Draft National Annex to Eurocode 8 for Malaysia and cost implication for residential buildings with thin size elements
|
|
|
- Primrose Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
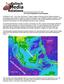
1 Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia Draft National Annex to Eurocode 8 for Malaysia and cost implication for residential buildings with thin size elements M.C. Hee Technical Committee for Eurocode 8 NA, The Institution of Engineers Malaysia. N.T.K. Lam Infrastructure Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, Australia. H.H. Tsang Centre for Sustainable Infrastructure, Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne, Australia. D.T.W. Looi Technical Committee for Eurocode 8 NA, The Institution of Engineers Malaysia. ABSTRACT: A hybrid design response spectrum is developed for Malaysia. A hybrid model consists of both local and distant earthquake. This paper gives a brief explanation on the development and application of seismic loading in Malaysia. Implementation of the proposed seismic loading in Malaysia, due to the aftermath of the Sumatra Earthquake that raised concerns on the structural stability of the buildings in Malaysia. Using the hybrid model, safety and cost implication are investigated for thin size elements commonly used in low rise link houses. These link houses are the most common type of dwellings found in Malaysia. The analysis is carried out taking into account of stiffness reduction and behaviour factor under EC8. The study concludes the impact of the proposed response spectra on the buildings of Malaysia. 1 INTRODUCTION For decades Malaysian Engineers have neglected Earthquake as a main design factor in buildings. However the major Sumatra earthquake in 2004 raised concerns throughout Malaysia. To address these concerns, The Institution of Engineers Malaysia (IEM) took the initiative and formed a Technical Committee on Earthquake Engineering publishing their first position paper in Initially the primary concern was the long distant earthquakes from neighbouring Indonesia. Until in 2010, Malaysia itself experienced a series of small earthquakes (M0.3 to M4.2) in the Bukit Tinggi fault zone (fig. 1). This generation of local earthquakes in an inactive intraplate fault further heightened the already raised concerns within the IEM technical committee categorising Malaysia as a low to moderate seismicity region. This also clarified doubts whether Malaysia, located on the stable Sunda plate required a seismic code or not. This lead to gathering of several technical meetings and symposiums by the earthquake committee and the development of the seismic response spectrum. The paper aims to introduce the development of the hybrid model developed for the Malaysian N.A to EC8 and the implication of earthquake design to low rise link houses in Malaysia. 2 DISTANT EARTHQUAKE Megathrust earthquakes such as Aceh 2004 (M9.3) and Nias 2005 (M8.7) from Indonesia, Sumatra are mainly caused by the movement of the Sunda Arc Subduction fault offshore of Sumatra (fig. 1), approximately 530 km 730 km from Peninsular Malaysia. 1
2 Figure 1. Distant and local earthquake faults in Peninsular Malaysia. A Uniform Hazard Spectrum (UHS) model for key cities of Malaysia for both 475 years and 2475 years return period has been developed by ARUP (Pappin et al., 2011) based in far field events. Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment (PSHA) has been undertaken for Malaysia based on historical earthquake data of 40 years from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) database starting from 1942, covering an area between latitude 14 S to 22 N and longitude 90 E to 132 E (Pappin et al., 2011). Note however that there are drawbacks of the Ground Motion Prediction Equation (GMPE) that was employed in the analysis as it was intended to be used for modelling distant large magnitude events making it inappropriate for modelling hazards that are associated with local earthquakes (or earthquakes occurring at close range to Malaysia). The originally developed UHS employed an early ground motion model that was developed by Pan et al. (2007) which required corrections as per recommendations by Megawati & Pan (2010). The IEM Technical Committee Working Group 1 was assigned the task of developing the design spectrum, using the original UHS (that was developed by ARUP) but had the results modified as per the latest work of Megawati and Pan (2010) and the latest development of CAM in order to achieve a better and updated UHS for long distant earthquakes. The Component Attenuation Model (CAM) as summarized in Lam et al. (2010) has been coded into programme GENQKE (Lam, 1999) for generating synthetic earthquake accelerograms based on stochastic simulations of the seismological model. CAM has successfully simulated distant earthquakes affecting Singapore (Lam et al., 2009). CAM has also been shown to be able to simulate ground motions that match the instrumental field recordings from major events including the Aceh earthquake of 2004 and the Nias earthquake of LOCAL EARTHQUAKE With the lack of data for local earthquakes, the major challenge came in the development of the local component of the hybrid model. There is very low frequency of occurrence of intraplate earthquakes in the Sunda plate. Developing a reliable model based on these low quantities of occurrence data is not statistically practicable. Since there is still seismic activity, these activities inside the plate are still comparable globally to areas with enough statistical data of intraplate events (Lam, 2015). Hence collection of intraplate records globally from different parts of the world with similar tectonic settings to develop a model of the rate of occurrence is adopted. An average global activity rate of intraplate earthquake of magnitude greater than 5.66 per square meter per second was estimated at 4.27 x by Bird (2010). Translating this as 2-3 events occurring in an area of 1 million square kilometer over a period of 50 years. From this translation it can be established that the occurrence of an earthquake in Peninsular Malaysia is 1 to 2 events per century. This does not mean that an event might not occur in 2
3 Malaysia in the coming future. Hence establishing the fact that earthquake events may occur even in Malaysia. A design Peak Ground Acceleration (PGA) of 0.1g for a return period of 2745 years is adopted, benchmarking with world average for intraplate earthquakes. 4 DEVELOPMENT OF HYBRID MODEL The developed hybrid models for rock sites for Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak and Sabah can be summarized in the form of schematic diagrams as shown in Figures 2a 2f and associated Table 1. Table 1 summarises PGA values that are recommended for Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak and Sabah for different importance classes for the Malaysian National Annex (NA) to EC8. The values inside the parentheses show the derivation of design PGA based on the importance factor recommended in the draft NA. In summary, the hybrid model is a combination of results from conventional PSHA of historical earthquakes from regional sources (Model 1) and results from PSHA based on broad source zone modelling in accordance with global seismicity data (Model 2). For Peninsular Malaysia, Model 2 dominates the demand at the short period range, whereas Model 1 dominates the demand at the long period range (fig. 2a - 2b). For Sarawak, Model 2 dominates the demand across the entire period range (fig. 2c 2d); and for Sabah, Model 1 dominates the whole response spectrum model (fig. 2e 2f). Figure 2a. Superimposing the two components for hybrid model for Peninsular Malaysia Figure 2b. Hybrid model for Peninsular Malaysia 3
4 Figure 2c. Superimposing the two components for hybrid model for Sarawak Figure 2d. Hybrid model for Sarawak Figure 2e. Superimposing the two components for hybrid model for Sabah 4
5 Importance Class Figure 2f. Hybrid model for Sabah Table 1. Design PGA on rock sites for Peninsular Malaysia,Sarawak and Sabah Descriptions Design PGA (g s) Peninsular Malaysia and Sarawak I Minor constructions 0.06 II III IV Ordinary buildings (individual dwellings or shops in low rise buildings) Buildings of large occupancies (condominiums, shopping centres, schools and public buildings) Lifeline built facilities (hospitals, emergency services, power plants and communication facilities) (~0.8 x 0.1/1.5) 0.07 (~0.1/1.5) Reference PGA (notional 475 years RP) 0.08 (~1.2 x 0.1/1.5) 0.10 (consistent with RP of 2475years) Design PGA (g s) Sabah 0.10 (~0.8 x 0.18/1.5) 0.12 (~0.18/1.5) Reference PGA (notional 475 years RP) 0.14 (~1.2 x 0.18/1.5) 0.18 (consistent with RP of 2475 years) 5 COST ANALYSIS FOR THIN SIZE ELEMENTS There are over thousands of single and double storey link houses in Malaysia. Being a common feature in Malaysia, the first question that comes to the minds of engineers is how susceptible these buildings are to an earthquake. In order to understand the implications of a seismic event and designing to earthquake loading in Malaysia, a cost study was undertaken to estimate whether there is a significant change in cost on a typical link house of single and double storey. The cost study will provide an easy to understand figure which indicates the amount of cost increase in Malaysia due to the introduction of the seismic design standard. 5.1 General Building description Link houses are a common feature in Malaysia, where buildings are developed with houses sharing a common partition wall. The houses are commonly 1 to 2 story high (fig. 3). 5
