Equivalent Conditions on Conjugate Unitary Matrices
|
|
|
- Silvester Mason
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Mathematics Trends and Technology (IJMTT Volume 42 Number 1- February 2017 Equivalent Conditions on Conjugate Unitary Matrices A. Govindarasu #, S.Sassicala #1 # Department of Mathematics, A.V.C. College (Autonomous Mannampandal, Mayiladuthurai Abstract Concept of conjugate unitary matrices are given. Some equivalent conditions on conjugate unitary matrices are obtained. Conditions related to secondary unitary matrices, hermitian, s-hermitian and involutary are also derived. AMS Classification 15A09, 15A57. Keywords Unitary matrix, secondary transpose of a matrix, conjugate secondary transpose of a matrix, conjugate unitary matrix. I. INTRODUCTION Anna Lee [1] has initiated the study of secondary symmetric matrices. Also she has shown that for a Complex matrix A, the usual transpose and secondary transpose are related as, where is the permutation matrix with units in its secondary diagonal. Also denotes the conjugate secondary transpose of. where [2]. In this paper our intension is to prove some equivalent conditions on conjugate unitary matrices. II. PRELIMINARIES AND NOTATIONS Let be the space of complex matrices of order n. For.,,,, denote transpose, conjugate, conjugate transpose, secondary transpose, conjugate secondary transpose of a matrix respectively. Also satisfies and is called unitary if [7]. is called conjugate normal if [3]. is called s-normal iff [6] is called secondary unitary (s-unitary if [5]. is called s-hermitian if A A A S. is called is called conjugate unitary if [4]. III. EQUIVALENT CONDITIONS ON CONJUGATE UNITARY MATRICES Theorem 3.1 Any two of the following imply the (i is conjugate unitary matrix (ii is hermitian (iii Proof (i and (ii (iii A Case (i ( is hermitian Case (ii ( is hermitian (ii and (iii (i (. ( is hermitian (3.1.1 Again take ( ( is hermitian (3.1.2 Therefore, from (3.1.1 and (3.1.2 we A is conjugate unitary matrix. (iii and (i (ii Case (i Pre multiplying the above equation by ( A is hermitian Case(ii ISSN: Page 64
2 International Journal of Mathematics Trends and Technology (IJMTT Volume 42 Number 1- February 2017 Post multiplying the above equation by ( A is hermitian Therefore,in both cases implies A is hermitian. Theorem 3.2: Any two of the following imply the (i is conjugate unitary matrix (ii is s-unitary (iii commutes with V ( Proof: (i and (ii (iii Case (i ( is s - unitary Taking conjugate transpose Post multiplying the above equation by V Case (ii Taking conjugate ( is s - unitary Post multiply the above equation by sides, we commutes with (ii and (iii (i is s unitary Taking conjugate transpose (3.2.1 = Taking conjugate transpose (3.2.2 Therefore from equations (3.2.1 and (3.2.2 we, (iii and (i (ii Case (i (3.2.3 Pre multiplying the above equation by Post multiplying equation (3.2.3 by (3.2.4 (3.2.5 Therefore, from (3.2.4 and (3.2.5, we Case (ii (3.2.6 Pre multiplying equation (3.2.6 by sides, we Post multiplying equation (3.2.6 by we (3.2.7 sides, (3.2.8 Therefore from equations (3.2.7 and (3.2.8, we Therefore, in both cases, implies is s-unitary matrix. Theorem 3.3: Any two of the following imply the (i is conjugate unitary matrix (ii is s hermitian (iii ISSN: Page 65
3 International Journal of Mathematics Trends and Technology (IJMTT Volume 42 Number 1- February 2017 Proof: (i and (ii (iii Case (i Case (ii Case (ii A ( ( is s- hermitian (ii and (iii (i ( V A is s- hermitian. Theorem3.4: Any two of the following imply the (i is conjugate unitary matrix (ii is skew hermitian (iii is Involutary Proof : (i and (ii (iii Case (i A (3.3.1 A V ( V Case (ii ( (ii and (iii (i (3.3.2 Therefore from equations (3.3.1 and (3.3.2 we is conjugate unitary matrix. (iii and (i (ii Case (i ( Again take (3.4.1 ISSN: Page 66
4 International Journal of Mathematics Trends and Technology (IJMTT Volume 42 Number 1- February 2017 Case (ii, (3.4.2 Therefore, from (3.4.1 and (3.4.2 we (iii and (ii (i Take (3.5.4, (3.5.5 Post multiplying equation (3.5.4 by sides, we, (3.5.6 Therefore, from equations (3.5.5 and (3.5.6, we, Therefore, in both cases, implies is s-unitary. (iii and (i (ii ( is s unitary Now we take (3.4.3 ( is hermitian (3.5.7 Therefore, from (3.4.3 and (3.4.4 we (3.4.4 ( is hermitian is skew-hermitian Theorem3.5: If then any two of the following imply the (i is s-unitary (ii is conjugate unitary (iii is hermitian Proof: Given that (i and (ii (iii is s- unitary is conjugate unitary is hermitian (ii and (iii (i Case (i (3.5.1 Post multiplying equation (3.5.1 by (3.5.2 ( is hermitian ( is hermitian, (3.5.8 Therefore, from equations (3.5.7 and (3.5.8, we is conjugate unitary matrix. Theorem 3.6: Any two of the following imply the (i is conjugate unitary matrix (ii is hermitian (iii Proof: (i and (ii (iii Case (i Take transpose (3.5.3 Therefore, from equations (3.5.2 and (3.5.3 we ISSN: Page 67
5 International Journal of Mathematics Trends and Technology (IJMTT Volume 42 Number 1- February 2017 Case (ii Again taking transpose Again take (3.6.1 is hermitian Taking transpose Taking transpose Therefore, in both cases we (ii and (iii (i. Again taking transpose Taking transpose (3.6.2 Therefore, from equations (3.6.1 and (3.6.2, we (iii and (ii (i is conjugate unitary matrix. Taking transpose is hermitian IV. CONCLUSION Some equivalent condition on conjugate unitary matrices are obtained. Conditions related to secondary unitary matrices, unitary matrices, hermitian, s-hermitian and involutary matrix are also derived. [6]. S. Krishnamoorthy and R. Vijayakumar, Some equivalent conditions on s-normal matrices, International Journal of Comtemporary Mathematical Sciences, Vol.4, No.29, pp , [7]. A.K. Sharma, Text book of matrix theory, DPH Mathematics series, 2004 REFERENCES [1]. Anna Lee, Secondary symmetric, secondary skew symmetric, secondary orthogonal matrices, Period. Math. Hungary, Vol. 7, pp , [2]. Anna Lee, On s-symmetric, s-skew symmetric and s- orthogonal matrices, Period. Math. Hungary, Vol. 7, pp , [3]. A. Faßbender and Kh.D.Ikramov, Conjugate-normal matrices: a survey, Lin. Alg. Appl., Vol. 429, pp , [4]. A. Govindarasu and S. Sassicala, Characterizations of conjugate unitary matrices, Journal of ultra scientist of physical science, Vol. 29, No. 1, pp , [5]. S. Krishnamoorthy and A. Govindarasu, On Secondary Unitary Matrices, International Journal of computational science and Mathematics, Vol.2, No.3, pp , ISSN: Page 68
Some Properties of Conjugate Unitary Matrices
 Volume 119 No. 6 2018, 75-88 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Some Properties of Conjugate Unitary Matrices A.Govindarasu and S.Sassicala
Volume 119 No. 6 2018, 75-88 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Some Properties of Conjugate Unitary Matrices A.Govindarasu and S.Sassicala
