Homework 2 due Friday, October 11 at 5 PM.
|
|
|
- Gabriel Beasley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Complex Riemann Surfaces Monday, October 07, :01 PM Homework 2 due Friday, October 11 at 5 PM. How should one choose the specific branches to define the Riemann surface? It is a subjective choice, but there are some that are more convenient to work with than others. Two approaches: Geometrically choose where the branch cuts are desired and then find the corresponding values of the angles to define the cuts. Simply make simple choices for the angles for the cuts and then deduce where the cuts are geometrically. To work from the desired picture for the branch cut: The natural choices for choosing the values of the angles at which to cut is that should be some multiple of, bearing in mind that the above branch cut must rely on some sort of cancellation of branch cuts associated to each branch point. And then experiment with these choices: A natural first try is When two branch cuts overlap (as here on the ray lying along the positive real axis:, the discontinuities might cancel so that there is no real branch cut. Let's check: ComplexAnalysis Page 1
2 The double branch cut corresponds to, where the angles jump to when the branch cut is crossed. So the jump in the angle as this double branch cut is crossed is and therefore the argument of F(z) changes by, so its value doesn't actually change across the jump, i.e., F(z) so defined is continuous across the double branch cut so it isn't actually a true branch cut. So we can actually define a branch of the function as follows: Comment: This turns out to be the same branch that would be defined if we had chosen the branch cuts to be at Let's find another branch with the same branch cut. The typical strategy is simply to shift the definition of the angle domains by some multiple of (so that one is simply making a different choice of angle, but the branch cuts are identical. For example: ComplexAnalysis Page 2
3 Notice that with this definition, every value of z will be associated to some values for the first branch, and the values for the second branch. Therefore the argument of F 2 (z) is shifted by relative to F 1 (z), so. This is not a general relationship between branches for all multivalued functions, just functions like this. Since there are only two branches, and we know that we must change branches at a branch cut, we conclude that the two branches defined above are glued to each other along the branch cut on the real axis within the interval [-1,1] and when this branch cut is crossed, one switches between the two branches. This is topologically the same Riemann surface as for (think Riemann sphere). Example with compounded branch cuts: Look for branch points. Clearly the inner square root has singularities at which implies. The log function will only have singularities when it is evaluated at. What values of z correspond to potential singularities of log? ComplexAnalysis Page 3
4 So the only possible branch points are at -1,1,13/12 Are they actually branch points? Following a small loop around z=-1 (or z=+1) which change the argument of the quantity inside of the square root by, so the square root itself will have a different value and the rest of the function (adding 5 and taking the log) does not collapse the two values. (there is no identity Therefore are actual branch points. What about z=13/12? Take a small loop around z=13/12. ComplexAnalysis Page 4
5 So on this loop, Notice that, depending on the branch of the square root, this either looks like evaluating log along a small circle about the value 10 or the value 0. Log doesn't have any singularity at 10, so following it about a small circle in the vicinity of 10 does not create any discontinuity. But following log about a small circle encircling the origin does create a discontinuity because the circle is traversed exactly once and 0 is a branch point for log. What this means is that 13/12 is a branch point for f(z) only on the part of the Riemann surface corresponding to one of the branches of the square root. Therefore different parts of the Riemann surface will have branch points appearing in one of the two following ways: ComplexAnalysis Page 5
6 Let's just to find our way make some concrete choices for angles to define the branch cuts and then see what geometric structures they correspond to. Express variables in polar form with respect to their branch points. We will just try to define a branch by making arbitrary cutting choices, and see what it produces. Out of lack of creativity, let's just make the same choices as one makes for defining principal branches This somewhat implicitly defines a branch of f(z) as follows: ComplexAnalysis Page 6
7 This works fine as a branch. But what is the branch cut structure in the complex plane? Note that the cut of the angle is not yet very explicit in terms of z. Let's make it explicit. The only way to get a solution is for But our choice of branch forbids this; it is impossible for So this putative branch cut isn't actually there on this branch! ComplexAnalysis Page 7
Introduce complex-valued transcendental functions via the complex exponential defined as:
 Complex exponential and logarithm Monday, September 30, 2013 1:59 PM Homework 2 posted, due October 11. Introduce complex-valued transcendental functions via the complex exponential defined as: where We'll
Complex exponential and logarithm Monday, September 30, 2013 1:59 PM Homework 2 posted, due October 11. Introduce complex-valued transcendental functions via the complex exponential defined as: where We'll
First some basics from multivariable calculus directly extended to complex functions.