6 Figure 3. Typical link houses in Malaysia A typical link house building (fig. 4a - 4b) developed in Malaysia common for the 3 regions of Malaysia (i.e. Peninsular Malaysia, Sabah and Sarawak) is chosen. The structure is built out of reinforced concrete of grade C20/25, reinforcing steel with yield strength of 460 MPa and 250 MPa, for longitudinal reinforcement and stirrups, respectively. Element sizing of the models are tabulated in Table 2. Two models were developed for each type of building, One was subjected to static loading and one was subjected to both static and earthquake loading. The two replicas was analysed and designed as assuming they are uncracked. They are subjected to pushover analysis in order to determine whether the sections are cracked or not. If the buildings fall under cracked sections, the property of the building is assumed cracked, thus reducing the stiffness of all members by 50% as per EC8 requirements. Figure 4a. 1 storey building Figure 4b. 2 storey building Table 2. Beam and Column Sizing for 1story and 2story building models 1 story building 2 story building Party Wall Beams 225x450 (mm) 225x450 (mm) Internal beams 125x450 (mm) 125x450 (mm) Party wall columns 225x300 (mm) 225x300 (mm) Internal Columns - 125x300 (mm) 6
7 5.2 Loading applied For gravity loads, a superimposed dead load of 2.5 kpa is adopted and a live load of 1.5 kpa as per Malaysian building regulations (Laws of Malaysia, 2006). Wind load is applied as per BS-EN , with a basic wind speed of 20 m/s inside city. Notional imperfection load is applied taking a maximum inclination of 1/200. This amounts to 0.5% of the ultimate dead and live. Earthquake loading is applied utilizing the Malaysian hybrid design spectrum. All buildings are assumed to be located in stiff soil similar to typical Malaysian soil conditions (Tsang et al., 2015). For computation of natural period, is a function of stiffness and mass of the building. The design seismic mass can be formulated using equation 1. Where G k and Q k the characteristic dead and imposed mass respectively. Ψ E is take as 0.3 taking into account the likelihood that imposed load is not present over the entire structure during the earthquake. 5.3 Pushover Analysis and Stiffness Reduction Under the clause of EC8, the stiffness of the cracked structural elements can be taken as 50% of its original un-cracked stiffness. In order to determine whether the structure is cracked or un-cracked, a pushover analysis is performed. The capacity curve (fig. 5a) gives the maximum displacement in meters of the building against lateral load in kilo newton. The building experiences its first crack at 360kN (α 1 ). Hence the pushover capacity curve was superimposed over the acceleration displacement response spectrum of Peninsular Malaysia to determine the performance point (fig. 5b). Since the performance point is above the α 1 (which is the first crack) indicating that the structure has cracked.. Hence concluding that the building has cracked and the analysis is carried out under cracked section properties. This reduction in stiffness increased the first mode period of the 1 storey from 0.25 s to 0.35 s and the 2-storey building from 0.48 s to 0.67 s. (1) Figure 5a. Pushover capacity curve Figure 5b. Pushover demand curve 5.4 Analysis and Results Cost Estimation is calculated under static load conditions (dead load, imposed load, wind load and notional imperfection load) and under combined static and earthquake load. 1 standard deviation is calculated with the 2 samples of 1 story and 2 story and applied to the costing to cover uncertainties. The highest percentage increase in cost for Sabah is 5% for the 2-storey building and 4.7% for 1 storey. Similarly the structural building cost increase for Peninsular Malaysia/Sarawak is 4.2% for 2- storey and 2.0% (fig. 6). Figure 7 summarises the base shear for the corresponding regions when subjected to earthquake. 7
8 Figure 6. Preliminary cost estimation (Structural building cost) Figure 7. Base shear graph 6 SUMMARY AND CONCLUDING REMARKS A hybrid model consisting of local and distant earthquake is developed for Malaysia dividing Malaysia into the 3 major regions, Peninsular Malaysia, Sabah and Sarawak. The reference PGA value based on a notional return period of 475 years is accordingly 0.07g (being 2/3 of 0.1g) for Peninsular Malaysia and Sarawak and 0.12g (being 2/3 of 0.18g) for Sabah. Cost estimation (with 1 standard deviation) for Peninsular Malaysia/Sarawak on typical link single 2.0% and double storey link houses 4.2 %. The highest cost increase in Sabah with 5% increase in cost for double storey link house and 4.7% for single storey link house. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: The authors would like to thank the IEM Earthquake Technical Committee for the technical and financial support given to conduct the research. Valuable intellectual inputs by Ir E.P. Lim and Mr A.Z. Zaeem along with the other active participants from EC8 TC are also gratefully acknowledged. REFERENCES: Atkinson G.M. and Boore D.M Earthquake ground-motion prediction equations for eastern North America, Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. 96 (6) Bird P., Kreemer C. and Holt W. E A long term forecast of shallow seismicity based on the global strain 8
9 rate map. Seismological Research Letters. 81 (2) Eurocode 8 Design of structures for earthquake resistance. EN Part 1: General rules, seismic actions and rules for buildings. IEM position document (2005, approved 2007). Position paper on issues related to earthquake. The Institution of Engineers, Malaysia. Lam N.T.K Program GENQKE User s Guide. Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, The University of Melbourne. Lam N.T.K., Tsang H.H., Lumantarna E. and Wilson J.L Local intraplate earthquakes considerations for Singapore. Institution of Engineering Singapore Part A: Civil & Structural Engineering. Published on line 21 November (In press) Lam N.T.K., Wilson J.L. and Tsang H.H Modelling Earthquake Ground Motions By Stochastic Methods. Stochastic Control. SCIYO Publisher. Chapter 23: Lam N.T.K., Balendra T., Wilson J.L. and Srikanth V Seismic Load Estimates of Distant Subduction Earthquakes Affecting Singapore. Engineering Structures. 31 (5) Laws of Malaysia Uniform Building By-Laws. MDC Publishers Printers Sdn. Bhd. Megawati K. and Pan T.C Ground-motion attenuation relationship for the Sumatran megathrust earthquakes. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics Pappin J.W., Yim P.H.I. and Koo C.H.R An approach for seismic design in Malaysia following the principles of Eurocode 8. IEM Jurutera (the monthly bulletin of the Institution of Engineers, Malaysia). October Issue Pan T.C., Megawati K. and Lim C.L Seismic shaking in Singapore due to past Sumatran earthquakes. Journal of Earthquake and Tsunami. 1 (1) Tsang H.H., Wilson J.L. and Lam N.T.K Recommended site classification scheme and design spectrum model for regions of low-to-moderate seismicity. Proceedings of the tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering, 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia. 9
Seismic Hazard Modelling for Malaysia
 Seismic Hazard Modelling for Malaysia Nelson Lam 1, Hing-Ho Tsang 2, Daniel Looi 3,Elisa Lumantarna 1 and John Wilson 2 1 Department of Infrastructure Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne,
Seismic Hazard Modelling for Malaysia Nelson Lam 1, Hing-Ho Tsang 2, Daniel Looi 3,Elisa Lumantarna 1 and John Wilson 2 1 Department of Infrastructure Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne,
An Approach for Seismic Design in Malaysia following the Principles of Eurocode 8
 An Approach for Seismic Design in Malaysia following the Principles of Eurocode 8 by Dr J. W. Pappin, Ms. P. H. I. Yim and Mr. C. H. R. Koo 1. INTRODUCTION Eurocode 8 is a useful document providing systematic
An Approach for Seismic Design in Malaysia following the Principles of Eurocode 8 by Dr J. W. Pappin, Ms. P. H. I. Yim and Mr. C. H. R. Koo 1. INTRODUCTION Eurocode 8 is a useful document providing systematic
Seismic site response analysis for Australia
 Seismic site response analysis for Australia Anita Amirsardari 1, Elisa Lumantarna 2, Helen M. Goldsworthy 3 1. Corresponding Author. PhD Candidate, Department of Infrastructure Engineering, University
Seismic site response analysis for Australia Anita Amirsardari 1, Elisa Lumantarna 2, Helen M. Goldsworthy 3 1. Corresponding Author. PhD Candidate, Department of Infrastructure Engineering, University
THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR
 JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
Intricacies of addressing distant and local earthquakes in Malaysia in the official design standard EC8 Malaysia NA
 Intricacies of addressing distant and local earthquakes in Malaysia in the official design standard EC8 Malaysia NA Jeffrey C. L. Chiang 1, Daniel T.W. Looi 2 and M.C. Hee 3 1. Corresponding Author. Dean
Intricacies of addressing distant and local earthquakes in Malaysia in the official design standard EC8 Malaysia NA Jeffrey C. L. Chiang 1, Daniel T.W. Looi 2 and M.C. Hee 3 1. Corresponding Author. Dean
Evaluation of the Seismic Load Level in Korea based on Global Earthquake Records
 Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 215, Sydney, Australia Evaluation of the Seismic Load Level in Korea based on
Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 215, Sydney, Australia Evaluation of the Seismic Load Level in Korea based on
Two-Day Symposium/Workshop on Earthquake Engineering In Malaysia and Asia Pacific Region 2013 By Ir. Ong Sang Woh and Engr.
