Chemistry 163B Thermodynamics Winter 2014
|
|
|
- Roland Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemistry 163B Thermodynamics Winter 2014 Thermodynamics is a really beautiful scientific story!! 1 2 rules of science Observations (QM vs Thermo) observations Thermodynamics is very working class in its origins: guiding principles predictions and applications based on principles quantum mechanics Effete spectra H = E thermodynamics canons Blue Collar S universe > observations: thermo heat observations: mechanical efficiency of steam engine Count Rumford, 1799 observed water turning into steam when canon barrel was bored work heat Sadi Carnot, 1824 efficiency of engines 5 6 1
2 guiding principles Applications U,H,S,G Conservation of heat and work (Joule, 1845) 1st LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS How does knowledge about efficiencies of steam engines, mechanical systems, etc, relate to processes in chemical, biological, and geological systems? Clausius, 1860 Entropy 2 nd LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS ANSWERED BY: Boltzmann, late 19 th century, molecular picture of entropy Clausius the thermodynamic functions U, H, and S (1 st and 2 nd laws) Boltzmann 7 J. W. Gibbs- arguably the frist great American scientist who combined the concepts of heat and entropy and proposed [Gibbs] Free Energy, G, a thermodynamic state function that leads to a whole spectrum of applications 8 from: Einstein s Autobiographical Notes types of problems that thermodynamics addresses (reactions) might 1. Under what conditions will a reaction occur? C (graphite) C (diamond) 30, ,000 atm 1000 K 3000 K 1 st artificially produced diamonds, 1954 at General Electric Labs 9 10 types of problems that thermodynamics addresses (equilibria) types of problems that thermodynamics addresses (biology) 2. How far will a reaction proceed (given enough time)? How do the thermal and entropic properties determine EQUILIBRIUM? How do the EQUILIBRIUM conditions depend on T,P? N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) 2NH 3 (g) what are best T,P for NH 3 products? The Haber Process 3. Chemical and physical changes in biological systems [K + ] inside cell [K+] outside what difference in [K + ] out vs [K + ] in can be tolerated before cell wall bursts or collapses? SiO 2 + CaCO 3 CaO SiO 2 + CO 2 (g) quartz calcite wollastonite geologic thermometer: The fraction of wollastonite in a rock sample can be used to estimate the temperature at which the rock metamorphosis occurred [the T at which the equilibrium was rapidly frozen] 11 low extracellular salt hypotonic (rupture) normal isotonic extracellular salt high hypertonic (collapse) 12 2
3 types of problems that thermodynamics addresses (biology) types of problems that thermodynamics addresses (ecology) 4. Why does an egg hard boil? (protein conformation) 5. Membrane potentials and ion concentrations in neurons. (electrochemistry and thermodynamics) 6. Thermodynamic feasibility of SO 2 removal SO 2 (g) S(s) + O 2 (g) what thermodynamics can t answer aims of class 1. How fast a reaction proceeds (kinetics, catalysts, enzymes; in chem 103, BMB 100, chem 163C) 2. Macroscopic thermodynamics does not prove or require hypotheses about molecular structure; however we will use our knowledge of molecular structure to get an atomic picture of thermodynamic processes. The quantitative connection is made by statistical thermodynamics: chem 163A chem 163B chem 163C 3. Although in chemistry 163B we will study how thermodynamics put limits on processes at equilibrium, there exists a whole other field of non-equilibrium thermodynamics. 1. Clear conceptual picture of thermodynamics 2. Ability to relate and apply thermodynamics to chemical and biological systems 3. PROBLEM SOLVING: Chemistry + Logic + Mathematics 4. How to do independent and advanced reading/research in areas that utilize thermodynamics. 5. THE GRAND PICTURE of how thermodynamics and quantum mechanics fit into our picture of nature. 6. Advanced mathematical techniques class administration Learn Thermodynamics course pages Chemistry 163B lectures: A MUST homework: A MUST Lectures Sections (start TOMORROW Tues, Jan 7; HW#1 Probs 1-4) Tutorial Event (starts THIS Thurs, Jan 9) Office hours (start TODAY Mon, Jan 6) LSS Tutor sections: required (A MUST) tutorial EVENT & Office Hours & LSS (for YOU!) midterms: 31 st January 26 th February final: 20 th March, 12:00-3:00 PM (last class 17 th March)
