SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF GEOTHERMAL FIELDS IN THE PANNONIAN BASIN - A CASE STUDY
|
|
|
- Brittney Mathews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROCEEDINGS. Twenty-Fm Workshop on OCoU~amal Raavou Engiuoxing Stanford University. Stanford. czlifomia, January SGP-TR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF GEOTHERMAL FIELDS IN THE PANNONIAN BASIN - A CASE STUDY Dumitru Panul, Horia Mitrofanl, Viorel S e d FORADEX SA, 5 Milcov St., Bucharest, Romania 2 DATA EXPERT S.R.L., Av. Alex. Serbanescu str. 49/221>, Bucharest I, Romania ABSTRACl- As suggested by the discusssion of Barker, 1988, on the influence of flow dimension on the late-time behaviour of the generalized line source solution, it was inferred that observed long term reservoir pressure decline was an outcome of the 1D (linear) flow geometry, indicated by well tests. The detrimental effects of the reservoir pressure decline can be partly mitigated by taking advantage of the two-phase flow which occurs when methane, originally dissolved m the geothermal brine, is released within the well bore. Sustainable artesiar withdrawal scenarios for existing geothermal fields are devised, based on an accurate prediction of bottomhole pressure decline trends and an adequate selection of the diameter ana length of the production tubing. Overall analysis and forecast are performed by an integrated reservoir & well bore simulator. INTRODUCTION Aquifers located in Pliocene detritic deposits of the Pannonian Basin (fig. 1) provide a significant part of the geothermal resources of Hungary, Slovakia, Slovenia, Croatia, Serbia and Romania (Arpasi, 1995, Franko et al., 1989, Rajver et al., 1995, Cubric and Jelic, 1995, Panu, 1995). Multi-layered reservoirs, occuring at m depth, include slightly consolidated sandstones interbedded with shales, saturated with low temperature (50-IOOOC) geothermal fluids. As a result of long term withdrawal, the well fields display a steady reservoir pressure decline trend and associated reductions of the extracted flowrates (Franko et al., 1989, Plavita and Cohut, 1990, Arpasi. 1995, Cubric and Jelic, 1995, Szita, 1995). Attempts to control pressure decline by reinjection have been performed in Hungary and Romania. However, Hungarian experiments are reported to be non-conclusive (Szita, 1995), while tests carried out in Romania definitely proved unsuccessful, due to the extremely high wellhead pressures required (50-90 bar).. Hodmez 0 LOO k Fig. 1. Panonian Basin. Main geothermal fields tapping Pliocene reservoirs. 507
2 ERV-CHARACTERIZATION ACCORDING TO WELL TESTS Based on single- and mu1ti:well tests and assuming a conventional radial flow model, described by the Theis-Jacob line source solution, reservoirs parameters such as transmissivity (MI) and storativity ($h) have been computed for geothermal wells which tap the Pliocene deposits of the Pannonian Basin (Franko et al., 1989, Plavita and Cohut, 1990, 1992). The computed parameters have been used to provide forecasts on the subsequent reservoir pressure drop, either for a specific well field (Plavita and Cohut, 1992), or for a whole region of the Pannonian Basin (Franko et al., 1989). However, no attempt was made to fit a simulated pressure evolution to long term data recorded during exploitation. I i g o 51 F simulated ualucs - linear flow mddd 0 0 = 0 recorded rater level atmulated vm1u.m - rsdlal flow model.... flaw rats at the production r.u reservoir indicates (Barker, 1988): a quasi-steady state can be reached only for flow dimensions equal to 2 (i.e. the commonly assumed radial cylindrical flow described by the Theis-Jacob solution), or more, On the contrary, the draw-down in a we11 is strongly time-dependent at flow dimensions smaller than 2. Sediment assemblages in the Pannonian Basin have been shown to derive from the progradation of delta systems into an isolated lacustrine basin (Vakarcs et al., 1994). The sandstones are channel fills and bars, while the siltstones and shales represent lower energy environments, such as interchannel and levee deposits. Under such circumstances, a 1D (linear) flow geometry might prove appropriate in describing the hydrodynamic behaviour of the reservoirs. Following Barker, 1988, the specific draw-down of a well of effective radius r, which taps a horizontal, homogenous aquifer that extends mainly along one dimension and displays constant throughflow area R, permeability k, porosity (I and composite (fluid and formation) compressibilty c, is: 1 Fig Tomnatic observation well. Draw-down history. When such a comparison is performed (fig. 2), it becomes obvious that although over short periods (a few months) modeled and observation data match, there is no more agreement when the long term (several years) reservoir pressure evolution is considered. According to the model, the maximum draw-down should stabilize after the first production-recovery cycle of one year, while the actual reservoir pressure continues to decline during the whole subsequent period. The pressure stabilization predicted by the model is characteristic for the assumed 2D flow geameuy, as the generalization at arbitrary flow dimensions of the line source solution for a horizontal, infinite 508 where, Ap is the differential pressure, q is the discharge and p is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid in the aquifer. Since the relationship is an asymptotic approximation of the exact solution, for interference tests it can only be used to model late time responses. As for single well tests, it applies to the entire time span over which records are normally performed. The validity of the ID model was first tested by plotting the bottomhole pressure recorded during single well build-up or draw-down tests against the square root of time. Figure 3 illustrates the results obtained in the geothermal well field of Jimbolia Romania. The distinct, increasingly gentler slopes
3 displayed by the diagrams suggest that hydraulic properties (permeability, storage capacity, throughflow area) improve away from the tested well. As a general rule, only poor productivity aquifer bodies have been intercepted by wells drilled so far, hence the pattern of the diagram probably reflects also an hierarchy in distribution: there are frequent linear aquifer bodies of low productivity, yet connected to fewer ones of moderate productivity, that at their turn are connected to even fewer high productivity reservoir sections, a.s.0. - <!D (linear) flow model: prewvt appropnstely plotted vs (time)'" a 0, C V %? 0.05 CXlIDwell 4630: shut-off at 25.0 I/r well 4630: flow star( with 25.0 I/s well 1563: nhul-off at 12.3 I/s : /60 1/ I2 24 4a Lime (houn) Fig. 3. Jimbolia geothermal field. Single well bottomhole pressure transients A rather similar pattern was obtained when plotting against the square root of time the results of a test performed on well FGV-1 Vlcany (Slovakia), published by Frank0 et al., 1989 (fig. 4). The correlation between pressure decline, flow rate and time. derived for the ultimate, late time period of the well tests, was subsequently used to simulate the evolution of pressure in the reservoir over the years since exploitation started. Figure 2 illustrates the draw-down history matching conducted for an observation well in the geothermal well field of Tomnatic, Romania. It clearly indicates that the assumed ID reservoir model is more appropriate than the alternative, 2D model. PRODUCTMTY ASSESSMENT, INCLUDING WELL BO RE EFFECT S Methane, originally dissolved in the geothermal water of the Pliocene reservoirs (1-2 m3/m3 gashater ratio), is released in the upper section of the well bores (Frank0 et al., 1989, Plavita and Cohut, 1990, 1992, Cubric and Jelic, 1995, Panu, 1995, Szita, 1995). The resulting two-phase flow regime controls the correlation between the bottomhole pressure evolution and that of the wellhead pressure. A well bore simulator, based on Orkiszewski, 1967, algorithm, is used in connection with a reservoir simulator, within the integrated software package GEOTHERM, developed by DATA EXPERT. The fundamental scheme of GEOTHERM can be described as follows: RESERVOIR BEHAVIOUR 0 Fig SO time (dsys) FGV-1 Vlcany geothermal well Single well bottomhole pressure transients TEMPERATURE Variable temperature input at the inflow depth is considered, in the form of an idow te&ermm versus total extracted fow rate correlation. PRESSURE Dianct procedures are available for two basic assumptions: + time-independent reservolr pressure ( the procedure devised for this case dso assumes that the effects of interference of other wells in the field can be neglected); + reservoir pressure decline during exploitation by assuming 1, 2 or 3D radial flow geometry; 509