 Complex Integration Tuesday, October 15, 2013 2:01 PM Our first objective is to develop a concept of integration of complex functions that interacts well with the notion of complex derivative. A certain
Complex Integration Tuesday, October 15, 2013 2:01 PM Our first objective is to develop a concept of integration of complex functions that interacts well with the notion of complex derivative. A certain
LECTURE-15 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS
 LECTURE-5 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS VED V. DATAR The purpose of this lecture is twofold - first, to characterize domains on which a holomorphic logarithm can be defined, and second, to show that
LECTURE-5 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS VED V. DATAR The purpose of this lecture is twofold - first, to characterize domains on which a holomorphic logarithm can be defined, and second, to show that
Note that. No office hours on Monday October 15 or Wednesday October 17. No class Tuesday October 16
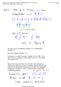 advprobnotes101207b Page 1 CDFS and coping with random variables that are not purely discrete nor absolutely continuouss Friday, October 12, 2007 2:10 PM Note that No office hours on Monday October 15
advprobnotes101207b Page 1 CDFS and coping with random variables that are not purely discrete nor absolutely continuouss Friday, October 12, 2007 2:10 PM Note that No office hours on Monday October 15
Cauchy Integral Formula Consequences
 Cauchy Integral Formula Consequences Monday, October 28, 2013 1:59 PM Homework 3 due November 15, 2013 at 5 PM. Last time we derived Cauchy's Integral Formula, which we will present in somewhat generalized
Cauchy Integral Formula Consequences Monday, October 28, 2013 1:59 PM Homework 3 due November 15, 2013 at 5 PM. Last time we derived Cauchy's Integral Formula, which we will present in somewhat generalized
Mittag-Leffler and Principle of the Argument
 Mittag-Leffler and Principle of the Argument Thursday, November 21, 2013 1:54 PM Homework 3 due Friday, November 22 at 5 PM. Homework 4 will be posted tonight, due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM. We'll
Mittag-Leffler and Principle of the Argument Thursday, November 21, 2013 1:54 PM Homework 3 due Friday, November 22 at 5 PM. Homework 4 will be posted tonight, due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM. We'll
0. Introduction 1 0. INTRODUCTION
 0. Introduction 1 0. INTRODUCTION In a very rough sketch we explain what algebraic geometry is about and what it can be used for. We stress the many correlations with other fields of research, such as
0. Introduction 1 0. INTRODUCTION In a very rough sketch we explain what algebraic geometry is about and what it can be used for. We stress the many correlations with other fields of research, such as
Homework 3: Complex Analysis
 Homework 3: Complex Analysis Course: Physics 23, Methods of Theoretical Physics (206) Instructor: Professor Flip Tanedo (flip.tanedo@ucr.edu) Due by: Friday, October 4 Corrected: 0/, problem 6 f(z) f(/z)
Homework 3: Complex Analysis Course: Physics 23, Methods of Theoretical Physics (206) Instructor: Professor Flip Tanedo (flip.tanedo@ucr.edu) Due by: Friday, October 4 Corrected: 0/, problem 6 f(z) f(/z)
Complex functions, single and multivalued.
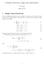 Complex functions, single and multivalued. D. Craig 2007 03 27 1 Single-valued functions All of the following functions can be defined via power series which converge for the entire complex plane, and
Complex functions, single and multivalued. D. Craig 2007 03 27 1 Single-valued functions All of the following functions can be defined via power series which converge for the entire complex plane, and
THE RESIDUE THEOREM. f(z) dz = 2πi res z=z0 f(z). C
 THE RESIDUE THEOREM ontents 1. The Residue Formula 1 2. Applications and corollaries of the residue formula 2 3. ontour integration over more general curves 5 4. Defining the logarithm 7 Now that we have
THE RESIDUE THEOREM ontents 1. The Residue Formula 1 2. Applications and corollaries of the residue formula 2 3. ontour integration over more general curves 5 4. Defining the logarithm 7 Now that we have
Homework 4: Mayer-Vietoris Sequence and CW complexes
 Homework 4: Mayer-Vietoris Sequence and CW complexes Due date: Friday, October 4th. 0. Goals and Prerequisites The goal of this homework assignment is to begin using the Mayer-Vietoris sequence and cellular
Homework 4: Mayer-Vietoris Sequence and CW complexes Due date: Friday, October 4th. 0. Goals and Prerequisites The goal of this homework assignment is to begin using the Mayer-Vietoris sequence and cellular
Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4
 Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4 Due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM Note that to get full credit on any problem in this class, you must solve the problems in an efficient and elegant manner,
Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4 Due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM Note that to get full credit on any problem in this class, you must solve the problems in an efficient and elegant manner,
G-GPE Explaining the equation for a circle
 G-GPE Explaining the equation for a circle Alignments to Content Standards: G-GPE.A.1 Task This problem examines equations defining different circles in the - plane. a. Use the Pythagorean theorem to find
G-GPE Explaining the equation for a circle Alignments to Content Standards: G-GPE.A.1 Task This problem examines equations defining different circles in the - plane. a. Use the Pythagorean theorem to find
MAE 143B - Homework 9
 MAE 43B - Homework 9 7.2 2 2 3.8.6.4.2.2 9 8 2 2 3 a) G(s) = (s+)(s+).4.6.8.2.2.4.6.8. Polar plot; red for negative ; no encirclements of, a.s. under unit feedback... 2 2 3. 4 9 2 2 3 h) G(s) = s+ s(s+)..2.4.6.8.2.4
MAE 43B - Homework 9 7.2 2 2 3.8.6.4.2.2 9 8 2 2 3 a) G(s) = (s+)(s+).4.6.8.2.2.4.6.8. Polar plot; red for negative ; no encirclements of, a.s. under unit feedback... 2 2 3. 4 9 2 2 3 h) G(s) = s+ s(s+)..2.4.6.8.2.4
Numerical results in ABJM theory
 Numerical results in ABJM theory Riccardo Conti Friday 3ʳᵈ March 2017 D. Bombardelli, A. Cavaglià, R. Conti and R. Tateo (in progress) Overview Purpose: Solving the Quantum Spectral Curve (QSC) equations
Numerical results in ABJM theory Riccardo Conti Friday 3ʳᵈ March 2017 D. Bombardelli, A. Cavaglià, R. Conti and R. Tateo (in progress) Overview Purpose: Solving the Quantum Spectral Curve (QSC) equations
Consequences of Continuity
 Consequences of Continuity James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University October 4, 2017 Outline 1 Domains of Continuous Functions 2 The
Consequences of Continuity James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University October 4, 2017 Outline 1 Domains of Continuous Functions 2 The
The Nuclear Force and Limitations to the Lorentz Electrostatic Force Equation
 The Nuclear Force and Limitations to the Lorentz Electrostatic Force Equation Author: Singer, Michael Date: 1 st May 2017 3 rd July 2018 Revision Abstract In Electromagnetic Field Theory it is the interaction