4 Van der Waals gas Sections week of 6 th January Variables of state: V, T, P (careful definitions) empirical TEMPERATURE: universal behavior of gas handout and pp. 4-5 VOLUME: MEASURED WITH A RULER TEMPERATURE: SEE IDEAL GAS THERMOMETER HANDOUT T eq =boiling water at 1atm PRESSURE: FORCE/AREA T eq =ice at 1atm EQUATION of STATE: RELATES P, V, T (more later) 21 Choose R so that T boiling -T ice = [n.b. curves for various gasses are cartoons but actual data would converge to limit] Pressure, Kinetic Energy, and Temperature SEE HANDOUT Ideal Gas Energy: Game Plan Handout #6 [E&R pp 2-4] for monatomic ideal gas from PV=n*kT and P=F/A use physics to relate pressure energy of gas 23 and thus for monatomic ideal gas E depends only on T!!! [in thermodynamic notation E U (internal energy)] 24 4
5 heuristic derivation of E=E(T) for ideal gas [U=U(T)] heuristic derivation 1. molecules all with same v x (all same v x is heuristic ) 2. elastic collision with wall mass velocity goes v x ö-v x 3. from physics 4. from physics 5. dp º Dp = 2m v x per collision (m is mass of particle) 6. total Dp in given time Dt, would depend on number of collisions in that interval 25,. 26 heuristic derivation heuristic derivation is density of molecules, Av x Dt is volume of rectangular box, is number of molecules colliding with area A 9. total heuristic derivation TAKE HOME MESSAGES 11. after some algebra and equating Good warm up of physics and equation derivation For a molecule with only kinetic energy (e.g. monatomic species), and ideal gas (no intermolecular forces) 12. in 3D with v x = v y = v z For monatomic ideal gas, E is function of only T; T constant î E constant
6 various equations of state (Raff Table 1.2) Some comments on the Van der Waals equation of state HW#1 1 HW#1 2-3 HW#1 * van der Waals equation van der Waals equation interpretation of parameters: b is correction for actual volume of atoms/molecules interpretation of parameters: a is correction for attractive forces of atoms/molecules a is associated with attractive forces volume available to molecules smaller than P bulk ª P ideal is greater than PªP meas measured at surface b is associated with repulsive forces 33 P bulk = 34 heuristic justification for attractive constant a van der Waals equation asymmetric attractive forces for molecule at surface molecule at surface has less momentum less than molecule in bulk PªP meas < P bulk P bulk =
7 van der Waals equation some trash talk on VDW eqn: inaccurate but instructive!!! (from other texts)? size repulsive attractive polarizability polarity Validity However, the Van der Waals model is not appropriate for rigorous quantitative calculations, remaining useful only for teaching and qualitative purposes. [1] Nowadays, Eq. 2.9 belongs to pedagogical physics: it is the simplest equation that illustrates several important concepts, but its accuracy is not satisfactory various equations of state (Raff Table 1.2) End of Lecture The Haber Process (thermodynamics and kinetics) heuristic Previously the problem had been that N 2 is a very stable molecule, and so most attempts to convert it to less stable molecules, such as NH 3, failed because of thermodynamic or entropy problems. The secret to the Haber-Bosch process proved to be a catalyst of iron with a small amount of aluminium added (aluminium was at the time an exotic and expensive metal that probably attracted Haber's attention as a novelty). The Haber- Bosch process operates at high pressure so as to shift the equilibrium to the right, and high temperature to increase the rates of the reaction. Of course, operating at high temperature actually shifted the reaction to the left, but the trade-off for faster rates was accepted. By removing the ammonia as liquid ammonia, the equilibrium is continuously shifted to the right. heu ris tic [hyoo-ris-tik or, often, yoo-] adjective 1. serving to indicate or point out; stimulating interest as a means of furthering investigation
