What can we learn about the neutron-star equation of state from inspiralling binary neutron stars?
|
|
|
- Madlyn Potter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 What can we learn about the neutron-star equation of state from inspiralling binary neutron stars? Ben Lackey, Les Wade University of Washington, Seattle Washington, 1 July 2014
2 What can we measure from the waveform? Phase shift during the inspiral from tidal interactions Tidal field E ij of one NS induces quadrupole moment Q ij in other NS Q ij = (EOS,M NS )E ij (EOS,M NS )MNSE 5 ij Increased quadrupole moment leads to more tightly bound system and additional quadrupole radiation
3 What can we measure from the waveform? Tidal effects first appear at same order as 5PN point-particle terms Leading term is a linear combination of the tidal deformabilities for each NS Results in a phase shift of ~1 cycle up to ISCO depending on the EOS h(f) / M5/6 f 7/6 e i (f) D L apple (f) =2 ft c c v = 8 h (PP-PN) ( )( )+ p 2 (M,, EOS)v 10 i 1 4 ( )( 1 2 ) 13 h + at 100Mpc No tidal, m 1 =1.35, m 2 =1.35 5PN tidal, m 1 =1.35, m 2 =1.35, L 1 =591, L 2 = t HsL
4 4-parameter EOS fit 37 Tabulated theoretical models 37 2 examples of fits loghp in dyneêcm 2 L nuclear density loghr in gêcm 3 L loghp in dyneêcm 2 L p 1 low density ρ0 variable ρ1 fixed ρ2 fixed Γ 2 Γ loghr in gêcm 3 L Γ 3 p( )= K 1 1, 0 < < 1 K 2 2, 1 < < 2 K 3 3, > 2
5 Current EOS constraints Causality: Speed of sound must be less than the speed of light in a stable neutron star v s = dp/d <c Maximum mass: EOS must be able to support the observed star with mass greater than 1.93M (lower limit on J )
6 Estimating EOS parameters from LIGO data Analogue of 2-step procedure described by Steiner, Lattimer, Brown (Astrophys. J. 722, 33) for mass-radius measurements They combined several mass-radius measurements from accreting neutron stars to estimate EOS parameters We will use estimates of M (M,, EOS) inspiral events to estimate EOS parameters from several BNS
7 Step 1: Estimate M (M,, EOS). Can estimate BNS parameters from Bayes theorem: Prior Likelihood Posterior p( d ~ n, H, I) = p(~ H, I)p(d n, ~ H, I) p(d n H, I) Evidence ~ = {,,,,D L,t c, c, M,, } d n : gravitational wave data from nth BNS system H: waveform model I : prior information about the parameters Posterior calculated with MCMC or estimated with Fisher matrix which assumes Gaussian likelihood and prior Marginalized distribution trivial Z to compute with MCMC or Fisher p(m,, d n, H, I) = p( d ~ n, H, I)d ~ marg
8 Step 2: Estimate EOS parameters Can estimate EOS parameters from Bayes theorem: Prior Likelihood Posterior p(~x d 1...d N, H, I) = p(~x H, I)p(d 1...d N ~x, H, I) p(d 1...d N H, I) Evidence ~x = {log(p 1 ), 1, 2, 3, M 1, 1,...,M N, N } d 1...d N : gravitational wave data from all N BNS events prior: Flat in EOS parameters except and M max 1.93M Likelihood: p(d 1,...,d N ~x, H, I) = NY n=1 v s = p dp/d apple c Marginalized posterior/quasilikelihood from single BNS event p(m n, n, n d n, H, I) n = (M n, n,eos) Perform MCMC simulation over the 4+2N parameters, then marginalize over the 2N mass parameters
9 Simulating a population of BNS events We chose the true EOS to be MPA1 Moderate EOS in middle of parameter space R(1.4M ) 12.5km, and M max 2.5M Sampled 50 BNS systems with SNR > 8 Individual masses distributed uniformly in (1.2M, 1.6M ) Sky position and distance distributed uniformly in volume Orientation distributed uniformly on unit sphere then calculated from masses and true EOS
10 EOS Parameters True values d marginalized PDFs 1 BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS d marginalized PDFs log(p 1 ) (dyne/cm 2 )
11 EOS Parameters BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS log(p 1 ) (dyne/cm 2 )
12 EOS Parameters BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS log(p 1 ) (dyne/cm 2 )
13 EOS Parameters BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS log(p 1 ) (dyne/cm 2 )
14 EOS function p( ) log(p) (dyn/cm 2 ) % confidence nuc nuc nuc 1 BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS p/ptrue log( ) (g/cm 3 )
15 EOS function p( ) log(p) (dyn/cm 2 ) % confidence nuc nuc nuc 1 BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS p/ptrue log( ) (g/cm 3 )
16 EOS function p( ) log(p) (dyn/cm 2 ) % confidence nuc nuc nuc 1 BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS p/ptrue log( ) (g/cm 3 )
17 EOS function p( ) log(p) (dyn/cm 2 ) % confidence nuc nuc nuc 1 BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS p/ptrue log( ) (g/cm 3 )
18 NS Radius and Tidal Deformability Del Pozzo et al. found (1.4M ) can be measured to +/-10% with 50 sources but the slope of (M) cannot be measured Fitting the EOS function p( ) instead of (M), and using known EOS information dramatically improves the measurement of (M) R (km) Simulated masses uniformly distributed in this range (10 36 g cm 2 s 2 ) BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS M(M ) M(M )
19 NS Radius and Tidal Deformability Del Pozzo et al. found (1.4M ) can be measured to +/-10% with 50 sources but the slope of (M) cannot be measured Fitting the EOS function p( ) instead of (M), and using known EOS information dramatically improves the measurement of (M) R (km) Simulated masses uniformly distributed in this range (10 36 g cm 2 s 2 ) BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS M(M ) M(M )
