Parabolas. Example. y = ax 2 + bx + c where a = 1, b = 0, c = 0. = x 2 + 6x [expanding] \ y = x 2 + 6x + 11 and so is of the form
|
|
|
- Cori Strickland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Parabolas NCEA evel Achievement Standard 9157 (Mathematics and Statistics.) Appl graphical methods in solving problems Methods include: graphs at curriculum level 7, their features and their equations transformations of graphs. Parabolas Parabolas are the graphs of quadratic functions, which are functions of the tpe = a + b + c where a, b and c are constant numbers. Chapter 7 Graphs of quadratics = a + b + c where a = ±1 The graphs of functions of the tpe = a + b + c, where a = ±1, can be obtained b filling in a table of values (as in Chapter 6) and joining the resulting points b a smooth curve. Eample The graphs of = (graph I), = ( + 3) + (graph II) and = 4 ( ) (graph III) are shown. Each of the equations of these three graphs can be epanded and simplified to the form = a + b + c where a = ±1 (as shown below). I: = is alread in the form = a + b + c where a = 1, b = 0, c = 0 II I 6 Domain = Reals, Range = 0 II: = ( + 3) + 4 = [epanding] III \ = and so is of the form = a + b + c where a = 1, b = 6 and c = Domain = Reals, Range = III: = 4 ( ) 4 = 4 ( 4 + 4) [epanding] = \ = + 4 and so is of the form = a + b + c where a = 1, b = 4 and c = 0 Domain = Reals, Range = 4 Note: If a (the coefficient of ) is negative, the graph is inverted. Graphs of = ±( a) + b The above eample illustrates that an graph of the tpe = ±( a) + b is congruent (identical in size and shape) to the graph of =, and has a verte (turning point) at (a,b). For eample, = ( + 3) + has a verte at (3,) which is a local minimum, and = 4 ( ) (which can be written as = ( ) + 4) has a verte at (,4), which is a local maimum. ESA Publications (NZ) td, Customer freephone:
2 4 Achievement Standard 9157 (Mathematics and Statistics.) Graphs of quadratics in factorised form Quadratic functions which are factorised are easil sketched, b plotting intercepts and finding the verte using the ais of smmetr. Functions whose graphs are congruent to = have factorised form = ( a)( b) where a and b are real numbers. Eample The graph of = ( 1)( 3) is shown (the parabola) along with the ais of smmetr 6 (the dotted vertical line = ). 4 Note the following important points: The intercept is 3, which is found b setting 4 = 0 in the equation. This gives = (0 1)(0 3) = 3 The intercepts are 1 and 3 which are found b setting = 0 in the equation. The ais of smmetr is midwa between the intercepts. Its equation is = 1 + 3, which is = The coordinates of the verte are (,1). The verte is found b substituting = (the equation of the ais of smmetr) into the equation. This gives = ( 1)( 3) = 1 A smooth curve is drawn through the intercepts and verte, so that a smmetrical graph results. If a graph is congruent to =, its factorised equation will be of the form = ( a)( b) or = ( a)(b ). Eample Q. Write down the equation in factorised form of the parabola shown. A. The graph is congruent to = and has intercepts 3 and 1. The equation of the parabola is therefore: = ( + 3)( 1) Alternativel, since ( 1) = 1, the equation can be written: = ( + 3)(1 ) Chapter 7 Activit 7B: Graphs of quadratics in factorised form Ans p a. Cop and complete in this table of values for the function = ( + 3)( 1) b. Use our table to draw the graph of = ( + 3)( 1) c. What are the coordinates of the intercepts of the graph ou have drawn? d. What are the coordinate of intercept of the graph ou have drawn? ESA Publications (NZ) td, Customer freephone:
3 e. What is the equation of the ais of smmetr of this graph? f. What are the coordinates of the verte of this graph? g. Write the equation of this parabola in the form = a + b + c.. a. Cop and complete the table and draw the graph of = ( + )( ) Chapter 7: Parabolas b. What is the equation of the ais of smmetr of this graph? c. What are the coordinates of the verte of this graph? d. What are the coordinates of the intercepts of this graph? e. Write the equation of this parabola in the form = a + b + c. 3. Write the equation in factored form for each of the parabolas (I, II, III) shown. Each is congruent to =. 6 II I III 6 Graphs of quadratics which can be factorised Quadratic functions which can be factorised are easil sketched, using the techniques discussed in the previous section. Eample = can be factorised to give = ( 1) ( 5) 6 The intercept is found b substituting = 0: = (0 1)(0 5) = 5 4 The intercepts are found b substituting = 0: ( 1)( 5) = 0 = 1 or = The ais of smmetr lies midwa between the intercepts and hence is the vertical line through = 3 4 The turning point will lie on the ais of smmetr and will have vertical coordinate: = (3 1) (3 5) = 4 [substituting = 3 into = ( 1)( 5)] \ the turning point is (3,4) Note: = can be written as = ( 3) 4 which is in the form = a( b) + c and thus could be sketched using the method described in the first eample. Chapter 7 ESA Publications (NZ) td, Customer freephone:
4 44 Achievement Standard 9157 (Mathematics and Statistics.) Activit 7C: Graphs of quadratics which can be factorised Ans p. 358 Draw a neat graph for each of the following quadratic functions, showing clearl: i. intercept ii. intercepts iii. turning points 1. = 3. = = ( 8) 4. = = = Graphs of = a + b + c when a 1 When b, c are both zero, the graphs are of the tpe = a. Eample Sketches of =, =, = 1 3 and = 1 are drawn b plotting a few points and joining them. (Take care to square the values before multipling b the coefficient. For eample, if = 1 then = 1 =.) = 3 = = = Note: The graph of = is the graph of = stretched verticall. The graph of = 1 3 is the graph of = compressed verticall. Chapter 7 The graph of = 1 is the graph of = compressed verticall and inverted. Activit 7D: Graphs of the form = a Ans p. 358 Sketch the graphs of the following quadratic functions. abel the coordinates of a point on each graph. 1. = 3. = 1 3. = 4. = 3 5. = 4 ESA Publications (NZ) td, Customer freephone:
5 Formulae NCEA evel Achievement Standard 9161 (Mathematics and Statistics.6) Appl algebraic methods in solving problems Methods include: manipulating algebraic epressions including rational epressions manipulating epressions with eponents. Chapter 0 Introduction The topics in this chapter provide a revision of the NCEA Mathematics evel 1 work on formulae. These topics are not assessed directl in evel, but are assumed knowledge throughout the evel course. Mathematical modelling Mathematical modelling involves epressing a relationship as a formula in which mathematical smbols and letters are used to represent variables. The abilit to do this accuratel and use the resulting formula is important in man situations. Eample Three quantities used in accounting are assets (A), proprietorship (P), and liabilities (). The relationship between these quantities is that assets are equal to the sum of proprietorship and liabilities. In mathematical form, the relationship can be epressed: A = P + Note: A, P and are variables, and the equation, A = P + is a formula for A in terms of the two variables, P and. Eample Q. The volume of a cone is one third of the product of its height and the area of its base. Epress this relationship in mathematical form. A. et the volume of the cone be V, the radius of the base be R, and the height be H. The base area is πr [formula for area of circle] the volume is V = 1 3 πr H [from information given] R H Eample Q. A trapezium is a quadrilateral with a pair of parallel sides. Find an epression for the area of the trapezium shown where one parallel side is one half the length of the other parallel side, and the distance between the two parallel 4 ESA Publications (NZ) td, Customer freephone:
