Rheology of granular flows: Role of the interstitial fluid
|
|
|
- Stephanie Patrick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rheology of granular flows: Role of the interstitial fluid Colorado 2003, USGS Olivier Pouliquen, IUSTI, CNRS, Aix-Marseille University Marseille, France
2 Motivations : debris flows, landslides, avalanches, silo Not Fault!!! Low level of pressure: kpa in natural events kpa in the experiments => Rigid and non breakable particles
3 Particles of different sizes + liquid (non newtonian) + complex topography + unsteady flows????????????????? In this talk : 1) rheology of dry granular flows? 2) What happen when coupling with the interstitial fluid matters?
4 Dry granular material: Collection of grains No cohesion No brownian motion No fluid interaction Only contact interactions But not so easy
5 Dry granular flows Different flow regimes Gas Liquid Solid
6 Dry granular flows Different flow regimes Gas Liquid Solid
7 Quasi-static deformations : Soil mechanics and plasticity «!solid!» Focus on initial deformation What happens :! at large deformations?! for fast deformations?
8 Dry granular flows Different flow regimes Gas Liquid Solid
9 Kinetic theory for rapid granular gases «!gas!» Binary collisions+inelastic collisions! constitutive equations coupling Density, velocity and granular temperature But if not enough energy is injected:! finite duration contact,! multiple contact,
10 Dry granular flows Different flow regimes Gas Liquid Solid
11
12 Different flow configurations studied both experimentally and numerically GDR Midi, Eur. Phys. J 04
13 P plane shear under controlled normal stress U Lois et al 2005 Da Cruz et al, PRE 05 GdR Midi, Eur. Phys. J 04 h P One imposes P and A single dimensionless number (inertial number) Shear stress "? Volume fraction #? (Savage 84, Ancey et al 99)
14 Inertial number * ratio between 2 times : : time scale of the mean shear : microscopic time for rearrangement
15 «!quasi-static!» «liquid» «!gas!» 0 1 I = " d P /#
16 P U Da Cruz et al, PRE 05 GdR Midi Eur. Phys. J 04 h P One imposes P and Shear stress "? Volume fraction #?
17 P " " = µ I ( )P " /P " = " I ( ) I = " d P /#
18 remark: No velocity weakening Peyneau & Roux PRE 08 Dacruz et al PRE 05
19 Forterre, Pouliquen ARFM 08 For spheres Data from Inclined plane exp. (Pouliquen 99) Inclined plane simulations (Baran et al 2006) Annular shear cell exp. (Sayed, Savage JFM, 84)
20 An empirical friction law: " = µ(i)p I = " d P /# µ(i) = µ s + µ 2 " µ s I 0 I +1
21 Constant pressure µ # I $ And shear at constant volume fraction?? Bagnold Proc. R. Soc 54 Lois et al PRE 07 Lemaitre PRE 05 Da Cruz et al PRE 05 f1 f2 # #
22 allows to describe (not perfectly) velocity profiles on inclined plane, Let s go further
23 Predicted velocity and volume fraction profiles Rheology µ(i) predicts - V % h (h-z) 1.5 and &=cte Gdr Midi et al, 2004, Da cruz et al 2002, Silbert et al Pb with thin flows and close to free surface Gdr Midi et al, 2004, Da cruz et al 2002, Rajchenbach 2003
24 allows to describe (not perfectly) velocity profiles on inclined plane, on pile, Let s go further
25 3D generalisation: a visco-plastic model (Jop et al Nature 06) assumptions : 1) P isotropic 2) and are colinear (Savage 83, Goddard 86, Schaeffer 87, ) Effective viscosity
26 3D generalisation of the friction law : granular flows as a viscoplastic fluid (Jop et al Nature 06) assumptions: 1) P isotropic 2) and are co-linear (Savage 83, Goddard 86, Schaeffer 87, ) Pressure dependent viscosity
27 flows on a heap : a full 3D problem (P. Jop et al Nature 06) Q W z/d y/d L = 1.5 m V(y,z)
28 Flow between rough lateral walls: Jop et al, Nature V surf gd h/d ,2 0 0,2 0,4 0,6 0,8 1 1,2 y/w ,2 0,4 0,6 0,8 1 y/w
29 Jop et al, Phys. Fluids 2007 Initiation of the flow?
30 Long wave instability in granular flows (Y. Forterre, JFM 06 )
31 Experimental Setup : forcing of the instability Power supply Function generator f, AGBF Stabilized alimentation Loudspeakers Slides projector Nozzle z y x h Photodiodes! Forterre and Pouliquen JFM 02
32 Instability threshold Forterre, JFM 06 Dispersion relation
33 Granular slumping (Lacaze and Kerswell 08) Lajeunesse et al Phys. Fluids 2004,2005 Lube et al JFM 2004, Larrieu et al JFM 2006, Staron & Hinch JFM 2005, Lacaze et al Phys. Fluids 2008 Lajeunesse et al 05
34 Lacaze and Kerswell (preprint 08)
35 Relative Success of the visco-plastic description. A starting point to adress other configurations (simulating the pressure dependent visco-plastic rheology is non trivial ) But there are problems when approaching the solid
36 Limits of the viscoplastic approach: 1) Quasistatic flows (shear band, finite size effect.) A need for non local approach 2) Transient flows when preparation plays a crucial role
37 Exponential tail Not predicted.. Velocity profile
38 Shear bands in quasi-static flow (Forterre & Pouliquen ARFM 08, Jop PRE 08) V/Vw y/d Howell et al PRL 99 Mueth et al Nature 00 Bocquet et al PRE 02 Not captured by the viscoplastic approach
39 Flow threshold hysteresis Finite size effects Not captured by the viscoplastic approach Limit of a local rheology?
40 to go further? Role of the fluctuations? Aranson and Tsimring PRE,01, Louge Phys. Fluids 03, Josserand et al 06 Lemaitre 02 Bazant 07 Nott 08 Behringer 08 Role of the correlations? Pouliquen et al 01, Ertas and Halsey 03, Mills et al 08 Jenkins and Chevoir 01, Jenkins Phys. Fluids 06, Radjai and Roux PRL Pouliquen PRL 04 Link with plasticity of other amorphous and glassy systems
41 F Evidence for non local effects: Microrheology experiments! Deflection angle (mrad) '=0 20 '! time (s) M. Van Hecke 2008 Pouliquen, Forterre, Nott
42
43 Self activated process Pouliquen & Forterre, Phil. Trans, 2009
44 Limits of the viscoplastic approach: 1) Quasistatic flows (shear band, finite size effect.) A need for non local approach 2) Transient flows when preparation plays a crucial role
45 Influence of the initial Volume fraction on the Collapse of a pile. Daerr & Douady 99
46 Quasi-static case : critical state theory # # c ( " " c ( Coupling Friction- dilatancy
47 Reynolds Dilatancy
48 Simple critical state theory P Dilatancy angle ( dx dy # assumption: critical " volume fraction # c # c ( (Radjai and Roux 98)
49 Visco plastic theory : shear rate dependence but no dilatancy critical state theory : dilatancy but no shear rate dependence Shear rate dependent critical state theory
50 Shear rate dependent critical state theory : I = " d P /#
51 3D generalisation :......
