Results for Exam 2_C1403_05: Mean grade = 80, Median grade = 82 For any questions on the exam, please post on the discussion board.
|
|
|
- Chester Perkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Results for Exam 2_C1403_05: Mean grade = 80, Median grade = 82 For any questions on the exam, please post on the discussion board.
2 Results of Course evalution after exam 2 Test: Class Survey after Exam 2 N/A: No Answer Helpfulness Please rank the following in terms of their assistance to you in preparing for the exam. Question 1: Class Lectures Question 2: a: very useful 69% b: useful 17% c: not useful 13% Homework assignments from the text a: very useful 20% b: useful 63% c: not useful 17% CourseWorks N/A Question 1: Courseworks worked well for me to obtain information on the course syllabus and exam materials. a: strongy agree 54% b: agree 41% c: disagree 5% Question 2: The quicktime movies were useful in clarifying and reinforcing concepts related to the course content in the book and lectures. a: Strongly agree 22% b: agree 58% c: disagree 18% Question 3: The powerpoint presentations were useful in clarifying and reinforcing concepts related to the course content in the book and lectures. Question 3: Multiple choice homework assignments a: very useful 47% b: useful 39% c: not useful 13% a: strongly agree 30% b: agree 61% c: disagree 7%
3 Exam N/A Question 1: On the average, how many hours per week have you spent preparing for the course by reading, studying for quizzes or completing homework assignments? Question 2: a: Less than 5 h 15% b: 5-10 h 45% c: h 28% d: h 7% e: More than 20 h 6% Please indicate your opinion of the exam. The exam covered materials that were stressed in the homework. a: strongly agree 17% b: agree 65% c: disagree 14% Question 4: The exam covered materials that were stressed in the practice multiple choice questions. a: strongly agree 29% b: agree 60% c: disagree 8% d: strongly disagree 4% Question 5: The exam covered materials that were stressed in the recitation sections. a: strongly agree 8% b: agree 49% c: disagree 30% d: strongly disagree 11% Question 3: lectures. d: strongly disagree 4% The exam covered materials that were stressed in the a: strongly agree 25% b: agree 63% c: disagree 8% d: strongly disagree 3% Question 6: Based on the information presented concerning the exam, the exam was fair. a: strongly agree 26% b: agree 60% c: disagree 11% d: strongly disagree 3%
4 Ratings N/A Question 1: Instructor: Organization and Preparation Question 4: Course: Appropriateness of Workload a: excellent 39% a: excellent 19% b: very good 44% b: very good 49% c: satisfactory 16% c: satisfactory 27% d: poor 2% d: poor 5% Question 2: Instructor: Approachability a: excellent 36% Question 5: N/A 0% Course: Overall Quality b: very good 42% a: excellent 18% c: satisfactory 19% b: very good 52% d: poor 2% c: satisfactory 25% d: poor 4% Question 3: Course: Amount Learned a: excellent 20% Question 6: Quality of Textbook b: very good 49% a: excellent 8% c: satisfactory 25% b: very good 33% d: poor 4% c: satisfactory 36% d: poor 15%
5 Chapter 18 Molecular orbitals and spectroscopy 18.1 Diatomic molecules 18.2 Polyatomic molecules 18.3 Conjugation of bonds and resonance structures 18.4 The interaction of light and matter (spectroscopy) 18.5 Photochemistry Atmospheric photochemistry Special Topic: Buckyballs (C 60 ) and molecules@c 60
6 18.3 Conjugation of bonds. Resonance structures Conjugation: delocalization from overlap of! orbitals Connection between MO theory and Lewis resonance structures MOs of conjugated molecules Conjugation of! orbitals and resonance Resonance: 1,3-butadiene and benzene Conjugation and light absorption
7 Two atoms: Ethylene (1) Lowest MO has no nodes; (2) each higher MO has one more node; (3) each MO has the symmetry of the molecule One node No nodes
8 Three atoms: Molecular pi orbitals No nodes (!) Two nodes (!") One node (Non bonding, nb) Energy ranking: p < nb <!" (order of nodes)
9 Four atoms: The! molecular orbitals for a 1,3-diene Three nodes Two nodes One node No nodes
10 Benzene: A closed ring has some special properties Three nodes: one orbital Two nodes; Two equal energy orbitals One node; Two equal energy orbitals No node; one orbital
11 Two descriptions of benzene Valence bond:! bonds localized Molecular orbital:! bonds delocalized
12 18.4 The interaction of light and molecules. Molecular spectroscopy Classifications of electromagnetic radiation: Spectral classification: X-ray, Ultraviolet, Visible, Infrared, Microwave, Radio Spectroscopic classification Electronic spectroscopy, Vibrational spectroscopy, Spin spectroscopy (Magnetic resonance) Absorption of light and color Photochemistry: photosynthesis, vision, atmospheric, toxic, theraputic
13 Photochemistry: involves electronically excited states
14 The distance and size scales of the electromagnetic spectrum
15 Energy Scales: Why the visible region works for vision Ultraviolet Region Chemical Bonds of DNA and Proteins Damaged Infrared Region Chemical Bonds Energy too low to make or break chemical bonds. 400 nm 500 nm 700 nm 71.5 kcal/mol 57.2 kcal/mol 40.8 kcal/mol Huge energies per photon. X-Rays 0.1 nm 300,000 kcal/mol Themal energies at room temperature ca 1 kcal/mole Tiny energies per photon. Microwaves 1,000,000 nm 0.03 kcal/mol
16 Photochemistry and spectroscopy both involve the absorption of photons to change a structure The configurations of electron, the vibrations of atoms, the orientation of spins
17 As conjugation is extended, the wavelength of absorption increases!"! Energy gap decreases: Wavelength increases beta Carotene
18 Photochemistry: the science of chemical reactions which occur from electronically excited states of molecules R + h# *R Chemical reactions *R is an electronically excited state Some important photochemical enents: Photosynthesis (electron transfer) Vision (cis-trans isomerization) Atmospheric: ozone layer (dissociation)
19 A widely read text on the subject of photochemistry
