STATUS OF THE CAVIAR DETECTOR AT LISE-GANIL
|
|
|
- Anthony Howard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STATUS OF THE CAVIAR DETECTOR AT LISE-GANIL L. Perrot #, IPNO-IN2P3-CNRS, Orsay, France S. Grévy, C. Houarner, R.Hue, C. Marry, GANIL, Caen, France S. M. Lukyanov, Yu. Penionzhkevich, FLNR JINR, Dubna, Russia Abstract Physics that motivated the building of the LISE magnetic spectrometer, main ideas exposed in the scientific council of GANIL June 4th 1981 by M. Brian and M. Fleury, were: atomic physics studies with stripped ions and the study of new isotopes produced by the fragmentation of beams. The LISE line is a doubly achromatic spectrometer (angle and position), with a resolution better than Since the first experiment done in 1984, several improvements of the spectrometer were performed: use of a achromatic degrader (1987, used for the first time in the world), building of the achromatic deviation and the Wien Filter (1990), building of a new selection dipole and associated vertical platform (1994), building of the new LISE2000 line (2001), use of the CAVIAR detector (2002), building of the CLIM target (2007). Despite an extreme international competition, the LISE spectrometer remains a world-leader equipment using more than 50 % and up to 90 % of the beam time available at GANIL. This paper presents the status of CAVIAR detector which consists of a MWPC dedicated to in flight particle position at the first dispersive plane of LISE. Since two years, intensive efforts were done with the objective to make available a plug and play detector for nuclear physic experiment. We will describe the system from MWPC up to acquisition system. As example few experimental results will be presented. INTRODUCTION In the energy domain of GANIL (from 30 up to 100 MeV/u), a large fraction of the reaction cross section goes into the fragmentation of the projectile. Fragments are emitted around 0 at velocities very close to the one of the incident beam, in a mass range which spreads from the projectile. A physics program with the goals to study exotic nuclei and secondary radioactive beams started in the early eighties [1]. LISE provides two main selection criteria in the identification process of reaction products. The first one is the magnetic rigidity (Bρ=Av/Q) given by the first analyzing dipole D31. Dispersion term of the section is typically 16.5mm/% of δp/p. Slits are placed at the dispersive plane with full aperture of ±45mm. The momentum acceptance is equal to Δp/p=2.72%. The second selection is the differential energy loss (de) of the ions in materials, by means of an achromatic degrader located in the intermediate focal plan of the spectrometer (cf. Fig. 1). The combination of Bρ and de measurements provides a selection to A 3 /Z 2 (with B the magnetic field, ρ the radius, A the mass number, v the velocity and Z the atomic number). Beam line acceptance is around 1msr. These two previous selections are the selection reference of LISE spectrometer. Figure 1: View of the LISE spectrometer. Essential beam lines elements can be located. CAVIAR and physics acquisition location are precise. # perrot@ipno.in2p3.fr
2 The angle of entry of the primary beam with respect to the axis of the spectrometer has been made variable (from 0 up to 3.5 ). This improvement allows the suppression of remaining incompletely stripped beam charge states in experiments with heavy beams (Z>30). A third selection was added in the early nineties for increasing the rejection power. In order to filter out a given velocity, it has been constructed a device in which an electrostatic and a magnetic field are crossed in a classical Wien filter [2]. The flight path between the target and the final focus is around 43m. The line was named LISE3. In 2001, the new line LISE2002 was built for increasing magnetic rigidity (until 4.2Tm) and beam line acceptance [3]. LISE2002 line is connected to old LISE line after the intermediate focal plane. It imposed quadruples and first dipole changing. More recently, according the various LISE features, a new rotating target was build. This target can accept beam power until to 2kW [4]. During an experiment carried out in 2002, a multi-wires proportional detector was placed in the dispersive plane of the spectrometer [5]. This detector named CAVIAR by the GANIL staff allowed the measuring of the magnetic rigidity of each fragment via its position in the focal plane, improving the mass-to-charge A/Q resolution. Activities on this detector began again in 2006 with α- source and beam test before a real experiment. During the two last years, various improvements have been done. We will present in this paper the status of the detector. We will first describe the detector. Next, we will give the methodology for tune the system. Finally, few results will be presented. CAVIAR DETECTOR To take the maximum benefit of the secondary beam intensity produced in the target, momentum selection slits of the LISE dispersive plane must be opened. Counting rate expected can be increasing by a factor 5. But the major difficulty is that heavy nuclides have too closed mass-to-charge A/Q ratio and time of flight (which is the case for fragmentation beams). For the full slits aperture, nuclides can not be distinguished. Contaminants rates can largely dominate the very low production rates of the interesting nuclide. Identification can be providing using a MWPC [6] placed at the dispersive focal point (cf. Fig. 1). Each wire detects the horizontal position of the particle at this point. With a coincidence between CAVIAR and detectors placed at the final focal plane (LISE2000 or LISE3) and a time of flight measurement, we can reconstruct precisely the mass-to-charge ratio event by event. Maximum counting rate per wire is 10 khz. FLNR JINR team performs MPWC and preamplifiers R&D according their great experience [7-8]. CAVIAR is a powerful tool for research and nuclear spectroscopy on nuclides produced with very low cross section. For example, it will concern nuclides closed the proton or the neutron drip-line. In addition, CAVIAR detector can be used during LISE tuning at the beginning of experiment. We obtain nuclides momentum distribution in the first LISE dispersive plane and optimize properly the spectrometer to the nuclide of interest. Mechanics The sensitive area of this detector is 96mm in the horizontal plane and 32mm in the vertical plane. These sizes are defined by the secondary beam sizes and maximum aperture of the slits in the dispersive plane. CAVIAR is composed by 96 wires of 10μm in diameter with 1mm step between each of them. Wires are gilded Tungsten. Two 1.5μm thicknesses Aluminum Cathodes foils are placed 3.4mm distance from anode (cf. Fig. 2). Figure 2: Mechanical view of the sensitive area of CAVIAR. Detector is filling with variable and less than 50mbar Isobutene (C 4 h 10 ). Two Kapton (C 22 H 10 N 2 O 5 ) windows of 8 μm thicknesses are used. They isolate the detector from beam line vacuum [9]. CAVIAR is a low interceptive detector for high energy beams. CAVIAR detector can be easily inserted in the beam line using a classical gage, which has connections on the top for high voltage, gas circulation and 96 out signals from wires. On the beam axis, CAVIAR is locating 45mm after the selection slits. Gas System The Isobutene was choosing for his cost and good properties to nuclides and energy range. For safety reason, gas filling system is located outside the experimental room (cf. Fig. 1). This gas unit, developed at GANIL, is inside the experimental room. We can control it by software. The gas unit system is working in a way to protect the detector in case of any trouble. Without gas regulation, valve is open to obtain the same vacuum in the detector and in the beam vacuum chamber. Signal Pre-amplification Directly fixed to the propeller, 6 boxes of 16 channels of pre-amplification are connected. Each wire is individually read out. Using this type of charges preamplifiers and due to ECM compatibility, we need
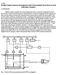
3 short lengths from wires up to PA entry. Figure 3 shows signals amplitudes after amplification. New tension preamplifiers have been recently built at JINR for take into account to eventual long distance between detector and preamplifiers. Tests with beam have been done in March Figure 5: Synoptic adopted for CAVIAR. Figure 3: Amplificated signals (50Ω adapt.). CAVIAR Acquisition System The 96 amplified signals are transport along 16 m cables until the acquisition system. Analog signals process is based on VME standard [10]. 6 DDM16 modules develop at GANIL are inserted [11]. Each DDM16 manage 16 channels. The module provides leading edge triggering, delay time and memorization. Scalers, tests, checkouts of analogical and logical signals are also available. When a particle passes truth CAVIAR detector, a signal can be induced on a wire. Signal is treated by associated DDM16 channel. The particle can be also detected by the detection system placed at the final focus point which is the master. The associated trigger generated by a validated event in the final detection system is transport until a TGV (Trigger Général VME) module with a CENTRUM receptor, which can correlate to the event number with the logical signal generated by the DDM16 (cf. Fig. 4). Figure 4: Synoptic adopted for CAVIAR. Due to beam line flight path, cables lengths and various signals treatments, all CAVIAR logical signals must be delayed to obtain the good memorization (cf. Fig. 5). CAVIAR memorization pattern is defining in 6 words of 16 bits. Finally, each DDM16 provide a Or of its 16 channels. The 6 resulting Or can be mixed for produced a single one. This Or logic can be use for the time measurement during the experiment. CAVIAR TUNING We will briefly describe up to now the method for tune the CAVIAR detector. First of all, detector must be connected to the line few days before the experiment. Vacuum in both chamber and detector must be in agreement with normal condition (around 10-6 mbar). Some test must be done with gas circulation for ensure that no gas leak occurs with the Kapton windows. At the experiment start, gas pressure must be chosen in agreement with the species and beam energy. At LISE, gas pressure will be typically 10mbar. High voltage value for the detector must be also prepares and checks. In order to protect the MWPC, current limit (of few μa) must be fixed for automatic switch-off the voltage. At LISE for 10mbar isobutene, optimum voltage will around -600V. During the experiment, any CAVIAR insertion in line must be done with beam off. With beam, observation of dedicated analogical signal to one wire can be done at oscilloscope. In that way we can increase progressively the high voltage until obtain signals like Figure 3. Then, threshold is applying just higher the noise (~13mV). Using dedicated CAVIAR scaler, we can flag wires with abnormal counting rate. Threshold can be changed individually wire by wire and observed at the oscilloscope (cf. Fig. 4). In order to verify if the detector tuning is well optimizing, slits just before CAVIAR can be closed at ±0.1mm for the primary beam. If more than one wire have signal with a too high statistics, it is an indication that the high voltage and threshold are not satisfying. With the close slits, we can also determine the center of the CAVIAR detector in the beam line. We have mention above that CAVIAR is a low interceptive detector. But, energy losses can be observed in the refocusing LISE section. Beams have to be recentered by decrease the current in the second LISE dipole D32 (cf. Fig. 1). Typically, with fragments at LISE, Bρ correction is around 0.5% (in energy, it is around 1%).