6 154 Achievement Standard 9161 (Mathematics and Statistics.6) sides is equal to one quarter of the length of the longer parallel side. Epress the area in terms of the length of the longer parallel side. A. et the length of the longer parallel side be and the area be A. The area of the trapezium is the sum of the areas of the two shaded triangles (as shown on the diagram, where the shorter parallel side is and the height is 4 ). Area of the smaller triangle is 1 4 = 16 1 Area of the larger triangle is 4 = 8 Area of the trapezium is A = 3 + = [area is half base height] [adding fractions] Activit 0A: Writing formulae Ans p. 385 Chapter 0 1. A pair of socks costs $D. Write an epression for the cost of the socks in cents.. a. Epress the time of 3 minutes in hours. b. Epress this same time in seconds. 3. Peter weighs kilograms and grams. a. Epress Peter s weight in grams. b. Epress his weight in kilograms. 4. A rectangle has length metres and width W centimetres. Write an epression for: a. the area in cm b. the area in m c. the perimeter in mm 5. A square has area 4 in square metres. Write an epression for: a. the perimeter in cm b. the perimeter in mm 6. A rightangled triangle has base b and height a. Both have the same unit. a. What is the area of the triangle? b. What is the length of the hpotenuse (the third side)? 7. a. Find an epression for the volume of the clinder shown. b. Find an epression for the total surface area of the clinder. 8. a. Find an epression for the perimeter of the shape shown. b. Find a formula for the area of this shape. z 9. a. What is the perimeter of the shape shown? b. What is the volume of the bo which forms when the shape is folded along the dotted lines? M ESA Publications (NZ) td, Customer freephone:
7 Chapter 0: Formulae The length of the closed bo shown is 4. The height and width of the bo are both half the length. a. Write down an epression for the volume of the bo. b. Write down an epression for the surface area of the bo. 4 Changing the subject of a formula The subject of a formula is a variable which appears alone on one side (usuall the left side) of the equals sign. The subject is epressed in terms of the other variables. Changing the subject of a formula means rearranging the formula (using inverse operations) so that another variable becomes the subject. Eample Q. Make the subject of = 6 A. = = [adding 6 to both sides] = + 6 [swapping sides] = + 6 [dividing both sides b ] Sometimes the variable to be made subject appears more than once in the formula. You will need to collect terms in this variable on one side and then factorise. Chapter 0 Eample Q. Make T the subject of AT + D = E T AT D A. = E + T AT + D = ET [multipling both sides b T] ET = AT + D [swapping sides] ET AT = D [collecting terms in T on one side] T(E A) = D [factorising ET AT ] T = D E A [dividing b E A (providing E A 0)] Note: D = 0 if E A = 0 [substituting E A = 0 in T(E A) = D] Squaring and taking the square root are inverses. Take care with signs when taking a square root (if = then = ± ). ESA Publications (NZ) td, Customer freephone:
8 answers Chapter 1: Coordinate geometr Activit 1A: Distance between points (page 4) 1. a. 3 b. 10 c. 13 d. 40 e. 41. a.. km b. 6.1 km c. 3.6 km d. 8.6 km e. 5.8 km km km 5. b. AB = 6, AC = 6, BC = 3 6. Side lengths are 40, 40, 3 7. (1,) 8. a. 5 cm b.. (1 dp) 9. = or a = 1 or 5 Activit 1B: Midpoints of line segments (page 6) 1. a. (3.5,6) b. (,) c. (4,3) d. (1.5,0) e. (0.5,4) f. (a + 1,a 1). (4,1) 3. (7,7) 4. 1 km east and km north of camp 5. a. 40 km west and 0 km north of island b. 60 km west and 40 km north of port a = 4, b = 9 8. midpoint AC = midpoint BD = ( 1, 1 ) 9. a. 4.7 b. QR = which is double Student proof Chapter : Gradient of a straight line Activit : The gradient of a straight line (page 9) 1. a. m = 1 3 b. m = 3 c. m = 1 d. m = e. m is undefined f. m = 0 4. Both lines have gradient 3. Both lines have gradient 3 4. Gradients are 1 and 3 5. Not parallel 6. Parallel 7. k = 3 8. k = 4 9. k = k = = 1 1. = = Proof (grad AB = grad BC = ) 17. Proof (grad AB = grad BC = 3) 18. a = a = a. 3 b. 3 c. The two lines are parallel 8 8 d. Student proof ESA Publications (NZ) td, Customer freephone:
9 Formulae and tables Eternall assessed standards Quadratics If a + b + c = 0 b ± b 4 ac then = a and = b 4ac ogarithms If = b then = log b log b () = log b + log b log b = log b log b log b ( n ) = n log b If = e then = log e (= In ) Calculus d d (n ) = n n 1 n d = Probabilit Z = µ σ n c n+ 1 Internall assessed standards Coordinate geometr 1 = m( 1 ) Sequences and series t n = a + (n 1)d S n = n [a + (n 1)d] t n = a r n 1 S n = a (1 r n ), r 1 1 r a S = for r < 1 1 r Statistics ( ) s = n IQR median ± 1.5 n Trigonometr a b c = = sina sinb sinc a = b + c bc cos A b + c a cos A = bc Area of triangle = 1 bc sin A Arc length = r θ Area of sector = 1 r θ Area of segment = 1 r (θ sin θ) ESA Publications (NZ) td, Customer freephone:
10 answers Inde absolute value 3, 83 absolute value function 87, 9 acceleration 1, 3 actual probabilit 75 algebraic equation 133 algebraic fractions 147 altitude 3 amplitude 75 antiderivative 19 antidifferentiation 19 arbitrar constant 19, 0 arc 15 arc length 15 area of sector 15 area rule (triangle) 119 arithmetic sequence 99 asmptote 34, 57, 69 average 41 ais of smmetr 4, 58 backtoback stemandleaf diagram 48 base (indices) 169 basechanging rule 69 bearings 10 bimodal 49 boundar line 339 boandwhisker plot 5, 58 calculus 197 Cartesian notation 198 categor variable 90 census 35 change of base rule 69 cluster sampling 37 clusters 47, 50 coefficient 144 collinear 9, 10 common denominator 149 common difference 99 common factor 143 common ratio 105 complement of event 79 compress 80 conclusion (inference) 65 concurrent 5 conditional probabilit 85 confidence interval 57 congruent 39, 4 constant term 161, 0 continuous population 95, 308 convention for labelling triangles 115 cosine (cos) 75 cosine rule 115 cube root 173 cubic functions 51 deca curve 65 decreasing function 3, 05 degree (polnomial) 51, 159, 161 denominator 146, 147 derivative 197 derived function 197 difference of two squares 144 differentiable 197 differentiating 197 discontinuit 58 discriminant 166 distance of point from line 3 distribution 47 distributive law 141 divisor 148 domain 30, 57, 60, 75 dot plot 47, 50 enlarge 80 equall likel outcomes 75, 76 equation of straight line 11 equation of tangent 03 event 75, 76 epanding 141 epected number or value 89 eperiment 75 eperimental distributions 307 eperimental probabilit 75, 3 ESA Publications (NZ) td, Customer freephone:
ZETA MATHS. Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist
 ZETA MATHS Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Epressions & Functions Page Logarithmic & Eponential Functions Addition Formulae. 3 Wave Function.... 4 Graphs of Functions. 5 Sets of Functions
ZETA MATHS Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Epressions & Functions Page Logarithmic & Eponential Functions Addition Formulae. 3 Wave Function.... 4 Graphs of Functions. 5 Sets of Functions
1.1 Laws of exponents Conversion between exponents and logarithms Logarithm laws Exponential and logarithmic equations 10
 CNTENTS Algebra Chapter Chapter Chapter Eponents and logarithms. Laws of eponents. Conversion between eponents and logarithms 6. Logarithm laws 8. Eponential and logarithmic equations 0 Sequences and series.
