Supplementary Information: Data Used in Computing Porosity, Pore Pressure, and
|
|
|
- Bertram Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GSA DATA REPOSITORY ITEM Supplementary Information: Data Used in Computing Porosity, Pore Pressure, and Effective Stress, and Results for Seismic Line 284 Accompanying: Tobin, H. & Saffer, D., Elevated Fluid Pressure and Extreme Mechanical Weakness of a Plate Boundary Thrust, Nankai Trough Subduction Zone The transform function used to compute porosity in the underthrust section from PSDM interval velocity is based on Hoffman and Tobin (23) and is shown in figure DR1. It uses a function that accounts explicitly for the changing mechanisms of sediment stiffening and concomitant velocity increase during compaction, cementation, and lithification (Erickson and Jarrard, 1998), parameterized to achieve a least-squares minimization of error for the borehole core data from this transect. The transform used in turn to compute maximum past effective stress in a given element of underthrust sediment from porosity (or its corollary, void ratio) is also locally calibrated to corrected borehole data (Figure DR2). We performed the computations shown in Figure 2 using the functions derived from these two analyses. In addition to Line 215 as presented in the main body, we performed an analogous analysis of a second seismic reflection line (line 284) taken from the same survey. Line 284 parallels Line 215 and lies ~ 7 m northeastward along strike of the trench and plate boundary décollement. PSDM velocity near the top of the underthrust section was extracted in the same way, and all calculations were performed using identical procedures. Results (Figure DR3) show very similar results to Line 215, and are entirely consistent with the results and conclusions presented for that line. Calculated pore fluid
2 GSA DATA REPOSITORY ITEM 29xxx pressure is generally slightly higher than for line 215, and therefore effective normal stress and resolved shear stress are slightly lower. Along line 284, resolved shear stress has a maximum value of 3.57 ±.5 MPa. Figure Legends Figure DR1. P-wave velocity vs. porosity for elastic rebound-corrected core sample data from Sites 1173, 1174, and 88, with several transform models (Hoffman and Tobin, 23). Core data are from underthrust interval only. HMM curve (Hyndman et al., 1993) is a commonly used fit to Site 88 data that includes the turbidites of the trench fill section, and would be inappropriate for this study on lithological grounds and also fit the data poorly. E+J curves (Erickson and Jarrard, 1998) are global average clastic sediment functions for normally consolidated and highly consolidated sections, computed using a threshold porosity formulation, merging a mechanical compaction based, concave-up function at high porosity with a cementation-dominated, convex-up function for porosity lower than the threshold value. The transform used in this study (solid line) uses the Erickson and Jarrard approach and a threshold porosity of.31 to fit the core data, minimize error, and best predict the porosity at higher velocity. For further details, see Hoffman and Tobin (24). Figure DR2. Void ratio vs. effective stress for reference Site 1173 (Saffer, 23). Values of void ratio were determined from shipboard measurement, and corrected for rebound; values of effective stress were calculated from rebound-corrected bulk density measurements, assuming hydrostatic pore pressure. Dashed line shows best-fit virgin compression curve.
3 GSA DATA REPOSITORY ITEM 29xxx Figure DR3. Velocity, pore fluid pressure, and effective stress calculation results for seismic line 284. All parameters are calculated as in figure 2.
4 GSA DATA REPOSITORY ITEM 29xxx Site 1173 Site 1174 Site 88 HMM curve E&J normal E&J high Least squares Velocity (km/s) High 1.8 Normal Porosity
5 GSA DATA REPOSITORY ITEM 29xxx 1.5 Site 1173 Void ratio Effective stress (kpa) Tobin & Saffer Figure S-2
6 GSA DATA 4 REPOSITORY ITEM 29xxx Stress or pressure (MPa) Velocity (m/s) Overburden (lithostatic) Hydrostatic pressure Calculated pore fluid pressure A B.8.4 Porosity Stress (MPa) 2 1 Expected effective stress (normal consolidation) Effective stress Shear stress 2, 15, 1, 5 Distance landward of trench (m) C -5 Tobin & Saffer Figure S-3
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B5, 2261, doi: /2002jb001787, 2003
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B5, 2261, doi:10.1029/2002jb001787, 2003 Pore pressure development and progressive dewatering in underthrust sediments at the Costa Rican subduction margin:
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B5, 2261, doi:10.1029/2002jb001787, 2003 Pore pressure development and progressive dewatering in underthrust sediments at the Costa Rican subduction margin:
PORE PRESSURE AND FLUID FLOW BENEATH THE FRONTAL THRUST OF THE KUMANO BASIN TRANSECT, JAPAN: INFLUENCE ON DÉCOLLEMENT PROPAGATION
 PORE PRESSURE AND FLUID FLOW BENEATH THE FRONTAL THRUST OF THE KUMANO BASIN TRANSECT, JAPAN: INFLUENCE ON DÉCOLLEMENT PROPAGATION By KATHERINE ROWE A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY
PORE PRESSURE AND FLUID FLOW BENEATH THE FRONTAL THRUST OF THE KUMANO BASIN TRANSECT, JAPAN: INFLUENCE ON DÉCOLLEMENT PROPAGATION By KATHERINE ROWE A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY
Effective stress and pore pressure in the Nankai accretionary prism off the Muroto Peninsula, southwestern Japan
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005002, 2008 Effective stress and pore pressure in the Nankai accretionary prism off the Muroto Peninsula, southwestern
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005002, 2008 Effective stress and pore pressure in the Nankai accretionary prism off the Muroto Peninsula, southwestern
Acoustic and mechanical properties of Nankai accretionary prism core samples
 Article Volume 12, Number 4 7 April 2011 Q0AD10, doi: ISSN: 1525 2027 Acoustic and mechanical properties of Nankai accretionary prism core samples Hugues Raimbourg JAMSTEC, Natsushima cho, Yokosuka 237
Article Volume 12, Number 4 7 April 2011 Q0AD10, doi: ISSN: 1525 2027 Acoustic and mechanical properties of Nankai accretionary prism core samples Hugues Raimbourg JAMSTEC, Natsushima cho, Yokosuka 237
Deformation and in situ stress in the Nankai Accretionary Prism from resistivity-at-bit images, ODP Leg 196
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L02602, doi:10.1029/2003gl018799, 2004 Deformation and in situ stress in the Nankai Accretionary Prism from resistivity-at-bit images, ODP Leg 196 L. C. McNeill,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L02602, doi:10.1029/2003gl018799, 2004 Deformation and in situ stress in the Nankai Accretionary Prism from resistivity-at-bit images, ODP Leg 196 L. C. McNeill,
Data report: frictional healing and compressibility of sheared sediment from fault zones, Sites C0004 and C0007 1
 Kinoshita, M., Tobin, H., Ashi, J., Kimura, G., Lallemant, S., Screaton, E.J., Curewitz, D., Masago, H., Moe, K.T., and the Expedition 31/315/31 Scientists Proceedings of the Integrated Ocean Drilling
Kinoshita, M., Tobin, H., Ashi, J., Kimura, G., Lallemant, S., Screaton, E.J., Curewitz, D., Masago, H., Moe, K.T., and the Expedition 31/315/31 Scientists Proceedings of the Integrated Ocean Drilling
12. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES ALONG THE DEVELOPING DÉCOLLEMENT IN THE NANKAI TROUGH: INFERENCES FROM 3-D SEISMIC REFLECTION DATA INVERSION AND LEG 190
