Synchronous Reluctance Motor Iron losses: Considering Machine Non-Linearity at MTPA, FW, and MTPV Operating Conditions
|
|
|
- Edwin Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Synchronous Reluctance Motor Iron losses: Considering Machine Non-Linearity at MTPA, FW, and MTPV Operating Conditions Hanafy Mahoud, Giacoo Bacco, Michele Degano, Nicola Bianchi and Chris Gerada Abstract Synchronous reluctance achine has high flux density fluctuations in the iron due to the high haronics results fro the rotor anisotropy. Thus, an accurate coputation of the iron losses is of paraount iportance, especially during the design stage. In this paper, a non-linear analytical odel considering the agnetic iron saturation and the slotting effect is proposed. The odel estiates accurately the iron losses at a wide range of operating speed. In addition, the accuracy of the non-linear odel when the achine is highly saturated, i.e. when it works along the MTPA trajectory, is presented and verified. The odel presented is general and can be applied to other configurations. A 36-slot four-pole achine, with three flux-barriers per pole is considered as a case study. Finite eleent analysis is used to validate the results achieved by eans of the non-linear analytical odel. Furtherore, an experiental setup is built to validate the siulation results. Index Ters Synchronous reluctance achine, Iron saturation, Non-linear analytical odels, Iron losses coputation, Finite eleent analysis. I. INTRODUCTION The iportance of deterining accurately the total iron losses in the whole otor structure is crucial even during the first design stage. In addition, the coputation tie of these losses is very iportant for reducing the diensioning phase in the product developent yields to a positive financial ipact. For that reason, the analytical odels are attractive tools for estiating these losses. Referring to the linear analytical odel presented in the literature [] [3], the over estiation of the iron losses results fro that linear odel leads to oversize the achine. Thus, it is necessary to find a fast and accurate analytical tool overcoe the assuptions of those linear odels. Fro the literature, it has been recognized that there are any approaches for coputing the iron losses of Synchronous reluctance (SynRel) achines. Most of the are based on the analysis, as in [4] [8], or on analytical H. Mahoud is with the Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Nottingha, NG7RD, Nottingha (UK), and also with the Departent of Electrical Power and Machines, Cairo University, 63 Giza, Egypt (e-ail: eng.hanafy4@yahoo.co, Hanafy.Mahoud@nottingha.ac.uk). G. Bacco and N. Bianchi are with the Departent of Industrial Engineering, University of Padova, 353 Padova, Italy (e-ail: giacoo.bacco@phd.unipd.it), (e-ail: nicola.bianchi@unipd.it; nicola.bianchi@dii.unipd.it). M. Degano and C. Gerada are with the Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Nottingha, NG7RD, Nottingha (UK), and also with the University of Nottingha Ningbo China, Ningbo, China. (e-ail: ichele.degano@nottingha.ac.uk), (e-ail: chris.gerada@nottingha.ac.uk) analysis for specific stator MMF and rotor geoetry, as in [], [3]. The analytical odel presented in [] considers all haronics of the stator MMF and is valid for a general rotor geoetry. However, it focuses only on the eddy current loss coputation in the stator teeth. Besides, the rotor end angles are optiized in order to iniize those losses disregarding their effect on the torque ripple, however it has a high ipact on reducing both stator teeth and yoke iron losses, as well [9]. The previous analysis has been carried out neglecting both: (a) the stator slotting effect, and (b) the agnetic iron saturation effect. These phenoena strongly affect the air-gap flux density distribution [] []. In fact, soe dips appear in the air-gap flux density distribution due to the agnetic reluctance variations in the air-gap caused by the slot openings [3] [6]. In addition, the agnetic voltage drops, occurring in the stator and rotor iron, liit the agnetic fluxes flowing through the iron parts of the otor. As a consequence, the flux density variations in these regions are reduced [], [7]. It has been observed that the iron losses coputed in [9] result to be overestiated, especially if they are coputed along the MTPA trajectory. To fill this gap, the ai of this paper is to include the achine non-linearities in the analytical odel so as to copute ore accurately the iron losses in various iron parts. An novel aspect introduced in this work, with respect to the presented stator yoke stator tooth stator slot shaft 3 rd barrier nd barrier st barrier channel q - axis nd island st island Fig. : Sketch of the SynRel achine under study. d - axis 3 rd island
2 odel in [], is the extension to the iron losses prediction in the various iron parts of the achine, not only in the stator teeth. The hysteresis losses are considered for the fundaental coponent, because of their significant aplitude, especially if the achine is working along the MTPA trajectory. Fig. reports a D sketch of SynRel achine showing the different iron parts of the stator, i.e. teeth and yoke, and the rotor, i.e., islands and channels. Once again, a 36-slot fourpole achine with three flux-barriers per pole is used, as an exaple, however, the non-linear analytical odel is general for a different nuber of poles, stator slots, flux-barriers, as can be recognized in [8], [9]. The design specifications, of the studied SynRel, are suarized in Table I. TABLE I: Geoetrical data of SynRel otor used in section III. Inner stator Diaeter D o Inner stator Diaeter D 5 Stack length L stk 4 Nuber of stator slots Q s 36 Nuber of stator pole pairs p s Air-gap length g.35 First flux barrier ends angle θ b 8 Second flux barrier ends angle θ b 5.4 Third flux barrier ends angle θ b The paper is organized as follows: Section II briefly describes the non-linear analytical odel. Section III reports the iron losses when the otor operate along the MTPA, FW, and MTPV trajectory, respectively. Furtherore, it shows the coparison between the linear and non-linear analyses results for all the above conditions. Section IV studies the ipact of the local saturation close to the iron ribs on the non-linear analytical odel accuracy. siulations and an experiental easureents validate the results obtained by eans of the analytical analyses. II. NON-LINEAR ANALYTICAL MODEL In this section, the analytical odel considers the sae pereance function discussed in [], [5]. Then, the air-gap flux density is updated. Its distribution is confired by the analysis, as shown in Fig.. Air-gap flux density [T] ϑ s [Elec. Deg.] Fig. : Air-gap flux density distribution at J = A/ and αi e = 8, i.e., along the MTPV trajectory. The agnetic voltage drop in the iron paths can be considered by eans of an additional equivalent voltage drop in the air-gap. In other words, the air-gap length is increased by a specific factor: the saturation factor K sat [], [6], []. Due to the coplex rotor structure, it is difficult to consider the agnetic saturation in both stator and rotor iron by eans of a unique equivalent factor. l ht wt ψ y(3) Ds De ψ y(9) ψ y(8) ψ y(7) ψ y(6) B t3 ψ y(5) ψ y(4) Fig. 3: The ain idea behind the ghost paths. ψ y(3) ψ y() ψ y() As shown in Fig. 3, the ghost flux line enters fro the tooth n and exits fro the tooth (n + Q s /p). It is equivalent to consider that every flux line travels for a full pole pitch. Referring to the stator, Fig. 3 shows that the agnetic voltage drop in each flux path ghost path occurs in the yoke and two teeth. Considering half of the path, the agnetic drop can be presented by K sattn in front to the n th tooth. It can be expressed as K sattn B y3 = + ψ t n + ψ ytn gh gn, n =,..., Q s /p () where ψ tn is the agnetic voltage drop in the n th tooth. ψ ytn is the agnetic drop which occurs in half the flux path in the stator yoke. The subscript yt indicates that the yoke drop is considered as an additional agnetic drop along the tooth. H gn is the field intensity in front of the n th tooth. The detailed coputations of both ψ tn and ψ ytn will be discussed later on. On the other hand, the voltage drop in the rotor islands and channels can be considered by adopting K satis,i to increase the air-gap in front of each rotor iron part. It can be coputed as K satis,i = + µ ψ isi gb gis,i, i =,..., N b + () where ψ isi is the agnetic voltage drop in the i th rotor island. B gis,i is the air-gap flux density in front to the i th island. Indeed, the coputation for the rotor channel is carried out when i = N b +. A. Magnetic voltage drop in the stator iron ) Stator teeth: The flux density variation in the n th stator tooth can be coputed as B tn ( ) = D w t γs+nα slot γ s+(n )α slot B g (ϑ s, ) dϑ s (3)
3 Then, fro the actual iron B-H curve, shown in Fig. 4, the field intensity is deterined. Hence, ψ tn can be coputed as B tn (t) H tn (t) ψ tn = H tn (t) h t (4) where h t is the height of the stator tooth. B [T] H [A/] x 5 Fig. 4: Magnetization curve of the ferroagnetic aterial used. ) Stator yoke: Starting fro a generic tooth, the actual flux flowing through the s th section of the stator yoke is coputed as φ ys n=s = w t L stk B tn w tl stk Q s /p n= s=q s/p s= n=s B tn (5) n= Consequently, the flux density, field intensity, and agnetic voltage drop in the s th section can be achieved as B ys (t) = φ y s (t) h y L stk H ys (t) ψ ys = H ys (t) l (6) where l = π(d e h y )/Q s is the average length of one backiron sector. The ghost flux line encounters Q s /p agnetic voltage drops along its path. These agnetic voltage drops can be sued, with the sign of the corresponding flux in the sae sector. At the end, the ghost flux line has gathered the sae overall agnetic voltage drop of the actual flux line of that particular tooth and can be expressed as n+ Qs p ψ ytn = ψ y [K] sign φ y [K], n =,..., Q s/p K=n (7) The occurs since half the path of the line is considered. As an exaple, the solid path shown in Fig. 3 starts fro tooth n = (below the first slot) and it ends in tooth n =. The total agnetic voltage drop associated to this line is ψ yt = ψ y + ψ y ψ y9 (8) On the other hand, the dotted path shown in Fig. 3 sees ψ yt5 = ψ y ψ y9 ψ y... ψ y3 = ψy5 (9) where the last equivalence is the ain assuption of this coputation. In fact it is like iplying that ψ y6 is equal and opposite to ψ y3, siilarly, ψ y7 to ψ y and so on. All ters are canceled out but the ter ψ y5. B. Magnetic voltage drop in the rotor iron Fig. 5 shows the actual flux paths in the different rotor iron parts, such as the flux enters in and exits fro each rotor island and channel. The flux flowing through the i th flux barrier is coputed as φ isi ( ) = φ ini ( ) φ b i ( ) + φ bi ( ) where φ bi ( ) is given by () φ bi ( ) = φ ini ( ) φ outi ( ) () By integrating the air-gap flux density, φ ini ( ) and φ outi ( ) are coputed as φ ini ( ) = φ outi ( ) = π p ϑ b i π p ϑ b i π p +ϑ b i B g (ϑ s, ) DL stk B g (ϑ s, ) DL stk π p +ϑ b i dϑ s () dϑ s (3) On the other hand, the flux flowing through the rotor channel is coputed as φ ch = φ chi φ cho (4) where φ chi and φ cho are derived by integrating the air-gap flux density as follows φ chi = φ cho = π p ϑ b Nb + π p +ϑ B g (ϑ s, t) DL stk B g (ϑ s, t) DL stk π p +ϑ b Nb + dϑ s (5) dϑ s (6) The aforeentioned island and channel fluxes are the d axis fluxes. The q axis flux for the islands and the channels is is is3 chi ch in3 b3 in b in b out out b out3 cho q-axis b3 d-axis Fig. 5: Actual flux paths in the different rotor iron parts.
