A TOOL FOR DETERMINATION FINITE SEISMIC SOURCE PARAMETERS VIA STOPPING PHASES METHOD
|
|
|
- Emerald Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A TOOL FOR DETERMINATION FINITE SEISMIC SOURCE PARAMETERS VIA STOPPING PHASES METHOD P. Kolář Institute of Geophysics, Czech Acad. of Sci. of Czech Rep. Abstract We present a special (interactive) tool for particular processing of seismograms from West Bohemia region. The purpose of the data investigation is to determine the parameter of (simplified) seismic source. There are given basic information about the seismic region, its activity, about the used method and about its particular realization. The developed tool is described including screen shots of the graphical interfaces. 1 Background and motivation West Bohemia region is definitely the most seismo-active region on the territory of Czech Republic. This fact has been recently confirmed by a seismic swarm which lasted from August 23 th till the end of September 2011 year see Fig. 1a,b. The seismic activity is one of the features of geodynamics processes which performed in this region. The West Bohemia seismic activity is not manifested by occurrence of singe events, but the individual events are clustered in so named seismic swarms. Such type of seismic activity is known also in other regions (e.g. Iceland, Sultz in France, north Italy), but it has been firstly investigated just in West Bohemia region in 19 th century. The swarm activity can be traces back to middle ages, however instrumental observation can be dated to beginning of 20 th century. Local network of (analogues) seismic station was build up on Germany part of the region in The modern, i.e. digital, observations were started during pronounced seismic swarm which occurred in 1985/86. At that time it was established WEBNET (Horálek et al., 2000) - a network of digital seismic stations. The WEBNET network continuously operates; of course during the time it was enlarged (up to contemporary number of about 20 stations), the equipment is permanently modernized, the network shape was tuned to optimum. Data transfer from selected stations is now continuous and on-line. At the beginning of digital seismic observations, the main effort was concentrated on basic data processing, e.g. routine pre-processing, event identification, location, magnitude determination. Lately, the investigated tasks were enlarged to time-spatial distribution study, seismic source mechanism determination of larger events (at the beginning only double couple model was considered, lately full 6 component seismic moment tensor were determined). Together with these tasks there were performed also some structural studies. During approximately last decade, such studies become a little bit routine (even if still they are of significant importance and by far not all the problems has been solved yet) and it has arisen a highly specialized studies, as e.g. determination parameters of a finite source mode. This is also the case of our study. The observed data are permanently subject of various studies see e.g. Stud. Geophys. et Geod., (2000, 2008 and 2009). Actual information about the West Bohemia activity can be found on wwwwebnet (2011a,b).
2 Figure 1a. Map of West Bohemia region with the epicenters of 2011 swarm (circles) and WEBNET stations (triangels) overtaken from wwwwebnet (2011b) Figure 1a Time distribution of the events versus magnitude of 2011 year swarm - overtaken from wwwwebnet (2011b) 2 Stopping phases method To model finite source we adopted Stopping phases method developed by Imanishi and Takeo (1998, 2002), which is based on relatively simple idea. Here, the seismic source is modeled as a rupture propagating radially from a nucleation point along the fault plane (the orientation of the fault plane is supposed to be known from previous study). The rupturing continues with constant velocity until the source boundary is reached; in our model the boundary is supposed to be of circular or elliptical shapes respectively. Note, that such models are considered to be suitable for relatively week events, which is definitely our case. For the rupture process can be identified in seismograms three phases: (i) first arrival wave, which corresponds to the beginning of the process (i.e. signals coming from the source nucleation point) and (ii) two so named stopping phases, which correspond to stopping points situated on the margin
3 of ruptured area. In a figurative way, the stopping phases can be understand as a changes in the course of observed displacement produced by finite source. When the rupture process reach the source boundary and fade in a particular direction, such a change results in a change of slope of displacement pulse, which can be (in twice differentiate displacement signal, i.e. in accelerogram) interpreted as a stopping phase. Or in another words (figurative way proposed Imanishi and Takeo) the source radiation can be reduced into three points, while the signals from all other point are mutually destroyed by deconstructive interference. Imanishi and Takeo (1998, 2002), derived stopping phases theory and methodology for their identification see also Appendix. The two stopping phases are in mutual relation as a pulse and its Hilbert transform, which is also the criterion for their identification. The time lags between these phases depend on source size, geometrical orientation of the finite source and also on the source-to-station path. Therefore first we have to search for the stopping phases in seismograms. The time delays between onset and these two stopping phases represent the input data, which are subject of inversion.. 3 Data processing While the above mentioned inversion is contemporary more or less routine process, the stopping phases identification it has appeared to be crucial. As soon as we started process real data it has appeared same features. We try to determine finite seismic source for selected events from West Bohemia seismic area from 2000 year and lately also from 2008 year (such a detail study as it is in our case, it is necessary delay for same time, as it is necessary to wait for results from others previous data processing). The processed data are partly low indexed and the signals suffer from partial disturbances (which origin is known only partly), that the stopping phases positions definitely cannot be determined automatically. Soon after the starting the study, it has appeared that all the picked stopping phases positions have to be checked and in necessary corrected interactively. To be able to do such interpretation effectively we have developed an interactive tool (created on MATLAB platform) which is briefly described in the next section. 4 Interactive tool realization To handle the exploited data in an effective way we have developed unique Tool for determination finite seismic source parameters via Stopping phase method. The code was written on MATLAB platform. In the Fig. 2 there is a screen shot of the tool main window, its basic features are given below: Main control window - header In the upper part there is a header, which displays principal information about the processed event, namely event identification, location, magnitude, source mechanism (all this data are taken form prearranged tables). Further there are displayed results of the two last inversion attempts (to be able to compare their results) and some control buttons are present. Main control window - display area Below, there are displayed individual records of processed event. There are 3 vertical columns: o Left column - seismograms On the left there are plotted seismograms (transversal component of acceleration, its Hilbert transform and Hilbert transform multiplied by -1; all these signal are used to calculate mutual correlation
4 Header (general data, controls, settings ) Inversion results (finite source parameters) Left column (seismograms, Hilbert transforms) Middle column (correlation maps) Right column (stopping phase positions, residuals) Figure 2. Screen shot of the main control window of the Tool
5 to determine stopping phases), the positions of interpreted stopping phases as well as seismic wave onset are marked. o Middle column: correlation maps In the middle column there are correlation maps. These maps are main mean for stopping phases identification: the stopping phases are defined as a point with highest mutual correlation. Unfortunately, the processed signal waveform are not simple enough and the point with maximal correlation does not necessary corresponds to the stopping phases. Therefore we check every automatic interpretation and if the stopping phase position appeared to be unrealistic and simultaneously there is a pronounced local maximum close to the expected stopping phases position, we prefer this interpretation as the more probable. Note, that such approach is also mention by the stopping phases method see Imanishi and Takeo (1998, 2002). Note also that the origin of false correlation is not exactly known probably it is some reflection of the signal on the subtle medium structure (which is not yet known in details). o Right column: numbers In the right column there are displayed values of stopping phases interpretation, inversions result, inversion residua and some control buttons. There are displayed the values of original (automatic) interpretation, their corrections if available and the various inversion result and their residua see below. In addition the tool enables to set length of interval of correlation, weight individual records and switched on/off particular record from the calculation. The number of records displayed can be changed to enable clear visibility of the investigated event; in the case of extend number of seismogram the plots are swapped BUBD TRC KOC HOPD POLD PLED SKC VAC LBC POC NKC KOPD KRC SNED LOUD STC OLV HRED HRC KAC ZHC LAC Figure 3. Schematic map of used stations map is bind to the on/off switched seismograms.