 Mikada, H., Moore, G.F., Taira, A., Becker, K., Moore, J.C., and Klaus, A. (Eds.) Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results Volume 190/196 12. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES ALONG THE DEVELOPING
Mikada, H., Moore, G.F., Taira, A., Becker, K., Moore, J.C., and Klaus, A. (Eds.) Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results Volume 190/196 12. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES ALONG THE DEVELOPING
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Abstract
 Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
An evaluation of factors influencing pore pressure in accretionary complexes: Implications for taper angle and wedge mechanics
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jb003990, 2006 An evaluation of factors influencing pore pressure in accretionary complexes: Implications for taper angle and wedge mechanics
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jb003990, 2006 An evaluation of factors influencing pore pressure in accretionary complexes: Implications for taper angle and wedge mechanics
23. FRONTAL THRUST, OREGON ACCRETIONARY PRISM: GEOMETRY, PHYSICAL PROPERTIES, AND FLUID PRESSURE 1
 Carson, B., Westbrook, G.K., Musgrave, R.J., and Suess, E. (Eds.), 1995 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 146 (Pt. 1) 23. FRONTAL THRUST, OREGON ACCRETIONARY PRISM: GEOMETRY,
Carson, B., Westbrook, G.K., Musgrave, R.J., and Suess, E. (Eds.), 1995 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 146 (Pt. 1) 23. FRONTAL THRUST, OREGON ACCRETIONARY PRISM: GEOMETRY,
Along-strike variations in underthrust sediment dewatering on the Nicoya margin, Costa Rica related to the updip limit of seismicity
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L04613, doi:10.1029/2003gl018863, 2004 Along-strike variations in underthrust sediment dewatering on the Nicoya margin, Costa Rica related to the updip limit of seismicity
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L04613, doi:10.1029/2003gl018863, 2004 Along-strike variations in underthrust sediment dewatering on the Nicoya margin, Costa Rica related to the updip limit of seismicity
8. ELASTIC PROPERTY CORRECTIONS APPLIED TO LEG 154 SEDIMENT, CEARA RISE 1
 Shackleton, N.J., Curry, W.., Richter, C., and ralower, T.J. (Eds.), 1997 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 154 8. ELSTIC PROPERTY CORRECTIONS PPLIED TO LEG 154 SEDIMENT,
Shackleton, N.J., Curry, W.., Richter, C., and ralower, T.J. (Eds.), 1997 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 154 8. ELSTIC PROPERTY CORRECTIONS PPLIED TO LEG 154 SEDIMENT,
Sections Rock Physics Seminar Alejandra Rojas
 Sections 1.1 1.3 Rock Physics Seminar Alejandra Rojas February 6 th, 2009 Outline Introduction Velocity Porosity relations for mapping porosity and facies Fluid substitution analysis 1.1 Introduction Discovering
Sections 1.1 1.3 Rock Physics Seminar Alejandra Rojas February 6 th, 2009 Outline Introduction Velocity Porosity relations for mapping porosity and facies Fluid substitution analysis 1.1 Introduction Discovering
Chapter 1: Acoustic and elastic properties of calcareous sediments siliceous diagenetic front on the eastern U.S.
 1 Chapter 1: Acoustic and elastic properties of calcareous sediments siliceous diagenetic front on the eastern U.S. continental slope across a 1.1 Abstract The Ocean Drilling Program drilled Hole 904A
1 Chapter 1: Acoustic and elastic properties of calcareous sediments siliceous diagenetic front on the eastern U.S. continental slope across a 1.1 Abstract The Ocean Drilling Program drilled Hole 904A
Geology 229 Engineering Geology. Lecture 5. Engineering Properties of Rocks (West, Ch. 6)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 5 Engineering Properties of Rocks (West, Ch. 6) Common mechanic properties: Density; Elastic properties: - elastic modulii Outline of this Lecture 1. Uniaxial rock
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 5 Engineering Properties of Rocks (West, Ch. 6) Common mechanic properties: Density; Elastic properties: - elastic modulii Outline of this Lecture 1. Uniaxial rock
I point out two possible paradoxical difficulties in the important target of the IODP in subduction zones, i.e.,
 Drilling the Seismogenic Zone: Some Paradoxes Tetsuzo Seno Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo (Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst., subumitted on January 16, 2003; accepted on July 22, 2003) Abstract
Drilling the Seismogenic Zone: Some Paradoxes Tetsuzo Seno Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo (Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst., subumitted on January 16, 2003; accepted on July 22, 2003) Abstract
PERMEABILITIES OF SUBDUCTION ZONE SEDIMENTS AND THEIR EFFECT ON PORE PRESSURE GENERATION
 PERMEABILITIES OF SUBDUCTION ZONE SEDIMENTS AND THEIR EFFECT ON PORE PRESSURE GENERATION By KUSALI R. GAMAGE A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
PERMEABILITIES OF SUBDUCTION ZONE SEDIMENTS AND THEIR EFFECT ON PORE PRESSURE GENERATION By KUSALI R. GAMAGE A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Brittle Deformation. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Liquefaction is the sudden loss of shear strength of a saturated sediment due to earthquake shaking. Nisqually earthquake 02/28/2001: Olympia, WA
 Liquefaction is the sudden loss of shear strength of a saturated sediment due to earthquake shaking Nisqually earthquake 02/28/2001: Olympia, WA The shear strength is controlled by the degree of grain-to-grain
Liquefaction is the sudden loss of shear strength of a saturated sediment due to earthquake shaking Nisqually earthquake 02/28/2001: Olympia, WA The shear strength is controlled by the degree of grain-to-grain
Estimation of Pore Pressure from Well logs: A theoretical analysis and Case Study from an Offshore Basin, North Sea
 P-217 Estimation of Pore Pressure from Well logs: A theoretical analysis and Case Study from an Offshore Basin, North Sea Pritam Bera Final Year, M.Sc.Tech. (Applied Geophysics) Summary This paper concerns
P-217 Estimation of Pore Pressure from Well logs: A theoretical analysis and Case Study from an Offshore Basin, North Sea Pritam Bera Final Year, M.Sc.Tech. (Applied Geophysics) Summary This paper concerns
Regional-Scale Salt Tectonics Modelling: Bench-Scale Validation and Extension to Field-Scale Predictions
 Software Limited Bench-Scale to Field-Scale Regional-Scale Salt Tectonics Modelling: Bench-Scale Validation and Extension to Field-Scale Predictions Thornton, Dean A., Roberts, Daniel T., Crook, Anthony
Software Limited Bench-Scale to Field-Scale Regional-Scale Salt Tectonics Modelling: Bench-Scale Validation and Extension to Field-Scale Predictions Thornton, Dean A., Roberts, Daniel T., Crook, Anthony
Tectonophysics 484 (2010) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Tectonophysics. journal homepage:
 Tectonophysics 484 (2010) 127 138 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Tectonophysics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tecto Effect of increased shear stress along a plate boundary fault
Tectonophysics 484 (2010) 127 138 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Tectonophysics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tecto Effect of increased shear stress along a plate boundary fault
Dynamic analysis. 1. Force and stress
 Dynamic analysis 1. Force and stress Dynamics is the part of structural geology that involves energy, force, stress, and strength. It's very important to distinguish dynamic concepts from kinematic ones.
