/ / / / /6 8 2x7/ / / / /10
|
|
|
- Norma Stephens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 <The Answers> Problem points Problem points TTAL pts / / / / /6 8 2x7/ / / / /10 /100 전체기준 : 전개과정은맞으나답이나 unit 이틀리면 -1 답은맞으나전개과정이약간틀렸을때 -1 식을전혀쓰지않고 ( 혹은흔적이전혀없고 ) 답만맞았을때 -1 (3 pts), -2 (4 pts 이상 ) 1. (Total 12 pts) (a) (2 pts) 부호틀리면모두감점 Cl 2(aq) e - Cl(aq) E (volts) 1.64 Cr (aq) e - + 2Cr The first half reaction (the reduction) is occurring at the cathode and the second half reaction (the oxidation) is occurring at the anode. ε cell = ε cathode - ε anode = 1.64 V V = 0.31 V (+2 pts, o partial points) (b) (3 pts) G = -nfe cell (+1 point) = -6 mol X C/mol X 0.31 V = kj (+3 pts) (c) (3 pts) G = -RTlnK = -nfe or E = (0.0592/n) logk (+1 point) ence lnk = - G /RT, K = exp(- G /RT) = exp(179.5 X 1000 J/mol / (8.314 J/molK X 298K) = 2.9 X ( ~10 31, order have to correct, 2 pts) (d) (4 pts) o o cell = cell log 10 (at 25 C) E E Q n by ernst equation (+2 pts) Q = (0.2 3 X 0.8 X )/( X [Cr 3+ ] 2 ) ence, 0.15 V = 0.31 V V / 6 X log((0.2 3 X 0.8 X )/( X [Cr 3+ ] 2 )) 6( ) V / V = -log (1.896/[Cr 3+ ] 2 ) = 1.896/[Cr 3+ ] 2, ence [Cr 3+ ] = 1.07 X 10-8 M ( ~10-8 M, order have to correct, 2 pts)
2 2. (Total 14 pts) (a) (3 pts) potential 안써도상관없음 Cathode: (aq) + 2 e 2 (g) (l) E o = 0.00 V Anode: 3 2 (l) (1/2) 2 (g) (aq) + 2 e E o = ( V) (6 2 (l) 2 (g) (aq) + 4 e ) 도정답인정 (b) (4 pts) 각 2 pts E(cathode) = E o (cathode) ( V / n hc ) log Q hc = 0.00 ( V / 2) log {P( 2 )/[ 3 + ] 2 } = 0.00 ( V / 2) log {1/ (10 7 ) 2 } = V = E ( 3 + (10 7 M) 2 (1 atm)) E(anode) = E o (anode) ( V / n hc ) log Q hc = ( V / 2) log {P( 2 )/[ 3 + ] 2 } = ( V / 2) log {1/ (10 7 ) 2 } = V = E( 2 (1 atm), 3 + (10 7 M) 2 ) (c) (3 pts) each of three: 1 pt E = E(cathode) E(anode) = V = V ( = E o ) Since E < 0, G > 0 nonspontaneous needs an external voltage, Decomposition potential of V. (d) (4 pts) reduction potential 계산안하고답만맞는경우각각 0.5 pt; reduction potential 비교시, Concentraion of acl using ernst eq. 고려하지않으면 -1 pt. Possible half-cell reactions at electrode: Cathode: a + (0.1 M) + e a(s) E o (a + a) = 2.71 V (10 7 M) + 2 e 2 (g) (l) E o ( ) = 0.00 V Anode: 2Cl (0.1 M) Cl 2 (g) + 2 e E o (Cl 2 Cl ) = 1.36 V 6 2 (l) 2 (g) (10 7 M) + 4 e E o ( 2, ) = V [ 3 + ] = [ ] = M, P( 2 ) = P(Cl 2 ) = P( 2 ) = 1 atm at 25 C >> Reduction potential for the first reaction: E(a + a) = E o (a + a) ( V / n hc ) log Q hc = 2.71 ( V / 1) log {1/[a + ]} = 2.71 ( V / 1) log {1/(0.1)} = = 2.77 V Smaller than V = E[ 3 + (10 7 M) 2 (1 atm)] Reduction of a + (aq) impossible! ence hydrogen will be generated at the cathode
3 >> Reduction potential for the third reaction: E(Cl 2 Cl ) = E o (Cl 2 Cl ) ( V / n hc ) log Q hc = 1.36 ( V / 1) log {[Cl ]/P(Cl 2 )} = 1.36 ( V / 1) log {(0.1) / 1} = 1.42 V Larger than V = E( 2 (1 atm), 3 + (10 7 M) 2 ) reduction of Cl 2 (g) possible, oxidation of Cl - is not plausible! ence, oxygen will be generated at the anode. 3. (Total 6 pts) (a) (3 pts) = 2kt +, so = 2kt + = (2 X 7.0 X 10 9 M -1 s -1 )(2 min X ) + = 6.0 X M ence [I 2 ] = M (b) (3 pts) formular, 0.6 M, 0.42 M, 각각 1 pt = 1/(2k[A] 0 ), so For [I] 0 = 0.6 M, =1/(2k[I] 0 ) = 1/2 X = 1.2 X s For [I] = 0.42 M, = = = 1.7 X s
4 4. (Total 9 pts) (a) (3 pts) k = A X exp(-e a /RT) lnk 1 -lnk 2 = ln(k 1 /k 2 ) = E a /R X (1/T 2 1/T 1 ) ence, E a = ln(k 1 /k 2 ) X R X 1/(1/T 2 1/T 1 ) = ln(0.76/0.87) X J/molK X 1/(1/1030K 1/1000K) = 38.6 kjmol -1 (b) (3 pts) from k = A X exp(-e a /RT) A = k / exp(-e a /RT) = 0.76 s -1 / exp ((-38.6 X 1000 J/mol) / (8.314 J/molK X 1000K)) = = 78.9 s -1 (c) (3 pts) from k = A X exp(-e a /RT) k at 1100 K = 78.9 s -1 X exp ((-38.6 X 1000 J/mol) / (8.314 J/molK X 1100K))= 1.16 s -1
5 5. (Total 8 pts) (a) (4 pts) (b) (4 pts)
6 6. (7 pts) B 2 pts, reduced mass 2 pt, length 3 pts We use the to find B, and then B to find r e.. The differences 5-4 and 6-5 are 20.8 and 20.5 cm -1, respectively, so average B = (20.65) = ± 0.2 cm -1. The reduced mass, µ, in kilograms, is µ = = amu( )( ) = X kg Then r e = [ ] 1/2 = X m (= Å) 7. (Total 12 pts) (a) (6 pts) 각 1 pt, 다맞았을경우 +1 pt (b) (6 pts) 각 1 pt, 다맞았을경우 +1 pt D E B A C
7 8. (Total 14 pts) 2 pts for a correct answer and -1 pt for a wrong answer (a) F The LUM of ethylene is an antibonding orbital (π*). An additional antibonding electron means - that the bond order decreases in C 2 4 compared to C 2 (b) F The transfer reduces the overall bond order of the molecule by 1. The C to C bond in the molecule in the excited state should be longer than it was in the ground state. Because the bond is weaker, its force constant is diminished, and the vibrational frequency of the C to C stretching mode is reduced. (c) F Delocalization of the double bonds in benzene should lower the energy for an electronic transition. Therefore, the absorption occurs at longer wavelength in benzene. (d) T El-Sayed s rule (e) F (f) T (g) F A strong absorption observed in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum of formaldehyde is attributed to a π π* transition. 9. (Total 8 pts) (a) (4 pts) 각 monomer 당 2 pts (b) (4 pts) 비슷하나 repeating unit 이약간틀렸을경우 2 pts The resulting polymer is poly(1-butene), and its repeating unit is following :
8 10. (Total 10 pts) (a) (3 pts) R R R R adenine guanine thymine cytosine (b) (3 pts) 각 hydrogen bonding 당 1 pt, 다맞는경우 +1 pt R R adenine thymine (c) (4 pts) 각 hydrogen bonding 당 1 pt, 다맞는경우 +1 pt R R guanine cytosine
9 2014 FALL Semester Final Examination For General Chemistry II (C103) Date: December 17 (Wed), Time Limit: 19:00 ~ 21:00 Write down your information neatly in the space provided below; print your Student ID in the upper right corner of every page. Professor ame Class Student I.D. umber ame Problem points Problem points TTAL pts 1 /12 6 /7 2 /14 7 /12 3 /6 8 /14 4 /9 9 /8 5 /8 10 /10 /100 ** This paper consists of 14 sheets with 10 problems (page 11: standard reduction potentials and 9 MR chemical shifts, page 12: fundamental constants, page 13: periodic table, page 14: claim form). Please check all page numbers before taking the exam. Write down your work and answers in the sheet. Please write down the unit of your answer when applicable. You will get 30% deduction for a missing unit. TICE: SCEDULES on RETUR and CLAIM of the MARKED EXAM PAPER. 1. Period, Location and Procedure 1) Return and Claim Period: December 19 (Friday, 11:00-13:00, 2 hrs) 2) Location: Creative Learning Bldg.(E11) Class Room A 407 B 408 C 409 3) Claim Procedure: Rule 1: Students cannot bring their own writing tools into the room. (Use a pen only provided by TA) Rule 2: With or without claim, you must submit the paper back to TA. (Do not go out of the room with it) (During the period, you can check the marked exam paper from your TA and should hand in the paper with a FRM for claims if you have any claims on it. The claim is permitted only on the period. Keep that in mind! A solution file with answers for the examination will be uploaded on 12/19 on the web.) 2. Final Confirmation 1) Period: December 20(Sat) 21(Sun) 2) Procedure: During this period, you can check the final score of the examination on the website again. To get more information, visit the website at 1. (Total 12 pts) The following reaction occurs in an electrochemical cell (25 C).