The Nuclear Force and Limitations to the Lorentz Electrostatic Force Equation Author: Singer, Michael Date: 1 st May 2017 3 rd July 2018 Revision Abstract In Electromagnetic Field Theory it is the interaction
LAURENT SERIES AND SINGULARITIES
 LAURENT SERIES AND SINGULARITIES Introduction So far we have studied analytic functions Locally, such functions are represented by power series Globally, the bounded ones are constant, the ones that get
LAURENT SERIES AND SINGULARITIES Introduction So far we have studied analytic functions Locally, such functions are represented by power series Globally, the bounded ones are constant, the ones that get
FOUNDATIONS OF ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY CLASS 24
 FOUNDATIONS OF ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY CLASS 24 RAVI VAKIL CONTENTS 1. Vector bundles and locally free sheaves 1 2. Toward quasicoherent sheaves: the distinguished affine base 5 Quasicoherent and coherent sheaves
FOUNDATIONS OF ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY CLASS 24 RAVI VAKIL CONTENTS 1. Vector bundles and locally free sheaves 1 2. Toward quasicoherent sheaves: the distinguished affine base 5 Quasicoherent and coherent sheaves
Mid Term-1 : Solutions to practice problems
 Mid Term- : Solutions to practice problems 0 October, 06. Is the function fz = e z x iy holomorphic at z = 0? Give proper justification. Here we are using the notation z = x + iy. Solution: Method-. Use
Mid Term- : Solutions to practice problems 0 October, 06. Is the function fz = e z x iy holomorphic at z = 0? Give proper justification. Here we are using the notation z = x + iy. Solution: Method-. Use
1 Implicit Differentiation
 MATH 1010E University Mathematics Lecture Notes (week 5) Martin Li 1 Implicit Differentiation Sometimes a function is defined implicitly by an equation of the form f(x, y) = 0, which we think of as a relationship
MATH 1010E University Mathematics Lecture Notes (week 5) Martin Li 1 Implicit Differentiation Sometimes a function is defined implicitly by an equation of the form f(x, y) = 0, which we think of as a relationship
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE
 MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE 1. Introduction Let D denote the unit disk and let D denote its boundary circle. Consider a piecewise continuous function on the boundary circle, {
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE 1. Introduction Let D denote the unit disk and let D denote its boundary circle. Consider a piecewise continuous function on the boundary circle, {
6.003: Signals and Systems
 6.003: Signals and Systems Discrete-Time Systems September 13, 2011 1 Homework Doing the homework is essential to understanding the content. Weekly Homework Assigments tutor (exam-type) problems: answers
6.003: Signals and Systems Discrete-Time Systems September 13, 2011 1 Homework Doing the homework is essential to understanding the content. Weekly Homework Assigments tutor (exam-type) problems: answers
MATH 434 Fall 2016 Homework 1, due on Wednesday August 31
 Homework 1, due on Wednesday August 31 Problem 1. Let z = 2 i and z = 3 + 4i. Write the product zz and the quotient z z in the form a + ib, with a, b R. Problem 2. Let z C be a complex number, and let
Homework 1, due on Wednesday August 31 Problem 1. Let z = 2 i and z = 3 + 4i. Write the product zz and the quotient z z in the form a + ib, with a, b R. Problem 2. Let z C be a complex number, and let
Complex Variables. Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit.
 Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit. 1. The TI-89 calculator says, reasonably enough, that x 1) 1/3 1 ) 3 = 8. lim
Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit. 1. The TI-89 calculator says, reasonably enough, that x 1) 1/3 1 ) 3 = 8. lim
Algebraic Topology I Homework Spring 2014
 Algebraic Topology I Homework Spring 2014 Homework solutions will be available http://faculty.tcu.edu/gfriedman/algtop/algtop-hw-solns.pdf Due 5/1 A Do Hatcher 2.2.4 B Do Hatcher 2.2.9b (Find a cell structure)
Algebraic Topology I Homework Spring 2014 Homework solutions will be available http://faculty.tcu.edu/gfriedman/algtop/algtop-hw-solns.pdf Due 5/1 A Do Hatcher 2.2.4 B Do Hatcher 2.2.9b (Find a cell structure)
Spring 2010 Exam 2. You may not use your books, notes, or any calculator on this exam.
 MTH 282 final Spring 2010 Exam 2 Time Limit: 110 Minutes Name (Print): Instructor: Prof. Houhong Fan This exam contains 6 pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if any pages are
MTH 282 final Spring 2010 Exam 2 Time Limit: 110 Minutes Name (Print): Instructor: Prof. Houhong Fan This exam contains 6 pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if any pages are
Synopsis of Complex Analysis. Ryan D. Reece
 Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Mathematics-I Prof. S.K. Ray Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Lecture 1 Real Numbers
 Mathematics-I Prof. S.K. Ray Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 1 Real Numbers In these lectures, we are going to study a branch of mathematics called
Mathematics-I Prof. S.K. Ray Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 1 Real Numbers In these lectures, we are going to study a branch of mathematics called
26.2. Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping 26.2 Introduction In this Section we consider two important features of complex functions. The Cauchy-Riemann equations provide a necessary and sufficient
Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping 26.2 Introduction In this Section we consider two important features of complex functions. The Cauchy-Riemann equations provide a necessary and sufficient
Ω Ω /ω. To these, one wants to add a fourth condition that arises from physics, what is known as the anomaly cancellation, namely that
 String theory and balanced metrics One of the main motivations for considering balanced metrics, in addition to the considerations already mentioned, has to do with the theory of what are known as heterotic
String theory and balanced metrics One of the main motivations for considering balanced metrics, in addition to the considerations already mentioned, has to do with the theory of what are known as heterotic
Consequences of Continuity
 Consequences of Continuity James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University October 4, 2017 Outline Domains of Continuous Functions The Intermediate
Consequences of Continuity James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University October 4, 2017 Outline Domains of Continuous Functions The Intermediate
CS/Ph120 Homework 1 Solutions
 CS/Ph0 Homework Solutions October, 06 Problem : State discrimination Suppose you are given two distinct states of a single qubit, ψ and ψ. a) Argue that if there is a ϕ such that ψ = e iϕ ψ then no measurement
CS/Ph0 Homework Solutions October, 06 Problem : State discrimination Suppose you are given two distinct states of a single qubit, ψ and ψ. a) Argue that if there is a ϕ such that ψ = e iϕ ψ then no measurement
Locus 6. More Root S 0 L U T I 0 N S. Note: All references to Figures and Equations whose numbers are not preceded by an "S"refer to the textbook.
