Study Effect of Residence Time on the Wear Rate for Polymer UBE / PMMA and Reinforced by the Nanometer ZnO
|
|
|
- Lauren Rosalyn Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Study Effect of Residence Time on the Wear Rate for Polymer UBE / PMMA and Reinforced by the Nanometer ZnO Zainab A. AL- Ramadhan 1, Fadhil k. Farhan 2, Widad A.Abd-ALhussein 3 1, 3 College of Education 2 Ministry of Science and Technology Abstract : In this study, Tribologicalproperties ( Wear, Friction, Dry lubricant), have been studied for (UPE/PMMA) bland polymer, reinforced with nano [ZnO]( 0vol %,1vol%2vol%, 3vol%, 4vol% and 5vol%). Ultrasonic dispersion technique used to prepare the nanocomposites specimens follow with cold casting technique using flash Teflon molds standard conditions. [Pin-on-disc] technique is used to measure wear rate,coefficient of friction and heat of friction. Tribological properties (Dry sliding wear rate) results show that values decreases progressively by succession of increase load and volume fraction of fillers. Scanning electron microscopy used were employed to aid interpretation results of sliding wear, and distribution nanoparticle in base matrix. Keyword: Tribological, dispersion, UPE/PMMA, nanocomposites 1. Introduction Nano particles are entities with diameters in the range of nm. This new field of nanoparticles is lying between the traditional fields of nanoparticles is lying physics. Therefore, a significant gap exists between these regimes with unique characteristics that neither obeys the law of physics nor quantum chemistry. The smaller is the particle, the higher is the surface-to-volume ratio. Thus more atoms t are once determined by the molecular structures are now end to reside on the surface than inside the particle itself. Particle chemical/mechanical properties that influenced by the defects on the surface [1]. The incorporation of fillers into a polymer matrix has shown tremendous promise in increasing longevity and achieving the desired mix of tribological properties in dry sliding. It is also attractive from processing consideration because the same processing methods as applicable to unfilled polymers can be used for filled polymers as well. A large number of tribological studies have been reported [2] to exhibit properties different from their micro scale counterparts. Since they have higher percentages of atoms on their surfaces, they are expected to be more active. In view of this, they would be expected to provide different tribological properties, hopefully beneficial. The wear resistance of polymer composites filled with micro particles depends on the modification of transfer film by the particulate filler material [3, 4]. Because of their high reactivity, nanoparticles should influence the transfer film more proactively than the micro particles. nanocomposite is a class of materials with unique physical properties and wide application potential in diverse areas [5]. Dispersion of nano scaled inorganic fillers into an organic polymer to form polymer nanocomposites has gained increasing interest in recent years. Controlling the nanostructure, composition and morphology of nano composites plays an essential role in their applications. Novel properties of nanocomposites can be obtained by successful imparting of the characteristics of parent constituents to a single material [6]. These materials differ from both pure polymers and inorganic fillers in some physical and nano scale inorganic fillers is opening pathways for engineering flexible composites that exhibit attractive mechanical, thermal, optical and electrical properties compared with conventional composites [7, 8]. [TiO 2,ZnO] is an important and attractive semi conductive material. It has drawn enormous attention due to its fantastic characteristics in thermal and electronics.polymers are widely used in aeronautics, automobiles, constructions, oil and gas industries, and so on. However, they are susceptible to damage by scratching and abrasive wear. Such processes impair the appearance and also reduce the mechanical strength by the introduction of flaws [9]. Polymers scratch and abrasive properties are of practical importance and the use of reinforced polymer composites is becoming more common. When nanoparticles are embedded in polymer, the resulted composite material is known as polymer nano composite. Nowadays, polymer composites are widely used in many situations where machine components are subjected to tribological loading conditions [10-14]. For such components, it is imperative to understand the wearing mechanism under specific sliding conditions. Furthermore, the ever-increasing demand for reliability and long life of machine parts (made of polymeric composite materials) are one of the main concerns that during design stage [14, 15]. In view of this, many researchers are interested to study the wear properties at different loadings and found that, different inorganic fillers show distinct effect on the wear behaviors of polymer composites, so the mechanism of filler in reducing wear has been largely focused [16-18]. The objective of this work is to investigate the friction and wear properties of particulate filled [TiO 2,ZnO] composites. 2. The aim of the Study 1) Fabrication of[zno]reinforced resin UPE/PMMAbased nanocompositewith/without filler content. 2) Dry sliding wear of composite samples under various operating conditions. 3) Study effect of filler content on sliding wear analysis. Paper ID: NOV
2 4) Besides the above all the objective is to develop new class of nanocomposites by incorporating [ZnO] reinforcing phases into a polymeric resin. Also this work is expected to introduce a new class of polymer composite that might find tribological applications. 3. Theory Recently the application of polymers has rapidly increased generally in technology and also as materials for rubbing components in various machines and devices. This is particularly connected with low cost of materials and manufacturing in large amount of components. When the polymeric materials are rubbing in tribological contacts it is very useful and often the lubrication is not necessary. The friction coefficient can be similar to the lubricated metallic or ceramic contacts. This kind of contact is often called as oilless[21. Since tribological phenomena involve the interaction between surfaces, it is important to reveal whether the metal particles are present on the composite surface. In our previous work we have shown that metallic particles can be found on the surface of the composite and are well dispersed, with the exception of SIC (micro and nanosized) which tends to form agglomerates as large as 30 microns in diameter [22]. In general, the wear mechanisms of materials include adhesion, abrasion, fatigue and impact, electrical and chemical wear. for polymeric materials adhesion, abrasion and fatigue wear are the dominant mechanisms. Although there is only little tendency of adhesion between ceramic materials and polymers, in many cases a film of transferred material can be formed on the ceramic surface (the hardest material) and thus adhesion can be stronger [23]. Figure (1) show the apparatus used in this study. According to the conditions of the Pin on disc- machine the wear rate are calculated according to the following equation[24]. =.(1) SD Where: : is the Wear weight loss of the specimen before and after the wear test (). =W 1 -W 2, W 1 : mass before Wear test (). W 2 : mass after Wear test (). SD: is the sliding distance (cm). SD= π. ϴ. D. t D: is the circular sliding diameter(cm). ϴ: is the no. of revolutions of the rotating disc (rev. /min). t: sliding distance time (second). And the Wear coefficient can be used the Archard s equation: Archard s Wear equation relates the Wear volume, to the normal load L, the sliding distance SD, and the inverse of hardness H VS, through a proportionality constant, often referred to as the Wear coefficient. = WRᵣ ρ W Coeff = WR.HV..(2). (3) SD.L W V : is the wear volume loss of the specimen before and after the wear test (mm 3 ). ρ= density of sample ( / cm 3 ) L (load): normal load applied on the sample (Newton). The sliding velocity(m / s) is evaluated from the relationship: Vs = (πdθ) 60.. (4) 4. Experimental Nanocomposite preparation and standards Nanocomposites are prepared by dispersing Nano[ZnO]kinetically by ultrasonication. To achieve better state of dispersion first the nanoparticales were Figure 1: Pin on- disc - machine [24] treated with alcoholicmedium (ethanol or acetone) for the deagglomeration of the particle bundles. The treated particles are then added to the blends resin and sonicated for 2 h at room temperature. Then the mixture is cured under vacuum at (363K) for 10 h followed by hardener addition by using simultaneous magnetic stirring (100 rpm), for an hour to Paper ID: NOV
