Status of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment
|
|
|
- Jeffery Holmes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: DOI /s Status of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment Z. Ahmed D.S. Akerib M.J. Attisha C.N. Bailey L. Baudis D.A. Bauer P.L. Brink P.P. Brusov R. Bunker B. Cabrera D.O. Caldwell C.L. Chang J. Cooley M.B. Crisler P. Cushman M. Daal F. DeJongh R. Dixon M.R. Dragowsky L. Duong R. Ferril E. Figueroa-Feliciano J. Filippini R.J. Gaitskell S.R. Golwala D.R. Grant R. Hennings-Yeomans D. Holmgren M.E. Huber S. Kamat S. Leclercq R. Mahapatra V. Mandic P. Meunier N. Mirabolfathi H. Nelson R.W. Ogburn M. Pyle X. Qiu E. Ramberg W. Rau A. Reisetter R.R. Ross T. Saab B. Sadoulet J. Sander R.W. Schnee D.N. Seitz B. Serfass K.M. Sundqvist J.-P.F. Thompson G. Wang S. Yellin J. Yoo B.A. Young Received: 22 July 2007 / Accepted: 15 September 2007 / Published online: 24 January 2008 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2008 N. Mirabolfathi for the CDMS collaboration. M.J. Attisha R.J. Gaitskell J.-P.F. Thompson Brown University, Providence, USA D.S. Akerib C.N. Bailey P.P. Brusov M.R. Dragowsky D.R. Grant R. Hennings-Yeomans S. Kamat R.W. Schnee Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, USA D.A. Bauer M.B. Crisler F. DeJongh R. Dixon D. Holmgren E. Ramberg J. Yoo Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, Batavia, IL 60510, USA R.R. Ross B. Sadoulet Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA B.A. Young Santa Clara University, Santa Clara, CA 95052, USA P. Cushman L. Duong X. Qiu A. Reisetter University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455, USA P.L. Brink B. Cabrera C.L. Chang J. Cooley R.W. Ogburn M. Pyle S. Yellin Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA M. Daal J. Filippini V. Mandic P. Meunier N. Mirabolfathi ( ) H. Nelson R.R. Ross B. Sadoulet D.N. Seitz B. Serfass K.M. Sundqvist University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA mirabol@cosmology.berkeley.edu
2 J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: Abstract The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search experiment (CDMS) is using Phonon+ Ionization detectors to search for Dark Matter in the form of Weakly Interactive Massive Particles (WIMPs). We report the current status of the experiment and its perspective to achieve the sensitivity goal of the cross section: σ WIMP-nucleon cm 2 (Spin independent). Keywords Dark Matter WIMP Transition Edge Sensor (TES) PACS Ly d 1 Introduction Over the last decade, a variety of cosmological observations have led to the construction of a concordance model of cosmology. In this very successful model, 23% of the Universe is composed of nonbaryonic dark matter [1]. Weakly Interactive Massive Particles (WIMPs) represent a generic class of candidates for this dark matter [2]. The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) seeks to detect WIMPs via their interaction with nuclei in crystals of Ge or Si at millikelvin temperatures. CDMS uses ZIP (Z-sensitive ionization and phonon) detectors [3] to discriminate between electronrecoils (most backgrounds) and nuclear-recoils (WIMPs and neutrons) on an eventby-event basis via a simultaneous measurement of ionization and athermal phonons. Bulk and surface electron-recoils are rejected using the relative amplitudes and timings of these signals. In particular the phonon timing parameters are faster for events occurring close to the ionization electrodes (Fig. 1 left). Since its installation at Soudan deep underground laboratory (2090 meters-waterequivalent), CDMS has completed two WIMP-search runs. The first run with one R. Bunker D.O. Caldwell R. Ferril R. Mahapatra J. Sander University of California, Santa Barbara, CA 93106, USA M.E. Huber University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center, Denver, CO, USA S. Leclercq T. Saab University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA Z. Ahmed S.R. Golwala G. Wang California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA L. Baudis RWTH Aachen University, Aachen 52074, Germany W. Rau Queen s University, Kingston, ON K7L 3N6, Canada E. Figueroa-Feliciano Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA L. Baudis Zurich University, Winterthurer str. 190, Zürich 8057, Switzerland
3 802 J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: Fig. 1 (Left) Ionization yield versus phonon timing parameter. Gray dots are the bulk electron-recoil events from a 133 Ba source, black cross are the near-surface electron recoils with lower yield but faster phonon pulses and the gray circles are nuclear recoils from 252 Cf. The rectangle indicates approximately the WIMPs signal region. (Right) Upper limits on the Spin-independent WIMPs-nucleon interaction; CDMS two previous runs combined [4]: black; CDMSII final projected: black dash; Xenon [5]: circle; EdelweissI [6]: cross. Filled regions indicate MSSM [7](light gray) and CMSSM [8](medium gray) models, as well as an interpretation of the DAMA/NaI annual modulation signal [9](black) stack of six ZIPs (called a Tower): g Ge and g Si, and the second with two Towers: g Ge and g Si. Detector response to electronrecoils and nuclear-recoils was calibrated in situ using radioactive gamma ( 133 Ba) and neutron ( 252 Cf) sources. A total of 52.6 and 74.5 live-days of WIMP search data were acquired from the first and the second runs respectively, yielding: kg-days exposure before cuts. A blind analysis was performed for the data of each run in which the nuclear recoil region was masked while the various analysis cuts were completed. Single WIMP candidates were found in each run consistent with the expectations for misidentified near surface electron-recoils [4, 10]. These results, with one event found in each of the two runs, may be combined and interpreted in terms of limits on the WIMP-nucleon interaction (Fig. 1 left). 2 CDMSII 5-Tower Run In August 2004 after nearly a year at 50 mk the experiment was warmed up to install several new upgrades. Chief among these were three new detector towers (18 more ZIPs) adding 3.25 kg of Ge to the previous 1.5 kg Ge ZIP detectors, 18 additional flexible circuits (strip-lines) to read them out and a Gifford-McMahon cryocooler to mitigate their extra heat load and to reduce the liquid helium consumption. The first CDMS WIMP search run (since October 2006) with five ZIP towers was stopped on March A total of 430 kg days WIMP exposure (before cuts) was accumulated during that period. An additional 223 kg days has been accumulated since March 2007 making the total CDMSII five-tower exposure accumulated up to this time 653 kg days before cuts. The blind analysis for this data is still ongoing and expected to be finalized this fall. Except for a short period when the CDMSII