 JURUTERA ONLINE 2014 CIVIL & STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING TECHNICAL DIVISION, IEM Two-Day Symposium/Workshop on Earthquake Engineering In Malaysia and Asia Pacific Region 2013 By Ir. Ong Sang Woh and Engr. Looi
JURUTERA ONLINE 2014 CIVIL & STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING TECHNICAL DIVISION, IEM Two-Day Symposium/Workshop on Earthquake Engineering In Malaysia and Asia Pacific Region 2013 By Ir. Ong Sang Woh and Engr. Looi
Malaysian Journal of Civil Engineering 22(1) : (2010) Malaysia
 AN INVESTIGATION ON THE ATTENUATION CHARACTERISTICS OF DISTANT GROUND MOTIONS IN PENINSULAR MALAYSIA BY COMPARING VALUES OF RECORDED WITH ESTIMATED PGA AND PGV Sherliza Zaini Sooria 1*, Sumio Sawada 2,
AN INVESTIGATION ON THE ATTENUATION CHARACTERISTICS OF DISTANT GROUND MOTIONS IN PENINSULAR MALAYSIA BY COMPARING VALUES OF RECORDED WITH ESTIMATED PGA AND PGV Sherliza Zaini Sooria 1*, Sumio Sawada 2,
A hybrid probabilistic seismic hazard analysis of a low and moderate seismic region: Sri Lanka a case study
 Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia A hybrid probabilistic seismic hazard analysis of a low
Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia A hybrid probabilistic seismic hazard analysis of a low
ATTENUATION FUNCTION RELATIONSHIP OF SUBDUCTION MECHANISM AND FAR FIELD EARTHQUAKE
 ATTENUATION FUNCTION RELATIONSHIP OF SUBDUCTION MECHANISM AND FAR FIELD EARTHQUAKE Rozaimi Mohd Noor 1, Saffuan Wan Ahmad 2, Azlan Adnan 1 and Ramli Nazir 1 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi
ATTENUATION FUNCTION RELATIONSHIP OF SUBDUCTION MECHANISM AND FAR FIELD EARTHQUAKE Rozaimi Mohd Noor 1, Saffuan Wan Ahmad 2, Azlan Adnan 1 and Ramli Nazir 1 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi
Seismic Vulnerability Assessment of Wood-frame Buildings in Southwestern British Columbia
 Seismic Vulnerability Assessment of Wood-frame Buildings in Southwestern British Columbia K. Goda University of Bristol, United Kingdom G.M. Atkinson University of Western Ontario, Canada ABSTRACT: The
Seismic Vulnerability Assessment of Wood-frame Buildings in Southwestern British Columbia K. Goda University of Bristol, United Kingdom G.M. Atkinson University of Western Ontario, Canada ABSTRACT: The
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND SEISMIC INPUT TO TSUNAMI MODELING FOR MICROZONATION OF MEURAXA DISTRICT CITY OF BANDA ACEH
 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND SEISMIC INPUT TO TSUNAMI MODELING FOR MICROZONATION OF MEURAXA DISTRICT CITY OF BANDA ACEH I W. Sengara 1, Hendarto 1, P. Sumiartha 1, H. Latief 1, S.B. Kusuma 1 and Munirwansjah
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND SEISMIC INPUT TO TSUNAMI MODELING FOR MICROZONATION OF MEURAXA DISTRICT CITY OF BANDA ACEH I W. Sengara 1, Hendarto 1, P. Sumiartha 1, H. Latief 1, S.B. Kusuma 1 and Munirwansjah
SEISMIC SLOPE STABILITY ASSESSMENT IN A MODERATE SEISMICITY REGION, HONG KONG
 SEISMIC SLOPE STABILITY ASSESSMENT IN A MODERATE SEISMICITY REGION, HONG KONG R.C.H. Koo, V. Kong 2, H.H. Tsang 3 and J.W. Pappin 4 Geotechnical Engineer, Ove Arup & Partners Hong Kong Ltd. 2 PhD Student,
SEISMIC SLOPE STABILITY ASSESSMENT IN A MODERATE SEISMICITY REGION, HONG KONG R.C.H. Koo, V. Kong 2, H.H. Tsang 3 and J.W. Pappin 4 Geotechnical Engineer, Ove Arup & Partners Hong Kong Ltd. 2 PhD Student,
Usability of the Next Generation Attenuation Equations for Seismic Hazard Assessment in Malaysia
 Azlan Adnan, Patrick Liq Yee Tiong, Yue Eng Chow/ International Journal of Engineering Vol. 2 Issue 1, Jan-Feb 212, pp.639-644 Usability of the Next Generation Attenuation Equations for Seismic Hazard
Azlan Adnan, Patrick Liq Yee Tiong, Yue Eng Chow/ International Journal of Engineering Vol. 2 Issue 1, Jan-Feb 212, pp.639-644 Usability of the Next Generation Attenuation Equations for Seismic Hazard
PROPOSED CHANGE TO THE 2012 BUILDING CODE O. REG. 332/12 AS AMENDED
 Ministry of Municipal Affairs PROPOSED CHANGE TO THE 2012 BUILDING CODE O. REG. 332/12 AS AMENDED CHANGE NUMBER: SOURCE: B-04-01-15 Ontario-NBC CODE REFERENCE: Division B / 4.1.8.2. Division B / 4.1.8.4.
Ministry of Municipal Affairs PROPOSED CHANGE TO THE 2012 BUILDING CODE O. REG. 332/12 AS AMENDED CHANGE NUMBER: SOURCE: B-04-01-15 Ontario-NBC CODE REFERENCE: Division B / 4.1.8.2. Division B / 4.1.8.4.
Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk
 Prepared for: The Municipality of Anchorage Planning Department and the Geotechnical Advisory Commission Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk Prepared
Prepared for: The Municipality of Anchorage Planning Department and the Geotechnical Advisory Commission Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk Prepared
Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code
 Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code Mark D. Petersen (U.S. Geological Survey) http://earthquake.usgs.gov/hazmaps/ Seismic hazard analysis
Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code Mark D. Petersen (U.S. Geological Survey) http://earthquake.usgs.gov/hazmaps/ Seismic hazard analysis
Ground Motion Studies for Critical Sites in North-West Bangladesh
 Science & Technology Conference 2011 Vienna, June 8-10, 2011 Ground Motion Studies for Critical Sites in North-West Bangladesh Dr. Tahmeed M. Al Hussaini Professor of Civil Engineering, Bangladesh University
Science & Technology Conference 2011 Vienna, June 8-10, 2011 Ground Motion Studies for Critical Sites in North-West Bangladesh Dr. Tahmeed M. Al Hussaini Professor of Civil Engineering, Bangladesh University
Soil-Structure Interaction in Nonlinear Pushover Analysis of Frame RC Structures: Nonhomogeneous Soil Condition
 ABSTRACT: Soil-Structure Interaction in Nonlinear Pushover Analysis of Frame RC Structures: Nonhomogeneous Soil Condition G. Dok ve O. Kırtel Res. Assist., Department of Civil Engineering, Sakarya University,
ABSTRACT: Soil-Structure Interaction in Nonlinear Pushover Analysis of Frame RC Structures: Nonhomogeneous Soil Condition G. Dok ve O. Kırtel Res. Assist., Department of Civil Engineering, Sakarya University,
Pushover Seismic Analysis of Bridge Structures
 Pushover Seismic Analysis of Bridge Structures Bernardo Frère Departamento de Engenharia Civil, Arquitectura e Georrecursos, Instituto Superior Técnico, Technical University of Lisbon, Portugal October
Pushover Seismic Analysis of Bridge Structures Bernardo Frère Departamento de Engenharia Civil, Arquitectura e Georrecursos, Instituto Superior Técnico, Technical University of Lisbon, Portugal October
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard.
 Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
Harmonized European standards for construction in Egypt
 Harmonized European standards for construction in Egypt EN 1998 - Design of structures for earthquake resistance Jean-Armand Calgaro Chairman of CEN/TC250 Organised with the support of the Egyptian Organization
Harmonized European standards for construction in Egypt EN 1998 - Design of structures for earthquake resistance Jean-Armand Calgaro Chairman of CEN/TC250 Organised with the support of the Egyptian Organization
Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design
 Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design *Jun-Kyoung Kim 1), Soung-Hoon Wee 2) and Seong-Hwa Yoo 2) 1) Department of Fire Protection and Disaster Prevention, Semyoung University,
Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design *Jun-Kyoung Kim 1), Soung-Hoon Wee 2) and Seong-Hwa Yoo 2) 1) Department of Fire Protection and Disaster Prevention, Semyoung University,
Seismic Hazard of Singapore and Malaysia
 Seismic Hazard of Singapore and Malaysia T Balendra 1 & Z. Li 1 Department of Civil Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore 1, Email: cvebalen@gmail.com ABSTRACT: This article reviews
Seismic Hazard of Singapore and Malaysia T Balendra 1 & Z. Li 1 Department of Civil Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore 1, Email: cvebalen@gmail.com ABSTRACT: This article reviews
L. Danciu, D. Giardini, J. Wößner Swiss Seismological Service ETH-Zurich Switzerland
 BUILDING CAPACITIES FOR ELABORATION OF NDPs AND NAs OF THE EUROCODES IN THE BALKAN REGION Experience on the field of seismic hazard zonation SHARE Project L. Danciu, D. Giardini, J. Wößner Swiss Seismological
BUILDING CAPACITIES FOR ELABORATION OF NDPs AND NAs OF THE EUROCODES IN THE BALKAN REGION Experience on the field of seismic hazard zonation SHARE Project L. Danciu, D. Giardini, J. Wößner Swiss Seismological
SOIL-BASEMENT STRUCTURE INTERACTION ANALYSIS ON DYNAMIC LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE ON BASEMENT WALL
 International Conference on Earthquake Engineering and Disaster Mitigation, Jakarta, April 1-15, SOIL-BASEMENT STRUCTURE INTERACTION ANALYSIS ON DYNAMIC LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE ON BASEMENT WALL Nurrachmad
International Conference on Earthquake Engineering and Disaster Mitigation, Jakarta, April 1-15, SOIL-BASEMENT STRUCTURE INTERACTION ANALYSIS ON DYNAMIC LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE ON BASEMENT WALL Nurrachmad
Comparison of response spectra from Australian earthquakes and North American attenuation models
 Comparison of response spectra from Australian earthquakes and North American attenuation models T. Dhu, T. Allen, P. Cummins, M. Leonard, D. Robinson and J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, ACT,
Comparison of response spectra from Australian earthquakes and North American attenuation models T. Dhu, T. Allen, P. Cummins, M. Leonard, D. Robinson and J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, ACT,
Hazard and Vulnerability of Moderate Seismicity Regions
 Hazard and Vulnerability of Moderate Seismicity Regions presented by Professor Tso-Chien PAN Dean, College of Engineering Director, 25 October 2010 DRM GDLN Session on Earthquake Vulnerability Reduction
Hazard and Vulnerability of Moderate Seismicity Regions presented by Professor Tso-Chien PAN Dean, College of Engineering Director, 25 October 2010 DRM GDLN Session on Earthquake Vulnerability Reduction
COLUMN INTERACTION EFFECT ON PUSH OVER 3D ANALYSIS OF IRREGULAR STRUCTURES
 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, Paper No. 6 COLUMN INTERACTION EFFECT ON PUSH OVER D ANALYSIS OF IRREGULAR STRUCTURES Jaime DE-LA-COLINA, MariCarmen HERNANDEZ
th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, Paper No. 6 COLUMN INTERACTION EFFECT ON PUSH OVER D ANALYSIS OF IRREGULAR STRUCTURES Jaime DE-LA-COLINA, MariCarmen HERNANDEZ
Assessment of New Zealand scaling procedure of ground motions for liquid storage tanks
 Assessment of New Zealand scaling procedure of ground motions for liquid storage tanks M. Ormeno, M. Geddes, T. Larkin & N. Chouw The University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand. 2014 NZSEE Conference
Assessment of New Zealand scaling procedure of ground motions for liquid storage tanks M. Ormeno, M. Geddes, T. Larkin & N. Chouw The University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand. 2014 NZSEE Conference
SITE RESPONSE ANALYSIS FOR SEISMIC DESIGN OF A 48-STOREY TOWER BUILDING IN JAKARTA
 SITE RESPONSE ANALYSIS FOR SEISMIC DESIGN OF A 48-STOREY TOWER BUILDING IN JAKARTA I Wayan Sengara 1, Davy Sukamta 2 and Putu Sumiartha 3 1 Head, Geotechnical Engineering Laboratory, Engineering Center
SITE RESPONSE ANALYSIS FOR SEISMIC DESIGN OF A 48-STOREY TOWER BUILDING IN JAKARTA I Wayan Sengara 1, Davy Sukamta 2 and Putu Sumiartha 3 1 Head, Geotechnical Engineering Laboratory, Engineering Center
Update on the It s Our Fault project
 Report 12.552 Date 29 October 2012 File 12/01/01 Committee Author CDEM Group Bruce Pepperell, Regional Manager, WREMO Update on the It s Our Fault project 1. Purpose To inform the CDEM Group of progress
Report 12.552 Date 29 October 2012 File 12/01/01 Committee Author CDEM Group Bruce Pepperell, Regional Manager, WREMO Update on the It s Our Fault project 1. Purpose To inform the CDEM Group of progress
WHAT SEISMIC HAZARD INFORMATION THE DAM ENGINEERS NEED FROM SEISMOLOGISTS AND GEOLOGISTS?
 WHAT SEISMIC HAZARD INFORMATION THE DAM ENGINEERS NEED FROM SEISMOLOGISTS AND GEOLOGISTS? Martin WIELAND 1 ABSTRACT For large dam projects a site-specific seismic hazard analysis is usually recommended.
WHAT SEISMIC HAZARD INFORMATION THE DAM ENGINEERS NEED FROM SEISMOLOGISTS AND GEOLOGISTS? Martin WIELAND 1 ABSTRACT For large dam projects a site-specific seismic hazard analysis is usually recommended.