 S 0 L U T I 0 N S More Root Locus 6 Note: All references to Figures and Equations whose numbers are not preceded by an "S"refer to the textbook. For the first transfer function a(s), the root locus is
S 0 L U T I 0 N S More Root Locus 6 Note: All references to Figures and Equations whose numbers are not preceded by an "S"refer to the textbook. For the first transfer function a(s), the root locus is
Pertubation10 Page 1
 Pertubation10 Page 1 Singular Perturbation Theory for Algebraic Equations Monday, February 22, 2010 1:58 PM Readings: Holmes, Sec. 1.5 Hinch, Secs. 1.2 & 1.3 Homework 1 due Thursday, February 25. Again
Pertubation10 Page 1 Singular Perturbation Theory for Algebraic Equations Monday, February 22, 2010 1:58 PM Readings: Holmes, Sec. 1.5 Hinch, Secs. 1.2 & 1.3 Homework 1 due Thursday, February 25. Again
Smooth Structure. lies on the boundary, then it is determined up to the identifications it 1 2
 132 3. Smooth Structure lies on the boundary, then it is determined up to the identifications 1 2 + it 1 2 + it on the vertical boundary and z 1/z on the circular part. Notice that since z z + 1 and z
132 3. Smooth Structure lies on the boundary, then it is determined up to the identifications 1 2 + it 1 2 + it on the vertical boundary and z 1/z on the circular part. Notice that since z z + 1 and z
Checking Consistency. Chapter Introduction Support of a Consistent Family
 Chapter 11 Checking Consistency 11.1 Introduction The conditions which define a consistent family of histories were stated in Ch. 10. The sample space must consist of a collection of mutually orthogonal
Chapter 11 Checking Consistency 11.1 Introduction The conditions which define a consistent family of histories were stated in Ch. 10. The sample space must consist of a collection of mutually orthogonal
(x 1, y 1 ) = (x 2, y 2 ) if and only if x 1 = x 2 and y 1 = y 2.
 1. Complex numbers A complex number z is defined as an ordered pair z = (x, y), where x and y are a pair of real numbers. In usual notation, we write z = x + iy, where i is a symbol. The operations of
1. Complex numbers A complex number z is defined as an ordered pair z = (x, y), where x and y are a pair of real numbers. In usual notation, we write z = x + iy, where i is a symbol. The operations of
Problem 1: (3 points) Recall that the dot product of two vectors in R 3 is
 Linear Algebra, Spring 206 Homework 3 Name: Problem : (3 points) Recall that the dot product of two vectors in R 3 is a x b y = ax + by + cz, c z and this is essentially the same as the matrix multiplication
Linear Algebra, Spring 206 Homework 3 Name: Problem : (3 points) Recall that the dot product of two vectors in R 3 is a x b y = ax + by + cz, c z and this is essentially the same as the matrix multiplication
We will begin by first solving this equation on a rectangle in 2 dimensions with prescribed boundary data at each edge.
 Page 1 Sunday, May 31, 2015 9:24 PM From our study of the 2-d and 3-d heat equation in thermal equlibrium another PDE which we will learn to solve. Namely Laplace's Equation we arrive at In 3-d In 2-d
Page 1 Sunday, May 31, 2015 9:24 PM From our study of the 2-d and 3-d heat equation in thermal equlibrium another PDE which we will learn to solve. Namely Laplace's Equation we arrive at In 3-d In 2-d
Gaussian integrals. Calvin W. Johnson. September 9, The basic Gaussian and its normalization
 Gaussian integrals Calvin W. Johnson September 9, 24 The basic Gaussian and its normalization The Gaussian function or the normal distribution, ep ( α 2), () is a widely used function in physics and mathematical
Gaussian integrals Calvin W. Johnson September 9, 24 The basic Gaussian and its normalization The Gaussian function or the normal distribution, ep ( α 2), () is a widely used function in physics and mathematical
The harmonic map flow
 Chapter 2 The harmonic map flow 2.1 Definition of the flow The harmonic map flow was introduced by Eells-Sampson in 1964; their work could be considered the start of the field of geometric flows. The flow
Chapter 2 The harmonic map flow 2.1 Definition of the flow The harmonic map flow was introduced by Eells-Sampson in 1964; their work could be considered the start of the field of geometric flows. The flow
Student: We have to buy a new access code? I'm afraid you have to buy a new one. Talk to the bookstore about that.
