (D) 55 (E) 66 2. The velocity of a particle
AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 REVIEW 4.1 4.4 Name Date Period NO CALCULATOR IS ALLOWED FOR THIS PORTION OF THE REVIEW. 1. 4 d dt (3t 2 + 2t 1) dt = 2 (A) 12 (B) 4 (C) 46 (D) 55 (E) 66 2. The velocity of a particle
(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)
![(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2) (a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)](/thumbs/85/92620692.jpg) . f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
. f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
 AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA CALCULUS AB SECTION I, Part A Time 55 minutes Number of questions 8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAM. Directions: Solve each of the following problems,
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA CALCULUS AB SECTION I, Part A Time 55 minutes Number of questions 8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAM. Directions: Solve each of the following problems,
dx. Ans: y = tan x + x2 + 5x + C
 Chapter 7 Differential Equations and Mathematical Modeling If you know one value of a function, and the rate of change (derivative) of the function, then yu can figure out many things about the function.
Chapter 7 Differential Equations and Mathematical Modeling If you know one value of a function, and the rate of change (derivative) of the function, then yu can figure out many things about the function.
CALCULUS EXPLORATION OF THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS. Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (Chain Rule Version): f t dt
 CALCULUS EXPLORATION OF THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS d d d d t dt 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: d f tdt d a d d 4 t dt d d a f t dt d d 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental
CALCULUS EXPLORATION OF THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS d d d d t dt 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: d f tdt d a d d 4 t dt d d a f t dt d d 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental
Answers to Some Sample Problems
 Answers to Some Sample Problems. Use rules of differentiation to evaluate the derivatives of the following functions of : cos( 3 ) ln(5 7 sin(3)) 3 5 +9 8 3 e 3 h 3 e i sin( 3 )3 +[ ln ] cos( 3 ) [ln(5)
Answers to Some Sample Problems. Use rules of differentiation to evaluate the derivatives of the following functions of : cos( 3 ) ln(5 7 sin(3)) 3 5 +9 8 3 e 3 h 3 e i sin( 3 )3 +[ ln ] cos( 3 ) [ln(5)
Part 1: Integration problems from exams
 . Find each of the following. ( (a) 4t 4 t + t + (a ) (b ) Part : Integration problems from 4-5 eams ) ( sec tan sin + + e e ). (a) Let f() = e. On the graph of f pictured below, draw the approimating
. Find each of the following. ( (a) 4t 4 t + t + (a ) (b ) Part : Integration problems from 4-5 eams ) ( sec tan sin + + e e ). (a) Let f() = e. On the graph of f pictured below, draw the approimating
cos 5x dx e dt dx 20. CALCULUS AB WORKSHEET ON SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM AND REVIEW Work the following on notebook paper. No calculator.
 WORKSHEET ON SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM AND REVIEW Work the following on notebook paper. No calculator. Find the derivative. Do not leave negative eponents or comple fractions in our answers. 4. 8 4 f
WORKSHEET ON SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM AND REVIEW Work the following on notebook paper. No calculator. Find the derivative. Do not leave negative eponents or comple fractions in our answers. 4. 8 4 f
BE SURE TO READ THE DIRECTIONS PAGE & MAKE YOUR NOTECARDS FIRST!! Part I: Unlimited and Continuous! (21 points)
 BE SURE TO READ THE DIRECTIONS PAGE & MAKE YOUR NOTECARDS FIRST!! Part I: United and Continuous! ( points) For #- below, find the its, if they eist.(#- are pt each) ) 7 ) 9 9 ) 5 ) 8 For #5-7, eplain why
BE SURE TO READ THE DIRECTIONS PAGE & MAKE YOUR NOTECARDS FIRST!! Part I: United and Continuous! ( points) For #- below, find the its, if they eist.(#- are pt each) ) 7 ) 9 9 ) 5 ) 8 For #5-7, eplain why
Answer Key 1973 BC 1969 BC 24. A 14. A 24. C 25. A 26. C 27. C 28. D 29. C 30. D 31. C 13. C 12. D 12. E 3. A 32. B 27. E 34. C 14. D 25. B 26.
 Answer Key 969 BC 97 BC. C. E. B. D 5. E 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. D. A. B. E. C. D 5. B 6. B 7. B 8. E 9. C. A. B. E. D. C 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. D 9. C. D. C. B. A. D 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. D. E. D. B. E. E 5. E.
