Probability Theory. Alea iacta est!
|
|
|
- Jodie Berry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Probability Theory Alea iacta est!
2 "Scientific theories which involve the properties of large aggregates of individuals [...] are liable to misinterpretation as soon as the statistical nature of the argument is lost sight of. " Ronald Aylmer Fisher ( )
3 An event is said to occur at random if its outcome is variable and unpredictable.
4 The classical interpretation The probability of an event is the ratio of the favourable outcomes to the possible outcomes. Pierre-Simon Laplace ( ) Example: A die is thrown with the result that "the count is five". There are six possible outcomes with only one being favourable. Thus, the probability of "the count is five" is one sixth.
5 The frequency interpretation The probability of an event in a sequence of events is the limit of the relative frequency of that event. John Venn ( ) Example: Throw a die several times and record the counts. The relative frequency of "the count is five" is about one sixth. The limit of the relative frequency is exactly one sixth.
6 The subjective interpretation The probability is a measure of the degree of belief. Frank P. Ramsey ( ) Example: suppose you bet that the score would be five; you bet a dollar and, if you win, you will receive six dollars: this is a fair bet.
7 The axiomatic interpretation The probability is whatever fulfils the axioms of the theory of probability. Andrei N. Kolmogorov ( )
8
9 Kolmogorov's Probability Calculus Let Ω be a non-empty set and let be a family of subsets of Ω that has Ω as a member, and that is closed under complementation (with respect to Ω) and union. Let P be a function from to the real numbers that fulfils 1. Non-negativity P(A) 0 for all A 2. Normalization P(Ω) = 1 3. Additivity P(A 1 A 2...) = P(A 1 )+P(A 2 )+... for all A 1, A 2,... with A i A j = Ø P is called a 'probability' and (Ω,, P) is called a 'probability space'. Foundations of the Theory of Probability (1933)
10 Game of Dice P=6/6 P=4/6 P=2/6 {1,2,3,4,5,6} Ω {1,2,3,4} {1,2,3,5} {1,2,3,6} {1,2,4,5} {1,2,4,6} {1,2,5,6} {1,3,4,5} {1,3,4,6} {1,3,5,6} {1,4,5,6} {2,3,4,5} {2,3,4,6} {2,3,5,6} {2,4,5,6} {3,4,5,6} {1,2} {1,3} {1,4} {1,5} {1,6} {2,3} {2,4} {2,5} {2,6} {3,4} {3,5} {3,6} {4,5} {4,6} {5,6} P=5/6 P=3/6 P=1/6 {1,2,3,4,5} {1,2,3,4,6} {1,2,3,5,6} {1,2,4,5,6} {1,3,4,5,6} {2,3,4,6,5} {1,2,3} {4,5,6} {1,2,4} {3,5,6} {1,2,5} {3,4,6} {1,2,6} {3,4,5} {1,3,4} {2,5,6} {1,3,5} {2,4,6} {1,3,6} {2,4,5} {1,4,5} {2,3,6} {1,4,6} {2,3,5} {1,5,6} {2,3,4} {1} {2} {3} {4} {5} {6} P=0/6 Ø
11 Measure Theoretical View of Probability Ω Ω A B A A C A B: Either event A, or event B, or both occur. A B: Both event A and event B occur simultaneously. A C : The complement, or opposite, of event A occurs. P(A B) = P(A)+P(B)-P(A B) P(A)+P(A C ) = P(A A C ) = P(Ω) = 1 P(A C ) = 1-P(A)
12 Independence of Events Two events A and B are called 'independent' if P(A B) = P(A) P(B)
13 Blood Pressure and Blood Lipids Some 25% of adult US Americans have high blood pressure. (A) Some 20% of adult US Americans have high blood lipid levels. (B) Some 17% of adult US Americans are both hypertensive and hyperlipidemic. (A B) P(A B) = 0.17 > 0.05 = = P(A) P(B)
14 Random Variables... map complex random events from real life onto a simple (most often numerical) scale X: number of times the first five dice show 6 X = 2 a 'realisation' of X
15 Discrete Random Variables X: number of times the first five dice show 6 X = 2 a 'realisation' of X Probability Function of X f(a)=p(x=a) for all possible values a of X
16 Binomial Distribution Bin(n,π) Model: n independent replications of a random experiment with binary outcome ("success","failure") and a constant success probability π in each replication X: number of successes f(k) = P(X = k) = n k π k (1 π) n k n k = n k (n k) = n! k!(n k)! 'binomial coefficient'
17 Coin Tossing n=5, k=3 π (1-π) π (1-π) π=π 3 (1-π) 2 (1-π) π π (1-π) π=π 3 (1-π) In how many different ways can 3 positions be chosen from 5 positions? = 10 = = 5! 3! 2!
18 Effectiveness of Antibiotics An antibiotic is effective in 85% of patients with a particular disease. What is the probability that 8 or more out of 10 patients given the drug will be cured? n=10, π=0.85, k=8, 9 or 10 P(X 8) = f(8) + f(9) + f(10) = = = = 0.820
19 Probability Function 0.4 Bin(10,0.85) 0.3 f(k) k
20 Continuous Random Variables X = 22.5 Distribution Function of X F(b)=P(X b) for real numbers b
21 Distribution Function 1,0 0,8 F(b) 0,6 0,4 0,2 0, b 0 F(b) 1 F(b) is monotonously increasing
22 Continuous Random Variable y b f(x) 'density' x F(b) = b f(x)dx y P(a < X b) = F(b) F(a) a b x
23 Independence of Random Variables Two random variables X and Y are called 'stochastically independent' if P(X a,y b) = P(X a) P(Y b) for any choice of real numbers a and b.
