Math 229: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Elementary approaches I: Variations on a theme of Euclid
|
|
|
- Brook Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 229: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Elementary approaches I: Variations on a theme of Euclid Like much of mathematics, the history of the distribution of primes begins with Euclid: Theorem (Euclid [IX, 20]. There are infinitely many primes. Euclid s justly famed argument, while often presented as a proof by contradiction, is readily framed as an effective (albeit rather inefficient construction: Proof: We inductively construct a sequence { } k>1 of primes, starting with p 1 = 2. Given primes p 1, p 2,..., p n, let P n = n, define N n = P n + 1, and let p n+1 be the smallest factor of N n. Then p n+1 is a prime no larger than N n and different from p 1,..., p n. Thus { } k>1 is an infinite sequence of distinct primes, Q.E.D. This answers Yes to the first asymptotic question to ask about π(x := #{p x : p is a positive prime} = 1, 0<p x p prime namely whether π(x as x. Moreover, the proof also gives an explicit upper bound on p n, and thus a lower bound on π(x. Theorem. For each integer n > 0, there are more than n primes p < 2 2n. Equivalently, we have 1 π(x > log 2 log 2 x for all x > 1. Proof : In the proof of Euclid s theorem, we may take p 1 = 2, and observe that p n+1 N n = 1 + n n 2. if equality were satisfied at each step we would have p n = 2 2n 1. Thus by induction we see that p n 2 2n 1, and of course the inequality is strict once n > 1. Therefore if x 2 2n 1 then < x for k = 1, 2,..., n, and so π(x n, Q.E.D. The P n + 1 trick has been adapted to prove some special cases of Dirichlet s theorem on primes in arithmetic progressions, which asserts that for relatively 1 The ubiquity of estimates involving log log x, log log log x, and beyond in analytic number theory has even inspired a joke: Q: What sound does a drowning analytic number theorist make? A: log log log log... I do not know who originated this joke; I was told it by B. Mazur, who heard it from R. Murty. 1
2 prime integers q > 0 and a there are infinitely many primes p a mod q. (We shall give the proof later in the course. Of course the case 1 mod 2 is trivial given Euclid. For 1 mod q with q = 3, 4, 6, start with p 1 = q 1 and define N n = qp n 1. More generally, for any quadratic character 2 χ there are infinitely many primes p with χ(p = 1; as a special case, given an odd prime q 0, there are infinitely many primes p which are quadratic nonresidues of q 0. [I m particularly fond of this argument because I was able to adapt it as the punchline of my doctoral thesis; see [Elkies 1987].] The case of χ(p = +1 is only a bit trickier. 3 For instance, to prove Dirichlet for (q, a = (4, 1, let p 1 = 5 and N n = 4Pn 2 + 1, and invoke Fermat s theorem on the prime factors of x 2 + y 2. Again this argument even yields an explicit lower bound on π(x, 1 mod 4 := #{p x : p is a positive prime congruent to 1 mod 4}, namely 4 for some positive constant C. π(x, 1 mod 4 > C log log x But Euclid s approach and its variations, however elegant, are not sufficient for our purposes. For one thing, numerical evidence suggests and we shall soon prove that log 2 log 2 x is a gross underestimate on π(x. For another, one cannot prove all cases of Dirichlet s theorem using only variations on the Euclid argument. 5 The elementary approaches to lower bounds on π(n in the next few lectures will address at least the first deficiency. Meanwhile we briefly consider upper bounds. Trivially π(x < x for all x. Since all primes except 2 are odd (and 1 is not prime, we have in fact π(x (x+1/2, and π(2m m for m = 1, 2, 3,.... Likewise since all but two primes are congruent to 1 or 5 mod 6 we have π(6m 2m + 1 for natural numbers m, and so π(x (x/3 + c 2 for some constant c 2. More generally, let p n be the n-th prime, and let 6 P n = n ; then by the Chinese Remainder Theorem only n ( 1 of the residue classes mod P n can contain any prime other than p 1,..., p n, whence ( n π(p n m < ( 1 m + n 2 We ll say much more about characters, quadratic and others, in a few weeks. An example is the Legendre symbol n (n/q 0 for some fixed odd prime q 0, or more generally any s nonempty product n i=1 (n/q i of such characters for distinct odd primes q 1,..., q s. 3 But enough so that a problem from a recent Qualifying Exam for our graduate students asked to prove that there are infinitely many primes congruent to 1 mod 4. 4 Even a drowning analytic number theorist knows that log log and log 2 log 2 are asymptotically within a constant factor of each other. What is that factor? 5 This is not a theorem, of course. How could one even define variation of the Euclid argument rigorously? But a Euclid-style argument for the infinitude of primes congruent to 2 mod 5 or mod 7 would already be quite impressive. 6 n By analogy with the factorial n! = i, this Pn is sometimes called the n-th i=1 primorial. 2
3 for all natural numbers m. Thus there is a constant c n such that ( n p π(x < k 1 x + c n (1 for all x. What happens to this upper bound as n? The coefficient of x decreases, and if it approaches zero that is, if (pk 1/ = 0 then π(x/x 0 as x. Otherwise we might expect that π(x/x approaches some positive constant, say κ. But then (pk 1/ should certainly vanish, because it contains a positive proportion of the factors of the infinite product n=2 ((n 1/n, whose partial products are N n=2 n 1 n = (N 1! N! = 1 N 0. Unfortunately it does not immediately follow from (1 that if ( (pk 1/ is positive then it equals lim x π(x/x; indeed for all we know so far the limit might not exist at all, and we can conclude only that lim sup x π(x x 1. (See the next-to-last Exercise below! But we can still use (1 to obtain an elementary proof that π(x/x 0 as x. Assume not. Then there exists κ > 0 and an infinite sequence x m such that π(x m > κx m for all m 1. Passing to a subsequence we may assume that the x m grow so rapidly that x m 1 < (κ/2x m for all m > 1. Then more than (κ/2x m of the primes p x m are in (x m 1, x m ]. Hence the product of (p 1/p over these primes is < 1 (κ/2 (why?, whence p x m ((p 1/p < (1 (κ/2 m. But then ( (pk 1/ = 0, and we already know that this implies the desired conclusion π(x/x 0. Notice that we have not yet proved that in fact (pk 1/ = 0. That is in fact true, and will be part of our next topic. Exercises 1. Fix an integer q > 2, and let G be a subgroup of (Z/qZ other than (Z/qZ itself. Prove that there are infinitely many primes whose residue modulo q is not in G. 2. Obtain explicit values of C and x 0 such that π(x, 1 mod 4 > C log log x for all x > x Use cyclotomic polynomials to show more generally that for any q 0, prime or not, there exist infinitely many primes congruent to 1 mod q 0. [Attributed to Euler in [Dickson 1919, Ch.XVIII], a chapter which gives much more information on the history of work on the distribution of primes up to about Note 3
