Low-Temperature Geothermometry and Geochronology in Basis Analysis Part 2: Fission track dating Nuclear physics, technique, statistics
|
|
|
- Joy Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Low-Temperature Geothermometry and Geochronology in Basis Analysis Part 2: Fission track dating Nuclear physics, technique, statistics István Dunkl Sedimentology, University of Göttingen 1) Intro: Where are the geotherms? Geothermometry in basins by: vitrinite reflectance, bitumen refl., graptolite refl., Raman spectroscopy, conodont alteration, spore colour, fluorescence, Rock-Eval, clay mineralogy 2) Fission track dating: - nuclear physics - age equation, statistics 3) Volcanic events (= formation ages) Basement exhumation (= cooling ages) 4) Complex T histories of basins & thermal modelling 5) Detrital geochronology (provenance by single-grain ages) 6) (U-Th)/He thermochronology 7) K/Ar, Ar/Ar, Luminescence, ESR and cosmogenic dating of sediments 8) U/Pb and U/Th dating of sediments
2 Geochronology Radioactive elements for geochronology 3H, 14C, 40K, 87Rb, 115In, 138La, 147Sm, 176Lu, 187Re, 235U, 238U, 232Th mother isotope daughter isotope
3 Geochronology Relative dating methods A relative age is the age of a fossil organism, rock, or geologic feature or event defined relative to other organisms, rocks, or features or events rather than in terms of years. (Paleontology, biostratigraphy, structural geology) Correlation methods in geochronology Like fossils, the chemical and physical characteristics of rocks, minerals, and organic materials can be used for correlation. (Paleomagnetic dating, tephrochronology, 87 Sr / 86 Sr geochronology, stable isotope records) Numeric Dating Methods (~radiometric dating) /absolute??? dating/ Numeric dating involves methods of determining the geologic age of a fossil, rock, or geologic feature or event given in units of time. [Ma, Myr, ka, kyr] ( 40 K/ 40 Ar, 40 Ar/ 39 Ar, Rb/Sr, Sm/Nd, U/Pb, U-series methods, Pb-210 geochronology, tritium dating, radiocarbon geochronology, fission track, (U-Th)/He, luminescence geochronology)
4 Geochronology Chronostratigraphy is concerned with age of strata and time relations; it is an attempt to organize the sequence of strata into units that relate to time, determine local time relations, and correlate globally and thus establish a standard global chronostratigraphic scale. The nomeclature involves chronzone, stage, and series. Chronostratigraphic units are bodies of rock that formed during a specific time interval; the chronostratigraphic unit represents all rock on globe that formed during the time interval. The boundaries of chronostratigraphic units are isochronous surfaces or time lines. The rank of chronostratigraphic units is based on time not thickness. Chronostratigraphic horizon is an isochronous stratigraphic surface; theoretically it has no thickness. In the real world we use very thin distinctive intervals; called markers, marker horizon, marker bed, key bed, time surface, datum. Geochronologic units are familiar names found on the geologic time scale; they relate time only and provide an arrangement of time units of worldwide scope for reference dates. The precision or effectiveness of geochronologic units decreases with size.
5 Thermochronology closure temperature Multimethod thermochronology Elevation profile (1 method) Exhuming mountains Vertical age distribution Elevation [meter a.s.l.] rising relief shifting isotherms samples young old Apatite fission track age
6 Thermochronology: nowadays the result is not a (house)number, but a thermal path Result of an unsuperwised thermal modelling - described well the known thermal events. [Danišík & Dunkl, 2004]
7 Thermochronometers typically apatite and zircon are used in low-t basin studies
8 Selection guide - U-containing accessory or rock-forming minerals (or glass) (apatite, zircon, sphene >> biotite, epidote, garnet...) YES: granitoid, intermediate-acid volcanites, tuff, sandstone, metapelite NO: limestone, clay, marl, basalt, greenschist *************** Good Question Collection, ordering and evaluation of existing data: geochronology, stratigraphy, organic maturation, diagenesis, structural geology, hydrogeology
9 Occurrence of sphene
10 Typical densities of common minerals
11 At the beginning: separation of apatite and zircon fractions
12 Radioactive elements for geochronology 3H, 14C, 40K, 87Rb, 115In, 138La, 147Sm, 176Lu, 187Re, 235U, 238U, 232Th mother isotope daughter isotope 0.7% 235U 207Pb 99.3% 238U 206Pb 238U fission decay
13 Fission tracks in an apatite crystal (polished and etched by nitric acid locality: Bohemian Massif)
14 Applicability depends on the track density (age & U content) [Wagner, 1978]
15 History of fission track geochronology Young (1958) Silk & Barnes (1959) Price & Walker (1962) (engineers of GE) Fleischer & Price (1964) Fleischer et al. (1964) Naeser (1967) Wagner etching tracks in LiF tracks in mica by TEM etching tracks in mica etching tracks in 29 minerals first dating apatite, sphene thermochronology
16 Fissionable isotopes and reactions natural fission induced fission 238 U neutrons from 238 Track production in an apatite crystal 235 ( α,n) and ( γ,n) 30.8 U reactions 235U Th 232U 244 Pu α-particles 3 [track/cm * year] Th Cm cosmic ray
17 TEM (transmission electron microscope) image of a latent fission track in zircon [Yada et al., 1987]
18 Cascade process creates "extended" and "point" defects along a track [Pellas & Perron, 1984] TEM image
19 "Thermal spike" model Temperature (x10,000 C) Time (sec) [Chadderton, 1965]
20
21 Some etchants apatite sphene zircon muscovite conc. time temp. [ C] HNO % 4.5 m - 10 s 21 HCl 37% m 90 HF-HCl-HNO3 6 m 20 NaOH cc m 130 H3PO4 cc. 1 m 375 NaOH 100 N 15m - 4 h 220 HF-H2SO h 150 NaOH-KOH eutekt 2-60 h 200 NaOH-KOH-LiOH eutekt 2-40 h 190 HF % m 21
22 Fission tracks in an apatite crystal (polished and etched by nitric acid locality: Bohemian Massif)
23
24 The etched tracks have blade shape in anisotropic crystals [Gleadow et al., 2002]
25 Dependence of etching time and track shape on metamictization
26 Metamictization of zircon [Zhang et al., 2000] [Woodhead et al., 1991]
27
28 Flow-chart of fission dating method (external detector procedure) [Gallagher et al, 1998]
29 Latent tracks in U containing minerals from the natural fission of 238-U Neutron irradiation produces induced fission tracks of 235-U external detector After polishing and etching: v B << v T etched induced tracks Number of induced tracks Ni = f( Fn, s, U content) (n,f) Number of spontaneous tracks Ns = f(age, U content)
30
31 Population method External detector method [Naeser et al., 1981]
32
33 Identification of etched fission tracks 1) Always straight line, pipe or cone. 2) Length max 20 µm, can not be more. 3) Random orientation. 4) Latent tracks disappear bu annealing, while dislocations remain etchable. f ρs = (U, λ f, time)
34 Heterogeneous track density (uranium concentration) in apatite crystals and prints [GÖochroology]
35 Etched crystal defects (~dislocations are curved, oriented and can be longer than a fission track) [GÖochroology]
36 Zeta method needs: age standards + U-glasses ζ = λ Age D e D λ ( ρ ) S ρ S = 1 ρ ln[ 1+ λdζ ρ D] λ ρ I D T STD I 1 STD g ρ D U-glass age standard samples irradiation package σ(ζ) 2 ζ σ(t)=t N N N S I D [ ] [Hurford & Green, 1983]
37 Automatic track counting Track Review software based on Coincidence mapping Advantages: faster,, no humans suffering Problems: - does not measure the track length and the straightness. - relatively slow and needs a lot of checking - does not estimate the parallel tracks and any other possible defects which seems like a track. [Gleadow et al., 2009]
38 New age? Measuring spontaneous tracks by microscope and U content by laser abblation ICP-MS [Hasebe et al., 2004]
39 New age? Measuring spontaneous tracks by microscope and U content by laser abblation ICP-MS Th232 U238 Ca43 Ce
40 Statistics Statistics Statistics Real value -1000% -100% +10% +10% +100% +1000% Sampling Storage, Preparation Analysis Presentation of results Interpretation Source: BASF
41 Hard rock - one age cluster one cluster more clusters "hard rock" age "soft rock"
42 Recommended data presentation dispersion (Galbraith & Laslett, 1993)? 2σ average U content Sample Cryst. Spontaneous Induced Dosimeter P(χ 2 ) Disp. FT age ± 1σ U Track length (n) Code ρ s (Ns) ρ i (Ni) ρ d (Nd) [%] [Ma] [ppm] [µm] (244) 12.3 (1244) 5.30 (3106) ± ± 2.2 (62) (295) 11.5 (1347) 5.24 (3106) ± ± 0.9 (50) (349) 12.5 (1636) 5.48 (3889) ± ± 1.2 (102) (341) 15.7 (1708) 5.41 (3889) ± ± 0.9 (104) [after Hurford, 1990]
43 Effect of the number of crystals
44 Sources of extra-poissonal error: (A) Non-uniform age of crystals, (B) Spatial variation of neutron fluence, (C) Inproper etching, Careless counting, Presence of track-like defects, Bad contact between mount and mica, Imprecise positioning, (D) Vertical inhomegeneity of uranium. [after Green, 1981]