24 Independence of Random Variables Examples Independent X: body height Y: time of consultation X: gender Y: hair colour Not Independent X: body mass index Y: age X: blood pressure Y: blood lipid level
25 Expected Value E(X) The expected value (or expectation or population mean) of a random variable indicates its average or central value. It is a useful summary value of the variable's distribution. discrete continuous E(X) = a P(X = a a) E(X) + = x f(x) dx
26 Game of Dice X: number of points in a single throw E(X) = 1 1 / / / / / / 6 = 3.5 Y: sum of points in two rolls E(Y) = 2 1 / / / / / / / / / / / 36 = 7
27 Law of Large Numbers X 1, X 2,, X n independent and identically distributed with E(X 1 ) =... = E(X n ) = µ X = X n + X n µ when n gets large
28 Game of Dice X i : count of a single throw (i=1,..,n) X : average count of n throws replicates X n=10 n=100 n=500
29 Variance Var(X) The (population) variance of a random variable is a nonnegative number which gives an idea of how widely spread the values of the random variable are likely to be; the larger the variance, the more scattered the observations are on average. Var(X) = E([X-E(X)] 2 ) Var(X) 'standard deviation'
30 Variance Var(X) E(X 1 ) E(X 2 ) Var(X 1 ) < Var(X 2 )
31 Game of Dice X: number of points in a single roll Var(X) = (1-3.5) 2 1 / 6 + (2-3.5) 2 1 / 6 + (3-3.5) 2 1 / 6 + (4-3.5) 2 1 / 6 + (5-3.5) 2 1 / 6 + (6-3.5) 2 1 / 6 = 2.9 Y: sum of points in two rolls Var(Y) = (2-7) 2 1 / 36 + (3-7) 2 2 / 36 + (4-7) 2 3 / 36 + (5-7) 2 4 / 36 + (6-7) 2 5 / 36 + (7-7) 2 6 / 36 +(8-7) 2 5 / 36 + (9-7) 2 4 / 36 + (10-7) 2 3 / 36 + (11-7) 2 2 / 36 + (12-7) 2 1 / 36 = 5.8
32 Some Computational Rules E(X+Y) = E(X) + E(Y) E(α X) = α E(X) Var(α X) = α 2 Var(X) if X and Y are independent E(X Y) = E(X) E(Y) Var(X+Y) = Var(X) + Var(Y)
33 Normal Distribution N(µ,σ 2 ) f(x) = 1 e (x µ) 2 2σ 2 σ 2π µ = E(X), σ 2 = Var(X)
34 Standard Normal Distribution N(0,1) z P(Z z)=φ(z)
35 Standardization of N(µ,σ 2 ) If X has a normal distribution with expected value µ and variance σ 2, then the random variable Z = X µ σ has a standard normal distribution. The distribution function F(b) of X fulfils F(b) = b Φ( µ σ )
36 Blood Pressure If the diastolic blood pressure of healthy individuals has a normal distribution with expected value µ=80 mmhg and standard deviation σ=10 mmhg, what is the probability that a randomly chosen individual has a blood pressure between 70 mmhg and 85 mmhg? P(70 X 85) = F(85) F(70) = = Φ( ) Φ( ) Φ( 0.5) Φ( 1) = =0.5328
37 Standard Normal Distribution N(0,1) P(-1.00 Z +1.00) = 0.68 P(µ-σ X µ+σ) = 0.68
38 Standard Normal Distribution N(0,1) P(Z 0.00) = 0.50= P(Z 0.00) P(X µ) = 0.50 = P(X µ)
39 Standard Normal Distribution N(0,1) P(-1.96 Z +1.96) = 0.95 P(µ-1.96σ X µ+1.96σ) = 0.95
40 Standard Normal Distribution N(0,1) P(Z 1.65) = 0.95 = P(Z -1.65) P(X µ+1.65σ) = 0.95 = P(X µ-1.65σ)
41 Normal Distribution N(µ,σ 2 ) N(0,1) N(1,1) N(0,4) N(0,0.25)
42 Central Limit Theorem X 1, X 2,, X n independent and identically distributed with expected value µ and variance σ 2 n σ X X n µ n Z with a standard normal Z, when n gets large
43 Galton Board A board which contains several rows of staggered but equally spaced nails, named after its inventor, Francis Galton ( )
44 Game of Dice 3.7 X : average count of n throws 3.6 X n=500 Frequency replicates 0 X
45 The (Almost) Universal Nature of Normality length oxygen consumption fecundity bill length weight
46 Summary -Probability theory, as a scientific discipline, is based upon Kolmogorov's axiomatic definition of probability. -Random variablesmap complex (real) events onto simple numerical scales; they can be discrete or continuous. -The distribution of a random variable is characterised by its probability function (discrete) or density (continuous). -Random variables are independent if the joint distribution equals the product of their individual distributions. -Important summary values of the distribution of random variables include the expected value and the variance. -The normal distribution is a universal, large-scale approximation of the "average" of other random variables.