Answer Key 969 BC 97 BC. C. E. B. D 5. E 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. D. A. B. E. C. D 5. B 6. B 7. B 8. E 9. C. A. B. E. D. C 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. D 9. C. D. C. B. A. D 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. D. E. D. B. E. E 5. E.
Final Value = Starting Value + Accumulated Change. Final Position = Initial Position + Displacement
 Accumulation, Particle Motion Big Ideas Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and Accumulation AP Calculus Course Description Goals page 6 Students should understand the meaning of the definite integral both
Accumulation, Particle Motion Big Ideas Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and Accumulation AP Calculus Course Description Goals page 6 Students should understand the meaning of the definite integral both
LSU AP Calculus Practice Test Day
 LSU AP Calculus Practice Test Day AP Calculus AB 2018 Practice Exam Section I Part A AP CALCULUS AB: PRACTICE EXAM SECTION I: PART A NO CALCULATORS ALLOWED. YOU HAVE 60 MINUTES. 1. If y = ( 1 + x 5) 3
LSU AP Calculus Practice Test Day AP Calculus AB 2018 Practice Exam Section I Part A AP CALCULUS AB: PRACTICE EXAM SECTION I: PART A NO CALCULATORS ALLOWED. YOU HAVE 60 MINUTES. 1. If y = ( 1 + x 5) 3
AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
 AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Work these problems on notebook paper. All work must be shown. Use your graphing calculator only on problems -55, 80-8, and 7. Find the - and y-intercepts and the domain
AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Work these problems on notebook paper. All work must be shown. Use your graphing calculator only on problems -55, 80-8, and 7. Find the - and y-intercepts and the domain
Welcome to Advanced Placement Calculus!! Summer Math
 Welcome to Advanced Placement Calculus!! Summer Math - 017 As Advanced placement students, your first assignment for the 017-018 school year is to come to class the very first day in top mathematical form.
Welcome to Advanced Placement Calculus!! Summer Math - 017 As Advanced placement students, your first assignment for the 017-018 school year is to come to class the very first day in top mathematical form.
AP Calculus BC 2015 Free-Response Questions
 AP Calculus BC 05 Free-Response Questions 05 The College Board. College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central
AP Calculus BC 05 Free-Response Questions 05 The College Board. College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central
AP Calculus AB/BC ilearnmath.net
 CALCULUS AB AP CHAPTER 1 TEST Don t write on the test materials. Put all answers on a separate sheet of paper. Numbers 1-8: Calculator, 5 minutes. Choose the letter that best completes the statement or
CALCULUS AB AP CHAPTER 1 TEST Don t write on the test materials. Put all answers on a separate sheet of paper. Numbers 1-8: Calculator, 5 minutes. Choose the letter that best completes the statement or
Ex. Find the derivative. Do not leave negative exponents or complex fractions in your answers.
 CALCULUS AB THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS AND REVIEW E. Find the derivative. Do not leave negative eponents or comple fractions in your answers. 4 (a) y 4 e 5 f sin (b) sec (c) g 5 (d) y 4
CALCULUS AB THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS AND REVIEW E. Find the derivative. Do not leave negative eponents or comple fractions in your answers. 4 (a) y 4 e 5 f sin (b) sec (c) g 5 (d) y 4
AP CALCULUS AB/CALCULUS BC 2017 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP CALCULUS AB/CALCULUS BC 07 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 H ( 0) = ( 9 7) = 6 4 H ( 0) = 9 An equation for the tangent line is y = 9 6 t. : slope : : tangent line : approimation The internal temperature
AP CALCULUS AB/CALCULUS BC 07 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 H ( 0) = ( 9 7) = 6 4 H ( 0) = 9 An equation for the tangent line is y = 9 6 t. : slope : : tangent line : approimation The internal temperature
All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.
 AP Calculus.4 Worksheet All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.. What is a difference quotient?. How do you find the slope of a curve (aka slope
AP Calculus.4 Worksheet All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.. What is a difference quotient?. How do you find the slope of a curve (aka slope
Name Class. 5. Find the particular solution to given the general solution y C cos x and the. x 2 y
 10 Differential Equations Test Form A 1. Find the general solution to the first order differential equation: y 1 yy 0. 1 (a) (b) ln y 1 y ln y 1 C y y C y 1 C y 1 y C. Find the general solution to the
10 Differential Equations Test Form A 1. Find the general solution to the first order differential equation: y 1 yy 0. 1 (a) (b) ln y 1 y ln y 1 C y y C y 1 C y 1 y C. Find the general solution to the
Chapter 6 Overview: Applications of Derivatives
 Chapter 6 Overview: Applications of Derivatives There are two main contets for derivatives: graphing and motion. In this chapter, we will consider the graphical applications of the derivative. Much of
Chapter 6 Overview: Applications of Derivatives There are two main contets for derivatives: graphing and motion. In this chapter, we will consider the graphical applications of the derivative. Much of
means Name a function whose derivative is 2x. x 4, and so forth.