4 J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: He- 4 He dilution refrigerator was warmed to 4 K for circulation cleaning on March 2007, it has been cold since July 2006 and is planned to run for at least another year. 3 CDMSII: A Background Free Experiment The dominant background observed in CDMSII at Soudan consists of electrons from radioactive contamination on the detector surfaces, which we refer to as betas reflecting the likelihood that most of these events arise from beta decay. We are expecting a better background rejection with respect to the previous CDMS runs mainly because: (A) Newer ZIPs in Tower 3, 4 and 5 are cleaner The analysis of the previous CDMSII data suggests that the total rate of surface events in the energy range kev is 1.7 kg 1 day 1, of which 0.21 detector 1 day 1 are single-scatter events, having a hit in one ZIP detector alone. Detailed studies of the surface events show that the bulk of this rate is due to decays of 210 Pb deposited by airborne radon. Our detectors are exposed to radon during fabrication, mounting and testing. We observe alpha particles in our detectors at a rate of 0.4 detector 1 day 1. We identify the predicted beta component by looking at coincident betas between nearest-neighbor detectors and their correlation to the corresponding alpha rates (Fig. 2). Using this method we are finding a factor of 3 less radon contamination in our newest detectors which we can associate with the newer detectors being exposed less to radon during fabrication and testing. (B) More uniform phonon parameters A detailed description of the ZIP detectors is given in [3]. Athermal phonons in a ZIP are measured by four sensors. Each phonon Fig. 2 (Left) 45 kev peak in the sum energy spectrum of beta-beta coincidences in neighboring detectors due to 210 Pb. The 210 Pb decay is rather complicated due to variety of emissions. Hence a broad peak at 45 kev is a reasonable expectation. (Right) Correlation of number of events in the 45 kev nearest-neighbor beta-beta sum peak vs. number of alpha events coincident between the same neighbors (alpha seen in one member of the pair, recoiling 206 Pb in the other)
5 804 J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: sensor covers one quadrant of one planar face of a disc shape Ge or Si absorber (diameter = 7.5 cm, thickness = 1 cm). The four phonon sensors are independently read out. Thus, one can use the relative amplitudes and delays of the four athermal phonon sensors to localize events in the absorber. An important aspect of the ZIPs is the dependence of the measured athermal phonon signal on the position of the events. A solution to achieve uniform detector response is to correct the phonon parameters with respect to event location, i.e. to make a lookup table of correction factors for the detector. Comparing these local averages with the desired values provides the correction [11]. Therefore it is very important for the phonon sensors to perform similarly, so that the differences between the phonon parameters depend only on the position of the events in the absorber. In order to achieve a uniform phonon response for our current run, a new Phonon sensor tuning procedure using a real-time analysis feedback tool was developed [12]. Figure 3 shows the comparison between the timing parameter distributions among the four phonon-sensors (same detector) between the previous and the current CDMS runs. In addition to the event position, the phonon pulse parameters may also depend on the recoil energy [11]. Compared to the previous CDMS analysis where this energy dependence would be corrected independent of the position of the events, we have included energy to the lookup table parameters for our most recent analysis. Our preliminary analysis shows that using this method, the detector response is indeed more uniform. Whereas the previous CDMS analysis corrected this energy dependence independently of the position of the events, our most recent analysis now includes energy in the lookup table parameters. Our preliminary analysis shows that using this method indeed results in a more uniform detector response. Fig. 3 (Color online) With the new phonon sensor tuning procedure the distributions of the phonon timing parameter become more uniform in the current CDMS data (Right) compared to the previous data (Left). Shown on both plots are the timing-parameter histograms for the four phonon sensors. Each histogram contains only events occurring in the region of the detector covered with the corresponding phonon-sensor (quadrant A, B, C or D)
6 J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: With these improvements available, we expect to have a more uniform detector phonon response hence to increase our signal cut efficiency. 4 Conclusion CDMSII is currently running with 30 ZIPs and aims to accumulate 1500 kg day of WIMP search exposure by the end of In addition to several upgrades to its previous setup at the Soudan deep underground laboratory, CDMSII now has better control of its backgrounds. With conservative estimates of background rejection efficiencies (2 misidentified event per 10 6 bulk gammas and 2 per every 10 3 surface betas) and considering all known background sources and rates, CDMSII should stay background-free and should detect WIMPs if: σ WIMP-nucleon > cm 2. Acknowledgements We gratefully acknowledge the technical and support staff at our many institutions who have made this experiment possible, as well as the financial support of the NSF and DOE. References 1. D.N. Spergel et al., Astrophys. J. Suppl. 148, 175 (2003) 2. G. Jungman et al., Phys. Rep. 267, 195 (1996) 3. T. Saab et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 444, 300 (2000) 4. D.S. Akerib et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, (2006) 5. Announced at APS 2007, Florida, USA, arxiv: V. Sanglard et al., Phys. Rev. D 71, (2005) 7. E.A. Baltz, P. Gondolo, Phys. Rev. D 67, (2003) 8. J.R. Ellis et al., Phys. Rev. D 71, (2005) 9. R. Bernabei et al., Rivista Nuovo Cimento 26N1, 1 (2003) 10. D.S. Akerib et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, (2004) 11. V. Mandic et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 520, 171 (2004) 12. N. Mirabolfathi et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 559, 417 (2006)
Present Status of the SuperCDMS program
 J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 818 823 DOI 10.1007/s10909-008-9740-7 Present Status of the SuperCDMS program D.S. Akerib C.N. Bailey D.A. Bauer P.L. Brink R. Bunker B. Cabrera D.O. Caldwell J. Cooley P. Cushman
J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 818 823 DOI 10.1007/s10909-008-9740-7 Present Status of the SuperCDMS program D.S. Akerib C.N. Bailey D.A. Bauer P.L. Brink R. Bunker B. Cabrera D.O. Caldwell J. Cooley P. Cushman
CDMS-II to SuperCDMS
 CDMS-II to SuperCDMS WIMP search at a zeptobarn Tobias Bruch University of Zürich 5 th Patras Workshop on Axions,WIMPs and WISPs University of Durham, 13 July 2009 CDMS-II 5 Tower setup 5 Towers a 6 detectors
CDMS-II to SuperCDMS WIMP search at a zeptobarn Tobias Bruch University of Zürich 5 th Patras Workshop on Axions,WIMPs and WISPs University of Durham, 13 July 2009 CDMS-II 5 Tower setup 5 Towers a 6 detectors