6 Secondary window - map At the separate window (see fig. 3), there is a separate map of the region with marked event epicenter, considered stations; the stations included/not included into inversion process are marked by different colors 5 Performed inversion(s) Stopping phases position interpreted (either automatically or interactively) are input data to the inversion. The data are piped into independent inversion code and the inversion is run. Then the inversion results are read and displayed in form of particular values as well as in a graphical form. We use BRST inversion designed by Boender et al., (1982) and Czendes, (1988), wwwbrst (2011). The inversion evaluation is relatively fast, so it appears to the user as semi-interactive. During the inversion we are seeking for values of two, three and four parameters. The considered circular seismic source is described by two parameters (namely source radius and rupture velocity). The elliptical source by four parameters (namely by principal axes, eccentricity, rupture velocity and ellipse orientation on the fault plane). As the rupture velocity and the source size showed sometimes coupling, we perform also inversion with fix value of rupture velocity. We display simultaneously results of the inversion and of the previous one. This enables effective comparison of different combination of input data sets. Note that results of inversion confirm theoretical relation r=30*10 (0.35 Ml) (1) which bound even magnitude and its radius derived (Fischer and Horálek, 2005). 6 Conclusions The developed code appears to be an effective tool for (sometime low indexed) data processing. The code is subject of continuous development and improvements. The exploited method is rather particular in its orientation, nevertheless observation indicates that the correlation can be useful for identification of other phases in seismograms which potentially open a way for detailed interpretation of subtle medium structure. Acknowledgement Presentation of this work is supported by grant: P210/10/1728 of the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (Z. Jechumtálová). References Boender, C.G.E., Rinnooy Kan, A.H.G. and Timmer, G.T.: 1982, A Stochastic method for global optimalisation, Mathematical programming, 22,
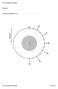
7 Csendes, T.: 1988, Nonlinear parameter estimation by global optimization Efficiency and reliability, Acta Cybernetica, VIII/4, Horálek, J., Fischer, T., Boušková, A., and Jedlička, P.: 2000, The Western Bohemia/Vogtland Region in the Light of the Webnet Network, Studia Geophys. et Geodet., 44, 2, Imanishi, K. and Takeo, M.: 1998, Estimates of fault dimensions for small earthquakes using stopping phases, Geophys. J. Let., 25, 15, pp Imanishi, K. and Takeo, M.: 2002, An inversion method to analyze rupture process of small earthquakes using stopping phases, J. Geophys. Res., 107, B3. Studia Geohpysica et Geodetica: 2000, (special issue devotes to West Bohemia topics): 44, 2 3. Studia Geohpysica et Geodetica: 2008, (special issue devotes to West Bohemia topics Part 1): 52, 4. Studia Geohpysica et Geodetica: 2009, (special issue devotes to West Bohemia topics Part 2): 53, 3. wwwbrst: 2011, access: 12 Jan wwwwebnet: 2011a, access: 15 Oct wwwwebnet: 2011b, access: 15 Oct Appendix: HOW and WHERE are Stopping phases generated To figuratively demonstrate in which points of the source the Stop phases are generated we developed a program which plots a simplified figure. The figure itself is 3D semi-interactive, here we present its screen shots. In the figures 4a,b it can be seen a circular source (r = 2.5 km, depth = 5 km ) and two stations (marked by triangles, epicentral distance 11.2 km [red] and 7.2 km [blue]). The apparent iso-chrones - i.e. lines which burst at the same time from the point of view of a particular station - are plotted as well as a ray from Stop points (asterisk) homogeneous medium model is supposed, i.e. the rays are straight (dotted) lines. Figure 4 a,b. Radiation of Stopping phases Contact information: P. Kolář, Institute of Geophysics, Czech Acad. of Sci., Boční II 1401, Praha 4 Spořilov, , Czech Republic, kolar@ig.cas.cz
VISUALIZATION OF THE FAULT SLIP CONNECTED WITH THE WEST BOHEMIA EARTHQUAKE SWARMS. Petr KOLÁŘ *, Bohuslav RŮŽEK, Alena BOUŠKOVÁ and Josef HORÁLEK
 Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 8, No. (6), 69 87, VISUALIZATION OF THE FAULT SLIP CONNECTED WITH THE WEST BOHEMIA EARTHQUAKE SWARMS Petr KOLÁŘ *, Bohuslav RŮŽEK, Alena BOUŠKOVÁ and Josef HORÁLEK Institute
Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 8, No. (6), 69 87, VISUALIZATION OF THE FAULT SLIP CONNECTED WITH THE WEST BOHEMIA EARTHQUAKE SWARMS Petr KOLÁŘ *, Bohuslav RŮŽEK, Alena BOUŠKOVÁ and Josef HORÁLEK Institute
FINITE SEISMIC SOURCE PARAMETERS INFERRED FROM STOPPING PHASES FOR SELECTED EVENTS OF WEST BOHEMIA 2000 SWARM
 Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 9, No. 4 (168), 435 447, 1 FINITE SEISMIC SOURCE PARAMETERS INFERRED FROM STOPPING PHASES FOR SELECTED EVENTS OF WEST BOHEMIA SWARM Petr KOLÁŘ * and Bohuslav RŮŽEK Institute
Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 9, No. 4 (168), 435 447, 1 FINITE SEISMIC SOURCE PARAMETERS INFERRED FROM STOPPING PHASES FOR SELECTED EVENTS OF WEST BOHEMIA SWARM Petr KOLÁŘ * and Bohuslav RŮŽEK Institute
Moho depth determination from waveforms of microearthquakes in the West Bohemia/Vogtland swarm area
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SOLID EARTH, VOL. 11, 137, doi:.29/2jb936, 213 Moho depth determination from waveforms of microearthquakes in the West Bohemia/Vogtland swarm area Pavla Hrubcová, 1 Václav
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SOLID EARTH, VOL. 11, 137, doi:.29/2jb936, 213 Moho depth determination from waveforms of microearthquakes in the West Bohemia/Vogtland swarm area Pavla Hrubcová, 1 Václav
REPLY TO THE OPEN LETTER
 Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 10, No. 1 (169), 41 45, 2013 DOI: 10.13168/AGG.2013.0003 REPLY TO THE OPEN LETTER TO CRUSTAL DEFORMATION MODELING OF THE WEST BOHEMIA SWARM AREA, CENTRAL EUROPE.Vladimír SCHENK
Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 10, No. 1 (169), 41 45, 2013 DOI: 10.13168/AGG.2013.0003 REPLY TO THE OPEN LETTER TO CRUSTAL DEFORMATION MODELING OF THE WEST BOHEMIA SWARM AREA, CENTRAL EUROPE.Vladimír SCHENK
Determination of prominent crustal discontinuities from waveforms of local earthquakes Pavla Hrubcová Václav Vavryčuk Alena Boušková Josef Horálek
 Determination of prominent crustal discontinuities from waveforms of local earthquakes avla Hrubcová Václav Vavryčuk Alena Boušková Josef Horálek Institute of Geophysics, Academy of ciences, rague, Czech
Determination of prominent crustal discontinuities from waveforms of local earthquakes avla Hrubcová Václav Vavryčuk Alena Boušková Josef Horálek Institute of Geophysics, Academy of ciences, rague, Czech
of other regional earthquakes (e.g. Zoback and Zoback, 1980). I also want to find out
 4. Focal Mechanism Solutions A way to investigate source properties of the 2001 sequence is to attempt finding well-constrained focal mechanism solutions to determine if they are consistent with those
4. Focal Mechanism Solutions A way to investigate source properties of the 2001 sequence is to attempt finding well-constrained focal mechanism solutions to determine if they are consistent with those
IMPLEMENT ROUTINE AND RAPID EARTHQUAKE MOMENT-TENSOR DETERMINATION AT THE NEIC USING REGIONAL ANSS WAVEFORMS
 Final Technical Report Award number: 05HQGR0062 IMPLEMENT ROUTINE AND RAPID EARTHQUAKE MOMENT-TENSOR DETERMINATION AT THE NEIC USING REGIONAL ANSS WAVEFORMS Lupei Zhu Saint Louis University Department
Final Technical Report Award number: 05HQGR0062 IMPLEMENT ROUTINE AND RAPID EARTHQUAKE MOMENT-TENSOR DETERMINATION AT THE NEIC USING REGIONAL ANSS WAVEFORMS Lupei Zhu Saint Louis University Department
Geodynamic Pattern of the West Bohemia during the October 2008 Earthquake Swarm
 10th Czech-Polish Workshop on RECENT GEODYNAMICS OF THE SUDETEN AND ADJACENT AREAS Szklarska Poręba, November 5-7, 2009 Geodynamic Pattern of the West Bohemia during the October 2008 Earthquake Swarm Vladimír
10th Czech-Polish Workshop on RECENT GEODYNAMICS OF THE SUDETEN AND ADJACENT AREAS Szklarska Poręba, November 5-7, 2009 Geodynamic Pattern of the West Bohemia during the October 2008 Earthquake Swarm Vladimír
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11492 Figure S1 Short-period Seismic Energy Release Pattern Imaged by F-net. (a) Locations of broadband seismograph stations in Japanese F-net used for the 0.5-2.0 Hz P wave back-projection
doi:10.1038/nature11492 Figure S1 Short-period Seismic Energy Release Pattern Imaged by F-net. (a) Locations of broadband seismograph stations in Japanese F-net used for the 0.5-2.0 Hz P wave back-projection
revised October 30, 2001 Carlos Mendoza
 Earthquake Sources in the circum-caribbean Region Puerto Rico Tsunami Mitigation and Warning Program Federal Emergency Management Agency Preliminary Report: Task 3 revised October 30, 2001 Carlos Mendoza
Earthquake Sources in the circum-caribbean Region Puerto Rico Tsunami Mitigation and Warning Program Federal Emergency Management Agency Preliminary Report: Task 3 revised October 30, 2001 Carlos Mendoza
S e i s m i c W a v e s
 Project Report S e i s m i c W a v e s PORTLAND STATE UNIVERSITY PHYSICS 213 SPRING TERM 2005 Instructor: Dr. Andres La Rosa Student Name: Prisciliano Peralta-Ramirez Table Of Contents 1. Cover Sheet 2.