45 The crystals have different track densities and thus...
46 The crystals have different counts and thus different error Number of tracks FT age ± 1s [Ma] ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 6
47 Average - but how? Pooled age: the sum of spontaneous counts divided by the sum of induced counts Mean age: arithmetic mean of the individual ratios of spontaneous to induced tracks Central age: weighted mean of log normal distribution of single grain ages rejection To weight, or not to weight that is the question: To be, or not to be- that is the question ρ RATIO w j ρs j = ρ w j i j need: type of distribution
48 What is an isochron plot?
49 The scatter comes from the low counts and from the "extra-poissonal" error A B
50 10 A-303.APA Dolomiti DO-2 "Knödel" - type 50 A-304.APA Dolomiti DO-7 "Spagetti" - type RhoS RhoS RhoI 10 RhoI 100
51 Outlier? What to do? RhoS RhoI 10^5 t/cm^2 RhoS 2 Dixon test p < 0.5% Grubbs test p < 1% 5 10 RhoI 10^5 t/cm^2 need: type of distribution
52 "Zero track grains" 0.1 A-154.DAT DA-AUST RhoS Ns RhoI 5 Ni 100
53 Probability density plot (PDP) / PDF function / Age spectrum Allocate each measurement a Gaussian curve of unit area reflecting its uncertainties
54 Radial plot s.d Age (value) Rel. error [%]
55 Usual presentation: radial plot + binned diagram + probability density plot Zircon FT ages [Dunkl et al., 2010]
István Dunkl Sedimentology, University of Göttingen
 Beckenanalyse 2: Analytic tools for basin analysis: thermometers and geochronometers [M.Geo.136b] Part 3: How to date low-temperature events? Fission track thermochronology University of Göttingen István
Beckenanalyse 2: Analytic tools for basin analysis: thermometers and geochronometers [M.Geo.136b] Part 3: How to date low-temperature events? Fission track thermochronology University of Göttingen István
Geothermometry - inorganic bench-marks
 Beckenanalyse 2: Analytic tools for basin analysis: thermometers and geochronometers [M.Geo.136b] Part 2b: How to measure the paleo-tempearture? (by inorganic methods) University of Göttingen István Dunkl
Beckenanalyse 2: Analytic tools for basin analysis: thermometers and geochronometers [M.Geo.136b] Part 2b: How to measure the paleo-tempearture? (by inorganic methods) University of Göttingen István Dunkl
Low-Temperature Geothermometry and Geochronology in Basis Analysis Part 4: Reconstruction of thermal histories of basins
 Low-Temperature Geothermometry and Geochronology in Basis Analysis Part 4: Reconstruction of thermal histories of basins István Dunkl Sedimentology, University of Göttingen http://www.sediment.uni-goettingen.de/staff/dunkl/
Low-Temperature Geothermometry and Geochronology in Basis Analysis Part 4: Reconstruction of thermal histories of basins István Dunkl Sedimentology, University of Göttingen http://www.sediment.uni-goettingen.de/staff/dunkl/
István Dunkl Sedimentology, University of Göttingen
 Beckenanalyse 2: Analytic tools for basin analysis: thermometers and geochronometers [M.Geo.136b] Part 5: FT Reconstruction of thermal evolution of basins University of Göttingen István Dunkl Sedimentology,
Beckenanalyse 2: Analytic tools for basin analysis: thermometers and geochronometers [M.Geo.136b] Part 5: FT Reconstruction of thermal evolution of basins University of Göttingen István Dunkl Sedimentology,
Intro to Quantitative Geology
 Introduction to Quantitative Geology Lesson 13.2 Low-temperature thermochronology Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi 4.12.17 3 Goals of this lecture Define low-temperature thermochronology Introduce
Introduction to Quantitative Geology Lesson 13.2 Low-temperature thermochronology Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi 4.12.17 3 Goals of this lecture Define low-temperature thermochronology Introduce
TABLE DR1. SUMMARY OF SHRIMP U-Pb ZIRCON RESULTS FOR SAMPLES D2-83 AND D2-24.