Dynamic analysis 1. Force and stress Dynamics is the part of structural geology that involves energy, force, stress, and strength. It's very important to distinguish dynamic concepts from kinematic ones.
Pressure and Compaction in the Rock Physics Space. Jack Dvorkin
 Pressure and Compaction in the Rock Physics Space Jack Dvorkin June 2002 0 200 Compaction of Shales Freshly deposited shales and clays may have enormous porosity of ~ 80%. The speed of sound is close to
Pressure and Compaction in the Rock Physics Space Jack Dvorkin June 2002 0 200 Compaction of Shales Freshly deposited shales and clays may have enormous porosity of ~ 80%. The speed of sound is close to
BPM37 Linking Basin Modeling with Seismic Attributes through Rock Physics
 BPM37 Linking Basin Modeling with Seismic Attributes through Rock Physics W. AlKawai* (Stanford University), T. Mukerji (Stanford University) & S. Graham (Stanford University) SUMMARY In this study, we
BPM37 Linking Basin Modeling with Seismic Attributes through Rock Physics W. AlKawai* (Stanford University), T. Mukerji (Stanford University) & S. Graham (Stanford University) SUMMARY In this study, we
4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration
 Title 4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration Authors Bloomer, D., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Reynolds, S., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Pavlova, M., Origin
Title 4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration Authors Bloomer, D., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Reynolds, S., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Pavlova, M., Origin
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116, B11102, doi: /2011jb008429, 2011
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008429, 2011 The South Ecuador subduction channel: Evidence for a dynamic mega shear zone from 2D fine scale seismic reflection imaging and
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008429, 2011 The South Ecuador subduction channel: Evidence for a dynamic mega shear zone from 2D fine scale seismic reflection imaging and
Marine Geology. Permeability porosity relationships of subduction zone sediments
 Marine Geology 279 (2011) 19 36 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Marine Geology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/margeo Permeability porosity relationships of subduction zone sediments
Marine Geology 279 (2011) 19 36 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Marine Geology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/margeo Permeability porosity relationships of subduction zone sediments
Deepwater Niger Delta fold-and-thrust belt modeled as a critical-taper wedge: The influence of a weak detachment on styles of fault-related folds
 Deepwater Niger Delta fold-and-thrust belt modeled as a critical-taper wedge: The influence of a weak detachment on styles of fault-related folds Frank Bilotti 1, Chris Guzofski 1, John H. Shaw 2 1 Chevron
Deepwater Niger Delta fold-and-thrust belt modeled as a critical-taper wedge: The influence of a weak detachment on styles of fault-related folds Frank Bilotti 1, Chris Guzofski 1, John H. Shaw 2 1 Chevron
Flood, R.D., Piper, D.J.W., Klaus, A., and Peterson, L.C. (Eds.), 1997 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol.