20 NS Radius and Tidal Deformability Del Pozzo et al. found (1.4M ) can be measured to +/-10% with 50 sources but the slope of (M) cannot be measured Fitting the EOS function p( ) instead of (M), and using known EOS information dramatically improves the measurement of (M) R (km) Simulated masses uniformly distributed in this range (10 36 g cm 2 s 2 ) BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS M(M ) M(M )
21 NS Radius and Tidal Deformability Del Pozzo et al. found (1.4M ) can be measured to +/-10% with 50 sources but the slope of (M) cannot be measured Fitting the EOS function p( ) instead of (M), and using known EOS information dramatically improves the measurement of (M) R (km) Simulated masses uniformly distributed in this range (10 36 g cm 2 s 2 ) BNS 5 BNS 20 BNS 50 BNS True EOS M(M ) M(M )
22 Fisher matrix versus MCMC Fisher matrix gives comparable results to lalinference_mcmc for loudest signals
23 Systematic errors in point particle waveform Injected TaylorF2, TaylorT1, TaylorT4 waveforms and used TaylorF2 as template
24 Higher mass NS observations Black-widow pulsars may have particularly high masses PSR B : PSR J : 2.40 ± 0.12M with lower limit 1.66M 2.68 ± 0.14M with lower limit 2.1M
25 Other EOS models
26 Other EOS models
27 Conclusion Detailed EOS information can be found from the inspiral of BNS systems with aligo Results are roughly equivalent to mass-radius observations Systematic errors from uncertainty in point-particle waveform are significant Unrelated to those in mass-radius observations
Measuring the Neutron-Star EOS with Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspiral
 Measuring the Neutron-Star EOS with Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspiral I. Astrophysical Constraints Jocelyn Read, Ben Lackey, Ben Owen, JF II. NRDA NS-NS Jocelyn Read, Charalampos Markakis, Masaru
Measuring the Neutron-Star EOS with Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspiral I. Astrophysical Constraints Jocelyn Read, Ben Lackey, Ben Owen, JF II. NRDA NS-NS Jocelyn Read, Charalampos Markakis, Masaru
Measuring the Neutron-Star EOS with Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspiral
 Measuring the Neutron-Star EOS with Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspiral John L Friedman Leonard E. Parker Center for Gravitation, Cosmology, and Asrtrophysics Measuring the Neutron-Star EOS with Gravitational
Measuring the Neutron-Star EOS with Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspiral John L Friedman Leonard E. Parker Center for Gravitation, Cosmology, and Asrtrophysics Measuring the Neutron-Star EOS with Gravitational
Studying the Effects of Tidal Corrections on Parameter Estimation
 Studying the Effects of Tidal Corrections on Parameter Estimation Leslie Wade Jolien Creighton, Benjamin Lackey, Evan Ochsner Center for Gravitation and Cosmology 1 Outline Background: Physical description
Studying the Effects of Tidal Corrections on Parameter Estimation Leslie Wade Jolien Creighton, Benjamin Lackey, Evan Ochsner Center for Gravitation and Cosmology 1 Outline Background: Physical description
Distinguishing boson stars from black holes and neutron stars with tidal interactions
 Distinguishing boson stars from black holes and neutron stars with tidal interactions Noah Sennett Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics (Albert Einstein Institute) Department of Physics, University
Distinguishing boson stars from black holes and neutron stars with tidal interactions Noah Sennett Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics (Albert Einstein Institute) Department of Physics, University
Cosmology with Gravitational Wave Detectors. Maya Fishbach
 Cosmology with Gravitational Wave Detectors Maya Fishbach Part I: Cosmography Compact Binary Coalescenses are Standard Sirens The amplitude* of a GW from a CBC is The timescale is Measuring amplitude,
Cosmology with Gravitational Wave Detectors Maya Fishbach Part I: Cosmography Compact Binary Coalescenses are Standard Sirens The amplitude* of a GW from a CBC is The timescale is Measuring amplitude,
, G RAVITATIONAL-WAVE. Kent Yagi. with N. Yunes. Montana State University. YKIS2013, Kyoto
 UNIVERSAL I-LOVE OVE-Q Q RELATIONSR IN Q R NEUTRON STARS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS TO ASTROPHYSICS STROPHYSICS,, GRAVITATIONAL G RAVITATIONAL-WAVE AVE, G AND FUNDAMENTAL PHYSICS Kent Yagi with N. Yunes Montana
UNIVERSAL I-LOVE OVE-Q Q RELATIONSR IN Q R NEUTRON STARS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS TO ASTROPHYSICS STROPHYSICS,, GRAVITATIONAL G RAVITATIONAL-WAVE AVE, G AND FUNDAMENTAL PHYSICS Kent Yagi with N. Yunes Montana
Inferring the Nuclear Equation of State Using Gravitational Waves from Binary Neutron Star Mergers
 Inferring the Nuclear Equation of State Using Gravitational Waves from Binary Neutron Star Mergers Samantha A. Usman 1 Advisors: Tjonnie Li 2, Alan Weinstein 2 1 Department of Physics, Syracuse University,
Inferring the Nuclear Equation of State Using Gravitational Waves from Binary Neutron Star Mergers Samantha A. Usman 1 Advisors: Tjonnie Li 2, Alan Weinstein 2 1 Department of Physics, Syracuse University,
Gravitational waves from NS-NS/BH-NS binaries
 Gravitational waves from NS-NS/BH-NS binaries Numerical-relativity simulation Masaru Shibata Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University Y. Sekiguchi, K. Kiuchi, K. Kyutoku,,H. Okawa, K.
Gravitational waves from NS-NS/BH-NS binaries Numerical-relativity simulation Masaru Shibata Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University Y. Sekiguchi, K. Kiuchi, K. Kyutoku,,H. Okawa, K.