CNTENTS Algebra Chapter Chapter Chapter Eponents and logarithms. Laws of eponents. Conversion between eponents and logarithms 6. Logarithm laws 8. Eponential and logarithmic equations 0 Sequences and series.
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE. Functions & Graphs
 STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
Mathematics. Mathematics 2. hsn.uk.net. Higher HSN22000
 hsn.uk.net Higher Mathematics UNIT Mathematics HSN000 This document was produced speciall for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that an copies or derivative works attribute the work to Higher Still
hsn.uk.net Higher Mathematics UNIT Mathematics HSN000 This document was produced speciall for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that an copies or derivative works attribute the work to Higher Still
Mathematics. Mathematics 2. hsn.uk.net. Higher HSN22000
 Higher Mathematics UNIT Mathematics HSN000 This document was produced speciall for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that an copies or derivative works attribute the work to Higher Still Notes. For
Higher Mathematics UNIT Mathematics HSN000 This document was produced speciall for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that an copies or derivative works attribute the work to Higher Still Notes. For
UNCORRECTED SAMPLE PAGES. 3Quadratics. Chapter 3. Objectives
 Chapter 3 3Quadratics Objectives To recognise and sketch the graphs of quadratic polnomials. To find the ke features of the graph of a quadratic polnomial: ais intercepts, turning point and ais of smmetr.
Chapter 3 3Quadratics Objectives To recognise and sketch the graphs of quadratic polnomials. To find the ke features of the graph of a quadratic polnomial: ais intercepts, turning point and ais of smmetr.
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae
 National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 4.676 4.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 00 to sig. figs.
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 4.676 4.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 00 to sig. figs.
Linear Equation Theory - 2
 Algebra Module A46 Linear Equation Theor - Copright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED June., 009 Linear Equation Theor - Statement of Prerequisite
Algebra Module A46 Linear Equation Theor - Copright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED June., 009 Linear Equation Theor - Statement of Prerequisite
Learning Goals. College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 101: College Algebra Final Exam Review Problems 1
 College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
ZETA MATHS. National 5 Mathematics Revision Checklist
 ZETA MATHS National 5 Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Expressions & Formulae Page Rounding Surds. Indices.... Algebra... Algebraic Fractions. Volumes. Gradient. 3 Circles.. 3 Relationships The
ZETA MATHS National 5 Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Expressions & Formulae Page Rounding Surds. Indices.... Algebra... Algebraic Fractions. Volumes. Gradient. 3 Circles.. 3 Relationships The
UNCORRECTED. To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: y = x 1 y 2 = x
 5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae
 National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 34.676 34.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 300 to sig. figs.
National 5 Learning Checklist Expressions & Formulae Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Rounding Round to decimal places 5.4 5. to d.p. 34.676 34.68 to d.p. Round to Significant Figures 76 300 to sig. figs.
Unit 3 Notes Mathematical Methods
 Unit 3 Notes Mathematical Methods Foundational Knowledge Created b Triumph Tutoring Copright info Copright Triumph Tutoring 07 Triumph Tutoring Pt Ltd ABN 60 607 0 507 First published in 07 All rights
Unit 3 Notes Mathematical Methods Foundational Knowledge Created b Triumph Tutoring Copright info Copright Triumph Tutoring 07 Triumph Tutoring Pt Ltd ABN 60 607 0 507 First published in 07 All rights
Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work
 Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work The summer assignment element should take no longer than hours to complete. Your summer assignment for each course must be submitted in the relevant first
Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work The summer assignment element should take no longer than hours to complete. Your summer assignment for each course must be submitted in the relevant first
NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS
 Mathematics Higher Prelim Eamination 04/05 Paper Assessing Units & + Vectors NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS Time allowed - hour 0 minutes Read carefully Calculators may NOT be used in this paper. Section A -
Mathematics Higher Prelim Eamination 04/05 Paper Assessing Units & + Vectors NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS Time allowed - hour 0 minutes Read carefully Calculators may NOT be used in this paper. Section A -
Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A)
 Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A) Updated 06/05/16 http://www.haesemathematics.com.au/ Note: Exercises in red text indicate material in the 10A textbook
Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A) Updated 06/05/16 http://www.haesemathematics.com.au/ Note: Exercises in red text indicate material in the 10A textbook
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge
 Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Coordinate geometry. + bx + c. Vertical asymptote. Sketch graphs of hyperbolas (including asymptotic behaviour) from the general
 A Sketch graphs of = a m b n c where m = or and n = or B Reciprocal graphs C Graphs of circles and ellipses D Graphs of hperbolas E Partial fractions F Sketch graphs using partial fractions Coordinate
A Sketch graphs of = a m b n c where m = or and n = or B Reciprocal graphs C Graphs of circles and ellipses D Graphs of hperbolas E Partial fractions F Sketch graphs using partial fractions Coordinate
1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. accurately drawn. x + 2. x + 4. x + 2
 1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. 2 x + 3 Diagram NOT accurately drawn x + 2 x + 4 x + 2 The length of the rectangle is 2x + 3. The width of the rectangle is x + 4. The length
1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. 2 x + 3 Diagram NOT accurately drawn x + 2 x + 4 x + 2 The length of the rectangle is 2x + 3. The width of the rectangle is x + 4. The length
QUADRATIC GRAPHS ALGEBRA 2. Dr Adrian Jannetta MIMA CMath FRAS INU0114/514 (MATHS 1) Quadratic Graphs 1/ 16 Adrian Jannetta
 QUADRATIC GRAPHS ALGEBRA 2 INU0114/514 (MATHS 1) Dr Adrian Jannetta MIMA CMath FRAS Quadratic Graphs 1/ 16 Adrian Jannetta Objectives Be able to sketch the graph of a quadratic function Recognise the shape