8 universal behavior of gas 43 8
Chemistry 163B Thermodynamics Winter 2013
 Chemistry 163B Thermodynamics Winter 2013 1 Thermodynamics is a really beautiful scientific story!! 2 1 rules of science observations guiding principles predictions and applications based on principles
Chemistry 163B Thermodynamics Winter 2013 1 Thermodynamics is a really beautiful scientific story!! 2 1 rules of science observations guiding principles predictions and applications based on principles
Chemistry 163B Thermodynamics Winter 2013
 Chemistry 163B Thermodynamics Winter 013 Thermodynamics is a really beautiful scientific story!! 1 rules of science Observations (QM vs Thermo) observations Thermodynamics is very working class in its
Chemistry 163B Thermodynamics Winter 013 Thermodynamics is a really beautiful scientific story!! 1 rules of science Observations (QM vs Thermo) observations Thermodynamics is very working class in its
Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing
 Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing 1 APPENDIX A: H f, G f, BUT S (no Δ, no sub f ) Hº f Gº f Sº 2 Third Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of any perfect crystalline substance approaches
Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing 1 APPENDIX A: H f, G f, BUT S (no Δ, no sub f ) Hº f Gº f Sº 2 Third Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of any perfect crystalline substance approaches
Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing
 Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing 1 APPENDIX A: H f, G f, BU S (no Δ, no sub f ) Hº f Gº f Sº 2 1 hird Law of hermodynamics he entropy of any perfect crystalline substance approaches
Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing 1 APPENDIX A: H f, G f, BU S (no Δ, no sub f ) Hº f Gº f Sº 2 1 hird Law of hermodynamics he entropy of any perfect crystalline substance approaches
Chemistry 163B Heuristic Tutorial Second Law, Statistics and Entropy falling apples excited state ground state chemistry 163B students
 Lecture 8 Chemistry B Winter 0 Introduction to nd Law Lower energy states are more stable Systems naturally go to lower energy???? Chemistry B Heuristic Tutorial Second Law, Statistics and Entropy falling
Lecture 8 Chemistry B Winter 0 Introduction to nd Law Lower energy states are more stable Systems naturally go to lower energy???? Chemistry B Heuristic Tutorial Second Law, Statistics and Entropy falling
Chemistry 163B. Concluding Factoids. and. Comments
 Chemistry 163B Concluding Factoids and Comments 1 neuron, resting potential http://projects.gw.utwente.nl/pi/sim/bovt/concep4.gif http://www.uta.edu/biology/westmoreland/classnotes/144/chapter_48_files/image009.jpg
Chemistry 163B Concluding Factoids and Comments 1 neuron, resting potential http://projects.gw.utwente.nl/pi/sim/bovt/concep4.gif http://www.uta.edu/biology/westmoreland/classnotes/144/chapter_48_files/image009.jpg
Grading System Text Book
 CHEM 240 Who am I? Thermodynamic studies Course for Engineering Students Dr. Mohamed Abdel Salam Assistant Professor of Physical Chemistry King Abdul Aziz University Jeddah KSA PhD in Nano Chemistry, Canada
CHEM 240 Who am I? Thermodynamic studies Course for Engineering Students Dr. Mohamed Abdel Salam Assistant Professor of Physical Chemistry King Abdul Aziz University Jeddah KSA PhD in Nano Chemistry, Canada
Lecture 03/30 Monday, March 30, :46 AM
 Chem 110A Page 1 Lecture 03/30 Monday, March 30, 2009 9:46 AM Notes 0330 Audio recording started: 10:02 AM Monday, March 30, 2009 Chapter 1: Ideal Gases Macroscopic properties of gases Equation of state
Chem 110A Page 1 Lecture 03/30 Monday, March 30, 2009 9:46 AM Notes 0330 Audio recording started: 10:02 AM Monday, March 30, 2009 Chapter 1: Ideal Gases Macroscopic properties of gases Equation of state
Chemistry 163B Heuristic Tutorial Second Law, Statistics and Entropy
