AN ELEMENTAL MACROE ECONOMIC MODEL FOR APPLIED ANALYSIS AT UNDERGRADUATE LEVEL
|
|
|
- Reginald Smith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECONOMICS AN ELEMENTAL MACROECONOMIC MODEL FOR ALIED ANALSIS AT UNDERGRADUATE LEVEL by Rod Tyrs Busin ss School Th Univrsity of Wst rn Australia and ANU Rsarch School of Economics DISCUSSION AER 11.11
2 An Elmntal Macroconomic Modl for Applid Analysis at Undrgraduat Lvl* Rod Tyrs UWA Businss School and ANU Rsarch School of Economics May 2011 Working aprs in Economics UWA Businss School DISCUSSION AER * Thanks ar du to Bn Smith and Matthw Bng, formr collagus at th ANU, with whom th original rprsntation of th modl prsntd was originally workd out and trialld sinc th 1990s. Thanks ar also du to Jurg Wbr and William Colman for usful discussions about applications to th third yar and honours lvls.
3 Abstract: A graphical rprsntation is offrd basd on a fairly standard formulation of an undrlying comparativ static modl for applid undrgraduat analysis. Contrary to standard practic th approach taks Walrasian quilibrium as its starting point and considrs markt failurs that includ nominal rigiditis as spcial cass. It thrfor builds intuition that cntrs on pric rathr than quantity adjustmnt following shocks. Byond this, its advantags includ that it offrs comparativ as of rprsntation of xtrnal shocks, which ar particularly important in small opn conomis, it uss intuitiv dmand-supply markt diagrams throughout and it provids th ability to st as clar targts for montary policy th xchang rat, th CI and th GD pric. Finally, it allows for forward xpctations so that it offrs usful insights for studnts into th conomic consquncs of financial shocks.
4 1. Introduction: Macroconomics is a vry old sub-disciplin to which approachs hav bn many and varid. Th challng is to captur ky charactristics of th conomy as a whol, which prsss toward gnral quilibrium analysis and conomic dynamics in ways that ar too tchnically advancd for th avrag undrgraduat. To avoid disguising fundamntal idas about macroconomic bhavior bhind advancd tchniqu, th undrgraduat taching of macroconomics has tndd to mphasiz short run comparativ statics. Most commonly, th approach uss aggrgat dmand and aggrgat supply, combind with Hicks (1937, 1980) IS-LM rprsntation. 1 Fixd pric lvls ar commonly assumd in th Kynsian tradition and thr is most oftn a Kynsian cross diagram th subtrranan mssag from which is to mphasiz that, in dtrmining GD, failurs of labour, product and financial markts ar th dfault cas, with output bing drivn by unintndd invntory changs. 2 Awkwardly, this tratmnt is usually prsntd to undrgraduats immdiatly following a smstr of microconomics that is dominatd by conomic storis about optimizing agnts and claring markts. Th approach dscribd hr was concivd to offr an altrnativ, on that avoids th difficult intuition of th quilibrium loci usd in AD-AS and IS-LM and th dfault concption of th conomy crippld by nominal rigiditis. It was concivd jointly with Bn Smith (2000) originally as a taching tool to offr an altrnativ rprsntation to th standard usd in principls and intrmdiat conomics courss. 3 It is cntrd on a flxibl pric lvl Mundll (1963) - Flming (1962) framwork with imprfct financial 1 Rcntly, as growth and conomic dynamics hav bcom mor cntral to th advancd taching of macroconomics lmnts such as comparativ stady stats and two-priod analysis hav bcom mor frquntly usd, as in Williamson (2011). Whil th associatd Walrasian approach is dsirabl, ths dynamic prspctivs can com at th cost of much intuition and institutional dtail (concrning, for xampl, th balanc shts and rols of cntral banks) that is mor commonly taught along sid th comparativ static modls. 2 This is vn tru of Hall and Taylor (1991) and th vry rcnt othrwis xcllnt tratmnt by Fnstra and Taylor (2008: Chaptr 7), who us th Kynsian cross diagram to driv th IS curv. An altrnativ markt diagram approach to this drivation is offrd in Sction Th rprsntation usd also drivs in part from th graphical modl offrd intrmdiat radrs in Mankiw (2004). It is also informd by frqunt discussions with Gram Wlls, whos txt (Wlls 1995) offrs a comprhnsiv covrag of advancd undrgraduat approachs and supporting vidnc mphasizing th Australian cas. 1
5 capital mobility, in which an opn financial capital markt xprincs inflows and outflows dpnding on yild diffrntials and xchang rat xpctations but dos not achiv uncovrd intrst parity. Th ky advantags it offrs ar 1) th as of rprsntation of xtrnal shocks, which ar particularly important in small opn conomis, 2) th us of mor intuitiv dmandsupply markt diagrams throughout, 3) th ndognity of th pric lvl, 4) th Walrasian starting point (rfrnc cas) with wag stickinss offrd as a spcial cas, 5) th ability to st as clar targts for montary policy th xchang rat, th CI and th GD pric, an advantag ovr th AD-AS IS-LM rprsntation in which th mony supply must b xognous, and 6) it incorporats xpctational variabls that allow th analysis of optimism and pssimism shocks stmming from information failurs in financial markts. Th graphical approach has bn usd in support of widr macroconomic analysis by Tyrs (2001), Robrts and Tyrs (2003) and Rs and Tyrs (2004). Th modl gnralizs radily into on suitabl for applid analysis in mor advancd classs and a two priod, multi-product vrsion is availabl for computr simulation using th frwar Rungm, a componnt of th Australian Gmpack modling packag. 4 Th nxt sction summariss th ky assumptions, th labour markt is prsntd in Sction 3 and consumption and saving ar discussd in Sction 4. Th small opn conomy financial capital markt is prsntd in Sction 5, th Forign Exchang markt in Sction 6 and th markt for mony in Sction 7. Th complt modl is assmbld in Sction 8 and mony nutrality is dmonstratd in Sction 9. Shocks with nominal wag rigidity ar considrd in Sction 10 and, for illustration, an unxpctd bond-financd fiscal xpansion is analysd in Sction 11 and a financial crisis in Sction 12. Links with 4 This modl and softwar wr routinly usd by studnts at intrmdiat and advancd lvls at th ANU through 2009 and thy ar in us by a third yar macroconomics class at th UWA Businss School. It has also bn usd for svral yars in training courss at th Australian Trasury. Applications of th computational modl appar in Tyrs and Rs (2004). Dtails ar availabl from th author. 2
6 th mor standard AD-AS IS-LM rprsntation ar formalizd in Sction 13 and conclusions ar offrd in Sction Ky assumptions: Short run: Th rlvant lngth of run is within th gstation priod of nw invstmnt, so that invstmnt placs dmands on th capital goods sctor but dos not add significantly to th productiv capital stock in th currnt priod (though it dos in futur priods, if modlld) so K K. Expctations: Much dpnds on xpctations and ths ar xognous in th comparativ static graphical rprsntation. Agnts form xpctations ovr th GD pric lvl,, th xchang rat, E, th lvl of futur privat disposabl incom, F, and th ral rat of rturn on installd capital nt of dprciation, r C. Ths thn bcom shiftrs in th graphical rprsntation. If ths ar lft inactiv, th modl gnrats changs in pric lvls, xchang rats and intrst rats but thy ar not anticipatd. No stady stat: Th ral intrst rat in th capital markt, r, gnrally diffrs from th nt rat of rturn on installd capital, r C : M K (1) r rc Financial assts ar bonds and mony: risk considrations ar not modld xplicitly, so assts ar consolidatd into bonds of short maturity (montary instrumnts) and of long maturity (th bulk of th collctiv asst portfolio and th ky instrumnts in saving and invstmnt), th yilds on which ar sparatd via th sgmntation thory of th yild curv. K No uncovrd intrst parity: In gnral, financial capital is imprfctly mobil intrnationally on th grounds that hom long maturity bonds ar diffrntiatd from thir 3
7 forign countrparts by considrations of risk and transaction cost. t rsponss to shocks to yild diffrntials and xchang rat xpctations do mov toward uncovrd intrst parity. An initially claring labour markt: Th rfrnc cas is Walrasian, in which all rprsntd markts clar. Th pric lvl is flxibl (ndognous) and, at last initially, th nominal wag is assumd to adjust to clar th labour markt. Onc changs in th pric lvl ar dtrmind, th ffcts of wag stickinss can thn b rsolvd. So mploymnt is initially constant at L L. Initial output in volum units is thrfor: (2) A, L, K A, L, K whr A is th xognous total factor productivity cofficint. 4
8 2. Th labour markt: Labour supply is inlastic on th grounds that mpirical studis find its short run lasticity to b small, and bcaus it is intuitiv for studnts to driv th labour supply curv from th trad-off btwn consumption and lisur with Cobb-Douglas prfrncs. 5 In this cas, incom and substitution ffcts offst on anothr, laving th labour supply curv vrtical. Labour dmand is drivn by production tchnology with th standard condition quating th mony wag, W, in $/workr yar, to th valu of th marginal product of labour, or th ral wag, w, to th marginal physical product of labour: (3) W A, L, K w M L LL L LL This quilibrium is illustratd in th labour markt diagram of Figur Invstmnt dpnds on th nt rat of rturn on installd capital: Th ral gross rat of rturn on an alrady installd machin is just th valu of its marginal product, M K, which is th annual incras to rvnu gnratd by th machin, dividd by th markt pric of th machin, K. Th nt rat of rturn just subtracts th rat of dprciation,. This is what drivs invstmnt dcisions. (4),, A L K rc MK K K KK K KK 5 Th most rcnt rsarch on th long run lasticity of labour supply (its rat of rspons to th ral wag) is from Ashnfltr, O., K. Doran and B. Schallr (2010), A shrd of crdibl vidnc on th long run lasticity of labour supply, NBER Working apr 15746, Cambridg MA. Evidnc on mploymnt contracts shows supply lasticitis around zro, whil vidnc from taxi drivrs who njoy a far rat incras suggsts a vry small ngativ numbr th incom ffcts of th far incras tndd to b vry slightly largr than th substitution ffcts from lisur to consumption. 5
9 Figur 1 w L S A, L, K w 0 =W 0 / L D : w ML A, K ) L L In th short run th capital stock is givn, so firms do not ncssarily hav th optimal quantity. In th long run stady stat, howvr, invstmnt taks plac until th ral nt rat of rturn on capital falls to th lvl of th ral financing cost or th opportunity cost of invstd funds (th ral rat of rturn that can b arnd on financial instrumnts, or that must b paid if bonds ar issud to financ th invstmnt, or th markt ral intrst rat), r. Th ral rat is prfrrd hr to th nominal rat on th assumption that capital gains ar xpctd to accru whn th pric of capital goods inflats at th sam rat as hom goods-srvics. So in th stady stat, but not in gnral, r c r. So, in th lngth of run to b considrd, xpctd changs in r, r driv invstmnt: C C if if rc rc r r th rturn will xcd th ral financing cost, th invstmnt will not b mad. This xpctd futur valu of this rat of rturn which is thn xognous. 6