 AP Slope Fields Worksheet Slope fields give us a great wa to visualize a famil of antiderivatives, solutions of differential equations. d Solving means Name a function whose derivative is. d Answers might
AP Slope Fields Worksheet Slope fields give us a great wa to visualize a famil of antiderivatives, solutions of differential equations. d Solving means Name a function whose derivative is. d Answers might
AP Calculus BC : The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 AP Calculus BC 415 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Tuesday, November 5, 008 Homework Answers 6. (a) approimately 0.5 (b) approimately 1 (c) approimately 1.75 38. 4 40. 5 50. 17 Introduction In
AP Calculus BC 415 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Tuesday, November 5, 008 Homework Answers 6. (a) approimately 0.5 (b) approimately 1 (c) approimately 1.75 38. 4 40. 5 50. 17 Introduction In
AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 6) (Mr. Surowski)
 AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 6) (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Suppose that f is an odd differentiable function. Then (A) f(1); (B) f (1) (C) f(1) f( 1) (D) 0 (E). 1 1 xf (x) =. The
AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 6) (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Suppose that f is an odd differentiable function. Then (A) f(1); (B) f (1) (C) f(1) f( 1) (D) 0 (E). 1 1 xf (x) =. The
AP Calculus BC. Free-Response Questions
 017 AP Calculus BC Free-Response Questions 017 The College Board. College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. 017 AP CALCULUS
017 AP Calculus BC Free-Response Questions 017 The College Board. College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. 017 AP CALCULUS
Math 2300 Calculus II University of Colorado
 Math 3 Calculus II University of Colorado Spring Final eam review problems: ANSWER KEY. Find f (, ) for f(, y) = esin( y) ( + y ) 3/.. Consider the solid region W situated above the region apple apple,
Math 3 Calculus II University of Colorado Spring Final eam review problems: ANSWER KEY. Find f (, ) for f(, y) = esin( y) ( + y ) 3/.. Consider the solid region W situated above the region apple apple,
Section 7.4 #1, 5, 6, 8, 12, 13, 44, 53; Section 7.5 #7, 10, 11, 20, 22; Section 7.7 #1, 4, 10, 15, 22, 44
 Math B Prof. Audrey Terras HW #4 Solutions Due Tuesday, Oct. 9 Section 7.4 #, 5, 6, 8,, 3, 44, 53; Section 7.5 #7,,,, ; Section 7.7 #, 4,, 5,, 44 7.4. Since 5 = 5 )5 + ), start with So, 5 = A 5 + B 5 +.
Math B Prof. Audrey Terras HW #4 Solutions Due Tuesday, Oct. 9 Section 7.4 #, 5, 6, 8,, 3, 44, 53; Section 7.5 #7,,,, ; Section 7.7 #, 4,, 5,, 44 7.4. Since 5 = 5 )5 + ), start with So, 5 = A 5 + B 5 +.
(i) find the points where f(x) is discontinuous, and classify each point of discontinuity.
 Math Final Eam - Practice Problems. A function f is graphed below. f() 5 4 8 7 5 4 4 5 7 8 4 5 (a) Find f(0), f( ), f(), and f(4) Find the domain and range of f (c) Find the intervals where f () is positive
Math Final Eam - Practice Problems. A function f is graphed below. f() 5 4 8 7 5 4 4 5 7 8 4 5 (a) Find f(0), f( ), f(), and f(4) Find the domain and range of f (c) Find the intervals where f () is positive
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Math 2250 Final Exam Practice Problem Solutions. f(x) = ln x x. 1 x. lim. lim. x x = lim. = lim 2
 Math 5 Final Eam Practice Problem Solutions. What are the domain and range of the function f() = ln? Answer: is only defined for, and ln is only defined for >. Hence, the domain of the function is >. Notice
Math 5 Final Eam Practice Problem Solutions. What are the domain and range of the function f() = ln? Answer: is only defined for, and ln is only defined for >. Hence, the domain of the function is >. Notice
Math 113 Final Exam Practice Problem Solutions. f(x) = ln x x. lim. lim. x x = lim. = lim 2
 Math 3 Final Eam Practice Problem Solutions. What are the domain and range of the function f() = ln? Answer: is only defined for, and ln is only defined for >. Hence, the domain of the function is >. Notice
Math 3 Final Eam Practice Problem Solutions. What are the domain and range of the function f() = ln? Answer: is only defined for, and ln is only defined for >. Hence, the domain of the function is >. Notice
Review for Exam 1. Calculus 1 Lia Vas. 1. Limits. Evaluate the following limits. x 1 x 2 3x + 2. x 1 x 2. (b) lim x. (h) lim x. x 2 x 6 x 2 2x 3.