4 are also coputed through the following approxiation φ isq = φ b,..., φ iqn b = φ b N b + φ b N b (7) φ chq = φ b N b The island q axis flux equations represent the average between the upper and lower barrier fluxes. In order to get the flux density in each i th island, all these fluxes are referred to the iddle section of the iron segent. For each i th island, the width w ri is known fro the drawing or coputed as in [], while the length is approxiated through therefore B isi = l isi = D ϑ bi + ϑ bi B isdi = φ isd i w ri L stk, B isqi = φ isq i l isi L stk B chd = φ chd, B chq = φ chq w ch L stk l ch L stk B isd i + B isq i, B ch = B chd + B chq (8) (9) where w ch = ( kair )D sin ( π p ϑ bn b ), lch = (D re +D ri )/, k air is the ratio between the su of the barriers thicknesses and the total length of the rotor along the q axis. C. Iterative approach The saturation factors reported in () and () are not fixed but they are iteratively coputed so as to adjust the agnetic odel paraeters. The nuber of the iterations depends on the saturation level in the achine iron parts. As an exaple, Fig. 6 explains the iterative approach for coputing K sattn in front of the n th tooth. III. ANALYSIS RESULTS AND VALIDATION In this section, the results of the linear odel at the operating points B (along MTPA trajectory) and B (along FW trajectory) are copared by the results of the non-linear odel. The current density is the sae for both operating conditions (J = 3A/ ) and the current vector angles are 45 and 8, respectively. For the sake of studying the odel accuracy at high saturation level, the coparison is repeated at current density J = 6A/. Furtherore, the non-linear odel is confired by the analysis in various operating points, along the MTPA trajectory, under the FW operation, and along the MTPV trajectory, i.e., at J = A/ and α e i = 8. Fro [], [9], it is recognized that the rotor losses are negligible coparing to the stator losses and can be neglected if the rotor is lainated and not rotating at very high speed. Therefore, the ain focus of this paper is on the stator iron losses coputation. A. MTPA operating condition Referring to the operating point B, Fig. 7 and Fig. 8 show the flux density variations in the stator teeth and yoke resulting K sat = K sat-prev. start read B g( θ s ) and actual iron B-H curve. define K sat-step =., Intial value of K sat =, Intial value of K sat-prev. =. x = copute K sat as in () and tn K sat-var = K sattn / K sat no x = if K sat-var >? end yes Iprove the air-gap flux density in front of the n-th stator tooth if x =? yes save K sattn = K sat Fig. 6: Iterative approach for coputing the accurate saturation factor in front to the n th stator tooth. fro the non-linear slotted odel. Three teeth are considered since there are three slots per pole and per phase. It is noted that there is a satisfactory agreeent between the iproved odel and the analysis. Table II shows the iron losses in the various iron parts of the stator core. The eddy current losses (due to all haronics) and the hysteresis loss (due to the fundaental haronic only) are reported. Again, the nonlinear analytical odel results are validated by eans of analysis, as shown in Table II. Coparing Table II with the corresponding Table III, which reports the iron losses resulting fro the linear analytical odel, it is noted that the iron losses are overestiated, by 9.5% with respect to those predicted by. This coparison rearks the accuracy of the non-linear analytical odel (axiu error approaches %) even if the local saturation close to the rotor iron ribs is disregarded. B. FW operating condition The non-linear analytical and odel results are copared together at the operating point B, as shown in Fig. 9, Fig., and Table IV. In FW conditions, there is a great reduction of the ain flux. As a consequence, the saturation level of the achine is low. The local saturation at the iron ribs is reduced too. This increases the accuracy of the non-linear no K sat = K sat-prev. K sat = K sat-prev. K sat-step
5 - Toothy Toothy ϑ [Elec.yDeg.] - (a) odel Toothy Toothy ϑ [Elec.yDeg.] (b) odel Fig. 7: Flux density variations in stator teeth at operating Point B resulting fro the non-linear odels. Yoketfluxtdensityt[T] ϑ [Elec.tDeg.] Fig. 8: Flux density variation in stator yoke at operating Point B resulting fro the non-linear odels. odel (axiu error.8%). Additionally, it is noted that, in point B the haronic losses are doinant, while the losses associated to the fundaental are quite low. This is due to both the relative increase of haronic content and the frequency. Siilarly, coparing Table IV to the corresponding results of the linear analytical odel, it is noted that the linear odel overestiates the coputed losses by 8.5%. Fro Table II and Table IV, it can be noted that the neglecting of the iron ribs becoes ore realistic at the FW operating condition and the odel error is reduced fro.5% (at point B) to.5% (at point B ). C. MTPV operating condition Hereafter, the otor is supplied with J = A/ and αi e = 8. It works at operation point along the MTPV TABLE II: Eddy current and hysteresis loss densities of the stator teeth and yoke at the operating point B resulting fro the non-linear analytical and odels. Iron part al h = h > h = h > Yoke First tooth Second tooth Third tooth Yoke First tooth Second tooth Third tooth al Stator tooth.4. Stator yoke Model error % TABLE III: Eddy current and hysteresis loss densities of the stator teeth and yoke at the operating point B resulting fro the linear analytical and odels. Iron part al h = h > h = h > Yoke First tooth Second tooth Third tooth Yoke First tooth Second tooth 9.84 Third tooth.5.3 al Stator tooth 3..7 Stator yoke Model error < % trajectory (point C). Fig. and Fig. show the flux density variations in the stator teeth and yoke estiated by the nonlinear analytical and odels. Hence, the stator core iron losses are estiated by both non-linear odels and reported in Table V. There is a good agreeent between both non-linear odels. The non-linear analytical odel overestiates the odel predicted losses by.5% only. When the otor runs along the MTPV operating trajectory, the current aplitude is reduced. Thus, the d axis current is reduced, and hence the ain flux of the achine is decreased ore than in the previous FW operating condition, as shown in Fig. and Fig.. In [], it is entioned that neglecting the iron saturation applied to the linear analytical odel is well suited to the MTPV operations due to low current density at this operating region. The linear analytical and odels are applied to the
6 Toothy Toothy [Elec.yDeg.] (a) odel Toothy Toothy [Elec.yDeg.] (b) odel Fig. 9: Flux density variations in stator teeth at operating Point B resulting fro the non-linear odels. Yoketfluxtdensityt[T] ϑ [Elec.tDeg.] Fig. : Flux density variation in stator yoke at operating Point B resulting fro the non-linear odels. sae operating point. The estiated iron losses are copared to those reported in Table V, hence, it is recognized that the iron losses resulting fro the linear odel are overestiated by 4.5%. To understand the effect of neglecting the iron saturation on the analytical odel accuracy, a sei non-linear odel conserving the stator slotting effect only is applied at the sae operating condition. It is recognized that this analytical odel overestiates the non-linear odel by.3%. IV. ACCURACY ROBUSTNESS OF THE NON-LINEAR ANALYTICAL MODEL The non-linear analytical odel does not consider the local saturation close to the rotor iron ribs. This local saturation interacts with the stator teeth and causes the different haronic contribution. This section ais to study the effect of this assuption on the accuracy of the iron losses coputations when the otor is highly saturated, i.e., it works along the MTPA TABLE IV: Eddy current and hysteresis loss densities of the stator teeth and yoke at the operating point B resulting fro the non-linear analytical and odels..5 Iron part al h = h > h = h > Yoke First tooth Second tooth Third tooth Yoke.6.86 First tooth.4.4 Second tooth.5.75 Third tooth al Stator tooth.8.7 Stator yoke Model error.5% Toothy Toothy e [Elec.yDeg.] (a) odel Toothy Toothy e [Elec.yDeg.] (b) odel Fig. : Flux density variations in stator teeth resulting fro the non-linear odels at the operating point C. trajectory. The accuracy of the non-linear analytical odel for coputing the other achine perforance paraeters at high saturation level has been checked in [], [6]. In this section, the odel accuracy is checked at J = 6 A/ and α e i = 59. Table VI reports the iron losses in the stator core at the aforeentioned operating condition. It is noted that, the non linear analytical odel overestiates the non-linear slotted odel by about %, uch better than the linear analytical odel which overestiates the losses by about 5% in this condition. In addition, Fig. and Fig. show a satisfactory agreeent between the non-
