Investigation of damage mechanisms of polymer concrete: Multivariable analysis based on temporal features extracted from acoustic emission signals
|
|
|
- Hannah Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Investigation of damage mechanisms of polymer concrete: Multivariable analysis based on temporal features extracted from acoustic emission signals Anne MAREC, Rachid BERBAOUI, Jean-Hugh TOMAS, Abderrahim EL MAHI, Rachid EL GUERJOUMA. LAUM, CNRS, Université du Maine, Avenue Olivier Messiaen, Le Mans Cedex 9, France Abstract The aim of this work is to identify and characterize the local damage in polymer concrete materials with the use of acoustic emission (AE). Polymer concrete materials are complex composites which damage and time-to-failure mechanisms still require a better understanding. The damage investigation in those materials is reached with the analysis of acoustic emission signals collected from static three point bending tests. Unsupervised pattern recognition analyses (fuzzy C-means clustering) associated with a principal component analysis are used for the classification of AE events. As few studies are reported in these materials, several model concrete samples are experimented in order to match each cluster with the corresponding damage mechanism of the material under investigation. This method provides the time dependency of each identified damage mechanism as a function of test time. We show through this approach that it is possible, using AE, to identify the most critical damage mechanisms leading to the final failure of the material. The possibility of assessing time to failure of the tested samples from AE is also investigated. Résumé Notre travail est dédié à l étude de l endommagement d un béton polymère au cours d essais statiques en flexion trois points. Notre contribution consiste à caractériser l endommagement par émission acoustique (EA), à identifier les signatures acoustiques des mécanismes d endommagement intervenant dans le matériau, à suivre l évolution de ces différents mécanismes au cours du temps et à identifier les plus critiques conduisant à la rupture du matériau. Différents échantillons de matériaux modèles (résine pure, résine-sable, résine-agrégats) et béton polymère (résine-sables-agrégats) sont considérés. Des techniques d analyse statistique multivariable (méthode de coalescence floue et analyse en composantes principales) sont utilisées afin de distinguer les signaux correspondants aux différents modes d'endommagement des matériaux. Les différents mécanismes d endommagement dans les matériaux (microfissuration de la résine, décohésion résine-agrégats et rupture d agrégats) sont identifiés en isolant des signaux d émission acoustique caractéristiques. Les premiers résultats obtenus sur ces matériaux complexes sont très encourageants, ils permettent de discriminer les différents mécanismes d endommagement et d identifier les plus critiques menant à la rupture final du matériau à partir de l analyse par l EA. Keywords Concrete Polymer, damage, acoustic emission, fracture.
2 1 Introduction Resin or polymer concrete possesses higher strength, higher ductility than conventional concrete. While their mechanical behaviour is mostly well known, their damage and time-tofailure mechanisms still require a better understanding. One of the aims of this paper is to identify the different damage mechanisms occurring in these materials and to estimate their remaining lifetime in a non destructive way. Acoustic Emission (AE), which represents the generation of transient ultrasonic waves in a material under load, is a useful tool that can be used in situ for structural health monitoring. One of the main issues of AE is to discriminate the different damage mechanisms from the detected AE signals. Most studies so far have used AE descriptors such as the amplitude and the energy of the signal to characterize the development of damage [1-3]. Each signal can be associated to a pattern composed of multiple relevant descriptors. Then the patterns can be divided into clusters representative of damage mechanisms according to their similarity by the use of multivariable data analyses based on pattern recognition algorithms [4]. As it is not possible to know exactly the origin of an emitted event and then to provide a training set of patterns belonging to several composite damage mechanisms, unsupervised pattern recognition is sometimes used with the problem of labelling the clusters [4]. Godin and al. [5] use this approach for clustering AE events with a Kohonen s neural network associated with the k-means algorithm. They obtain interesting results on unidirectional fiber-matrix and cross-ply composites AE data during tensile tests. However, it is less effective for complex composite materials such polymer concrete for instance. In order to improve the classification process for these complex materials, fuzzy C- means clustering [6] associated with a principal component analysis (PCA) are proposed in this paper. 2 Materials and tests The test specimens were constituted of polymer concrete. The matrix was made of epoxy resin and fine sand of average diameter equal to 0.4 mm, with a volume fraction of sand equal to 40%. The aggregates were of average diameter equal to 2 mm with a volume fraction of 30% (volume fraction of the matrix equal to 70%). The three-point bending tests are performed using an Instron 8500 Digital Servo hydraulic testing system. The specimen dimensions are 15 x 40 x 160 mm, as shown in Fig mm 160 mm Figure 1. Geometry of specimen and position of transducers A two channels EPA Acoustic Emission device is used. AE measurements are achieved by the means of two resonant Micro-80 sensors with a frequency band 100 khz - 1 MHz and a peak of resonance around 300 khz, coupled on the faces of the specimens with silicon grease. The calibration of each test uses a pencil lead break procedure in order to generate repeatable AE signals. Several time-based descriptors are calculated by the acquisition system for each AE event: the amplitude, the energy, the duration, the rise time, the number of times the amplitude of the event goes beyond the given amplitude threshold (called counts)... These collected parameters are used as input descriptors in the proposed classification method. 3 Multivariable data clustering of Acoustic Emission signals
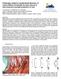
3 Each AE signal can be associated to a pattern composed of multiple relevant features extracted from the random AE waveforms such as the amplitude of the signal, its energy, etc. Thus, the d time-based parameters collected from n AE waveforms are the components of the n input pattern vectors used for the classification. Then the patterns can be divided into clusters representative of damage mechanisms according to their similarity with the use of multivariable data analyses based on pattern recognition algorithms. As it is not possible to know exactly the origin of an emitted event and then to provide a training set of patterns belonging to several composite damage mechanisms, unsupervised pattern recognition analyses, which provide a multidimensional data classification, are used with the problem of labeling the clusters. Here the Fuzzy C-means Clustering Method (FCM) [2,3,4] is used for the automatic classification into M classes representative of M damage mechanisms. It uses fuzzy partitioning so that each pattern vector x j (j=1,n) can belong to each cluster ωi (i=1,m) with different membership grades u i (x j ) between 0 and 1, which represents the membership value of the j th pattern vector x j to the cluster ωi. FCM is an iterative algorithm which runs with the steps presented in table 3. By iteratively updating the cluster centers and the membership grades for each pattern, FCM iteratively moves the cluster centers to the right location within the data set. The FCM is associated with a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) [5,6]. The basic goal in PCA is to reduce the dimension of the data. PCA is also used here to visualize the clusters provided by the automatic classification performed with the FCM. The proposed method permits to identify the damage mechanisms and to follow the time development of each damage mechanism till the final global fracture of the sample. Table 1. Fuzzy C-means Clustering algorithm. Data - n input pattern vectors x j (j=1,n) Parameters - M clusters ωi (i=1,m) - q iteration steps - Fuzzy degree f (f=2) - Threshold ε (0 < ε < 1), which defines the number of q iterations Initialization - Randomly initialization of membership matrix with values (in [0,1]) that represent the membership values u i (x j ) of the n patterns x j (j=1,n) to each cluster ωi (i=1,m) Iterations n f [ u ] j= i ( x j ) x 1 j - Calculation of cluster centers C i : Ci = n f u ( x ) j= 1 [ ] - Calculation of Euclidean distance d(x j,c i ) between the pattern vector x j and the cluster center C i - Calculation of membership matrix U : 1 2 /( 1) (, ) ( ) = M f d x j Ci u i x j k= 1 (, ) d x j Ck - Iterations until the improvement over the previous iteration is below ε : U q U q 1 < ε i j 4 Results and discussion In this material, three damage mechanisms can potentially occur within the material: matrix cracking, interfacial decohesion, gravel failure. The fuzzy C-means clustering method is applied to the actual material with three clusters that potentially correspond to the three damage mechanisms. The five descriptors used are the energy, the amplitude, the rise time, the counts and the duration of the signals. A PCA is achieved in order to visualize the results