Homework 4 Solution, due July 23
 Homework 4 Solution, due July 23 Random Variables Problem 1. Let X be the random number on a die: from 1 to. (i) What is the distribution of X? (ii) Calculate EX. (iii) Calculate EX 2. (iv) Calculate Var
Homework 4 Solution, due July 23 Random Variables Problem 1. Let X be the random number on a die: from 1 to. (i) What is the distribution of X? (ii) Calculate EX. (iii) Calculate EX 2. (iv) Calculate Var
Review of Probability. CS1538: Introduction to Simulations
 Review of Probability CS1538: Introduction to Simulations Probability and Statistics in Simulation Why do we need probability and statistics in simulation? Needed to validate the simulation model Needed
Review of Probability CS1538: Introduction to Simulations Probability and Statistics in Simulation Why do we need probability and statistics in simulation? Needed to validate the simulation model Needed
Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals
 Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge January 22nd, 2008 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture 1: Probability
Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge January 22nd, 2008 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture 1: Probability
Recitation 2: Probability
 Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Appendix A : Introduction to Probability and stochastic processes
 A-1 Mathematical methods in communication July 5th, 2009 Appendix A : Introduction to Probability and stochastic processes Lecturer: Haim Permuter Scribe: Shai Shapira and Uri Livnat The probability of
A-1 Mathematical methods in communication July 5th, 2009 Appendix A : Introduction to Probability and stochastic processes Lecturer: Haim Permuter Scribe: Shai Shapira and Uri Livnat The probability of
Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision]
![Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision]](/thumbs/93/111285649.jpg) Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] 1 Definition of Probability 1.1 Experiment An experiment is any procedure whose outcome is uncertain ffl toss a coin ffl throw a die ffl buy a lottery
Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] 1 Definition of Probability 1.1 Experiment An experiment is any procedure whose outcome is uncertain ffl toss a coin ffl throw a die ffl buy a lottery
STAT2201. Analysis of Engineering & Scientific Data. Unit 3
 STAT2201 Analysis of Engineering & Scientific Data Unit 3 Slava Vaisman The University of Queensland School of Mathematics and Physics What we learned in Unit 2 (1) We defined a sample space of a random
STAT2201 Analysis of Engineering & Scientific Data Unit 3 Slava Vaisman The University of Queensland School of Mathematics and Physics What we learned in Unit 2 (1) We defined a sample space of a random
Random Variables. Saravanan Vijayakumaran Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay
 1 / 13 Random Variables Saravanan Vijayakumaran sarva@ee.iitb.ac.in Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay August 8, 2013 2 / 13 Random Variable Definition A real-valued
1 / 13 Random Variables Saravanan Vijayakumaran sarva@ee.iitb.ac.in Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay August 8, 2013 2 / 13 Random Variable Definition A real-valued
LECTURE 1. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
 LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
Probabilistic models
 Probabilistic models Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became
Probabilistic models Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became
Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes
 Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Week 12-13: Discrete Probability
 Week 12-13: Discrete Probability November 21, 2018 1 Probability Space There are many problems about chances or possibilities, called probability in mathematics. When we roll two dice there are possible
Week 12-13: Discrete Probability November 21, 2018 1 Probability Space There are many problems about chances or possibilities, called probability in mathematics. When we roll two dice there are possible
M378K In-Class Assignment #1
 The following problems are a review of M6K. M7K In-Class Assignment # Problem.. Complete the definition of mutual exclusivity of events below: Events A, B Ω are said to be mutually exclusive if A B =.
The following problems are a review of M6K. M7K In-Class Assignment # Problem.. Complete the definition of mutual exclusivity of events below: Events A, B Ω are said to be mutually exclusive if A B =.
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics
 Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
Notes 12 Autumn 2005
 MAS 08 Probability I Notes Autumn 005 Conditional random variables Remember that the conditional probability of event A given event B is P(A B) P(A B)/P(B). Suppose that X is a discrete random variable.
MAS 08 Probability I Notes Autumn 005 Conditional random variables Remember that the conditional probability of event A given event B is P(A B) P(A B)/P(B). Suppose that X is a discrete random variable.
Recap of Basic Probability Theory
 02407 Stochastic Processes Recap of Basic Probability Theory Uffe Høgsbro Thygesen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark 2800 Kgs. Lyngby Denmark Email: uht@imm.dtu.dk
02407 Stochastic Processes Recap of Basic Probability Theory Uffe Høgsbro Thygesen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark 2800 Kgs. Lyngby Denmark Email: uht@imm.dtu.dk
Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability
 Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability Overview Lecturer Email Office Homework Webpage Dr Jonathan Cumming j.a.cumming@durham.ac.uk CM233 None! http://maths.dur.ac.uk/stats/people/jac/singleb/ 1 Introduction
Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability Overview Lecturer Email Office Homework Webpage Dr Jonathan Cumming j.a.cumming@durham.ac.uk CM233 None! http://maths.dur.ac.uk/stats/people/jac/singleb/ 1 Introduction
More than one variable
 Chapter More than one variable.1 Bivariate discrete distributions Suppose that the r.v. s X and Y are discrete and take on the values x j and y j, j 1, respectively. Then the joint p.d.f. of X and Y, to
Chapter More than one variable.1 Bivariate discrete distributions Suppose that the r.v. s X and Y are discrete and take on the values x j and y j, j 1, respectively. Then the joint p.d.f. of X and Y, to
Recap of Basic Probability Theory
 02407 Stochastic Processes? Recap of Basic Probability Theory Uffe Høgsbro Thygesen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark 2800 Kgs. Lyngby Denmark Email: uht@imm.dtu.dk
02407 Stochastic Processes? Recap of Basic Probability Theory Uffe Høgsbro Thygesen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark 2800 Kgs. Lyngby Denmark Email: uht@imm.dtu.dk
Notes on Mathematics Groups
 EPGY Singapore Quantum Mechanics: 2007 Notes on Mathematics Groups A group, G, is defined is a set of elements G and a binary operation on G; one of the elements of G has particularly special properties
EPGY Singapore Quantum Mechanics: 2007 Notes on Mathematics Groups A group, G, is defined is a set of elements G and a binary operation on G; one of the elements of G has particularly special properties
Chapter 2. Continuous random variables
 Chapter 2 Continuous random variables Outline Review of probability: events and probability Random variable Probability and Cumulative distribution function Review of discrete random variable Introduction
Chapter 2 Continuous random variables Outline Review of probability: events and probability Random variable Probability and Cumulative distribution function Review of discrete random variable Introduction
Part IA Probability. Definitions. Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua. Lent 2015
 Part IA Probability Definitions Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Part IA Probability Definitions Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Topic 5 Basics of Probability
 Topic 5 Basics of Probability Equally Likely Outcomes and the Axioms of Probability 1 / 13 Outline Equally Likely Outcomes Axioms of Probability Consequences of the Axioms 2 / 13 Introduction A probability
Topic 5 Basics of Probability Equally Likely Outcomes and the Axioms of Probability 1 / 13 Outline Equally Likely Outcomes Axioms of Probability Consequences of the Axioms 2 / 13 Introduction A probability
The enumeration of all possible outcomes of an experiment is called the sample space, denoted S. E.g.: S={head, tail}
 Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
5. Conditional Distributions
 1 of 12 7/16/2009 5:36 AM Virtual Laboratories > 3. Distributions > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 5. Conditional Distributions Basic Theory As usual, we start with a random experiment with probability measure P on an
1 of 12 7/16/2009 5:36 AM Virtual Laboratories > 3. Distributions > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 5. Conditional Distributions Basic Theory As usual, we start with a random experiment with probability measure P on an
5 CORRELATION. Expectation of the Binomial Distribution I The Binomial distribution can be defined as: P(X = r) = p r q n r where p + q = 1 and 0 r n
 5 CORRELATION The covariance of two random variables gives some measure of their independence. A second way of assessing the measure of independence will be discussed shortly but first the expectation
5 CORRELATION The covariance of two random variables gives some measure of their independence. A second way of assessing the measure of independence will be discussed shortly but first the expectation
Lecture 1: Basics of Probability
 Lecture 1: Basics of Probability (Luise-Vitetta, Chapter 8) Why probability in data science? Data acquisition is noisy Sampling/quantization external factors: If you record your voice saying machine learning
Lecture 1: Basics of Probability (Luise-Vitetta, Chapter 8) Why probability in data science? Data acquisition is noisy Sampling/quantization external factors: If you record your voice saying machine learning
Origins of Probability Theory
 1 16.584: INTRODUCTION Theory and Tools of Probability required to analyze and design systems subject to uncertain outcomes/unpredictability/randomness. Such systems more generally referred to as Experiments.