10 4. Consumption and saving: Hr a simpl incom tax rul is usd with a Kynsian consumption quation in prsnt and xpctd futur disposabl incom, masurd in ral volum quivalnts. All units ar product volums. Govrnmnt spnding, G, is a ral xognous policy variabl. (5) Elmntal tax rul: T t (6) Ral privat consumption C, rac bcrcc Tc F F TF (7) Ral privat saving:, S F, r T C, F, r (8) Total ral domstic saving:,,,,, S G r S r T G D F F To rflct consumption smoothing bhaviour, privat saving rsponds positivly to currnt disposabl incom and ngativly to xpctd futur disposabl incom. Th substitution ffcts ar assumd to dominat whn changs in bond yilds occur, so that privat saving also rsponds positivly to th ral yild on saving instrumnts (long maturity bonds), r. 5. Th small opn conomy financial capital markt: This is th markt that matchs saving to invstmnt. Units ar quivalnt volums of goods and srvics. (9) Ral invstmnt (brak-vn + nt): rc b N I I I K Hr th ratio of th xpctd nt rat of rturn on installd capital and th currnt ral long bond yild is closly rlatd to Tobin s Q, sinc th numrator dtrmins th currnt markt valu of capital assts and th dnominator dtrmins th ral cost of 7 r
11 financing thir rplacmnt. (10) Nt forign invstmnt dmand: NFI, G, r,,, c r I rc r SD F, G, r (11) Capital account nt inflows: *, R, NF *, R, KA r r S r r R Whr KA rprsnts th nt provision by forignrs of funds to financ a surplus of imports ovr xports (currnt account or CA dficit), S NF is nt forign saving, or th privat componnt of ths inflows, dpndnt on th forign bond yild, r*, th hom bond yild, r, and any (xognous) xpctation of a ral xchang rat chang, R. Th ral xchang rat hr has th financial dfinition, so it riss with apprciations. Th chang in th sock of official forign rsrvs, R, is an xognous montary policy variabl and, consistnt with th small opn conomy assumption, th forign bond yild, r*, is also xognous. This dpndnc implis somthing short of th ral vrsion of uncovrd intrst parity r r* /. Indd, S NF is influncd by dparturs from uncovrd intrst R R parity, th lattr applying only in a stady stat: R (12) SNF asf bsf r r*. R Th siz of th slop of this curv, b SF, thn dtrmins how quickly th solution approachs uncovrd intrst parity. Small valus suggst capital controls and larg valus suggst high lvls of financial capital mobility. Allowing dparturs from uncovrd intrst parity admits rality in a way that avoids th application inflxibility of approachs that impos it. 6 Th small opn conomy financial capital markt quilibrium is thn obtaind by finding th hom bond yild, r, that rndrs: 6 Th xcllnt gnral macroconomics txt by Blanchard and Shn (2004) is a cas in point. 8
12 (13), F,, c, c, D, F,, *, R, NF *, R, NFI G r r I r r S G r KA r r S r r R Onc th supply sid quilibrium has bn dtrmind, GD, or, is known. All th othr variabls in this quilibrium condition ar xognous, xcpt th hom long bond yild, r, which is radily solvd for. From this, thn, th ral valu of nt financial inflows on th capital account, KA, also mrgs. Critically, with claranc of th labour markt, th capital account balanc is sn to dpnd only on financial variabls, not on trad and th currnt account. Th quilibrium in this small opn conomy financial capital markt is illustratd as in Figur 2, with th curvs showing only thir shiftrs in parnthss. Figur 2 r KA(ΔR, R,r*) r 0 I-S D =, NFI F, G, r c KA- KA 0 0 KA+ 9
13 6. Th markt for forign xchang: First dfin th xchang rats. Th ral xchang rat is th numbr of rprsntativ forign product-srvic bundls that can b acquird in xchang for a singl hom product-srvic bundl. It is thrfor th common currncy ratio of th pric of hom goods to that of forign goods, bst rprsntd by th rspctiv GD prics, and But * is xprssd in forign currncy and so rquirs convrsion at th nominal xchang rat, E. Thus, if that is also dfind financially (apprciating whn it riss) w hav that: (14). R E * * / E Bcaus th capital account 7 must balanc th currnt account and th lattr is linkd to th valus of imports and xports in hom $, th balanc of paymnts in hom $ is: Bo KA CA 0 (15) KA S I CA N X M D whr N is nt factor incom from abroad. Imports, M, and xports, X, both dpnd on th ral xchang rat. *. Consistnt with th practic adoptd in rprsnting th financial capital markt, this should also b xprssd in quivalnt ral volums of hom product. Sinc N dpnds mainly on past invstmnts abroad, considr hraftr that N is an xognous constant, xprssd in ral trms and so in units of forign output. Rdfining th X and M in hom product quivalnts, th balanc bcoms: N (16) KA SD I CA X M Exports ar forign dmands for hom goods, which, lik any product dmand, dpnd positivly on forign incom and ngativly on th rlativ pric of hom goods or th ral xchang rat. Imports ar hom dmand for forign goods and so will dpnd R 7 This is hr dfind as th complmnt of th currnt account. It is thrfor th sum of what is commonly rfrrd to as th capital account, th financial account and th balanc on rsrvs. 10
14 positivly on hom incom, or GD, and ngativly on for rlativ pric of forign goods (th invrs of th ral xchang rat). For an intuitiv diagram, xprss ths in trms of th invrs of th ral xchang rat th rlativ pric of forign goods. So th currnt account dficit is: * 1 (17) CA N M, X, R R R Nt import dmand, or xcss dmand for goods, is thrfor unambiguously downward sloping in th rlativ pric of forign goods or positivly dpndnt on th ral xchang rat. Nt factor incom has th opposit dpndnc, howvr, though this is a pur valuation ffct, whras th trad flows combin valuation with volum adjustmnt ffcts. W will assum th trad account to dominat, so that th currnt account dficit can b writtn: * 1 (18) CA CA,, R Th currnt account masurs th nt inflow of paymnts associatd with currnt transactions, hr masurd as th quivalnt volum of hom goods. A dficit mans a nt outflow. This is th quivalnt of a nt outflow of forign xchang, matchd by a nt inflow of forign xchang arising out of financial flows in th financial capital markt. But w know from that markt that th nt inflow of forign xchang associatd with asst transactions is KA. And, so long as th labour markt clars, th quivalnt quantity of hom products is alrady boltd down. So th ral xchang rat adjusts to nsur that th balanc of paymnts dos actually balanc: Bo KA CA 0 (19) * 1 KA CA,, R 11
15 Th only ndognous variabls in this rlationship ar and R, but has alrady bn dtrmind in th labour markt. So this rlationship rvals th ral xchang rat, as shown graphically in Figur 3. Knowing and R, M and X can b obtaind by back solving if ndd. 7. Dmand sid, nominal part: Sinc th maturity of financial assts mattrs, a not on th yild curv is usful at th outst. Financial assts ar hr gnralisd as bonds. No risk considrations ar xplicit in th modl, xcpt to th xtnt to which thy diffrntiat hom from forign bonds and thrfor caus th failur of uncovrd intrst parity, lading to imprfct financial capital mobility vn whr no capital controls ar prsnt. But cntral banks dominat trad in mony markt instrumnts of maturity lss than a yar, whil th collctiv portfolio compriss mainly long trm instrumnts, which might b thought of hr as 10 yar bonds. Th yilds on short and long instrumnts do not mov togthr through tim, with short rats bing altrd by cntral banks in th managmnt of hom businss cycls whil long rats mov mor smoothly through tim and thir markts ar mor intgratd across countris, rflcting thir rol in quating th global supply of saving to global invstmnt dmand. 8 For ths rasons, th hom ral long bond yild is th quilibrating variabl in th financial capital markt. And, sinc long instrumnts dominat th collctiv portfolio th nominal long bond yild is th opportunity cost of holding mony. Th two ar rlatd as r i L, whr is th xpctd rat of inflation. A convntional cash in advanc constraint is assumd to undrli th dmand for ral mony balancs, which thn dpnds on GD, rprsnting transactions dmand, and th 8 Th rats ar kpt sparat by thr standard thoris of th yild curv, of which th most tlling is th sgmntation thory. Whn short rats ar low compard with long rats, th gap is sustaind by th transaction costs that would b incurrd wr a squnc of short contracts to rplac a singl long contract. 12
16 nominal long trm bond rat (20) md md, i m D, r Figur 3 S F (from financial capital markt) 1/ R 1/ R 0 R CA+ CA 0 0 CA- CA, * Whr is an xognous risk prmium that may b shiftd upward by pssimism about th prformanc of financial instrumnts othr than mony. Thus, whn financial instrumnts appar riskir, th opportunity cost of holding mony may not b as larg as th currnt long trm ral yild vn aftr adjustmnt for xpctd inflation. Th supply of mony bgins with th montary bas, M B, which cntral banks control by committing to trad in short trm instrumnts until xcss dmand at a dsignatd short yild is rducd to zro. Th rlationship btwn short rats and M B nd not b mad xplicit hr, howvr. Th mony multiplir thn links th montary bas to th 13
17 nominal mony supply and thnc to th supply of ral mony balancs. (21) M S 1 c MB c Whr c is th public s cash to dposit ratio and is th rsrv to dposit ratio of banks and othr financial institutions. So th supply of ral mony balancs can thn b quatd with its dmand in a claring mony markt. (22) D, M 1 M i M i S B S B S S c m r m c If th montary bas is considrd an xognous policy instrumnt, dtrmind by dclard lvls of i S in a sparat procss, th xpctd inflation rat is xognous, as ar th paramtrs c, and, th only ndognous unknown is th pric lvl,, or th xchang rat btwn hom mony and hom goods-srvics. Th diagram in Figur 4, unconvntionally, uss th ral intrst rat on th vrtical but, convntionally, ral mony balancs on th horizontal. GD, as a proxy for transactions dmand, xpctd inflation,, and th risk factor,, ar thn shiftrs of th mony dmand function, with th lattr two always xognous. As abov, th mony markt quilibrium is whr: M (23) m, D,, r S Th only variabl that rmains to b calculatd is th nominal xchang rat. If th forign pric lvl, *, is xognous, consistnt with th small country assumption, thn th nominal xchang rat, E, can b obtaind by transforming th standard xprssion 14
18 (14) for th now known ral xchang rat in trms of th known hom pric lvl: (24) * E R. Figur 4 r m S From financial capital mkt r 0 D + - +,, m m M S 8. Th complt modl: Th modl assmbls graphically on a squnc that follows from th dfault assumption of Walrasian quilibrium th simultanous claranc of all four intr-rlatd markts: th labour markt, th financial capital markt and th markts for hom and forign mony. Th graphical (and, if ndd, th numrical) solutions ar rcursiv, commncing with th labour markt and moving through th othr markts, all of which hav quantity axs that ar xprssd in quivalnt volums of hom products. 15