Project Report S e i s m i c W a v e s PORTLAND STATE UNIVERSITY PHYSICS 213 SPRING TERM 2005 Instructor: Dr. Andres La Rosa Student Name: Prisciliano Peralta-Ramirez Table Of Contents 1. Cover Sheet 2.
3.3. Waveform Cross-Correlation, Earthquake Locations and HYPODD
 3.3. Waveform Cross-Correlation, Earthquake Locations and HYPODD 3.3.1 Method More accurate relative earthquake locations depend on more precise relative phase arrival observations so I exploit the similarity
3.3. Waveform Cross-Correlation, Earthquake Locations and HYPODD 3.3.1 Method More accurate relative earthquake locations depend on more precise relative phase arrival observations so I exploit the similarity
The 2016, October 26, Central Italy Earthquake Origin Time 17:10:36 UTC, M L(ISNet) =5.3; M W(ISNet) =5.6
 The 2016, October 26, Central Italy Earthquake Origin Time 17:10:36 UTC, M L(ISNet) =5.3; M W(ISNet) =5.6 RISSC-Lab: Laboratorio di RIcerca in Sismologia Sperimentale e Computazionale The event as seen
The 2016, October 26, Central Italy Earthquake Origin Time 17:10:36 UTC, M L(ISNet) =5.3; M W(ISNet) =5.6 RISSC-Lab: Laboratorio di RIcerca in Sismologia Sperimentale e Computazionale The event as seen
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 20, 30 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Aki, Scaling law
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 20, 30 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Aki, Scaling law
Data Repository: Seismic and Geodetic Evidence For Extensive, Long-Lived Fault Damage Zones
 DR2009082 Data Repository: Seismic and Geodetic Evidence For Extensive, Long-Lived Fault Damage Zones Fault Zone Trapped Wave Data and Methods Fault zone trapped waves observed for 2 shots and 5 local
DR2009082 Data Repository: Seismic and Geodetic Evidence For Extensive, Long-Lived Fault Damage Zones Fault Zone Trapped Wave Data and Methods Fault zone trapped waves observed for 2 shots and 5 local
CLUSTERING OF 2008 WEST BOHEMIAN SEISMIC SWARM MECHANISMS AND ITS POSSIBLE INTERPRETATION
 Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 15, No. 1 (189), 27 40, 2018 DOI: 10.13168/AGG.2018.0001 journal homepage: https://www.irsm.cas.cz/acta ORIGINAL PAPER CLUSTERING OF 2008 WEST BOHEMIAN SEISMIC SWARM MECHANISMS
Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol. 15, No. 1 (189), 27 40, 2018 DOI: 10.13168/AGG.2018.0001 journal homepage: https://www.irsm.cas.cz/acta ORIGINAL PAPER CLUSTERING OF 2008 WEST BOHEMIAN SEISMIC SWARM MECHANISMS
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story
 Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source
 Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
Widespread Ground Motion Distribution Caused by Rupture Directivity during the 2015 Gorkha, Nepal Earthquake
 Widespread Ground Motion Distribution Caused by Rupture Directivity during the 2015 Gorkha, Nepal Earthquake Kazuki Koketsu 1, Hiroe Miyake 2, Srinagesh Davuluri 3 and Soma Nath Sapkota 4 1. Corresponding
Widespread Ground Motion Distribution Caused by Rupture Directivity during the 2015 Gorkha, Nepal Earthquake Kazuki Koketsu 1, Hiroe Miyake 2, Srinagesh Davuluri 3 and Soma Nath Sapkota 4 1. Corresponding
SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley)
 SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley) This practical deals with surface waves, which are usually the largest amplitude arrivals on the seismogram. The velocity at which surface waves propagate
SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley) This practical deals with surface waves, which are usually the largest amplitude arrivals on the seismogram. The velocity at which surface waves propagate
Determining the Earthquake Epicenter: Japan
 Practice Name: Hour: Determining the Earthquake Epicenter: Japan Measuring the S-P interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest of the world.
Practice Name: Hour: Determining the Earthquake Epicenter: Japan Measuring the S-P interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest of the world.
BROADBAND STRONG MOTION SIMULATION OF THE 2004 NIIGATA- KEN CHUETSU EARTHQUAKE: SOURCE AND SITE EFFECTS
 Third International Symposium on the Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion Grenoble, France, 30 August - 1 September 2006 Paper Number: 105 BROADBAND STRONG MOTION SIMULATION OF THE 2004 NIIGATA-
Third International Symposium on the Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion Grenoble, France, 30 August - 1 September 2006 Paper Number: 105 BROADBAND STRONG MOTION SIMULATION OF THE 2004 NIIGATA-
volcanic tremor and Low frequency earthquakes at mt. vesuvius M. La Rocca 1, D. Galluzzo 2 1
 volcanic tremor and Low frequency earthquakes at mt. vesuvius M. La Rocca 1, D. Galluzzo 2 1 Università della Calabria, Cosenza, Italy 2 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia Osservatorio Vesuviano,
volcanic tremor and Low frequency earthquakes at mt. vesuvius M. La Rocca 1, D. Galluzzo 2 1 Università della Calabria, Cosenza, Italy 2 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia Osservatorio Vesuviano,
Earthquake Lab Introduction: Purpose: Method: Equipment needed: Fundamental Concepts and Key Terms:
 Earthquake Lab Introduction: Seismology is that branch of the geological sciences which is concerned with the study of earthquakes. Purpose: The purpose of this exercise is to introduce some fundamental
Earthquake Lab Introduction: Seismology is that branch of the geological sciences which is concerned with the study of earthquakes. Purpose: The purpose of this exercise is to introduce some fundamental
What happened before the last five strong earthquakes in Greece: Facts and open questions
 86 Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B 82 (2006) [Vol. 82, What happened before the last five strong earthquakes in Greece: Facts and open questions By Panayiotis A. VAROTSOS ) Solid State Section and Solid Earth
86 Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B 82 (2006) [Vol. 82, What happened before the last five strong earthquakes in Greece: Facts and open questions By Panayiotis A. VAROTSOS ) Solid State Section and Solid Earth
25th Seismic Research Review - Nuclear Explosion Monitoring: Building the Knowledge Base
 KARATAU, MAKANCHI, AND LOCATION IN WESTERN CHINA Lee K. Steck, George E. Randall, Michael L. Begnaud, Charlotte A. Rowe, and Aaron A. Velasco Los Alamos National Laboratory Sponsored by National Nuclear
KARATAU, MAKANCHI, AND LOCATION IN WESTERN CHINA Lee K. Steck, George E. Randall, Michael L. Begnaud, Charlotte A. Rowe, and Aaron A. Velasco Los Alamos National Laboratory Sponsored by National Nuclear
Preliminary slip model of M9 Tohoku earthquake from strongmotion stations in Japan - an extreme application of ISOLA code.
