(b) Answer the following Explain addition polymerization with example. 2. Give the difference between paint and varnish.
|
|
|
- Wilfred Lester
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Diploma Engineering Semester I/II Examination WINTER 2013 Subject code: Date: 20/12/2013 Subject Name: Applied Science - II (CHEMISTRY) Time: 10:30 TO 1:00 Total Marks: 70 Instructions: 1. Attempt five questions. 2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks. 4. Each question carry equal marks (14 marks) Q.1 (a) Answer the following. (Any Four) 8 1. Explain full meaning of 92 U 235 & 7 N Give molecular weight of CaCl 2 and MgCl Calculate the P H of 0.01 N NaOH solution. 4. Give the characteristics of lubricants. 5. What is ionic bond? Give one example of it. 6. Define- Acid number and Saponification number. (b) Answer the following Explain addition polymerization with example. 2. Give the difference between paint and varnish. Q.2 (a) What is Degree of ionization? Explain the factors affecting to the degree of ionization. (a) What is buffer solution? Give the types of buffer solution with suitable examples. Q.2 (b) What is covalent bond? Give the types of covalent bond and explain polar characteristics of covalent bond. (b) Calculate the temporary, permanent and total hardness of the water sample containing following salts- Ca(HCO 3 ) 2 = 16.2ppm, CaCl 2 = 33.3 ppm, MgCl 2 =9.5 ppm, MgSO 4 = 24.0 ppm Q.2 (c) Give the difference between hard water and soft water. 4 (c) Give the difference between thermo plastics and thermo setting plastics. 4 Q.3 (a) Explain- permutit process use for softening of hard water with chemical 5 reactions. (a) What is Hydrogen bond? Give the significance of hydrogen bond. 5 Q.3 (b) Describe- Vulcanization of rubber and give the uses of rubber. 5 1/3
2 (b) What is lubricant and lubrication? Explain the types of lubricant with suitable 5 examples. Q.3 (c) What is corrosion? Explain water line corrosion with neat sketch. 4 (c) What is insulating material? Give the types of insulating material with suitable examples. 4 Q.4 (a) Describe the construction, working and principal of electrochemical cell with chemical reaction. Give the function of salt bridge in galvanic cell. 7 Q.4 (b) Write- Aufbau s and Hund s principals. 4 (b) Draw the structures of Sulphur and Phosphorous. 4 Q.4 (c) What is ph? Give the importance of ph measurement in various fields. 3 (c) List the factors affecting to the rate of corrosion. 3 Q.5 Answer the following questions. (a) Describe the Construction and working of standard Hydrogen cell. 5 (b) Explain- Electroplating and Galvanizing. 5 (c) Describe P-type semi-conductors. 4 *************** gaujratai Anauvaad pa`.1 (A) naicao Aapaolaa pa`fnaaonaa jvaaba Aapaao. (kaoe pana caar) U 235 Anao 7 N 14 naao sampauna* Aqa* samajavaao. 2. CaCl 2 Anao MgCl 2 naao ANauBaar lakaao N NaOH naa Z<avaNanaI P H ganaao. 4. snaohkaonaa gaunaqamaao* jnaavaao. 5. Aayainak bamqa kaonao khovaaya? taonaum Aok }dahrna Aapaao. 6. vyaakyaa Aapaao- AoisaD AaMk Anao saabaukrna AaMk. (ba) naicao Aapaolaa pa`fnaaonaa jvaaba Aapaao yaaogasaila bahuqatktaa }dahrna saihta samajavaao. 2. taolai rmga Anao vaaina*sa vaccaonaao tafavata Aapaao. pa`.2 (A) AayanaIkrNa AMSa AoTlao SauM? AayanaIkrNa AMSa }par Asar krtaa pairbalao samajavaao. 5 Aqavaa (A) bafr Z<avaNa AoTlao SauM? bafr Z<avaNanaa pa`karao }dahrna saihta lakaao. 5 pa`.2 (ba) sahsamyaaojk bamqa AoTlao SauM? sahsamyaaojk bamqanaa pa`karao jnaavai, sahsamyaaojk bamqanaum Qa`uivaya laxana samajavaao. Aqavaa 2/3 5
3 (ba) paanainaa namaunaamaam xaaraonaum pa`maana naicao maujba Co, taao taonai xainak kiznataa, kayamai kiznataa Anao kula kiznataa SaaoQaao. Ca(HCO 3 ) 2 = 16.2 paipaiaoma, MgCl 2 = 9.5 paipaiaoma, CaCl 2 = 33.3 paipaiaoma, MgSO 4 = 24.0 paipaiaoma. 5 pa`.2 (k) kzina paanai Anao narma paanai vaccaonaao tafavata Aapaao. 4 Aqavaa (k) taapamaana saunamya(qamaao* plaaistk) Anao taapamaana sqaaipata (qamaao* saoitmga plaaistk ) vaccaonaao tafavata Aapaao. 4 pa`.3 (A) kzina paanainao narma banaavavaa maatonai parmyautit paqqaita rasaayanaik pa`ik`yaa AapaI 5 samajavaao. Aqavaa (A) haed<aojna bamqa kaonao khovaaya? haed<aojnanaum mahtva jnaavaao. 5 pa`.3 (ba) rbar naum valkonaikrna samajavai rbarnaa }payaaogaao jnaavaao. 5 Aqavaa (ba) snaohk Anao snaohna AoTlao SauM? snaohknaa pa`karao }dahrna AapaI samajavaao. 5 pa`.3 (k) xaarna AoTlao SauM? paanainai sapaati naicao qatau xaarna AakRita daori vana*vaao. 4 Aqavaa (k) ivasamvaahi padaqa* AoTlao SauM? ivasamvaahi padaqa*naa pa`karao }dahrna saihta lakaao. 4 pa`.4 (A) ivaqauta rasaayanaik kaoyanaao isaqqaamta, rcanaa Anao kaya* paqqaita rasaayanaik pa`ik`yaaaao AapaI samajavaao. ivaqauta rasaayanaik kaoyamaam xaar saotaunaum kaya* jnaavaao. 7 pa`.4 (ba) Aa}fbaa} Anao humd naa isaqqaamtaao lakaao. 4 Aqavaa (ba) salfr Anao faosfrsa ANau nai AakRita darao. 4 pa`.4 (k) ph AoTlao SauM? ivaivaqa xao~aomaam ph maapananai Agatyataa vana*vaao. 3 Aqavaa (k) xaarna }par Asar krtaa pairbalaonai yaadi Aapaao. 3 pa`.5 naicao Aapaolaa pa`fnaaonaa jvaaba Aapaao. (A) haed<aojna ivaqarta Qa`uvanaI rcanaa Anao kaya* paqqaita samajavaao. 5 (ba) elaokt<aoplaotimga Anao gaolvaonaaejimga samajavaao. 5 (k) P-pa`karnaa AQa*vaahkao samajavaao. 4 *************** 3/3
4 Seat No.: Enrolment No. Subject code: GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Diploma Sem-II Examination July 2010 Subject Name: Applied Science II Date: 06 / /2010 Time: 03:00pm - :30pm Total Marks: 70 Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks. 4. English version Authentic Q.1 Answer the Following : 14 (a) Give electronic configuration of 26 Fe and explain meaning of 92 U 235 (b) What do you mean by Buffer solution? State main uses of this solution. (c) Give standard conditions used to measure electrode potential. (d) Define the terms: (i) Neutralisation number or Acid value (ii) Saponification number (e) What is vulcanisation of rubber? State its advantages. (f) State main constituents of Paints. (g) Give shape of P orbitals. Q.2 (a) Answer the Following : (i) Define degree of ionization (ii) 100 ppm = degree clark. (iii) Define ph. (iv) Explain in short sheradizing. (v) Define Lubricant and Lubrication. (vi) Define Electron affinity. (vii) State any two characteristics of good refractory. (b) Answer the Following : (i) Give importance of Hydrogen Bond. (ii) Explain Oxidation and Reduction process with suitable example. (b) Answer the Following : (i) Give differences between Paint and Varnish. (ii) What is Electrolysis? Explain Electrolysis of CuSo 4 Solution. Q.3 Answer the Following : (a) Derive the equation of Ionic Constant for weak acid. (b) Calculate ph of M H 2 SO 4 (c) Explain Electrotyping. Q.3 Answer the Following : (a) Write short note on N Type semiconductor. (b) Calculate ph of 10-4 M NaOH. (c) Explain Galvanising and Metal Clading. Q.4 Answer the Following : (a) Explain Construction & working of Electrochemical cell. (b) Explain Chlorination of water. (c) State properties and uses of Glass wool and Thermo Cole. 1