4 in a two-dimension subspace. The results are presented in figure 2 with the three identified clusters : A signal, B signals and C signals. The three families are well separated and discriminated. In order to identify precisely the mechanisms and to put in front of each AE signature a damage mechanism, we have considered in what follows some model materials in three points bending tests, starting from the pure resin and finishing by the actual concrete in order to match each cluster with the corresponding damage mechanism. Another point to clear concern the interface decohesion. While the matrix contains sand and gravel it is important to study the possibility to discriminate the two associated damage mechanisms (matrix sand decohesion and matrix gravel decohesion). Figure 2. : PCA visualization of the fuzzy C-means clustering (94% information kept) of three points bending tests on synthetic concretes. A signal is representative of matrix cracking, B signal of matrix gravel decohesion and C signal of gravel failure 4.1 Pure resin: Samples of pure resin were considered in a three points bending test. The aim of this experiment is to identify the signals corresponding to matrix cracking. Indeed, one type of signals is observed in this test with the amplitude range db, with waveform features similar to those of the cluster 1 (Fig. 3). Thus, the patterns of cluster 1 are built from signals similar to A signals which correspond to matrix cracking. Therefore, cluster 1 is representative of matrix cracking. a b Figure 3. a) AE Amplitude distribution for pure resin concretes, b) Corresponding detected signals: A signal (matrix cracking). 4.2 Gravel and resin concretes (no fine sand) : The aim of this experiment is to verify if the concrete without fine sand have a different damage behavior as actual concrete that contain fine sand. In this test, we obtain the same three kinds of signals as in the actual synthetic concretes. They correspond to matrix cracking (A signals) as shown above, and two
5 other signals, probably gravel/resin decohesion and gravel failure (Fig. 4). One can conclude that the sand matrix interface is stronger than the matrix gravel interface. To confirm this observation one must consider a sample with solely fine sand and resin. a b Figure 4. a) Detected signals in gravel and resin concrete a) gravel/resin debounding, b) gravel failure 4.3 Fine sand and resin concretes (no gravel) : The aim of this experiment is to generate matrix cracking and potential fine sand/matrix decohesion. Indeed, two kinds of signals are found. About 90% have amplitude in the range db, with waveform features similar to those observed in the tests on pure resin (Fig. 5a). Thus, they correspond to A signals. 10% of signals have amplitude mainly in the range db (Fig. 5a) and waveform features quite different from the A signals, with shorter rise time and higher energy. They correspond probably to the fine sand/matrix decohesion and are similar to the signals of the cluster 2 in the actual concrete but less energetic (Fig. 5b). The fine sand/matrix decohesion damage mechanism is then present but seems to be a secondary mechanism giving rise to few AE. a b Figure 5. a) Amplitude distribution of fine sand and resin concretes, b) Fine sand/matrix decohesion signal. 5 Time dependency damage mechanisms In order to identify the evolution of each damage mechanism with time, the clustering method is applied to the actual concretes (6692 AE events). The same descriptors are used to compose the patterns. The number of clusters set for classifying the data is three. The obtained clusters are composed of patterns whose amplitude are in the range from 40 to 70 db for 84% (cluster 1), in the range db for 15 % (cluster 2) and in the range
6 db for 1% (cluster 3). The time dependency of the different damage types (Fig 6) shows that the matrix cracking are the most important damage mechanisms, the interfacial decohesion begin from the starting of the experiment and are less numerous than the matrix cracking. At the end of the tests, few C signals, referring to the gravel failure appear and lead to the failure of the material. This is a very important result showing that the damage mechanisms don t have the same dynamic. Figure 6. Time dependency of the identified damage types 6 Conclusions Fuzzy C-means clustering method is coupled with a principal component analysis to discriminate different damage mechanisms from AE signals and to visualize the classification into classes. Clustering is done with the typical temporal descriptors of AE waveforms. The resulting clusters clearly identify the damage mechanisms in complex composite materials as polymer concretes. This unsupervised method also shows the time evolution of damage mechanisms in these materials till the final failure. The perspectives of this work are to define more time-scale descriptors to include them in the clustering method in order to improve the identification of damage mechanisms of polymer concrete. References 1. K. Ono, Acoustic emission, Encyclopedia of Acoustics, Wiley, New York, V. Kostopoulos, T.H. Loutas, A. Kontsos, G. Sotiriadis, Y.Z. Pappas, On the identification of the failure mechanisms in oxide/oxide composites using acoustic emission, NDT&E International 36 (2003) D.-J. Yoon, W. Weiss, S.P. Shah, Assessing damage corroded reinforced concrete using in acoustic emission, Journal of Engineering Mechanics (2000) N. Godin, S. Huguet, R. Gaertner, L. Salmon, Clustering of acoustic emission signals collected during tensile tests on unidirectional glass/polyester composites using supervised and unsupervised classifiers, NDT&E International 37 (2004) N. Godin, S. Huguet, R. Gaertner, Integration of the Kohonen s self-organising map and k- means algorithm for the segmentation of the AE data collected during tensile tests on cross-ply composites, NDT&E International 38 (2005) Bezdek, J.C., (1981) "Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algortithms", Plenum, New-York.
PATTERN RECOGNITION OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION SIGNAL DURING THE MODE I FRACTURE MECHANISMS IN CARBON-EPOXY COMPOSITE
 More info about this article: h Czech Society for Nondestructive Testing 32 nd European Conference on Acoustic Emission Testing Prague, Czech Republic, September 7-9, 26 PATTERN RECOGNITION OF ACOUSTIC
More info about this article: h Czech Society for Nondestructive Testing 32 nd European Conference on Acoustic Emission Testing Prague, Czech Republic, September 7-9, 26 PATTERN RECOGNITION OF ACOUSTIC
A normalization method for life-time prediction of composite materials
 A normalization method for life-time prediction of composite materials M. Darwiche a, G. Bousaleh b, M. Feuilloy c, D. Schang c and R. El Guerjouma a a Laboratoire d acoustique de l université du Maine,
A normalization method for life-time prediction of composite materials M. Darwiche a, G. Bousaleh b, M. Feuilloy c, D. Schang c and R. El Guerjouma a a Laboratoire d acoustique de l université du Maine,
Advanced Acoustic Emission Data Analysis Pattern Recognition & Neural Networks Software
 Applications Advanced Acoustic Emission Data Analysis Pattern Recognition & Neural Networks Software www.envirocoustics.gr, info@envirocoustics.gr www.pacndt.com, sales@pacndt.com FRP Blade Data Analysis
Applications Advanced Acoustic Emission Data Analysis Pattern Recognition & Neural Networks Software www.envirocoustics.gr, info@envirocoustics.gr www.pacndt.com, sales@pacndt.com FRP Blade Data Analysis
Characterization of Microcracking in Polymer Concrete Using Multiple Scattered Waves Under Steady-State Vibration Conditions
 RESEARCH IN NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION 2017, VOL. 28, NO. 1, 18 27 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09349847.2016.1262977 Characterization of Microcracking in Polymer Concrete Using Multiple Scattered Waves Under
RESEARCH IN NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION 2017, VOL. 28, NO. 1, 18 27 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09349847.2016.1262977 Characterization of Microcracking in Polymer Concrete Using Multiple Scattered Waves Under
Some elements for improving interpretation of concrete electrical resistivity
 Some elements for improving interpretation of concrete electrical resistivity Jean-François LATASTE 1, Stéphane LAURENS 2, Andrzej MOCZKO 3 1 Université Bordeaux 1, Talence, France, jf.lataste@ghymac.u-bordeaux1.fr
Some elements for improving interpretation of concrete electrical resistivity Jean-François LATASTE 1, Stéphane LAURENS 2, Andrzej MOCZKO 3 1 Université Bordeaux 1, Talence, France, jf.lataste@ghymac.u-bordeaux1.fr
PEMFC on line diagnosis via acoustic emission measurements. B. Legros, P.-X. Thivel*, Y Bultel, R.P. Nogueira
 PEMFC on line diagnosis via acoustic emission measurements B. Legros, P.-X. Thivel*, Y Bultel, R.P. Nogueira Laboratory of electrochemistry and physico-chemistry of materials and interfaces (LEPMI) Science
PEMFC on line diagnosis via acoustic emission measurements B. Legros, P.-X. Thivel*, Y Bultel, R.P. Nogueira Laboratory of electrochemistry and physico-chemistry of materials and interfaces (LEPMI) Science
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION WAVEFORMS AND. M.Ohtsu Department of Civil and Environmental Eng. Kumamoto University Kumamoto 860, Japan
 QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION WAVEFORMS AND PRACTICAL APPLICATION TO CIVIL STRUCTURES IN JAPAN M.Ohtsu Department of Civil and Environmental Eng. Kumamoto University Kumamoto 860, Japan INTRODUCTION
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION WAVEFORMS AND PRACTICAL APPLICATION TO CIVIL STRUCTURES IN JAPAN M.Ohtsu Department of Civil and Environmental Eng. Kumamoto University Kumamoto 860, Japan INTRODUCTION
Acoustic emission analysis for failure identification in composite materials
 Acoustic emission analysis for failure identification in composite materials Markus G. R. Sause Experimental Physics II Institute of Physics University of Augsburg 1. Motivation 2. Methods of AE analysis
Acoustic emission analysis for failure identification in composite materials Markus G. R. Sause Experimental Physics II Institute of Physics University of Augsburg 1. Motivation 2. Methods of AE analysis
Keywords: Adhesively bonded joint, laminates, CFRP, stacking sequence
 THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS GLOBAL AND LOCAL INFLUENCE OF STACKING SEQUENCE ON THE STRENGTH OF ADHESIVELY BONDED JOINTS OF CFRP LAMINATES J. Rousseau*, P. Satthamnuwong DRIVE,
THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS GLOBAL AND LOCAL INFLUENCE OF STACKING SEQUENCE ON THE STRENGTH OF ADHESIVELY BONDED JOINTS OF CFRP LAMINATES J. Rousseau*, P. Satthamnuwong DRIVE,
Interlaminar fracture characterization in composite materials by using acoustic emission
 5th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace, 13-15th November 2013, Singapore Interlaminar fracture characterization in composite materials by using acoustic emission Ian SILVERSIDES 1, Ahmed MASLOUHI
5th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace, 13-15th November 2013, Singapore Interlaminar fracture characterization in composite materials by using acoustic emission Ian SILVERSIDES 1, Ahmed MASLOUHI
EVALUATION OF DAMAGES DUE TO ALKALI-SILICA REACTION WITH ACOUSTICS TECHNIQUES. DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW NONLINEAR METHOD.