 Preliminary slip model of M9 Tohoku earthquake from strongmotion stations in Japan - an extreme application of ISOLA code. J. Zahradnik 1), F. Gallovic 1), E. Sokos 2) G-A. Tselentis 2) 1) Charles University
Preliminary slip model of M9 Tohoku earthquake from strongmotion stations in Japan - an extreme application of ISOLA code. J. Zahradnik 1), F. Gallovic 1), E. Sokos 2) G-A. Tselentis 2) 1) Charles University
ERTH2020 Introduction to Geophysics The Seismic Method. 1. Basic Concepts in Seismology. 1.1 Seismic Wave Types
 ERTH2020 Introduction to Geophysics The Seismic Method 1. Basic Concepts in Seismology 1.1 Seismic Wave Types Existence of different wave types The existence of different seismic wave types can be understood
ERTH2020 Introduction to Geophysics The Seismic Method 1. Basic Concepts in Seismology 1.1 Seismic Wave Types Existence of different wave types The existence of different seismic wave types can be understood
Dangerous tsunami threat off U.S. West Coast
 Earthquakes Ch. 12 Dangerous tsunami threat off U.S. West Coast Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? It s the shaking and trembling of the Earth s crust due to plate movement. The plates move, rocks along
Earthquakes Ch. 12 Dangerous tsunami threat off U.S. West Coast Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? It s the shaking and trembling of the Earth s crust due to plate movement. The plates move, rocks along
Earthquake information
 Name: Date: Block Earthquake information The graph below shows travel time in minutes and distance traveled for primary and secondary waves. Primary and secondary waves start at the same time but do not
Name: Date: Block Earthquake information The graph below shows travel time in minutes and distance traveled for primary and secondary waves. Primary and secondary waves start at the same time but do not
Seismic Waves. 1. Seismic Deformation
 Types of Waves 1. Seismic Deformation Seismic Waves When an earthquake fault ruptures, it causes two types of deformation: static; and dynamic. Static deformation is the permanent displacement of the ground
Types of Waves 1. Seismic Deformation Seismic Waves When an earthquake fault ruptures, it causes two types of deformation: static; and dynamic. Static deformation is the permanent displacement of the ground
ON NEAR-FIELD GROUND MOTIONS OF NORMAL AND REVERSE FAULTS FROM VIEWPOINT OF DYNAMIC RUPTURE MODEL
 1 Best Practices in Physics-based Fault Rupture Models for Seismic Hazard Assessment of Nuclear ON NEAR-FIELD GROUND MOTIONS OF NORMAL AND REVERSE FAULTS FROM VIEWPOINT OF DYNAMIC RUPTURE MODEL Hideo AOCHI
1 Best Practices in Physics-based Fault Rupture Models for Seismic Hazard Assessment of Nuclear ON NEAR-FIELD GROUND MOTIONS OF NORMAL AND REVERSE FAULTS FROM VIEWPOINT OF DYNAMIC RUPTURE MODEL Hideo AOCHI
RELOCATION OF THE MACHAZE AND LACERDA EARTHQUAKES IN MOZAMBIQUE AND THE RUPTURE PROCESS OF THE 2006 Mw7.0 MACHAZE EARTHQUAKE
 RELOCATION OF THE MACHAZE AND LACERDA EARTHQUAKES IN MOZAMBIQUE AND THE RUPTURE PROCESS OF THE 2006 Mw7.0 MACHAZE EARTHQUAKE Paulino C. FEITIO* Supervisors: Nobuo HURUKAWA** MEE07165 Toshiaki YOKOI** ABSTRACT
RELOCATION OF THE MACHAZE AND LACERDA EARTHQUAKES IN MOZAMBIQUE AND THE RUPTURE PROCESS OF THE 2006 Mw7.0 MACHAZE EARTHQUAKE Paulino C. FEITIO* Supervisors: Nobuo HURUKAWA** MEE07165 Toshiaki YOKOI** ABSTRACT
The Mw 6.2 Leonidio, southern Greece earthquake of January 6, 2008: Preliminary identification of the fault plane.
 The Mw 6.2 Leonidio, southern Greece earthquake of January 6, 28: Preliminary identification of the fault plane. J. Zahradnik 1, E. Sokos 2, A.Serpetsidaki 2, and G A.Tselentis 2 1 Charles University in
The Mw 6.2 Leonidio, southern Greece earthquake of January 6, 28: Preliminary identification of the fault plane. J. Zahradnik 1, E. Sokos 2, A.Serpetsidaki 2, and G A.Tselentis 2 1 Charles University in
AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING
 CO 2 TRACCS INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP Bucharest, 2 September, 2012 AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING M. Semih YÜCEMEN Department of Civil Engineering and Earthquake Studies
CO 2 TRACCS INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP Bucharest, 2 September, 2012 AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING M. Semih YÜCEMEN Department of Civil Engineering and Earthquake Studies
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR
 A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
60 C From Bicycle to Space. Dionysis Konstantinou Corina Toma. Space Travel
 60 C From Bicycle to Space Dionysis Konstantinou Corina Toma C Space Travel From Bicycle Length to Space of the CDay61 introduction Imagine travelling from one planet to another Why is it that we have
60 C From Bicycle to Space Dionysis Konstantinou Corina Toma C Space Travel From Bicycle Length to Space of the CDay61 introduction Imagine travelling from one planet to another Why is it that we have
Inversion of travel times to estimate Moho depth in Shillong Plateau and Kinematic implications through stress analysis of Northeastern India
 Inversion of travel times to estimate Moho depth in Shillong Plateau and Kinematic implications through stress analysis of Northeastern India by Saurabh Baruah Geoscience Division North-East Institute
Inversion of travel times to estimate Moho depth in Shillong Plateau and Kinematic implications through stress analysis of Northeastern India by Saurabh Baruah Geoscience Division North-East Institute
Earthquake Focal Mechanisms and Waveform Modeling
 Earthquake Focal Mechanisms and Waveform Modeling Rengin Gök Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory USA RELEMR Workshop İstanbul 2008 Gudmundar E. Sigvaldason The Dynamic Earth, USGS The size of the event