7 Yoketfluxtdensityt[T] e [Elec.tDeg.] Fig. : Flux density variation in stator yoke resulting fro the non-linear odels at the operating point C. TABLE V: Eddy current and hysteresis loss densities of the stator teeth and yoke resulting fro the non-linear odels at the operating point C. Iron part al h = h > h = h > Yoke First tooth Second tooth Third tooth Yoke.35.4 First tooth.7.3 Second tooth Third tooth.6.7 al Stator tooth Stator yoke.63.7 Model error.5% - Toothy Toothy [Elec.yDeg.] - (a) odel [Elec.yDeg.] (b) odel Toothy Toothy Fig. 3: Flux density variations in stator teeth at J = 6A/ and αi e = 59 resulting fro the non-linear odels. Yoketfluxtdensityt[T] - linear analytical and odels. TABLE VI: Eddy current and hysteresis loss densities of the stator teeth and yoke at J = 6A/ and αi e = 59 resulting fro the non-linear odels. Iron part al h = h > h = h > Yoke First tooth Second tooth Third tooth Yoke First tooth Second tooth Third tooth al Stator tooth Stator yoke.6.5 Model error % Finally, an experiental validation is carried out by validating the output power/torque ap of both the siulation ϑ [Elec.tDeg.] Fig. 4: Flux density variation in stator yoke at J = 6A/ and α e i = 59 resulting fro the non-linear odels. and the experiental easureents. This can be carried by fixing the input power for both the siulation and the actual otor under the experiental test. An indication of an accurate losses coputation can be achieved if the output power of both siulation and test are atched, for the sae input power. The experiental validation of the output torque ap is shown in Fig. 5. It is noted that there is a satisfactory agreeent between siulation results and experiental easureents. V. CONCLUSIONS This paper describes a rapid non-linear analytical odel for coputing the iron losses in SynRel achine. This odel is well suited to copute the flux density variation in the various iron parts of the SynRel achine. It allows the iron losses to be coputed in any iron part. The non-linear odel is checked in a wide operating speed range. Thus, the coputations are carried out at the operating points B (MTPA),
8 Peak q-axis current [A] analytical Peak d-axis current [A] experiental Fig. 5: Torque ap results fro the experiental easureents and the siulation. B (FW), and C (MTPV). The achine speed, saturation level, and haronic contribution are copletely different in these operating conditions. It is noted that the non-linear odel exhibits a good agreeent with the analysis. The results of the non-linear odel are also copared with the linear odel so as to evaluate the iproveent occurred in the iron losses coputations. It is noted that the error is reduced fro 9.5% to.5%, fro 8.5% to.5%, and fro 4.5% to.5%, at the operating points B, B, and C, respectively. Although the current aplitude is reduced at the operating point C (MTPV), the iron agnetic saturation affects the result accuracy. This can be noted fro the results of the linear slotted analytical odel result. The error of this sei nonlinear odel is.3% which is, of course, higher than that of the non-linear analytical odel. In addition, the non-linear odel is checked when the achine is saturated at current density 6A/ along the MTPA trajectory. Even if the saturation level is doubled, the non-linear odel results are satisfactory, yielding a slight overestiation of the losses around % with respect the coputation. This overestiation could be useful for the sake of safety for considering the anufacturing process effects on the agnetic properties of the achine iron. The non-linear analytical odel is a quick tool to estiate the iron losses of the achine. For one electric period, the siulation tie is about seconds. This advantage of the odel is very iportant for reducing the diensioning phase in the otor developent yields to a positive financial ipact. RERENCES [] M. Barcaro and N. Bianchi, Air-gap flux density distortion and iron losses in anisotropic synchronous otors, in IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 46, no., pp. 6, Jan. [] L. Ma, M. Sanada, S. Morioto, and Y. Takeda, Iron loss prediction considering the rotational field and flux density haronics in IPMSM and SynRM, IEE Proceedings - Electric Power Applications, vol. 5, no. 6, pp , Nov 3. [3] G. Pellegrino, P. Guglieli, A. Vagati, and F. Villata, Core losses and torque ripple in IPM achines: Dedicated odeling and design tradeoff, in IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 46, no. 6, pp , Nov. [4] M. J. Kaper, F. S. V. der Merwe, and S. Williason, Direct finite eleent design optiisation of the cageless reluctance synchronous achine, IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, vol., no. 3, pp , Sep 996. [5] J. H. Lee, I. K. Lee, Y. H. Cho, and T. W. Yun, Characteristics analysis and optiu design of anisotropy rotor synchronous reluctance otor using coupled finite eleent ethod and response surface ethodology, IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 45, no., pp , Oct 9. [6] P. Hudak, V. Hrabovcova, P. Rafajdus, and J. Mihok, Core loss analysis of the reluctance synchronous otor with barrier rotors, Journal of Electrical Engineering, vol. 55, pp , 4. [7] F. Leonardi, T. Matsuo, and T. A. Lipo, Iron loss calculation for synchronous reluctance achines, in Proceedings of International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systes for Industrial Growth, vol., Jan 996, pp vol.. [8] T. Rainosoa, I. Rasoanarivo, and F. M. Sargos, Reluctance network analysis of high power synchronous reluctance otor with saturation and iron losses considerations, in 6 th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Portoroz, Slovenia, Aug 6, pp [9] H. Mahoud, M. Degano, G. Bacco, N. Bianchi, and C. Gerada, Synchronous reluctance otor iron losses: al odel and optiization, In IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE 8), in press. [] P. Akiki, M. H. Hassan, J. C. Vannier, M. Bensetti, B. DagusÃ, D. Prieto, and M. McClelland, Non-linear analytical odel for a ultiv-shape IPM with concentrated winding, in 6 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, Sept 6, pp [] H. Mahoud, N. Chiodetto, and N. Bianchi, Magnetic field analytical coputation in synchronous reluctance achines considering the iron saturation, In IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE 6), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 8- Sept, 6. [] D. Prieto, P. Dessante, J. C. Vannier, B. DagusÃ, X. Jannot, and J. Saint-Michel, Multi-physic analytical odel for a saturated peranent agnet assisted synchronous reluctance otor, IET Electric Power Applications, vol., no. 5, pp , 6. [3] Z. Zhu and D. Howe, Instantaneous agnetic field distribution in brushless peranent agnet dc otors. iii. effect of stator slotting, IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 9, no., pp. 43 5, Jan 993. [4] J. Gieras, al approach to cogging torque calculation of PM brushless otors, IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 3 36, Sept 4. [5] D. Zarko, D. Ban, and T. Lipo, al calculation of agnetic field distribution in the slotted air gap of a surface peranent-agnet otor using coplex relative air-gap pereance, IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 4, no. 7, pp , July 6. [6] H. Mahoud and N. Bianchi, Nonlinear analytical odel of eccentric synchronous reluctance achines considering the iron saturation and slotting effect, IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 53, no. 3, pp. 7 5, May 7. [7] M. Ojaghi and S. Nasiri, Modeling eccentric squirrel-cage induction otors with slotting effect and saturable teeth reluctances, IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, vol. 9, no. 3, pp , Sept 4. [8] H. Mahoud and N. Bianchi, Eccentricity in synchronous reluctance otors;part I: al and finite-eleent odels, in IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, vol. 3, no., pp , June 5. [9] G. Bacco and N. Bianchi, Choice of flux-barriers position in synchronous reluctance achines, in 7 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Oct 7, pp [] K. Abbaszadeh and F. R. Ala, On-load field coponent separation in surface-ounted peranent-agnet otors using an iproved conforal apping ethod, in IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 5, no., pp., Feb 6. [] N. Bianchi, H. Mahoud, and S. Bolognani, Fast synthesis of peranent agnet assisted synchronous reluctance otors, in IET Electric Power Applications, vol., no. 5, pp. 3 38, 6.