The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update
 The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update 01-October-2009 Christophe Vigny Directeur de recherches at CNRS Laboratoire de Géologie Geoscience Dept. Of ENS,
The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update 01-October-2009 Christophe Vigny Directeur de recherches at CNRS Laboratoire de Géologie Geoscience Dept. Of ENS,
Chapter 6 Seismic Design of Bridges. Kazuhiko Kawashima Tokyo Institute of Technology
 Chapter 6 Seismic Design of Bridges Kazuhiko Kawashima okyo Institute of echnology Seismic Design Loading environment (dead, live, wind, earthquake etc) Performance criteria for gravity (deflection, stresses)
Chapter 6 Seismic Design of Bridges Kazuhiko Kawashima okyo Institute of echnology Seismic Design Loading environment (dead, live, wind, earthquake etc) Performance criteria for gravity (deflection, stresses)
Damage Estimation of the Road Bridge Structure Using the Seismic Hazard map for BCM in Hokkaido, Japan
 Damage Estimation of the Road Bridge Structure Using the Seismic Hazard map for BCM in Hokkaido, Japan T. Sato & H. Nishi Civil Engineerring Research Institute for Cold Region, PWRI,Japan T. Ikeda & Y.
Damage Estimation of the Road Bridge Structure Using the Seismic Hazard map for BCM in Hokkaido, Japan T. Sato & H. Nishi Civil Engineerring Research Institute for Cold Region, PWRI,Japan T. Ikeda & Y.
Lecture-09 Introduction to Earthquake Resistant Analysis & Design of RC Structures (Part I)
 Lecture-09 Introduction to Earthquake Resistant Analysis & Design of RC Structures (Part I) By: Prof Dr. Qaisar Ali Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar www.drqaisarali.com 1 Topics Introduction Earthquake
Lecture-09 Introduction to Earthquake Resistant Analysis & Design of RC Structures (Part I) By: Prof Dr. Qaisar Ali Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar www.drqaisarali.com 1 Topics Introduction Earthquake
SEISMIC BASE ISOLATION
 SEISMIC BASE ISOLATION DESIGN OF BASE ISOLATION SYSTEMS IN BUILDINGS FILIPE RIBEIRO DE FIGUEIREDO SUMMARY The current paper aims to present the results of a study for the comparison of different base isolation
SEISMIC BASE ISOLATION DESIGN OF BASE ISOLATION SYSTEMS IN BUILDINGS FILIPE RIBEIRO DE FIGUEIREDO SUMMARY The current paper aims to present the results of a study for the comparison of different base isolation
Distribution Restriction Statement Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
 CECW-ET Engineer Manual 1110-2-6050 Department of the Army U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Washington, DC 20314-1000 EM 1110-2-6050 30 June 1999 Engineering and Design RESPONSE SPECTRA AND SEISMIC ANALYSIS
CECW-ET Engineer Manual 1110-2-6050 Department of the Army U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Washington, DC 20314-1000 EM 1110-2-6050 30 June 1999 Engineering and Design RESPONSE SPECTRA AND SEISMIC ANALYSIS
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon
 Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
Vertical to Horizontal (V/H) Ratios for Large Megathrust Subduction Zone Earthquakes
 Vertical to Horizontal (V/H) Ratios for Large Megathrust Subduction Zone Earthquakes N.J. Gregor Consultant, Oakland, California, USA N.A. Abrahamson University of California, Berkeley, USA K.O. Addo BC
Vertical to Horizontal (V/H) Ratios for Large Megathrust Subduction Zone Earthquakes N.J. Gregor Consultant, Oakland, California, USA N.A. Abrahamson University of California, Berkeley, USA K.O. Addo BC
Incorporating simulated Hikurangi subduction interface spectra into probabilistic hazard calculations for Wellington
 Incorporating simulated Hikurangi subduction interface spectra into probabilistic hazard calculations for Wellington G.H. McVerry & C. Holden GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New Zealand. 2014 NZSEE Conference
Incorporating simulated Hikurangi subduction interface spectra into probabilistic hazard calculations for Wellington G.H. McVerry & C. Holden GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New Zealand. 2014 NZSEE Conference
A Modified Response Spectrum Analysis Procedure (MRSA) to Determine the Nonlinear Seismic Demands of Tall Buildings
 Fawad A. Najam Pennung Warnitchai Asian Institute of Technology (AIT), Thailand Email: fawad.ahmed.najam@ait.ac.th A Modified Response Spectrum Analysis Procedure (MRSA) to Determine the Nonlinear Seismic
Fawad A. Najam Pennung Warnitchai Asian Institute of Technology (AIT), Thailand Email: fawad.ahmed.najam@ait.ac.th A Modified Response Spectrum Analysis Procedure (MRSA) to Determine the Nonlinear Seismic
[Hussain, 4(9): September 2017] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor
![[Hussain, 4(9): September 2017] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor [Hussain, 4(9): September 2017] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor](/thumbs/89/98828424.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES SEISMIC ANALYSIS OF MULTI STOREYED BUILDING WITH SOFT STOREY Mohammed Irfan Hussain* *Asst. Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Chaitanya Institute
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES SEISMIC ANALYSIS OF MULTI STOREYED BUILDING WITH SOFT STOREY Mohammed Irfan Hussain* *Asst. Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Chaitanya Institute
Geo-Marine Letters Volume 36, 2016, electronic supplementary material
 1 Geo-Marine Letters Volume 36, 016, electronic supplementary material Submarine landslides offshore Vancouver Island along the northern Cascadia margin, British Columbia: why preconditioning is likely
1 Geo-Marine Letters Volume 36, 016, electronic supplementary material Submarine landslides offshore Vancouver Island along the northern Cascadia margin, British Columbia: why preconditioning is likely
PEAK GROUND HORIZONTAL ACCELERATION ATTENUATION RELATIONSHIP FOR LOW MAGNITUDES AT SHORT DISTANCES IN SOUTH INDIAN REGION
 PEAK GROUND HORIZONTAL ACCELERATION ATTENUATION RELATIONSHIP FOR LOW MAGNITUDES AT SHORT DISTANCES IN SOUTH INDIAN REGION C.Srinivasan 1, M.L.Sharma 2, J. Kotadia 2 and Y.A.Willy 1 1. National Institute
PEAK GROUND HORIZONTAL ACCELERATION ATTENUATION RELATIONSHIP FOR LOW MAGNITUDES AT SHORT DISTANCES IN SOUTH INDIAN REGION C.Srinivasan 1, M.L.Sharma 2, J. Kotadia 2 and Y.A.Willy 1 1. National Institute
Comparison between Different Shapes of Structure by Response Spectrum Method of Dynamic Analysis
 Open Journal of Civil Engineering, 2016, 6, 131-138 Published Online March 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojce http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojce.2016.62012 Comparison between Different Shapes
Open Journal of Civil Engineering, 2016, 6, 131-138 Published Online March 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojce http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojce.2016.62012 Comparison between Different Shapes
Inelastic shear response of RC coupled structural walls
 Inelastic shear response of RC coupled structural walls E. Morariu EDIT Structural, Bucuresti, Rumania. T. Isakovic, N. Eser & M. Fischinger Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, University of Ljubljana,
Inelastic shear response of RC coupled structural walls E. Morariu EDIT Structural, Bucuresti, Rumania. T. Isakovic, N. Eser & M. Fischinger Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, University of Ljubljana,
Modeling Of Earthquake Ground Motion for Tbilisi Region
 P a g e 2 Vol. 10 Issue 3 (Ver 1.0) July 2010 Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Modeling Of Earthquake Ground Motion for Tbilisi Region P. Rekvava 1 k. Mdivani 2 GJRE Classification E (FOR) 090702,
P a g e 2 Vol. 10 Issue 3 (Ver 1.0) July 2010 Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Modeling Of Earthquake Ground Motion for Tbilisi Region P. Rekvava 1 k. Mdivani 2 GJRE Classification E (FOR) 090702,
FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA
 FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA Myo Thant 1, Hiroshi Kawase 2, Subagyo Pramumijoyo 3, Heru Hendrayana
FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA Myo Thant 1, Hiroshi Kawase 2, Subagyo Pramumijoyo 3, Heru Hendrayana
CITIES WITHOUT A SEISMIC CODE I: HAZARD ASSESSMENT
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 129 CITIES WITHOUT A SEISMIC CODE I: HAZARD ASSESSMENT Kusnowidjaja MEGAWATI 1, Nelson T.K. LAM 2, Adrian
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 129 CITIES WITHOUT A SEISMIC CODE I: HAZARD ASSESSMENT Kusnowidjaja MEGAWATI 1, Nelson T.K. LAM 2, Adrian
Alireza Mehdipanah BEHAVIOUR OF BUILDINGS FEATURING TRANSFER BEAMS IN THE REGIONS OF LOW TO MODERATE SEISMICITY
 BEHAVIOUR OF BUILDINGS FEATURING TRANSFER BEAMS IN THE REGIONS OF LOW TO MODERATE SEISMICITY Alireza Mehdipanah PhD Candidate at The University of Melbourne SUPERVISORS: A/PROF. NELSON LAM DR. ELISA LUMANTARNA
BEHAVIOUR OF BUILDINGS FEATURING TRANSFER BEAMS IN THE REGIONS OF LOW TO MODERATE SEISMICITY Alireza Mehdipanah PhD Candidate at The University of Melbourne SUPERVISORS: A/PROF. NELSON LAM DR. ELISA LUMANTARNA
Representative ground-motion ensembles for several major earthquake scenarios in New Zealand
 Representative ground-motion ensembles for several major earthquake scenarios in New Zealand K. Tarbali & B.A. Bradley Department of Civil and Natural Resources Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch.