19 1. In th claring labour markt GD () is dtrmind. 2. Onc is known, privat and govrnmnt saving is known and so th opn conomy financial capital markt can b drawn. This dtrmins both th hom long bond yild and th nt inflows on th capital account, KA. 3. Th nt supply of forign xchang from th financial capital markt is KA and th xcss dmand for forign xchang in currnt intrnational transactions is th currnt account balanc, dfind as th dficit CA. For a balanc of paymnts, ths must b quatd in th forign xchang markt diagram. This yilds th ral xchang rat. 4. Th ral long bond rat from th financial capital markt, combind with th xognous xpctd inflation and risk factor, indicat th quantity of ral mony balancs dmandd. To bring supply into quality with this, for a givn short bond yild and hnc a givn montary bas and nominal mony supply, th pric lvl must adjust. This is th xchang rat btwn mony and hom goodssrvics in which th dmand for ral mony balancs is masurd. Th quilibrium pric lvl mrgs from th mony markt diagram. 5. Th nominal xchang rat thn follows from th ral xchang rat and th hom pric lvl. In th st of diagrams in Figur 5, th labour markt is omittd sinc Walrasian quilibrium implis claranc and a fixd lvl of GD,. Only th dmand sid is rprsntd. Arrows indicat th rcursiv solution in th Walrasian cas. 16
20 Figur 5 r r KA(ΔR,,r*) m S R r 0 r 0 I-S D = NFI, F, G, r c m, D, KA- KA 0 0 KA+ m M S S F 1/ R 1/ R 0 R E * CA, * CA+ CA 0 0 CA- 17
21 9. Mony nutrality: Th nutrality of mony whn thr ar no nominal rigiditis (all markts clar as in th Walrasian rfrnc cas) is an ssntial tst. It is radily sn from th rcursiv solution, abov and th masurmnt of all th horizontal axs in ral hom productsrvic volum quivalnts. Th ffct of a surpris (unxpctd) 10% hlicoptr xpansion in th nominal mony supply at ach stag is: 1. In th claring labour markt, labour supply dpnds on consumption-lisur prfrncs and labour dmand dpnds on th production tchnology, nithr of which bars any dirct rlationship with th supply of mony and so GD () is unaltrd. 2. In th financial capital markt, privat saving masurd as th ral volum of consumption dnid and this dpnds only on ral variabls, including th ral intrst rat or long bond yild. Th sam is tru for govrnmnt saving, hom invstmnt and for financial invstors xchanging assts intrnationally. Thr is thrfor no chang in th financial capital markt du to a ris in th supply of mony. 3. Th nt supply of forign xchang from th financial capital markt, KA, and th currnt account balanc, CA, ar both hr masurd in trms of quivalnt volums of hom products-srvics and nithr has any dirct dpndnc on th supply of hom mony. No chang thrfor occurs in this markt ithr. 4. In th sam way, th mony markt is charactrisd in trms of ral mony balancs with dpndnc on th ral hom long bond yild. Thr is thrfor no chang in th ral supply of mony. Thus: 18
22 M S (24) ms. So th xcss supply of mony rducs its valu rlativ to goods-srvics and so th GD pric riss by 10%. 5. With no chang to th ral xchang rat th nw rlativ abundanc of hom mony rducs its valu rlativ to forign mony and so th nominal xchang rat dprciats by 10%. (25) R E * 6. Finally, in th claring labour markt th markt-claring ral wag, w, is unchangd, which thn rquirs that th nominal wag riss by 10%. (26) W w Thus, an unxpctd hlicoptr mony xpansion has no ffct on variabls masurd in ral trms (as quivalnt volums of hom goods-srvics). Only nominal variabls (thos masurd in trms of $) ar altrd, and in ach cas thy chang by th sam proportion as for th nominal mony supply. 10. Shocks with a rigid nominal wag: Th rcommndd approach in th us of th graphical vrsion of this modl is mrly to dtrmin whthr any shock, or combination of shocks, is xpansionary or contractionary. A graphical solution for th nw lvl of GD is difficult sinc itrations ar rquird. This is a disadvantag rlativ to th standard AD-AS, IS-LM approach, which gos dirctly to an quilibrium lvl of GD with nominal rigiditis. 19
23 Itrations bgin with th application of th shock or shocks to th graphics on th initial assumption that th labour markt clars. Considr th simplst cas; that of th montary xpansion considrd in th prvious sction. This causs no changs to th dmand sid diagrams but thr is an inflation. Th ffct of this in a labour markt with a fixd nominal wag is thn to rais mploymnt abov th initial quilibrium lvl. 9 Figur 6 w L S w W / 0 0 0, L, A, L, K w W / L D : w ML A, K L L 1 L ) Thus, an unanticipatd montary xpansion is xpansionary of mploymnt and GD. To find th nw lvl of GD, th implications of th labour markt rsult of Figur 6 ar assssd using th dmand sid diagrams of Figur 5. Almost all curvs shift with a ris in output and no chang in th xpctational variabls. Th consquncs ar 9 If th initial lvl of unmploymnt is th minimum fasibl, this implis a transition to gratr us of ovrtim contracts and tmporary immigration. 20
24 1. A rducd long bond yild and an xpandd KA dficit (or rducd KA surplus; xpandd CA surplus or rducd dficit), as savings ris with xpandd GD. 2. Th xpandd CA surplus dprciats th ral xchang rat, which also follows from th nw rlativ abundanc of hom products-srvics compard with forign products-srvics. 3. Th lowr ral intrst rat rducs th opportunity cost of holding mony and so ral mony balancs xpand. Bcaus th nominal mony supply rmains fixd, th scarcity valu of mony riss rlativ to hom goods-srvics and so th pric lvl falls. 4. From (24), th ffct on th nominal xchang rat is indtrminat, sinc th ral xchang rat dprciats and th pric lvl falls. In gnral, this scond itration yilds a smallr nt inflation from th initial montary xpansion th sharing of th ffcts btwn pric and quantity adjustmnts. Furthr itrations ar thn possibl, but ths ar not ndd if all that is rquird is to distinguish xpansionary from contractionary ffcts. Indd, th ky to GD ffcts is th chang in th GD pric lvl,. If an unanticipatd inflation rsults th shock is xpansionary, if th rsult is a dflation, thn th ffct is contractionary. 11. Bond-financd fiscal xpansion: This xrcis illustrats th choic of montary targt. It draws th following conclusions: 1. that unanticipatd fiscal xpansions do rais output and mploymnt if thy ar prmittd to caus unanticipatd inflations but not othrwis, hnc th dpndnc of th rsult on th targt of montary policy 21
25 2. if thy caus inflations, th ffctivnss of fiscal xpansions in raising output and mploymnt is rducd th gratr is financial capital mobility. An unanticipatd, dbt financd ris in G adds to th supply of bonds sking purchas by savrs. Bond prics fall and yilds ris, crowding out som privat invstmnt. Nt inflows on th capital account ris (or bcom lss ngativ in th cas of a capital account dficit) as financial invstors ar attractd to hom bonds and th ral xchang rat apprciats. 10 Th analysis is illustratd in Figur 7. Commncing with th Walrasian rfrnc cas, GD is initially unaffctd and th shock occurs in th financial capital markt. Th ris in G rducs domstic saving and shifts th I-S D or NFI curv to th right. Th highr ral bond yild and th lss ngativ or mor positiv capital account balanc mrg from th financial capital markt. Th ral apprciation thn ariss in th forign xchang markt. In th mony markt th highr bond yild, again assuming no anticipation of any subsqunt inflation, raiss th opportunity cost of holding mony and rducs ral mony balancs. Hr is whr th targt of montary policy mattrs. If th targt is th mony supply itslf, implying that th cntral bank holds th short rat constant, thn thr is an xcss supply of mony so its valu falls rlativ to hom goods-srvics and thr is an inflation. Rturning to th labour markt, this tim with a fixd nominal wag, th inflation is sn to caus a ris in mploymnt and thrfor in GD, so th shock is xpansionary. 10 Of cours, if th shock and its immdiat ffcts ar anticipatd, Ricardian quivalnc ariss and privat saving could ris sufficintly to offst th ffcts of th xpansion. This can b illustratd with th graphical modl but what follows focuss on th unanticipatd cas. 22
26 Figur 7 r r KA(ΔR,,r*) m S m S R r 1 r 1 r 0 r 0 I-S D = NFI, F, G, r c m, D, KA- KA 0 0 KA+ m M ' S ' M S S F 1/ R 1/ R 0 1/ R 1 R E, E * R * CA, CA+ CA 0 CA 1 0 CA- * 23
27 If th targt of montary policy is th pric lvl, say, 11 thn a montary contraction is rquird. Thr is no inflation and hnc no xpansion in mploymnt and GD. Thus, an indpndnt cntral bank that targts product pric stability compltly nullifis th powr of fiscal policy. For th final conclusion, th intrnational mobility of financial capital dpnds on th slop of th KA curv in th financial capital markt. Th flattr this curv (th mor mobil is financial capital or th mor substitutabl ar hom with forign bonds), th smallr th ris in th hom bond yild and hnc th smallr th contraction in ral mony balancs. This mans that, if th targt of montary policy is th mony supply itslf, thn th ncssary inflation is smallr and so is th powr of th fiscal xpansion to rais mploymnt and output. Of cours, thr ar cass in which fiscal xpansions can b xpctd to b ffctiv vn with indpndnt inflation-targting cntral banks. An obvious on is th cas illustratd most strongly during th GFC in th US, th UK and Japan, whr th powr of montary policy was xhaustd th liquidity trap, which fixs th nominal mony supply so that fiscal xpansions hav traction ovr th pric lvl and so can offst dflationary tndncis. Evn if cntral banks rtain traction ovr th pric lvl, thr is also a rol for fiscal policy in circumstancs illustratd at th outst of th GFC, whr pssimism shocks tmporarily rais th shar of saving that gos to mony holdings, thus incrasing th mony shar of th collctiv portfolio. In this cas a ris in th privat saving rat dos not caus an quivalnt spnd on nw capital goods. If govrnmnts can issu bonds to soak up som of that mony accumulation and spnd th procds on hom goods-srvics quickly nough, thy can forstall th downturn. This is a tall ordr for fiscal policy, howvr, which is notoriously slow acting. 11 * Th targt can b th consumr pric lvl, rcognizing that C Av, E 24. Bcaus th xchang rat would apprciat, holding this constant would lad to a GD pric inflation and so h shock would b xpansionary, though by an amount that dpnds on th shar of imports in hom consumption.
28 12. ssimism shock th ffcts of a financial crisis This is a usful illustration of th application of xpctation shocks. Two typs of financial crisis might b considrd. Financial collapss that ar local and isolatd prcipitat capital flights and runs on th hom currncy. Ths ar radily modlld as upward shocks to r*, th forign bond yild, intndd to rprsnt riss in th hom asst risk prmium. Th analysis starts in th financial capital markt with a shift in th KA curv and is, thraftr, quit straightforward. That said, th simplicity of th analysis dos dpnd on th lvl to which th consquncs ar anticipatd and hnc whthr th shock is complicatd by changs in th xpctational variabls. It also dpnds on th complxity of th policy rsponss. In th cas of th Asian financial crisis of , th runs on Asian currncis wr only arrstd onc th currncis had bn forcd to float and by substantial mony-financd fiscal xpansions. That said, all ths shocks ar radily rprsntd. rhaps th bst illustration of th application of xpctations shocks, howvr, is th GFC. It commncd with th ralisation across financial markts that US and UK assts wr ovr-valud and hnc US housholds wr struck by a substantial walth cut. This was xacrbatd by associatd balanc sht problms in ky financial institutions, confidnc in which was suddnly rodd. Whil, during th arly stags of th GFC thr wr lmnts of capital flight, this was not th primary caus of its main conomic impact. Rprsntation in th modl rquirs th following xognous shocks: F : housholds xpct futur disposabl incom to b lowr and thrfor incras saving to smooth consumption forward rc : invstors anticipat lowr futur ral nt rturns on nw capital c, : housholds los confidnc in thir financial institutions and sk gratr liquidity, as wll as a highr cash to dposit ratio 25
