Focusing of Parametric X-ray Radiation from a Bent Crystal
|
|
|
- Caitlin Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Focusing of Parametric X-ray Radiation from a Bent Crystal A.V. Shchagin Kharkov Institute of Physics and Technology, Kharkov 608, Ukraine shchagin@kipt.kharkov.ua Abstract An idea of producing a focused parametric X-ray radiation (PXR) is presented. The PXR is emitted by relativistic charged particles channeling along a bent crystal. Then the PXR emitted from the whole length of the bent crystal is going to the focus. Some properties of focused PXR are estimated for typical experimental conditions and possible applications are discussed. The experiment for observation of focused PXR is proposed. PACS: m; 6.80.Cb, p, h Key words: parametric X-ray radiation, channeling particles, bent crystal, focusing of X-rays Introduction A possibility of steering charged particles motion by a bent crystal has first been predicted in Ref. []. The steering can be realized for particles which are traveling through a long bent crystal in the channeling regime []. The channeling particles may be deflected, if the crystal is bent smoothly enough. Experiments on proton beam deflection, focusing and extraction [3] by bent crystals have been performed, e.g., in Serpukhov at 70 GeV [4, 5], CERN at 0 GeV [6] and at 450 GeV [7,8], Fermilab at 900 GeV [9]. The steering of positive particles at planar channeling is most effective (see, e.g., [7]). Bent crystals of about several centimeters in length are generally used in the experiments. These crystals seem to be convenient for production of focused parametric X-ray radiation (PXR) by channeling relativistic particles. Experimental studies of PXR from relativistic electrons moving through a thin crystal have been performed since 985 to gain an insight into the PXR properties and to develop a new source of quasimonochromatic polarized X-ray beam. The PXR has its maximum intensity in the vicinity of Bragg direction relative to the crystallographic plane (PXR reflection). The PXR reflection from crystals was observed and studied at electron beam energies ranging from several MeV to several GeV, and at PXR energies from a few kev to hundreds of kev. The validity of kinematical theory [0] for the description of PXR properties has been demonstrated in the most of related publications. General information about the nature, properties and investigations of the PXR, as well as references to original papers can be found, e.g., in reviews [-4]. The experiment on observation of PXR from protons has been described in Ref. [5]. However, the
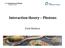
2 PXR from particles channeling in a bent crystal has not been studied as yet, so far as we know. Crystals usually have a number of crystallographic planes aligned at different directions. Therefore, relativistic particles emit a number of PXR reflections at Bragg directions relative to these crystallographic planes (see, e.g. [6]). In the present paper we will show a possibility of focusing the PXR generated in a bent crystal by channeling particles and consider some of its properties. The experiment for observation of focused PXR is also proposed. How to focus PXR Let us suppose that relativistic charged particles are moving in the channeling regime along a bent crystalline plate, as it is shown in Fig.. The bent crystal is cylindrical in shape, R being the radius, and f is the axis of the cylinder. The particles are channeling along the crystallographic planes denoted by the reciprocal lattice vector g!. In this paper we will consider PXR reflections from crystallographic planes aligned at 45 " relative to the particle trajectory and perpendicular to the plane of Fig. a. These crystallographic planes are denoted by the reciprocal lattice vectors g! and g!. The PXR reflections from these planes are going perpendicularly to the particle trajectory and the crystalline plate surface. The PXR reflections from g! are going from the whole plate to the axis f, or, in other words, are focused. The PXR reflections from g! are going in opposite directions, i.e., from the axis f. Thus, the PXR generated on the crystallographic planes g! in the whole bent crystal of several centimeters in length will be collected (focused) at the axis f. The properties of the PXR reflection generated at the right angle to the particle beam in thin crystals have been studied in several papers. The image of the whole PXR reflection at the right angle to the particle beam was first observed in Ref. [7], its polarization was considered in [8] and a detailed structure of the yield angular distribution was studied in [9]. The shape of angular distribution of the yield may be found, e.g., in figures of Refs. [7, 9, 4]. The shape of angular distribution of linear polarization directions in the PXR reflection at the right angle to the particle trajectory may be found, e.g., in figures of Refs. [8,4]. The angular distribution of the PXR yield in the reflection at the right angle to the particle trajectory has two maxima in the plane of Fig. b. Therefore the PXR will be focused at two points F and F at the axis f at an angular distance of about γ eff one from another. Here, γ eff is the effective relativistic factor in the medium [4], γeff = γ + χ0, where γ is the relativistic factor of incident particles, χ 0 is the dielectric susceptibility of the medium. The PXR is linearly polarized in the vicinity of points F and F. The linear polarization direction is practically in the plane of Fig. b. Thus, the focused PXR is linearly polarized in the plane of Fig. b.
3 Apart from the PXR emission, the particles moving through the crystalline plate ionize crystal atoms and thus make them emit the characteristic X-ray radiation (CXR). The CXR is isotropic and not focused, but it exists at points F and F, too. Estimations of some properties of focused PXR To understand the main features of focused PXR, let us estimate them for typical experimental conditions. As an example, we performed calculations for 450 GeV protons channeling along the crystallographic plane (0) with the reciprocal! g =< > lattice vector 0 (see Fig. ) in the Si single-crystal plate, 0.5 mm in thickness and l cryst = 5 cm in length, with the curvature radius R = 5 m. The PXR reflections under consideration are generated at crystallographic planes parallel to!! the ones denoted by the reciprocal lattice vectors g =< 00 > and g =< 0 0 >. The calculations were performed using formulae from Refs. [, 4, 0] derived within the framework of the Ter-Mikaelian theory [0]. The focused PXR reflections are going to the points F and F from the crystallographic planes having a nonzero structure factor parallel to (00), these are (400), (800), ( 00). The PXR reflections from higher-index planes have substantially lower yields. The PXR reflections from similar crystallographic planes, that are parallel to (00), are going in opposite directions from the axis f. The particular case of channeling radiation diffraction [] is not considered in the present estimations. The crystallographic axis < 0 > is aligned along the proton beam in the above-considered example. To avoid axial channeling in the experiment, one needs to provide misalignment of the crystal lattice in the (0) plane for a small angle, which is somewhat larger than the critical channeling angle. The critical channeling angle for the Si single crystal at a proton energy of 450 GeV is about 5 0 radian []. The main features of PXR emission, the positions of points 3 F, F and the properties of focused PXR will change insignificantly at such a small misalignment. The PXR properties are functions of the relativistic factor of the incident particle and the absolute value of particle charge [0,,0]. Therefore, the results of present calculations might be valid for 45 MeV positrons and electrons, which have the same relativistic factor. However, the motion of these particles in a long crystal can differ from the motion of protons. For example, a significant part of high-energy protons can move through a long bent crystal in the channeling regime [,4-9]. But electrons strongly scatter at channeling. So far as we know, there have been no publications about experimental research on the channeling of positrons in bent crystals and on generation of PXR by positrons in any crystals. Besides, the yield of CXR at.74 kev due to K-shell ionization of Si atoms by 450 GeV protons was estimated in accordance with the recommendations from Ref. []. In the calculations, the K-shell ionization cross section for Si atoms was taken to be 943 barn. This cross section value was calculated for 45 MeV electrons having the same relativistic factor as that of 450 GeV protons. The effect