 Calculus 1 Lia Vas Review for Eam 1 1. Limits. Evaluate the following limits. (a) lim 1 1 3 + (c) lim 3 3 (e) lim 3 5 + (g) lim 5 + 3 (i) lim 3 3 (k) lim 3 (b) lim 1 3 + (d) lim 3 (f) lim h 0 1 (+h) 1
Calculus 1 Lia Vas Review for Eam 1 1. Limits. Evaluate the following limits. (a) lim 1 1 3 + (c) lim 3 3 (e) lim 3 5 + (g) lim 5 + 3 (i) lim 3 3 (k) lim 3 (b) lim 1 3 + (d) lim 3 (f) lim h 0 1 (+h) 1
The region enclosed by the curve of f and the x-axis is rotated 360 about the x-axis. Find the volume of the solid formed.
 Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
sin x (B) sin x 1 (C) sin x + 1
 ANSWER KEY Packet # AP Calculus AB Eam Multiple Choice Questions Answers are on the last page. NO CALCULATOR MAY BE USED IN THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION. On the AP Eam, you will have minutes to answer
ANSWER KEY Packet # AP Calculus AB Eam Multiple Choice Questions Answers are on the last page. NO CALCULATOR MAY BE USED IN THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION. On the AP Eam, you will have minutes to answer
Find the following limits. For each one, if it does not exist, tell why not. Show all necessary work.
 Calculus I Eam File Spring 008 Test #1 Find the following its. For each one, if it does not eist, tell why not. Show all necessary work. 1.) 4.) + 4 0 1.) 0 tan 5.) 1 1 1 1 cos 0 sin 3.) 4 16 3 1 6.) For
Calculus I Eam File Spring 008 Test #1 Find the following its. For each one, if it does not eist, tell why not. Show all necessary work. 1.) 4.) + 4 0 1.) 0 tan 5.) 1 1 1 1 cos 0 sin 3.) 4 16 3 1 6.) For
UBC-SFU-UVic-UNBC Calculus Exam Solutions 7 June 2007
 This eamination has 15 pages including this cover. UBC-SFU-UVic-UNBC Calculus Eam Solutions 7 June 007 Name: School: Signature: Candidate Number: Rules and Instructions 1. Show all your work! Full marks
This eamination has 15 pages including this cover. UBC-SFU-UVic-UNBC Calculus Eam Solutions 7 June 007 Name: School: Signature: Candidate Number: Rules and Instructions 1. Show all your work! Full marks
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 3
 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part FTC Part Worksheet 5: Basic Rules, Initial Value Problems, Rewriting Integrands A. It s time to find anti-derivatives algebraically. Instead of saying the anti-derivative
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part FTC Part Worksheet 5: Basic Rules, Initial Value Problems, Rewriting Integrands A. It s time to find anti-derivatives algebraically. Instead of saying the anti-derivative
Unit #6 Basic Integration and Applications Homework Packet
 Unit #6 Basic Integration and Applications Homework Packet For problems, find the indefinite integrals below.. x 3 3. x 3x 3. x x 3x 4. 3 / x x 5. x 6. 3x x3 x 3 x w w 7. y 3 y dy 8. dw Daily Lessons and
Unit #6 Basic Integration and Applications Homework Packet For problems, find the indefinite integrals below.. x 3 3. x 3x 3. x x 3x 4. 3 / x x 5. x 6. 3x x3 x 3 x w w 7. y 3 y dy 8. dw Daily Lessons and
AP CALCULUS BC 2015 SCORING GUIDELINES
 05 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 5 Consider the function f =, where k is a nonzero constant. The derivative of f is given by k f = k ( k). (a) Let k =, so that f =. Write an equation for the line tangent
05 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 5 Consider the function f =, where k is a nonzero constant. The derivative of f is given by k f = k ( k). (a) Let k =, so that f =. Write an equation for the line tangent
AP Calculus BC Summer Assignment 2018
 AP Calculus BC Summer Assignment 018 Name: When you come back to school, I will epect you to have attempted every problem. These skills are all different tools that we will pull out of our toolbo at different
AP Calculus BC Summer Assignment 018 Name: When you come back to school, I will epect you to have attempted every problem. These skills are all different tools that we will pull out of our toolbo at different
Solutions to the Exercises of Chapter 8
 8A Domains of Functions Solutions to the Eercises of Chapter 8 1 For 7 to make sense, we need 7 0or7 So the domain of f() is{ 7} For + 5 to make sense, +5 0 So the domain of g() is{ 5} For h() to make