4 WELL BORE BEHAVIOUR COOLING A power law relates the cooling of the geothermal fluid along the well bore (linear temperature drop assumed) to total extracted flow rate. PRESSURE DROP pressure drop within the actual casing and tubing COntigLUatiOn of the Well can be simulated for liquid only and two-phase (either bubble, or slug flow) conditions. as g-., - Wl 1524 Downhole RessureDevlaiion Completedlntervd The predictions provided by these basic functions are integrated into assessments of the wellhead thermal and discharge performance. DEVELO PINENT OF A SUSTAINABLE EXPLOITATION SCEN ARIO An example of sustainable exploitation scenario devised by using GEOTHERM is given for well 1524, in the geothermal field of Sannicolau Mare, Romania. The considered well does not interfere with other wells in the field, as it taps a distinct reservoir. First the well bore flow regime parameters (roughness and free methane content) are calibrated, by checking simulated pressure profiles against recorded downhole pressure profiles (fig 5). In the given example, a first guess of "zero gadwater ratio" proves to be unsatisfactory: in the upper section of the well bore, where presumably free gas is released from the solution, the deviation between the simulated and the recorded pressures is severe. Yet when an appropriate gadwater ratio of 1.55 m3im3 is chosen, the deviation becomes close to zero all along the well bore. A sigdkant deviation still persists only at the wellhead, as a result of carbonate scaling whch sometimes may clog the upper few tens ot meters of the existing production tubing. Further, the relationship which describes the reservoir behaviour (pressure versus flow rate and time) is calibrated against the history of shut-off piezometric levels and against shut-off and flowing well bottomhole pressures (fig. 6). Fig. 5. Recorded minus simulated downhole pressure profiles Finally, the simulated bottomhole pressure is used in connection with simulated "up the well bore" pressure drops, in order to reconstruct the wellhead pressure evolution, which is checked against actually recorded wellhead pressures (fig. 6). When an overall satisfactory match between the recorded and the modeled pressure values has been achieved, the simulation is extrapolated in the future, according to a hypothetical withdrawal scenario (fig. 7)- The configuration of an artesian well bore discharging two-phase (gas-water) fluid normally includes a production tubing, introduced inside the casing. Its main purpose is to force the two-phase flow through an area smaller than that of the casing, which, according to specific conditions, may result in a significantly smaller pressure drop and in correspondingly enhanced artesian flowrates, or prolonged artesian lifetime. The tubing can be also extracted,priodically, to be cleaned of scaling products. As a result of complex behaviour due to two-phase flow, optimum tubing selection is a trial and error process, conducted by observing the criterion "the highest wellhead pressure for the required flow rate". As figure 7 indicates, for the same exploitation scenario, alternative tubing configurations result in 510
5 I yeor 2-1.m 4 E B s $ io.oo l6.w woterlevelevocmon a I I 'so 1964 I lw3 Waf Fig. 6. Well 1524 Sanuicolau Mare Production history 51 1
6 - P 1 A.0 c. p? 120 P Extmctedflwrate toting 5' X 220 m 0.20 i ' ~ " ' l ' ' l ' ~ l ' ~ l ' ~ 1 ~ ' l ' % w2 mvea tubing7'x220m Fig. 7. Well 1524 Sannicolau Mare Simulated wellhead pressure history and forecast 512
7 dramatically different artesian lifetimes. The most critical parameter appears to be the tubing diameter: 5 1/2" can secure an artesian lifetime of 10 years, as compared to both the immediately nmwer 5" and the immediately wider 7", which are not able to sustain the required free flow regime for more than 4, and respectively 3 years. For a given tubing diameter, the tubing length has to be appropriately selected as well. Wellhead pressures secured by stepwise increasing tubing lengths are successively computed for the considered provisional flow rate (fig. 8). The tubing length which provides the highest wellhead pressure is identified as a result ,.. I...,..,...,,,* and duration of withdrawal, but also the adopted well bore configuration. The authors wish to thank the company FORADEX for the permission to publish the observation data and the simulation results. We are also grateful to our colleagues Felicia Serban, Otilia Militaru. Cristina Radu. Magdalena Stoia and Mihaela Preda for their assistance in preparing and processing the data. Arpasi, M. (1995). "Country update from Hungary", Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress, Florence, My, Barker, J..k (1988), "A generalized radial flow model for hydraulic tests in fractured rock", Water Resources Research, 24, curng cenga [mi Fig. 8. Well 1524 Sannicolau Mare. Simulated wellhead pressure as a function of the 5 1/2" tubing length, for a discharge of 18 Us. CONCLUSIONS 1. Inability to control declining reservoir pressures and to secure desired artesian discharges hindered the exploitation of Pliocene geothermal reservoirs in the Pannoniah Basin. 2. An appropriate reservoir engineering approach integrates the influence of specific factors: the prevailingly ID reservoir development and the extensive two-phase flow within the well bore. 3. The related software GEOTHERM readily evaluates existing and alternative exploitation schemes. Attributes of sustainable development scenarios devised in this way are not only the rates Cubric, 5;. and Jelic, K. (1995), "Geothermal resource potential of the Republic of Croatia", Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress, Florence, My, Franko, 0.. Bodis, D., Fendek, M., Remsik, A., Janci, J. and Kral, M. (1989). "Methods of research and evaluation of geothermal resources in pore environment of Pannonian Basin", Zapadne Karpaty, Ser. Hydrogeologia a Inz. Geol., 8, Geol. Ust. D. Shua, Bratislava, Oriciszewski, J. (1967), "Predicting two-phase pressure drops in vertical pipe", Journal of Petroleum Technology, June, Panu, D. (1995), "Geothermal resources in Romania - Results and prospects ", Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress, Florence, Italy, Plavita, R. and Cohut, I. (1990). "Interference tests in the Western Plain of Romania", Geothermal Resources Council Transactions, 14,