QUADRATIC GRAPHS ALGEBRA 2 INU0114/514 (MATHS 1) Dr Adrian Jannetta MIMA CMath FRAS Quadratic Graphs 1/ 16 Adrian Jannetta Objectives Be able to sketch the graph of a quadratic function Recognise the shape
May 27, QUADRATICS.notebook. Apr 26 17:43. Apr 26 18:27. Apr 26 18:40. Apr 28 10:22. Apr 28 10:34. Apr 28 10:33. Starter
 1. Factorise: 2 - - 6 2. Solve for : 2( + 1) = - 1 3. Factorise: 2-25 To solve quadratic equations.. Factorise: 2 2-8 5. State the gradient of the line: + 12 = 2 Apr 26 17:3 Apr 26 18:27 Solving Quadratic
1. Factorise: 2 - - 6 2. Solve for : 2( + 1) = - 1 3. Factorise: 2-25 To solve quadratic equations.. Factorise: 2 2-8 5. State the gradient of the line: + 12 = 2 Apr 26 17:3 Apr 26 18:27 Solving Quadratic
Mathematics. Mathematics 1. hsn.uk.net. Higher HSN21000
 Higher Mathematics UNIT Mathematics HSN000 This document was produced speciall for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that an copies or derivative works attribute the work to Higher Still Notes. For
Higher Mathematics UNIT Mathematics HSN000 This document was produced speciall for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that an copies or derivative works attribute the work to Higher Still Notes. For
206 Calculus and Structures
 06 Calculus and Structures CHAPTER 4 CURVE SKETCHING AND MAX-MIN II Calculus and Structures 07 Copright Chapter 4 CURVE SKETCHING AND MAX-MIN II 4. INTRODUCTION In Chapter, we developed a procedure for
06 Calculus and Structures CHAPTER 4 CURVE SKETCHING AND MAX-MIN II Calculus and Structures 07 Copright Chapter 4 CURVE SKETCHING AND MAX-MIN II 4. INTRODUCTION In Chapter, we developed a procedure for
absolute value The distance of a number from zero on a real number line.
 G L O S S A R Y A absolute value The distance of a number from zero on a real number line. acute angle An angle whose measure is less than 90. acute triangle A triangle in which each of the three interior
G L O S S A R Y A absolute value The distance of a number from zero on a real number line. acute angle An angle whose measure is less than 90. acute triangle A triangle in which each of the three interior
1 k. cos tan? Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. 1. A sequence is defined by the recurrence relation u 2u 1, u 3.
 Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
ALGEBRA 1 CP FINAL EXAM REVIEW
 ALGEBRA CP FINAL EXAM REVIEW Alg CP Sem Eam Review 0 () Page of 8 Chapter 8: Eponents. Write in rational eponent notation. 7. Write in radical notation. Simplif the epression.. 00.. 6 6. 7 7. 6 6 8. 8
ALGEBRA CP FINAL EXAM REVIEW Alg CP Sem Eam Review 0 () Page of 8 Chapter 8: Eponents. Write in rational eponent notation. 7. Write in radical notation. Simplif the epression.. 00.. 6 6. 7 7. 6 6 8. 8
Trigonometric. equations. Topic: Periodic functions and applications. Simple trigonometric. equations. Equations using radians Further trigonometric
 Trigonometric equations 6 sllabusref eferenceence Topic: Periodic functions and applications In this cha 6A 6B 6C 6D 6E chapter Simple trigonometric equations Equations using radians Further trigonometric
Trigonometric equations 6 sllabusref eferenceence Topic: Periodic functions and applications In this cha 6A 6B 6C 6D 6E chapter Simple trigonometric equations Equations using radians Further trigonometric
and y f ( x ). given the graph of y f ( x ).
 FUNCTIONS AND RELATIONS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES:. Concept of function f : f ( ) : domain, range; image (value). Odd and even functions Composite functions f g; Identit function. One-to-one and man-to-one functions.
FUNCTIONS AND RELATIONS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES:. Concept of function f : f ( ) : domain, range; image (value). Odd and even functions Composite functions f g; Identit function. One-to-one and man-to-one functions.
e x for x 0. Find the coordinates of the point of inflexion and justify that it is a point of inflexion. (Total 7 marks)
 Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Module 3, Section 4 Analytic Geometry II
 Principles of Mathematics 11 Section, Introduction 01 Introduction, Section Analtic Geometr II As the lesson titles show, this section etends what ou have learned about Analtic Geometr to several related
Principles of Mathematics 11 Section, Introduction 01 Introduction, Section Analtic Geometr II As the lesson titles show, this section etends what ou have learned about Analtic Geometr to several related
Differentiation and applications
 FS O PA G E PR O U N C O R R EC TE D Differentiation and applications. Kick off with CAS. Limits, continuit and differentiabilit. Derivatives of power functions.4 C oordinate geometr applications of differentiation.5
FS O PA G E PR O U N C O R R EC TE D Differentiation and applications. Kick off with CAS. Limits, continuit and differentiabilit. Derivatives of power functions.4 C oordinate geometr applications of differentiation.5
Pure Core 1. Revision Notes
 Pure Core Revision Notes Ma 06 Pure Core Algebra... Indices... Rules of indices... Surds... 4 Simplifing surds... 4 Rationalising the denominator... 4 Quadratic functions... 5 Completing the square....
Pure Core Revision Notes Ma 06 Pure Core Algebra... Indices... Rules of indices... Surds... 4 Simplifing surds... 4 Rationalising the denominator... 4 Quadratic functions... 5 Completing the square....
1.2 Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus
 1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
Mathematics syllabus for Grade 11 and 12 For Bilingual Schools in the Sultanate of Oman
 03 04 Mathematics syllabus for Grade and For Bilingual Schools in the Sultanate of Oman Prepared By: A Stevens (Qurum Private School) M Katira (Qurum Private School) M Hawthorn (Al Sahwa Schools) In Conjunction
03 04 Mathematics syllabus for Grade and For Bilingual Schools in the Sultanate of Oman Prepared By: A Stevens (Qurum Private School) M Katira (Qurum Private School) M Hawthorn (Al Sahwa Schools) In Conjunction
LESSON #42 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART 2 COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
YEAR 10 PROGRAM TERM 1 TERM 2 TERM 3 TERM 4
 YEAR 10 PROGRAM TERM 1 1. Revision of number operations 3 + T wk 2 2. Expansion 3 + T wk 4 3. Factorisation 7 + T wk 6 4. Algebraic Fractions 4 + T wk 7 5. Formulae 5 + T wk 9 6. Linear Equations 10 +T
YEAR 10 PROGRAM TERM 1 1. Revision of number operations 3 + T wk 2 2. Expansion 3 + T wk 4 3. Factorisation 7 + T wk 6 4. Algebraic Fractions 4 + T wk 7 5. Formulae 5 + T wk 9 6. Linear Equations 10 +T
Sample Problems For Grade 9 Mathematics. Grade. 1. If x 3
 Sample roblems For 9 Mathematics DIRECTIONS: This section provides sample mathematics problems for the 9 test forms. These problems are based on material included in the New York Cit curriculum for 8.