8A Domains of Functions Solutions to the Eercises of Chapter 8 1 For 7 to make sense, we need 7 0or7 So the domain of f() is{ 7} For + 5 to make sense, +5 0 So the domain of g() is{ 5} For h() to make
Regent College Maths Department. Core Mathematics 4 Trapezium Rule. C4 Integration Page 1
 Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics Trapezium Rule C Integration Page Integration It might appear to be a bit obvious but you must remember all of your C work on differentiation if you are
Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics Trapezium Rule C Integration Page Integration It might appear to be a bit obvious but you must remember all of your C work on differentiation if you are
Unit #3 Rules of Differentiation Homework Packet
 Unit #3 Rules of Differentiation Homework Packet In the table below, a function is given. Show the algebraic analysis that leads to the derivative of the function. Find the derivative by the specified
Unit #3 Rules of Differentiation Homework Packet In the table below, a function is given. Show the algebraic analysis that leads to the derivative of the function. Find the derivative by the specified
All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.
 AP Calculus.1 Worksheet Day 1 All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit. 1. The only way to guarantee the eistence of a it is to algebraically prove
AP Calculus.1 Worksheet Day 1 All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit. 1. The only way to guarantee the eistence of a it is to algebraically prove
Chapter 4 Overview: Definite Integrals
 Chapter Overview: Definite Integrals In the Introduction to this book, we pointed out that there are four tools or operations in Calculus. This chapter presents the fourth the Definite Integral. Where
Chapter Overview: Definite Integrals In the Introduction to this book, we pointed out that there are four tools or operations in Calculus. This chapter presents the fourth the Definite Integral. Where
APPM 1360 Final Exam Spring 2016
 APPM 36 Final Eam Spring 6. 8 points) State whether each of the following quantities converge or diverge. Eplain your reasoning. a) The sequence a, a, a 3,... where a n ln8n) lnn + ) n!) b) ln d c) arctan
APPM 36 Final Eam Spring 6. 8 points) State whether each of the following quantities converge or diverge. Eplain your reasoning. a) The sequence a, a, a 3,... where a n ln8n) lnn + ) n!) b) ln d c) arctan
AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (104 points)
 AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (0 points) This packet is a review of some Precalculus topics and some Calculus topics. It is to be done NEATLY and on a SEPARATE sheet of paper. Use your discretion
AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (0 points) This packet is a review of some Precalculus topics and some Calculus topics. It is to be done NEATLY and on a SEPARATE sheet of paper. Use your discretion
Understanding Part 2 of The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 Understanding Part of The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Worksheet 8: The Graph of F () What is an Anti-Derivative? Give an eample that is algebraic: and an eample that is graphical: eample : Below is
Understanding Part of The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Worksheet 8: The Graph of F () What is an Anti-Derivative? Give an eample that is algebraic: and an eample that is graphical: eample : Below is
Applications of Derivatives
 Applications of Derivatives Big Ideas Connecting the graphs of f, f, f Differentiability Continuity Continuity Differentiability Critical values Mean Value Theorem for Derivatives: Hypothesis: If f is
Applications of Derivatives Big Ideas Connecting the graphs of f, f, f Differentiability Continuity Continuity Differentiability Critical values Mean Value Theorem for Derivatives: Hypothesis: If f is
K. Function Analysis. ). This is commonly called the first derivative test. f ( x) is concave down for values of k such that f " ( k) < 0.