8 Plavita, R. and Cohut, I. (1992). "Industrial Szita, G. (1995). "The situation of harnessing prospects for the Sacuieni geothermal area in Bihor geothermal energy in Hungary", Proceedings of the county, Romania", Geothermics, 21, World Geothermal Congress, Florence, Italy, Rajver, D., Ravnik, D., Zlebnik, L. and Cebulj, A. (1995), "Utilization of geothermal energy in Vakarcs, G., Vail, P.R., Tari, G., Pogacsas, Gy., Slovenia", Proceedings of the World Geothermal Mattick, R.E. and Szabo, A. (1994), "Third-order Congress, Florence, Italy, Middle Miocene-Early Pliocene depositional sequences in the prograding delta complex of the Pannonian Basin", Tectonophysics, 240,
HEAT TRANSFER IN A LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL WELL
 HEAT TRANSFER IN A LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL WELL Marcel Rosca University of Oradea, Armata Romana 5, RO-37 Oradea, Romania Key Words: low enthalpy, numerical modeling, wellbore heat transfer, Oradea reservoir,
HEAT TRANSFER IN A LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL WELL Marcel Rosca University of Oradea, Armata Romana 5, RO-37 Oradea, Romania Key Words: low enthalpy, numerical modeling, wellbore heat transfer, Oradea reservoir,
EVALUATING HEAT FLOW AS A TOOL FOR ASSESSING GEOTHERMAL RESOURCES
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31-February 2, 2005 SGP-TR-176 EVALUATING HEAT FLOW AS A TOOL FOR ASSESSING GEOTHERMAL
PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31-February 2, 2005 SGP-TR-176 EVALUATING HEAT FLOW AS A TOOL FOR ASSESSING GEOTHERMAL
INTERPRETATION OF INTERFERENCE EFFECTS IN THREE PRODUCTION WELLS IN THE KAWERAU GEOTHERMAL FIELD, NEW ZEALAND. Lynell Stevens and Kevin J Koorey
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-First Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 22-24, 1996 SGP-TR-151 INTERPRETATION OF INTERFERENCE EFFECTS IN THREE PRODUCTION
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-First Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 22-24, 1996 SGP-TR-151 INTERPRETATION OF INTERFERENCE EFFECTS IN THREE PRODUCTION
THERMAL STIMULATION OF GEOTHERMAL WELLS: A REVIEW OF FIELD DATA. Auckland, New Zealand 2 Mighty River Power
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 11-13, 2013 SGP-TR-198 THERMAL STIMULATION OF GEOTHERMAL WELLS: A REVIEW OF FIELD
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 11-13, 2013 SGP-TR-198 THERMAL STIMULATION OF GEOTHERMAL WELLS: A REVIEW OF FIELD
Numerical Simulation Study of the Mori Geothermal Field, Japan
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2010 Bali, Indonesia, 25-29 April 2010 Numerical Simulation Study of the Mori Geothermal Field, Japan Kazuyoshi Osada 1, Mineyuki Hanano 2, Kei Sato 1, Tatsuya Kajiwara
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2010 Bali, Indonesia, 25-29 April 2010 Numerical Simulation Study of the Mori Geothermal Field, Japan Kazuyoshi Osada 1, Mineyuki Hanano 2, Kei Sato 1, Tatsuya Kajiwara
Rate Transient Analysis COPYRIGHT. Introduction. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Learning Objectives Rate Transient Analysis Core Introduction This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define the rate time analysis Distinguish between traditional pressure transient
Learning Objectives Rate Transient Analysis Core Introduction This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define the rate time analysis Distinguish between traditional pressure transient
Inflow Performance 1
 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Radial Flow Equation 3. Straight Line Inflow Performance Relationship 4. Vogel Inflow Performance Relationship 5. Other Inflow Performance Relationship 6. Establishing
1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Radial Flow Equation 3. Straight Line Inflow Performance Relationship 4. Vogel Inflow Performance Relationship 5. Other Inflow Performance Relationship 6. Establishing
Developing Geothermal Energy in Croatia by Using Old Oil Wells for Power Generation
 PROCEEDINGS, 41st Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 22-24, 2016 SGP-TR-209 Developing Geothermal Energy in Croatia by Using Old Oil Wells
PROCEEDINGS, 41st Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 22-24, 2016 SGP-TR-209 Developing Geothermal Energy in Croatia by Using Old Oil Wells
RESERVOIR MODELING OF GEOTHERMAL ENERGY PRODUCTION FROM STRATIGRAPHIC RESERVOIRS IN THE GREAT BASIN
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February -3, 23 SGP-TR-98 RESERVOIR MODELING OF GEOTHERMAL ENERGY PRODUCTION FROM STRATIGRAPHIC
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February -3, 23 SGP-TR-98 RESERVOIR MODELING OF GEOTHERMAL ENERGY PRODUCTION FROM STRATIGRAPHIC
GeothermEx, Inc. GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FOR THE SCIENTIFIC OBSERVATION HOLE PROGRAM, KILAUEA EAST RIFT ZONE, HAWAII TASK 1 REPORT
 (415) 527 9876 CABLE ADDRESS- GEOTHERMEX TELEX 709152 STEAM UD FAX (415) 527-8164 Geotherm Ex, Inc. RICHMOND. CALIFORNIA 94804-5829 GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FOR THE SCIENTIFIC OBSERVATION
(415) 527 9876 CABLE ADDRESS- GEOTHERMEX TELEX 709152 STEAM UD FAX (415) 527-8164 Geotherm Ex, Inc. RICHMOND. CALIFORNIA 94804-5829 GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FOR THE SCIENTIFIC OBSERVATION
Assessing the Effect of Realistic Reservoir Features on the Performance of Sedimentary Geothermal Systems
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 39, 205 Assessing the Effect of Realistic Reservoir Features on the Performance of Sedimentary Geothermal Systems Luis E. Zerpa, JaeKyoung Cho, and Chad Augustine 2 Colorado School
GRC Transactions, Vol. 39, 205 Assessing the Effect of Realistic Reservoir Features on the Performance of Sedimentary Geothermal Systems Luis E. Zerpa, JaeKyoung Cho, and Chad Augustine 2 Colorado School
PRELIMINARY EFFORTS TO COUPLE TETRAD WITH GEOPHYSICS MODELS
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 28-30, 2002 SGP-TR-171 PRELIMINARY EFFORTS TO COUPLE TETRAD WITH GEOPHYSICS MODELS
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 28-30, 2002 SGP-TR-171 PRELIMINARY EFFORTS TO COUPLE TETRAD WITH GEOPHYSICS MODELS
CALCULATION OF STEAM AND WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITIES USING FIELD PRODUCTION DATA, WITH LABORATORY VERIFICATION
 CALCULATION OF STEAM AND WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITIES USING FIELD PRODUCTION DATA, WITH LABORATORY VERIFICATION Jericho L. P. Reyes, Chih-Ying Chen, Keen Li and Roland N. Horne Stanford Geothermal Program,
CALCULATION OF STEAM AND WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITIES USING FIELD PRODUCTION DATA, WITH LABORATORY VERIFICATION Jericho L. P. Reyes, Chih-Ying Chen, Keen Li and Roland N. Horne Stanford Geothermal Program,
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE THREE-MATERIAL DOWNHOLE FLOW FIELD IN HYDROTHERMAL JET DRILLING
 2017 WJTA-IMCA Conference and Expo October 25-27, 2017 New Orleans, Louisiana Paper NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE THREE-MATERIAL DOWNHOLE FLOW FIELD IN HYDROTHERMAL JET DRILLING Xianzhi Song, Zehao Lyu, Haizhu
2017 WJTA-IMCA Conference and Expo October 25-27, 2017 New Orleans, Louisiana Paper NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE THREE-MATERIAL DOWNHOLE FLOW FIELD IN HYDROTHERMAL JET DRILLING Xianzhi Song, Zehao Lyu, Haizhu
Geothermal Resources of Romania
 Marcel G. Roșca University of Oradea, Romania Faculty of Energy Engineering and Industrial Management Energy Engineering Department mrosca@uoradea.ro 1. Introduction 2. Hydrothermal resources 3. Potential
Marcel G. Roșca University of Oradea, Romania Faculty of Energy Engineering and Industrial Management Energy Engineering Department mrosca@uoradea.ro 1. Introduction 2. Hydrothermal resources 3. Potential
AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF BOILING HEAT CONVECTION WITH RADIAL FLOW IN A FRACTURE