 Chemistry 163B Heuristic Tutorial Second Law, Statistics and Entropy 3 Lower energy states are more stable Systems naturally go to lower energy???? falling apples excited state ground state chemistry 163B
Chemistry 163B Heuristic Tutorial Second Law, Statistics and Entropy 3 Lower energy states are more stable Systems naturally go to lower energy???? falling apples excited state ground state chemistry 163B
fiziks Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT-JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES
 Content-Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics 1. Kinetic theory of gases..(1-13) 1.1 Basic assumption of kinetic theory 1.1.1 Pressure exerted by a gas 1.2 Gas Law for Ideal gases: 1.2.1 Boyle s Law 1.2.2
Content-Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics 1. Kinetic theory of gases..(1-13) 1.1 Basic assumption of kinetic theory 1.1.1 Pressure exerted by a gas 1.2 Gas Law for Ideal gases: 1.2.1 Boyle s Law 1.2.2
Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Answer Key
 1 Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Answer Key Made by Montgomery High School montyscioly@gmail.com 2 Questions are worth between 1 to 3 points. Show calculations for all open-ended math questions
1 Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Answer Key Made by Montgomery High School montyscioly@gmail.com 2 Questions are worth between 1 to 3 points. Show calculations for all open-ended math questions
PHY 6500 Thermal and Statistical Physics - Fall 2017
 PHY 6500 Thermal and Statistical Physics - Fall 2017 Time: M, F 12:30 PM 2:10 PM. From 08/30/17 to 12/19/17 Place: Room 185 Physics Research Building Lecturer: Boris Nadgorny E-mail: nadgorny@physics.wayne.edu
PHY 6500 Thermal and Statistical Physics - Fall 2017 Time: M, F 12:30 PM 2:10 PM. From 08/30/17 to 12/19/17 Place: Room 185 Physics Research Building Lecturer: Boris Nadgorny E-mail: nadgorny@physics.wayne.edu
CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT, PORTLAND STATE UNIVERSITY
 CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT, PORTLAND STATE UNIVERSITY CHEMISTRY 440/540, PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY. FALL, 2014 Venue: CR 250 Instructor: R. H. Simoyi (SB2 372) Syllabus: The chapters and page numbers referred to in
CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT, PORTLAND STATE UNIVERSITY CHEMISTRY 440/540, PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY. FALL, 2014 Venue: CR 250 Instructor: R. H. Simoyi (SB2 372) Syllabus: The chapters and page numbers referred to in
CHAPTER 11: Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids. Are there any IDEAL GASES? The van der Waals equation corrects for deviations from ideality
 CHAPTER 11: Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids Are there any IDEAL GASES? The van der Waals equation corrects for deviations from ideality Does the KMT break down? Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. Gas
CHAPTER 11: Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids Are there any IDEAL GASES? The van der Waals equation corrects for deviations from ideality Does the KMT break down? Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. Gas
Chemistry Physical Chemistry I Fall 2017
 Chemistry 309 - Physical Chemistry I Fall 2017 Instructor: Office Hours: Dr. Samuel A. Abrash C208 Gottwald Science Center Work: 289-8248 Home: 323-7363 Cell: 363-2597 sabrash@richmond.edu www.richmond.edu/~sabrash
Chemistry 309 - Physical Chemistry I Fall 2017 Instructor: Office Hours: Dr. Samuel A. Abrash C208 Gottwald Science Center Work: 289-8248 Home: 323-7363 Cell: 363-2597 sabrash@richmond.edu www.richmond.edu/~sabrash
Chemistry 223H1 Fall Term 2010
 Chemistry 223H1 Fall Term 2010 Instructor: Dr. D.F. McIntosh Email: dmcintos@chem.utoronto.ca Office hour: Thursdays 3:00 4:00 pm Rm 223 in Lash Miller Lectures: T : LM 159 3:00 4:30 pm F : LM 159 2:00
Chemistry 223H1 Fall Term 2010 Instructor: Dr. D.F. McIntosh Email: dmcintos@chem.utoronto.ca Office hour: Thursdays 3:00 4:00 pm Rm 223 in Lash Miller Lectures: T : LM 159 3:00 4:30 pm F : LM 159 2:00