Earthquake Focal Mechanisms and Waveform Modeling Rengin Gök Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory USA RELEMR Workshop İstanbul 2008 Gudmundar E. Sigvaldason The Dynamic Earth, USGS The size of the event
Moveout approximation for P waves in a homogeneous VTI medium
 Moveout approximation for P waves in a homogeneous VTI medium Véronique Farra 1 and Ivan Pšenčík 2 1 Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Université Paris Diderot, UMR 7154 CNRS,
Moveout approximation for P waves in a homogeneous VTI medium Véronique Farra 1 and Ivan Pšenčík 2 1 Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Université Paris Diderot, UMR 7154 CNRS,
A. Locate the Epicenter
 Name: Block: Earthquake Lab The goal of this portion of the lab is to learn how recording of earthquakes seismograms are used to locate earthquakes, determine their magnitudes, and to understand the sense
Name: Block: Earthquake Lab The goal of this portion of the lab is to learn how recording of earthquakes seismograms are used to locate earthquakes, determine their magnitudes, and to understand the sense
How Do We Know Where an Earthquake Originated? Teacher's Guide
 How Do We Know Where an Earthquake Originated? Teacher's Guide Standard Addressed: Grades 6-8: Scientific Inquiry 1 B/1, 2 Mathematical Inquiry 2 C/2 Technology and Science 3 A/2 Processes that shape the
How Do We Know Where an Earthquake Originated? Teacher's Guide Standard Addressed: Grades 6-8: Scientific Inquiry 1 B/1, 2 Mathematical Inquiry 2 C/2 Technology and Science 3 A/2 Processes that shape the
SEISMIC DATA PROCESSING ON THE BASIS OF POLARIZATION ANALYSIS
 SEISMIC DATA PROCESSING ON THE BASIS OF POLARIZATION ANALYSIS V.B. Zaalishvili Sc. Doctor (Phys.-math.), D.A. Melkov Sc. Candidate (Tech.) Center of Geophysical Investigations of Vladikavkaz Scientific
SEISMIC DATA PROCESSING ON THE BASIS OF POLARIZATION ANALYSIS V.B. Zaalishvili Sc. Doctor (Phys.-math.), D.A. Melkov Sc. Candidate (Tech.) Center of Geophysical Investigations of Vladikavkaz Scientific
Analysis of the 29th May 2008 Ölfus earthquake and aftershock sequence using three-component t processing on ICEARRAY
 Analysis of the 29th May 2008 Ölfus earthquake and aftershock sequence using three-component t processing on ICEARRAY Benedikt Halldórsson Steven J. Gibbons International Symposium on Strong-motion Earthquake
Analysis of the 29th May 2008 Ölfus earthquake and aftershock sequence using three-component t processing on ICEARRAY Benedikt Halldórsson Steven J. Gibbons International Symposium on Strong-motion Earthquake
STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION OF A MATERIAL EXHIBITING NEGATIVE STIFFNESS
 International Conference on Engineering Vibration Ljubljana, Slovenia, 7-0 September 05 STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION OF A MATERIAL EXHIBITING NEGATIVE STIFFNESS Zuzana Dimitrovová*, Jan Heczo, Helder C. Rodrigues
International Conference on Engineering Vibration Ljubljana, Slovenia, 7-0 September 05 STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION OF A MATERIAL EXHIBITING NEGATIVE STIFFNESS Zuzana Dimitrovová*, Jan Heczo, Helder C. Rodrigues
APPLICATION OF RECEIVER FUNCTION TECHNIQUE TO WESTERN TURKEY
 APPLICATION OF RECEIVER FUNCTION TECHNIQUE TO WESTERN TURKEY Timur TEZEL Supervisor: Takuo SHIBUTANI MEE07169 ABSTRACT In this study I tried to determine the shear wave velocity structure in the crust
APPLICATION OF RECEIVER FUNCTION TECHNIQUE TO WESTERN TURKEY Timur TEZEL Supervisor: Takuo SHIBUTANI MEE07169 ABSTRACT In this study I tried to determine the shear wave velocity structure in the crust
Module 7: Plate Tectonics and Earth's Structure Topic 4 Content : Earthquakes Presentation Notes. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes 1 Topic 4 Content: Earthquakes Presentation Notes Earthquakes are vibrations within the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy from rocks that break under extreme stress. Earthquakes
Earthquakes 1 Topic 4 Content: Earthquakes Presentation Notes Earthquakes are vibrations within the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy from rocks that break under extreme stress. Earthquakes
Kirchhoff prestack depth migration in simple models of various anisotropy
 Kirchhoff prestack depth migration in simple models of various anisotropy Václav Bucha Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University, Ke Karlovu, 6 Praha, Czech Republic,
Kirchhoff prestack depth migration in simple models of various anisotropy Václav Bucha Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University, Ke Karlovu, 6 Praha, Czech Republic,
crustal volume of the swarm. This initiated interest and concern that another
 3. Earthquae locations Data from permanent seismic networs located the 2001 Enola mainshoc within the crustal volume of the 1982-84 swarm. This initiated interest and concern that another 1982-lie sequence
3. Earthquae locations Data from permanent seismic networs located the 2001 Enola mainshoc within the crustal volume of the 1982-84 swarm. This initiated interest and concern that another 1982-lie sequence
BRIEF ARTICLE THE AUTHOR
 BRIEF ARTICLE THE AUTHOR 1 2 THE AUTHOR S Pd K Pd S mantle OC IC CMB Figure 1 Figure 1. Illustration of the SPdKS / SKPdS ray-paths with sub-segments labeled. SPdKS is an SKS that intersects the source-side
BRIEF ARTICLE THE AUTHOR 1 2 THE AUTHOR S Pd K Pd S mantle OC IC CMB Figure 1 Figure 1. Illustration of the SPdKS / SKPdS ray-paths with sub-segments labeled. SPdKS is an SKS that intersects the source-side
JOINT ACCURATE TIME-FREQUENCY AND HIGH-RESOLUTION ARRAY ANALYSIS, A TOOL FOR SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATION?