Properties of k - CentroSymmetric and k Skew CentroSymmetric Matrices
 International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematical Sciences. ISSN 0972-9828 Volume 10, Number 1 (2017), pp. 99-106 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Properties of k - CentroSymmetric
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematical Sciences. ISSN 0972-9828 Volume 10, Number 1 (2017), pp. 99-106 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Properties of k - CentroSymmetric
On Sums of Conjugate Secondary Range k-hermitian Matrices
 Thai Journal of Mathematics Volume 10 (2012) Number 1 : 195 202 www.math.science.cmu.ac.th/thaijournal Online ISSN 1686-0209 On Sums of Conjugate Secondary Range k-hermitian Matrices S. Krishnamoorthy,
Thai Journal of Mathematics Volume 10 (2012) Number 1 : 195 202 www.math.science.cmu.ac.th/thaijournal Online ISSN 1686-0209 On Sums of Conjugate Secondary Range k-hermitian Matrices S. Krishnamoorthy,
CHAPTER 2 -idempotent matrices
 CHAPTER 2 -idempotent matrices A -idempotent matrix is defined and some of its basic characterizations are derived (see [33]) in this chapter. It is shown that if is a -idempotent matrix then it is quadripotent
CHAPTER 2 -idempotent matrices A -idempotent matrix is defined and some of its basic characterizations are derived (see [33]) in this chapter. It is shown that if is a -idempotent matrix then it is quadripotent
Secondary κ-kernel Symmetric Fuzzy Matrices
 Intern. J. Fuzzy Mathematical rchive Vol. 5, No. 2, 24, 89-94 ISSN: 232 3242 (P), 232 325 (online) Published on 2 December 24 www.researchmathsci.org International Journal of Secondary κ-ernel Symmetric
Intern. J. Fuzzy Mathematical rchive Vol. 5, No. 2, 24, 89-94 ISSN: 232 3242 (P), 232 325 (online) Published on 2 December 24 www.researchmathsci.org International Journal of Secondary κ-ernel Symmetric
Range Symmetric Matrices in Indefinite Inner Product Space
 Intern. J. Fuzzy Mathematical Archive Vol. 5, No. 2, 2014, 49-56 ISSN: 2320 3242 (P), 2320 3250 (online) Published on 20 December 2014 www.researchmathsci.org International Journal of Range Symmetric Matrices
Intern. J. Fuzzy Mathematical Archive Vol. 5, No. 2, 2014, 49-56 ISSN: 2320 3242 (P), 2320 3250 (online) Published on 20 December 2014 www.researchmathsci.org International Journal of Range Symmetric Matrices
Is there a Small Skew Cayley Transform with Zero Diagonal?
 Is there a Small Skew Cayley Transform with Zero Diagonal? Abstract The eigenvectors of an Hermitian matrix H are the columns of some complex unitary matrix Q. For any diagonal unitary matrix Ω the columns
Is there a Small Skew Cayley Transform with Zero Diagonal? Abstract The eigenvectors of an Hermitian matrix H are the columns of some complex unitary matrix Q. For any diagonal unitary matrix Ω the columns
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear Algebra
 SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 1.1. Introduction Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 1.1. Introduction Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
Inequalities For Singular Values And Traces Of Quaternion Hermitian Matrices
 Inequalities For Singular Values And Traces Of Quaternion Hermitian Matrices K. Gunasekaran M. Rahamathunisha Ramanujan Research Centre, PG and Research Department of Mathematics, Government Arts College
Inequalities For Singular Values And Traces Of Quaternion Hermitian Matrices K. Gunasekaran M. Rahamathunisha Ramanujan Research Centre, PG and Research Department of Mathematics, Government Arts College
Quantum Computing Lecture 2. Review of Linear Algebra
 Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
1 Linear Algebra Problems
 Linear Algebra Problems. Let A be the conjugate transpose of the complex matrix A; i.e., A = A t : A is said to be Hermitian if A = A; real symmetric if A is real and A t = A; skew-hermitian if A = A and
Linear Algebra Problems. Let A be the conjugate transpose of the complex matrix A; i.e., A = A t : A is said to be Hermitian if A = A; real symmetric if A is real and A t = A; skew-hermitian if A = A and
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear Algebra
 1.1. Introduction SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
1.1. Introduction SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
Symmetric and anti symmetric matrices
 Symmetric and anti symmetric matrices In linear algebra, a symmetric matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its transpose. Formally, matrix A is symmetric if. A = A Because equal matrices have equal
Symmetric and anti symmetric matrices In linear algebra, a symmetric matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its transpose. Formally, matrix A is symmetric if. A = A Because equal matrices have equal
Group representations
 Group representations A representation of a group is specified by a set of hermitian matrices that obey: (the original set of NxN dimensional matrices for SU(N) or SO(N) corresponds to the fundamental
Group representations A representation of a group is specified by a set of hermitian matrices that obey: (the original set of NxN dimensional matrices for SU(N) or SO(N) corresponds to the fundamental
MOORE-PENROSE INVERSE IN AN INDEFINITE INNER PRODUCT SPACE
 J. Appl. Math. & Computing Vol. 19(2005), No. 1-2, pp. 297-310 MOORE-PENROSE INVERSE IN AN INDEFINITE INNER PRODUCT SPACE K. KAMARAJ AND K. C. SIVAKUMAR Abstract. The concept of the Moore-Penrose inverse
J. Appl. Math. & Computing Vol. 19(2005), No. 1-2, pp. 297-310 MOORE-PENROSE INVERSE IN AN INDEFINITE INNER PRODUCT SPACE K. KAMARAJ AND K. C. SIVAKUMAR Abstract. The concept of the Moore-Penrose inverse
Phys 201. Matrices and Determinants
 Phys 201 Matrices and Determinants 1 1.1 Matrices 1.2 Operations of matrices 1.3 Types of matrices 1.4 Properties of matrices 1.5 Determinants 1.6 Inverse of a 3 3 matrix 2 1.1 Matrices A 2 3 7 =! " 1
Phys 201 Matrices and Determinants 1 1.1 Matrices 1.2 Operations of matrices 1.3 Types of matrices 1.4 Properties of matrices 1.5 Determinants 1.6 Inverse of a 3 3 matrix 2 1.1 Matrices A 2 3 7 =! " 1
Linear Algebra Section 2.6 : LU Decomposition Section 2.7 : Permutations and transposes Wednesday, February 13th Math 301 Week #4
 Linear Algebra Section. : LU Decomposition Section. : Permutations and transposes Wednesday, February 1th Math 01 Week # 1 The LU Decomposition We learned last time that we can factor a invertible matrix
Linear Algebra Section. : LU Decomposition Section. : Permutations and transposes Wednesday, February 1th Math 01 Week # 1 The LU Decomposition We learned last time that we can factor a invertible matrix
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators.
 MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators. Adjoint operator and adjoint matrix Given a linear operator L on an inner product space V, the adjoint of L is a transformation
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators. Adjoint operator and adjoint matrix Given a linear operator L on an inner product space V, the adjoint of L is a transformation
Ep Matrices and Its Weighted Generalized Inverse
 Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3850-3856 ISSN: 2249-6645 ABSTRACT: If A is a con s S.Krishnamoorthy 1 and B.K.N.MuthugobaI 2 Research Scholar Ramanujan Research Centre, Department of Mathematics, Govt.
Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3850-3856 ISSN: 2249-6645 ABSTRACT: If A is a con s S.Krishnamoorthy 1 and B.K.N.MuthugobaI 2 Research Scholar Ramanujan Research Centre, Department of Mathematics, Govt.
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing 2D SYSTEMS & PRELIMINARIES Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 Two Dimensional Fourier & Z-transform Toeplitz & Circulant Matrices Orthogonal & Unitary Matrices Block Matrices
Digital Image Processing 2D SYSTEMS & PRELIMINARIES Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 Two Dimensional Fourier & Z-transform Toeplitz & Circulant Matrices Orthogonal & Unitary Matrices Block Matrices
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Chemistry 5.76 Revised February, 1982 NOTES ON MATRIX METHODS
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Chemistry 5.76 Revised February, 198 NOTES ON MATRIX METHODS 1. Matrix Algebra Margenau and Murphy, The Mathematics of Physics and Chemistry, Chapter 10, give almost
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Chemistry 5.76 Revised February, 198 NOTES ON MATRIX METHODS 1. Matrix Algebra Margenau and Murphy, The Mathematics of Physics and Chemistry, Chapter 10, give almost
Linear Algebra: Matrix Eigenvalue Problems
 CHAPTER8 Linear Algebra: Matrix Eigenvalue Problems Chapter 8 p1 A matrix eigenvalue problem considers the vector equation (1) Ax = λx. 8.0 Linear Algebra: Matrix Eigenvalue Problems Here A is a given
CHAPTER8 Linear Algebra: Matrix Eigenvalue Problems Chapter 8 p1 A matrix eigenvalue problem considers the vector equation (1) Ax = λx. 8.0 Linear Algebra: Matrix Eigenvalue Problems Here A is a given
ELEMENTARY MATRIX ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY MATRIX ALGEBRA Third Edition FRANZ E. HOHN DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. Mineola, New York CONTENTS CHAPTER \ Introduction to Matrix Algebra 1.1 Matrices 1 1.2 Equality of Matrices 2 13 Addition
ELEMENTARY MATRIX ALGEBRA Third Edition FRANZ E. HOHN DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. Mineola, New York CONTENTS CHAPTER \ Introduction to Matrix Algebra 1.1 Matrices 1 1.2 Equality of Matrices 2 13 Addition
Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane.
 Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane c Sateesh R. Mane 2018 8 Lecture 8 8.1 Matrices July 22, 2018 We shall study
Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane c Sateesh R. Mane 2018 8 Lecture 8 8.1 Matrices July 22, 2018 We shall study
Assignment 12. O = O ij O kj = O kj O ij. δ ik = O ij
 Assignment 12 Arfken 4.1.1 Show that the group of n n orthogonal matrices On has nn 1/2 independent parameters. First we need to realize that a general orthogonal matrix, O, has n 2 elements or parameters,
Assignment 12 Arfken 4.1.1 Show that the group of n n orthogonal matrices On has nn 1/2 independent parameters. First we need to realize that a general orthogonal matrix, O, has n 2 elements or parameters,
CLASSICAL GROUPS DAVID VOGAN
 CLASSICAL GROUPS DAVID VOGAN 1. Orthogonal groups These notes are about classical groups. That term is used in various ways by various people; I ll try to say a little about that as I go along. Basically
CLASSICAL GROUPS DAVID VOGAN 1. Orthogonal groups These notes are about classical groups. That term is used in various ways by various people; I ll try to say a little about that as I go along. Basically
Mathematical Methods for Engineers and Scientists 1
 K.T. Tang Mathematical Methods for Engineers and Scientists 1 Complex Analysis, Determinants and Matrices With 49 Figures and 2 Tables fyj Springer Part I Complex Analysis 1 Complex Numbers 3 1.1 Our Number
K.T. Tang Mathematical Methods for Engineers and Scientists 1 Complex Analysis, Determinants and Matrices With 49 Figures and 2 Tables fyj Springer Part I Complex Analysis 1 Complex Numbers 3 1.1 Our Number
Mathematics. EC / EE / IN / ME / CE. for
 Mathematics for EC / EE / IN / ME / CE By www.thegateacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Mathematics Linear Algebra: Matrix Algebra, Systems of Linear Equations, Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Probability
Mathematics for EC / EE / IN / ME / CE By www.thegateacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Mathematics Linear Algebra: Matrix Algebra, Systems of Linear Equations, Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Probability
Lecture notes on Quantum Computing. Chapter 1 Mathematical Background
 Lecture notes on Quantum Computing Chapter 1 Mathematical Background Vector states of a quantum system with n physical states are represented by unique vectors in C n, the set of n 1 column vectors 1 For
Lecture notes on Quantum Computing Chapter 1 Mathematical Background Vector states of a quantum system with n physical states are represented by unique vectors in C n, the set of n 1 column vectors 1 For
Homework 1 Elena Davidson (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I)
 CS 106 Spring 2004 Homework 1 Elena Davidson 8 April 2004 Problem 1.1 Let B be a 4 4 matrix to which we apply the following operations: 1. double column 1, 2. halve row 3, 3. add row 3 to row 1, 4. interchange
CS 106 Spring 2004 Homework 1 Elena Davidson 8 April 2004 Problem 1.1 Let B be a 4 4 matrix to which we apply the following operations: 1. double column 1, 2. halve row 3, 3. add row 3 to row 1, 4. interchange
Matrices. Chapter What is a Matrix? We review the basic matrix operations. An array of numbers a a 1n A = a m1...