Temperature and Heat. Ken Intriligator s week 4 lectures, Oct 21, 2013
 Temperature and Heat Ken Intriligator s week 4 lectures, Oct 21, 2013 This week s subjects: Temperature and Heat chapter of text. All sections. Thermal properties of Matter chapter. Omit the section there
Temperature and Heat Ken Intriligator s week 4 lectures, Oct 21, 2013 This week s subjects: Temperature and Heat chapter of text. All sections. Thermal properties of Matter chapter. Omit the section there
Chem 350: Statistical Mechanics and Chemical Kinetics. Spring Preface. Introduction 2
 Preface Introduction 2 Statistical Mechanics and Chemical Kinetics: Syllabus Textbook: Thermodynamics, Statistical Thermodynamics and Kinetics 3 rd ed by Thomas Engel and Philip Reid Additional Resource
Preface Introduction 2 Statistical Mechanics and Chemical Kinetics: Syllabus Textbook: Thermodynamics, Statistical Thermodynamics and Kinetics 3 rd ed by Thomas Engel and Philip Reid Additional Resource
Physical Chemistry Using Mathcad
 Platform: Windows Requires: 4 MB hard disk space; includes the Mathcad Engine Available for ground shipment This book does two things: 1) Teaches the aspects of Mathcad that are most useful for solving
Platform: Windows Requires: 4 MB hard disk space; includes the Mathcad Engine Available for ground shipment This book does two things: 1) Teaches the aspects of Mathcad that are most useful for solving
Chemistry Physical Chemistry I Fall 2018
 Chemistry 309 - Physical Chemistry I Fall 2018 Instructor: Office Hours: Dr. Samuel A. Abrash C-208 Gottwald Science Center Work: 289-8248 Home: 323-7363 Cell: 363-2597 sabrash@richmond.edu www.richmond.edu/~sabrash
Chemistry 309 - Physical Chemistry I Fall 2018 Instructor: Office Hours: Dr. Samuel A. Abrash C-208 Gottwald Science Center Work: 289-8248 Home: 323-7363 Cell: 363-2597 sabrash@richmond.edu www.richmond.edu/~sabrash
Contents. 1 Introduction and guide for this text 1. 2 Equilibrium and entropy 6. 3 Energy and how the microscopic world works 21
 Preface Reference tables Table A Counting and combinatorics formulae Table B Useful integrals, expansions, and approximations Table C Extensive thermodynamic potentials Table D Intensive per-particle thermodynamic
Preface Reference tables Table A Counting and combinatorics formulae Table B Useful integrals, expansions, and approximations Table C Extensive thermodynamic potentials Table D Intensive per-particle thermodynamic
CHEM GENERAL CEMISTRY
 CHEM 100-12 GENERAL CEMISTRY Course Synopsis: The fundamental principles of chemistry, including atomic and molecular structure, bonding, elementary thermochemistry and thermodynamics, oxidation-reduction
CHEM 100-12 GENERAL CEMISTRY Course Synopsis: The fundamental principles of chemistry, including atomic and molecular structure, bonding, elementary thermochemistry and thermodynamics, oxidation-reduction
GENERAL CHEMISTRY II - Chem 206. GENERAL CHEMISTRY II - Chem 206
 GENERAL CHEMISTRY II - Chem 206 Be curious o How do they determine how many calories are in food? o Why do we put salt on the roads in winter? o What does Beano do? o Why do stalactites and stalagmites
GENERAL CHEMISTRY II - Chem 206 Be curious o How do they determine how many calories are in food? o Why do we put salt on the roads in winter? o What does Beano do? o Why do stalactites and stalagmites
Announcements 13 Nov 2014
 Announcements 13 Nov 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 3 starts on Tues Nov 25 a. Covers Ch 9-12, HW 18-24 b. Late fee on Wed after Thanksgiving, 3 pm c. Closes on Thursday after Thanksgiving, 3 pm d. Jerika review
Announcements 13 Nov 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 3 starts on Tues Nov 25 a. Covers Ch 9-12, HW 18-24 b. Late fee on Wed after Thanksgiving, 3 pm c. Closes on Thursday after Thanksgiving, 3 pm d. Jerika review
NY Times 11/25/03 Physics L 22 Frank Sciulli slide 1
 NY Times /5/03 slide Thermodynamics and Gases Last Time specific heats phase transitions Heat and Work st law of thermodynamics heat transfer conduction convection radiation Today Kinetic Theory of Gases