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 25-27, 1999 SGP-TR-162 AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF BOILING HEAT CONVECTION
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 25-27, 1999 SGP-TR-162 AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF BOILING HEAT CONVECTION
Geochemical Modelling of Low-Temperature Geothermal Fields from Bihor County, Romania
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Geochemical Modelling of Low-Temperature Geothermal Fields from Bihor County, Romania Oana Stǎnǎşel, Iulian Stǎnǎşel University
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Geochemical Modelling of Low-Temperature Geothermal Fields from Bihor County, Romania Oana Stǎnǎşel, Iulian Stǎnǎşel University
PRESSURE PERTURBATIONS IN TWO PHASE GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ASSOCIATED WITH SEISMISITY
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 27-29, 2003 SGP-TR-173 PRESSURE PERTURBATIONS IN TWO PHASE GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 27-29, 2003 SGP-TR-173 PRESSURE PERTURBATIONS IN TWO PHASE GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR
Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS
 Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
Numerical Simulation of Devolution and Evolution of Steam-Water Two-Phase Zone in a Fractured Geothermal Reservoir at Ogiri, Japan
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 37, 2013 Numerical Simulation of Devolution and Evolution of Steam-Water Two-Phase Zone in a Fractured Geothermal Reservoir at Ogiri, Japan Yohei Tateishi 1, Ryuichi Itoi 1, Toshiaki
GRC Transactions, Vol. 37, 2013 Numerical Simulation of Devolution and Evolution of Steam-Water Two-Phase Zone in a Fractured Geothermal Reservoir at Ogiri, Japan Yohei Tateishi 1, Ryuichi Itoi 1, Toshiaki
Chapter Seven. For ideal gases, the ideal gas law provides a precise relationship between density and pressure:
 Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR SIMULATION
 LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR SIMULATION Miklos ANTICS GEOPRODUCTION CONSULTANTS (GPC) Paris Nord 2, 4, rue de la Perdrix, Lot 9, B.P. 53 95946 ROISSY CDG CEDEX, France e-mail: m.antics@geoproduction.fr
LOW ENTHALPY GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR SIMULATION Miklos ANTICS GEOPRODUCTION CONSULTANTS (GPC) Paris Nord 2, 4, rue de la Perdrix, Lot 9, B.P. 53 95946 ROISSY CDG CEDEX, France e-mail: m.antics@geoproduction.fr
Pros and Cons against Reasonable Development of Unconventional Energy Resources
 Pros and Cons against Reasonable Development of Unconventional Energy Resources Associate Professor Shteryo LYOMOV, Ph.D. Presentation outline Energy resources; Conventional and Unconventional energy resources;
Pros and Cons against Reasonable Development of Unconventional Energy Resources Associate Professor Shteryo LYOMOV, Ph.D. Presentation outline Energy resources; Conventional and Unconventional energy resources;
Trevor M. Hunta and Warwick M. %slingb
 PROCEEDINGS, Nineteenth Workshop on Geothennal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 16-2, 1994 SGP-TR-147 Estimation of reservoir permeability using gravity change measurements
PROCEEDINGS, Nineteenth Workshop on Geothennal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 16-2, 1994 SGP-TR-147 Estimation of reservoir permeability using gravity change measurements
Determination of Productivity for Separate Layers in a Geothermal Well based on Well Log Temperature
 Determination of Productivity for Separate Layers in a Geothermal Well based on Well Log Temperature E. TORHAČ 1, J. KROPE 2, D. GORIČANEC 2 1 Nafta-Geoterm d.o.o., Mlinska ulica 5, 9220 Lendava, 2 Faculty
Determination of Productivity for Separate Layers in a Geothermal Well based on Well Log Temperature E. TORHAČ 1, J. KROPE 2, D. GORIČANEC 2 1 Nafta-Geoterm d.o.o., Mlinska ulica 5, 9220 Lendava, 2 Faculty
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS
 THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
The Effects of Adsorption and Desorption on Production and Reinjection in Vapor- Dominated Geothermal Fields
 Home et al The Effects of Adsorption and Desorption on Production and Reinjection in Vapor- Dominated Geothermal Fields Roland N Horne, Henry J Ramey, Jr, Shubo Shang, Antonio Correa, John Hornbrook Stanford
Home et al The Effects of Adsorption and Desorption on Production and Reinjection in Vapor- Dominated Geothermal Fields Roland N Horne, Henry J Ramey, Jr, Shubo Shang, Antonio Correa, John Hornbrook Stanford
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Lab-scale Investigation of a Multi Well Enhanced Geothermal Reservoir
 PROCEEDINGS, 43rd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 12-14, 2018 SGP-TR-213 Lab-scale Investigation of a Multi Well Enhanced Geothermal Reservoir
PROCEEDINGS, 43rd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 12-14, 2018 SGP-TR-213 Lab-scale Investigation of a Multi Well Enhanced Geothermal Reservoir
Thermal Performance Implications of Flow Orientation Relative to Fracture Shear Offset in Enhanced Geothermal Systems
 PROCEEDINGS, 44th Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 11-13, 2019 SGP-TR-214 Thermal Performance Implications of Flow Orientation Relative to
PROCEEDINGS, 44th Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 11-13, 2019 SGP-TR-214 Thermal Performance Implications of Flow Orientation Relative to
TEMPERATURE GEOTHERMAL SYSTEM *.BY. Roger F. Harrison Salt Lake City, Utah. C; K. Blair
 - * f c * -6 9 -.I. lcal '. DEVELOPMENT AND TESTSNG OF A SMALL MODERATE TEMPERATURE GEOTHERMAL SYSTEM *.BY Roger F. Harrison Terra Tek, Inc. Salt Lake City, Utah C; K. Blair Terra Tek, Inc. - Salt Lake
- * f c * -6 9 -.I. lcal '. DEVELOPMENT AND TESTSNG OF A SMALL MODERATE TEMPERATURE GEOTHERMAL SYSTEM *.BY Roger F. Harrison Terra Tek, Inc. Salt Lake City, Utah C; K. Blair Terra Tek, Inc. - Salt Lake
On The Determination of Transmissibility and Storage Coefficients from Pumping Test Data
 Circular No. 38 1952 STATE OF ILLINOIS On The Determination of Transmissibility and Storage Coefficients from Pumping Test Data Issued by Department of Registration and Education C. HOBART ENGLE, Director
Circular No. 38 1952 STATE OF ILLINOIS On The Determination of Transmissibility and Storage Coefficients from Pumping Test Data Issued by Department of Registration and Education C. HOBART ENGLE, Director
Oil and Gas Well Performance
 Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY OF SIBAYAK GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR, NORTH SUMATRA, INDONESIA
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 21 SGP-TR-168 NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY OF SIBAYAK GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR,
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 21 SGP-TR-168 NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY OF SIBAYAK GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR,
The use of straddle packer testing to hydraulically characterize rock boreholes for contaminant transport studies
 The use of straddle packer testing to hydraulically characterize rock boreholes for contaminant transport studies Patryk Quinn, John Cherry, Beth Parker Presentation for the Solinst Symposium November
The use of straddle packer testing to hydraulically characterize rock boreholes for contaminant transport studies Patryk Quinn, John Cherry, Beth Parker Presentation for the Solinst Symposium November
Thermal Modeling of the Mountain Home Geothermal Area
 PROCEEDINGS, 41st Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 22-24, 2016 SGP-TR-209 Thermal Modeling of the Mountain Home Geothermal Area Sabodh K.