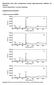
3 homogenization. The prepared samples are treated at (353K) for 6 h in the oven to remove the moisture contents of the samples. The samples are placed between two metal plates under pressure to reduce porosity forming during hardening, before mechanical and thermal measurements, the surfaces of the specimens are mechanically polished to minimize the influence of surface flaws, mainly the porosity. To prepare the nano composite samples, molds are made from Teflon. The mold smeared by wax before the mixture is poured into the mold after homogeneity. To calculation the weight of blends resin and [ Nano ZnO] used Sensitive electronic balance. 5. Testing Equipment and Techniques Wear experiments have been conducted in the Pin-on-disc type friction and wear monitor which was used to evaluate the wear behavior of the composite, against hardened ground steel disc. The wear test was performed on Pin-ondisc apparatus. In this test the flat end of cylindrical specimen 10 mm in diameter and 30 mm length was fixed in chuck jaws to prevent specimens from rotation during the test. Axial load was applied to the pins against the plane surface of the rotating disc. Each specimen was weighed before the experiment and after it by a digital balance having sensitivity of The duration of the experiment was controlled by stopwatch. The average value of the weight loss percentage as a function of test time was calculated. From weight loss of the specimens. [Pin - on disc] test apparatus which produced by local company named (Al furat company) was used to measure the wear rates of the previous prepared samples, the used disc in this work is made from steel material with hardness(55hrc). The wear tests were performed in air at room temperature ~(25.C) with different variables included:- [26] 1) The applied loads: (5) Newton. 2) The distance from the centre of sample to the centre of disc (7cm). 3) The testing time (t): (5,10,15 and 20) min. 4) The distance sliding D= 7 cm Wear rate was estimated by measuring the mass loss in the specimen after each test and mass loss, in the specimen was obtained. Wear rate which relates to the mass loss to sliding distance, was calculated using the expressions, the wear rates are calculated according to equation (1), and the specific wear rate is employed. This is defined as the volume loss of the nanocomposite per unit sliding distance and per unit applied normal load. Often the inverse of specific wear rate expressed in terms of the volumetric wear rate calculated using equation (2). The wear rate coefficient using equation (4), It is necessary to mention the following: The surface of all specimens under study were cleaned and grinded to become smoother (without scratches) before the test. Sensitive electronic balance (type- AE160 Metler, 4 digits) was used to measure the weights of samples before and after the wear test [27]. 6. Results and discuses Experimental data on the slide wear loss of filled and unfilled Nano[,ZnO]composite samples are shown in Figs(2,3,4and5) for different sliding time (5,10,15and 20N) and sliding velocity(3.48 m/s). Tables [1,2,3and 4] shows the results pertaining to the coefficient of wear rate of filled and unfilled Nano[ZnO]nanocomposite system. It is observed from the Figures and Table that there is a strong inter-dependence between the friction coefficient and wear loss irrespective of the loads and sliding velocities employed. The SEM photographs of select combinations of filled and unfilled Nano[ZnO]samples subjected to slide wear are shown in Figs. (6,7,8 and 9) respectively.the tribologicalproperties are studied for 0%,1v%, 2v%,3%,4% and 5v% Nano [ZnO]filled nanocomposite it is different observedthat, because of variation in the amount of the additive and this is due to agglomeration winning in the polymer matrix. After this the wear rate increased for reinforcing of Nano ZnO atdifferent load and time 10 min see Tables and Figures (2,3,4and5). From this, it is observed that the nanocomposite filled with 1vol% ZnOnanoparticles exhibits lowest wear rate in comparison with the wear rate of pure blend. It is also observed that, the wear rate difference is very low. There after increasing the percentage of,znonanoparticles, wear rate of nanocomposite is increased. The same trend is observed for 5,10,15 and 20 load as shown in Figures(2,3,4and5). This indicates that the filler content played a key role in the wear property of blend - based nanocomposites and this a good agreement with reference [28].From the SEM examinations Figures( 6,7,8 and 9) ofzno filled nanocomposites, it is clearly observed that the 1 v% and 2 v% Sic nanoparticles are mixed thoroughly in polymer matrix without any aggregation of ZnOnanoparticles (Figure 7&8)). The surface is also smooth for 1v% and 2 v%nanoznonanocomposites. From the SEM images (Figure 9), it is observed that, there is an aggregation of ZnOnanoparticles in the polymer matrix by reinforcing 5wt%based on this examination, we infer that,zno at low percentages distributed uniformly on the subsurfaceof the blend nanocomposite, which reduces the destructionof blend during wear process. Also observed, the higher percentages of reinforcing nanoparticles in the polymer matrix leads to aggregation and this a good agreement with reference [28]. Table 1: [T =5, Load = 5N, S D = cm] 10-8 Cm 3 /cm Kg/ m 3 Neat % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO Paper ID: NOV
4 Table 2: [T10, Load = 5N, S D =208810cm] cm 3 /cm Kg/ m 3 Neat % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO Table 3: [T =15 Load = 5N, S D = cm] cm 3 /cm Kg/ m 3 Neat % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO Table 4: [T =20 Load = 5N, S D = cm] mm 3 /cm Kg/m 3 Neat % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO % ZnO Figure 2: Wear Loss Values Figure 3: Wear Rate Values Paper ID: NOV
5 Figure 4: Wear Volume Values Figure 5: Wear coefficient value Figure 6: SEM of neat Figure 7: SEM of 1% Nano- ZnO Paper ID: NOV
6 7. Conclusions International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR) Figure 8: SEM of 3% Nano- ZnO Figure 9: SEM of 5% Nano- ZnO The following points can be concluded from the present study: 1) It can be noticed that the (blend) resin has higher wear rates compared with the [ZnO] nanocomposite. 2) The wear rates increases for both materials with increase of the applied load, at higher applied load, the wear rates of all materials under study increase when the sliding velocity and time test is increased. 3) It is clear that the order of magnitude of experimental wear rates is about in the range(10-5 ) /cm. 4) The wear and friction coefficient decreased with increase the time and percentage ZnO]. References [1] K.J. Klabunde.. Nanocrystals as Stoichiometric Reagents with Unique Surface Chemistry. J. Phys. Chem. Vol.100: pp (1996) [2] M.R. Scanlon, R.C. Cammrata.. Mechanical Properties of nano composite granular metal thin films. J. Appl. Phys.Vol. 76,pp (1994). [3] Z.P. Lu, K. Friedrich.. On sliding friction and wear of PEEK and its composites. Wear (2),pp ,(1995). [4] J. Vande Voort, S. Bahadur.. The growth and bonding of transfer film and the role of CuS and PTFE in the tribological behavior of PEEK. Wear (1),pp (1995). [5] Balazs AC, Emrick T, Russel TP.. Nanoparticle polymer composites: where two small worlds meet. Science.Vol. 314,pp (2006). [6] Tang EJ, Cheng GX, Ma XL.. Preparation of nano- ZnO/PMMA composite particles via grafting of the co polymer onto the surface of Zinc oxide nano particles powder technol.vol. 161,pp (2006). [7] Lin Y, Boker A He JB, Sill K, Xiang HQ,and Abetz C,. Self-directed self-assembly of nano particle / copolymer mixtures. Nature.Vol. 434,pp ,(2005). [8] Zhnag MQ, Yu G, Zeng HM, Zhang HB, and Hou YH. Two step percolation in polymer blends filled with carbon black. Macromolecules.Vol. 31,pp (1998). [9] M.J. Adams,. An experimental study of the nano scratches behavior of poly (Methyl methacrylate). Wear.Vol. 251,pp (2001). [10] Chand N, and Naik A Neogi S. Three - body abrasive wearof short glass fibre polyster composite. Wear.Vol. 242(1-2),pp ,(2002). [11] Edwards KL, An overview of the technology of the fibrereinforced plastics for design purposes. Mater design.vol. 19(1-2),pp (1998). [12] Tripathy BS, Furey MJ.. Tribological behavior of unidirectional graphite-epoxy and carbon-peek composites. Wear , pp (1993). [13] Kishore, Sampathkumaran P, Seetharamu S, Vynatheya S, Murali A, Kumar RK.. SEM observations of the effect and velocity and load on the sliding wear characteristics of glass fabric-epoxy composites with different fillers. Wear.Vol. 237(1),pp (2000). [14] Hasim P, Nihat T. Effect of load and speed on the behavior of woven glass fabrics and aramid fibrereinforced. 