 Physics 1-21-09 Wednesday Daily Homework Statistics 118 Responses Mean: 0.944 Median: 0.96 Do we want to turn the front lights off? This okay? A friend of mine used to visit a psychology class back in
Physics 1-21-09 Wednesday Daily Homework Statistics 118 Responses Mean: 0.944 Median: 0.96 Do we want to turn the front lights off? This okay? A friend of mine used to visit a psychology class back in
The Hurewicz Theorem
 The Hurewicz Theorem April 5, 011 1 Introduction The fundamental group and homology groups both give extremely useful information, particularly about path-connected spaces. Both can be considered as functors,
The Hurewicz Theorem April 5, 011 1 Introduction The fundamental group and homology groups both give extremely useful information, particularly about path-connected spaces. Both can be considered as functors,
Law of Trichotomy and Boundary Equations
 Law of Trichotomy and Boundary Equations Law of Trichotomy: For any two real numbers a and b, exactly one of the following is true. i. a < b ii. a = b iii. a > b The Law of Trichotomy is a formal statement
Law of Trichotomy and Boundary Equations Law of Trichotomy: For any two real numbers a and b, exactly one of the following is true. i. a < b ii. a = b iii. a > b The Law of Trichotomy is a formal statement
Theorems. Theorem 1.11: Greatest-Lower-Bound Property. Theorem 1.20: The Archimedean property of. Theorem 1.21: -th Root of Real Numbers
 Page 1 Theorems Wednesday, May 9, 2018 12:53 AM Theorem 1.11: Greatest-Lower-Bound Property Suppose is an ordered set with the least-upper-bound property Suppose, and is bounded below be the set of lower
Page 1 Theorems Wednesday, May 9, 2018 12:53 AM Theorem 1.11: Greatest-Lower-Bound Property Suppose is an ordered set with the least-upper-bound property Suppose, and is bounded below be the set of lower
1 Discussion on multi-valued functions
 Week 3 notes, Math 7651 1 Discussion on multi-valued functions Log function : Note that if z is written in its polar representation: z = r e iθ, where r = z and θ = arg z, then log z log r + i θ + 2inπ
Week 3 notes, Math 7651 1 Discussion on multi-valued functions Log function : Note that if z is written in its polar representation: z = r e iθ, where r = z and θ = arg z, then log z log r + i θ + 2inπ
PHIL 422 Advanced Logic Inductive Proof
 PHIL 422 Advanced Logic Inductive Proof 1. Preamble: One of the most powerful tools in your meta-logical toolkit will be proof by induction. Just about every significant meta-logical result relies upon
PHIL 422 Advanced Logic Inductive Proof 1. Preamble: One of the most powerful tools in your meta-logical toolkit will be proof by induction. Just about every significant meta-logical result relies upon
THE SIMPLE PROOF OF GOLDBACH'S CONJECTURE. by Miles Mathis
 THE SIMPLE PROOF OF GOLDBACH'S CONJECTURE by Miles Mathis miles@mileswmathis.com Abstract Here I solve Goldbach's Conjecture by the simplest method possible. I do this by first calculating probabilites
THE SIMPLE PROOF OF GOLDBACH'S CONJECTURE by Miles Mathis miles@mileswmathis.com Abstract Here I solve Goldbach's Conjecture by the simplest method possible. I do this by first calculating probabilites
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
Explicit Examples of Strebel Differentials
 Explicit Examples of Strebel Differentials arxiv:0910.475v [math.dg] 30 Oct 009 1 Introduction Philip Tynan November 14, 018 In this paper, we investigate Strebel differentials, which are a special class
Explicit Examples of Strebel Differentials arxiv:0910.475v [math.dg] 30 Oct 009 1 Introduction Philip Tynan November 14, 018 In this paper, we investigate Strebel differentials, which are a special class
LAB 8: INTEGRATION. Figure 1. Approximating volume: the left by cubes, the right by cylinders
 LAB 8: INTGRATION The purpose of this lab is to give intuition about integration. It will hopefully complement the, rather-dry, section of the lab manual and the, rather-too-rigorous-and-unreadable, section
LAB 8: INTGRATION The purpose of this lab is to give intuition about integration. It will hopefully complement the, rather-dry, section of the lab manual and the, rather-too-rigorous-and-unreadable, section
CS1210 Lecture 23 March 8, 2019
 CS1210 Lecture 23 March 8, 2019 HW5 due today In-discussion exams next week Optional homework assignment next week can be used to replace a score from among HW 1 3. Will be posted some time before Monday
CS1210 Lecture 23 March 8, 2019 HW5 due today In-discussion exams next week Optional homework assignment next week can be used to replace a score from among HW 1 3. Will be posted some time before Monday
The Derivative of a Function
 The Derivative of a Function James K Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 1, 2017 Outline A Basic Evolutionary Model The Next Generation
The Derivative of a Function James K Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 1, 2017 Outline A Basic Evolutionary Model The Next Generation
MITOCW watch?v=rf5sefhttwo
 MITOCW watch?v=rf5sefhttwo The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=rf5sefhttwo The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free. To
f(s) e -i n π s/l d s
 Pointwise convergence of complex Fourier series Let f(x) be a periodic function with period l defined on the interval [,l]. The complex Fourier coefficients of f( x) are This leads to a Fourier series
Pointwise convergence of complex Fourier series Let f(x) be a periodic function with period l defined on the interval [,l]. The complex Fourier coefficients of f( x) are This leads to a Fourier series
Geometric Series and the Ratio and Root Test
 Geometric Series and the Ratio and Root Test James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 5, 2018 Outline 1 Geometric Series
Geometric Series and the Ratio and Root Test James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 5, 2018 Outline 1 Geometric Series
Braid groups, their applications and connections
 Braid groups, their applications and connections Fred Cohen University of Rochester KITP Knotted Fields July 1, 2012 Introduction: Artin s braid groups are at the confluence of several basic mathematical
Braid groups, their applications and connections Fred Cohen University of Rochester KITP Knotted Fields July 1, 2012 Introduction: Artin s braid groups are at the confluence of several basic mathematical
Math 396. Bijectivity vs. isomorphism
 Math 396. Bijectivity vs. isomorphism 1. Motivation Let f : X Y be a C p map between two C p -premanifolds with corners, with 1 p. Assuming f is bijective, we would like a criterion to tell us that f 1
Math 396. Bijectivity vs. isomorphism 1. Motivation Let f : X Y be a C p map between two C p -premanifolds with corners, with 1 p. Assuming f is bijective, we would like a criterion to tell us that f 1
Each is equal to CP 1 minus one point, which is the origin of the other: (C =) U 1 = CP 1 the line λ (1, 0) U 0
 Algebraic Curves/Fall 2015 Aaron Bertram 1. Introduction. What is a complex curve? (Geometry) It s a Riemann surface, that is, a compact oriented twodimensional real manifold Σ with a complex structure.
Algebraic Curves/Fall 2015 Aaron Bertram 1. Introduction. What is a complex curve? (Geometry) It s a Riemann surface, that is, a compact oriented twodimensional real manifold Σ with a complex structure.
REVIEW REVIEW. Quantum Field Theory II
 Quantum Field Theory II PHYS-P 622 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory Chapters: 13, 14, 16-21, 26-28, 51, 52, 61-68, 44, 53, 69-74, 30-32, 84-86, 75,
Quantum Field Theory II PHYS-P 622 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory Chapters: 13, 14, 16-21, 26-28, 51, 52, 61-68, 44, 53, 69-74, 30-32, 84-86, 75,
Quantum Field Theory II
 Quantum Field Theory II PHYS-P 622 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory Chapters: 13, 14, 16-21, 26-28, 51, 52, 61-68, 44, 53, 69-74, 30-32, 84-86, 75,
Quantum Field Theory II PHYS-P 622 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory Chapters: 13, 14, 16-21, 26-28, 51, 52, 61-68, 44, 53, 69-74, 30-32, 84-86, 75,
We saw in Section 5.1 that a limit of the form. arises when we compute an area.
 INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS Equation 1 We saw in Section 5.1 that a limit of the form n lim f ( x *) x n i 1 i lim[ f ( x *) x f ( x *) x... f ( x *) x] n 1 2 arises when we compute an area. n We also saw that
INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS Equation 1 We saw in Section 5.1 that a limit of the form n lim f ( x *) x n i 1 i lim[ f ( x *) x f ( x *) x... f ( x *) x] n 1 2 arises when we compute an area. n We also saw that
, p 1 < p 2 < < p l primes.
 Solutions Math 347 Homework 1 9/6/17 Exercise 1. When we take a composite number n and factor it into primes, that means we write it as a product of prime numbers, usually in increasing order, using exponents
Solutions Math 347 Homework 1 9/6/17 Exercise 1. When we take a composite number n and factor it into primes, that means we write it as a product of prime numbers, usually in increasing order, using exponents
Chapter 6: The metric space M(G) and normal families
 Chapter 6: The metric space MG) and normal families Course 414, 003 04 March 9, 004 Remark 6.1 For G C open, we recall the notation MG) for the set algebra) of all meromorphic functions on G. We now consider
Chapter 6: The metric space MG) and normal families Course 414, 003 04 March 9, 004 Remark 6.1 For G C open, we recall the notation MG) for the set algebra) of all meromorphic functions on G. We now consider
Homework 4: Hard-Copy Homework Due Wednesday 2/17
 Homework 4: Hard-Copy Homework Due Wednesday 2/17 Special instructions for this homework: Please show all work necessary to solve the problems, including diagrams, algebra, calculus, or whatever else may
Homework 4: Hard-Copy Homework Due Wednesday 2/17 Special instructions for this homework: Please show all work necessary to solve the problems, including diagrams, algebra, calculus, or whatever else may
From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism. U : ϕ U(U U ) ϕ U (U U )
 3 Riemann surfaces 3.1 Definitions and examples From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism ϕ U from U to an open set V in R 2. If two such neighbourhoods U,
3 Riemann surfaces 3.1 Definitions and examples From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism ϕ U from U to an open set V in R 2. If two such neighbourhoods U,
Review of scalar field theory. Srednicki 5, 9, 10
 Review of scalar field theory Srednicki 5, 9, 10 2 The LSZ reduction formula based on S-5 In order to describe scattering experiments we need to construct appropriate initial and final states and calculate
Review of scalar field theory Srednicki 5, 9, 10 2 The LSZ reduction formula based on S-5 In order to describe scattering experiments we need to construct appropriate initial and final states and calculate
IV. Conformal Maps. 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability. 2. Automorphisms of the Riemann sphere: Möbius transformations
 MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
MA424, S13 HW #6: Homework Problems 1. Answer the following, showing all work clearly and neatly. ONLY EXACT VALUES WILL BE ACCEPTED.
 MA424, S13 HW #6: 44-47 Homework Problems 1 Answer the following, showing all work clearly and neatly. ONLY EXACT VALUES WILL BE ACCEPTED. NOTATION: Recall that C r (z) is the positively oriented circle
MA424, S13 HW #6: 44-47 Homework Problems 1 Answer the following, showing all work clearly and neatly. ONLY EXACT VALUES WILL BE ACCEPTED. NOTATION: Recall that C r (z) is the positively oriented circle
Linear Independence Reading: Lay 1.7
 Linear Independence Reading: Lay 17 September 11, 213 In this section, we discuss the concept of linear dependence and independence I am going to introduce the definitions and then work some examples and
Linear Independence Reading: Lay 17 September 11, 213 In this section, we discuss the concept of linear dependence and independence I am going to introduce the definitions and then work some examples and
A SURVEY ON THE MONODROMY GROUPS OF ALGEBRAIC FUNCTIONS
 A SURVEY ON THE MONODROMY GROUPS OF ALGEBRAIC FUNCTIONS HANNAH SANTA CRUZ Abstract. The study of polynomials is one of the most ancient subjects in mathematics, dating back to the Babylonian s search for
A SURVEY ON THE MONODROMY GROUPS OF ALGEBRAIC FUNCTIONS HANNAH SANTA CRUZ Abstract. The study of polynomials is one of the most ancient subjects in mathematics, dating back to the Babylonian s search for
Connectedness. Proposition 2.2. The following are equivalent for a topological space (X, T ).
 Connectedness 1 Motivation Connectedness is the sort of topological property that students love. Its definition is intuitive and easy to understand, and it is a powerful tool in proofs of well-known results.
Connectedness 1 Motivation Connectedness is the sort of topological property that students love. Its definition is intuitive and easy to understand, and it is a powerful tool in proofs of well-known results.