Identification of the Surface Event Background in the CDMS II Experiment. Sunil Golwala for the CDMS II Collaboration Caltech August 21, 2008
 Identification of the Surface Event Background in the CDMS II Experiment Sunil Golwala for the CDMS II Collaboration Caltech August 21, 28 Surface Event Background in CDMS II Identification of Surface
Identification of the Surface Event Background in the CDMS II Experiment Sunil Golwala for the CDMS II Collaboration Caltech August 21, 28 Surface Event Background in CDMS II Identification of Surface
WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT
 WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT P.L. BRINK, L. BAUDIS, B. CABRERA, J.P. CASTLE, C. CHANG AND T. SAAB Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94350, USA R. J. GAITSKELL
WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT P.L. BRINK, L. BAUDIS, B. CABRERA, J.P. CASTLE, C. CHANG AND T. SAAB Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94350, USA R. J. GAITSKELL
Limits on spin-dependent WIMP-nucleon interactions from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search
 PHYSICAL REVIEW D 73, 011102(R) (2006) Limits on spin-dependent WIMP-nucleon interactions from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search D. S. Akerib, 1 M. S. Armel-Funkhouser, 2 M. J. Attisha, 3 C. N. Bailey,
PHYSICAL REVIEW D 73, 011102(R) (2006) Limits on spin-dependent WIMP-nucleon interactions from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search D. S. Akerib, 1 M. S. Armel-Funkhouser, 2 M. J. Attisha, 3 C. N. Bailey,
Supporting Online Material for
 Originally published 11 February 21; corrected 26 March 21 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1186112/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Dark Matter Search Results from the CDMS II Experiment
Originally published 11 February 21; corrected 26 March 21 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1186112/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Dark Matter Search Results from the CDMS II Experiment
New Results from the CDMS-II experiment
 New Results from the CDMS-II experiment University of Zürich for the CDMS Collaboration DPG Meeting, 3 March 2008, University of Freiburg Outline Introducing the experiment Detection principle Low yield
New Results from the CDMS-II experiment University of Zürich for the CDMS Collaboration DPG Meeting, 3 March 2008, University of Freiburg Outline Introducing the experiment Detection principle Low yield
Recent Results from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search. Bruno Serfass - UC Berkeley on behalf of the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations
 Recent Results from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Bruno Serfass - UC Berkeley on behalf of the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations CDMS/SuperCDMS Collaborations DOE NSF California Institute of Technology
Recent Results from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Bruno Serfass - UC Berkeley on behalf of the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations CDMS/SuperCDMS Collaborations DOE NSF California Institute of Technology
Analysis of the low-energy electron-recoil spectrum of the CDMS experiment
 Analysis of the low-energy electron-recoil spectrum of the CDMS experiment The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Analysis of the low-energy electron-recoil spectrum of the CDMS experiment The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Constraints on Low-Mass WIMP Signals from CDMS. Steven W. Leman (MIT) 18 March 2011 Rencontres de Moriond EW La Thuile, Valle d Aosta, Italy
 Constraints on Low-Mass WIMP Signals from CDMS Steven W. Leman (MIT) 18 March 2011 Rencontres de Moriond EW La Thuile, Valle d Aosta, Italy CDMS Members California Institute of Technology Z. Ahmed, J.
Constraints on Low-Mass WIMP Signals from CDMS Steven W. Leman (MIT) 18 March 2011 Rencontres de Moriond EW La Thuile, Valle d Aosta, Italy CDMS Members California Institute of Technology Z. Ahmed, J.
Pushing the Limits: Dark Matter Search with SuperCDMS. Wolfgang Rau Queen s University Kingston For the SuperCDMS Collaboration
 Pushing the Limits: Dark Matter Search with Wolfgang Rau Queen s University Kingston For the Collaboration Dark Matter Velocity Observed Zwicky Expected (Kepler) Radius Rubin Luminous Matter (< 1 %) Ordinary
Pushing the Limits: Dark Matter Search with Wolfgang Rau Queen s University Kingston For the Collaboration Dark Matter Velocity Observed Zwicky Expected (Kepler) Radius Rubin Luminous Matter (< 1 %) Ordinary
Scalability of the SuperCDMS experiment
 Scalability of the SuperCDMS experiment Daniel Brandt dbrandt@slac.stanford.edu KIPAC, SLAC National Accelerator Lab Detecting dark matter The majority of the mass energy in the Universe is dark matter»
Scalability of the SuperCDMS experiment Daniel Brandt dbrandt@slac.stanford.edu KIPAC, SLAC National Accelerator Lab Detecting dark matter The majority of the mass energy in the Universe is dark matter»
CDMS. Vuk Mandic. 13. July 2010
 Dark Matter Direct Detection: CDMS Vuk Mandic University of Minnesota 13. July 2010 CDMS II Collaboration California Institute of Technology Z. Ahmed, J. Filippini, S.R. Golwala, D. Moore, R.W. Ogburn
Dark Matter Direct Detection: CDMS Vuk Mandic University of Minnesota 13. July 2010 CDMS II Collaboration California Institute of Technology Z. Ahmed, J. Filippini, S.R. Golwala, D. Moore, R.W. Ogburn
The CDMS-II Dark Matter Search and SuperCDMS
 The CDMS-II Dark Matter Search and SuperCDMS R. W. Ogburn IV Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA For the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) currently sets
The CDMS-II Dark Matter Search and SuperCDMS R. W. Ogburn IV Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA For the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) currently sets
The complex vacuum configurations contribute to an extra non-perturbative term in the QCD Lagrangian[1],
![The complex vacuum configurations contribute to an extra non-perturbative term in the QCD Lagrangian[1], The complex vacuum configurations contribute to an extra non-perturbative term in the QCD Lagrangian[1],](/thumbs/95/126083812.jpg) Detection of Axions LI, LONG Duke University October 18, 2017 Abstract Physicsts proposed axions as a solution to the strong-cp problem of QCD. Axions turn out also to be a candidate of dark matter which
Detection of Axions LI, LONG Duke University October 18, 2017 Abstract Physicsts proposed axions as a solution to the strong-cp problem of QCD. Axions turn out also to be a candidate of dark matter which
Search for Axions with the CDMS Experiment
 PRL 13, 1418 (9) P H Y S I C A L R E V I E W L E T T E R S Search for Axions with the CDMS Experiment Z. Ahmed, 1 D. S. Akerib, S. Arrenberg, 17 C. N. Bailey, D. Balakishiyeva, 15 L. Baudis, 17 D. A. Bauer,