252(11-12),pp (2002). [15] Srivastava VK,and Pathak JP. Friction and wear properties of bushing bearing of graphite filled short glass fibre composite in dry sliding. Wear.Vol. 197(1-2),pp (1996). [16] Z.-Z. Zhang, Q.-J. Xue, W.-M. Liu, W.C. Shen.. Wear.Vol. 210,p (1997). [17] L. Yu, W. Liu, Q. Xue.. J. Appl. Polym Sci.Vol. 68,p.1643,(1998). [18] L. YU, S. Bahadur, A. Kapoor.. Waer.Vol. 214,p.54.(1998). [19] Awham M. and H. Sadeer [Study of The Wear Rate of Some Polymer Materials In Different Conditions], Applied Science Department, University of Technology/ Baghdad (2010). [20] B. Aldousiri,1 A. Shalwan [A Review on Tribological Behaviour of PolymericComposites and Future Reinforcements], Received 28 May 2013; Accepted June (2013). [21] Samyn P.: Tribophysical interpretation of scaling effects in friction and wear for polymers, Ph.D. Dissertation, Ghent University,( 2006). [22] W.Brosto w, A.Buchman, E.Buchman, and O.Olea- Mejia, Polymer Eng. Sci.Vol.48,.p 1977, (2008). [23] M.H.Cho, S.Bahadur, and J.W.Andere gg, Tribol. Internat. 39, 1436 (2006). [24] M. Salih, M. M. Salih, "American J. of Appl. Sci.,Vol.6, PP. ( ),(2009). [25] Handbook Goodfellow GmbHPostfach 13 43D Bad Nauheim GermanyApril ( 2012.) Paper ID: NOV
7 [26] ASTM standards Annual hand book of, Section 3,03,02, ASTM G-99 Phildelphia, USA.(1995). [27] M. Salih, M. M. Salih, "American J. of Appl. Sci.,Vol.6, PP. ( ),(2009). [28] M.Jun,M.S.Mo,X.S.Du,S.R.Dai,andI.Luck, Studyof epoxy toughened by in situ formed rubber nanoparticles, Journal ofapplied Polymer Science,vol.110,pp ,(2008). Paper ID: NOV
DEVELOP WEAR-RESISTANT POLYMERIC COMPOSITES BY USING NANOPARTICLES
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS DEVELOP WEAR-RESISTANT POLYMERIC COMPOSITES BY USING NANOPARTICLES 1 Abstract L. Chang 1 *, K. Friedrich 2 1 School of Aerospace, Mechanical & Mechatronic
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS DEVELOP WEAR-RESISTANT POLYMERIC COMPOSITES BY USING NANOPARTICLES 1 Abstract L. Chang 1 *, K. Friedrich 2 1 School of Aerospace, Mechanical & Mechatronic
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 105 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 05 (05 ) 858 864 6th BSME International Conference on Thermal Engineering (ICTE 04) Experimental investigation on friction coefficient
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 05 (05 ) 858 864 6th BSME International Conference on Thermal Engineering (ICTE 04) Experimental investigation on friction coefficient
Mechanical Properties of Epoxy/Al 2 O 3 Nanocomposites
 Mechanical Properties of Epoxy/Al 2 O 3 Nanocomposites M. J. Kadhim*, A. K. Abdullah, I. A. Al-Ajaj, and A. S. Khalil Department of Physics, College of Science, Baghdad University, Baghdad, Iraq. Abstract
Mechanical Properties of Epoxy/Al 2 O 3 Nanocomposites M. J. Kadhim*, A. K. Abdullah, I. A. Al-Ajaj, and A. S. Khalil Department of Physics, College of Science, Baghdad University, Baghdad, Iraq. Abstract
The Effect of Surface Functionalization of Graphene on the Electrical Conductivity of Epoxy-based Conductive Nanocomposites
 The Effect of Surface Functionalization of Graphene on the Electrical Conductivity of Epoxy-based Conductive Nanocomposites Behnam Meschi Amoli 1,2,3,4, Josh Trinidad 1,2,3,4, Norman Y. Zhou 1,3,5, Boxin
The Effect of Surface Functionalization of Graphene on the Electrical Conductivity of Epoxy-based Conductive Nanocomposites Behnam Meschi Amoli 1,2,3,4, Josh Trinidad 1,2,3,4, Norman Y. Zhou 1,3,5, Boxin
Study of electrostatic potential induced by friction
 Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics 2014 1 Study of electrostatic potential induced by friction Shiyu Hu, Yuanyue Zhang, Tianmin Shao* State Key Lab of Tribology, Tsinghua University shaotm@tsinghua.edu.cn
Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics 2014 1 Study of electrostatic potential induced by friction Shiyu Hu, Yuanyue Zhang, Tianmin Shao* State Key Lab of Tribology, Tsinghua University shaotm@tsinghua.edu.cn
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 2, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 2, 2017, 1476 1480 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF CDSE QUANTUM DOTS IN POLY (3-HEXYLTHIOPHENE)(P3HT) PREPARED
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 2, 2017, 1476 1480 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF CDSE QUANTUM DOTS IN POLY (3-HEXYLTHIOPHENE)(P3HT) PREPARED
The Effect of Surface Functionalization of Graphene on the Electrical Conductivity of Epoxy-based Conductive Nanocomposites
 The Effect of Surface Functionalization of Graphene on the Electrical Conductivity of Epoxy-based Conductive Nanocomposites by Behnam Meschi Amoli, PhD Institute for Polymer Research, Waterloo Institute
The Effect of Surface Functionalization of Graphene on the Electrical Conductivity of Epoxy-based Conductive Nanocomposites by Behnam Meschi Amoli, PhD Institute for Polymer Research, Waterloo Institute
CHEM-C2410: Materials Science from Microstructures to Properties Composites: basic principles
 CHEM-C2410: Materials Science from Microstructures to Properties Composites: basic principles Mark Hughes 14 th March 2017 Today s learning outcomes To understand the role of reinforcement, matrix and
CHEM-C2410: Materials Science from Microstructures to Properties Composites: basic principles Mark Hughes 14 th March 2017 Today s learning outcomes To understand the role of reinforcement, matrix and
Studies on Furan Polymer Concrete
 Studies on Furan Polymer Concrete Rajesh Katiyar 1, Shobhit Shukla 2 1Associate Professor, Department of Chemical engineering, H.B.T.U., Kanpur-208002, India 2Research Scholar, Department of Chemical engineering
Studies on Furan Polymer Concrete Rajesh Katiyar 1, Shobhit Shukla 2 1Associate Professor, Department of Chemical engineering, H.B.T.U., Kanpur-208002, India 2Research Scholar, Department of Chemical engineering
Effect of Graphene and Silica Fillers on Mechanical Properties of Polymer Nano Composites
 International Journal of Advances in Scientific Research and Engineering (ijasre) E-ISSN : 2454-8006 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7324/ijasre.2017.32510 Vol.3 (9) Oct - 2017 Effect of Graphene and Silica
International Journal of Advances in Scientific Research and Engineering (ijasre) E-ISSN : 2454-8006 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7324/ijasre.2017.32510 Vol.3 (9) Oct - 2017 Effect of Graphene and Silica
IMPROVEMENT IN MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MODIFIED GRAPHENE/EPOXY NANOCOMPOSITES
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS IMPROVEMENT IN MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MODIFIED 1 Introduction Since first successfully separated from graphite by micromechanical cleavage [1], graphene
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS IMPROVEMENT IN MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MODIFIED 1 Introduction Since first successfully separated from graphite by micromechanical cleavage [1], graphene
Fabrication and Characterization of Nanometer-sized AgCl/PMMA Hybrid Materials
 Modern Applied Science November, 2008 Fabrication and Characterization of Nanometer-sized AgCl/PMMA Hybrid Materials Xiangting Dong (Corresponding author), Jinxian Wang, Xiuli Feng School of Chemistry