10 3Cl 2(aq) + 2Cr3+ (aq) (l) 3Cl(aq) + Cr (aq) (aq) (a) Calculate E for this cell. (b) Calculate G for this cell. (c) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction. (d) At p 0, with [Cr ] = 0.8 M and [Cl 2 ] = 0.15 M, and [Cl] = 0.2 M, the cell potential is found to equal 0.15 V. Calculate the concentration of Cr 3+ (aq) in the cell.
11 2. (Total 14 pts) Consider the electrolysis of pure water /2 2 (a) Write the half-cell reactions for the cathode and anode. (b) Assuming that the hydrogen and oxygen are produced at atmospheric pressure, calculate the reduction potential for each half-reaction at p = 7. (c) What is the overall cell potential? Is the reaction spontaneous? ow much potential should be applied for the electrolysis of pure water to occur? (d) Suppose you apply 1.5 V on 0.1 M aqueous solution of acl. Which substances will be generated in the cathode and in the anode, respectively? (Rationalize your explanation based on the analysis of the reduction potential of each substance present in the solution.)
12 3. (Total 6 pts) Iodine atoms combine to form molecular iodine in the gas phase : I(g) + I(g) I 2 (g) This reaction follows second-order kinetics with k = M -1 s -1 at 23 o C. (a) If the initial concentration of I was M, calculate the concentration after 2 min. (b) Calculate the half-life of the reaction if the initial concentration of I is 0.6 M and if it is 0.42 M. 4. (Total 9 pts) The rate constant of the first-order reaction 2 2 (g) 2 2 (g) + 2 (g) is 0.76 s -1 at 1000 K and 0.87 s -1 at 1030 K. (a) Calculate the activation energy (E a ) of the reaction. (b) Calculate the pre-exponential factor (A, from the Arrhrenius equation) of the reaction. (c) What would be the predicted rate constant at 1100 K?
13 5. (Total 8 pts) The conversion of dissolved carbon dioxide in blood to C 3 - and 3 + is catalyzed by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase. The Michaelis-nten constants for this enzyme and substrate are K m = moll -1 and k 2 = s -1. (a) What is the maximum rate of reaction of carbon dioxide if the enzyme concentration is M? (b) At what C 2 concentration will the rate of decomposition be 30% of that calculated in part (a)?
14 6. (7 pts) Following figure is a pure rotational spectrum for Cl. The line positions of the fourth, fifth, and sixth lines of the spectrum shown in the figure are = cm -1, = cm -1, and = cm -1. Find the equilibrium bond length r e for Cl. ote that. (m = 1.00, m Cl = 35.00)
15 7. (Total 12 pts) (a) Predict the number of peaks (set of peaks generated by spin-spin coupling is counted as one peak) in the proton MR spectrum of the following compounds. (b) Below are the 1 MR spectra (DMS-d 6, 300 Mz) of five different compounds. Assign the spectra to each compounds. Refer the 1 MR chemical shift chart. A B 3 2 PPM PPM 1 0 C D PPM PPM E PPM
16 8. (Total 14 pts) Classify each of the following statements as True (T) or False (F). You will get 2 pts for a correct answer and -1 pt for a wrong answer. (a) If an ethylene molecule gains an additional electron to give the C 2-4 ion, the bond order of the carbon-carbon bond will increase. (b) If an electron in the π orbital of C 2 4 is excited by a photon to the π* orbital, the vibrational frequency in the excited state will be higher than in the ground state. (c) The structure of the molecules cyclohexene and benzene are shown below. cyclohexene benzene The absorption of ultraviolet light by benzene occurs at shorter wavelength. (d) Intersystem crossing is enhanced between states of different orbital configurations for organic molecules containing only the lighter elements. (e) Φ p s are small for molecules that have rapid S 1 T n intersystem crossing rates. (f) Bacteria have a single photosynthetic system that absorbs longer wavelengths than plants and does not produce holes sufficiently oxidizing to oxidize water. (g) A strong absorption observed in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum of formaldehyde is attributed to an n π* transition. 9. (Total 8 pts) (a) The following structure is the repeating unit of Kevlar, a mechanically strong fiber used to make
17 bulletproof vests. Draw two monomer chemical structures for Kevlar. (b) Draw the repeating unit of the polymer which is formed when peroxides are added to C 3 C 2 C=C 2 at a high temperature and pressure.
18 10. (Total 10 pts) (a) The primary genetic material of biological systems is DA. DA is made up of four types of nucleotides which have different bases. Those are adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine. Below are the structures of four bases. Write the name of each base below the structure. R R R R adenine (b) Adenine and thymine can form two intermolecular hydrogen bonding which enable the formation of DA double helix. Indicate these two hydrogen bonds from the molecular structure of these two bases. R adenine thymine (c) Guanine and cytosine can form three intermolecular hydrogen bonding which enable the formation of DA double helix. Indicate these three hydrogen bonds from the molecular structure of these two bases. guanine cytosine
19 <Standard Reduction Potentials at 25 o C and 1 MR chemical shifts>
20
21
22 Claim Form for General Chemistry Examination Page ( / ) Class:, Professor ame:, I.D.# :, ame: If you have any claims on the marked paper, please write down them on this form and submit this with your paper in the assigned place. (And this form should be attached on the top of the marked paper with a stapler.) Please, copy this sheet if you need more before use. By Student By TA Accepted? Yes( ) or o( ) Question # Claims Yes: Pts (+/-) o: Reasons
23 2014 FALL Semester Midterm Examination For General Chemistry II (C103) Date: ctober 22 (Wed), Time Limit: 19:00 ~ 21:00 Write down your information neatly in the space provided below; print your Student ID in the upper right corner of every page. Professor ame Class Student I.D. umber ame Problem points Problem points TTAL pts 1 /6 6 /10 2 /10 7 /13 3 /8 8 /10 4 /11 9 /12 5 /14 10 /6 /100 ** This paper consists of 14 sheets with 10 problems (page 12: fundamental constants, page 13: periodic table, page 14: claim form). Please check all page numbers before taking the exam. Write down your work and answers in the sheet. Please write down the unit of your answer when applicable. You will get 30% deduction for a missing unit. TICE: SCEDULES on RETUR and CLAIM of the MARKED EXAM PAPER. ( 채점답안지분배및이의신청일정 ) 1. Period, Location, and Procedure 1) Return and Claim Period: ctober 27 (Mon, 6:30 ~ 7:30 p.m.) 2) Location: Room for quiz session 3) Procedure: Rule 1: Students cannot bring their own writing tools into the room. (Use a pen only provided by TA) Rule 2: With or without claim, you must submit the paper back to TA. (Do not go out of the room with it) If you have any claims on it, you can submit the claim paper with your opinion. After writing your opinions on the claim form, attach it to your mid-term paper with a stapler. Give them to TA. 2. Final Confirmation 1) Period: ctober 30 (Thu) ctober 31 (Fri) 2) Procedure: During this period, you can check the final score of the examination on the website. ** For further information, please visit General Chemistry website at 1
24 <The Answers> Problem points Problem points TTAL pts 1 6/ /10 2 2x5/10 7 2x / / / / /12 / / /6 전체기준 : 계산문제위주이므로부분점수를최소한으로줄것. 전개과정은맞으나답이나 unit 이틀리면 -1 답은맞으나전개과정이약간틀렸을때 -1 식을전혀쓰지않고 ( 혹은흔적이전혀없고 ) 답만맞았을때 -1 (3 pts), -2 (4 pts 이상 ) 1. (Total 6 pts) Kirchhoff s law 적용 4 pts, Cp 2 pts p, rxn = v P P - v R P = 2 P[ 2 (l)] - 2 P[ 2 (g)] - P[ 2 (g)] = 2(75.3 J mol -1 K -1 ) 2(28.8 J mol -1 K -1 ) J mol -1 K -1 = 63.6 J mol -1 K -1 Using Kirchhoff s law gives Δ rxn (T 2 ) = Δ rxn (T 1 ) + p, rxn ΔT = kj mol -1 + (63.6 J mol -1 K -1 )( K K)( ) = kj mol -1 (eat capacities are generally given in units of J mol -1 K -1, whereas enthalpies are usually in units of kj mol -1 so we must always be careful to include the conversion from joules to kilojoules in these types of calculations.) 2. (Total 10 pts) 각각맞으면 1pt 씩, 틀리면 -0.5 pt (a) F (an isolated system.) (b) T (c) F (only for an isolated system) (d) T (e) F ((3/2)(1+1+2*(-2))R = (3/2)(2-2)R) (f) F (i.e. phase change)
25 (g) T (h) F (for pure substance) (i) F (opposite to the 2 nd thermodynamic law) (j) T 3. (Total 8 pts) (a) (4 pts) 2 pts for each Δ Fe = nc P ΔT = (1.00 mol)(25.1 J K -1 mol -1 )( K) = J ΔS Fe = nc P ln = (1.00 mol)(25.1 J K -1 mol -1 ) ln = J K -1 (b) (4 pts) 2 pts for each The entropy S is a function of state, and the initial and final states of the piece of iron are the same as in part a). Therefore ΔS Fe = J K -1. The reservoir of water gains the 2510 J of heat from the piece of iron at a constant temperature of K. Therefore ΔS water = 2510 J / K = J K -1. ΔS total = ΔS Fe + ΔS water = 1.36 J K (Total 11 pts) (a) (8 pts) 2 pts for each q = vap + ncp T = 2.00 mol 23.4 kj/mol + 2 mol 38 J/molK 58 K = 51.2 kj w = -P V = P = nrt = 2.00 mol J/molK 298 K = 4.96 kj U = q + w =51208 J J = 46.2 kj The reaction is conducted at constant pressure of 1 atm. ence, = q. = 51.2 kj (b) (3 pts) S vap = q rev /T = vap /T = ( J/mol) / 240 K = 97.5 J mol -1 K -1
26 5. (Total 14 pts) (a) (2 pts) [PCl 5 ] = 3.00 mol/l, [PCl 3 ] = 6.00 mol/l, [Cl 2 ] = 1.00 mol/l, Q = = 3.00/6.00*1.00 = 0.5 Q K, hence the reaction is not at equilibrium. (b) (2 pts) Q < K, hence the reaction will proceed to the right direction to form PCl 5. (c) (5 pts) 2 nd order equation 까지세웠으나약간틀렸을경우 2 pts PCl 3 + Cl 2 PCl 5 initial conc (mol/l) change in conc (mol/l) -x -x +x equilibrium 6-x 1-x 3+x conc (mol/l) K c = = (3+x)/[(6-x)(1-x)] = 0.56 ence 0.56x x = 0 Solve the quadratic equation to get x = 9.2 or is physically nonsensical. x=0.07 ence, [PCl 5 ] = 3.07 mol L -1, [PCl 3 ] = 5.93 mol L -1, [Cl 2 ] = 0.93 mol L -1 at equilibrium (d) (3 pts) 구하지않고정성적인답만썼을경우 1 pt f (PCl 3 (g)) = kj/mol. f (PCl 5 (g)) = kj/mol. ence, the enthalpy of reaction = f (PCl 5 (g)) ( f (PCl 3 (g)) + f (Cl 2 (g))) = = 87.9 kj/mol (Exothermic reaction) If the temperature is increased, PCl 5 will be consumed to form more chlorine gas (Le Chatelier s principle). (e) (2 pts) If the volume is decreased, chlorine will be consumed to form more PCl 5 (Le Chatelier s principle).