 Data Repository Item, Siddoway p. 1 DR20008 TABLE DR1. SUMMARY OF SHRIMP U-Pb ZIRCON RESULTS FOR SAMPLES D2-83 AND D2-24. Grain Spot U (ppm) Th (ppm) Th/U Pb * (ppm) 204 Pb 206 Pb f 208 % 238 U 206 Pb
Data Repository Item, Siddoway p. 1 DR20008 TABLE DR1. SUMMARY OF SHRIMP U-Pb ZIRCON RESULTS FOR SAMPLES D2-83 AND D2-24. Grain Spot U (ppm) Th (ppm) Th/U Pb * (ppm) 204 Pb 206 Pb f 208 % 238 U 206 Pb
Thermochronology, cosmogenic isotopes and dating of young sedimentary rocks Part 8: Usage of U-Pb and U-Th geochronology in sedimentary environment
 Thermochronology, cosmogenic isotopes and dating of young sedimentary rocks Part 8: Usage of U-Pb and U-Th geochronology in sedimentary environment István Dunkl http://www.sediment.uni-goettingen.de/staff/dunkl/
Thermochronology, cosmogenic isotopes and dating of young sedimentary rocks Part 8: Usage of U-Pb and U-Th geochronology in sedimentary environment István Dunkl http://www.sediment.uni-goettingen.de/staff/dunkl/
István Dunkl Sedimentology, University of Göttingen
 Beckenanalyse 2: Analytic tools for basin analysis: thermometers and geochronometers [M.Geo.136b] Part 2a: How to measure the paleo-tempearture? (by organic methods) University of Göttingen István Dunkl
Beckenanalyse 2: Analytic tools for basin analysis: thermometers and geochronometers [M.Geo.136b] Part 2a: How to measure the paleo-tempearture? (by organic methods) University of Göttingen István Dunkl
Diffusion in minerals and melts
 Diffusion in minerals and melts There are three types of diffusion in a rock Surface diffusion essentially over a 2 dimensional area Grain-boundary diffusion along grain boundaries, slower than surface
Diffusion in minerals and melts There are three types of diffusion in a rock Surface diffusion essentially over a 2 dimensional area Grain-boundary diffusion along grain boundaries, slower than surface
Doing Time: Apatite Fission Track Analysis in Undergraduate Geoscience Courses
 Doing Time: Apatite Fission Track Analysis in Undergraduate Geoscience Courses Annia K. Fayon Irene M. Duranczyk Donna L. Whitney Department of Post-Secondary Teaching and Learning, University of Minnesota,
Doing Time: Apatite Fission Track Analysis in Undergraduate Geoscience Courses Annia K. Fayon Irene M. Duranczyk Donna L. Whitney Department of Post-Secondary Teaching and Learning, University of Minnesota,
CHAPTER 2: Fission Track Thermochronometry - AFT 19 The main transformation of fission track thermochronometry took place in the early 198 s when a re
 CHAPTER 2: Fission Track Thermochronometry - AFT 18 2-2 Apatite Fission Track Thermochronometry (AFTT) 2-2-1 History Improved understanding of how the Earth s crust has behaved in response to climate-erosion
CHAPTER 2: Fission Track Thermochronometry - AFT 18 2-2 Apatite Fission Track Thermochronometry (AFTT) 2-2-1 History Improved understanding of how the Earth s crust has behaved in response to climate-erosion
Die Blei-Blei Methoden
 Die Blei-Blei Methoden Pb produced by radioactive decay of U & Th 238 U 206 Pb (half-life 4.47 Ga) 235 U 207 Pb (half-life 0.70 Ga) 232 Th 208 Pb (half-life 14 Ga) non-radiogenic 204 Pb used as reference
Die Blei-Blei Methoden Pb produced by radioactive decay of U & Th 238 U 206 Pb (half-life 4.47 Ga) 235 U 207 Pb (half-life 0.70 Ga) 232 Th 208 Pb (half-life 14 Ga) non-radiogenic 204 Pb used as reference
5. Chronostratigraphy and Geological Time
 5. Chronostratigraphy and Geological Time Chronostratigraphy is the unifying construct that defines (ideally by international agreement) boundaries for systems, series, and stages. Chronostratigraphy is
5. Chronostratigraphy and Geological Time Chronostratigraphy is the unifying construct that defines (ideally by international agreement) boundaries for systems, series, and stages. Chronostratigraphy is
GEOL 562 Notes: U-Series and Th-series nuclides. Guide Questions: Reading: White, Lecture 10 Faure and Mensing Ch. 20
 GEOL 562 Notes: U-Series and Th-series nuclides Reading: White, Lecture 0 Faure and Mensing Ch. 20 Motivation: Up to now we have dealt with long half-life nuclides (all left over from the birth of the
GEOL 562 Notes: U-Series and Th-series nuclides Reading: White, Lecture 0 Faure and Mensing Ch. 20 Motivation: Up to now we have dealt with long half-life nuclides (all left over from the birth of the
Radiometric Dating of Lake Sediments
 Radiometric Dating of Lake Sediments NORIKO HASEBE Institute of Nature and Environmental Technology, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Ishikawa 920-1192, JAPAN I. Introduction Lake sediments yield records
Radiometric Dating of Lake Sediments NORIKO HASEBE Institute of Nature and Environmental Technology, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Ishikawa 920-1192, JAPAN I. Introduction Lake sediments yield records
Determination of zeta values for fission-track age calibration using thermal neutron irradiation at the JRR- reactor of JAEA, Japan
 Jour. Geol. Soc. Japan, Vol. 115, No. 3, p. 141 145, March 2009 note Determination of zeta values for fission-track age calibration using thermal neutron irradiation at the JRR- reactor of JAEA, Japan
Jour. Geol. Soc. Japan, Vol. 115, No. 3, p. 141 145, March 2009 note Determination of zeta values for fission-track age calibration using thermal neutron irradiation at the JRR- reactor of JAEA, Japan
Chapter 3 Time and Geology
 Chapter 3 Time and Geology Finding the age of rocks: Relative versus Actual Dating The science that deals with determining the ages of rocks is called geochronology. Methods of Dating Rocks 1. Relative
Chapter 3 Time and Geology Finding the age of rocks: Relative versus Actual Dating The science that deals with determining the ages of rocks is called geochronology. Methods of Dating Rocks 1. Relative
Table of Isotopic Masses and Natural Abudances
 Table of Isotopic Masses and Natural Abudances in amu, where 1amu = 1/12 mass 12 C Atomic weight element = M i (abun i )+M j (abun j ) + Four types of radioactive decay 1) alpha (α) decay - 4 He nucleus
Table of Isotopic Masses and Natural Abudances in amu, where 1amu = 1/12 mass 12 C Atomic weight element = M i (abun i )+M j (abun j ) + Four types of radioactive decay 1) alpha (α) decay - 4 He nucleus
Chapter 3 Time and Geology
 Chapter 3 Time and Geology Methods of Dating Rocks 1. Relative dating - Using fundamental principles of geology (Steno's Laws, Fossil Succession, etc.) to determine the relative ages of rocks (which rocks
Chapter 3 Time and Geology Methods of Dating Rocks 1. Relative dating - Using fundamental principles of geology (Steno's Laws, Fossil Succession, etc.) to determine the relative ages of rocks (which rocks
Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles
 Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles Introduction - An appreciation for the immensity of geologic time is essential for understanding the history of our planet - Geologists use two references for time
Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles Introduction - An appreciation for the immensity of geologic time is essential for understanding the history of our planet - Geologists use two references for time
DR GSA data repository. Data Repository Item, Foeken et al. (G19572), p. 1. Apatite (U-Th)/He analysis
 Data Repository Item, Foeken et al. (G19572), p. 1 DR2003115 GSA data repository Apatite (U-Th)/He analysis During sampling, the first 10cm of rock was removed to avoid possible He loss due to insolation