 EVALUATION OF DAMAGES DUE TO ALKALI-SILICA REACTION WITH ACOUSTICS TECHNIQUES. DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW NONLINEAR METHOD. Apedovi S. Kodjo (1, 2), Patrice Rivard (1), Frederic Cohen-Tenoudji (3) and Jean-Louis
EVALUATION OF DAMAGES DUE TO ALKALI-SILICA REACTION WITH ACOUSTICS TECHNIQUES. DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW NONLINEAR METHOD. Apedovi S. Kodjo (1, 2), Patrice Rivard (1), Frederic Cohen-Tenoudji (3) and Jean-Louis
Vibration damping in polygonal plates using the acoustic black hole effect: model based on the image source method
 Vibration damping in polygonal plates using the acoustic black hole effect: model based on the image source method Jacques Cuenca a,b, Adrien Pelat a, François Gautier a a. Laboratoire d Acoustique de
Vibration damping in polygonal plates using the acoustic black hole effect: model based on the image source method Jacques Cuenca a,b, Adrien Pelat a, François Gautier a a. Laboratoire d Acoustique de
Hilbert-Huang Transform versus Fourier based analysis for diffused ultrasonic waves structural health monitoring in polymer based composite materials
 Proceedings of the Acoustics 212 Nantes Conference 23-27 April 212, Nantes, France Hilbert-Huang Transform versus Fourier based analysis for diffused ultrasonic waves structural health monitoring in polymer
Proceedings of the Acoustics 212 Nantes Conference 23-27 April 212, Nantes, France Hilbert-Huang Transform versus Fourier based analysis for diffused ultrasonic waves structural health monitoring in polymer
NEURAL NETWORK BURST PRESSURE PREDICTION IN COMPOSITE OVERWRAPPED PRESSURE VESSELS
 NEURAL NETWORK BURST PRESSURE PREDICTION IN COMPOSITE OVERWRAPPED PRESSURE VESSELS ERIC v. K. HILL, SETH-ANDREW T. DION, JUSTIN O. KARL, NICHOLAS S. SPIVEY and JAMES L. WALKER II* Aerospace Engineering
NEURAL NETWORK BURST PRESSURE PREDICTION IN COMPOSITE OVERWRAPPED PRESSURE VESSELS ERIC v. K. HILL, SETH-ANDREW T. DION, JUSTIN O. KARL, NICHOLAS S. SPIVEY and JAMES L. WALKER II* Aerospace Engineering
ème Congrès annuel, Section technique, ATPPC th Annual Meeting, PAPTAC
 2000-86 ème Congrès annuel, Section technique, ATPPC 2000-86th Annual Meeting, PAPTAC Use of components of formation for predicting print quality and physical properties of newsprint Jean-Philippe Bernié,
2000-86 ème Congrès annuel, Section technique, ATPPC 2000-86th Annual Meeting, PAPTAC Use of components of formation for predicting print quality and physical properties of newsprint Jean-Philippe Bernié,
Combined Acoustic Emission and Thermographic Testing of Fibre Composites
 19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Combined Acoustic Emission and Thermographic Testing of Fibre Composites Matthias GOLDAMMER 1, Markus G. R. SAUSE 2, Detlef RIEGER 1 1 Siemens AG
19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Combined Acoustic Emission and Thermographic Testing of Fibre Composites Matthias GOLDAMMER 1, Markus G. R. SAUSE 2, Detlef RIEGER 1 1 Siemens AG
In Situ Ultrasonic NDT of Fracture and Fatigue in Composites
 ECNDT 26 - Mo.2.6.5 In Situ Ultrasonic NDT of Fracture and Fatigue in Composites I. SOLODOV, K. PFLEIDERER, and G. BUSSE Institute for Polymer Testing and Polymer Science (IKP), Non-destructive Testing
ECNDT 26 - Mo.2.6.5 In Situ Ultrasonic NDT of Fracture and Fatigue in Composites I. SOLODOV, K. PFLEIDERER, and G. BUSSE Institute for Polymer Testing and Polymer Science (IKP), Non-destructive Testing
REGRESSION MODELING FOR STRENGTH AND TOUGHNESS EVALUATION OF HYBRID FIBRE REINFORCED CONCRETE
 REGRESSION MODELING FOR STRENGTH AND TOUGHNESS EVALUATION OF HYBRID FIBRE REINFORCED CONCRETE S. Eswari 1, P. N. Raghunath and S. Kothandaraman 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Pondicherry Engineering
REGRESSION MODELING FOR STRENGTH AND TOUGHNESS EVALUATION OF HYBRID FIBRE REINFORCED CONCRETE S. Eswari 1, P. N. Raghunath and S. Kothandaraman 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Pondicherry Engineering
Local Strain and Damage Measurements on a Composite with Digital Image Correlation and Acoustic Emission
 Local Strain and Damage Measurements on a Composite with Digital Image Correlation and Acoustic Emission Camille Flament, Michelle Salvia, Bruno Berthel, Gérard Crosland To cite this version: Camille Flament,
Local Strain and Damage Measurements on a Composite with Digital Image Correlation and Acoustic Emission Camille Flament, Michelle Salvia, Bruno Berthel, Gérard Crosland To cite this version: Camille Flament,
The parametric propagation in underwater acoustics : experimental results
 The parametric propagation in underwater acoustics : experimental results E. Bouttard, V. Labat, O. Bou Matar, Thierry Chonavel To cite this version: E. Bouttard, V. Labat, O. Bou Matar, Thierry Chonavel.
The parametric propagation in underwater acoustics : experimental results E. Bouttard, V. Labat, O. Bou Matar, Thierry Chonavel To cite this version: E. Bouttard, V. Labat, O. Bou Matar, Thierry Chonavel.
AE Source Orientation by Plate Wave Analysis * Michael R. Gorman Aeronautics and Astronautics Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943
 AE Source Orientation by Plate Wave Analysis * Michael R. Gorman Aeronautics and Astronautics Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943 William H. Prosser NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA 23665
AE Source Orientation by Plate Wave Analysis * Michael R. Gorman Aeronautics and Astronautics Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943 William H. Prosser NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA 23665
APPLICATION OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION METHOD DURING CYCLIC LOADING OF CONCRETE BEAM
 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=21866 Abstract IX th NDT in PROGRESS October 9 11, 2017, Prague, Czech Republic APPLICATION OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION METHOD DURING CYCLIC LOADING OF CONCRETE
More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=21866 Abstract IX th NDT in PROGRESS October 9 11, 2017, Prague, Czech Republic APPLICATION OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION METHOD DURING CYCLIC LOADING OF CONCRETE
The parametric propagation in underwater acoustics: experimental results
 The parametric propagation in underwater acoustics: experimental results E. Bouttard a, V. Labat a, O. Bou Matar b and T. Chonavel c a Institut de Recherche de l Ecole Navale (EA 3634), BCRM Brest CC 600
The parametric propagation in underwater acoustics: experimental results E. Bouttard a, V. Labat a, O. Bou Matar b and T. Chonavel c a Institut de Recherche de l Ecole Navale (EA 3634), BCRM Brest CC 600
DAMAGE MODELLING OF A SATIN SEPCARB COMPOSITE
 DAMAGE MODELLING OF A SATIN SEPCARB COMPOSITE X. Aubard 1, C. Cluzel 2,3, P. Ladevèze 2 and J.N. Périé 2 1 SEP Division de SNECMA, Le Haillan BP 37, 33165 St MEDARD-EN-JALLES, FRANCE 2 LMT Cachan, E.N.S.