PROCEEDINGS, 41st Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 22-24, 2016 SGP-TR-209 Thermal Modeling of the Mountain Home Geothermal Area Sabodh K.
18 Single vertical fractures
 18 Single vertical fractures 18.1 Introduction If a well intersects a single vertical fracture, the aquifer s unsteady drawdown response to pumping differs significantly from that predicted by the Theis
18 Single vertical fractures 18.1 Introduction If a well intersects a single vertical fracture, the aquifer s unsteady drawdown response to pumping differs significantly from that predicted by the Theis
Verification of Archie Constants Using Special Core Analysis and Resistivity Porosity Cross Plot Using Picket Plot Method
 Int'l Journal of Computing, Communications & Instrumentation Engg. (IJCCIE) Vol. 4, Issue (207) ISSN 2349-469 EISSN 2349-477 Verification of Archie Constants Using Special Core Analysis and Resistivity
Int'l Journal of Computing, Communications & Instrumentation Engg. (IJCCIE) Vol. 4, Issue (207) ISSN 2349-469 EISSN 2349-477 Verification of Archie Constants Using Special Core Analysis and Resistivity
Examination of a geothermal system from a porous geothermal reservoir in the Pannonian Basin in Hungary
 PROCEEDINGS, Fourtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 26-28, 2015 SGP-TR-204 Examination of a geothermal system from a porous geothermal
PROCEEDINGS, Fourtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 26-28, 2015 SGP-TR-204 Examination of a geothermal system from a porous geothermal
Introduction to Well Hydraulics Fritz R. Fiedler
 Introduction to Well Hydraulics Fritz R. Fiedler A well is a pipe placed in a drilled hole that has slots (screen) cut into it that allow water to enter the well, but keep the aquifer material out. A well
Introduction to Well Hydraulics Fritz R. Fiedler A well is a pipe placed in a drilled hole that has slots (screen) cut into it that allow water to enter the well, but keep the aquifer material out. A well
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Groundwater Chapter 10 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois Co Jennifer Cole Northeastern University
Essentials of Geology, 11e Groundwater Chapter 10 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois Co Jennifer Cole Northeastern University
Introduction to Oil&Gas Well Drilling
 Introduction to Oil&Gas Well Drilling Drilling Introduction to Oil&Gas Well Drilling The term drilling indicates the whole complex of operations necessary to construct wells of circular section applying
Introduction to Oil&Gas Well Drilling Drilling Introduction to Oil&Gas Well Drilling The term drilling indicates the whole complex of operations necessary to construct wells of circular section applying
CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS USING RESISTIVITY
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 01 SGP-TR-194 CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 01 SGP-TR-194 CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS
SPE Comparison of Numerical vs Analytical Models for EUR Calculation and Optimization in Unconventional Reservoirs
 SPE-180209 Comparison of Numerical vs Analytical Models for EUR Calculation and Optimization in Unconventional Reservoirs A. Moinfar, J.C. Erdle, K. Patel, Computer Modelling Group Inc. Motivation Analytical
SPE-180209 Comparison of Numerical vs Analytical Models for EUR Calculation and Optimization in Unconventional Reservoirs A. Moinfar, J.C. Erdle, K. Patel, Computer Modelling Group Inc. Motivation Analytical
RESULTS OF STIMULATION TREATMENTS AT THE GEOTHERMAL RESEARCH WELLS IN GROß SCHÖNEBECK/GERMANY
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Third Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 8-3, 8 SGP-TR-185 RESULTS OF STIMULATION TREATMENTS AT THE GEOTHERMAL RESEARCH
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Third Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 8-3, 8 SGP-TR-185 RESULTS OF STIMULATION TREATMENTS AT THE GEOTHERMAL RESEARCH
From 2D Seismic to Hydrodynamic Modelling
 From 2D Seismic to Hydrodynamic Modelling A Complex Study of Turbidites in a Petroleum-Bearing Basin Marcell Lux, HC Exploration Geologist Ahmed Amran, HC Exploration Advisor Marianna Vincze, Geomodel
From 2D Seismic to Hydrodynamic Modelling A Complex Study of Turbidites in a Petroleum-Bearing Basin Marcell Lux, HC Exploration Geologist Ahmed Amran, HC Exploration Advisor Marianna Vincze, Geomodel
A HYBRID SEMI-ANALYTICAL AND NUMERICAL METHOD FOR MODELING WELLBORE HEAT TRANSMISSION
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31-February 2, 5 SGP-TR-176 A HYBRID SEMI-ANALYTICAL AND NUMERICAL METHOD FOR MODELING
PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31-February 2, 5 SGP-TR-176 A HYBRID SEMI-ANALYTICAL AND NUMERICAL METHOD FOR MODELING
Discrete Element Modeling of Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Coupling in Enhanced Geothermal Reservoirs
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California Discrete Element Modeling of Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Coupling in Enhanced Geothermal Reservoirs
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California Discrete Element Modeling of Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Coupling in Enhanced Geothermal Reservoirs
Reservoir Management Background OOIP, OGIP Determination and Production Forecast Tool Kit Recovery Factor ( R.F.) Tool Kit
 Reservoir Management Background 1. OOIP, OGIP Determination and Production Forecast Tool Kit A. Volumetrics Drainage radius assumption. B. Material Balance Inaccurate when recovery factor ( R.F.) < 5 to
Reservoir Management Background 1. OOIP, OGIP Determination and Production Forecast Tool Kit A. Volumetrics Drainage radius assumption. B. Material Balance Inaccurate when recovery factor ( R.F.) < 5 to
REINJECTION INTO WELL ST0902 AND TRACER TESTING IN THE XIONGXIAN GEOTHERMAL FIELD, HEBEI PROVINCE, CHINA
 GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME Reports 2010 Orkustofnun, Grensásvegur 9, Number 25 IS-108 Reykjavík, Iceland REINJECTION INTO WELL ST0902 AND TRACER TESTING IN THE XIONGXIAN GEOTHERMAL FIELD, HEBEI PROVINCE,
GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME Reports 2010 Orkustofnun, Grensásvegur 9, Number 25 IS-108 Reykjavík, Iceland REINJECTION INTO WELL ST0902 AND TRACER TESTING IN THE XIONGXIAN GEOTHERMAL FIELD, HEBEI PROVINCE,
The Ketzin Test Site (former CO 2 Sink-project)
 The Ketzin Test Site (former CO 2 Sink-project) - Experiences and results gained during 32 months of operation - Axel Liebscher & Ketzin Team The Ketzin Test Site ~ 25 km west of Berlin located in the
The Ketzin Test Site (former CO 2 Sink-project) - Experiences and results gained during 32 months of operation - Axel Liebscher & Ketzin Team The Ketzin Test Site ~ 25 km west of Berlin located in the
Pressure Transient Analysis COPYRIGHT. Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Pressure Transient Analysis Core Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives
Pressure Transient Analysis Core Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives
Numerical Analysis of Transient Steam-Water Two-Phase Flow in Geothermal Production Wells with Multiple Feed Zones
 ROCEEDINGS, 4nd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 3-5, 07 SG-TR- Numerical Analysis of Transient Steam-Water Two-hase Flow in Geothermal roduction