4 of channeling was not taken into account in the present estimations of CXR yield, as it is not expected to be very significant at high particle energies (see Refs. in []). The calculations were performed for a uniform distribution of protons in the crystalline plate thickness. The radiation excited by channeling protons is going to points F and F across the plate, and is attenuated by the Si crystal. The attenuation of radiation in the plate was taken into account in the calculations. Results and discussion The results of calculations are presented in Table. The spectrum of X-ray radiation at points F and F has four spectral peaks in the kev energy range, this being convenient for registration by standard X-ray spectrometric detectors. The peak at.74 kev is due to a non-focused non-polarized CXR, which is produced mainly by protons moving in a 3.3 µ m layer at a concave side of the plate. This layer thickness is determined by X-ray attenuation in a Si crystal (see Table ). Thus, only a little part of the total number of protons passing through the plate produces the CXR that reaches the points F and F. The other spectral peaks are due to a focused polarized PXR. The spectral peaks of focused PXR at E = 6.46,.9, 9.37 kev are produced mainly by protons moving in the 37 µ m layer at a concave side of the plate, in the 70 µ m layer at the same side of the plate, and in almost the whole crystalline plate thickness respectively. The radiation sources for different spectral peaks are specifically distributed in the crystal thickness. Therefore, the measurements and analysis of relative intensities of spectral peaks would permit the estimation of beam proton distribution in the crystal thickness. This can be done for the whole crystalline plate or for its separate part, provided that other parts of the plate are screened, and the X-ray detector can see only this separate part of the crystal. The CXR from the 3.3 µ m layer at a convex side of the bent crystal may be registered by an X-ray detector installed opposite to a convex side of the bent crystal, as the CXR is isotropic and non-focused. Angular divergence (convergence) of focused PXR may be controlled by changing the radius of curvature R of the bent crystal. Thus, we have an X-ray source of several centimeters in size, with a provided smooth tuning of the divergence (convergence). This monochromatic source of polarized X-rays with a possibility of smooth tuning of divergence may be useful for calibration of largeaperture X-ray equipment, for example, X-ray space telescopes [6]. The divergence (convergence) of PXR reflections from channeling particles is cryst the plane of Fig. a. The focused PXR generated by channeling positive relativistic particles in a long crystal can provide a natural PXR spectral peak of extremely narrow width. The natural spectral peak width of focused PXR may be of microelectronvolts range at PXR spectral peak energy of about 0 kev [3]. l R 4 at
5 The experiment on observation of focused PXR may be performed at a facility with a crystal bent for steering the proton beam having the channeling 7 p particles intensity of about or above 0. It can be seen from Table that all s spectral peaks have comparable intensities, and thus, can be measured simultaneously by a spectrometric X-ray detector. The X-ray detector, being about cm square, should be installed at point F or F at the axis f. The PXR from non-channeled particles can be rejected by registering X-rays in coincidence with the particles that have passed through the bent crystal in the channeling regime. There should be vacuum connection between the bent crystal and the X-ray detector in order to observe soft X-rays, because of their attenuation in air. X-rays of energies.74 and 6.46 will be absorbed practically completely over a distance of 5 m in air. However, observation of higher-energy focused PXR is possible in air. The X-rays of energies.9 and 9.37 kev will be attenuated by factors of about 0.3 and 0.60, respectively, at 5 m in air. The energies of all spectral peaks are practically independent of incident relativistic particle energy. Yet, their intensities can increase (decrease) with an increasing (decreasing) incident proton energy [,0]. Acknowledgements The author is thankful to E.N. Tsyganov for discussions during the meeting, [3,4] and more recently, to X. Artru and I. Endo and V.V. Sotnikov. This work was presented as an oral paper at Workshop [5]. The paper became possible partially due to grant STCU 030. References [] E.N. Tsyganov, Fermilab TM-68, Batavia (976). [] V.M. Biryukov, Yu.A. Chesnokov, V.I. Kotov, Uspekhi Fizicheskikh Nauk,64 (994) [in Russian]. Physics-Uspekhi 37 (994) [in English]. [3] E. Tsyganov, The Future of Accelerator Physics, ed. T. Tajima, AIP Conf. Proc. No. 356 (AIP, New York, 996), pp [4] A.A. Asseev, M.Yu. Gorin, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. B 9 (996) 0-4. [5] Yu.A. Chesnokov, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. B 9 (996) [6] K. Elsener, G. Fidecaro, M. Gyr, W. Herr, J. Klem, U. Mikkelsen, S.P. Møller, E. Uggerhøj, G. Vuagnin, E. Weisse, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. B 9 (996) [7] A. Baurichter, K. Kirsebom, R. Medenwaldt, S.P. Møller, T. Worm, E. Uggerhøj, C. Biino, M. Clément, N. Doble, K. Elsener, L. Gatignon, P. Grafström, U. Mikkelsen, A. Freund, Z. Vilakazi, P. Siffert, M. Hage-Ali, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. B 9 (996)
6 [8] N. Doble, L. Gatigton, P. Grafstrom, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. B 9 (996) [9] C.T. Murphy, R. Carrigan, D. Chen, G. Jackson, N. Mokhov, H.-J. Shih, B. Cox, V. Golovatyuk, A. McManus, A. Bogacz, D. Cline, S. Ramachandran, J. Rhoades, J. Rosenzweig, B. Newberger, J.A. Ellison, S. Baker, C.R. Sun, W. Gabella, E. Tsyganov, A. Taratin, A. Asseev, V. Biryukov, A. Khanzadeev, T. Prokofieva, V. Samsonov, G. Solodov, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. B 9 (996) [0] M.L. Ter-Mikaelian, High-Energy Electromagnetic Processes in Condensed Media, Edition of Armenian Academy of Sciences, Erevan, 969 [in Russian]. Wiley-Interscience, New York, 97 [in English]. [] M.L. Ter-Mikaelian, Uspekhi Fizicheskikh Nauk, 7 (00) [in Russian]. Physics-Uspekhi 44 (00) [in English]. [] A.V. Shchagin, X.K. Maruyama, Parametric X-rays, in: Acceleratorbased atomic physics technique and applications, eds. S.M. Shafroth, J.C. Austin (AIP Press, New York, 997) pp [3] P. Rullhusen, A. Artru, P. Dhez, Novel radiation sources using relativistic electrons, World Scientific Publishers, Singapore, 998. [4] A.V. Shchagin, Investigations and properties of PXR, in: Electronphoton interactions in dense media, ed. by H. Wiedemann, NATO Science Series, II Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry, Vol. 49, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht/Boston/London, 00, pp [5] V.P. Afanasenko, V.G. Baryshevsky, R.F. Zuevsky, A.S. Lobko, A.A. Moskatelnikov, S.B. Nurushev, V.V. Panov, V.P. Potsilujko, V.V. Rykalin, S.V. Skorokhod, D.S. Shvarkov Phys. Lett. A 70 (99) [6] A.V. Shchagin, N.A. Khizhnyak, R.B. Fiorito, D.W. Rule, X. Artru, Nucl. Instr. and Meth B 73 (00) [7] R.B. Fiorito, D.W. Rule, M.A. Piestrup, X.K. Maruyama, R.M. Silzer, D.M. Skopik, A.V. Shchagin, Phys. Rev. E 5 (995) R759-R76. [8] A.V. Shchagin, Phys. Lett. A 47 (998) [9] A.V. Shchagin, Phys. Lett. A 6 (999) [0] A.V. Shchagin, N.A. Khizhnyak, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. B 9 (996) 5-. [] T. Ikeda, Y. Matsuda, H. Nitta, Y.H. Ohtsuki, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. B, 5 (996) [] A.V. Shchagin, V.I. Pristupa, N.A. Khizhnyak, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. B 48 (994) 9-3. [3] A.V. Shchagin, to be published. [4] A.V. Shchagin, The Future of Accelerator Physics, ed. T. Tajima, AIP Conf. Proc. No. 356 (AIP, New York, 996), pp [5] A.V. Shchagin, at Workshop Relativistic Channeling and Related Coherent Phenomena, March 3 6, 004, INFL-Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, Frascati, Italy. 6
7 7 Table. Table. Properties of CXR and focused PXR from 450 GeV protons channeling in a bent Si single-crystal plate, 0.5 mm in thickness and 5 cm in length, along the crystallographic plane (0). The radius of crystal curvature is 5 m. The origin of radiation (CXR or focused PXR) and polarization properties of the radiation are given in the first and second columns of the table, where E is the energy of spectral peaks of radiation, γ eff is the inverse effective relativistic factor (for comparison, the inverse relativistic factor of incident 450 GeV protons is 3 γ =.08 0 ), F is the distance between points F and F, T e is the e-fold attenuation length of radiation having the energy E in a Si single crystal, I is the number of quanta per proton per cm at points F and F with X-ray attenuation in the crystal taken into account for the total number of channeling protons randomly distributed in the plate thickness. Radiation Polarization E, kev γ Fmm, eff e T in Si, µ m I, quanta cm p + 7 CXR Si No PXR(400) Linear PXR(800) Linear PXR( 00) Linear
8 8 g! g! p + g! p + p + R a b γ - eff f F f F Fig.. Production of focused PXR by particles channeling in a bent crystalline plate. The side and front views are shown in Figs. a and b, respectively. The particle beam is indicated by arrows p +. The particles are channeling along the crystallographic planes denoted by the reciprocal lattice vector g!. The singlecrystal plate is cylindrical in shape with a radius of curvature R around the axis f. The angular distributions of the yields in the PXR reflections are shown schematically for three points at the plate. Wavy lines with arrows show the radiation propagation direction in the PXR reflections. PXR reflections from crystallographic planes denoted by the reciprocal lattice vector g! are focused at points F and F at the axis f. PXR reflections from crystallographic planes denoted by the reciprocal lattice vector g! are going in opposite directions. The PXR focused at points F and F is linearly polarized practically in the plane of Fig. b.