DAMAGE MODELLING OF A SATIN SEPCARB COMPOSITE X. Aubard 1, C. Cluzel 2,3, P. Ladevèze 2 and J.N. Périé 2 1 SEP Division de SNECMA, Le Haillan BP 37, 33165 St MEDARD-EN-JALLES, FRANCE 2 LMT Cachan, E.N.S.
COMPARISON OF COHESIVE ZONE MODELS USED TO PREDICT DELAMINATION INITIATED FROM FREE-EDGES : VALIDATION AGAINST EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
 COMPARISON OF COHESIVE ZONE MODELS USED TO PREDICT DELAMINATION INITIATED FROM FREE-EDGES : VALIDATION AGAINST EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS A. Uguen 1, L. Zubillaga 2, A. Turon 3, N. Carrère 1 1 Laboratoire Brestois
COMPARISON OF COHESIVE ZONE MODELS USED TO PREDICT DELAMINATION INITIATED FROM FREE-EDGES : VALIDATION AGAINST EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS A. Uguen 1, L. Zubillaga 2, A. Turon 3, N. Carrère 1 1 Laboratoire Brestois
Probabilistic approach to crack mode classification in concrete under uniaxial compression
 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=22316 Probabilistic approach to crack mode classification in concrete under uniaxial compression Deepak Suthar 1 Jayant Srivastava 2 J. M. Kabinesh
More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=22316 Probabilistic approach to crack mode classification in concrete under uniaxial compression Deepak Suthar 1 Jayant Srivastava 2 J. M. Kabinesh
EWGAE 2010 Vienna, 8th to 10th September
 EWGAE 21 Vienna, 8th to 1th September Influence of Specimen Geometry on Acoustic Emission Signals in Fiber Reinforced Composites: FEM-Simulations and Experiments Markus G. R. SAUSE, Siegfried HORN University
EWGAE 21 Vienna, 8th to 1th September Influence of Specimen Geometry on Acoustic Emission Signals in Fiber Reinforced Composites: FEM-Simulations and Experiments Markus G. R. SAUSE, Siegfried HORN University
QUANTITATIVE DAMAGE ESTIMATION OF CONCRETE CORE BASED ON AE RATE PROCESS ANALYSIS
 QUANTITATIVE DAMAGE ESTIMATION OF CONCRETE CORE BASED ON AE RATE PROCESS ANALYSIS MASAYASU OHTSU and TETSUYA SUZUKI 1 Kumamoto University, Kumamoto 860-8555, Japan 2 Nippon Suiko Consultants Co., Kumamoto
QUANTITATIVE DAMAGE ESTIMATION OF CONCRETE CORE BASED ON AE RATE PROCESS ANALYSIS MASAYASU OHTSU and TETSUYA SUZUKI 1 Kumamoto University, Kumamoto 860-8555, Japan 2 Nippon Suiko Consultants Co., Kumamoto
MOMENT TENSORS OF IN-PLANE WAVES ANALYZED BY SIGMA-2D
 MOMENT TENSORS OF IN-PLANE WAVES ANALYZED BY SIGMA-2D MASAYASU OHTSU 1, KENTARO OHNO 1 and MARVIN A. HAMSTAD 2 1) Graduate School of Science and Technology, Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan. 2) Department
MOMENT TENSORS OF IN-PLANE WAVES ANALYZED BY SIGMA-2D MASAYASU OHTSU 1, KENTARO OHNO 1 and MARVIN A. HAMSTAD 2 1) Graduate School of Science and Technology, Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan. 2) Department
ANALYSIS OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION SIGNALS PRODUCED BY DIFFERENT CARBON FIBRE REINFORCED PLASTIC LAMINATES
 ANALYSIS OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION SIGNALS PRODUCED BY DIFFERENT CARBON FIBRE REINFORCED PLASTIC LAMINATES V. Lopresto 1, C. Leone 1, G. Caprino 1 and I. de Iorio 2 1 Dept. of Materials and Production Engineering,
ANALYSIS OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION SIGNALS PRODUCED BY DIFFERENT CARBON FIBRE REINFORCED PLASTIC LAMINATES V. Lopresto 1, C. Leone 1, G. Caprino 1 and I. de Iorio 2 1 Dept. of Materials and Production Engineering,
Ultimate Compression After Impact Load Prediction in Graphite/Epoxy Coupons Using Neural Network and Multivariate Statistical Analyses
 Dissertations and Theses Spring 2011 Ultimate Compression After Impact Load Prediction in Graphite/Epoxy Coupons Using Neural Network and Multivariate Statistical Analyses Alexandre David Grégoire Embry-Riddle
Dissertations and Theses Spring 2011 Ultimate Compression After Impact Load Prediction in Graphite/Epoxy Coupons Using Neural Network and Multivariate Statistical Analyses Alexandre David Grégoire Embry-Riddle
ISSN: ISO 9001:2008 Certified International Journal of Engineering Science and Innovative Technology (IJESIT) Volume 2, Issue 4, July 2013
 Delamination Studies in Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites K.Kantha Rao, Dr P. Shailesh, K. Vijay Kumar 1 Associate Professor, Narasimha Reddy Engineering College Hyderabad. 2 Professor, St. Peter s Engineering
Delamination Studies in Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites K.Kantha Rao, Dr P. Shailesh, K. Vijay Kumar 1 Associate Professor, Narasimha Reddy Engineering College Hyderabad. 2 Professor, St. Peter s Engineering
Accuracy of flaw localization algorithms: application to structures monitoring using ultrasonic guided waves
 Première journée nationale SHM-France Accuracy of flaw localization algorithms: application to structures monitoring using ultrasonic guided waves Alain Le Duff Groupe Signal Image & Instrumentation (GSII),
Première journée nationale SHM-France Accuracy of flaw localization algorithms: application to structures monitoring using ultrasonic guided waves Alain Le Duff Groupe Signal Image & Instrumentation (GSII),
Bayesian model updating and boundary element method applied to concrete fracture testing.
 Bayesian model updating and boundary element method applied to concrete fracture testing. Pierre Beaurepaire a, Sergio Gustavo Ferreira Cordeiro b, Edson Denner Leonel b, Alaa Chateauneuf a a. Université
Bayesian model updating and boundary element method applied to concrete fracture testing. Pierre Beaurepaire a, Sergio Gustavo Ferreira Cordeiro b, Edson Denner Leonel b, Alaa Chateauneuf a a. Université
DAMAGE ASSESSMENT OF REINFORCED CONCRETE USING ULTRASONIC WAVE PROPAGATION AND PATTERN RECOGNITION
 II ECCOMAS THEMATIC CONFERENCE ON SMART STRUCTURES AND MATERIALS C.A. Mota Soares et al. (Eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, July 18-21, 2005 DAMAGE ASSESSMENT OF REINFORCED CONCRETE USING ULTRASONIC WAVE PROPAGATION
II ECCOMAS THEMATIC CONFERENCE ON SMART STRUCTURES AND MATERIALS C.A. Mota Soares et al. (Eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, July 18-21, 2005 DAMAGE ASSESSMENT OF REINFORCED CONCRETE USING ULTRASONIC WAVE PROPAGATION
MODELING OF THE BEHAVIOR OF WOVEN LAMINATED COMPOSITES UNTIL RUPTURE