5 Q. 4 Answer the Following : (a) What is Polymerisation? Explain Condesation Polymerisation with suitable example. (b) Give Differences between Thermoplastics & Thermosetting Plastics. (c) (i) What type of Lubricant you will select for cutting tools. (ii) State only main Additives of Lubricants. Q.5 Answer the Following : (a) Explain Ion Exchange Method for Softening of Hard water. (b) Write Formula, Properties & Uses of following materials: (i) Polyvinyl Chloride(PVC) (ii) Neoprene rubber (c) Following salts are dissolved in a sample of water. Calculate its total hardness in French degree: Mg(HCO 3 ) 2 = 1.46 mg/ltr MgCl 2 = 19.0 mg/ltr Mg SO 4 = 6.0 mg/ltr Q.5 Answer the Following : (a) List the effects of hard water when it is used in boiler. Explain scale & sludge formation and its prevention. (b) Define Covalent Bond. Explain bond formation in case of CCl 4. (c) Ionic constant (Ka) of 0.01 M CH 3 COOH solution is Calculate concentration of H 3 O +. Q.1 14 (a) 26Fe >,[S8=MGG\] A\WFZ6 H6FJM VG[ 92 U 235 GM ;\5"}6 VY",BMP (b) AOZ N=FJ6 V[8,[ X]\m AOZ N=FJ6GL D]bI p5imlutfvm H6FJMP (c) >,[S8=M0 5M8MlgXI, DF5JF DF8[GL 5 DFl6T XZTM H6FJMP (d) jifbif VF5M (i) G8:YLSZ6 VF\S VYJF V[l;0 D}<I (ii) ;FA]SZ6 VF\S (e) ZaAZG\] J<S[GF>h[XG V[8,[ X]\m T[GF OFINFVM H6FJMP (f) 5[>g8DF\ VFJ[,F D]?I 38SMGF GFD H6FJM (g) P S1FSMGL VFS'lT NMZMP Q.2 GLR[GF HJFA,BM (a) (i) VFIGLSZ6 V\XGL jifbif VF5MP (ii) 100 ppm = l0u L S,F"SP (iii) ph GL jifbif VF5MP (iv) l;z[0f>hl\u 5 ls'if 8}\SDF\ H6FJMP (v) :G[CS VG[ :G[CGGL jifbif VF5MP (vi) >,[S8=MG A\W]TFGL jifbif VF5MP (b) (i) CF>0=MHG A\WG\] DCtJ ;DHFJMP (ii) VMlS;0[XG VG[ lz0sxg VW"5 ls'if pnfcz6 ;lct ;DHFJMP VYJF (b) GLR[GF HJFA VF5Mo (i) 5[>g8 VG[ JFlG"X JrR[GF TOFJTGF D]bI D]NFVM H6FJMP (ii) ljw]tljefhg V[8,[ X\]m CuSo 4 GF N=FJ6G\] ljw]tljefhg ;DHFJMP Q.3 GLR[GF HJFA,BM (a) lga"/ V[l;0 DF8[ VFIlGS VR/F\SG\] ;}+ TFZJMP (b) of M H 2 SO 4 N=FJ6GL ph XMWMP (c) ;DHFJM o >,[S8=M8F>5L\U VYJF 2
6 Q.3 Q.4 Q. 4 Q.5 Q.5 (a) N 5 SFZGF VW"JFCS 5Z 8\}S GM\W,BMP (b) 10-4 M NaOH N=FJ6GL ph XMWMP (c) ;DHFJMo U[<J[GF>lh\U VG[ D[8, S,[l0\U (a) ljw}tzf;fil6s SMQF V[8,[ X\]m T[GL ZRGF VG[ SFI" ;DHFJMP (b) 5F6LGF S,MZLG[XG ljx[ ;DHFJMP (c) u,f;j], VG[ YDM"SM, GF U]6WDM" VG[ p5imum H6FJFP VYJF (a) AC]38STF V[8,[ X\]m ;\WGG AC]W8STF IMuI pnfcz6 J0[ ;DHFJMP (b) TF5;]GdI %,Fl:8S VG[ TF5:YFl5T %,Fl:8S JrR[ TOFJTGF D]bI D]NFVM H6FJMP (c) (i) S8L\U 8]<; DF8[ TD[ SIF 5 SFZGF :G[CSGL 5\;NUL SZXMm (ii) :G[CSDF\ pd[zjfdf\ VFJTF IMUtDSMGF\ GFD H6FJM (a) Sl9G 5F6LG[ GZD AGFJJF DF8[GL VFIG v ljlgdi 5wWlT ;DHFJMP (b) GLR[ NXF"J[,F 5NFYM"GF ZF;FIl6S ;]+4 U]6WD" VG[ p5imum H6FJMP (i) 5Ml,lJGF>, S,MZF>0 (PVC) (ii) lgim5 LG ZAZP (c) 5F6LGF V[S GD}GFDF\ GLR[ NXF"jIF 5 DF6GF 1FFZ VMU/[,F K[P T[GL S], Sl9GTF O \[R l0u LDF\ D[/JMP Mg(HCO 3 ) 2 = 1.46 mg/ltr MgCl 2 = 19.0 mg/ltr Mg SO 4 = 6.0 mg/ltr VYJF (a) AM>,ZDF\ Sl9G 5F6L JF5ZTF\ pnejtl D]xS[,LVM H6FJMP KFZL VG[ VJD,G\] lgdf"6 VG[ T[G[ V8SF JJFGF p5fim H6FJMP (b) ;C;\IMHS A\WGL jifbif VF5MP CCl 4. DF\ A\WG\] lgdf"6 ;DHFJMP (c) 0.01 M CH 3 COOH GM VFIlGS VR/F\S 10-4 K[P TM H 3 O + VFIGGL ;F\N=TF U6MP ********** 3
7 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Diploma Sem-II examination June 2009 Date: 23 / 06 / 2009 Subject code: Subject ame: Applied Science-II (Chemistry) Time: 10:30am-1:00pm Total Marks: 70 Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks. Q.1 (a) Answer the following. 1 Differentiate orbit and orbital 2 Explain the factors affecting the degree of Ionization. (b) Answer the following. 1 What is corrosion? Explain the mechanism of atmospheric corrosion. 2 Explain demineralization method for making soft water with figure. Write equations evolved in it. (c) Answer the following. 1 Define : (I) Flash point (II) Neutralization number 2 Define: oil point. Write the main constituents of it. Q.2 (a) Fill in the blanks. 1 Molecular weight of Platinum ( 78 Pt 191 ) = 2 ph of pure water is 3 A transparent homogeneous liquid made by dissolving resins into drying oil is known as 4 In pitting corrosion area of cathode is than that of anode ppm = degree clerk. 6 For measurement of Pensky Marten apparatus. 7 is used in vulcanization of Rubber. (b) Answer the following 1 Explain the problems occur due to hard water used in boiler. Give its remedies. 2 Write short note on Redwood viscometer. 3 Explain structures of bakelite and Nylon 6,6. Write their usage. (b) Answer the following 1 Explain the structure of molecular solids. Draw sketches of sulphur and phosphorus molecules. 2 Write short notes on: Electroplating and Electrotyping. 3 Explain the construction of Electrochemical cell. Q.3 (a) Write Auf Bau principle. Give electronic configuration of (b) (1) 16 S (2) 17 Co (3) 26Fe What is buffer solution? Give its types and Explain any three applications of buffer solutions
8 (c) A sample of hard water gave on analysis the following results. 1 Ca(HCO 3 ) 2 = 8.1 mg / L 2 Mg(HCO 3 ) 2 = 7.3 mg / L 3 CaSO 4 = 13.6 mg / L 4 MgCl 2 = 9.5 mg / L Atomic weight: H = 1, C = 12, O = 16, Mg = 24, Ca = 40, S = 32, Cl = 35.5 Q.3 (a) What is half cell. Explain construction and working of standard hydrogen half cell. (b) Define: (1) Lubrication (2) Lubricant. Explain fluid film lubrication. (c) What is polymerization? Give its types. Explain any one of them. Q.4 (a) Give meaning of 11 Na 23, 17 Cl 35, 25 Mn 55, 92 U 235 (b) Define: ph. Calculate the ph of M H 2 SO 4 solution. [log 4 = ] (c) Explain factors that affect the rate of corrosion. Q. 4 (a) Explain permutit method. (b) Write about selection of lubricants for 1 Cutting tools 2 Steam turbine (c) Write difference between thermoplastics and thermo setting plastic. Q.5 (a) What is insulating material? Give their ideal characteristics. Write about properties of Glass-Wool and thermo Cole. (b) What are the additives? Write their purpose. (c) Explain chlorination of water by bleaching powder. Q.5 (a) Explain Galvanizing and Tinning of metals. (b) Write difference between metallic conductors and solutions of electrolytes. (c) Explain formation of Hydrogen bond with example. Write its types and significance. : : :. 3 :. :. Q.1. ( ) ( ) ( )?. ( ) -.. 2
9 ( ).-( ) ( ) ( ) -( ),. Q.2. ( ) ( ) ( ) ( PT ) ph= ( ) ( ) = ( ) ( ) Q-2. ( ). ( ). 02 ( )., ( ). ( ). ( ).( ) ( ) 02 ( ). 02 Q-3 ( )... (1)S 16 (2)Co 17 (3)Fe ( )?. ( ). (1)Ca(Hco 3 ) 2= 8.1. / (2)Mg(Hco 3 ) 2 =7.3. / (2)Caso 4=13.6. / (3)Mg Cl 2 =9.5. / [ =H=1,C=12, O=16,Mg= 24, Ca=40.S=32,Cl=35.5],. 3
10 Q.3 ( )?. ( ) (1) (2).. ( )?. Q.4 ( ). (1) 11 Na 23 (2) 17 Cl 35 (3) 25 Mn 55 (4) 92 U 238. ( ) PH H 2 So 4 PH. [Log 10 4=0.6021] ( ). Q.4 ( ). ( ). (1) (2) ( ). Q.5 ( )?.. ( )?. ( ). Q.5 ( ). ( ). ( ).. ************** 4
11 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Diploma Sem-II Remedial Examination September 2009 Subject code: Subject Name: App. Sci. II Date: 18 / 09 / 2009 Time: 03:00pm- :30pm Total Marks: 70 Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks. 4. English version Authentic Q.1 Answer the following questions. (a) Give the electronic configuration of (1) 26 Fe (2) 14 Si (3) 11 Na (4) 20 Ca (b) Write the industrial applications of electrolytes. (c) Calculate the ph of 0.0 M HCl solution. [ log 5 = ] Q.2 Answer the following questions. (a) Filling the blanks. (1) Silica and fire clay are the example of Refractory. (2) A heating process of added sulpher in Natural rubber is. (3) impurities added Ge or Si is know as P-type semiconductor. (4) ph of acid is less than and that of base is more than. (5) In pitting corrosion area of cathode is than area of anode. (6) Galvanizing is coating. (7) Mg(HCO 3 ) 2 is produced hardness in water. (b) (1) Define: (i) Fire point (ii) Drop point (iii) Saponification number (2) Give the example of basic refractories. 03 (b) (1) Define: (i) orbital (ii) hard water (iii) polymer (2) Write the applications of buffer solutions 03 Q.3 Answer the following questions. (a) Explain Auf Bau principle. (b) Write only the names of factors affecting the degree of ionization. (c) What is Electro chemical series? State importance of it. Q.3 Answer the following questions. (a) Write the bad effect of using hard water in boiler. (b) Explain boundary lubrication with diagram. (c) Classify refractories. Give examples of each. 1