52 Application to a dry flow: Initiation of flow on an inclined plane: z different )
53 z z Initially dense z z Initially loose Comparison with DEM simulations with N. Taberlet
54
55 Changing time scales by putting the granular material in water (Cassar et al, Phys. Fluids 06) DV recorder d=112 µm glass beads Laser P.C!P
56 Dry Immersed
57 A naive idea : fluid only plays a role by changing the time scale of rearrangements " = P µ(i) with I = ( t micro viscous : dry :
58 µ=tg) Idry Ivisc Cassar et al. Phys. Fluids 05
59 Submarine flows on heap Doppler et al, JFM 07 Flow rate Velocity profile
60 And dilatancy??? And Pore pressure?? Cf In Faults Rice JGR 75, Rudnicki JGR 84,
61 How to explain the variety of landslides observed in nature? Iverson et al, (2000) Science Large scale experiments in the USGS facility
62 Dense preparation Courtesy of Dick Iverson
63 Loose preparation Courtesy of Dick Iverson
64 Pore Pressure feedback argument (Iverson Rev. Geo. 97, JGR 05) Loose case Dense case &!! Fluid expelled! P fluid!! P eff "! Friction "! Less friction between grains &"! Fluid sucked! P fluid "! P eff!! Friction!! higher friction between grains In faults: rice JGR 75, Rudnicki JGR 84,
65 A simple experiment: Dense sample Loose sample
66 Experimental setup (Pailha et al 08) Glass beads : 160µm Liquid: mixture of water and Ucon oil: *= kg/m.s *= kg/m.s 20cm 7cm 1m
67 Experimental procedure 0.60 Compaction by taps 0.59! Result of sedimentation # tap 15 20
68 Velocity of the Free surface Typical results Surface velocity (mm/s) ,&i=0.568 &i=0.571,&i=0.562 &i=0.578 &i=0.584 &i=0.588,&i= =25º h=5mm *= Pa.s Pressure under The avalanche Pore pressure (Pa) Time (s) (Pailha et al Pof 08)
69 Velocity of the Free surface Typical results Surface velocity (mm/s) ,&i=0.568 &i=0.571,&i=0.562 &i=0.578 Loose &i<&c &i=0.584 &i=0.588,&i=0.592 Dense &i>&c +=25º h=5mm *= Pa.s Pressure under The avalanche Pore pressure (Pa) Time (s) (Pailha et al Pof 08)
70 Triggering time in the dense case
71 Triggering time + =25 + = = 28 + = 30 h=3.7 mm h=6.1 mm Time (s) *= kg/m.s Phi
72 Deformation Surface velocity (mm.s -1 ) Time (s) Surface velocity (mm.s -1 ) !i=0.588!i=0.584!i= Deformation For initial preparation erased
73 Two phase flow model 1 Coupling with the liquid: Two phase equations Fluids mechanics 2 Rheology of the granular phase 3 Dilatancy Granular matter Soil mechanics
74 submarine avalanches : Depth averaged approach (Pitman and Le 05) : z h )
75 Submarine granular avalanches: Shear rate critical state theory (Cassar et al 05, Doppler et al 07 ) Particle -fluid coupling Relative weight Viscous drag due to the Vertical displacement
76 µ Calibration of the model looking at the steady state I µ ( I ) v x10-3! " ( eq I ) v 2 I 3 4x10-3! start K A single free Parameter K "
77 Velocity Predictions : Pressure u (mm.s-1) Pore pressure (Pa) t (s) t (s) u (mm.s-1) Pore pressure (Pa) t (s) t (s)
78 Scaling of the triggering time t/t0 Different h Different viscosities
79 Pore Pressure Maximum acceleration
80 Conclusions for submarine avalanches A simple critical state approach+ a viscoplastic rheology + two phase flow equations!semi quantitative predictions in the complex dynamics of the flow initiation of submarine avalanches Beyond the depth averaged approach? Question of the numerical implementation of such models?
81 Index matching method Mickael Pailha unpublished
82 Conclusions for constitutive modeling of granular flows Visco-plastic approach gives the order zero of viscous behavior of granular flows It can serve as a base for further developments: -irregular particles? -cohesive particles? -polydispersed materials? -breakable particles? (dilatancy, underwater granular flows, cohesive flows ) -link with the microscopic physics? -how to capture non local effects (role of fluctuations, link with glassy systems,.)?
83 Towards more complex granular media: Polydispersed : Felix et Thomas PRE 04 Rognon et al 06 Cohesive granular matter: Rognon et al 08 Halsey et al 06 Richefeu et al 06 granular matter with fluid interactions
84 Merci à Mickael Pailha Pierre Jop, Cyril Cassar Yoël Forterre Pascale Aussillous Maxime Nicolas Prabhu Nott Jeff Morris Neil Balmforth Bruno Andreotti Olivier Dauchot
Lecture 6: Flow regimes fluid-like
 Granular Flows 1 Lecture 6: Flow regimes fluid-like Quasi-static granular flows have plasticity laws, gaseous granular flows have kinetic theory -- how to model fluid-like flows? Intermediate, dense regime:
Granular Flows 1 Lecture 6: Flow regimes fluid-like Quasi-static granular flows have plasticity laws, gaseous granular flows have kinetic theory -- how to model fluid-like flows? Intermediate, dense regime:
Dry granular flows: gas, liquid or solid?
 Dry granular flows: gas, liquid or solid? Figure 1: Forterre & Pouliquen, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mechanics, 2008 1 Characterizing size and size distribution Grains are not uniform (size, shape, ) Statistical
Dry granular flows: gas, liquid or solid? Figure 1: Forterre & Pouliquen, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mechanics, 2008 1 Characterizing size and size distribution Grains are not uniform (size, shape, ) Statistical
Simple shear flow of collisional granular-fluid mixtures
 Manuscript Click here to download Manuscript: Manuscript_r1.docx 1 Simple shear flow of collisional granular-fluid mixtures 2 3 4 5 D. Berzi 1 1 Department of Environmental, Hydraulic, Infrastructure,
Manuscript Click here to download Manuscript: Manuscript_r1.docx 1 Simple shear flow of collisional granular-fluid mixtures 2 3 4 5 D. Berzi 1 1 Department of Environmental, Hydraulic, Infrastructure,
SIMULATION OF A 2D GRANULAR COLUMN COLLAPSE ON A RIGID BED
 1 SIMULATION OF A 2D GRANULAR COLUMN COLLAPSE ON A RIGID BED WITH LATERAL FRICTIONAL EFFECTS High slope results and comparison with experimental data Nathan Martin1, Ioan Ionescu2, Anne Mangeney1,3 François
1 SIMULATION OF A 2D GRANULAR COLUMN COLLAPSE ON A RIGID BED WITH LATERAL FRICTIONAL EFFECTS High slope results and comparison with experimental data Nathan Martin1, Ioan Ionescu2, Anne Mangeney1,3 François
A two-phase flow description of the initiation of submarine granular avalanches
 Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 A two-phase flow description of the initiation of submarine granular avalanches By M I C K A Ë L P A I L H A A N D O L I V I E R P O U L I Q U E
Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 A two-phase flow description of the initiation of submarine granular avalanches By M I C K A Ë L P A I L H A A N D O L I V I E R P O U L I Q U E
Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology
 CEA-Saclay/SPEC; Group Instabilities and Turbulence Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology Olivier Dauchot together with many contributors: D. Bonamy, E. Bertin, S. Deboeuf, B. Andreotti,
CEA-Saclay/SPEC; Group Instabilities and Turbulence Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology Olivier Dauchot together with many contributors: D. Bonamy, E. Bertin, S. Deboeuf, B. Andreotti,
Dry granular flows: rheological measurements of the I
 Dry granular flows: rheological measurements of the I -rheology A. Fall 1, G. Ovarlez 1,2, D. Hautemayou 1, C. Mézière 1, J.-N. Roux 1 and F. Chevoir 1 1 Université Paris Est, Laboratoire Navier (CNRS,
Dry granular flows: rheological measurements of the I -rheology A. Fall 1, G. Ovarlez 1,2, D. Hautemayou 1, C. Mézière 1, J.-N. Roux 1 and F. Chevoir 1 1 Université Paris Est, Laboratoire Navier (CNRS,
Extended kinetic theory applied to dense, granular, simple shear flows
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Diego Berzi Extended kinetic theory applied to dense, granular, simple shear flows Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract We apply the Extended
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Diego Berzi Extended kinetic theory applied to dense, granular, simple shear flows Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract We apply the Extended
A Two-Phase Solid/Fluid Model for Dense Granular Flows including Dilatancy Effects
 23-26th May 2016, GdR EGRIN, Piriac-sur-Mer A Two-Phase Solid/Fluid Model for Dense Granular Flows including Dilatancy Effects Anne Mangeney1,1 F. Bouchut2, E. Fernandez-Nieto3, G. Narbona-Reina3, and
23-26th May 2016, GdR EGRIN, Piriac-sur-Mer A Two-Phase Solid/Fluid Model for Dense Granular Flows including Dilatancy Effects Anne Mangeney1,1 F. Bouchut2, E. Fernandez-Nieto3, G. Narbona-Reina3, and
On granular rheology in bedload transport
 On granular rheology in bedload transport R. Maurin a, J. Chauchat b, B. Chareyre c and P. Frey a. Irstea, Grenoble, UR ETGR, Univ. Grenoble Alpes. raphael.maurin@irstea.fr b. LEGI, CNRS UMR 5519, Univ.