NY Times /5/03 slide Thermodynamics and Gases Last Time specific heats phase transitions Heat and Work st law of thermodynamics heat transfer conduction convection radiation Today Kinetic Theory of Gases
Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Team Name: Team Number: Score: / 43. Made by Montgomery High School -
 1 Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Team Name: Team Number: Score: / 43 Made by Montgomery High School - montyscioly@gmail.com 2 Questions are worth between 1 and 3 points. Show calculations for all
1 Test Exchange Thermodynamics (C) Test Team Name: Team Number: Score: / 43 Made by Montgomery High School - montyscioly@gmail.com 2 Questions are worth between 1 and 3 points. Show calculations for all
Introduction to Chemical Thermodynamics. D. E. Manolopoulos First Year (13 Lectures) Michaelmas Term
 Introduction to Chemical Thermodynamics D. E. Manolopoulos First Year (13 Lectures) Michaelmas Term Lecture Synopsis 1. Introduction & Background. Le Chatelier s Principle. Equations of state. Systems
Introduction to Chemical Thermodynamics D. E. Manolopoulos First Year (13 Lectures) Michaelmas Term Lecture Synopsis 1. Introduction & Background. Le Chatelier s Principle. Equations of state. Systems
Pure Substance Properties and Equation of State
 Pure Substance Properties and Equation of State Pure Substance Content Pure Substance A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout is called a pure substance. Water, nitrogen, helium, and
Pure Substance Properties and Equation of State Pure Substance Content Pure Substance A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout is called a pure substance. Water, nitrogen, helium, and
HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICS PHY 522 Fall, 2010
 HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICS PHY 522 Fall, 2010 I. INSTRUCTOR Professor Lance De Long Office: CP363 (257-4775) Labs: CP75, CP158 (257-8883), ASTeCC A041 Office Hours: M 10:30-11:30 a.m.; T 8:30-9:30 a.m. II.
HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICS PHY 522 Fall, 2010 I. INSTRUCTOR Professor Lance De Long Office: CP363 (257-4775) Labs: CP75, CP158 (257-8883), ASTeCC A041 Office Hours: M 10:30-11:30 a.m.; T 8:30-9:30 a.m. II.
School of Chemical & Biological Engineering, Konkuk University
 School of Chemical & Biological Engineering, Konkuk University Chemistry is the science concerned with the composition, structure, and properties of matter, as well as the changes it undergoes during chemical
School of Chemical & Biological Engineering, Konkuk University Chemistry is the science concerned with the composition, structure, and properties of matter, as well as the changes it undergoes during chemical
CHEM 116 Phase Changes and Phase Diagrams
 CHEM 116 Phase Changes and Phase Diagrams Lecture 4 Prof. Sevian Please turn in extra credit assignments at the very beginning of class. Today s agenda Finish chapter 10 Partial pressures Vapor pressure
CHEM 116 Phase Changes and Phase Diagrams Lecture 4 Prof. Sevian Please turn in extra credit assignments at the very beginning of class. Today s agenda Finish chapter 10 Partial pressures Vapor pressure
Collective Effects. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics
 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 1, 17 March 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Collective
1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 1, 17 March 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Collective
CHEM1100 Summary Notes Module 2
 CHEM1100 Summary Notes Module 2 Lecture 14 Introduction to Kinetic Theory & Ideal Gases What are Boyle s and Charles Laws? Boyle s Law the pressure of a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional
CHEM1100 Summary Notes Module 2 Lecture 14 Introduction to Kinetic Theory & Ideal Gases What are Boyle s and Charles Laws? Boyle s Law the pressure of a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional
Fig Note the three different types of systems based on the type of boundary between system and surroundings.