1 16.584: INTRODUCTION Theory and Tools of Probability required to analyze and design systems subject to uncertain outcomes/unpredictability/randomness. Such systems more generally referred to as Experiments.
Examples of random experiment (a) Random experiment BASIC EXPERIMENT
 Random experiment A random experiment is a process leading to an uncertain outcome, before the experiment is run We usually assume that the experiment can be repeated indefinitely under essentially the
Random experiment A random experiment is a process leading to an uncertain outcome, before the experiment is run We usually assume that the experiment can be repeated indefinitely under essentially the
EE514A Information Theory I Fall 2013
 EE514A Information Theory I Fall 2013 K. Mohan, Prof. J. Bilmes University of Washington, Seattle Department of Electrical Engineering Fall Quarter, 2013 http://j.ee.washington.edu/~bilmes/classes/ee514a_fall_2013/
EE514A Information Theory I Fall 2013 K. Mohan, Prof. J. Bilmes University of Washington, Seattle Department of Electrical Engineering Fall Quarter, 2013 http://j.ee.washington.edu/~bilmes/classes/ee514a_fall_2013/
1 Presessional Probability
 1 Presessional Probability Probability theory is essential for the development of mathematical models in finance, because of the randomness nature of price fluctuations in the markets. This presessional
1 Presessional Probability Probability theory is essential for the development of mathematical models in finance, because of the randomness nature of price fluctuations in the markets. This presessional
Brief Review of Probability
 Brief Review of Probability Nuno Vasconcelos (Ken Kreutz-Delgado) ECE Department, UCSD Probability Probability theory is a mathematical language to deal with processes or experiments that are non-deterministic
Brief Review of Probability Nuno Vasconcelos (Ken Kreutz-Delgado) ECE Department, UCSD Probability Probability theory is a mathematical language to deal with processes or experiments that are non-deterministic
PROBABILITY CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES UNIT OVERVIEW
 CHAPTER 16 PROBABILITY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Concept of probability is used in accounting and finance to understand the likelihood of occurrence or non-occurrence of a variable. It helps in developing financial
CHAPTER 16 PROBABILITY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Concept of probability is used in accounting and finance to understand the likelihood of occurrence or non-occurrence of a variable. It helps in developing financial
Lecture 10: Probability distributions TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019
 Lecture 10: Probability distributions DANIEL WELLER TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019 Agenda What is probability? (again) Describing probabilities (distributions) Understanding probabilities (expectation) Partial
Lecture 10: Probability distributions DANIEL WELLER TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019 Agenda What is probability? (again) Describing probabilities (distributions) Understanding probabilities (expectation) Partial
STAT 430/510 Probability Lecture 7: Random Variable and Expectation
 STAT 430/510 Probability Lecture 7: Random Variable and Expectation Pengyuan (Penelope) Wang June 2, 2011 Review Properties of Probability Conditional Probability The Law of Total Probability Bayes Formula
STAT 430/510 Probability Lecture 7: Random Variable and Expectation Pengyuan (Penelope) Wang June 2, 2011 Review Properties of Probability Conditional Probability The Law of Total Probability Bayes Formula
Probability theory basics
 Probability theory basics Michael Franke Basics of probability theory: axiomatic definition, interpretation, joint distributions, marginalization, conditional probability & Bayes rule. Random variables:
Probability theory basics Michael Franke Basics of probability theory: axiomatic definition, interpretation, joint distributions, marginalization, conditional probability & Bayes rule. Random variables:
Probability Theory and Applications
 Probability Theory and Applications Videos of the topics covered in this manual are available at the following links: Lesson 4 Probability I http://faculty.citadel.edu/silver/ba205/online course/lesson
Probability Theory and Applications Videos of the topics covered in this manual are available at the following links: Lesson 4 Probability I http://faculty.citadel.edu/silver/ba205/online course/lesson
Set Theory. Pattern Recognition III. Michal Haindl. Set Operations. Outline
 Set Theory A, B sets e.g. A = {ζ 1,...,ζ n } A = { c x y d} S space (universe) A,B S Outline Pattern Recognition III Michal Haindl Faculty of Information Technology, KTI Czech Technical University in Prague
Set Theory A, B sets e.g. A = {ζ 1,...,ζ n } A = { c x y d} S space (universe) A,B S Outline Pattern Recognition III Michal Haindl Faculty of Information Technology, KTI Czech Technical University in Prague
MA : Introductory Probability
 MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
Lecture 1. Chapter 1. (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 ( ). 1. What is Statistics?
 Lecture 1 (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 (2.1 --- 2.6). Chapter 1 1. What is Statistics? 2. Two definitions. (1). Population (2). Sample 3. The objective of statistics.