Modern Applied Science November, 2008 Fabrication and Characterization of Nanometer-sized AgCl/PMMA Hybrid Materials Xiangting Dong (Corresponding author), Jinxian Wang, Xiuli Feng School of Chemistry
Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Nanocomposites
 12 S. Singha and M. J. Thomas: Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Nanocomposites Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Nanocomposites Santanu Singha and M. Joy Thomas High Voltage Laboratory Department of Electrical
12 S. Singha and M. J. Thomas: Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Nanocomposites Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Nanocomposites Santanu Singha and M. Joy Thomas High Voltage Laboratory Department of Electrical
Change in physico-mechanical and thermal properties of polyamide / silica nanocomposite film
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 7, Issue 6 (June 2013), PP. 01-05 Change in physico-mechanical and thermal properties
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 7, Issue 6 (June 2013), PP. 01-05 Change in physico-mechanical and thermal properties
STUDY ON FRICTION AND DRY SLIDING WEAR BEHAVIOR OF CENOSPHERE FILLED VINYLESTER COMPOSITES
 (AGUIJST) 08, Vol. No., Jul-Dec e-issn: 55-09; p-issn: 55-808 STUDY ON FRICTION AND DRY SLIDING WEAR BEHAVIOR OF CENOSPHERE FILLED VINYLESTER COMPOSITES Sunil Thakur, S.R. Chauhan Department of Mechanical
(AGUIJST) 08, Vol. No., Jul-Dec e-issn: 55-09; p-issn: 55-808 STUDY ON FRICTION AND DRY SLIDING WEAR BEHAVIOR OF CENOSPHERE FILLED VINYLESTER COMPOSITES Sunil Thakur, S.R. Chauhan Department of Mechanical
ENHANCED THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY OF EPOXY BASED COMPOSITES WITH SELF-ASSEMBLED GRAPHENE-PA HYBRIDS
 ENHANCED THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY OF EPOXY BASED COMPOSITES WITH SELF-ASSEMBLED GRAPHENE-PA HYBRIDS Di. Wu 1, Gang. Li 2 *, XiaoPing. Yang 1 (1 State Key Laboratory of Organic-Inorganic Composites; Beijing
ENHANCED THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY OF EPOXY BASED COMPOSITES WITH SELF-ASSEMBLED GRAPHENE-PA HYBRIDS Di. Wu 1, Gang. Li 2 *, XiaoPing. Yang 1 (1 State Key Laboratory of Organic-Inorganic Composites; Beijing
Supporting Information: PDMS Nanocomposites for Heat Transfer Enhancement in. Microfluidic Platforms
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information: PDMS Nanocomposites for Heat Transfer Enhancement in Microfluidic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information: PDMS Nanocomposites for Heat Transfer Enhancement in Microfluidic
[83] RMUTP Research Journal: Special Issue 2014 The 4 th RMUTP International conference: Textiles and Fashion
![[83] RMUTP Research Journal: Special Issue 2014 The 4 th RMUTP International conference: Textiles and Fashion [83] RMUTP Research Journal: Special Issue 2014 The 4 th RMUTP International conference: Textiles and Fashion](/thumbs/88/115954002.jpg) [83] : 2014 FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF FIBER REINFORCED NANOCOMPOSITES Rajesh Mishra 1*, Richa Tiwari 1, Jiri Militky 1 & B.K.Behera 2 1 Faculty of Textile Engineering, Technical University of Liberec,
[83] : 2014 FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF FIBER REINFORCED NANOCOMPOSITES Rajesh Mishra 1*, Richa Tiwari 1, Jiri Militky 1 & B.K.Behera 2 1 Faculty of Textile Engineering, Technical University of Liberec,
ISSN: ISO 9001:2008 Certified International Journal of Engineering Science and Innovative Technology (IJESIT) Volume 2, Issue 4, July 2013
 Delamination Studies in Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites K.Kantha Rao, Dr P. Shailesh, K. Vijay Kumar 1 Associate Professor, Narasimha Reddy Engineering College Hyderabad. 2 Professor, St. Peter s Engineering
Delamination Studies in Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites K.Kantha Rao, Dr P. Shailesh, K. Vijay Kumar 1 Associate Professor, Narasimha Reddy Engineering College Hyderabad. 2 Professor, St. Peter s Engineering
STUDY ON FRICTION PERFORMANCE OF CARBON/CARBON COMPOSITE UNDER LUBRICATION CONDITION
 STUDY ON FRICTION PERFORMANCE OF CARBON/CARBON COMPOSITE UNDER LUBRICATION CONDITION Yewei Fu, Hejun Li, Jie Fei, Guosheng Yang National Key Laboratory of Thermostructure of Composite Materials, Northwestern
STUDY ON FRICTION PERFORMANCE OF CARBON/CARBON COMPOSITE UNDER LUBRICATION CONDITION Yewei Fu, Hejun Li, Jie Fei, Guosheng Yang National Key Laboratory of Thermostructure of Composite Materials, Northwestern
Nanocomposite Fabrication Through Particle Surface Initiated Polymerization
 Nanocomposite Fabrication Through Particle Surface Initiated Polymerization Zhanhu Guo 1, Sung Park 2, H. Thomas Hahn 1 (1) Multifunctional Composite Lab, Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering Department,
Nanocomposite Fabrication Through Particle Surface Initiated Polymerization Zhanhu Guo 1, Sung Park 2, H. Thomas Hahn 1 (1) Multifunctional Composite Lab, Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering Department,
Synthesis, Characterization and Tribological Evaluation of SDS stabilized. Antiwear Lubricant Additives
 Supporting Information Synthesis, Characterization and Tribological Evaluation of SDS stabilized Magnesium-Doped-Zinc Oxide (Zn 0.88 Mg 0. O) Nanoparticles as Efficient Antiwear Lubricant Additives Kalyani,
Supporting Information Synthesis, Characterization and Tribological Evaluation of SDS stabilized Magnesium-Doped-Zinc Oxide (Zn 0.88 Mg 0. O) Nanoparticles as Efficient Antiwear Lubricant Additives Kalyani,
Multi-Layer Coating of Ultrathin Polymer Films on Nanoparticles of Alumina by a Plasma Treatment
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Vol. 635 2001 Materials Research Society Multi-Layer Coating of Ultrathin Polymer Films on Nanoparticles of Alumina by a Plasma Treatment Donglu Shi, Zhou Yu, S. X. Wang 1, Wim J.
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Vol. 635 2001 Materials Research Society Multi-Layer Coating of Ultrathin Polymer Films on Nanoparticles of Alumina by a Plasma Treatment Donglu Shi, Zhou Yu, S. X. Wang 1, Wim J.
Charpy Impact Response of Glass Fiber Reinforced Composite with Nano Graphene Enhanced Epoxy
 Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Scinces ISSN 2303-4521 Vol.5, No.3, November 2017, pp. 341~346 Available online at: http://pen.ius.edu.ba Charpy Impact Response of Glass Fiber Reinforced Composite
Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Scinces ISSN 2303-4521 Vol.5, No.3, November 2017, pp. 341~346 Available online at: http://pen.ius.edu.ba Charpy Impact Response of Glass Fiber Reinforced Composite
FRACTURE TOUGHENING MECHANISMS IN NANOPARTICLE AND MICRO- PARTICLE REINFORCED EPOXY SYSTEMS USING MULTI-SCALE ANALYSIS
 FRACTURE TOUGHENING MECHANISMS IN NANOPARTICLE AND MICRO- PARTICLE REINFORCED EPOXY SYSTEMS USING MULTI-SCALE ANALYSIS By BENJAMIN BOESL A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY
FRACTURE TOUGHENING MECHANISMS IN NANOPARTICLE AND MICRO- PARTICLE REINFORCED EPOXY SYSTEMS USING MULTI-SCALE ANALYSIS By BENJAMIN BOESL A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY
Application of Nano-ZnO on Antistatic Finishing to the Polyester Fabric
 Modern Applied Science January, 2009 Application of Nano-ZnO on Antistatic Finishing to the Polyester Fabric Fan Zhang & Junling Yang School of Material Science and Chemical Engineer Tianjin Polytechnic
Modern Applied Science January, 2009 Application of Nano-ZnO on Antistatic Finishing to the Polyester Fabric Fan Zhang & Junling Yang School of Material Science and Chemical Engineer Tianjin Polytechnic
CHAPTER 4 MODELING OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF POLYMER COMPOSITES
 CHAPTER 4 MODELING OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF POLYMER COMPOSITES 4. Introduction Fillers added to polymer matrices as additives are generally intended for decreasing the cost (by increase in bulk) of
CHAPTER 4 MODELING OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF POLYMER COMPOSITES 4. Introduction Fillers added to polymer matrices as additives are generally intended for decreasing the cost (by increase in bulk) of
Halloysite. Nanotubes Epoxy. NanoComposites
 Halloysite Halloysite Nanotubes Nanotubes Epoxy Epoxy NanoComposites NanoComposites Songshan Zeng Christopher Reyes Songshan Zeng Christopher Reyes Epoxy Chemistry Epoxy systems consist of a liquid epoxy