 CHAPTER 1 LECTURE NOTES System, Surroundings, and States Fig. 1.4 Note the three different types of systems based on the type of boundary between system and surroundings. Intensive and Extensive Properties
CHAPTER 1 LECTURE NOTES System, Surroundings, and States Fig. 1.4 Note the three different types of systems based on the type of boundary between system and surroundings. Intensive and Extensive Properties
Collective Effects. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics
 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 1, 17 March 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Collective
Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 1, 17 March 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Collective
Chapter 13, Chemical Equilibrium
 Chapter 13, Chemical Equilibrium You may have gotten the impression that when 2 reactants mix, the ensuing rxn goes to completion. In other words, reactants are converted completely to products. We will
Chapter 13, Chemical Equilibrium You may have gotten the impression that when 2 reactants mix, the ensuing rxn goes to completion. In other words, reactants are converted completely to products. We will
Chem 105 Friday 3 Dec 2010
 Chem 105 Friday 3 Dec 010 Today: Kinetic-molecular theory Diffusion and effusion Course Questionnaires Real gases & Van der Waals equation Hour Exam 4 (Chap 9, 10, 11) Friday. Dec 10 A practice exam will
Chem 105 Friday 3 Dec 010 Today: Kinetic-molecular theory Diffusion and effusion Course Questionnaires Real gases & Van der Waals equation Hour Exam 4 (Chap 9, 10, 11) Friday. Dec 10 A practice exam will
Application of the First Law To The Construction of an Engine
 CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Fall 2014 Application of the First Law To The Construction of an Engine So, now we are in the thick of it. We have established a method for measuring the Internal Energy change
CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Fall 2014 Application of the First Law To The Construction of an Engine So, now we are in the thick of it. We have established a method for measuring the Internal Energy change
Equilibrium Lesson Plan and Handout for Chemistry I. High Tech High. Jay A. Haron, Ph.D. April 24, 2007
 Chemical Equilibrium Lesson Plan 1.. Equilibrium Lesson Plan and Handout for Chemistry I High Tech High Jay A. Haron, Ph.D. April 24, 2007. Chemical Equilibrium Lesson Plan 2 Equilibrium Lesson Plan and
Chemical Equilibrium Lesson Plan 1.. Equilibrium Lesson Plan and Handout for Chemistry I High Tech High Jay A. Haron, Ph.D. April 24, 2007. Chemical Equilibrium Lesson Plan 2 Equilibrium Lesson Plan and
Pine Hill Public Schools Curriculum
 Pine Hill Public Schools Curriculum Content Area: Course Title/ Grade Level: AP Chemistry / 11 or 12th grade Unit 1: Mathematics of Chemistry Duration: 1 week Unit 2: Atoms, molecules and Ions Duration:
Pine Hill Public Schools Curriculum Content Area: Course Title/ Grade Level: AP Chemistry / 11 or 12th grade Unit 1: Mathematics of Chemistry Duration: 1 week Unit 2: Atoms, molecules and Ions Duration:
Similarities and differences:
 How does the system reach equilibrium? I./9 Chemical equilibrium I./ Equilibrium electrochemistry III./ Molecules in motion physical processes, non-reactive systems III./5-7 Reaction rate, mechanism, molecular
How does the system reach equilibrium? I./9 Chemical equilibrium I./ Equilibrium electrochemistry III./ Molecules in motion physical processes, non-reactive systems III./5-7 Reaction rate, mechanism, molecular
Chapter 19 Entropy Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 20-1
 Chapter 19 Entropy Slide 20-1 Ch 19 & 20 material What to focus on? Just put out some practice problems Ideal gas how to find P/V/T changes. E.g., gas scaling, intro to the ideal gas law, pressure cooker,
Chapter 19 Entropy Slide 20-1 Ch 19 & 20 material What to focus on? Just put out some practice problems Ideal gas how to find P/V/T changes. E.g., gas scaling, intro to the ideal gas law, pressure cooker,
Chapter 10. Thermal Physics
 Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermal Physics Thermal physics is the study of Temperature Heat How these affect matter Thermal Physics, cont Descriptions require definitions of temperature, heat and internal
Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermal Physics Thermal physics is the study of Temperature Heat How these affect matter Thermal Physics, cont Descriptions require definitions of temperature, heat and internal
Physics 112 Spring 2014
 Physics 112 Spring 2014 Phys 112 (S12) Syllabus/introduction 1 Goals Deeper understanding of concepts: less mysterious Entropy Free energy Chemical potential Statistical mechanics fluctuations kinetic
Physics 112 Spring 2014 Phys 112 (S12) Syllabus/introduction 1 Goals Deeper understanding of concepts: less mysterious Entropy Free energy Chemical potential Statistical mechanics fluctuations kinetic
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS. Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5
 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
Kinetic Molecular Theory, Weak Interactions, States of Matter (Why do liquids & solids exist?)