27 6. (Total 10 pts) (a) (3 pts) From van t off equation applied in the vapor pressure case, ln(4.23/0.4034) = vap /(8.315 J/molK)[1/273.5 K 1/223.15] vap = kj mol -1 (b) (4 pts) In vaporization case P 3(g) = K (equation 1) (c) (3 pts) ormal boiling point is temperature where vapor pressure is 1 atm. From equation 1, T = vap / ( S vap RlnP) = (23820 J/mol) / (99.20 J/molK J/molK ln1) = K
28 7. (Total 13 pts) 2 pts for (a-c, e, f); 3 pts for (d), circle 1 pt + reason 1 pt; ( a ) (2 pts ) Con j ugate base has more resonance structures. (b) (2 pts ) Con j ugate base has more resonance structures. ( c ) (2 pts ) CF 3 C CCl 3 C F is more electronegative than Cl. (d) (3 pts ) 2 Con j ugate base has more resonance structures over the nitro group. 2 ( e ) (2 pts ) is more electronegative than. (f) (2 pts ) + 2 Protonated amine is more acidic.
29 For (d), additional stabilization by the nitro group 8. (Total 10 pts) (a) (2 pts) In applying the enderson-asselbalch equation, n A = n aa = mol, and p = pk a =4.75 (b) (2 pts) n A = mol, n aa = mol; p = log 10 (0.015/0.005) = 5.23 (c) (4 pts) 2 pts for each ote that solution (b), which contains more salt, has a higher p as expected since the salt is basic. The added strong base will react stoichiometrically with A, thereby reducing the amount n A, and increasing n aa. For (a), n A = = mol; n aa = = mol p= log 10 (0.012/0.008) = 4.93, an increase of 0.18 For (b), n A = = mol; n aa = = mol p= log 10 (0.017/0.003) = 5.50, an increase of 0.27 (d) (2 pts) If the solution is unbuffered, the acid present to yield p = 4.75 is negligible compared to the added base, and the p is determined entirely by the a: p = -log 10 (0.002 mol/0.1l) = 1.70 and p 12.30, an increase of p 7.55.
30 9. (Total 12 pts) (a) (10 pts) the second equation 4 pts, the first equation 6 pts Very high formation constant indicates that most of the Cu 2+ would exist as a complex-ion with the cyanide anion upon mixing. Limiting reagent is CuCl 2. ence, Initial Cu(C) 4 2- concentration: 0.02 M Initial C - concentration: = 0.02 M. C - hydrolyzes water C C + - C C initial conc (M) 0.02 ~0 0 change in conc (M) -x +x +x equilibrium conc (M) 0.02-x x x [C][ - ]/[C - ] = x 2 /(0.02 x) = K b = K w /K a = /( ) = Solving the quadratic equation for x gives, x = [C - ] = = M Cu(C) 4 2- (aq) Cu 2+ (aq) + 4C - (aq) K = 1/K f = Cu(C)4 2- Cu 2+ 4C - initial conc (M) 0.02 ~ change in conc (M) -x +x +4x equilibrium conc (M) 0.02-x x x [Cu 2+ ][C - ] 4 /[Cu(C) 4 2- ] = [x*( x) 4 ]/(0.02 x) (x* )/(0.02) = K = x = [Cu 2+ ] = M (b) (2 pts) [ - ] = 5.61 X 10-4 [ 3 + ] = K w /[ - ] = / ( ) = p = 10.7
31 10. (Total 6 pts) K sp of CaC 3 2 pts Use the letter C to refer to CaC 3 and B to refer to BaC 3. For CaC 3 : S C = 7 X 10-3 g L -1 X = 7 X 10-5 mol L -1 so that K sp,c = S 2 C = 5 X 10-9 Write the K sp expressions for dissolution of the two carbonates and divide one by the other: Just after the precipitation of CaC 3 has begun, both dissolution reactions are at equilibrium, and the concentration of Ba 2+ has been reduced to 0.10 of what it was originally. Therefore K sp,b = (0.10) K sp,c = 0.10 (5 X 10-9 ) = 5 X 10-10
32 1. (Total 6 pts) The standard enthalpy change for the reaction 2 2 (g) + 2 (g) 2 2 (l) is kj mol -1 at 25 o C. Calculate the value of Δ rxn at 100 o C, assuming that all C p o values are independent of temperature. (C p o is 29.4, 28.8, and 75.3 J mol -1 K -1 for 2 (g), 2 (g), and 2 (l), respectively.) 2. (Total 10 pts) Classify each of the following statements as True (T) or False (F). You will get 1 pt for a correct answer, and -0.5 pt for a wrong answer. (a) A bomb calorimeter in which benzene is burned is a thermodynamically closed system. (b) V (volume) and S (entropy) are both state functions and extensive properties. (c) The total energy of a system is always conserved. 2
33 (d) The constant-pressure heat capacity is always larger than the constant-volume heat capacity. (e) According to the equipartition theorem of energy, a nonlinear ideal gas molecule containing atoms has 3 degree of freedom and thus can contribute (3/2)R to C v. (f) Enthalpy change is always stored as bond energies. (g) Entropy of the isolated system always increases in any spontaneous processes. (h) Entropy approaches to zero as temperature decreases to 0 K for any substance in its equilibrium. (i) There is a device that can transfer heat withdrawn from a reservoir completely into work with no other effect. (j) 2 has the higher molar heat capacity than. 3
34 3. (Total 8 pts) Iron has a heat capacity of 25.1 J K -1 mol -1, approximately independent of temperature between 0 o C and 100 o C. (a) Calculate the enthalpy and entropy change of 1.00 mol iron as it is cooled at atmospheric pressure from 100 o C to 0 o C. (b) A piece of iron weighting g and at 100 o C is placed in a large reservoir of water held at 0 o C. It cools irreversibly until its temperature equals that of the water. Assuming the water reservoir is large enough that its temperature remains close to 0 o C, calculate the entropy changes for the iron and the water and the total entropy change in this process. 4
35 4. (Total 11 pts) (a) Calculate q, w,, and U for the following reaction. (Assume that the gas behaves ideally and that the volume occupied by the liquid is negligible.) 2.00 mol 3 (l, 1 atm, 240 K) 2.00 mol 3 (g, 1 atm, 298 K) - ormal boiling point of liquid ammonia: 240 K - Enthalpy of vaporization at 240 K: 23.4 kj mol -1 - C p of ammonia: 38 J K -1 mol -1 (b) Calculate the entropy of vaporization of ammonia at 240 K. 5. (Total 14 pts) In the following reaction, PCl 3 (g) + Cl 2 (g) PCl 5 (g) K = 0.56 (L mol -1 ) at 250 C 1.50 mol PCl 5, 3.00 mol PCl 3, 0.50 mol Cl 2 are present in a L reaction vessel at 250 C ( f (PCl 3 (g)) = kj mol -1, f (PCl 5 (g)) = kj mol -1 ). (a) Is the reaction at equilibrium? Write the reason for your statement. 5
36 (b) If not, in which direction is it proceeding? (c) What are the equilibrium compositions (mol L -1 ) of all chemical substances? (d) nce the equilibrium is reached, if the temperature is increased to 300 C, do you expect more chlorine gas to be consumed or generated? (e) nce the equilibrium is reached, if you compress the vessel to half the volume, do you expect more chlorine gas to be consumed or generated? 6
37 6. (Total 10 pts) The vapor pressure of ammonia at 50 C is atm. At 0 C, it is atm. Assume that vap and S vap are approximately independent of temperature. (a) Calculate the molar enthalpy of vaporization of ammonia. (b) Calculate the molar entropy of vaporization of ammonia. (c) Calculate the normal boiling temperature of ammonia liquid. 7
38 7. (Total 13 pts) Between two chemical structures shown below, circle the substances with a more acidic proton (evaluate the acidity of the bold protons, a-f), and briefly explain the reason. ( a ) (b) ( c ) CF 3 C CCl 3 C (d) 2 2 ( e ) (f) + 2 8
39 8. (Total 10 pts) Find the p of acetic acid (A)/ sodium acetate (aa) buffer solutions made from (a) 50 ml 0.20 M A and 50 ml 0.20 M aa (b) 25 ml 0.20 M A and 75 ml 0.20 M aa. (c) Calculate the change in p when 80 mg a (s) is added to each of these solutions (a and b). (d) Compare the results with adding the same amount of a to an unbuffered solution of the same p and volume as solution (a). eglect the change in volume on adding a (s) (pk a of A is 4.75). 9
40 9. (Total 12 pts) (a) Calculate the concentration of Cu 2+ (aq) in an aqueous solution that contains ml of CuCl 2 and 0.1 mol of ac in 1.0 L (pk a of C is 9.21). Cu 2+ (aq) + 4C - (aq) Cu(C) 2-4 (aq) K f = 2.0 X (b) What is the p of the resulting solution? 10
41 10. (Total 6 pts) The solubility of CaC 3 in water is about 7 mg L -1. Show how one can calculate the solubility product of BaC 3 from this information and from the fact that when sodium carbonate solution is added slowly to a solution containing equimolar concentrations of Ca 2+ and Ba 2+, no CaC 3 is formed until about 90% of the Ba 2+ has been precipitated as BaC 3. 11
42 12
43 13
44 Claim Form for General Chemistry Examination Page ( / ) Class:, Professor ame:, I.D.# :, ame: If you have any claims on the marked paper, please write down them on this form and submit this with your paper in the assigned place. (And this form should be attached on the top of the marked paper with a stapler.) Please, copy this sheet if you need more before use. By Student By TA Accepted? Yes( ) or o( ) Question # Claims Yes: Pts (+/-) o: Reasons 14
2007 Fall Semester Mid-term Examination For General Chemistry II. Class Student Number Name
 Time Limit: 7:00 ~ 9:00 p.m. 2007 Fall Semester Mid-term Examination For General Chemistry II Professor Name Class Student Number Name Problem No. Scores (points) Problem No. Scores (points) TOTAL 1 /12
Time Limit: 7:00 ~ 9:00 p.m. 2007 Fall Semester Mid-term Examination For General Chemistry II Professor Name Class Student Number Name Problem No. Scores (points) Problem No. Scores (points) TOTAL 1 /12
Name AP CHEM / / Collected AP Exam Essay Answers for Chapter 16
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected AP Exam Essay Answers for Chapter 16 1980 - #7 (a) State the physical significance of entropy. Entropy (S) is a measure of randomness or disorder in a system. (b) From each of
Name AP CHEM / / Collected AP Exam Essay Answers for Chapter 16 1980 - #7 (a) State the physical significance of entropy. Entropy (S) is a measure of randomness or disorder in a system. (b) From each of
2015 SPRING Semester Midterm Examination For General Chemistry I
 2015 SPRING Semester Midterm Examination For General Chemistry I Date: April 22 (Wed), Time Limit: 19:00 ~ 21:00 Write down your information neatly in the space provided below; print your Student ID in
2015 SPRING Semester Midterm Examination For General Chemistry I Date: April 22 (Wed), Time Limit: 19:00 ~ 21:00 Write down your information neatly in the space provided below; print your Student ID in
FRONT PAGE FORMULA SHEET - TEAR OFF
 FRONT PAGE FORMULA SHEET - TEAR OFF N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013
FRONT PAGE FORMULA SHEET - TEAR OFF N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013
CHEM J-2 June 2006 HCO 2. Calculate the osmotic pressure of a solution of 1.0 g of glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) in 1500 ml of water at 37 C.