Halloysite Halloysite Nanotubes Nanotubes Epoxy Epoxy NanoComposites NanoComposites Songshan Zeng Christopher Reyes Songshan Zeng Christopher Reyes Epoxy Chemistry Epoxy systems consist of a liquid epoxy
Polymerveredelung durch Nanotechnologie:
 Polymerveredelung durch Nanotechnologie: Hoch transparente Werkstoffe für die Laserbeschriftung Project House Functional Polymers @ Interfaces and Surfaces DECHEMA, Frankfurt, March 9 th 2005 Dr. Ralf
Polymerveredelung durch Nanotechnologie: Hoch transparente Werkstoffe für die Laserbeschriftung Project House Functional Polymers @ Interfaces and Surfaces DECHEMA, Frankfurt, March 9 th 2005 Dr. Ralf
Structure and properties of polyurethane nanocomposites modified by dibutyl phosphate boehmite
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 26, No. 2, 2008 Structure and properties of polyurethane nanocomposites modified by dibutyl phosphate boehmite J. RYSZKOWSKA *, M. JURCZYK Warsaw University of Technology,
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 26, No. 2, 2008 Structure and properties of polyurethane nanocomposites modified by dibutyl phosphate boehmite J. RYSZKOWSKA *, M. JURCZYK Warsaw University of Technology,
A facile procedure to fabricate nano. calcium carbonate/polymer-based. superhydrophobic surfaces
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information
Innovative use of ultrasound in the manufacture of paints and coatings
 COMPOSITES 2011 American Composites Manufacturers Association February 2-4, 2011 Ft. Lauderdale, Florida USA Innovative use of ultrasound in the manufacture of paints and coatings by Kathrin Hielscher,
COMPOSITES 2011 American Composites Manufacturers Association February 2-4, 2011 Ft. Lauderdale, Florida USA Innovative use of ultrasound in the manufacture of paints and coatings by Kathrin Hielscher,
Semi-Additive Process for Low Loss Build-Up Material in High Frequency Signal Transmission Substrates
 Semi-Additive Process for Low Loss Build-Up Material in High Frequency Signal Transmission Substrates Fei Peng 1, Naomi Ando 2, Roger Bernards 1, Bill Decesare 1 1 MacDermid Enthone Electronics Solutions,
Semi-Additive Process for Low Loss Build-Up Material in High Frequency Signal Transmission Substrates Fei Peng 1, Naomi Ando 2, Roger Bernards 1, Bill Decesare 1 1 MacDermid Enthone Electronics Solutions,
Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics. Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi
 Supporting Information: Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi Experimental Section 1.1 Materials The MWNT
Supporting Information: Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi Experimental Section 1.1 Materials The MWNT
Polymer Nanocomposites: Introduction
 Chapter 1 Polymer Nanocomposites: Introduction Downloaded via 148.251.232.83 on April 5, 2019 at 22:23:00 (UTC). See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published
Chapter 1 Polymer Nanocomposites: Introduction Downloaded via 148.251.232.83 on April 5, 2019 at 22:23:00 (UTC). See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published
New method for dynamic tribological test of engineering polymers
 New method for dynamic tribological test of engineering polymers Á. SARANKÓ, R. KERESZTES, G. KALÁCSKA Szent István University, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Technology, saranko.adam@gmail.com Szent
New method for dynamic tribological test of engineering polymers Á. SARANKÓ, R. KERESZTES, G. KALÁCSKA Szent István University, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Technology, saranko.adam@gmail.com Szent
TESTING of AGGREGATES for CONCRETE
 TESTING of AGGREGATES for CONCRETE The properties of the aggregates affect both the fresh and hardened properties of concrete. It is crucial to know the properties of the aggregates to be used in the making
TESTING of AGGREGATES for CONCRETE The properties of the aggregates affect both the fresh and hardened properties of concrete. It is crucial to know the properties of the aggregates to be used in the making
The study on physical and mechanical properties of latex/graphene oxide composite film
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The study on physical and mechanical properties of latex/graphene oxide composite film To cite this article: S Gea et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The study on physical and mechanical properties of latex/graphene oxide composite film To cite this article: S Gea et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
White Paper: Transparent High Dielectric Nanocomposite
 Zhiyun (Gene) Chen, Ph.D., Vice President of Engineering Pixelligent Technologies 64 Beckley Street, Baltimore, Maryland 2224 Email: zchen@pixelligent.com February 205 Abstract High dielectric constant
Zhiyun (Gene) Chen, Ph.D., Vice President of Engineering Pixelligent Technologies 64 Beckley Street, Baltimore, Maryland 2224 Email: zchen@pixelligent.com February 205 Abstract High dielectric constant
Supplementary information. Derivatization and Interlaminar Debonding of Graphite-Iron Nanoparticles Hybrid
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Supplementary information Derivatization and Interlaminar Debonding of Graphite-Iron
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Supplementary information Derivatization and Interlaminar Debonding of Graphite-Iron
Radar absorbing properties of carbon nanotubes/polymer composites in the V-band
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 39, No. 2, April 2016, pp. 451 456. c Indian Academy of Sciences. Radar absorbing properties of carbon nanotubes/polymer composites in the V-band E A ZAKHARYCHEV 1,, E N RAZOV 1,2,
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 39, No. 2, April 2016, pp. 451 456. c Indian Academy of Sciences. Radar absorbing properties of carbon nanotubes/polymer composites in the V-band E A ZAKHARYCHEV 1,, E N RAZOV 1,2,
Failure analysis of serial pinned joints in composite materials
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 18, April 2011, pp. 102-110 Failure analysis of serial pinned joints in composite materials Alaattin Aktaş* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 18, April 2011, pp. 102-110 Failure analysis of serial pinned joints in composite materials Alaattin Aktaş* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING
 CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING 6.1 TEST RIG SETUP FOR THE FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS Knowing the frictional coefficient is important for the determination of wear loss and power loss
CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING 6.1 TEST RIG SETUP FOR THE FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS Knowing the frictional coefficient is important for the determination of wear loss and power loss
The influence of oxide nanaoparticles on the thermal properties of polymer matrix
 The influence of oxide nanaoparticles on the thermal properties of polymer matrix Branka Pilić, Oskar Bera, Mirjana Jovičić, Jelena Pavličević, Tanja Radusin International Workshop Eco-sustainable Food
The influence of oxide nanaoparticles on the thermal properties of polymer matrix Branka Pilić, Oskar Bera, Mirjana Jovičić, Jelena Pavličević, Tanja Radusin International Workshop Eco-sustainable Food
Mechanical Behaviors Study of Epoxy Resins Reinforced with Nano-SiO 2 Particles Jian Zheng, Xiong Chen, Deng Jia, Xin Tong
 International Conference on Materials, Environmental and Biological Engineering (MEBE 2015) Mechanical Behaviors Study of Epoxy Resins Reinforced with Nano-SiO 2 Particles Jian Zheng, Xiong Chen, Deng
International Conference on Materials, Environmental and Biological Engineering (MEBE 2015) Mechanical Behaviors Study of Epoxy Resins Reinforced with Nano-SiO 2 Particles Jian Zheng, Xiong Chen, Deng
STUDY ON FRICTION TEMPERATURE OF UHMWPE/MULTILAYER GRAPHENE/PARAFFIN NANOCOMPOSITES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 12, No. 4, October-December 2017, p. 1215-1221 STUDY ON FRICTION TEMPERATURE OF UHMWPE/MULTILAYER GRAPHENE/PARAFFIN NANOCOMPOSITES B. PAN ab*, T.
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 12, No. 4, October-December 2017, p. 1215-1221 STUDY ON FRICTION TEMPERATURE OF UHMWPE/MULTILAYER GRAPHENE/PARAFFIN NANOCOMPOSITES B. PAN ab*, T.