 Third International Symposium on the Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion Grenoble, France, 30 August - 1 September 2006 Paper Number: 152 JOINT ACCURATE TIME-FREQUENCY AND HIGH-RESOLUTION ARRAY
Third International Symposium on the Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion Grenoble, France, 30 August - 1 September 2006 Paper Number: 152 JOINT ACCURATE TIME-FREQUENCY AND HIGH-RESOLUTION ARRAY
Outstanding Problems. APOSTOLOS S. PAPAGEORGIOU University of Patras
 NEAR-FAULT GROUND MOTIONS: Outstanding Problems APOSTOLOS S. PAPAGEORGIOU University of Patras Outline Characteristics of near-fault ground motions Near-fault strong ground motion database A mathematical
NEAR-FAULT GROUND MOTIONS: Outstanding Problems APOSTOLOS S. PAPAGEORGIOU University of Patras Outline Characteristics of near-fault ground motions Near-fault strong ground motion database A mathematical
LAB 3: GLOBAL SEISMOLOGY
 NAME: LAB TIME: LAB 3: GLOBAL SEISMOLOGY This lab will introduce you to the basic concepts of global seismology and the Earth s interior structure. This is a hybrid assignment: some aspects can be done
NAME: LAB TIME: LAB 3: GLOBAL SEISMOLOGY This lab will introduce you to the basic concepts of global seismology and the Earth s interior structure. This is a hybrid assignment: some aspects can be done
Earthquake patterns in the Flinders Ranges - Temporary network , preliminary results
 Earthquake patterns in the Flinders Ranges - Temporary network 2003-2006, preliminary results Objectives David Love 1, Phil Cummins 2, Natalie Balfour 3 1 Primary Industries and Resources South Australia
Earthquake patterns in the Flinders Ranges - Temporary network 2003-2006, preliminary results Objectives David Love 1, Phil Cummins 2, Natalie Balfour 3 1 Primary Industries and Resources South Australia
Assessing the solution quality of the earthquake location problem
 Semesterarbeit HS 2008 Department of Earth Sciences ETH Zurich Assessing the solution quality of the earthquake location problem Sabrina Schönholzer Supervisor: Technical Supervisor: Prof. Dr. E. Kissling
Semesterarbeit HS 2008 Department of Earth Sciences ETH Zurich Assessing the solution quality of the earthquake location problem Sabrina Schönholzer Supervisor: Technical Supervisor: Prof. Dr. E. Kissling
km. step. 0.5km. Ishihara km. al., Rayleigh. cavity. cavity
 .9-1.1.25-.5km : 1955 1985 step.5km 2km Tameguri Ishihara, 199 Ishihara1985 et al., 21 1.1-1.5 Uhira and Takeo, P 1994 2 Rayleigh 1999 198 cavity P cavity 2km Sakurajima KAB KOM N 51-5 m/s V P D LP HAR
.9-1.1.25-.5km : 1955 1985 step.5km 2km Tameguri Ishihara, 199 Ishihara1985 et al., 21 1.1-1.5 Uhira and Takeo, P 1994 2 Rayleigh 1999 198 cavity P cavity 2km Sakurajima KAB KOM N 51-5 m/s V P D LP HAR
Dynamic Triggering Semi-Volcanic Tremor in Japanese Volcanic Region by The 2016 Mw 7.0 Kumamoto Earthquake
 Dynamic Triggering Semi-Volcanic Tremor in Japanese Volcanic Region by The 016 Mw 7.0 Kumamoto Earthquake Heng-Yi Su 1 *, Aitaro Kato 1 Department of Earth Sciences, National Central University, Taoyuan
Dynamic Triggering Semi-Volcanic Tremor in Japanese Volcanic Region by The 016 Mw 7.0 Kumamoto Earthquake Heng-Yi Su 1 *, Aitaro Kato 1 Department of Earth Sciences, National Central University, Taoyuan
ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B. Figure 6. Student Registration No. ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Version 2
 ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Figure 6 Student Registration No UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series UG Examination 014-15 SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS WITH FIELDCOURSE
ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Figure 6 Student Registration No UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series UG Examination 014-15 SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS WITH FIELDCOURSE
Special edition paper Development of Shinkansen Earthquake Impact Assessment System
 Development of Shinkansen Earthquake Impact Assessment System Makoto Shimamura*, Keiichi Yamamura* Assuring safety during earthquakes is a very important task for the Shinkansen because the trains operate
Development of Shinkansen Earthquake Impact Assessment System Makoto Shimamura*, Keiichi Yamamura* Assuring safety during earthquakes is a very important task for the Shinkansen because the trains operate
Determination of the Rydberg constant, Moseley s law, and screening constant (Item No.: P )
 Determination of the Rydberg constant, Moseley s law, and screening constant (Item No.: P2541001) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: ILIAS Education Level: Physik Topic: Hochschule Subtopic: Moderne
Determination of the Rydberg constant, Moseley s law, and screening constant (Item No.: P2541001) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: ILIAS Education Level: Physik Topic: Hochschule Subtopic: Moderne
Human Arm. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory. 2.1 Equation of Motion for a Rotating Rigid Body
 Human Arm Equipment: Capstone, Human Arm Model, 45 cm rod, sensor mounting clamp, sensor mounting studs, 2 cord locks, non elastic cord, elastic cord, two blue pasport force sensors, large table clamps,
Human Arm Equipment: Capstone, Human Arm Model, 45 cm rod, sensor mounting clamp, sensor mounting studs, 2 cord locks, non elastic cord, elastic cord, two blue pasport force sensors, large table clamps,
MODELING OF HIGH-FREQUENCY WAVE RADIATION PROCESS ON THE FAULT PLANE FROM THE ENVELOPE FITTING OF ACCELERATION RECORDS
 MODELING OF HIGH-FREQUENCY WAVE RADIATION PROCESS ON THE FAULT PLANE FROM THE ENVELOPE FITTING OF ACCELERATION RECORDS Yasumaro KAKEHI 1 SUMMARY High-frequency (higher than 1 Hz) wave radiation processes
MODELING OF HIGH-FREQUENCY WAVE RADIATION PROCESS ON THE FAULT PLANE FROM THE ENVELOPE FITTING OF ACCELERATION RECORDS Yasumaro KAKEHI 1 SUMMARY High-frequency (higher than 1 Hz) wave radiation processes
SEISMOTECTONIC ANALYSIS OF A COMPLEX FAULT SYSTEM IN ITALY: THE
 SEISMOTECTONIC ANALYSIS OF A COMPLEX FAULT SYSTEM IN ITALY: THE GARFAGNANA-NORTH (NORTHERN TUSCANY) LINE. Eva Claudio 1, Eva Elena 2, Scafidi Davide 1, Solarino Stefano 2, Turino Chiara 1 1 Dipartimento
SEISMOTECTONIC ANALYSIS OF A COMPLEX FAULT SYSTEM IN ITALY: THE GARFAGNANA-NORTH (NORTHERN TUSCANY) LINE. Eva Claudio 1, Eva Elena 2, Scafidi Davide 1, Solarino Stefano 2, Turino Chiara 1 1 Dipartimento
THREE-DIMENSIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF STRONG GROUND MOTION IN THE NEAR-FAULT AREA
 THREE-DIMENSIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF STRONG GROUND MOTION IN THE NEAR-FAULT AREA Rajesh RUPAKHETY 1 and Ragnar SIGBJÖRNSSON 2 ABSTRACT This works presents an analysis of three-dimensional characteristics
THREE-DIMENSIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF STRONG GROUND MOTION IN THE NEAR-FAULT AREA Rajesh RUPAKHETY 1 and Ragnar SIGBJÖRNSSON 2 ABSTRACT This works presents an analysis of three-dimensional characteristics
Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion
 4 th IASPEI / IAEE International Symposium: Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion August 23 26, 2011 University of California Santa Barbara LONG-PERIOD (3 TO 10 S) GROUND MOTIONS IN AND AROUND THE
4 th IASPEI / IAEE International Symposium: Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion August 23 26, 2011 University of California Santa Barbara LONG-PERIOD (3 TO 10 S) GROUND MOTIONS IN AND AROUND THE
EXPERIMENT 4 ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION
 EXPERIMENT 4 ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION INTRODUCTION This experiment explores the meaning of displacement; velocity, acceleration and the relationship that exist between them. An understanding of these concepts
EXPERIMENT 4 ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION INTRODUCTION This experiment explores the meaning of displacement; velocity, acceleration and the relationship that exist between them. An understanding of these concepts
FOCAL MECHANISM DETERMINATION USING WAVEFORM DATA FROM A BROADBAND STATION IN THE PHILIPPINES