ROCEEDINGS, 4nd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 3-5, 07 SG-TR- Numerical Analysis of Transient Steam-Water Two-hase Flow in Geothermal roduction
Lab 9: Petroleum and groundwater
 Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 9: Petroleum and groundwater Petroleum (oil) is a multi-component liquid refined to generate different hydrocarbons, such as heptane (a component of gasoline) and waxes. For the
Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 9: Petroleum and groundwater Petroleum (oil) is a multi-component liquid refined to generate different hydrocarbons, such as heptane (a component of gasoline) and waxes. For the
Hijiori HDR Reservoir Evaluation by Micro-Earthquake Observation
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 38, 2014 Hijiori HDR Reservoir Evaluation by Micro-Earthquake Observation Hideshi Kaieda Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry, Abiko, Chiba, Japan Keywords HDR,
GRC Transactions, Vol. 38, 2014 Hijiori HDR Reservoir Evaluation by Micro-Earthquake Observation Hideshi Kaieda Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry, Abiko, Chiba, Japan Keywords HDR,
OVERVIEW OF THE WAIRAKEI-TAUHARA SUBSIDENCE INVESTIGATION PROGRAM
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31 - February 2, 2011 SGP-TR-191 OVERVIEW OF THE WAIRAKEI-TAUHARA SUBSIDENCE INVESTIGATION
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Sixth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31 - February 2, 2011 SGP-TR-191 OVERVIEW OF THE WAIRAKEI-TAUHARA SUBSIDENCE INVESTIGATION
A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi
 A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi Austria E-mail: listen+talk(a),magnet.at Abstract A thorough analysis of hydrologic pumping tests requires
A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi Austria E-mail: listen+talk(a),magnet.at Abstract A thorough analysis of hydrologic pumping tests requires
SPE Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow
 SPE 10262 Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow Prijambodo, R.,U. of Tulsa Raghavan, R., U. of Tulsa Reynolds, A.C., U. of Tulsa 1985 SPEJ Abstract The pressure response
SPE 10262 Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow Prijambodo, R.,U. of Tulsa Raghavan, R., U. of Tulsa Reynolds, A.C., U. of Tulsa 1985 SPEJ Abstract The pressure response
Slobodan Kolbah 1. DELINEATION OF DEEP WATER-BODIES
 Deep Transboundary Water-Bodies: Exploration & Management in the Pannonian Basin of the Republic of Croatia UNESCO-IAH-UNEP Conference, Paris, Slobodan Kolbah INA Naftaplin Oil & Gas Exploration & Producing
Deep Transboundary Water-Bodies: Exploration & Management in the Pannonian Basin of the Republic of Croatia UNESCO-IAH-UNEP Conference, Paris, Slobodan Kolbah INA Naftaplin Oil & Gas Exploration & Producing
Franco D'Amore,Claudio Calore and Romano Celati. Istituto Internazionale per le Ricerche Geotermiche (CNR) Via del Buongusto 1, Pisa, Italy
 Proceedings Seventh Workshop Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford, December 1981. SGP-TR-55. T W W WOLUTON OF THE COMPOSTON OF THE FLUD FRO4 SERRAZZANO ZONE (LARDERELLO) Franco D'Amore,Claudio Calore
Proceedings Seventh Workshop Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford, December 1981. SGP-TR-55. T W W WOLUTON OF THE COMPOSTON OF THE FLUD FRO4 SERRAZZANO ZONE (LARDERELLO) Franco D'Amore,Claudio Calore
Soils, Hydrogeology, and Aquifer Properties. Philip B. Bedient 2006 Rice University
 Soils, Hydrogeology, and Aquifer Properties Philip B. Bedient 2006 Rice University Charbeneau, 2000. Basin Hydrologic Cycle Global Water Supply Distribution 3% of earth s water is fresh - 97% oceans 1%
Soils, Hydrogeology, and Aquifer Properties Philip B. Bedient 2006 Rice University Charbeneau, 2000. Basin Hydrologic Cycle Global Water Supply Distribution 3% of earth s water is fresh - 97% oceans 1%
Carbon Sequestration in Basalts: Laboratory Studies and Field Demonstration
 Carbon Sequestration in Basalts: Laboratory Studies and Field Demonstration H. T. Schaef B.P. McGrail Workshop on Geologic Capture and Sequestration of Carbon Stanford University November 28, 2017 Needles
Carbon Sequestration in Basalts: Laboratory Studies and Field Demonstration H. T. Schaef B.P. McGrail Workshop on Geologic Capture and Sequestration of Carbon Stanford University November 28, 2017 Needles
NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS
 NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS This document may contain copyrighted materials These materials have been made available for use in research, teaching, and private study, but may not be used for
NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS This document may contain copyrighted materials These materials have been made available for use in research, teaching, and private study, but may not be used for
11/22/2010. Groundwater in Unconsolidated Deposits. Alluvial (fluvial) deposits. - consist of gravel, sand, silt and clay
 Groundwater in Unconsolidated Deposits Alluvial (fluvial) deposits - consist of gravel, sand, silt and clay - laid down by physical processes in rivers and flood plains - major sources for water supplies
Groundwater in Unconsolidated Deposits Alluvial (fluvial) deposits - consist of gravel, sand, silt and clay - laid down by physical processes in rivers and flood plains - major sources for water supplies
Reservoir Engineering Aspects of Unconventional Reservoirs A Brief Introduction
 Reservoir Engineering Aspects of Unconventional Reservoirs A Brief Introduction Tom BLASINGAME Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116 (USA) +1.979.255.8808 t-blasingame@tamu.edu
Reservoir Engineering Aspects of Unconventional Reservoirs A Brief Introduction Tom BLASINGAME Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116 (USA) +1.979.255.8808 t-blasingame@tamu.edu
Effects of depositional and diagenetic heterogeneitites on fluid flow in Plio -- Pleistocene reefal carbonates of the Southern Dominican Republic
 Viviana Díaz was born in Puerto Rico and received her undergraduate degree from the University of Puerto Rico and her Master's at the University of North Carolina. She is currently working on her PhD at
Viviana Díaz was born in Puerto Rico and received her undergraduate degree from the University of Puerto Rico and her Master's at the University of North Carolina. She is currently working on her PhD at
Hydraulic Characteristics of the Basel 1 Enhanced Geothermal System
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 33, 9 Hydraulic Characteristics of the Basel 1 Enhanced Geothermal System Florentin Ladner and Markus O. Häring Geothermal Explorers International Ltd, Switzerland Keywords Geothermal,
GRC Transactions, Vol. 33, 9 Hydraulic Characteristics of the Basel 1 Enhanced Geothermal System Florentin Ladner and Markus O. Häring Geothermal Explorers International Ltd, Switzerland Keywords Geothermal,
INFERRING RELATIVE PERMEABILITY FROM RESISTIVITY WELL LOGGING
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 3-February 2, 25 SGP-TR-76 INFERRING RELATIVE PERMEABILITY FROM RESISTIVITY WELL LOGGING
PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 3-February 2, 25 SGP-TR-76 INFERRING RELATIVE PERMEABILITY FROM RESISTIVITY WELL LOGGING
A New Combinational Terminology for Geothermal Systems