 Chapter Matrices We review the basic matrix operations What is a Matrix? An array of numbers a a n A = a m a mn with m rows and n columns is a m n matrix Element a ij in located in position (i, j The elements
Chapter Matrices We review the basic matrix operations What is a Matrix? An array of numbers a a n A = a m a mn with m rows and n columns is a m n matrix Element a ij in located in position (i, j The elements
1 Matrices and vector spaces
 Matrices and vector spaces. Which of the following statements about linear vector spaces are true? Where a statement is false, give a counter-example to demonstrate this. (a) Non-singular N N matrices
Matrices and vector spaces. Which of the following statements about linear vector spaces are true? Where a statement is false, give a counter-example to demonstrate this. (a) Non-singular N N matrices
Lecture 6: Vector Spaces II - Matrix Representations
 1 Key points Lecture 6: Vector Spaces II - Matrix Representations Linear Operators Matrix representation of vectors and operators Hermite conjugate (adjoint) operator Hermitian operator (self-adjoint)
1 Key points Lecture 6: Vector Spaces II - Matrix Representations Linear Operators Matrix representation of vectors and operators Hermite conjugate (adjoint) operator Hermitian operator (self-adjoint)
Preliminary/Qualifying Exam in Numerical Analysis (Math 502a) Spring 2012
 Instructions Preliminary/Qualifying Exam in Numerical Analysis (Math 502a) Spring 2012 The exam consists of four problems, each having multiple parts. You should attempt to solve all four problems. 1.
Instructions Preliminary/Qualifying Exam in Numerical Analysis (Math 502a) Spring 2012 The exam consists of four problems, each having multiple parts. You should attempt to solve all four problems. 1.
Computational Foundations of Cognitive Science. Definition of the Inverse. Definition of the Inverse. Definition Computation Properties
 al Foundations of Cognitive Science Lecture 1: s; Frank Keller School of Informatics University of Edinburgh keller@inf.ed.ac.uk February, 010 1 Reading: Anton and Busby, Chs..,.6 Frank Keller al Foundations
al Foundations of Cognitive Science Lecture 1: s; Frank Keller School of Informatics University of Edinburgh keller@inf.ed.ac.uk February, 010 1 Reading: Anton and Busby, Chs..,.6 Frank Keller al Foundations
1. Foundations of Numerics from Advanced Mathematics. Linear Algebra
 Foundations of Numerics from Advanced Mathematics Linear Algebra Linear Algebra, October 23, 22 Linear Algebra Mathematical Structures a mathematical structure consists of one or several sets and one or
Foundations of Numerics from Advanced Mathematics Linear Algebra Linear Algebra, October 23, 22 Linear Algebra Mathematical Structures a mathematical structure consists of one or several sets and one or
2. Introduction to quantum mechanics
 2. Introduction to quantum mechanics 2.1 Linear algebra Dirac notation Complex conjugate Vector/ket Dual vector/bra Inner product/bracket Tensor product Complex conj. matrix Transpose of matrix Hermitian
2. Introduction to quantum mechanics 2.1 Linear algebra Dirac notation Complex conjugate Vector/ket Dual vector/bra Inner product/bracket Tensor product Complex conj. matrix Transpose of matrix Hermitian
Matrix Operations. Linear Combination Vector Algebra Angle Between Vectors Projections and Reflections Equality of matrices, Augmented Matrix
 Linear Combination Vector Algebra Angle Between Vectors Projections and Reflections Equality of matrices, Augmented Matrix Matrix Operations Matrix Addition and Matrix Scalar Multiply Matrix Multiply Matrix
Linear Combination Vector Algebra Angle Between Vectors Projections and Reflections Equality of matrices, Augmented Matrix Matrix Operations Matrix Addition and Matrix Scalar Multiply Matrix Multiply Matrix
FFTs in Graphics and Vision. The Laplace Operator
 FFTs in Graphics and Vision The Laplace Operator 1 Outline Math Stuff Symmetric/Hermitian Matrices Lagrange Multipliers Diagonalizing Symmetric Matrices The Laplacian Operator 2 Linear Operators Definition:
FFTs in Graphics and Vision The Laplace Operator 1 Outline Math Stuff Symmetric/Hermitian Matrices Lagrange Multipliers Diagonalizing Symmetric Matrices The Laplacian Operator 2 Linear Operators Definition:
Computational Methods CMSC/AMSC/MAPL 460. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Ramani Duraiswami, Dept. of Computer Science
 Computational Methods CMSC/AMSC/MAPL 460 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Ramani Duraiswami, Dept. of Computer Science Eigen Values of a Matrix Recap: A N N matrix A has an eigenvector x (non-zero) with corresponding
Computational Methods CMSC/AMSC/MAPL 460 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Ramani Duraiswami, Dept. of Computer Science Eigen Values of a Matrix Recap: A N N matrix A has an eigenvector x (non-zero) with corresponding
arxiv: v3 [math.ra] 22 Aug 2014
![arxiv: v3 [math.ra] 22 Aug 2014 arxiv: v3 [math.ra] 22 Aug 2014](/thumbs/91/105622575.jpg) arxiv:1407.0331v3 [math.ra] 22 Aug 2014 Positivity of Partitioned Hermitian Matrices with Unitarily Invariant Norms Abstract Chi-Kwong Li a, Fuzhen Zhang b a Department of Mathematics, College of William
arxiv:1407.0331v3 [math.ra] 22 Aug 2014 Positivity of Partitioned Hermitian Matrices with Unitarily Invariant Norms Abstract Chi-Kwong Li a, Fuzhen Zhang b a Department of Mathematics, College of William
Math 108b: Notes on the Spectral Theorem
 Math 108b: Notes on the Spectral Theorem From section 6.3, we know that every linear operator T on a finite dimensional inner product space V has an adjoint. (T is defined as the unique linear operator
Math 108b: Notes on the Spectral Theorem From section 6.3, we know that every linear operator T on a finite dimensional inner product space V has an adjoint. (T is defined as the unique linear operator
Index. book 2009/5/27 page 121. (Page numbers set in bold type indicate the definition of an entry.)