4 DDM16 delays are the same for all CAVIAR logical signals. They are fixed only when Trigger come from the acquisition of the experiment (cf. Fig. 4). CAVIAR memorization is valid when the forehead of rise delay logical signal of CAVIAR is inside the memorization window (cf. Fig. 4, green and blue curves). Various parameters have to be known or determine in order to reconstruct the mass-to-charge ratio during the experiment. All of these next parameters are used for calculate the nuclide speed and for the nuclide localization on CAVIAR (see appendix for explanation). Wire value (W c ) in the beam line center on the horizontal axis. As we have already seen, it is achieved by closing the selection slits at ±0.1mm. Time of flight (ToF) measurement have to be known from CAVIAR and from the final detection. Absolute calibration must be determined. The magnetic rigidity of the first (Bρ D31 ) and the second (Bρ D32 ) section must be known. At LISE, RMN measurement will provide the field gradients. Magnetic rigidities are determined by multiplication of the field by the radius of the dipole. Path length (L) between LISE target and CAVIAR and also LISE target and final detection [9]. The dispersive transport matrix term T16 at the CAVIAR position has to be known. For LISE3 standard optics, we have T16=16.1mm/% of δp/p. We can notice that different optics are available for the LISE spectrometer. Checks must be done during the experiment. In that way, we take advantage of the various checks out of CAVIAR signals (analog, prompt and delayed signals), memorization window and DDM16 scalers. Spectra produced on line during the experiment like CAVIAR profile and his multiplicity will be also some good additional checks. EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS Different tests and experiment have been realized sine Few of them are now presented. α-source Measurements For detector checks, it can be useful to use radioactive 3 α-source emitter (α energies<6mev). CAVIAR detector can be inserted between the radioactive source and a Silicon detector. The Silicon junction detector is using for precise energy deposition measurements and simulation the physics detector (like in a real experiment). Electronic treatments to Silicon detector is a classical spectrometry electronic. We can study α energy losses in CAVIAR and detected in the Silicon detector. Figure 6 present the α energy spectra measured with the Silicon detector for CAVIAR off line, in line with and without gaz. We can observe that α lose almost half of its energy in CAVIAR, contribution of gas is not negligible. Careful calculations using TRIM code [12] have very well reproduced these experimental results. It is important to well understand contribution of the energy loss in CAVIAR. In real experiment at LISE, we remind that nuclides energies are very high (more than 30MeV/u); energies losses in CAVIAR will be around 1%. Figure 6: α energy loss in a Silicon detector. An important parameter is the wires number touched per nuclides pass across CAVIAR. This parameter is the multiplicity. It depends to the beam divergence characteristics, high voltage and threshold. There will also be an impact on the localization accuracy of the nuclide in CAVIAR (cf. Fig. 7). Figure 7: Example of CAVIAR event multiplicity. Krypton High Energy Beam An experiment has been realized using a 78 Kr 33+ primary beam at 70MeV/u. LISE target was a 500μm Beryllium. Heavy ions of high atomic number (here Z=36) impose a low gas pressure to 6mbar. High voltage apply to CAVIAR was -513V. Figure 8: Determination of the atomic number Z as a function of the mass to charge A/Q using CAVIAR. Experiment has been performed using a Silicon junction at the final focus point in LISE D4. This single detector provides nuclides identification (atomic number Z) by measurements of particles energy losses and time of
5 flight. Selection slits in the dispersive plane was open at ±42.5mm. From the CAVIAR mass to charge reconstruction and the atomic number determination from energy loss in the silicon detector, we can obtain a complete identification of particles (cf. Fig. 8). We can observe that nuclides are well separated. Various nuclides charge states are also identified. Case of heavy ions like Krypton area of the nuclides chart is an extreme case of the CAVIAR contribution. More low ions produce with less charge states will be largely easier for clear separation. Finally, using contour selection in Z%A/Q distribution, we can determine the momentum distribution for few nuclides (cf. Fig. 9). Figure 9: Distribution of selected nuclides in the LISE dispersive plane. CONCLUSION In this paper, we have presented the status of the CAVIAR detector at LISE GANIL. This MWPC measure the horizontal position of each fragment in the first dispersive plane of the spectrometer. We can determine precisely the mass to charge ratio of each particle during experiment. Since 2006, various improvement have been done like new preamplifiers, dedicated acquisition system based on VME standard. Some efforts must be done to the cables, connectors and ECM before preamplifiers with the objective of noise reduction. CAVIAR detector offers new possibilities to the LISE spectrometer. It will be certainly an interesting tool for SPIRAL2 beams that will be available APPENDIX We give here formulas for determine the nuclides massto-charge A/Q knowing its position in the dispersive plane and its time of flight (see appendix A in ref. [8]). For each event, we have to determine the average CAVIAR wire (W a ) touched knowing his multiplicity N mult and wires touched W i : W a = W i /N mult. Knowing the central wire W c, the dispersion is X disp =W a -W c. With the LISE magnetic rigidity of the first section (Bρ D31 ) and the matrix dispersive term T 16 in the plane of CAVIAR, we can determine the single magnetic rigidity Bρ W like: X = Disp Bρ + W Bρ D 31 1 (1) T 16 Finally, knowing the path length L and the measured time of flight T, we determine the mass-to-charge ratio: A BρW c = Q M βγ UMA With c the speed light, β=l/(ct), γ the Lorentz factor and M UMA the atomic mass unit. REFERENCES [1] R. Anne et al., The achromatic Spectrometer LISE at GANIL, NIM, A257, (1987), [2] R. Anne, A.C. Mueller, LISE3: a magnetic spectrometer-wien Filter combination for the secondary beam production. NIM, B70 (1995), [3] R. Anne, LISE2000, Preprint GANIL, P [4] S. Grévy, R. Hue, CLIM: the new rotating target for exotic nuclei production at LISE spectrometer, 24th World Conference of the International Nuclear Target Development Society - INTDS2008, Caen: France (2008). [5] S.M. Lukyanov et al., Experimental evidence for the particle stability of 34 Ne and 37 Na, J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 28 (2008), L41-L45. [6] F. Sauli, Principles of operation of multiwire proportional and drift chambers, Lectures given in the Academic Training Programme of CERN, CERN 77-09, 3 May [7] R.A. Asaturyan et al. The Multiwire Proportional Chambers Coordinate System of MULTI Set-Up, Instruments and Experimental Techniques, V 42, N3, 1999, pp [8] R.A. Astabatyan, Set-Up on the basics of multiwire proportional and ionization chambers for radioactive beam experiments, Preprint JINR, E , Dubna, [9] L. Perrot, Le détecteur CAVIAR, Preprint GANIL, R 07 04, HAL: in2p , version 1 [10] W. D. Peterson, Versa Module Eurocard, VMEbus International Trade Association, USA, [11] C. Houarner, L. Olivier Discriminator Delay Memorization 16 Channels and CAVIAR Acquisition System Guide, Preprints GANIL, December 2008, Documentation/VME/DDM16. [12] J. F. Ziegler, J. P. Biersack and U. Littmark, The Stopping and Range of Ions in Solids, Pergamon Press, New York, 1985 (new edition in 2009). (2)
Status of the caviar detector at LISE-GANIL
 Status of the caviar detector at LISE-GANIL L. Perrot, S. Grévy, C. Houarner, R. Hue, C. Marry, S.M. Lukyanov, Yu. Penionshkevitch To cite this version: L. Perrot, S. Grévy, C. Houarner, R. Hue, C. Marry,
Status of the caviar detector at LISE-GANIL L. Perrot, S. Grévy, C. Houarner, R. Hue, C. Marry, S.M. Lukyanov, Yu. Penionshkevitch To cite this version: L. Perrot, S. Grévy, C. Houarner, R. Hue, C. Marry,
Minicourse on Experimental techniques at the NSCL Fragment Separators
 Minicourse on Experimental techniques at the NSCL Fragment Separators Thomas Baumann National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University e-mail: baumann@nscl.msu.edu August 2, 2001
Minicourse on Experimental techniques at the NSCL Fragment Separators Thomas Baumann National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University e-mail: baumann@nscl.msu.edu August 2, 2001
Secondary beam production with fragment separators
 Secondary beam production with fragment separators Introduction Application Statistics Monte Carlo calculation of fragment transmission EBSS tutorial The code operates under MS Windows environment and
Secondary beam production with fragment separators Introduction Application Statistics Monte Carlo calculation of fragment transmission EBSS tutorial The code operates under MS Windows environment and
MARS status report for : Development of rare isotope beams of 25 Si, 6 He, 9 Li, 23 Si, and 22 Si
 MARS status report for 2015-2016: Development of rare isotope beams of 25 Si, 6 He, 9 Li, 23 Si, and 22 Si B.T. Roeder, A. Saastamoinen, and M.R.D. Rodrigues 1 1 Instituto de Física, Universidade de São
MARS status report for 2015-2016: Development of rare isotope beams of 25 Si, 6 He, 9 Li, 23 Si, and 22 Si B.T. Roeder, A. Saastamoinen, and M.R.D. Rodrigues 1 1 Instituto de Física, Universidade de São
The heavy-ion magnetic spectrometer PRISMA
 Nuclear Physics A 701 (2002) 217c 221c www.elsevier.com/locate/npe The heavy-ion magnetic spectrometer PRISMA A.M. Stefanini a,,l.corradi a,g.maron a,a.pisent a,m.trotta a, A.M. Vinodkumar a, S. Beghini
Nuclear Physics A 701 (2002) 217c 221c www.elsevier.com/locate/npe The heavy-ion magnetic spectrometer PRISMA A.M. Stefanini a,,l.corradi a,g.maron a,a.pisent a,m.trotta a, A.M. Vinodkumar a, S. Beghini
LISE++ tutorial. The tutorial walks you through the required steps to try to fulfill the experimentalists requests:
 LISE++ tutorial D. Bazin* Summer School on Exotic Beam Physics NSCL / Michigan State University In this tutorial you impersonate a Radioactive beam physicist who is asked to prepare for producing a radioactive
LISE++ tutorial D. Bazin* Summer School on Exotic Beam Physics NSCL / Michigan State University In this tutorial you impersonate a Radioactive beam physicist who is asked to prepare for producing a radioactive
version ISOL METHOD MASS SEPARATOR MASHA CHARGE STATES...5
 version 6.5 Contents: 1. ISOL METHOD... 2 1.1. MASS SEPARATOR MASHA...3 1.2. CHARGE STATES...5 2. OTHER... 6 2.1. ELECTRIC DIPOLE: SEPARATION PLANE...6 2.2. WEDGE ANGLE DIALOG...6 2.3. MSP-144 MODIFICATION...7
version 6.5 Contents: 1. ISOL METHOD... 2 1.1. MASS SEPARATOR MASHA...3 1.2. CHARGE STATES...5 2. OTHER... 6 2.1. ELECTRIC DIPOLE: SEPARATION PLANE...6 2.2. WEDGE ANGLE DIALOG...6 2.3. MSP-144 MODIFICATION...7
Production and Separation of Radioactive Beams. Mg and 20 Na with MARS
 Production and Separation of Radioactive Beams 20 Mg and 20 Na with MARS Gopal Subedi, Colby College REU 2009, Cyclotron Institute, TAMU Advisor: Dr. Robert E. Tribble August 23, 2009 1 Overview Motivation
Production and Separation of Radioactive Beams 20 Mg and 20 Na with MARS Gopal Subedi, Colby College REU 2009, Cyclotron Institute, TAMU Advisor: Dr. Robert E. Tribble August 23, 2009 1 Overview Motivation
Wien filter revision. version Contents: Setting Wien filter in LISE++ Transport solution of Wien-filter optics
 Wien filter revision Contents: Setting Wien filter in LISE++ version 8.5.43 Transport solution of Wien-filter optics Classical solution for the dispersion coefficient Dispersion as a function of fields,
Wien filter revision Contents: Setting Wien filter in LISE++ version 8.5.43 Transport solution of Wien-filter optics Classical solution for the dispersion coefficient Dispersion as a function of fields,
Information about the T9 beam line and experimental facilities
 Information about the T9 beam line and experimental facilities The incoming proton beam from the PS accelerator impinges on the North target and thus produces the particles for the T9 beam line. The collisions
Information about the T9 beam line and experimental facilities The incoming proton beam from the PS accelerator impinges on the North target and thus produces the particles for the T9 beam line. The collisions
THE ACCULINNA AND ACCULINNA-2 RADIOACTIVE ION BEAM FACILITY AT DUBNA: STATUS AND PERSPECTIVES
 THE ACCULINNA AND ACCULINNA-2 RADIOACTIVE ION BEAM FACILITY AT DUBNA: STATUS AND PERSPECTIVES Grzegorz Kamiński for the ACCULINNA group FLNR, JINR, DUBNA International Nuclear Physics Conference (INPC2016)
THE ACCULINNA AND ACCULINNA-2 RADIOACTIVE ION BEAM FACILITY AT DUBNA: STATUS AND PERSPECTIVES Grzegorz Kamiński for the ACCULINNA group FLNR, JINR, DUBNA International Nuclear Physics Conference (INPC2016)
GANIL STATUS REPORT. B. Jacquot, F. Chautard, A.Savalle, & Ganil Staff GANIL-DSM/CEA,IN2P3/CNRS, BP 55027, Caen Cedex, France.