 MODELING OF THE BEHAVIOR OF WOVEN LAMINATED COMPOSITES UNTIL RUPTURE Jean Paul Charles, Christian Hochard,3, Pierre Antoine Aubourg,3 Eurocopter, 375 Marignane cedex, France Unimeca, 6 rue J. Curie, 3453
MODELING OF THE BEHAVIOR OF WOVEN LAMINATED COMPOSITES UNTIL RUPTURE Jean Paul Charles, Christian Hochard,3, Pierre Antoine Aubourg,3 Eurocopter, 375 Marignane cedex, France Unimeca, 6 rue J. Curie, 3453
Estimation of Seismic Damage for Optimum Management of Irrigation Infrastructures in Service Conditions using Elastic Waves Information
 Estimation of Seismic Damage for Optimum Management of Irrigation Infrastructures in Service Conditions using Elastic Waves Information Tetsuya Suzuki Faculty of Agriculture, Niigata University 950-2181,
Estimation of Seismic Damage for Optimum Management of Irrigation Infrastructures in Service Conditions using Elastic Waves Information Tetsuya Suzuki Faculty of Agriculture, Niigata University 950-2181,
Damage Inspection of Fiber Reinforced Polymer-Concrete Systems using a Distant Acoustic-Laser NDE Technique
 SPIE Smart Structures/NDE March 11, 2010, San Diego, CA Session 10: Civil Infrastructure Health Monitoring I Damage Inspection of Fiber Reinforced Polymer-Concrete Systems using a Distant Acoustic-Laser
SPIE Smart Structures/NDE March 11, 2010, San Diego, CA Session 10: Civil Infrastructure Health Monitoring I Damage Inspection of Fiber Reinforced Polymer-Concrete Systems using a Distant Acoustic-Laser
DAMAGE MECHANICS MODEL FOR OFF-AXIS FATIGUE BEHAVIOR OF UNIDIRECTIONAL CARBON FIBER-REINFORCED COMPOSITES AT ROOM AND HIGH TEMPERATURES
 DAMAGE MECHANICS MODEL FOR OFF-AXIS FATIGUE BEHAVIOR OF UNIDIRECTIONAL CARBON FIBER-REINFORCED COMPOSITES AT ROOM AND HIGH TEMPERATURES M. Kawai Institute of Engineering Mechanics University of Tsukuba,
DAMAGE MECHANICS MODEL FOR OFF-AXIS FATIGUE BEHAVIOR OF UNIDIRECTIONAL CARBON FIBER-REINFORCED COMPOSITES AT ROOM AND HIGH TEMPERATURES M. Kawai Institute of Engineering Mechanics University of Tsukuba,
A STUDY ON FATIGUE CRACK GROWTH IN CONCRETE IN THE PRE-PARIS REGION
 VIII International Conference on Fracture Mechanics of Concrete and Concrete Structures FraMCoS-8 J.G.M. Van Mier, G. Ruiz, C. Andrade, R.C. Yu and X.X. Zhang (Eds) A STUDY ON FATIGUE CRACK GROWTH IN CONCRETE
VIII International Conference on Fracture Mechanics of Concrete and Concrete Structures FraMCoS-8 J.G.M. Van Mier, G. Ruiz, C. Andrade, R.C. Yu and X.X. Zhang (Eds) A STUDY ON FATIGUE CRACK GROWTH IN CONCRETE
Unsupervised Learning Methods
 Structural Health Monitoring Using Statistical Pattern Recognition Unsupervised Learning Methods Keith Worden and Graeme Manson Presented by Keith Worden The Structural Health Monitoring Process 1. Operational
Structural Health Monitoring Using Statistical Pattern Recognition Unsupervised Learning Methods Keith Worden and Graeme Manson Presented by Keith Worden The Structural Health Monitoring Process 1. Operational
LAMB WAVES GENERATION USING A TRANSDUCER EMBEDDED IN A COMPOSITE PLATE
 LAMB WAVES GENERATION USING A TRANSDUCER EMBEDDED IN A COMPOSITE PLATE Emmanuel Moulin 1, Jamal Assaad 1, Christophe Delebarre 1 and Daniel Osmont 2 1 IEMN, UMR CNRS 9929, OAE Department, Université de
LAMB WAVES GENERATION USING A TRANSDUCER EMBEDDED IN A COMPOSITE PLATE Emmanuel Moulin 1, Jamal Assaad 1, Christophe Delebarre 1 and Daniel Osmont 2 1 IEMN, UMR CNRS 9929, OAE Department, Université de
Simulation of Dynamic Delamination and Mode I Energy Dissipation
 Simulation of Dynamic Delamination and Mode I Energy Dissipation Muhammad Ilyas, Christine Espinosa 1, Frédéric Lachaud and Michel Salaün Université de Toulouse ISAE, DMSM, 1 Avenue Edouard Belin, 3154
Simulation of Dynamic Delamination and Mode I Energy Dissipation Muhammad Ilyas, Christine Espinosa 1, Frédéric Lachaud and Michel Salaün Université de Toulouse ISAE, DMSM, 1 Avenue Edouard Belin, 3154
Structural Health Monitoring of fibre composite structures by Acoustic Emission Analysis
 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=23604 Structural Health Monitoring of fibre composite structures by Acoustic Emission Analysis Lars Schubert 1, Eberhard Schulze 1, Robert Neubeck 1
More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=23604 Structural Health Monitoring of fibre composite structures by Acoustic Emission Analysis Lars Schubert 1, Eberhard Schulze 1, Robert Neubeck 1
FAVIMAT (AI)ROBOT2 FAVIGRAPH. Automatic Single-Fibre Testers
 FAVIMAT (AI)ROBOT2 FAVIGRAPH Automatic Single-Fibre Testers Single-Fibre Testers FAVIMAT and FAVIGRAPH The FAVIMAT testing methods Testing and evaluation of a wide range of fibre properties are essential
FAVIMAT (AI)ROBOT2 FAVIGRAPH Automatic Single-Fibre Testers Single-Fibre Testers FAVIMAT and FAVIGRAPH The FAVIMAT testing methods Testing and evaluation of a wide range of fibre properties are essential
CHARACTERIZATION AND DAMAGE EVOLUTION OF S.M.C COMPOSITES MATERIALS BY ULTRASONIC METHOD
 CHARACTERIZATION AND DAMAGE EVOLUTION OF S.M.C COMPOSITES MATERIALS BY ULTRASONIC METHOD M. SAYARI, D.BAPTISTE, M. BOCQUET AND J.FITOUSSI Laboratoire de Microstructure et Mécanique des Matériaux, URA CNRS
CHARACTERIZATION AND DAMAGE EVOLUTION OF S.M.C COMPOSITES MATERIALS BY ULTRASONIC METHOD M. SAYARI, D.BAPTISTE, M. BOCQUET AND J.FITOUSSI Laboratoire de Microstructure et Mécanique des Matériaux, URA CNRS
The effects of time correlations in subcritical fracture. An acoustic analysis
 The effects of time correlations in subcritical fracture. An acoustic analysis M. Stojanova a, S. Santucci b, L. Vanel a, O. Ramos a a. Institut Lumière Matière, UMR56 Université Lyon -CNRS, Université
The effects of time correlations in subcritical fracture. An acoustic analysis M. Stojanova a, S. Santucci b, L. Vanel a, O. Ramos a a. Institut Lumière Matière, UMR56 Université Lyon -CNRS, Université
On the study of elastic wave scattering and Rayleigh wave velocity measurement of concrete with steel bar
 NDT&E International 33 (2000) 401 407 www.elsevier.com/locate/ndteint On the study of elastic wave scattering and Rayleigh wave velocity measurement of concrete with steel bar T.-T. Wu*, J.-H. Sun, J.-H.
NDT&E International 33 (2000) 401 407 www.elsevier.com/locate/ndteint On the study of elastic wave scattering and Rayleigh wave velocity measurement of concrete with steel bar T.-T. Wu*, J.-H. Sun, J.-H.