 page 121 Index (Page numbers set in bold type indicate the definition of an entry.) A absolute error...26 componentwise...31 in subtraction...27 normwise...31 angle in least squares problem...98,99 approximation
page 121 Index (Page numbers set in bold type indicate the definition of an entry.) A absolute error...26 componentwise...31 in subtraction...27 normwise...31 angle in least squares problem...98,99 approximation
MATH 213 Linear Algebra and ODEs Spring 2015 Study Sheet for Midterm Exam. Topics
 MATH 213 Linear Algebra and ODEs Spring 2015 Study Sheet for Midterm Exam This study sheet will not be allowed during the test Books and notes will not be allowed during the test Calculators and cell phones
MATH 213 Linear Algebra and ODEs Spring 2015 Study Sheet for Midterm Exam This study sheet will not be allowed during the test Books and notes will not be allowed during the test Calculators and cell phones
determinantal conjecture, Marcus-de Oliveira, determinants, normal matrices,
 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 BOUNDARY MATRICES AND THE MARCUS-DE OLIVEIRA DETERMINANTAL CONJECTURE AMEET SHARMA Abstract. We present notes on the Marcus-de Oliveira conjecture. The conjecture concerns the region in the
1 3 4 5 6 7 8 BOUNDARY MATRICES AND THE MARCUS-DE OLIVEIRA DETERMINANTAL CONJECTURE AMEET SHARMA Abstract. We present notes on the Marcus-de Oliveira conjecture. The conjecture concerns the region in the
Problem set 2. Math 212b February 8, 2001 due Feb. 27
 Problem set 2 Math 212b February 8, 2001 due Feb. 27 Contents 1 The L 2 Euler operator 1 2 Symplectic vector spaces. 2 2.1 Special kinds of subspaces....................... 3 2.2 Normal forms..............................
Problem set 2 Math 212b February 8, 2001 due Feb. 27 Contents 1 The L 2 Euler operator 1 2 Symplectic vector spaces. 2 2.1 Special kinds of subspaces....................... 3 2.2 Normal forms..............................
What is the Matrix? Linear control of finite-dimensional spaces. November 28, 2010
 What is the Matrix? Linear control of finite-dimensional spaces. November 28, 2010 Scott Strong sstrong@mines.edu Colorado School of Mines What is the Matrix? p. 1/20 Overview/Keywords/References Advanced
What is the Matrix? Linear control of finite-dimensional spaces. November 28, 2010 Scott Strong sstrong@mines.edu Colorado School of Mines What is the Matrix? p. 1/20 Overview/Keywords/References Advanced
Matrix Inequalities by Means of Block Matrices 1
 Mathematical Inequalities & Applications, Vol. 4, No. 4, 200, pp. 48-490. Matrix Inequalities by Means of Block Matrices Fuzhen Zhang 2 Department of Math, Science and Technology Nova Southeastern University,
Mathematical Inequalities & Applications, Vol. 4, No. 4, 200, pp. 48-490. Matrix Inequalities by Means of Block Matrices Fuzhen Zhang 2 Department of Math, Science and Technology Nova Southeastern University,
Algebra I Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.701 Algebra I Fall 007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.701 007 Geometry of the Special Unitary
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.701 Algebra I Fall 007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.701 007 Geometry of the Special Unitary
Geometry of the Special Unitary Group
 Geometry of the Special Unitary Group The elements of SU 2 are the unitary 2 2 matrices with determinant 1. It is not hard to see that they have the form a 1) ) b, b ā with āa+bb = 1. This is the transpose
Geometry of the Special Unitary Group The elements of SU 2 are the unitary 2 2 matrices with determinant 1. It is not hard to see that they have the form a 1) ) b, b ā with āa+bb = 1. This is the transpose
Distribution for the Standard Eigenvalues of Quaternion Matrices
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 7, 01, no. 17, 831-838 Distribution for the Standard Eigenvalues of Quaternion Matrices Shahid Qaisar College of Mathematics and Statistics, Chongqing University
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 7, 01, no. 17, 831-838 Distribution for the Standard Eigenvalues of Quaternion Matrices Shahid Qaisar College of Mathematics and Statistics, Chongqing University
A Proof of Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Through Linear Algebra due to Derksen. Anant R. Shastri. February 13, 2011
 A Proof of Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Through Linear Algebra due to Derksen February 13, 2011 MA106-Linear Algebra 2011 MA106-Linear Algebra 2011 We present a proof of the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
A Proof of Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Through Linear Algebra due to Derksen February 13, 2011 MA106-Linear Algebra 2011 MA106-Linear Algebra 2011 We present a proof of the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
Lecture 8 : Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
 CPS290: Algorithmic Foundations of Data Science February 24, 2017 Lecture 8 : Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Lecturer: Kamesh Munagala Scribe: Kamesh Munagala Hermitian Matrices It is simpler to begin with
CPS290: Algorithmic Foundations of Data Science February 24, 2017 Lecture 8 : Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Lecturer: Kamesh Munagala Scribe: Kamesh Munagala Hermitian Matrices It is simpler to begin with
Assignment 11 (C + C ) = (C + C ) = (C + C) i(c C ) ] = i(c C) (AB) = (AB) = B A = BA 0 = [A, B] = [A, B] = (AB BA) = (AB) AB
![Assignment 11 (C + C ) = (C + C ) = (C + C) i(c C ) ] = i(c C) (AB) = (AB) = B A = BA 0 = [A, B] = [A, B] = (AB BA) = (AB) AB Assignment 11 (C + C ) = (C + C ) = (C + C) i(c C ) ] = i(c C) (AB) = (AB) = B A = BA 0 = [A, B] = [A, B] = (AB BA) = (AB) AB](/thumbs/82/86038312.jpg) Arfken 3.4.6 Matrix C is not Hermition. But which is Hermitian. Likewise, Assignment 11 (C + C ) = (C + C ) = (C + C) [ i(c C ) ] = i(c C ) = i(c C) = i ( C C ) Arfken 3.4.9 The matrices A and B are both
Arfken 3.4.6 Matrix C is not Hermition. But which is Hermitian. Likewise, Assignment 11 (C + C ) = (C + C ) = (C + C) [ i(c C ) ] = i(c C ) = i(c C) = i ( C C ) Arfken 3.4.9 The matrices A and B are both
Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2
 Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University February 6, 2018 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 February 6, 2018
Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University February 6, 2018 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 February 6, 2018
Math Abstract Linear Algebra Fall 2011, section E1 Practice Final. This is a (long) practice exam. The real exam will consist of 6 problems.
 Math 416 - Abstract Linear Algebra Fall 2011, section E1 Practice Final Name: This is a (long) practice exam. The real exam will consist of 6 problems. In the real exam, no calculators, electronic devices,
Math 416 - Abstract Linear Algebra Fall 2011, section E1 Practice Final Name: This is a (long) practice exam. The real exam will consist of 6 problems. In the real exam, no calculators, electronic devices,
Matched, Lossless, Reciprocal Devices
 /3/7 Matched reciprocal lossless 73 /9 Matched, Lossless, Reciprocal Devices As we discussed earlier, a device can be lossless or reciprocal. In addition, we can likewise classify it as being matched.
/3/7 Matched reciprocal lossless 73 /9 Matched, Lossless, Reciprocal Devices As we discussed earlier, a device can be lossless or reciprocal. In addition, we can likewise classify it as being matched.