PRL 13, 1418 (9) P H Y S I C A L R E V I E W L E T T E R S Search for Axions with the CDMS Experiment Z. Ahmed, 1 D. S. Akerib, S. Arrenberg, 17 C. N. Bailey, D. Balakishiyeva, 15 L. Baudis, 17 D. A. Bauer,
Results from CRESST and CDMS
 Results from CRESST and CDMS Syracuse University CDMS Thanks to Federica Petricca & Franz Proebst of CRESST for sharing slides and information November 14, 2011 CRESST target: CRESST Target Material scintillating
Results from CRESST and CDMS Syracuse University CDMS Thanks to Federica Petricca & Franz Proebst of CRESST for sharing slides and information November 14, 2011 CRESST target: CRESST Target Material scintillating
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results
 A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
First CDMS II Five-Tower Results. Sunil Golwala SLAC Summer Institute 2008 August 7, 2008
 First CDMS II Five-Tower Results Sunil Golwala SLAC Summer Institute 2008 August 7, 2008 Overview Why and how do we look for WIMP dark matter? Candidate WIMPs from particle physics The Cryogenic Dark Matter
First CDMS II Five-Tower Results Sunil Golwala SLAC Summer Institute 2008 August 7, 2008 Overview Why and how do we look for WIMP dark matter? Candidate WIMPs from particle physics The Cryogenic Dark Matter
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 24 Jun 2004
 LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment
 Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment Kevin A. McCarthy Massachusetts Institute of Technology On behalf of the SuperCDMS and CDMS Collaborations
Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment Kevin A. McCarthy Massachusetts Institute of Technology On behalf of the SuperCDMS and CDMS Collaborations
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Dark Matter Search. Dark Matter
 Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
CDMS and SuperCDMS. SLAC Summer Institute - CDMS. August 2, 2007 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS
 CDMS and SuperCDMS SLAC Summer Institute August 2, 2007 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS CDMS-II science results - less than 1 evt / kg of Ge / month Status of CDMS-II 5-Tower
CDMS and SuperCDMS SLAC Summer Institute August 2, 2007 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS CDMS-II science results - less than 1 evt / kg of Ge / month Status of CDMS-II 5-Tower
Search for Weakly Interacting Massive Particles with CDMS and XENON
 Search for Weakly Interacting Massive Particles with CDMS and XENON Elena Aprile 1,2, Laura Baudis 3,4, Blas Cabrera 5,6 1 Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University,
Search for Weakly Interacting Massive Particles with CDMS and XENON Elena Aprile 1,2, Laura Baudis 3,4, Blas Cabrera 5,6 1 Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University,
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search. Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration
 SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project
 Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
Search for Inelastic Dark Matter with the CDMS experiment. Sebastian Arrenberg Universität Zürich Doktorierendenseminar 2010 Zürich,
 Search for Inelastic Dark Matter with the CDMS experiment Sebastian Arrenberg Universität Zürich Doktorierendenseminar 2010 Zürich, 30.08.2010 The CDMS experiment - 19 Ge and 11 Si semiconductor detectors
Search for Inelastic Dark Matter with the CDMS experiment Sebastian Arrenberg Universität Zürich Doktorierendenseminar 2010 Zürich, 30.08.2010 The CDMS experiment - 19 Ge and 11 Si semiconductor detectors
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST
 Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Phonon Quasidiffusion in Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Large Germanium Detectors
 Phonon Quasidiffusion in Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Large Germanium Detectors arxiv:1107.3575v1 [physics.ins-det] 18 Jul 2011 S.W. Leman a, B. Cabrera b, K.A. McCarthy a, M. Pyle b, R. Resch c, B. Sadoulet
Phonon Quasidiffusion in Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Large Germanium Detectors arxiv:1107.3575v1 [physics.ins-det] 18 Jul 2011 S.W. Leman a, B. Cabrera b, K.A. McCarthy a, M. Pyle b, R. Resch c, B. Sadoulet
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter
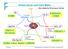 Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors
 Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors Complementarity between Dark Matter Searches & Collider Experiments Miniworkshop before SUSY06 at Irvine -
Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors Complementarity between Dark Matter Searches & Collider Experiments Miniworkshop before SUSY06 at Irvine -
Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search: Charge Transport and Phonon Emission in Ge 100 Crystals at 40 mk
 J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 443 447 DOI 10.1007/s10909-007-9666-5 Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search: Charge Transport and Phonon Emission in Ge 100 Crystals at 40 mk K.M. Sundqvist B. Sadoulet
J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 443 447 DOI 10.1007/s10909-007-9666-5 Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search: Charge Transport and Phonon Emission in Ge 100 Crystals at 40 mk K.M. Sundqvist B. Sadoulet
Monte Carlo Comparisons to a Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Detector with low Transition-Edge-Sensor Transition Temperature
 SLAC-PUB-199 Monte Carlo Comparisons to a Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Detector with low Transition-Edge-Sensor Transition Temperature S.W. Leman a, K.A. McCarthy a, P.L. Brink b, B. Cabrera b, M. Cherry
SLAC-PUB-199 Monte Carlo Comparisons to a Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Detector with low Transition-Edge-Sensor Transition Temperature S.W. Leman a, K.A. McCarthy a, P.L. Brink b, B. Cabrera b, M. Cherry
PoS(VERTEX 2009)026. Dark Matter search with Ge detectors. Paul L. Brink 1
 Dark Matter search with Ge detectors Paul L. Brink 1 Dept. of Physics, Stanford University 382 Via Pueblo Mall, Stanford, CA 943405, USA E-mail: pbrink@stanford.edu The direct detection of Dark Matter,
Dark Matter search with Ge detectors Paul L. Brink 1 Dept. of Physics, Stanford University 382 Via Pueblo Mall, Stanford, CA 943405, USA E-mail: pbrink@stanford.edu The direct detection of Dark Matter,
Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE
 Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE Kyungeun E. Lim (on behalf of the CUORE collaboration) Oct. 30. 015, APS Division of Nuclear Physics meeting, Santa Fe, NM The CUORE Experiment CUORE
Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE Kyungeun E. Lim (on behalf of the CUORE collaboration) Oct. 30. 015, APS Division of Nuclear Physics meeting, Santa Fe, NM The CUORE Experiment CUORE
SuperCDMS at SNOLAB. What is CDMS? Technical Progress. Collaboration. Funding. Schedule and Needs. Why is SuperCDMS 25 kg timely?