Sample roblems For 9 Mathematics DIRECTIONS: This section provides sample mathematics problems for the 9 test forms. These problems are based on material included in the New York Cit curriculum for 8.
Methods for Advanced Mathematics (C3) Coursework Numerical Methods
 Woodhouse College 0 Page Introduction... 3 Terminolog... 3 Activit... 4 Wh use numerical methods?... Change of sign... Activit... 6 Interval Bisection... 7 Decimal Search... 8 Coursework Requirements on
Woodhouse College 0 Page Introduction... 3 Terminolog... 3 Activit... 4 Wh use numerical methods?... Change of sign... Activit... 6 Interval Bisection... 7 Decimal Search... 8 Coursework Requirements on
Sophomore Year: Algebra II Textbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012
 Sophomore Year: Algebra II Tetbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012 Course Description: The purpose of this course is to give students a strong foundation
Sophomore Year: Algebra II Tetbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012 Course Description: The purpose of this course is to give students a strong foundation
KEY IDEAS. Chapter 1 Function Transformations. 1.1 Horizontal and Vertical Translations Pre-Calculus 12 Student Workbook MHR 1
 Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations A translation can move the graph of a function up or down (vertical translation) and right or left (horizontal translation). A translation
Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations A translation can move the graph of a function up or down (vertical translation) and right or left (horizontal translation). A translation
JUST IN TIME MATERIAL GRADE 11 KZN DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION CURRICULUM GRADES DIRECTORATE TERM
 JUST IN TIME MATERIAL GRADE 11 KZN DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION CURRICULUM GRADES 10 1 DIRECTORATE TERM 1 017 This document has been compiled by the FET Mathematics Subject Advisors together with Lead Teachers.
JUST IN TIME MATERIAL GRADE 11 KZN DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION CURRICULUM GRADES 10 1 DIRECTORATE TERM 1 017 This document has been compiled by the FET Mathematics Subject Advisors together with Lead Teachers.
Pure Core 2. Revision Notes
 Pure Core Revision Notes June 06 Pure Core Algebra... Polynomials... Factorising... Standard results... Long division... Remainder theorem... 4 Factor theorem... 5 Choosing a suitable factor... 6 Cubic
Pure Core Revision Notes June 06 Pure Core Algebra... Polynomials... Factorising... Standard results... Long division... Remainder theorem... 4 Factor theorem... 5 Choosing a suitable factor... 6 Cubic
The Grade Descriptors below are used to assess work and student progress in Mathematics from Year 7 to
 Jersey College for Girls Assessment criteria for KS3 and KS4 Mathematics In Mathematics, students are required to become familiar, confident and competent with a range of content and procedures described
Jersey College for Girls Assessment criteria for KS3 and KS4 Mathematics In Mathematics, students are required to become familiar, confident and competent with a range of content and procedures described
MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 NOTES
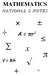 MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 NOTES A = πr 2 ± V = lbh π + - INDEX: page 1 Chapter 1: Fractions page 3 Chapter 2: Percentages page 5 Chapter 3: Surds page 7 Chapter 4: Indices, including Scientific Notation and
MATHEMATICS NATIONAL 5 NOTES A = πr 2 ± V = lbh π + - INDEX: page 1 Chapter 1: Fractions page 3 Chapter 2: Percentages page 5 Chapter 3: Surds page 7 Chapter 4: Indices, including Scientific Notation and
Answer Explanations. The SAT Subject Tests. Mathematics Level 1 & 2 TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE
 The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
Quadratic Functions Objective: To be able to graph a quadratic function and identify the vertex and the roots.
 Name: Quadratic Functions Objective: To be able to graph a quadratic function and identif the verte and the roots. Period: Quadratic Function Function of degree. Usuall in the form: We are now going to
Name: Quadratic Functions Objective: To be able to graph a quadratic function and identif the verte and the roots. Period: Quadratic Function Function of degree. Usuall in the form: We are now going to
Mathematics. Polynomials and Quadratics. hsn.uk.net. Higher. Contents. Polynomials and Quadratics 52 HSN22100
 Higher Mathematics UNIT OUTCOME 1 Polnomials and Quadratics Contents Polnomials and Quadratics 5 1 Quadratics 5 The Discriminant 54 Completing the Square 55 4 Sketching Parabolas 57 5 Determining the Equation
Higher Mathematics UNIT OUTCOME 1 Polnomials and Quadratics Contents Polnomials and Quadratics 5 1 Quadratics 5 The Discriminant 54 Completing the Square 55 4 Sketching Parabolas 57 5 Determining the Equation
(c) Find the gradient of the graph of f(x) at the point where x = 1. (2) The graph of f(x) has a local maximum point, M, and a local minimum point, N.
 Calculus Review Packet 1. Consider the function f() = 3 3 2 24 + 30. Write down f(0). Find f (). Find the gradient of the graph of f() at the point where = 1. The graph of f() has a local maimum point,
Calculus Review Packet 1. Consider the function f() = 3 3 2 24 + 30. Write down f(0). Find f (). Find the gradient of the graph of f() at the point where = 1. The graph of f() has a local maimum point,
y intercept Gradient Facts Lines that have the same gradient are PARALLEL
 CORE Summar Notes Linear Graphs and Equations = m + c gradient = increase in increase in intercept Gradient Facts Lines that have the same gradient are PARALLEL If lines are PERPENDICULAR then m m = or
CORE Summar Notes Linear Graphs and Equations = m + c gradient = increase in increase in intercept Gradient Facts Lines that have the same gradient are PARALLEL If lines are PERPENDICULAR then m m = or
Grade 12 Mathematics. unimaths.co.za. Revision Questions. (Including Solutions)
 Grade 12 Mathematics Revision Questions (Including Solutions) unimaths.co.za Get read for universit mathematics b downloading free lessons taken from Unimaths Intro Workbook. Visit unimaths.co.za for more
Grade 12 Mathematics Revision Questions (Including Solutions) unimaths.co.za Get read for universit mathematics b downloading free lessons taken from Unimaths Intro Workbook. Visit unimaths.co.za for more
Perth Academy Mathematics Department Intermediate 2 Unit 3 Revision Pack. Contents:
 Perth Academ Mathematics Department Intermediate Unit Revision Pack Contents: Algebraic Operations: Fractions Fractions Formulae Surds Indices Quadratic Functions: Y = a Y = a + b Y = ( + a) + b Turning
Perth Academ Mathematics Department Intermediate Unit Revision Pack Contents: Algebraic Operations: Fractions Fractions Formulae Surds Indices Quadratic Functions: Y = a Y = a + b Y = ( + a) + b Turning
APPENDIXES. B Coordinate Geometry and Lines C. D Trigonometry E F. G The Logarithm Defined as an Integral H Complex Numbers I
 APPENDIXES A Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values B Coordinate Geometr and Lines C Graphs of Second-Degree Equations D Trigonometr E F Sigma Notation Proofs of Theorems G The Logarithm Defined as
APPENDIXES A Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values B Coordinate Geometr and Lines C Graphs of Second-Degree Equations D Trigonometr E F Sigma Notation Proofs of Theorems G The Logarithm Defined as
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the City University of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE. MTH06 Review Sheet y 6 2x + 5 y.
 BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the Cit Universit of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE MTH06 Review Sheet. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: n n 0 n + n ( 9 )( ) + + 6 + 9ab
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the Cit Universit of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE MTH06 Review Sheet. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: n n 0 n + n ( 9 )( ) + + 6 + 9ab
Name: Richard Montgomery High School Department of Mathematics. Summer Math Packet. for students entering. Algebra 2/Trig*
 Name: Richard Montgomer High School Department of Mathematics Summer Math Packet for students entering Algebra 2/Trig* For the following courses: AAF, Honors Algebra 2, Algebra 2 (Please go the RM website
Name: Richard Montgomer High School Department of Mathematics Summer Math Packet for students entering Algebra 2/Trig* For the following courses: AAF, Honors Algebra 2, Algebra 2 (Please go the RM website
Nova Scotia Examinations Mathematics 12 Web Sample 2. Student Booklet
 Nova Scotia Eaminations Mathematics Web Sample Student Booklet General Instructions - WEB SAMPLE* This eamination is composed of two sections with the following suggested time allotment: Selected-Response
Nova Scotia Eaminations Mathematics Web Sample Student Booklet General Instructions - WEB SAMPLE* This eamination is composed of two sections with the following suggested time allotment: Selected-Response
Functions and Graphs TERMINOLOGY
 5 Functions and Graphs TERMINOLOGY Arc of a curve: Part or a section of a curve between two points Asmptote: A line towards which a curve approaches but never touches Cartesian coordinates: Named after
5 Functions and Graphs TERMINOLOGY Arc of a curve: Part or a section of a curve between two points Asmptote: A line towards which a curve approaches but never touches Cartesian coordinates: Named after
Mathematics. Polynomials and Quadratics. hsn.uk.net. Higher. Contents. Polynomials and Quadratics 1. CfE Edition
 Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Quadratics EF 1 The Discriminant EF 3 3 Completing the Square EF 4 4 Sketching Parabolas EF 7 5 Determining the Equation of a Parabola RC 9 6 Solving Quadratic Inequalities
Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Quadratics EF 1 The Discriminant EF 3 3 Completing the Square EF 4 4 Sketching Parabolas EF 7 5 Determining the Equation of a Parabola RC 9 6 Solving Quadratic Inequalities
Brief Revision Notes and Strategies
 Brief Revision Notes and Strategies Straight Line Distance Formula d = ( ) + ( y y ) d is distance between A(, y ) and B(, y ) Mid-point formula +, y + M y M is midpoint of A(, y ) and B(, y ) y y Equation
Brief Revision Notes and Strategies Straight Line Distance Formula d = ( ) + ( y y ) d is distance between A(, y ) and B(, y ) Mid-point formula +, y + M y M is midpoint of A(, y ) and B(, y ) y y Equation
1 x
 Unit 1. Calculus Topic 4: Increasing and decreasing functions: turning points In topic 4 we continue with straightforward derivatives and integrals: Locate turning points where f () = 0. Determine the
Unit 1. Calculus Topic 4: Increasing and decreasing functions: turning points In topic 4 we continue with straightforward derivatives and integrals: Locate turning points where f () = 0. Determine the
Glossary. Also available at BigIdeasMath.com: multi-language glossary vocabulary flash cards. An equation that contains an absolute value expression
 Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
Higher School Certificate
 Higher School Certificate Mathematics HSC Stle Questions (Section ) FREE SAMPLE J.P.Kinn-Lewis Higher School Certificate Mathematics HSC Stle Questions (Section ) J.P.Kinn-Lewis First published b John
Higher School Certificate Mathematics HSC Stle Questions (Section ) FREE SAMPLE J.P.Kinn-Lewis Higher School Certificate Mathematics HSC Stle Questions (Section ) J.P.Kinn-Lewis First published b John
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the City University of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE. MTH06 Review Sheet y 6 2x + 5 y.
 BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the Cit Universit of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE MTH06 Review Sheet. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: n n 0 n + n ( 9 ) ( ) + + 6 + 9ab
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the Cit Universit of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE MTH06 Review Sheet. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: n n 0 n + n ( 9 ) ( ) + + 6 + 9ab
c) domain {x R, x 3}, range {y R}
 Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
ERRATA. MATHEMATICS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL STUDENT MATHEMATICS HL (Core) (3rd edition)
 ERRATA MATHEMATICS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL STUDENT MATHEMATICS HL (Core) (rd edition) Third edition - 07 third reprint The following erratum was made on 5/Jul/07 page 6 REVIEW SET 0A 0 b, 0 b Show that if
ERRATA MATHEMATICS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL STUDENT MATHEMATICS HL (Core) (rd edition) Third edition - 07 third reprint The following erratum was made on 5/Jul/07 page 6 REVIEW SET 0A 0 b, 0 b Show that if
The region enclosed by the curve of f and the x-axis is rotated 360 about the x-axis. Find the volume of the solid formed.
 Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS
 H Mathematics Higher Paper Practice Paper A Time allowed hour minutes NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS Read carefull Calculators ma NOT be used in this paper. Section A Questions ( marks) Instructions for completion
H Mathematics Higher Paper Practice Paper A Time allowed hour minutes NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS Read carefull Calculators ma NOT be used in this paper. Section A Questions ( marks) Instructions for completion
3. TRANSLATED PARABOLAS
 3. TRANSLATED PARABOLAS The Parabola with Verte V(h, k) and Aes Parallel to the ais Consider the concave up parabola with verte V(h, k) shown below. This parabola is obtained b translating the parabola
3. TRANSLATED PARABOLAS The Parabola with Verte V(h, k) and Aes Parallel to the ais Consider the concave up parabola with verte V(h, k) shown below. This parabola is obtained b translating the parabola
Higher. Polynomials and Quadratics. Polynomials and Quadratics 1
 Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Quadratics EF 1 The Discriminant EF 3 3 Completing the Square EF 4 4 Sketching Parabolas EF 7 5 Determining the Equation of a Parabola RC 9 6 Solving Quadratic Inequalities
Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Quadratics EF 1 The Discriminant EF 3 3 Completing the Square EF 4 4 Sketching Parabolas EF 7 5 Determining the Equation of a Parabola RC 9 6 Solving Quadratic Inequalities
MATH 60 Review Problems for Final Exam
 MATH 60 Review Problems for Final Eam Scientific Calculators Onl - Graphing Calculators Not Allowed NO CLASS NOTES PERMITTED Evaluate the epression for the given values. m 1) m + 3 for m = 3 2) m 2 - n2
MATH 60 Review Problems for Final Eam Scientific Calculators Onl - Graphing Calculators Not Allowed NO CLASS NOTES PERMITTED Evaluate the epression for the given values. m 1) m + 3 for m = 3 2) m 2 - n2
Created by T. Madas. Candidates may use any calculator allowed by the regulations of this examination.