4 that 4P 2 n + 1 is the fourth cyclotomic polynomial evaluated at 2P n.] Show that again the number of such primes x grows at least as fast as some multiple of log log x (that is, for every q 0 there exist constants C > 0 and x 0 such that for every x > x 0 there are at least C log log x primes p x congruent to 1 mod q Show that there are infinitely many primes congruent to 4 mod 5. If you know about the arithmetic of cyclotomic number fields, prove more generally that if G 0 is a subgroup of (Z/qZ and G is a subgroup of G 0 other than G 0 itself then there are infinitely many primes whose residue mod q is in G 0 but not in G. Obtain an explicit log log bound as before. 5. [A much later proof of the infinitude of primes that curiously gives the same bound π(x > log 2 log 2 (x.] Recall that the m-th Fermat number F m is defined by F m = 2 2m + 1 (m = 0, 1, 2,.... Prove that F m and F m are relatively prime unless m = m. Conclude that there are at least n primes p F n 1, and thus that π(x > log 2 log 2 x. 6. [A warning about limits.] Let {q k } be a sequence of primes, or even of natural numbers that are relatively prime in pairs; set κ = (qk 1/q k ; and let {a k } be an arbitrary sequence of integers. For x > 0 let ϖ(x be the number of positive integers q x such that q a k mod q k for all k. Prove that lim sup x ϖ(x/x κ, but that there are choices of {a k } for which ϖ(x/x 0 as x, even if κ > [Analytic number theory without Euclid.] Even though we re starting our exposition with Euclid, there are questions and techniques that can precede even the infinitude of primes. An example is lower bounds on Euler s phi-function φ(q = # ( (Z/qZ = #{a 0 a < q, gcd(a, q = 1} = q p q p 1 p (q a positive integer. Clearly φ(q q, with equality only for q = 1; but often (in analytic number theory and elsewhere it is useful to know that φ(q is not too much smaller than q, either for any given q or on average. i Prove that for all ɛ > 0 there exists C ɛ > 0 such that φ(q > C ɛ q 1 ɛ for all q. [Only finitely many of the factors (p 1/p can be smaller than p ɛ.] ii Prove that there exists c > 0 such that x q=1 φ(x > cx2 for all positive integers x. [Since x q=1 q = (x2 + x/2, the lower bound on x q=1 φ(x says in effect that φ(q 2cq on average.] Naturally, more precise results on the distribution of primes will let us obtain sharper results, such as the dependence of C ɛ on ɛ; e.g. the fact that C ɛ cannot be chosen independent of ɛ is tantamount to lim inf q(φ(q/q = 0, which is in turn equivalent to (pk 1/ = 0. For part (ii, it is easy to obtain this bound with 2c = 1 (1/p2. The actual asymptotic average of φ(q/q is usually described as the probability that two randomly chosen integers are relatively prime. This is wellknown to be 1/ζ(2 = 6/π 2 ; this is not too hard to prove (see Exercise 7 of the next installment, though there are still nontrivial questions concerning the error term x φ(x q=1 x2 /(2ζ(2. 4
5 Digression Even a piece of mathematics as venerable as Euclid s proof of the infinitude of primes can continue to suggest very difficult problems. For instance, let p n be the n-th prime and P n = n as before. We know that P n + 1 must contain a new prime factor, which cannot be p n+1 once n > 1 (if only because P n 1 must also contain a new prime factor. Does it happen infinitely often that p n+1 is a factor of P n + 1? [This is the case for n = 1, 7, 232, 430, and no other n < 10 5.] What of the primality of P n + 1 itself? It is well-known that P n + 1 is prime for n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, but P = = As of early 2010, only seventeen n > 5 have been found for which P n + 1 is prime, of which the smallest is 11 and the largest is Again it is not known whether this happens infinitely often. Likewise for the primality of P n 1 and its divisibility by p n+1. For another variation, define q 1 = 2 and, for n > 0, let q n+1 be the smallest prime factor of ( n q k + 1. The sequence {q n } n=1 starts 2, 3, 7, 43, 13, 53, 5, , , 139, 2801, 11,... For instance, q 5 = 13 because = 1807 = Is this Euclid- Mullin sequence [Sloane, A000945] a permutation of the sequence of primes? Probably yes, but proving this will likely be intractable for the foreseeable future. The same is true for the infinitude of primes of the form P n ± 1, and of n such that p n+1 P n ± 1. It should not even be obvious that one should expect that these four sets are all infinite. The heuristics supporting this expectation rely on results on the distribution of primes that we shall develop in the next few weeks. References [Dickson 1919] Dickson, L.E.: History of the Theory of Numbers, Vol. I: Divisibility and Primality. Washington: Carnegie Inst., [Euclid] Euclid, Elements. [Elkies 1987] Elkies, N.D.: The existence of infinitely many supersingular primes for every elliptic curve over Q, Invent. Math. 89 (1987, ; See also: Supersingular primes for elliptic curves over real number fields, Compositio Math. 72 (1989, [Sloane] Sloane, N.J.A.: On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. 7 Sequence A in [Sloane], where the primality of P is attributed to Eric W. Weisstein, March 13, For the analogous question concerning P n 1, see Sequence A and A
= 1 2x. x 2 a ) 0 (mod p n ), (x 2 + 2a + a2. x a ) 2
 8. p-adic numbers 8.1. Motivation: Solving x 2 a (mod p n ). Take an odd prime p, and ( an) integer a coprime to p. Then, as we know, x 2 a (mod p) has a solution x Z iff = 1. In this case we can suppose
8. p-adic numbers 8.1. Motivation: Solving x 2 a (mod p n ). Take an odd prime p, and ( an) integer a coprime to p. Then, as we know, x 2 a (mod p) has a solution x Z iff = 1. In this case we can suppose
SQUARE PATTERNS AND INFINITUDE OF PRIMES
 SQUARE PATTERNS AND INFINITUDE OF PRIMES KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction Numerical data suggest the following patterns for prime numbers p: 1 mod p p = 2 or p 1 mod 4, 2 mod p p = 2 or p 1, 7 mod 8, 2 mod
SQUARE PATTERNS AND INFINITUDE OF PRIMES KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction Numerical data suggest the following patterns for prime numbers p: 1 mod p p = 2 or p 1 mod 4, 2 mod p p = 2 or p 1, 7 mod 8, 2 mod
Part II. Number Theory. Year
 Part II Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2017 Paper 3, Section I 1G 70 Explain what is meant by an Euler pseudoprime and a strong pseudoprime. Show that 65 is an Euler
Part II Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2017 Paper 3, Section I 1G 70 Explain what is meant by an Euler pseudoprime and a strong pseudoprime. Show that 65 is an Euler
Know the Well-ordering principle: Any set of positive integers which has at least one element contains a smallest element.