 GANIL STATUS REPORT B. Jacquot, F. Chautard, A.Savalle, & Ganil Staff GANIL-DSM/CEA,IN2P3/CNRS, BP 55027, 4076 Caen Cedex, France Abstract The GANIL-Spiral facility (Caen, France) is dedicated to the acceleration
GANIL STATUS REPORT B. Jacquot, F. Chautard, A.Savalle, & Ganil Staff GANIL-DSM/CEA,IN2P3/CNRS, BP 55027, 4076 Caen Cedex, France Abstract The GANIL-Spiral facility (Caen, France) is dedicated to the acceleration
THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI
 THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI M. Winkler 1,2, H. Geissel 2,1,, G. Münzenberg 2, V. Shiskine 2, H. Weick 2, H. Wollnik 1, M. Yavor 3 1 University of Giessen, Germany, 2 GSI, Germany, 3 Institute for Analytical
THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI M. Winkler 1,2, H. Geissel 2,1,, G. Münzenberg 2, V. Shiskine 2, H. Weick 2, H. Wollnik 1, M. Yavor 3 1 University of Giessen, Germany, 2 GSI, Germany, 3 Institute for Analytical
An Introduction to. Ion-Optics. Series of Five Lectures JINA, University of Notre Dame Sept. 30 Dec. 9, Georg P. Berg
 An Introduction to Ion-Optics Series of Five Lectures JINA, University of Notre Dame Sept. 30 Dec. 9, 2005 Georg P. Berg 1 The Lecture Series 1 st Lecture: 9/30/05, 2:00 pm: Definitions, Formalism, Examples
An Introduction to Ion-Optics Series of Five Lectures JINA, University of Notre Dame Sept. 30 Dec. 9, 2005 Georg P. Berg 1 The Lecture Series 1 st Lecture: 9/30/05, 2:00 pm: Definitions, Formalism, Examples
Physics with Exotic Nuclei
 Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
two-proton radioactivity discovery of two-proton radioactivity experimental results with TPC s future studies
 two-proton radioactivity discovery of two-proton radioactivity experimental results with TPC s future studies Bertram Blank CEN Bordeaux-Gradignan EPS European Nuclear Physics Conference 2009 Spring meeting
two-proton radioactivity discovery of two-proton radioactivity experimental results with TPC s future studies Bertram Blank CEN Bordeaux-Gradignan EPS European Nuclear Physics Conference 2009 Spring meeting
Review of ISOL-type Radioactive Beam Facilities
 Review of ISOL-type Radioactive Beam Facilities, CERN Map of the nuclear landscape Outline The ISOL technique History and Geography Isotope Separation On-Line Existing facilities First generation facilities
Review of ISOL-type Radioactive Beam Facilities, CERN Map of the nuclear landscape Outline The ISOL technique History and Geography Isotope Separation On-Line Existing facilities First generation facilities
discovery of two-proton radioactivity future studies Bertram Blank, CEN Bordeaux-Gradignan Hirschegg, january 2008
 two-proton radioactivity discovery of two-proton radioactivity Experimental results with TPC future studies Bertram Blank, CEN Bordeaux-Gradignan Hirschegg, 14-18 january 2008 alpha emission of 4 He 2
two-proton radioactivity discovery of two-proton radioactivity Experimental results with TPC future studies Bertram Blank, CEN Bordeaux-Gradignan Hirschegg, 14-18 january 2008 alpha emission of 4 He 2
RITU and the GREAT Spectrometer
 RITU and the GREAT Spectrometer Cath Scholey Department of Physics University of Jyväskylä 19 th March 2006 3rd TASCA Detector Group Meeting, GSI Darmstadt C. Scholey (JYFL, Finland) RITU and the GREAT
RITU and the GREAT Spectrometer Cath Scholey Department of Physics University of Jyväskylä 19 th March 2006 3rd TASCA Detector Group Meeting, GSI Darmstadt C. Scholey (JYFL, Finland) RITU and the GREAT
Alpha-energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer (Item No.: P )
 Alpha-energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer (Item No.: P2522015) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: ILIAS Education Level: Physik Topic: Hochschule Subtopic: Moderne Physik Experiment:
Alpha-energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer (Item No.: P2522015) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: ILIAS Education Level: Physik Topic: Hochschule Subtopic: Moderne Physik Experiment:
Alpha-Energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer
 Physical Structure of Matter Radioactivity Alpha-Energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer What you can learn about Decay series Radioactive equilibrium Isotopic properties Decay energy
Physical Structure of Matter Radioactivity Alpha-Energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer What you can learn about Decay series Radioactive equilibrium Isotopic properties Decay energy
Rare isotope beams production using fusion-fission reactions
 Rare isotope beams production using fusion-fission reactions O.B.Tarasov, 1 O.Delaune, 2,a F.Farget, 2 A.M.Amthor, 2,b B.Bastin, 2 D.Bazin, 1 B.Blank, 3 L.Caceres, 2 A.Chbihi, 2 B.Fernandez-Domnguez, 4
Rare isotope beams production using fusion-fission reactions O.B.Tarasov, 1 O.Delaune, 2,a F.Farget, 2 A.M.Amthor, 2,b B.Bastin, 2 D.Bazin, 1 B.Blank, 3 L.Caceres, 2 A.Chbihi, 2 B.Fernandez-Domnguez, 4
An Introduction to the Ion-Optics of Magnet Spectrometers
 An Introduction to the Ion-Optics of Magnet Spectrometers U. Tokyo, RIKEN The 14 th RIBF Nuclear Physics Seminar Series of Three Lectures CNS, University of Tokyo February 27, 2006 Georg P. Berg University
An Introduction to the Ion-Optics of Magnet Spectrometers U. Tokyo, RIKEN The 14 th RIBF Nuclear Physics Seminar Series of Three Lectures CNS, University of Tokyo February 27, 2006 Georg P. Berg University
DEVELOPMENT OF JINR FLNR HEAVY-ION ACCELERATOR COMPLEX IN THE NEXT 7 YEARS
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2010.. 7, º 7(163).. 827Ä834 ˆ ˆŠ ˆ ˆŠ Š ˆ DEVELOPMENT OF JINR FLNR HEAVY-ION ACCELERATOR COMPLEX IN THE NEXT 7 YEARS G. Gulbekyan, B. Gikal, I. Kalagin, N. Kazarinov Joint Institute for Nuclear
Ó³ Ÿ. 2010.. 7, º 7(163).. 827Ä834 ˆ ˆŠ ˆ ˆŠ Š ˆ DEVELOPMENT OF JINR FLNR HEAVY-ION ACCELERATOR COMPLEX IN THE NEXT 7 YEARS G. Gulbekyan, B. Gikal, I. Kalagin, N. Kazarinov Joint Institute for Nuclear
Assembly and test runs of decay detector for ISGMR study. J. Button, R. Polis, C. Canahui, Krishichayan, Y. -W. Lui, and D. H.
 Assembly and test runs of decay detector for ISGMR study J. Button, R. Polis, C. Canahui, Krishichayan, Y. -W. Lui, and D. H. Youngblood 1. ΔE- ΔE - E Plastic Scintillator Array Decay Detector In order
Assembly and test runs of decay detector for ISGMR study J. Button, R. Polis, C. Canahui, Krishichayan, Y. -W. Lui, and D. H. Youngblood 1. ΔE- ΔE - E Plastic Scintillator Array Decay Detector In order
Detectors in Nuclear and High Energy Physics. RHIG summer student meeting June 2014
 Detectors in Nuclear and High Energy Physics RHIG summer student meeting June 2014 Physics or Knowledge of Nature Experimental Data Analysis Theory ( application) Experimental Data Initial Conditions /
Detectors in Nuclear and High Energy Physics RHIG summer student meeting June 2014 Physics or Knowledge of Nature Experimental Data Analysis Theory ( application) Experimental Data Initial Conditions /
Beam Diagnostics and Instrumentation JUAS, Archamps Peter Forck Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschnung (GSI)
 Beam Diagnostics and Instrumentation JUAS, Archamps Peter Forck Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschnung (GSI), 2003, A dedicated proton accelerator for 1p-physics at the future GSI Demands facilities for
Beam Diagnostics and Instrumentation JUAS, Archamps Peter Forck Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschnung (GSI), 2003, A dedicated proton accelerator for 1p-physics at the future GSI Demands facilities for
ORTEC AN34 Experiment 10 Compton Scattering
 EQUIPMENT NEEDED FROM ORTEC 113 Preamplifier (2 ea.) TRUMP-PCI-2K MCA System including suitable PC operating Windows 98/2000/XP (other ORTEC MCAs may be used) 266 Photomultiplier Tube Base (2 ea.) 4001A/4002D
EQUIPMENT NEEDED FROM ORTEC 113 Preamplifier (2 ea.) TRUMP-PCI-2K MCA System including suitable PC operating Windows 98/2000/XP (other ORTEC MCAs may be used) 266 Photomultiplier Tube Base (2 ea.) 4001A/4002D
Kaon Identification at NA62. Institute of Physics Particle, Astroparticle, and Nuclear Physics groups Conference 2015
 Kaon Identification at NA62 Institute of Physics Particle, Astroparticle, and Nuclear Physics groups Conference 2015 Francis Newson April 2015 Kaon Identification at NA62 K πνν NA48 and NA62 K + π + νν
Kaon Identification at NA62 Institute of Physics Particle, Astroparticle, and Nuclear Physics groups Conference 2015 Francis Newson April 2015 Kaon Identification at NA62 K πνν NA48 and NA62 K + π + νν
OPERATION STATUS OF HIGH INTENSITY ION BEAMS AT GANIL
 OPERATION STATUS OF HIGH INTENSITY ION BEAMS AT GANIL F. Chautard, G. Sénécal, GANIL, Caen, France Abstract The Grand Accélérateur National d s Lourds (GANIL, Fig. ) facility (Caen, France) is dedicated
OPERATION STATUS OF HIGH INTENSITY ION BEAMS AT GANIL F. Chautard, G. Sénécal, GANIL, Caen, France Abstract The Grand Accélérateur National d s Lourds (GANIL, Fig. ) facility (Caen, France) is dedicated
SIMULATION OF LASER INDUCED NUCLEAR REACTIONS
 NUCLEAR PHYSICS SIMULATION OF LASER INDUCED NUCLEAR REACTIONS K. SPOHR 1, R. CHAPMAN 1, K. LEDINGHAM 2,3, P. MCKENNA 2,3 1 The Institute of Physical Research, University of Paisley, Paisley PA1 2BE, UK
NUCLEAR PHYSICS SIMULATION OF LASER INDUCED NUCLEAR REACTIONS K. SPOHR 1, R. CHAPMAN 1, K. LEDINGHAM 2,3, P. MCKENNA 2,3 1 The Institute of Physical Research, University of Paisley, Paisley PA1 2BE, UK
Measurement of the n_tof beam profile in the second experimental area (EAR2) using a silicon detector
 Measurement of the n_tof beam profile in the second experimental area (EAR) using a silicon detector Fidan Suljik Supervisors: Dr. Massimo Barbagallo & Dr. Federica Mingrone September 8, 7 Abstract A new
Measurement of the n_tof beam profile in the second experimental area (EAR) using a silicon detector Fidan Suljik Supervisors: Dr. Massimo Barbagallo & Dr. Federica Mingrone September 8, 7 Abstract A new
INITIAL RESULTS OF THE COMMISSIONING OF THE HRIBF RECOIL MASS SPECTROMETER
 INITIAL RESULTS OF THE COMMISSIONING OF THE HRIBF RECOIL MASS SPECTROMETER C. J. Gross Physics Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 37831 and Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education,
INITIAL RESULTS OF THE COMMISSIONING OF THE HRIBF RECOIL MASS SPECTROMETER C. J. Gross Physics Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 37831 and Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education,
Performance of high pressure Xe/TMA in GEMs for neutron and X-ray detection
 Performance of high pressure Xe/TMA in GEMs for neutron and X-ray detection R. Kreuger, C. W. E. van Eijk, Member, IEEE, F. A. F. Fraga, M. M. Fraga, S. T. G. Fetal, R. W. Hollander, Member, IEEE, L. M.