20 Vision: Early theories of light were theories of vision. Photosynthesis: Life requires the capture, storage and release of the sun s energy. Wald Calvin Marcus Nobel in Medicine Mechanism of Vision Nobels in Chemistry Mechanism of Photosynthesis
21 Solar Radiation What wavelengths are present? This depends on the wavelengths given off by the sun AND the wavelengths absorbed by the atmosphere
22 Photochemistry and spectroscopy of the atmosphere Penetration of electromagnetic radiation through the atmosphere
23 Water + Carbon dioxide = Food (carbohydrates) + Oxygen Sun: like a bell ringing out light
24 Chlorophyll
25 Photosynthesis: Ch + h# *Ch (electrically excited) *Ch + Q Ch + + Q - (electron transfer) Photosynthesis: 6 H 2 O + 6 CO 2 = C 6 H 12 O O 2 Sun
26 Vision: triggered by a photochemical reaction
27 The effect of photoexcitation of a! electron to a!!* orbital: the double bond is broken! 2 electronic configuration: double bond keeps the molecule planar and prevents twisting about the C=C bond (!) 1 (!*) 1 electronic configuration: double bond broken and twisting occurs about the C-C bond
28 Rotation about a C=C* bond causes cis-trans isomerization The photochemical change which triggers vision. A simple cis-trans isomerization: rotation about a double bond. H cis = same side trans = opposite side H h! H O H O cis-retinal trans-retinal The cis to trans isomerization triggers vision
29 Vision results from the change of a shape of ca.2 nm = 0.2 x 10-9 m 15Å trans-retinal 13Å cis-retinal 13Å 15Å
30 Atmospheric photochemistry: production and destruction of ozone Photodissociation of O 2 : O 2 + h# O + O Reaction of O with O 2 : O + O 2 O 3 Ozone protection: O 3 absorbs light whose wavelength is in the nm region of the spectrum Fluorocarbons absorb light and produce Cl atoms Cl atoms react with O 3 to destroy the ozone: Cl + O 3 ClO + O 2
31 Photochemistry and biology Photons can be toxic (cause DNA bases to dimerize) Photons can be therapeutic: phototherapy Photons can track thoughts, one molecule at a time Photons can image whole bodies and search for disease
32 Phototoxicity: Damage to DNA DNA 2 Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid
33 DNA: UV photochemistry Photons cause two DNA bases to link: this kills the cells containing the irradiated DNA
34 Singlet molecular oxygen: and excited state of ordinary oxygen The Aufbau of the MOs of O 2 3! u * 1" g * 1" u 3! g 2p Hund s rule states: When there are two electrons to be placed in two orbitals of equal energy, the lowest energy configuration places one electron in each orbital with parallel spins, a triplet state 2! u 2! g 2s O O
35 Electronic states of molecular oxygen: two low lying singlet states E [kj. Mol -1 ] " g + 1! g 37.5 kcal/mol, kj/mol, cm -1 $ R = 6.7 min (to 1! g ) # g 1! g 22.4 kcal/mol, 94.2 kj/mol 7882 cm -1 $ R = 64.6 min 0 3 " g - 1! g (ground state)
36 Direct spectroscopic detection of 1 O 2 $ 3 O 2 + h#: phosphorescence at 1270 nm tetraphenylporphine 3 O 2 + h# C ; 3 hours CDCl 3 O O! t1/2 = 5 h 25 0 C + 1 O 2 Photochemical generation of endoperoxide Thermal decomposition of endoperoxide O 2 phosphorescence in CCl intensity O 2 3 O 2 + h# (1270 nm) 1 " 1! nm 3 " " (nm)
37 Photodynamic Therapy using singlet oxygen Porphyrin injected into patient Only the affected organ irradiated with light 1 O 2 kills cancer cells in irradiated area (Abs nm) Patient cured!
38 Irradiating babies with jaundice causes a photochemical change that causes the jaundice pigment to become water soluble and to be excreted
39 NOBEL PRIZE The BIG One! SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION CRISIS ANOMALIES REVOLUTIONARY SCIENCE NEW PARADIGM PARADIGM REINFORCED RESISTANT PUZZLES NORMAL SCIENCE YES NO CONVENTIONAL PARADIGMS GENERATE PUZZLES SOLVE PUZZLES? Flow diagram for revolutionary science:extraordinary claims that become accepted and are integrated into normal science.
40 Different forms of elemental carbon: from diamond to graphite to buckyballs! Diamond Graphite C 60 He@C60
41 An Extraordinary Claim: Carbon can exist in an elemental form that has a structure reminiscent to a soccer ball. The first evidence for the special stability of C 60 Discovery of C 60 Buckyballs Pathological Science or Revolutionary Science? Would you have predicted a Nobel Prize?
42 Robert Curl Harold Kroto Richard Smalley The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1996 for the discovery of fullerene The proposal of Buckeyballs turned out to be revolutionary science
43 Buckyballs pulled into nanowires: Carbon nanotubes!
44 Nanodevices: A carbon nanocar rolling on a gold surface Thanks to Whitney Zoller
45 Putting H 2 inside a buckyball! Open the buckyball, pressure in gaseous H 2, close buckyball! Professor Koichi Komatsu (Kyoto University)
46
Frequency of scores on exam 2. Grade = n(right)/28 x 100
 1 Frequency of scores on exam 2 Grade = n(right)/28 x 100 2 Photochemistry and biology Photons can be toxic (cause DNA bases to dimerize) Photons can be therapeutic: phototherapy Photons can track thoughts,
1 Frequency of scores on exam 2 Grade = n(right)/28 x 100 2 Photochemistry and biology Photons can be toxic (cause DNA bases to dimerize) Photons can be therapeutic: phototherapy Photons can track thoughts,
Quantum Chemistry. NC State University. Lecture 5. The electronic structure of molecules Absorption spectroscopy Fluorescence spectroscopy
 Quantum Chemistry Lecture 5 The electronic structure of molecules Absorption spectroscopy Fluorescence spectroscopy NC State University 3.5 Selective absorption and emission by atmospheric gases (source:
Quantum Chemistry Lecture 5 The electronic structure of molecules Absorption spectroscopy Fluorescence spectroscopy NC State University 3.5 Selective absorption and emission by atmospheric gases (source:
Chemistry 200: Basic Chemistry and Applications Course Syllabus: Spring
 Chemistry 200: Basic Chemistry and Applications Course Syllabus: Spring 2017 2018 Course Instructors Faraj Hasanayn; Office of Faraj Hasanayn: Chem Bldg. Rm 522 Office Hours: TBA Email: fh19@aub.edu.lb.