29 : financial institutions hdg against runs by holding mor cash on rsrv Th changs in th cash to dposit ratio and th rsrv ratio rducd th mony multiplir and wr th rason th Fd s attmptd montary xpansions smd lik pushing on a pic of string. Short rats would b lowrd and th montary bas xpandd but th mony supply did not ris. But, bfor w can s th ffct of this w must know what happnd to ral mony balancs and for that w nd th ntir dmand sid of th modl. Th shocks ar imposd in Figur 8, assuming that th targt of montary policy is th pric lvl and that th cntral bank is capabl of dfnding it, so. Not that th diagram is hr drawn for a currnt account dficit, in plac of th 0 surpluss rprsntd in Figurs 2, 3, 5 and 7. From Figur 8 it is clar that pssimism on th part of both savrs and invstors causs th I SD NFIF, rc curv to contract to th lft sinc, at any hom bond yild, invstors ar prpard to supply fwr financing bonds and housholds rstrict thir consumption in th currnt priod in ordr to sav for th apparntly infrior futur. Th long bond yild falls, th currnt account dficit falls and th ral xchang rat dprciats. If th cntral bank is abl to dfnd th domstic pric lvl, this indicats that th nominal xchang rat also falls. In th mony markt, incrasd liquidity prfrnc causs th dmand curv to shift to th right and so th quilibrium volum of ral mony balancs xpands du to th lowr opportunity cost of holding mony but that xpansion is mad largr by th incrasd liquidity prfrnc. Th ky qustion now ariss: is th cntral bank capabl of dfnding th pric lvl whn a larg ris in th mony supply is rquird? That this could b a tall ordr is clar from (22), hr r-xprssd: (27) md 1 M S MB is MB is c ms c 26
30 Figur 8 r KA r m S m S r 0 r 0 r 1 r 1 NFI I-S D = F, rc md KA- 0 KA 1 KA 0 KA+ m M 0 S 0 M S 0 1/ R S F 1/ R 1 1/ R 0 R E * CA, CA+ 0 CA 1 CA 0 CA- * 27
31 Not only is th ris in ral mony balancs doubl barrlld but, bcaus th mony multiplir falls, th montary bas must ris by vn mor and hnc th short intrst rat must fall considrably. From this it is not surprising that th US and th UK, whn subjctd to ths shocks in 2008, rachd liquidity traps so quickly. Th nxt qustion is, if a liquidity trap is rachd and th montary bas cannot b raisd furthr by convntional mans thn mony is in xcss dmand and th valu of goodssrvics in trms of mony falls thr is a dflation. In Figur 6 a dflationary shock clarly contracts mploymnt and GD. So, what is to b don? Wll, not that th montary bas, and hnc th ral mony supply, ar stalld. This is th prcis circumstanc undr which a fiscal xpansion was sn in Sction 11 to b xpansionary. That is, th fiscal xpansion in ths circumstancs offsts th dflation and so contributs to limiting th rsulting contraction. 13. Links with th standard AD-AS, IS-LM rprsntation Th algbra that undrlis this modl is standard and so it is not surprising that loci of quilibrium combinations of, and r, or i r, which is what AD, AS, IS and LM ar, follow dirctly from it. Th advantag of th tratmnt offrd hr is that th abstraction of quilibrium loci is not rquird. All diagrams hav tru dmand and supply curvs Th opn conomy aggrgat dmand curv This is th st of combinations of (, ) for which th dmand sid of th conomy (th capital, mony and forign xchang markts) is in quilibrium. It is not an ordinary dmand curv. Also, bcaus th mony supply must b an xognous shiftr of th AD curv, it dos not rprsnt wll th modrn rol of th cntral bank. This is bcaus th mony supply nd not b xognous, and indd it is not if th cntral bank has an altrnativ targt, as in most of th analytical xampls of th prvious sctions. 28
32 To driv th AD curv for th cas whr th cntral bank targts th mony supply, imagin that thr is a supply sid shock so. Th diagrams for th financial capital markt and th mony markt can thn b usd to calculat th associatd chang in th 0 pric lvl, as in Figur 9. Th initial quilibrium combination is, 0. A scond combination ariss whn w hav th ris in GD to 1. At highr GD thr is mor incom and mor saving so, othr things qual, thr is lss xcss dmand for forign funds to financ hom invstmnt, or mor dmand for hom bonds, so highr bond prics and lowr yilds. In th mony markt, lowr opportunity cost, combind with highr transactions dmand, ncssitats incrasd ral mony balancs. With th mony supply xognous this crats xcss dmand for mony rlativ to goods-srvics and so a lowr pric lvl rsults. Figur 9 r r m S 0 KA m S 1 m D ( 1 ) r 0 NFI( 0 ) r 1 m D ( 0 ) NFI( 1 > 0 ) KA- 0 KA 0 KA+ m M S 0 M S 1 29
33 By slcting a rang of supply sid shocks and calculating th chang in th pric lvl for ach a downward sloping AD curv is mappd out. Th shiftrs of th curv ar shown in Figur 10, whr th dirctional signs indicat th ffcts of th shiftrs on th pric lvl for any givn quantity, Aggrgat supply Th Walrasian cas, which fixs th lvls of mploymnt and GD in a claring labour markt, yilds what is oftn rfrrd to as th long run quilibrium in GD and th Figur AD(r c, G, r*,r, R,M S ) 0 1 pric lvl, yilding a vrtical long run aggrgat supply curv. 12 Th commonly drawn short run aggrgat supply curv, SAS, is spcific to a givn fixd nominal wag 12 Sinc th modl is constructd to fit th short run intrval within th gstation priod of invstmnt, th long run offrs many diffrncs in addition to th claring labour markt. This titl is thrfor mislading. It is bttr thought of as th Walrasian aggrgat supply curv. 30
34 rat. It is radily drivd from th production function, not spcifid hr, from (3), as th rlationship btwn GD and th pric lvl for a particular fixd nominal wag, W. (28) W A, L, K w M L,,, L L L L W L W K L LL 13.3 Th IS curv This is simply an altrnativ rprsntation of th financial capital markt, of Figur 2, from which it tracks quilibrium combinations of th lvl of GD and th intrst rat. It is obtaind in th sam way as for th AD curv, by applying supply sid shocks to, which shift th I S D = NFI curv, and obsrving changs in th quilibrium yild on long bonds. Incrasd GD raiss incom and saving, and thrfor th dmand for hom bonds, so it rducs thir yild, rndring th IS curv downward sloping and shiftd by all th xognous variabls that influnc th financial capital markt Th LM curv This is a rprsntation of th mony markt, of Figur 4. Th quantity of ral mony balancs (M S / ) is fixd and GD is shockd. Th long bond yild at which that particular quantity of ral mony balancs would b chosn is thn solvd for. Th gratr is transactions dmand for mony, th highr th opportunity cost must b to justify this choic, and so th LM curv is upward sloping in th intrst rat. Again, th shiftrs includ all th xognous paramtrs in Figur Th Bo curv A common addition to th IS-LM approach for opn conomy macroconomics is th Bo curv. 13 This is usually addd to th IS-LM diagram and, again, it rprsnts combinations (, r) at which thr is a balanc of paymnts (KA=-CA). This curv must 13 This curv was originally addd by Mundll (1963) and Flming (1962). It is clarly xplaind in many txts. Two cognt xampls ar Lvacic and Rbmann (1989) and Wlls (1995). 31
35 pass through th intrsction of th IS and LM curvs sinc thr can b no conomy wid quilibrium without a balanc of paymnts. To nsur that it dos, th xchang rat must b mad ndognous. In standard applications, domstic pric lvls at hom and abroad ar fixd and hnc, whn shocks ar applid, th upward or downward shifts in Bo as it follows th common quilibrium in th financial and mony markts, indicat nominal apprciations or dprciations. This is a clvr addition though, in a flx pric nvironmnt it nds to b formulatd in trms of th ral xchang rat. Onc this is don, howvr, som xtrnal shocks bcom difficult to implmnt. For xampl, a capital flight, stimulatd by a ris in th risk prmium-adjustd forign bond yild, r*, cannot radily b dmonstratd sinc r* is a shiftr in both th IS and Bo curvs. 14. Conclusion Dspit th many and various viws and analytical approachs to macroconomic analysis, th most common approach to training undrgraduat conomics majors is via th AD-AS IS-LM approach with its Kynsian prcpts and its rlianc on graphical rprsntation of quilibrium loci. Hr, a graphical rprsntation is offrd basd on a standard formulation of an undrlying comparativ static macroconomic modl. It taks Walrasian quilibrium as its starting point and considrs nominal rigiditis as spcial cass. It thrfor builds intuition that cntrs on pric rathr than quantity adjustmnt following shocks. In addition, it offrs comparativ as of rprsntation of xtrnal shocks, which ar particularly important in small opn conomis, it uss intuitiv dmand-supply markt diagrams throughout and it provids th ability to st as clar targts for montary policy th xchang rat, th CI and th GD pric. Finally, it allows for forward xpctations so that it offrs usful insights for studnts into th conomic consquncs of financial shocks. 32
36 Rfrncs Blanchard and Shn, Macroconomics: Australian Edition, arson/rntic Hall. Fnstra, R.C. and A.M. Taylor, Intrnational Macroconomics, Nw ork: Worth ublishrs. Flming, J.M., Domstic financial policis undr fixd and undr flxibl xchang rats, Intrnational Montary Fund Staff aprs, 9: Hall, R.E. and J.B. Taylor, Macroconomics, 3 rd Edition, W.W. Norton. Hicks, J.R., Mr Kyns and th Classics : a suggstd intrprtation, Economtrica, 5: , IS-LM: an xplanation, Journal of ost Kynsian Economics, 3: Lvacic, R. and A. Rbmann, Macroconomics: An Introduction to Kynsian- Noclassical Controvrsis, Macmillan. Mankiw, N. G., Macroconomics, Fifth Edition, Nw ork: Worth ublishrs. Mundll, R.A., Capital mobility and stabilisation policy undr fixd and flxibl xchang rats, Canadian Journal of Economics and olitical Scinc, 29: Smith, B., Introduction to Macroconomics, arson Australia. Rs, L. and R. Tyrs, Trad rform in th short run: China s WTO accssion, Journal of Asian Economics 15(1): 1-31, January-Fbruary. Robrts, I. and R. Tyrs, China s xchang rat policy: th cas for gratr flxibility, Asian Economic Journal, 17(2): Tyrs, R., China aftr th crisis: th lmntal macroconomics, Asian Economic Journal, 15(2): , August. Tyrs, R. and L. Rs, On th robustnss of short run gains from trad libralisation, Discussion apr D 474, Cntr for Economic olicy Rsarch, Australian National Univrsity. Wlls, G., Macroconomics, Mlbourn: Thomas Nlson. Williamson, S., Macroconomics, Fourth Edition, Boston MA: arson Addison- Wsly. 33