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach
 Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Microwave absorbing properties of activated carbon fibre polymer composites
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 34, No. 1, February 2011, pp. 75 79. c Indian Academy of Sciences. Microwave absorbing properties of activated carbon fibre polymer composites TIANCHUN ZOU, NAIQIN ZHAO, CHUNSHENG
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 34, No. 1, February 2011, pp. 75 79. c Indian Academy of Sciences. Microwave absorbing properties of activated carbon fibre polymer composites TIANCHUN ZOU, NAIQIN ZHAO, CHUNSHENG
Bifunctional hairy silica nanoparticles towards high-performance additives for lubricant Tianyi Sui, Baoyu Song*, Yu-ho Wen, Feng Zhang
 Bifunctional hairy silica nanoparticles towards high-performance additives for lubricant Tianyi Sui, Baoyu Song*, Yu-ho Wen, Feng Zhang Supplementary information 1. XPS survey spectra of BHSNs 5 4 O1s
Bifunctional hairy silica nanoparticles towards high-performance additives for lubricant Tianyi Sui, Baoyu Song*, Yu-ho Wen, Feng Zhang Supplementary information 1. XPS survey spectra of BHSNs 5 4 O1s
FUNCTIONALIZATION OF GRAPHENE NANOPLATELETS WITH AN ELASTOMER CTBN AND THE EFFECT ON THE VINYL ESTER NANOCOMPOSITES
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS FUNCTIONALIZATION OF GRAPHENE NANOPLATELETS WITH AN ELASTOMER CTBN AND THE EFFECT ON THE VINYL ESTER NANOCOMPOSITES S. G. Ji 1, D. Kim 1, D. Cho 1
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS FUNCTIONALIZATION OF GRAPHENE NANOPLATELETS WITH AN ELASTOMER CTBN AND THE EFFECT ON THE VINYL ESTER NANOCOMPOSITES S. G. Ji 1, D. Kim 1, D. Cho 1
Fabrication of Carbon Nanotubes/Phenolic Nano-Composite and Its Electrical and Thermal Conductivity Measurements
 Fabrication of Carbon Nanotubes/Phenolic Nano-Composite and Its Electrical and Thermal Conductivity Measurements Chie Gau 1 *, Shuo-Ying Chen 1, Hsin-Luen Tsai 2, Syh-Tsang Jenq 1, Cheng-Ching Lee 3,Yu-Der
Fabrication of Carbon Nanotubes/Phenolic Nano-Composite and Its Electrical and Thermal Conductivity Measurements Chie Gau 1 *, Shuo-Ying Chen 1, Hsin-Luen Tsai 2, Syh-Tsang Jenq 1, Cheng-Ching Lee 3,Yu-Der
Cronicon CHEMISTRY. Research Article. Rheological Properties of NBR-PVC Blend
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS CHEMISTRY Research Article Rheological Properties of NBR-PVC Blend Mohammed H Al-Maamori 1, Ali I Al-Mosawi 2 *, Shaymaa Abbas Abdulsada 3 and Haider A Yasser 1 1 College of Engineering
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS CHEMISTRY Research Article Rheological Properties of NBR-PVC Blend Mohammed H Al-Maamori 1, Ali I Al-Mosawi 2 *, Shaymaa Abbas Abdulsada 3 and Haider A Yasser 1 1 College of Engineering
Influence of Processing on Morphology, Electrical Conductivity and Flexural Properties of Exfoliated Graphite Nanoplatelets Polyamide Nanocomposites
 Carbon Letters Vol. 11, No. 4 December 2010 pp. 279-284 Influence of Processing on Morphology, Electrical Conductivity and Flexural Properties of Exfoliated Graphite Nanoplatelets Polyamide Nanocomposites
Carbon Letters Vol. 11, No. 4 December 2010 pp. 279-284 Influence of Processing on Morphology, Electrical Conductivity and Flexural Properties of Exfoliated Graphite Nanoplatelets Polyamide Nanocomposites
Preparation and Study of Some Electrical Properties of PVA-Ni(NO 3 ) 2 Composites
 International Letters of Chemistry, Physics and Astronomy Online: 2014-10-23 ISSN: 2299-3843, Vol. 40, pp 36-42 doi:10.18052/www.scipress.com/ilcpa.40.36 2015 SciPress Ltd., Switzerland Preparation and
International Letters of Chemistry, Physics and Astronomy Online: 2014-10-23 ISSN: 2299-3843, Vol. 40, pp 36-42 doi:10.18052/www.scipress.com/ilcpa.40.36 2015 SciPress Ltd., Switzerland Preparation and
IMPACT PROPERTIES OF POLYMERIC NANOCOMPOSITES WITH DIFFERENT SHAPE OF NANOPARTICLES. Robert VALEK a, Jaroslav HELL a
 IMPACT PROPERTIES OF POLYMERIC NANOCOMPOSITES WITH DIFFERENT SHAPE OF NANOPARTICLES Robert VALEK a, Jaroslav HELL a a SVUM, a. s., Podnikatelska 565, 19 11 Prague, Czech Republic, valek@svum.cz Abstract
IMPACT PROPERTIES OF POLYMERIC NANOCOMPOSITES WITH DIFFERENT SHAPE OF NANOPARTICLES Robert VALEK a, Jaroslav HELL a a SVUM, a. s., Podnikatelska 565, 19 11 Prague, Czech Republic, valek@svum.cz Abstract
CHEM-E2200: Polymer blends and composites Fibre architecture and principles of reinforcement
 CHEM-E2200: Polymer blends and composites Fibre architecture and principles of reinforcement Mark Hughes 19 th September 2016 Outline Fibre architecture Volume fraction and the rule of mixtures Principle
CHEM-E2200: Polymer blends and composites Fibre architecture and principles of reinforcement Mark Hughes 19 th September 2016 Outline Fibre architecture Volume fraction and the rule of mixtures Principle
Fibrillated Cellulose and Block Copolymers as a Modifiers of Unsaturated Polyester Nanocomposites
 Fibrillated Cellulose and Block Copolymers as a Modifiers of Unsaturated Polyester Nanocomposites Daniel H. Builes, Hugo Hernández, Laida Cano, Agnieszka Tercjak Group Materials + Technologies Polymeric
Fibrillated Cellulose and Block Copolymers as a Modifiers of Unsaturated Polyester Nanocomposites Daniel H. Builes, Hugo Hernández, Laida Cano, Agnieszka Tercjak Group Materials + Technologies Polymeric
Experimental Analysis of Tribological Properties of Lubricating Oil Using Nanoparticle Additives
 ISSN 2395-1621 Experimental Analysis of Tribological Properties of Lubricating Oil Using Nanoparticle Additives #1 S.N.Mandlik, #2 Prof. S.R.Nimbalkar 1 mandliksantosh8@gmail.com 2 nimbalkarsr@pravaraengg.org.in
ISSN 2395-1621 Experimental Analysis of Tribological Properties of Lubricating Oil Using Nanoparticle Additives #1 S.N.Mandlik, #2 Prof. S.R.Nimbalkar 1 mandliksantosh8@gmail.com 2 nimbalkarsr@pravaraengg.org.in
Effect of surface fluorination and sulphonation on the adhesion and tribological properties of polymers
 Plasticheskie Massy, No. 8, 2006, pp. 17-19 Effect of surface fluorination and sulphonation on the adhesion and tribological properties of polymers V. G. Nazarov, V. P. Stolyarov, L. A. Evlampieva, and
Plasticheskie Massy, No. 8, 2006, pp. 17-19 Effect of surface fluorination and sulphonation on the adhesion and tribological properties of polymers V. G. Nazarov, V. P. Stolyarov, L. A. Evlampieva, and
Influence of roughness parameters on coefficient of friction under lubricated conditions
 Sādhanā Vol. 33, Part 3, June 2008, pp. 181 190. Printed in India Influence of roughness parameters on coefficient of friction under lubricated conditions PRADEEP L MENEZES 1, KISHORE 1 and SATISH V KAILAS
Sādhanā Vol. 33, Part 3, June 2008, pp. 181 190. Printed in India Influence of roughness parameters on coefficient of friction under lubricated conditions PRADEEP L MENEZES 1, KISHORE 1 and SATISH V KAILAS
Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application
 Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements for Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics VII 307 Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application T.
Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements for Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics VII 307 Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application T.
A NEW GENERATION OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS: CARBON NANOTUBES INCORPORATED TO CONCRETE AND POLYMERIC MATRIX
 A NEW GENERATION OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS: CARBON NANOTUBES INCORPORATED TO CONCRETE AND POLYMERIC MATRIX Javier Grávalos, Juan Manuel Mieres and Santiago González R&D Department, NECSO Entrecanales Cubiertas
A NEW GENERATION OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS: CARBON NANOTUBES INCORPORATED TO CONCRETE AND POLYMERIC MATRIX Javier Grávalos, Juan Manuel Mieres and Santiago González R&D Department, NECSO Entrecanales Cubiertas
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 17(2) (2013), pp. 36-44 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229-6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Polyamide/Clay
Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 17(2) (2013), pp. 36-44 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229-6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Polyamide/Clay
Available online at ScienceDirect. The Malaysian International Tribology Conference 2013, MITC2013
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 68 ( 2013 ) 7 11 The Malaysian International Tribology Conference 2013, MITC2013 The Effect of External Grit Particle Size on
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 68 ( 2013 ) 7 11 The Malaysian International Tribology Conference 2013, MITC2013 The Effect of External Grit Particle Size on
Comparative Analysis of Dielectric Properties of Enamel Filled with Various Nanofillers such as ZrO 2, Al 2 O 3, CNT and ZnO
 Comparative Analysis of Dielectric Properties of Enamel Filled with Various Nanofillers such as,, and D. Edison Selvaraj Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Mepco Schlenk Engineering
Comparative Analysis of Dielectric Properties of Enamel Filled with Various Nanofillers such as,, and D. Edison Selvaraj Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Mepco Schlenk Engineering
Composite Materials. Fibre-Matrix Interfaces. There is nothing there really except the two of you (or the fiber and matrix).