12 \\ \\ Q.4 Answer the following questions. (a) Explain bond formation in NaCl. (b) Explain the atmospheric corrosion. (c) Write a short note on pitting corrosion. Q. 4 Answer the following questions. (a) Distinguish between Thermoplastic and Thermosetting plastic. (b) Explain the addition polymerization with proper example. (c) Give classification of lubricant with suitable example. Q.5 Answer the following questions. (a) A sample of hard water gives in the following result. Calculate temporary hardness, permanent hardness and total hardness. Ca(HCO 3 ) 2 = 8.1 mg / L, CaCl 2 = 11.1 mg / L, Mg(HCO 3 ) 2 = 29.2 mg / L, MgCl 2 = 47.5 mg / L, MgSO 4 = 6.0 mg / L, CaSO 4 = 6.8 mg / L (b) Explain fluid film lubrication. (c) State the constituents of oil paints. Q.5 Answer the following questions. (a) Explain the types of H bond with suitable example. (b) Write a short note on (1) Electro refining (2) Electro typing (c) Explain the construction and working of electro chemical cell. 5 \ \`Gv! 5 \ \`G `GvZ GLR[GF 5`GF[GF HJFA VF5F[ V GL[RGFG\.,[S8=,GLS A\WFZ6 VF5F[ (1) 26 Fe (2) 14 Si (3) 11 Na (4) 20 Ca A ljw]t ljefhif[gf[ VF{WF[ULS p5if[u,bf[ S 0.0 M Hcl GF N FJ6GL Ph U6M slog 5=0.6990) V BF,L HuIF 5\]ZF[! Z[TL VG[ VluGHLT DF8LV[ PPPPPPPPPPPPPPPP pqdf pnfcz6 K[P Z S]NZTL ZAZDF\ U\WS pd[zl UZD SZJFGL 5wWlTG[ PPPPPPPPPPPPPPPP SC[ K[P # Ge S[ Si DF\ PPPPPPPPPPPPPPPGL VX]lwWVF[ pd[zjfyl P 5 SFZGF[ VW"JFCS AG[ K[P $ V[;L0 PH PPPPPPPPYL VF[KL VG[ A[.HGL PH PPPPPPPPPPPPPYL JW] CF[I K[P 5 5L8L\U 1FFZ6DF\ V[GF[0LS lj:tfz S\YF[0LS lj:tfz SZTF PPPPPPPPPPPPPPP CF[I K[P & U[<J[ GF.hL\U PPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPP G]\ VFJZ6 K[P * Mg(HCO 3 ) 2 5F6LGL PPPPPPPPPPPPPPPS9LGTF pt5gg SZ[ K[P A s!f jifbif VF5F[P 03 VP VFU lagn] AP Z[,F lagn] SP ;FA]GLSZ6 V\S szf A[.hLS pqdf ;CGF pnfcz6m VF5F[P A VYJF s!f jifbif VF5F[P 03 VP S1FS AP ;bt 5F6L #P AC]W8S szf AOZ N FJ6GL p5if[ultf,bf[p 2
13 5 `Gv# 5 `Gv# 5 `Gv$ 5 `Gv$ 5 `Gv5 5 `Gv5 GL[RGF 5 `GF[GF pttz VF5F[P V VFpO AFp GF[ l;wwf\t ;DHFJF[P A VFIGLSZ6 V\X p5z V;Z SZTF 5lZA/M,BF[P S ljw]t Z;FI6 z[6l V[8,[ X]\ m T[GL VUtITF,BF[P VYJF GL[RGF 5 `GF[GF pttz VF5F[P V ;BT 5F6LYL YTL BZFA V;ZF[,BF[P A ;LDFJTL" :G[CG GL VFS'lT ;lct ;DHFJF[P S pqdf;cg]\ JUL"SZ6 pnfcz6 ;lct SZF[P GL[RGF 5 `GF[GF pttz VF5F[P V Nacl A\W ZRGFVF[ ;DHFJF[P A JFTFZ6YL YT]\ 1FFZ6 ;DHFJF[P S 5L8L\U 1FFZ6 p5z 8}\SGF[\W,BF[P VYJF GL[RGF 5 `GF[GF pttz VF5F[P V YDM";[\8L\U VG[ YDM"%,F:8LS JrR[GF[ TOFJT,BF[P A IF[UXL, AC]W8STF IF[uI pnfcz6 ;lct ;DHFJF[P S :G[CSG]\ JUL"SZ6 IF[uI pnfcz6 ;lct ;DHFJF[P V GL[RGF 5 `GF[GF pttz VF5F[P ;BT 5F6LGF V[S GD]GFG]\ 5lZ6FD GLR[ D]HA K[P TF[ T[GL :YF. S9LGTF V:YF. S9LGTF TYF S], S9LGTF U6F[P Ca(HCO 3 ) 2 = 8.1 mg / L, CaCl 2 = 11.1 mg / L, Mg(HCO 3 ) 2 = 29.2 mg / L, MgCl 2 = 47.5 mg / L, MgSO 4 = 6.0 mg / L, CaSO 4 = 6.8 mg / L A TZ, 50 :G[CG ;DHFJF[P S Z\UGF W8SF[ H6FJF[P VYJF GL[RGF 5 `GF[GF pttz VF5F[P V H A\WGF 5 SFZ pnfcz6 ;lct ;DHFJF[P A 8}\SGF[\W,BF[P!P WFT] X]lwWSZ6 ZP.,[S8=M 8F.5L\U S ljh Z;FIl6S ;[,GL ZRGF VG[ SFIF["H6FJF[P ********** 3
14 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Diploma Semester II Remedial Examination December Subject code: Subject Name: Applied Science-II Date: 13 /12 /2010 Time: am pm Total Marks: 70 Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks. Q.1 (a) Explain auf-bau principle and give electronic configuration of following element. (i) 26 Fe (ii)14 Si (b) Write the name of the salts producing hardness of water and calculate the ph of 0.0N H2so4 solution. (c) Define: (i) Fire point (ii) safonification no. (iii) Ionization energy (iv) electron affinity Q.2 (a) (i) Differentiate between orbit and orbital. (ii) state the properties of insulating materials. (b) Define and explain electro chemical cell with construction and working. (b) Write the type of chemical bond and explain Ionic bond. Q.3 (a) Define electro chemical series and importance of electro chemical series in understanding the corrosion of metals. (b) Explain in brief ph and its importance in various field. (c) Define Degree of ionization and explain what factor affect on Degree of ionization. Q.3 (a) Explain buffer solution,give types of buffer solution and its importance. (b) Write short note on : (i)pitting corrosion (ii) electro platting (c) Write short note on : N-type semi conductors. Q.4 (a) Explain in brief ion exchange process. (b) List the effect of hard water when used in boiler and explain the reason formation of scale and sludge and its prevention. (c) A sample of water on analysis gives the following results. Calculate temporary hardness, permanent hardness, total hardness. Mg(HCO3)2 =7.3 mg/lit. CaSO4 = 27.2 mg/lit. Ca(HCO3)2 =81 mg/lit. MgCl2 = 19.0 mg/lit. Q. 4 (a) Explain three method of express the hardness of water. (b) Define lubrication and give the types of lubrication and explain fluid film lubrication. (c) What properties will you consider while selecting a lubricant for (i)cutting tools (ii) gears 1
15 Q.5 (a) Explain polymerization with suitable example. (b) What is paints? Explain constituents(ingredient) of paints and their function. (c) Distinguish between thermo plastic polymer and thermo setting polymer. Q.5 (a) Define adhesive and give their types with suitable example. (b) Write short note on : (i)refractory (ii) vulcanization (c) Distinguish between paint and varnish 5 `Gv! V VFpOAFp GM l;wwf\t ;DHFJL GLR[GF TtJMGL.,[S8=MGLS ZRGF,BMP s!f 26 Fe szf 14 Si A 5F6LDF\ Sl9GTF pt5gg SZTF\ 1FFZMGF GFD,BMP VG[0.0N H2so4 GF - FJ6GL 5LV[R XMWMP S jifbif VF5MP s!f VFUlAN]\ szf ;FA]GLSZ6 VF\S s#f VFIGLSZ6 XlST s$f.,[s8=mga\w]tf 5 `GvZ V s!ftofjt VF5M o S1FF VG[ S1FS szf VJFCS 5NFY"GF U]6WDM" H6FJMP A JLH ZF;FIl6S SMQFGL jifbif VF5L T[G]\ A\WFZ6 VG[ SFI" ;DHFJMP VYJF A ZF;FIl6S A\WGF 5 SFZ H6FJL VFIMGLS A\W ;DHFJMP 5 `Gv# V JLH ZF;FIl6S z[6lgl jifbif VF5L WFT] 1FFZ6DF\ T[G]\ X]\ DCtJ K[ T[ ;DHFJMP A 5L V[R ljx[ 8}\SDF\ ;DHFJL T[G]\ H]NF H]NF 1F[+MDF\ DCtJ ;DHFJMP S VFIGLSZ6 V\XGL jifbif VF5L SIF SIF 5ZLA/M VFIGLSZ6 V\XG[ V;Z SZ[ K[ T[ ;DHFJMP VYJF 5 `Gv# V AOZ - FJ6GL jifbif VF5L T[GF 5 SFZ VG[ DCtJ ;DHFJMP A 8}\SGM\W,BMP s!f 5L8L\U 1FFZ6 szf.,[s8=m%,[8l\u S 8}\SGM\W,BMP V[Gv8F.5 VW"JFCS 5 `Gv$ V VFIG V[1FR[\H 5wWlT ljx[ 8}\SDF\ ;DHFJMP A Sl9G 5F6LGF AM.,ZDF\ p5imuyl pt5gg YTL V;ZM H6FJMP :S[, VG[ :,h pt5gg YJFGF SFZ6M VG[ ZMSJF DF8[GF p5fi,bmp S V[S 5F6LGF GD}GFGM 5'yYSZ6 SZTF\ GLR[ D]HAGF 5lZ6FD D/[ K[P TM 5F6LGL 1Fl6S S9LGTF4SFIDL S9LGTF VG[ S], S9LGTF XMWMP Mg(HCO3)2 =7.3 mg/lit. CaSO4 = 27.2 mg/lit. Ca(HCO3)2 =81 mg/lit. MgCl2 = 19.0 mg/lit. VYJF 5 `Gv$ V 5F6LGL S9LGTFG[ NXF"JJFGL +6 ZLTM ;DHFJMP A :G[CGGL jifbif VF5L :G[CGGF 5 SFZ H6FJL TZ,50 :G[CG ;DHFJMP S s!fs8l\u 8]<; VG[ szfuli;" DF8[ TD[ SIF 5 SFZGF U]6WDM" JF/F :G[CSGM p5imu SZXMP 5 `Gv5 V IMuI pnfcz6 VF5L AC],LSZ6GL 5 ls IF ;DHFJMP A 5[.g8 X]\ K[ m 5[.g8GF A\WFZ6 s38smf VG[ T[VMGF SFIM" H6FJMP S TOFJT VF5MP o YDM"%,F:8LS 5M,LDZ VG[ YDM";[8L\U 5M,LDZ VYJF 5 `Gv5 V VF;\HSM sv[0[;ljfgl jifbif VF5L T[DGF IMuI pnfcz6 ;FY[ 5 SFZ H6FJMP A 8}\SGM\W,BMP s!f ZLOZ[S8ZL szf J<S[GF.h[XG S TOFJT VF5M o 5[.g8 VG[ JFlG"; ********** 2