 Flood, R.D., Piper, D.J.W., Klaus, A., and Peterson, L.C. (Eds.), 1997 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 155 29. THE COMPRESSIONAL-WAVE VELOCITY OF AMAZON FAN SEDIMENTS:
Flood, R.D., Piper, D.J.W., Klaus, A., and Peterson, L.C. (Eds.), 1997 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 155 29. THE COMPRESSIONAL-WAVE VELOCITY OF AMAZON FAN SEDIMENTS:
Michael Stipp Department of Marine Geodynamics, GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, Kiel, Germany
 Article Volume 14, Number 00 00 Month 2013 doi: ISSN: 1525-2027 Strong sediments at the deformation front, and weak sediments at the rear of the Nankai accretionary prism, revealed by triaxial deformation
Article Volume 14, Number 00 00 Month 2013 doi: ISSN: 1525-2027 Strong sediments at the deformation front, and weak sediments at the rear of the Nankai accretionary prism, revealed by triaxial deformation
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks
 An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
Soil Properties - II
 Soil Properties - II Amit Prashant Indian Institute of Technology andhinagar Short Course on eotechnical Aspects of Earthquake Engineering 04 08 March, 2013 Seismic Waves Earthquake Rock Near the ground
Soil Properties - II Amit Prashant Indian Institute of Technology andhinagar Short Course on eotechnical Aspects of Earthquake Engineering 04 08 March, 2013 Seismic Waves Earthquake Rock Near the ground
Controlled-source electromagnetic imaging of the Middle America Trench o"shore Nicaragua
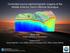 Controlled-source electromagnetic imaging of the Middle America Trench o"shore Nicaragua Kerry Key Scripps Institution of Oceanography Collaborators: Samer Naif (SIO, now LDEO), Steven Constable (SIO),
Controlled-source electromagnetic imaging of the Middle America Trench o"shore Nicaragua Kerry Key Scripps Institution of Oceanography Collaborators: Samer Naif (SIO, now LDEO), Steven Constable (SIO),
42. POROSITY AND VELOCITY VS. DEPTH AND EFFECTIVE STRESS IN CARBONATE SEDIMENTS 1
 Duncan, R. A., Backman, J., Peterson, L. C, et al., 1990 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 115 42. POROSITY AND VELOCITY VS. DEPTH AND EFFECTIVE STRESS IN ONATE SEDIMENTS
Duncan, R. A., Backman, J., Peterson, L. C, et al., 1990 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 115 42. POROSITY AND VELOCITY VS. DEPTH AND EFFECTIVE STRESS IN ONATE SEDIMENTS
Th SBT1 14 Seismic Characters of Pore Pressure Due to Smectite-to-illite Transition
 Th SBT1 14 Seismic Characters of Pore Pressure Due to Smectite-to-illite Transition X. Qin* (University of Houston) & D. Han (University of Houston) SUMMARY In this study, we strive to understand unloading
Th SBT1 14 Seismic Characters of Pore Pressure Due to Smectite-to-illite Transition X. Qin* (University of Houston) & D. Han (University of Houston) SUMMARY In this study, we strive to understand unloading
Tectonics. Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting GNH7/GG09/GEOL4002 EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE HAZARD
 Tectonics Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting Plane strain 3 Strain occurs only in a plane. In the third direction strain is zero. 1 ε 2 = 0 3 2 Assumption of plane strain for faulting e.g., reverse fault:
Tectonics Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting Plane strain 3 Strain occurs only in a plane. In the third direction strain is zero. 1 ε 2 = 0 3 2 Assumption of plane strain for faulting e.g., reverse fault:
Toward a dynamic concept of the subduction channel at erosive convergent margins with implications for interplate material transfer
 Article Volume 13, Number 1 10 February 2012 Q02003, doi:10.1029/2011gc003846 ISSN: 1525-2027 Toward a dynamic concept of the subduction channel at erosive convergent margins with implications for interplate
Article Volume 13, Number 1 10 February 2012 Q02003, doi:10.1029/2011gc003846 ISSN: 1525-2027 Toward a dynamic concept of the subduction channel at erosive convergent margins with implications for interplate
Dynamic Subsidence and Uplift of the Colorado Plateau. Supplementary Material
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2010177 Liu and Gurnis Dynamic Subsidence and Uplift of the Colorado Plateau Supplementary Material Lijun Liu and Michael Gurnis Seismological Laboratory California Institute of Technology
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2010177 Liu and Gurnis Dynamic Subsidence and Uplift of the Colorado Plateau Supplementary Material Lijun Liu and Michael Gurnis Seismological Laboratory California Institute of Technology
Numerical modelling: The governing equation used in this study is: (K T ) c T H 0,
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012254 Cozzens and Spinelli Numerical modelling: The governing equation used in this study is: (K T ) c T H 0, where K is thermal conductivity, T is temperature, ρ is density, c is
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012254 Cozzens and Spinelli Numerical modelling: The governing equation used in this study is: (K T ) c T H 0, where K is thermal conductivity, T is temperature, ρ is density, c is
STRUCfURAL RESTORATION AND APPUCA TION OF DYNAMIC COULOMB WEDGE THEORY TO THE NANKAI TROUGH ACCRETIONARY WEDGE TOE
 41f>S STRUCfURAL RESTORATION AND APPUCA TION OF DYNAMIC COULOMB WEDGE THEORY TO THE NANKAI TROUGH ACCRETIONARY WEDGE TOE A THESIS SUBMfI'IED TO THE GRADUATE DIVISION OF THE UNIVERSITY OF HAW AI'I IN PARTIAL
41f>S STRUCfURAL RESTORATION AND APPUCA TION OF DYNAMIC COULOMB WEDGE THEORY TO THE NANKAI TROUGH ACCRETIONARY WEDGE TOE A THESIS SUBMfI'IED TO THE GRADUATE DIVISION OF THE UNIVERSITY OF HAW AI'I IN PARTIAL
16 Rainfall on a Slope
 Rainfall on a Slope 16-1 16 Rainfall on a Slope 16.1 Problem Statement In this example, the stability of a generic slope is analyzed for two successive rainfall events of increasing intensity and decreasing
Rainfall on a Slope 16-1 16 Rainfall on a Slope 16.1 Problem Statement In this example, the stability of a generic slope is analyzed for two successive rainfall events of increasing intensity and decreasing
7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS
 7-1 7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS 7.1 THE MOHR CIRCLE The discussions in Chapters and 5 were largely concerned with vertical stresses. A more detailed examination of soil behaviour requires a knowledge
7-1 7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS 7.1 THE MOHR CIRCLE The discussions in Chapters and 5 were largely concerned with vertical stresses. A more detailed examination of soil behaviour requires a knowledge
Evaluation of Stress and Strain Induced by the Rock Compaction on a Hydrocarbon Well Completion Using Contact Interfaces with Abaqus
 Evaluation of Stress and Strain Induced by the Rock Compaction on a Hydrocarbon Well Completion Using Contact Interfaces with Abaqus G. Capasso and G. Musso * eni E&P, S. Donato Milanese, MI, Italy * now
Evaluation of Stress and Strain Induced by the Rock Compaction on a Hydrocarbon Well Completion Using Contact Interfaces with Abaqus G. Capasso and G. Musso * eni E&P, S. Donato Milanese, MI, Italy * now
3D simulations of an injection test done into an unsaturated porous and fractured limestone
 3D simulations of an injection test done into an unsaturated porous and fractured limestone A. Thoraval *, Y. Guglielmi, F. Cappa INERIS, Ecole des Mines de Nancy, FRANCE *Corresponding author: Ecole des
3D simulations of an injection test done into an unsaturated porous and fractured limestone A. Thoraval *, Y. Guglielmi, F. Cappa INERIS, Ecole des Mines de Nancy, FRANCE *Corresponding author: Ecole des
Shear stresses on megathrusts: Implications for mountain building behind subduction zones
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jb003916, 2006 Shear stresses on megathrusts: Implications for mountain building behind subduction zones Simon Lamb 1 Received 30 June 2005;
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jb003916, 2006 Shear stresses on megathrusts: Implications for mountain building behind subduction zones Simon Lamb 1 Received 30 June 2005;
and reservoir simulation. Figure 1. Interdependence of experimental, poromechanical, and field study variables. 1 GeoFluids 2020_v2.