 Composite Materials Fibre-Matrix Interfaces There is nothing there really except the two of you (or the fiber and matrix). Composite Parameters Fibre properties Composite Interfaces Matrix properties Fibre
Composite Materials Fibre-Matrix Interfaces There is nothing there really except the two of you (or the fiber and matrix). Composite Parameters Fibre properties Composite Interfaces Matrix properties Fibre
A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal
 Supporting information A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal Actuator via Gradient Infiltration Dajie Zhang #, Jie Liu //#, Bo Chen *, Yong Zhao, Jingxia Wang * //, Tomiki Ikeda, Lei Jiang //. CAS
Supporting information A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal Actuator via Gradient Infiltration Dajie Zhang #, Jie Liu //#, Bo Chen *, Yong Zhao, Jingxia Wang * //, Tomiki Ikeda, Lei Jiang //. CAS
Rheological and mechanical properties of epoxy composites modified with montmorillonite nanoparticles
 Plasticheskie Massy, No. 3, 2011, pp. 56 60 Rheological and mechanical properties of epoxy composites modified with montmorillonite nanoparticles S.O. Il in, 1 I.Yu. Gorbunova, 2 E.P. Plotnikova, 1 and
Plasticheskie Massy, No. 3, 2011, pp. 56 60 Rheological and mechanical properties of epoxy composites modified with montmorillonite nanoparticles S.O. Il in, 1 I.Yu. Gorbunova, 2 E.P. Plotnikova, 1 and
Experimental Investigation of Tribological Properties Using Nanoparticles as Modifiers in Lubricating Oil
 Experimental Investigation of Tribological Properties Using Nanoparticles as Modifiers in Lubricating Oil Mr. A.B. Najan 1, Dr. R.R. Navthar 2, Mr. M.J. Gitay 3 1,2 PG Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
Experimental Investigation of Tribological Properties Using Nanoparticles as Modifiers in Lubricating Oil Mr. A.B. Najan 1, Dr. R.R. Navthar 2, Mr. M.J. Gitay 3 1,2 PG Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
Effect of Graphene Nanoplatelets on Compatibility of Polypropylene and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate
 Effect of Graphene Nanoplatelets on Compatibility of Polypropylene and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Jason Peng a, Bei Kai Huang a, Da Qu a a, Chang Jae Yoo a Department of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering,
Effect of Graphene Nanoplatelets on Compatibility of Polypropylene and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Jason Peng a, Bei Kai Huang a, Da Qu a a, Chang Jae Yoo a Department of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering,
D.B.Kawadkar 1, Dr.D.V.Bhope, 2 S.D. Khamankar 3
 Evaluation of Stress Concentration in Plate with Cutout and its Experimental Verification D.B.Kawadkar, Dr.D.V.Bhope, 2 S.D. Khamankar 3 Student, IV Semester, M.Tech (CAD/CAM) Mechanical Engineering Department,
Evaluation of Stress Concentration in Plate with Cutout and its Experimental Verification D.B.Kawadkar, Dr.D.V.Bhope, 2 S.D. Khamankar 3 Student, IV Semester, M.Tech (CAD/CAM) Mechanical Engineering Department,
Graphene oxide hydrogel at solid/liquid interface
 Electronic Supplementary Information Graphene oxide hydrogel at solid/liquid interface Jiao-Jing Shao, Si-Da Wu, Shao-Bo Zhang, Wei Lv, Fang-Yuan Su and Quan-Hong Yang * Key Laboratory for Green Chemical
Electronic Supplementary Information Graphene oxide hydrogel at solid/liquid interface Jiao-Jing Shao, Si-Da Wu, Shao-Bo Zhang, Wei Lv, Fang-Yuan Su and Quan-Hong Yang * Key Laboratory for Green Chemical
Notes on Rubber Friction
 Notes on Rubber Friction 2011 A G Plint Laws of Friction: In dry sliding between a given pair of materials under steady conditions, the coefficient of friction may be almost constant. This is the basis
Notes on Rubber Friction 2011 A G Plint Laws of Friction: In dry sliding between a given pair of materials under steady conditions, the coefficient of friction may be almost constant. This is the basis
GRAPHENE BASED POLY(VINYL ALCOHOL) NANOCOMPOSITES: EFFECT OF HUMIDITY CONTENT
 THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS GRAPHENE BASED POLY(VINYL ALCOHOL) NANOCOMPOSITES: EFFECT OF HUMIDITY CONTENT A. Pegoretti 1 *, M. Traina 2 1 Department of Industrial Engineering,
THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS GRAPHENE BASED POLY(VINYL ALCOHOL) NANOCOMPOSITES: EFFECT OF HUMIDITY CONTENT A. Pegoretti 1 *, M. Traina 2 1 Department of Industrial Engineering,
Lecture No. (1) Introduction of Polymers
 Lecture No. (1) Introduction of Polymers Polymer Structure Polymers are found in nature as proteins, cellulose, silk or synthesized like polyethylene, polystyrene and nylon. Some natural polymers can also
Lecture No. (1) Introduction of Polymers Polymer Structure Polymers are found in nature as proteins, cellulose, silk or synthesized like polyethylene, polystyrene and nylon. Some natural polymers can also
Dielectric constant measurement of P3HT, polystyrene, and polyethylene
 Dielectric constant measurement of P3HT, polystyrene, and polyethylene Supervisor: prof. dr. J.C. Hummelen Daily supervisor: Jenny Douvogianni Name: Si Chen (s2660482) 1. Introduction Dielectric constant
Dielectric constant measurement of P3HT, polystyrene, and polyethylene Supervisor: prof. dr. J.C. Hummelen Daily supervisor: Jenny Douvogianni Name: Si Chen (s2660482) 1. Introduction Dielectric constant
DETERMINATION OF GLASS TRANSITION TEMPERATURE FOR POLYESTER / GRAPHENE OXIDE AND POLYESTER / GRAPHITE COMPOSITE BY TMA AND DSC
 DETERMINATION OF GLASS TRANSITION TEMPERATURE FOR POLYESTER / GRAPHENE OXIDE AND POLYESTER / GRAPHITE COMPOSITE BY TMA AND DSC M. Bastiurea 1, M. S. Bastiurea 1, G. Andrei 1, M. Murarescu 2, D. Dumitru
DETERMINATION OF GLASS TRANSITION TEMPERATURE FOR POLYESTER / GRAPHENE OXIDE AND POLYESTER / GRAPHITE COMPOSITE BY TMA AND DSC M. Bastiurea 1, M. S. Bastiurea 1, G. Andrei 1, M. Murarescu 2, D. Dumitru
Supplementary Information. Seeding Approach to Noble Metal Decorated Conducting Polymer Nanofiber Network
 Supplementary Information Seeding Approach to Noble Metal Decorated Conducting Polymer Nanofiber Network Zhen Liu, Selcuk Poyraz, Yang Liu, Xinyu Zhang* Department of Polymer and Fiber Engineering, Auburn
Supplementary Information Seeding Approach to Noble Metal Decorated Conducting Polymer Nanofiber Network Zhen Liu, Selcuk Poyraz, Yang Liu, Xinyu Zhang* Department of Polymer and Fiber Engineering, Auburn
Hardness and wear resistance of carbon nanotube reinforced Cu matrix nanocomposites
 Materials Science and Engineering A 449 451 (2007) 46 50 Hardness and wear resistance of carbon nanotube reinforced Cu matrix nanocomposites Kyung Tae Kim, Seung Il Cha, Soon Hyung Hong Department of Materials
Materials Science and Engineering A 449 451 (2007) 46 50 Hardness and wear resistance of carbon nanotube reinforced Cu matrix nanocomposites Kyung Tae Kim, Seung Il Cha, Soon Hyung Hong Department of Materials
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
 B05D PROCESSES FOR APPLYING LIQUIDS OR OTHER FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL (apparatus for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces B05B, B05C; {coating of foodstuffs A23P 20/17,
B05D PROCESSES FOR APPLYING LIQUIDS OR OTHER FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL (apparatus for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces B05B, B05C; {coating of foodstuffs A23P 20/17,
MODELLING INTERACTION EFFECT OF NANOSILICA PARTICLES ON NANOSILICA/EPOXY COMPOSITE STIFFNESS
 MODELLING INTERACTION EFFECT OF NANOSILICA PARTICLES ON NANOSILICA/EPOXY COMPOSITE STIFFNESS Mulyadi a*, I. Gitman a, C. Pinna a, C. Soutis b a Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Sheffield,
MODELLING INTERACTION EFFECT OF NANOSILICA PARTICLES ON NANOSILICA/EPOXY COMPOSITE STIFFNESS Mulyadi a*, I. Gitman a, C. Pinna a, C. Soutis b a Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Sheffield,
NITRILE RUBBER (NBR) NANOCOMPOSITES BASED ON DIFFERENT FILLER GEOMETRIES (Nanocalcium carbonate, Carbon nanotube and Nanoclay)
 CHAPTER 5 NITRILE RUBBER (NBR) NANOCOMPOSITES BASED ON DIFFERENT FILLER GEOMETRIES (Nanocalcium carbonate, Carbon nanotube and Nanoclay) 5.1 Introduction Nanocalcium carbonate (NCC) is a particulate nanofiller
CHAPTER 5 NITRILE RUBBER (NBR) NANOCOMPOSITES BASED ON DIFFERENT FILLER GEOMETRIES (Nanocalcium carbonate, Carbon nanotube and Nanoclay) 5.1 Introduction Nanocalcium carbonate (NCC) is a particulate nanofiller
Lead-Free Ceramic-Polymer Composites for Embedded Capacitor and Piezoelectric Applications P. Kumar *
 Lead-Free Ceramic-Polymer Composites for Embedded Capacitor and Piezoelectric Applications P. Kumar * Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, Odisha, India, 769008 Correspondence
Lead-Free Ceramic-Polymer Composites for Embedded Capacitor and Piezoelectric Applications P. Kumar * Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, Odisha, India, 769008 Correspondence
RHEOLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THERMOSETTING RES- IN SYSTEM WITH THERMOPLASTIC FUNCTIONAL LAYER
 21 st International Conference on Composite Materials Xi an, 20-25 th August 2017 RHEOLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THERMOSETTING RES- IN SYSTEM WITH THERMOPLASTIC FUNCTIONAL LAYER W. Surjoseputro 1, G.