Improvements on Geometric Means Related to the Tracy-Singh Products of Positive Matrices
 MATEMATIKA, 2005, Volume 21, Number 2, pp. 49 65 c Department of Mathematics, UTM. Improvements on Geometric Means Related to the Tracy-Singh Products of Positive Matrices 1 Adem Kilicman & 2 Zeyad Al
MATEMATIKA, 2005, Volume 21, Number 2, pp. 49 65 c Department of Mathematics, UTM. Improvements on Geometric Means Related to the Tracy-Singh Products of Positive Matrices 1 Adem Kilicman & 2 Zeyad Al
Matched, Lossless, Reciprocal Devices
 /6/009 Matched reciprocal lossless present / Matched, Lossless, Reciprocal Devices As we discussed earlier, a device can be lossless or reciprocal. In addition, we can likewise classify it as being matched.
/6/009 Matched reciprocal lossless present / Matched, Lossless, Reciprocal Devices As we discussed earlier, a device can be lossless or reciprocal. In addition, we can likewise classify it as being matched.
Means of unitaries, conjugations, and the Friedrichs operator
 J. Math. Anal. Appl. 335 (2007) 941 947 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmaa Means of unitaries, conjugations, and the Friedrichs operator Stephan Ramon Garcia Department of Mathematics, Pomona College, Claremont,
J. Math. Anal. Appl. 335 (2007) 941 947 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmaa Means of unitaries, conjugations, and the Friedrichs operator Stephan Ramon Garcia Department of Mathematics, Pomona College, Claremont,
Lecture 10: Eigenvectors and eigenvalues (Numerical Recipes, Chapter 11)
 Lecture 1: Eigenvectors and eigenvalues (Numerical Recipes, Chapter 11) The eigenvalue problem, Ax= λ x, occurs in many, many contexts: classical mechanics, quantum mechanics, optics 22 Eigenvectors and
Lecture 1: Eigenvectors and eigenvalues (Numerical Recipes, Chapter 11) The eigenvalue problem, Ax= λ x, occurs in many, many contexts: classical mechanics, quantum mechanics, optics 22 Eigenvectors and
Physics 129B, Winter 2010 Problem Set 4 Solution
 Physics 9B, Winter Problem Set 4 Solution H-J Chung March 8, Problem a Show that the SUN Lie algebra has an SUN subalgebra b The SUN Lie group consists of N N unitary matrices with unit determinant Thus,
Physics 9B, Winter Problem Set 4 Solution H-J Chung March 8, Problem a Show that the SUN Lie algebra has an SUN subalgebra b The SUN Lie group consists of N N unitary matrices with unit determinant Thus,
On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian Block-Matrices
 On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices Antoine Mhanna To cite this version: Antoine Mhanna On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices 016 HAL Id: hal-0131860
On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices Antoine Mhanna To cite this version: Antoine Mhanna On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices 016 HAL Id: hal-0131860
University of Colorado at Denver Mathematics Department Applied Linear Algebra Preliminary Exam With Solutions 16 January 2009, 10:00 am 2:00 pm
 University of Colorado at Denver Mathematics Department Applied Linear Algebra Preliminary Exam With Solutions 16 January 2009, 10:00 am 2:00 pm Name: The proctor will let you read the following conditions
University of Colorado at Denver Mathematics Department Applied Linear Algebra Preliminary Exam With Solutions 16 January 2009, 10:00 am 2:00 pm Name: The proctor will let you read the following conditions
On A Special Case Of A Conjecture Of Ryser About Hadamard Circulant Matrices
 Applied Mathematics E-Notes, 1(01), 18-188 c ISSN 1607-510 Available free at mirror sites of http://www.math.nthu.edu.tw/amen/ On A Special Case Of A Conjecture Of Ryser About Hadamard Circulant Matrices
Applied Mathematics E-Notes, 1(01), 18-188 c ISSN 1607-510 Available free at mirror sites of http://www.math.nthu.edu.tw/amen/ On A Special Case Of A Conjecture Of Ryser About Hadamard Circulant Matrices
CLASS 12 ALGEBRA OF MATRICES
 CLASS 12 ALGEBRA OF MATRICES Deepak Sir 9811291604 SHRI SAI MASTERS TUITION CENTER CLASS 12 A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers or functions. The numbers or functions are called the elements
CLASS 12 ALGEBRA OF MATRICES Deepak Sir 9811291604 SHRI SAI MASTERS TUITION CENTER CLASS 12 A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers or functions. The numbers or functions are called the elements
Example: Filter output power. maximization. Definition. Eigenvalues, eigenvectors and similarity. Example: Stability of linear systems.
 Lecture 2: Eigenvalues, eigenvectors and similarity The single most important concept in matrix theory. German word eigen means proper or characteristic. KTH Signal Processing 1 Magnus Jansson/Emil Björnson
Lecture 2: Eigenvalues, eigenvectors and similarity The single most important concept in matrix theory. German word eigen means proper or characteristic. KTH Signal Processing 1 Magnus Jansson/Emil Björnson
Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering
 Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering Lectures 13 15, Tuesday 8 th and Friday 11 th November 016 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE
Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering Lectures 13 15, Tuesday 8 th and Friday 11 th November 016 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE
An Interpolation Problem by Completely Positive Maps and its. Quantum Cloning
 An Interpolation Problem by Completely Positive Maps and its Application in Quantum Cloning College of Mathematics and Information Science, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi an, China, 710062 gzhihua@tom.com
An Interpolation Problem by Completely Positive Maps and its Application in Quantum Cloning College of Mathematics and Information Science, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi an, China, 710062 gzhihua@tom.com
Properties of Matrix Arithmetic
 Properties of Matrix Arithmetic I've given examples which illustrate how you can do arithmetic with matrices. Now I'll give precise definitions of the various matrix operations. This will allow me to prove
Properties of Matrix Arithmetic I've given examples which illustrate how you can do arithmetic with matrices. Now I'll give precise definitions of the various matrix operations. This will allow me to prove
Matrix Factorization and Analysis
 Chapter 7 Matrix Factorization and Analysis Matrix factorizations are an important part of the practice and analysis of signal processing. They are at the heart of many signal-processing algorithms. Their
Chapter 7 Matrix Factorization and Analysis Matrix factorizations are an important part of the practice and analysis of signal processing. They are at the heart of many signal-processing algorithms. Their
Review 1 Math 321: Linear Algebra Spring 2010
 Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico Review 1 Math 321: Linear Algebra Spring 2010 This is a review for Midterm 1 that will be on Thursday March 11th, 2010. The main topics
Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico Review 1 Math 321: Linear Algebra Spring 2010 This is a review for Midterm 1 that will be on Thursday March 11th, 2010. The main topics
A property of orthogonal projectors
 Linear Algebra and its Applications 354 (2002) 35 39 www.elsevier.com/locate/laa A property of orthogonal projectors Jerzy K. Baksalary a,, Oskar Maria Baksalary b,tomaszszulc c a Department of Mathematics,