Performance of high pressure Xe/TMA in GEMs for neutron and X-ray detection R. Kreuger, C. W. E. van Eijk, Member, IEEE, F. A. F. Fraga, M. M. Fraga, S. T. G. Fetal, R. W. Hollander, Member, IEEE, L. M.
Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca n
 Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca 297 118 +3n Yu.S.Tsyganov, A.M.Sukhov, A.N.Polyakov Abstract Two decay chains originated from the even-even isotope 294 118 produced in the
Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca 297 118 +3n Yu.S.Tsyganov, A.M.Sukhov, A.N.Polyakov Abstract Two decay chains originated from the even-even isotope 294 118 produced in the
RADIOACTIVITY IN THE AIR
 RADIOACTIVITY IN THE AIR REFERENCES M. Sternheim and J. Kane, General Physics (See the discussion on Half Life) Evans, The Atomic Nucleus, pp. 518-522 Segre, Nuclei and Particles, p. 156 See HEALTH AND
RADIOACTIVITY IN THE AIR REFERENCES M. Sternheim and J. Kane, General Physics (See the discussion on Half Life) Evans, The Atomic Nucleus, pp. 518-522 Segre, Nuclei and Particles, p. 156 See HEALTH AND
N/Z influence on the level density parameter
 EPJ Web of Conferences 88, 00030 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20158800030 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2015 N/Z influence on the level density parameter G. Ademard 1,L.Augey
EPJ Web of Conferences 88, 00030 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20158800030 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2015 N/Z influence on the level density parameter G. Ademard 1,L.Augey
Neutron Structure Functions and a Radial Time Projection Chamber
 Neutron Structure Functions and a Radial Time Projection Chamber Stephen Bültmann Old Dominion University for the BoNuS Collaboration The Structure of the Neutron The BoNuS Experiment at CLAS A New Proton
Neutron Structure Functions and a Radial Time Projection Chamber Stephen Bültmann Old Dominion University for the BoNuS Collaboration The Structure of the Neutron The BoNuS Experiment at CLAS A New Proton
Experimental data analysis at the MASHA setup. Prepared by: Abeer M. Attia Supervisor: Lubos Krupa LOGO. Aleksey Novoselov
 Experimental data analysis at the MASHA setup Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions JINR, Dubna, Russia Prepared by: Abeer M. Attia Supervisor: Lubos Krupa LOGO Aleksey Novoselov Flerov Laboratory of
Experimental data analysis at the MASHA setup Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions JINR, Dubna, Russia Prepared by: Abeer M. Attia Supervisor: Lubos Krupa LOGO Aleksey Novoselov Flerov Laboratory of
High efficiency 3 He neutron detector TETRA for DESIR.
 DESIR workshop, May 2010 High efficiency 3 He neutron detector TETRA for DESIR. Yuri Penionzhkevich Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna Beta Decay of Exotic Nuclei: Goal to study Neutron emission
DESIR workshop, May 2010 High efficiency 3 He neutron detector TETRA for DESIR. Yuri Penionzhkevich Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna Beta Decay of Exotic Nuclei: Goal to study Neutron emission
DUBNA CYCLOTRONS STATUS AND PLANS
 DUBNA CYCLOTRONS STATUS AND PLANS B.N. Gikal *, S.L. Bogomolov, S.N. Dmitriev, G.G. Gulbekyan, M.G. Itkis, V.V. Kalagin, Yu.Ts. Oganessian, V.A. Sokolov Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Moscow
DUBNA CYCLOTRONS STATUS AND PLANS B.N. Gikal *, S.L. Bogomolov, S.N. Dmitriev, G.G. Gulbekyan, M.G. Itkis, V.V. Kalagin, Yu.Ts. Oganessian, V.A. Sokolov Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Moscow
Calibration of the Modular Neutron Array (MoNA)
 Calibration of the Modular Neutron Array (MoNA) Robert Pepin Gonzaga University ~1~ Calibration of the Modular Neutron Array (MoNA): Figure 1 - A rendering of the Modular Neutron Array In recent years
Calibration of the Modular Neutron Array (MoNA) Robert Pepin Gonzaga University ~1~ Calibration of the Modular Neutron Array (MoNA): Figure 1 - A rendering of the Modular Neutron Array In recent years
Progress in measuring GMR in unstable nuclei: Decay detector calibration and inverse reaction experiment. J. Button, Y.-W. Lui, and D.H.
 Progress in measuring GMR in unstable nuclei: Decay detector calibration and inverse reaction experiment J. Button, Y.-W. Lui, and D.H. Youngblood I. Introduction The Giant Monopole Resonance (GMR) is
Progress in measuring GMR in unstable nuclei: Decay detector calibration and inverse reaction experiment J. Button, Y.-W. Lui, and D.H. Youngblood I. Introduction The Giant Monopole Resonance (GMR) is
The experiment at JINR: status and physics program
 The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
Joint Institute for Nuclear Research. Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions. University Center LABORATORY WORK
 Joint Institute for Nuclear Research Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions University Center LABORATORY WORK TOF measurement of the charged particles using the MCP detector Supervisor: Dauren Aznabayev
Joint Institute for Nuclear Research Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions University Center LABORATORY WORK TOF measurement of the charged particles using the MCP detector Supervisor: Dauren Aznabayev
SYNTHESIS OF SUPERHEAVY ELEMENTS USING THE MASS SPECTROMETER MASHA
 SYNTHESIS OF SUPERHEAVY ELEMENTS USING THE MASS SPECTROMETER MASHA Students Timofei Tikhomirov - RB Kevin Li - RSA Alesya Lebedevich - RB Maurice Mashau - RSA Supervisor Krupa Lubosh Flerov Laboratiory
SYNTHESIS OF SUPERHEAVY ELEMENTS USING THE MASS SPECTROMETER MASHA Students Timofei Tikhomirov - RB Kevin Li - RSA Alesya Lebedevich - RB Maurice Mashau - RSA Supervisor Krupa Lubosh Flerov Laboratiory
MEASUREMENT AND DETECTION OF RADIATION
 MEASUREMENT AND DETECTION OF RADIATION Second Edition Nicholas Tsoulfanidis University of Missouri-Rolla Ж Taylor &Francis * Publishers since I79H CONTENTS Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second
MEASUREMENT AND DETECTION OF RADIATION Second Edition Nicholas Tsoulfanidis University of Missouri-Rolla Ж Taylor &Francis * Publishers since I79H CONTENTS Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second
Equalisation of the PMT response to charge particles for the Lucid detector of the ATLAS experiment
 Equalisation of the PMT response to charge particles for the Lucid detector of the ATLAS experiment Camilla Vittori Department of Physics, University of Bologna, Italy Summer Student Program 2014 Supervisor
Equalisation of the PMT response to charge particles for the Lucid detector of the ATLAS experiment Camilla Vittori Department of Physics, University of Bologna, Italy Summer Student Program 2014 Supervisor
DSSSD based Spectrometer of the Dubna Gas-Filled Recoil Separator
 DSSSD based Spectrometer of Dubna Gas-Filled Recoil Separator Yury S. Tsyganov Abstract Recently, in DGFRS related experiments discoveries of new superheavy elements Z=114-118 were successfully performed.