 The first exam will be on Monday, June 8, 202. The syllabus will be sections. and.2 in Lax, and the number theory handout found on the class web site, plus the handout on the method of successive squaring
The first exam will be on Monday, June 8, 202. The syllabus will be sections. and.2 in Lax, and the number theory handout found on the class web site, plus the handout on the method of successive squaring
ECEN 5022 Cryptography
 Elementary Algebra and Number Theory University of Colorado Spring 2008 Divisibility, Primes Definition. N denotes the set {1, 2, 3,...} of natural numbers and Z denotes the set of integers {..., 2, 1,
Elementary Algebra and Number Theory University of Colorado Spring 2008 Divisibility, Primes Definition. N denotes the set {1, 2, 3,...} of natural numbers and Z denotes the set of integers {..., 2, 1,
AN EASY GENERALIZATION OF EULER S THEOREM ON THE SERIES OF PRIME RECIPROCALS
 AN EASY GENERALIZATION OF EULER S THEOREM ON THE SERIES OF PRIME RECIPROCALS PAUL POLLACK Abstract It is well-known that Euclid s argument can be adapted to prove the infinitude of primes of the form 4k
AN EASY GENERALIZATION OF EULER S THEOREM ON THE SERIES OF PRIME RECIPROCALS PAUL POLLACK Abstract It is well-known that Euclid s argument can be adapted to prove the infinitude of primes of the form 4k
Lecture notes: Algorithms for integers, polynomials (Thorsten Theobald)
 Lecture notes: Algorithms for integers, polynomials (Thorsten Theobald) 1 Euclid s Algorithm Euclid s Algorithm for computing the greatest common divisor belongs to the oldest known computing procedures
Lecture notes: Algorithms for integers, polynomials (Thorsten Theobald) 1 Euclid s Algorithm Euclid s Algorithm for computing the greatest common divisor belongs to the oldest known computing procedures
CHAPTER 6. Prime Numbers. Definition and Fundamental Results
 CHAPTER 6 Prime Numbers Part VI of PJE. Definition and Fundamental Results 6.1. Definition. (PJE definition 23.1.1) An integer p is prime if p > 1 and the only positive divisors of p are 1 and p. If n
CHAPTER 6 Prime Numbers Part VI of PJE. Definition and Fundamental Results 6.1. Definition. (PJE definition 23.1.1) An integer p is prime if p > 1 and the only positive divisors of p are 1 and p. If n
A Few Primality Testing Algorithms
 A Few Primality Testing Algorithms Donald Brower April 2, 2006 0.1 Introduction These notes will cover a few primality testing algorithms. There are many such, some prove that a number is prime, others
A Few Primality Testing Algorithms Donald Brower April 2, 2006 0.1 Introduction These notes will cover a few primality testing algorithms. There are many such, some prove that a number is prime, others
MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY FOURTH LECTURE
 MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY FOURTH LECTURE 1. Introduction Everybody knows that three hours after 10:00, the time is 1:00. That is, everybody is familiar with modular arithmetic, the usual arithmetic of the
MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY FOURTH LECTURE 1. Introduction Everybody knows that three hours after 10:00, the time is 1:00. That is, everybody is familiar with modular arithmetic, the usual arithmetic of the
Applied Cryptography and Computer Security CSE 664 Spring 2018
 Applied Cryptography and Computer Security Lecture 12: Introduction to Number Theory II Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Lecture Outline This time we ll finish the
Applied Cryptography and Computer Security Lecture 12: Introduction to Number Theory II Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Lecture Outline This time we ll finish the
(Primes and) Squares modulo p
 (Primes and) Squares modulo p Paul Pollack MAA Invited Paper Session on Accessible Problems in Modern Number Theory January 13, 2018 1 of 15 Question Consider the infinite arithmetic progression Does it
(Primes and) Squares modulo p Paul Pollack MAA Invited Paper Session on Accessible Problems in Modern Number Theory January 13, 2018 1 of 15 Question Consider the infinite arithmetic progression Does it
An integer p is prime if p > 1 and p has exactly two positive divisors, 1 and p.
 Chapter 6 Prime Numbers Part VI of PJE. Definition and Fundamental Results Definition. (PJE definition 23.1.1) An integer p is prime if p > 1 and p has exactly two positive divisors, 1 and p. If n > 1
Chapter 6 Prime Numbers Part VI of PJE. Definition and Fundamental Results Definition. (PJE definition 23.1.1) An integer p is prime if p > 1 and p has exactly two positive divisors, 1 and p. If n > 1
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory The Selberg (quadratic) sieve and some applications
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory The Selberg (quadratic) sieve and some applications An elementary and indeed naïve approach to the distribution of primes is the following argument: an
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory The Selberg (quadratic) sieve and some applications An elementary and indeed naïve approach to the distribution of primes is the following argument: an
Math 4400/6400 Homework #8 solutions. 1. Let P be an odd integer (not necessarily prime). Show that modulo 2,
 MATH 4400 roblems. Math 4400/6400 Homework # solutions 1. Let P be an odd integer not necessarily rime. Show that modulo, { P 1 0 if P 1, 7 mod, 1 if P 3, mod. Proof. Suose that P 1 mod. Then we can write
MATH 4400 roblems. Math 4400/6400 Homework # solutions 1. Let P be an odd integer not necessarily rime. Show that modulo, { P 1 0 if P 1, 7 mod, 1 if P 3, mod. Proof. Suose that P 1 mod. Then we can write
2 Arithmetic. 2.1 Greatest common divisors. This chapter is about properties of the integers Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}.
 2 Arithmetic This chapter is about properties of the integers Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}. (See [Houston, Chapters 27 & 28]) 2.1 Greatest common divisors Definition 2.16. If a, b are integers, we say
2 Arithmetic This chapter is about properties of the integers Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}. (See [Houston, Chapters 27 & 28]) 2.1 Greatest common divisors Definition 2.16. If a, b are integers, we say
ON VALUES OF CYCLOTOMIC POLYNOMIALS. V
 Math. J. Okayama Univ. 45 (2003), 29 36 ON VALUES OF CYCLOTOMIC POLYNOMIALS. V Dedicated to emeritus professor Kazuo Kishimoto on his seventieth birthday Kaoru MOTOSE In this paper, using properties of
Math. J. Okayama Univ. 45 (2003), 29 36 ON VALUES OF CYCLOTOMIC POLYNOMIALS. V Dedicated to emeritus professor Kazuo Kishimoto on his seventieth birthday Kaoru MOTOSE In this paper, using properties of
PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY. Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice a prime.
 PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. This is a list of exercises on Number Theory. Miguel A. Lerma Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice
PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. This is a list of exercises on Number Theory. Miguel A. Lerma Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice
PRIME NUMBERS YANKI LEKILI
 PRIME NUMBERS YANKI LEKILI We denote by N the set of natural numbers: 1,2,..., These are constructed using Peano axioms. We will not get into the philosophical questions related to this and simply assume
PRIME NUMBERS YANKI LEKILI We denote by N the set of natural numbers: 1,2,..., These are constructed using Peano axioms. We will not get into the philosophical questions related to this and simply assume
Proofs of the infinitude of primes
 Proofs of the infinitude of primes Tomohiro Yamada Abstract In this document, I would like to give several proofs that there exist infinitely many primes. 0 Introduction It is well known that the number
Proofs of the infinitude of primes Tomohiro Yamada Abstract In this document, I would like to give several proofs that there exist infinitely many primes. 0 Introduction It is well known that the number
8 Primes and Modular Arithmetic
 8 Primes and Modular Arithmetic 8.1 Primes and Factors Over two millennia ago already, people all over the world were considering the properties of numbers. One of the simplest concepts is prime numbers.
8 Primes and Modular Arithmetic 8.1 Primes and Factors Over two millennia ago already, people all over the world were considering the properties of numbers. One of the simplest concepts is prime numbers.