9 Hanafy Mahoud received the bachelor s degree and the M.Sc. degree in electrical engineering in 9 and respectively, fro Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt. During his M.Sc. period he worked on faults detection and perforance analysis of the induction achines. He received his a PhD degree fro Padova University, Italy. Now, he is a Research Fellow at the PEMC group, Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nottingha University, UK. His research activities deals with the analysis of synchronous peranent agnet and reluctance achines, focusing on analytical and finite eleent odeling, faulty conditions analyses. Besides, his current research interests are high efficiency achine design for the advanced propulsion systes, as well as analytical odeling of various electrical achines. Giacoo Bacco (s 5) received both the BS in Energy Engineering in 3 and the MS in Electrical Engineering in 6 fro the University of Padova, Padova, Italy. Currently he is a PhD student of the Departent of Industrial Engineering at the sae University. His research interests are focused in the analysis and design of synchronous achines, in particular synchronous reluctance (REL) otors. Michele Degano (M 5) received the Laurea degree in electrical engineering fro the University of Trieste, Trieste, Italy, in, and the Ph.D. degree in industrial engineering fro the University of Padova, Padova, Italy, in 5. During his doctoral studies, he cooperated with several local copanies for the design of peranent-agnet achines. In 5, he joined the Power Electronics, Machines and Control Group, The University of Nottingha, Nottingha, U.K., as a Research Fellow, where he is currently an Assistant Professor teaching advanced courses on electrical achines. His ain research interests include design and optiization of peranent-agnet achines, reluctance and peranent-agnet-assisted synchronous reluctance otors through genetic optiization techniques, for autootive and aerospace applications, ranging fro sall to large power. Nicola Bianchi (M 98 SM 9 F 4) received the M.Sc. and Ph.D. degrees in electrical engineering fro the University of Padova, Padua, Italy, in 99 and 995, respectively. In 998, he joined the Departent of Electrical Engineering, University of Padova, as an Assistant Professor. Since 5, he has been an Associate Professor of electrical achines, converters, and drives. His activity is conducted in the Electric Drive Laboratory, Departent of Electrical Engineering, University of Padova. His teaching activity deals with the design ethods of electrical achines, where he introduced the finite-eleent analysis of achines. He is the author or coauthor of several scientific papers and international books on electrical achines and drives. He is recipient of five awards for best conference and journal papers His research activity is in the field of design of electrical achines, particularly for drive applications, in which he is responsible for various projects for local and foreign industries. He is an IEEE Fellow eber and a eber of the Electric Machines Coittee and the Electrical Drives Coittee of the IEEE Industry Applications Society. He served as technical progra chair for IEEE ECCE 4 and is Associate Editor of IEEE Trans on IA and IET-EPA proceedings. Chris Gerada (M 5 SM ) received the Ph.D. degree in nuerical odelling of electrical achines fro The University of Nottingha, Nottingha, U.K., in 5. He was a Researcher with The University of Nottingha, working on highperforance electrical drives and on the design and odelling of electroagnetic actuators for aerospace applications. Since 6, he has been the Project Manager of the GE Aviation Strategic Partnership. In 8, he becae a Lecturer in electrical achines, in, as an Associate Professor, and in 3, a Professor at The University of Nottingha. His ain research interests include the design and odelling of high-perforance electric drives and achines. Prof. Gerada serves as an Associate Editor for the IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS and is the Chair of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society Electrical Machines Coittee.
This is a repository copy of Analytical optimisation of electromagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance motor.
 This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
Designing a Permanent Magnet Linear Generator Multi Air-gap Structure using the Finite Element Method.
 Designing a Peranent Magnet Linear Generator Multi Air-gap Structure using the Finite Eleent Method. Pierre Kenfack, Daniel Matt, and Philippe Enrici Institute of Electronics and Systes, University Montpellier,
Designing a Peranent Magnet Linear Generator Multi Air-gap Structure using the Finite Eleent Method. Pierre Kenfack, Daniel Matt, and Philippe Enrici Institute of Electronics and Systes, University Montpellier,
Dimensioning of a permanent magnets motor with double rotor for electric vehicle
 SETIT 007 4 th International Conference: Sciences of Electronic, Technologies of Inforation and Telecounications arch 5-9, 007 TUISIA iensioning of a peranent agnets otor with double rotor for electric
SETIT 007 4 th International Conference: Sciences of Electronic, Technologies of Inforation and Telecounications arch 5-9, 007 TUISIA iensioning of a peranent agnets otor with double rotor for electric
Design of 25 KA Current Injection Transformer Core with Finite Element Method
 1 Design of 5 KA Current Injection Transforer Core ith Finite Eleent Method HOSSEIN HEYDARI, MOHSEN ARIANNEJAD, FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran Abstract.Since Current
1 Design of 5 KA Current Injection Transforer Core ith Finite Eleent Method HOSSEIN HEYDARI, MOHSEN ARIANNEJAD, FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran Abstract.Since Current
Torque Performance and Permanent Magnet Arrangement for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
 Extended Summary pp.954 960 Torque Performance and Permanent Magnet Arrangement for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Naohisa Matsumoto Student Member (Osaka Prefecture University, matumoto@eis.osakafu-u.ac.jp)
Extended Summary pp.954 960 Torque Performance and Permanent Magnet Arrangement for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Naohisa Matsumoto Student Member (Osaka Prefecture University, matumoto@eis.osakafu-u.ac.jp)
9. Operation Principle of the Electric Machines
 9. Operation Principle of the Electric Machines J Electric Machines Operation Principle Ø An electric achine consists of two electric circuits coupled by eans of a agnetic flu, that is linked with both
9. Operation Principle of the Electric Machines J Electric Machines Operation Principle Ø An electric achine consists of two electric circuits coupled by eans of a agnetic flu, that is linked with both
Sensorless Control of Induction Motor Drive Using SVPWM - MRAS Speed Observer
 Journal of Eerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 2 (3): 509-513 Journal Scholarlink of Eerging Research Trends Institute in Engineering Journals, 2011 and Applied (ISSN: 2141-7016)
Journal of Eerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 2 (3): 509-513 Journal Scholarlink of Eerging Research Trends Institute in Engineering Journals, 2011 and Applied (ISSN: 2141-7016)
DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF INDUCTION MACHINES CONSIDERING THE IRON LOSSES
 DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF INDUCTION MACHINES CONSIDERING THE IRON LOSSES TRUC PHAM-DINH A thesis subitted in partial fulfilent of the requireents of Liverpool John Moores University for the degree of Doctor
DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF INDUCTION MACHINES CONSIDERING THE IRON LOSSES TRUC PHAM-DINH A thesis subitted in partial fulfilent of the requireents of Liverpool John Moores University for the degree of Doctor
Zero speed sensorless drive capability of fractional slot inset PM machine
 Zero speed sensorless drive capability of fractional slot inset PM Adriano Faggion Nicola Bianchi Silverio Bolognani Emanuele Fornasiero Electric Drives Laboratory Department of Industrial Engineering
Zero speed sensorless drive capability of fractional slot inset PM Adriano Faggion Nicola Bianchi Silverio Bolognani Emanuele Fornasiero Electric Drives Laboratory Department of Industrial Engineering
Control of Brushless DC Motor with Direct Torque and Indirect Flux using SVPWM Technique
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(2), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i2/71211, Septeber 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Control of Brushless DC Motor with Direct Torque
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(2), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i2/71211, Septeber 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Control of Brushless DC Motor with Direct Torque
Basic Experiments for High-Torque, Low-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor and a Technique for Reducing Cogging Torque
 Basic Experients for High-Torque, Low-Speed Peranent Magnet Synchronous Motor and a Technique for educing Cogging Torque Kouichi Sato, Jung-Seob Shin, Takafui Koseki and Yasuaki Aoyaa Φ Abstract -- Fully
Basic Experients for High-Torque, Low-Speed Peranent Magnet Synchronous Motor and a Technique for educing Cogging Torque Kouichi Sato, Jung-Seob Shin, Takafui Koseki and Yasuaki Aoyaa Φ Abstract -- Fully
CFD-Parametric Study in Stator Heat Transfer of an Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Machine
 World Acadey of Science, Engineering and Technology CFD-Paraetric Study in Stator Heat Transfer of an Axial Flux Peranent Magnet Machine Alireza Rasekh, Peter Sergeant, Jan Vierendeels Abstract This paper
World Acadey of Science, Engineering and Technology CFD-Paraetric Study in Stator Heat Transfer of an Axial Flux Peranent Magnet Machine Alireza Rasekh, Peter Sergeant, Jan Vierendeels Abstract This paper
ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND PARAMETRIC STUDY OF LATERAL IMPACT BEHAVIOR OF PRESSURIZED PIPELINES AND INFLUENCE OF INTERNAL PRESSURE
 DRAFT Proceedings of the ASME 014 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE014 Noveber 14-0, 014, Montreal, Quebec, Canada IMECE014-36371 ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND PARAMETRIC
DRAFT Proceedings of the ASME 014 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE014 Noveber 14-0, 014, Montreal, Quebec, Canada IMECE014-36371 ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND PARAMETRIC
Performance analysis of variable speed multiphase induction motor with pole phase modulation
 ARCHIVES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 65(3), pp. 425-436 (2016) DOI 10.1515/aee-2016-0031 Performance analysis of variable speed multiphase induction motor with pole phase modulation HUIJUAN LIU, JUN
ARCHIVES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 65(3), pp. 425-436 (2016) DOI 10.1515/aee-2016-0031 Performance analysis of variable speed multiphase induction motor with pole phase modulation HUIJUAN LIU, JUN
Lecture 7: Synchronous Motor Drives
 1 / 46 Lecture 7: Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 46 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises you
1 / 46 Lecture 7: Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 46 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises you
L2 IntroSurvey. EIEN20 Design of Electrical Machines, IEA, Today s goal. L2: Variety of electrical machines.