 FOCAL MECHANISM DETERMINATION USING WAVEFORM DATA FROM A BROADBAND STATION IN THE PHILIPPINES Vilma Castillejos Hernandez Supervisor: Tatsuhiko Hara MEE10508 ABSTRACT We performed time domain moment tensor
FOCAL MECHANISM DETERMINATION USING WAVEFORM DATA FROM A BROADBAND STATION IN THE PHILIPPINES Vilma Castillejos Hernandez Supervisor: Tatsuhiko Hara MEE10508 ABSTRACT We performed time domain moment tensor
OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION 3 WHAT'S MISSING? 4 OBJECTIVES 5
 OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION 3 WHAT'S MISSING? 4 OBJECTIVES 5 DISTORTION OF SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 6 PRINCIPLE 7 SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 8 EFFECT OF RECORDING INSTRUMENTS 9 SEISMOMETERS 9 CORRECTION FOR FREQUENCY
OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION 3 WHAT'S MISSING? 4 OBJECTIVES 5 DISTORTION OF SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 6 PRINCIPLE 7 SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 8 EFFECT OF RECORDING INSTRUMENTS 9 SEISMOMETERS 9 CORRECTION FOR FREQUENCY
ATTENUATION OF PEAK HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL ACCELERATION IN THE DINARIDES AREA
 ATTENUATION OF PEAK HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL ACCELERATION IN THE DINARIDES AREA MARIJAN HERAK, SNJEZANA MARKUSIC AND INES IVANtic University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia Summary: Peak acceleration attenuation
ATTENUATION OF PEAK HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL ACCELERATION IN THE DINARIDES AREA MARIJAN HERAK, SNJEZANA MARKUSIC AND INES IVANtic University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia Summary: Peak acceleration attenuation
Earthquake location at teleseismic distances from 3-component records (Tutorial with exercise by hand)
 Topic Author Version Earthquake location at teleseismic distances from 3-component records (Tutorial with exercise by hand) Peter Bormann (formerly GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, D-14473 Potsdam,
Topic Author Version Earthquake location at teleseismic distances from 3-component records (Tutorial with exercise by hand) Peter Bormann (formerly GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, D-14473 Potsdam,
Measuring seismicity in the Groningen Field. Bernard Dost, Elmer Ruigrok, Jesper Spetzler, Gert-Jan van den Hazel, Jordi Domingo
 Measuring seismicity in the Groningen Field Bernard Dost, Elmer Ruigrok, Jesper Spetzler, Gert-Jan van den Hazel, Jordi Domingo Monitoring induced seismicity in the Netherlands. Instrumentation and network
Measuring seismicity in the Groningen Field Bernard Dost, Elmer Ruigrok, Jesper Spetzler, Gert-Jan van den Hazel, Jordi Domingo Monitoring induced seismicity in the Netherlands. Instrumentation and network
SIMULATED SEISMOGRAMS
 SIMULATED SEISMOGRAMS Great Falls, Montana I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I 8:03 8:04 8:05 8:06 8:07 P-wave arrival S-wave arrival Little Rock, Arkansas I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
SIMULATED SEISMOGRAMS Great Falls, Montana I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I 8:03 8:04 8:05 8:06 8:07 P-wave arrival S-wave arrival Little Rock, Arkansas I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
PEAT SEISMOLOGY Lecture 12: Earthquake source mechanisms and radiation patterns II
 PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 12: Earthquake source mechanisms and radiation patterns II Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Waveform modelling P-wave first-motions
PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 12: Earthquake source mechanisms and radiation patterns II Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Waveform modelling P-wave first-motions
Estimation of Peak Ground Acceleration for Delhi Region using Finsim, a Finite Fault Simulation Technique
 215 Estimation of Peak Ground Acceleration for Delhi Region using Finsim, a Finite Fault Simulation Technique NEELIMA SATYAM. D* and K. S. RAO** * Earthquake Engineering Research Centre, International
215 Estimation of Peak Ground Acceleration for Delhi Region using Finsim, a Finite Fault Simulation Technique NEELIMA SATYAM. D* and K. S. RAO** * Earthquake Engineering Research Centre, International
B = 8 0 NI/[r (5) 3/2 ],
![B = 8 0 NI/[r (5) 3/2 ], B = 8 0 NI/[r (5) 3/2 ],](/thumbs/80/82433821.jpg) ELECTRON BEAM IN A MAGNETIC FIELD Introduction: A charged body moving relative to a magnetic field experiences a force which is perpendicular to both the velocity of the particle and to the magnetic field.
ELECTRON BEAM IN A MAGNETIC FIELD Introduction: A charged body moving relative to a magnetic field experiences a force which is perpendicular to both the velocity of the particle and to the magnetic field.
Objective: You will learn to interpret a seismogram and, using differences in seismic waves, locate the epicenter of an earthquake.
 Earth Science Dynamic Crust Name Period Finding Epicenters Lab# Introduction: Earthquakes occur when there is movement along a fault. The friction between rock masses rubbing against one another generates
Earth Science Dynamic Crust Name Period Finding Epicenters Lab# Introduction: Earthquakes occur when there is movement along a fault. The friction between rock masses rubbing against one another generates
Radiation. Laboratory exercise - Astrophysical Radiation Processes. Magnus Gålfalk Stockholm Observatory 2007
 Radiation Laboratory exercise - Astrophysical Radiation Processes Magnus Gålfalk Stockholm Observatory 2007 1 1 Introduction The electric (and magnetic) field pattern from a single charged particle can
Radiation Laboratory exercise - Astrophysical Radiation Processes Magnus Gålfalk Stockholm Observatory 2007 1 1 Introduction The electric (and magnetic) field pattern from a single charged particle can
Northern Tanzanian Earthquakes: Fault orientations, and depth distribution
 Northern Tanzanian Earthquakes: Fault orientations, and depth distribution Stewart Rouse (NC A&T Physics) Penn State University SROP Mentors: Dr. Andy Nyblade & Dr. Rick Brazier July 27, 2005 1.0 Introduction
Northern Tanzanian Earthquakes: Fault orientations, and depth distribution Stewart Rouse (NC A&T Physics) Penn State University SROP Mentors: Dr. Andy Nyblade & Dr. Rick Brazier July 27, 2005 1.0 Introduction
4.2 Solutionfor the ElastodynamicGreenFunctioninaHomogeneous, Isotropic,UnboundedMedium 73
 4.2 Solutionfor the ElastodynamicGreenFunctioninaHomogeneous, Isotropic,UnboundedMedium 73 data used in earthquake engineering are occasionally collected in the near field. But when one takes up in more
4.2 Solutionfor the ElastodynamicGreenFunctioninaHomogeneous, Isotropic,UnboundedMedium 73 data used in earthquake engineering are occasionally collected in the near field. But when one takes up in more
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2
 Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2 Apr 15 8:52 PM What are seismic waves? How are earthquakes measured? How is an earthquake located? Apr 15 8:54 PM 1 What are seismic waves An earthquake is the
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2 Apr 15 8:52 PM What are seismic waves? How are earthquakes measured? How is an earthquake located? Apr 15 8:54 PM 1 What are seismic waves An earthquake is the
Dynamic source inversion for physical parameters controlling the 2017 Lesvos earthquake
 Dynamic source inversion for physical parameters controlling the 2017 Lesvos earthquake F. Kostka 1, E. Sokos 2, J. Zahradník 1, F. Gallovič 1 1 Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics and
Dynamic source inversion for physical parameters controlling the 2017 Lesvos earthquake F. Kostka 1, E. Sokos 2, J. Zahradník 1, F. Gallovič 1 1 Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics and
TECTONIC MOVEMENTS MONITORING OF SUDETIC MARGINAL FAULT USING SHORT GPS BASELINES
 POSTER PAPER SESSION TECTONIC MOVEMENTS MONITORING OF SUDETIC MARGINAL FAULT USING SHORT GPS ASELINES ernard Kontny Department of Geodesy and Photogrammetry Agricultural University of Wroclaw, Poland Abstract