 UT GeoFluids 2020 Research Plan Peter B. Flemings1, John T. Germaine2, Maria A. Nikolinakou3 1. pflemings@jsg.utexas.edu, 2. john.germaine@tufts.edu. 3. mariakat@mail.utexas.edu Executive summary The UT
UT GeoFluids 2020 Research Plan Peter B. Flemings1, John T. Germaine2, Maria A. Nikolinakou3 1. pflemings@jsg.utexas.edu, 2. john.germaine@tufts.edu. 3. mariakat@mail.utexas.edu Executive summary The UT
4 Undrained Cylindrical Cavity Expansion in a Cam-Clay Medium
 Undrained Cylindrical Cavity Expansion in a Cam-Clay Medium 4-1 4 Undrained Cylindrical Cavity Expansion in a Cam-Clay Medium 4.1 Problem Statement The stress and pore pressure changes due to the expansion
Undrained Cylindrical Cavity Expansion in a Cam-Clay Medium 4-1 4 Undrained Cylindrical Cavity Expansion in a Cam-Clay Medium 4.1 Problem Statement The stress and pore pressure changes due to the expansion
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen?
 San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
ROCK PHYSICS MODELING FOR LITHOLOGY PREDICTION USING HERTZ- MINDLIN THEORY
 ROCK PHYSICS MODELING FOR LITHOLOGY PREDICTION USING HERTZ- MINDLIN THEORY Ida Ayu PURNAMASARI*, Hilfan KHAIRY, Abdelazis Lotfy ABDELDAYEM Geoscience and Petroleum Engineering Department Universiti Teknologi
ROCK PHYSICS MODELING FOR LITHOLOGY PREDICTION USING HERTZ- MINDLIN THEORY Ida Ayu PURNAMASARI*, Hilfan KHAIRY, Abdelazis Lotfy ABDELDAYEM Geoscience and Petroleum Engineering Department Universiti Teknologi
Hydrogeophysics - Seismics
 Hydrogeophysics - Seismics Matthias Zillmer EOST-ULP p. 1 Table of contents SH polarized shear waves: Seismic source Case study: porosity of an aquifer Seismic velocities for porous media: The Frenkel-Biot-Gassmann
Hydrogeophysics - Seismics Matthias Zillmer EOST-ULP p. 1 Table of contents SH polarized shear waves: Seismic source Case study: porosity of an aquifer Seismic velocities for porous media: The Frenkel-Biot-Gassmann
Deformation history recorded in accreted sediments in an evolved portion of the Nankai accretionary prism
 Deformation history recorded in accreted sediments in an evolved portion of the Nankai accretionary prism Kohtaro Ujiie Research Program for Plate Dynamics, Institute for Frontier Research on Earth Evolution
Deformation history recorded in accreted sediments in an evolved portion of the Nankai accretionary prism Kohtaro Ujiie Research Program for Plate Dynamics, Institute for Frontier Research on Earth Evolution
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics
 Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Module 5: Failure Criteria of Rock and Rock masses. Contents Hydrostatic compression Deviatoric compression
 FAILURE CRITERIA OF ROCK AND ROCK MASSES Contents 5.1 Failure in rocks 5.1.1 Hydrostatic compression 5.1.2 Deviatoric compression 5.1.3 Effect of confining pressure 5.2 Failure modes in rocks 5.3 Complete
FAILURE CRITERIA OF ROCK AND ROCK MASSES Contents 5.1 Failure in rocks 5.1.1 Hydrostatic compression 5.1.2 Deviatoric compression 5.1.3 Effect of confining pressure 5.2 Failure modes in rocks 5.3 Complete
The Frictional Regime
 The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
Origin of Overpressure and Pore Pressure Prediction in Carbonate Reservoirs of the Abadan Plain Basin
 Origin of Overpressure and Pore Pressure Prediction in Carbonate Reservoirs of the Abadan Plain Basin Vahid Atashbari Australian School of Petroleum The University of Adelaide This thesis is submitted
Origin of Overpressure and Pore Pressure Prediction in Carbonate Reservoirs of the Abadan Plain Basin Vahid Atashbari Australian School of Petroleum The University of Adelaide This thesis is submitted
So I have a Seismic Image, But what is in that Image?
 P-513 So I have a Seismic Image, But what is in that Image? Dr. Nader C. Dutta, Schlumberger Introduction and background Migration involves repositioning of returned signals in a seismic experiment to
P-513 So I have a Seismic Image, But what is in that Image? Dr. Nader C. Dutta, Schlumberger Introduction and background Migration involves repositioning of returned signals in a seismic experiment to
Competing Effect of Pore Fluid and Texture -- Case Study
 Competing Effect of Pore Fluid and Texture -- Case Study Depth (m) Sw Sxo. m Poisson's Ratio.. GOC.1 5 7 8 9 P-Impedance OWC 15 GR.. RHOB.5 1 Saturation...5. 1. 1.5 Vs (km/s).. Poisson's Ratio 5 7 P-Impedance
Competing Effect of Pore Fluid and Texture -- Case Study Depth (m) Sw Sxo. m Poisson's Ratio.. GOC.1 5 7 8 9 P-Impedance OWC 15 GR.. RHOB.5 1 Saturation...5. 1. 1.5 Vs (km/s).. Poisson's Ratio 5 7 P-Impedance
Read & Learn Earthquakes & Faults
 Read Earthquakes & Faults Read the provided article. Use the information in the reading to answer the questions on the task cards on your answer sheet. Make sure your answers are in the correct spot on
Read Earthquakes & Faults Read the provided article. Use the information in the reading to answer the questions on the task cards on your answer sheet. Make sure your answers are in the correct spot on
What is the role of the Nankai Frontal prism in tsunamigenic earthquakes & slow slip?