48 K. B. Korotchenko, Yu. L. Pivovarov, Y. Takabayashi where n is the number of quantum states, L is the normalization length (N = 1 for axial channel
 Pis'ma v ZhETF, vol. 95, iss. 8, pp. 481 { 485 c 01 April 5 Quantum Eects for Parametric X-ray Radiation during Channeling: Theory and First Experimental Observation K. B. Korotchenko 1), Yu. L. Pivovarov,
Pis'ma v ZhETF, vol. 95, iss. 8, pp. 481 { 485 c 01 April 5 Quantum Eects for Parametric X-ray Radiation during Channeling: Theory and First Experimental Observation K. B. Korotchenko 1), Yu. L. Pivovarov,
Characterization of thick graded Si 1 x Ge x /Si layers grown by low energy plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 215 (24) 235 239 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Characterization of thick graded Si 1 x Ge x /Si layers grown by low energy plasma enhanced chemical
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 215 (24) 235 239 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Characterization of thick graded Si 1 x Ge x /Si layers grown by low energy plasma enhanced chemical
Bent crystals as a tool for manipulation of ultra-relativistic electron beams. Institut fur Kernphysik, Johannes Gutenberg Universitat Mainz, Germany
 Bent crystals as a tool for manipulation of ultra-relativistic electron beams 1 INFN Sezione di Ferrara via Saragat 1 44122 Ferrara, Italy E-mail: laura.bandiera@cern.ch E. Bagli, G. Germogli, V. Guidi,
Bent crystals as a tool for manipulation of ultra-relativistic electron beams 1 INFN Sezione di Ferrara via Saragat 1 44122 Ferrara, Italy E-mail: laura.bandiera@cern.ch E. Bagli, G. Germogli, V. Guidi,
JLab Nov. 1. R. Avakian
 JLab Nov. 1 R. Avakian Coherent radiation in Crystalls 1. Coherent Bremsstrahlung (CBS) 2. Parametric X-ray Radiation 3. Channeling Radiation (ChR) 4. String Of Strings (SOS) Different types of radiations
JLab Nov. 1 R. Avakian Coherent radiation in Crystalls 1. Coherent Bremsstrahlung (CBS) 2. Parametric X-ray Radiation 3. Channeling Radiation (ChR) 4. String Of Strings (SOS) Different types of radiations
ADVANCED PHOTON SOURCES AND THEIR APPLICATIONS
 ADVANCED PHOTON SOURCES AND THEIR APPLICATIONS JLab Oct 29 R. Avakian R.H. Avakian Yerevan Physics Institute & Stanford Linear Accelerator Center NATO ADVANCED WORKSHOP Advanced Photon Sources And Their
ADVANCED PHOTON SOURCES AND THEIR APPLICATIONS JLab Oct 29 R. Avakian R.H. Avakian Yerevan Physics Institute & Stanford Linear Accelerator Center NATO ADVANCED WORKSHOP Advanced Photon Sources And Their
Studies of Nanotube Channeling for. Efficient Beam Scraping at Accelerators
 Studies of Nanotube Channeling for Efficient Beam Scraping at Accelerators V.M. Biryukov 1,, S. Bellucci 2 1 Institute for High Energy Physics, Pobedy 1, Protvino, RU-142281, Russia 2 INFN - Laboratori
Studies of Nanotube Channeling for Efficient Beam Scraping at Accelerators V.M. Biryukov 1,, S. Bellucci 2 1 Institute for High Energy Physics, Pobedy 1, Protvino, RU-142281, Russia 2 INFN - Laboratori
Baryshevsky V., Gurinovich A., Gurnevich E., Lobko A.
 Baryshevsky V., Gurinovich A., Gurnevich E., Lobko A. Research Institute for Nuclear Problems Minsk Belarus INP In the Executive Summary of the first International Workshop Physics for Health in Europe
Baryshevsky V., Gurinovich A., Gurnevich E., Lobko A. Research Institute for Nuclear Problems Minsk Belarus INP In the Executive Summary of the first International Workshop Physics for Health in Europe
A Study of RHIC Crystal Collimation
 A Study of RHIC Crystal Collimation arxiv:hep-ex/0111021v1 7 Nov 2001 D.Trbojevic, BNL, USA, V.Biryukov, IHEP, Protvino, Russia, M.Harrison, B.Parker, P.Thompson, and A. Stevens, BNL, USA, N.Mokhov and
A Study of RHIC Crystal Collimation arxiv:hep-ex/0111021v1 7 Nov 2001 D.Trbojevic, BNL, USA, V.Biryukov, IHEP, Protvino, Russia, M.Harrison, B.Parker, P.Thompson, and A. Stevens, BNL, USA, N.Mokhov and
The limits of volume reflection in bent crystals
 The limits of volume reflection in bent crystals V.M. Biryukov Institute for High Energy Physics, Protvino, 142281, Russia Abstract We show that theory predictions for volume reflection in bent crystals
The limits of volume reflection in bent crystals V.M. Biryukov Institute for High Energy Physics, Protvino, 142281, Russia Abstract We show that theory predictions for volume reflection in bent crystals
Single and Multiple Volume Reflections of Ultra-Relativistic Electrons in a Bent Crystal as Tools for Intense Production of Electromagnetic Radiation
 Single and Multiple Volume Reflections of Ultra-Relativistic Electrons in a Bent Crystal as Tools for Intense Production of Electromagnetic Radiation L Bandiera 1,2, A Mazzolari 1,2*, E Bagli 1,2, A Berra
Single and Multiple Volume Reflections of Ultra-Relativistic Electrons in a Bent Crystal as Tools for Intense Production of Electromagnetic Radiation L Bandiera 1,2, A Mazzolari 1,2*, E Bagli 1,2, A Berra
1,0 0,8. Coefficient 0,6 0,4 0,2
 UA9: Crystal Collimation Experiment at CERN S.B. Dabagov (Resp. Loc.), A. Babaev (Osp.), O. Bogdanov (Postdoc), G. Claps (Bors.), A. Dik (Bors.), E. Frolov (Bors.), D. Hampai (art. 23), F. Murtas Participant
UA9: Crystal Collimation Experiment at CERN S.B. Dabagov (Resp. Loc.), A. Babaev (Osp.), O. Bogdanov (Postdoc), G. Claps (Bors.), A. Dik (Bors.), E. Frolov (Bors.), D. Hampai (art. 23), F. Murtas Participant
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH Status for 2017, CERN NA63 6. June 2017 U.I. Uggerhøj, T.N. Wistisen 1) Department of Physics and Astronomy, Aarhus University, Denmark NA63 Abstract In the NA63
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH Status for 2017, CERN NA63 6. June 2017 U.I. Uggerhøj, T.N. Wistisen 1) Department of Physics and Astronomy, Aarhus University, Denmark NA63 Abstract In the NA63
V.G. Baryshevsky. Institute for Nuclear Problems, Belarusian State University, Minsk, Belarus