37 D NUMBER AUTHORS ECONOMICS DISCUSSION AERS 2009 TITLE L, A.T. ENTR INTO UNIVERSIT: ARE THE CHILDREN OF IMMIGRANTS DISADVANTAGED? Wu,. CHINA S CAITAL STOCK SERIES B REGION AND SECTOR Chn, M.H. UNDERSTANDING WORLD COMMODIT RICES RETURNS, VOLATILIT AND DIVERSIFACATION Vlagic, R. UWA DISCUSSION AERS IN ECONOMICS: THE FIRST McLur, M. ROALTIES FOR REGIONS: ACCOUNTABILIT AND SUSTAINABILIT Chn, A. and Gronwold, N. REDUCING REGIONAL DISARITIES IN CHINA: AN EVALUATION OF ALTERNATIVE OLICIES Gronwold, N. and Haggr, A. THE REGIONAL ECONOMIC EFFECTS OF IMMIGRATION: SIMULATION RESULTS FROM A SMALL CGE MODEL Clmnts, K. and Chn, D. AFFLUENCE AND FOOD: SIMLE WA TO INFER INCOMES Clmnts, K. and Maspp, M. A SELF-REFLECTIVE INVERSE DEMAND SSTEM Jons, C. MEASURING WESTERN AUSTRALIAN HOUSE RICES: METHODS AND IMLICATIONS Siddiqu, M.A.B. WESTERN AUSTRALIA-JAAN MINING CO-OERATION: AN HISTORICAL OVERVIEW Wbr, E.J. RE-INDUSTRIAL BIMETALLISM: THE INDEX COIN HTHESIS McLur, M. ARETO AND IGOU ON OHELIMIT, UTILIT AND WELFARE: IMLICATIONS FOR UBLIC FINANCE Wbr, E.J. WILFRED EDWARD GRAHAM SALTER: THE MERITS OF A CLASSICAL ECONOMIC EDUCATION Tyrs, R. and Huang, L. COMBATING CHINA S EXORT CONTRACTION: FISCAL EXANSION OR ACCELERATED INDUSTRIAL REFORM Zwifl,., laff, D. and Kühn, J. IS REGULATING THE SOLVENC OF BANKS COUNTER- RODUCTIVE? Clmnts, K. THE HD CONFERENCE REACHES ADULTHOOD McLur, M. THIRT EARS OF ECONOMICS: UWA AND THE WA BRANCH OF THE ECONOMIC SOCIET FROM 1963 TO Harris, R.G. and Robrtson,. TRADE, WAGES AND SKILL ACCUMULATION IN THE EMERGING GIANTS ng, J., Cui, J., Qin, F. and Gronwold, N. STOCK RICES AND THE MACRO ECONOM IN CHINA Chn, A. and Gronwold, N. REGIONAL EQUALIT AND NATIONAL DEVELOMENT IN CHINA: IS THERE A TRADE-OFF? 34
38 D NUMBER AUTHORS ECONOMICS DISCUSSION AERS TITLE Hndry, D.F. RESEARCH AND THE ACADEMIC: A TALE OF TWO CULTURES McLur, M., Turkington, D. and Wbr, E.J. A CONVERSATION WITH ARNOLD ZELLNER Butlr, D.J., Burbank, V.K. and Chisholm, J.S. THE FRAMES BEHIND THE GAMES: LAER S ERCETIONS OF RISONER S DILEMMA, CHICKEN, DICTATOR, AND ULTIMATUM GAMES Harris, R.G., Robrtson,.E. and Xu, J.. THE INTERNATIONAL EFFECTS OF CHINA S GROWTH, TRADE AND EDUCATION BOOMS Clmnts, K.W., Mongy, S. and Si, J. THE DNAMICS OF NEW RESOURCE ROJECTS A ROGRESS REORT Costllo, G., Frasr,. and Gronwold, N. HOUSE RICES, NON-FUNDAMENTAL COMONENTS AND INTERSTATE SILLOVERS: THE AUSTRALIAN EXERIENCE Clmnts, K. REORT OF THE 2009 HD CONFERENCE IN ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS Robrtson,.E. INVESTMENT LED GROWTH IN INDIA: HINDU FACT OR MTHOLOG? Fu, D., Wu,. and Tang,. THE EFFECTS OF OWNERSHI STRUCTURE AND INDUSTR CHARACTERISTICS ON EXORT ERFORMANCE Wu,. INNOVATION AND ECONOMIC GROWTH IN CHINA Stphns, B.J. THE DETERMINANTS OF LABOUR FORCE STATUS AMONG INDIGENOUS AUSTRALIANS Davis, M. FINANCING THE BURRA BURRA MINES, SOUTH AUSTRALIA: LIQUIDIT ROBLEMS AND RESOLUTIONS Tyrs, R. and Zhang,. ARECIATING THE RENMINBI Clmnts, K.W., Lan,. and Sah, S.. THE BIG MAC INDEX TWO DECADES ON AN EVALUATION OF BURGERNOMICS Robrtson,.E. and Xu, J.. IN CHINA S WAKE: HAS ASIA GAINED FROM CHINA S GROWTH? Clmnts, K.W. and Izan, H.. THE A ARIT MATRIX: A TOOL FOR ANALSING THE STRUCTURE OF A Gao, G. WORLD FOOD DEMAND Wu,. INDIGENOUS INNOVATION IN CHINA: IMLICATIONS FOR SUSTAINABLE GROWTH Robrtson,.E. DECIHERING THE HINDU GROWTH EIC Stvns, G. RESERVE BANK OF AUSTRALIA-THE ROLE OF FINANCE
39 10.21 Widmr,.K., Zwifl,. and Farsi, M. ACCOUNTING FOR HETEROGENEIT IN THE MEASUREMENT OF HOSITAL ERFORMANCE McLur, M. ASSESSMENTS OF A. C. IGOU S FELLOWSHI THESES oon, A.R. THE ECONOMICS OF NONLINEAR RICING: EVIDENCE FROM AIRFARES AND GROCER RICES Halprin, D. FORECASTING METALS RETURNS: A BAESIAN DECISION THEORETIC AROACH Clmnts, K.W. and Si. J. THE INVESTMENT ROJECT IELINE: COST ESCALATION, LEAD-TIME, SUCCESS, FAILURE AND SEED Chn, A., Gronwold, N. and Haggr, A.J. THE REGIONAL ECONOMIC EFFECTS OF A REDUCTION IN CARBON EMISSIONS Siddiqu, A., Slvanathan, E.A. and Slvanathan, S. REMITTANCES AND ECONOMIC GROWTH: EMIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM BANGLADESH, INDIA AND SRI LANKA 36
40 D NUMBER AUTHORS ECONOMICS DISCUSSION AERS 2011 TITLE Robrtson,.E. DEE IMACT: CHINA AND THE WORLD ECONOM Kang, C. and L, S.H. BEING KNOWLEDGEABLE OR SOCIABLE? DIFFERENCES IN RELATIVE IMORTANCE OF COGNITIVE AND NON-COGNITIVE SKILLS Turkington, D. DIFFERENT CONCETS OF MATRIX CALCULUS Golly, J. and Tyrs, R. CONTRASTING GIANTS: DEMOGRAHIC CHANGE AND ECONOMIC ERFORMANCE IN CHINA AND INDIA Collins, J., Bar, B. and Wbr, E.J. ECONOMIC GROWTH AND EVOLUTION: ARENTAL REFERENCE FOR QUALIT AND QUANTIT OF OFFSRING Turkington, D. ON THE DIFFERENTIATION OF THE LOG LIKELIHOOD FUNCTION USING MATRIX CALCULUS Gronwold, N. and atrson, J.E.H. STOCK RICES AND EXCHANGE RATES IN AUSTRALIA: ARE COMMODIT RICES THE MISSING LINK? Chn, A. and Gronwold, N. REDUCING REGIONAL DISARITIES IN CHINA: IS INVESTMENT ALLOCATION OLIC EFFECTIVE? Williams, A., Birch, E. and Hancock,. THE IMACT OF ON-LINE LECTURE RECORDINGS ON STUDENT ERFORMANCE awly, J. and Wbr, E.J. INVESTMENT AND TECHNICAL ROGRESS IN THE G7 COUNTRIES AND AUSTRALIA Tyrs, R. AN ELEMENTAL MACROECONOMIC MODEL FOR ALIED ANALSIS AT UNDERGRADUATE LEVEL Clmnts, K.W. and Gao, G. QUALIT, QUANTIT, SENDING AND RICES Tyrs, R. and Zhang,. JAAN S ECONOMIC RECOVER: INSIGHTS FROM MULTI-REGION DNAMICS McLur, M. A. C. IGOU S REJECTION OF ARETO S LAW Kristoffrsn, I. THE SUBJECTIVE WELLBEING SCALE: HOW REASONABLE IS THE CARDINALIT ASSUMTION? Clmnts, K.W., Izan, H.. and Lan,. VOLATILIT AND STOCK RICE INDEXES arkinson, M. SHANN MEMORIAL LECTURE 2011: SUSTAINABLE WELLBEING AN ECONOMIC FUTURE FOR AUSTRALIA 37
Diploma Macro Paper 2
 Diploma Macro Papr 2 Montary Macroconomics Lctur 6 Aggrgat supply and putting AD and AS togthr Mark Hays 1 Exognous: M, G, T, i*, π Goods markt KX and IS (Y, C, I) Mony markt (LM) (i, Y) Labour markt (P,
Diploma Macro Papr 2 Montary Macroconomics Lctur 6 Aggrgat supply and putting AD and AS togthr Mark Hays 1 Exognous: M, G, T, i*, π Goods markt KX and IS (Y, C, I) Mony markt (LM) (i, Y) Labour markt (P,
dr Bartłomiej Rokicki Chair of Macroeconomics and International Trade Theory Faculty of Economic Sciences, University of Warsaw
 dr Bartłomij Rokicki Chair of Macroconomics and Intrnational Trad Thory Faculty of Economic Scincs, Univrsity of Warsaw dr Bartłomij Rokicki Opn Economy Macroconomics Small opn conomy. Main assumptions
dr Bartłomij Rokicki Chair of Macroconomics and Intrnational Trad Thory Faculty of Economic Scincs, Univrsity of Warsaw dr Bartłomij Rokicki Opn Economy Macroconomics Small opn conomy. Main assumptions
The Open Economy in the Short Run
 Economics 442 Mnzi D. Chinn Spring 208 Social Scincs 748 Univrsity of Wisconsin-Madison Th Opn Economy in th Short Run This st of nots outlins th IS-LM modl of th opn conomy. First, it covrs an accounting
Economics 442 Mnzi D. Chinn Spring 208 Social Scincs 748 Univrsity of Wisconsin-Madison Th Opn Economy in th Short Run This st of nots outlins th IS-LM modl of th opn conomy. First, it covrs an accounting
4. Money cannot be neutral in the short-run the neutrality of money is exclusively a medium run phenomenon.
 PART I TRUE/FALSE/UNCERTAIN (5 points ach) 1. Lik xpansionary montary policy, xpansionary fiscal policy rturns output in th mdium run to its natural lvl, and incrass prics. Thrfor, fiscal policy is also
PART I TRUE/FALSE/UNCERTAIN (5 points ach) 1. Lik xpansionary montary policy, xpansionary fiscal policy rturns output in th mdium run to its natural lvl, and incrass prics. Thrfor, fiscal policy is also
Chapter 13 Aggregate Supply
 Chaptr 13 Aggrgat Supply 0 1 Larning Objctivs thr modls of aggrgat supply in which output dpnds positivly on th pric lvl in th short run th short-run tradoff btwn inflation and unmploymnt known as th Phillips
Chaptr 13 Aggrgat Supply 0 1 Larning Objctivs thr modls of aggrgat supply in which output dpnds positivly on th pric lvl in th short run th short-run tradoff btwn inflation and unmploymnt known as th Phillips
Exchange rates in the long run (Purchasing Power Parity: PPP)
 Exchang rats in th long run (Purchasing Powr Parity: PPP) Jan J. Michalk JJ Michalk Th law of on pric: i for a product i; P i = E N/ * P i Or quivalntly: E N/ = P i / P i Ida: Th sam product should hav
Exchang rats in th long run (Purchasing Powr Parity: PPP) Jan J. Michalk JJ Michalk Th law of on pric: i for a product i; P i = E N/ * P i Or quivalntly: E N/ = P i / P i Ida: Th sam product should hav
Chapter 14 Aggregate Supply and the Short-run Tradeoff Between Inflation and Unemployment
 Chaptr 14 Aggrgat Supply and th Short-run Tradoff Btwn Inflation and Unmploymnt Modifid by Yun Wang Eco 3203 Intrmdiat Macroconomics Florida Intrnational Univrsity Summr 2017 2016 Worth Publishrs, all
Chaptr 14 Aggrgat Supply and th Short-run Tradoff Btwn Inflation and Unmploymnt Modifid by Yun Wang Eco 3203 Intrmdiat Macroconomics Florida Intrnational Univrsity Summr 2017 2016 Worth Publishrs, all
Inflation and Unemployment
 C H A P T E R 13 Aggrgat Supply and th Short-run Tradoff Btwn Inflation and Unmploymnt MACROECONOMICS SIXTH EDITION N. GREGORY MANKIW PowrPoint Slids by Ron Cronovich 2008 Worth Publishrs, all rights rsrvd
C H A P T E R 13 Aggrgat Supply and th Short-run Tradoff Btwn Inflation and Unmploymnt MACROECONOMICS SIXTH EDITION N. GREGORY MANKIW PowrPoint Slids by Ron Cronovich 2008 Worth Publishrs, all rights rsrvd
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
+ f. e f. Ch. 8 Inflation, Interest Rates & FX Rates. Purchasing Power Parity. Purchasing Power Parity
 Ch. 8 Inlation, Intrst Rats & FX Rats Topics Purchasing Powr Parity Intrnational Fishr Ect Purchasing Powr Parity Purchasing Powr Parity (PPP: Th purchasing powr o a consumr will b similar whn purchasing
Ch. 8 Inlation, Intrst Rats & FX Rats Topics Purchasing Powr Parity Intrnational Fishr Ect Purchasing Powr Parity Purchasing Powr Parity (PPP: Th purchasing powr o a consumr will b similar whn purchasing
The Ramsey Model. Reading: Firms. Households. Behavior of Households and Firms. Romer, Chapter 2-A;
 Th Ramsy Modl Rading: Romr, Chaptr 2-A; Dvlopd by Ramsy (1928), latr dvlopd furthr by Cass (1965) and Koopmans (1965). Similar to th Solow modl: labor and knowldg grow at xognous rats. Important diffrnc:
Th Ramsy Modl Rading: Romr, Chaptr 2-A; Dvlopd by Ramsy (1928), latr dvlopd furthr by Cass (1965) and Koopmans (1965). Similar to th Solow modl: labor and knowldg grow at xognous rats. Important diffrnc:
The van der Waals interaction 1 D. E. Soper 2 University of Oregon 20 April 2012
 Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
r m r m 1 r m 2 y 1 y 2
 An Explanation (Using th ISLM Modl) of How Volatilit in Expctations About th Profitabilit of Futur Invstmnt Projcts Can Mak Aggrgat Dmand Itslf Volatil. Th ISLM modl is a combination of two conomic modls;
An Explanation (Using th ISLM Modl) of How Volatilit in Expctations About th Profitabilit of Futur Invstmnt Projcts Can Mak Aggrgat Dmand Itslf Volatil. Th ISLM modl is a combination of two conomic modls;
Higher order derivatives
 Robrto s Nots on Diffrntial Calculus Chaptr 4: Basic diffrntiation ruls Sction 7 Highr ordr drivativs What you nd to know alrady: Basic diffrntiation ruls. What you can larn hr: How to rpat th procss of
Robrto s Nots on Diffrntial Calculus Chaptr 4: Basic diffrntiation ruls Sction 7 Highr ordr drivativs What you nd to know alrady: Basic diffrntiation ruls. What you can larn hr: How to rpat th procss of
11/11/2018. Chapter 14 8 th and 9 th edition. Aggregate Supply and the Short-run Tradeoff Between Inflation and Unemployment.