16 Seat No.: Enrolment No. Date:23/06/2011 GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Diploma Engineering Sem. II nd - Examination June/July Subject code: Subject Name: Applied science-ii [Chemistry] Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks. 4. English Version Authentic. Time: 02:30 pm :00 pm Total Marks: 70 Q.1 (a) Answer The following question.(any three) (1) Draw the shape of S & P orbital. (2) Give electronic configuration of 17 Cl & 26Fe. (3) Explain the full meaning of 11 Na 23 & 92 U 235. (4) Write the industrial application of electrolyte. (b) Filling the blanks : (1) PH + POH =. (2) 100 ppm = degree clerk. (3) is used in vulcanization of Rubber. (4) Galvenizing is coating. (5) For measurement of pensky marten Apparatus is used. (6) Molecular weight of ( 78 pt 191 ) =. (7) Grephite is lubricant. Q.2 (a) (b) (b) Answer the following question. (1) Explain Auf-bau principle. (2) Define :Ionisation energy & Electron effinity. (3) Explain meaning of Atomic Number & Mass Number. Answer the following question. (1) Write the name of factors effecting the degree of Ionisation. (2) Calculate PH of 0.2 M HCl. (3) What is Buffer solution.explain it s types with suitable example Answer the following question. (1) Explain Ionic bond formation with suitable example. (2) Give the characteristics of covalent compound. (3) Write Importance of Hydrogen bond. Q.3 (a) Answer the following question. (1) Explain construction and working of Electrochemical cell. (2) Explain factors that effect the rate of corrosion. (3) Which are different methods used to protect Metals. 1
17 (b) (1) Explain in brief PH and its importance. (2) What is N- type semiconductor. (3) Write standard conditions for Hydrogen electrode. Q.3 (a) Answer the following question. (1) Give the name & formula of salt causes permanent hardness. (2) Write chemical equation involve in Zeolite method. (3) Explain Ion exchange process. (b) (1) State the various systems to express the hardness of water. (2) Sample of water contain following data.calculate its Temporary,permanent and Total hardness. Ca(HCO 3 ) 2 = 81mg/lit Mg(HCO 3 ) 2 =16.2 mg/lit CaCl 2 =77.7mg/lit, MgCl 2 =19.0mg/lit, CaSO 4 =6.8mg/lit, MgSO4 =6.0mg/lit. Q.4 (a) Answer the following question. (1) Discuss different methods of purification of water. (2) Write effect of hard water when it is use in Boiler. (b) Answer the following question. (1) Define: Lubricant. Give the Functions of Lubricant. (2) Explain Boundary Lubrication. Q.4 (a) Answer the following question. (1) Give the classification of Lubricants. (2) Define :Flash point, Cloud point,neutralisation Number,Emulsification number. (b) Answer the following question. (1) Explain pitting corrosion. (2) Explain electrochemical series.write its importance. Q.5 (a) Answer the following question. (1) Distinguish between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic. (2) Explain vulcanization of rubber and its advantage. (b) Answer the following question. (1) Distinguish between Paint & Varnishes. (2) Explain characteristics of good Adhesives. Q.5 (a) Answer the following question. (1) Write constituent of oil paint & varnish. (2) Give preparation & properties of Nylon66 polymer. (b) Answer the following question. (1) Give properties of Refractorie. (2) Define Insulating material & Give its type. (3) Classification of Refractories. (PTO) 2
18 ન.૧ (અ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. (ક ઇપણ ણ ) ૦૭ (૧) S અન P ક કન આક ર દ ર. (૨) ૧૭ Cl23 & ૨૬ Fe ન ઇલ નક સ રચન લખ. (3) ૧૧ Na ૨૩ & ૯૨ U 235 ન સ ણ અથ સમ વ. (૪) વ ત વભ ય ન ઔ ગક ઉપય ગ લખ. (બ) ખ લ જ ય ર. (૧) PH + POH =. ૦૭ (૨) 100 ppm =.ડ લ ક. (૩) રબરન વ કન કરણમ (૪) તરન ગ વ ન ઇ ઝ ગ કહ છ. ન ઉપય ગ થ ય છ. (૫) પ ન ક મ ટ ન સ ધનન ઉપય ગ ન મ પનમ થ ય છ. (૬) ૭૮pt191 મ અ ભ ર (૭) ફ ઇટ ન હક છ. છ. ન.૨ (અ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧) આઉફ-બ ઉ ન સ ધ ત સમ વ. (૨) ય ય :આયન કરણ શ ત & ઇલ ન બ ત. (૩) પરમ મ ક અન પરમ ભ ર ન અથ સમ વ. (બ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧) આય નકરણ શ પર અસર કરત પ રબળ લખ. (૨) ૦.૨ M HCl ન વણન PH ગણ. (૩) બફર વણ ઍટલ.ય ય ઉદ હરણ સહ ત ત ન ક ર સમ વ. અથવ (બ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (1) ય ય ઉદ હરણ સહ ત આય નક બ ધન રચન સમ વ. 3
19 (૨) સહસ ય જક સ ય જન ન લ ણકત ઓ આપ. (૩) હ ઇ જન બ ધન અ યત લખ. ન.૩ (અ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧) વ ત વભજન ક ષ ન રચન અન ક ય સમ વ. (૨) રણન દર પર અસર કરત પ રબળ સમ વ. (૩) ધ ન ર ણ મ ટન દ દ પ ધ ત કઇ? (બ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧) PH અન ત ન અગ યત મ સમ વ. (૨) N ક રન અધ વ હક ઍટલ? (૩)હ ઇ જન ઇલ ડન મ ણ ત શરત લખ. અથવ ન.૩ (અ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧)ક યમ ઠ નત ન ર ન ન મ અન આપ. (૨) ઝ ય લ ઇટ પ ધ તન ર સ ય ણક સમ કરણ લખ. (૩) આયન વ નમય પ ત સમ વ. (બ)(૧) પ ણ ન ક ઠ નત દશ વવ ન દ દ ર ત લખ. ૦૭ (૨) પ ણ ન ન ન ન વગત ન ચ જબ છ ત ન ક યમ, ણક તથ લ ક ઠનત ગણ. Ca(HCO 3 ) 2 =81 mg/lit, Mg(HCO 3 ) 2 = 16.2mg/lit CaCl 2 =77.7mg/lit, MgCl 2 =19.0 mg/lit, Caso 4 =6.8mg/lit,MgSo 4 =6.0mg/lit. ન.૪ (અ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. (૧) પ ણ ન ધકરણન દ દ ર ત ન ચચ કર. ૦૭ (૨) બ ઇલરમ ક ઠન પ ણ થ થત અસર લખ. (બ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧) ય ય અપ. ક ટ. ક ટન ક ય અપ. (૨) સ મ વત ન હન સમ વ. 4
20 અથવ.૪ (અ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧) ક ટ વગ કરણ અપ. (૨) ય ય : ભડક બ,વ દળ બ,તટ થ કરણ ક, પ યસ કરણ ક. (બ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧) પ ટ ગ રણ સમ વ. (૨) વ તર સ ય ણક ણ સમ વ ત ન અગ યત લખ..૫ (અ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧) થમ લ ટક અન થમ સ ટ ગ લ ટક વ ચ ન તફ વત. (૨) ર બર કન કરણ અન ત ન ફ યદ સમ વ. (બ) ન ચ ન ન ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧) ર ગ અન વ ન શ વ ચ ન તફ વત. (૨) સ ર આસ જક ન લ ણ ત ઓ સમ વ. અથવ.૫ (અ) ન ન ન ચ ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧) ર ગ અન વ ન શન ઘટક લખ. (૨) ન યલ ન ૬૬ ન બન વટ & ણધમ આપ. (બ) ન ન ન ચ ન જવ બ આપ. ૦૭ (૧) ઉ મ સહન ણધમ અપ. (૨) ય ય : વસ વ હ પદ થ & ત ન ક ર અપ. (૩) ઉ મ સહ વગ કરણ. ************** 5
21 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Diploma Engineering - SEMESTER II EXAMINATION WINTER 2012 Subject code: Date: 15/01/2013 Subject Name: Applied Science-II Time: am pm Total Marks: 70 Instructions: 1. Attempt any five questions. 2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks. 4. English version is considered to be Authentic. Q.1 (a) Answer the following (1) Define the term: (a) Ionization energy (b) Electrolyte (2) State Auf-Bau s principle (3) Give electronic configuration of (a) 17 Cl 35 (b) 26 Fe 56 (4) Give characteristics of ionic substances (5) What are refractories and give its classification (6) Give the types of electrolytes with suitable examples (7) Write the name of monomers used in (a) PVC (b) Terelyne Q.2 Answer the following (a) (b) Fill in the gaps (1) Alumina and Magnesia are example of refractories (2) As dilution of aqueous solution increases, the degree of ionization (3) Nylon 6,6 is formed by polymerization reaction. (4) The value of first ionization energy is than second ionization energy (5) The no. of neutrons in the atom of 11 Na 23 is (6) The shape of P orbital is (7) The solution which resists the change in hydrogen ion concentration is known as (1) Define (i) Viscosity index (ii) Flash point (iii) fire point (2) Write only Chemical reactions occurring in Ion exchange process For removal of hardness (b) (1) Explain condensation polymerization with suitable example (2) State properties and uses of Thermocole and glass wool 03 Q.3 Answer the following (a) What is Buffer solution? Give its types with suitable examples (b) (c) Explain construction and working of Galvanic cell Explain the importance of ph in various fields of Engineering Q.3 (a) Explain Hydrogen bond and give its significance (b) (c) Define: Degree of ionization,state the factors affecting degree of ionization Define ph and calculate the ph of Acidic solution containing 0.001M concentration of H 3 O + 1