 The phenomena of spin rotation and depolarization of highenergy particles in bent and straight crystals at Large Hadron Collider (LHC) and Future Circular Collider (FCC) energies and the possibility to
The phenomena of spin rotation and depolarization of highenergy particles in bent and straight crystals at Large Hadron Collider (LHC) and Future Circular Collider (FCC) energies and the possibility to
CHANNELING 2014 CHARGED & NEUTRAL PARTICLES CHANNELING PHENOMENA, Capri (Napoli), Italy, October 5-10, 2014
 CHANNELING 2014 CHARGED & NEUTRAL PARTICLES CHANNELING PHENOMENA, Capri (Napoli), Italy, October 5-10, 2014 Spontaneous and Induced Radiation of Relativistic Electrons/Positrons in Natural and Photonic
CHANNELING 2014 CHARGED & NEUTRAL PARTICLES CHANNELING PHENOMENA, Capri (Napoli), Italy, October 5-10, 2014 Spontaneous and Induced Radiation of Relativistic Electrons/Positrons in Natural and Photonic
Theoretical Analysis of Orientation Distribution Function Reconstruction of Textured Polycrystal by Parametric X-rays
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Theoretical Analysis of Orientation Distribution Function Reconstruction of Textured Polycrystal by Parametric X-rays Related content - Possibilities
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Theoretical Analysis of Orientation Distribution Function Reconstruction of Textured Polycrystal by Parametric X-rays Related content - Possibilities
Status and Results of the UA9 Crystal Collimation Experiment at the CERN-SPS
 HB2012 - Beijing - 18 September 2012 Status and Results of the UA9 Crystal Collimation Experiment at the CERN-SPS Simone Montesano (CERN) for the UA9 collaboration Silicon strip crystal Outline Crystal
HB2012 - Beijing - 18 September 2012 Status and Results of the UA9 Crystal Collimation Experiment at the CERN-SPS Simone Montesano (CERN) for the UA9 collaboration Silicon strip crystal Outline Crystal
arxiv: v1 [physics.acc-ph] 10 Nov 2015
![arxiv: v1 [physics.acc-ph] 10 Nov 2015 arxiv: v1 [physics.acc-ph] 10 Nov 2015](/thumbs/88/116910375.jpg) arxiv:1511.03175v1 [physics.acc-ph] 10 Nov 2015 Relaxation of axially confined 400 GeV/c protons to planar channeling in a bent crystal L. Bandiera 1, A. Mazzolari 1, E. Bagli 1, G. Germogli 1, V. Guidi
arxiv:1511.03175v1 [physics.acc-ph] 10 Nov 2015 Relaxation of axially confined 400 GeV/c protons to planar channeling in a bent crystal L. Bandiera 1, A. Mazzolari 1, E. Bagli 1, G. Germogli 1, V. Guidi
Determination of parameters of cascade showers in the water calorimeter using 3D-distribution of Cherenkov light
 in the water calorimeter using 3D-distribution of Cherenkov light 1, A.G. Bogdanov, S.S. Khokhlov, V.A. Khomyakov, V.V. Kindin, A.A. Petrukhin, V.V. Shutenko, I.I. Yashin National Research Nuclear University
in the water calorimeter using 3D-distribution of Cherenkov light 1, A.G. Bogdanov, S.S. Khokhlov, V.A. Khomyakov, V.V. Kindin, A.A. Petrukhin, V.V. Shutenko, I.I. Yashin National Research Nuclear University
Experiments on deflection of charged particles using silicon crystals at. Proton Synchrotron (KEK(
 Experiments on deflection of charged particles using silicon crystals at REFER ring (Hiroshima( University) and Proton Synchrotron (KEK( KEK) S. Sawada KEK High Energy Accelerator Research Organization
Experiments on deflection of charged particles using silicon crystals at REFER ring (Hiroshima( University) and Proton Synchrotron (KEK( KEK) S. Sawada KEK High Energy Accelerator Research Organization
LASER-COMPTON SCATTERING AS A POTENTIAL BRIGHT X-RAY SOURCE
 Copyright(C)JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data 2003, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Vol.46 74 ISSN 1097-0002 LASER-COMPTON SCATTERING AS A POTENTIAL BRIGHT X-RAY SOURCE K. Chouffani 1, D. Wells
Copyright(C)JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data 2003, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Vol.46 74 ISSN 1097-0002 LASER-COMPTON SCATTERING AS A POTENTIAL BRIGHT X-RAY SOURCE K. Chouffani 1, D. Wells
Geant4 simulations of the lead fluoride calorimeter
 Geant4 simulations of the lead fluoride calorimeter A.A. Savchenko a, *, A.A. Tishchenko a, S.B. Dabagov a,b, A. Anastasi b,c, G. Venanzoni b, M.N. Strikhanov a (et al.) a National Research Nuclear University
Geant4 simulations of the lead fluoride calorimeter A.A. Savchenko a, *, A.A. Tishchenko a, S.B. Dabagov a,b, A. Anastasi b,c, G. Venanzoni b, M.N. Strikhanov a (et al.) a National Research Nuclear University
Particle Refraction, Reflection and Channeling by Laser Beams
 Particle Refraction, Reflection and Channeling by Laser Beams X. Artru 1), K.A. Ispirian 2)* and M.K. Ispiryan 3) 1) Institut de Physique Nucleare de Lyon, CNRS/IN2P3 and Universite Claude-Bernard Lyon-1
Particle Refraction, Reflection and Channeling by Laser Beams X. Artru 1), K.A. Ispirian 2)* and M.K. Ispiryan 3) 1) Institut de Physique Nucleare de Lyon, CNRS/IN2P3 and Universite Claude-Bernard Lyon-1
188 L. Jakubowski and M.J. Sadowski temperature. Some examples of the registered X-ray images are shown in Fig.1. Figure 1. X-ray pinhole images from
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 32, no. 1, March, 2002 187 Hot-Spots in Plasma-Focus Discharges as Intense Sources of Different Radiation Pulses L. Jakubowski and M.J. Sadowski The Andrzej Soltan Institute
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 32, no. 1, March, 2002 187 Hot-Spots in Plasma-Focus Discharges as Intense Sources of Different Radiation Pulses L. Jakubowski and M.J. Sadowski The Andrzej Soltan Institute
Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility
 2 nd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with Intense Laser and Heavy Ion Beams, May 14-15, Moscow Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility S.A. Pikuz Jr., I.Yu. Skobelev, A.Ya. Faenov, T.A.
2 nd EMMI Workshop on Plasma Physics with Intense Laser and Heavy Ion Beams, May 14-15, Moscow Investigations on warm dense plasma with PHELIX facility S.A. Pikuz Jr., I.Yu. Skobelev, A.Ya. Faenov, T.A.