Data Repository Item, Foeken et al. (G19572), p. 1 DR2003115 GSA data repository Apatite (U-Th)/He analysis During sampling, the first 10cm of rock was removed to avoid possible He loss due to insolation
Header. Volcanic matrix from three basalts and one dacite sample from the Black Mountains and Black Hills, respectively, were separated to perform
 DR000 Data Repository Item Geochronology Sample Preparation and Analysis Volcanic matrix from three basalts and one dacite sample from the Black Mountains and Black Hills, respectively, were separated
DR000 Data Repository Item Geochronology Sample Preparation and Analysis Volcanic matrix from three basalts and one dacite sample from the Black Mountains and Black Hills, respectively, were separated
Radiogenic Isotopes. W. F. McDonough 1 1 Department of Earth Sciences and Research Center for
 Radiogenic Isotopes W. F. McDonough 1 1 Department of Earth Sciences and Research Center for Neutrino Science, Tohoku University, Sendai 980-8578, Japan (Dated: May 17, 2018) I. SUMMRY Isotope systems
Radiogenic Isotopes W. F. McDonough 1 1 Department of Earth Sciences and Research Center for Neutrino Science, Tohoku University, Sendai 980-8578, Japan (Dated: May 17, 2018) I. SUMMRY Isotope systems
Chapter 11 (Geologic Time)
 Chapter 11 (Geologic Time) Knowing the chronology of events is crucial for interpreting geologic history. One of the early figures in geology, James Hutton, observed of geologic time that there is "No
Chapter 11 (Geologic Time) Knowing the chronology of events is crucial for interpreting geologic history. One of the early figures in geology, James Hutton, observed of geologic time that there is "No
Geochronology Using U,Th-Pb; U,Th-He; U,Th-He; Sm-Nd; Re- Os; Lu-Hf and the Evolution of the Earth s Mantle and Crust
 Geochronology Using U,Th-Pb; U,Th-He; U,Th-He; Sm-Nd; Re- Os; Lu-Hf and the Evolution of the Earth s Mantle and Crust Reading for this topic, from White s notes: Chapter 3: (U,Th-Pb) read up to, but not
Geochronology Using U,Th-Pb; U,Th-He; U,Th-He; Sm-Nd; Re- Os; Lu-Hf and the Evolution of the Earth s Mantle and Crust Reading for this topic, from White s notes: Chapter 3: (U,Th-Pb) read up to, but not
Zircon Fission-Track Dating of NIED Nojima Fault Drilling Cores at Hirabayashi Borehole
 Technical Zircon Note Fission-Track of the National Dating Research of NIED Institute Nojima Fault for Earth Drilling Science Cores at and Hirabayashi Disaster Prevention, Borehole R. No. Yamada 272; et
Technical Zircon Note Fission-Track of the National Dating Research of NIED Institute Nojima Fault for Earth Drilling Science Cores at and Hirabayashi Disaster Prevention, Borehole R. No. Yamada 272; et
II. Knowing and Understanding the Six Principles of Stratigraphy:
 Student Name(s): Physical Geology 101 Laboratory Relative Dating of Rocks Using Stratigraphic Principles Grade: I. Introduction & Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to learn and apply the concepts of
Student Name(s): Physical Geology 101 Laboratory Relative Dating of Rocks Using Stratigraphic Principles Grade: I. Introduction & Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to learn and apply the concepts of
Dating Single Zircon by Fission-Track and U-Pb Methods-A Case Study on a Granite at the Cooper Basin HFR Site, Australia-
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 1 Bali, Indonesia, 5-9 April 1 Dating Single Zircon by Fission-Track and U-Pb Methods-A Case Study on a Granite at the Cooper Basin HFR Site, Australia- Hisatoshi
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 1 Bali, Indonesia, 5-9 April 1 Dating Single Zircon by Fission-Track and U-Pb Methods-A Case Study on a Granite at the Cooper Basin HFR Site, Australia- Hisatoshi
Quiz Three (9:30-9:35 AM)
 Quiz Three (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 7 & 8: Dating Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1. William Smith and Water 2. Stratigraphic Principles 3.
Quiz Three (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 7 & 8: Dating Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1. William Smith and Water 2. Stratigraphic Principles 3.
The additional parameters - a short introduction to the data handling with TRACKKEY 4.1
 published in: OnTrack v. 11/1, 19-22 (2001) The additional parameters - a short introduction to the data handling with TRACKKEY 4.1 István Dunkl 1,2 istvan.dunkl@uni-tuebingen.de 1): Institut für Geologie
published in: OnTrack v. 11/1, 19-22 (2001) The additional parameters - a short introduction to the data handling with TRACKKEY 4.1 István Dunkl 1,2 istvan.dunkl@uni-tuebingen.de 1): Institut für Geologie
The Geology of Pacific Northwest Rocks & Minerals Activity 1: Geologic Time
 Name: Age: I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt is made to determine
Name: Age: I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt is made to determine
Thermal Footprints in Time: Exploring the Crust using Thermochronometry Brent McInnes Director, John de Laeter Centre
 Thermal Footprints in Time: Exploring the Crust using Thermochronometry Brent McInnes Director, John de Laeter Centre Noreen Evans, Brad McDonald and Martin Danisik Curtin University Introduction Heat
Thermal Footprints in Time: Exploring the Crust using Thermochronometry Brent McInnes Director, John de Laeter Centre Noreen Evans, Brad McDonald and Martin Danisik Curtin University Introduction Heat
Geological record of flat-slab induced extension in the Southern Peruvian forearc
 GSA Data Repository 2017239 Geological record of flatslab induced extension in the Southern Peruvian forearc Mélanie Noury, Mélody Philippon, Matthias Bernet, JeanLouis Paquette, and Thierry Sempere Contents
GSA Data Repository 2017239 Geological record of flatslab induced extension in the Southern Peruvian forearc Mélanie Noury, Mélody Philippon, Matthias Bernet, JeanLouis Paquette, and Thierry Sempere Contents
6. Relative and Absolute Dating
 6. Relative and Absolute Dating Adapted by Sean W. Lacey & Joyce M. McBeth (2018) University of Saskatchewan from Deline B, Harris R, & Tefend K. (2015) "Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology". First
6. Relative and Absolute Dating Adapted by Sean W. Lacey & Joyce M. McBeth (2018) University of Saskatchewan from Deline B, Harris R, & Tefend K. (2015) "Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology". First
GEOLOGIC EVENTS SEDIMENTARY ROCKS FAULTING FOLDING TILTING
 RELATIVE TIME (DATING) ABSOLUTE TIME (DATING) GEOLOGIC TIME List the order in which events occurred, without regard to the amount of time separating them. Refers to the age of a rock in relation to other
RELATIVE TIME (DATING) ABSOLUTE TIME (DATING) GEOLOGIC TIME List the order in which events occurred, without regard to the amount of time separating them. Refers to the age of a rock in relation to other
Coupling basement and detrital thermochronology to constrain Meso-Cenozoic intramontane basin evolution in the northern Tien Shan (Central Asia)
 FACULTY OF SCIENCES Master of Science in geology Coupling basement and detrital thermochronology to constrain Meso-Cenozoic intramontane basin evolution in the northern Tien Shan (Central Asia) Simon Nachtergaele
FACULTY OF SCIENCES Master of Science in geology Coupling basement and detrital thermochronology to constrain Meso-Cenozoic intramontane basin evolution in the northern Tien Shan (Central Asia) Simon Nachtergaele
SCIENTIFIC DATING IN ARCHAEOLOGY