Lecture 1 (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 (2.1 --- 2.6). Chapter 1 1. What is Statistics? 2. Two definitions. (1). Population (2). Sample 3. The objective of statistics.
MATH MW Elementary Probability Course Notes Part I: Models and Counting
 MATH 2030 3.00MW Elementary Probability Course Notes Part I: Models and Counting Tom Salisbury salt@yorku.ca York University Winter 2010 Introduction [Jan 5] Probability: the mathematics used for Statistics
MATH 2030 3.00MW Elementary Probability Course Notes Part I: Models and Counting Tom Salisbury salt@yorku.ca York University Winter 2010 Introduction [Jan 5] Probability: the mathematics used for Statistics
MATHEMATICS 154, SPRING 2009 PROBABILITY THEORY Outline #11 (Tail-Sum Theorem, Conditional distribution and expectation)
 MATHEMATICS 154, SPRING 2009 PROBABILITY THEORY Outline #11 (Tail-Sum Theorem, Conditional distribution and expectation) Last modified: March 7, 2009 Reference: PRP, Sections 3.6 and 3.7. 1. Tail-Sum Theorem
MATHEMATICS 154, SPRING 2009 PROBABILITY THEORY Outline #11 (Tail-Sum Theorem, Conditional distribution and expectation) Last modified: March 7, 2009 Reference: PRP, Sections 3.6 and 3.7. 1. Tail-Sum Theorem
Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com
 1 School of Oriental and African Studies September 2015 Department of Economics Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com Gujarati D. Basic Econometrics, Appendix
1 School of Oriental and African Studies September 2015 Department of Economics Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com Gujarati D. Basic Econometrics, Appendix
Bayesian statistics, simulation and software
 Module 1: Course intro and probability brush-up Department of Mathematical Sciences Aalborg University 1/22 Bayesian Statistics, Simulations and Software Course outline Course consists of 12 half-days
Module 1: Course intro and probability brush-up Department of Mathematical Sciences Aalborg University 1/22 Bayesian Statistics, Simulations and Software Course outline Course consists of 12 half-days
What is Probability? Probability. Sample Spaces and Events. Simple Event
 What is Probability? Probability Peter Lo Probability is the numerical measure of likelihood that the event will occur. Simple Event Joint Event Compound Event Lies between 0 & 1 Sum of events is 1 1.5
What is Probability? Probability Peter Lo Probability is the numerical measure of likelihood that the event will occur. Simple Event Joint Event Compound Event Lies between 0 & 1 Sum of events is 1 1.5
Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Fall 2015
 L645 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Fall 2015 1 / 34 To start out the course, we need to know something about statistics and This is only an introduction; for a fuller understanding, you would
L645 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Fall 2015 1 / 34 To start out the course, we need to know something about statistics and This is only an introduction; for a fuller understanding, you would
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics
 SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics Lecture 13: Expectation and Variance and joint distributions Purnamrita Sarkar Department of Statistics and Data Science The University of Texas at Austin
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics Lecture 13: Expectation and Variance and joint distributions Purnamrita Sarkar Department of Statistics and Data Science The University of Texas at Austin
Solutionbank S1 Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mathematics
 Heinemann Solutionbank: Statistics S Page of Solutionbank S Exercise A, Question Write down whether or not each of the following is a discrete random variable. Give a reason for your answer. a The average
Heinemann Solutionbank: Statistics S Page of Solutionbank S Exercise A, Question Write down whether or not each of the following is a discrete random variable. Give a reason for your answer. a The average
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability. Elements of Probability. Conditional probability. Sequential Calculation of Probability
 Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability Set Theory Elements of Probability Conditional probability Sequential Calculation of Probability Total Probability and Bayes Rule Independence Counting EE 178/278A: Basic
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability Set Theory Elements of Probability Conditional probability Sequential Calculation of Probability Total Probability and Bayes Rule Independence Counting EE 178/278A: Basic
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna 1
 Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna 1 Introduction Probability theory was originated from gambling theory Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna 2 History of Probability Galileo
Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna 1 Introduction Probability theory was originated from gambling theory Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna 2 History of Probability Galileo
Bayes Theorem. Jan Kracík. Department of Applied Mathematics FEECS, VŠB - TU Ostrava
 Jan Kracík Department of Applied Mathematics FEECS, VŠB - TU Ostrava Introduction Bayes theorem fundamental theorem in probability theory named after reverend Thomas Bayes (1701 1761) discovered in Bayes
Jan Kracík Department of Applied Mathematics FEECS, VŠB - TU Ostrava Introduction Bayes theorem fundamental theorem in probability theory named after reverend Thomas Bayes (1701 1761) discovered in Bayes
Lecture 2: Review of Basic Probability Theory
 ECE 830 Fall 2010 Statistical Signal Processing instructor: R. Nowak, scribe: R. Nowak Lecture 2: Review of Basic Probability Theory Probabilistic models will be used throughout the course to represent
ECE 830 Fall 2010 Statistical Signal Processing instructor: R. Nowak, scribe: R. Nowak Lecture 2: Review of Basic Probability Theory Probabilistic models will be used throughout the course to represent
Quick Tour of Basic Probability Theory and Linear Algebra
 Quick Tour of and Linear Algebra Quick Tour of and Linear Algebra CS224w: Social and Information Network Analysis Fall 2011 Quick Tour of and Linear Algebra Quick Tour of and Linear Algebra Outline Definitions
Quick Tour of and Linear Algebra Quick Tour of and Linear Algebra CS224w: Social and Information Network Analysis Fall 2011 Quick Tour of and Linear Algebra Quick Tour of and Linear Algebra Outline Definitions
Math 151. Rumbos Fall Solutions to Review Problems for Exam 2. Pr(X = 1) = ) = Pr(X = 2) = Pr(X = 3) = p X. (k) =
 Math 5. Rumbos Fall 07 Solutions to Review Problems for Exam. A bowl contains 5 chips of the same size and shape. Two chips are red and the other three are blue. Draw three chips from the bowl at random,
Math 5. Rumbos Fall 07 Solutions to Review Problems for Exam. A bowl contains 5 chips of the same size and shape. Two chips are red and the other three are blue. Draw three chips from the bowl at random,
Example 1. The sample space of an experiment where we flip a pair of coins is denoted by:
 Chapter 8 Probability 8. Preliminaries Definition (Sample Space). A Sample Space, Ω, is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment. Such a sample space is considered discrete if Ω has finite cardinality.