 L: Variety of electrical achines Machine construction: an overview Transforer is it achine too? Today s goal ntroduction to achine construction Constructional layouts and echanical arrangeents Supply &
L: Variety of electrical achines Machine construction: an overview Transforer is it achine too? Today s goal ntroduction to achine construction Constructional layouts and echanical arrangeents Supply &
Cogging Torque Reduction in Surface-mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Axial Pole Pairing
 EVS28 KINTEX, Korea, May 3-6, 215 Cogging Torque Reduction in Surface-mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Axial Pole Pairing Soo-Gyung Lee 1, Kyung-Tae Jung 1, Seung-Hee Chai 1, and Jung-Pyo
EVS28 KINTEX, Korea, May 3-6, 215 Cogging Torque Reduction in Surface-mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Axial Pole Pairing Soo-Gyung Lee 1, Kyung-Tae Jung 1, Seung-Hee Chai 1, and Jung-Pyo
Research and Experiments on Electromagnetic Field Induced by Two. Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Inforation Technology (ICMIT 16) Research and Experients on Electroagnetic Field Induced by Two Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Inforation Technology (ICMIT 16) Research and Experients on Electroagnetic Field Induced by Two Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
INTERIOR Permanent Magnet (IPM) machines have been
 1 Permanent Magnet minimization in PM-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance motors for wide speed range P. Guglielmi, B. Boazzo, E. Armando, G. Pellegrino and A. Vagati Department of Electrical Engineering -
1 Permanent Magnet minimization in PM-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance motors for wide speed range P. Guglielmi, B. Boazzo, E. Armando, G. Pellegrino and A. Vagati Department of Electrical Engineering -
Simplified Thermal Model of a Radial Flux Motor for Electric Vehicle Application
 Journal of Asian Electric Vehicles, Volue 8, Nuber 2, Deceber 2010 Siplified Theral Model of a adial Flux Motor for Electric Vehicle Application Moez Ayadi 1, Hana Kebaili 2, Mohaed Aine Fakhfakh 3, and
Journal of Asian Electric Vehicles, Volue 8, Nuber 2, Deceber 2010 Siplified Theral Model of a adial Flux Motor for Electric Vehicle Application Moez Ayadi 1, Hana Kebaili 2, Mohaed Aine Fakhfakh 3, and
A Pulley System Apparatus for a Laboratory Experience in Dynamics
 A Pulley Syste Apparatus for a Laboratory Experience in Dynaics Chris J. Kobus and Yin-Ping Chang Oakland University, Rochester, MI 48309-4478 Eail: cjkobus@oakland.edu Abstract This paper describes a
A Pulley Syste Apparatus for a Laboratory Experience in Dynaics Chris J. Kobus and Yin-Ping Chang Oakland University, Rochester, MI 48309-4478 Eail: cjkobus@oakland.edu Abstract This paper describes a
Accuracy of the Scaling Law for Experimental Natural Frequencies of Rectangular Thin Plates
 The 9th Conference of Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand 9- October 005, Phuket, Thailand Accuracy of the caling Law for Experiental Natural Frequencies of Rectangular Thin Plates Anawat Na songkhla
The 9th Conference of Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand 9- October 005, Phuket, Thailand Accuracy of the caling Law for Experiental Natural Frequencies of Rectangular Thin Plates Anawat Na songkhla
Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyramidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular Cross-Sectional Area
 Proceedings of the 006 WSEAS/IASME International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Miai, Florida, USA, January 18-0, 006 (pp13-18) Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyraidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular
Proceedings of the 006 WSEAS/IASME International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Miai, Florida, USA, January 18-0, 006 (pp13-18) Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyraidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular
Using Modular Pole for Multi-Objective Design Optimization of a Linear Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
 Using Modular Pole for Multi-Objective Design Optiization of a Linear Peranent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Particle Swar Optiization (PSO) C. Lucas*, Z. Nasiri-Gheidari** and F. Tootoonchian*** Abstract:
Using Modular Pole for Multi-Objective Design Optiization of a Linear Peranent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Particle Swar Optiization (PSO) C. Lucas*, Z. Nasiri-Gheidari** and F. Tootoonchian*** Abstract:
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS/IASME Int. Conf. on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Tenerife, Spain, December 16-18,
 Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS/IASME Int. Conf. on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Tenerife, Spain, December 16-18, 2006 196 A Method for the Modeling and Analysis of Permanent
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS/IASME Int. Conf. on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Tenerife, Spain, December 16-18, 2006 196 A Method for the Modeling and Analysis of Permanent
Analytical Method for Predicting the Air-Gap Flux Density of Dual-Rotor Permanent- Magnet (DRPM) Machine
 Analytical Method for Predicting the Air-Gap Flux Density of Dual-Rotor Permanent- Magnet (DRPM) Machine W.Xie, G.Dajaku*, D.Gerling Institute for Electrical Drives and Actuators, University of Federal
Analytical Method for Predicting the Air-Gap Flux Density of Dual-Rotor Permanent- Magnet (DRPM) Machine W.Xie, G.Dajaku*, D.Gerling Institute for Electrical Drives and Actuators, University of Federal
Cogging Torque Reduction in Surface-mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Axial Pole Pairing
 EVS28 KINTEX, Korea, May 3-6, 215 Cogging Torque Reduction in Surface-mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Axial Pole Pairing Soo-Gyung Lee 1, Kyung-Tae Jung 1, Seung-Hee Chai 1, and Jung-Pyo
EVS28 KINTEX, Korea, May 3-6, 215 Cogging Torque Reduction in Surface-mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Axial Pole Pairing Soo-Gyung Lee 1, Kyung-Tae Jung 1, Seung-Hee Chai 1, and Jung-Pyo
Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition. Perceptrons and Support Vector Machines
 Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley osig 1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 6 27 February 2018 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector achines Notation...2 Linear odels...3 Lines, Planes
Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley osig 1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 6 27 February 2018 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector achines Notation...2 Linear odels...3 Lines, Planes
Keywords: Electric Machines, Rotating Machinery, Stator faults, Fault tolerant control, Field Weakening, Anisotropy, Dual rotor, 3D modeling
 Analysis of Electromagnetic Behavior of Permanent Magnetized Electrical Machines in Fault Modes M. U. Hassan 1, R. Nilssen 1, A. Røkke 2 1. Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Norwegian University
Analysis of Electromagnetic Behavior of Permanent Magnetized Electrical Machines in Fault Modes M. U. Hassan 1, R. Nilssen 1, A. Røkke 2 1. Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Norwegian University
Faraday's Law Warm Up
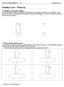 Faraday's Law-1 Faraday's Law War Up 1. Field lines of a peranent agnet For each peranent agnet in the diagra below draw several agnetic field lines (or a agnetic vector field if you prefer) corresponding
Faraday's Law-1 Faraday's Law War Up 1. Field lines of a peranent agnet For each peranent agnet in the diagra below draw several agnetic field lines (or a agnetic vector field if you prefer) corresponding
Cogging torque reduction of Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (IPMSM)
 Scientia Iranica D (2018) 25(3), 1471{1477 Sharif University of Technology Scientia Iranica Transactions D: Computer Science & Engineering and Electrical Engineering http://scientiairanica.sharif.edu Cogging
Scientia Iranica D (2018) 25(3), 1471{1477 Sharif University of Technology Scientia Iranica Transactions D: Computer Science & Engineering and Electrical Engineering http://scientiairanica.sharif.edu Cogging
Analysis of Anti-Notch Method to the Reduction of the Cogging Torque in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 12, December-2016 1301 Analysis of Anti-Notch Method to the Reduction of the Cogging Torque in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 12, December-2016 1301 Analysis of Anti-Notch Method to the Reduction of the Cogging Torque in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator
WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN 2011
 WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN 011 WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING 011 SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN WIRELESS
WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN 011 WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING 011 SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN WIRELESS
COMPLEX FOURIER SERIES MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A UNIVERSAL MOTOR SUPPLIED BY A TRIAC
 Zeszyty Probleowe Maszyny Elektryczne Nr 2/23 (99) 59 Pavel Záskaliý, Ján Kaňuch Technical University of Košice, Slovakia COMPLEX FOURIER SERIES MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A UNIVERSAL MOTOR SUPPLIED BY A TRIAC
Zeszyty Probleowe Maszyny Elektryczne Nr 2/23 (99) 59 Pavel Záskaliý, Ján Kaňuch Technical University of Košice, Slovakia COMPLEX FOURIER SERIES MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A UNIVERSAL MOTOR SUPPLIED BY A TRIAC
A note on the multiplication of sparse matrices
 Cent. Eur. J. Cop. Sci. 41) 2014 1-11 DOI: 10.2478/s13537-014-0201-x Central European Journal of Coputer Science A note on the ultiplication of sparse atrices Research Article Keivan Borna 12, Sohrab Aboozarkhani
Cent. Eur. J. Cop. Sci. 41) 2014 1-11 DOI: 10.2478/s13537-014-0201-x Central European Journal of Coputer Science A note on the ultiplication of sparse atrices Research Article Keivan Borna 12, Sohrab Aboozarkhani
Design tradeoffs between constant power speed range, uncontrolled generator operation and rated current of IPM motor drives
 Design tradeoffs between constant power speed range, uncontrolled generator operation and rated current of IPM motor drives G. Pellegrino Member, IEEE gianmario.pellegrino@polito.it A. Vagati Fellow, IEEE