 What is the role of the Nankai Frontal prism in tsunamigenic earthquakes & slow slip? A Core-Log-Seismic Integration Investigation at Sea: Synthesis and New Directions in research building on NanTroSEIZE
What is the role of the Nankai Frontal prism in tsunamigenic earthquakes & slow slip? A Core-Log-Seismic Integration Investigation at Sea: Synthesis and New Directions in research building on NanTroSEIZE
Empirical trends of velocity- porosity and velocity-density in shallow sediment in Kerala- Konkan Basin on the west coast of India
 P-444 Summary Empirical trends of velocity- porosity and velocity-density in shallow sediment in Kerala- Konkan Basin on the west coast of India Maheswar Ojha*, Kalachand Sain, NGRI During the expedition
P-444 Summary Empirical trends of velocity- porosity and velocity-density in shallow sediment in Kerala- Konkan Basin on the west coast of India Maheswar Ojha*, Kalachand Sain, NGRI During the expedition
Accretionary prisms in subduction earthquake cycles: The theory of dynamic Coulomb wedge
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jb004094, 2006 Accretionary prisms in subduction earthquake cycles: The theory of dynamic Coulomb wedge Kelin Wang
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jb004094, 2006 Accretionary prisms in subduction earthquake cycles: The theory of dynamic Coulomb wedge Kelin Wang
Th LHR2 04 Quantification of Reservoir Pressure-sensitivity Using Multiple Monitor 4D Seismic Data
 Th LHR2 04 Quantification of Reservoir -sensitivity Using Multiple Monitor 4D Seismic Data V.E. Omofoma* (Heriot-Watt University) & C. MacBeth (Heriot-Watt University) SUMMARY Key to quantitative interpretation
Th LHR2 04 Quantification of Reservoir -sensitivity Using Multiple Monitor 4D Seismic Data V.E. Omofoma* (Heriot-Watt University) & C. MacBeth (Heriot-Watt University) SUMMARY Key to quantitative interpretation
Sand Control Rock Failure
 Sand Control Rock Failure Why? A bit of Mechanics on rock failure How? Some choices that depend on the rock What is moving? Sand grains? Fines? 3/14/2009 1 Young s Modulus, E Young s Modulus is a material
Sand Control Rock Failure Why? A bit of Mechanics on rock failure How? Some choices that depend on the rock What is moving? Sand grains? Fines? 3/14/2009 1 Young s Modulus, E Young s Modulus is a material
A new model for pore pressure prediction Fuyong Yan* and De-hua Han, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston Keyin Ren, Nanhai West Corporation, CNOOC
 A new model for pore pressure prediction Fuyong Yan* and De-hua Han, Rock hysics Lab, University of Houston Keyin Ren, Nanhai West Corporation, CNOOC Summary Eaton s equation is the most popularly used
A new model for pore pressure prediction Fuyong Yan* and De-hua Han, Rock hysics Lab, University of Houston Keyin Ren, Nanhai West Corporation, CNOOC Summary Eaton s equation is the most popularly used
Faults, Fossils, Rocks and Minerals Review:
 Faults, Fossils, Rocks and Minerals Review: 1. The preserved remains or traces of organisms that lived in the past are. - Fossils 2. How do Fossils form? - A dead organism becomes buried in sediment 3.
Faults, Fossils, Rocks and Minerals Review: 1. The preserved remains or traces of organisms that lived in the past are. - Fossils 2. How do Fossils form? - A dead organism becomes buried in sediment 3.
Th D Interpolation and Extrapolation of Sparse Well Data Using Rock Physics Principles - Applications to Anisotropic VMB
 Th-04-07 3D Interpolation and Extrapolation of Sparse Well Data Using Rock Physics Principles - Applications to Anisotropic VMB R. Bachrach* (Schlumberger WesternGeco) & K. Osypov (Schlumberger WesternGeco)
Th-04-07 3D Interpolation and Extrapolation of Sparse Well Data Using Rock Physics Principles - Applications to Anisotropic VMB R. Bachrach* (Schlumberger WesternGeco) & K. Osypov (Schlumberger WesternGeco)
Effective Stress-Porosity Relationship above and Within the Oil Window in the North Sea Basin
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 3(1): 32-38, 2011 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2011 Received: September 03, 2010 Accepted: November 27, 2010 Published:
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 3(1): 32-38, 2011 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2011 Received: September 03, 2010 Accepted: November 27, 2010 Published:
Characterization of in situ elastic properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments on the Blake Ridge
 17 Chapter 2: Characterization of in situ elastic properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments on the Blake Ridge 2.1 Abstract During ODP Leg 164, shear sonic velocity and other geophysical logs were acquired
17 Chapter 2: Characterization of in situ elastic properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments on the Blake Ridge 2.1 Abstract During ODP Leg 164, shear sonic velocity and other geophysical logs were acquired
Yasuhiro Yamada Department of Earth Resources Engineering, Kyoto University, Kyoto , Japan u.ac.
 Article Volume 12, Number 7 19 July 2011 Q0AD15, doi:10.1029/2010gc003365 ISSN: 1525 2027 Structural styles across the Nankai accretionary prism revealed from LWD borehole images and their correlation
Article Volume 12, Number 7 19 July 2011 Q0AD15, doi:10.1029/2010gc003365 ISSN: 1525 2027 Structural styles across the Nankai accretionary prism revealed from LWD borehole images and their correlation
Calibration of the petro-elastic model (PEM) for 4D seismic studies in multi-mineral rocks Amini, Hamed; Alvarez, Erick Raciel
 Heriot-Watt University Heriot-Watt University Research Gateway Calibration of the petro-elastic model (PEM) for 4D seismic studies in multi-mineral rocks Amini, Hamed; Alvarez, Erick Raciel DOI: 10.3997/2214-4609.20132136
Heriot-Watt University Heriot-Watt University Research Gateway Calibration of the petro-elastic model (PEM) for 4D seismic studies in multi-mineral rocks Amini, Hamed; Alvarez, Erick Raciel DOI: 10.3997/2214-4609.20132136
Geological perspectives on consolidation of clay-rich marine sediments
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 18, NO. B4, 2197, doi:1.129/21jb652, 23 Geological perspectives on consolidation of clay-rich marine sediments D. E. Karig Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 18, NO. B4, 2197, doi:1.129/21jb652, 23 Geological perspectives on consolidation of clay-rich marine sediments D. E. Karig Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences,
3D Mohr diagram to explain reactivation of pre-existing planes due to changes in applied stresses
 Rock Stress and Earthquakes Xie (ed.) 2010 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-0-415-60165-8 3D Mohr diagram to explain reactivation of pre-existing planes due to changes in applied stresses S.-S.
Rock Stress and Earthquakes Xie (ed.) 2010 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-0-415-60165-8 3D Mohr diagram to explain reactivation of pre-existing planes due to changes in applied stresses S.-S.