Chapter 8 Probability 8. Preliminaries Definition (Sample Space). A Sample Space, Ω, is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment. Such a sample space is considered discrete if Ω has finite cardinality.
1 The Basic Counting Principles
 1 The Basic Counting Principles The Multiplication Rule If an operation consists of k steps and the first step can be performed in n 1 ways, the second step can be performed in n ways [regardless of how
1 The Basic Counting Principles The Multiplication Rule If an operation consists of k steps and the first step can be performed in n 1 ways, the second step can be performed in n ways [regardless of how
n(1 p i ) n 1 p i = 1 3 i=1 E(X i p = p i )P(p = p i ) = 1 3 p i = n 3 (p 1 + p 2 + p 3 ). p i i=1 P(X i = 1 p = p i )P(p = p i ) = p1+p2+p3
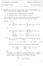 Introduction to Probability Due:August 8th, 211 Solutions of Final Exam Solve all the problems 1. (15 points) You have three coins, showing Head with probabilities p 1, p 2 and p 3. You perform two different
Introduction to Probability Due:August 8th, 211 Solutions of Final Exam Solve all the problems 1. (15 points) You have three coins, showing Head with probabilities p 1, p 2 and p 3. You perform two different
Probabilistic models
 Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became the definitive formulation
Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became the definitive formulation
Basic Probability. Introduction
 Basic Probability Introduction The world is an uncertain place. Making predictions about something as seemingly mundane as tomorrow s weather, for example, is actually quite a difficult task. Even with
Basic Probability Introduction The world is an uncertain place. Making predictions about something as seemingly mundane as tomorrow s weather, for example, is actually quite a difficult task. Even with
CSC Discrete Math I, Spring Discrete Probability
 CSC 125 - Discrete Math I, Spring 2017 Discrete Probability Probability of an Event Pierre-Simon Laplace s classical theory of probability: Definition of terms: An experiment is a procedure that yields
CSC 125 - Discrete Math I, Spring 2017 Discrete Probability Probability of an Event Pierre-Simon Laplace s classical theory of probability: Definition of terms: An experiment is a procedure that yields
Lecture 3 - Axioms of Probability
 Lecture 3 - Axioms of Probability Sta102 / BME102 January 25, 2016 Colin Rundel Axioms of Probability What does it mean to say that: The probability of flipping a coin and getting heads is 1/2? 3 What
Lecture 3 - Axioms of Probability Sta102 / BME102 January 25, 2016 Colin Rundel Axioms of Probability What does it mean to say that: The probability of flipping a coin and getting heads is 1/2? 3 What
Summary of basic probability theory Math 218, Mathematical Statistics D Joyce, Spring 2016
 8. For any two events E and F, P (E) = P (E F ) + P (E F c ). Summary of basic probability theory Math 218, Mathematical Statistics D Joyce, Spring 2016 Sample space. A sample space consists of a underlying
8. For any two events E and F, P (E) = P (E F ) + P (E F c ). Summary of basic probability theory Math 218, Mathematical Statistics D Joyce, Spring 2016 Sample space. A sample space consists of a underlying
Probability Theory and Random Variables
 Probability Theory and Random Variables One of the most noticeable aspects of many computer science related phenomena is the lack of certainty. When a job is submitted to a batch oriented computer system,
Probability Theory and Random Variables One of the most noticeable aspects of many computer science related phenomena is the lack of certainty. When a job is submitted to a batch oriented computer system,
Lecture 1: Review on Probability and Statistics
 STAT 516: Stochastic Modeling of Scientific Data Autumn 2018 Instructor: Yen-Chi Chen Lecture 1: Review on Probability and Statistics These notes are partially based on those of Mathias Drton. 1.1 Motivating
STAT 516: Stochastic Modeling of Scientific Data Autumn 2018 Instructor: Yen-Chi Chen Lecture 1: Review on Probability and Statistics These notes are partially based on those of Mathias Drton. 1.1 Motivating
Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables. Conditional Probability and Independence. Functions of a Random Variable
 Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables Probability Spaces Conditional Probability and Independence Random Variables Functions of a Random Variable Generation of a Random Variable Jointly Distributed
Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables Probability Spaces Conditional Probability and Independence Random Variables Functions of a Random Variable Generation of a Random Variable Jointly Distributed
Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of
 Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of repetitions. (p229) That is, probability is a long-term
Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of repetitions. (p229) That is, probability is a long-term
Aarti Singh. Lecture 2, January 13, Reading: Bishop: Chap 1,2. Slides courtesy: Eric Xing, Andrew Moore, Tom Mitchell
 Machine Learning 0-70/5 70/5-78, 78, Spring 00 Probability 0 Aarti Singh Lecture, January 3, 00 f(x) µ x Reading: Bishop: Chap, Slides courtesy: Eric Xing, Andrew Moore, Tom Mitchell Announcements Homework
Machine Learning 0-70/5 70/5-78, 78, Spring 00 Probability 0 Aarti Singh Lecture, January 3, 00 f(x) µ x Reading: Bishop: Chap, Slides courtesy: Eric Xing, Andrew Moore, Tom Mitchell Announcements Homework
1 INFO Sep 05
 Events A 1,...A n are said to be mutually independent if for all subsets S {1,..., n}, p( i S A i ) = p(a i ). (For example, flip a coin N times, then the events {A i = i th flip is heads} are mutually
Events A 1,...A n are said to be mutually independent if for all subsets S {1,..., n}, p( i S A i ) = p(a i ). (For example, flip a coin N times, then the events {A i = i th flip is heads} are mutually
Introduction to probability theory
 Introduction to probability theory Fátima Sánchez Cabo Institute for Genomics and Bioinformatics, TUGraz f.sanchezcabo@tugraz.at 07/03/2007 - p. 1/35 Outline Random and conditional probability (7 March)
Introduction to probability theory Fátima Sánchez Cabo Institute for Genomics and Bioinformatics, TUGraz f.sanchezcabo@tugraz.at 07/03/2007 - p. 1/35 Outline Random and conditional probability (7 March)