Multiscale analyses of the behaviour and damage of composite materials
 Multiscale analyses of the behaviour and damage of composite materials Presented by Didier BAPTISTE ENSAM, LIM, UMR CNRS 8006 151 boulevard de l hôpital l 75013 PARIS, France Research works from: K.Derrien,
Multiscale analyses of the behaviour and damage of composite materials Presented by Didier BAPTISTE ENSAM, LIM, UMR CNRS 8006 151 boulevard de l hôpital l 75013 PARIS, France Research works from: K.Derrien,
Transactions on Information and Communications Technologies vol 6, 1994 WIT Press, ISSN
 Prediction of composite laminate residual strength based on a neural network approach R. Teti & G. Caprino Department of Materials and Production Engineering, University of Naples 'Federico II', Abstract
Prediction of composite laminate residual strength based on a neural network approach R. Teti & G. Caprino Department of Materials and Production Engineering, University of Naples 'Federico II', Abstract
Mechanical modelling of SiC/SiC composites and design criteria
 Mechanical modelling of SiC/SiC composites and design criteria F. Bernachy CEA, DEN/DMN/SRMA/LC2M, Gif-sur-Yvette, France L. Gélébart CEA, DEN/DMN/SRMA/LC2M, Gif-sur-Yvette, France J. Crépin Centre des
Mechanical modelling of SiC/SiC composites and design criteria F. Bernachy CEA, DEN/DMN/SRMA/LC2M, Gif-sur-Yvette, France L. Gélébart CEA, DEN/DMN/SRMA/LC2M, Gif-sur-Yvette, France J. Crépin Centre des
Machine Learning 11. week
 Machine Learning 11. week Feature Extraction-Selection Dimension reduction PCA LDA 1 Feature Extraction Any problem can be solved by machine learning methods in case of that the system must be appropriately
Machine Learning 11. week Feature Extraction-Selection Dimension reduction PCA LDA 1 Feature Extraction Any problem can be solved by machine learning methods in case of that the system must be appropriately
GLOBAL MONITORING OF CONCRETE BRIDGE USING ACOUSTIC EMISSION
 GLOBAL MONITORING OF CONCRETE BRIDGE USING ACOUSTIC EMISSION T. SHIOTANI, D. G. AGGELIS 1 and O. MAKISHIMA 2 Department of Urban Management, Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, C1-2- 236,
GLOBAL MONITORING OF CONCRETE BRIDGE USING ACOUSTIC EMISSION T. SHIOTANI, D. G. AGGELIS 1 and O. MAKISHIMA 2 Department of Urban Management, Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, C1-2- 236,
Experimental study of the behaviour of reinforced highstrength concrete short corbels
 Materials and Structures/Matériaux et Constructions, Vol. 34, April 2001, pp 155-162 Experimental study of the behaviour of reinforced highstrength concrete short corbels M. Bourget 1, Y. Delmas 1 and
Materials and Structures/Matériaux et Constructions, Vol. 34, April 2001, pp 155-162 Experimental study of the behaviour of reinforced highstrength concrete short corbels M. Bourget 1, Y. Delmas 1 and
WILEY STRUCTURAL HEALTH MONITORING A MACHINE LEARNING PERSPECTIVE. Charles R. Farrar. University of Sheffield, UK. Keith Worden
 STRUCTURAL HEALTH MONITORING A MACHINE LEARNING PERSPECTIVE Charles R. Farrar Los Alamos National Laboratory, USA Keith Worden University of Sheffield, UK WILEY A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Preface
STRUCTURAL HEALTH MONITORING A MACHINE LEARNING PERSPECTIVE Charles R. Farrar Los Alamos National Laboratory, USA Keith Worden University of Sheffield, UK WILEY A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Preface
1. Introduction. 2. Testing strategy. Daniel HUELSBUSCH 1, Frank WALTHER 1
 6th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace, 12-14th November 2014, Madrid, Spain - www.ndt.net/app.aerondt2014 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=16947 Damage detection and fatigue
6th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace, 12-14th November 2014, Madrid, Spain - www.ndt.net/app.aerondt2014 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=16947 Damage detection and fatigue
Acoustic Emission Location Experiment Research on Stope Roof Breakage Boundaries Time-Varying Process
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2015, 9, 797-805 797 Open Access Acoustic Emission Location Experiment Research on Stope Roof Breakage Boundaries
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2015, 9, 797-805 797 Open Access Acoustic Emission Location Experiment Research on Stope Roof Breakage Boundaries
A RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR STABILITY AND FAILURE OF THIN- WALLED COMPOSITE COLUMNS WITH OPEN CROSS-SECTION
 A RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR STABILITY AND FAILURE OF THIN- WALLED COMPOSITE COLUMNS WITH OPEN CROSS-SECTION H. Debski a*, J. Bienias b, P. Jakubczak b a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Machine
A RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR STABILITY AND FAILURE OF THIN- WALLED COMPOSITE COLUMNS WITH OPEN CROSS-SECTION H. Debski a*, J. Bienias b, P. Jakubczak b a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Machine
DELAMINATION IN MODE I AND II OF CARBON FIBRE COMPOSITE MATERIALS : FIBRE ORIENTATION INFLUENCE
 DELAMINATION IN MODE I AND II OF CARBON FIBRE COMPOSITE MATERIALS : FIBRE ORIENTATION INFLUENCE F. LACHAUD 1,2, R. PIQUET 2, L. MICHEL 1 2 LMT, IUT de énie Mécanique, 50, Chemin des Maraîchers, 31077 TOULOUSE
DELAMINATION IN MODE I AND II OF CARBON FIBRE COMPOSITE MATERIALS : FIBRE ORIENTATION INFLUENCE F. LACHAUD 1,2, R. PIQUET 2, L. MICHEL 1 2 LMT, IUT de énie Mécanique, 50, Chemin des Maraîchers, 31077 TOULOUSE
Numerical modelling of elastic-plastic deformation at crack tips in composite material under stress wave loading
 JOURNAL DE PHYSIQUE IV Colloque C8, supplément au Journal de Physique III, Volume 4, septembre 1994 C8-53 Numerical modelling of elastic-plastic deformation at crack tips in composite material under stress
JOURNAL DE PHYSIQUE IV Colloque C8, supplément au Journal de Physique III, Volume 4, septembre 1994 C8-53 Numerical modelling of elastic-plastic deformation at crack tips in composite material under stress
Effect of tire type on strains occurring in asphalt concrete layers
 Effect of tire type on strains occurring in asphalt concrete layers Grellet D., Doré G., & Bilodeau J.-P. Department of Civil Engineering, Laval University, Québec, Canada ABSTRACT: The three main causes
Effect of tire type on strains occurring in asphalt concrete layers Grellet D., Doré G., & Bilodeau J.-P. Department of Civil Engineering, Laval University, Québec, Canada ABSTRACT: The three main causes
Challenges related to standardized detection of crack initiation thresholds for lower-bound or ultra-long-term strength prediction of rock
 Challenges related to standardized detection of crack initiation thresholds for lower-bound or ultra-long-term strength prediction of rock E. Ghazvinian*, M. Diederichs* & J. Archibald *Dept. of Geological
Challenges related to standardized detection of crack initiation thresholds for lower-bound or ultra-long-term strength prediction of rock E. Ghazvinian*, M. Diederichs* & J. Archibald *Dept. of Geological
A probabilistic method to predict fatigue crack initiation
 International Journal of Fracture (2006) 137:9 17 DOI 10.1007/s10704-005-3074-0 Springer 2006 A probabilistic method to predict fatigue crack initiation SALIL. S. KULKARNI, L. SUN, B. MORAN, S. KRISHNASWAMY
International Journal of Fracture (2006) 137:9 17 DOI 10.1007/s10704-005-3074-0 Springer 2006 A probabilistic method to predict fatigue crack initiation SALIL. S. KULKARNI, L. SUN, B. MORAN, S. KRISHNASWAMY
Positive and Nondestructive Identification of Acrylic-Based Coatings
 Positive and Nondestructive Identification of Acrylic-Based Coatings Using Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis with the Agilent 4300 Handheld FTIR Application Note Materials Testing and Research
Positive and Nondestructive Identification of Acrylic-Based Coatings Using Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis with the Agilent 4300 Handheld FTIR Application Note Materials Testing and Research
Rapid Bridge Deck Condition Assessment Using Three- Dimensional Visualization of Impact Echo Data
 Rapid Bridge Deck Condition Assessment Using Three- Dimensional Visualization of Impact Echo Data Nenad GUCUNSKI 1, Zhe WANG 2, Tong FANG 2, Ali MAHER 1 1 Rutgers University, Piscataway, New Jersey, U.S.A.,
Rapid Bridge Deck Condition Assessment Using Three- Dimensional Visualization of Impact Echo Data Nenad GUCUNSKI 1, Zhe WANG 2, Tong FANG 2, Ali MAHER 1 1 Rutgers University, Piscataway, New Jersey, U.S.A.,
DAMAGE EVALUATION OF CRACKED CONCRETE BY DECAT
 VIII International Conference on Fracture Mechanics of Concrete and Concrete Structures FraMCoS-8 J.G.M. Van Mier, G. Ruiz, C. Andrade, R.C. Yu and X.X. Zhang (Eds) DAMAGE EVALUATION OF CRACKED CONCRETE