Reservoir Rock Properties COPYRIGHT. Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Learning Objectives Reservoir Rock Properties Core Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability This section will cover the following learning objectives: Explain why petroleum fluids are found in underground
Learning Objectives Reservoir Rock Properties Core Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability This section will cover the following learning objectives: Explain why petroleum fluids are found in underground
GSA Data Repository
 GSA Data Repository 2014300 Permeability reduction of fractured rhyolite in volcanic conduits and its control on eruption cyclicity Satoshi Okumura & Osamu Sasaki Typical Displacement During Compression
GSA Data Repository 2014300 Permeability reduction of fractured rhyolite in volcanic conduits and its control on eruption cyclicity Satoshi Okumura & Osamu Sasaki Typical Displacement During Compression
J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science)
 29829. One 4D geomechanical model and its many applications J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science) Main objectives (i) Field case study demonstrating application
29829. One 4D geomechanical model and its many applications J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science) Main objectives (i) Field case study demonstrating application
Simplified In-Situ Stress Properties in Fractured Reservoir Models. Tim Wynn AGR-TRACS
 Simplified In-Situ Stress Properties in Fractured Reservoir Models Tim Wynn AGR-TRACS Before the What and the How is Why Potential decrease in fault seal capacity Potential increase in natural fracture
Simplified In-Situ Stress Properties in Fractured Reservoir Models Tim Wynn AGR-TRACS Before the What and the How is Why Potential decrease in fault seal capacity Potential increase in natural fracture
A Transformation from Acoustic and Density Properties to Reservoir Properties applied to Krishna Godavari Basin, India
 P-439 Summary A Transformation from Acoustic and Density Properties to Reservoir Properties applied to Krishna Godavari Basin, India Debjani Bhowmick*and Deepak K. Gupta, Indian School of Mines Uma Shankar
P-439 Summary A Transformation from Acoustic and Density Properties to Reservoir Properties applied to Krishna Godavari Basin, India Debjani Bhowmick*and Deepak K. Gupta, Indian School of Mines Uma Shankar
Production-induced stress change in and above a reservoir pierced by two salt domes: A geomechanical model and its applications
 Production-induced stress change in and above a reservoir pierced by two salt domes: A geomechanical model and its applications Peter Schutjens, Jeroen Snippe, Hassan Mahani, Jane Turner, Joel Ita and
Production-induced stress change in and above a reservoir pierced by two salt domes: A geomechanical model and its applications Peter Schutjens, Jeroen Snippe, Hassan Mahani, Jane Turner, Joel Ita and
UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS
 UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS ROCK DEFORMATION Tectonic forces exert different types of stress on rocks in different geologic environments. STRESS The first, called confining stress
UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS ROCK DEFORMATION Tectonic forces exert different types of stress on rocks in different geologic environments. STRESS The first, called confining stress
D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test.
 (d) COMPRESSIBILITY AND CONSOLIDATION D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test. (a) Plot the e - σ curve. (b)
(d) COMPRESSIBILITY AND CONSOLIDATION D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test. (a) Plot the e - σ curve. (b)
DOWN-HOLE SEISMIC SURVEY AND VERTICAL ELECTRIC SOUNDINGS RABASKA PROJECT, LÉVIS, QUÉBEC. Presented to :
 DOWN-HOLE SEISMIC SURVEY AND VERTICAL ELECTRIC SOUNDINGS RABASKA PROJECT, LÉVIS, QUÉBEC Presented to : TERRATECH 455, René-Lévesque Blvd. West Montreal, Québec HZ 1Z3 Presented by : GEOPHYSICS GPR INTERNATIONAL
DOWN-HOLE SEISMIC SURVEY AND VERTICAL ELECTRIC SOUNDINGS RABASKA PROJECT, LÉVIS, QUÉBEC Presented to : TERRATECH 455, René-Lévesque Blvd. West Montreal, Québec HZ 1Z3 Presented by : GEOPHYSICS GPR INTERNATIONAL
EFFECTS OF HIGH PORE PRESSURE ON PERFORATION TUNNELS IN BOTH HIGH AND MODERATE COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH ROCKS IPS 16-43
 2016 INTERNATIONAL PERFORATING SYMPOSIUM GALVESTON EFFECTS OF HIGH PORE PRESSURE ON PERFORATION TUNNELS IN BOTH HIGH AND MODERATE COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH ROCKS May 10TH, 2016 2016 Halliburton. All Rights
2016 INTERNATIONAL PERFORATING SYMPOSIUM GALVESTON EFFECTS OF HIGH PORE PRESSURE ON PERFORATION TUNNELS IN BOTH HIGH AND MODERATE COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH ROCKS May 10TH, 2016 2016 Halliburton. All Rights
OTC We attribute the high values of density porosity above the oil- Copyright 2001, Offshore Technology Conference
 OTC 13103 Stress-Controlled Porosity in Overpressured Sands at Bullwinkle (GC65), Deepwater Gulf of Mexico P.B. Flemings, J. Comisky, X. Liu, and J.A. Lupa, Pennsylvania State University Copyright 2001,
OTC 13103 Stress-Controlled Porosity in Overpressured Sands at Bullwinkle (GC65), Deepwater Gulf of Mexico P.B. Flemings, J. Comisky, X. Liu, and J.A. Lupa, Pennsylvania State University Copyright 2001,
Splay fault and megathrust earthquake slip in the Nankai Trough
 Earth Planets Space, 53, 243 248, 2001 Splay fault and megathrust earthquake slip in the Nankai Trough Phil R. Cummins, Takane Hori, and Yoshiyuki Kaneda Frontier Research Program for Subduction Dynamics,
Earth Planets Space, 53, 243 248, 2001 Splay fault and megathrust earthquake slip in the Nankai Trough Phil R. Cummins, Takane Hori, and Yoshiyuki Kaneda Frontier Research Program for Subduction Dynamics,
6298 Stress induced azimuthally anisotropic reservoir - AVO modeling
 6298 Stress induced azimuthally anisotropic reservoir - AVO modeling M. Brajanovski* (Curtin University of Technology), B. Gurevich (Curtin University of Technology), D. Nadri (CSIRO) & M. Urosevic (Curtin
6298 Stress induced azimuthally anisotropic reservoir - AVO modeling M. Brajanovski* (Curtin University of Technology), B. Gurevich (Curtin University of Technology), D. Nadri (CSIRO) & M. Urosevic (Curtin
Fault Rocks. EARS5136 slide 1