On granular rheology in bedload transport R. Maurin a, J. Chauchat b, B. Chareyre c and P. Frey a. Irstea, Grenoble, UR ETGR, Univ. Grenoble Alpes. raphael.maurin@irstea.fr b. LEGI, CNRS UMR 5519, Univ.
Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors
 Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors L. Staron, F. Radjai & J.-P. Vilotte Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge CB3 0WA, UK. Laboratoire de Mécanique et Génie
Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors L. Staron, F. Radjai & J.-P. Vilotte Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge CB3 0WA, UK. Laboratoire de Mécanique et Génie
Granular materials and pattern formation
 Granular materials and pattern formation Ask not what you can do for pattern formation, ask what pattern formation can do for you! sand dunes flowing layers vibrated layers avalanche Granular materials
Granular materials and pattern formation Ask not what you can do for pattern formation, ask what pattern formation can do for you! sand dunes flowing layers vibrated layers avalanche Granular materials
epl draft Stresses in smooth flows of dense granular media
 epl draft Stresses in smooth flows of dense granular media Martin Depken 1, Jeremy B. Lechman 2, Martin van Hecke 3, Wim van Saarloos 1 and Gary S. Grest 2 1 Instituut Lorentz, Universiteit Leiden, Postbus
epl draft Stresses in smooth flows of dense granular media Martin Depken 1, Jeremy B. Lechman 2, Martin van Hecke 3, Wim van Saarloos 1 and Gary S. Grest 2 1 Instituut Lorentz, Universiteit Leiden, Postbus
GRANULAR MEDIA. Between Fluid and Solid
 GRANULAR MEDIA Between Fluid and Solid Sand, rice, sugar, snow,cement...although ubiquitous in our daily lives, granular media still challenge engineers and fascinate researchers. This book provides the
GRANULAR MEDIA Between Fluid and Solid Sand, rice, sugar, snow,cement...although ubiquitous in our daily lives, granular media still challenge engineers and fascinate researchers. This book provides the
Scaling laws in granular flows down rough inclined planes
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 3 MARCH 1999 Scaling laws in granular flows down rough inclined planes O. Pouliquen a) LadHyX, Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau cedex, France Received 15 July 1998;
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 3 MARCH 1999 Scaling laws in granular flows down rough inclined planes O. Pouliquen a) LadHyX, Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau cedex, France Received 15 July 1998;
Collapse dynamics and runout of dense granular materials in a fluid
 Collapse dynamics and runout of dense granular materials in a fluid Vincent Topin, Yann Monerie, Frédéric Perales, Farhang Radjai To cite this version: Vincent Topin, Yann Monerie, Frédéric Perales, Farhang
Collapse dynamics and runout of dense granular materials in a fluid Vincent Topin, Yann Monerie, Frédéric Perales, Farhang Radjai To cite this version: Vincent Topin, Yann Monerie, Frédéric Perales, Farhang
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 103 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 103 (2015 ) 237 245 The 13 th Hypervelocity Impact Symposium Strength of Granular Materials in Transient and Steady State Rapid
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 103 (2015 ) 237 245 The 13 th Hypervelocity Impact Symposium Strength of Granular Materials in Transient and Steady State Rapid
From Frictional to Viscous Behavior: Three Dimensional Imaging and Rheology of Gravitational Suspensions
 From Frictional to Viscous Behavior: Three Dimensional Imaging and Rheology of Gravitational Suspensions thing not achieved in previous studies of gravitational suspensions [3, 5, 17, 18]. Second, extensive
From Frictional to Viscous Behavior: Three Dimensional Imaging and Rheology of Gravitational Suspensions thing not achieved in previous studies of gravitational suspensions [3, 5, 17, 18]. Second, extensive
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 23 Jun 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 23 Jun 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 23 Jun 2005](/thumbs/72/67842732.jpg) Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 arxiv:cond-mat/56584v2 [cond-mat.soft] 23 Jun 25 Rheology of surface granular flows By ASHISH V. ORPE AND D. V. KHAKHAR Department of Chemical Engineering,
Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 arxiv:cond-mat/56584v2 [cond-mat.soft] 23 Jun 25 Rheology of surface granular flows By ASHISH V. ORPE AND D. V. KHAKHAR Department of Chemical Engineering,
Segregation Effects in Granular Collapses
 Segregation Effects in Granular Collapses Joshua S. Caplan, Saran Tunyasuvunakool, Stuart B. Dalziel & Nathalie M. Vriend Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge,
Segregation Effects in Granular Collapses Joshua S. Caplan, Saran Tunyasuvunakool, Stuart B. Dalziel & Nathalie M. Vriend Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge,
Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media
 Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media David Chen May 13, 2010 Abstract A continuum description of avalanches in granular systems is presented. The model is based on hydrodynamic equations coupled
Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media David Chen May 13, 2010 Abstract A continuum description of avalanches in granular systems is presented. The model is based on hydrodynamic equations coupled
Dry and wet granular flows. Diego Berzi
 Dry and wet granular flows Diego Berzi Outline 2 What? Why? How? When? Who? Where? Then? What? Granular flows many solid moving particles 3 particle mass is large (at least 10 20 molecular masses). Hence,
Dry and wet granular flows Diego Berzi Outline 2 What? Why? How? When? Who? Where? Then? What? Granular flows many solid moving particles 3 particle mass is large (at least 10 20 molecular masses). Hence,
Some recent models and simulations for granular flows
 Some recent models and simulations for granular flows François Bouchut LAMA, CNRS & Université Paris-Est all collaborations with Anne Mangeney Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris HYP2016, Aachen, August
Some recent models and simulations for granular flows François Bouchut LAMA, CNRS & Université Paris-Est all collaborations with Anne Mangeney Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris HYP2016, Aachen, August
Granular column collapses: further experimental results