Chemistry 200: Basic Chemistry and Applications Course Syllabus: Spring 2017 2018 Course Instructors Faraj Hasanayn; Office of Faraj Hasanayn: Chem Bldg. Rm 522 Office Hours: TBA Email: fh19@aub.edu.lb.
NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE AND INTRODUCTION TO MASS SPECTROMETRY
 NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE AND INTRODUCTION TO MASS SPECTROMETRY A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Identify and explain the processes involved in proton ( 1 H) and carbon-13 ( 13 C) nuclear magnetic resonance
NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE AND INTRODUCTION TO MASS SPECTROMETRY A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Identify and explain the processes involved in proton ( 1 H) and carbon-13 ( 13 C) nuclear magnetic resonance
Chemistry 304B, Spring 1999 Lecture 5 1. UV Spectroscopy:
 Chemistry 304B, Spring 1999 Lecture 5 1 Ultraviolet spectroscopy; UV Spectroscopy: Infrared spectroscopy; Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy General basis of spectroscopy: Shine light at a collection
Chemistry 304B, Spring 1999 Lecture 5 1 Ultraviolet spectroscopy; UV Spectroscopy: Infrared spectroscopy; Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy General basis of spectroscopy: Shine light at a collection
Covalent Bonding: Orbitals
 Hybridization and the Localized Electron Model Covalent Bonding: Orbitals A. Hybridization 1. The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new orbitals of equal
Hybridization and the Localized Electron Model Covalent Bonding: Orbitals A. Hybridization 1. The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new orbitals of equal
Assumed knowledge. Chemistry 2. Learning outcomes. Electronic spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules. Franck-Condon Principle (reprise)
 Chemistry 2 Lecture 11 Electronic spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules Assumed knowledge For bound excited states, transitions to the individual vibrational levels of the excited state are observed with
Chemistry 2 Lecture 11 Electronic spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules Assumed knowledge For bound excited states, transitions to the individual vibrational levels of the excited state are observed with
Lectures Spectroscopy. Fall 2012
 Lectures 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2012 1 spectroscopic principles (Chem 1M/1N exps. #6 and #11) 4 1 spectroscopic excitations ( E = h = hc/ ; = c ) (nm) (sec -1 ) radiation technique molecular excitation
Lectures 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2012 1 spectroscopic principles (Chem 1M/1N exps. #6 and #11) 4 1 spectroscopic excitations ( E = h = hc/ ; = c ) (nm) (sec -1 ) radiation technique molecular excitation
Photochemical principles
 Chapter 1 Photochemical principles Dr. Suzan A. Khayyat 1 Photochemistry Photochemistry is concerned with the absorption, excitation and emission of photons by atoms, atomic ions, molecules, molecular
Chapter 1 Photochemical principles Dr. Suzan A. Khayyat 1 Photochemistry Photochemistry is concerned with the absorption, excitation and emission of photons by atoms, atomic ions, molecules, molecular
Lectures Spectroscopy. Fall 2012
 Lectures 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2012 1 spectroscopic principles (Chem 1M/1N exps. #6 and #11) 4 spectroscopic excitations ( E = h = hc/ ; = c ) (nm) (sec -1 ) radiation technique molecular excitation
Lectures 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2012 1 spectroscopic principles (Chem 1M/1N exps. #6 and #11) 4 spectroscopic excitations ( E = h = hc/ ; = c ) (nm) (sec -1 ) radiation technique molecular excitation
and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
ANNOUNCEMENTS. If you have questions about your exam 2 grade, write to me or Chapter 8 homework due April. 13 th.
 ANNOUNCEMENTS If you have questions about your exam 2 grade, write to me or Chem200@mail.sdsu.edu. Chapter 8 homework due April. 13 th. Chapter 9 home work due April. 20th. Exam 3 is 4/14 at 2 pm. LECTURE
ANNOUNCEMENTS If you have questions about your exam 2 grade, write to me or Chem200@mail.sdsu.edu. Chapter 8 homework due April. 13 th. Chapter 9 home work due April. 20th. Exam 3 is 4/14 at 2 pm. LECTURE
MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY Chapter 10.8, Morrison and Boyd
 MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY Chapter 10.8, Morrison and Boyd more understanding: why oxygen is paramagnetic, why H2 + exists; explanation of excited electronic states (e.g., visible spectra) eliminates need
MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY Chapter 10.8, Morrison and Boyd more understanding: why oxygen is paramagnetic, why H2 + exists; explanation of excited electronic states (e.g., visible spectra) eliminates need
Ch4 and Ch5. Atomic History and the Atom
 Ch4 and Ch5 Atomic History and the Atom Ch4.2 What are atoms? Atoms are the smallest part of an element that still has the element s properties. Ch. 4.3 The Atom is Defined 400 B.C. the Greek philosopher
Ch4 and Ch5 Atomic History and the Atom Ch4.2 What are atoms? Atoms are the smallest part of an element that still has the element s properties. Ch. 4.3 The Atom is Defined 400 B.C. the Greek philosopher
Honors Ch3 and Ch4. Atomic History and the Atom
 Honors Ch3 and Ch4 Atomic History and the Atom Ch. 3.1 The Atom is Defined 400 B.C. the Greek philosopher Democritus said that the world was made of two things: Empty space and tiny particles called atoms
Honors Ch3 and Ch4 Atomic History and the Atom Ch. 3.1 The Atom is Defined 400 B.C. the Greek philosopher Democritus said that the world was made of two things: Empty space and tiny particles called atoms
Chapter 13. Conjugated Unsaturated Systems. +,., - Allyl. What is a conjugated system? AllylicChlorination (High Temperature)
 What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
on-line spectroscopy 1!!! Chemistry 1B Fall 2013 Chemistry 1B, Fall 2013 Lecture Spectroscopy Lectures Spectroscopy Fall 2013
 Lecture 190 Spectroscopy Flipping the lecture discussion Flip teaching (or flipped classroom) is a form of blended learning in which students learn new content online by watching video lectures, usually