Euclidean prime generators
 Euclidean prime generators Andrew R. Booker, Bristol University Bristol, UK Carl Pomerance, Dartmouth College (emeritus) Hanover, New Hampshire, USA (U. Georgia, emeritus) Integers Conference, Carrollton,
Euclidean prime generators Andrew R. Booker, Bristol University Bristol, UK Carl Pomerance, Dartmouth College (emeritus) Hanover, New Hampshire, USA (U. Georgia, emeritus) Integers Conference, Carrollton,
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Primes in arithmetic progressions: Dirichlet characters and L-functions
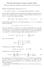 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Primes in arithmetic progressions: Dirichlet characters and L-functions Dirichlet extended Euler s analysis from π(x) to π(x, a mod q) := #{p x : p is a
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Primes in arithmetic progressions: Dirichlet characters and L-functions Dirichlet extended Euler s analysis from π(x) to π(x, a mod q) := #{p x : p is a
Winter Camp 2009 Number Theory Tips and Tricks
 Winter Camp 2009 Number Theory Tips and Tricks David Arthur darthur@gmail.com 1 Introduction This handout is about some of the key techniques for solving number theory problems, especially Diophantine
Winter Camp 2009 Number Theory Tips and Tricks David Arthur darthur@gmail.com 1 Introduction This handout is about some of the key techniques for solving number theory problems, especially Diophantine
IRREDUCIBILITY TESTS IN F p [T ]
![IRREDUCIBILITY TESTS IN F p [T ] IRREDUCIBILITY TESTS IN F p [T ]](/thumbs/96/128966602.jpg) IRREDUCIBILITY TESTS IN F p [T ] KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction Let F p = Z/(p) be a field of prime order. We will discuss a few methods of checking if a polynomial f(t ) F p [T ] is irreducible that are
IRREDUCIBILITY TESTS IN F p [T ] KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction Let F p = Z/(p) be a field of prime order. We will discuss a few methods of checking if a polynomial f(t ) F p [T ] is irreducible that are
Chapter 4. Characters and Gauss sums. 4.1 Characters on finite abelian groups
 Chapter 4 Characters and Gauss sums 4.1 Characters on finite abelian groups In what follows, abelian groups are multiplicatively written, and the unit element of an abelian group A is denoted by 1 or 1
Chapter 4 Characters and Gauss sums 4.1 Characters on finite abelian groups In what follows, abelian groups are multiplicatively written, and the unit element of an abelian group A is denoted by 1 or 1
1, for s = σ + it where σ, t R and σ > 1
 DIRICHLET L-FUNCTIONS AND DEDEKIND ζ-functions FRIMPONG A. BAIDOO Abstract. We begin by introducing Dirichlet L-functions which we use to prove Dirichlet s theorem on arithmetic progressions. From there,
DIRICHLET L-FUNCTIONS AND DEDEKIND ζ-functions FRIMPONG A. BAIDOO Abstract. We begin by introducing Dirichlet L-functions which we use to prove Dirichlet s theorem on arithmetic progressions. From there,
. As the binomial coefficients are integers we have that. 2 n(n 1).
 Math 580 Homework. 1. Divisibility. Definition 1. Let a, b be integers with a 0. Then b divides b iff there is an integer k such that b = ka. In the case we write a b. In this case we also say a is a factor
Math 580 Homework. 1. Divisibility. Definition 1. Let a, b be integers with a 0. Then b divides b iff there is an integer k such that b = ka. In the case we write a b. In this case we also say a is a factor
MATH 310: Homework 7
 1 MATH 310: Homework 7 Due Thursday, 12/1 in class Reading: Davenport III.1, III.2, III.3, III.4, III.5 1. Show that x is a root of unity modulo m if and only if (x, m 1. (Hint: Use Euler s theorem and
1 MATH 310: Homework 7 Due Thursday, 12/1 in class Reading: Davenport III.1, III.2, III.3, III.4, III.5 1. Show that x is a root of unity modulo m if and only if (x, m 1. (Hint: Use Euler s theorem and
Elementary Number Theory MARUCO. Summer, 2018
 Elementary Number Theory MARUCO Summer, 2018 Problem Set #0 axiom, theorem, proof, Z, N. Axioms Make a list of axioms for the integers. Does your list adequately describe them? Can you make this list as
Elementary Number Theory MARUCO Summer, 2018 Problem Set #0 axiom, theorem, proof, Z, N. Axioms Make a list of axioms for the integers. Does your list adequately describe them? Can you make this list as
Notes on Systems of Linear Congruences
 MATH 324 Summer 2012 Elementary Number Theory Notes on Systems of Linear Congruences In this note we will discuss systems of linear congruences where the moduli are all different. Definition. Given the
MATH 324 Summer 2012 Elementary Number Theory Notes on Systems of Linear Congruences In this note we will discuss systems of linear congruences where the moduli are all different. Definition. Given the
Lecture 11 - Basic Number Theory.
 Lecture 11 - Basic Number Theory. Boaz Barak October 20, 2005 Divisibility and primes Unless mentioned otherwise throughout this lecture all numbers are non-negative integers. We say that a divides b,
Lecture 11 - Basic Number Theory. Boaz Barak October 20, 2005 Divisibility and primes Unless mentioned otherwise throughout this lecture all numbers are non-negative integers. We say that a divides b,
This is a recursive algorithm. The procedure is guaranteed to terminate, since the second argument decreases each time.
 8 Modular Arithmetic We introduce an operator mod. Let d be a positive integer. For c a nonnegative integer, the value c mod d is the remainder when c is divided by d. For example, c mod d = 0 if and only
8 Modular Arithmetic We introduce an operator mod. Let d be a positive integer. For c a nonnegative integer, the value c mod d is the remainder when c is divided by d. For example, c mod d = 0 if and only
On The Weights of Binary Irreducible Cyclic Codes
 On The Weights of Binary Irreducible Cyclic Codes Yves Aubry and Philippe Langevin Université du Sud Toulon-Var, Laboratoire GRIM F-83270 La Garde, France, {langevin,yaubry}@univ-tln.fr, WWW home page:
On The Weights of Binary Irreducible Cyclic Codes Yves Aubry and Philippe Langevin Université du Sud Toulon-Var, Laboratoire GRIM F-83270 La Garde, France, {langevin,yaubry}@univ-tln.fr, WWW home page:
1. multiplication is commutative and associative;
 Chapter 4 The Arithmetic of Z In this chapter, we start by introducing the concept of congruences; these are used in our proof (going back to Gauss 1 ) that every integer has a unique prime factorization.
Chapter 4 The Arithmetic of Z In this chapter, we start by introducing the concept of congruences; these are used in our proof (going back to Gauss 1 ) that every integer has a unique prime factorization.
ORDERS OF ELEMENTS IN A GROUP
 ORDERS OF ELEMENTS IN A GROUP KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction Let G be a group and g G. We say g has finite order if g n = e for some positive integer n. For example, 1 and i have finite order in C, since
ORDERS OF ELEMENTS IN A GROUP KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction Let G be a group and g G. We say g has finite order if g n = e for some positive integer n. For example, 1 and i have finite order in C, since
Counting points on elliptic curves over F q
 Counting points on elliptic curves over F q Christiane Peters DIAMANT-Summer School on Elliptic and Hyperelliptic Curve Cryptography September 17, 2008 p.2 Motivation Given an elliptic curve E over a finite
Counting points on elliptic curves over F q Christiane Peters DIAMANT-Summer School on Elliptic and Hyperelliptic Curve Cryptography September 17, 2008 p.2 Motivation Given an elliptic curve E over a finite
Math 324, Fall 2011 Assignment 7 Solutions. 1 (ab) γ = a γ b γ mod n.