 IYGB GCE Mathematics SYN Advanced Level Snoptic Paper C Difficult Rating: 3.895 Time: 3 hours Candidates ma use an calculator allowed b the regulations of this eamination. Information for Candidates This
IYGB GCE Mathematics SYN Advanced Level Snoptic Paper C Difficult Rating: 3.895 Time: 3 hours Candidates ma use an calculator allowed b the regulations of this eamination. Information for Candidates This
CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW
 NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
Unit 10 - Graphing Quadratic Functions
 Unit - Graphing Quadratic Functions PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multipl polnomials students should be able to factor polnomials students should be able to identif
Unit - Graphing Quadratic Functions PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multipl polnomials students should be able to factor polnomials students should be able to identif
Circle Theorems. Angles at the circumference are equal. The angle in a semi-circle is x The angle at the centre. Cyclic Quadrilateral
 The angle in a semi-circle is 90 0 Angles at the circumference are equal. A B They must come from the same arc. Look out for a diameter. 2x Cyclic Quadrilateral Opposite angles add up to 180 0 A They must
The angle in a semi-circle is 90 0 Angles at the circumference are equal. A B They must come from the same arc. Look out for a diameter. 2x Cyclic Quadrilateral Opposite angles add up to 180 0 A They must
SAMPLE. A Gallery of Graphs. To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relationships: y = x 1,
 Objectives C H A P T E R 5 A Galler of Graphs To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relationships: =, =, = / and + =. To be able to sketch the graphs and simple transformations of these
Objectives C H A P T E R 5 A Galler of Graphs To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relationships: =, =, = / and + =. To be able to sketch the graphs and simple transformations of these
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 The Quadratic Function (Vertex Form): Translations. and axis of symmetry is at x a.
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 Verte form of Quadratic Relations The epression a p q defines a quadratic relation called the verte form with a horizontal translation of p units and vertical translation of
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 Verte form of Quadratic Relations The epression a p q defines a quadratic relation called the verte form with a horizontal translation of p units and vertical translation of
IB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd edition. Quadratics. 112 min 110 marks. y l
 IB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd edition Quadratics 112 min 110 marks 1. The following diagram shows a straight line l. 10 8 y l 6 4 2 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 (a) Find the equation of the line l. The line
IB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd edition Quadratics 112 min 110 marks 1. The following diagram shows a straight line l. 10 8 y l 6 4 2 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 (a) Find the equation of the line l. The line
2 year GCSE Scheme of Work
 2 year GCSE Scheme of Work Year 10 Pupils follow the 2 year Pearsons/Edexcel Scheme of Work FOUNDATION ROUTE HIGHER ROUTE YEAR 4 YEAR 5 YEAR 4 YEAR 5 GCSE (9-1) Foundation GCSE (9-1) Foundation GCSE (9-1)
2 year GCSE Scheme of Work Year 10 Pupils follow the 2 year Pearsons/Edexcel Scheme of Work FOUNDATION ROUTE HIGHER ROUTE YEAR 4 YEAR 5 YEAR 4 YEAR 5 GCSE (9-1) Foundation GCSE (9-1) Foundation GCSE (9-1)
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function 2
 Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
Model Paper WITH ANSWERS. Higher Maths
 Model Paper WITH ANSWERS Higher Maths This model paper is free to download and use for revision purposes. The paper, which may include a limited number of previously published SQA questions, has been specially
Model Paper WITH ANSWERS Higher Maths This model paper is free to download and use for revision purposes. The paper, which may include a limited number of previously published SQA questions, has been specially
ARE YOU READY FOR CALCULUS?? Name: Date: Period:
 ARE YOU READY FOR CALCULUS?? Name: Date: Period: Directions: Complete the following problems. **You MUST show all work to receive credit.**(use separate sheets of paper.) Problems with an asterisk (*)
ARE YOU READY FOR CALCULUS?? Name: Date: Period: Directions: Complete the following problems. **You MUST show all work to receive credit.**(use separate sheets of paper.) Problems with an asterisk (*)
f(x) = 2x 2 + 2x - 4
 4-1 Graphing Quadratic Functions What You ll Learn Scan the tet under the Now heading. List two things ou will learn about in the lesson. 1. Active Vocabular 2. New Vocabular Label each bo with the terms
4-1 Graphing Quadratic Functions What You ll Learn Scan the tet under the Now heading. List two things ou will learn about in the lesson. 1. Active Vocabular 2. New Vocabular Label each bo with the terms
Assessment Report. Level 2, Mathematics
 Assessment Report Level 2, 2006 Mathematics Manipulate algebraic expressions and solve equations (90284) Draw straightforward non-linear graphs (90285) Find and use straightforward derivatives and integrals
Assessment Report Level 2, 2006 Mathematics Manipulate algebraic expressions and solve equations (90284) Draw straightforward non-linear graphs (90285) Find and use straightforward derivatives and integrals
Quadratics NOTES.notebook November 02, 2017
 1) Find y where y = 2-1 and a) = 2 b) = -1 c) = 0 2) Epand the brackets and simplify: (m + 4)(2m - 3) To find the equation of quadratic graphs using substitution of a point. 3) Fully factorise 4y 2-5y
1) Find y where y = 2-1 and a) = 2 b) = -1 c) = 0 2) Epand the brackets and simplify: (m + 4)(2m - 3) To find the equation of quadratic graphs using substitution of a point. 3) Fully factorise 4y 2-5y
Mathematics Paper 1 (Non-Calculator)
 H National Qualifications CFE Higher Mathematics - Specimen Paper F Duration hour and 0 minutes Mathematics Paper (Non-Calculator) Total marks 60 Attempt ALL questions. You ma NOT use a calculator. Full
H National Qualifications CFE Higher Mathematics - Specimen Paper F Duration hour and 0 minutes Mathematics Paper (Non-Calculator) Total marks 60 Attempt ALL questions. You ma NOT use a calculator. Full
Newbattle Community High School National 5 Mathematics. Key Facts Q&A
 Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing National 5 Maths to take turns reading a
Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing National 5 Maths to take turns reading a
MATHEMATICS Higher Grade - Paper I (Non~calculator)
 Prelim Eamination 005 / 006 (Assessing Units & ) MATHEMATICS Higher Grade - Paper I (Non~calculator) Time allowed - hour 0 minutes Read Carefully. Calculators may not be used in this paper.. Full credit
Prelim Eamination 005 / 006 (Assessing Units & ) MATHEMATICS Higher Grade - Paper I (Non~calculator) Time allowed - hour 0 minutes Read Carefully. Calculators may not be used in this paper.. Full credit
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time)
 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 998 MATHEMATICS / UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions. ALL questions are of equal value.