 CEM1405 2006-J-2 June 2006 Draw Lewis structures of ozone, 3, and the formate anion, C 2, including resonance hybrids where appropriate. 3 C 2 3 C C Calculate the osmotic pressure of a solution of 1.0
CEM1405 2006-J-2 June 2006 Draw Lewis structures of ozone, 3, and the formate anion, C 2, including resonance hybrids where appropriate. 3 C 2 3 C C Calculate the osmotic pressure of a solution of 1.0
Chem GENERAL CHEMISTRY II
 GENERAL CHEMISTRY II CHEM 206 /2 51 Final Examination December 19, 2006 1900-2200 Dr. Cerrie ROGERS x x programmable calculators must be reset Chem 206 --- GENERAL CHEMISTRY II LAST NAME: STUDENT NUMBER:
GENERAL CHEMISTRY II CHEM 206 /2 51 Final Examination December 19, 2006 1900-2200 Dr. Cerrie ROGERS x x programmable calculators must be reset Chem 206 --- GENERAL CHEMISTRY II LAST NAME: STUDENT NUMBER:
1 /13 7 /12 2 /6 8 /9 3 /14 9 /6 4 /7 10 /9 5 /13 11 /5 6 /6
 2013 FALL Semester Midterm Examination For General Chemistry II (CH103) Date: October 24 (Thu), Time Limit: 14:30 ~ 17:00 Write down your information neatly in the space provided below; print your Student
2013 FALL Semester Midterm Examination For General Chemistry II (CH103) Date: October 24 (Thu), Time Limit: 14:30 ~ 17:00 Write down your information neatly in the space provided below; print your Student
Chem 204 Spring 2014 Name PRACTICE EXAM I. There are 9 pages (counting this one) and a periodic table.
 Chem 204 Spring 2014 ame TA/Section PRACTICE EXAM I This Examination is worth 100 points. There are 9 pages (counting this one) and a periodic table. o books, notes, cellphones, anything with earbuds/earphones,
Chem 204 Spring 2014 ame TA/Section PRACTICE EXAM I This Examination is worth 100 points. There are 9 pages (counting this one) and a periodic table. o books, notes, cellphones, anything with earbuds/earphones,
1 /10 6 /10 2 /5 7 /5 3 /10 8 /10 4 /10 9 /10 5 /10 10 /20
 2009 FALL Semester Midterm Examination For General Chemistry II (CHEM103) Date: October 21, 2009 (Wed), Time Limit: 7:00 ~ 9:00 p.m. Write down your information neatly in the space provided below; print
2009 FALL Semester Midterm Examination For General Chemistry II (CHEM103) Date: October 21, 2009 (Wed), Time Limit: 7:00 ~ 9:00 p.m. Write down your information neatly in the space provided below; print
Chemistry 1A, Spring 2009 Midterm 3 April 13, 2009
 Chemistry 1A, Spring 2009 Midterm 3 April 13, 2009 (90 min, closed book) Name: SID: TA Name: There are 20 Multiple choice questions worth 3 points each. There are 3, multi-part short answer questions.
Chemistry 1A, Spring 2009 Midterm 3 April 13, 2009 (90 min, closed book) Name: SID: TA Name: There are 20 Multiple choice questions worth 3 points each. There are 3, multi-part short answer questions.
ph = pk a + log 10{[base]/[acid]}
![ph = pk a + log 10{[base]/[acid]} ph = pk a + log 10{[base]/[acid]}](/thumbs/91/106996519.jpg) FRONT PAGE FORMULA SHEET - TEAR OFF N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5)( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar
FRONT PAGE FORMULA SHEET - TEAR OFF N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5)( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar
Chemistry 1A, Spring 2007 Midterm Exam 3 April 9, 2007 (90 min, closed book)
 Chemistry 1A, Spring 2007 Midterm Exam 3 April 9, 2007 (90 min, closed book) Name: KEY SID: TA Name: 1.) Write your name on every page of this exam. 2.) This exam has 34 multiple choice questions. Fill
Chemistry 1A, Spring 2007 Midterm Exam 3 April 9, 2007 (90 min, closed book) Name: KEY SID: TA Name: 1.) Write your name on every page of this exam. 2.) This exam has 34 multiple choice questions. Fill
AP CHEMISTRY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES
 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 (10 points) Answer the following questions that relate to the chemistry of halogen oxoacids. (a) Use the information in the table below to answer part (a)(i). Acid HOCl
2009 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 (10 points) Answer the following questions that relate to the chemistry of halogen oxoacids. (a) Use the information in the table below to answer part (a)(i). Acid HOCl
ph = pk a + log 10{[base]/[acid]}
![ph = pk a + log 10{[base]/[acid]} ph = pk a + log 10{[base]/[acid]}](/thumbs/90/103664826.jpg) FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5)( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5)( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
CHM 151 Practice Final Exam
 CM 151 Practice Final Exam 1. ow many significant figures are there in the result of 5.52 divided by 3.745? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 (e) 5 2. ow many significant figures are there in the answer when 9.021
CM 151 Practice Final Exam 1. ow many significant figures are there in the result of 5.52 divided by 3.745? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 (e) 5 2. ow many significant figures are there in the answer when 9.021
ph = pk a + log 10 {[base]/[acid]}
![ph = pk a + log 10 {[base]/[acid]} ph = pk a + log 10 {[base]/[acid]}](/thumbs/80/80846619.jpg) FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
Chem. 1B Final Practice Test 2 Solutions
 First letter of last name Chem. 1B Final Practice Test 2 Solutions Name Print Neatly. You will lose 1 point if I cannot read your name or perm number. Student Number If you are sitting next to someone
First letter of last name Chem. 1B Final Practice Test 2 Solutions Name Print Neatly. You will lose 1 point if I cannot read your name or perm number. Student Number If you are sitting next to someone
Chemistry 122 Wrap-Up Review Kundell
 Chapter 11 Chemistry 122 Wrap-Up Review Kundell 1. The enthalpy (heat) of vaporization for ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH) is 43.3 kj/mol. How much heat, in kilojoules, is required to vaporize 115 g of ethanol at
Chapter 11 Chemistry 122 Wrap-Up Review Kundell 1. The enthalpy (heat) of vaporization for ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH) is 43.3 kj/mol. How much heat, in kilojoules, is required to vaporize 115 g of ethanol at
B 2 Fe(s) O 2(g) Fe 2 O 3 (s) H f = -824 kj mol 1 Iron reacts with oxygen to produce iron(iii) oxide as represented above. A 75.