 J. Fluid Mech. (2007), vol. 575, pp. 177 186. c 2007 Cambridge University Press doi:10.1017/s0022112006004563 Printed in the United Kingdom 177 Granular column collapses: further experimental results ERICA
J. Fluid Mech. (2007), vol. 575, pp. 177 186. c 2007 Cambridge University Press doi:10.1017/s0022112006004563 Printed in the United Kingdom 177 Granular column collapses: further experimental results ERICA
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 Mar 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 Mar 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 Mar 2003](/thumbs/83/87420074.jpg) Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 arxiv:cond-mat/0303017v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 Mar 2003 Long surface wave instability in dense granular flows. By YOËL FORTERRE and OLIVIER POULIQUEN
Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 arxiv:cond-mat/0303017v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 Mar 2003 Long surface wave instability in dense granular flows. By YOËL FORTERRE and OLIVIER POULIQUEN
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 10 Dec 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 10 Dec 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 10 Dec 2002](/thumbs/93/113489424.jpg) Europhysics Letters PREPRINT Wall effects on granular heap stability arxiv:cond-mat/0209040v2 [cond-mat.soft] 10 Dec 2002 S. Courrech du Pont 1, P. Gondret 1, B. Perrin 2 and M. Rabaud 1 1 F.A.S.T. Universités
Europhysics Letters PREPRINT Wall effects on granular heap stability arxiv:cond-mat/0209040v2 [cond-mat.soft] 10 Dec 2002 S. Courrech du Pont 1, P. Gondret 1, B. Perrin 2 and M. Rabaud 1 1 F.A.S.T. Universités
Temporally Heterogeneous Dynamics in Granular Flows
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Publications Department of Physics 3-25 Temporally Heterogeneous Dynamics in Granular Flows Leo Silbert Southern Illinois University Carbondale, lsilbert@physics.siu.edu
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Publications Department of Physics 3-25 Temporally Heterogeneous Dynamics in Granular Flows Leo Silbert Southern Illinois University Carbondale, lsilbert@physics.siu.edu
Received 07/04/2015; Accepted d/m/2015
 Rev. Cuba Fis. 32, 37 (2015) ARTÍCULOS ORIGINALES VELOCITY PROFILE OF GRANULAR FLOWS DOWN A HEAP DESCRIBED BY DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS PERFIL DE VELOCIDADES DE UN FLUJO GRANULAR EN UNA PILA CUASI-BIDIMENSIONAL
Rev. Cuba Fis. 32, 37 (2015) ARTÍCULOS ORIGINALES VELOCITY PROFILE OF GRANULAR FLOWS DOWN A HEAP DESCRIBED BY DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS PERFIL DE VELOCIDADES DE UN FLUJO GRANULAR EN UNA PILA CUASI-BIDIMENSIONAL
Turbulentlike Quantitative Analysis on Energy Dissipation in Vibrated Granular Media
 Copyright 011 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.71, no., pp.149-155, 011 Turbulentlike Quantitative Analysis on Energy Dissipation in Vibrated Granular Media Zhi Yuan Cui 1, Jiu Hui Wu 1 and Di Chen Li 1 Abstract:
Copyright 011 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.71, no., pp.149-155, 011 Turbulentlike Quantitative Analysis on Energy Dissipation in Vibrated Granular Media Zhi Yuan Cui 1, Jiu Hui Wu 1 and Di Chen Li 1 Abstract:
Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow
 Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow Namiko Mitarai Department of Chemistry and Physics of Condensed Matter, Graduate School of Science, Kyushu University, Japan. A thesis submitted
Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow Namiko Mitarai Department of Chemistry and Physics of Condensed Matter, Graduate School of Science, Kyushu University, Japan. A thesis submitted
Olivier Roche, Santiago Montserrat, Yarko Niño, Aldo Tamburrino. HAL Id: hal
 Experimental observations of water-like behavior of initially fluidized, dam break granular flows and their relevance for the propagation of ash-rich pyroclastic flows Olivier Roche, Santiago Montserrat,
Experimental observations of water-like behavior of initially fluidized, dam break granular flows and their relevance for the propagation of ash-rich pyroclastic flows Olivier Roche, Santiago Montserrat,
Discrete simulation of dense flows of polyhedral grains down a rough inclined plane
 Discrete simulation of dense flows of polyhedral grains down a rough inclined plane Emilien Azéma, Yannick Descantes, Nicolas Roquet, Jean-Noël Roux, François Chevoir To cite this version: Emilien Azéma,
Discrete simulation of dense flows of polyhedral grains down a rough inclined plane Emilien Azéma, Yannick Descantes, Nicolas Roquet, Jean-Noël Roux, François Chevoir To cite this version: Emilien Azéma,
Sediment transport and dunes in pipe flow
 Sediment transport and dunes in pipe flow Malika Ouriemi, Julien Chauchat, Pascale Aussillous, Marc Médale, Elisabeth Guazzelli To cite this version: Malika Ouriemi, Julien Chauchat, Pascale Aussillous,
Sediment transport and dunes in pipe flow Malika Ouriemi, Julien Chauchat, Pascale Aussillous, Marc Médale, Elisabeth Guazzelli To cite this version: Malika Ouriemi, Julien Chauchat, Pascale Aussillous,
Tuning granular matter rheology using externally supplied vibrations
 Flowing Matter 2017 23-27 January 2017 PORTO Tuning granular matter rheology using externally supplied vibrations Laboratory : LEMTA, Nancy (France) Team «Rheophysics and hydrodynamics of complex fluids»
Flowing Matter 2017 23-27 January 2017 PORTO Tuning granular matter rheology using externally supplied vibrations Laboratory : LEMTA, Nancy (France) Team «Rheophysics and hydrodynamics of complex fluids»
Granular and Particle-Laden Flows
 Granular and Particle-Laden Flows 1 September to 19 December 2003 Report from the Organisers: JMNT Gray (Manchester), K Hutter (Darmstadt), JT Jenkins (Cornell), T Mullin (Manchester) Scientific Background
Granular and Particle-Laden Flows 1 September to 19 December 2003 Report from the Organisers: JMNT Gray (Manchester), K Hutter (Darmstadt), JT Jenkins (Cornell), T Mullin (Manchester) Scientific Background
L O N G I T U D I N A L V O R T I C E S I N G R A N U L A R F L O W S
 L O N G I T U D I N A L V O R T I C E S I N G R A N U L A R F L O W S Yoël FORTERRE, Olivier POULIQUEN Institut Universitaire des Sstèmes Thermiques et Industriels (UMR 6595 CNRS) 5, rue Enrico Fermi 13453
L O N G I T U D I N A L V O R T I C E S I N G R A N U L A R F L O W S Yoël FORTERRE, Olivier POULIQUEN Institut Universitaire des Sstèmes Thermiques et Industriels (UMR 6595 CNRS) 5, rue Enrico Fermi 13453