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 998 MATHEMATICS / UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions. ALL questions are of equal value.
G r a d e 1 1 P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s ( 3 0 S ) Final Practice Exam Answer Key
 G r a d e P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s ( 3 0 S ) Final Practice Eam Answer Key G r a d e P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s Final Practice Eam Answer Key Name: Student Number:
G r a d e P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s ( 3 0 S ) Final Practice Eam Answer Key G r a d e P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s Final Practice Eam Answer Key Name: Student Number:
Lesson 9.1 Using the Distance Formula
 Lesson. Using the Distance Formula. Find the eact distance between each pair of points. a. (0, 0) and (, ) b. (0, 0) and (7, ) c. (, 8) and (, ) d. (, ) and (, 7) e. (, 7) and (8, ) f. (8, ) and (, 0)
Lesson. Using the Distance Formula. Find the eact distance between each pair of points. a. (0, 0) and (, ) b. (0, 0) and (7, ) c. (, 8) and (, ) d. (, ) and (, 7) e. (, 7) and (8, ) f. (8, ) and (, 0)
MATHEMATICS LEVEL 2 TEST FORM B Continued
 Mathematics Level Test Form B For each of the following problems, decide which is the BEST of the choices given. If the eact numerical value is not one of the choices, select the choice that best approimates
Mathematics Level Test Form B For each of the following problems, decide which is the BEST of the choices given. If the eact numerical value is not one of the choices, select the choice that best approimates
Higher. Integration 1
 Higher Mathematics Contents Indefinite Integrals RC Preparing to Integrate RC Differential Equations A Definite Integrals RC 7 Geometric Interpretation of A 8 Areas between Curves A 7 Integrating along
Higher Mathematics Contents Indefinite Integrals RC Preparing to Integrate RC Differential Equations A Definite Integrals RC 7 Geometric Interpretation of A 8 Areas between Curves A 7 Integrating along
Mathematics Placement Examination (MPE)
 Practice Problems for Mathematics Placement Eamination (MPE) Revised June, 011 When ou come to New Meico State Universit, ou ma be asked to take the Mathematics Placement Eamination (MPE) Your inital placement
Practice Problems for Mathematics Placement Eamination (MPE) Revised June, 011 When ou come to New Meico State Universit, ou ma be asked to take the Mathematics Placement Eamination (MPE) Your inital placement
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the City University of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE. MTH06 Review Sheet y 6 2x + 5 y.
 BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the Cit Universit of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE MTH06 Review Sheet. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: n n 0 n +n ( 9 )( ) + + 6 + 9ab a+b
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the Cit Universit of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS & COMPUTER SCIENCE MTH06 Review Sheet. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: n n 0 n +n ( 9 )( ) + + 6 + 9ab a+b
GCSE Higher Tier Practice Questions
 GCSE Higher Tier Practice Questions GCSE Higher Tier Practice Questions Contents: Topic Page Solving Linear, Quadratic and Simultaneous Equations Algebra: Factorising Practice and Fractions Changing Subjects
GCSE Higher Tier Practice Questions GCSE Higher Tier Practice Questions Contents: Topic Page Solving Linear, Quadratic and Simultaneous Equations Algebra: Factorising Practice and Fractions Changing Subjects
MATHEMATICS LEVEL 2. MATHEMATICS LEVEL 2 Continued GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE USE THIS SPACE FOR SCRATCHWORK. 1. If xy 0 and 3x = 0.
 MATHEMATICS LEVEL For each of the following problems, decide which is the BEST of the choices given. If the eact numerical value is not one of the choices, select the choice that best approimates this
MATHEMATICS LEVEL For each of the following problems, decide which is the BEST of the choices given. If the eact numerical value is not one of the choices, select the choice that best approimates this
Figure 5.1 shows some scaffolding in which some of the horizontal pieces are 2 m long and others are 1 m. All the vertical pieces are 2 m.
 A place for everthing, and everthing in its place. samuel smiles (8 904) Coordinate geometr Figure. shows some scaffolding in which some of the horizontal pieces are m long and others are m. All the vertical
A place for everthing, and everthing in its place. samuel smiles (8 904) Coordinate geometr Figure. shows some scaffolding in which some of the horizontal pieces are m long and others are m. All the vertical
Solve Quadratics Using the Formula
 Clip 6 Solve Quadratics Using the Formula a + b + c = 0, = b± b 4 ac a ) Solve the equation + 4 + = 0 Give our answers correct to decimal places. ) Solve the equation + 8 + 6 = 0 ) Solve the equation =
Clip 6 Solve Quadratics Using the Formula a + b + c = 0, = b± b 4 ac a ) Solve the equation + 4 + = 0 Give our answers correct to decimal places. ) Solve the equation + 8 + 6 = 0 ) Solve the equation =
Power Functions. A polynomial expression is an expression of the form a n. x n 2... a 3. ,..., a n. , a 1. A polynomial function has the form f(x) a n
 1.1 Power Functions A rock that is tossed into the water of a calm lake creates ripples that move outward in a circular pattern. The area, A, spanned b the ripples can be modelled b the function A(r) πr,
1.1 Power Functions A rock that is tossed into the water of a calm lake creates ripples that move outward in a circular pattern. The area, A, spanned b the ripples can be modelled b the function A(r) πr,
Analisis Mata Pelajaran
 99 SPM 2008 [ 756/1 ] [ 756/2 ] Additional Mathematic Analisis Mata Pelajaran Analsis of Additional Mathematic ( 2004-2007 ) NO TOPICS PAPER 1 PAPER 2 2004 2005 2006 2007 2004 2005 2006 2007 1 Functions
99 SPM 2008 [ 756/1 ] [ 756/2 ] Additional Mathematic Analisis Mata Pelajaran Analsis of Additional Mathematic ( 2004-2007 ) NO TOPICS PAPER 1 PAPER 2 2004 2005 2006 2007 2004 2005 2006 2007 1 Functions
Higher Tier - Algebra revision
 Higher Tier - Algebra revision Contents: Indices Epanding single brackets Epanding double brackets Substitution Solving equations Solving equations from angle probs Finding nth term of a sequence Simultaneous
Higher Tier - Algebra revision Contents: Indices Epanding single brackets Epanding double brackets Substitution Solving equations Solving equations from angle probs Finding nth term of a sequence Simultaneous