Applications of Neutron-Star Universal Relations to Gravitational Wave Observations
 Applications of Neutron-Star Universal Relations to Gravitational Wave Observations Department of Physics, Montana State University INT, Univ. of Washington, Seattle July 3rd 2014 Universal Relations:
Applications of Neutron-Star Universal Relations to Gravitational Wave Observations Department of Physics, Montana State University INT, Univ. of Washington, Seattle July 3rd 2014 Universal Relations:
arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 25 Mar 2013
![arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 25 Mar 2013 arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 25 Mar 2013](/thumbs/84/91225932.jpg) Extracting equation of state parameters from black hole-neutron star mergers: aligned-spin black holes and a preliminary waveform model Benjamin D. Lackey 1, Koutarou Kyutoku 2, Masaru Shibata 3, Patrick
Extracting equation of state parameters from black hole-neutron star mergers: aligned-spin black holes and a preliminary waveform model Benjamin D. Lackey 1, Koutarou Kyutoku 2, Masaru Shibata 3, Patrick
GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral
 GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral Lazzaro Claudia for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 25 October 2017 GW170817 PhysRevLett.119.161101
GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral Lazzaro Claudia for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 25 October 2017 GW170817 PhysRevLett.119.161101
Inadequacies of the Fisher Matrix in Gravitational-wave Parameter Estimation
 Inadequacies of the Fisher Matrix in Gravitational-wave Parameter Estimation Carl Rodriguez Ilya Mandel Ben Farr The Problem Advanced LIGO receives a signal: Past the initial detection, all science potential
Inadequacies of the Fisher Matrix in Gravitational-wave Parameter Estimation Carl Rodriguez Ilya Mandel Ben Farr The Problem Advanced LIGO receives a signal: Past the initial detection, all science potential
Constraints on Neutron Star Sttructure and Equation of State from GW170817
 Constraints on Neutron Star Sttructure and Equation of State from GW170817 J. M. Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University March 12, 2018 INT-JINA GW170817 12 March, 2018 GW170817
Constraints on Neutron Star Sttructure and Equation of State from GW170817 J. M. Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University March 12, 2018 INT-JINA GW170817 12 March, 2018 GW170817
Four ways of doing cosmography with gravitational waves
 Four ways of doing cosmography with gravitational waves Chris Van Den Broeck National Institute for Subatomic Physics Amsterdam, The Netherlands StronG BaD Workshop, Oxford, Mississippi, 27 February -
Four ways of doing cosmography with gravitational waves Chris Van Den Broeck National Institute for Subatomic Physics Amsterdam, The Netherlands StronG BaD Workshop, Oxford, Mississippi, 27 February -
Equation of state constraints from modern nuclear interactions and observation
 Equation of state constraints from modern nuclear interactions and observation Kai Hebeler Seattle, March 12, 218 First multi-messenger observations of a neutron star merger and its implications for nuclear
Equation of state constraints from modern nuclear interactions and observation Kai Hebeler Seattle, March 12, 218 First multi-messenger observations of a neutron star merger and its implications for nuclear
Probing the High-Density Behavior of Symmetry Energy with Gravitational Waves
 Probing the High-Density Behavior of Symmetry Energy with Gravitational Waves Farrukh J. Fattoyev Bao-An Li, William G. Newton Texas A&M University-Commerce 27 th Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics
Probing the High-Density Behavior of Symmetry Energy with Gravitational Waves Farrukh J. Fattoyev Bao-An Li, William G. Newton Texas A&M University-Commerce 27 th Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans. Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04
 LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
Constraints on Compact Star Radii and the Equation of State From Gravitational Waves, Pulsars and Supernovae
 Constraints on Compact Star Radii and the Equation of State From Gravitational Waves, Pulsars and Supernovae J. M. Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University September 13, 2016 Collaborators:
Constraints on Compact Star Radii and the Equation of State From Gravitational Waves, Pulsars and Supernovae J. M. Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University September 13, 2016 Collaborators:
Search for compact binary systems in LIGO data
 Search for compact binary systems in LIGO data Thomas Cokelaer On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Cardiff University, U.K. LIGO-G060630-00-Z Plan 1) Overview What kind of gravitational waves
Search for compact binary systems in LIGO data Thomas Cokelaer On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Cardiff University, U.K. LIGO-G060630-00-Z Plan 1) Overview What kind of gravitational waves
Simulations of neutron star mergers: Status and prospects
 Simulations of neutron star mergers: Status and prospects David Radice 1,2 1 Research Associate, Princeton University 2 Taplin Member, Institute for Advanced Study First multi-messenger observations of
Simulations of neutron star mergers: Status and prospects David Radice 1,2 1 Research Associate, Princeton University 2 Taplin Member, Institute for Advanced Study First multi-messenger observations of
The Impact of Gravitational Waves: Detectability and Signatures
 The Impact of Gravitational Waves: Detectability and Signatures Jenna Klemkowsky Wheeling Jesuit University Summer 2013 University of Florida International Research Experience for Undergraduates University
The Impact of Gravitational Waves: Detectability and Signatures Jenna Klemkowsky Wheeling Jesuit University Summer 2013 University of Florida International Research Experience for Undergraduates University
Universal Relations for the Moment of Inertia in Relativistic Stars
 Universal Relations for the Moment of Inertia in Relativistic Stars Cosima Breu Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main Astro Coffee Motivation Crab-nebula (de.wikipedia.org/wiki/krebsnebel) neutron stars
Universal Relations for the Moment of Inertia in Relativistic Stars Cosima Breu Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main Astro Coffee Motivation Crab-nebula (de.wikipedia.org/wiki/krebsnebel) neutron stars
Constraining the Radius of Neutron Stars Through the Moment of Inertia
 Constraining the Radius of Neutron Stars Through the Moment of Inertia Neutron star mergers: From gravitational waves to nucleosynthesis International Workshop XLV on Gross Properties of Nuclei and Nuclear
Constraining the Radius of Neutron Stars Through the Moment of Inertia Neutron star mergers: From gravitational waves to nucleosynthesis International Workshop XLV on Gross Properties of Nuclei and Nuclear
Ref. PRL 107, (2011)
 Kenta Kiuchi, Y. Sekiguchi, K. Kyutoku, M. Shibata Ref. PRL 107, 051102 (2011) Y TP YUKAWA INSTITUTE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS Introduction Coalescence of binary neutron stars Promising source of GWs Verification
Kenta Kiuchi, Y. Sekiguchi, K. Kyutoku, M. Shibata Ref. PRL 107, 051102 (2011) Y TP YUKAWA INSTITUTE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS Introduction Coalescence of binary neutron stars Promising source of GWs Verification
Extracting Equation of State Parameters from Black Hole-Neutron Star Mergers
 Extracting Equation of State Parameters from Black Hole-Neutron Star Mergers Benjamin D. Lackey 1, Koutarou Kyutoku, Masaru Shibata, Patrick R. Brady 1, John L. Friedman 1 this is white 1 Department of
Extracting Equation of State Parameters from Black Hole-Neutron Star Mergers Benjamin D. Lackey 1, Koutarou Kyutoku, Masaru Shibata, Patrick R. Brady 1, John L. Friedman 1 this is white 1 Department of
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO
 Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO Duncan Brown University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Inspiral Working Group LIGO-G030671-00-Z S1 Binary
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO Duncan Brown University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Inspiral Working Group LIGO-G030671-00-Z S1 Binary
Gravitational waves (...and GRB central engines...) from neutron star mergers
 Gravitational waves (...and GRB central engines...) from neutron star mergers Roland Oechslin MPA Garching, SFB/TR 7 Ringberg Workshop, 27.3.2007 In this talk: -Intro: -Overview & Motivation -Neutron star
Gravitational waves (...and GRB central engines...) from neutron star mergers Roland Oechslin MPA Garching, SFB/TR 7 Ringberg Workshop, 27.3.2007 In this talk: -Intro: -Overview & Motivation -Neutron star
Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: What could the Signal tell us?
 Outline Harald Dimmelmeier harrydee@mpa-garching.mpg.de Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: What could the Signal tell us? Work done at the MPA in Garching Dimmelmeier, Font, Müller, Astron.