Design tradeoffs between constant power speed range, uncontrolled generator operation and rated current of IPM motor drives G. Pellegrino Member, IEEE gianmario.pellegrino@polito.it A. Vagati Fellow, IEEE
DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS *
 IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
Magnetorheological Fluid for Levitation Migration Technology
 66 The Open Materials Science Journal, 2011, 5, 66-71 Magnetorheological Fluid for Levitation Migration Technology Guang Yang * and ZhuPing Chen * Open Access Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Jiei University,
66 The Open Materials Science Journal, 2011, 5, 66-71 Magnetorheological Fluid for Levitation Migration Technology Guang Yang * and ZhuPing Chen * Open Access Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Jiei University,
16.30/31 September 24, 2010 Prof. J. P. How and Prof. E. Frazzoli Due: October 15, 2010 T.A. B. Luders /31 Lab #1
 16.30/31 Septeber 24, 2010 Prof. J. P. How and Prof. E. Frazzoli Due: October 15, 2010 T.A. B. Luders 16.30/31 Lab #1 1 Introduction The Quanser helicopter is a echanical device that eulates the flight
16.30/31 Septeber 24, 2010 Prof. J. P. How and Prof. E. Frazzoli Due: October 15, 2010 T.A. B. Luders 16.30/31 Lab #1 1 Introduction The Quanser helicopter is a echanical device that eulates the flight
Self-Erecting Inverted Pendulum: Swing up and Stabilization Control
 Self-Erecting Inverted Pendulu: Swing up and Stabilization Control S. McGilvray (Winner of the IEEE Life Meber ward for best paper fro the Central Canada Council for the IEEE Student Paper Contest, ) Contents
Self-Erecting Inverted Pendulu: Swing up and Stabilization Control S. McGilvray (Winner of the IEEE Life Meber ward for best paper fro the Central Canada Council for the IEEE Student Paper Contest, ) Contents
Ufuk Demirci* and Feza Kerestecioglu**
 1 INDIRECT ADAPTIVE CONTROL OF MISSILES Ufuk Deirci* and Feza Kerestecioglu** *Turkish Navy Guided Missile Test Station, Beykoz, Istanbul, TURKEY **Departent of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
1 INDIRECT ADAPTIVE CONTROL OF MISSILES Ufuk Deirci* and Feza Kerestecioglu** *Turkish Navy Guided Missile Test Station, Beykoz, Istanbul, TURKEY **Departent of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
2.141 Modeling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems Assignment #2
 2.141 Modeling and Siulation of Dynaic Systes Assignent #2 Out: Wednesday Septeber 20, 2006 Due: Wednesday October 4, 2006 Proble 1 The sketch shows a highly siplified diagra of a dry-dock used in ship
2.141 Modeling and Siulation of Dynaic Systes Assignent #2 Out: Wednesday Septeber 20, 2006 Due: Wednesday October 4, 2006 Proble 1 The sketch shows a highly siplified diagra of a dry-dock used in ship
Data-Driven Imaging in Anisotropic Media
 18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
On Constant Power Water-filling
 On Constant Power Water-filling Wei Yu and John M. Cioffi Electrical Engineering Departent Stanford University, Stanford, CA94305, U.S.A. eails: {weiyu,cioffi}@stanford.edu Abstract This paper derives
On Constant Power Water-filling Wei Yu and John M. Cioffi Electrical Engineering Departent Stanford University, Stanford, CA94305, U.S.A. eails: {weiyu,cioffi}@stanford.edu Abstract This paper derives
Loss Modeling and Analysis of the Nuna Solar Car Drive System
 March 9 April 1 International Conference on Ecologic Vehicles & Renewable Energies Loss Modeling and Analysis of the Nuna Solar Car Drive Syste George C.M. Arkesteijn CSE ENGI EAD Drives, Sieens Nederland
March 9 April 1 International Conference on Ecologic Vehicles & Renewable Energies Loss Modeling and Analysis of the Nuna Solar Car Drive Syste George C.M. Arkesteijn CSE ENGI EAD Drives, Sieens Nederland
Vibration Characteristics of Cardboard Inserts in Shells
 2003-01-1489 Vibration Characteristics of Cardboard Inserts in Shells Martin G. Foulkes and Jaes P. De Clerck General Motors Corporation Raendra Singh he Ohio State University Copyright 2003 SAE International
2003-01-1489 Vibration Characteristics of Cardboard Inserts in Shells Martin G. Foulkes and Jaes P. De Clerck General Motors Corporation Raendra Singh he Ohio State University Copyright 2003 SAE International
Optimum Design of Assembled Cavity Dies for Precision Forging Process
 International Syposiu on Material, Energy and Environent Enginee (ISM3E 2015) Optiu Design of Assebled Cavity Dies for Precision Forging Process Jun-song Jin1 and Xin-yun Wang1,* 1 State Key Laboratory
International Syposiu on Material, Energy and Environent Enginee (ISM3E 2015) Optiu Design of Assebled Cavity Dies for Precision Forging Process Jun-song Jin1 and Xin-yun Wang1,* 1 State Key Laboratory
Analytical Model for Sizing the Magnets of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines
 Journal of Electrical Engineering 3 (2015) 134-141 doi: 10.17265/2328-2223/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Analytical Model for Sizing Magnets of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines George Todorov and
Journal of Electrical Engineering 3 (2015) 134-141 doi: 10.17265/2328-2223/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Analytical Model for Sizing Magnets of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines George Todorov and
Application of Eddy Current Damping Effect to Design a Novel Magnetic Damper
 2nd International Foru on Electrical Engineering and Autoation (IFEEA 2015) Application of Eddy Current Daping Effect to Design a Novel Magnetic Daper Xiao Denghong*1 Zhou Xiaohong1 Gao yong1 Quan Dongliang1
2nd International Foru on Electrical Engineering and Autoation (IFEEA 2015) Application of Eddy Current Daping Effect to Design a Novel Magnetic Daper Xiao Denghong*1 Zhou Xiaohong1 Gao yong1 Quan Dongliang1
Grid performance models using Design of Experiments (DoE) methods
 Grid perforance odels using Design of Experients (DoE) ethods IEPC 25-139 Presented at the 29 th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Princeton University, October 31 Noveber, 25 Michael Tartz
Grid perforance odels using Design of Experients (DoE) ethods IEPC 25-139 Presented at the 29 th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Princeton University, October 31 Noveber, 25 Michael Tartz
MSEC MODELING OF DEGRADATION PROCESSES TO OBTAIN AN OPTIMAL SOLUTION FOR MAINTENANCE AND PERFORMANCE
 Proceeding of the ASME 9 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference MSEC9 October 4-7, 9, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA MSEC9-8466 MODELING OF DEGRADATION PROCESSES TO OBTAIN AN OPTIMAL
Proceeding of the ASME 9 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference MSEC9 October 4-7, 9, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA MSEC9-8466 MODELING OF DEGRADATION PROCESSES TO OBTAIN AN OPTIMAL
1 Analysis of heat transfer in a single-phase transformer
 Assignent -7 Analysis of heat transr in a single-phase transforer The goal of the first assignent is to study the ipleentation of equivalent circuit ethod (ECM) and finite eleent ethod (FEM) for an electroagnetic
Assignent -7 Analysis of heat transr in a single-phase transforer The goal of the first assignent is to study the ipleentation of equivalent circuit ethod (ECM) and finite eleent ethod (FEM) for an electroagnetic
Now multiply the left-hand-side by ω and the right-hand side by dδ/dt (recall ω= dδ/dt) to get:
 Equal Area Criterion.0 Developent of equal area criterion As in previous notes, all powers are in per-unit. I want to show you the equal area criterion a little differently than the book does it. Let s
Equal Area Criterion.0 Developent of equal area criterion As in previous notes, all powers are in per-unit. I want to show you the equal area criterion a little differently than the book does it. Let s
An Approximate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity Increase in the Intermediate Ballistics Period
 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF THE ENERGETIC CONSUMPTION FOR SOIL DIGGING MACHINES IN GREENHOUSES
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 3 (5) - 00 Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF THE ENERGETIC CONSUMPTION FOR SOIL DIGGING MACHINES
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 3 (5) - 00 Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF THE ENERGETIC CONSUMPTION FOR SOIL DIGGING MACHINES
Regular paper. Use of Evolutionary Approach for Multiobjective Optimization of Losses and Mass in Permanent Magnet Motor
 N. Ben hadj, S. Tounsi R. Neji F. Sellai Regular paper Use of Evolutionary Approach for Multiobjective Optiization of Losses and Mass in Peranent Magnet Motor For Electric Vehicles (EVs), Weight and losses
N. Ben hadj, S. Tounsi R. Neji F. Sellai Regular paper Use of Evolutionary Approach for Multiobjective Optiization of Losses and Mass in Peranent Magnet Motor For Electric Vehicles (EVs), Weight and losses
SOME ASPECTS OF THE MAGNETIC FIELD DISTRIBUTION PROBLEMS OF LINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR
 International Journal on Technical and Physical Probles of Engineering (IJTPE) Published by International Organization of IOTPE ISSN 2077-3528 IJTPE Journal www.iotpe.co ijtpe@iotpe.co June 2014 Issue
International Journal on Technical and Physical Probles of Engineering (IJTPE) Published by International Organization of IOTPE ISSN 2077-3528 IJTPE Journal www.iotpe.co ijtpe@iotpe.co June 2014 Issue
Ştefan ŞTEFĂNESCU * is the minimum global value for the function h (x)
 7Applying Nelder Mead s Optiization Algorith APPLYING NELDER MEAD S OPTIMIZATION ALGORITHM FOR MULTIPLE GLOBAL MINIMA Abstract Ştefan ŞTEFĂNESCU * The iterative deterinistic optiization ethod could not
7Applying Nelder Mead s Optiization Algorith APPLYING NELDER MEAD S OPTIMIZATION ALGORITHM FOR MULTIPLE GLOBAL MINIMA Abstract Ştefan ŞTEFĂNESCU * The iterative deterinistic optiization ethod could not
Chapter 2: Introduction to Damping in Free and Forced Vibrations
 Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
CONTROL SYSTEMS, ROBOTICS, AND AUTOMATION Vol. IX Uncertainty Models For Robustness Analysis - A. Garulli, A. Tesi and A. Vicino
 UNCERTAINTY MODELS FOR ROBUSTNESS ANALYSIS A. Garulli Dipartiento di Ingegneria dell Inforazione, Università di Siena, Italy A. Tesi Dipartiento di Sistei e Inforatica, Università di Firenze, Italy A.