 International Journal of Geosciences, 2013, 4, 43-48 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2013.41005 Published Online January 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg) A New Combinational Terminology for Geothermal
International Journal of Geosciences, 2013, 4, 43-48 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2013.41005 Published Online January 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg) A New Combinational Terminology for Geothermal
SPE ATCE 2013 Special Session So We Frac'd the Well, Now What? Reservoir Engineering Aspects of Unconventional Reservoirs
 SPE ATCE 2013 Special Session So We Frac'd the Well, Now What? Reservoir Engineering Aspects of Unconventional Reservoirs Tom BLASINGAME Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116
SPE ATCE 2013 Special Session So We Frac'd the Well, Now What? Reservoir Engineering Aspects of Unconventional Reservoirs Tom BLASINGAME Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116
Daniel C. Reda and Roger R. Eaton Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque, New Mexico
 -21 8- INFLUENCE OF STEAM/WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITY MODELS ON PREDICTED GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR PERFORMANCE: A SENSITIVITY STUDY INTRODUCTION /STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM Daniel C. Reda and Roger R. Eaton
-21 8- INFLUENCE OF STEAM/WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITY MODELS ON PREDICTED GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR PERFORMANCE: A SENSITIVITY STUDY INTRODUCTION /STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM Daniel C. Reda and Roger R. Eaton
TWO DIFFERENT ROLES OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL DEVELOPMENT
 TWO DIFFERENT ROLES OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL DEVELOPMENT Mineyuki Hanano Japan Metals & Chemicals Co., Ltd., 1-3-6 Saien, Morioka-city, Iwate 020-0024, Japan, email: hananom@jmc.co.jp Key Words: geothermal
TWO DIFFERENT ROLES OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL DEVELOPMENT Mineyuki Hanano Japan Metals & Chemicals Co., Ltd., 1-3-6 Saien, Morioka-city, Iwate 020-0024, Japan, email: hananom@jmc.co.jp Key Words: geothermal
ANALYTICAL AND NUMERICAL MODELLING OF COLD WATER INJECTION INTO HORIZONTAL RESERVOIRS
 GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME Reports 00 Orkustofnun, Grensásvegur 9, Number 4 IS-108 Reykjavík, Iceland ANALYTICAL AND NUMERICAL MODELLING OF COLD WATER INJECTION INTO HORIZONTAL RESERVOIRS Hennadiy Chetveryk,
GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME Reports 00 Orkustofnun, Grensásvegur 9, Number 4 IS-108 Reykjavík, Iceland ANALYTICAL AND NUMERICAL MODELLING OF COLD WATER INJECTION INTO HORIZONTAL RESERVOIRS Hennadiy Chetveryk,
Integrated Approach to Drilling Project in Unconventional Reservoir Using Reservoir Simulation
 Integrated Approach to Drilling Project in Unconventional Reservoir Using Reservoir Simulation Jerzy Stopa 1,*, Rafał Wiśniowski 1, Paweł Wojnarowski 1, Damian Janiga 1, and Krzysztof Skrzypaszek 1 1 AGH
Integrated Approach to Drilling Project in Unconventional Reservoir Using Reservoir Simulation Jerzy Stopa 1,*, Rafał Wiśniowski 1, Paweł Wojnarowski 1, Damian Janiga 1, and Krzysztof Skrzypaszek 1 1 AGH
Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot
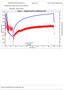 BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
REGIONAL GEOLOGY IN KHMER BASIN
 CONTENTS 1-Khmere Basin 2-Regional Geology Khmer Basin 3-Regime Tectonic 4-Seismic Database -a/ Acquisition Data -b/ Prospect Angkor -C/ Cross Section Seismic 5-Play Type -a/ Play Schematic -b/ Structure
CONTENTS 1-Khmere Basin 2-Regional Geology Khmer Basin 3-Regime Tectonic 4-Seismic Database -a/ Acquisition Data -b/ Prospect Angkor -C/ Cross Section Seismic 5-Play Type -a/ Play Schematic -b/ Structure
Fr CO2 02 Fault Leakage Detection From Pressure Transient Analysis
 Fr CO2 2 Fault Detection From Pressure Transient Analysis A. Shchipanov *, L. Kollbotn, R. Berenblyum IRIS Summary of reservoir fluids from injection site, e.g. through faults, is one of the key risks
Fr CO2 2 Fault Detection From Pressure Transient Analysis A. Shchipanov *, L. Kollbotn, R. Berenblyum IRIS Summary of reservoir fluids from injection site, e.g. through faults, is one of the key risks
Optimisation of Well Trajectory and Hydraulic Fracture Design in a Poor Formation Quality Gas-Condensate Reservoir
 Optimisation of Well Trajectory and Hydraulic Fracture Design in a Poor Formation Quality Gas-Condensate Reservoir Tipping, André Carlo Torres de Carvalho at8865@my.bristol.ac.uk Masters in Petroleum Engineering,
Optimisation of Well Trajectory and Hydraulic Fracture Design in a Poor Formation Quality Gas-Condensate Reservoir Tipping, André Carlo Torres de Carvalho at8865@my.bristol.ac.uk Masters in Petroleum Engineering,
XYZ COMPANY LTD. Prepared For: JOHN DOE. XYZ et al Knopcik 100/ W5/06 PAS-TRG. Dinosaur Park Formation
 All depths reported in mkb TVD per EUB requirements. All pressures reported in (a) per EUB requirements. 9.01 used as atmospheric pressure adjustment to convert from gauge to absolute pressure. XYZ COMPANY
All depths reported in mkb TVD per EUB requirements. All pressures reported in (a) per EUB requirements. 9.01 used as atmospheric pressure adjustment to convert from gauge to absolute pressure. XYZ COMPANY
 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 40-50 50-60 60-70 70-80 80-90 90-100 Fresh Water What we will cover The Hydrologic Cycle River systems Floods Groundwater Caves and Karst Topography Hot springs Distribution of water in
12 10 8 6 4 2 0 40-50 50-60 60-70 70-80 80-90 90-100 Fresh Water What we will cover The Hydrologic Cycle River systems Floods Groundwater Caves and Karst Topography Hot springs Distribution of water in
APPLICATION OF SELF-POTENTIAL MEASUREMENTS TO GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ENGINEERING: CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURED RESERVOIRS
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Fifth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 1-3, 2010 SGP-TR-188 APPLICATION OF SELF-POTENTIAL MEASUREMENTS TO GEOTHERMAL
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Fifth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 1-3, 2010 SGP-TR-188 APPLICATION OF SELF-POTENTIAL MEASUREMENTS TO GEOTHERMAL
Analysis of stress variations with depth in the Permian Basin Spraberry/Dean/Wolfcamp Shale
 ARMA 15-189 Analysis of stress variations with depth in the Permian Basin Spraberry/Dean/Wolfcamp Shale Xu, Shaochuan and Zoback, M.D. Stanford University, Stanford, California, USA Copyright 2015 ARMA,
ARMA 15-189 Analysis of stress variations with depth in the Permian Basin Spraberry/Dean/Wolfcamp Shale Xu, Shaochuan and Zoback, M.D. Stanford University, Stanford, California, USA Copyright 2015 ARMA,
Tesorillo Project Presentation Spain. June 2013
 Tesorillo Project Presentation Spain June 2013 Highlights Two contiguous license areas total 38,000ha (94,000 acres), Cadiz province, southern Spain License contains 1956 Almarchal-1, which flowed gas
Tesorillo Project Presentation Spain June 2013 Highlights Two contiguous license areas total 38,000ha (94,000 acres), Cadiz province, southern Spain License contains 1956 Almarchal-1, which flowed gas