21 st International Conference on Composite Materials Xi an, 20-25 th August 2017 RHEOLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THERMOSETTING RES- IN SYSTEM WITH THERMOPLASTIC FUNCTIONAL LAYER W. Surjoseputro 1, G.
INVESTIGATION OF FRICTION HYSTERESIS USING A LABORATORY- SCALE TRIBOMETER
 INVESTIGATION OF FRICTION HYSTERESIS USING A LABORATORY- SCALE TRIBOMETER P. D. Neis 1,2, P. De Baets 2, Y. Perez Delgado 2 and N. F. Ferreira 1 1 Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil 2 Ghent
INVESTIGATION OF FRICTION HYSTERESIS USING A LABORATORY- SCALE TRIBOMETER P. D. Neis 1,2, P. De Baets 2, Y. Perez Delgado 2 and N. F. Ferreira 1 1 Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil 2 Ghent
Modern Additive Technology - a view into the future
 Introduction Modern Additive Technology - a view into the future Dr. Jürgen Omeis, Dr. Guillaume Jaunky BYK-Chemie GmbH, Wesel, Germany Reviewing the current literature of colloids and interfacial materials,
Introduction Modern Additive Technology - a view into the future Dr. Jürgen Omeis, Dr. Guillaume Jaunky BYK-Chemie GmbH, Wesel, Germany Reviewing the current literature of colloids and interfacial materials,
TRANSPORT BEHAVIOUR OF XYLENE THROUGH COMPATIBILIZED LOW DENSITY POLYETHYLENE COMPOSITE
 TRANSPORT BEHAVIOUR OF XYLENE THROUGH COMPATIBILIZED LOW DENSITY POLYETHYLENE COMPOSITE Genevieve C. Onuegbu Department of Polymer and Textile Engineering, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Imo
TRANSPORT BEHAVIOUR OF XYLENE THROUGH COMPATIBILIZED LOW DENSITY POLYETHYLENE COMPOSITE Genevieve C. Onuegbu Department of Polymer and Textile Engineering, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Imo
Home-built Apparatus for Measuring Thermal Conductivity of Glass and Polymer Materials
 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1657 2014 Materials Research Society DOI: 10.1557/opl.2014. 375 Home-built Apparatus for Measuring Thermal Conductivity of Glass and Polymer Materials William R. Heffner
Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1657 2014 Materials Research Society DOI: 10.1557/opl.2014. 375 Home-built Apparatus for Measuring Thermal Conductivity of Glass and Polymer Materials William R. Heffner
INFLUENCE OF NORMAL FORCE AND HUMIDITY ON FRICTION AND WEAR OF UNLUBRICATED STEEL/ STEEL COUPLES
 INFLUENCE OF NORMAL FORCE AND HUMIDITY ON FRICTION AND WEAR OF UNLUBRICATED STEEL/ STEEL COUPLES D. KLAFFKE Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM), Lab. VIII.2, Unter den Eichen 87,
INFLUENCE OF NORMAL FORCE AND HUMIDITY ON FRICTION AND WEAR OF UNLUBRICATED STEEL/ STEEL COUPLES D. KLAFFKE Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM), Lab. VIII.2, Unter den Eichen 87,
Thermal Conduction in Graphite Flake-Epoxy Composites using Infrared Microscopy
 Thermal Conduction in Graphite Flake-Epoxy Composites using Infrared Microscopy Rajath Kantharaj 1, Ishan Srivastava 1, Kunal R. Thaker 1, Aalok U. Gaitonde 1, Alexandra Bruce 2, John Howarter 2, Timothy
Thermal Conduction in Graphite Flake-Epoxy Composites using Infrared Microscopy Rajath Kantharaj 1, Ishan Srivastava 1, Kunal R. Thaker 1, Aalok U. Gaitonde 1, Alexandra Bruce 2, John Howarter 2, Timothy
Electronic Supplementary Information. Three-Dimensional Multilayer Graphene Web for Polymer Nanocomposites with
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Three-Dimensional Multilayer Graphene Web for Polymer
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Three-Dimensional Multilayer Graphene Web for Polymer
Ferroelectric Zinc Oxide Nanowire Embedded Flexible. Sensor for Motion and Temperature Sensing
 Supporting information for: Ferroelectric Zinc Oxide Nanowire Embedded Flexible Sensor for Motion and Temperature Sensing Sung-Ho Shin 1, Dae Hoon Park 1, Joo-Yun Jung 2, Min Hyung Lee 3, Junghyo Nah 1,*
Supporting information for: Ferroelectric Zinc Oxide Nanowire Embedded Flexible Sensor for Motion and Temperature Sensing Sung-Ho Shin 1, Dae Hoon Park 1, Joo-Yun Jung 2, Min Hyung Lee 3, Junghyo Nah 1,*
applied as UV protective films
 Nanocomposite gels via in-situ photoinitiation and disassembly of TiO 2 -Clay composites with polymers applied as UV protective films Chuanan Liao, Qing Wu, Teng Su, Da Zhang, Qingsheng Wu and Qigang Wang*
Nanocomposite gels via in-situ photoinitiation and disassembly of TiO 2 -Clay composites with polymers applied as UV protective films Chuanan Liao, Qing Wu, Teng Su, Da Zhang, Qingsheng Wu and Qigang Wang*
Functionalized flexible MOF as filler in mixed matrix membranes for highly selective separation of CO 2 from CH 4 at elevated pressures
 -Supplementary info file- Functionalized flexible MOF as filler in mixed matrix membranes for highly selective separation of CO 2 from CH 4 at elevated pressures Beatriz Zornoza a, Alberto Martinez-Joaristi
-Supplementary info file- Functionalized flexible MOF as filler in mixed matrix membranes for highly selective separation of CO 2 from CH 4 at elevated pressures Beatriz Zornoza a, Alberto Martinez-Joaristi
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF BAMBOO FIBRE WITH GRAPHENE AS A FILLER MATERIAL IN POLYESTER COMPOSITE
 Volume 119 No. 7 2018, 989-1000 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF BAMBOO FIBRE WITH GRAPHENE AS A FILLER MATERIAL
Volume 119 No. 7 2018, 989-1000 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF BAMBOO FIBRE WITH GRAPHENE AS A FILLER MATERIAL
Finite element modelling of infinitely wide Angle-ply FRP. laminates
 www.ijaser.com 2012 by the authors Licensee IJASER- Under Creative Commons License 3.0 editorial@ijaser.com Research article ISSN 2277 9442 Finite element modelling of infinitely wide Angle-ply FRP laminates
www.ijaser.com 2012 by the authors Licensee IJASER- Under Creative Commons License 3.0 editorial@ijaser.com Research article ISSN 2277 9442 Finite element modelling of infinitely wide Angle-ply FRP laminates
Friction at high sliding speed of WC-6Co pin versus steel disc AISI 1045: estimation of the contact temperature
 Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 3 Number 2 29 141 Friction at high sliding speed of WC-6Co pin versus steel disc AISI 145: estimation of the contact temperature T. KAGNAYA 1,2, C. BOHER 1, L. LAMBERT
Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 3 Number 2 29 141 Friction at high sliding speed of WC-6Co pin versus steel disc AISI 145: estimation of the contact temperature T. KAGNAYA 1,2, C. BOHER 1, L. LAMBERT
Synthesis and Properties of Polymethyl Methacrylate/Nanodiamond Composite Material
 International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation (ICECTT 2015) Synthesis and Properties of Polymethyl Methacrylate/Nanodiamond Composite Material Lifang Ma 1,2,a, Guoliang
International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation (ICECTT 2015) Synthesis and Properties of Polymethyl Methacrylate/Nanodiamond Composite Material Lifang Ma 1,2,a, Guoliang
Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil
 Supplementary Information Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil Kai Feng, Yewen Cao and Peiyi Wu* State key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of
Supplementary Information Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil Kai Feng, Yewen Cao and Peiyi Wu* State key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of