22 Q.4 Answer the following (a) What are adhesives? Give characteristics of Good adhesive (b) (c) Give classification of lubricants with examples Distinguish between the Paint and Varnish Q. 4 (a) What is electrolysis? Explain refining of impure Cu by electrolysis (b) (c) Explain Zeolite process for softening of hard water Write the functions of ingredients of paints Q.5 Answer the following (a) Explain Fluid film lubrication with diagram (b) Water sample contains the following salts present in it.find (i) Temporary hardness(ii) Permanent hardness (iii) Total hardness of water sample in ppm Ca(HCO3)2 = 81 mg/litre CaSO4 = 13.6 mg/litre Mg(HCO3)2 = 14.6 mg/litre MgCl2 = 19.0 mg/litre (c) Explain Vulcanization of rubber with its advantages Q.5 (a) Explain covalent bond and write its characteristics (b) (c) State the essential properties of lubricants used for Cutting tools and Steam turbine Write short note on method of Anodic and Cathodic protection of metal -૧ (અ) ન ચ ન ન જવ બ આપ. ************ જર ત (1) ન ચ ન પદ ન ય ય આપ. (અ) આયન કરણ શ ત (બ) વ ત વભ જય (2) આઉફ-બ ઉ ન નયમ જણ વ. (3) (અ) 17 Cl 35 ( ) 2 6 Fe 56 ન ઇલ ક ન ક બ ધ રણ લખ. (4) આય ન ક પદ થ ન લ ણકત ઓ આપ. (5) ઉ મ સહ પદ થ એટલ? ત વગ કરણ કર. (6) ય ય ઉદ હરણ સ હત વ ત વભ જયન ક ર જણ વ. (7) (અ) પ.વ.સ.(બ) ટ ર લ ન ન બન વટ મ ટ વપર ત મ ન મરન ન મ લખ 14-૨ 14 (અ) ખ લ જ ય ર (1) એ મ ન અન મ ન શ ય ઉ મ સહ ઉદ હરણ છ. (2) મ વણન મ દત વધ ત મ આયન કરણ શન યમ થ ય છ.. 2
23 (3) ન યલ ન 6,6 ન બન વટ બ ધટકટ ય ર થ ય છ (4) થમ આયન કરણ શ કત ય તય આયન કરણ શ કતન ય કરત હ ય છ. (5) 11 Na 23 ન પરમ મ નન સ ય હ ય છ. (6) p ક કન આક ર હ ય છ. (7) જલ ય વણ હ ઇ જનન આયનન સ ત મ થત ફ રફ રન તક ર કર ત વણ કહ વ ય (બ) (બ) (1) ય ય આપ. (અ) ન ધત ક (બ)ભડક બ (ક) આગ બ (2) પ ણ ન ક ઠનત ર કરવ મ ટ ન આયન વ નમય પ ધ તમ થત મ ર સ ય ણક કય ઓ લખ. (1) ય ય ઉદ હરણ સ હત સ ઘનન બ ઘટકત વશ સમ વ. (2) લ સ લ અન થમ ક લન ણધમ અન ઉપય ગ જણ વ ન ચ ન ન જવ બ આપ (અ) (બ) (ક) બફર વણ એટલ? ય ય ઉદ હરણ સ હત બફર વણન ક ર જણ વ. ગ વ નક ક ષન રચન અન ક ય પ ધ ત સમ વ. ઇજન ર ન દ દ મ ph ન અગ યત સમ વ. અથવ (અ) હ ઇ જન બ ધ વશ સમ વ અન ત મહ વ જણ વ. (બ) આયન કરણ શ પદન ય ય આપ અન આયન કરણ શન અસર કરત પર બળ જણ વ. (ક) ph ન ય ય આપ M હ ઇ જન આયન(H 3 O + ) ન સ ત ધર વત એ સ ડક વણ ph ય ગણ. -૪ (અ) (બ) (ક) ન ચ ન ન જવ બ આપ સ સગ પદ થ એટલ? સ ર સ સગ પદ થ ન ખ સયત જણ વ. ઉદ હરણ સ હત ન હક વગ કરણ લખ. ત લ ર ગ અન વ ન વ ચ ન ભ દ જણ વ. અથવ -૪ (અ) વ ત વભ જન એટલ શ? વ ત વભ જન ર અ ધ ત બ (Cu) 3
24 (બ) ધ કરણ સમ વ. ક ઠન પ ણ ન નરમ બન વવ મ ટ ન ઝ ય લ ઇટ પ ધ ત વશ સમ વ (ક) ત લ ર ગમ વપર ત ઘટક ન ક ય લખ. ૦૪-5 -5 ન ચ ન ન જવ બ આપ (અ) તરલ-પડ ન હન આ ત સ હત સમ વ (બ) (ક) પ ણ ન ન ન થકરણ કરત ત મ રહ લ ર મ ણ ન ચ મ ણ મ. પ ણ મ રહ લ (i) ણક ક ઠનત (ii) ક યમ ક ઠનત અન (iii) લ ક ઠનત મ ણ શ ધ. Ca(HCO3)2 = 81 mg/litre CaSO4 = 13.6 mg/litre Mg(HCO3)2 = 14.6 mg/litre MgCl2 = 19.0 mg/litre ( H=01, C = 12, O = 16, Mg = 24, S = 32, Cl = 35.5,Ca = 40 ) વ ક ન ઇઝ શનન ફ ઇદ ઓ સ હત રબર વ ક ન ઇઝ શન સમ વ. અથવ (અ) સહસ ય જક બ ધ સમ વ.ત ન લ ણકત ઓ લખ. (બ) (ક) ક ટ ગ સ અન ટ મ ટબ ઇન મ ટ વપર ત ન હક ન જ ર ણધમ જણ વ ધ ન એન ડક અન ક થ ડક ર ણ મ ટ ન ર ત ઉપર કન ધ લખ. ૦૪ ૦૪ ************ 4
Gujarat Post office (MTS) Main Exam Study material part 2
 Gujarat Post office (MTS) Main Exam Study material part 2 1) Map શબ દ ક ન પરથ બન લ છ? નકશ મ ટ અ ગ જ શબ દ Map લ ટટન શબ દ Mappa અથવ Mappa mundi પરથ બન લ છ. ત ન અ થ હ થર મ લ કદન ક પડન ટ કડ થ ય છ. ઈ.સ.840મ
Gujarat Post office (MTS) Main Exam Study material part 2 1) Map શબ દ ક ન પરથ બન લ છ? નકશ મ ટ અ ગ જ શબ દ Map લ ટટન શબ દ Mappa અથવ Mappa mundi પરથ બન લ છ. ત ન અ થ હ થર મ લ કદન ક પડન ટ કડ થ ય છ. ઈ.સ.840મ
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Diploma Engineering - SEMESTER II (CtoD) EXAMINATION WINTER 2014
 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Diploma Engineering - SEMESTER II (CtoD) EXAMINATION WINTER 2014 Subject Code: C320903 Date: 29-12-2014 Subject Name: D. C. CIRCUIT Time: 10:30
Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Diploma Engineering - SEMESTER II (CtoD) EXAMINATION WINTER 2014 Subject Code: C320903 Date: 29-12-2014 Subject Name: D. C. CIRCUIT Time: 10:30
Physical Setting & Earth Science. Glossary. High School Level. English / Gujarati
 High School Level Glossary Physical Setting & Earth Science Glossary English / Gujarati Translation of Physical Setting & Earth Science terms based on the Coursework for Physical Setting & Earth Science
High School Level Glossary Physical Setting & Earth Science Glossary English / Gujarati Translation of Physical Setting & Earth Science terms based on the Coursework for Physical Setting & Earth Science
GUJARAT VIDYAPEETH : AHMEDABAD M.D.
 GUJARAT VIDYAPEETH : AHMEDABAD MIC-101:Introduction and Historical Developments in Microbiology (Syllabus of theoretical portion) (With Effect From 1 st July, 2016) (Total Teaching Hours=30, Credit=02)
GUJARAT VIDYAPEETH : AHMEDABAD MIC-101:Introduction and Historical Developments in Microbiology (Syllabus of theoretical portion) (With Effect From 1 st July, 2016) (Total Teaching Hours=30, Credit=02)
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Applications, Volume XII, Issue III, March 18, ISSN
 International Journal of Computer Engineering and Applications, STRING SIMILARITY BASED ON PHONETIC IN GUJARATI LANGUAGE USING GUJSIM ALGORITHM Chandrakant D. Patel 1, Dr. Jayesh M. Patel 2 1 Research
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Applications, STRING SIMILARITY BASED ON PHONETIC IN GUJARATI LANGUAGE USING GUJSIM ALGORITHM Chandrakant D. Patel 1, Dr. Jayesh M. Patel 2 1 Research
જ.ક ર. ૮૮/૨૦૧૬-૧૭ જગ મ ન ન ભ : વયક ય ક ર જ ભ બ ત કળ સ ત ર તલમન ભદદન ળ પ ર ધ મ ક, લ ગ-૨
 જ.ક ર. ૮૮/૨૦૧૬-૧૭ જગ મ ન ન ભ : વયક ય ક ર જ ભ બ ત કળ સ ત ર તલમન ભદદન ળ પ ર ધ મ ક, લ ગ-૨ બ ગ-૧ અન બ ગ-૨ ન ૧૫૦ તભતનટન વ યક પ રશ નત રન પ ર થતભક કવ ટ ન અભ મ વક રભ પ ર થતભક કવ ટ ન અભ મ વક રભ બ ગ-૧ ભ ધ મભ: ગજય
જ.ક ર. ૮૮/૨૦૧૬-૧૭ જગ મ ન ન ભ : વયક ય ક ર જ ભ બ ત કળ સ ત ર તલમન ભદદન ળ પ ર ધ મ ક, લ ગ-૨ બ ગ-૧ અન બ ગ-૨ ન ૧૫૦ તભતનટન વ યક પ રશ નત રન પ ર થતભક કવ ટ ન અભ મ વક રભ પ ર થતભક કવ ટ ન અભ મ વક રભ બ ગ-૧ ભ ધ મભ: ગજય
fresh bond and on usual terms and conditions. Rule is made absolute accordingly. Direct service is permitted.
 242 ACQUITTAL AND BAIL CASES ABC 2013 (I) rs on n on usul trms n onitions. Rul is m solut orinly. Dirt srvi is prmitt. Rsult: - Applition sus. ABC 2013 (I) 242GUJ ACQUITTAL & BAIL CASES HIGH COURT OF GUJARAT
242 ACQUITTAL AND BAIL CASES ABC 2013 (I) rs on n on usul trms n onitions. Rul is m solut orinly. Dirt srvi is prmitt. Rsult: - Applition sus. ABC 2013 (I) 242GUJ ACQUITTAL & BAIL CASES HIGH COURT OF GUJARAT
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS UNIT I: POLYMERS AND BUILDING MATERIALS
 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS UNIT I: POLYMERS AND BUILDING MATERIALS 1. Define polymer. Give one example. 2. What is monomer? Give one example. 3. What is polymerization? 4. What is degree of polymerization?
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS UNIT I: POLYMERS AND BUILDING MATERIALS 1. Define polymer. Give one example. 2. What is monomer? Give one example. 3. What is polymerization? 4. What is degree of polymerization?
Equilibria in electrolytes solutions and water hardness
 Equilibria in electrolytes solutions and water hardness by Urszula LelekBorkowska Electrolytes When the substance dissolved in water or other solvent exhibits electrical conductivity it is called an electrolyte.