Outline Harald Dimmelmeier harrydee@mpa-garching.mpg.de Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: What could the Signal tell us? Work done at the MPA in Garching Dimmelmeier, Font, Müller, Astron.
Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3
 Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3 Tom Dent (Albert Einstein Institute, Hannover) Chris Pankow (CIERA/Northwestern) for the LIGO and Virgo Collaborations DCC: LIGO-G1800370
Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3 Tom Dent (Albert Einstein Institute, Hannover) Chris Pankow (CIERA/Northwestern) for the LIGO and Virgo Collaborations DCC: LIGO-G1800370
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 20 Mar 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 20 Mar 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 20 Mar 2018](/thumbs/80/80793243.jpg) Draft version March 22, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 TIDAL DEFORMABILITY FROM GW170817 AS A DIRECT PROBE OF THE NEUTRON STAR RADIUS Carolyn A. Raithel, Feryal Özel,
Draft version March 22, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 TIDAL DEFORMABILITY FROM GW170817 AS A DIRECT PROBE OF THE NEUTRON STAR RADIUS Carolyn A. Raithel, Feryal Özel,
TIDAL LOVE NUMBERS OF NEUTRON STARS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 677:116Y10, 008 April 0 # 008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. TIDAL LOVE NUMBERS OF NEUTRON STARS Tanja Hinderer Center for Radiophysics
The Astrophysical Journal, 677:116Y10, 008 April 0 # 008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. TIDAL LOVE NUMBERS OF NEUTRON STARS Tanja Hinderer Center for Radiophysics
EOS Constraints From Neutron Stars
 EOS Constraints From Neutron Stars J. M. Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University January 17, 2016 Bridging Nuclear and Gravitational Physics: the Dense Matter Equation of State
EOS Constraints From Neutron Stars J. M. Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University January 17, 2016 Bridging Nuclear and Gravitational Physics: the Dense Matter Equation of State
Gravitational waves from neutron-star binaries
 Gravitational waves from neutron-star binaries - Constraining Neutron Star EOS - Masaru Shibata Center for Gravitational Physics, Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University Outline 0. Brief
Gravitational waves from neutron-star binaries - Constraining Neutron Star EOS - Masaru Shibata Center for Gravitational Physics, Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University Outline 0. Brief
Neutron-star mergers:
 Neutron-star mergers: Predictions by numerical relativity Masaru Shibata Center for Gravitational Physics, Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University Many people are exploring NS binaries
Neutron-star mergers: Predictions by numerical relativity Masaru Shibata Center for Gravitational Physics, Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University Many people are exploring NS binaries
Bayesian methods in the search for gravitational waves
 Bayesian methods in the search for gravitational waves Reinhard Prix Albert-Einstein-Institut Hannover Bayes forum Garching, Oct 7 2016 Statistics as applied Probability Theory Probability Theory: extends
Bayesian methods in the search for gravitational waves Reinhard Prix Albert-Einstein-Institut Hannover Bayes forum Garching, Oct 7 2016 Statistics as applied Probability Theory Probability Theory: extends
LIGO Observational Results
 LIGO Observational Results Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin Milwaukee on behalf of LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Science Goals Direct verification of two dramatic predictions of Einstein s general
LIGO Observational Results Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin Milwaukee on behalf of LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Science Goals Direct verification of two dramatic predictions of Einstein s general
Gravitational waves from binary neutron stars
 Gravitational waves from binary neutron stars Koutarou Kyutoku High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK), Institute of Particle and Nuclear Studies 2018/11/12 QNP2018 satellite at Tokai 1 Plan
Gravitational waves from binary neutron stars Koutarou Kyutoku High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK), Institute of Particle and Nuclear Studies 2018/11/12 QNP2018 satellite at Tokai 1 Plan
Neutron Star Observations and Their Implications for the Nuclear Equation of State
 Neutron Star Observations and Their Implications for the Nuclear Equation of State J. M. Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University May 24, 2016 24 May, 2016, JINA-CEE International
Neutron Star Observations and Their Implications for the Nuclear Equation of State J. M. Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University May 24, 2016 24 May, 2016, JINA-CEE International
James Clark For The LSC
 A search for gravitational waves associated with the August 2006 timing glitch of the http://arxiv.org/abs/1011.1357 Vela pulsar James Clark For The LSC Introduction This talk: first search for GWs associated
A search for gravitational waves associated with the August 2006 timing glitch of the http://arxiv.org/abs/1011.1357 Vela pulsar James Clark For The LSC Introduction This talk: first search for GWs associated
Parameter estimation for signals from compact binary inspirals injected into LIGO data
 IOP PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 26 (2009) 204010 (10pp) CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY doi:10.1088/0264-9381/26/20/204010 Parameter estimation for signals from compact binary inspirals injected into
IOP PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 26 (2009) 204010 (10pp) CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY doi:10.1088/0264-9381/26/20/204010 Parameter estimation for signals from compact binary inspirals injected into
Searching for Intermediate Mass Black Holes mergers
 Searching for Intermediate Mass Black Holes mergers G. A. Prodi, Università di Trento and INFN for the LIGO Scientific collaboration and the Virgo collaboration special credits to Giulio Mazzolo and Chris
Searching for Intermediate Mass Black Holes mergers G. A. Prodi, Università di Trento and INFN for the LIGO Scientific collaboration and the Virgo collaboration special credits to Giulio Mazzolo and Chris
arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 12 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 12 Oct 2015 arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 12 Oct 2015](/thumbs/88/115710989.jpg) Parameter estimation using a complete signal and inspiral templates for low mass binary black holes with Advanced LIGO sensitivity arxiv:5.4399v [gr-qc] Oct 5 Hee-Suk Cho E-mail: chohs439@pusan.ac.kr Korea
Parameter estimation using a complete signal and inspiral templates for low mass binary black holes with Advanced LIGO sensitivity arxiv:5.4399v [gr-qc] Oct 5 Hee-Suk Cho E-mail: chohs439@pusan.ac.kr Korea
Status and Prospects for LIGO