Lecture 190 Spectroscopy Flipping the lecture discussion Flip teaching (or flipped classroom) is a form of blended learning in which students learn new content online by watching video lectures, usually
Randa AbiRafi Jaber Office: Chem Bldg. Rm 212 Office Hrs: Tue, Wed 11:00 Thu: 2:00 3:00 pm
 Faraj Hasanayn Office Chem Bldg. Rm 522 Office Hrs: Mon: 10:30 11:30 am Tuesday: 1:30 2:30 pm, and by appointment Email: fh19@aub.edu.lb, Phone Ext: 3994 Randa AbiRafi Jaber Office: Chem Bldg. Rm 212 Office
Faraj Hasanayn Office Chem Bldg. Rm 522 Office Hrs: Mon: 10:30 11:30 am Tuesday: 1:30 2:30 pm, and by appointment Email: fh19@aub.edu.lb, Phone Ext: 3994 Randa AbiRafi Jaber Office: Chem Bldg. Rm 212 Office
Conjugated Systems. With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn
 Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Topics Spectroscopy. Fall 2016
 Topics 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2016 1 SPECTROSCOPY: short wavelength regions ESCA (photoelectron) and UV handout 2 alert approach for spectroscopy material not straight from text chapter must FOLLOW videos,
Topics 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2016 1 SPECTROSCOPY: short wavelength regions ESCA (photoelectron) and UV handout 2 alert approach for spectroscopy material not straight from text chapter must FOLLOW videos,
CHEM Inorganic Chemistry for High School Teachers II (Spring 2014)
 CHEM 821 -- Inorganic Chemistry for High School Teachers II (Spring 2014) 3 credit hours Online Format (January 13 May 8, 2014) Instructor: Christopher L. Exstrom Office: 405C Bruner Hall of Science Phone:
CHEM 821 -- Inorganic Chemistry for High School Teachers II (Spring 2014) 3 credit hours Online Format (January 13 May 8, 2014) Instructor: Christopher L. Exstrom Office: 405C Bruner Hall of Science Phone:
Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy
 Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated Systems - Conjugated systems have alternating single and double bonds. For example: C=C C=C C=C and C=C C=O - This is not conjugated because the double
Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated Systems - Conjugated systems have alternating single and double bonds. For example: C=C C=C C=C and C=C C=O - This is not conjugated because the double
Chapter 2 Protecting the Ozone Layer. The Ozone Hole
 Today (Tues 2/24) Newspaper Articles: Ciara Rodwell and Melissa Regan Intro to Ozone, Ozone Hole, & Chapter 2 Light, matter, and human health! Laboratory: Experiment 4 You design investigation Start Ozone
Today (Tues 2/24) Newspaper Articles: Ciara Rodwell and Melissa Regan Intro to Ozone, Ozone Hole, & Chapter 2 Light, matter, and human health! Laboratory: Experiment 4 You design investigation Start Ozone
Overview of Photosynthesis
 Overview of Photosynthesis In photosynthesis, green plants absorb energy from the sun and use the energy to drive an endothermic reaction, the reaction between carbon dioxide and water that produces glucose
Overview of Photosynthesis In photosynthesis, green plants absorb energy from the sun and use the energy to drive an endothermic reaction, the reaction between carbon dioxide and water that produces glucose
Chemistry 1B-AL, Fall 2016 Topics Spectroscopy
 Chemistry 1BAL, Fall 2016 Topics 1920 Spectroscopy Topics 1920 Spectroscopy SPECTROSCOPY: short wavelength regions ESCA (photoelectron) and UV Fall 2016 handout 1 2 alert spectroscopy handout approach
Chemistry 1BAL, Fall 2016 Topics 1920 Spectroscopy Topics 1920 Spectroscopy SPECTROSCOPY: short wavelength regions ESCA (photoelectron) and UV Fall 2016 handout 1 2 alert spectroscopy handout approach
Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer
 Chapter 2: Protecting the zone Layer Why do we need to do to protect the ozone layer? Isn t ozone hazardous to human health? Why is the ozone layer getting smaller? What can we do (if anything) to help
Chapter 2: Protecting the zone Layer Why do we need to do to protect the ozone layer? Isn t ozone hazardous to human health? Why is the ozone layer getting smaller? What can we do (if anything) to help
Introduction ENERGY. Heat Electricity Electromagnetic irradiation (light)
 Photochemistry Introduction ENERGY Heat Electricity Electromagnetic irradiation (light) Vision: Triggered by a photochemical reaction Is red in the dark? The answer must be NO - Since what we see as colour
Photochemistry Introduction ENERGY Heat Electricity Electromagnetic irradiation (light) Vision: Triggered by a photochemical reaction Is red in the dark? The answer must be NO - Since what we see as colour
General Chemistry I (2012) Lecture by B. H. Hong
 3.8 The Limitations of Lewis's Theory 3.9 Molecular Orbitals The valence-bond (VB) and molecular orbital (MO) theories are both procedures for constructing approximate wavefunctions of electrons. The MO
3.8 The Limitations of Lewis's Theory 3.9 Molecular Orbitals The valence-bond (VB) and molecular orbital (MO) theories are both procedures for constructing approximate wavefunctions of electrons. The MO
Topics Spectroscopy. Fall 2016
 Topics 1920 Spectroscopy Fall 2016 1 SPECTROSCOPY: short wavelength regions ESCA (photoelectron) and UV handout 2 1 alert approach for spectroscopy material not straight from text chapter must FOLLOW videos,
Topics 1920 Spectroscopy Fall 2016 1 SPECTROSCOPY: short wavelength regions ESCA (photoelectron) and UV handout 2 1 alert approach for spectroscopy material not straight from text chapter must FOLLOW videos,
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 3. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 3 Quantum Transitions The energy of a photon can also be transferred to an elementary particle by adsorption if the energy of the photon exactly matches the
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 3 Quantum Transitions The energy of a photon can also be transferred to an elementary particle by adsorption if the energy of the photon exactly matches the
Fluorescence and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
 Fluorescence and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy Murphy, B. (2017). Fluorescence and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Lecture 3. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College