Representative ground-motion ensembles for several major earthquake scenarios in New Zealand K. Tarbali & B.A. Bradley Department of Civil and Natural Resources Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch.
Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan
 Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan M.A. Shah Micro Seismic Studies Programme, Islamabad, Pakistan Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Islamabad, Pakistan M.
Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan M.A. Shah Micro Seismic Studies Programme, Islamabad, Pakistan Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Islamabad, Pakistan M.
The 10 th Anniversary of the Newcastle Earthquake -
 The 10 th Anniversary of the Newcastle Earthquake - Lessons Learnt Proceedings of a conference held by the Australian Earthquake Engineering Society Sydney, New South Wales 1999 This work was published
The 10 th Anniversary of the Newcastle Earthquake - Lessons Learnt Proceedings of a conference held by the Australian Earthquake Engineering Society Sydney, New South Wales 1999 This work was published
Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments
 Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments Vicki-Ann Dimas 1,2 and Gary Gibson 3 1. Corresponding Author. Seismic Hazard Analyst, Seismology Research
Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments Vicki-Ann Dimas 1,2 and Gary Gibson 3 1. Corresponding Author. Seismic Hazard Analyst, Seismology Research
Seismic Hazard Assessment and Site Response Evaluation in Hong Kong. Abstract
 Seismic Hazard Assessment and Site Response Evaluation in Hong Kong J. W. Pappin and R. Koo. Director, Ove Arup & Partners Hong Kong Ltd, Level, 8 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong Email : Jack.pappin@arup.com.
Seismic Hazard Assessment and Site Response Evaluation in Hong Kong J. W. Pappin and R. Koo. Director, Ove Arup & Partners Hong Kong Ltd, Level, 8 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong Email : Jack.pappin@arup.com.
Modelling Strong Ground Motions for Subduction Events in the Wellington Region, New Zealand
 Proceedings of the Ninth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Society 14-16 April, 2011, Auckland, New Zealand Modelling Strong Ground Motions for Subduction Events
Proceedings of the Ninth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Society 14-16 April, 2011, Auckland, New Zealand Modelling Strong Ground Motions for Subduction Events
Comparison of Structural Models for Seismic Analysis of Multi-Storey Frame Buildings
 Comparison of Structural Models for Seismic Analysis of Multi-Storey Frame Buildings Dj. Ladjinovic, A. Raseta, A. Radujkovic & R. Folic University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Technical Sciences, Novi Sad,
Comparison of Structural Models for Seismic Analysis of Multi-Storey Frame Buildings Dj. Ladjinovic, A. Raseta, A. Radujkovic & R. Folic University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Technical Sciences, Novi Sad,
Eleventh U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering Integrating Science, Engineering & Policy June 25-29, 2018 Los Angeles, California
 Eleventh U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering Integrating Science, Engineering & Policy June 25-29, 2018 Los Angeles, California Site-Specific MCE R Response Spectra for Los Angeles Region
Eleventh U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering Integrating Science, Engineering & Policy June 25-29, 2018 Los Angeles, California Site-Specific MCE R Response Spectra for Los Angeles Region
Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington
 Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington A. Christophersen, D.A. Rhoades, R.J. Van Dissen, C. Müller, M.W. Stirling, G.H. McVerry & M.C. Gerstenberger GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New
Time-varying and long-term mean aftershock hazard in Wellington A. Christophersen, D.A. Rhoades, R.J. Van Dissen, C. Müller, M.W. Stirling, G.H. McVerry & M.C. Gerstenberger GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New
Comparison of Base Shear Force Method in the Seismic Design Codes of China, America and Europe
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Vols. 66-69 (202) pp 2345-2352 Online available since 202/May/4 at www.scientific.net (202) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:0.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.66-69.2345
Applied Mechanics and Materials Vols. 66-69 (202) pp 2345-2352 Online available since 202/May/4 at www.scientific.net (202) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:0.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.66-69.2345
PADANG EARTHQUAKE, WEST SUMATRA ON MARCH 6, 2007
 PADANG EARTHQUAKE, WEST SUMATRA ON MARCH 6, 2007 EARTHQUAKE DETAILS The U. S. Geological Survey (USGS) informed a strong earthquake struck west Sumatra on Tuesday March 6, 2007 at 10:49 with a magnitude
PADANG EARTHQUAKE, WEST SUMATRA ON MARCH 6, 2007 EARTHQUAKE DETAILS The U. S. Geological Survey (USGS) informed a strong earthquake struck west Sumatra on Tuesday March 6, 2007 at 10:49 with a magnitude
Geotechnical Site Classification and Croatian National Annex for EC 8
 Geotechnical Site Classification and Croatian National Annex for EC 8 by Predrag Kvasnika University of Zagreb Faculty of Mining-Geology and Petroleum engineering Outline General Motivation Site classification
Geotechnical Site Classification and Croatian National Annex for EC 8 by Predrag Kvasnika University of Zagreb Faculty of Mining-Geology and Petroleum engineering Outline General Motivation Site classification
Susitna-Watana Hydroelectric Project (FERC No ) Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Study Study Plan Section 16.6
 (FERC No. 14241) Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Study Study Plan Section 16.6 Initial Study Report Part A: Sections 1-6, 8-9 Prepared for Prepared by MWH / Fugro June 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction...
(FERC No. 14241) Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Study Study Plan Section 16.6 Initial Study Report Part A: Sections 1-6, 8-9 Prepared for Prepared by MWH / Fugro June 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction...