Probabilistic Systems Analysis Spring 2018 Lecture 6. Random Variables: Probability Mass Function and Expectation
 EE 178 Probabilistic Systems Analysis Spring 2018 Lecture 6 Random Variables: Probability Mass Function and Expectation Probability Mass Function When we introduce the basic probability model in Note 1,
EE 178 Probabilistic Systems Analysis Spring 2018 Lecture 6 Random Variables: Probability Mass Function and Expectation Probability Mass Function When we introduce the basic probability model in Note 1,
PCMI Introduction to Random Matrix Theory Handout # REVIEW OF PROBABILITY THEORY. Chapter 1 - Events and Their Probabilities
 PCMI 207 - Introduction to Random Matrix Theory Handout #2 06.27.207 REVIEW OF PROBABILITY THEORY Chapter - Events and Their Probabilities.. Events as Sets Definition (σ-field). A collection F of subsets
PCMI 207 - Introduction to Random Matrix Theory Handout #2 06.27.207 REVIEW OF PROBABILITY THEORY Chapter - Events and Their Probabilities.. Events as Sets Definition (σ-field). A collection F of subsets
Analysis of Engineering and Scientific Data. Semester
 Analysis of Engineering and Scientific Data Semester 1 2019 Sabrina Streipert s.streipert@uq.edu.au Example: Draw a random number from the interval of real numbers [1, 3]. Let X represent the number. Each
Analysis of Engineering and Scientific Data Semester 1 2019 Sabrina Streipert s.streipert@uq.edu.au Example: Draw a random number from the interval of real numbers [1, 3]. Let X represent the number. Each
Math 493 Final Exam December 01
 Math 493 Final Exam December 01 NAME: ID NUMBER: Return your blue book to my office or the Math Department office by Noon on Tuesday 11 th. On all parts after the first show enough work in your exam booklet
Math 493 Final Exam December 01 NAME: ID NUMBER: Return your blue book to my office or the Math Department office by Noon on Tuesday 11 th. On all parts after the first show enough work in your exam booklet
Mathematics 426 Robert Gross Homework 9 Answers
 Mathematics 4 Robert Gross Homework 9 Answers. Suppose that X is a normal random variable with mean µ and standard deviation σ. Suppose that PX > 9 PX
Mathematics 4 Robert Gross Homework 9 Answers. Suppose that X is a normal random variable with mean µ and standard deviation σ. Suppose that PX > 9 PX
Why study probability? Set theory. ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables
 ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables Readings from G&S: Chapter 1. Section 2.1, Section 2.3, Section 2.4, Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.5, Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section
ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables Readings from G&S: Chapter 1. Section 2.1, Section 2.3, Section 2.4, Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.5, Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section
Course: ESO-209 Home Work: 1 Instructor: Debasis Kundu
 Home Work: 1 1. Describe the sample space when a coin is tossed (a) once, (b) three times, (c) n times, (d) an infinite number of times. 2. A coin is tossed until for the first time the same result appear
Home Work: 1 1. Describe the sample space when a coin is tossed (a) once, (b) three times, (c) n times, (d) an infinite number of times. 2. A coin is tossed until for the first time the same result appear
2.1 Elementary probability; random sampling
 Chapter 2 Probability Theory Chapter 2 outlines the probability theory necessary to understand this text. It is meant as a refresher for students who need review and as a reference for concepts and theorems
Chapter 2 Probability Theory Chapter 2 outlines the probability theory necessary to understand this text. It is meant as a refresher for students who need review and as a reference for concepts and theorems
Introduction to Probability and Stocastic Processes - Part I
 Introduction to Probability and Stocastic Processes - Part I Lecture 1 Henrik Vie Christensen vie@control.auc.dk Department of Control Engineering Institute of Electronic Systems Aalborg University Denmark
Introduction to Probability and Stocastic Processes - Part I Lecture 1 Henrik Vie Christensen vie@control.auc.dk Department of Control Engineering Institute of Electronic Systems Aalborg University Denmark
4th IIA-Penn State Astrostatistics School July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatory, Kavalur
 4th IIA-Penn State Astrostatistics School July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatory, Kavalur Laws of Probability, Bayes theorem, and the Central Limit Theorem Rahul Roy Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi. Adapted
4th IIA-Penn State Astrostatistics School July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatory, Kavalur Laws of Probability, Bayes theorem, and the Central Limit Theorem Rahul Roy Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi. Adapted
Lecture 1. ABC of Probability
 Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 1. ABC of Probability January 16, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 1 January 16, 2013 1 / 9 Agenda Sample Spaces Realizations, Events Axioms of Probability
Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 1. ABC of Probability January 16, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 1 January 16, 2013 1 / 9 Agenda Sample Spaces Realizations, Events Axioms of Probability
Statistical Inference
 Statistical Inference Lecture 1: Probability Theory MING GAO DASE @ ECNU (for course related communications) mgao@dase.ecnu.edu.cn Sep. 11, 2018 Outline Introduction Set Theory Basics of Probability Theory
Statistical Inference Lecture 1: Probability Theory MING GAO DASE @ ECNU (for course related communications) mgao@dase.ecnu.edu.cn Sep. 11, 2018 Outline Introduction Set Theory Basics of Probability Theory
Basic Statistics and Probability Chapter 3: Probability
 Basic Statistics and Probability Chapter 3: Probability Events, Sample Spaces and Probability Unions and Intersections Complementary Events Additive Rule. Mutually Exclusive Events Conditional Probability
Basic Statistics and Probability Chapter 3: Probability Events, Sample Spaces and Probability Unions and Intersections Complementary Events Additive Rule. Mutually Exclusive Events Conditional Probability
Probability measures A probability measure, P, is a real valued function from the collection of possible events so that the following