VIII International Conference on Fracture Mechanics of Concrete and Concrete Structures FraMCoS-8 J.G.M. Van Mier, G. Ruiz, C. Andrade, R.C. Yu and X.X. Zhang (Eds) DAMAGE EVALUATION OF CRACKED CONCRETE
Experimental damage analysis of concrete structures using the vibration signature - Part II: located damage (crack)
 Experimental damage analysis of concrete structures using the vibration signature - Part II: located damage (crack) Z. Boukria, A. Limam Abstract This paper reports on an experimental non-destructive method
Experimental damage analysis of concrete structures using the vibration signature - Part II: located damage (crack) Z. Boukria, A. Limam Abstract This paper reports on an experimental non-destructive method
Effects with a matrix crack on monitoring by electrical resistance method
 Adv. Composite Mater., Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 107 120 (2004) VSP 2004. Also available online - www.vsppub.com Effects with a matrix crack on monitoring by electrical resistance method AKIRA TODOROKI, MIHO
Adv. Composite Mater., Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 107 120 (2004) VSP 2004. Also available online - www.vsppub.com Effects with a matrix crack on monitoring by electrical resistance method AKIRA TODOROKI, MIHO
Real Time Failure Detection in Smart Structures using Wavelet Analysis
 Real Time Failure Detection in Smart Structures using Wavelet Analysis M-F. Dandine a, D. Necsulescu b LPMI Laboratoire M.I., ENSAM, 2 bd du Ronceray, 49035 Angers, France a Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Real Time Failure Detection in Smart Structures using Wavelet Analysis M-F. Dandine a, D. Necsulescu b LPMI Laboratoire M.I., ENSAM, 2 bd du Ronceray, 49035 Angers, France a Department of Mechanical Engineering,
DEVELOPMENT OF THERMOELASTIC STRESS ANALYSIS AS A NON-DESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION TOOL
 DEVELOPMENT OF THERMOELASTIC STRESS ANALYSIS AS A NON-DESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION TOOL S. Quinn*, R.K. Fruehmann and J.M. Dulieu-Barton School of Engineering Sciences University of Southampton Southampton SO17
DEVELOPMENT OF THERMOELASTIC STRESS ANALYSIS AS A NON-DESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION TOOL S. Quinn*, R.K. Fruehmann and J.M. Dulieu-Barton School of Engineering Sciences University of Southampton Southampton SO17
Influence of fines on the resistance to liquefaction of a clayey sand
 Ground Improvement (24) 8, No. 1, 1 5 1 Influence of fines on the resistance to liquefaction of a clayey sand R. BOUFERRA and I. SHAHROUR Laboratoire de Mécanique de Lille, University of Sciences and Technologies
Ground Improvement (24) 8, No. 1, 1 5 1 Influence of fines on the resistance to liquefaction of a clayey sand R. BOUFERRA and I. SHAHROUR Laboratoire de Mécanique de Lille, University of Sciences and Technologies
LECTURE NO. 4-5 INTRODUCTION ULTRASONIC * PULSE VELOCITY METHODS
 LECTURE NO. 4-5 ULTRASONIC * PULSE VELOCITY METHODS Objectives: To introduce the UPV methods To briefly explain the theory of pulse propagation through concrete To explain equipments, procedures, calibrations,
LECTURE NO. 4-5 ULTRASONIC * PULSE VELOCITY METHODS Objectives: To introduce the UPV methods To briefly explain the theory of pulse propagation through concrete To explain equipments, procedures, calibrations,
Finite Element Modeling of Ultrasonic Transducers for Polymer Characterization
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Finite Element Modeling of Ultrasonic Transducers for Polymer Characterization Serena De Paolis *, Francesca Lionetto and Alfonso Maffezzoli
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Finite Element Modeling of Ultrasonic Transducers for Polymer Characterization Serena De Paolis *, Francesca Lionetto and Alfonso Maffezzoli
ULTRASONIC PULSE METHOD THE CEMENT STRENGTH EVALUATION TOOL
 ULTRASONIC PULSE METHOD THE CEMENT STRENGTH EVALUATION TOOL Jiri BROZOVSKY (1), Jiri ZACH (1) (1) TIBME, FCE, Brno University of Technology,and Czech Republic Abstract The spectrum of control and laboratory
ULTRASONIC PULSE METHOD THE CEMENT STRENGTH EVALUATION TOOL Jiri BROZOVSKY (1), Jiri ZACH (1) (1) TIBME, FCE, Brno University of Technology,and Czech Republic Abstract The spectrum of control and laboratory
CSC Neural Networks. Perceptron Learning Rule
 CSC 302 1.5 Neural Networks Perceptron Learning Rule 1 Objectives Determining the weight matrix and bias for perceptron networks with many inputs. Explaining what a learning rule is. Developing the perceptron
CSC 302 1.5 Neural Networks Perceptron Learning Rule 1 Objectives Determining the weight matrix and bias for perceptron networks with many inputs. Explaining what a learning rule is. Developing the perceptron
QUESTION BANK Composite Materials
 QUESTION BANK Composite Materials 1. Define composite material. 2. What is the need for composite material? 3. Mention important characterits of composite material 4. Give examples for fiber material 5.
QUESTION BANK Composite Materials 1. Define composite material. 2. What is the need for composite material? 3. Mention important characterits of composite material 4. Give examples for fiber material 5.
NEURAL NETWORK TECHNIQUES FOR BURST PRESSURE PREDICTION IN KEVLAR/EPOXY PRESSURE VESSELS USING ACOUSTIC EMISSION DATA
 Abstract NEURAL NETWORK TECHNIQUES FOR BURST PRESSURE PREDICTION IN KEVLAR/EPOXY PRESSURE VESSELS USING ACOUSTIC EMISSION DATA ERIC v. K. HILL, MICHAEL D. SCHEPPA, ZACHARY D. SAGER and ISADORA P. THISTED
Abstract NEURAL NETWORK TECHNIQUES FOR BURST PRESSURE PREDICTION IN KEVLAR/EPOXY PRESSURE VESSELS USING ACOUSTIC EMISSION DATA ERIC v. K. HILL, MICHAEL D. SCHEPPA, ZACHARY D. SAGER and ISADORA P. THISTED
Fatigue of stay cables inside end fittings high frequencies of wind induced vibrations
 D. Siegert, P. Brevet Laboratoire Central des Ponts et Chaussées, France Fatigue of stay cables inside end fittings high frequencies of wind induced vibrations Summary A twenty year old stay cable was
D. Siegert, P. Brevet Laboratoire Central des Ponts et Chaussées, France Fatigue of stay cables inside end fittings high frequencies of wind induced vibrations Summary A twenty year old stay cable was
CHAPTER 3 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
 Experimental Study 42 CHAPTER 3 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY 3.1. INTRODUCTION The experimental study that has been carried out in this thesis has two main objectives: 1. Characterise the concrete behaviour in mode
Experimental Study 42 CHAPTER 3 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY 3.1. INTRODUCTION The experimental study that has been carried out in this thesis has two main objectives: 1. Characterise the concrete behaviour in mode
DYNAMICS AND DAMAGE ASSESSMENT IN IMPACTED CROSS-PLY CFRP PLATE UTILIZING THE WAVEFORM SIMULATION OF LAMB WAVE ACOUSTIC EMISSION
 DYNAMICS AND DAMAGE ASSESSMENT IN IMPACTED CROSS-PLY CFRP PLATE UTILIZING THE WAVEFORM SIMULATION OF LAMB WAVE ACOUSTIC EMISSION ABSTRACT Y. MIZUTAMI, H. NISHINO, M. TAKEMOTO and K. ONO* Aoyama Gakuin
DYNAMICS AND DAMAGE ASSESSMENT IN IMPACTED CROSS-PLY CFRP PLATE UTILIZING THE WAVEFORM SIMULATION OF LAMB WAVE ACOUSTIC EMISSION ABSTRACT Y. MIZUTAMI, H. NISHINO, M. TAKEMOTO and K. ONO* Aoyama Gakuin
We Prediction of Geological Characteristic Using Gaussian Mixture Model
 We-07-06 Prediction of Geological Characteristic Using Gaussian Mixture Model L. Li* (BGP,CNPC), Z.H. Wan (BGP,CNPC), S.F. Zhan (BGP,CNPC), C.F. Tao (BGP,CNPC) & X.H. Ran (BGP,CNPC) SUMMARY The multi-attribute
We-07-06 Prediction of Geological Characteristic Using Gaussian Mixture Model L. Li* (BGP,CNPC), Z.H. Wan (BGP,CNPC), S.F. Zhan (BGP,CNPC), C.F. Tao (BGP,CNPC) & X.H. Ran (BGP,CNPC) SUMMARY The multi-attribute
Detection and Survey of Interface Defects Within a Pavement Structure with Ultrasonic Pulse Echo
 Detection and Survey of Interface Defects Within a Pavement Structure with Ultrasonic Pulse Echo Jean Michel Simonin, Géraldine Villain To cite this version: Jean Michel Simonin, Géraldine Villain. Detection
Detection and Survey of Interface Defects Within a Pavement Structure with Ultrasonic Pulse Echo Jean Michel Simonin, Géraldine Villain To cite this version: Jean Michel Simonin, Géraldine Villain. Detection
Correlation between the internal length, the fracture process zone and size effect in model materials
 Available online at www.rilem.net Materials and Structures 38 (March 2005) 201-210 Correlation between the internal length, the fracture process zone and size effect in model materials K. Haidar 1, G.
Available online at www.rilem.net Materials and Structures 38 (March 2005) 201-210 Correlation between the internal length, the fracture process zone and size effect in model materials K. Haidar 1, G.