 SCIENTIFIC DATING IN ARCHAEOLOGY Tsuneto Nagatomo 1. AGE DETERMINATION IN ARCHAEOLOGY Relative Age: stratigraphy, typology Absolute Chronology: historical data Age Determination by (natural) Scientific
SCIENTIFIC DATING IN ARCHAEOLOGY Tsuneto Nagatomo 1. AGE DETERMINATION IN ARCHAEOLOGY Relative Age: stratigraphy, typology Absolute Chronology: historical data Age Determination by (natural) Scientific
1) Radioactive Decay, Nucleosynthesis, and Basic Geochronology
 1) Radioactive Decay, Nucleosynthesis, and Basic Geochronology Reading (all from White s Notes) Lecture 1: Introduction And Physics Of The Nucleus: Skim Lecture 1: Radioactive Decay- Read all Lecture 3:
1) Radioactive Decay, Nucleosynthesis, and Basic Geochronology Reading (all from White s Notes) Lecture 1: Introduction And Physics Of The Nucleus: Skim Lecture 1: Radioactive Decay- Read all Lecture 3:
Ge 11a, 2014, Lecture 3 Radioactivity and quantitative geochronology
 Ge 11a, 2014, Lecture 3 Radioactivity and quantitative geochronology Radioactive decay Antoine Henri Becquerel Discovered spontaneous radioactivity Marie Skłodowska-Curie Explored spontaneous radioactivity
Ge 11a, 2014, Lecture 3 Radioactivity and quantitative geochronology Radioactive decay Antoine Henri Becquerel Discovered spontaneous radioactivity Marie Skłodowska-Curie Explored spontaneous radioactivity
geologic age of Earth - about 4.6 billion years
 Geologic Time Geologic Time geologic age of Earth - about 4.6 billion years Geologic Time very difficult to appreciate from our human perspective necessary to understand history of Earth two basic ways
Geologic Time Geologic Time geologic age of Earth - about 4.6 billion years Geologic Time very difficult to appreciate from our human perspective necessary to understand history of Earth two basic ways
Intro to Quantitative Geology
 Introduction to Quantitative Geology Lesson 13.1 Basic concepts of thermochronology Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi 4.12.17 3 Goals of this lecture Introduce the basic concepts of thermochronology
Introduction to Quantitative Geology Lesson 13.1 Basic concepts of thermochronology Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi 4.12.17 3 Goals of this lecture Introduce the basic concepts of thermochronology
Bishop Ussher (1650) Absolute Age Dating. Early attempts at the age of the Earth
 Absolute Age Dating Relative age dating just says that one rock unit or geologic event is younger or older than another Dave is older than Steve Absolute age dating gives a number to the age Dave is 89
Absolute Age Dating Relative age dating just says that one rock unit or geologic event is younger or older than another Dave is older than Steve Absolute age dating gives a number to the age Dave is 89
7) Applications of Nuclear Radiation in Science and Technique (1) Analytical applications (Radiometric titration)
 7) Applications of Nuclear Radiation in Science and Technique (1) (Radiometric titration) The radioactive material is indicator Precipitation reactions Complex formation reactions Principle of a precipitation
7) Applications of Nuclear Radiation in Science and Technique (1) (Radiometric titration) The radioactive material is indicator Precipitation reactions Complex formation reactions Principle of a precipitation
GEOL 562 Notes: U-Series and Th-series nuclides. Guide Questions: Reading: White, Lecture 10
 GEOL 562 Notes: U-Series and Th-series nuclides Reading: White, Lecture 10 Motivation: Up to now we have dealt with long half-life nuclides (all left over from the birth of the solar system). What are
GEOL 562 Notes: U-Series and Th-series nuclides Reading: White, Lecture 10 Motivation: Up to now we have dealt with long half-life nuclides (all left over from the birth of the solar system). What are
Helium diffusion experiments give nuclear evidence for a young world
 RATE project Helium diffusion experiments give nuclear evidence for a young world 1.5 billion years of nuclear decay occurred between 4,000 and 8,000 years ago Updated! D. Russell Humphreys, Ph.D. Institute
RATE project Helium diffusion experiments give nuclear evidence for a young world 1.5 billion years of nuclear decay occurred between 4,000 and 8,000 years ago Updated! D. Russell Humphreys, Ph.D. Institute
GEOLOGY 1--Physical Geology Lecture #2, 2/9/2006
 Topics: GEOLOGY 1--Physical Geology Lecture #2, 2/9/2006 Lithospheric plates and their motions Types of plate boundaries or margins The present is the key to the past Relative Time Numerical Age Age of
Topics: GEOLOGY 1--Physical Geology Lecture #2, 2/9/2006 Lithospheric plates and their motions Types of plate boundaries or margins The present is the key to the past Relative Time Numerical Age Age of
Geology Laboratory - GEOL 101. Ray Rector - Instructor
 GEOLOGIC DATING LAB Principles and Applications Geology Laboratory - GEOL 101 Ray Rector - Instructor Earth s Age and History How Old Is the Earth? How Can We Determine Earth s Geologic History? Two Primary
GEOLOGIC DATING LAB Principles and Applications Geology Laboratory - GEOL 101 Ray Rector - Instructor Earth s Age and History How Old Is the Earth? How Can We Determine Earth s Geologic History? Two Primary
GEOLOGIC DATING LAB Principles and Applications
 GEOLOGIC DATING LAB Principles and Applications Geology Laboratory - GEOL 101 Ray Rector - Instructor Earth s Age and History How Old Is the Earth? How Can We Determine Earth s Geologic History? Scientific
GEOLOGIC DATING LAB Principles and Applications Geology Laboratory - GEOL 101 Ray Rector - Instructor Earth s Age and History How Old Is the Earth? How Can We Determine Earth s Geologic History? Scientific
Radioactive Decay and Geochronology
 EESC2200 Solid Earth Homework 3 Due Wed. October 8 in class. Radioactive Decay and Geochronology Useful information for the calculations is at the end of the problem set, including a portion of the Chart
EESC2200 Solid Earth Homework 3 Due Wed. October 8 in class. Radioactive Decay and Geochronology Useful information for the calculations is at the end of the problem set, including a portion of the Chart
Unit 2 Lesson 3 Absolute Dating. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 It s About Time! How can the absolute age of rock be determined? Determining the actual age of an event or object in years is called absolute dating. Scientists often use radioactive isotopes to find the
It s About Time! How can the absolute age of rock be determined? Determining the actual age of an event or object in years is called absolute dating. Scientists often use radioactive isotopes to find the
2812 *address correspondence to: File DR1: Detailed description of U-Pb and Hf-isotope results from each sample
 Sauer, K.B., Gordon, S.M., Miller, R.B., Vervoort, J.D., and Fisher, C.M., 2018, Provenance and metamorphism of the Swakane Gneiss: Implications for incorporation of sediment into the deep levels of the
Sauer, K.B., Gordon, S.M., Miller, R.B., Vervoort, J.D., and Fisher, C.M., 2018, Provenance and metamorphism of the Swakane Gneiss: Implications for incorporation of sediment into the deep levels of the
Chapter 09 Geologic Time
 Physical Geology 1330 116-S&R 1 Chapter 09 Geologic Time Lectures 12 & 13 Dr. Mike Murphy mmurphy@mail.uh.edu 333-S&R-1 www.uh.edu/~mamurph2/homepage.html Two Ways to Date Geologic Events 1. Relative Dating
Physical Geology 1330 116-S&R 1 Chapter 09 Geologic Time Lectures 12 & 13 Dr. Mike Murphy mmurphy@mail.uh.edu 333-S&R-1 www.uh.edu/~mamurph2/homepage.html Two Ways to Date Geologic Events 1. Relative Dating
Calculations. λ old. λ new