Fluorescence and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy Murphy, B. (2017). Fluorescence and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Lecture 3. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
17.1 Classes of Dienes
 W 2/1 Due: HW14, spec03 Due: n/a M 2/6 Lecture HW14 grading Lect17a Conjugated π systems Lecture quiz Lect17b Lab Lab02 Qual Analysis II (cont) 7-1 17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for
W 2/1 Due: HW14, spec03 Due: n/a M 2/6 Lecture HW14 grading Lect17a Conjugated π systems Lecture quiz Lect17b Lab Lab02 Qual Analysis II (cont) 7-1 17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for
Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Key Words Conjugated Diene Resonance Structures Dienophiles Concerted Reaction Pericyclic Reaction Cycloaddition Reaction Bridged Bicyclic Compound Cyclic
Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Key Words Conjugated Diene Resonance Structures Dienophiles Concerted Reaction Pericyclic Reaction Cycloaddition Reaction Bridged Bicyclic Compound Cyclic
progressive electromagnetic wave
 LECTURE 11 Ch17 A progressive electromagnetic wave is a self-supporting, energy-carrying disturbance that travels free of its source. The light from the Sun travels through space (no medium) for only 8.3
LECTURE 11 Ch17 A progressive electromagnetic wave is a self-supporting, energy-carrying disturbance that travels free of its source. The light from the Sun travels through space (no medium) for only 8.3
Increasing energy. ( 10 4 cm -1 ) ( 10 2 cm -1 )
 The branch of science which deals with the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter is called spectroscopy The energy absorbed or emitted in each transition corresponds to a definite frequency
The branch of science which deals with the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter is called spectroscopy The energy absorbed or emitted in each transition corresponds to a definite frequency
Lecture 2 nmr Spectroscopy
 Lecture 2 nmr Spectroscopy Pages 427 430 and Chapter 13 Molecular Spectroscopy Molecular spectroscopy: the study of the frequencies of electromagnetic radiation that are absorbed or emitted by substances
Lecture 2 nmr Spectroscopy Pages 427 430 and Chapter 13 Molecular Spectroscopy Molecular spectroscopy: the study of the frequencies of electromagnetic radiation that are absorbed or emitted by substances
Excited State Processes
 Excited State Processes Photophysics Fluorescence (singlet state emission) Phosphorescence (triplet state emission) Internal conversion (transition to singlet gr. state) Intersystem crossing (transition
Excited State Processes Photophysics Fluorescence (singlet state emission) Phosphorescence (triplet state emission) Internal conversion (transition to singlet gr. state) Intersystem crossing (transition
Tentative content material to be covered for Exam 2 (Wednesday, November 2, 2005)
 Tentative content material to be covered for Exam 2 (Wednesday, November 2, 2005) Chapter 16 Quantum Mechanics and the Hydrogen Atom 16.1 Waves and Light 16.2 Paradoxes in Classical Physics 16.3 Planck,
Tentative content material to be covered for Exam 2 (Wednesday, November 2, 2005) Chapter 16 Quantum Mechanics and the Hydrogen Atom 16.1 Waves and Light 16.2 Paradoxes in Classical Physics 16.3 Planck,
Chapter 9. Covalent Bonding: Orbitals
 Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals EXERCISE! Draw the Lewis structure for methane, CH 4. What is the shape of a methane molecule? tetrahedral What are the bond angles? 109.5 o H H C H H Copyright Cengage
Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals EXERCISE! Draw the Lewis structure for methane, CH 4. What is the shape of a methane molecule? tetrahedral What are the bond angles? 109.5 o H H C H H Copyright Cengage
π* orbitals do not Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomics
 Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomics CHEM 2060 Lecture 26: MO theory contd L26-1 Molecular orbitals can be formed pictorially by looking at the way in which atomic orbitals overlap. Let s look
Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomics CHEM 2060 Lecture 26: MO theory contd L26-1 Molecular orbitals can be formed pictorially by looking at the way in which atomic orbitals overlap. Let s look
New σ bond closes a ring. Loss of one π bond and gain of one σ bond
 CHAPTER 1 Pericyclic Reactions 1.1 INTRODUCTION Pericyclic reactions are defined as the reactions that occur by a concerted cyclic shift of electrons. This definition states two key points that characterise
CHAPTER 1 Pericyclic Reactions 1.1 INTRODUCTION Pericyclic reactions are defined as the reactions that occur by a concerted cyclic shift of electrons. This definition states two key points that characterise
SAM Teachers Guide Photosynthesis
 SAM Teachers Guide Photosynthesis Overview This activity focuses on how certain molecules called pigments interact with light and determine the color of plants. Students explore how molecules such as chlorophyll
SAM Teachers Guide Photosynthesis Overview This activity focuses on how certain molecules called pigments interact with light and determine the color of plants. Students explore how molecules such as chlorophyll
CHAPTER 13 Molecular Spectroscopy 2: Electronic Transitions
 CHAPTER 13 Molecular Spectroscopy 2: Electronic Transitions I. General Features of Electronic spectroscopy. A. Visible and ultraviolet photons excite electronic state transitions. ε photon = 120 to 1200
CHAPTER 13 Molecular Spectroscopy 2: Electronic Transitions I. General Features of Electronic spectroscopy. A. Visible and ultraviolet photons excite electronic state transitions. ε photon = 120 to 1200
Introduction. Electromagnetic Waves. Electromagnetic Waves
 Introduction Much of the information we know about electrons comes from studies of interactions of light and matter. In the early 1900 s, scientists discovered that light has properties of both a wave
Introduction Much of the information we know about electrons comes from studies of interactions of light and matter. In the early 1900 s, scientists discovered that light has properties of both a wave
Optical Spectroscopy 1 1. Absorption spectroscopy (UV/vis)