Site specific seismic hazard assessment a case study of Guanyin offshore wind farm 場址特定地震危害度評估 - 以觀音離岸風力發電廠為例
 Site specific seismic hazard assessment a case study of Guanyin offshore wind farm 場址特定地震危害度評估 - 以觀音離岸風力發電廠為例 Supervisor : Dr. Chyi-Tyi Lee and Dr. Kuo-Fong Ma Speaker : Jia-Cian Gao 2018/04/26 1 1. A
Site specific seismic hazard assessment a case study of Guanyin offshore wind farm 場址特定地震危害度評估 - 以觀音離岸風力發電廠為例 Supervisor : Dr. Chyi-Tyi Lee and Dr. Kuo-Fong Ma Speaker : Jia-Cian Gao 2018/04/26 1 1. A
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS. Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1
 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 Seismic Hazard Analysis Deterministic procedures Probabilistic procedures USGS hazard
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 Seismic Hazard Analysis Deterministic procedures Probabilistic procedures USGS hazard
Damping Scaling of Response Spectra for Shallow CCCCCCCCCrustalstallPaper Crustal Earthquakes in Active Tectonic Title Line Regions 1 e 2
 Damping Scaling of Response Spectra for Shallow CCCCCCCCCrustalstallPaper Crustal Earthquakes in Active Tectonic Title Line Regions 1 e 2 S. Rezaeian U.S. Geological Survey, Golden, CO, USA Y. Bozorgnia
Damping Scaling of Response Spectra for Shallow CCCCCCCCCrustalstallPaper Crustal Earthquakes in Active Tectonic Title Line Regions 1 e 2 S. Rezaeian U.S. Geological Survey, Golden, CO, USA Y. Bozorgnia
Seismic Performance of RC Building Using Spectrum Response and Pushover Analyses
 Seismic Performance of RC Building Using Spectrum Response and Pushover Analyses Mehani Youcef (&), Kibboua Abderrahmane, and Chikh Benazouz National Earthquake Engineering Research Center (CGS), Algiers,
Seismic Performance of RC Building Using Spectrum Response and Pushover Analyses Mehani Youcef (&), Kibboua Abderrahmane, and Chikh Benazouz National Earthquake Engineering Research Center (CGS), Algiers,
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative VANUATU September 211 Country Risk Profile: VANUATU is expected to incur, on average, 48 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative VANUATU September 211 Country Risk Profile: VANUATU is expected to incur, on average, 48 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and
Commentary Appendix A DEVELOPMENT OF MAXIMUM CONSIDERED EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTION MAPS FIGURES THROUGH
 Commentary Appendix A DEVELOPMENT OF MAXIMUM CONSIDERED EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTION MAPS FIGURES 3.3-1 THROUGH 3.3-14 BACKGROUND The maps used in the Provisions through 1994 provided the A a (effective peak
Commentary Appendix A DEVELOPMENT OF MAXIMUM CONSIDERED EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTION MAPS FIGURES 3.3-1 THROUGH 3.3-14 BACKGROUND The maps used in the Provisions through 1994 provided the A a (effective peak
PROBABILISTIC PERFORMANCE-BASED SEISMIC DEMAND MODEL FOR R/C FRAME BUILDINGS
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1547 PROBABILISTIC PERFORMANCE-BASED SEISMIC DEMAND MODEL FOR R/C FRAME BUILDINGS Srdjan JANKOVIC 1 and
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1547 PROBABILISTIC PERFORMANCE-BASED SEISMIC DEMAND MODEL FOR R/C FRAME BUILDINGS Srdjan JANKOVIC 1 and
SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT AND SITE RESPONSE EVALUATION IN HONG KONG
 Proceedings of the SECED Young Engineers Conference - March 00, University of Bath, Bath, UK SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT AND SITE RESPONSE EVALUATION IN HONG KONG Raymond Koo, Vickie Kong, Matthew Free,,
Proceedings of the SECED Young Engineers Conference - March 00, University of Bath, Bath, UK SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT AND SITE RESPONSE EVALUATION IN HONG KONG Raymond Koo, Vickie Kong, Matthew Free,,
Overview of National Seismic Hazard Maps for the next National Building Code
 Overview of National Seismic Hazard Maps for the next National Building Code John Adams Earthquakes Canada Geological Survey of Canada Copyright. Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, 2004 CSCE Workshop
Overview of National Seismic Hazard Maps for the next National Building Code John Adams Earthquakes Canada Geological Survey of Canada Copyright. Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, 2004 CSCE Workshop
SAFETY CHECK OF SONDUR DAM FOR CHANGED SEISMIC CONDITION Aryak shori 1, R.K.Tripthi 2 and M. K. Verma 3
 ABSTRACT SAFETY CHECK OF SONDUR DAM FOR CHANGED SEISMIC CONDITION Aryak shori 1, R.K.Tripthi 2 and M. K. Verma 3 The paper presents Seismic Hazard Analysis (SHA) of Sondur dam situated in Chhattisgarh
ABSTRACT SAFETY CHECK OF SONDUR DAM FOR CHANGED SEISMIC CONDITION Aryak shori 1, R.K.Tripthi 2 and M. K. Verma 3 The paper presents Seismic Hazard Analysis (SHA) of Sondur dam situated in Chhattisgarh
DETERMINATION OF PERFORMANCE POINT IN CAPACITY SPECTRUM METHOD
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
Seismic risk assessment of conventional steel constructions to the hazard of three earthquake types in Southwestern British Columbia
 Seismic risk assessment of conventional steel constructions to the hazard of three earthquake types in Southwestern British Columbia F.E. Pina Department of Civil Engineering, Universidad de Santiago de
Seismic risk assessment of conventional steel constructions to the hazard of three earthquake types in Southwestern British Columbia F.E. Pina Department of Civil Engineering, Universidad de Santiago de
Environmental Contours for Determination of Seismic Design Response Spectra
 Environmental Contours for Determination of Seismic Design Response Spectra Christophe Loth Modeler, Risk Management Solutions, Newark, USA Jack W. Baker Associate Professor, Dept. of Civil and Env. Eng.,
Environmental Contours for Determination of Seismic Design Response Spectra Christophe Loth Modeler, Risk Management Solutions, Newark, USA Jack W. Baker Associate Professor, Dept. of Civil and Env. Eng.,
Analysis of post-elastic damage measures in Nonlinear Dynamic Analyses of RC structures
 Analysis of post-elastic damage measures in Nonlinear Dynamic Analyses of RC structures Cristina Cantagallo 1), Guido Camata 2) and Enrico Spacone 3) 1), 2), 3) Department of Engineering and Geology, University
Analysis of post-elastic damage measures in Nonlinear Dynamic Analyses of RC structures Cristina Cantagallo 1), Guido Camata 2) and Enrico Spacone 3) 1), 2), 3) Department of Engineering and Geology, University
Development of Earthquake Risk-Targeted Ground Motions for Indonesian Earthquake Resistance Building Code SNI
 Development of Earthquake Risk-Targeted Ground Motions for Indonesian Earthquake Resistance Building Code SNI 1726-2012 I WayanSengara Associate Professor, Faculty of Civil and Environment Engineering,
Development of Earthquake Risk-Targeted Ground Motions for Indonesian Earthquake Resistance Building Code SNI 1726-2012 I WayanSengara Associate Professor, Faculty of Civil and Environment Engineering,
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TUVALU is expected to incur, on average,. million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones. In the next 5 years, has
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TUVALU is expected to incur, on average,. million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones. In the next 5 years, has
SHAKE MAPS OF STRENGTH AND DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS FOR ROMANIAN VRANCEA EARTHQUAKES
 SHAKE MAPS OF STRENGTH AND DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS FOR ROMANIAN VRANCEA EARTHQUAKES D. Lungu 1 and I.-G. Craifaleanu 2 1 Professor, Dept. of Reinforced Concrete Structures, Technical University of Civil Engineering
SHAKE MAPS OF STRENGTH AND DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS FOR ROMANIAN VRANCEA EARTHQUAKES D. Lungu 1 and I.-G. Craifaleanu 2 1 Professor, Dept. of Reinforced Concrete Structures, Technical University of Civil Engineering