 Chaptr 14 8 th and 9 th dition Aggrgat Supply and th Short-run Tradoff Btwn Inflation and Unmploymnt W covr modls of aggrgat supply in which output dpnds positivly on th pric lvl in th short run. th short-run
Chaptr 14 8 th and 9 th dition Aggrgat Supply and th Short-run Tradoff Btwn Inflation and Unmploymnt W covr modls of aggrgat supply in which output dpnds positivly on th pric lvl in th short run. th short-run
ME 321 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines S. Lambert Winter 2002
 3.4 Forc Analysis of Linkas An undrstandin of forc analysis of linkas is rquird to: Dtrmin th raction forcs on pins, tc. as a consqunc of a spcifid motion (don t undrstimat th sinificanc of dynamic or
3.4 Forc Analysis of Linkas An undrstandin of forc analysis of linkas is rquird to: Dtrmin th raction forcs on pins, tc. as a consqunc of a spcifid motion (don t undrstimat th sinificanc of dynamic or
Two Products Manufacturer s Production Decisions with Carbon Constraint
 Managmnt Scinc and Enginring Vol 7 No 3 pp 3-34 DOI:3968/jms9335X374 ISSN 93-34 [Print] ISSN 93-35X [Onlin] wwwcscanadant wwwcscanadaorg Two Products Manufacturr s Production Dcisions with Carbon Constraint
Managmnt Scinc and Enginring Vol 7 No 3 pp 3-34 DOI:3968/jms9335X374 ISSN 93-34 [Print] ISSN 93-35X [Onlin] wwwcscanadant wwwcscanadaorg Two Products Manufacturr s Production Dcisions with Carbon Constraint
VALUING SURRENDER OPTIONS IN KOREAN INTEREST INDEXED ANNUITIES
 VALUING SURRENDER OPTIONS IN KOREAN INTEREST INDEXED ANNUITIES Changi Kim* * Dr. Changi Kim is Lcturr at Actuarial Studis Faculty of Commrc & Economics Th Univrsity of Nw South Wals Sydny NSW 2052 Australia.
VALUING SURRENDER OPTIONS IN KOREAN INTEREST INDEXED ANNUITIES Changi Kim* * Dr. Changi Kim is Lcturr at Actuarial Studis Faculty of Commrc & Economics Th Univrsity of Nw South Wals Sydny NSW 2052 Australia.
EXST Regression Techniques Page 1
 EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
A Propagating Wave Packet Group Velocity Dispersion
 Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
COMPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAMS Optical Sciences 627 W.J. Dallas (Monday, April 04, 2005, 8:35 AM) PART I: CHAPTER TWO COMB MATH.
 C:\Dallas\0_Courss\03A_OpSci_67\0 Cgh_Book\0_athmaticalPrliminaris\0_0 Combath.doc of 8 COPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAS Optical Scincs 67 W.J. Dallas (onday, April 04, 005, 8:35 A) PART I: CHAPTER TWO COB ATH
C:\Dallas\0_Courss\03A_OpSci_67\0 Cgh_Book\0_athmaticalPrliminaris\0_0 Combath.doc of 8 COPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAS Optical Scincs 67 W.J. Dallas (onday, April 04, 005, 8:35 A) PART I: CHAPTER TWO COB ATH
Differential Equations
 Prfac Hr ar m onlin nots for m diffrntial quations cours that I tach hr at Lamar Univrsit. Dspit th fact that ths ar m class nots, th should b accssibl to anon wanting to larn how to solv diffrntial quations
Prfac Hr ar m onlin nots for m diffrntial quations cours that I tach hr at Lamar Univrsit. Dspit th fact that ths ar m class nots, th should b accssibl to anon wanting to larn how to solv diffrntial quations
u x v x dx u x v x v x u x dx d u x v x u x v x dx u x v x dx Integration by Parts Formula
 7. Intgration by Parts Each drivativ formula givs ris to a corrsponding intgral formula, as w v sn many tims. Th drivativ product rul yilds a vry usful intgration tchniqu calld intgration by parts. Starting
7. Intgration by Parts Each drivativ formula givs ris to a corrsponding intgral formula, as w v sn many tims. Th drivativ product rul yilds a vry usful intgration tchniqu calld intgration by parts. Starting
Intermediate Macroeconomics: New Keynesian Model
 Intrmdiat Macroconomics: Nw Kynsian Modl Eric Sims Univrsity of Notr Dam Fall 23 Introduction Among mainstram acadmic conomists and policymakrs, th lading altrnativ to th ral businss cycl thory is th Nw
Intrmdiat Macroconomics: Nw Kynsian Modl Eric Sims Univrsity of Notr Dam Fall 23 Introduction Among mainstram acadmic conomists and policymakrs, th lading altrnativ to th ral businss cycl thory is th Nw
CS 361 Meeting 12 10/3/18
 CS 36 Mting 2 /3/8 Announcmnts. Homwork 4 is du Friday. If Friday is Mountain Day, homwork should b turnd in at my offic or th dpartmnt offic bfor 4. 2. Homwork 5 will b availabl ovr th wknd. 3. Our midtrm
CS 36 Mting 2 /3/8 Announcmnts. Homwork 4 is du Friday. If Friday is Mountain Day, homwork should b turnd in at my offic or th dpartmnt offic bfor 4. 2. Homwork 5 will b availabl ovr th wknd. 3. Our midtrm
Chapter 13 GMM for Linear Factor Models in Discount Factor form. GMM on the pricing errors gives a crosssectional
 Chaptr 13 GMM for Linar Factor Modls in Discount Factor form GMM on th pricing rrors givs a crosssctional rgrssion h cas of xcss rturns Hors rac sting for charactristic sting for pricd factors: lambdas
Chaptr 13 GMM for Linar Factor Modls in Discount Factor form GMM on th pricing rrors givs a crosssctional rgrssion h cas of xcss rturns Hors rac sting for charactristic sting for pricd factors: lambdas
Addition of angular momentum
 Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
General Notes About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidelines
 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
Addition of angular momentum
 Addition of angular momntum April, 07 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat
Addition of angular momntum April, 07 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
Applied Econometrics and International Development. AEID.Vol. 6-1 (2006)
 Applid Economtrics and Intrnational Dvlopmnt. AEID.Vol. 6-1 (2006) DETERMINANTS OF EXCHANGE RATE FLUCTUATIONS FOR VENEZUELA: APPLICATION OF AN EXTENDED MUNDELL-FLEMING MODEL HSING, u * Abstract Applying
Applid Economtrics and Intrnational Dvlopmnt. AEID.Vol. 6-1 (2006) DETERMINANTS OF EXCHANGE RATE FLUCTUATIONS FOR VENEZUELA: APPLICATION OF AN EXTENDED MUNDELL-FLEMING MODEL HSING, u * Abstract Applying
What are those βs anyway? Understanding Design Matrix & Odds ratios
 Ral paramtr stimat WILD 750 - Wildlif Population Analysis of 6 What ar thos βs anyway? Undrsting Dsign Matrix & Odds ratios Rfrncs Hosmr D.W.. Lmshow. 000. Applid logistic rgrssion. John Wily & ons Inc.
Ral paramtr stimat WILD 750 - Wildlif Population Analysis of 6 What ar thos βs anyway? Undrsting Dsign Matrix & Odds ratios Rfrncs Hosmr D.W.. Lmshow. 000. Applid logistic rgrssion. John Wily & ons Inc.
Problem Set 6 Solutions
 6.04/18.06J Mathmatics for Computr Scinc March 15, 005 Srini Dvadas and Eric Lhman Problm St 6 Solutions Du: Monday, March 8 at 9 PM in Room 3-044 Problm 1. Sammy th Shark is a financial srvic providr
6.04/18.06J Mathmatics for Computr Scinc March 15, 005 Srini Dvadas and Eric Lhman Problm St 6 Solutions Du: Monday, March 8 at 9 PM in Room 3-044 Problm 1. Sammy th Shark is a financial srvic providr
Search sequence databases 3 10/25/2016
 Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Einstein Equations for Tetrad Fields
 Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
The Matrix Exponential
 Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
There is an arbitrary overall complex phase that could be added to A, but since this makes no difference we set it to zero and choose A real.
 Midtrm #, Physics 37A, Spring 07. Writ your rsponss blow or on xtra pags. Show your work, and tak car to xplain what you ar doing; partial crdit will b givn for incomplt answrs that dmonstrat som concptual
Midtrm #, Physics 37A, Spring 07. Writ your rsponss blow or on xtra pags. Show your work, and tak car to xplain what you ar doing; partial crdit will b givn for incomplt answrs that dmonstrat som concptual
The Matrix Exponential
 Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by Dan Klain Vrsion 28928 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix () A A k I + A + k!
Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by Dan Klain Vrsion 28928 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix () A A k I + A + k!
Bifurcation Theory. , a stationary point, depends on the value of α. At certain values
 Dnamic Macroconomic Thor Prof. Thomas Lux Bifurcation Thor Bifurcation: qualitativ chang in th natur of th solution occurs if a paramtr passs through a critical point bifurcation or branch valu. Local
Dnamic Macroconomic Thor Prof. Thomas Lux Bifurcation Thor Bifurcation: qualitativ chang in th natur of th solution occurs if a paramtr passs through a critical point bifurcation or branch valu. Local
Answer Homework 5 PHA5127 Fall 1999 Jeff Stark
 Answr omwork 5 PA527 Fall 999 Jff Stark A patint is bing tratd with Drug X in a clinical stting. Upon admiion, an IV bolus dos of 000mg was givn which yildd an initial concntration of 5.56 µg/ml. A fw
Answr omwork 5 PA527 Fall 999 Jff Stark A patint is bing tratd with Drug X in a clinical stting. Upon admiion, an IV bolus dos of 000mg was givn which yildd an initial concntration of 5.56 µg/ml. A fw
MEASURING ECONOMIC IMPACT OF A DISASTER WITHOUT DOUBLE COUNTING: A THEORETICAL ANALYSIS
 MEASURING ECONOMIC IMPACT OF A DISASTER WITHOUT DOUBLE COUNTING: A THEORETICAL ANALYSIS ABSTRACT : H. Tatano and K. Nakano Profssor, Disastr Prvntion Rsarch Institut, Kyoto Univrsity, Uji. Japan Ph.D Candidat,
MEASURING ECONOMIC IMPACT OF A DISASTER WITHOUT DOUBLE COUNTING: A THEORETICAL ANALYSIS ABSTRACT : H. Tatano and K. Nakano Profssor, Disastr Prvntion Rsarch Institut, Kyoto Univrsity, Uji. Japan Ph.D Candidat,
Estimation of apparent fraction defective: A mathematical approach
 Availabl onlin at www.plagiarsarchlibrary.com Plagia Rsarch Library Advancs in Applid Scinc Rsarch, 011, (): 84-89 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Estimation of apparnt fraction dfctiv: A mathmatical
Availabl onlin at www.plagiarsarchlibrary.com Plagia Rsarch Library Advancs in Applid Scinc Rsarch, 011, (): 84-89 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Estimation of apparnt fraction dfctiv: A mathmatical
Homotopy perturbation technique
 Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
ph People Grade Level: basic Duration: minutes Setting: classroom or field site
 ph Popl Adaptd from: Whr Ar th Frogs? in Projct WET: Curriculum & Activity Guid. Bozman: Th Watrcours and th Council for Environmntal Education, 1995. ph Grad Lvl: basic Duration: 10 15 minuts Stting:
ph Popl Adaptd from: Whr Ar th Frogs? in Projct WET: Curriculum & Activity Guid. Bozman: Th Watrcours and th Council for Environmntal Education, 1995. ph Grad Lvl: basic Duration: 10 15 minuts Stting:
A. Limits and Horizontal Asymptotes ( ) f x f x. f x. x "±# ( ).
 A. Limits and Horizontal Asymptots What you ar finding: You can b askd to find lim x "a H.A.) problm is asking you find lim x "# and lim x "$#. or lim x "±#. Typically, a horizontal asymptot algbraically,
A. Limits and Horizontal Asymptots What you ar finding: You can b askd to find lim x "a H.A.) problm is asking you find lim x "# and lim x "$#. or lim x "±#. Typically, a horizontal asymptot algbraically,
Elements of Statistical Thermodynamics
 24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
Calculus concepts derivatives
 All rasonabl fforts hav bn mad to mak sur th nots ar accurat. Th author cannot b hld rsponsibl for any damags arising from th us of ths nots in any fashion. Calculus concpts drivativs Concpts involving
All rasonabl fforts hav bn mad to mak sur th nots ar accurat. Th author cannot b hld rsponsibl for any damags arising from th us of ths nots in any fashion. Calculus concpts drivativs Concpts involving
That is, we start with a general matrix: And end with a simpler matrix:
 DIAGON ALIZATION OF THE STR ESS TEN SOR INTRO DUCTIO N By th us of Cauchy s thorm w ar abl to rduc th numbr of strss componnts in th strss tnsor to only nin valus. An additional simplification of th strss
DIAGON ALIZATION OF THE STR ESS TEN SOR INTRO DUCTIO N By th us of Cauchy s thorm w ar abl to rduc th numbr of strss componnts in th strss tnsor to only nin valus. An additional simplification of th strss
8 Equilibrium Analysis in a Pure Exchange Model
 8 Equilibrium Analysis in a Pur Exchang Modl So far w hav only discussd dcision thory. That is, w hav lookd at consumr choic problms on th form s.t. p 1 x 1 + p 2 x 2 m: max u (x 1 ; x 2 ) x 1 ;x 2 Th
8 Equilibrium Analysis in a Pur Exchang Modl So far w hav only discussd dcision thory. That is, w hav lookd at consumr choic problms on th form s.t. p 1 x 1 + p 2 x 2 m: max u (x 1 ; x 2 ) x 1 ;x 2 Th
Fourier Transforms and the Wave Equation. Key Mathematics: More Fourier transform theory, especially as applied to solving the wave equation.