 Status and Prospects for LIGO Crab Pulsar St Thomas, Virgin Islands Barry C. Barish Caltech 17-March-06 LIGO Livingston, Louisiana 4 km 17-March-06 Confronting Gravity - St Thomas 2 LIGO Hanford Washington
Status and Prospects for LIGO Crab Pulsar St Thomas, Virgin Islands Barry C. Barish Caltech 17-March-06 LIGO Livingston, Louisiana 4 km 17-March-06 Confronting Gravity - St Thomas 2 LIGO Hanford Washington
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves
 Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Barry C. Barish Caltech Argonne National Laboratory 16-Jan-04 LIGO-G030523-00-M
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Barry C. Barish Caltech Argonne National Laboratory 16-Jan-04 LIGO-G030523-00-M
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 26 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 26 Oct 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 26 Oct 2015](/thumbs/95/125324935.jpg) EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:1510.07515v1 [astro-ph.he] 26 Oct 2015 Neutron Star Radii, Universal Relations, and the Role of Prior Distributions A. W. Steiner 1,2, J. M. Lattimer
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:1510.07515v1 [astro-ph.he] 26 Oct 2015 Neutron Star Radii, Universal Relations, and the Role of Prior Distributions A. W. Steiner 1,2, J. M. Lattimer
The effect of f - modes on the gravitational waves during a binary inspiral
 The effect of f - modes on the gravitational waves during a binary inspiral Tanja Hinderer (AEI Potsdam) PRL 116, 181101 (2016), arxiv:1602.00599 and arxiv:1608.01907? A. Taracchini F. Foucart K. Hotokezaka
The effect of f - modes on the gravitational waves during a binary inspiral Tanja Hinderer (AEI Potsdam) PRL 116, 181101 (2016), arxiv:1602.00599 and arxiv:1608.01907? A. Taracchini F. Foucart K. Hotokezaka
Gravitational Waves. Masaru Shibata U. Tokyo
 Gravitational Waves Masaru Shibata U. Tokyo 1. Gravitational wave theory briefly 2. Sources of gravitational waves 2A: High frequency (f > 10 Hz) 2B: Low frequency (f < 10 Hz) (talk 2B only in the case
Gravitational Waves Masaru Shibata U. Tokyo 1. Gravitational wave theory briefly 2. Sources of gravitational waves 2A: High frequency (f > 10 Hz) 2B: Low frequency (f < 10 Hz) (talk 2B only in the case
Long-term strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups
 Longterm strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups Barry Barish APPEC Meeting London, UK 29Jan04 International Interferometer Network Simultaneously detect signal (within msec) LIGO
Longterm strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups Barry Barish APPEC Meeting London, UK 29Jan04 International Interferometer Network Simultaneously detect signal (within msec) LIGO
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 11 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 11 Dec 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 11 Dec 2008](/thumbs/89/97949908.jpg) Constraints on a phenomenologically parameterized neutron-star equation of state Jocelyn S. Read 1, Benjamin D. Lackey 1, Benjamin J. Owen 2, and John L. Friedman 1 1 Department of Physics, University
Constraints on a phenomenologically parameterized neutron-star equation of state Jocelyn S. Read 1, Benjamin D. Lackey 1, Benjamin J. Owen 2, and John L. Friedman 1 1 Department of Physics, University
Symmetry Energy Constraints From Neutron Stars and Experiment
 Symmetry Energy Constraints From Neutron Stars and Experiment Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University 17 January 2012 Collaborators: E. Brown (MSU), K. Hebeler (OSU), C.J. Pethick (NORDITA),
Symmetry Energy Constraints From Neutron Stars and Experiment Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University 17 January 2012 Collaborators: E. Brown (MSU), K. Hebeler (OSU), C.J. Pethick (NORDITA),
Gravity. Newtonian gravity: F = G M1 M2/r 2
 Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity : Gravity is a manifestation of curvature of 4- dimensional (3 space + 1 time) space-time produced by matter (metric equation? g μν = η μν ) If the curvature
Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity : Gravity is a manifestation of curvature of 4- dimensional (3 space + 1 time) space-time produced by matter (metric equation? g μν = η μν ) If the curvature
Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life
 Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life Romain Gouaty LAPP - Université de Savoie - CNRS/IN2P3 On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life Romain Gouaty LAPP - Université de Savoie - CNRS/IN2P3 On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Extreme Properties of Neutron Stars
 Extreme Properties of The most compact and massive configurations occur when the low-density equation of state is soft and the high-density equation of state is stiff (Koranda, Stergioulas & Friedman 1997).
Extreme Properties of The most compact and massive configurations occur when the low-density equation of state is soft and the high-density equation of state is stiff (Koranda, Stergioulas & Friedman 1997).
Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles
 Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles Éric Chassande-Mottin AstroParticule et Cosmologie, Paris et collaborateurs : Satya Mohapatra, Miriam Miele, Laura Cadonati, Zacharya Nemtzow Outline
Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles Éric Chassande-Mottin AstroParticule et Cosmologie, Paris et collaborateurs : Satya Mohapatra, Miriam Miele, Laura Cadonati, Zacharya Nemtzow Outline
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL, PHYSICAL AND NATURAL SCIENCES. AUTHOR Francesco Torsello SUPERVISOR Prof. Valeria Ferrari
 FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL, PHYSICAL AND NATURAL SCIENCES AUTHOR Francesco SUPERVISOR Prof. Valeria Ferrari Internal structure of a neutron star M [ 1, 2] M n + p + e + µ 0.3km; atomic nuclei +e 0.5km; PRM
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL, PHYSICAL AND NATURAL SCIENCES AUTHOR Francesco SUPERVISOR Prof. Valeria Ferrari Internal structure of a neutron star M [ 1, 2] M n + p + e + µ 0.3km; atomic nuclei +e 0.5km; PRM
Gravitational radiation from compact binaries in scalar-tensor gravity
 Gravitational radiation from compact binaries in scalar-tensor gravity Ryan Lang University of Florida 10th International LISA Symposium May 23, 2014 Testing general relativity General relativity has withstood
Gravitational radiation from compact binaries in scalar-tensor gravity Ryan Lang University of Florida 10th International LISA Symposium May 23, 2014 Testing general relativity General relativity has withstood
Modeling gravitational waves from compact-object binaries
 Modeling gravitational waves from compact-object binaries Andrea Taracchini (Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics, Albert Einstein Institute Potsdam, Germany) [https://dcc.ligo.org/g1602133]
Modeling gravitational waves from compact-object binaries Andrea Taracchini (Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics, Albert Einstein Institute Potsdam, Germany) [https://dcc.ligo.org/g1602133]