UNCERTAINTY MODELS FOR ROBUSTNESS ANALYSIS A. Garulli Dipartiento di Ingegneria dell Inforazione, Università di Siena, Italy A. Tesi Dipartiento di Sistei e Inforatica, Università di Firenze, Italy A.
Hysteresis model for magnetic materials using the Jiles-Atherton model
 Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
Analytical and numerical computation of the no-load magnetic field in induction motors
 Analytical and numerical computation of the no-load induction motors Dan M. Ionel University of Glasgow, Glasgow, Scotland, UK and Mihai V. Cistelecan Research Institute for Electrical Machines, Bucharest
Analytical and numerical computation of the no-load induction motors Dan M. Ionel University of Glasgow, Glasgow, Scotland, UK and Mihai V. Cistelecan Research Institute for Electrical Machines, Bucharest
SPECTRUM sensing is a core concept of cognitive radio
 World Acadey of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Electronics and Counication Engineering Vol:6, o:2, 202 Efficient Detection Using Sequential Probability Ratio Test in Mobile
World Acadey of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Electronics and Counication Engineering Vol:6, o:2, 202 Efficient Detection Using Sequential Probability Ratio Test in Mobile
2 Q 10. Likewise, in case of multiple particles, the corresponding density in 2 must be averaged over all
 Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
IN modern society that various systems have become more
 Developent of Reliability Function in -Coponent Standby Redundant Syste with Priority Based on Maxiu Entropy Principle Ryosuke Hirata, Ikuo Arizono, Ryosuke Toohiro, Satoshi Oigawa, and Yasuhiko Takeoto
Developent of Reliability Function in -Coponent Standby Redundant Syste with Priority Based on Maxiu Entropy Principle Ryosuke Hirata, Ikuo Arizono, Ryosuke Toohiro, Satoshi Oigawa, and Yasuhiko Takeoto
A Simplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the Weaving Machines with Automatic Filling Repair
 Proceedings of the 6th SEAS International Conference on Siulation, Modelling and Optiization, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 006 0 A Siplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the eaving
Proceedings of the 6th SEAS International Conference on Siulation, Modelling and Optiization, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 006 0 A Siplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the eaving
Design and Analysis of the Dimension of the PMs for the DMMSM using EMCM Jian-guo BU, Xu-dong LAN, Kai-xiong LV and Ming ZHOU
 2016 International Conference on Advanced anufacture Technology and Industrial Application (ATIA 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-387-8 Design and Analysis of the Dimension of the Ps for the DS using EC Jian-guo
2016 International Conference on Advanced anufacture Technology and Industrial Application (ATIA 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-387-8 Design and Analysis of the Dimension of the Ps for the DS using EC Jian-guo
Multi Degrees of Freedom Maglev System with Permanent Magnet Motion Control
 Multi Degrees of Freedo Maglev Syste with Peranent Magnet Motion Control Cui Tianshi A dissertation subitted to Kochi University of Technology in partial fulfillent of the requireents for the degree of
Multi Degrees of Freedo Maglev Syste with Peranent Magnet Motion Control Cui Tianshi A dissertation subitted to Kochi University of Technology in partial fulfillent of the requireents for the degree of
An Improved Particle Filter with Applications in Ballistic Target Tracking
 Sensors & ransducers Vol. 72 Issue 6 June 204 pp. 96-20 Sensors & ransducers 204 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co An Iproved Particle Filter with Applications in Ballistic arget racing
Sensors & ransducers Vol. 72 Issue 6 June 204 pp. 96-20 Sensors & ransducers 204 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co An Iproved Particle Filter with Applications in Ballistic arget racing
Block designs and statistics
 Bloc designs and statistics Notes for Math 447 May 3, 2011 The ain paraeters of a bloc design are nuber of varieties v, bloc size, nuber of blocs b. A design is built on a set of v eleents. Each eleent
Bloc designs and statistics Notes for Math 447 May 3, 2011 The ain paraeters of a bloc design are nuber of varieties v, bloc size, nuber of blocs b. A design is built on a set of v eleents. Each eleent
THE magnetic fluxes in the stator and rotor yokes of
 Analytical Calculation of Yoke Flux Patterns in Fractional-Slot Permanent Magnet Machines Astrid Røkke and Robert Nilssen Department of Electric Power Engineering, Norwegian University of Science and Technology,
Analytical Calculation of Yoke Flux Patterns in Fractional-Slot Permanent Magnet Machines Astrid Røkke and Robert Nilssen Department of Electric Power Engineering, Norwegian University of Science and Technology,
Extension of CSRSM for the Parametric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels
 Extension of CSRSM for the Paraetric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels Guilhe Mollon 1, Daniel Dias 2, and Abdul-Haid Soubra 3, M.ASCE 1 LGCIE, INSA Lyon, Université de Lyon, Doaine scientifique
Extension of CSRSM for the Paraetric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels Guilhe Mollon 1, Daniel Dias 2, and Abdul-Haid Soubra 3, M.ASCE 1 LGCIE, INSA Lyon, Université de Lyon, Doaine scientifique
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measurement Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES
 Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Model Fitting. CURM Background Material, Fall 2014 Dr. Doreen De Leon
 Model Fitting CURM Background Material, Fall 014 Dr. Doreen De Leon 1 Introduction Given a set of data points, we often want to fit a selected odel or type to the data (e.g., we suspect an exponential
Model Fitting CURM Background Material, Fall 014 Dr. Doreen De Leon 1 Introduction Given a set of data points, we often want to fit a selected odel or type to the data (e.g., we suspect an exponential
Department of Electronic and Optical Engineering, Ordnance Engineering College, Shijiazhuang, , China
 6th International Conference on Machinery, Materials, Environent, Biotechnology and Coputer (MMEBC 06) Solving Multi-Sensor Multi-Target Assignent Proble Based on Copositive Cobat Efficiency and QPSO Algorith
6th International Conference on Machinery, Materials, Environent, Biotechnology and Coputer (MMEBC 06) Solving Multi-Sensor Multi-Target Assignent Proble Based on Copositive Cobat Efficiency and QPSO Algorith
Predictive Control of Outer-Rotor Five-Phase BLDC Generators Applicable for Off-Shore. Wind Power Plants
 ١ ٢ Predictive Control of Outer-Rotor Five-Phase BLDC Generators Applicable for Off-Shore Wind Power Plants ٣ ٤ Rain SALEHI ARASHLOO Mehdi SALEHIFAR 2 Jose Luis ROMERAL MARINEZ 3 Juan Manuel 4 MORENO ٥
١ ٢ Predictive Control of Outer-Rotor Five-Phase BLDC Generators Applicable for Off-Shore Wind Power Plants ٣ ٤ Rain SALEHI ARASHLOO Mehdi SALEHIFAR 2 Jose Luis ROMERAL MARINEZ 3 Juan Manuel 4 MORENO ٥
Unified Torque Expressions of AC Machines. Qian Wu
 Unified Torque Expressions of AC Machines Qian Wu Outline 1. Review of torque calculation methods. 2. Interaction between two magnetic fields. 3. Unified torque expression for AC machines. Permanent Magnet
Unified Torque Expressions of AC Machines Qian Wu Outline 1. Review of torque calculation methods. 2. Interaction between two magnetic fields. 3. Unified torque expression for AC machines. Permanent Magnet
A Comparative Study of Two Permanent Magnet Motors Structures with Interior and Exterior Rotor
 Journal of Asian Electric Vehicles, Volue 8, Nuber, June A Coparative Stuy of Two Peranent Magnet Motors Structures with Interior an Exterior Rotor Mohae Chaieb, Naourez Ben Haj, Jalila Kaouthar Kaoun
Journal of Asian Electric Vehicles, Volue 8, Nuber, June A Coparative Stuy of Two Peranent Magnet Motors Structures with Interior an Exterior Rotor Mohae Chaieb, Naourez Ben Haj, Jalila Kaouthar Kaoun
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH European Laboratory for Particle Physics
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCEAR RESEARCH European aboratory for Particle Physics shc Projects shc Project Report 47 EDDY CURRENT MODEING AND MEASURING IN FAST-PUSED RESISTIVE MAGNETS P. Arpaia,2, M. Buzio
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCEAR RESEARCH European aboratory for Particle Physics shc Projects shc Project Report 47 EDDY CURRENT MODEING AND MEASURING IN FAST-PUSED RESISTIVE MAGNETS P. Arpaia,2, M. Buzio
Comparison of Several Improved Versions of Particle Swarm Optimizer Algorithm for Parameter Estimation of Squirrel-Cage Induction Motors
 Jurnal Intelek (014) Vol 8(): 7-35 Coparison of everal Iproved Versions of Particle war Optiizer Algorith for Paraeter Estiation of quirrel-cage Induction Motors *Mohaad Yazdani-Asrai 1, Mehran Taghipour
Jurnal Intelek (014) Vol 8(): 7-35 Coparison of everal Iproved Versions of Particle war Optiizer Algorith for Paraeter Estiation of quirrel-cage Induction Motors *Mohaad Yazdani-Asrai 1, Mehran Taghipour
Multi-Dimensional Hegselmann-Krause Dynamics
 Multi-Diensional Hegselann-Krause Dynaics A. Nedić Industrial and Enterprise Systes Engineering Dept. University of Illinois Urbana, IL 680 angelia@illinois.edu B. Touri Coordinated Science Laboratory