 1 2004 B 2 Fe(s) + 3 2 O 2(g) Fe 2 O 3 (s) H f = -824 kj mol 1 Iron reacts with oxygen to produce iron(iii) oxide as represented above. A 75.0 g sample of Fe(s) is mixed with 11.5 L of O 2 (g) at 2.66
1 2004 B 2 Fe(s) + 3 2 O 2(g) Fe 2 O 3 (s) H f = -824 kj mol 1 Iron reacts with oxygen to produce iron(iii) oxide as represented above. A 75.0 g sample of Fe(s) is mixed with 11.5 L of O 2 (g) at 2.66
CHEMISTRY 107 Section 501 Final Exam Version A December 12, 2016 Dr. Larry Brown
 NAME: (print) UIN #: CHEMISTRY 107 Section 501 Final Exam Version A December 12, 2016 Dr. Larry Brown This is a 2-hour exam, and contains 11 problems. There should be 14 numbered pages, including this
NAME: (print) UIN #: CHEMISTRY 107 Section 501 Final Exam Version A December 12, 2016 Dr. Larry Brown This is a 2-hour exam, and contains 11 problems. There should be 14 numbered pages, including this
BCIT Fall Chem Exam #2
 BCIT Fall 2017 Chem 3310 Exam #2 Name: Attempt all questions in this exam. Read each question carefully and give a complete answer in the space provided. Part marks given for wrong answers with partially
BCIT Fall 2017 Chem 3310 Exam #2 Name: Attempt all questions in this exam. Read each question carefully and give a complete answer in the space provided. Part marks given for wrong answers with partially
CHEMpossible. Final Exam Review
 CHEMpossible Final Exam Review 1. Given the following pair of reactions and their equilibrium constants: 2NO 2 (g) 2NO (g) + O 2 (g) K c = 15.5 2NO (g) + Cl 2 (g) 2 NOCl (g) K c = 3.20 10-3 Calculate a
CHEMpossible Final Exam Review 1. Given the following pair of reactions and their equilibrium constants: 2NO 2 (g) 2NO (g) + O 2 (g) K c = 15.5 2NO (g) + Cl 2 (g) 2 NOCl (g) K c = 3.20 10-3 Calculate a
CHM 2046 Final Exam Review: Chapters 11 18
 Chapter 11 1. Which of the following has the lowest boiling point? a. NH 3 b. CH 3 Cl c. NaCl d. CO 2 e. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 2. Which of the following has the lowest vapor pressure? a. CH 3 F b. CH
Chapter 11 1. Which of the following has the lowest boiling point? a. NH 3 b. CH 3 Cl c. NaCl d. CO 2 e. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 2. Which of the following has the lowest vapor pressure? a. CH 3 F b. CH
Intermolecular Forces 2 nd Semester Review Questions and Problems
 Intermolecular Forces 2 nd Semester Review Questions and Problems 1. Complete the following table: Molecule Lewis Structure Molecule Shape Polar/Nonpolar CS 2 H 3 O + CdBr 2 CHI 3 2. What makes the dipole
Intermolecular Forces 2 nd Semester Review Questions and Problems 1. Complete the following table: Molecule Lewis Structure Molecule Shape Polar/Nonpolar CS 2 H 3 O + CdBr 2 CHI 3 2. What makes the dipole
Saturday Study Session 1 3 rd Class Student Handout Thermochemistry
 Saturday Study Session 1 3 rd Class Student Handout Thermochemistry Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. C 2 H 4 (g) + 3 O 2 (g) 2 CO 2 (g)
Saturday Study Session 1 3 rd Class Student Handout Thermochemistry Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. C 2 H 4 (g) + 3 O 2 (g) 2 CO 2 (g)
Chemical Thermodynamics
 Quiz A 42.8 ml solution of ammonia (NH 3 ) is titrated with a solution of 0.9713 M hydrochloric acid. The initial reading on the buret containing the HCl was 47.13 ml and the final reading when the endpoint
Quiz A 42.8 ml solution of ammonia (NH 3 ) is titrated with a solution of 0.9713 M hydrochloric acid. The initial reading on the buret containing the HCl was 47.13 ml and the final reading when the endpoint
AP* Thermodynamics Free Response Questions page 1. Essay Questions
 AP* Thermodynamics Free Response Questions page 1 Essay Questions 1991 The reaction represented above is a reversible reaction. BCl 3 (g) + NH 3 (g) Cl 3 BNH 3 (s) (a) Predict the sign of the entropy change,
AP* Thermodynamics Free Response Questions page 1 Essay Questions 1991 The reaction represented above is a reversible reaction. BCl 3 (g) + NH 3 (g) Cl 3 BNH 3 (s) (a) Predict the sign of the entropy change,
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy. Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy Chapter 8 1 Chemical Thermodynamics Chemical Thermodynamics is the study of the energetics of a chemical reaction. Thermodynamics deals with the absorption or
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy Chapter 8 1 Chemical Thermodynamics Chemical Thermodynamics is the study of the energetics of a chemical reaction. Thermodynamics deals with the absorption or
Chemistry 112, Fall 2006, Section 1 (Garman and Heuck) Final Exam A (100 points) 19 Dec 2006
 Chemistry 112, Fall 2006, Section 1 (Garman and Heuck) (100 points) 19 Dec 2006 Name: YOU MUST: Put your name and student ID on the bubble sheet correctly. Put the exam version on the bubble sheet on the
Chemistry 112, Fall 2006, Section 1 (Garman and Heuck) (100 points) 19 Dec 2006 Name: YOU MUST: Put your name and student ID on the bubble sheet correctly. Put the exam version on the bubble sheet on the
Thermodynamics- Chapter 19 Schedule and Notes
 Thermodynamics- Chapter 19 Schedule and Notes Date Topics Video cast DUE Assignment during class time One Review of thermodynamics ONE and TWO Review of thermo Wksheet Two 19.1-4; state function THREE
Thermodynamics- Chapter 19 Schedule and Notes Date Topics Video cast DUE Assignment during class time One Review of thermodynamics ONE and TWO Review of thermo Wksheet Two 19.1-4; state function THREE
Topics in the November 2009 Exam Paper for CHEM1101
 November 2009 Topics in the November 2009 Exam Paper for CHEM1101 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 2009-N-2: 2009-N-3: 2009-N-4: 2009-N-5: 2009-N-6: 2009-N-7: 2009-N-8: 2009-N-9: 2009-N-10:
November 2009 Topics in the November 2009 Exam Paper for CHEM1101 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 2009-N-2: 2009-N-3: 2009-N-4: 2009-N-5: 2009-N-6: 2009-N-7: 2009-N-8: 2009-N-9: 2009-N-10:
Chemistry 10401, Sections H*, Spring 2015 Prof. T. Lazaridis Final examination, May 18, Last Name: First Name:
 The City College of New York Chemistry Department Chemistry 10401, Sections H*, Spring 2015 Prof. T. Lazaridis Final examination, May 18, 2015 Last Name: First Name: Instructions: There are 13 questions
The City College of New York Chemistry Department Chemistry 10401, Sections H*, Spring 2015 Prof. T. Lazaridis Final examination, May 18, 2015 Last Name: First Name: Instructions: There are 13 questions
Disorder and Entropy. Disorder and Entropy
 Disorder and Entropy Suppose I have 10 particles that can be in one of two states either the blue state or the red state. How many different ways can we arrange those particles among the states? All particles
Disorder and Entropy Suppose I have 10 particles that can be in one of two states either the blue state or the red state. How many different ways can we arrange those particles among the states? All particles
Chapter Eighteen. Thermodynamics
 Chapter Eighteen Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Study of energy changes during observed processes Purpose: To predict spontaneity of a process Spontaneity: Will process go without assistance? Depends
Chapter Eighteen Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Study of energy changes during observed processes Purpose: To predict spontaneity of a process Spontaneity: Will process go without assistance? Depends
Topics in the November 2008 Exam Paper for CHEM1612
 November 2008 Topics in the November 2008 Exam Paper for CHEM1612 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 2008-N-2: 2008-N-3: 2008-N-4: 2008-N-5: 2008-N-6: 2008-N-7: 2008-N-8: 2008-N-9: 2008-N-10:
November 2008 Topics in the November 2008 Exam Paper for CHEM1612 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 2008-N-2: 2008-N-3: 2008-N-4: 2008-N-5: 2008-N-6: 2008-N-7: 2008-N-8: 2008-N-9: 2008-N-10:
General Chemistry I Final Exam 100 pts Fall 2010
 General Chemistry I Final Exam 100 pts Fall 2010 Name This is a closed-book exam: the only reference materials you may use are a periodic table of the elements, a table of enthalpies of formation, and
General Chemistry I Final Exam 100 pts Fall 2010 Name This is a closed-book exam: the only reference materials you may use are a periodic table of the elements, a table of enthalpies of formation, and
Name Final Exam Spring 2002 Page (16 points) Acetylsalicylic acid, the molecule pictured here, is better known as aspirin.
 Name Final Exam Spring 2002 Page 1 1. (16 points) Acetylsalicylic acid, the molecule pictured here, is better known as aspirin. 1 A D 2 B 3 4 Describing the bonding in aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid. (a)
Name Final Exam Spring 2002 Page 1 1. (16 points) Acetylsalicylic acid, the molecule pictured here, is better known as aspirin. 1 A D 2 B 3 4 Describing the bonding in aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid. (a)
Bonus Final Exam 3. 1 Calculate the heat of reaction,δh 0 rxn, for the following reaction as written at 298 K: g 2H 2 CH 4. g CF 4.
 Bonus Final Exam 3 1 Calculate the heat of reaction,δh rxn, for the following reaction as written at 298 K: CH 4 2F 2 CF 4 2H 2 substance CH 4 CF 4 ΔH f kj/mol 75 68 (A) ΔH rxn 23 kj (B) ΔH rxn 914 kj
Bonus Final Exam 3 1 Calculate the heat of reaction,δh rxn, for the following reaction as written at 298 K: CH 4 2F 2 CF 4 2H 2 substance CH 4 CF 4 ΔH f kj/mol 75 68 (A) ΔH rxn 23 kj (B) ΔH rxn 914 kj
AP Chemistry. Free-Response Questions
 2018 AP Chemistry Free-Response Questions College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online
2018 AP Chemistry Free-Response Questions College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online
Chemistry 1A, Fall 2006 Final Exam, Version B Dec 12, 2006 (180 min, closed book)
 Name: SID: GSI Name: Chemistry 1A, Fall 2006 Final Exam, Version B Dec 12, 2006 (180 min, closed book) There are 60 Multiple choice questions worth 4.34 points each. There are 13 short answer questions.