Linear Algebra and its Applications 354 (2002) 35 39 www.elsevier.com/locate/laa A property of orthogonal projectors Jerzy K. Baksalary a,, Oskar Maria Baksalary b,tomaszszulc c a Department of Mathematics,
Lecture 3: Matrix and Matrix Operations
 Lecture 3: Matrix and Matrix Operations Representation, row vector, column vector, element of a matrix. Examples of matrix representations Tables and spreadsheets Scalar-Matrix operation: Scaling a matrix
Lecture 3: Matrix and Matrix Operations Representation, row vector, column vector, element of a matrix. Examples of matrix representations Tables and spreadsheets Scalar-Matrix operation: Scaling a matrix
Matrix Representation
 Matrix Representation Matrix Rep. Same basics as introduced already. Convenient method of working with vectors. Superposition Complete set of vectors can be used to express any other vector. Complete set
Matrix Representation Matrix Rep. Same basics as introduced already. Convenient method of working with vectors. Superposition Complete set of vectors can be used to express any other vector. Complete set
Orthogonal Symmetric Toeplitz Matrices
 Orthogonal Symmetric Toeplitz Matrices Albrecht Böttcher In Memory of Georgii Litvinchuk (1931-2006 Abstract We show that the number of orthogonal and symmetric Toeplitz matrices of a given order is finite
Orthogonal Symmetric Toeplitz Matrices Albrecht Böttcher In Memory of Georgii Litvinchuk (1931-2006 Abstract We show that the number of orthogonal and symmetric Toeplitz matrices of a given order is finite
MATH 511 ADVANCED LINEAR ALGEBRA SPRING 2006
 MATH 511 ADVANCED LINEAR ALGEBRA SPRING 2006 Sherod Eubanks HOMEWORK 2 2.1 : 2, 5, 9, 12 2.3 : 3, 6 2.4 : 2, 4, 5, 9, 11 Section 2.1: Unitary Matrices Problem 2 If λ σ(u) and U M n is unitary, show that
MATH 511 ADVANCED LINEAR ALGEBRA SPRING 2006 Sherod Eubanks HOMEWORK 2 2.1 : 2, 5, 9, 12 2.3 : 3, 6 2.4 : 2, 4, 5, 9, 11 Section 2.1: Unitary Matrices Problem 2 If λ σ(u) and U M n is unitary, show that
Math 407: Linear Optimization
 Math 407: Linear Optimization Lecture 16: The Linear Least Squares Problem II Math Dept, University of Washington February 28, 2018 Lecture 16: The Linear Least Squares Problem II (Math Dept, University
Math 407: Linear Optimization Lecture 16: The Linear Least Squares Problem II Math Dept, University of Washington February 28, 2018 Lecture 16: The Linear Least Squares Problem II (Math Dept, University
18.06 Problem Set 8 - Solutions Due Wednesday, 14 November 2007 at 4 pm in
 806 Problem Set 8 - Solutions Due Wednesday, 4 November 2007 at 4 pm in 2-06 08 03 Problem : 205+5+5+5 Consider the matrix A 02 07 a Check that A is a positive Markov matrix, and find its steady state
806 Problem Set 8 - Solutions Due Wednesday, 4 November 2007 at 4 pm in 2-06 08 03 Problem : 205+5+5+5 Consider the matrix A 02 07 a Check that A is a positive Markov matrix, and find its steady state
ACM 104. Homework Set 5 Solutions. February 21, 2001
 ACM 04 Homework Set 5 Solutions February, 00 Franklin Chapter 4, Problem 4, page 0 Let A be an n n non-hermitian matrix Suppose that A has distinct eigenvalues λ,, λ n Show that A has the eigenvalues λ,,
ACM 04 Homework Set 5 Solutions February, 00 Franklin Chapter 4, Problem 4, page 0 Let A be an n n non-hermitian matrix Suppose that A has distinct eigenvalues λ,, λ n Show that A has the eigenvalues λ,,
Phase space, Tangent-Linear and Adjoint Models, Singular Vectors, Lyapunov Vectors and Normal Modes
 Phase space, Tangent-Linear and Adjoint Models, Singular Vectors, Lyapunov Vectors and Normal Modes Assume a phase space of dimension N where Autonomous governing equations with initial state: = is a state
Phase space, Tangent-Linear and Adjoint Models, Singular Vectors, Lyapunov Vectors and Normal Modes Assume a phase space of dimension N where Autonomous governing equations with initial state: = is a state
Numerical Methods I Eigenvalue Problems
 Numerical Methods I Eigenvalue Problems Aleksandar Donev Courant Institute, NYU 1 donev@courant.nyu.edu 1 MATH-GA 2011.003 / CSCI-GA 2945.003, Fall 2014 October 2nd, 2014 A. Donev (Courant Institute) Lecture
Numerical Methods I Eigenvalue Problems Aleksandar Donev Courant Institute, NYU 1 donev@courant.nyu.edu 1 MATH-GA 2011.003 / CSCI-GA 2945.003, Fall 2014 October 2nd, 2014 A. Donev (Courant Institute) Lecture
REVERSALS ON SFT S. 1. Introduction and preliminaries
 Trends in Mathematics Information Center for Mathematical Sciences Volume 7, Number 2, December, 2004, Pages 119 125 REVERSALS ON SFT S JUNGSEOB LEE Abstract. Reversals of topological dynamical systems
Trends in Mathematics Information Center for Mathematical Sciences Volume 7, Number 2, December, 2004, Pages 119 125 REVERSALS ON SFT S JUNGSEOB LEE Abstract. Reversals of topological dynamical systems
Math 215 HW #11 Solutions
 Math 215 HW #11 Solutions 1 Problem 556 Find the lengths and the inner product of 2 x and y [ 2 + ] Answer: First, x 2 x H x [2 + ] 2 (4 + 16) + 16 36, so x 6 Likewise, so y 6 Finally, x, y x H y [2 +
Math 215 HW #11 Solutions 1 Problem 556 Find the lengths and the inner product of 2 x and y [ 2 + ] Answer: First, x 2 x H x [2 + ] 2 (4 + 16) + 16 36, so x 6 Likewise, so y 6 Finally, x, y x H y [2 +
The Singular Value Decomposition
 The Singular Value Decomposition Philippe B. Laval KSU Fall 2015 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) SVD Fall 2015 1 / 13 Review of Key Concepts We review some key definitions and results about matrices that will
The Singular Value Decomposition Philippe B. Laval KSU Fall 2015 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) SVD Fall 2015 1 / 13 Review of Key Concepts We review some key definitions and results about matrices that will
Trades in complex Hadamard matrices
 Trades in complex Hadamard matrices Padraig Ó Catháin Ian M. Wanless School of Mathematical Sciences, Monash University, VIC 3800, Australia. February 9, 2015 Abstract A trade in a complex Hadamard matrix
Trades in complex Hadamard matrices Padraig Ó Catháin Ian M. Wanless School of Mathematical Sciences, Monash University, VIC 3800, Australia. February 9, 2015 Abstract A trade in a complex Hadamard matrix
(c) Only when AB = BA d) only when AB BA. find the first column of its inverse,
 . Find the symmetric and the skew symmetric part of 2 0 3 7 5 9 3 respectively 2. n n n B B, where & B are two matrix above result true (a) lways (b) Never (c) Only when B = B d) only when B B 3. Find
. Find the symmetric and the skew symmetric part of 2 0 3 7 5 9 3 respectively 2. n n n B B, where & B are two matrix above result true (a) lways (b) Never (c) Only when B = B d) only when B B 3. Find
Research Article k-kernel Symmetric Matrices
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2009, Article ID 926217, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2009/926217 Research Article k-kernel Symmetric Matrices
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2009, Article ID 926217, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2009/926217 Research Article k-kernel Symmetric Matrices
Numerical Linear Algebra Homework Assignment - Week 2
 Numerical Linear Algebra Homework Assignment - Week 2 Đoàn Trần Nguyên Tùng Student ID: 1411352 8th October 2016 Exercise 2.1: Show that if a matrix A is both triangular and unitary, then it is diagonal.