Silver Thin Film Characterization
 Silver Thin Film Characterization.1 Introduction Thin films of Ag layered structures, typically less than a micron in thickness, are tailored to achieve desired functional properties. Typical characterization
Silver Thin Film Characterization.1 Introduction Thin films of Ag layered structures, typically less than a micron in thickness, are tailored to achieve desired functional properties. Typical characterization
Highenergy Nuclear Optics of Polarized Particles
 Highenergy Nuclear Optics of Polarized Particles Vladimir G. Baryshevsky Research Institute for Nuclear Problems Belarusian State University 1> World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI
Highenergy Nuclear Optics of Polarized Particles Vladimir G. Baryshevsky Research Institute for Nuclear Problems Belarusian State University 1> World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI
BREMSSTRAHLUNG IN A THIN LAYER OF MATTER AT HIGH ENERGY
 BREMSSTRAHLUNG IN A THIN LAYER OF MATTER AT HIGH ENERGY S.P. Fomin, A.S. Fomin, N.F. Shul ga Akhiezer Institute for Theoretical Physics National Science Center Kharkov Institute of Physics & Technology
BREMSSTRAHLUNG IN A THIN LAYER OF MATTER AT HIGH ENERGY S.P. Fomin, A.S. Fomin, N.F. Shul ga Akhiezer Institute for Theoretical Physics National Science Center Kharkov Institute of Physics & Technology
Crystal Channeling Radiation and Volume Reflection Experiments at SLAC
 Crystal Channeling Radiation and Volume Reflection Experiments at SLAC Robert Noble, Andrei Seryi, Jim Spencer, Gennady Stupakov SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Talk originally given at 4 th Crystal
Crystal Channeling Radiation and Volume Reflection Experiments at SLAC Robert Noble, Andrei Seryi, Jim Spencer, Gennady Stupakov SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Talk originally given at 4 th Crystal
NEGATIVE PARTICLE PLANAR AND AXIAL CHANNELING AND CHANNELING COLLIMATION
 NEGATIVE PARTICLE PLANAR AND AXIAL CHANNELING AND CHANNELING COLLIMATION RICHARD A. CARRIGAN, JR. Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory *, Batavia, IL 60510, USA While information exists on high energy
NEGATIVE PARTICLE PLANAR AND AXIAL CHANNELING AND CHANNELING COLLIMATION RICHARD A. CARRIGAN, JR. Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory *, Batavia, IL 60510, USA While information exists on high energy
On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination of the air-fluorescence yield
 arxiv:1207.2913v1 [astro-ph.im] 12 Jul 2012 On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination of the air-fluorescence yield J. Rosado, P. Gallego, D. García-Pinto, F. Blanco and
arxiv:1207.2913v1 [astro-ph.im] 12 Jul 2012 On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination of the air-fluorescence yield J. Rosado, P. Gallego, D. García-Pinto, F. Blanco and
X-Ray Radiation Channeling through Micro-Channel Plates: spectroscopy with a Synchrotron Radiation Beam
 X-Ray Radiation Channeling through Micro-Channel Plates: spectroscopy with a Synchrotron Radiation Beam M.I. Mazuritskiy a, S.B. Dabagov b,c, A. Marcelli b, K. Dziedzic-Kocurek d and A.M. Lerer a a Southern
X-Ray Radiation Channeling through Micro-Channel Plates: spectroscopy with a Synchrotron Radiation Beam M.I. Mazuritskiy a, S.B. Dabagov b,c, A. Marcelli b, K. Dziedzic-Kocurek d and A.M. Lerer a a Southern
arxiv: v1 [physics.acc-ph] 29 Nov 2014
![arxiv: v1 [physics.acc-ph] 29 Nov 2014 arxiv: v1 [physics.acc-ph] 29 Nov 2014](/thumbs/81/84321120.jpg) CRYSTAL Simulation Code and New Coherent Effects in Bent Crystal at the LHC A. I. Sytov, V. V. Tikhomirov arxiv:1412.0110v1 [physics.acc-ph] 29 Nov 2014 Research Institute for Nuclear Problems, Bobruiskaya
CRYSTAL Simulation Code and New Coherent Effects in Bent Crystal at the LHC A. I. Sytov, V. V. Tikhomirov arxiv:1412.0110v1 [physics.acc-ph] 29 Nov 2014 Research Institute for Nuclear Problems, Bobruiskaya
ON THE DISCOVERY OF COHERENT BREMSSTRAHLUNG IN A SINGLE CRYSTAL AT THE FRASCATI NATIONAL LABORATORIES
 ON THE DISCOVERY OF COHERENT BREMSSTRAHLUNG IN A SINGLE CRYSTAL AT THE FRASCATI NATIONAL LABORATORIES G. BARBIELLINIl, G.P. MURTAS2, AND S.B. DABAGOV 2 3 /) University o/trieste, Via Valerio 2, 34127 Trieste,
ON THE DISCOVERY OF COHERENT BREMSSTRAHLUNG IN A SINGLE CRYSTAL AT THE FRASCATI NATIONAL LABORATORIES G. BARBIELLINIl, G.P. MURTAS2, AND S.B. DABAGOV 2 3 /) University o/trieste, Via Valerio 2, 34127 Trieste,
Exercise 1 Atomic line spectra 1/9
 Exercise 1 Atomic line spectra 1/9 The energy-level scheme for the hypothetical one-electron element Juliettium is shown in the figure on the left. The potential energy is taken to be zero for an electron
Exercise 1 Atomic line spectra 1/9 The energy-level scheme for the hypothetical one-electron element Juliettium is shown in the figure on the left. The potential energy is taken to be zero for an electron
Channeling of high-energy particles in a multi-wall nanotube
 Physics Letters B 608 (005) 53 58 www.elsevier.com/locate/physletb Channeling of high-energy particles in a multi-wall nanotube S. Bellucci a,v.m.biryukov b,a.cordelli a a INFN, Laboratori Nazionali di
Physics Letters B 608 (005) 53 58 www.elsevier.com/locate/physletb Channeling of high-energy particles in a multi-wall nanotube S. Bellucci a,v.m.biryukov b,a.cordelli a a INFN, Laboratori Nazionali di
Transition radiation and di raction radiation. Similarities and di erences
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 145 (1998) 169±179 Transition radiation and di raction radiation. Similarities and di erences A.P. Potylitsyn 1 Institute for Nuclear Physics, Tomsk
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 145 (1998) 169±179 Transition radiation and di raction radiation. Similarities and di erences A.P. Potylitsyn 1 Institute for Nuclear Physics, Tomsk
A New Non Intercepting Beam Size Diagnostics Using Diffraction Radiation from a Slit
 L A B O R A T O R I N A Z I O N A L I D I F R A S C A T I SIS Pubblicazioni LNF 96/04 (P) 3 Settembre 1996 A New Non Intercepting Beam Size Diagnostics Using Diffraction Radiation from a Slit M. Castellano
L A B O R A T O R I N A Z I O N A L I D I F R A S C A T I SIS Pubblicazioni LNF 96/04 (P) 3 Settembre 1996 A New Non Intercepting Beam Size Diagnostics Using Diffraction Radiation from a Slit M. Castellano
Channeling of high-energy particles in bent crystals ± Experiments at the CERN SPS
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 164±165 (2000) 27±43 www.elsevier.nl/locate/nimb Channeling of high-energy particles in bent crystals ± Experiments at the CERN SPS A. Baurichter a,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 164±165 (2000) 27±43 www.elsevier.nl/locate/nimb Channeling of high-energy particles in bent crystals ± Experiments at the CERN SPS A. Baurichter a,
on basis of the Geant4 simulations
 Optimization of BaF 2 PAL-spectrometer geometry on basis of the Geant4 simulations L.Yu. Dubov 2, V.I. Grafutin 1, Yu.V. Funtikov 1, Yu.V. Shtotsky 2, L.V. Elnikova 1 1 FSBI RF SSC Institute for Theoretical
Optimization of BaF 2 PAL-spectrometer geometry on basis of the Geant4 simulations L.Yu. Dubov 2, V.I. Grafutin 1, Yu.V. Funtikov 1, Yu.V. Shtotsky 2, L.V. Elnikova 1 1 FSBI RF SSC Institute for Theoretical
and another with a peak frequency ω 2
 Physics Qualifying Examination Part I 7-Minute Questions September 13, 2014 1. A sealed container is divided into two volumes by a moveable piston. There are N A molecules on one side and N B molecules
Physics Qualifying Examination Part I 7-Minute Questions September 13, 2014 1. A sealed container is divided into two volumes by a moveable piston. There are N A molecules on one side and N B molecules
Thin Calorimetry for Cosmic-Ray Studies Outside the Earth s Atmosphere. 1 Introduction
 Thin Calorimetry for Cosmic-Ray Studies Outside the Earth s Atmosphere Richard WIGMANS Department of Physics, Texas Tech University, Lubbock TX 79409-1051, USA (wigmans@ttu.edu) Abstract Cosmic ray experiments
Thin Calorimetry for Cosmic-Ray Studies Outside the Earth s Atmosphere Richard WIGMANS Department of Physics, Texas Tech University, Lubbock TX 79409-1051, USA (wigmans@ttu.edu) Abstract Cosmic ray experiments
A Crystal Routine for Collimation Studies in Circular Proton Accelerators
 A Crystal Routine for Collimation Studies in Circular Proton Accelerators D. Mirarchi a,b, G. Hall b, S. Redaelli a, W. Scandale a a CER, European Organization for uclear Research, CH-2 Geneva 2, Switzerland