 What is CDMS? SuperCDMS at SNOLAB Why is SuperCDMS 25 kg timely? Technical Progress CDMS II running at Soudan (4.5 kg Ge) Detectors Cryogenics Backgrounds Electronics Infrastructure Collaboration Addition
What is CDMS? SuperCDMS at SNOLAB Why is SuperCDMS 25 kg timely? Technical Progress CDMS II running at Soudan (4.5 kg Ge) Detectors Cryogenics Backgrounds Electronics Infrastructure Collaboration Addition
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search
 Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 8 Jul 2005
 CDMS December 3, 25 Exclusion Limits on the WIMP-Nucleon Cross-Section from the First Run of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search in the Soudan Underground Lab arxiv:astro-ph/579 v 8 Jul 25 D.S. Akerib, M.S.
CDMS December 3, 25 Exclusion Limits on the WIMP-Nucleon Cross-Section from the First Run of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search in the Soudan Underground Lab arxiv:astro-ph/579 v 8 Jul 25 D.S. Akerib, M.S.
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment. 1 Abstract. 2 Introduction
 Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 4 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 4 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 4 Nov 2017](/thumbs/89/101192102.jpg) arxiv:1711.01488v1 [physics.ins-det] 4 Nov 017 Current status and projected sensitivity of COSINE-0 WG Thompson, on behalf of the COSINE-0 Collaboration Department of Physics, Yale University, New Haven,
arxiv:1711.01488v1 [physics.ins-det] 4 Nov 017 Current status and projected sensitivity of COSINE-0 WG Thompson, on behalf of the COSINE-0 Collaboration Department of Physics, Yale University, New Haven,
Sensitivity of sodium iodide cryogenic scintillation-phonon detectors to WIMP signals
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Sensitivity of sodium iodide cryogenic scintillation-phonon detectors to WIMP signals To cite this article: M Clark et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Sensitivity of sodium iodide cryogenic scintillation-phonon detectors to WIMP signals To cite this article: M Clark et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012](/thumbs/75/71468977.jpg) Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:1201.3685v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012 M. Pyle 1 D.A. Bauer 2 B. Cabrera 1 J. Hall 2 R.W. Schnee 4 R. Basu Thakur
Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:1201.3685v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012 M. Pyle 1 D.A. Bauer 2 B. Cabrera 1 J. Hall 2 R.W. Schnee 4 R. Basu Thakur
The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) : Status and future. Kipac SLAC April 2009
 The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) : Status and future Kipac SLAC April 2009 Department of Physics, Stanford University KIPAC associate member CDMS The CDMS Collaboration Caltech Z. Ahmed, S. Golwala,
The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) : Status and future Kipac SLAC April 2009 Department of Physics, Stanford University KIPAC associate member CDMS The CDMS Collaboration Caltech Z. Ahmed, S. Golwala,
PoS(idm2008)010. The PICASSO Dark Matter Search Project. A. Davour for the PICASSO collaboration Queen s University
 The PICASSO Dark Matter Search Project A. Davour for the PICASSO collaboration Queen s University E-mail: adavour@owl.phy.queensu.ca PICASSO is an array of bubble detectors constructed to search for spin
The PICASSO Dark Matter Search Project A. Davour for the PICASSO collaboration Queen s University E-mail: adavour@owl.phy.queensu.ca PICASSO is an array of bubble detectors constructed to search for spin
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 4 Oct 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 4 Oct 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 4 Oct 2014](/thumbs/94/119519658.jpg) Maximum Likelihood Analysis of Low Energy CDMS II Germanium Data arxiv:14.3v1 [astro-ph.co] 4 Oct 214 R. Agnese, 19 A.J. Anderson, 4 D. Balakishiyeva, 19 R. Basu Thakur, 2, 2 D.A. Bauer, 2 J. Billard,
Maximum Likelihood Analysis of Low Energy CDMS II Germanium Data arxiv:14.3v1 [astro-ph.co] 4 Oct 214 R. Agnese, 19 A.J. Anderson, 4 D. Balakishiyeva, 19 R. Basu Thakur, 2, 2 D.A. Bauer, 2 J. Billard,
SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS
 SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS David G. Cerdeño Institute for Theoretical Physics Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for the SuperCDMS Collaboration Hints for low-mass WIMPs in direct detection
SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS David G. Cerdeño Institute for Theoretical Physics Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for the SuperCDMS Collaboration Hints for low-mass WIMPs in direct detection
Status of the CUORE and CUORE-0 experiments at Gran Sasso
 Status of the CUORE and CUORE-0 experiments at Gran Sasso S. Di Domizio INFN and University of Genova for the CUORE collaboration Weak Interactions and Neutrinos Natal, September 19 2013 Neutrinoless double
Status of the CUORE and CUORE-0 experiments at Gran Sasso S. Di Domizio INFN and University of Genova for the CUORE collaboration Weak Interactions and Neutrinos Natal, September 19 2013 Neutrinoless double
Search for low-mass WIMPs with Spherical Detectors : NEWS-LSM and NEWS-SNO
 Search for low-mass WIMPs with Spherical Detectors : NEWS-LSM and NEWS-SNO G. Gerbier 1 for the NEWS collaboration 2, 1 Queen s University, Physics Department, Kingston, Canada 2 New Experiments With Spheres
Search for low-mass WIMPs with Spherical Detectors : NEWS-LSM and NEWS-SNO G. Gerbier 1 for the NEWS collaboration 2, 1 Queen s University, Physics Department, Kingston, Canada 2 New Experiments With Spheres
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches
 Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 22 Dec 2016
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 22 Dec 2016 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 22 Dec 2016](/thumbs/83/87421236.jpg) Results from the DM-Ice17 Dark Matter Experiment at the South Pole arxiv:161.0746v1 [physics.ins-det] Dec 016, on behalf of the DM-Ice Collaboration Department of Physics and Wright Laboratory, Yale University
Results from the DM-Ice17 Dark Matter Experiment at the South Pole arxiv:161.0746v1 [physics.ins-det] Dec 016, on behalf of the DM-Ice Collaboration Department of Physics and Wright Laboratory, Yale University
Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS
 Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS TeV 2006, Madison - August 30, 2006 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS Summary of current status of Direct
Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS TeV 2006, Madison - August 30, 2006 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS Summary of current status of Direct
Position calibration of cryogenic dark matter detectors
 Abstract Position calibration of cryogenic dark matter detectors Aliya Merali University of Florida REU Participant, Summer 2010 Advisor: Dr. Tarek Saab Preparations for a position calibration of cryogenic
Abstract Position calibration of cryogenic dark matter detectors Aliya Merali University of Florida REU Participant, Summer 2010 Advisor: Dr. Tarek Saab Preparations for a position calibration of cryogenic
arxiv: v3 [physics.ins-det] 4 Oct 2013
![arxiv: v3 [physics.ins-det] 4 Oct 2013 arxiv: v3 [physics.ins-det] 4 Oct 2013](/thumbs/75/71537465.jpg) arxiv:1305.405v3 [physics.ins-det] 4 Oct 013 Demonstration of Surface Electron Rejection with Interleaved Germanium Detectors for Dark Matter Searches R. Agnese, 18 A.J. Anderson, 4 D. Balakishiyeva, 18
arxiv:1305.405v3 [physics.ins-det] 4 Oct 013 Demonstration of Surface Electron Rejection with Interleaved Germanium Detectors for Dark Matter Searches R. Agnese, 18 A.J. Anderson, 4 D. Balakishiyeva, 18
Investigation of pulse shapes and time constants for NaI scintillation pulses produced by low energy electrons from beta decay
 11 November 1999 Ž. Physics Letters B 467 1999 132 136 Investigation of pulse shapes and time constants for NaI scintillation pulses produced by low energy electrons from beta decay N.J.T. Smith a, P.F.
11 November 1999 Ž. Physics Letters B 467 1999 132 136 Investigation of pulse shapes and time constants for NaI scintillation pulses produced by low energy electrons from beta decay N.J.T. Smith a, P.F.
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions
 Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
The 46g BGO bolometer
 Nature, 3 The g BGO bolometer 1 Photograph of the heat [g BGO] and light [Ge; =5 mm] bolometers: see Fig. 1c for description Current events: Amplification gains: 8, (heat channel) &, (light channel). The
Nature, 3 The g BGO bolometer 1 Photograph of the heat [g BGO] and light [Ge; =5 mm] bolometers: see Fig. 1c for description Current events: Amplification gains: 8, (heat channel) &, (light channel). The
Status of the CUORE and CUORE-0 experiments at Gran Sasso
 Status of the CUORE and CUORE-0 experiments at Gran Sasso S. Di Domizio INFN and University of Genova for the CUORE collaboration Les Rencontres de Physique de la Vallée d'aoste La Thuile, February 25
Status of the CUORE and CUORE-0 experiments at Gran Sasso S. Di Domizio INFN and University of Genova for the CUORE collaboration Les Rencontres de Physique de la Vallée d'aoste La Thuile, February 25
the first prototype for a scintillating bolometer double beta decay experiment.
 the first prototype for a scintillating bolometer double beta decay experiment. On behalf of CUPID-INFN collaboration Cuore Upgrade with Particle IDentification In the middle of 2015 INFN decided to support
the first prototype for a scintillating bolometer double beta decay experiment. On behalf of CUPID-INFN collaboration Cuore Upgrade with Particle IDentification In the middle of 2015 INFN decided to support
cryogenic calorimeter with particle identification for double beta decay search
 cryogenic calorimeter with particle identification for double beta decay search Cuore Upgrade with Particle IDentification In the middle of 2015 INFN decided to support CUPID activity to develop: CUPID-0:
cryogenic calorimeter with particle identification for double beta decay search Cuore Upgrade with Particle IDentification In the middle of 2015 INFN decided to support CUPID activity to develop: CUPID-0:
Looking for WIMPs A Review
 Looking for WIMPs A Review Beatriz E. Burrola Gabilondo There is currently a race to find out what dark matter actually is. Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) are a strong candidate for dark
Looking for WIMPs A Review Beatriz E. Burrola Gabilondo There is currently a race to find out what dark matter actually is. Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) are a strong candidate for dark
DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO
 Search for Dark Matter WIMPs: SuperCDMS Soudan Soudan and SNOLAB leading to GEODM at DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO - September 17, 2009 Blas Cabrera - Stanford
Search for Dark Matter WIMPs: SuperCDMS Soudan Soudan and SNOLAB leading to GEODM at DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO - September 17, 2009 Blas Cabrera - Stanford
Beta Screening Options
 Beta Screening Options in an Underground Low-Background Counting Facility Case Western Reserve University Based on work with or by Dan Akerib, Eric Dahl, Raul Hennings-Yeoman, Tom Shutt (Case), Luis DeViveiros
Beta Screening Options in an Underground Low-Background Counting Facility Case Western Reserve University Based on work with or by Dan Akerib, Eric Dahl, Raul Hennings-Yeoman, Tom Shutt (Case), Luis DeViveiros
Review of dark matter direct detection experiments
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 79, No. 5 journal of November 2012 physics pp. 1045 1057 Review of dark matter direct detection experiments RUPAK MAHAPATRA Department of Physics and Astronomy,
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 79, No. 5 journal of November 2012 physics pp. 1045 1057 Review of dark matter direct detection experiments RUPAK MAHAPATRA Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS
 Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS SuperCDMS Science Coordinator Syracuse University arxiv: 1304.4279 1304.3706 1203.1309 A New Order 0.01% Visible H, He 0.5% ENERGY Metals Dark Matter
Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS SuperCDMS Science Coordinator Syracuse University arxiv: 1304.4279 1304.3706 1203.1309 A New Order 0.01% Visible H, He 0.5% ENERGY Metals Dark Matter
Dark Matter. and TPC Technologies
 Dark Matter and TPC Technologies The Physics Case for WIMPs Status of the Field:event by event discrimination Elements of a roadmap Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute for