Name: SID: GSI Name: Chemistry 1A, Fall 2006 Final Exam, Version B Dec 12, 2006 (180 min, closed book) There are 60 Multiple choice questions worth 4.34 points each. There are 13 short answer questions.
Chemistry 1A, Spring 2008 Midterm Exam III, Version A April 14, 2008 (90 min, closed book)
 Chemistry 1A, Spring 2008 Midterm Exam III, Version A April 14, 2008 (90 min, closed book) Name: KEY SID: A Name: 1.) Write your name on every page of this exam. 2.) his exam has 15 multiple-choice questions
Chemistry 1A, Spring 2008 Midterm Exam III, Version A April 14, 2008 (90 min, closed book) Name: KEY SID: A Name: 1.) Write your name on every page of this exam. 2.) his exam has 15 multiple-choice questions
Thermochemistry: the study of energy (in the from of heat) changes that accompany physical & chemical changes
 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry: the study of energy (in the from of heat) changes that accompany physical & chemical changes heat flows from high to low (hot cool) endothermic reactions: absorb energy
Thermochemistry Thermochemistry: the study of energy (in the from of heat) changes that accompany physical & chemical changes heat flows from high to low (hot cool) endothermic reactions: absorb energy
AP Chemistry Big Idea Review
 Name: AP Chemistry Big Idea Review Background The AP Chemistry curriculum is based on 6 Big Ideas and many Learning Objectives associated with each Big Idea. This review will cover all of the Big Ideas
Name: AP Chemistry Big Idea Review Background The AP Chemistry curriculum is based on 6 Big Ideas and many Learning Objectives associated with each Big Idea. This review will cover all of the Big Ideas
Homework 11 - Second Law & Free Energy
 HW11 - Second Law & Free Energy Started: Nov 1 at 9:0am Quiz Instructions Homework 11 - Second Law & Free Energy Question 1 In order for an endothermic reaction to be spontaneous, endothermic reactions
HW11 - Second Law & Free Energy Started: Nov 1 at 9:0am Quiz Instructions Homework 11 - Second Law & Free Energy Question 1 In order for an endothermic reaction to be spontaneous, endothermic reactions
Thermodynamics. Thermodynamics of Chemical Reactions. Enthalpy change
 Thermodynamics 1 st law (Cons of Energy) Deals with changes in energy Energy in chemical systems Total energy of an isolated system is constant Total energy = Potential energy + kinetic energy E p mgh
Thermodynamics 1 st law (Cons of Energy) Deals with changes in energy Energy in chemical systems Total energy of an isolated system is constant Total energy = Potential energy + kinetic energy E p mgh
Chemistry 112, Spring 2006 Prof. Metz Final Exam Name Each question is worth 4 points, unless otherwise noted
 Chemistry 112, Spring 2006 Prof. Metz Final Exam Name Each question is worth 4 points, unless otherwise noted 1. The predominant intermolecular attractive force in solid sodium is: (A) metallic (B) ionic
Chemistry 112, Spring 2006 Prof. Metz Final Exam Name Each question is worth 4 points, unless otherwise noted 1. The predominant intermolecular attractive force in solid sodium is: (A) metallic (B) ionic
ph = pk a + log 10{[base]/[acid]}
![ph = pk a + log 10{[base]/[acid]} ph = pk a + log 10{[base]/[acid]}](/thumbs/91/105823399.jpg) FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5)( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5)( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
CHEM 10123/10125, Exam 3
 CHEM 10123/10125, Exam 3 April 4, 2012 (50 minutes) Name (please print) Please box your answers, and remember that significant figures, phases (for chemical equations), and units do count! 1. (18 points)
CHEM 10123/10125, Exam 3 April 4, 2012 (50 minutes) Name (please print) Please box your answers, and remember that significant figures, phases (for chemical equations), and units do count! 1. (18 points)
Chapter 16. Thermodynamics. Thermochemistry Review. Calculating H o rxn. Predicting sign for H o rxn. Creative Commons License
 Chapter 16 Thermodynamics GCC CHM152 Creative Commons License Images and tables in this file have been used from the following sources: OpenStax: Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0. ChemWiki (CC
Chapter 16 Thermodynamics GCC CHM152 Creative Commons License Images and tables in this file have been used from the following sources: OpenStax: Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0. ChemWiki (CC
Chem 1A, Fall 2015, Midterm Exam 3. Version A November 17, 2015 (Prof. Head-Gordon) 2. Student ID: TA:
 Chem 1A, Fall 2015, Midterm Exam 3. Version A November 17, 2015 (Prof. Head-Gordon) 2 Name: Student ID: TA: Contents: 6 pages A. Multiple choice (10 points) B. Thermochemistry and Equilibria (12 points)
Chem 1A, Fall 2015, Midterm Exam 3. Version A November 17, 2015 (Prof. Head-Gordon) 2 Name: Student ID: TA: Contents: 6 pages A. Multiple choice (10 points) B. Thermochemistry and Equilibria (12 points)
St. John s College High School Mr. Trubic AP Midterm Review Packet 2
 Name Date Directions: Read each question carefully and write your response in the space provided following each question. Your responses to these questions will be scored on the basis of the accuracy and
Name Date Directions: Read each question carefully and write your response in the space provided following each question. Your responses to these questions will be scored on the basis of the accuracy and
Chemistry 1A, Fall 2006 Final Exam, Version B Dec 12, 2006 (180 min, closed book)
 Name: SID: GSI Name: Chemistry 1A, Fall 2006 Final Exam, Version B Dec 12, 2006 (180 min, closed book) There are 60 Multiple choice questions worth 4.34 points each. There are 13 short answer questions.
Name: SID: GSI Name: Chemistry 1A, Fall 2006 Final Exam, Version B Dec 12, 2006 (180 min, closed book) There are 60 Multiple choice questions worth 4.34 points each. There are 13 short answer questions.
Questions 1-2 Consider the atoms of the following elements. Assume that the atoms are in the ground state. a. S b. Ca c. Ga d. Sb e.
 AP Chemistry Fall Semester Practice Exam 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE PORTION: Write the letter for the correct answer to the following questions on the provided answer sheet. Each multiple choice question is worth
AP Chemistry Fall Semester Practice Exam 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE PORTION: Write the letter for the correct answer to the following questions on the provided answer sheet. Each multiple choice question is worth
Name:. Correct Questions = Wrong Questions =.. Unattempt Questions = Marks =
 Name:. Correct Questions = Wrong Questions =.. Unattempt Questions = Marks = 1. Which salt is colorless? (A) KMn 4 (B) BaS 4 (C) Na 2 Cr 4 (D) CoCl 2 2. Which 0.10 M aqueous solution exhibits the lowest
Name:. Correct Questions = Wrong Questions =.. Unattempt Questions = Marks = 1. Which salt is colorless? (A) KMn 4 (B) BaS 4 (C) Na 2 Cr 4 (D) CoCl 2 2. Which 0.10 M aqueous solution exhibits the lowest
Chem. 1B Final Practice First letter of last name
 Chem. 1B Final Practice First letter of last name Name Student Number All work must be shown on the exam for partial credit. Points will be taken off for incorrect or no units. Calculators are allowed.
Chem. 1B Final Practice First letter of last name Name Student Number All work must be shown on the exam for partial credit. Points will be taken off for incorrect or no units. Calculators are allowed.
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19. Chemical Thermodynamics Sample Exercise 19.2 (p. 819) Elemental mercury is a silver liquid at room temperature. Its normal freezing point is -38.9 o C, and its molar enthalpy of fusion is H
Chapter 19. Chemical Thermodynamics Sample Exercise 19.2 (p. 819) Elemental mercury is a silver liquid at room temperature. Its normal freezing point is -38.9 o C, and its molar enthalpy of fusion is H
FORMULA SHEET (tear off)
 FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
CH302 Spring 2009 Practice Exam 1 (a fairly easy exam to test basic concepts)
 CH302 Spring 2009 Practice Exam 1 (a fairly easy exam to test basic concepts) 1) Complete the following statement: We can expect vapor pressure when the molecules of a liquid are held together by intermolecular
CH302 Spring 2009 Practice Exam 1 (a fairly easy exam to test basic concepts) 1) Complete the following statement: We can expect vapor pressure when the molecules of a liquid are held together by intermolecular
FORMULA SHEET (tear off)
 FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
Chem. 1B Final Practice
 Chem. 1B Final Practice Name Student Number All work must be shown on the exam for partial credit. Points will be taken off for incorrect or no units and for the incorrect number of significant figures.
Chem. 1B Final Practice Name Student Number All work must be shown on the exam for partial credit. Points will be taken off for incorrect or no units and for the incorrect number of significant figures.
Entropy, Free Energy, and Equilibrium
 Entropy, Free Energy, and Equilibrium Chapter 17 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Spontaneous Physical and Chemical Processes A waterfall runs
Entropy, Free Energy, and Equilibrium Chapter 17 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Spontaneous Physical and Chemical Processes A waterfall runs
Chem 127, Final Exam December 14, 2001
 I. (55 points) This part of the final corresponds to Exam I. It covers the material in Chapters 1, 2 and 3. A. (8 points) Fill in the empty boxes with the appropriate symbol, number, word or charge. Nuclear
I. (55 points) This part of the final corresponds to Exam I. It covers the material in Chapters 1, 2 and 3. A. (8 points) Fill in the empty boxes with the appropriate symbol, number, word or charge. Nuclear
Chem Hughbanks Final Exam, May 11, 2011
 Chem 107 - Hughbanks Final Exam, May 11, 2011 Name (Print) UIN # Section 503 Exam 3, Version # A On the last page of this exam, you ve been given a periodic table and some physical constants. You ll probably
Chem 107 - Hughbanks Final Exam, May 11, 2011 Name (Print) UIN # Section 503 Exam 3, Version # A On the last page of this exam, you ve been given a periodic table and some physical constants. You ll probably
CHM 1046 FINAL REVIEW
 CHM 1046 FINAL REVIEW Prepared & Presented By: Marian Ayoub PART I Chapter Description 6 Thermochemistry 11 States of Matter; Liquids and Solids 12 Solutions 13 Rates of Reactions 18 Thermodynamics and
CHM 1046 FINAL REVIEW Prepared & Presented By: Marian Ayoub PART I Chapter Description 6 Thermochemistry 11 States of Matter; Liquids and Solids 12 Solutions 13 Rates of Reactions 18 Thermodynamics and
CHEMISTRY 110 Final EXAM Dec 17, 2012 FORM A
 CEMISTRY 110 Final EXAM Dec 17, 2012 FORM A 1. Given the following reaction which of the following statements is true? Fe(s) + CuCl 2 (aq)! Cu(s) + FeCl 2 (aq) A. Iron is oxidized and copper is reduced.