2 Discrete Dynamical Systems (DDS)
 2 Discrete Dynamical Systems (DDS) 2.1 Basics A Discrete Dynamical System (DDS) models the change (or dynamics) of single or multiple populations or quantities in which the change occurs deterministically
2 Discrete Dynamical Systems (DDS) 2.1 Basics A Discrete Dynamical System (DDS) models the change (or dynamics) of single or multiple populations or quantities in which the change occurs deterministically
Research Methods in Mathematics Homework 4 solutions
 Research Methods in Mathematics Homework 4 solutions T. PERUTZ (1) Solution. (a) Since x 2 = 2, we have (p/q) 2 = 2, so p 2 = 2q 2. By definition, an integer is even if it is twice another integer. Since
Research Methods in Mathematics Homework 4 solutions T. PERUTZ (1) Solution. (a) Since x 2 = 2, we have (p/q) 2 = 2, so p 2 = 2q 2. By definition, an integer is even if it is twice another integer. Since
Chapter 6: Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity Tuesday, September 17, :00 PM. Circular Motion. Rotational kinematics
 Ch6 Page 1 Chapter 6: Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM Circular Motion Rotational kinematics We'll discuss the basics of rotational kinematics in this chapter;
Ch6 Page 1 Chapter 6: Circular Motion, Orbits, and Gravity Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM Circular Motion Rotational kinematics We'll discuss the basics of rotational kinematics in this chapter;
implies that if we fix a basis v of V and let M and M be the associated invertible symmetric matrices computing, and, then M = (L L)M and the
 Math 395. Geometric approach to signature For the amusement of the reader who knows a tiny bit about groups (enough to know the meaning of a transitive group action on a set), we now provide an alternative
Math 395. Geometric approach to signature For the amusement of the reader who knows a tiny bit about groups (enough to know the meaning of a transitive group action on a set), we now provide an alternative
THE MANDELSTAM REPRESENTATION IN PERTURBATION THEORY
 THE MANDELSTAM REPRESENTATION IN PERTURBATION THEORY P. V. Landshoff, J. C. Polkinghorne, and J. C. Taylor University of Cambridge, Cambridge, England (presented by J. C. Polkinghorne) 1. METHODS The aim
THE MANDELSTAM REPRESENTATION IN PERTURBATION THEORY P. V. Landshoff, J. C. Polkinghorne, and J. C. Taylor University of Cambridge, Cambridge, England (presented by J. C. Polkinghorne) 1. METHODS The aim
A PRIMER ON SESQUILINEAR FORMS
 A PRIMER ON SESQUILINEAR FORMS BRIAN OSSERMAN This is an alternative presentation of most of the material from 8., 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5 and 8.8 of Artin s book. Any terminology (such as sesquilinear form
A PRIMER ON SESQUILINEAR FORMS BRIAN OSSERMAN This is an alternative presentation of most of the material from 8., 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5 and 8.8 of Artin s book. Any terminology (such as sesquilinear form
Getting Started with Communications Engineering
 1 Linear algebra is the algebra of linear equations: the term linear being used in the same sense as in linear functions, such as: which is the equation of a straight line. y ax c (0.1) Of course, if we
1 Linear algebra is the algebra of linear equations: the term linear being used in the same sense as in linear functions, such as: which is the equation of a straight line. y ax c (0.1) Of course, if we
Homework 3 due Monday, November 19 at 5 PM. Hint added to Problem 2.2.
 advprobnotes111607b Page 1 Covariance and conditional probability Friday, November 16, 2007 1:59 PM Homework 3 due Monday, November 19 at 5 PM. Hint added to Problem 2.2. If we have two random variables
advprobnotes111607b Page 1 Covariance and conditional probability Friday, November 16, 2007 1:59 PM Homework 3 due Monday, November 19 at 5 PM. Hint added to Problem 2.2. If we have two random variables
Geometric Aspects of Sturm-Liouville Problems I. Structures on Spaces of Boundary Conditions
 Geometric Aspects of Sturm-Liouville Problems I. Structures on Spaces of Boundary Conditions QINGKAI KONG HONGYOU WU and ANTON ZETTL Abstract. We consider some geometric aspects of regular Sturm-Liouville
Geometric Aspects of Sturm-Liouville Problems I. Structures on Spaces of Boundary Conditions QINGKAI KONG HONGYOU WU and ANTON ZETTL Abstract. We consider some geometric aspects of regular Sturm-Liouville
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4
 MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4 Harmonic conjugates 4.1 Check that each of the functions u(x, y) below is harmonic at every (x, y) R 2, and find the unique harmonic conjugate, v(x, y), satisfying v(0,
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4 Harmonic conjugates 4.1 Check that each of the functions u(x, y) below is harmonic at every (x, y) R 2, and find the unique harmonic conjugate, v(x, y), satisfying v(0,
Advanced Calculus Questions
 Advanced Calculus Questions What is here? This is a(n evolving) collection of challenging calculus problems. Be warned - some of these questions will go beyond the scope of this course. Particularly difficult
Advanced Calculus Questions What is here? This is a(n evolving) collection of challenging calculus problems. Be warned - some of these questions will go beyond the scope of this course. Particularly difficult
SUBAREA I MATHEMATIC REASONING AND COMMUNICATION Understand reasoning processes, including inductive and deductive logic and symbolic logic.
 SUBAREA I MATHEMATIC REASONING AND COMMUNICATION 0001. Understand reasoning processes, including inductive and deductive logic and symbolic logic. Conditional statements are frequently written in "if-then"
SUBAREA I MATHEMATIC REASONING AND COMMUNICATION 0001. Understand reasoning processes, including inductive and deductive logic and symbolic logic. Conditional statements are frequently written in "if-then"
Notes 7 Analytic Continuation
 ECE 6382 Fall 27 David R. Jackson Notes 7 Analtic Continuation Notes are from D. R. Wilton, Dept. of ECE Analtic Continuation of Functions We define analtic continuation as the process of continuing a
ECE 6382 Fall 27 David R. Jackson Notes 7 Analtic Continuation Notes are from D. R. Wilton, Dept. of ECE Analtic Continuation of Functions We define analtic continuation as the process of continuing a
PH 1120 Term D, 2017
 PH 1120 Term D, 2017 Study Guide 4 / Objective 13 The Biot-Savart Law \ / a) Calculate the contribution made to the magnetic field at a \ / specified point by a current element, given the current, location,
PH 1120 Term D, 2017 Study Guide 4 / Objective 13 The Biot-Savart Law \ / a) Calculate the contribution made to the magnetic field at a \ / specified point by a current element, given the current, location,
B Elements of Complex Analysis
 Fourier Transform Methods in Finance By Umberto Cherubini Giovanni Della Lunga Sabrina Mulinacci Pietro Rossi Copyright 21 John Wiley & Sons Ltd B Elements of Complex Analysis B.1 COMPLEX NUMBERS The purpose
Fourier Transform Methods in Finance By Umberto Cherubini Giovanni Della Lunga Sabrina Mulinacci Pietro Rossi Copyright 21 John Wiley & Sons Ltd B Elements of Complex Analysis B.1 COMPLEX NUMBERS The purpose
HOMEWORK 7 SOLUTIONS
 HOMEWORK 7 SOLUTIONS MA11: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 17 (1) Using the method of Lagrange multipliers, find the largest and smallest values of the function f(x, y) xy on the ellipse x + y 1. Solution: The
HOMEWORK 7 SOLUTIONS MA11: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 17 (1) Using the method of Lagrange multipliers, find the largest and smallest values of the function f(x, y) xy on the ellipse x + y 1. Solution: The
Lecture 20: Further graphing
 Lecture 20: Further graphing Nathan Pflueger 25 October 2013 1 Introduction This lecture does not introduce any new material. We revisit the techniques from lecture 12, which give ways to determine the
Lecture 20: Further graphing Nathan Pflueger 25 October 2013 1 Introduction This lecture does not introduce any new material. We revisit the techniques from lecture 12, which give ways to determine the
Mathematical Background. e x2. log k. a+b a + b. Carlos Moreno uwaterloo.ca EIT e π i 1 = 0.