Using Repeat Microgravity Measurements to Track Reinjection in Liquid-Dominated Fields
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 25 Antalya, Turkey, 24-29 April 25 Using Repeat Microgravity Measurements to Track Reinjection in Liquid-Dominated Fields Trevor M. Hunt Institute of Geological &
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 25 Antalya, Turkey, 24-29 April 25 Using Repeat Microgravity Measurements to Track Reinjection in Liquid-Dominated Fields Trevor M. Hunt Institute of Geological &
SPADES: Swift Production Data Analysis and Diagnostics Engine for Shale Reservoirs
 SPADES: Swift Production Data Analysis and Diagnostics Engine for Shale Reservoirs Xu Xue April 8, 017 Motivation Production data analysis software for shale gas/oil reservoirs Model free analysis of production
SPADES: Swift Production Data Analysis and Diagnostics Engine for Shale Reservoirs Xu Xue April 8, 017 Motivation Production data analysis software for shale gas/oil reservoirs Model free analysis of production
NUMERICAL TYPES OF MODELING OF GEOTHERMAL RESOURCES
 Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea, Seria Geografie, Tom XIX, 2009, pag. 233-238 NUMERICAL TYPES OF MODELING OF GEOTHERMAL RESOURCES Elena ZIERLER 1, Maria DURGĂU 2 Résumé: Types de modélisation numérique
Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea, Seria Geografie, Tom XIX, 2009, pag. 233-238 NUMERICAL TYPES OF MODELING OF GEOTHERMAL RESOURCES Elena ZIERLER 1, Maria DURGĂU 2 Résumé: Types de modélisation numérique
Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals COPYRIGHT. Introduction
 Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals Why This Module is Important Introduction Fundamental understanding of the flow through rocks is extremely important to understand the behavior of the reservoir Permeability
Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals Why This Module is Important Introduction Fundamental understanding of the flow through rocks is extremely important to understand the behavior of the reservoir Permeability
Evaluation of Low Resistivity Laminated Shaly Sand Reservoirs
 Evaluation of Low Resistivity Laminated Shaly Sand Reservoirs Summary Dr S S Prasad, C S Sajith & S S Bakshi Sub Surface Team, Mehsana Asset, ONGC, Palavasna, Mehsana, Gujarat E-mail : shivshankarp@gmailcom
Evaluation of Low Resistivity Laminated Shaly Sand Reservoirs Summary Dr S S Prasad, C S Sajith & S S Bakshi Sub Surface Team, Mehsana Asset, ONGC, Palavasna, Mehsana, Gujarat E-mail : shivshankarp@gmailcom
Microseismicity applications in hydraulic fracturing monitoring
 Available online atwww.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2016, 8 (4):13-19 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Microseismicity
Available online atwww.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2016, 8 (4):13-19 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Microseismicity
Scoping Calculations of TBM Advancement in Flysch and Breccias of Strait-of-Gibraltar Tunnel
 EURO:TUN 2009 2 nd International Conference on Computational Methods in Tunnelling Ruhr University Bochum, 9-11 September 2009 Aedificatio Publishers, 369-376 Scoping Calculations of TBM Advancement in
EURO:TUN 2009 2 nd International Conference on Computational Methods in Tunnelling Ruhr University Bochum, 9-11 September 2009 Aedificatio Publishers, 369-376 Scoping Calculations of TBM Advancement in
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR THE RAPID ESTIMATION OF DRAINAGE VOLUME, PRESSURE AND WELL RATES. A Thesis NEHA GUPTA
 A NOVEL APPROACH FOR THE RAPID ESTIMATION OF DRAINAGE VOLUME, PRESSURE AND WELL RATES A Thesis by NEHA GUPTA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR THE RAPID ESTIMATION OF DRAINAGE VOLUME, PRESSURE AND WELL RATES A Thesis by NEHA GUPTA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
Considerations for Infill Well Development in Low Permeability Reservoirs
 Considerations for Infill Well Development in Low Permeability Reservoirs George Waters Technical Manager Unconventional Completions September 9, 2014 Topics Continuous Improvement in Field Development
Considerations for Infill Well Development in Low Permeability Reservoirs George Waters Technical Manager Unconventional Completions September 9, 2014 Topics Continuous Improvement in Field Development
IMWA Proceedings 1987 International Mine Water Association
 COAL MINE DEWATERING AS A KEY ASPECT IN PRE-MINE FEASIBILITY PLANNING IN THE SEMI-ARID WESTERN UNITED STATES Phillip E. Brown Consultant in Geohydrology 1401 Monaco Parkway Denver, Colorado 87220 USA Marcie
COAL MINE DEWATERING AS A KEY ASPECT IN PRE-MINE FEASIBILITY PLANNING IN THE SEMI-ARID WESTERN UNITED STATES Phillip E. Brown Consultant in Geohydrology 1401 Monaco Parkway Denver, Colorado 87220 USA Marcie
TOUGH2 Flow Simulator Used to Simulate an Electric Field of a Reservoir With a Conductive Tracer for Fracture Characterization
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 36, 2012 TOUGH2 Flow Simulator Used to Simulate an Electric Field of a Reservoir With a Conductive Tracer for Fracture Characterization Lilja Magnusdottir and Roland N. Horne Stanford
GRC Transactions, Vol. 36, 2012 TOUGH2 Flow Simulator Used to Simulate an Electric Field of a Reservoir With a Conductive Tracer for Fracture Characterization Lilja Magnusdottir and Roland N. Horne Stanford
Introduction to Formation Evaluation Abiodun Matthew Amao
 Introduction to Formation Evaluation By Abiodun Matthew Amao Monday, September 09, 2013 Well Logging PGE 492 1 Lecture Outline What is formation evaluation? Why do we evaluate formation? What do we evaluate?
Introduction to Formation Evaluation By Abiodun Matthew Amao Monday, September 09, 2013 Well Logging PGE 492 1 Lecture Outline What is formation evaluation? Why do we evaluate formation? What do we evaluate?
GEOELEC Prospective for Geothermal Electricity in Europe
 GEOELEC Prospective for Geothermal Electricity in Europe 3 rd Regional Workshop Italy, France, Slovenia and the Balkans Philippe Calcagno Burkhard Sanner Chrystel Dezayes BRGM EGEC BRGM Milano, 05/12/2011
GEOELEC Prospective for Geothermal Electricity in Europe 3 rd Regional Workshop Italy, France, Slovenia and the Balkans Philippe Calcagno Burkhard Sanner Chrystel Dezayes BRGM EGEC BRGM Milano, 05/12/2011
HDR PROJECT SOULTZ: HYDRAULIC AND SEISMIC OBSERVATIONS DURING STIMULATION OF THE 3 DEEP WELLS BY MASSIVE WATER INJECTIONS
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Second Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 22-24, 27 SGP-TR-183 HDR PROJECT SOULTZ: HYDRAULIC AND SEISMIC OBSERVATIONS DURING
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Second Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 22-24, 27 SGP-TR-183 HDR PROJECT SOULTZ: HYDRAULIC AND SEISMIC OBSERVATIONS DURING
Modeling pressure response into a fractured zone of Precambrian basement to understand deep induced-earthquake hypocenters from shallow injection
 Modeling pressure response into a fractured zone of Precambrian basement to understand deep induced-earthquake hypocenters from shallow injection S. Raziperchikolaee 1 and J. F. Miller 1 Abstract Analysis
Modeling pressure response into a fractured zone of Precambrian basement to understand deep induced-earthquake hypocenters from shallow injection S. Raziperchikolaee 1 and J. F. Miller 1 Abstract Analysis