CEMISTRY 110 Final EXAM Dec 17, 2012 FORM A 1. Given the following reaction which of the following statements is true? Fe(s) + CuCl 2 (aq)! Cu(s) + FeCl 2 (aq) A. Iron is oxidized and copper is reduced.
CHEM N-2 November 2014
 CHEM1612 2014-N-2 November 2014 Explain the following terms or concepts. Le Châtelier s principle 1 Used to predict the effect of a change in the conditions on a reaction at equilibrium, this principle
CHEM1612 2014-N-2 November 2014 Explain the following terms or concepts. Le Châtelier s principle 1 Used to predict the effect of a change in the conditions on a reaction at equilibrium, this principle
Brown, LeMay Ch 5 AP Chemistry Monta Vista High School
 Brown, LeMay Ch 5 AP Chemistry Monta Vista High School 1 From Greek therme (heat); study of energy changes in chemical reactions Energy: capacity do work or transfer heat Joules (J), kilo joules (kj) or
Brown, LeMay Ch 5 AP Chemistry Monta Vista High School 1 From Greek therme (heat); study of energy changes in chemical reactions Energy: capacity do work or transfer heat Joules (J), kilo joules (kj) or
CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2010 FINAL EXAM FORM C Section 502 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT PART 1
 NAME (Block Print) CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2010 FINAL EXAM FORM C Section 502 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT Directions: (1) Put your name on PART 1 and your name and signature on PART 2 of the exam where indicated.
NAME (Block Print) CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2010 FINAL EXAM FORM C Section 502 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT Directions: (1) Put your name on PART 1 and your name and signature on PART 2 of the exam where indicated.
Topics in the November 2014 Exam Paper for CHEM1101
 November 2014 Topics in the November 2014 Exam Paper for CHEM1101 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 2014-N-2: 2014-N-3: 2014-N-4: 2014-N-5: 2014-N-7: 2014-N-8: 2014-N-9: 2014-N-10: 2014-N-11:
November 2014 Topics in the November 2014 Exam Paper for CHEM1101 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 2014-N-2: 2014-N-3: 2014-N-4: 2014-N-5: 2014-N-7: 2014-N-8: 2014-N-9: 2014-N-10: 2014-N-11:
Topics in the June 2006 Exam Paper for CHEM1901
 June 006 Topics in the June 006 Exam Paper for CHEM1901 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 006-J-: 006-J-3: 006-J-4: 006-J-5: 006-J-6: 006-J-7: 006-J-8: 006-J-9: 006-J-10: 006-J-11: 006-J-1:
June 006 Topics in the June 006 Exam Paper for CHEM1901 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 006-J-: 006-J-3: 006-J-4: 006-J-5: 006-J-6: 006-J-7: 006-J-8: 006-J-9: 006-J-10: 006-J-11: 006-J-1:
2. Explain why the ph of unbuffered water is generally around 5.7
 CHEM 108b FINAL EXAM The exam is worth a total of 100 points. Each problem is worth five points. Show all work for partial credit. Don t forget to label units and check whether equations are balanced if
CHEM 108b FINAL EXAM The exam is worth a total of 100 points. Each problem is worth five points. Show all work for partial credit. Don t forget to label units and check whether equations are balanced if
CHE 107 FINAL EXAMINATION December 10, 2012
 CHE 107 FINAL EXAMINATION December 10, 2012 University of Kentucky Department of Chemistry READ THESE DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY BEFORE STARTING THE EXAMINATION! It is extremely important that you fill in the
CHE 107 FINAL EXAMINATION December 10, 2012 University of Kentucky Department of Chemistry READ THESE DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY BEFORE STARTING THE EXAMINATION! It is extremely important that you fill in the
Department of Chemistry Memorial University of Newfoundland Chemistry 1050
 Department of Chemistry Memorial University of Newfoundland Chemistry 1050 Fall 2012 Final Examination Time 3 hours NAME: MUN Student Number: Circle your professor s name. Robert Davis Christopher Flinn
Department of Chemistry Memorial University of Newfoundland Chemistry 1050 Fall 2012 Final Examination Time 3 hours NAME: MUN Student Number: Circle your professor s name. Robert Davis Christopher Flinn
Chemistry 223 Spring 2012 Oregon State University Exam 2 May 24, 2012 Drs. Nafshun, Watson, Richardson
 Chemistry 223 Spring 2012 Oregon State University Exam 2 May 24, 2012 Drs. Nafshun, Watson, Richardson Instructions: You should have with you several number two pencils, an eraser, your 3" x 5" note card,
Chemistry 223 Spring 2012 Oregon State University Exam 2 May 24, 2012 Drs. Nafshun, Watson, Richardson Instructions: You should have with you several number two pencils, an eraser, your 3" x 5" note card,
Chemistry 2000 Spring 2006 Final Examination
 Chemistry 2000 Spring 2006 Final Examination Name: Student number: Time: 3 hours Aids allowed: Calculator Instructions: Answer all questions in the spaces provided. You can use the backs of pages for scratch
Chemistry 2000 Spring 2006 Final Examination Name: Student number: Time: 3 hours Aids allowed: Calculator Instructions: Answer all questions in the spaces provided. You can use the backs of pages for scratch
Chem 112, Fall 05 (Garman/Weis) Final Exam A, 12/20/2005 (Print Clearly) +2 points
 +2 points Before you begin, make sure that your exam has all 10 pages. There are 24 required problems worth 4 points apiece, unless otherwise noted, and two 4-point extra credit problems. Stay focused,
+2 points Before you begin, make sure that your exam has all 10 pages. There are 24 required problems worth 4 points apiece, unless otherwise noted, and two 4-point extra credit problems. Stay focused,
40S CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM PROBLEM REVIEW SHEET:
 40S CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM PROBLEM REVIEW SHEET: **THIS IS NOT A COMPLETE REVIEW. CONTINUE TO READ ALL COURSE NOTES, GO OVER ALL WORKSHEETS, HANDOUTS, AND THE MID-TERM EXAM TO BE BETTER PREPARED. To prepare
40S CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM PROBLEM REVIEW SHEET: **THIS IS NOT A COMPLETE REVIEW. CONTINUE TO READ ALL COURSE NOTES, GO OVER ALL WORKSHEETS, HANDOUTS, AND THE MID-TERM EXAM TO BE BETTER PREPARED. To prepare
CY 102: Physical Chemistry End Semester May 3, 2004
 CY 102: Physical Chemistry End Semester May 3, 2004 Answer All Questions R = (8.314 J = 0.0821 atm dm 3 ) K -1 mol -1 Trouton s constant = 88 J K -1 mol -1 F = 96,500 Cmol -1. Question 1: Fill in the blanks
CY 102: Physical Chemistry End Semester May 3, 2004 Answer All Questions R = (8.314 J = 0.0821 atm dm 3 ) K -1 mol -1 Trouton s constant = 88 J K -1 mol -1 F = 96,500 Cmol -1. Question 1: Fill in the blanks
Chem 152 Final. You will have 1 hour and 50 minutes. Do not begin the exam until you are instructed to start. Best of luck.
 Chem 152 Final Section: Name: You will have 1 hour and 50 minutes. Do not begin the exam until you are instructed to start. Best of luck. Question 1 /80 Question 2 /20 Question 3 /20 Question 4 /20 Question
Chem 152 Final Section: Name: You will have 1 hour and 50 minutes. Do not begin the exam until you are instructed to start. Best of luck. Question 1 /80 Question 2 /20 Question 3 /20 Question 4 /20 Question
Chemistry II Midterm Exam April 24, 2009
 Chemistry II Midterm Exam April 24, 2009 Constants R = 8.314 J / mol K = 0.08314 Lbar / K mol = 8.314 L kpa / K mol F = 9.6485 10 4 C/mol h = 6.63 10-34 J s h = 1.05 10-34 J s k = 1.3806504 10 23 J / K
Chemistry II Midterm Exam April 24, 2009 Constants R = 8.314 J / mol K = 0.08314 Lbar / K mol = 8.314 L kpa / K mol F = 9.6485 10 4 C/mol h = 6.63 10-34 J s h = 1.05 10-34 J s k = 1.3806504 10 23 J / K
Autumn Semester. Basic Chemistry for Engineering/ Fundamental Inorganic Chemistry Final Exam. 18 February Time: 60 minutes
 Basic Chemistry Final Exam 1 Name: Student number: Instructions: Autumn Semester Basic Chemistry for Engineering/ Fundamental Inorganic Chemistry Final Exam 18 February 2013 Time: 60 minutes Answer any
Basic Chemistry Final Exam 1 Name: Student number: Instructions: Autumn Semester Basic Chemistry for Engineering/ Fundamental Inorganic Chemistry Final Exam 18 February 2013 Time: 60 minutes Answer any
1. Read all questions thoroughly and answer each question completely. ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN IN ORDER TO RECEIVE ANY CREDIT.
 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Read all questions thoroughly and answer each question completely. ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN IN ORDER TO RECEIVE ANY CREDIT. 2. You will be allowed to use only the given sheet of thermodynamic
INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Read all questions thoroughly and answer each question completely. ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN IN ORDER TO RECEIVE ANY CREDIT. 2. You will be allowed to use only the given sheet of thermodynamic
Final Exam Review Chem 110 MJ Bojan
 Final Exam Review hem 110 MJ Bojan EM 110 EXAM Final Exam Fri. May 3 10:10am noon Locations are assigned by section and are posted on the Web. (IGNORE e-lion listings) http://courses.chem.psu.edu/chem110spring!