 Lur 7 Fourir Transforms and th Wav Euation Ovrviw and Motivation: W first discuss a fw faturs of th Fourir transform (FT), and thn w solv th initial-valu problm for th wav uation using th Fourir transform
Lur 7 Fourir Transforms and th Wav Euation Ovrviw and Motivation: W first discuss a fw faturs of th Fourir transform (FT), and thn w solv th initial-valu problm for th wav uation using th Fourir transform
(Upside-Down o Direct Rotation) β - Numbers
 Amrican Journal of Mathmatics and Statistics 014, 4(): 58-64 DOI: 10593/jajms0140400 (Upsid-Down o Dirct Rotation) β - Numbrs Ammar Sddiq Mahmood 1, Shukriyah Sabir Ali,* 1 Dpartmnt of Mathmatics, Collg
Amrican Journal of Mathmatics and Statistics 014, 4(): 58-64 DOI: 10593/jajms0140400 (Upsid-Down o Dirct Rotation) β - Numbrs Ammar Sddiq Mahmood 1, Shukriyah Sabir Ali,* 1 Dpartmnt of Mathmatics, Collg
The pn junction: 2 Current vs Voltage (IV) characteristics
 Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Sec 2.3 Modeling with First Order Equations
 Sc.3 Modling with First Ordr Equations Mathmatical modls charactriz physical systms, oftn using diffrntial quations. Modl Construction: Translating physical situation into mathmatical trms. Clarly stat
Sc.3 Modling with First Ordr Equations Mathmatical modls charactriz physical systms, oftn using diffrntial quations. Modl Construction: Translating physical situation into mathmatical trms. Clarly stat
Cramér-Rao Inequality: Let f(x; θ) be a probability density function with continuous parameter
 WHEN THE CRAMÉR-RAO INEQUALITY PROVIDES NO INFORMATION STEVEN J. MILLER Abstract. W invstigat a on-paramtr family of probability dnsitis (rlatd to th Parto distribution, which dscribs many natural phnomna)
WHEN THE CRAMÉR-RAO INEQUALITY PROVIDES NO INFORMATION STEVEN J. MILLER Abstract. W invstigat a on-paramtr family of probability dnsitis (rlatd to th Parto distribution, which dscribs many natural phnomna)
Background: We have discussed the PIB, HO, and the energy of the RR model. In this chapter, the H-atom, and atomic orbitals.
 Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
cycle that does not cross any edges (including its own), then it has at least
 W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
Forces. Quantum ElectroDynamics. α = = We have now:
 W hav now: Forcs Considrd th gnral proprtis of forcs mdiatd by xchang (Yukawa potntial); Examind consrvation laws which ar obyd by (som) forcs. W will nxt look at thr forcs in mor dtail: Elctromagntic
W hav now: Forcs Considrd th gnral proprtis of forcs mdiatd by xchang (Yukawa potntial); Examind consrvation laws which ar obyd by (som) forcs. W will nxt look at thr forcs in mor dtail: Elctromagntic
SECTION where P (cos θ, sin θ) and Q(cos θ, sin θ) are polynomials in cos θ and sin θ, provided Q is never equal to zero.
 SETION 6. 57 6. Evaluation of Dfinit Intgrals Exampl 6.6 W hav usd dfinit intgrals to valuat contour intgrals. It may com as a surpris to larn that contour intgrals and rsidus can b usd to valuat crtain
SETION 6. 57 6. Evaluation of Dfinit Intgrals Exampl 6.6 W hav usd dfinit intgrals to valuat contour intgrals. It may com as a surpris to larn that contour intgrals and rsidus can b usd to valuat crtain
Economics 201b Spring 2010 Solutions to Problem Set 3 John Zhu
 Economics 20b Spring 200 Solutions to Problm St 3 John Zhu. Not in th 200 vrsion of Profssor Andrson s ctur 4 Nots, th charactrization of th firm in a Robinson Cruso conomy is that it maximizs profit ovr
Economics 20b Spring 200 Solutions to Problm St 3 John Zhu. Not in th 200 vrsion of Profssor Andrson s ctur 4 Nots, th charactrization of th firm in a Robinson Cruso conomy is that it maximizs profit ovr
LINEAR DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION WITH A POSITIVE AND A NEGATIVE TERM
 Elctronic Journal of Diffrntial Equations, Vol. 2003(2003), No. 92, pp. 1 6. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://jd.math.swt.du or http://jd.math.unt.du ftp jd.math.swt.du (login: ftp) LINEAR DELAY DIFFERENTIAL
Elctronic Journal of Diffrntial Equations, Vol. 2003(2003), No. 92, pp. 1 6. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://jd.math.swt.du or http://jd.math.unt.du ftp jd.math.swt.du (login: ftp) LINEAR DELAY DIFFERENTIAL
Quasi-Classical States of the Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Application of the IS MP IA model to the Singapore economy and policy implications. Abstract
 Application of th IS MP IA modl to th Singapor conomy and policy implications Yu Hsing Southastrn Louisiana Univrsity Abstract Extnding th IS MP IA modl (omr, 2000, w find that quilibrium output in Singapor
Application of th IS MP IA modl to th Singapor conomy and policy implications Yu Hsing Southastrn Louisiana Univrsity Abstract Extnding th IS MP IA modl (omr, 2000, w find that quilibrium output in Singapor
Derangements and Applications
 2 3 47 6 23 Journal of Intgr Squncs, Vol. 6 (2003), Articl 03..2 Drangmnts and Applications Mhdi Hassani Dpartmnt of Mathmatics Institut for Advancd Studis in Basic Scincs Zanjan, Iran mhassani@iasbs.ac.ir
2 3 47 6 23 Journal of Intgr Squncs, Vol. 6 (2003), Articl 03..2 Drangmnts and Applications Mhdi Hassani Dpartmnt of Mathmatics Institut for Advancd Studis in Basic Scincs Zanjan, Iran mhassani@iasbs.ac.ir
4. (5a + b) 7 & x 1 = (3x 1)log 10 4 = log (M1) [4] d = 3 [4] T 2 = 5 + = 16 or or 16.
![4. (5a + b) 7 & x 1 = (3x 1)log 10 4 = log (M1) [4] d = 3 [4] T 2 = 5 + = 16 or or 16. 4. (5a + b) 7 & x 1 = (3x 1)log 10 4 = log (M1) [4] d = 3 [4] T 2 = 5 + = 16 or or 16.](/thumbs/86/93688166.jpg) . 7 7 7... 7 7 (n )0 7 (M) 0(n ) 00 n (A) S ((7) 0(0)) (M) (7 00) 8897 (A). (5a b) 7 7... (5a)... (M) 7 5 5 (a b ) 5 5 a b (M)(A) So th cofficint is 75 (A) (C) [] S (7 7) (M) () 8897 (A) (C) [] 5. x.55
. 7 7 7... 7 7 (n )0 7 (M) 0(n ) 00 n (A) S ((7) 0(0)) (M) (7 00) 8897 (A). (5a b) 7 7... (5a)... (M) 7 5 5 (a b ) 5 5 a b (M)(A) So th cofficint is 75 (A) (C) [] S (7 7) (M) () 8897 (A) (C) [] 5. x.55
2.3 Matrix Formulation
 23 Matrix Formulation 43 A mor complicatd xampl ariss for a nonlinar systm of diffrntial quations Considr th following xampl Exampl 23 x y + x( x 2 y 2 y x + y( x 2 y 2 (233 Transforming to polar coordinats,
23 Matrix Formulation 43 A mor complicatd xampl ariss for a nonlinar systm of diffrntial quations Considr th following xampl Exampl 23 x y + x( x 2 y 2 y x + y( x 2 y 2 (233 Transforming to polar coordinats,
6.1 Integration by Parts and Present Value. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 6.1 Intgration by Parts and Prsnt Valu Copyright Cngag Larning. All rights rsrvd. Warm-Up: Find f () 1. F() = ln(+1). F() = 3 3. F() =. F() = ln ( 1) 5. F() = 6. F() = - Objctivs, Day #1 Studnts will b
6.1 Intgration by Parts and Prsnt Valu Copyright Cngag Larning. All rights rsrvd. Warm-Up: Find f () 1. F() = ln(+1). F() = 3 3. F() =. F() = ln ( 1) 5. F() = 6. F() = - Objctivs, Day #1 Studnts will b
Evaluating Reliability Systems by Using Weibull & New Weibull Extension Distributions Mushtak A.K. Shiker
 Evaluating Rliability Systms by Using Wibull & Nw Wibull Extnsion Distributions Mushtak A.K. Shikr مشتاق عبذ الغني شخير Univrsity of Babylon, Collg of Education (Ibn Hayan), Dpt. of Mathmatics Abstract
Evaluating Rliability Systms by Using Wibull & Nw Wibull Extnsion Distributions Mushtak A.K. Shikr مشتاق عبذ الغني شخير Univrsity of Babylon, Collg of Education (Ibn Hayan), Dpt. of Mathmatics Abstract
u r du = ur+1 r + 1 du = ln u + C u sin u du = cos u + C cos u du = sin u + C sec u tan u du = sec u + C e u du = e u + C
 Tchniqus of Intgration c Donald Kridr and Dwight Lahr In this sction w ar going to introduc th first approachs to valuating an indfinit intgral whos intgrand dos not hav an immdiat antidrivativ. W bgin
Tchniqus of Intgration c Donald Kridr and Dwight Lahr In this sction w ar going to introduc th first approachs to valuating an indfinit intgral whos intgrand dos not hav an immdiat antidrivativ. W bgin
Differentiation of Exponential Functions
 Calculus Modul C Diffrntiation of Eponntial Functions Copyright This publication Th Northrn Albrta Institut of Tchnology 007. All Rights Rsrvd. LAST REVISED March, 009 Introduction to Diffrntiation of
Calculus Modul C Diffrntiation of Eponntial Functions Copyright This publication Th Northrn Albrta Institut of Tchnology 007. All Rights Rsrvd. LAST REVISED March, 009 Introduction to Diffrntiation of
MATH 319, WEEK 15: The Fundamental Matrix, Non-Homogeneous Systems of Differential Equations
 MATH 39, WEEK 5: Th Fundamntal Matrix, Non-Homognous Systms of Diffrntial Equations Fundamntal Matrics Considr th problm of dtrmining th particular solution for an nsmbl of initial conditions For instanc,
MATH 39, WEEK 5: Th Fundamntal Matrix, Non-Homognous Systms of Diffrntial Equations Fundamntal Matrics Considr th problm of dtrmining th particular solution for an nsmbl of initial conditions For instanc,
1 Minimum Cut Problem
 CS 6 Lctur 6 Min Cut and argr s Algorithm Scribs: Png Hui How (05), Virginia Dat: May 4, 06 Minimum Cut Problm Today, w introduc th minimum cut problm. This problm has many motivations, on of which coms
CS 6 Lctur 6 Min Cut and argr s Algorithm Scribs: Png Hui How (05), Virginia Dat: May 4, 06 Minimum Cut Problm Today, w introduc th minimum cut problm. This problm has many motivations, on of which coms
Homework #3. 1 x. dx. It therefore follows that a sum of the
 Danil Cannon CS 62 / Luan March 5, 2009 Homwork # 1. Th natural logarithm is dfind by ln n = n 1 dx. It thrfor follows that a sum of th 1 x sam addnd ovr th sam intrval should b both asymptotically uppr-
Danil Cannon CS 62 / Luan March 5, 2009 Homwork # 1. Th natural logarithm is dfind by ln n = n 1 dx. It thrfor follows that a sum of th 1 x sam addnd ovr th sam intrval should b both asymptotically uppr-
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory
 Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
A Prey-Predator Model with an Alternative Food for the Predator, Harvesting of Both the Species and with A Gestation Period for Interaction
 Int. J. Opn Problms Compt. Math., Vol., o., Jun 008 A Pry-Prdator Modl with an Altrnativ Food for th Prdator, Harvsting of Both th Spcis and with A Gstation Priod for Intraction K. L. arayan and. CH. P.