INTERNAL STRAIN MEASUREMENTS IN CFRP PLATES SUBJECTED TO IMPACT LOAD USING FBG SENSORS
 INTERNAL STRAIN MEASUREMENTS IN CFRP PLATES SUBJECTED TO IMPACT LOAD USING FBG SENSORS J. Frieden, J. Cugnoni, J. Botsis, Th. Gmür, D. Coric Laboratoire de Mécanique appliquée et d Analyse de Fiabilité
INTERNAL STRAIN MEASUREMENTS IN CFRP PLATES SUBJECTED TO IMPACT LOAD USING FBG SENSORS J. Frieden, J. Cugnoni, J. Botsis, Th. Gmür, D. Coric Laboratoire de Mécanique appliquée et d Analyse de Fiabilité
High Dimensional Discriminant Analysis
 High Dimensional Discriminant Analysis Charles Bouveyron 1,2, Stéphane Girard 1, and Cordelia Schmid 2 1 LMC IMAG, BP 53, Université Grenoble 1, 38041 Grenoble cedex 9 France (e-mail: charles.bouveyron@imag.fr,
High Dimensional Discriminant Analysis Charles Bouveyron 1,2, Stéphane Girard 1, and Cordelia Schmid 2 1 LMC IMAG, BP 53, Université Grenoble 1, 38041 Grenoble cedex 9 France (e-mail: charles.bouveyron@imag.fr,
ECE 521. Lecture 11 (not on midterm material) 13 February K-means clustering, Dimensionality reduction
 ECE 521 Lecture 11 (not on midterm material) 13 February 2017 K-means clustering, Dimensionality reduction With thanks to Ruslan Salakhutdinov for an earlier version of the slides Overview K-means clustering
ECE 521 Lecture 11 (not on midterm material) 13 February 2017 K-means clustering, Dimensionality reduction With thanks to Ruslan Salakhutdinov for an earlier version of the slides Overview K-means clustering
DYNAMIC DELAMINATION OF AERONAUTIC STRUCTURAL COMPOSITES BY USING COHESIVE FINITE ELEMENTS
 DYNAMIC DELAMINATION OF AERONAUTIC STRUCTURAL COMPOSITES BY USING COHESIVE FINITE ELEMENTS M. Ilyas, F. Lachaud 1, Ch. Espinosa and M. Salaün Université de Toulouse, ISAE/DMSM, 1 avenue Edouard Belin,
DYNAMIC DELAMINATION OF AERONAUTIC STRUCTURAL COMPOSITES BY USING COHESIVE FINITE ELEMENTS M. Ilyas, F. Lachaud 1, Ch. Espinosa and M. Salaün Université de Toulouse, ISAE/DMSM, 1 avenue Edouard Belin,
ScienceDirect. Study of acoustic emission in a compression test of andesite rock
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 9 (2015 ) 292 297 International Congress of Science and Technology of Metallurgy and Materials, SAM CONAMET 2014 Study
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 9 (2015 ) 292 297 International Congress of Science and Technology of Metallurgy and Materials, SAM CONAMET 2014 Study
EVALUATION OF DAMAGE DEVELOPMENT FOR NCF COMPOSITES WITH A CIRCULAR HOLE BASED ON MULTI-SCALE ANALYSIS
 THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS EVALUATION OF DAMAGE DEVELOPMENT FOR NCF COMPOSITES WITH A CIRCULAR HOLE BASED ON MULTI-SCALE ANALYSIS T. Kurashiki 1 *, Y. Matsushima 1, Y. Nakayasu
THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS EVALUATION OF DAMAGE DEVELOPMENT FOR NCF COMPOSITES WITH A CIRCULAR HOLE BASED ON MULTI-SCALE ANALYSIS T. Kurashiki 1 *, Y. Matsushima 1, Y. Nakayasu
EFFECT OF BASALT FIBRE HYBRIDIZATION ON THE LOW VELOCITY IMPACT BEHAVIOUR OF WOVEN CARBON FIBRE/EPOXY LAMINATES
 THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS EFFECT OF BASALT FIBRE HYBRIDIZATION ON THE LOW L. Ferrante 1, F. Sarasini 1*, J. Tirillò 1, M. Valente 1, T. Valente 1, S. Cioffi 2, S. Iannace
THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS EFFECT OF BASALT FIBRE HYBRIDIZATION ON THE LOW L. Ferrante 1, F. Sarasini 1*, J. Tirillò 1, M. Valente 1, T. Valente 1, S. Cioffi 2, S. Iannace
Natural frequency evaluation of a cracked RC beam with or without composite strengthening for a damage assessment
 Available online at www.rilem.net Materials and Structures 38 (December ) 86-873 Natural frequency evaluation of a craced RC beam with or without composite strengthening for a damage assessment M. Massenzio,
Available online at www.rilem.net Materials and Structures 38 (December ) 86-873 Natural frequency evaluation of a craced RC beam with or without composite strengthening for a damage assessment M. Massenzio,
How to Sparsify the Singular Value Decomposition with Orthogonal Components
 How to Sparsify the Singular Value Decomposition with Orthogonal Components Vincent Guillemot, Aida Eslami, Arnaud Gloaguen 3, Arthur Tenenhaus 3, & Hervé Abdi 4 Institut Pasteur C3BI, USR 3756 IP CNRS
How to Sparsify the Singular Value Decomposition with Orthogonal Components Vincent Guillemot, Aida Eslami, Arnaud Gloaguen 3, Arthur Tenenhaus 3, & Hervé Abdi 4 Institut Pasteur C3BI, USR 3756 IP CNRS
Evaluation of transverse elastic properties of fibers used in composite materials by laser resonant ultrasound spectroscopy
 Evaluation of transverse elastic properties of fibers used in composite materials by laser resonant ultrasound spectroscopy Denis Mounier, Christophe Poilâne, Cécile Bûcher, Pascal Picart To cite this
Evaluation of transverse elastic properties of fibers used in composite materials by laser resonant ultrasound spectroscopy Denis Mounier, Christophe Poilâne, Cécile Bûcher, Pascal Picart To cite this
Load transfers and arching effects in granular soil layer
 Load transfers and arching effects in granular soil layer Bastien Chevalier, Gaël Combe & Pascal Villard Laboratoire 3S-R : Sols, Solides Structures et Risques BP 53-38041 Grenoble cedex 9 France bastien.chevalier@ujf-grenoble.fr
Load transfers and arching effects in granular soil layer Bastien Chevalier, Gaël Combe & Pascal Villard Laboratoire 3S-R : Sols, Solides Structures et Risques BP 53-38041 Grenoble cedex 9 France bastien.chevalier@ujf-grenoble.fr
EFFECT OF THERMAL FATIGUE ON INTRALAMINAR CRACKING IN LAMINATES LOADED IN TENSION
 EFFECT OF THERMAL FATIGUE ON INTRALAMINAR CRACKING IN LAMINATES LOADED IN TENSION J.Varna and R.Joffe Dept of Applied Physics and Mechanical Engineering Lulea University of Technology, SE 97187, Lulea,
EFFECT OF THERMAL FATIGUE ON INTRALAMINAR CRACKING IN LAMINATES LOADED IN TENSION J.Varna and R.Joffe Dept of Applied Physics and Mechanical Engineering Lulea University of Technology, SE 97187, Lulea,
Lecture 3: Pattern Classification
 EE E6820: Speech & Audio Processing & Recognition Lecture 3: Pattern Classification 1 2 3 4 5 The problem of classification Linear and nonlinear classifiers Probabilistic classification Gaussians, mixtures
EE E6820: Speech & Audio Processing & Recognition Lecture 3: Pattern Classification 1 2 3 4 5 The problem of classification Linear and nonlinear classifiers Probabilistic classification Gaussians, mixtures
Artificial Neural Networks. Edward Gatt
 Artificial Neural Networks Edward Gatt What are Neural Networks? Models of the brain and nervous system Highly parallel Process information much more like the brain than a serial computer Learning Very
Artificial Neural Networks Edward Gatt What are Neural Networks? Models of the brain and nervous system Highly parallel Process information much more like the brain than a serial computer Learning Very
ISRM Congress 2015 Proceedings - Int l Symposium on Rock Mechanics - ISBN: ACOUSTIC EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF SHALE
 ACOUSTIC EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF SHALE * Z. Moradian, Q. B. Li, S. Morgan, B. Gonçalves da Silva, J. T. Germaine, H. H. Einstein Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Massachusetts Institute
ACOUSTIC EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF SHALE * Z. Moradian, Q. B. Li, S. Morgan, B. Gonçalves da Silva, J. T. Germaine, H. H. Einstein Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Massachusetts Institute
Bayesian Knowledge Fusion in Prognostics and Health Management A Case Study
 Bayesian Knowledge Fusion in Prognostics and Health Management A Case Study Masoud Rabiei Mohammad Modarres Center for Risk and Reliability University of Maryland-College Park Ali Moahmamd-Djafari Laboratoire
Bayesian Knowledge Fusion in Prognostics and Health Management A Case Study Masoud Rabiei Mohammad Modarres Center for Risk and Reliability University of Maryland-College Park Ali Moahmamd-Djafari Laboratoire
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Optics and Lasers in Engineering
 Optics and Lasers in Engineering 47 (29) 156 162 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics and Lasers in Engineering journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optlaseng Fiber optic acoustic emission
Optics and Lasers in Engineering 47 (29) 156 162 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Optics and Lasers in Engineering journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optlaseng Fiber optic acoustic emission