Numerical Linear Algebra Homework Assignment - Week 2 Đoàn Trần Nguyên Tùng Student ID: 1411352 8th October 2016 Exercise 2.1: Show that if a matrix A is both triangular and unitary, then it is diagonal.
Trace Inequalities for a Block Hadamard Product
 Filomat 32:1 2018), 285 292 https://doiorg/102298/fil1801285p Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://wwwpmfniacrs/filomat Trace Inequalities for
Filomat 32:1 2018), 285 292 https://doiorg/102298/fil1801285p Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://wwwpmfniacrs/filomat Trace Inequalities for
Linear Algebra Linear Algebra : Matrix decompositions Monday, February 11th Math 365 Week #4
 Linear Algebra Linear Algebra : Matrix decompositions Monday, February 11th Math Week # 1 Saturday, February 1, 1 Linear algebra Typical linear system of equations : x 1 x +x = x 1 +x +9x = 0 x 1 +x x
Linear Algebra Linear Algebra : Matrix decompositions Monday, February 11th Math Week # 1 Saturday, February 1, 1 Linear algebra Typical linear system of equations : x 1 x +x = x 1 +x +9x = 0 x 1 +x x
Review of Linear Algebra
 Review of Linear Algebra Definitions An m n (read "m by n") matrix, is a rectangular array of entries, where m is the number of rows and n the number of columns. 2 Definitions (Con t) A is square if m=
Review of Linear Algebra Definitions An m n (read "m by n") matrix, is a rectangular array of entries, where m is the number of rows and n the number of columns. 2 Definitions (Con t) A is square if m=
Math 250B Midterm I Information Fall 2018
 Math 250B Midterm I Information Fall 2018 WHEN: Wednesday, September 26, in class (no notes, books, calculators I will supply a table of integrals) EXTRA OFFICE HOURS: Sunday, September 23 from 8:00 PM
Math 250B Midterm I Information Fall 2018 WHEN: Wednesday, September 26, in class (no notes, books, calculators I will supply a table of integrals) EXTRA OFFICE HOURS: Sunday, September 23 from 8:00 PM
Functional determinants
 Functional determinants based on S-53 We are going to discuss situations where a functional determinant depends on some other field and so it cannot be absorbed into the overall normalization of the path
Functional determinants based on S-53 We are going to discuss situations where a functional determinant depends on some other field and so it cannot be absorbed into the overall normalization of the path
Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012
 PHYS 20602 Handout 1 Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012 Handout Contents Examples Classes Examples for Lectures 1 to 4 (with hints at end) Definitions of groups and vector
PHYS 20602 Handout 1 Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012 Handout Contents Examples Classes Examples for Lectures 1 to 4 (with hints at end) Definitions of groups and vector
Mathematical Formulation of the Superposition Principle
 Mathematical Formulation of the Superposition Principle Superposition add states together, get new states. Math quantity associated with states must also have this property. Vectors have this property.
Mathematical Formulation of the Superposition Principle Superposition add states together, get new states. Math quantity associated with states must also have this property. Vectors have this property.
NOTES ON BILINEAR FORMS
 NOTES ON BILINEAR FORMS PARAMESWARAN SANKARAN These notes are intended as a supplement to the talk given by the author at the IMSc Outreach Programme Enriching Collegiate Education-2015. Symmetric bilinear
NOTES ON BILINEAR FORMS PARAMESWARAN SANKARAN These notes are intended as a supplement to the talk given by the author at the IMSc Outreach Programme Enriching Collegiate Education-2015. Symmetric bilinear
A VERY BRIEF LINEAR ALGEBRA REVIEW for MAP 5485 Introduction to Mathematical Biophysics Fall 2010
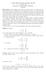 A VERY BRIEF LINEAR ALGEBRA REVIEW for MAP 5485 Introduction to Mathematical Biophysics Fall 00 Introduction Linear Algebra, also known as matrix theory, is an important element of all branches of mathematics
A VERY BRIEF LINEAR ALGEBRA REVIEW for MAP 5485 Introduction to Mathematical Biophysics Fall 00 Introduction Linear Algebra, also known as matrix theory, is an important element of all branches of mathematics
A = 3 B = A 1 1 matrix is the same as a number or scalar, 3 = [3].
![A = 3 B = A 1 1 matrix is the same as a number or scalar, 3 = [3]. A = 3 B = A 1 1 matrix is the same as a number or scalar, 3 = [3].](/thumbs/78/77913594.jpg) Appendix : A Very Brief Linear ALgebra Review Introduction Linear Algebra, also known as matrix theory, is an important element of all branches of mathematics Very often in this course we study the shapes
Appendix : A Very Brief Linear ALgebra Review Introduction Linear Algebra, also known as matrix theory, is an important element of all branches of mathematics Very often in this course we study the shapes
We use the overhead arrow to denote a column vector, i.e., a number with a direction. For example, in three-space, we write
 1 MATH FACTS 11 Vectors 111 Definition We use the overhead arrow to denote a column vector, ie, a number with a direction For example, in three-space, we write The elements of a vector have a graphical
1 MATH FACTS 11 Vectors 111 Definition We use the overhead arrow to denote a column vector, ie, a number with a direction For example, in three-space, we write The elements of a vector have a graphical