RHEOMETRY OF DENSE GRANULAR COLLAPSE ON INCLINED PLANES
 RHEOMETRY OF DENSE GRANULAR COLLAPSE ON INCLINED PLANES A Thesis Submitted To the Faculty of Graduate Studies and Research In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the Degree of Masters of Applied
RHEOMETRY OF DENSE GRANULAR COLLAPSE ON INCLINED PLANES A Thesis Submitted To the Faculty of Graduate Studies and Research In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the Degree of Masters of Applied
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 11 Jun 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 11 Jun 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 11 Jun 2002](/thumbs/81/84185960.jpg) Granular flow down a rough inclined plane: transition between thin and thick piles arxiv:cond-mat/0206188v1 [cond-mat.soft] 11 Jun 2002 Leonardo E. Silbert, James W. Landry, and Gary S. Grest Sandia National
Granular flow down a rough inclined plane: transition between thin and thick piles arxiv:cond-mat/0206188v1 [cond-mat.soft] 11 Jun 2002 Leonardo E. Silbert, James W. Landry, and Gary S. Grest Sandia National
SOME ISSUES AND PERSPECTIVES IN GRANULAR PHYSICS
 1 SOME ISSUES AND PERSPECTIVES IN GRANULAR PHYSICS Jean-Noël Roux Laboratoire des Matériaux et des Structures du Génie Civil Unité Mixte de Recherche LCPC-ENPC-CNRS Institut Navier, Champs-sur-Marne, France
1 SOME ISSUES AND PERSPECTIVES IN GRANULAR PHYSICS Jean-Noël Roux Laboratoire des Matériaux et des Structures du Génie Civil Unité Mixte de Recherche LCPC-ENPC-CNRS Institut Navier, Champs-sur-Marne, France
The erosion of granular beds under the action of fluid shearing flows
 The erosion of granular beds under the action of fluid shearing flows Pascale Aussillous, Julien Chauchat a, Malika Ouriemi b, Marc Médale, Mickaël Pailha c,yannick Peysson b, and Élisabeth Guazzelli,
The erosion of granular beds under the action of fluid shearing flows Pascale Aussillous, Julien Chauchat a, Malika Ouriemi b, Marc Médale, Mickaël Pailha c,yannick Peysson b, and Élisabeth Guazzelli,
IMPLEMENTATION OF NON-NEWTONIAN RHEOLOGY FOR GRANULAR FLOW SIMULATION
 9. National Conference on Computational Mechanics MekIT 17 B. Skallerud and H I Andersson (Eds) IMPLEMENTATION OF NON-NEWTONIAN RHEOLOGY FOR GRANULAR FLOW SIMULATION Petter Fornes 1,, Hans Bihs 1 and Steinar
9. National Conference on Computational Mechanics MekIT 17 B. Skallerud and H I Andersson (Eds) IMPLEMENTATION OF NON-NEWTONIAN RHEOLOGY FOR GRANULAR FLOW SIMULATION Petter Fornes 1,, Hans Bihs 1 and Steinar
Unsteady granular flows down an inclined plane
 Unsteady granular flows down an inclined plane Stanislav Parez, Einat Aharonov, Renaud Toussaint To cite this version: Stanislav Parez, Einat Aharonov, Renaud Toussaint. Unsteady granular flows down an
Unsteady granular flows down an inclined plane Stanislav Parez, Einat Aharonov, Renaud Toussaint To cite this version: Stanislav Parez, Einat Aharonov, Renaud Toussaint. Unsteady granular flows down an
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 24 Jun 2011
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 24 Jun 2011 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 24 Jun 2011](/thumbs/74/70999009.jpg) Dense granular flow around a penetrating object: Experiments and hydrodynamic model A. Seguin 1, Y. Bertho 1, P. Gondret 1, and J. Crassous 2 1 Univ Paris-Sud 11, Univ Paris 6, CNRS, Lab FAST, Bât. 52,
Dense granular flow around a penetrating object: Experiments and hydrodynamic model A. Seguin 1, Y. Bertho 1, P. Gondret 1, and J. Crassous 2 1 Univ Paris-Sud 11, Univ Paris 6, CNRS, Lab FAST, Bât. 52,
Towards prediction of fines captures
 Towards prediction of fines captures over the wide range of depositional environments occurring simultaneously in a typical facility Luca Sittoni, Jill Hanssen, Hugo van Es, Jan van Kester, Rob Uittenbogaard,
Towards prediction of fines captures over the wide range of depositional environments occurring simultaneously in a typical facility Luca Sittoni, Jill Hanssen, Hugo van Es, Jan van Kester, Rob Uittenbogaard,
Discrete element investigation of rate effects on the asymptotic behaviour of granular materials
 Discrete element investigation of rate effects on the asymptotic behaviour of granular materials David MAŠÍN a,1 and Jan JERMAN a a Faculty of Science, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic Abstract.
Discrete element investigation of rate effects on the asymptotic behaviour of granular materials David MAŠÍN a,1 and Jan JERMAN a a Faculty of Science, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic Abstract.
Rheology of granular flows across the transition from soft to rigid particles
 PHYSICAL REVIEW FLUIDS 2, 102301(R) (2017) Rheology of granular flows across the transition from soft to rigid particles Adeline Favier de Coulomb, 1 Mehdi Bouzid, 2 Philippe Claudin, 1 Eric Clément, 1
PHYSICAL REVIEW FLUIDS 2, 102301(R) (2017) Rheology of granular flows across the transition from soft to rigid particles Adeline Favier de Coulomb, 1 Mehdi Bouzid, 2 Philippe Claudin, 1 Eric Clément, 1
Discrete Element Modelling in Granular Mechanics WUHAN seminars, China, 28th august-2nd september 2017
 Discrete Element Modelling in Granular Mechanics WUHAN seminars, China, 28th august-2nd september 2017 F. DARVE, L. SIBILLE, F. DUFOUR Laboratoire Sols, Solides, Structures, Risques, INPG-UGA-CNRS, Grenoble,
Discrete Element Modelling in Granular Mechanics WUHAN seminars, China, 28th august-2nd september 2017 F. DARVE, L. SIBILLE, F. DUFOUR Laboratoire Sols, Solides, Structures, Risques, INPG-UGA-CNRS, Grenoble,
Towards hydrodynamic simulations of wet particle systems
 The 7th World Congress on Particle Technology (WCPT7) Towards hydrodynamic simulations of wet particle systems Sudeshna Roy a*, Stefan Luding a, Thomas Weinhart a a Faculty of Engineering Technology, MESA+,
The 7th World Congress on Particle Technology (WCPT7) Towards hydrodynamic simulations of wet particle systems Sudeshna Roy a*, Stefan Luding a, Thomas Weinhart a a Faculty of Engineering Technology, MESA+,
Rheometer: Procedure: Part A: Viscosity v Time
 Rheometer A fluid is defined as a substance that deforms continuously under the action of a shear stress, no matter how small the shear stress may be. Without shear stress, there will be no deformation.
Rheometer A fluid is defined as a substance that deforms continuously under the action of a shear stress, no matter how small the shear stress may be. Without shear stress, there will be no deformation.