 Fault Rocks EARS5136 slide 1 Fault rocks Fault rock types Examples of deformation features in cores Microstructures Porosity and permeability Lithological and lithification control EARS5136 slide 2 Deformation
Fault Rocks EARS5136 slide 1 Fault rocks Fault rock types Examples of deformation features in cores Microstructures Porosity and permeability Lithological and lithification control EARS5136 slide 2 Deformation
Heat flow distribution on the floor of Nankai Trough off Kumano and implications for the geothermal regime of subducting sediments
 JAMSTEC Rep. Res. Dev., Volume 8, November 2008, 13 28 Original paper Heat flow distribution on the floor of Nankai Trough off Kumano and implications for the geothermal regime of subducting sediments
JAMSTEC Rep. Res. Dev., Volume 8, November 2008, 13 28 Original paper Heat flow distribution on the floor of Nankai Trough off Kumano and implications for the geothermal regime of subducting sediments
Time-lapse (4D) seismic effects: Reservoir sensitivity to stress and water saturation
 Time-lapse (4D) seismic effects: Reservoir sensitivity to stress and water saturation Sunday O. Amoyedo*, Kurt J. Marfurt and Roger M. Slatt, The University of Oklahoma. Summary Knowledge of reservoir
Time-lapse (4D) seismic effects: Reservoir sensitivity to stress and water saturation Sunday O. Amoyedo*, Kurt J. Marfurt and Roger M. Slatt, The University of Oklahoma. Summary Knowledge of reservoir
Exam Deformatie en Metamorfose van de Korst Educatorium zaal ALFA
 Naam Studentnummer... Exam Deformatie en Metamorfose van de Korst Educatorium zaal ALFA Do not forget to put your name and student number on each of the question and answer sheets and to return both of
Naam Studentnummer... Exam Deformatie en Metamorfose van de Korst Educatorium zaal ALFA Do not forget to put your name and student number on each of the question and answer sheets and to return both of
Crustal Deformation. Earth Systems 3209
 Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
USE OF CWT ACOUSTIC VELOCITY MEASUREMENT ON CUTTINGS FOR EVALUATION OF PORE PRESSURE
 SCA2006-53 1/6 USE OF CWT ACOUSTIC VELOCITY MEASUREMENT ON CUTTINGS FOR EVALUATION OF PORE PRESSURE P. Budak, S. Falkowicz, Oil and Gas Institute, Krakow, Poland This paper was prepared for presentation
SCA2006-53 1/6 USE OF CWT ACOUSTIC VELOCITY MEASUREMENT ON CUTTINGS FOR EVALUATION OF PORE PRESSURE P. Budak, S. Falkowicz, Oil and Gas Institute, Krakow, Poland This paper was prepared for presentation
Prediction technique of formation pressure
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 01 (January. 2016), V3 PP 29-34 www.iosrjen.org Prediction technique of formation pressure Wu Shangxin 1 1.
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 01 (January. 2016), V3 PP 29-34 www.iosrjen.org Prediction technique of formation pressure Wu Shangxin 1 1.
6. THE BOREHOLE ENVIRONMENT. 6.1 Introduction. 6.2 Overburden Pressures
 6. THE BOREHOLE ENVIRONMENT 6.1 Introduction Wireline logging has a single clearly defined purpose: to give accurate and representative data on the physical properties of the rock formations and fluids
6. THE BOREHOLE ENVIRONMENT 6.1 Introduction Wireline logging has a single clearly defined purpose: to give accurate and representative data on the physical properties of the rock formations and fluids
Methods of Interpreting Ground Stress Based on Underground Stress Measurements and Numerical Modelling
 University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2006 Methods of Interpreting Ground Stress Based on Underground Stress Measurements and
University of Wollongong Research Online Coal Operators' Conference Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2006 Methods of Interpreting Ground Stress Based on Underground Stress Measurements and
Unjacketed bulk compressibility of sandstone in laboratory experiments. R. M. Makhnenko 1 and J. F. Labuz 1
 481 Unjacketed bulk compressibility of sandstone in laboratory experiments R. M. Makhnenko 1 and J. F. Labuz 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455; PH (612)
481 Unjacketed bulk compressibility of sandstone in laboratory experiments R. M. Makhnenko 1 and J. F. Labuz 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455; PH (612)
NanTroSEIZE Stage 1 expeditions: introduction and synthesis of key results 1
 Kinoshita, M., Tobin, H., Ashi, J., Kimura, G., Lallement, S., Screaton, E.J., Curewitz, D., Masago, H., Moe, K.T., and the Expedition 314/315/316 Scientists Proceedings of the Integrated Ocean Drilling
Kinoshita, M., Tobin, H., Ashi, J., Kimura, G., Lallement, S., Screaton, E.J., Curewitz, D., Masago, H., Moe, K.T., and the Expedition 314/315/316 Scientists Proceedings of the Integrated Ocean Drilling
8. HYDROSTATIC CONSOLIDATION TESTS OF UNDEFORMED, CLAY-RICH SAMPLES FROM THE BARBADOS ACCRETIONARY PRISM, LEG 156 1
 Moore, J.C., Klaus, A., et al., 1998 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Initial Reports, Vol. 171A 8. HYDROSTATIC CONSOLIDATION TESTS OF UNDEFORMED, CLAY-RICH SAMPLES FROM THE BARBADOS ACCRETIONARY
Moore, J.C., Klaus, A., et al., 1998 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Initial Reports, Vol. 171A 8. HYDROSTATIC CONSOLIDATION TESTS OF UNDEFORMED, CLAY-RICH SAMPLES FROM THE BARBADOS ACCRETIONARY
OP-13. PROCEDURES FOR DESIGN OF EMBANKMENT
 Page 1 of 8 WORK INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGINEERS TYC Compiled by : LSS Checked by : GSS Approved by : OP-13. PROCEDURES FOR DESIGN OF EMBANKMENT Page of 8 13.0 13.1. OVERALL PROCEDURES This section will briefly
Page 1 of 8 WORK INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGINEERS TYC Compiled by : LSS Checked by : GSS Approved by : OP-13. PROCEDURES FOR DESIGN OF EMBANKMENT Page of 8 13.0 13.1. OVERALL PROCEDURES This section will briefly
College of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric Sciences, Oregon State University, 104 CEOAS Administration Building, Corvallis, Oregon 97330, USA 2
 THEMED ISSUE: Subduction Top to Bottom 2 GEOSPHERE GEOSPHERE, v. 13, no. 5 doi:1.113/ges1498.1 Hydrothermal circulation and the thermal structure of shallow subduction zones Robert N. Harris 1, Glenn A.
THEMED ISSUE: Subduction Top to Bottom 2 GEOSPHERE GEOSPHERE, v. 13, no. 5 doi:1.113/ges1498.1 Hydrothermal circulation and the thermal structure of shallow subduction zones Robert N. Harris 1, Glenn A.