 Optical Spectroscopy 1 1. Absorption spectroscopy (UV/vis) 2 2. Circular dichroism (optical activity) CD / ORD 3 3. Fluorescence spectroscopy and energy transfer Electromagnetic Spectrum Electronic Molecular
Optical Spectroscopy 1 1. Absorption spectroscopy (UV/vis) 2 2. Circular dichroism (optical activity) CD / ORD 3 3. Fluorescence spectroscopy and energy transfer Electromagnetic Spectrum Electronic Molecular
CHEM Chapter 6. Basic Quantum Chemistry (Homework). WL36
 CHEM 1411. Chapter 6. Basic Quantum Chemistry (Homework). WL36 1. The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom found its greatest support in experimental work on the photoelectric effect. A) True B) False 2. A
CHEM 1411. Chapter 6. Basic Quantum Chemistry (Homework). WL36 1. The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom found its greatest support in experimental work on the photoelectric effect. A) True B) False 2. A
Atomic Structure and Periodicity
 Atomic Structure and Periodicity Atoms and isotopes: Isotopes-#p + same for all but mass number is different b/c of # n o Average atomic mass is weighted average of all the isotopes for an element Average
Atomic Structure and Periodicity Atoms and isotopes: Isotopes-#p + same for all but mass number is different b/c of # n o Average atomic mass is weighted average of all the isotopes for an element Average
CHEM 261 Notes Nov 22, 2017 REVIEW:
 155 CEM 261 Notes Nov 22, 2017 REVIEW: Recall how we can show the energy levels of the atomic orbitals of C. If the C is sp 2 hybridized, two of the 2p orbitals combine with the 2s orbital to form two
155 CEM 261 Notes Nov 22, 2017 REVIEW: Recall how we can show the energy levels of the atomic orbitals of C. If the C is sp 2 hybridized, two of the 2p orbitals combine with the 2s orbital to form two
Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy :
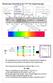 Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy : X-ray: core electron excitation UV: valance electronic excitation IR: molecular vibrations Radio waves: Nuclear spin states (in a magnetic field) The wavelength
Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy : X-ray: core electron excitation UV: valance electronic excitation IR: molecular vibrations Radio waves: Nuclear spin states (in a magnetic field) The wavelength
Lecture 16 C1403 October 31, Molecular orbital theory: molecular orbitals and diatomic molecules
 Lecture 16 C1403 October 31, 2005 18.1 Molecular orbital theory: molecular orbitals and diatomic molecules 18.2 Valence bond theory: hybridized orbitals and polyatomic molecules Bond order, bond lengths,
Lecture 16 C1403 October 31, 2005 18.1 Molecular orbital theory: molecular orbitals and diatomic molecules 18.2 Valence bond theory: hybridized orbitals and polyatomic molecules Bond order, bond lengths,
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion #1: A body continues at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by a force. Why doesn t the soccer ball move on its own? What causes a soccer ball to roll
Newton s Laws of Motion #1: A body continues at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by a force. Why doesn t the soccer ball move on its own? What causes a soccer ball to roll
WELCOME TO CHEM 110 CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES PROF:
 WELCOME TO CHEM 110 CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES PROF: John Asbury SECTIONS: 1-131 13 LECTURES: MWF 9:05 Forum Dr. Asbury Office Hours 3 5 pm, Wed. and Thurs. Room 112 Chem. Building Chemistry building Whitmore
WELCOME TO CHEM 110 CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES PROF: John Asbury SECTIONS: 1-131 13 LECTURES: MWF 9:05 Forum Dr. Asbury Office Hours 3 5 pm, Wed. and Thurs. Room 112 Chem. Building Chemistry building Whitmore
Review Outline Chemistry 1B, Fall 2012
 Review Outline Chemistry 1B, Fall 2012 -------------------------------------- Chapter 12 -------------------------------------- I. Experiments and findings related to origin of quantum mechanics A. Planck:
Review Outline Chemistry 1B, Fall 2012 -------------------------------------- Chapter 12 -------------------------------------- I. Experiments and findings related to origin of quantum mechanics A. Planck:
Chemistry 218 Spring Molecular Structure
 Chemistry 218 Spring 2015-2016 Molecular Structure R. Sultan COURSE SYLLABUS Email: rsultan@aub.edu.lb Homepage: http://staff.aub.edu.lb/~rsultan/ Lectures: 12:30-13:45 T, Th. 101 Chemistry Textbook: P.
Chemistry 218 Spring 2015-2016 Molecular Structure R. Sultan COURSE SYLLABUS Email: rsultan@aub.edu.lb Homepage: http://staff.aub.edu.lb/~rsultan/ Lectures: 12:30-13:45 T, Th. 101 Chemistry Textbook: P.
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA
 CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
Lecture 18, March 2, 2015 graphene, bucky balls, bucky tubes
 Lecture 18, March 2, 2015 graphene, bucky balls, bucky tubes Elements of Quantum Chemistry with Applications to Chemical Bonding and Properties of Molecules and Solids Course number: Ch125a; Room 115 BI
Lecture 18, March 2, 2015 graphene, bucky balls, bucky tubes Elements of Quantum Chemistry with Applications to Chemical Bonding and Properties of Molecules and Solids Course number: Ch125a; Room 115 BI
Chemistry 213 Practical Spectroscopy
 Chemistry 213 Practical Spectroscopy Dave Berg djberg@uvic.ca Elliott 314 A course in determining structure by spectroscopic methods Different types of spectroscopy afford different information about molecules
Chemistry 213 Practical Spectroscopy Dave Berg djberg@uvic.ca Elliott 314 A course in determining structure by spectroscopic methods Different types of spectroscopy afford different information about molecules
Ozone in the Atmosphere
 Ozone in the Atmosphere Why are we concerned with ozone? This simple molecule affects us in very important ways. It protects us, as well as all animals and plants on our planet, from the harm that ultraviolet
Ozone in the Atmosphere Why are we concerned with ozone? This simple molecule affects us in very important ways. It protects us, as well as all animals and plants on our planet, from the harm that ultraviolet
A. 24 B. 27 C. 30 D. 32 E. 33. A. It is impossible to tell from the information given. B. 294 mm C. 122 mm D. 10 mm E. 60 mm A. 1 H B. C. D. 19 F " E.
 CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 1 Sept. 24, 2012 FORM A 1. A microwave oven uses 2.45! 10 9 Hz electromagnetic waves to heat food. What is the wavelength of this radiation in mm? A. It is impossible to tell from the
CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 1 Sept. 24, 2012 FORM A 1. A microwave oven uses 2.45! 10 9 Hz electromagnetic waves to heat food. What is the wavelength of this radiation in mm? A. It is impossible to tell from the
Chapter 10 Theories of Covalent Bonding
 Chapter 10 Theories of Covalent Bonding 1 Atomic Orbitals Molecules Bonding and 2 Molecular Structure Questions How are molecules held together? Why is O 2 paramagnetic? And how is this property connected
Chapter 10 Theories of Covalent Bonding 1 Atomic Orbitals Molecules Bonding and 2 Molecular Structure Questions How are molecules held together? Why is O 2 paramagnetic? And how is this property connected
Announcements Self-inductance. Self-inductance. RL Circuit. RL Circuit, cont 3/11/2011. Chapter (not.9-.10) τ = R. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 21.8-13(not.9-.10) Electromagnetic Announcements Clicker quizzes NO LONGER GRADED! WebAssign HW Set 8 due this Friday Problems cover material from Chapters 21-22 Office hours: My office hours today
Chapter 21.8-13(not.9-.10) Electromagnetic Announcements Clicker quizzes NO LONGER GRADED! WebAssign HW Set 8 due this Friday Problems cover material from Chapters 21-22 Office hours: My office hours today
Mock Exam Which elements have a single s electron in their outermost shell? a. Na, Al, Ar b. Cl, I, Br c. Cl, O, N d.
 Mock Exam 2 1. What is Aufbau s principle? a. Electrons have a negative one charge b. Electrons have opposite spins c. Electrons fill the lowest-energy atomic orbitals of a ground-state first d. The radius
Mock Exam 2 1. What is Aufbau s principle? a. Electrons have a negative one charge b. Electrons have opposite spins c. Electrons fill the lowest-energy atomic orbitals of a ground-state first d. The radius
Valence Bond Theory - Description
 Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
Molecular Geometry. Introduction
 Molecular Geometry Introduction In this lab, you will explore how the geometry and structure of molecules are influenced by the number of bonding electron pairs and lone pairs of electrons around different
Molecular Geometry Introduction In this lab, you will explore how the geometry and structure of molecules are influenced by the number of bonding electron pairs and lone pairs of electrons around different
The many forms of carbon
 The many forms of carbon Carbon is not only the basis of life, it also provides an enormous variety of structures for nanotechnology. This versatility is connected to the ability of carbon to form two
The many forms of carbon Carbon is not only the basis of life, it also provides an enormous variety of structures for nanotechnology. This versatility is connected to the ability of carbon to form two
Infrared Spectroscopy
 Infrared Spectroscopy The Interaction of Light with Matter Electric fields apply forces to charges, according to F = qe In an electric field, a positive charge will experience a force, but a negative charge
Infrared Spectroscopy The Interaction of Light with Matter Electric fields apply forces to charges, according to F = qe In an electric field, a positive charge will experience a force, but a negative charge
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life. Biology Photosynthesis
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Biology 2201 3.2 The Process of Photosynthesis Photosynthesis The process by which an organism captures the energy of the sun to convert CO 2 and water into glucose. Light
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Biology 2201 3.2 The Process of Photosynthesis Photosynthesis The process by which an organism captures the energy of the sun to convert CO 2 and water into glucose. Light
Experiment #9. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
 Introduction Experiment #9. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of light with matter. This interaction can be in the form of the absorption or the emission of electromagnetic
Introduction Experiment #9. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of light with matter. This interaction can be in the form of the absorption or the emission of electromagnetic
Nature of the Chemical Bond with applications to catalysis, materials science, nanotechnology, surface science, bioinorganic chemistry, and energy
 Lecture 22, November 16, 2016 Graphite, graphene, bucky balls, bucky tubes Nature of the Chemical Bond with applications to catalysis, materials science, nanotechnology, surface science, bioinorganic chemistry,
Lecture 22, November 16, 2016 Graphite, graphene, bucky balls, bucky tubes Nature of the Chemical Bond with applications to catalysis, materials science, nanotechnology, surface science, bioinorganic chemistry,
CHEM J-2 June 2014
 CHEM1611 014-J- June 014 Reaction of nitrogen-14 with a neutron forms two products, one of which is carbon-14. Radiocarbon dating involves the carbon-14 isotope which undergoes β-decay (emission of an
CHEM1611 014-J- June 014 Reaction of nitrogen-14 with a neutron forms two products, one of which is carbon-14. Radiocarbon dating involves the carbon-14 isotope which undergoes β-decay (emission of an
CHEM6416 Theory of Molecular Spectroscopy 2013Jan Spectroscopy frequency dependence of the interaction of light with matter
 CHEM6416 Theory of Molecular Spectroscopy 2013Jan22 1 1. Spectroscopy frequency dependence of the interaction of light with matter 1.1. Absorption (excitation), emission, diffraction, scattering, refraction
CHEM6416 Theory of Molecular Spectroscopy 2013Jan22 1 1. Spectroscopy frequency dependence of the interaction of light with matter 1.1. Absorption (excitation), emission, diffraction, scattering, refraction
Chapter 10. VSEPR Model: Geometries
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Farthest apart
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Farthest apart
Energy can be transformed from one form to another
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture you will be able to: Photosynthesis 1. Understand that ENERGY can be transformed from one form to another. 2. Know that energy exist in two forms; free energy
LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture you will be able to: Photosynthesis 1. Understand that ENERGY can be transformed from one form to another. 2. Know that energy exist in two forms; free energy
Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Diene: molecule with two double bonds Conjugated diene: alternating double and single bonds
 Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Diene: molecule with two double bonds Conjugated diene: alternating double and single bonds C-C single bond lkene Diene C=C double bonds Conjugate
Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Diene: molecule with two double bonds Conjugated diene: alternating double and single bonds C-C single bond lkene Diene C=C double bonds Conjugate
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes REVIEW... Q Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC OZONE (in
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes REVIEW... Q Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC OZONE (in
Because light behaves like a wave, we can describe it in one of two ways by its wavelength or by its frequency.