Debris Flows: Recent Advances in Experiments and Modeling
 Debris Flows: Recent dvances in Experiments and Modeling Diego Berzi a, James T. Jenkins b, Michele Larcher c a Department of Environmental, Hydraulic, Infrastructures and Surveying Engineering, Politecnico
Debris Flows: Recent dvances in Experiments and Modeling Diego Berzi a, James T. Jenkins b, Michele Larcher c a Department of Environmental, Hydraulic, Infrastructures and Surveying Engineering, Politecnico
Modelling of dispersed, multicomponent, multiphase flows in resource industries Section 4: Non-Newtonian fluids and rheometry (PART 1)
 Modelling of dispersed, multicomponent, multiphase flows in resource industries Section 4: Non-Newtonian fluids and rheometry (PART 1) Globex Julmester 2017 Lecture #3 05 July 2017 Agenda Lecture #3 Section
Modelling of dispersed, multicomponent, multiphase flows in resource industries Section 4: Non-Newtonian fluids and rheometry (PART 1) Globex Julmester 2017 Lecture #3 05 July 2017 Agenda Lecture #3 Section
Mass Wasting. Requirements for Mass Wasting. Slope Stability. Geol 104: mass wasting
 Mass Wasting Movement of earth materials downslope, driven by Gravitational Forces. Landslides - general term for rock or soil movement. In U.S., on average, mass wasting causes 1 to 2 billion dollars
Mass Wasting Movement of earth materials downslope, driven by Gravitational Forces. Landslides - general term for rock or soil movement. In U.S., on average, mass wasting causes 1 to 2 billion dollars
Figure 3: Problem 7. (a) 0.9 m (b) 1.8 m (c) 2.7 m (d) 3.6 m
 1. For the manometer shown in figure 1, if the absolute pressure at point A is 1.013 10 5 Pa, the absolute pressure at point B is (ρ water =10 3 kg/m 3, ρ Hg =13.56 10 3 kg/m 3, ρ oil = 800kg/m 3 ): (a)
1. For the manometer shown in figure 1, if the absolute pressure at point A is 1.013 10 5 Pa, the absolute pressure at point B is (ρ water =10 3 kg/m 3, ρ Hg =13.56 10 3 kg/m 3, ρ oil = 800kg/m 3 ): (a)
Joe Goddard, Continuum modeling of granular media
 Joe Goddard, jgoddard@ucsd.edu Continuum modeling of granular media This talk summarizes a recent survey [1] of the interesting phenomenology and the prominent régimes of granular flow which also offers
Joe Goddard, jgoddard@ucsd.edu Continuum modeling of granular media This talk summarizes a recent survey [1] of the interesting phenomenology and the prominent régimes of granular flow which also offers
An Experimental Study of the Elastic Theory for Granular Flows
 An Experimental Study of the Elastic Theory for Granular Flows Tongtong Guo and Charles S. Campbell Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA
An Experimental Study of the Elastic Theory for Granular Flows Tongtong Guo and Charles S. Campbell Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA
Viscoelasticity. Basic Notions & Examples. Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity. Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies. Non-linear behavior
 Viscoelasticity Basic Notions & Examples Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies Non-linear behavior Viscoelastic Behavior Generic Viscoelasticity: exhibition of both
Viscoelasticity Basic Notions & Examples Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies Non-linear behavior Viscoelastic Behavior Generic Viscoelasticity: exhibition of both
Discontinuous shear thickening occurs in suspensions whose
 Revealing the frictional transition in shear-thickening suspensions Cécile Clavaud a,1, Antoine érut a, loen Metzger a, and Yoël Forterre a a Aix Marseille Univ, CNRS, Institut Universitaire des Systèmes
Revealing the frictional transition in shear-thickening suspensions Cécile Clavaud a,1, Antoine érut a, loen Metzger a, and Yoël Forterre a a Aix Marseille Univ, CNRS, Institut Universitaire des Systèmes
Overcoming paradoxes of Drucker-Prager theory for unconsolidated granular matter. (Dated: January 23, 2014)
 Overcoming paradoxes of Drucker-Prager theory for unconsolidated granular matter (Dated: January 23, 2014) 1 Abstract Drucker-Prager model of granular matter contradicts to experiments in several aspects
Overcoming paradoxes of Drucker-Prager theory for unconsolidated granular matter (Dated: January 23, 2014) 1 Abstract Drucker-Prager model of granular matter contradicts to experiments in several aspects
Modelling of dispersed, multicomponent, multiphase flows in resource industries. Section 3: Examples of analyses conducted for Newtonian fluids
 Modelling of dispersed, multicomponent, multiphase flows in resource industries Section 3: Examples of analyses conducted for Newtonian fluids Globex Julmester 017 Lecture # 04 July 017 Agenda Lecture
Modelling of dispersed, multicomponent, multiphase flows in resource industries Section 3: Examples of analyses conducted for Newtonian fluids Globex Julmester 017 Lecture # 04 July 017 Agenda Lecture
Behavior of model cohesive granular materials in the dense flow regime
 Behavior of model cohesive granular materials in the dense flow regime Pierre Rognon 1,2, François Chevoir 1,, Mohamed Naaïm 2 & Jean-Noël Roux 1 1 LMSGC, Institut Navier, 2 allée Kepler, 7742 Champs sur
Behavior of model cohesive granular materials in the dense flow regime Pierre Rognon 1,2, François Chevoir 1,, Mohamed Naaïm 2 & Jean-Noël Roux 1 1 LMSGC, Institut Navier, 2 allée Kepler, 7742 Champs sur
IX. Mass Wasting Processes
 IX. Mass Wasting Processes 1. Deris Flows Flow types: Deris flow, lahar (volcanic), mud flow (few gravel, no oulders) Flowing mixture of water, clay, silt, sand, gravel, oulder, etc. Flowing is liquefied
IX. Mass Wasting Processes 1. Deris Flows Flow types: Deris flow, lahar (volcanic), mud flow (few gravel, no oulders) Flowing mixture of water, clay, silt, sand, gravel, oulder, etc. Flowing is liquefied
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Aug 2006
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Aug 2006 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Aug 2006](/thumbs/88/117723838.jpg) Velocity Correlations in Dense Gravity Driven Granular Chute Flow arxiv:cond-mat/6864v [cond-mat.soft] 29 Aug 26 Oleh Baran, Deniz Ertaş, and Thomas C. Halsey Corporate Strategic Research, ExxonMobil Research
Velocity Correlations in Dense Gravity Driven Granular Chute Flow arxiv:cond-mat/6864v [cond-mat.soft] 29 Aug 26 Oleh Baran, Deniz Ertaş, and Thomas C. Halsey Corporate Strategic Research, ExxonMobil Research
Auto-acoustic compaction in steady shear flows: Experimental evidence for. suppression of shear dilatancy by internal acoustic vibration
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Auto-acoustic compaction in steady shear flows: Experimental evidence for suppression of shear dilatancy by internal acoustic vibration Nicholas J. van der Elst 1*, Emily E. Brodsky 1, Pierre-Yves
1 2 3 4 5 6 Auto-acoustic compaction in steady shear flows: Experimental evidence for suppression of shear dilatancy by internal acoustic vibration Nicholas J. van der Elst 1*, Emily E. Brodsky 1, Pierre-Yves
(2.1) Is often expressed using a dimensionless drag coefficient:
 1. Introduction Multiphase materials occur in many fields of natural and engineering science, industry, and daily life. Biological materials such as blood or cell suspensions, pharmaceutical or food products,
1. Introduction Multiphase materials occur in many fields of natural and engineering science, industry, and daily life. Biological materials such as blood or cell suspensions, pharmaceutical or food products,
Summer School: Granular Materials from Simulations to Astrophysical Applications
 Summer School: Granular Materials from Simulations to Astrophysical Applications Hosted by CSCAMM and the University of Maryland Burgers Program in Fluid Dynamics Organizers: Derek Richardson, Astronomy
Summer School: Granular Materials from Simulations to Astrophysical Applications Hosted by CSCAMM and the University of Maryland Burgers Program in Fluid Dynamics Organizers: Derek Richardson, Astronomy
Friction law for dense granular flows: application to the motion of a mass down a rough inclined plane
 J. Fluid Mech. (22), vol. 453, pp. 133 151. c 22 Cambridge University Press DOI: 1.117/S2211216796 Printed in the United Kingdom 133 Friction law for dense granular flows: application to the motion of
J. Fluid Mech. (22), vol. 453, pp. 133 151. c 22 Cambridge University Press DOI: 1.117/S2211216796 Printed in the United Kingdom 133 Friction law for dense granular flows: application to the motion of
Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics
 Computational Biology Group (CoBi), D-BSSE, ETHZ Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil MSc Computational Biology 2015/16 7. Mai 2016 2 / 57 Contents 1 Introduction to Elastic Materials
Computational Biology Group (CoBi), D-BSSE, ETHZ Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil MSc Computational Biology 2015/16 7. Mai 2016 2 / 57 Contents 1 Introduction to Elastic Materials
Inclined plane rheometry of a dense granular suspension
 Inclined plane rheometry of a dense granular suspension C. Bonnoit, T. Darnige, E. Clement, and A. Lindner a) Laboratoire de Physique et Mécanique des Milieux Hétégogènes (PMMH), UMR 7636, CNRS-ESPCI,
Inclined plane rheometry of a dense granular suspension C. Bonnoit, T. Darnige, E. Clement, and A. Lindner a) Laboratoire de Physique et Mécanique des Milieux Hétégogènes (PMMH), UMR 7636, CNRS-ESPCI,
Collapses of two-dimensional granular columns
 Collapses of two-dimensional granular columns Gert Lube, 1 Herbert E. Huppert, 2 R. Stephen J. Sparks, 3 and Armin Freundt 1 1 Research Division Dynamics of the Ocean Floor, IFM-GEOMAR, Leibniz Institute
Collapses of two-dimensional granular columns Gert Lube, 1 Herbert E. Huppert, 2 R. Stephen J. Sparks, 3 and Armin Freundt 1 1 Research Division Dynamics of the Ocean Floor, IFM-GEOMAR, Leibniz Institute
Sand transport over a barchan dune
 Sand transport over a barchan dune F. Charru (1), V. Laval (1) 1. IMFT, Toulouse, France - corresponding author: francois.charru@imft.fr Abstract The present work investigates an important and yet unsolved
Sand transport over a barchan dune F. Charru (1), V. Laval (1) 1. IMFT, Toulouse, France - corresponding author: francois.charru@imft.fr Abstract The present work investigates an important and yet unsolved
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses.