Multi-Diensional Hegselann-Krause Dynaics A. Nedić Industrial and Enterprise Systes Engineering Dept. University of Illinois Urbana, IL 680 angelia@illinois.edu B. Touri Coordinated Science Laboratory
Hybrid System Identification: An SDP Approach
 49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control Deceber 15-17, 2010 Hilton Atlanta Hotel, Atlanta, GA, USA Hybrid Syste Identification: An SDP Approach C Feng, C M Lagoa, N Ozay and M Sznaier Abstract The
49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control Deceber 15-17, 2010 Hilton Atlanta Hotel, Atlanta, GA, USA Hybrid Syste Identification: An SDP Approach C Feng, C M Lagoa, N Ozay and M Sznaier Abstract The
EFFECT OF SURFACE ASPERITY TRUNCATION ON THERMAL CONTACT CONDUCTANCE
 EFFECT OF SURFACE ASPERITY TRUNCATION ON THERMAL CONTACT CONDUCTANCE Fernando H. Milanez *, M. M. Yovanovich, J. R. Culha Microelectronics Heat Transfer Laboratory Departent of Mechanical Engineering University
EFFECT OF SURFACE ASPERITY TRUNCATION ON THERMAL CONTACT CONDUCTANCE Fernando H. Milanez *, M. M. Yovanovich, J. R. Culha Microelectronics Heat Transfer Laboratory Departent of Mechanical Engineering University
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations, Simple Harmonic Motion
 Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
Index Terms: Placement machines, placement head, pick-and-place, electronics assembly equipment, constant force. I. INTRODUCTION
 CONSTANT FORCE LINEAR PERMANENT MAGNET ACTUATORS Johannes J.H. Paulides, Meber, Laurentiu Encica, Meber, Koen J. Meessen Student Meber, and Elena A. Loonova, Senior Meber Abstract: In applications, such
CONSTANT FORCE LINEAR PERMANENT MAGNET ACTUATORS Johannes J.H. Paulides, Meber, Laurentiu Encica, Meber, Koen J. Meessen Student Meber, and Elena A. Loonova, Senior Meber Abstract: In applications, such
Interactive Markov Models of Evolutionary Algorithms
 Cleveland State University EngagedScholarship@CSU Electrical Engineering & Coputer Science Faculty Publications Electrical Engineering & Coputer Science Departent 2015 Interactive Markov Models of Evolutionary
Cleveland State University EngagedScholarship@CSU Electrical Engineering & Coputer Science Faculty Publications Electrical Engineering & Coputer Science Departent 2015 Interactive Markov Models of Evolutionary
Nonmonotonic Networks. a. IRST, I Povo (Trento) Italy, b. Univ. of Trento, Physics Dept., I Povo (Trento) Italy
 Storage Capacity and Dynaics of Nononotonic Networks Bruno Crespi a and Ignazio Lazzizzera b a. IRST, I-38050 Povo (Trento) Italy, b. Univ. of Trento, Physics Dept., I-38050 Povo (Trento) Italy INFN Gruppo
Storage Capacity and Dynaics of Nononotonic Networks Bruno Crespi a and Ignazio Lazzizzera b a. IRST, I-38050 Povo (Trento) Italy, b. Univ. of Trento, Physics Dept., I-38050 Povo (Trento) Italy INFN Gruppo
Determining a Function for the Damping Coefficient of a laminated Stack
 DOI: 10.435/UB.OVGU-017-093 TECHNISCHE MECHANIK, 37, -5, (017), 161 170 subitted: June 9, 017 Deterining a Function for the Daping Coefficient of a lainated Stack C. Zahalka, K. Ellerann The design of
DOI: 10.435/UB.OVGU-017-093 TECHNISCHE MECHANIK, 37, -5, (017), 161 170 subitted: June 9, 017 Deterining a Function for the Daping Coefficient of a lainated Stack C. Zahalka, K. Ellerann The design of
Analytical Study of AC Magnetic Susceptibility of (Bi, Pb) Sr-Ca-Cu-O Superconducting Systems Using Bean Critical State Model
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 43 : 353-359 (9) Analytical Study of AC Magnetic Susceptibility of (Bi, Pb) Sr-Ca-Cu-O Superconducting Systes Using Bean Critical State Model Supreya Trivijitkase *, Adisak Boonchun,
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 43 : 353-359 (9) Analytical Study of AC Magnetic Susceptibility of (Bi, Pb) Sr-Ca-Cu-O Superconducting Systes Using Bean Critical State Model Supreya Trivijitkase *, Adisak Boonchun,
Key-Words: - Electrical Engineering education, simulation, power electronics, high voltages. with the classic methods of theory and experimental work.
 New ethods in experiental work along with siulation odeling and analysis in the laboratories of the Electrical Engineering Departent of the T.E.I of Larissa. ATHANASIOS MAGLARAS, JOHN ANDRITSOS, GEORGE
New ethods in experiental work along with siulation odeling and analysis in the laboratories of the Electrical Engineering Departent of the T.E.I of Larissa. ATHANASIOS MAGLARAS, JOHN ANDRITSOS, GEORGE
PERIODIC STEADY STATE ANALYSIS, EFFECTIVE VALUE,
 PERIODIC SEADY SAE ANALYSIS, EFFECIVE VALUE, DISORSION FACOR, POWER OF PERIODIC CURRENS t + Effective value of current (general definition) IRMS i () t dt Root Mean Square, in Czech boo denoted I he value
PERIODIC SEADY SAE ANALYSIS, EFFECIVE VALUE, DISORSION FACOR, POWER OF PERIODIC CURRENS t + Effective value of current (general definition) IRMS i () t dt Root Mean Square, in Czech boo denoted I he value
The proofs of Theorem 1-3 are along the lines of Wied and Galeano (2013).
 A Appendix: Proofs The proofs of Theore 1-3 are along the lines of Wied and Galeano (2013) Proof of Theore 1 Let D[d 1, d 2 ] be the space of càdlàg functions on the interval [d 1, d 2 ] equipped with
A Appendix: Proofs The proofs of Theore 1-3 are along the lines of Wied and Galeano (2013) Proof of Theore 1 Let D[d 1, d 2 ] be the space of càdlàg functions on the interval [d 1, d 2 ] equipped with
POLITECNICO DI TORINO Repository ISTITUZIONALE
 POLITECNICO DI TORINO Repository ISTITUZIONALE Ferrite Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines: a General Approach Original Ferrite Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines: a General Approach / A. Vagati;
POLITECNICO DI TORINO Repository ISTITUZIONALE Ferrite Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines: a General Approach Original Ferrite Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines: a General Approach / A. Vagati;
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines
 Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley ENSIAG 2 / osig 1 Second Seester 2012/2013 Lesson 20 2 ay 2013 Kernel ethods and Support Vector achines Contents Kernel Functions...2 Quadratic
Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley ENSIAG 2 / osig 1 Second Seester 2012/2013 Lesson 20 2 ay 2013 Kernel ethods and Support Vector achines Contents Kernel Functions...2 Quadratic
970 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 48, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2012
 970 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 48, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2012 Control Method Suitable for Direct-Torque-Control-Based Motor Drive System Satisfying Voltage and Current Limitations Yukinori
970 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 48, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2012 Control Method Suitable for Direct-Torque-Control-Based Motor Drive System Satisfying Voltage and Current Limitations Yukinori
Torsion Experiment. Encoder #3 ( 3 ) Third encoder/disk for Model 205a only. Figure 1: ECP Torsion Experiment
 Torsion Experient Introduction For the Torsion lab, there are two required experients to perfor and one extra credit assignent at the end. In experient 1, the syste paraeters need to be identified so that
Torsion Experient Introduction For the Torsion lab, there are two required experients to perfor and one extra credit assignent at the end. In experient 1, the syste paraeters need to be identified so that
Influence of different rotor magnetic circuit structure on the performance. permanent magnet synchronous motor
 ARCHIVES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 66(3), pp. 583-594 (2017) DOI 10.1515/aee-2017-0044 Influence of different rotor magnetic circuit structure on the performance of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ARCHIVES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 66(3), pp. 583-594 (2017) DOI 10.1515/aee-2017-0044 Influence of different rotor magnetic circuit structure on the performance of permanent magnet synchronous motor
A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS FOR BLAST ALLEVIATION
 International Journal of Aerospace and Lightweight Structures Vol. 3, No. 1 (2013) 109 133 c Research Publishing Services DOI: 10.3850/S201042862013000550 A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS
International Journal of Aerospace and Lightweight Structures Vol. 3, No. 1 (2013) 109 133 c Research Publishing Services DOI: 10.3850/S201042862013000550 A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS
Optical Properties of Plasmas of High-Z Elements
 Forschungszentru Karlsruhe Techni und Uwelt Wissenschaftlishe Berichte FZK Optical Properties of Plasas of High-Z Eleents V.Tolach 1, G.Miloshevsy 1, H.Würz Project Kernfusion 1 Heat and Mass Transfer
Forschungszentru Karlsruhe Techni und Uwelt Wissenschaftlishe Berichte FZK Optical Properties of Plasas of High-Z Eleents V.Tolach 1, G.Miloshevsy 1, H.Würz Project Kernfusion 1 Heat and Mass Transfer
The Wilson Model of Cortical Neurons Richard B. Wells
 The Wilson Model of Cortical Neurons Richard B. Wells I. Refineents on the odgkin-uxley Model The years since odgkin s and uxley s pioneering work have produced a nuber of derivative odgkin-uxley-like
The Wilson Model of Cortical Neurons Richard B. Wells I. Refineents on the odgkin-uxley Model The years since odgkin s and uxley s pioneering work have produced a nuber of derivative odgkin-uxley-like