DSSSD based Spectrometer of Dubna Gas-Filled Recoil Separator Yury S. Tsyganov Abstract Recently, in DGFRS related experiments discoveries of new superheavy elements Z=114-118 were successfully performed.
A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Status of the magnetic spectrometer PRISMA
 Status of the magnetic spectrometer PRISMA E. Fioretto INFN Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro 1 PRISMA in vacuum mode Dipole 50 cm 120 cm 60 +130 Quadrupole 30 cm Beam Target 2-20 Rotating platform PRISMA:
Status of the magnetic spectrometer PRISMA E. Fioretto INFN Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro 1 PRISMA in vacuum mode Dipole 50 cm 120 cm 60 +130 Quadrupole 30 cm Beam Target 2-20 Rotating platform PRISMA:
7. Particle identification
 7. Particle identification in general, momentum of a particle measured in a spectrometer and another observable is used to identity the species velocity time-of-flight Cherenkov threshold transition radiation
7. Particle identification in general, momentum of a particle measured in a spectrometer and another observable is used to identity the species velocity time-of-flight Cherenkov threshold transition radiation
Measurement of Beam Profile
 Measurement of Beam Profile The beam width can be changed by focusing via quadruples. Transverse matching between ascending accelerators is done by focusing. Profiles have to be controlled at many locations.
Measurement of Beam Profile The beam width can be changed by focusing via quadruples. Transverse matching between ascending accelerators is done by focusing. Profiles have to be controlled at many locations.
Optimization of the SIS100 Lattice and a Dedicated Collimation System for Ionisation Losses
 Optimization of the SIS100 Lattice and a Dedicated Collimation System for Ionisation Losses P. Spiller, K. Blasche, B. Franczak, J. Stadlmann, and C. Omet GSI Darmstadt, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract:
Optimization of the SIS100 Lattice and a Dedicated Collimation System for Ionisation Losses P. Spiller, K. Blasche, B. Franczak, J. Stadlmann, and C. Omet GSI Darmstadt, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract:
Fission Fragment characterization with FALSTAFF at NFS
 EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 01001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134201001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Fission characterization with FALSTAFF at NFS D. Doré 1, F. Farget 2,
EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 01001 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134201001 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Fission characterization with FALSTAFF at NFS D. Doré 1, F. Farget 2,
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 9 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 9 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 9 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/113031417.jpg) Improvement of charge resolution for radioactive heavy ions at relativistic energies using a hybrid detector system J.W. Zhao a, B.H. Sun a,b,c,, L.C. He a, G.S. Li a, W.J. Lin a, C.Y. Liu a, Z. Liu d,
Improvement of charge resolution for radioactive heavy ions at relativistic energies using a hybrid detector system J.W. Zhao a, B.H. Sun a,b,c,, L.C. He a, G.S. Li a, W.J. Lin a, C.Y. Liu a, Z. Liu d,
Experiment for synthesis of neutrondeficient
 Experiment for synthesis of neutrondeficient isotopes Hua Bin Yang ( 杨华彬 ) Institute of modern Physics, CAS Tutored by Professor Zai Guo Gan ( 甘再国 ) Outline Motivation @ Estimation Experimental purposes
Experiment for synthesis of neutrondeficient isotopes Hua Bin Yang ( 杨华彬 ) Institute of modern Physics, CAS Tutored by Professor Zai Guo Gan ( 甘再国 ) Outline Motivation @ Estimation Experimental purposes
arxiv: v2 [nucl-ex] 6 Oct 2008
![arxiv: v2 [nucl-ex] 6 Oct 2008 arxiv: v2 [nucl-ex] 6 Oct 2008](/thumbs/88/114593371.jpg) he ime Projection Chamber for the ALICE Experiment C. Lippmann and the ALICE PC Collaboration CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland he ime Projection Chamber of the ALICE Experiment has been installed in the
he ime Projection Chamber for the ALICE Experiment C. Lippmann and the ALICE PC Collaboration CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland he ime Projection Chamber of the ALICE Experiment has been installed in the
Investigation of nuclear Equation of State (EoS) is an attractive subject not only for nuclear
 First Experiment of SπRIT-TPC at SAMURAI in RIKEN-RIBF for SπRIT Collaboration RIKEN, Nishina Center, RIKEN, Japan E-mail: mizuki@riken.jp Investigation of nuclear Equation of State (EoS) is an attractive
First Experiment of SπRIT-TPC at SAMURAI in RIKEN-RIBF for SπRIT Collaboration RIKEN, Nishina Center, RIKEN, Japan E-mail: mizuki@riken.jp Investigation of nuclear Equation of State (EoS) is an attractive
REFERENCE SOURCES FOR THE CALIBRATION OF THE AUTOCORRELATION SINGLE-CRYSTAL SCINTILLATION TIME SPECTROMETER
 REFERENCE SOURCES FOR THE CALIBRATION OF THE AUTOCORRELATION SINGLE-CRYSTAL SCINTILLATION TIME SPECTROMETER V.A. MOROZOV 1, N.V. MOROZOVA 1, T. BĂDICĂ 2, D. DELEANU 2,3, D. GHIŢĂ 2, S. PASCU 2,3 1 Joint
REFERENCE SOURCES FOR THE CALIBRATION OF THE AUTOCORRELATION SINGLE-CRYSTAL SCINTILLATION TIME SPECTROMETER V.A. MOROZOV 1, N.V. MOROZOVA 1, T. BĂDICĂ 2, D. DELEANU 2,3, D. GHIŢĂ 2, S. PASCU 2,3 1 Joint
Appendix A2. Particle Accelerators and Detectors The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Geneva, Switzerland on the Border of France.
 Appendix A. Particle Accelerators and Detectors The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Geneva, Switzerland on the Border of France. Prepared by: Arash Akbari-Sharbaf Why Build Accelerators? Probe deeper From
Appendix A. Particle Accelerators and Detectors The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Geneva, Switzerland on the Border of France. Prepared by: Arash Akbari-Sharbaf Why Build Accelerators? Probe deeper From
Particle Energy Loss in Matter
 Particle Energy Loss in Matter Charged particles, except electrons, loose energy when passing through material via atomic excitation and ionization These are protons, pions, muons, The energy loss can
Particle Energy Loss in Matter Charged particles, except electrons, loose energy when passing through material via atomic excitation and ionization These are protons, pions, muons, The energy loss can
Examples for experiments that can be done at the T9 beam line
 Examples for experiments that can be done at the T9 beam line Example 1: Use muon tomography to look for hidden chambers in pyramids (2016 winning proposal, Pyramid hunters) You may know computer tomography
Examples for experiments that can be done at the T9 beam line Example 1: Use muon tomography to look for hidden chambers in pyramids (2016 winning proposal, Pyramid hunters) You may know computer tomography
BEAM BEAM. cathode anode cathode
 High-rate axial-field ioniza2on chamber for par2cle iden2fica2on of radioac2ve beams, J. Vadas, Varinderjit Singh, G. Visser, A. Alexander, J. Huston, B.B. Wiggins, A. Chbihi, M. Famiano, M. Bischak To
High-rate axial-field ioniza2on chamber for par2cle iden2fica2on of radioac2ve beams, J. Vadas, Varinderjit Singh, G. Visser, A. Alexander, J. Huston, B.B. Wiggins, A. Chbihi, M. Famiano, M. Bischak To
Bolometry. H. Kroegler Assciazione Euratom-ENEA sulla Fusione, Frascati (Italy)
 Bolometry H. Kroegler Assciazione Euratom-ENEA sulla Fusione, Frascati (Italy) Revised May 28, 2002 1. Radiated power Time and space resolved measurements of the total plasma radiation can be done by means
Bolometry H. Kroegler Assciazione Euratom-ENEA sulla Fusione, Frascati (Italy) Revised May 28, 2002 1. Radiated power Time and space resolved measurements of the total plasma radiation can be done by means
Tracking properties of the ATLAS Transition Radiation Tracker (TRT)
 2 racking properties of the ALAS ransition Radiation racker (R) 3 4 5 6 D V Krasnopevtsev on behalf of ALAS R collaboration National Research Nuclear University MEPhI (Moscow Engineering Physics Institute),
2 racking properties of the ALAS ransition Radiation racker (R) 3 4 5 6 D V Krasnopevtsev on behalf of ALAS R collaboration National Research Nuclear University MEPhI (Moscow Engineering Physics Institute),
«Analysis at GANIL»
 «Analysis at GANIL» AGATA@VAMOS Outline o o AGATA @ Ganil - AGATA@VAMOS - Gamma ray spectroscopy around the Coulomb barrier VAMOS : large acceptance spectrometer - VAMOS detection setup - Detection what
«Analysis at GANIL» AGATA@VAMOS Outline o o AGATA @ Ganil - AGATA@VAMOS - Gamma ray spectroscopy around the Coulomb barrier VAMOS : large acceptance spectrometer - VAMOS detection setup - Detection what
Calorimetry in particle physics experiments
 Calorimetry in particle physics experiments Unit N. 9 The NA48 ECAL example (LKR) Roberta Arcidiacono R. Arcidiacono Calorimetry 1 Lecture overview The requirements Detector layout & construction Readout
Calorimetry in particle physics experiments Unit N. 9 The NA48 ECAL example (LKR) Roberta Arcidiacono R. Arcidiacono Calorimetry 1 Lecture overview The requirements Detector layout & construction Readout
GEM at CERN. Leszek Ropelewski CERN PH-DT2 DT2-ST & TOTEM
 GEM at CERN Leszek Ropelewski CERN PH-DT2 DT2-ST & TOTEM MicroStrip Gas Chamber Semiconductor industry technology: Photolithography Etching Coating Doping A. Oed Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A263 (1988) 351.