 8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
Modified Kinetic Theory Applied to the Shear Flows of Granular Materials
 Modified Kinetic Theory Applied to the Shear Flows of Granular Materials Yifei Duan, 1) Zhi-Gang Feng, 1,a) Efstathios E. Michaelides, 2) Shaolin Mao 3) 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, UTSA, San
Modified Kinetic Theory Applied to the Shear Flows of Granular Materials Yifei Duan, 1) Zhi-Gang Feng, 1,a) Efstathios E. Michaelides, 2) Shaolin Mao 3) 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, UTSA, San
Confined flow of suspensions modeled by a frictional rheology
 Confined flow of suspensions modeled by a frictional rheology Brice Lecampion 1, Dmitry I. Garagash 2 1 Schlumberger, 1 cours du Triangle, 92936 Paris La Defense, France 2 Department of Civil and Resource
Confined flow of suspensions modeled by a frictional rheology Brice Lecampion 1, Dmitry I. Garagash 2 1 Schlumberger, 1 cours du Triangle, 92936 Paris La Defense, France 2 Department of Civil and Resource
Fluid Mechanics Introduction
 Fluid Mechanics Introduction Fluid mechanics study the fluid under all conditions of rest and motion. Its approach is analytical, mathematical, and empirical (experimental and observation). Fluid can be
Fluid Mechanics Introduction Fluid mechanics study the fluid under all conditions of rest and motion. Its approach is analytical, mathematical, and empirical (experimental and observation). Fluid can be
file:///d /suhasini/suha/office/html2pdf/ _editable/slides/module%202/lecture%206/6.1/1.html[3/9/2012 4:09:25 PM]
![file:///d /suhasini/suha/office/html2pdf/ _editable/slides/module%202/lecture%206/6.1/1.html[3/9/2012 4:09:25 PM] file:///d /suhasini/suha/office/html2pdf/ _editable/slides/module%202/lecture%206/6.1/1.html[3/9/2012 4:09:25 PM]](/thumbs/96/126781421.jpg) Objectives_template Objectives In this section you will learn the following Introduction Different Theories of Earth Pressure Lateral Earth Pressure For At Rest Condition Movement of the Wall Different
Objectives_template Objectives In this section you will learn the following Introduction Different Theories of Earth Pressure Lateral Earth Pressure For At Rest Condition Movement of the Wall Different
The role of interparticle forces in the fluidization of micro and nanoparticles
 The role of interparticle forces in the fluidization of micro and nanoparticles A. Castellanos POWDER FLOW 2009 London, December 16 Acknowledgements The experimental work presented here has been done in
The role of interparticle forces in the fluidization of micro and nanoparticles A. Castellanos POWDER FLOW 2009 London, December 16 Acknowledgements The experimental work presented here has been done in
Fluid dynamics - viscosity and. turbulent flow
 Fluid dynamics - viscosity and Fluid statics turbulent flow What is a fluid? Density Pressure Fluid pressure and depth Pascal s principle Buoyancy Archimedes principle Fluid dynamics Reynolds number Equation
Fluid dynamics - viscosity and Fluid statics turbulent flow What is a fluid? Density Pressure Fluid pressure and depth Pascal s principle Buoyancy Archimedes principle Fluid dynamics Reynolds number Equation
Granular packings: internal states, quasi-static rheology
 1 Granular packings: internal states, quasi-static rheology Main tool : grain-level numerical simulation...... of assemblies of spherical grains (3D)... comparisons with experiments on glass beads geometry
1 Granular packings: internal states, quasi-static rheology Main tool : grain-level numerical simulation...... of assemblies of spherical grains (3D)... comparisons with experiments on glass beads geometry
GRAVITY-DRIVEN FLOW OF GRAINS THROUGH PIPES: A ONE-DIMENSIONAL MODEL
 IV Journeys in Multiphase Flows (JEM217) March 27-31, 217 - São Paulo, Brazil Copyright c 217 by ABCM PaperID: JEM-217-1 GRAVITY-DRIVEN FLOW OF GRAINS THROUGH PIPES: A ONE-DIMENSIONAL MODEL Carlos A. Alvarez
IV Journeys in Multiphase Flows (JEM217) March 27-31, 217 - São Paulo, Brazil Copyright c 217 by ABCM PaperID: JEM-217-1 GRAVITY-DRIVEN FLOW OF GRAINS THROUGH PIPES: A ONE-DIMENSIONAL MODEL Carlos A. Alvarez
arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 30 Jul 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 30 Jul 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 30 Jul 2004](/thumbs/77/76691732.jpg) Relation between dry granular flow regimes and morphology of deposits: formation of levées in pyroclastic deposits arxiv:cond-mat/5v [cond-mat.stat-mech] Jul Gwenaëlle Félix and Nathalie Thomas Laboratoire
Relation between dry granular flow regimes and morphology of deposits: formation of levées in pyroclastic deposits arxiv:cond-mat/5v [cond-mat.stat-mech] Jul Gwenaëlle Félix and Nathalie Thomas Laboratoire
Rheology of concentrated hard-sphere suspensions
 Rheology of concentrated hard-sphere suspensions Complex behaviour in a simple system Wilson Poon School of Physics & Astronomy, The University of Edinburgh Rut Besseling Lucio Isa ( ETH, Zürich) Khoa
Rheology of concentrated hard-sphere suspensions Complex behaviour in a simple system Wilson Poon School of Physics & Astronomy, The University of Edinburgh Rut Besseling Lucio Isa ( ETH, Zürich) Khoa
Experimentally determined distribution of granular-flow characteristics in collisional bed load transport
 Experimentally determined distribution of granular-flow characteristics in collisional bed load transport Václav Matoušek 1,*, Štěpán Zrostlík 1, Luigi Fraccarollo 2, Anna Prati 2, and Michele Larcher
Experimentally determined distribution of granular-flow characteristics in collisional bed load transport Václav Matoušek 1,*, Štěpán Zrostlík 1, Luigi Fraccarollo 2, Anna Prati 2, and Michele Larcher
Fluid Mechanics Prof. T.I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture - 17 Laminar and Turbulent flows
 Fluid Mechanics Prof. T.I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 17 Laminar and Turbulent flows Welcome back to the video course on fluid mechanics. In
Fluid Mechanics Prof. T.I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 17 Laminar and Turbulent flows Welcome back to the video course on fluid mechanics. In
Lecture 3: Fundamentals of Fluid Flow: fluid properties and types; Boundary layer structure; unidirectional flows
 GEOL 440 Sedimentology and stratigraphy: processes, environments and deposits Lecture 3: Fundamentals of Fluid Flow: fluid properties and types; Boundary layer structure; unidirectional flows Why study
GEOL 440 Sedimentology and stratigraphy: processes, environments and deposits Lecture 3: Fundamentals of Fluid Flow: fluid properties and types; Boundary layer structure; unidirectional flows Why study