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
NPTEL/IITM. Molecular Spectroscopy Lectures 1 & 2. Prof.K. Mangala Sunder Page 1 of 15. Topics. Part I : Introductory concepts Topics
 Molecular Spectroscopy Lectures 1 & 2 Part I : Introductory concepts Topics Why spectroscopy? Introduction to electromagnetic radiation Interaction of radiation with matter What are spectra? Beer-Lambert
Molecular Spectroscopy Lectures 1 & 2 Part I : Introductory concepts Topics Why spectroscopy? Introduction to electromagnetic radiation Interaction of radiation with matter What are spectra? Beer-Lambert
17.1 Classes of Dienes
 17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for dienes: Cumulated: pi bonds are adjacent. Conjugated: pi bonds are separated by exactly ONE single bond. Isolated: pi bonds are separated by any distance
17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for dienes: Cumulated: pi bonds are adjacent. Conjugated: pi bonds are separated by exactly ONE single bond. Isolated: pi bonds are separated by any distance
Name: Class: Date: 3. How many lone pairs of electrons are assigned to the carbon atom in carbon monoxide? a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3
 Class: Date: Midterm 3, Fall 2009 Record your name on the top of this exam and on the scantron form. Record the test ID letter in the top right box of the scantron form. Record all of your answers on the
Class: Date: Midterm 3, Fall 2009 Record your name on the top of this exam and on the scantron form. Record the test ID letter in the top right box of the scantron form. Record all of your answers on the
Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation
 Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Molecular Geometry. Introduction
 Molecular Geometry Introduction In this lab, you will explore how the geometry and structure of molecules are influenced by the number of bonding electron pairs and lone pairs of electrons around different
Molecular Geometry Introduction In this lab, you will explore how the geometry and structure of molecules are influenced by the number of bonding electron pairs and lone pairs of electrons around different
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH
 C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE The Electromagnetic Spectrum The Wave
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE The Electromagnetic Spectrum The Wave
MO theory is better for spectroscopy (Exited State Properties; Ionization)
 CHEM 2060 Lecture 25: MO Theory L25-1 Molecular Orbital Theory (MO theory) VB theory treats bonds as electron pairs. o There is a real emphasis on this point (over-emphasis actually). VB theory is very
CHEM 2060 Lecture 25: MO Theory L25-1 Molecular Orbital Theory (MO theory) VB theory treats bonds as electron pairs. o There is a real emphasis on this point (over-emphasis actually). VB theory is very
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 7 NATURE OF LIGHT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM When white light passes through a prism, it spreads out into a rainbow of colours, with red at one end and
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 7 NATURE OF LIGHT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM When white light passes through a prism, it spreads out into a rainbow of colours, with red at one end and
Chapter 10. VSEPR Model: Geometries
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Two bonds Two
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Two bonds Two
Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy
 Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy Chromophore The part of a molecule responsible for imparting color, are called as chromospheres. OR The functional groups containing multiple bonds capable of absorbing
Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy Chromophore The part of a molecule responsible for imparting color, are called as chromospheres. OR The functional groups containing multiple bonds capable of absorbing
Chemistry 1B. Fall Lectures Coordination Chemistry
 Chemistry 1B Fall 2012 Lectures 13-14 Coordination Chemistry 1 LISTEN UP!!! WE WILL ONLY COVER LIMITED PARTS OF CHAPTER 19 (pp. 933-937; 946-948; 958-966) [940-944;952-954;963-970] 7th 2 good reasons for
Chemistry 1B Fall 2012 Lectures 13-14 Coordination Chemistry 1 LISTEN UP!!! WE WILL ONLY COVER LIMITED PARTS OF CHAPTER 19 (pp. 933-937; 946-948; 958-966) [940-944;952-954;963-970] 7th 2 good reasons for
7a. Structure Elucidation: IR and 13 C-NMR Spectroscopies (text , , 12.10)
 2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7a.1 7a. Structure Elucidation: IR and 13 C-NMR Spectroscopies (text 11.1 11.5, 12.1 12.5, 12.10) A. Electromagnetic Radiation Energy is
2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7a.1 7a. Structure Elucidation: IR and 13 C-NMR Spectroscopies (text 11.1 11.5, 12.1 12.5, 12.10) A. Electromagnetic Radiation Energy is
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 7 Introduction to Spectroscopy
 Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 7 Introduction to Spectroscopy Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of radiant energy and matter. The electromagnetic spectrum diagram is shown below to use a reference.
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 7 Introduction to Spectroscopy Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of radiant energy and matter. The electromagnetic spectrum diagram is shown below to use a reference.
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: Photosynthesis
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: Photosynthesis Unit Objective I can compare the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in terms of energy flow, reactants, and products. During this
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: Photosynthesis Unit Objective I can compare the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in terms of energy flow, reactants, and products. During this
Topic 8: Beyond Light
 Topic 8: Beyond Light The Sun is the most abundant source of direct natural light on the Earth. There are other forms of energy, invisible, that are also supplied by this source. The tiny band of visible
Topic 8: Beyond Light The Sun is the most abundant source of direct natural light on the Earth. There are other forms of energy, invisible, that are also supplied by this source. The tiny band of visible
Course Syllabus. Department: Science & Technology. Date: April I. Course Prefix and Number: CHM 212. Course Name: Organic Chemistry II
 Department: Science & Technology Date: April 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: CHM 212 Course Name: Organic Chemistry II Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 5 credit hours and 7 (3:3:1) contact
Department: Science & Technology Date: April 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: CHM 212 Course Name: Organic Chemistry II Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 5 credit hours and 7 (3:3:1) contact
light-dependent reactions (i.e., light reactions)
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1. Understand that ENERGY can be transformed from one form to another. 2. Know that energy exist in two forms; free energy - available
LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1. Understand that ENERGY can be transformed from one form to another. 2. Know that energy exist in two forms; free energy - available
February 8, 2018 Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 7 UV-Vis spectroscopy February 8, 2018 First Midterm Exam When: Wednesday, 2/14 When: 7-9 PM (please do not be late) Where: WEL 2.122 This room!!! What: Covers material through today s lecture
Lecture 7 UV-Vis spectroscopy February 8, 2018 First Midterm Exam When: Wednesday, 2/14 When: 7-9 PM (please do not be late) Where: WEL 2.122 This room!!! What: Covers material through today s lecture
Conjugated Dienes. Chapter 14 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John E. McMurry
 Conjugated Dienes Chapter 14 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John E. McMurry 1 Dienes Propadiene (allene) is a cumulated diene 1,3-Butadiene is a conjugated diene. 1,4-Pentadiene is an isolated diene.
Conjugated Dienes Chapter 14 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John E. McMurry 1 Dienes Propadiene (allene) is a cumulated diene 1,3-Butadiene is a conjugated diene. 1,4-Pentadiene is an isolated diene.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy
 Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