Int. J. Opn Problms Compt. Math., Vol., o., Jun 008 A Pry-Prdator Modl with an Altrnativ Food for th Prdator, Harvsting of Both th Spcis and with A Gstation Priod for Intraction K. L. arayan and. CH. P.
Pipe flow friction, small vs. big pipes
 Friction actor (t/0 t o pip) Friction small vs larg pips J. Chaurtt May 016 It is an intrsting act that riction is highr in small pips than largr pips or th sam vlocity o low and th sam lngth. Friction
Friction actor (t/0 t o pip) Friction small vs larg pips J. Chaurtt May 016 It is an intrsting act that riction is highr in small pips than largr pips or th sam vlocity o low and th sam lngth. Friction
econstor Make Your Publications Visible.
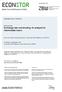 constor Mak Your Publications Visibl. A Srvic o Wirtschat Cntr zbwlibniz-inormationszntrum conomics Natividad-Carlos Fidlina B. Working Papr xchang-rat ovrshooting: An analysis or intrmdiat macro Discussion
constor Mak Your Publications Visibl. A Srvic o Wirtschat Cntr zbwlibniz-inormationszntrum conomics Natividad-Carlos Fidlina B. Working Papr xchang-rat ovrshooting: An analysis or intrmdiat macro Discussion
 Mor Tutorial at www.dumblittldoctor.com Work th problms without a calculator, but us a calculator to chck rsults. And try diffrntiating your answrs in part III as a usful chck. I. Applications of Intgration
Mor Tutorial at www.dumblittldoctor.com Work th problms without a calculator, but us a calculator to chck rsults. And try diffrntiating your answrs in part III as a usful chck. I. Applications of Intgration
Abstract Interpretation: concrete and abstract semantics
 Abstract Intrprtation: concrt and abstract smantics Concrt smantics W considr a vry tiny languag that manags arithmtic oprations on intgrs valus. Th (concrt) smantics of th languags cab b dfind by th funzcion
Abstract Intrprtation: concrt and abstract smantics Concrt smantics W considr a vry tiny languag that manags arithmtic oprations on intgrs valus. Th (concrt) smantics of th languags cab b dfind by th funzcion
Introduction to Arithmetic Geometry Fall 2013 Lecture #20 11/14/2013
 18.782 Introduction to Arithmtic Gomtry Fall 2013 Lctur #20 11/14/2013 20.1 Dgr thorm for morphisms of curvs Lt us rstat th thorm givn at th nd of th last lctur, which w will now prov. Thorm 20.1. Lt φ:
18.782 Introduction to Arithmtic Gomtry Fall 2013 Lctur #20 11/14/2013 20.1 Dgr thorm for morphisms of curvs Lt us rstat th thorm givn at th nd of th last lctur, which w will now prov. Thorm 20.1. Lt φ:
Market power, Growth and Unemployment
 Markt powr, Growth and Unmploymnt Pitro F Prtto Dpartmnt of Economics, Duk Univrsity Jun 13, 2011 Abstract I prsnt a modl whr firms and workrs st wags abov th markt-claring lvl Unmploymnt is thus gnratd
Markt powr, Growth and Unmploymnt Pitro F Prtto Dpartmnt of Economics, Duk Univrsity Jun 13, 2011 Abstract I prsnt a modl whr firms and workrs st wags abov th markt-claring lvl Unmploymnt is thus gnratd
Brief Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
 Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
On the Hamiltonian of a Multi-Electron Atom
 On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
Environmental Policy and Time Consistency: Emission Taxes and Emissions Trading
 Environmntal Policy and Tim Consistncy: Emission Taxs and Emissions Trading Ptr W. Knndy 1 and Bnoît Laplant 2 1 Dpartmnt of Economics, Univrsity of Victoria, Victoria, British Columbia V8W 2Y2, Canada.
Environmntal Policy and Tim Consistncy: Emission Taxs and Emissions Trading Ptr W. Knndy 1 and Bnoît Laplant 2 1 Dpartmnt of Economics, Univrsity of Victoria, Victoria, British Columbia V8W 2Y2, Canada.
orbiting electron turns out to be wrong even though it Unfortunately, the classical visualization of the
 Lctur 22-1 Byond Bohr Modl Unfortunatly, th classical visualization of th orbiting lctron turns out to b wrong vn though it still givs us a simpl way to think of th atom. Quantum Mchanics is ndd to truly
Lctur 22-1 Byond Bohr Modl Unfortunatly, th classical visualization of th orbiting lctron turns out to b wrong vn though it still givs us a simpl way to think of th atom. Quantum Mchanics is ndd to truly
Observer Bias and Reliability By Xunchi Pu
 Obsrvr Bias and Rliability By Xunchi Pu Introduction Clarly all masurmnts or obsrvations nd to b mad as accuratly as possibl and invstigators nd to pay carful attntion to chcking th rliability of thir
Obsrvr Bias and Rliability By Xunchi Pu Introduction Clarly all masurmnts or obsrvations nd to b mad as accuratly as possibl and invstigators nd to pay carful attntion to chcking th rliability of thir
Data Assimilation 1. Alan O Neill National Centre for Earth Observation UK
 Data Assimilation 1 Alan O Nill National Cntr for Earth Obsrvation UK Plan Motivation & basic idas Univariat (scalar) data assimilation Multivariat (vctor) data assimilation 3d-Variational Mthod (& optimal
Data Assimilation 1 Alan O Nill National Cntr for Earth Obsrvation UK Plan Motivation & basic idas Univariat (scalar) data assimilation Multivariat (vctor) data assimilation 3d-Variational Mthod (& optimal
4037 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Lvl MARK SCHEME for th Octobr/Novmbr 0 sris 40 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 40/ Papr, maimum raw mark 80 This mark schm is publishd as an aid to tachrs and candidats,
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Lvl MARK SCHEME for th Octobr/Novmbr 0 sris 40 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 40/ Papr, maimum raw mark 80 This mark schm is publishd as an aid to tachrs and candidats,
Extraction of Doping Density Distributions from C-V Curves
 Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
Dealing with quantitative data and problem solving life is a story problem! Attacking Quantitative Problems
 Daling with quantitati data and problm soling lif is a story problm! A larg portion of scinc inols quantitati data that has both alu and units. Units can sa your butt! Nd handl on mtric prfixs Dimnsional
Daling with quantitati data and problm soling lif is a story problm! A larg portion of scinc inols quantitati data that has both alu and units. Units can sa your butt! Nd handl on mtric prfixs Dimnsional
Exam 1. It is important that you clearly show your work and mark the final answer clearly, closed book, closed notes, no calculator.
 Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
While there is a consensus that monetary policy must be
 Optimal Montary Policy in an Economy with Sticky Nominal Wags Evan F. Konig Rsarch Officr Fdral Rsrv Bank of Dallas Whil thr is a consnsus that montary policy must b conductd within a framwork in which
Optimal Montary Policy in an Economy with Sticky Nominal Wags Evan F. Konig Rsarch Officr Fdral Rsrv Bank of Dallas Whil thr is a consnsus that montary policy must b conductd within a framwork in which
A Sub-Optimal Log-Domain Decoding Algorithm for Non-Binary LDPC Codes
 Procdings of th 9th WSEAS Intrnational Confrnc on APPLICATIONS of COMPUTER ENGINEERING A Sub-Optimal Log-Domain Dcoding Algorithm for Non-Binary LDPC Cods CHIRAG DADLANI and RANJAN BOSE Dpartmnt of Elctrical
Procdings of th 9th WSEAS Intrnational Confrnc on APPLICATIONS of COMPUTER ENGINEERING A Sub-Optimal Log-Domain Dcoding Algorithm for Non-Binary LDPC Cods CHIRAG DADLANI and RANJAN BOSE Dpartmnt of Elctrical
EEO 401 Digital Signal Processing Prof. Mark Fowler
 EEO 401 Digital Signal Procssing Prof. Mark Fowlr Dtails of th ot St #19 Rading Assignmnt: Sct. 7.1.2, 7.1.3, & 7.2 of Proakis & Manolakis Dfinition of th So Givn signal data points x[n] for n = 0,, -1
EEO 401 Digital Signal Procssing Prof. Mark Fowlr Dtails of th ot St #19 Rading Assignmnt: Sct. 7.1.2, 7.1.3, & 7.2 of Proakis & Manolakis Dfinition of th So Givn signal data points x[n] for n = 0,, -1
Math 34A. Final Review
 Math A Final Rviw 1) Us th graph of y10 to find approimat valus: a) 50 0. b) y (0.65) solution for part a) first writ an quation: 50 0. now tak th logarithm of both sids: log() log(50 0. ) pand th right
Math A Final Rviw 1) Us th graph of y10 to find approimat valus: a) 50 0. b) y (0.65) solution for part a) first writ an quation: 50 0. now tak th logarithm of both sids: log() log(50 0. ) pand th right
First derivative analysis
 Robrto s Nots on Dirntial Calculus Chaptr 8: Graphical analysis Sction First drivativ analysis What you nd to know alrady: How to us drivativs to idntiy th critical valus o a unction and its trm points
Robrto s Nots on Dirntial Calculus Chaptr 8: Graphical analysis Sction First drivativ analysis What you nd to know alrady: How to us drivativs to idntiy th critical valus o a unction and its trm points
Transitional Probability Model for a Serial Phases in Production
 Jurnal Karya Asli Lorkan Ahli Matmatik Vol. 3 No. 2 (2010) pag 49-54. Jurnal Karya Asli Lorkan Ahli Matmatik Transitional Probability Modl for a Srial Phass in Production Adam Baharum School of Mathmatical
Jurnal Karya Asli Lorkan Ahli Matmatik Vol. 3 No. 2 (2010) pag 49-54. Jurnal Karya Asli Lorkan Ahli Matmatik Transitional Probability Modl for a Srial Phass in Production Adam Baharum School of Mathmatical
Derivation of Electron-Electron Interaction Terms in the Multi-Electron Hamiltonian
 Drivation of Elctron-Elctron Intraction Trms in th Multi-Elctron Hamiltonian Erica Smith Octobr 1, 010 1 Introduction Th Hamiltonian for a multi-lctron atom with n lctrons is drivd by Itoh (1965) by accounting
Drivation of Elctron-Elctron Intraction Trms in th Multi-Elctron Hamiltonian Erica Smith Octobr 1, 010 1 Introduction Th Hamiltonian for a multi-lctron atom with n lctrons is drivd by Itoh (1965) by accounting
1973 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 97 AP Calculus AB: Sction I 9 Minuts No Calculator Not: In this amination, ln dnots th natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to th bas ).. ( ) d= + C 6 + C + C + C + C. If f ( ) = + + + and ( ), g=
97 AP Calculus AB: Sction I 9 Minuts No Calculator Not: In this amination, ln dnots th natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to th bas ).. ( ) d= + C 6 + C + C + C + C. If f ( ) = + + + and ( ), g=
3 Finite Element Parametric Geometry
 3 Finit Elmnt Paramtric Gomtry 3. Introduction Th intgral of a matrix is th matrix containing th intgral of ach and vry on of its original componnts. Practical finit lmnt analysis rquirs intgrating matrics,
3 Finit Elmnt Paramtric Gomtry 3. Introduction Th intgral of a matrix is th matrix containing th intgral of ach and vry on of its original componnts. Practical finit lmnt analysis rquirs intgrating matrics,
Computing and Communications -- Network Coding
 89 90 98 00 Computing and Communications -- Ntwork Coding Dr. Zhiyong Chn Institut of Wirlss Communications Tchnology Shanghai Jiao Tong Univrsity China Lctur 5- Nov. 05 0 Classical Information Thory Sourc
89 90 98 00 Computing and Communications -- Ntwork Coding Dr. Zhiyong Chn Institut of Wirlss Communications Tchnology Shanghai Jiao Tong Univrsity China Lctur 5- Nov. 05 0 Classical Information Thory Sourc