 Introduction Potassium is abundant in planetary crusts and is a major constituent of several common mineral phases, including potassium feldspar, muscovite, biotite, and hornblende. The radioactive decay
Introduction Potassium is abundant in planetary crusts and is a major constituent of several common mineral phases, including potassium feldspar, muscovite, biotite, and hornblende. The radioactive decay
Additional Analytical Methods. Detrital zircon samples were collected from nine fine-, medium-, and coarse-grained
 GSA Data Repository 2016214 Leary, R.J., DeCelles, P.G., Quade, J., Gehrels, G.E., and Waanders, G., 2016, The Liuqu Conglomerate, southern Tibet: Early Miocene basin development related to deformation
GSA Data Repository 2016214 Leary, R.J., DeCelles, P.G., Quade, J., Gehrels, G.E., and Waanders, G., 2016, The Liuqu Conglomerate, southern Tibet: Early Miocene basin development related to deformation
published sources and U-Pb geochronology performed in this study. We analyzed six
 Data Repository: Uba, Strecker, and Schmitt U-Pb radiometric dating The age controls for the stable isotopic records presented here are from both published sources and U-Pb geochronology performed in this
Data Repository: Uba, Strecker, and Schmitt U-Pb radiometric dating The age controls for the stable isotopic records presented here are from both published sources and U-Pb geochronology performed in this
Trace Elements - Definitions
 Trace Elements - Definitions Elements that are not stoichiometric constituents in phases in the system of interest For example, IG/MET systems would have different trace elements than aqueous systems Do
Trace Elements - Definitions Elements that are not stoichiometric constituents in phases in the system of interest For example, IG/MET systems would have different trace elements than aqueous systems Do
AMHERST COLLEGE Department of Geology GEOLOGY 41 - Environmental and Solid Earth Geophysics Lab 2: Geochronology Solution
 AMHERST COLLEGE Department of Geology GEOLOGY 41 - Environmental and Solid Earth Geophysics Lab 2: Geochronology Solution U/Pb data aliquot # U (ppm) Pb (ppm) 206 Pb/ 204 Pb 207 Pb/ 204 Pb 208 Pb/ 204
AMHERST COLLEGE Department of Geology GEOLOGY 41 - Environmental and Solid Earth Geophysics Lab 2: Geochronology Solution U/Pb data aliquot # U (ppm) Pb (ppm) 206 Pb/ 204 Pb 207 Pb/ 204 Pb 208 Pb/ 204
Structure of Phu Phan Range in the Khorat Plateau: Its Apatite Fission Track Ages and Geological Syntheses
 Structure of Phu Phan Range in the Khorat Plateau: Its Apatite Fission Track Ages and Geological Syntheses Apivut Veeravinantanakul 1, Pitsanupong Kanjanapayont 2,*, Arak Sangsompong 1 Noriko Hasebe 2
Structure of Phu Phan Range in the Khorat Plateau: Its Apatite Fission Track Ages and Geological Syntheses Apivut Veeravinantanakul 1, Pitsanupong Kanjanapayont 2,*, Arak Sangsompong 1 Noriko Hasebe 2
Introduction to Archaeology: Notes 9 Chronology, part 2 Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Trapped-charge dating methods Several different kinds, one basic
 Introduction to Archaeology: Notes 9 Chronology, part 2 Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Trapped-charge dating methods Several different kinds, one basic principle All measure the accumulated damage (displaced
Introduction to Archaeology: Notes 9 Chronology, part 2 Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Trapped-charge dating methods Several different kinds, one basic principle All measure the accumulated damage (displaced
Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale
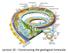 Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale Geologic Time Discovering the magnitude of the Earth s past was a momentous development in the history of humanity This discovery forever altered our perception
Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale Geologic Time Discovering the magnitude of the Earth s past was a momentous development in the history of humanity This discovery forever altered our perception
Geochronology. study of 'Earth time' Historical Geology. study of the physical and biological evolution of the Earth & its life
 http://talc.geo.umn.edu/courses/100i/1001kirkby/ss6.html Page I of II 3/17/2006 Geochronology study of 'Earth time' time scale of geologic processes & methods of measuring time Historical Geology study
http://talc.geo.umn.edu/courses/100i/1001kirkby/ss6.html Page I of II 3/17/2006 Geochronology study of 'Earth time' time scale of geologic processes & methods of measuring time Historical Geology study
K/Ar AND Ar/Ar DATING
 K K/Ar AND Ar/Ar DATING R M Twyman, University of York, York, UK ª 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. Introduction Radiometric dating methods measure the decay of naturally occurring radioactive isotopes,
K K/Ar AND Ar/Ar DATING R M Twyman, University of York, York, UK ª 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. Introduction Radiometric dating methods measure the decay of naturally occurring radioactive isotopes,
Issues of the Age of the Earth Parts 1 & 2
 Issues of the Age of the Earth Parts 1 & 2 Why is Age such an issue? Incomprehensible ages make evolution seem possible. In billions of years anything can happen Impossible to test possible to construct
Issues of the Age of the Earth Parts 1 & 2 Why is Age such an issue? Incomprehensible ages make evolution seem possible. In billions of years anything can happen Impossible to test possible to construct
The principle of fossil succession allows strata in different parts of the world to be correlated, and worldwide relative ages to be worked out
 Correlating beds using index fossils Stratigraphic Classification: Piles of stratified rocks need to be classified. A formation is an easily identifiable rock unit that differs from layers above and below
Correlating beds using index fossils Stratigraphic Classification: Piles of stratified rocks need to be classified. A formation is an easily identifiable rock unit that differs from layers above and below
Timing of Geologic Events. Geologic Time Terms. Laws / Principles of Stratigraphy
 Geologic Time Terms Hadean Archean Proterozoic Phanerozoic Paleozoic Mesozoic Cenozoic(Tertiary) Cambrian Unconformity Angular unconformity Half-life Alpha particle Beta particle Gamma ray Neutron UT How
Geologic Time Terms Hadean Archean Proterozoic Phanerozoic Paleozoic Mesozoic Cenozoic(Tertiary) Cambrian Unconformity Angular unconformity Half-life Alpha particle Beta particle Gamma ray Neutron UT How
GSA DATA REPOSITORY Topuz et al. ANALYTICAL PROCEDURE
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013062 Topuz et al. ANALYTICAL PROCEDURE 40 Ar/ 39 Ar Dating Samples were selected, prepared and analysed following procedures described in Rolland et al. (2008). Pure white mica and
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013062 Topuz et al. ANALYTICAL PROCEDURE 40 Ar/ 39 Ar Dating Samples were selected, prepared and analysed following procedures described in Rolland et al. (2008). Pure white mica and
Spot Name U-Pb ages (Ma) Plagioclase ages (Ma) Biotite age (Ma) Whole rock age (Ma)
 Table 1. Average U-Pb ages from this study in comparison with previous ages from Sherrod and Tosdal (1991, and references therein). Previous study ages are reported as ranges including uncertainty (i.e.
Table 1. Average U-Pb ages from this study in comparison with previous ages from Sherrod and Tosdal (1991, and references therein). Previous study ages are reported as ranges including uncertainty (i.e.