Final Exam Review hem 110 MJ Bojan EM 110 EXAM Final Exam Fri. May 3 10:10am noon Locations are assigned by section and are posted on the Web. (IGNORE e-lion listings) http://courses.chem.psu.edu/chem110spring!
10 NEET 31 Years 11. The enthalpy of fusion of water is kcal/mol. The molar entropy change for the melting of ice at
 6 Thermodynamics. A gas is allowed to expand in a well insulated container against a constant external pressure of.5 atm from an initial volume of.50 L to a final volume of 4.50 L. The change in internal
6 Thermodynamics. A gas is allowed to expand in a well insulated container against a constant external pressure of.5 atm from an initial volume of.50 L to a final volume of 4.50 L. The change in internal
CHEM 108 (Spring-2008)
 CHEM 108 (Spring-2008) Final Exam (106 pts) Name: --------------------------------------------------------------------------, CLID # -------------------------------- LAST NAME, First (Circle the alphabet
CHEM 108 (Spring-2008) Final Exam (106 pts) Name: --------------------------------------------------------------------------, CLID # -------------------------------- LAST NAME, First (Circle the alphabet
2nd Semester Exam Review. C. K eq = [N 2][H 2 ]
![2nd Semester Exam Review. C. K eq = [N 2][H 2 ] 2nd Semester Exam Review. C. K eq = [N 2][H 2 ]](/thumbs/82/85457292.jpg) Name: ate: 1. Which pair of formulas represents the empirical formula and the molecular formula of a compound?. H 2 O, 4 H 6 O 4. HO, 6 H 12 O 6 8. Given the reaction at equilibrium: N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g)
Name: ate: 1. Which pair of formulas represents the empirical formula and the molecular formula of a compound?. H 2 O, 4 H 6 O 4. HO, 6 H 12 O 6 8. Given the reaction at equilibrium: N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g)
CHEMISTRY 202 Hour Exam II. Dr. D. DeCoste T.A (60 pts.) 31 (20 pts.) 32 (40 pts.)
 CHEMISTRY 202 Hour Exam II October 27, 2015 Dr. D. DeCoste Name Signature T.A. This exam contains 32 questions on 11 numbered pages. Check now to make sure you have a complete exam. You have two hours
CHEMISTRY 202 Hour Exam II October 27, 2015 Dr. D. DeCoste Name Signature T.A. This exam contains 32 questions on 11 numbered pages. Check now to make sure you have a complete exam. You have two hours
Midterm Exam III. CHEM 181: Introduction to Chemical Principles November 25, 2014 Answer Key
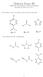 Midterm Exam III EM 181: Introduction to hemical Principles ovember 25, 2014 Answer Key 1. For reference, here are the pk a values for three weak acids: 3 pk a = 7.2 pk a = 4.8 pk a = 15 ow consider this
Midterm Exam III EM 181: Introduction to hemical Principles ovember 25, 2014 Answer Key 1. For reference, here are the pk a values for three weak acids: 3 pk a = 7.2 pk a = 4.8 pk a = 15 ow consider this
THERMODYNAMICS I. TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A. Review of Definitions 1. Thermodynamics = Study of the exchange of heat, energy and work between a system
 THERMODYNAMICS I. TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A. Review of Definitions 1. Thermodynamics = Study of the exchange of heat, energy and work between a system and its surroundings. a. System = That part of universe
THERMODYNAMICS I. TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A. Review of Definitions 1. Thermodynamics = Study of the exchange of heat, energy and work between a system and its surroundings. a. System = That part of universe
Name: Student code: The average kinetic energy of an argon atom is the same as that of a water droplet.
 T-11 ame 5 pts Student code 25 75 1-1. The mass of a water droplet m = V ρ = [(4/3) π r 3 ] ρ = (4/3) π (0.5x10-6 m) 3 (1.0 g/cm 3 ) = 5.2x10-16 kg 10 Average kinetic energy at 27 o C KE = mv 2 /2 = (5.2x10-16
T-11 ame 5 pts Student code 25 75 1-1. The mass of a water droplet m = V ρ = [(4/3) π r 3 ] ρ = (4/3) π (0.5x10-6 m) 3 (1.0 g/cm 3 ) = 5.2x10-16 kg 10 Average kinetic energy at 27 o C KE = mv 2 /2 = (5.2x10-16
AP* Electrochemistry Free Response Questions page 1
 Galvanic (Voltaic) Cells 1988 Average score = 5.02 a) two points Sn ---> Sn 2+ + 2e Ag + + e ---> Ag AP* Electrochemistry Free Response Questions page 1 b) two points 2 Ag + + Sn ---> 2 Ag + Sn 2+ E =
Galvanic (Voltaic) Cells 1988 Average score = 5.02 a) two points Sn ---> Sn 2+ + 2e Ag + + e ---> Ag AP* Electrochemistry Free Response Questions page 1 b) two points 2 Ag + + Sn ---> 2 Ag + Sn 2+ E =
Name (Print) Section # or TA. 1. You may use a crib sheet which you prepared in your own handwriting. This may be
 Name (Print) Section # or TA 1. You may use a crib sheet which you prepared in your own handwriting. This may be one 8-1/2 by 11 inch sheet of paper with handwriting only on one side. 2. You may use a
Name (Print) Section # or TA 1. You may use a crib sheet which you prepared in your own handwriting. This may be one 8-1/2 by 11 inch sheet of paper with handwriting only on one side. 2. You may use a
40S CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM PROBLEM REVIEW SHEET:
 40S CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM PROBLEM REVIEW SHEET: **THIS IS NOT A COMPLETE REVIEW. CONTINUE TO READ ALL COURSE NOTES, GO OVER ALL WORKSHEETS, HANDOUTS, AND THE UNIT TESTS TO BE BETTER PREPARED. To prepare
40S CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM PROBLEM REVIEW SHEET: **THIS IS NOT A COMPLETE REVIEW. CONTINUE TO READ ALL COURSE NOTES, GO OVER ALL WORKSHEETS, HANDOUTS, AND THE UNIT TESTS TO BE BETTER PREPARED. To prepare
CHEMISTRY 102B Hour Exam II. Dr. D. DeCoste T.A.
 CHEMISTRY 10B Hour Exam II March 19, 015 Dr. D. DeCoste Name Signature T.A. This exam contains questions on 9 numbered pages. Check now to make sure you have a complete exam. You have one hour and thirty
CHEMISTRY 10B Hour Exam II March 19, 015 Dr. D. DeCoste Name Signature T.A. This exam contains questions on 9 numbered pages. Check now to make sure you have a complete exam. You have one hour and thirty
Chem 12 Exam 3. Basic Skills Section. 1. What is the chemical formula for aluminum nitrate?
 Chem 1 Exam Basic Skills Section 1. What is the chemical formula for aluminum nitrate? a) Al(N ) b) AlN c) Al(N ) d) Al (N ) e) Al (N ). What are the spectator ions in the solution after the complete neutralization
Chem 1 Exam Basic Skills Section 1. What is the chemical formula for aluminum nitrate? a) Al(N ) b) AlN c) Al(N ) d) Al (N ) e) Al (N ). What are the spectator ions in the solution after the complete neutralization
McCord CH301 Exam 5 Dec 5, 2017
 425 version last name first name signature McCord CH301 Exam 5 Dec 5, 2017 50070 BUR 106 Tuesday TTh 9:30 am - 11 pm Remember to refer to the Periodic Table handout that is separate from this exam copy.
425 version last name first name signature McCord CH301 Exam 5 Dec 5, 2017 50070 BUR 106 Tuesday TTh 9:30 am - 11 pm Remember to refer to the Periodic Table handout that is separate from this exam copy.
CHEMISTRY. Section II (Total time 95 minutes) Part A Time 55 minutes YOU MAY USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR PART A.
 CHEMISTRY Section II (Total time 95 minutes) Part A Time 55 minutes YOU MAY USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR PART A. CLEARLY SHOW THE METHOD USED AND THE STEPS INVOLVED IN ARRIVING AT YOUR ANSWERS. It is to your
CHEMISTRY Section II (Total time 95 minutes) Part A Time 55 minutes YOU MAY USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR PART A. CLEARLY SHOW THE METHOD USED AND THE STEPS INVOLVED IN ARRIVING AT YOUR ANSWERS. It is to your
ANSWERS CIRCLE CORRECT SECTION
 CHEMISTRY 162 - EXAM I June 08, 2009 Name: SIGN: RU ID Number Choose the one best answer for each question and write the letter preceding it in the appropriate space on this answer sheet. Only the answer
CHEMISTRY 162 - EXAM I June 08, 2009 Name: SIGN: RU ID Number Choose the one best answer for each question and write the letter preceding it in the appropriate space on this answer sheet. Only the answer
Molar heat capacity, C p J K 1 mol 1. o C
 CHEM1109 2009-N-2 November 2009 The thermite reaction is written below. Show that the heat released in this reaction is sufficient for the iron to be produced as molten metal. 2Al(s) + Fe 2 O 3 (s) Al
CHEM1109 2009-N-2 November 2009 The thermite reaction is written below. Show that the heat released in this reaction is sufficient for the iron to be produced as molten metal. 2Al(s) + Fe 2 O 3 (s) Al
1 /9 6 /7 2 /15 7 /14 3 /5 8 /13 4 /10 9 /10 5 /7 10 /10
 2017 FALL Semester Midterm Examination For General Chemistry II (CH103) Date: ctober 18 (Wed), Time Limit: 19:00 ~ 21:00 Write down your information neatly in the space provided below; print your Student
2017 FALL Semester Midterm Examination For General Chemistry II (CH103) Date: ctober 18 (Wed), Time Limit: 19:00 ~ 21:00 Write down your information neatly in the space provided below; print your Student