A Crystal Routine for Collimation Studies in Circular Proton Accelerators D. Mirarchi a,b, G. Hall b, S. Redaelli a, W. Scandale a a CER, European Organization for uclear Research, CH-2 Geneva 2, Switzerland
Particles and Waves Particles Waves
 Particles and Waves Particles Discrete and occupy space Exist in only one location at a time Position and velocity can be determined with infinite accuracy Interact by collisions, scattering. Waves Extended,
Particles and Waves Particles Discrete and occupy space Exist in only one location at a time Position and velocity can be determined with infinite accuracy Interact by collisions, scattering. Waves Extended,
Quantitative Assessment of Scattering Contributions in MeV-Industrial X-ray Computed Tomography
 11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=16530 Quantitative Assessment of Scattering
11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=16530 Quantitative Assessment of Scattering
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION AT THE ONSET OF THE QUANTUM REGIME
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION AT THE ONSET OF THE QUANTUM REGIME DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY, AARHUS UNIVERSITY MOTIVATION Test of quantum mechanical calculations of synchrotron
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION AT THE ONSET OF THE QUANTUM REGIME DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY, AARHUS UNIVERSITY MOTIVATION Test of quantum mechanical calculations of synchrotron
CRYM: a channeling emulation program based on the latest experimental data
 CRYM: a channeling emulation program based on the latest experimental data Said Hasan Università degli studi dell Insubria INFN Milano Bicocca Channeling 2008 Erice Summary CRYM stands for Crystal Model
CRYM: a channeling emulation program based on the latest experimental data Said Hasan Università degli studi dell Insubria INFN Milano Bicocca Channeling 2008 Erice Summary CRYM stands for Crystal Model
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH Status for 018, CERN NA63 May 30th 018 C.F. Nielsen and U.I. Uggerhøj Department of Physics and Astronomy, Aarhus University, Denmark T.N. Wistisen and A. Di
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH Status for 018, CERN NA63 May 30th 018 C.F. Nielsen and U.I. Uggerhøj Department of Physics and Astronomy, Aarhus University, Denmark T.N. Wistisen and A. Di
Scattering Lecture. February 24, 2014
 Scattering Lecture February 24, 2014 Structure Determination by Scattering Waves of radiation scattered by different objects interfere to give rise to an observable pattern! The wavelength needs to close
Scattering Lecture February 24, 2014 Structure Determination by Scattering Waves of radiation scattered by different objects interfere to give rise to an observable pattern! The wavelength needs to close
INTRODUCING CHANNELING EFFECT
 INTRODUCING CHANNELING EFFECT Enrico Bagli on the behalf of G4CMP working group Motivation Geant4 is a toolkit for the simulation of the passage of particles through matter. Its areas of application include
INTRODUCING CHANNELING EFFECT Enrico Bagli on the behalf of G4CMP working group Motivation Geant4 is a toolkit for the simulation of the passage of particles through matter. Its areas of application include
M2 TP. Low-Energy Electron Diffraction (LEED)
 M2 TP Low-Energy Electron Diffraction (LEED) Guide for report preparation I. Introduction: Elastic scattering or diffraction of electrons is the standard technique in surface science for obtaining structural
M2 TP Low-Energy Electron Diffraction (LEED) Guide for report preparation I. Introduction: Elastic scattering or diffraction of electrons is the standard technique in surface science for obtaining structural
U n 3 n Ba Kr (D) Br (C) Kr (B) Rb (E) 94 37
 1984 36. The critical angle for a transparent material in air is 30. The index of refraction of the material is most nearly (A) 0.33 (B) 0.50 (C) 1.0 (D) 1.5 (E) 2.0 37. An object is placed as shown in
1984 36. The critical angle for a transparent material in air is 30. The index of refraction of the material is most nearly (A) 0.33 (B) 0.50 (C) 1.0 (D) 1.5 (E) 2.0 37. An object is placed as shown in
SELF-ATTENUATION FACTORS IN GAMMA-RAY SPECTROMETRY M. KORUN * )
 Attenuation M. Korun in gamma-ray spectrometry SELF-ATTENUATION FACTORS IN GAMMA-RAY SPECTROMETRY M. KORUN * ) J. Stefan Institute, Jamova 39, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia * matjaz.korun@ijs.si The relation
Attenuation M. Korun in gamma-ray spectrometry SELF-ATTENUATION FACTORS IN GAMMA-RAY SPECTROMETRY M. KORUN * ) J. Stefan Institute, Jamova 39, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia * matjaz.korun@ijs.si The relation
Feasibility of measuring the magnetic dipole moments of the charm baryons at the LHC using bent crystals
 Feasibility of measuring the magnetic dipole moments of the charm baryons at the LHC using bent crystals Alex Fomin Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire Université Paris-Sud/IN2P3, Orsay, France NSC
Feasibility of measuring the magnetic dipole moments of the charm baryons at the LHC using bent crystals Alex Fomin Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire Université Paris-Sud/IN2P3, Orsay, France NSC
remsstrahlung 1 Bremsstrahlung
 remsstrahlung 1 Bremsstrahlung remsstrahlung 2 Bremsstrahlung A fast moving charged particle is decelerated in the Coulomb field of atoms. A fraction of its kinetic energy is emitted in form of real photons.
remsstrahlung 1 Bremsstrahlung remsstrahlung 2 Bremsstrahlung A fast moving charged particle is decelerated in the Coulomb field of atoms. A fraction of its kinetic energy is emitted in form of real photons.
ANALYSIS OF LUMINESCENCE SPECTRA OF SUBSTRATE-FREE ICOSAHEDRAL AND CRYSTALLINE CLUSTERS OF ARGON
 ANALYSIS OF LUMINESCENCE SPECTRA OF SUBSTRATE-FREE ICOSAHEDRAL AND CRYSTALLINE CLUSTERS OF ARGON Yu.S. Doronin, V.L. Vakula, G.V. Kamarchuk, A.A. Tkachenko, V.N. Samovarov B. Verkin Institute for Low Temperature
ANALYSIS OF LUMINESCENCE SPECTRA OF SUBSTRATE-FREE ICOSAHEDRAL AND CRYSTALLINE CLUSTERS OF ARGON Yu.S. Doronin, V.L. Vakula, G.V. Kamarchuk, A.A. Tkachenko, V.N. Samovarov B. Verkin Institute for Low Temperature
Light ion recoil detector
 Light ion recoil detector Overall design The detector for light (target-like) particles is a substantial part of the R3B setup. It allows registration of recoils in coincidence with the heavy fragments,
Light ion recoil detector Overall design The detector for light (target-like) particles is a substantial part of the R3B setup. It allows registration of recoils in coincidence with the heavy fragments,
Observational Prospects for Quark Nugget Dark Matter
 Observational Prospects for Quark Nugget Dark Matter Kyle Lawson University of British Columbia Partially based on material reviewed in http://arxiv.org/abs/1305.6318 Outline Baryogenesis (matter/antimatter
Observational Prospects for Quark Nugget Dark Matter Kyle Lawson University of British Columbia Partially based on material reviewed in http://arxiv.org/abs/1305.6318 Outline Baryogenesis (matter/antimatter
Interaction of Ionizing Radiation with Matter
 Type of radiation charged particles photonen neutronen Uncharged particles Charged particles electrons (β - ) He 2+ (α), H + (p) D + (d) Recoil nuclides Fission fragments Interaction of ionizing radiation
Type of radiation charged particles photonen neutronen Uncharged particles Charged particles electrons (β - ) He 2+ (α), H + (p) D + (d) Recoil nuclides Fission fragments Interaction of ionizing radiation
Shadowing of the electromagnetic field of a relativistic electron
 Channeling 2008, Erice, 26 oct. 1 nov. Shadowing of the electromagnetic field of a relativistic electron X.Artru 1, G. Naumenko 2, Yu. Popov 3, A. Potylitsyn 3, and L. Sukhikh 3 1 Institut de Physique
Channeling 2008, Erice, 26 oct. 1 nov. Shadowing of the electromagnetic field of a relativistic electron X.Artru 1, G. Naumenko 2, Yu. Popov 3, A. Potylitsyn 3, and L. Sukhikh 3 1 Institut de Physique
PoS(EPS-HEP2017)533. First Physics Results of AWAKE, a Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN. Patric Muggli, Allen Caldwell
 First Physics Results of AWAKE, a Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN Patric Muggli, Max Planck Institute for Physics E-mail: muggli@mpp.mpg.de AWAKE is a plasma wakefield acceleration experiment