G-100 Lectures 12 & 13 Clocks in Rocks
 A riddle: G-100 Lectures 12 & 13 Clocks in Rocks This thing all things devours: Birds, beasts, trees, flowers; Gnaws iron, bites steel, Grinds hard stones to meal; Slays king, ruins town, And beats high
A riddle: G-100 Lectures 12 & 13 Clocks in Rocks This thing all things devours: Birds, beasts, trees, flowers; Gnaws iron, bites steel, Grinds hard stones to meal; Slays king, ruins town, And beats high
R.J. Stewart, B. Hallet, P.K. Zeitler, M.A. Malloy, C. M. Allen and D. Trippett. Nature of sand samples collected downstream of Brahmaputra Canyon
 Data Repository, Stewart, Text and Figure DR 1, page 1 Data Repository 2008179 "Brahmaputra Sediment Flux Dominated by Highly Localized Rapid Erosion from the Easternmost Himalaya" R.J. Stewart, B. Hallet,
Data Repository, Stewart, Text and Figure DR 1, page 1 Data Repository 2008179 "Brahmaputra Sediment Flux Dominated by Highly Localized Rapid Erosion from the Easternmost Himalaya" R.J. Stewart, B. Hallet,
Recap: Element Segregation
 Recap: Earth is Structured A) Metal Core and Silicate mantle and Crust B) Deduced by: -Observation of crust and mantle derived rocks -Seismic structure (P and S waves) -Knowledge of Earth mass deduced
Recap: Earth is Structured A) Metal Core and Silicate mantle and Crust B) Deduced by: -Observation of crust and mantle derived rocks -Seismic structure (P and S waves) -Knowledge of Earth mass deduced
Pleistocene Terrace Deposits of the Crystal Geyser Area e. r G. P5 5o. M1/Qal. M3 3y M4 M5 M5. 5o M6y P6. M1/Qal
 0 M6 C O N T O UR IN T E R V A L 4 0 F E E T NO R T H A ME R IC A N V E R T IC A L D A T UM O F 1 9 8 8 500 METERS KILOMETERS 0.5 S C A L E 1 : 1 2,0 0 0 r M1/Qal USU-780 P6 1000 1 5o M6y P6 y M4 M5 M5
0 M6 C O N T O UR IN T E R V A L 4 0 F E E T NO R T H A ME R IC A N V E R T IC A L D A T UM O F 1 9 8 8 500 METERS KILOMETERS 0.5 S C A L E 1 : 1 2,0 0 0 r M1/Qal USU-780 P6 1000 1 5o M6y P6 y M4 M5 M5
Sequestration of Radioactive Wastes: The Oklo Experiment (Gabon)
 Sequestration of Radioactive Wastes: The Oklo Experiment (Gabon) Advantages of Nuclear Power At the site of generation, the only major environmental impact is waste heat. Given the high energy content
Sequestration of Radioactive Wastes: The Oklo Experiment (Gabon) Advantages of Nuclear Power At the site of generation, the only major environmental impact is waste heat. Given the high energy content
Unit A (225 m.y. old) Unit B (how old is it?) Unit C (275 m.y. old)
 Radiometric Dating Relative dating techniques are based on principles can be used to differentiate the relative age rock units and landforms. Relative dating techniques by themselves cannot be used to
Radiometric Dating Relative dating techniques are based on principles can be used to differentiate the relative age rock units and landforms. Relative dating techniques by themselves cannot be used to
Geol. 655 Isotope Geochemistry
 GEOCHRONOLOGY I We have now discussed many of the basic aspects of radiogenic isotope geochemistry and we can now consider how it is applied to solving questions about the Earth. We will begin by discussing
GEOCHRONOLOGY I We have now discussed many of the basic aspects of radiogenic isotope geochemistry and we can now consider how it is applied to solving questions about the Earth. We will begin by discussing
Breeding et al., Data Repository Material Figure DR1. Athens. Study Area
 Breeding, Ague, and Brocker 1 Figure DR1 21 o 24 Greece o A 38 o Athens Tinos 37 o Syros Attic-Cycladic Blueschist Belt Syros Kampos B Study Area Ermoupoli N Vari Unit Cycladic HP-LT Unit Marble horizons
Breeding, Ague, and Brocker 1 Figure DR1 21 o 24 Greece o A 38 o Athens Tinos 37 o Syros Attic-Cycladic Blueschist Belt Syros Kampos B Study Area Ermoupoli N Vari Unit Cycladic HP-LT Unit Marble horizons
Isotope Geochem Notes (U,Th-Pb; Sm-Nd; Re-Os; Lu-Hf)
 Isotope Geochem Notes (U,Th-Pb; Sm-Nd; Re-Os; Lu-Hf) Reading for this topic: White, Nos. 7,8,9,11. Guide questions: What are the special features of the U,Th - Pb system that make it uniquely useful for
Isotope Geochem Notes (U,Th-Pb; Sm-Nd; Re-Os; Lu-Hf) Reading for this topic: White, Nos. 7,8,9,11. Guide questions: What are the special features of the U,Th - Pb system that make it uniquely useful for
Geologic Time: Hutton s Outcrop at Siccar Point. How do we determine age (relative & absolute) What is the age of the earth? How do we know?
 Geologic Time: How do we determine age (relative & absolute) What is the age of the earth? How do we know? What is the age of the Earth? A. 4.44 million years B. 1 million years C. 4.55 billion years D.
Geologic Time: How do we determine age (relative & absolute) What is the age of the earth? How do we know? What is the age of the Earth? A. 4.44 million years B. 1 million years C. 4.55 billion years D.
Source- to- Sink in the Stra/graphic Record
 Source- to- Sink in the Stra/graphic Record Capturing the Long-Term, Deep-Time Evolution of Sedimentary Systems Stephan A. Graham Stanford University Brian W. Romans Chevron Energy Technology Co. Jacob
Source- to- Sink in the Stra/graphic Record Capturing the Long-Term, Deep-Time Evolution of Sedimentary Systems Stephan A. Graham Stanford University Brian W. Romans Chevron Energy Technology Co. Jacob
Stratigraphy and Geologic Time. How old are the rocks?
 Stratigraphy and Geologic Time How old are the rocks? 1 Questions What is the difference between Absolute and Relative dating? How old is the Earth? How can we use fossils to date rocks? How are the absolute
Stratigraphy and Geologic Time How old are the rocks? 1 Questions What is the difference between Absolute and Relative dating? How old is the Earth? How can we use fossils to date rocks? How are the absolute
ENVI.2030L Geologic Time
 Name ENVI.2030L Geologic Time I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt
Name ENVI.2030L Geologic Time I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt
GEOLOGICAL LOG INTERPRETATION TUTORIAL
 GEOLOGICAL LOG INTERPRETATION TUTORIAL Text and Figures by Geoff Bohling and John Doveton The following pages will familiarize you with the basics of the geological interpretation of common logs as they
GEOLOGICAL LOG INTERPRETATION TUTORIAL Text and Figures by Geoff Bohling and John Doveton The following pages will familiarize you with the basics of the geological interpretation of common logs as they
Telling Geologic Time
 Telling Geologic Time Trilobite fossils these arthropods went extinct during the great extinction at the end of the Permian Period ~250 Ma ka = kilo-annum Ma = Mega-annum Ga = Giga-annum Relative dating
Telling Geologic Time Trilobite fossils these arthropods went extinct during the great extinction at the end of the Permian Period ~250 Ma ka = kilo-annum Ma = Mega-annum Ga = Giga-annum Relative dating
Chapter 17. Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles
 Chapter 17 Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles Introduction The Grand Canyon - Major John Wesley Powell, in 1869, led a group of explorers down the Colorado River. Powell was impressed with the geology
Chapter 17 Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles Introduction The Grand Canyon - Major John Wesley Powell, in 1869, led a group of explorers down the Colorado River. Powell was impressed with the geology
from the Sierra Nevada Fault Project
 Open File Report OF-AR-15 New Mexico Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources A division of New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology 40 Ar/ 39 Ar Geochronology Results from the Sierra Nevada Fault
Open File Report OF-AR-15 New Mexico Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources A division of New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology 40 Ar/ 39 Ar Geochronology Results from the Sierra Nevada Fault
Chapter 8 TIMING THE GEOLOGIC RECORD
 Chapter 8 Fossils (cont.): Petrified Forest, Arizona. These ancient logs are millions of years old. Their substance was completely replaced by silica, which preserved all the original details of form.