GEM at CERN Leszek Ropelewski CERN PH-DT2 DT2-ST & TOTEM MicroStrip Gas Chamber Semiconductor industry technology: Photolithography Etching Coating Doping A. Oed Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A263 (1988) 351.
Tracking at the LAND/R B setup on 17
 3 Tracking at the LAND/R B setup on 17 the example of Ne(γ,2p)15O R. Plag*, J. Marganiec 21. Januar 2011 Dedicated to the students of LAND/R3B Outline rp process and motivation coulomb dissociation as
3 Tracking at the LAND/R B setup on 17 the example of Ne(γ,2p)15O R. Plag*, J. Marganiec 21. Januar 2011 Dedicated to the students of LAND/R3B Outline rp process and motivation coulomb dissociation as
Nuclear Physics at the Lanzhou Storage Ring
 Nuclear Physics at the Lanzhou Storage Ring M.Wang, H.S.Xu, Y.H.Zhang, X.L.Tu, X.W.Ma Institute of Modern Physics, CAS, 730000 Lanzhou, China Since the last conference stori 08, progresses have been made
Nuclear Physics at the Lanzhou Storage Ring M.Wang, H.S.Xu, Y.H.Zhang, X.L.Tu, X.W.Ma Institute of Modern Physics, CAS, 730000 Lanzhou, China Since the last conference stori 08, progresses have been made
Direct and β-delayed multi-proton emission from atomic nuclei with a time projection chamber: the cases of 43 Cr, 45 Fe, and 51 Ni
 Eur. Phys. J. A () 8: 79 DOI./epja/i-79- Regular Article Experimental Physics THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL A Direct and β-delayed multi-proton emission from atomic nuclei with a time projection chamber:
Eur. Phys. J. A () 8: 79 DOI./epja/i-79- Regular Article Experimental Physics THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL A Direct and β-delayed multi-proton emission from atomic nuclei with a time projection chamber:
ALICE A Large Ion Collider Experiment
 ALICE A Large Ion Collider Experiment Purpose: study the physics of strongly interacting matter at extreme energy densities CERN LHC: Colliding Pb ions at E CM =5.5 A TeV, p-p, light ions collisions 84
ALICE A Large Ion Collider Experiment Purpose: study the physics of strongly interacting matter at extreme energy densities CERN LHC: Colliding Pb ions at E CM =5.5 A TeV, p-p, light ions collisions 84
Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon
 Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon Mohammad QH 1* and Maghdid HA 2 1 Department of Physics, College of Science, Raparin University, Sulaimanyah, Iraqi Kurdistan, Iraq 2 Department of Physics,
Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon Mohammad QH 1* and Maghdid HA 2 1 Department of Physics, College of Science, Raparin University, Sulaimanyah, Iraqi Kurdistan, Iraq 2 Department of Physics,
Alpha-Gamma discrimination by Pulse Shape in LaBr 3 :Ce and LaCl 3 :Ce
 Alpha-Gamma discrimination by Pulse Shape in LaBr 3 :Ce and LaCl 3 :Ce F.C.L. Crespi 1,2, F.Camera 1,2, N. Blasi 2, A.Bracco 1,2, S. Brambilla 2, B. Million 2, R. Nicolini 1,2, L.Pellegri 1, S. Riboldi
Alpha-Gamma discrimination by Pulse Shape in LaBr 3 :Ce and LaCl 3 :Ce F.C.L. Crespi 1,2, F.Camera 1,2, N. Blasi 2, A.Bracco 1,2, S. Brambilla 2, B. Million 2, R. Nicolini 1,2, L.Pellegri 1, S. Riboldi
Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment
 Simone Valdré Grand Accélérateur National d Ions Lourds Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment Nusym 2017 GANIL, Maison d hôtes September 7 th, 2017 ISOFAZIA experiment at LNS Aim of this work Study
Simone Valdré Grand Accélérateur National d Ions Lourds Recent results from the ISOFAZIA experiment Nusym 2017 GANIL, Maison d hôtes September 7 th, 2017 ISOFAZIA experiment at LNS Aim of this work Study
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NEUTRON FIELDS PRODUCED IN PROTON REACTIONS WITH HEAVY TARGETS. Nuclear Physics Institute AS CR, Rez Czech Republic
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NEUTRON FIELDS PRODUCED IN PROTON REACTIONS WITH HEAVY TARGETS A. Kugler, V. Wagner Nuclear Physics Institute AS CR, 25068 Rez Czech Republic I. Introduction One of important aspects
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NEUTRON FIELDS PRODUCED IN PROTON REACTIONS WITH HEAVY TARGETS A. Kugler, V. Wagner Nuclear Physics Institute AS CR, 25068 Rez Czech Republic I. Introduction One of important aspects
Development of Ring-Imaging Cherenkov Counter for Heavy Ions
 Development of Ring-Imaging Cherenkov Counter for Heavy Ions Masahiro Machida Tokyo University of Science New Facilities and Instrumentation INPC 2016 Collaborators 2 Tokyo University of Science M. Machida,
Development of Ring-Imaging Cherenkov Counter for Heavy Ions Masahiro Machida Tokyo University of Science New Facilities and Instrumentation INPC 2016 Collaborators 2 Tokyo University of Science M. Machida,
Radioactivity at the limits of nuclear existence
 Radioactivity at the limits of nuclear existence Zenon Janas Institute of Experimental Physics University of Warsaw Chart of nuclei - stable - β + - β - - α - fission - p p and 2p radioactivty proton radioactivity
Radioactivity at the limits of nuclear existence Zenon Janas Institute of Experimental Physics University of Warsaw Chart of nuclei - stable - β + - β - - α - fission - p p and 2p radioactivty proton radioactivity
Fission-yield data. Karl-Heinz Schmidt
 Fission-yield data Karl-Heinz Schmidt Topical day From nuclear data to a reliable estimate of spent fuel decay heat October 26, 2017 SCK CEN Lakehouse, Mol, Belgium Lay out Introduction Stages of the fission
Fission-yield data Karl-Heinz Schmidt Topical day From nuclear data to a reliable estimate of spent fuel decay heat October 26, 2017 SCK CEN Lakehouse, Mol, Belgium Lay out Introduction Stages of the fission
A Measurement of Monoenergetic Neutrons from 9 Be(p,n) 9 B
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, No. 4, April 1998, pp. 462 467 A Measurement of Monoenergetic Neutrons from 9 Be(p,n) 9 B J. H. Kim, H. Bhang, J. H. Ha, J. C. Kim, M. J. Kim, Y. D. Kim
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, No. 4, April 1998, pp. 462 467 A Measurement of Monoenergetic Neutrons from 9 Be(p,n) 9 B J. H. Kim, H. Bhang, J. H. Ha, J. C. Kim, M. J. Kim, Y. D. Kim
The Island of of Inversion from a nuclear moments perspective
 The Island of of Inversion from a nuclear moments perspective Gerda Neyens Instituut voor Kern- en Stralingsfysica, K.U. Leuven, Belgium the LISE-NMR collaboration @ GANIL: E437 (,32,33 g-factors) E437a
The Island of of Inversion from a nuclear moments perspective Gerda Neyens Instituut voor Kern- en Stralingsfysica, K.U. Leuven, Belgium the LISE-NMR collaboration @ GANIL: E437 (,32,33 g-factors) E437a
GEM: A new concept for electron amplification in gas detectors
 GEM: A new concept for electron amplification in gas detectors F. Sauli, Nucl. Instr. & Methods in Physics Research A 386 (1997) 531-534 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Two-step amplification: MWPC combined
GEM: A new concept for electron amplification in gas detectors F. Sauli, Nucl. Instr. & Methods in Physics Research A 386 (1997) 531-534 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Two-step amplification: MWPC combined
Mass Determination of Rn and Hg isotopes using MASHA
 Mass Determination of Rn and Hg isotopes using MASHA Alfred M. Sehone Lumkile Msebi Oleg Lishyk Stanislav Stanishevski Yuliya Brechko Supervisor Krupa Lubosh Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear reactions, JINR,
Mass Determination of Rn and Hg isotopes using MASHA Alfred M. Sehone Lumkile Msebi Oleg Lishyk Stanislav Stanishevski Yuliya Brechko Supervisor Krupa Lubosh Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear reactions, JINR,
The neutron multiplicity study at spontaneous fission of short-lived isotopes (z > 100) using VASSILISSA recoil separator
 The neutron multiplicity study at spontaneous fission of short-lived isotopes (z > 100) using VASSILISSA recoil separator Svirikhin A.I. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia Manipal University,
The neutron multiplicity study at spontaneous fission of short-lived isotopes (z > 100) using VASSILISSA recoil separator Svirikhin A.I. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia Manipal University,
Fig. 1 Sketch of the experimental setup for PFN investigation.