Continuous-wave gravitational radiation from pulsar glitch recovery
 1 Continuous-wave gravitational radiation from pulsar glitch recovery Mark Bennett Anthony van Eysden & Andrew Melatos University of Melbourne 1 September 2010, ET WG4 Nice Meeting 2 Talk Outline Pulsar
1 Continuous-wave gravitational radiation from pulsar glitch recovery Mark Bennett Anthony van Eysden & Andrew Melatos University of Melbourne 1 September 2010, ET WG4 Nice Meeting 2 Talk Outline Pulsar
arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 29 Jul 2013
![arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 29 Jul 2013 arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 29 Jul 2013](/thumbs/79/80174898.jpg) Equation-of-state-independent relations in neutron stars arxiv:14.52v2 [gr-qc] 29 Jul 13 Andrea Maselli, 1, 2 Vitor Cardoso, 3, 4, 5 Valeria Ferrari, 2 Leonardo Gualtieri, 2 and Paolo Pani 3, 6 1 Institute
Equation-of-state-independent relations in neutron stars arxiv:14.52v2 [gr-qc] 29 Jul 13 Andrea Maselli, 1, 2 Vitor Cardoso, 3, 4, 5 Valeria Ferrari, 2 Leonardo Gualtieri, 2 and Paolo Pani 3, 6 1 Institute
Rate (Upper Limit) Calculation
 117 Chapter 9 Rate (Upper Limit) Calculation Whether the search results in a small number of detection candidates or more, we can bound the rate of CBCs in the (nearby) universe. Depending on the significance
117 Chapter 9 Rate (Upper Limit) Calculation Whether the search results in a small number of detection candidates or more, we can bound the rate of CBCs in the (nearby) universe. Depending on the significance
GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY
 GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY A. Melatos (Melbourne) 1. GW: physics & astronomy 2. Current- & next-gen detectors & searches 3. Burst sources: CBC, SN GR, cosmology 4. Periodic sources: NS subatomic physics
GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY A. Melatos (Melbourne) 1. GW: physics & astronomy 2. Current- & next-gen detectors & searches 3. Burst sources: CBC, SN GR, cosmology 4. Periodic sources: NS subatomic physics
Miscellany : Long Run Behavior of Bayesian Methods; Bayesian Experimental Design (Lecture 4)
 Miscellany : Long Run Behavior of Bayesian Methods; Bayesian Experimental Design (Lecture 4) Tom Loredo Dept. of Astronomy, Cornell University http://www.astro.cornell.edu/staff/loredo/bayes/ Bayesian
Miscellany : Long Run Behavior of Bayesian Methods; Bayesian Experimental Design (Lecture 4) Tom Loredo Dept. of Astronomy, Cornell University http://www.astro.cornell.edu/staff/loredo/bayes/ Bayesian
Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves
 Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan (LIGO Laboratory / Caltech) For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration American Physical Society April Meeting May 4, 2004 Denver,
Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan (LIGO Laboratory / Caltech) For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration American Physical Society April Meeting May 4, 2004 Denver,
Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars
 Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars Ian Jones D.I.Jones@soton.ac.uk General Relativity Group, Southampton University Ian Jones Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars 1/23
Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars Ian Jones D.I.Jones@soton.ac.uk General Relativity Group, Southampton University Ian Jones Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars 1/23
Gravitational-wave Detectability of Equal-Mass Black-hole Binaries With Aligned Spins
 Intro Simulations Results Gravitational-wave Detectability of Equal-Mass Black-hole Binaries With Aligned Spins Jennifer Seiler Christian Reisswig, Sascha Husa, Luciano Rezzolla, Nils Dorband, Denis Pollney
Intro Simulations Results Gravitational-wave Detectability of Equal-Mass Black-hole Binaries With Aligned Spins Jennifer Seiler Christian Reisswig, Sascha Husa, Luciano Rezzolla, Nils Dorband, Denis Pollney
LIGO and the Quest for Gravitational Waves
 LIGO and the Quest for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) LIGO-G030523-00-M Barry C. Barish Caltech UT Austin 24-Sept-03 1 A Conceptual
LIGO and the Quest for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) LIGO-G030523-00-M Barry C. Barish Caltech UT Austin 24-Sept-03 1 A Conceptual
arxiv:gr-qc/ v1 4 Dec 2003
 Testing the LIGO Inspiral Analysis with Hardware Injections arxiv:gr-qc/0312031 v1 4 Dec 2003 Duncan A. Brown 1 for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
Testing the LIGO Inspiral Analysis with Hardware Injections arxiv:gr-qc/0312031 v1 4 Dec 2003 Duncan A. Brown 1 for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
Numerical trial for cleaning of gravitational wave foreground by neutron star binaries in DECIGO
 Numerical trial for cleaning of gravitational wave foreground by neutron star binaries in DECIGO Mitsuru Tokuda, Nobuyuki Kanda Osaka City University Olbers Paradox Heinrich Wilhelm Matthäus Olbers (1758-1840)
Numerical trial for cleaning of gravitational wave foreground by neutron star binaries in DECIGO Mitsuru Tokuda, Nobuyuki Kanda Osaka City University Olbers Paradox Heinrich Wilhelm Matthäus Olbers (1758-1840)
GRAVITATIONAL-WAVE ASTRONOMY WITH COALESCING COMPACT BINARIES: DETECTION AND PARAMETER ESTIMATION WITH ADVANCED DETECTORS
 GRAVITATIONAL-WAVE ASTRONOMY WITH COALESCING COMPACT BINARIES: DETECTION AND PARAMETER ESTIMATION WITH ADVANCED DETECTORS RORY JAMES EDWIN SMITH A thesis submitted to the University of Birmingham for the
GRAVITATIONAL-WAVE ASTRONOMY WITH COALESCING COMPACT BINARIES: DETECTION AND PARAMETER ESTIMATION WITH ADVANCED DETECTORS RORY JAMES EDWIN SMITH A thesis submitted to the University of Birmingham for the
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems
 Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems Stephen Fairhurst Cardiff University and LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Outline Motivation Searching for Coalescing Binaries Latest Results
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems Stephen Fairhurst Cardiff University and LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Outline Motivation Searching for Coalescing Binaries Latest Results
Gravitational waveforms for data analysis of spinning binary black holes
 Gravitational waveforms for data analysis of spinning binary black holes Andrea Taracchini (Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics, Albert Einstein Institute Potsdam, Germany) [https://dcc.ligo.org/g1700243]
Gravitational waveforms for data analysis of spinning binary black holes Andrea Taracchini (Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics, Albert Einstein Institute Potsdam, Germany) [https://dcc.ligo.org/g1700243]
arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 8 Sep 2015
![arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 8 Sep 2015 arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 8 Sep 2015](/thumbs/76/73274989.jpg) Measuring violations of General Relativity from single gravitational wave detection by non-spinning binary systems: higher-order asymptotic analysis arxiv:1509.048v1 [gr-qc] 8 Sep 015 1,, 3, a Rhondale