 Math 324, Fall 2011 Assignment 7 Solutions Exercise 1. (a) Suppose a and b are both relatively prime to the positive integer n. If gcd(ord n a, ord n b) = 1, show ord n (ab) = ord n a ord n b. (b) Let
Math 324, Fall 2011 Assignment 7 Solutions Exercise 1. (a) Suppose a and b are both relatively prime to the positive integer n. If gcd(ord n a, ord n b) = 1, show ord n (ab) = ord n a ord n b. (b) Let
Chapter 1. Introduction to prime number theory. 1.1 The Prime Number Theorem
 Chapter 1 Introduction to prime number theory 1.1 The Prime Number Theorem In the first part of this course, we focus on the theory of prime numbers. We use the following notation: we write f( g( as if
Chapter 1 Introduction to prime number theory 1.1 The Prime Number Theorem In the first part of this course, we focus on the theory of prime numbers. We use the following notation: we write f( g( as if
Arithmetic Statistics Lecture 1
 Arithmetic Statistics Lecture 1 Álvaro Lozano-Robledo Department of Mathematics University of Connecticut May 28 th CTNT 2018 Connecticut Summer School in Number Theory Question What is Arithmetic Statistics?
Arithmetic Statistics Lecture 1 Álvaro Lozano-Robledo Department of Mathematics University of Connecticut May 28 th CTNT 2018 Connecticut Summer School in Number Theory Question What is Arithmetic Statistics?
4 PRIMITIVE ROOTS Order and Primitive Roots The Index Existence of primitive roots for prime modulus...
 PREFACE These notes have been prepared by Dr Mike Canfell (with minor changes and extensions by Dr Gerd Schmalz) for use by the external students in the unit PMTH 338 Number Theory. This booklet covers
PREFACE These notes have been prepared by Dr Mike Canfell (with minor changes and extensions by Dr Gerd Schmalz) for use by the external students in the unit PMTH 338 Number Theory. This booklet covers
Math 109 HW 9 Solutions
 Math 109 HW 9 Solutions Problems IV 18. Solve the linear diophantine equation 6m + 10n + 15p = 1 Solution: Let y = 10n + 15p. Since (10, 15) is 5, we must have that y = 5x for some integer x, and (as we
Math 109 HW 9 Solutions Problems IV 18. Solve the linear diophantine equation 6m + 10n + 15p = 1 Solution: Let y = 10n + 15p. Since (10, 15) is 5, we must have that y = 5x for some integer x, and (as we
CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ω(q) AND ν(q)
 CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ωq) AND νq) GEORGE E. ANDREWS, DONNY PASSARY, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Recently, Andrews, Dixit and Yee introduced partition
CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ωq) AND νq) GEORGE E. ANDREWS, DONNY PASSARY, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Recently, Andrews, Dixit and Yee introduced partition
A Guide to Arithmetic
 A Guide to Arithmetic Robin Chapman August 5, 1994 These notes give a very brief resumé of my number theory course. Proofs and examples are omitted. Any suggestions for improvements will be gratefully
A Guide to Arithmetic Robin Chapman August 5, 1994 These notes give a very brief resumé of my number theory course. Proofs and examples are omitted. Any suggestions for improvements will be gratefully
Dirichlet s Theorem. Martin Orr. August 21, The aim of this article is to prove Dirichlet s theorem on primes in arithmetic progressions:
 Dirichlet s Theorem Martin Orr August 1, 009 1 Introduction The aim of this article is to prove Dirichlet s theorem on primes in arithmetic progressions: Theorem 1.1. If m, a N are coprime, then there
Dirichlet s Theorem Martin Orr August 1, 009 1 Introduction The aim of this article is to prove Dirichlet s theorem on primes in arithmetic progressions: Theorem 1.1. If m, a N are coprime, then there
Projects on elliptic curves and modular forms
 Projects on elliptic curves and modular forms Math 480, Spring 2010 In the following are 11 projects for this course. Some of the projects are rather ambitious and may very well be the topic of a master
Projects on elliptic curves and modular forms Math 480, Spring 2010 In the following are 11 projects for this course. Some of the projects are rather ambitious and may very well be the topic of a master
1 Overview and revision
 MTH6128 Number Theory Notes 1 Spring 2018 1 Overview and revision In this section we will meet some of the concerns of Number Theory, and have a brief revision of some of the relevant material from Introduction
MTH6128 Number Theory Notes 1 Spring 2018 1 Overview and revision In this section we will meet some of the concerns of Number Theory, and have a brief revision of some of the relevant material from Introduction
198 VOLUME 46/47, NUMBER 3
 LAWRENCE SOMER Abstract. Rotkiewicz has shown that there exist Fibonacci pseudoprimes having the forms p(p + 2), p(2p 1), and p(2p + 3), where all the terms in the products are odd primes. Assuming Dickson
LAWRENCE SOMER Abstract. Rotkiewicz has shown that there exist Fibonacci pseudoprimes having the forms p(p + 2), p(2p 1), and p(2p + 3), where all the terms in the products are odd primes. Assuming Dickson
Math 110 HW 3 solutions
 Math 0 HW 3 solutions May 8, 203. For any positive real number r, prove that x r = O(e x ) as functions of x. Suppose r
Math 0 HW 3 solutions May 8, 203. For any positive real number r, prove that x r = O(e x ) as functions of x. Suppose r
Lecture 7: More Arithmetic and Fun With Primes
 IAS/PCMI Summer Session 2000 Clay Mathematics Undergraduate Program Advanced Course on Computational Complexity Lecture 7: More Arithmetic and Fun With Primes David Mix Barrington and Alexis Maciel July
IAS/PCMI Summer Session 2000 Clay Mathematics Undergraduate Program Advanced Course on Computational Complexity Lecture 7: More Arithmetic and Fun With Primes David Mix Barrington and Alexis Maciel July
Chapter 9 Mathematics of Cryptography Part III: Primes and Related Congruence Equations
 Chapter 9 Mathematics of Cryptography Part III: Primes and Related Congruence Equations Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1 Chapter 9 Objectives
Chapter 9 Mathematics of Cryptography Part III: Primes and Related Congruence Equations Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1 Chapter 9 Objectives
Corollary 4.2 (Pepin s Test, 1877). Let F k = 2 2k + 1, the kth Fermat number, where k 1. Then F k is prime iff 3 F k 1
 4. Primality testing 4.1. Introduction. Factorisation is concerned with the problem of developing efficient algorithms to express a given positive integer n > 1 as a product of powers of distinct primes.
4. Primality testing 4.1. Introduction. Factorisation is concerned with the problem of developing efficient algorithms to express a given positive integer n > 1 as a product of powers of distinct primes.