SPH Molecules - a model of granular materials
 SPH Molecules - a model of granular materials Tatiana Capone DITS, Univeristy of Roma (la Sapienza) Roma, Italy Jules Kajtar School of Mathematical Sciences Monash University Vic. 3800, Australia Joe Monaghan
SPH Molecules - a model of granular materials Tatiana Capone DITS, Univeristy of Roma (la Sapienza) Roma, Italy Jules Kajtar School of Mathematical Sciences Monash University Vic. 3800, Australia Joe Monaghan
Coupling dense and dilute granular flows in a high shear Mi-Pro granulator
 Coupling dense and dilute granular flows in a high shear Mi-Pro granulator Master s Thesis within the Innovative and Sustainable Chemical Engineering programme EVA MARÍA GÓMEZ FINO Department of Chemical
Coupling dense and dilute granular flows in a high shear Mi-Pro granulator Master s Thesis within the Innovative and Sustainable Chemical Engineering programme EVA MARÍA GÓMEZ FINO Department of Chemical
Grainsize Evolution in Open Systems
 Grainsize Evolution in Open Systems Benjy Marks and Itai Einav Abstract Granular flows are often characterised by spatial and temporal variations in their grainsize distribution. These variations are generally
Grainsize Evolution in Open Systems Benjy Marks and Itai Einav Abstract Granular flows are often characterised by spatial and temporal variations in their grainsize distribution. These variations are generally
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 24 Oct 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 24 Oct 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 24 Oct 2010](/thumbs/92/109049696.jpg) The role of dilation and confining stresses in shear thickening of dense suspensions arxiv:1010.4921v1 [cond-mat.soft] 24 Oct 2010 Eric Brown and Heinrich M. Jaeger James Franck Institute, The University
The role of dilation and confining stresses in shear thickening of dense suspensions arxiv:1010.4921v1 [cond-mat.soft] 24 Oct 2010 Eric Brown and Heinrich M. Jaeger James Franck Institute, The University
Frictional rheologies have a wide range of applications in engineering
 A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
Small particles in a viscous fluid. Part 2. Sedimentation of particles. Sedimentation of an isolated sphere. Part 2. Sedimentation of particles
 Small particles in a viscous fluid Course in three parts. A quick course in micro-hydrodynamics 2. Sedimentation of particles 3. Rheology of suspensions Good textbook for parts & 2: A Physical Introduction
Small particles in a viscous fluid Course in three parts. A quick course in micro-hydrodynamics 2. Sedimentation of particles 3. Rheology of suspensions Good textbook for parts & 2: A Physical Introduction
6. Basic basic equations I ( )
 6. Basic basic equations I (4.2-4.4) Steady and uniform flows, streamline, streamtube One-, two-, and three-dimensional flow Laminar and turbulent flow Reynolds number System and control volume Continuity
6. Basic basic equations I (4.2-4.4) Steady and uniform flows, streamline, streamtube One-, two-, and three-dimensional flow Laminar and turbulent flow Reynolds number System and control volume Continuity
Drained Against Undrained Behaviour of Sand
 Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 54 (2007), No. 3, pp. 207 222 IBW PAN, ISSN 1231 3726 Drained Against Undrained Behaviour of Sand Andrzej Sawicki, Waldemar Świdziński Institute
Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 54 (2007), No. 3, pp. 207 222 IBW PAN, ISSN 1231 3726 Drained Against Undrained Behaviour of Sand Andrzej Sawicki, Waldemar Świdziński Institute
Fluid Mechanics. du dy
 FLUID MECHANICS Technical English - I 1 th week Fluid Mechanics FLUID STATICS FLUID DYNAMICS Fluid Statics or Hydrostatics is the study of fluids at rest. The main equation required for this is Newton's
FLUID MECHANICS Technical English - I 1 th week Fluid Mechanics FLUID STATICS FLUID DYNAMICS Fluid Statics or Hydrostatics is the study of fluids at rest. The main equation required for this is Newton's
Principles of Convection
 Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
Testing various constitutive equations for debris flow modelling
 Hydrology, Water Resources and Ecology in Headwaters (Proceedings of the HeadWater'98 Conference held at Meran/Merano, Italy, April 1998). IAHS Publ. no. 48, 1998. 49 Testing various constitutive equations
Hydrology, Water Resources and Ecology in Headwaters (Proceedings of the HeadWater'98 Conference held at Meran/Merano, Italy, April 1998). IAHS Publ. no. 48, 1998. 49 Testing various constitutive equations
Forces on bins: The effect of random friction
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 57, NUMBER 3 MARCH 1998 Forces on bins: The effect of random friction E. Bruce Pitman* Department of Mathematics, State University of New York, Buffalo, New York 14214 Received
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 57, NUMBER 3 MARCH 1998 Forces on bins: The effect of random friction E. Bruce Pitman* Department of Mathematics, State University of New York, Buffalo, New York 14214 Received
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing.
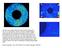 This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
Study of flow landslide impact forces on protection structures with the Material Point Method
 Study of flow landslide impact forces on protection structures with the Material Point Method F. Ceccato DICEA University of Padua, Italy ABSTRACT: to assess the potential damage caused by a landslide
Study of flow landslide impact forces on protection structures with the Material Point Method F. Ceccato DICEA University of Padua, Italy ABSTRACT: to assess the potential damage caused by a landslide
JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials
 JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials Drienerburght, University of Twente, February 25 - March 1, 2013 Speakers: Dirk van der Ende - Nico Gray - Detlef Lohse - Stefan Luding
JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials Drienerburght, University of Twente, February 25 - March 1, 2013 Speakers: Dirk van der Ende - Nico Gray - Detlef Lohse - Stefan Luding
Quasistatic behavior and force transmission in packing of irregular polyhedral particles
 Quasistatic behavior and force transmission in packing of irregular polyhedral particles Emilien Azéma, Farhang Radjai, Gilles Saussine To cite this version: Emilien Azéma, Farhang Radjai, Gilles Saussine.
Quasistatic behavior and force transmission in packing of irregular polyhedral particles Emilien Azéma, Farhang Radjai, Gilles Saussine To cite this version: Emilien Azéma, Farhang Radjai, Gilles Saussine.