 1) Title Prompt Fission Neutron Investigation with Frisch-gridded Twin Back-to-back Ionization Chamber. 2) Introduction Modern models consider the nuclear fission process as a result of competition between
1) Title Prompt Fission Neutron Investigation with Frisch-gridded Twin Back-to-back Ionization Chamber. 2) Introduction Modern models consider the nuclear fission process as a result of competition between
The Alice Experiment Felix Freiherr von Lüdinghausen
 The Alice Experiment Felix Freiherr von Lüdinghausen Alice, who is Alice? Alice is A Large Ion Collider Experiment. Worldwide hit in 1977 for the band Smokie Alice is the dedicated heavy ion experiment
The Alice Experiment Felix Freiherr von Lüdinghausen Alice, who is Alice? Alice is A Large Ion Collider Experiment. Worldwide hit in 1977 for the band Smokie Alice is the dedicated heavy ion experiment
First lifetime measurements in the 78 Ni region with AGATA and VAMOS at GANIL
 First lifetime measurements in the 78 Ni region with AGATA and VAMOS at GANIL Clément Delafosse Institut de Physique Nucléaire d Orsay for the E669 collaboration Colloque GANIL 2017 - Amboise Physics motivation
First lifetime measurements in the 78 Ni region with AGATA and VAMOS at GANIL Clément Delafosse Institut de Physique Nucléaire d Orsay for the E669 collaboration Colloque GANIL 2017 - Amboise Physics motivation
Radioactivity and Ionizing Radiation
 Radioactivity and Ionizing Radiation QuarkNet summer workshop June 24-28, 2013 1 Recent History Most natural phenomena can be explained by a small number of simple rules. You can determine what these rules
Radioactivity and Ionizing Radiation QuarkNet summer workshop June 24-28, 2013 1 Recent History Most natural phenomena can be explained by a small number of simple rules. You can determine what these rules
FARCOS Femtoscope Array for Correlations & Spectroscopy
 FARCOS Femtoscope Array for Correlations & Spectroscopy Overview of project and physics inputs Present status (mechanics, electronics) and perspectives for the use with GET electronics G. Cardella, INFN-Catania
FARCOS Femtoscope Array for Correlations & Spectroscopy Overview of project and physics inputs Present status (mechanics, electronics) and perspectives for the use with GET electronics G. Cardella, INFN-Catania
Angular and energy distributions of the prompt fission neutrons from thermal neutron-induced fission of 239 Pu
 Angular and energy distributions of the prompt fission neutrons from thermal neutron-induced fission of 239 Pu Vorobyev AS, Shcherbakov OA, Gagarski AM, Val ski GV, Petrov GA National Research Center Kurchatov
Angular and energy distributions of the prompt fission neutrons from thermal neutron-induced fission of 239 Pu Vorobyev AS, Shcherbakov OA, Gagarski AM, Val ski GV, Petrov GA National Research Center Kurchatov
Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor To cite this article: T Ino et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 528 012039 View the article
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor To cite this article: T Ino et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 528 012039 View the article
PANDA Muon System Prototype
 PANDA Muon System Prototype Victor Abazov 1, Gennady Alexeev 1, Maxim Alexeev 2, Vladimir Frolov 1, Georgy Golovanov 1, Sergey Kutuzov 1, Alexei Piskun 1, Alexander Samartsev 1, Valeri Tokmenin 1, Alexander
PANDA Muon System Prototype Victor Abazov 1, Gennady Alexeev 1, Maxim Alexeev 2, Vladimir Frolov 1, Georgy Golovanov 1, Sergey Kutuzov 1, Alexei Piskun 1, Alexander Samartsev 1, Valeri Tokmenin 1, Alexander
Research related to Geant4 in Korea Heavy-Ion Medical Accelerator
 Research related to Geant4 in Korea Heavy-Ion Medical Accelerator for Cyclotron Based Carbon Therapy Facility Garam Hahn(garam@kirams.re.kr), Beam Physics Team KIRAMS 2012.12.15 Introduction KHIMA(Korea
Research related to Geant4 in Korea Heavy-Ion Medical Accelerator for Cyclotron Based Carbon Therapy Facility Garam Hahn(garam@kirams.re.kr), Beam Physics Team KIRAMS 2012.12.15 Introduction KHIMA(Korea
Exotic Nuclei II. Neutron-rich nuclides. Michael Thoennessen FRIB/NSCL Michigan State University
 Exotic Nuclei II Neutron-rich nuclides Michael Thoennessen FRIB/NSCL Michigan State University Most neutron-rich nuclides N/Z = 1 n X not a nuclide but a nucleon N/Z = 3 8 He 11 Li: N/Z = 2.67 N/Z = 3
Exotic Nuclei II Neutron-rich nuclides Michael Thoennessen FRIB/NSCL Michigan State University Most neutron-rich nuclides N/Z = 1 n X not a nuclide but a nucleon N/Z = 3 8 He 11 Li: N/Z = 2.67 N/Z = 3
STATUS REPORT ON SPIRAL1 F. Chautard October 2 nd, 2007
 STATUS REPORT ON SPIRAL1 F. Chautard October 2 nd, 2007 Assessment of GANIL/SPIRAL operation Technical achievements Present R&D Possible developments SPIRAL: Radioactive ion beams with «ISOL» method since
STATUS REPORT ON SPIRAL1 F. Chautard October 2 nd, 2007 Assessment of GANIL/SPIRAL operation Technical achievements Present R&D Possible developments SPIRAL: Radioactive ion beams with «ISOL» method since
Performance of the ALICE Muon Trigger system in Pb Pb collisions
 Performance of the ALICE Muon Trigger system in Pb Pb collisions, for the ALICE collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica Sperimentale dell Università di Torino and Sezione INFN di Torino, Turin, Italy Laboratoire
Performance of the ALICE Muon Trigger system in Pb Pb collisions, for the ALICE collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica Sperimentale dell Università di Torino and Sezione INFN di Torino, Turin, Italy Laboratoire
NSCL and Physics and Astronomy Department, Michigan State University Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics
 National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory An overview Ana D. Becerril NSCL and Physics and Astronomy Department, Michigan State University Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics University of North
National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory An overview Ana D. Becerril NSCL and Physics and Astronomy Department, Michigan State University Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics University of North
Beam diagnostics: Alignment of the beam to prevent for activation. Accelerator physics: using these sensitive particle detectors.
 Beam Loss Monitors When energetic beam particles penetrates matter, secondary particles are emitted: this can be e, γ, protons, neutrons, excited nuclei, fragmented nuclei... Spontaneous radiation and
Beam Loss Monitors When energetic beam particles penetrates matter, secondary particles are emitted: this can be e, γ, protons, neutrons, excited nuclei, fragmented nuclei... Spontaneous radiation and
SPIRAL 2 Commissioning Status
 SPIRAL 2 Commissioning Status Jean-Michel Lagniel (GANIL) for the SPIRAL 2 Team With thanks to the SPIRAL 2 team Page 1 Menu 1- SPIRAL 2 facility (Phase 1) presentation 2- Injector commisionning (Sources
SPIRAL 2 Commissioning Status Jean-Michel Lagniel (GANIL) for the SPIRAL 2 Team With thanks to the SPIRAL 2 team Page 1 Menu 1- SPIRAL 2 facility (Phase 1) presentation 2- Injector commisionning (Sources