Equilibria in electrolytes solutions and water hardness by Urszula LelekBorkowska Electrolytes When the substance dissolved in water or other solvent exhibits electrical conductivity it is called an electrolyte.
V;ZSFZS JU"B\0 lx1f6 શ ક ષક ત લ મ મ ટ ન MT ત લ મ વર ગ સ નલ ક. ચ હ ણ લ ક ચરર ડ ય ટ - ર જક ટ L/O/G/O 5/29/2014 સ નલ ક. ચ હ ણ, લ કચરર, ડ ય ટ- ર જક ટ
 1 V;ZSFZS JU"B\0 lx1f6 L/O/G/O શ ક ષક ત લ મ મ ટ ન MT ત લ મ વર ગ સ નલ ક. ચ હ ણ લ ક ચરર ડ ય ટ - JU"jIJCFZ jilstut VlEUD lx1f6 5 ls IFGM GFGM EFU 5 tifig 5 ls IF 2 asrkirk vgd (SxN n)c[n) bibti[ pr aifir)t
1 V;ZSFZS JU"B\0 lx1f6 L/O/G/O શ ક ષક ત લ મ મ ટ ન MT ત લ મ વર ગ સ નલ ક. ચ હ ણ લ ક ચરર ડ ય ટ - JU"jIJCFZ jilstut VlEUD lx1f6 5 ls IFGM GFGM EFU 5 tifig 5 ls IF 2 asrkirk vgd (SxN n)c[n) bibti[ pr aifir)t
ABC 2011 (II) 111 GUJ
 Arvini Mnkll Ptl Vs. Stt o Gujrt &Anr (Guj) 111 s not on to t otr ontntions nvss y lrn vots pprin on l o t rsptiv prtis s impun omplint/ Criminl Cs is rquir to qus n st si on t orsi roun lon. 11. In viw
Arvini Mnkll Ptl Vs. Stt o Gujrt &Anr (Guj) 111 s not on to t otr ontntions nvss y lrn vots pprin on l o t rsptiv prtis s impun omplint/ Criminl Cs is rquir to qus n st si on t orsi roun lon. 11. In viw
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
2011 ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY - II
 Set No. 1 1. (a) with suitable examples explain addition polymerization, condensation polymerization and co-polymerization. (b) Give a brief account of conducting polymers. (c) Write the preparation, properties
Set No. 1 1. (a) with suitable examples explain addition polymerization, condensation polymerization and co-polymerization. (b) Give a brief account of conducting polymers. (c) Write the preparation, properties
1. 5ZL1FF 5]l:TSFGF VF 5FGF 5Z E}ZL q SF/L AM, 5M.g85[G YL ljutm T]Z\T EZJLP 5[lg;,GM p5imu ;J"YF lglqfâ K[P
![1. 5ZL1FF 5]l:TSFGF VF 5FGF 5Z E}ZL q SF/L AM, 5M.g85[G YL ljutm T]Z\T EZJLP 5[lg;,GM p5imu ;JYF lglqfâ K[P 1. 5ZL1FF 5]l:TSFGF VF 5FGF 5Z E}ZL q SF/L AM, 5M.g85[G YL ljutm T]Z\T EZJLP 5[lg;,GM p5imu ;JYF lglqfâ K[P](/thumbs/92/111014534.jpg) This booklet contains 28 printed pages. VF 5]l:TSFDF\ 28 5FGF D]lãT K[P PAPER 1 : PHYSICS, MATHEMATICS & CHEMISTRY 5ZL1FF 5]l:TSF v 1 o EF{lTS XF:+4 Ul6T VG[ Z;FI6 XF:+ Do not open this Test Booklet until
This booklet contains 28 printed pages. VF 5]l:TSFDF\ 28 5FGF D]lãT K[P PAPER 1 : PHYSICS, MATHEMATICS & CHEMISTRY 5ZL1FF 5]l:TSF v 1 o EF{lTS XF:+4 Ul6T VG[ Z;FI6 XF:+ Do not open this Test Booklet until
Time Allowed: 1:45 hours
 9 th LAHORE BOARD 2014 Group I 1) Explain double covalent bond with the help of an example. 2) How do atoms follow octet rule? 3) Explain polar covalent bond with an example. 4) Define pressure. Write
9 th LAHORE BOARD 2014 Group I 1) Explain double covalent bond with the help of an example. 2) How do atoms follow octet rule? 3) Explain polar covalent bond with an example. 4) Define pressure. Write
Downloaded from
 I.I.T.Foundation - XI Chemistry MCQ #10 Time: 45 min Student's Name: Roll No.: Full Marks: 90 Solutions I. MCQ - Choose Appropriate Alternative 1. Molarity is the number of moles of a solute dissolved
I.I.T.Foundation - XI Chemistry MCQ #10 Time: 45 min Student's Name: Roll No.: Full Marks: 90 Solutions I. MCQ - Choose Appropriate Alternative 1. Molarity is the number of moles of a solute dissolved
Angel International SchoolManipay
 Grade OL Angel International SchoolManipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2016 Chemistry Duration: 3 Hours 1. Which property is common to calcium, potassium and sodium? a) Their atoms all lose two electrons
Grade OL Angel International SchoolManipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2016 Chemistry Duration: 3 Hours 1. Which property is common to calcium, potassium and sodium? a) Their atoms all lose two electrons
Questions Booklet. UNIT 1: Principles & Applications of Science I CHEMISTRY SECTION. Level 3 Applied Science. Name:.. Teacher:..
 Level 3 Applied Science UNIT 1: Principles & Applications of Science I CHEMISTRY SECTION Questions Booklet Name:.. Teacher:.. Level 3 Applied Science 2017-2018 Unit 1 (Chemistry) 1 1. State the relative
Level 3 Applied Science UNIT 1: Principles & Applications of Science I CHEMISTRY SECTION Questions Booklet Name:.. Teacher:.. Level 3 Applied Science 2017-2018 Unit 1 (Chemistry) 1 1. State the relative
Chemistry Standard level Paper 1
 M15/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX Chemistry Standard level Paper 1 Thursday 14 May 2015 (afternoon) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all
M15/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX Chemistry Standard level Paper 1 Thursday 14 May 2015 (afternoon) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all
materials and their properties
 materials and their properties macroscopic properties phase state strength / stiffness electrical conductivity chemical properties color / transparence spectroscopical properties surface properties density
materials and their properties macroscopic properties phase state strength / stiffness electrical conductivity chemical properties color / transparence spectroscopical properties surface properties density
MAHARASHTRASTATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) WINTER 6 EXAMINATION Model ject Code: 703 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in themodel answer
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) WINTER 6 EXAMINATION Model ject Code: 703 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in themodel answer
Name: Regents Chemistry Date:
 Name: Date: 1. The reaction CuO + CO CO 2 + Cu is an example of (A) reduction, only (B) oxidation, only (C) both oxidation and reduction (D) neither oxidation nor reduction 6. In which compound does chlorine
Name: Date: 1. The reaction CuO + CO CO 2 + Cu is an example of (A) reduction, only (B) oxidation, only (C) both oxidation and reduction (D) neither oxidation nor reduction 6. In which compound does chlorine
(i) Voltameter consist of a vessel, two electrodes and electrolytic solution.
 Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry which deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes taking place in redox reactions i.e., how chemical energy produced
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry which deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes taking place in redox reactions i.e., how chemical energy produced
(c) Na is deposited at the cathode (d) Na appears at the anode
 year chemiry n0tes new CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY MCQS Q.1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy
year chemiry n0tes new CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY MCQS Q.1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy
MAHARASHTRASTATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: Answer
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) WINTER 6 EXAMINATION Model ject Code: 703 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in themodel answer
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) WINTER 6 EXAMINATION Model ject Code: 703 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in themodel answer
Course Title: Engineering Chemistry(Group-2) (Code: )
 GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM Course Title: Engineering Chemistry(Group-2) (Code: 3300006) Diploma Programmes in which this course is offered Biomedical Engineering,
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM Course Title: Engineering Chemistry(Group-2) (Code: 3300006) Diploma Programmes in which this course is offered Biomedical Engineering,
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E.)
 Name: Index No. School:. Candidate s Sign.... Date:... 233/1 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 JULY /AUGUST 2011 TIME: 2 HOURS Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E.) Chemistry Paper 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO THE
Name: Index No. School:. Candidate s Sign.... Date:... 233/1 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 JULY /AUGUST 2011 TIME: 2 HOURS Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E.) Chemistry Paper 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO THE
Electrochemistry Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid
 Electrochemistry 18.1 Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid 18.3 Voltaic (or Galvanic) Cells: Generating Electricity from Spontaneous Chemical Reactions 18.4 Standard Electrode Potentials 18.7 Batteries:
Electrochemistry 18.1 Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid 18.3 Voltaic (or Galvanic) Cells: Generating Electricity from Spontaneous Chemical Reactions 18.4 Standard Electrode Potentials 18.7 Batteries:
Chemistry 12. Resource Exam B. Exam Booklet
 Chemistry 12 Resource Exam B Exam Booklet Contents: 21 pages Examination: 2 hours 50 multiple-choice questions in the Exam Booklet Additional Time Permitted: 60 minutes Province of British Columbia PART
Chemistry 12 Resource Exam B Exam Booklet Contents: 21 pages Examination: 2 hours 50 multiple-choice questions in the Exam Booklet Additional Time Permitted: 60 minutes Province of British Columbia PART
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry. Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry. Notes.
 Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Chapter 3 Engineering Science for Microsystems Design and Fabrication
 Lectures on MEMS and MICROSYSTEMS DESIGN and MANUFACTURE Chapter 3 Engineering Science for Microsystems Design and Fabrication In this Chapter, we will present overviews of the principles of physical and
Lectures on MEMS and MICROSYSTEMS DESIGN and MANUFACTURE Chapter 3 Engineering Science for Microsystems Design and Fabrication In this Chapter, we will present overviews of the principles of physical and
Redox reactions & electrochemistry
 Redox reactions & electrochemistry Electrochemistry Electrical energy ; Chemical energy oxidation/reduction = redox reactions Electrochemistry Zn + Cu 2+ º Zn 2+ + Cu Oxidation-reduction reactions always
Redox reactions & electrochemistry Electrochemistry Electrical energy ; Chemical energy oxidation/reduction = redox reactions Electrochemistry Zn + Cu 2+ º Zn 2+ + Cu Oxidation-reduction reactions always
Unit 13 Electrochemistry Review
 1. What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in NaNO2? A) +1 B) +2 C) +3 D) +4 2. Given the reaction that occurs in an electrochemical cell: Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) During this reaction, the
1. What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in NaNO2? A) +1 B) +2 C) +3 D) +4 2. Given the reaction that occurs in an electrochemical cell: Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) During this reaction, the
(c) dilute solution of glucose (d) chloroform 12 Which one of the following represents the same net reaction as the electrolysis of aqueous H2SO4
 1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. covalent ionic non-metallic
 1 The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. (a) (i) Choose a word from the box to complete the sentence. covalent ionic non-metallic Electrolysis takes place when electricity
1 The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. (a) (i) Choose a word from the box to complete the sentence. covalent ionic non-metallic Electrolysis takes place when electricity
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E.
 MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - II - SET -A 020 Periodic Table, Chemical bonding, Acid, Bases and Salts, Practical Work, Mole Concept, Electrolysis Chemistry
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - II - SET -A 020 Periodic Table, Chemical bonding, Acid, Bases and Salts, Practical Work, Mole Concept, Electrolysis Chemistry
SCHOOL YEAR CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12
 SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. During oxidation, one or more electrons
SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. During oxidation, one or more electrons
UNIVERSITY OF SIERRA LEONE FOURAH BAY COLLEGE. FIRST EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B. Sc. HONOURS LEVEL I SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION
 UNIVERSITY OF SIERRA LEONE FOURAH BAY COLLEGE CHEM 221 FIRST EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B. Sc. HONOURS LEVEL I SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION FRIDAY 21 st SEPTEMBER 2018 09.30 12.45 CHEM 221 FURTHER INORGANIC
UNIVERSITY OF SIERRA LEONE FOURAH BAY COLLEGE CHEM 221 FIRST EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B. Sc. HONOURS LEVEL I SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION FRIDAY 21 st SEPTEMBER 2018 09.30 12.45 CHEM 221 FURTHER INORGANIC
(c) Dr. Payal B. Joshi
 Polymer (Greek: poly=many; mer=part) Made up of large molecules characterized by repeating units called monomers held together by covalent bonds Functionality To act as monomer, it must have at least two
Polymer (Greek: poly=many; mer=part) Made up of large molecules characterized by repeating units called monomers held together by covalent bonds Functionality To act as monomer, it must have at least two
AP Questions: Electrochemistry
 AP Questions: Electrochemistry I 2 + 2 S 2O 2-3 2 I - + S 4O 2-6 How many moles of I 2 was produced during the electrolysis? The hydrogen gas produced at the cathode during the electrolysis was collected
AP Questions: Electrochemistry I 2 + 2 S 2O 2-3 2 I - + S 4O 2-6 How many moles of I 2 was produced during the electrolysis? The hydrogen gas produced at the cathode during the electrolysis was collected
 Mark scheme Answers Marks (a) (i) 2.8.4 4 (b) (i) Decreases // Become smaller Proton number / Positive charges increases // Forces of attraction increases (c) Achieved octet electron arrangement // Has
Mark scheme Answers Marks (a) (i) 2.8.4 4 (b) (i) Decreases // Become smaller Proton number / Positive charges increases // Forces of attraction increases (c) Achieved octet electron arrangement // Has
MC 17 C SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section.
 Question 1. (a) SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Choose from the following list of substances, as to what matches the description from to given below : [Bronze,
Question 1. (a) SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Choose from the following list of substances, as to what matches the description from to given below : [Bronze,
Chem 42 Final Review Sheet Mr. J. Fassler Spring 2018
 Chem 42 Final Review Sheet Mr. J. Fassler Spring 2018 These problems are given to help you review concepts you may have forgotten. Old tests, quizzes and review sheets are also important in studying. Chapter
Chem 42 Final Review Sheet Mr. J. Fassler Spring 2018 These problems are given to help you review concepts you may have forgotten. Old tests, quizzes and review sheets are also important in studying. Chapter
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) TIME: 3 Hours Tuesday afternoon 09/10/2007
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) TIME: 3 Hours Tuesday afternoon 09/10/2007
ELECTROCHEMISTRY OXIDATION-REDUCTION
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes
 Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes Chemical Activity (or Chemical Reactivity) is the measure of the reactivity of elements. If an element has high activity, then it means that the element is willing to
Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes Chemical Activity (or Chemical Reactivity) is the measure of the reactivity of elements. If an element has high activity, then it means that the element is willing to
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST
 GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW. C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3. A. Fe B. CO
 CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
1. How many significant digits are there in each of the following measurements? (½ mark each) a) ha b) s. c) d) 0.
 SCH 4U_07-08 SCH3U: REVIEW NAME: (TOTAL SCORE = 80) 1. How many significant digits are there in each of the following measurements? (½ mark each) a) 204.45 ha b) 18.23 s c) 380 000 d) 0.00560 g 2. Name
SCH 4U_07-08 SCH3U: REVIEW NAME: (TOTAL SCORE = 80) 1. How many significant digits are there in each of the following measurements? (½ mark each) a) 204.45 ha b) 18.23 s c) 380 000 d) 0.00560 g 2. Name
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells of a galvanic cell?
 Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
Course Title: Basics Chemistry (Group-4) (Code: )
 GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM Course Title: Basics (Group-4) (Code: 3300011) Diploma Programmes in which this course is offered Chemical Engineering, Printing Technology,
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM Course Title: Basics (Group-4) (Code: 3300011) Diploma Programmes in which this course is offered Chemical Engineering, Printing Technology,
 Electronic configurations, Auf-bau principle, Pauli principle, Hunds rule 1. Which of the following statements in relation to the hydrogen atom is correct? 1) 3s and 3p orbitals are of lower energy than
Electronic configurations, Auf-bau principle, Pauli principle, Hunds rule 1. Which of the following statements in relation to the hydrogen atom is correct? 1) 3s and 3p orbitals are of lower energy than
(i) The atomic number of an atom is the number of... (ii) The mass number of an atom is the number of...
 C2 Essential Questions Atomic Structure Q1.This question is about atomic structure and elements. (a) Complete the sentences. (i) The atomic number of an atom is the number of... (ii) The mass number of
C2 Essential Questions Atomic Structure Q1.This question is about atomic structure and elements. (a) Complete the sentences. (i) The atomic number of an atom is the number of... (ii) The mass number of
CHEM J-14 June 2014
 CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
METRO CENTRAL EDUCATION DISTRICT GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) SEPTEMBER 2016
 METRO CENTRAL EDUCATION DISTRICT GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) SEPTEMBER 2016 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 14 numbered pages and 4 data sheets. PHYSICAL SCIENCES/P2
METRO CENTRAL EDUCATION DISTRICT GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) SEPTEMBER 2016 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 14 numbered pages and 4 data sheets. PHYSICAL SCIENCES/P2
3. Solids cannot conduct electricity because the ions cannot move freely 4. Electrolytic cell
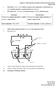 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Section A: Summary Notes
 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 25 AUGUST 2015 Section A: Summary Notes Important definitions: Oxidation: the loss of electrons by a substance during a chemical reaction Reduction: the gain of electrons by a substance
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 25 AUGUST 2015 Section A: Summary Notes Important definitions: Oxidation: the loss of electrons by a substance during a chemical reaction Reduction: the gain of electrons by a substance
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
2. What is the charge of the nucleus in an atom of oxygen-17? (1) 0 (2) 2 (3) +8 (4) +17
 60 Most Missed Chemistry Regents Exams Questions 1. In the wave-mechanical model, an orbital is a region of space in an atom where there is (1) a high probability of finding an electron (2) a high probability
60 Most Missed Chemistry Regents Exams Questions 1. In the wave-mechanical model, an orbital is a region of space in an atom where there is (1) a high probability of finding an electron (2) a high probability
CET Q UESTIONS QUESTIONS
 CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL
 *P15* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2009 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions from Section A All questions carry
*P15* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2009 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions from Section A All questions carry
Unit 4: Chemical Changes (Higher Content)
 Metals react with oxygen to produce metal oxides. E.g. Copper + Oxygen > Copper Oxide The reactions are oxidation reactions because the metals gain oxygen. Reactivity of Metals Metal Extraction Metals
Metals react with oxygen to produce metal oxides. E.g. Copper + Oxygen > Copper Oxide The reactions are oxidation reactions because the metals gain oxygen. Reactivity of Metals Metal Extraction Metals
SAURASHTRA UNIVERSITY STRUCTURE OF THE COURSES. SUBJECT : GEOGRAPHY B.A. ALL SEMESTER (Revised Syllabus in Force from: June-2016)
 SAURASHTRA UNIVERSITY STRUCTURE OF THE COURSES 0F SUBJECT : GEOGRAPHY B.A. ALL SEMESTER (Revised Syllabus in Force from: June-2016) Page 1 of 49 Sr No Level Sem Course Group SAURASHTRA UNIVERSITY ARTS
SAURASHTRA UNIVERSITY STRUCTURE OF THE COURSES 0F SUBJECT : GEOGRAPHY B.A. ALL SEMESTER (Revised Syllabus in Force from: June-2016) Page 1 of 49 Sr No Level Sem Course Group SAURASHTRA UNIVERSITY ARTS
 CHEMISTRY 112 FINAL EXAM June 24, 2013 FORM A 1. The following data was obtained for a reaction. The slope of the line is!2.8 " 10 3 K and the intercept is!0.44. What is the activation energy of the reaction?
CHEMISTRY 112 FINAL EXAM June 24, 2013 FORM A 1. The following data was obtained for a reaction. The slope of the line is!2.8 " 10 3 K and the intercept is!0.44. What is the activation energy of the reaction?
Practice I: Chemistry IGCSE
 Practice I: Chemistry IGCSE cristian.obiol@gmail.com 1) Explain the following processes related to changes of states of matter. -Melting:... -Vaporization:... -Freezing:... -Condensation:... -Sublimation:...
Practice I: Chemistry IGCSE cristian.obiol@gmail.com 1) Explain the following processes related to changes of states of matter. -Melting:... -Vaporization:... -Freezing:... -Condensation:... -Sublimation:...