A Few New Facts about the EKG Sequence
 1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 11 (2008), Article 08.4.2 A Few New Facts about the EKG Sequence Piotr Hofman and Marcin Pilipczuk Department of Mathematics, Computer Science and Mechanics
1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 11 (2008), Article 08.4.2 A Few New Facts about the EKG Sequence Piotr Hofman and Marcin Pilipczuk Department of Mathematics, Computer Science and Mechanics
10 Problem 1. The following assertions may be true or false, depending on the choice of the integers a, b 0. a "
 Math 4161 Dr. Franz Rothe December 9, 2013 13FALL\4161_fall13f.tex Name: Use the back pages for extra space Final 70 70 Problem 1. The following assertions may be true or false, depending on the choice
Math 4161 Dr. Franz Rothe December 9, 2013 13FALL\4161_fall13f.tex Name: Use the back pages for extra space Final 70 70 Problem 1. The following assertions may be true or false, depending on the choice
Primes in arithmetic progressions
 (September 26, 205) Primes in arithmetic progressions Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ [This document is http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/m/mfms/notes 205-6/06 Dirichlet.pdf].
(September 26, 205) Primes in arithmetic progressions Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ [This document is http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/m/mfms/notes 205-6/06 Dirichlet.pdf].
Definition 6.1 (p.277) A positive integer n is prime when n > 1 and the only positive divisors are 1 and n. Alternatively
 6 Prime Numbers Part VI of PJE 6.1 Fundamental Results Definition 6.1 (p.277) A positive integer n is prime when n > 1 and the only positive divisors are 1 and n. Alternatively D (p) = { p 1 1 p}. Otherwise
6 Prime Numbers Part VI of PJE 6.1 Fundamental Results Definition 6.1 (p.277) A positive integer n is prime when n > 1 and the only positive divisors are 1 and n. Alternatively D (p) = { p 1 1 p}. Otherwise
How To Test If a Polynomial Is Identically Zero?
 How To Test If a Polynomial Is Identically Zero? det(a G ) is a polynomial in n 2 variables. There are exponentially many terms in det(a G ). Expanding the determinant polynomial is not feasible. Too many
How To Test If a Polynomial Is Identically Zero? det(a G ) is a polynomial in n 2 variables. There are exponentially many terms in det(a G ). Expanding the determinant polynomial is not feasible. Too many
A SURVEY OF PRIMALITY TESTS
 A SURVEY OF PRIMALITY TESTS STEFAN LANCE Abstract. In this paper, we show how modular arithmetic and Euler s totient function are applied to elementary number theory. In particular, we use only arithmetic
A SURVEY OF PRIMALITY TESTS STEFAN LANCE Abstract. In this paper, we show how modular arithmetic and Euler s totient function are applied to elementary number theory. In particular, we use only arithmetic
Polygonal Numbers, Primes and Ternary Quadratic Forms
 Polygonal Numbers, Primes and Ternary Quadratic Forms Zhi-Wei Sun Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, P. R. China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/ zwsun August 26, 2009 Modern number theory has
Polygonal Numbers, Primes and Ternary Quadratic Forms Zhi-Wei Sun Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, P. R. China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/ zwsun August 26, 2009 Modern number theory has
Equidivisible consecutive integers
 & Equidivisible consecutive integers Ivo Düntsch Department of Computer Science Brock University St Catherines, Ontario, L2S 3A1, Canada duentsch@cosc.brocku.ca Roger B. Eggleton Department of Mathematics
& Equidivisible consecutive integers Ivo Düntsch Department of Computer Science Brock University St Catherines, Ontario, L2S 3A1, Canada duentsch@cosc.brocku.ca Roger B. Eggleton Department of Mathematics
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 On Runs of Residues Author(s): D. H. Lehmer and Emma Lehmer Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 13, No. 1 (Feb., 1962), pp. 102-106 Published by: American Mathematical Society
On Runs of Residues Author(s): D. H. Lehmer and Emma Lehmer Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 13, No. 1 (Feb., 1962), pp. 102-106 Published by: American Mathematical Society
Math 314 Course Notes: Brief description
 Brief description These are notes for Math 34, an introductory course in elementary number theory Students are advised to go through all sections in detail and attempt all problems These notes will be
Brief description These are notes for Math 34, an introductory course in elementary number theory Students are advised to go through all sections in detail and attempt all problems These notes will be
Standard forms for writing numbers
 Standard forms for writing numbers In order to relate the abstract mathematical descriptions of familiar number systems to the everyday descriptions of numbers by decimal expansions and similar means,
Standard forms for writing numbers In order to relate the abstract mathematical descriptions of familiar number systems to the everyday descriptions of numbers by decimal expansions and similar means,
On the Cardinality of Mersenne Primes
 On the Cardinality of Mersenne Primes Garimella Rama Murthy, Associate Professor, International Institute of Information Technology (IIIT), Gachibowli, Hyderabad-32,AP,INDIA ABSTRACT In this research paper,
On the Cardinality of Mersenne Primes Garimella Rama Murthy, Associate Professor, International Institute of Information Technology (IIIT), Gachibowli, Hyderabad-32,AP,INDIA ABSTRACT In this research paper,
Rational Points on Conics, and Local-Global Relations in Number Theory
 Rational Points on Conics, and Local-Global Relations in Number Theory Joseph Lipman Purdue University Department of Mathematics lipman@math.purdue.edu http://www.math.purdue.edu/ lipman November 26, 2007
Rational Points on Conics, and Local-Global Relations in Number Theory Joseph Lipman Purdue University Department of Mathematics lipman@math.purdue.edu http://www.math.purdue.edu/ lipman November 26, 2007
Bipartite Perfect Matching
 Bipartite Perfect Matching We are given a bipartite graph G = (U, V, E). U = {u 1, u 2,..., u n }. V = {v 1, v 2,..., v n }. E U V. We are asked if there is a perfect matching. A permutation π of {1, 2,...,
Bipartite Perfect Matching We are given a bipartite graph G = (U, V, E). U = {u 1, u 2,..., u n }. V = {v 1, v 2,..., v n }. E U V. We are asked if there is a perfect matching. A permutation π of {1, 2,...,
Discrete Logarithms. Let s begin by recalling the definitions and a theorem. Let m be a given modulus. Then the finite set
 Discrete Logarithms Let s begin by recalling the definitions and a theorem. Let m be a given modulus. Then the finite set Z/mZ = {[0], [1],..., [m 1]} = {0, 1,..., m 1} of residue classes modulo m is called
Discrete Logarithms Let s begin by recalling the definitions and a theorem. Let m be a given modulus. Then the finite set Z/mZ = {[0], [1],..., [m 1]} = {0, 1,..., m 1} of residue classes modulo m is called
CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ω(q) AND ν(q)
 CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ωq) AND νq) GEORGE E. ANDREWS, DONNY PASSARY, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Recently, Andrews, Dixit, and Yee introduced partition
CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ωq) AND νq) GEORGE E. ANDREWS, DONNY PASSARY, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Recently, Andrews, Dixit, and Yee introduced partition
SPECIAL CASES OF THE CLASS NUMBER FORMULA
 SPECIAL CASES OF THE CLASS NUMBER FORMULA What we know from last time regarding general theory: Each quadratic extension K of Q has an associated discriminant D K (which uniquely determines K), and an
SPECIAL CASES OF THE CLASS NUMBER FORMULA What we know from last time regarding general theory: Each quadratic extension K of Q has an associated discriminant D K (which uniquely determines K), and an
The number of ways to choose r elements (without replacement) from an n-element set is. = r r!(n r)!.