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Algorithms for Uncertainty Quantification
 Algorithms for Uncertainty Quantification Tobias Neckel, Ionuț-Gabriel Farcaș Lehrstuhl Informatik V Summer Semester 2017 Lecture 2: Repetition of probability theory and statistics Example: coin flip Example
Algorithms for Uncertainty Quantification Tobias Neckel, Ionuț-Gabriel Farcaș Lehrstuhl Informatik V Summer Semester 2017 Lecture 2: Repetition of probability theory and statistics Example: coin flip Example
Probability Review. Chao Lan
 Probability Review Chao Lan Let s start with a single random variable Random Experiment A random experiment has three elements 1. sample space Ω: set of all possible outcomes e.g.,ω={1,2,3,4,5,6} 2. event
Probability Review Chao Lan Let s start with a single random variable Random Experiment A random experiment has three elements 1. sample space Ω: set of all possible outcomes e.g.,ω={1,2,3,4,5,6} 2. event
Probability and random variables. Sept 2018
 Probability and random variables Sept 2018 2 The sample space Consider an experiment with an uncertain outcome. The set of all possible outcomes is called the sample space. Example: I toss a coin twice,
Probability and random variables Sept 2018 2 The sample space Consider an experiment with an uncertain outcome. The set of all possible outcomes is called the sample space. Example: I toss a coin twice,
Lecture 2: Repetition of probability theory and statistics
 Algorithms for Uncertainty Quantification SS8, IN2345 Tobias Neckel Scientific Computing in Computer Science TUM Lecture 2: Repetition of probability theory and statistics Concept of Building Block: Prerequisites:
Algorithms for Uncertainty Quantification SS8, IN2345 Tobias Neckel Scientific Computing in Computer Science TUM Lecture 2: Repetition of probability theory and statistics Concept of Building Block: Prerequisites:
Announcements. Topics: To Do:
 Announcements Topics: In the Probability and Statistics module: - Sections 1 + 2: Introduction to Stochastic Models - Section 3: Basics of Probability Theory - Section 4: Conditional Probability; Law of
Announcements Topics: In the Probability and Statistics module: - Sections 1 + 2: Introduction to Stochastic Models - Section 3: Basics of Probability Theory - Section 4: Conditional Probability; Law of
ECE 302: Chapter 02 Probability Model
 ECE 302: Chapter 02 Probability Model Fall 2018 Prof Stanley Chan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University 1 / 35 1. Probability Model 2 / 35 What is Probability? It is a number.
ECE 302: Chapter 02 Probability Model Fall 2018 Prof Stanley Chan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University 1 / 35 1. Probability Model 2 / 35 What is Probability? It is a number.
Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables. Conditional Probability and Independence. Functions of a Random Variable
 Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables Probability Spaces Conditional Probability and Independence Random Variables Functions of a Random Variable Generation of a Random Variable Jointly Distributed
Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables Probability Spaces Conditional Probability and Independence Random Variables Functions of a Random Variable Generation of a Random Variable Jointly Distributed
ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 2 MATH00040 SEMESTER / Probability
 ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 2 MATH00040 SEMESTER 2 2017/2018 DR. ANTHONY BROWN 5.1. Introduction to Probability. 5. Probability You are probably familiar with the elementary
ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 2 MATH00040 SEMESTER 2 2017/2018 DR. ANTHONY BROWN 5.1. Introduction to Probability. 5. Probability You are probably familiar with the elementary
Classical Probability
 Chapter 1 Classical Probability Probability is the very guide of life. Marcus Thullius Cicero The original development of probability theory took place during the seventeenth through nineteenth centuries.
Chapter 1 Classical Probability Probability is the very guide of life. Marcus Thullius Cicero The original development of probability theory took place during the seventeenth through nineteenth centuries.
Lecture notes for probability. Math 124
 Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
4.1 Expected value of a discrete random variable. Suppose we shall win $i if the die lands on i. What is our ideal average winnings per toss?
 Chapter 4 Mathematical Expectation 4.1 Expected value of a discrete random variable Examples: (a) Given 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. What is the average? (b) Toss an unbalanced die 1 times. Lands on 1 2 3 4 5 6 Probab..1.3.1.2.2.1
Chapter 4 Mathematical Expectation 4.1 Expected value of a discrete random variable Examples: (a) Given 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. What is the average? (b) Toss an unbalanced die 1 times. Lands on 1 2 3 4 5 6 Probab..1.3.1.2.2.1
ECE 302, Final 3:20-5:20pm Mon. May 1, WTHR 160 or WTHR 172.
 ECE 302, Final 3:20-5:20pm Mon. May 1, WTHR 160 or WTHR 172. 1. Enter your name, student ID number, e-mail address, and signature in the space provided on this page, NOW! 2. This is a closed book exam.
ECE 302, Final 3:20-5:20pm Mon. May 1, WTHR 160 or WTHR 172. 1. Enter your name, student ID number, e-mail address, and signature in the space provided on this page, NOW! 2. This is a closed book exam.
Some Concepts of Probability (Review) Volker Tresp Summer 2018
 Some Concepts of Probability (Review) Volker Tresp Summer 2018 1 Definition There are different way to define what a probability stands for Mathematically, the most rigorous definition is based on Kolmogorov
Some Concepts of Probability (Review) Volker Tresp Summer 2018 1 Definition There are different way to define what a probability stands for Mathematically, the most rigorous definition is based on Kolmogorov
Probability Theory Review
 Cogsci 118A: Natural Computation I Lecture 2 (01/07/10) Lecturer: Angela Yu Probability Theory Review Scribe: Joseph Schilz Lecture Summary 1. Set theory: terms and operators In this section, we provide
Cogsci 118A: Natural Computation I Lecture 2 (01/07/10) Lecturer: Angela Yu Probability Theory Review Scribe: Joseph Schilz Lecture Summary 1. Set theory: terms and operators In this section, we provide