Dark Matter and TPC Technologies The Physics Case for WIMPs Status of the Field:event by event discrimination Elements of a roadmap Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute for
Dark Matter Searches. Marijke Haffke University of Zürich
 University of Zürich Structure Ι. Introduction - Dark Matter - WIMPs Ι Ι. ΙΙΙ. ΙV. V. Detection - Philosophy & Methods - Direct Detection Detectors - Scintillators - Bolometer - Liquid Noble Gas Detectors
University of Zürich Structure Ι. Introduction - Dark Matter - WIMPs Ι Ι. ΙΙΙ. ΙV. V. Detection - Philosophy & Methods - Direct Detection Detectors - Scintillators - Bolometer - Liquid Noble Gas Detectors
Dark Matter Direct Detection
 Dark Matter Direct Detection Who will win the race? Prof. Rupak Mahapatra Texas A&M University COSMO/CosPA, 2010 Dark Matter Direct Detection Anyone can win the race!! Prof. Rupak Mahapatra Texas A&M University
Dark Matter Direct Detection Who will win the race? Prof. Rupak Mahapatra Texas A&M University COSMO/CosPA, 2010 Dark Matter Direct Detection Anyone can win the race!! Prof. Rupak Mahapatra Texas A&M University
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector
 XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
Status of the AMoRE experiment searching for neutrinoless double beta decay of 100 Mo
 Status of the AMoRE experiment searching for neutrinoless double beta decay of 100 Mo Hyon-Suk Jo Center for Underground Physics Institute for Basic Science INPC 2016 - Adelaide Convention Centre, Australia
Status of the AMoRE experiment searching for neutrinoless double beta decay of 100 Mo Hyon-Suk Jo Center for Underground Physics Institute for Basic Science INPC 2016 - Adelaide Convention Centre, Australia
Background optimization for a new spherical gas detector for very light WIMP detection
 Background optimization for a new spherical gas detector for very light WIMP detection a, I. Giomataris b, G. Gerbier b, J. Derré b, M. Gros b, P. Magnier b, D. Jourde b, E.Bougamont b, X-F. Navick b,
Background optimization for a new spherical gas detector for very light WIMP detection a, I. Giomataris b, G. Gerbier b, J. Derré b, M. Gros b, P. Magnier b, D. Jourde b, E.Bougamont b, X-F. Navick b,
Bubble Chambers for Direct Dark Matter Searches in COUPP
 Bubble Chambers for Direct Dark Matter Searches in COUPP Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB 8th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs and WISPs Chicago IL, USA; July 22, 2012 Eric Va zquez-ja uregui PATRAS 2012 July
Bubble Chambers for Direct Dark Matter Searches in COUPP Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB 8th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs and WISPs Chicago IL, USA; July 22, 2012 Eric Va zquez-ja uregui PATRAS 2012 July
The COSINUS project. development of new NaI- based detectors for dark ma6er search. STATUS report Karoline Schäffner
 The COSINUS project development of new NaI- based detectors for dark ma6er search STATUS report 2016 Karoline Schäffner SCATTERING SCENARIO Dark matter particles scatter off nuclei elastically coherently:
The COSINUS project development of new NaI- based detectors for dark ma6er search STATUS report 2016 Karoline Schäffner SCATTERING SCENARIO Dark matter particles scatter off nuclei elastically coherently:
Dark Matter Searches. Andrew Wagner SASS Presentation April 8, 2009
 Dark Matter Searches SASS Presentation April 8, 2009 Outline If its Dark how do we know its there? What could it be? (What is it?) How could it be directly detected? What are present limits set by two
Dark Matter Searches SASS Presentation April 8, 2009 Outline If its Dark how do we know its there? What could it be? (What is it?) How could it be directly detected? What are present limits set by two
COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection
 COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB Rencontres de Moriond 2013 La Thuille, Italy; March 9-16, 2013 COUPP bubble chambers Target material: superheated CF 3 I spin-dependent/independent
COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB Rencontres de Moriond 2013 La Thuille, Italy; March 9-16, 2013 COUPP bubble chambers Target material: superheated CF 3 I spin-dependent/independent
Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments
 Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX, USA E-mail: cooley@physics.smu.edu The past year has yielded several new results from the direct detection
Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX, USA E-mail: cooley@physics.smu.edu The past year has yielded several new results from the direct detection
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background
 Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment
 The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE
 Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE Europhysics Conference on High-Energy Physics 2011 Cecilia G. Maiano on behalf of CUORE collaboration Contents The Bolometric Technique The CUORE experiment
Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE Europhysics Conference on High-Energy Physics 2011 Cecilia G. Maiano on behalf of CUORE collaboration Contents The Bolometric Technique The CUORE experiment
THE CRYOGENIC UNDERGROUND OBSERVATORY FOR RARE EVENTS: STATUS AND PROSPECTS
 THE CRYOGENIC UNDERGROUND OBSERVATORY FOR RARE EVENTS: STATUS AND PROSPECTS Eric B. Norman Dept. of Nuclear Engineering Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA U. S. A. Recent results in n physics Neutrinos
THE CRYOGENIC UNDERGROUND OBSERVATORY FOR RARE EVENTS: STATUS AND PROSPECTS Eric B. Norman Dept. of Nuclear Engineering Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA U. S. A. Recent results in n physics Neutrinos
AMoRE 0 experiment using low temperature 40 Ca 100 MoO 4 calorimeters
 AMoRE 0 experiment using low temperature 40 Ca 100 MoO 4 calorimeters Yong-Hamb Kim On behalf of AMoRE collaboration Institute for Basic Science (IBS) Korea Research Institute for Standards and Science
AMoRE 0 experiment using low temperature 40 Ca 100 MoO 4 calorimeters Yong-Hamb Kim On behalf of AMoRE collaboration Institute for Basic Science (IBS) Korea Research Institute for Standards and Science
A Known Unknown: Directly Detecting the Missing Mass of the Universe - The US Perspective