 The first exam will be on Friday, September 23, 2011. The syllabus will be sections 0.1 through 0.4 and 0.6 in Nagpaul and Jain, and the corresponding parts of the number theory handout found on the class
The first exam will be on Friday, September 23, 2011. The syllabus will be sections 0.1 through 0.4 and 0.6 in Nagpaul and Jain, and the corresponding parts of the number theory handout found on the class
Number Theory Proof Portfolio
 Number Theory Proof Portfolio Jordan Rock May 12, 2015 This portfolio is a collection of Number Theory proofs and problems done by Jordan Rock in the Spring of 2014. The problems are organized first by
Number Theory Proof Portfolio Jordan Rock May 12, 2015 This portfolio is a collection of Number Theory proofs and problems done by Jordan Rock in the Spring of 2014. The problems are organized first by
Representing numbers as the sum of squares and powers in the ring Z n
 Representing numbers as the sum of squares powers in the ring Z n Rob Burns arxiv:708.03930v2 [math.nt] 23 Sep 207 26th September 207 Abstract We examine the representation of numbers as the sum of two
Representing numbers as the sum of squares powers in the ring Z n Rob Burns arxiv:708.03930v2 [math.nt] 23 Sep 207 26th September 207 Abstract We examine the representation of numbers as the sum of two
Numbers, Groups and Cryptography. Gordan Savin
 Numbers, Groups and Cryptography Gordan Savin Contents Chapter 1. Euclidean Algorithm 5 1. Euclidean Algorithm 5 2. Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic 9 3. Uniqueness of Factorization 14 4. Efficiency
Numbers, Groups and Cryptography Gordan Savin Contents Chapter 1. Euclidean Algorithm 5 1. Euclidean Algorithm 5 2. Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic 9 3. Uniqueness of Factorization 14 4. Efficiency
A polytime proof of correctness of the Rabin-Miller algorithm from Fermat s Little Theorem
 A polytime proof of correctness of the Rabin-Miller algorithm from Fermat s Little Theorem Grzegorz Herman and Michael Soltys November 24, 2008 Abstract Although a deterministic polytime algorithm for
A polytime proof of correctness of the Rabin-Miller algorithm from Fermat s Little Theorem Grzegorz Herman and Michael Soltys November 24, 2008 Abstract Although a deterministic polytime algorithm for
Journal of Combinatorics and Number Theory 1(2009), no. 1, ON SUMS OF PRIMES AND TRIANGULAR NUMBERS. Zhi-Wei Sun
 Journal of Combinatorics and Number Theory 1(009), no. 1, 65 76. ON SUMS OF PRIMES AND TRIANGULAR NUMBERS Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 10093, People s Republic of China
Journal of Combinatorics and Number Theory 1(009), no. 1, 65 76. ON SUMS OF PRIMES AND TRIANGULAR NUMBERS Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 10093, People s Republic of China
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security
 Outline Quadratic residues Useful tests Digital Signatures CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Lecture 14 Michael J. Fischer Department of Computer Science Yale University March 1, 2010 Michael
Outline Quadratic residues Useful tests Digital Signatures CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Lecture 14 Michael J. Fischer Department of Computer Science Yale University March 1, 2010 Michael
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2018 Alistair Sinclair and Yun Song Note 6
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2018 Alistair Sinclair and Yun Song Note 6 1 Modular Arithmetic In several settings, such as error-correcting codes and cryptography, we sometimes
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2018 Alistair Sinclair and Yun Song Note 6 1 Modular Arithmetic In several settings, such as error-correcting codes and cryptography, we sometimes
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2014 Anant Sahai Note 7
 EECS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2014 Anant Sahai Note 7 Polynomials Polynomials constitute a rich class of functions which are both easy to describe and widely applicable in topics
EECS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2014 Anant Sahai Note 7 Polynomials Polynomials constitute a rich class of functions which are both easy to describe and widely applicable in topics
Number Theory. Henry Liu, 6 July 2007
 Number Theory Henry Liu, 6 July 007 1. Introduction In one sentence, number theory is the area of mathematics which studies the properties of integers. Some of the most studied subareas are the theories
Number Theory Henry Liu, 6 July 007 1. Introduction In one sentence, number theory is the area of mathematics which studies the properties of integers. Some of the most studied subareas are the theories
MATH 4400 SOLUTIONS TO SOME EXERCISES. 1. Chapter 1
 MATH 4400 SOLUTIONS TO SOME EXERCISES 1.1.3. If a b and b c show that a c. 1. Chapter 1 Solution: a b means that b = na and b c that c = mb. Substituting b = na gives c = (mn)a, that is, a c. 1.2.1. Find
MATH 4400 SOLUTIONS TO SOME EXERCISES 1.1.3. If a b and b c show that a c. 1. Chapter 1 Solution: a b means that b = na and b c that c = mb. Substituting b = na gives c = (mn)a, that is, a c. 1.2.1. Find
2.1 Convergence of Sequences
 Chapter 2 Sequences 2. Convergence of Sequences A sequence is a function f : N R. We write f) = a, f2) = a 2, and in general fn) = a n. We usually identify the sequence with the range of f, which is written
Chapter 2 Sequences 2. Convergence of Sequences A sequence is a function f : N R. We write f) = a, f2) = a 2, and in general fn) = a n. We usually identify the sequence with the range of f, which is written
Part IA Numbers and Sets
 Part IA Numbers and Sets Definitions Based on lectures by A. G. Thomason Notes taken by Dexter Chua Michaelmas 2014 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Part IA Numbers and Sets Definitions Based on lectures by A. G. Thomason Notes taken by Dexter Chua Michaelmas 2014 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics. Mathematical Induction
 Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics Mathematical Induction Instructor: Dr. Blerina Xhabli Department of Mathematics, University of Houston https://www.math.uh.edu/ blerina Email: blerina@math.uh.edu Fall 2018
Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics Mathematical Induction Instructor: Dr. Blerina Xhabli Department of Mathematics, University of Houston https://www.math.uh.edu/ blerina Email: blerina@math.uh.edu Fall 2018
Elementary Properties of the Integers
 Elementary Properties of the Integers 1 1. Basis Representation Theorem (Thm 1-3) 2. Euclid s Division Lemma (Thm 2-1) 3. Greatest Common Divisor 4. Properties of Prime Numbers 5. Fundamental Theorem of
Elementary Properties of the Integers 1 1. Basis Representation Theorem (Thm 1-3) 2. Euclid s Division Lemma (Thm 2-1) 3. Greatest Common Divisor 4. Properties of Prime Numbers 5. Fundamental Theorem of
The Chinese Remainder Theorem
 The Chinese Remainder Theorem R. C. Daileda February 19, 2018 1 The Chinese Remainder Theorem We begin with an example. Example 1. Consider the system of simultaneous congruences x 3 (mod 5), x 2 (mod
The Chinese Remainder Theorem R. C. Daileda February 19, 2018 1 The Chinese Remainder Theorem We begin with an example. Example 1. Consider the system of simultaneous congruences x 3 (mod 5), x 2 (mod
Abstracts of papers. Amod Agashe
 Abstracts of papers Amod Agashe In this document, I have assembled the abstracts of my work so far. All of the papers mentioned below are available at http://www.math.fsu.edu/~agashe/math.html 1) On invisible
Abstracts of papers Amod Agashe In this document, I have assembled the abstracts of my work so far. All of the papers mentioned below are available at http://www.math.fsu.edu/~agashe/math.html 1) On invisible
Euler s, Fermat s and Wilson s Theorems
 Euler s, Fermat s and Wilson s Theorems R. C. Daileda February 17, 2018 1 Euler s Theorem Consider the following example. Example 1. Find the remainder when 3 103 is divided by 14. We begin by computing
Euler s, Fermat s and Wilson s Theorems R. C. Daileda February 17, 2018 1 Euler s Theorem Consider the following example. Example 1. Find the remainder when 3 103 is divided by 14. We begin by computing
Writing proofs for MATH 61CM, 61DM Week 1: basic logic, proof by contradiction, proof by induction
 Writing proofs for MATH 61CM, 61DM Week 1: basic logic, proof by contradiction, proof by induction written by Sarah Peluse, revised by Evangelie Zachos and Lisa Sauermann September 27, 2016 1 Introduction
Writing proofs for MATH 61CM, 61DM Week 1: basic logic, proof by contradiction, proof by induction written by Sarah Peluse, revised by Evangelie Zachos and Lisa Sauermann September 27, 2016 1 Introduction
2x 1 7. A linear congruence in modular arithmetic is an equation of the form. Why is the solution a set of integers rather than a unique integer?
 Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic 25 SECTION C Solving Linear Congruences By the end of this section you will be able to solve congruence equations determine the number of solutions find the multiplicative
Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic 25 SECTION C Solving Linear Congruences By the end of this section you will be able to solve congruence equations determine the number of solutions find the multiplicative
WHAT IS SPECIAL ABOUT THE DIVISORS OF 24?
 WHAT IS SPECIAL ABOUT THE DIVISORS OF 24? SUNIL K. CHEBOLU It is a miracle that the human mind can string a thousand arguments together without getting itself into contradictions. 1. Introduction Eugene
WHAT IS SPECIAL ABOUT THE DIVISORS OF 24? SUNIL K. CHEBOLU It is a miracle that the human mind can string a thousand arguments together without getting itself into contradictions. 1. Introduction Eugene
The running time of Euclid s algorithm
 The running time of Euclid s algorithm We analyze the worst-case running time of EUCLID as a function of the size of and Assume w.l.g. that 0 The overall running time of EUCLID is proportional to the number
The running time of Euclid s algorithm We analyze the worst-case running time of EUCLID as a function of the size of and Assume w.l.g. that 0 The overall running time of EUCLID is proportional to the number
MATH 25 CLASS 21 NOTES, NOV Contents. 2. Subgroups 2 3. Isomorphisms 4
 MATH 25 CLASS 21 NOTES, NOV 7 2011 Contents 1. Groups: definition 1 2. Subgroups 2 3. Isomorphisms 4 1. Groups: definition Even though we have been learning number theory without using any other parts
MATH 25 CLASS 21 NOTES, NOV 7 2011 Contents 1. Groups: definition 1 2. Subgroups 2 3. Isomorphisms 4 1. Groups: definition Even though we have been learning number theory without using any other parts
Discrete Math, Fourteenth Problem Set (July 18)
 Discrete Math, Fourteenth Problem Set (July 18) REU 2003 Instructor: László Babai Scribe: Ivona Bezakova 0.1 Repeated Squaring For the primality test we need to compute a X 1 (mod X). There are two problems
Discrete Math, Fourteenth Problem Set (July 18) REU 2003 Instructor: László Babai Scribe: Ivona Bezakova 0.1 Repeated Squaring For the primality test we need to compute a X 1 (mod X). There are two problems
Outline. Number Theory and Modular Arithmetic. p-1. Definition: Modular equivalence a b [mod n] (a mod n) = (b mod n) n (a-b)
![Outline. Number Theory and Modular Arithmetic. p-1. Definition: Modular equivalence a b [mod n] (a mod n) = (b mod n) n (a-b) Outline. Number Theory and Modular Arithmetic. p-1. Definition: Modular equivalence a b [mod n] (a mod n) = (b mod n) n (a-b)](/thumbs/79/79558181.jpg) Great Theoretical Ideas In CS Victor Adamchik CS - Lecture Carnegie Mellon University Outline Number Theory and Modular Arithmetic p- p Working modulo integer n Definitions of Z n, Z n Fundamental lemmas
Great Theoretical Ideas In CS Victor Adamchik CS - Lecture Carnegie Mellon University Outline Number Theory and Modular Arithmetic p- p Working modulo integer n Definitions of Z n, Z n Fundamental lemmas
Elementary Number Theory Review. Franz Luef
 Elementary Number Theory Review Principle of Induction Principle of Induction Suppose we have a sequence of mathematical statements P(1), P(2),... such that (a) P(1) is true. (b) If P(k) is true, then
Elementary Number Theory Review Principle of Induction Principle of Induction Suppose we have a sequence of mathematical statements P(1), P(2),... such that (a) P(1) is true. (b) If P(k) is true, then
Theoretical Cryptography, Lecture 13
 Theoretical Cryptography, Lecture 13 Instructor: Manuel Blum Scribe: Ryan Williams March 1, 2006 1 Today Proof that Z p has a generator Overview of Integer Factoring Discrete Logarithm and Quadratic Residues
Theoretical Cryptography, Lecture 13 Instructor: Manuel Blum Scribe: Ryan Williams March 1, 2006 1 Today Proof that Z p has a generator Overview of Integer Factoring Discrete Logarithm and Quadratic Residues
Math 324 Summer 2012 Elementary Number Theory Notes on Mathematical Induction
 Math 4 Summer 01 Elementary Number Theory Notes on Mathematical Induction Principle of Mathematical Induction Recall the following axiom for the set of integers. Well-Ordering Axiom for the Integers If
Math 4 Summer 01 Elementary Number Theory Notes on Mathematical Induction Principle of Mathematical Induction Recall the following axiom for the set of integers. Well-Ordering Axiom for the Integers If
Lecture 11: Cantor-Zassenhaus Algorithm
 CS681 Computational Number Theory Lecture 11: Cantor-Zassenhaus Algorithm Instructor: Piyush P Kurur Scribe: Ramprasad Saptharishi Overview In this class, we shall look at the Cantor-Zassenhaus randomized
CS681 Computational Number Theory Lecture 11: Cantor-Zassenhaus Algorithm Instructor: Piyush P Kurur Scribe: Ramprasad Saptharishi Overview In this class, we shall look at the Cantor-Zassenhaus randomized
Contest Number Theory
 Contest Number Theory Andre Kessler December 7, 2008 Introduction Number theory is one of the core subject areas of mathematics. It can be somewhat loosely defined as the study of the integers. Unfortunately,
Contest Number Theory Andre Kessler December 7, 2008 Introduction Number theory is one of the core subject areas of mathematics. It can be somewhat loosely defined as the study of the integers. Unfortunately,
QUADRATIC CONGRUENCES FOR COHEN - EISENSTEIN SERIES.
 QUADRATIC CONGRUENCES FOR COHEN - EISENSTEIN SERIES. P. GUERZHOY The notion of quadratic congruences was introduced in the recently appeared paper [1]. In this note we present another, somewhat more conceptual
QUADRATIC CONGRUENCES FOR COHEN - EISENSTEIN SERIES. P. GUERZHOY The notion of quadratic congruences was introduced in the recently appeared paper [1]. In this note we present another, somewhat more conceptual