Downloaded from Unit - 15 POLYMERS. Points to Remember
 Unit - 15 POLYMERS Points to Remember 1. Polymers are defined as high molecular mass macromolecules which consist of repeating structural units derived from the appropriate monomers. 2. In presence of
Unit - 15 POLYMERS Points to Remember 1. Polymers are defined as high molecular mass macromolecules which consist of repeating structural units derived from the appropriate monomers. 2. In presence of
Atomic Structure. Same atomic number Different mass number
 Mass number Number of protons and neutrons Atomic number Number of protons Atomic Structure Cl 35 17 Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons - these atoms are called isotopes of
Mass number Number of protons and neutrons Atomic number Number of protons Atomic Structure Cl 35 17 Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons - these atoms are called isotopes of
Oxidation numbers are charges on each atom. Oxidation-Reduction. Oxidation Numbers. Electrochemical Reactions. Oxidation and Reduction
 Oxidation-Reduction Oxidation numbers are charges on each atom. 1 2 Electrochemical Reactions Oxidation Numbers In electrochemical reactions, electrons are transferred from one species to another. In order
Oxidation-Reduction Oxidation numbers are charges on each atom. 1 2 Electrochemical Reactions Oxidation Numbers In electrochemical reactions, electrons are transferred from one species to another. In order
Fall 2011 CHEM Test 4, Form A
 Fall 2011 CHEM 1110.40413 Test 4, Form A Part I. Multiple Choice: Clearly circle the best answer. (60 pts) Name: 1. The common constituent in all acid solutions is A) H 2 SO 4 B) H 2 C) H + D) OH 2. Which
Fall 2011 CHEM 1110.40413 Test 4, Form A Part I. Multiple Choice: Clearly circle the best answer. (60 pts) Name: 1. The common constituent in all acid solutions is A) H 2 SO 4 B) H 2 C) H + D) OH 2. Which
Water - HW. PSI Chemistry
 Water - HW PSI Chemistry Name 1) In a single molecule of water, the two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by A) hydrogen bonds. B) nonpolar covalent bonds. C) polar covalent bonds. D) ionic
Water - HW PSI Chemistry Name 1) In a single molecule of water, the two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by A) hydrogen bonds. B) nonpolar covalent bonds. C) polar covalent bonds. D) ionic
For more information visit
 Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry which deals with the chemical changes caused in the matter by passage of electric current and conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa.
Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry which deals with the chemical changes caused in the matter by passage of electric current and conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa.
Solved Examples On Electrochemistry
 Solved Examples On Electrochemistry Example 1. Find the charge in coulomb on 1 g-ion of Charge on one ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 coulomb Thus, charge on one g-ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 6.02 10 23 = 2.89
Solved Examples On Electrochemistry Example 1. Find the charge in coulomb on 1 g-ion of Charge on one ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 coulomb Thus, charge on one g-ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 6.02 10 23 = 2.89
Chemistry 102 Chapter 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS
 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
NEW ERA SENIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL, NIZAMPURA SUMMER HOLIDAY ASSIGNMENT CLASS: IX
 (P.T.O.) NEW ERA SENIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL, NIZAMPURA SUMMER HOLIDAY ASSIGNMENT CLASS: IX NAME: ROLL NO.: DIV.: ENGLISH 1) Read the book Three men in a boat.write any three funny incidents of the story.
(P.T.O.) NEW ERA SENIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL, NIZAMPURA SUMMER HOLIDAY ASSIGNMENT CLASS: IX NAME: ROLL NO.: DIV.: ENGLISH 1) Read the book Three men in a boat.write any three funny incidents of the story.
Regents review Electrochemistry(redox)
 2011-2012 1. Chlorine has an oxidation state of +3 in the compound A) HClO B) HClO2 C) HClO3 D) HClO4 2. What is the oxidation number of iodine in KIO4? A) +1 B) 1 C) +7 D) 7 3. What is the oxidation number
2011-2012 1. Chlorine has an oxidation state of +3 in the compound A) HClO B) HClO2 C) HClO3 D) HClO4 2. What is the oxidation number of iodine in KIO4? A) +1 B) 1 C) +7 D) 7 3. What is the oxidation number
Chemistry. Electrochemistry.
 Chemistry Electrochemistry www.testprepkart.com Table of Content 1. Electrolytes and Electrolysis.. Faraday s laws of electrolysis. 3. Metallic and Electrolytic conductors. 4. Electrolytic conduction.
Chemistry Electrochemistry www.testprepkart.com Table of Content 1. Electrolytes and Electrolysis.. Faraday s laws of electrolysis. 3. Metallic and Electrolytic conductors. 4. Electrolytic conduction.
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) PHYSICAL SCIENCE (Second Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010
 NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) PHYSICAL SCIENCE (Second Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 (10021002) 11 March (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 A non-programmable scientific calculator may be used.
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) PHYSICAL SCIENCE (Second Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 (10021002) 11 March (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 A non-programmable scientific calculator may be used.
S4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES
 S4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES 1. The Mole One mole of a substance = GRAM FORMULA MASS e.g. H 2 SO 4 RAM from databook pg.7 2H 2 x 1 = 2 1S 1 x 32 = 32 4O 4 x 16 = 64 98g Mass = number of moles x Mass of 1
S4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES 1. The Mole One mole of a substance = GRAM FORMULA MASS e.g. H 2 SO 4 RAM from databook pg.7 2H 2 x 1 = 2 1S 1 x 32 = 32 4O 4 x 16 = 64 98g Mass = number of moles x Mass of 1
Electrochemistry Pearson Education, Inc. Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School AP Chemistry
 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School AP Chemistry Electricity from Chemistry Many chemical reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions electron transfer
2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School AP Chemistry Electricity from Chemistry Many chemical reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions electron transfer
************************************************************************************** NSS1 ( )
 Yan Oi Tong Tin Ka Ping Secondary School NSS1 Chemistry Teaching Schedule (2018 2021) NSS1 Chemistry (2018 2021) / Teaching Schedule / P.1 **************************************************************************************
Yan Oi Tong Tin Ka Ping Secondary School NSS1 Chemistry Teaching Schedule (2018 2021) NSS1 Chemistry (2018 2021) / Teaching Schedule / P.1 **************************************************************************************
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan
 YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
Unit 8: Redox and Electrochemistry
 May 20, 2014 Unit 8: Redox and Electrochemistry http://www.firefly.org/firefly-pictures.html Oxidation Number numbers assigned to atoms that allow us to keep track of electrons. Rule #1: Oxidation number
May 20, 2014 Unit 8: Redox and Electrochemistry http://www.firefly.org/firefly-pictures.html Oxidation Number numbers assigned to atoms that allow us to keep track of electrons. Rule #1: Oxidation number
Question Bank Physical Chemistry & Material of Construction (CH-4-G) 1.Thermodynamics
 Question Bank Physical Chemistry & Material of Construction (CH-4-G) 1.Thermodynamics 1. Define the following terms and give its example I. System II. Surrounding III. Boundries IV. Homogeneous system
Question Bank Physical Chemistry & Material of Construction (CH-4-G) 1.Thermodynamics 1. Define the following terms and give its example I. System II. Surrounding III. Boundries IV. Homogeneous system
VPKBIET, FE SEMESTER - II ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY THEORY QUESTION BANK
 VPKBIET, FE 2017-18 SEMESTER - II ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY THEORY QUESTION BANK UNIT- I: WATER TECHNOLOGY Q1. Describe Demineralisation process of softening of hard water. What are its advantages over Zeolite
VPKBIET, FE 2017-18 SEMESTER - II ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY THEORY QUESTION BANK UNIT- I: WATER TECHNOLOGY Q1. Describe Demineralisation process of softening of hard water. What are its advantages over Zeolite
Redox and Electrochemistry
 Redox and Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemistry in Action! 2 Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers The oxidation number of any uncombined element is 0. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the
Redox and Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemistry in Action! 2 Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers The oxidation number of any uncombined element is 0. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the
8. Draw Lewis structures and determine molecular geometry based on VSEPR Theory
 Chemistry Grade 12 Outcomes 1 Quantum Chemistry and Atomic Structure Unit I 1. Perform calculations on wavelength, frequency and energy. 2. Have an understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. 3. Relate
Chemistry Grade 12 Outcomes 1 Quantum Chemistry and Atomic Structure Unit I 1. Perform calculations on wavelength, frequency and energy. 2. Have an understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. 3. Relate
1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number
 General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
Chapter 7 Electrochemistry
 Chapter 7 Electrochemistry Outside class reading Levine: pp. 417 14.4 Galvanic cells: pp. 423 14.5 types of reversible electrodes 7.6.1 Basic concepts of electrochemical apparatus (1) Electrochemical apparatus
Chapter 7 Electrochemistry Outside class reading Levine: pp. 417 14.4 Galvanic cells: pp. 423 14.5 types of reversible electrodes 7.6.1 Basic concepts of electrochemical apparatus (1) Electrochemical apparatus
Q1. The table below shows the boiling points of some hydrogen compounds formed by Group 6 elements. S H 2 O H 2. Boiling point / K
 Q1. The table below shows the boiling points of some hydrogen compounds formed by Group 6 elements. H O H S H Se H Te Boiling point / K 373 1 3 71 (a) State the strongest type of intermolecular force in
Q1. The table below shows the boiling points of some hydrogen compounds formed by Group 6 elements. H O H S H Se H Te Boiling point / K 373 1 3 71 (a) State the strongest type of intermolecular force in
HonorsChemistry 2nd Semester Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name HonorsChemistry 2nd Semester Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which process releases energy? 1) A) bond formation
Exam Name HonorsChemistry 2nd Semester Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which process releases energy? 1) A) bond formation
Unit 13 Redox Reactions & Electrochemistry Ch. 19 & 20 of your book.
 Unit 13 Redox Reactions & Electrochemistry Ch. 19 & 20 of your book. Early Booklet E.C.: + 2 Unit 13 Hwk. Pts.: / 32 Unit 13 Lab Pts.: / 32 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N Learning Targets
Unit 13 Redox Reactions & Electrochemistry Ch. 19 & 20 of your book. Early Booklet E.C.: + 2 Unit 13 Hwk. Pts.: / 32 Unit 13 Lab Pts.: / 32 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N Learning Targets
MC 17 C - 6 SECTION - I
 SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Question 1. (a) Name the gas in each of the following : An alkaline gas which gives dense white fumes with hydrogen chloride.
SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Question 1. (a) Name the gas in each of the following : An alkaline gas which gives dense white fumes with hydrogen chloride.
CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL
 *P15* Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2012 Triailscrúdú na hardteistiméireachta, 2012 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions
*P15* Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2012 Triailscrúdú na hardteistiméireachta, 2012 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions
States of matter
 3.1.3.4 States of matter 261 minutes 257 marks Page 1 of 30 Q1. (a) Describe the bonding in a metal. Explain why magnesium has a higher melting point than sodium. (4) (b) Why do diamond and graphite both
3.1.3.4 States of matter 261 minutes 257 marks Page 1 of 30 Q1. (a) Describe the bonding in a metal. Explain why magnesium has a higher melting point than sodium. (4) (b) Why do diamond and graphite both