First Physics Results of AWAKE, a Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN Patric Muggli, Max Planck Institute for Physics E-mail: muggli@mpp.mpg.de AWAKE is a plasma wakefield acceleration experiment
Physics 126 Practice Exam #4 Professor Siegel
 Physics 126 Practice Exam #4 Professor Siegel Name: Lab Day: 1. Light is usually thought of as wave-like in nature and electrons as particle-like. In which one of the following instances does light behave
Physics 126 Practice Exam #4 Professor Siegel Name: Lab Day: 1. Light is usually thought of as wave-like in nature and electrons as particle-like. In which one of the following instances does light behave
General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18
 95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
Preparing for a Crystal Experiment Proposal
 Preparing for a Crystal Experiment Proposal U. Wienands, SLAC Special thanks to S. Mack, U. Ottawa SULI Student 2011. Channeling in Crystals * Discovered in the 60s: Atoms lined up in strings or planes,
Preparing for a Crystal Experiment Proposal U. Wienands, SLAC Special thanks to S. Mack, U. Ottawa SULI Student 2011. Channeling in Crystals * Discovered in the 60s: Atoms lined up in strings or planes,
 Name : Roll No. :.. Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech/SEM-2/PH-201/2010 2010 ENGINEERING PHYSICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are
Name : Roll No. :.. Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech/SEM-2/PH-201/2010 2010 ENGINEERING PHYSICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are
Photonuclear Reactions and Nuclear Transmutation. T. Tajima 1 and H. Ejiri 2
 Draft Photonuclear Reactions and Nuclear Transmutation T. Tajima 1 and H. Ejiri 2 1) Kansai JAERI 2) JASRI/SPring-8, Mikazuki-cho, Sayou-gun, Hyougo, 679-5198 JAPAN Abstract Photonuclear reactions are
Draft Photonuclear Reactions and Nuclear Transmutation T. Tajima 1 and H. Ejiri 2 1) Kansai JAERI 2) JASRI/SPring-8, Mikazuki-cho, Sayou-gun, Hyougo, 679-5198 JAPAN Abstract Photonuclear reactions are
Beam halo formation in high-intensity beams
 Beam halo formation in high-intensity beams Alexei V. Fedotov,1,2 Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973, USA Abstract Studies of beam halo became an unavoidable feature of high-intensity machines
Beam halo formation in high-intensity beams Alexei V. Fedotov,1,2 Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973, USA Abstract Studies of beam halo became an unavoidable feature of high-intensity machines
Surface Sensitivity & Surface Specificity
 Surface Sensitivity & Surface Specificity The problems of sensitivity and detection limits are common to all forms of spectroscopy. In its simplest form, the question of sensitivity boils down to whether
Surface Sensitivity & Surface Specificity The problems of sensitivity and detection limits are common to all forms of spectroscopy. In its simplest form, the question of sensitivity boils down to whether
On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination of the air-fluorescence yield
 EPJ Web of Conferences 53, 10001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20135310001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination
EPJ Web of Conferences 53, 10001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20135310001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 On the energy deposition by electrons in air and the accurate determination
Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na. Ellen Simmons
 Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na Ellen Simmons 1 Contents Introduction Review of the Types of Radiation Charged Particle Radiation Detection Review of Semiconductor
Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na Ellen Simmons 1 Contents Introduction Review of the Types of Radiation Charged Particle Radiation Detection Review of Semiconductor
Interaction theory Photons. Eirik Malinen
 Interaction theory Photons Eirik Malinen Introduction Interaction theory Dosimetry Radiation source Ionizing radiation Atoms Ionizing radiation Matter - Photons - Charged particles - Neutrons Ionizing
Interaction theory Photons Eirik Malinen Introduction Interaction theory Dosimetry Radiation source Ionizing radiation Atoms Ionizing radiation Matter - Photons - Charged particles - Neutrons Ionizing
For the next several lectures, we will be looking at specific photon interactions with matter. In today s lecture, we begin with the photoelectric
 For the next several lectures, we will be looking at specific photon interactions with matter. In today s lecture, we begin with the photoelectric effect. 1 The objectives of today s lecture are to identify
For the next several lectures, we will be looking at specific photon interactions with matter. In today s lecture, we begin with the photoelectric effect. 1 The objectives of today s lecture are to identify
Theory English (Official)
 Q3-1 Large Hadron Collider (10 points) Please read the general instructions in the separate envelope before you start this problem. In this task, the physics of the particle accelerator LHC (Large Hadron
Q3-1 Large Hadron Collider (10 points) Please read the general instructions in the separate envelope before you start this problem. In this task, the physics of the particle accelerator LHC (Large Hadron
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 559
 Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS
 CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS Background Charged Particles Heavy charged particles Charged particles with Mass > m e α, proton, deuteron, heavy ion (e.g., C +, Fe + ), fission fragment, muon, etc. α is
CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS Background Charged Particles Heavy charged particles Charged particles with Mass > m e α, proton, deuteron, heavy ion (e.g., C +, Fe + ), fission fragment, muon, etc. α is
Geant4 simulations of the full-size calorimeter for muon G-2 experiment
 The 7th International Conference "Charged & Neutral Particles Channeling Phenomena Channeling 2016" Our work was performed using resources of NRNU MEPhI highperformance computing center. Geant4 simulations
The 7th International Conference "Charged & Neutral Particles Channeling Phenomena Channeling 2016" Our work was performed using resources of NRNU MEPhI highperformance computing center. Geant4 simulations
Radiation and the Atom
 Radiation and the Atom PHYS Lecture Departamento de Física Instituto Superior de Engenharia do Porto cav@isep.ipp.pt Overview SI Units and Prefixes Radiation Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum
Radiation and the Atom PHYS Lecture Departamento de Física Instituto Superior de Engenharia do Porto cav@isep.ipp.pt Overview SI Units and Prefixes Radiation Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW POSITRON LIFETIME SPECTROSCOPY TECHNIQUE FOR DEFECT CHARACTERIZATION IN THICK MATERIALS
 Copyright JCPDS - International Centre for Diffraction Data 2004, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 47. 59 DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW POSITRON LIFETIME SPECTROSCOPY TECHNIQUE FOR DEFECT CHARACTERIZATION IN
Copyright JCPDS - International Centre for Diffraction Data 2004, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 47. 59 DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW POSITRON LIFETIME SPECTROSCOPY TECHNIQUE FOR DEFECT CHARACTERIZATION IN
PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM. Student Number. The last two pages of the exam have some equations and some physical constants.
 PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Name Student Number CHECK ONE: Instructor 1 10:00 Instructor 2 1:00 Note that problems 1-19 are worth 2 points each, while problem 20 is worth 15 points and problems 21 and
PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Name Student Number CHECK ONE: Instructor 1 10:00 Instructor 2 1:00 Note that problems 1-19 are worth 2 points each, while problem 20 is worth 15 points and problems 21 and
III. Energy Deposition in the Detector and Spectrum Formation
 1 III. Energy Deposition in the Detector and Spectrum Formation a) charged particles Bethe-Bloch formula de 4πq 4 z2 e 2m v = NZ ( ) dx m v ln ln 1 0 2 β β I 0 2 2 2 z, v: atomic number and velocity of
1 III. Energy Deposition in the Detector and Spectrum Formation a) charged particles Bethe-Bloch formula de 4πq 4 z2 e 2m v = NZ ( ) dx m v ln ln 1 0 2 β β I 0 2 2 2 z, v: atomic number and velocity of
is the minimum stopping potential for which the current between the plates reduces to zero.