 A Known Unknown: Directly Detecting the Missing Mass of the Universe - The US Perspective Gaitskell Brown University, Department of Physics Particle Astrophysics Group gaitskell@brown.edu see information
A Known Unknown: Directly Detecting the Missing Mass of the Universe - The US Perspective Gaitskell Brown University, Department of Physics Particle Astrophysics Group gaitskell@brown.edu see information
Chapter 12. Dark Matter
 Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal 128 Chapter 12 Dark Matter Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal Baryonic Dark Matter Brightness & Rotation Curve of NGC3198 Brightness Rotation Curve measured expected
Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal 128 Chapter 12 Dark Matter Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal Baryonic Dark Matter Brightness & Rotation Curve of NGC3198 Brightness Rotation Curve measured expected
Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE
 Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE Marco Vignati University of Rome La Sapienza & INFN Rome on behalf of the CUORE collaboration Panic 11, July 5, MIT 988 TeO crystals Ton scale bolometric
Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE Marco Vignati University of Rome La Sapienza & INFN Rome on behalf of the CUORE collaboration Panic 11, July 5, MIT 988 TeO crystals Ton scale bolometric
Study well-shaped germanium detectors for lowbackground
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study well-shaped germanium detectors for lowbackground counting To cite this article: W-Z Wei et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 606 012019 View the
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study well-shaped germanium detectors for lowbackground counting To cite this article: W-Z Wei et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 606 012019 View the
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
The next generation dark matter hunter: XENON1T status and perspective
 The next generation dark matter hunter: XENON1T status and perspective A. Rizzo a on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Department of Astrophysics, Columbia University in the City of New York, USA Abstract.
The next generation dark matter hunter: XENON1T status and perspective A. Rizzo a on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Department of Astrophysics, Columbia University in the City of New York, USA Abstract.
Direct dark matter search with XMASS. K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration
 Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III
 The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
The BetaCage, an ultra-sensitive screener for surface contamination
 The BetaCage, an ultra-sensitive screener for surface contamination R. Bunker, Z. Ahmed, M.A. Bowles, S.R. Golwala, D.R. Grant, M. Kos,, R.H. Nelson, R.W. Schnee, A. Rider, B. Wang and A. Zahn arxiv:1404.5803v1
The BetaCage, an ultra-sensitive screener for surface contamination R. Bunker, Z. Ahmed, M.A. Bowles, S.R. Golwala, D.R. Grant, M. Kos,, R.H. Nelson, R.W. Schnee, A. Rider, B. Wang and A. Zahn arxiv:1404.5803v1
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 15 Feb 2005
 The XENON Dark Matter Experiment Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027 age@astro.columbia.edu
The XENON Dark Matter Experiment Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027 age@astro.columbia.edu
Whither WIMP Dark Matter Search? Pijushpani Bhattacharjee AstroParticle Physics & Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata
 Whither WIMP Dark Matter Search? AstroParticle Physics & Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata 1/51 2/51 Planck 2015 Parameters of the Universe 3/51 Discovery of Dark Matter Fritz
Whither WIMP Dark Matter Search? AstroParticle Physics & Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata 1/51 2/51 Planck 2015 Parameters of the Universe 3/51 Discovery of Dark Matter Fritz
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Universität Zürich E-mail: marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Liquid noble gases have proven a great potential as detector medium for dark matter searches. Particles interacting in these media produce ionized and
Universität Zürich E-mail: marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Liquid noble gases have proven a great potential as detector medium for dark matter searches. Particles interacting in these media produce ionized and
Latest results of EDELWEISS II
 Latest results of EDELWEISS II Ana Torrentó CEA/IRFU/SPP Saclay Rencontres de Moriond 2011 «EW and Unified Theories» WIMP search Motivated by the «WIMP miracle» Very small rate of WIMPnucleus scattering
Latest results of EDELWEISS II Ana Torrentó CEA/IRFU/SPP Saclay Rencontres de Moriond 2011 «EW and Unified Theories» WIMP search Motivated by the «WIMP miracle» Very small rate of WIMPnucleus scattering
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 1 Nov 2011
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 1 Nov 2011 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 1 Nov 2011](/thumbs/96/128749111.jpg) Title : will be set by the publisher Editors : will be set by the publisher EAS Publications Series, Vol.?, 211 arxiv:1111.22v1 [physics.ins-det] 1 Nov 211 STATUS AND PROSPECTS OF THE DMTPC DIRECTIONAL
Title : will be set by the publisher Editors : will be set by the publisher EAS Publications Series, Vol.?, 211 arxiv:1111.22v1 [physics.ins-det] 1 Nov 211 STATUS AND PROSPECTS OF THE DMTPC DIRECTIONAL
The XENON1T experiment
 The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
Low energy neutron propagation in MCNPX and GEANT4
 Low energy neutron propagation in and R. Lemrani a M. Robinson b V. A. Kudryavtsev b M. De Jesus c G. Gerbier a N. J. C. Spooner b arxiv:hep-ex/06030 v1 17 Jan 2006 a DAPNIA-SPP, CEA-Saclay, Gif-Sur-Yvette,
Low energy neutron propagation in and R. Lemrani a M. Robinson b V. A. Kudryavtsev b M. De Jesus c G. Gerbier a N. J. C. Spooner b arxiv:hep-ex/06030 v1 17 Jan 2006 a DAPNIA-SPP, CEA-Saclay, Gif-Sur-Yvette,
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter
 Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Light Dark Matter and XENON100. For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University
 Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