Nonlinear static analysis PUSHOVER
 Nonlinear static analysis PUSHOVER Adrian DOGARIU European Erasmus Mundus Master Course Sustainable Constructions under Natural Hazards and Catastrophic Events 520121-1-2011-1-CZ-ERA MUNDUS-EMMC Structural
Nonlinear static analysis PUSHOVER Adrian DOGARIU European Erasmus Mundus Master Course Sustainable Constructions under Natural Hazards and Catastrophic Events 520121-1-2011-1-CZ-ERA MUNDUS-EMMC Structural
Seismic Evaluation of Tailing Storage Facility
 Australian Earthquake Engineering Society 2010 Conference, Perth, Western Australia Seismic Evaluation of Tailing Storage Facility Jonathan Z. Liang 1, David Elias 2 1 Senior Geotechnical Engineer, GHD
Australian Earthquake Engineering Society 2010 Conference, Perth, Western Australia Seismic Evaluation of Tailing Storage Facility Jonathan Z. Liang 1, David Elias 2 1 Senior Geotechnical Engineer, GHD
DISPLACEMENT MODELLING OF INTRAPLATE EARTHQUAKES
 ISET Journal of Earthquake Technology, Paper No. 439, Vol. 41, No. 1, March 24, pp. 15-52 DISPLACEMENT MODELLING OF INTRAPLATE EARTHQUAKES Nelson Lam and John Wilson Department of Civil and Environmental
ISET Journal of Earthquake Technology, Paper No. 439, Vol. 41, No. 1, March 24, pp. 15-52 DISPLACEMENT MODELLING OF INTRAPLATE EARTHQUAKES Nelson Lam and John Wilson Department of Civil and Environmental
NONLINEAR SEISMIC SOIL-STRUCTURE (SSI) ANALYSIS USING AN EFFICIENT COMPLEX FREQUENCY APPROACH
 NONLINEAR SEISMIC SOIL-STRUCTURE (SSI) ANALYSIS USING AN EFFICIENT COMPLEX FREQUENCY APPROACH Dan M. GHIOCEL 1 ABSTRACT The paper introduces a novel approach for modeling nonlinear hysteretic behavior
NONLINEAR SEISMIC SOIL-STRUCTURE (SSI) ANALYSIS USING AN EFFICIENT COMPLEX FREQUENCY APPROACH Dan M. GHIOCEL 1 ABSTRACT The paper introduces a novel approach for modeling nonlinear hysteretic behavior
CONSIDERATION OF EARTHQUAKES IN THE DESIGN OF THE MACAU TOWER
 CONSIDERATION OF EARTHQUAKES IN THE DESIGN OF THE MACAU TOWER Dejan R NOVAKOV 1, Rob D JURY 2 And Mark S SPENCER 3 SUMMARY Macau Tower, a 338 m tall communication and observation tower currently under
CONSIDERATION OF EARTHQUAKES IN THE DESIGN OF THE MACAU TOWER Dejan R NOVAKOV 1, Rob D JURY 2 And Mark S SPENCER 3 SUMMARY Macau Tower, a 338 m tall communication and observation tower currently under
CAPACITY SPECTRUM FOR STRUCTURES ASYMMETRIC IN PLAN
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 004 Paper No. 653 CAPACITY SPECTRUM FOR STRUCTURES ASYMMETRIC IN PLAN B. K. Raghu Prasad 1, A. Seetha Ramaiah and A.
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 004 Paper No. 653 CAPACITY SPECTRUM FOR STRUCTURES ASYMMETRIC IN PLAN B. K. Raghu Prasad 1, A. Seetha Ramaiah and A.
CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY
 32 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 GENERAL In 1910, the seismological society of America identified the three groups of earthquake problems, the associated ground motions and the effect on structures. Indeed
32 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 GENERAL In 1910, the seismological society of America identified the three groups of earthquake problems, the associated ground motions and the effect on structures. Indeed
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH BOARD. TRB Webinar Program Direct Displacement Based Seismic Design of Bridges. Thursday, June 22, :00-3:30 PM ET
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH BOARD TRB Webinar Program Direct Displacement Based Seismic Design of Bridges Thursday, June 22, 2017 2:00-3:30 PM ET The Transportation Research Board has met the standards and
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH BOARD TRB Webinar Program Direct Displacement Based Seismic Design of Bridges Thursday, June 22, 2017 2:00-3:30 PM ET The Transportation Research Board has met the standards and
Severe accident risk assessment for Nuclear. Power Plants
 PSA 2017- September 2017 IRSN Severe accident risk assessment for Nuclear * Power Plants * Enhancing nuclear safety An original approach to derive seismic fragility curves - Application to a PWR main steam
PSA 2017- September 2017 IRSN Severe accident risk assessment for Nuclear * Power Plants * Enhancing nuclear safety An original approach to derive seismic fragility curves - Application to a PWR main steam
Preview Mode: ON Earthquake Risk in Stable, Intraplate Regions: the Case. of Perth, Australia. Historical Seismicity in the Perth Region
 Preview Mode: ON Earthquake Risk in Stable, Intraplate Regions: the Case Editor s note: There is often a tendency to discount earthquake risk in of Perth, Australia 02.2010 AIRCurrents regions where earthquakes
Preview Mode: ON Earthquake Risk in Stable, Intraplate Regions: the Case Editor s note: There is often a tendency to discount earthquake risk in of Perth, Australia 02.2010 AIRCurrents regions where earthquakes
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TIMOR-LESTE September Timor-Leste is expected to incur, on average, 5.9 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones.
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Assessment And Financing Initiative TIMOR-LESTE September Timor-Leste is expected to incur, on average, 5.9 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and tropical cyclones.
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake
 News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN
 EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN A MODERATE SEISMICITY REGION, HONG KONG
 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -, 4 Paper No. 9 SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN A MODERATE SEISMICITY REGION, HONG KONG Matthew FREE, Jack PAPPIN, Raymond KOO
th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -, 4 Paper No. 9 SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN A MODERATE SEISMICITY REGION, HONG KONG Matthew FREE, Jack PAPPIN, Raymond KOO
Probabilistic damage control seismic design of bridges using structural reliability concept
 Probabilistic damage control seismic design of bridges using structural reliability concept A. Saini Doctoral Student, University of Nevada, Reno, NV, USA A. Vosooghi Bridge Engineer III, Ph.D., P.E.,
Probabilistic damage control seismic design of bridges using structural reliability concept A. Saini Doctoral Student, University of Nevada, Reno, NV, USA A. Vosooghi Bridge Engineer III, Ph.D., P.E.,
Seismic Source Characterization in Siting New Nuclear Power Plants in the Central and Eastern United States
 Seismic Source Characterization in Siting New Nuclear Power Plants in the Central and Eastern United States ABSTRACT : Yong Li 1 and Nilesh Chokshi 2 1 Senior Geophysicist, 2 Deputy Director of DSER Nuclear
Seismic Source Characterization in Siting New Nuclear Power Plants in the Central and Eastern United States ABSTRACT : Yong Li 1 and Nilesh Chokshi 2 1 Senior Geophysicist, 2 Deputy Director of DSER Nuclear
Comparative study between the push-over analysis and the method proposed by the RPA for the evaluation of seismic reduction coefficient
 33, Issue (27) 5-23 Journal of Advanced Research in Materials Science Journal homepage: www.akademiabaru.com/arms.html ISSN: 2289-7992 Comparative study between the push-over analysis and the method proposed
33, Issue (27) 5-23 Journal of Advanced Research in Materials Science Journal homepage: www.akademiabaru.com/arms.html ISSN: 2289-7992 Comparative study between the push-over analysis and the method proposed
Recolouring GSHAP: Challenging the status quo of Australian earthquake hazard
 Recolouring GSHAP: Challenging the status quo of Australian earthquake hazard Trevor Allen, Jonathan Griffin, Dan Clark, Hadi Ghasemi, Mark Leonard & Theodora Volti Australia in the Global Context SCRs
Recolouring GSHAP: Challenging the status quo of Australian earthquake hazard Trevor Allen, Jonathan Griffin, Dan Clark, Hadi Ghasemi, Mark Leonard & Theodora Volti Australia in the Global Context SCRs