 Module 1 :Quantum Mechanics Chapter 2 : Introduction to Quantum ideas Introduction to Quantum ideas We will now consider some experiments and their implications, which introduce us to quantum ideas. The
Module 1 :Quantum Mechanics Chapter 2 : Introduction to Quantum ideas Introduction to Quantum ideas We will now consider some experiments and their implications, which introduce us to quantum ideas. The
 Electromagnetic Waves Properties. The electric and the magnetic field, associated with an electromagnetic wave, propagating along the z=axis. Can be represented by E = E kˆ, = iˆ E = E ˆj, = ˆj b) E =
Electromagnetic Waves Properties. The electric and the magnetic field, associated with an electromagnetic wave, propagating along the z=axis. Can be represented by E = E kˆ, = iˆ E = E ˆj, = ˆj b) E =
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.acc-ph] 16 Mar 2004
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.acc-ph] 16 Mar 2004 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.acc-ph] 16 Mar 2004](/thumbs/77/75798433.jpg) arxiv:physics/0403082v1 [physics.acc-ph] 16 Mar 2004 Channeling of Positrons through Periodically Bent Crystals: on Feasibility of Crystalline Undulator and Gamma-Laser 1. Introduction A. V. Korol, A.
arxiv:physics/0403082v1 [physics.acc-ph] 16 Mar 2004 Channeling of Positrons through Periodically Bent Crystals: on Feasibility of Crystalline Undulator and Gamma-Laser 1. Introduction A. V. Korol, A.
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
Cauchois Johansson x-ray spectrograph for kev energy range
 REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS VOLUME 72, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 2001 Cauchois Johansson x-ray spectrograph for 1.5 400 kev energy range E. O. Baronova a) and M. M. Stepanenko RRC Kurchatov Institute, 123182,
REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS VOLUME 72, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 2001 Cauchois Johansson x-ray spectrograph for 1.5 400 kev energy range E. O. Baronova a) and M. M. Stepanenko RRC Kurchatov Institute, 123182,
SSRL XAS Beam Lines Soft X-ray
 SSRL SMB Summer School July 20, 2010 SSRL XAS Beam Lines Soft X-ray Thomas Rabedeau SSRL Beam Line Development Objective/Scope Objective - develop a better understanding of the capabilities and limitations
SSRL SMB Summer School July 20, 2010 SSRL XAS Beam Lines Soft X-ray Thomas Rabedeau SSRL Beam Line Development Objective/Scope Objective - develop a better understanding of the capabilities and limitations
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 23 Mar 2015
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 23 Mar 2015 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 23 Mar 2015](/thumbs/88/115933437.jpg) Bremsstrahlung from relativistic heavy ions in a fixed target experiment at the LHC arxiv:1503.06621v1 [nucl-ex] 23 Mar 2015 Abstract Rune E. Mikkelsen, Allan H. Sørensen, Ulrik I. Uggerhøj Department
Bremsstrahlung from relativistic heavy ions in a fixed target experiment at the LHC arxiv:1503.06621v1 [nucl-ex] 23 Mar 2015 Abstract Rune E. Mikkelsen, Allan H. Sørensen, Ulrik I. Uggerhøj Department
2. Passage of Radiation Through Matter
 2. Passage of Radiation Through Matter Passage of Radiation Through Matter: Contents Energy Loss of Heavy Charged Particles by Atomic Collision (addendum) Cherenkov Radiation Energy loss of Electrons and
2. Passage of Radiation Through Matter Passage of Radiation Through Matter: Contents Energy Loss of Heavy Charged Particles by Atomic Collision (addendum) Cherenkov Radiation Energy loss of Electrons and
X-ray imaging with parametric X-rays (PXR) from a lithium fluoride (LiF) crystal
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 560 (2006) 589 597 www.elsevier.com/locate/nima X-ray imaging with parametric X-rays (PXR) from a lithium fluoride (LiF) crystal B. Sones, Y. Danon,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 560 (2006) 589 597 www.elsevier.com/locate/nima X-ray imaging with parametric X-rays (PXR) from a lithium fluoride (LiF) crystal B. Sones, Y. Danon,
The ELTEST Experiment
 The ELTEST Experiment R. Pozzoli, M. Cavenago, F. De Luca, M. De Poli, V. Petrillo, M. Romè, L. Serafini, G. Bettega, and A. Illiberi INFN Sezione di Milano and Dipartimento di Fisica Università di Milano
The ELTEST Experiment R. Pozzoli, M. Cavenago, F. De Luca, M. De Poli, V. Petrillo, M. Romè, L. Serafini, G. Bettega, and A. Illiberi INFN Sezione di Milano and Dipartimento di Fisica Università di Milano
A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Passage of particles through matter
 Passage of particles through matter Alexander Khanov PHYS6260: Experimental Methods is HEP Oklahoma State University September 11, 2017 Delta rays During ionization, the energy is transferred to electrons
Passage of particles through matter Alexander Khanov PHYS6260: Experimental Methods is HEP Oklahoma State University September 11, 2017 Delta rays During ionization, the energy is transferred to electrons
Advantages of axially aligned crystals used in positron production at future linear colliders
 PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS, VOLUME 6, 091003 (2003) Advantages of axially aligned crystals used in positron production at future linear colliders X. Artru, 1 R. Chehab, 2 M.
PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS, VOLUME 6, 091003 (2003) Advantages of axially aligned crystals used in positron production at future linear colliders X. Artru, 1 R. Chehab, 2 M.
DEFLECTION OF PROTON BEAMS BY CRYSTAL MISCUT SURFACE
 ISTITUTO NAZIONALE DI FISICA NUCLEARE LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI FRASCATI INFN-14-05/LNF 5 th March 014 DEFLECTION OF PROTON BEAMS BY CRYSTAL MISCUT SURFACE A.A. Babaev 1,, and S.B. Dabagov 3,4 1 INFN Sezione
ISTITUTO NAZIONALE DI FISICA NUCLEARE LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI FRASCATI INFN-14-05/LNF 5 th March 014 DEFLECTION OF PROTON BEAMS BY CRYSTAL MISCUT SURFACE A.A. Babaev 1,, and S.B. Dabagov 3,4 1 INFN Sezione
Technical University of Denmark
 Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
Transmission Electron Microscopy
 L. Reimer H. Kohl Transmission Electron Microscopy Physics of Image Formation Fifth Edition el Springer Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Transmission Electron Microscopy... 1 1.1.1 Conventional Transmission
L. Reimer H. Kohl Transmission Electron Microscopy Physics of Image Formation Fifth Edition el Springer Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Transmission Electron Microscopy... 1 1.1.1 Conventional Transmission
APEX CARE INSTITUTE FOR PG - TRB, SLET AND NET IN PHYSICS
 Page 1 1. Within the nucleus, the charge distribution A) Is constant, but falls to zero sharply at the nuclear radius B) Increases linearly from the centre, but falls off exponentially at the surface C)
Page 1 1. Within the nucleus, the charge distribution A) Is constant, but falls to zero sharply at the nuclear radius B) Increases linearly from the centre, but falls off exponentially at the surface C)
What the radio signal tells about the cosmic-ray air shower
 EPJ Web of Conferences 3, 0800 (03) DOI:./epjconf/0330800 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 03 What the radio signal tells about the cosmic-ray air shower Olaf Scholten,a, Krijn D. de
EPJ Web of Conferences 3, 0800 (03) DOI:./epjconf/0330800 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 03 What the radio signal tells about the cosmic-ray air shower Olaf Scholten,a, Krijn D. de
PARTICLE ACCELERATORS
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE PARTICLE ACCELERATORS Particle accelerators are used to accelerate elementary particles to very high energies for: Production of radioisotopes Probing the structure of matter There
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE PARTICLE ACCELERATORS Particle accelerators are used to accelerate elementary particles to very high energies for: Production of radioisotopes Probing the structure of matter There
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION I-2 MEDICAL IMAGING Reading Activity Answers IB Assessment Statements Option I-2, Medical Imaging: X-Rays I.2.1. I.2.2. I.2.3. Define
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION I-2 MEDICAL IMAGING Reading Activity Answers IB Assessment Statements Option I-2, Medical Imaging: X-Rays I.2.1. I.2.2. I.2.3. Define
CHANNELING IN DIRECT DARK MATTER DETECTION
 CHANNELING IN DIRECT DARK MATTER DETECTION Nassim Bozorgnia UCLA Based on work in progress with G. Gelmini and P. Gondolo SNOWPAC 2010 Outline Channeling and blocking in crystals Channeling effect in direct
CHANNELING IN DIRECT DARK MATTER DETECTION Nassim Bozorgnia UCLA Based on work in progress with G. Gelmini and P. Gondolo SNOWPAC 2010 Outline Channeling and blocking in crystals Channeling effect in direct