Measuring violations of General Relativity from single gravitational wave detection by non-spinning binary systems: higher-order asymptotic analysis arxiv:1509.048v1 [gr-qc] 8 Sep 015 1,, 3, a Rhondale
Testing GR with Compact Object Binary Mergers
 Testing GR with Compact Object Binary Mergers Frans Pretorius Princeton University The Seventh Harvard-Smithsonian Conference on Theoretical Astrophysics : Testing GR with Astrophysical Systems May 16,
Testing GR with Compact Object Binary Mergers Frans Pretorius Princeton University The Seventh Harvard-Smithsonian Conference on Theoretical Astrophysics : Testing GR with Astrophysical Systems May 16,
EINSTEIN TELESCOPE rd. 3 generation GW detector
 EINSTEIN TELESCOPE rd 3 generation GW detector http://www.et-gw.eu/ Dorota Gondek-Rosińska University of Zielona Góra w imieniu polskiego ET konsorcjum (UW, UZG, UwB, PW, CAMK, IMPAN ) Gravitational wave
EINSTEIN TELESCOPE rd 3 generation GW detector http://www.et-gw.eu/ Dorota Gondek-Rosińska University of Zielona Góra w imieniu polskiego ET konsorcjum (UW, UZG, UwB, PW, CAMK, IMPAN ) Gravitational wave
Extracting Neutron Star Radii from the Tidal Deformability of GW170817
 Extracting Neutron Star Radii from the Tidal Deformability of GW170817 Carolyn Raithel Feryal Özel and Dimitrios Psaltis University of Arizona March 12, 2018 INT Symposium on GW170817 First measurement
Extracting Neutron Star Radii from the Tidal Deformability of GW170817 Carolyn Raithel Feryal Özel and Dimitrios Psaltis University of Arizona March 12, 2018 INT Symposium on GW170817 First measurement
Neutron star coalescences A good microphysics laboratory
 Neutron star coalescences A good microphysics laboratory Rubén M. Cabezón Grup d Astronomia i Astrofísica Dept. de Física i Enginyeria Nuclear UPC (Barcelona) In this talk: o Motivation o What is a neutron
Neutron star coalescences A good microphysics laboratory Rubén M. Cabezón Grup d Astronomia i Astrofísica Dept. de Física i Enginyeria Nuclear UPC (Barcelona) In this talk: o Motivation o What is a neutron
Strong field tests of Gravity using Gravitational Wave observations
 Strong field tests of Gravity using Gravitational Wave observations K. G. Arun Chennai Mathematical Institute Astronomy, Cosmology & Fundamental Physics with GWs, 04 March, 2015 indig K G Arun (CMI) Strong
Strong field tests of Gravity using Gravitational Wave observations K. G. Arun Chennai Mathematical Institute Astronomy, Cosmology & Fundamental Physics with GWs, 04 March, 2015 indig K G Arun (CMI) Strong
Neutron Stars. Melissa Louie
 Neutron Stars Melissa Louie 11-08-10 Outline History, Formation, Properties Detection Pulsars Crab Nebula Pulsar Pulsar Timing Pulsars in Binary Systems Isolated Neutron Stars J185635-3754 Summary 2 The
Neutron Stars Melissa Louie 11-08-10 Outline History, Formation, Properties Detection Pulsars Crab Nebula Pulsar Pulsar Timing Pulsars in Binary Systems Isolated Neutron Stars J185635-3754 Summary 2 The
GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University. Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne]
![GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University. Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne] GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University. Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne]](/thumbs/79/79556320.jpg) GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne] Summary of talk Review of observational upper limits and current and planned
GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne] Summary of talk Review of observational upper limits and current and planned
GR Simulations of Neutron Star-Neutron Star & Black Hole-Neutron Star Binaries
 GR Simulations of Neutron Star-Neutron Star & Black Hole-Neutron Star Binaries Masaru Shibata Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University Introduction: Why NS-NS/BH-NS simulations are important?
GR Simulations of Neutron Star-Neutron Star & Black Hole-Neutron Star Binaries Masaru Shibata Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University Introduction: Why NS-NS/BH-NS simulations are important?
Gravitational wave from neutron star
 Gravitational wave from neutron star phase transition Shu Lin 2018.11.4 ATHIC 2018, Hefei based on 1810.00528, Gaoqing Cao, SL Outline Introduction GW from binary neutron star merger GW generation from
Gravitational wave from neutron star phase transition Shu Lin 2018.11.4 ATHIC 2018, Hefei based on 1810.00528, Gaoqing Cao, SL Outline Introduction GW from binary neutron star merger GW generation from
S. V. Dhurandhar IUCAA Pune, India
 Extended hierarchical search (EHS) for inspiraling compact binaries S. V. Dhurandhar IUCAA Pune, India * A. Sengupta, A. Lazzarini, P. Shawhan LIGO-G040556-00-R Plan of the Talk The 1-step (flat) search
Extended hierarchical search (EHS) for inspiraling compact binaries S. V. Dhurandhar IUCAA Pune, India * A. Sengupta, A. Lazzarini, P. Shawhan LIGO-G040556-00-R Plan of the Talk The 1-step (flat) search
Detecting the next Galactic supernova
 Detecting the next Galactic supernova Nicolas Arnaud on behalf of the Virgo-LAL group Now fellow at LHCb-CERN Moriond Gravitation 2003 GW supernova amplitudes Burst online filter performances Comparison
Detecting the next Galactic supernova Nicolas Arnaud on behalf of the Virgo-LAL group Now fellow at LHCb-CERN Moriond Gravitation 2003 GW supernova amplitudes Burst online filter performances Comparison
Physics and Astrophysics with Gravitational. Ground Based Interferometers
 Physics and Astrophysics with Gravitational Waves from Compact Binary Coalescence in Ground Based Interferometers by Katherine L. Grover A thesis submitted to the University of Birmingham for the degree
Physics and Astrophysics with Gravitational Waves from Compact Binary Coalescence in Ground Based Interferometers by Katherine L. Grover A thesis submitted to the University of Birmingham for the degree
Errors in History Matching by. Zohreh Tavassoli Jonathan Carter Peter King Department of Earth Science & Engineering Imperial College, London, UK
 Errors in History Matching by Zohreh Tavassoli Jonathan Carter Peter King Department of Earth Science & Engineering Imperial College London UK Introduction History Matching is used to find parameters in
Errors in History Matching by Zohreh Tavassoli Jonathan Carter Peter King Department of Earth Science & Engineering Imperial College London UK Introduction History Matching is used to find parameters in
Gravitational Wave Astronomy the sound of spacetime. Marc Favata Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics
 Gravitational Wave Astronomy the sound of spacetime Marc Favata Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics What are gravitational waves? Oscillations in the gravitational field ripples in the curvature of
Gravitational Wave Astronomy the sound of spacetime Marc Favata Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics What are gravitational waves? Oscillations in the gravitational field ripples in the curvature of
Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S691 S696 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68883-6 Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data Gabriela González
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S691 S696 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68883-6 Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data Gabriela González
On the detectability of post-newtonian eects. in gravitational-wave emission of a coalescing. binary 1. Institute of Mathematics
 On the detectability of post-newtonian eects in gravitational-wave emission of a coalescing binary 1 ANDRZEJ KR OLAK a KOSTAS D. KOKKOTAS b GERHARD SCH AFER c PostScript processed by the SLAC/DESY Libraries
On the detectability of post-newtonian eects in gravitational-wave emission of a coalescing binary 1 ANDRZEJ KR OLAK a KOSTAS D. KOKKOTAS b GERHARD SCH AFER c PostScript processed by the SLAC/DESY Libraries
Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: Current state and future prospects
 Gravitational Waves from Core Collapse Harald Dimmelmeier harrydee@mpa-garching.mpg.de Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: Current state and future prospects Work done with E. Müller (MPA)
Gravitational Waves from Core Collapse Harald Dimmelmeier harrydee@mpa-garching.mpg.de Gravitational Waves from Supernova Core Collapse: Current state and future prospects Work done with E. Müller (MPA)
LIGO S2 Inspiral Hardware Injections
 LIGO S2 Inspiral Hardware Injections Steve Fairhurst University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee LSC Inspiral Working Group GWDAW December 19, 2003. LIGO-G030688-00-Z Introduction Hardware injections provide a good
LIGO S2 Inspiral Hardware Injections Steve Fairhurst University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee LSC Inspiral Working Group GWDAW December 19, 2003. LIGO-G030688-00-Z Introduction Hardware injections provide a good
Systematic Errors in Neutron Star Radius Measurements. Cole Miller University of Maryland and Joint Space-Science Institute
 Systematic Errors in Neutron Star Radius Measurements Cole Miller University of Maryland and Joint Space-Science Institute 1 Outline Key point: M max >2 M s is solid, but all current NS radius estimates
Systematic Errors in Neutron Star Radius Measurements Cole Miller University of Maryland and Joint Space-Science Institute 1 Outline Key point: M max >2 M s is solid, but all current NS radius estimates
M.Alessandra Papa. Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee. ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune
 Gravitational Wave Data Analysis M.Alessandra Papa Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune Gravitational wave data analysis * legacy
Gravitational Wave Data Analysis M.Alessandra Papa Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune Gravitational wave data analysis * legacy
GENERAL RELATIVISTIC SIMULATIONS OF NS BINARIES. Bruno Giacomazzo University of Trento and INFN-TIFPA, Italy
 GENERAL RELATIVISTIC SIMULATIONS OF NS BINARIES Bruno Giacomazzo University of Trento and INFN-TIFPA, Italy WHY SO INTERESTING? Due to their duration and dynamics, NS-NS and NS-BH binaries are very good
GENERAL RELATIVISTIC SIMULATIONS OF NS BINARIES Bruno Giacomazzo University of Trento and INFN-TIFPA, Italy WHY SO INTERESTING? Due to their duration and dynamics, NS-NS and NS-BH binaries are very good
continuous waves from rotating neutron stars
 continuous waves from rotating neutron stars Matthew Pitkin - University of Glasgow DAWN Workshop 7 May 2015 LIGO G1500603 0 continuous wave sources Rotating neutron stars with a non-axisymmetric deformation
continuous waves from rotating neutron stars Matthew Pitkin - University of Glasgow DAWN Workshop 7 May 2015 LIGO G1500603 0 continuous wave sources Rotating neutron stars with a non-axisymmetric deformation
State of LIGO. Barry Barish. S1 sensitivities. LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km LIGO-G M
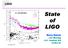 S1 sensitivities -- GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km State of h 0 LIGO Barry Barish LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov-03 Goals and Priorities LSC -Aug 02 Interferometer performance» Integrate commissioning
S1 sensitivities -- GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km State of h 0 LIGO Barry Barish LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov-03 Goals and Priorities LSC -Aug 02 Interferometer performance» Integrate commissioning
HPC in Physics. (particularly astrophysics) Reuben D. Budiardja Scientific Computing National Institute for Computational Sciences
 HPC in Physics (particularly astrophysics) Reuben D. Budiardja Scientific Computing National Institute for Computational Sciences 1 Gravitational Wave Einstein s Unfinished Symphony Marcia Bartuciak Predicted
HPC in Physics (particularly astrophysics) Reuben D. Budiardja Scientific Computing National Institute for Computational Sciences 1 Gravitational Wave Einstein s Unfinished Symphony Marcia Bartuciak Predicted
Neutron stars in globular clusters as tests of nuclear physics
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 87, 521 c SAIt 2016 Memorie della Neutron stars in globular clusters as tests of nuclear physics S. Guillot Instituto de Astrofisica Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile Macul, Santiago,
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 87, 521 c SAIt 2016 Memorie della Neutron stars in globular clusters as tests of nuclear physics S. Guillot Instituto de Astrofisica Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile Macul, Santiago,
Testing relativity with gravitational waves
 Testing relativity with gravitational waves Michał Bejger (CAMK PAN) ECT* workshop New perspectives on Neutron Star Interiors Trento, 10.10.17 (DCC G1701956) Gravitation: Newton vs Einstein Absolute time
Testing relativity with gravitational waves Michał Bejger (CAMK PAN) ECT* workshop New perspectives on Neutron Star Interiors Trento, 10.10.17 (DCC G1701956) Gravitation: Newton vs Einstein Absolute time
Searching for Big Bang relicts with LIGO. Stefan W. Ballmer For the LSC/VIRGO collaboration GW2010, University of Minnesota October 16, 2010
 Searching for Big Bang relicts with LIGO Stefan W. Ballmer For the LSC/VIRGO collaboration GW2010, University of Minnesota October 16, 2010 Outline The search for a stochastic GW background» Motivation»
Searching for Big Bang relicts with LIGO Stefan W. Ballmer For the LSC/VIRGO collaboration GW2010, University of Minnesota October 16, 2010 Outline The search for a stochastic GW background» Motivation»
Sources of Gravitational Waves
 1 Sources of Gravitational Waves Joan Centrella Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics NASA/GSFC Gravitational Interaction of Compact Objects KITP May 12-14, 2003 A Different Type of Astronomical Messenger
1 Sources of Gravitational Waves Joan Centrella Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics NASA/GSFC Gravitational Interaction of Compact Objects KITP May 12-14, 2003 A Different Type of Astronomical Messenger