 K. Function Analysis What you are finding: You have a function f ( ). You want to find intervals where f ( ) is increasing and decreasing, concave up and concave down. You also want to find values of where
K. Function Analysis What you are finding: You have a function f ( ). You want to find intervals where f ( ) is increasing and decreasing, concave up and concave down. You also want to find values of where
AB 1: Find lim. x a.
 AB 1: Find lim x a f ( x) AB 1 Answer: Step 1: Find f ( a). If you get a zero in the denominator, Step 2: Factor numerator and denominator of f ( x). Do any cancellations and go back to Step 1. If you
AB 1: Find lim x a f ( x) AB 1 Answer: Step 1: Find f ( a). If you get a zero in the denominator, Step 2: Factor numerator and denominator of f ( x). Do any cancellations and go back to Step 1. If you
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
1969 AP Calculus BC: Section I
 969 AP Calculus BC: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Note: In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e).. t The asymptotes of the graph of the parametric
969 AP Calculus BC: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Note: In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e).. t The asymptotes of the graph of the parametric
FUNCTIONS (1.1) 2. Use the graph at the right to find the following. Assume the domain is 3 x 11. A. Find f (0). B. On what interval(s) is f( x)
 FUNCTIONS (.). As you travel at a constant speed from Tucson to Bisbee, you pass through Benson. Sketch possible graphs to represent the functions below. Label the aes and any important features of your
FUNCTIONS (.). As you travel at a constant speed from Tucson to Bisbee, you pass through Benson. Sketch possible graphs to represent the functions below. Label the aes and any important features of your
Integration Techniques for the AB exam
 For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
AP Calculus BC 2011 Free-Response Questions
 AP Calculus BC 11 Free-Response Questions About the College Board The College Board is a mission-driven not-for-profit organization that connects students to college success and opportunity. Founded in
AP Calculus BC 11 Free-Response Questions About the College Board The College Board is a mission-driven not-for-profit organization that connects students to college success and opportunity. Founded in
CALCULUS I. Practice Problems. Paul Dawkins
 CALCULUS I Practice Problems Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... iii Outline... iii Review... Introduction... Review : Functions... Review : Inverse Functions... 6 Review : Trig Functions... 6 Review
CALCULUS I Practice Problems Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... iii Outline... iii Review... Introduction... Review : Functions... Review : Inverse Functions... 6 Review : Trig Functions... 6 Review
 1A (13) 1. Find an equation for the tangent line to the graph of y = 3 3y +3at the point ( ; 1). The first thing to do is to check that the values =, y =1satisfy the given equation. They do. Differentiating
1A (13) 1. Find an equation for the tangent line to the graph of y = 3 3y +3at the point ( ; 1). The first thing to do is to check that the values =, y =1satisfy the given equation. They do. Differentiating
e x for x 0. Find the coordinates of the point of inflexion and justify that it is a point of inflexion. (Total 7 marks)
 Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
AP Calculus AB/IB Math SL2 Unit 1: Limits and Continuity. Name:
 AP Calculus AB/IB Math SL Unit : Limits and Continuity Name: Block: Date:. A bungee jumper dives from a tower at time t = 0. Her height h (in feet) at time t (in seconds) is given by the graph below. In
AP Calculus AB/IB Math SL Unit : Limits and Continuity Name: Block: Date:. A bungee jumper dives from a tower at time t = 0. Her height h (in feet) at time t (in seconds) is given by the graph below. In
M151B Practice Problems for Exam 1
 M151B Practice Problems for Eam 1 Calculators will not be allowed on the eam. Unjustified answers will not receive credit. 1. Compute each of the following its: 1a. 1b. 1c. 1d. 1e. 1 3 4. 3. sin 7 0. +
M151B Practice Problems for Eam 1 Calculators will not be allowed on the eam. Unjustified answers will not receive credit. 1. Compute each of the following its: 1a. 1b. 1c. 1d. 1e. 1 3 4. 3. sin 7 0. +
Review Sheet for Second Midterm Mathematics 1300, Calculus 1
 Review Sheet for Second Midterm Mathematics 300, Calculus. For what values of is the graph of y = 5 5 both increasing and concave up? >. 2. Where does the tangent line to y = 2 through (0, ) intersect
Review Sheet for Second Midterm Mathematics 300, Calculus. For what values of is the graph of y = 5 5 both increasing and concave up? >. 2. Where does the tangent line to y = 2 through (0, ) intersect