POSTER PAPER SESSION TECTONIC MOVEMENTS MONITORING OF SUDETIC MARGINAL FAULT USING SHORT GPS ASELINES ernard Kontny Department of Geodesy and Photogrammetry Agricultural University of Wroclaw, Poland Abstract
San Francisco Bay Area Earthquake Simulations: A step toward a Standard Physical Earthquake Model
 San Francisco Bay Area Earthquake Simulations: A step toward a Standard Physical Earthquake Model Steven N. Ward Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA,
San Francisco Bay Area Earthquake Simulations: A step toward a Standard Physical Earthquake Model Steven N. Ward Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA,
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
RECIPE FOR PREDICTING STRONG GROUND MOTIONS FROM FUTURE LARGE INTRASLAB EARTHQUAKES
 RECIPE FOR PREDICTING STRONG GROUND MOTIONS FROM FUTURE LARGE INTRASLAB EARTHQUAKES T. Sasatani 1, S. Noguchi, T. Maeda 3, and N. Morikawa 4 1 Professor, Graduate School of Engineering, Hokkaido University,
RECIPE FOR PREDICTING STRONG GROUND MOTIONS FROM FUTURE LARGE INTRASLAB EARTHQUAKES T. Sasatani 1, S. Noguchi, T. Maeda 3, and N. Morikawa 4 1 Professor, Graduate School of Engineering, Hokkaido University,
Seismic Source Mechanism
 Seismic Source Mechanism Yuji Yagi (University of Tsukuba) Earthquake Earthquake is a term used to describe both failure process along a fault zone, and the resulting ground shaking and radiated seismic
Seismic Source Mechanism Yuji Yagi (University of Tsukuba) Earthquake Earthquake is a term used to describe both failure process along a fault zone, and the resulting ground shaking and radiated seismic
Earthquake Engineering GE / CE - 479/679
 Earthquake Engineering GE / CE - 479/679 Topic 4. Seismometry John G. Anderson Director February 4-6, 2003 1 Wood-Anderson Seismograph Important because: Principles of operation are widely used. Basis
Earthquake Engineering GE / CE - 479/679 Topic 4. Seismometry John G. Anderson Director February 4-6, 2003 1 Wood-Anderson Seismograph Important because: Principles of operation are widely used. Basis
RELATION BETWEEN RAYLEIGH WAVES AND UPLIFT OF THE SEABED DUE TO SEISMIC FAULTING
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 1359 RELATION BETWEEN RAYLEIGH WAVES AND UPLIFT OF THE SEABED DUE TO SEISMIC FAULTING Shusaku INOUE 1,
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 1359 RELATION BETWEEN RAYLEIGH WAVES AND UPLIFT OF THE SEABED DUE TO SEISMIC FAULTING Shusaku INOUE 1,
Reexamination of moment tensors for initial motion of explosion earthquakes using borehole seismograms at Sakurajima volcano, Japan
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 53, 63 68, 2001 Reexamination of moment tensors for initial motion of explosion earthquakes using borehole seismograms at Sakurajima volcano, Japan Takeshi Tameguri, Masato
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 53, 63 68, 2001 Reexamination of moment tensors for initial motion of explosion earthquakes using borehole seismograms at Sakurajima volcano, Japan Takeshi Tameguri, Masato
LAB 6 SUPPLEMENT. G141 Earthquakes & Volcanoes
 G141 Earthquakes & Volcanoes Name LAB 6 SUPPLEMENT Using Earthquake Arrival Times to Locate Earthquakes In last week's lab, you used arrival times of P- and S-waves to locate earthquakes from a local seismograph
G141 Earthquakes & Volcanoes Name LAB 6 SUPPLEMENT Using Earthquake Arrival Times to Locate Earthquakes In last week's lab, you used arrival times of P- and S-waves to locate earthquakes from a local seismograph
Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels
 Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels Jeffrey B. Carruthers Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University jbc@bu.edu Sachin Padma Department of Electrical and
Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels Jeffrey B. Carruthers Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University jbc@bu.edu Sachin Padma Department of Electrical and
27th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 EVALUATION OF CROSS-CORRELATION METHODS ON A MASSIVE SCALE FOR ACCURATE RELOCATION OF SEISMIC EVENTS Won-Young Kim, Paul G. Richards, David P. Schaff, Felix Waldhauser, and Jian Zhang Lamont-Doherty Earth
EVALUATION OF CROSS-CORRELATION METHODS ON A MASSIVE SCALE FOR ACCURATE RELOCATION OF SEISMIC EVENTS Won-Young Kim, Paul G. Richards, David P. Schaff, Felix Waldhauser, and Jian Zhang Lamont-Doherty Earth
Seismic Waves in Complex 3 D Structures, 26 (2016), (ISSN , online at
 Kirchhoff prestack depth migration in simple orthorhombic and triclinic models with differently rotated elasticity tensor: comparison with zero-offset travel-time perturbations Václav Bucha Department
Kirchhoff prestack depth migration in simple orthorhombic and triclinic models with differently rotated elasticity tensor: comparison with zero-offset travel-time perturbations Václav Bucha Department
28th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 BASIC RESEARCH ON SEISMIC AND INFRASONIC MONITORING OF THE EUROPEAN ARCTIC Frode Ringdal, Tormod Kværna, Svein Mykkeltveit, Steven J. Gibbons, and Johannes Schweitzer NORSAR Sponsored by Army Space and
BASIC RESEARCH ON SEISMIC AND INFRASONIC MONITORING OF THE EUROPEAN ARCTIC Frode Ringdal, Tormod Kværna, Svein Mykkeltveit, Steven J. Gibbons, and Johannes Schweitzer NORSAR Sponsored by Army Space and
Seismogram Interpretation. Seismogram Interpretation
 Travel times in the Earth Ray paths, phases and their name Wavefields in the Earth: SH waves, P-SV waves Seismic Tomography Receiver Functions Seismogram Example Long-period transverse displacement for
Travel times in the Earth Ray paths, phases and their name Wavefields in the Earth: SH waves, P-SV waves Seismic Tomography Receiver Functions Seismogram Example Long-period transverse displacement for
29th Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 IMPROVING MAGNITUDE DETECTION THRESHOLDS USING MULTI-STATION, MULTI-EVENT, AND MULTI-PHASE METHODS David Schaff and Felix Waldhauser Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University Sponsored by Air
IMPROVING MAGNITUDE DETECTION THRESHOLDS USING MULTI-STATION, MULTI-EVENT, AND MULTI-PHASE METHODS David Schaff and Felix Waldhauser Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University Sponsored by Air
The Reynolds experiment
 Chapter 13 The Reynolds experiment 13.1 Laminar and turbulent flows Let us consider a horizontal pipe of circular section of infinite extension subject to a constant pressure gradient (see section [10.4]).
Chapter 13 The Reynolds experiment 13.1 Laminar and turbulent flows Let us consider a horizontal pipe of circular section of infinite extension subject to a constant pressure gradient (see section [10.4]).
RECURSIVE SUBSPACE IDENTIFICATION IN THE LEAST SQUARES FRAMEWORK
 RECURSIVE SUBSPACE IDENTIFICATION IN THE LEAST SQUARES FRAMEWORK TRNKA PAVEL AND HAVLENA VLADIMÍR Dept of Control Engineering, Czech Technical University, Technická 2, 166 27 Praha, Czech Republic mail:
RECURSIVE SUBSPACE IDENTIFICATION IN THE LEAST SQUARES FRAMEWORK TRNKA PAVEL AND HAVLENA VLADIMÍR Dept of Control Engineering, Czech Technical University, Technická 2, 166 27 Praha, Czech Republic mail:
FEASIBILITY STUDY ON EARTHQUAKE EARLY WARNING SYSTEM FOR THE CITY OF LIMA, PERU, USING A NEWLY DEPLOYED STRONG-MOTION NETWORK
 FEASIBILITY STUDY ON EARTHQUAKE EARLY WARNING SYSTEM FOR THE CITY OF LIMA, PERU, USING A NEWLY DEPLOYED STRONG-MOTION NETWORK Cinthia CALDERON MEE1771 Supervisor: Takumi HAYASHIDA Toshiaki YOKOI ABSTRACT
FEASIBILITY STUDY ON EARTHQUAKE EARLY WARNING SYSTEM FOR THE CITY OF LIMA, PERU, USING A NEWLY DEPLOYED STRONG-MOTION NETWORK Cinthia CALDERON MEE1771 Supervisor: Takumi HAYASHIDA Toshiaki YOKOI ABSTRACT
Geology 554 -Wilson Environmental and Exploration Geophysics II Computer Lab - Seismic Resolution I
 Geology 554 -Wilson Environmental and Exploration Geophysics II Computer Lab - Seismic Resolution I In this lab we will examine the response of a thinning layer and use it to develop an understanding of
Geology 554 -Wilson Environmental and Exploration Geophysics II Computer Lab - Seismic Resolution I In this lab we will examine the response of a thinning layer and use it to develop an understanding of