 Mathematical Background Carlos Moreno cmoreno @ uwaterloo.ca EIT-4103 N k=0 log k 0 e x2 e π i 1 = 0 dx a+b a + b https://ece.uwaterloo.ca/~cmoreno/ece250 Mathematical Background Standard reminder to set
Mathematical Background Carlos Moreno cmoreno @ uwaterloo.ca EIT-4103 N k=0 log k 0 e x2 e π i 1 = 0 dx a+b a + b https://ece.uwaterloo.ca/~cmoreno/ece250 Mathematical Background Standard reminder to set
8 Wyner Honors Algebra II Fall 2013
 8 Wyner Honors Algebra II Fall 2013 CHAPTER THREE: SOLVING EQUATIONS AND SYSTEMS Summary Terms Objectives The cornerstone of algebra is solving algebraic equations. This can be done with algebraic techniques,
8 Wyner Honors Algebra II Fall 2013 CHAPTER THREE: SOLVING EQUATIONS AND SYSTEMS Summary Terms Objectives The cornerstone of algebra is solving algebraic equations. This can be done with algebraic techniques,
MITOCW ocw f99-lec23_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec23_300k -- and lift-off on differential equations. So, this section is about how to solve a system of first order, first derivative, constant coefficient linear equations. And if
MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec23_300k -- and lift-off on differential equations. So, this section is about how to solve a system of first order, first derivative, constant coefficient linear equations. And if
MA30056: Complex Analysis. Exercise Sheet 7: Applications and Sequences of Complex Functions
 MA30056: Complex Analysis Exercise Sheet 7: Applications and Sequences of Complex Functions Please hand solutions in at the lecture on Monday 6th March..) Prove Gauss Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Hint:
MA30056: Complex Analysis Exercise Sheet 7: Applications and Sequences of Complex Functions Please hand solutions in at the lecture on Monday 6th March..) Prove Gauss Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Hint:
Chapter 2. Matrix Arithmetic. Chapter 2
 Matrix Arithmetic Matrix Addition and Subtraction Addition and subtraction act element-wise on matrices. In order for the addition/subtraction (A B) to be possible, the two matrices A and B must have the
Matrix Arithmetic Matrix Addition and Subtraction Addition and subtraction act element-wise on matrices. In order for the addition/subtraction (A B) to be possible, the two matrices A and B must have the
1 Closest Pair of Points on the Plane
 CS 31: Algorithms (Spring 2019): Lecture 5 Date: 4th April, 2019 Topic: Divide and Conquer 3: Closest Pair of Points on a Plane Disclaimer: These notes have not gone through scrutiny and in all probability
CS 31: Algorithms (Spring 2019): Lecture 5 Date: 4th April, 2019 Topic: Divide and Conquer 3: Closest Pair of Points on a Plane Disclaimer: These notes have not gone through scrutiny and in all probability
Comments about Chapter 3 of the Math 5335 (Geometry I) text Joel Roberts November 5, 2003; revised October 18, 2004
 Comments about Chapter 3 of the Math 5335 (Geometry I) text Joel Roberts November 5, 2003; revised October 18, 2004 Contents: Heron's formula (Theorem 8 in 3.5). 3.4: Another proof of Theorem 6. 3.7: The
Comments about Chapter 3 of the Math 5335 (Geometry I) text Joel Roberts November 5, 2003; revised October 18, 2004 Contents: Heron's formula (Theorem 8 in 3.5). 3.4: Another proof of Theorem 6. 3.7: The
Definition We say that a topological manifold X is C p if there is an atlas such that the transition functions are C p.
 13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
THE ENVELOPE OF LINES MEETING A FIXED LINE AND TANGENT TO TWO SPHERES
 6 September 2004 THE ENVELOPE OF LINES MEETING A FIXED LINE AND TANGENT TO TWO SPHERES Abstract. We study the set of lines that meet a fixed line and are tangent to two spheres and classify the configurations
6 September 2004 THE ENVELOPE OF LINES MEETING A FIXED LINE AND TANGENT TO TWO SPHERES Abstract. We study the set of lines that meet a fixed line and are tangent to two spheres and classify the configurations
Theory of algebraic functions on the Riemann Sphere
 Mathematica Aeterna, Vol. 3, 2013, no. 2, 83-101 Theory of algebraic functions on the Riemann Sphere John Nixon Brook Cottage The Forge, Ashburnham Battle, East Sussex TN33 9PH, U.K. email: john.h.nixon@spamcop.net
Mathematica Aeterna, Vol. 3, 2013, no. 2, 83-101 Theory of algebraic functions on the Riemann Sphere John Nixon Brook Cottage The Forge, Ashburnham Battle, East Sussex TN33 9PH, U.K. email: john.h.nixon@spamcop.net