Chapter 8 Fossils (cont.): Petrified Forest, Arizona. These ancient logs are millions of years old. Their substance was completely replaced by silica, which preserved all the original details of form.
Dating methods Stragraphic or geologic methods. Thomas INGICCO
 Dating methods Stragraphic or geologic methods Thomas INGICCO Electro-spin resonance (ESR) An electron can be represented by a negatively charged sphere animated of a rotational movement on itself. This
Dating methods Stragraphic or geologic methods Thomas INGICCO Electro-spin resonance (ESR) An electron can be represented by a negatively charged sphere animated of a rotational movement on itself. This
Name: Period: Half-life and Radiometric Dating
 Name: Period: Half-life and Radiometric Dating Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to understand half-life and how it is used in determining the age of materials. Students will also understand the limitations
Name: Period: Half-life and Radiometric Dating Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to understand half-life and how it is used in determining the age of materials. Students will also understand the limitations
Lecture Outline Friday Feb. 21 Wednesday Feb. 28, 2018
 Lecture Outline Friday Feb. 21 Wednesday Feb. 28, 2018 Questions? Key Points for today What are the 5 relative age dating principles and how do you apply the principles to determine a geologic history
Lecture Outline Friday Feb. 21 Wednesday Feb. 28, 2018 Questions? Key Points for today What are the 5 relative age dating principles and how do you apply the principles to determine a geologic history
Workshop Mendoza, Argentina April 11-15, 2016
 Workshop Mendoza, Argentina April 11-15, 2016 Geochronology of Uranium Deposits Why is geochronology of uranium deposits important? Source Transport Mechanism Geological Environment or Depositional Mechanism
Workshop Mendoza, Argentina April 11-15, 2016 Geochronology of Uranium Deposits Why is geochronology of uranium deposits important? Source Transport Mechanism Geological Environment or Depositional Mechanism
Low temperature thermal history reconstruction using apatite. fission-track length distribution and apatite U-Th/He age
 Low temperature thermal history reconstruction using apatite fission-track length distribution and apatite U-Th/He age Ruxin Ding a, b, * a School of Earth Science and Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University,
Low temperature thermal history reconstruction using apatite fission-track length distribution and apatite U-Th/He age Ruxin Ding a, b, * a School of Earth Science and Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University,
Radiometric Dating and the Age of the Earth
 Radiometric Dating and the Age of the Earth How to tell time: Relative Time: putting events in time order. Law of Superposition Correlation of rock layers using fossils. There is a wonderful order and
Radiometric Dating and the Age of the Earth How to tell time: Relative Time: putting events in time order. Law of Superposition Correlation of rock layers using fossils. There is a wonderful order and
CLOSURE TEMPERATURES OF ACCESSORY MINERALS
 DR2005002 Flowers et al. CLOSURE TEMPERATURES OF ACCESSORY MINERALS The range of Pb diffusivity in accessory minerals provides the opportunity to reconstruct detailed thermal histories using the U-Pb isotopic
DR2005002 Flowers et al. CLOSURE TEMPERATURES OF ACCESSORY MINERALS The range of Pb diffusivity in accessory minerals provides the opportunity to reconstruct detailed thermal histories using the U-Pb isotopic
Guided Notes Geologic History
 Guided Notes Geologic History Relative Age Sequence of Events Correlation Techniques Volcanic Ash Markers Index Fossils Geologic Time Scale Evolution Radioactive Dating 9) How has Earth changed over time?
Guided Notes Geologic History Relative Age Sequence of Events Correlation Techniques Volcanic Ash Markers Index Fossils Geologic Time Scale Evolution Radioactive Dating 9) How has Earth changed over time?
dating of geological samples by laser ablation ICPMS
 U-Th-Pb dating of geological samples by laser ablation ICPMS Winter Conference on Plasma Spectrochemistry Fort Lauderdale, Florida, January 3, 2004 Short course ST-19 Jan Košler 1 and Mike Tubrett 2 1.
U-Th-Pb dating of geological samples by laser ablation ICPMS Winter Conference on Plasma Spectrochemistry Fort Lauderdale, Florida, January 3, 2004 Short course ST-19 Jan Košler 1 and Mike Tubrett 2 1.
Determining Absolute Age
 CHAPTER 8 SECTION 2 The Rock Record Determining Absolute Age KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: Why can t scientists use rates of erosion and deposition as the only ways
CHAPTER 8 SECTION 2 The Rock Record Determining Absolute Age KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: Why can t scientists use rates of erosion and deposition as the only ways
Formative mechanism of inhomogeneous distribution of fractures, an example of the Toki Granite, Central Japan
 Formative mechanism of inhomogeneous distribution of fractures, an example of the Toki Granite, Central Japan Eiji SASAO (1), Takashi YUGUCHI (2), Yasuto ITOH (3), Takashi INOUE (3) and Masayuki ISHIBASHI
Formative mechanism of inhomogeneous distribution of fractures, an example of the Toki Granite, Central Japan Eiji SASAO (1), Takashi YUGUCHI (2), Yasuto ITOH (3), Takashi INOUE (3) and Masayuki ISHIBASHI
An 80 milligram sample of a radioactive isotope decays to 5 milligrams in 32 days. What is the half-life of this element?
 An 80 milligram sample of a radioactive isotope decays to 5 milligrams in 32 days. What is the half-life of this element? A. 8 days B. 2 days C. 6 days D. 4 days An original sample of a radioisotope had
An 80 milligram sample of a radioactive isotope decays to 5 milligrams in 32 days. What is the half-life of this element? A. 8 days B. 2 days C. 6 days D. 4 days An original sample of a radioisotope had
Apatite fission-track and Re-Os geochronology of the Xuefeng uplift, China: Temporal implications for dry gas associated hydrocarbon systems
 GSA Data Repository 2016163 Apatite fission-track and Re-Os geochronology of the Xuefeng uplift, China: Temporal implications for dry gas associated hydrocarbon systems Xiang Ge 1,2, Chuanbo Shen 1*, David
GSA Data Repository 2016163 Apatite fission-track and Re-Os geochronology of the Xuefeng uplift, China: Temporal implications for dry gas associated hydrocarbon systems Xiang Ge 1,2, Chuanbo Shen 1*, David
DATA REPOSITORY ITEMS
 Gunnell page 1 DATA REPOSITORY ITEMS Stratigraphy and rifting age The Lower sequence (0.6 km of inner-shelfal and dolomitic limestone) currently forms the sharp-rimmed morphology of the escarpment, while
Gunnell page 1 DATA REPOSITORY ITEMS Stratigraphy and rifting age The Lower sequence (0.6 km of inner-shelfal and dolomitic limestone) currently forms the sharp-rimmed morphology of the escarpment, while
XM1/331 XM1/331 BLFX-3 XM1/331
 a b AkC AkC strontian fluoro-apatite clinopyroxene phlogopite K-richterite XM1/331 clinopyroxene XM1/331 Fe-Ti ox c d clinopyroxene kric AkC ilmenite Sr-barite AkC XM1/331 BLFX-3 Supplementary Figure 1.
a b AkC AkC strontian fluoro-apatite clinopyroxene phlogopite K-richterite XM1/331 clinopyroxene XM1/331 Fe-Ti ox c d clinopyroxene kric AkC ilmenite Sr-barite AkC XM1/331 BLFX-3 Supplementary Figure 1.