 Kinetic Molecular Theory, Weak Interactions, States of Matter (Why do liquids & solids exist?) Themes for the day: 1. What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory? 2. ow do #1 & weak interactions help us with
Kinetic Molecular Theory, Weak Interactions, States of Matter (Why do liquids & solids exist?) Themes for the day: 1. What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory? 2. ow do #1 & weak interactions help us with
Big Idea 1: Structure of Matter Learning Objective Check List
 Big Idea 1: Structure of Matter Learning Objective Check List Structure of Matter Mole Concept: Empirical Formula, Percent Composition, Stoichiometry Learning objective 1.1 The student can justify the
Big Idea 1: Structure of Matter Learning Objective Check List Structure of Matter Mole Concept: Empirical Formula, Percent Composition, Stoichiometry Learning objective 1.1 The student can justify the
Introduction to Chemical Thermodynamics. (10 Lectures) Michaelmas Term
 Introduction to Chemical Thermodynamics Dr. D. E. Manolopoulos First Year (0 Lectures) Michaelmas Term Lecture Synopsis. Introduction & Background. Le Chatelier s Principle. Equations of state. Systems
Introduction to Chemical Thermodynamics Dr. D. E. Manolopoulos First Year (0 Lectures) Michaelmas Term Lecture Synopsis. Introduction & Background. Le Chatelier s Principle. Equations of state. Systems
Table of Contents [ttc]
![Table of Contents [ttc] Table of Contents [ttc]](/thumbs/89/97960614.jpg) Table of Contents [ttc] 1. Equilibrium Thermodynamics I: Introduction Thermodynamics overview. [tln2] Preliminary list of state variables. [tln1] Physical constants. [tsl47] Equations of state. [tln78]
Table of Contents [ttc] 1. Equilibrium Thermodynamics I: Introduction Thermodynamics overview. [tln2] Preliminary list of state variables. [tln1] Physical constants. [tsl47] Equations of state. [tln78]
Lecture 40: Equilibrium 1
 Lecture 40: Equilibrium 1 Read: BLB 15.1 15.3 HW: BLB 15:13,14,21 Sup 15:1 4 Know: concept of equilibrium equilibrium constant (K eq ) derivation of K p /K c relationship what magnitude of K eq means FINAL
Lecture 40: Equilibrium 1 Read: BLB 15.1 15.3 HW: BLB 15:13,14,21 Sup 15:1 4 Know: concept of equilibrium equilibrium constant (K eq ) derivation of K p /K c relationship what magnitude of K eq means FINAL
Dr. Fus Chemistry 1220 SPRING 2013 CHECKLIST: MW CLASS
 CHEMISTRY 1220 SPRING 2013 CHECKLIST: MW CLASS LECTURE #1: MONDAY, JANUARY 7 th Syllabus overview, course expectations, Mastering Chemistry registration, Polleverywhere registration, www.drfus.com Before
CHEMISTRY 1220 SPRING 2013 CHECKLIST: MW CLASS LECTURE #1: MONDAY, JANUARY 7 th Syllabus overview, course expectations, Mastering Chemistry registration, Polleverywhere registration, www.drfus.com Before
CHEMISTRY Survey of Physical Chemistry. Course Text Book References General Information McGill Policy statements Course outline
 CHEMISTRY Survey of Physical Chemistry Course Text Book References General Information McGill Policy statements Course outline COURSE CONTENT: (Top) The lecture recordings are available under MyCourses.
CHEMISTRY Survey of Physical Chemistry Course Text Book References General Information McGill Policy statements Course outline COURSE CONTENT: (Top) The lecture recordings are available under MyCourses.
Lecture 24. Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Lecture 4 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory Today s Topics: Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory of Gases Phase equilibria and phase diagrams Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is an idealized model for real gases that
Lecture 4 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory Today s Topics: Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory of Gases Phase equilibria and phase diagrams Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is an idealized model for real gases that
Thermal Physics. Energy and Entropy
 Thermal Physics Energy and Entropy Written by distinguished physics educator, this fresh introduction to thermodynamics, statistical mechanics and the study of matter is ideal for undergraduate courses.
Thermal Physics Energy and Entropy Written by distinguished physics educator, this fresh introduction to thermodynamics, statistical mechanics and the study of matter is ideal for undergraduate courses.
Chemistry. Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations. NC State University
 Chemistry Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations NC State University Thermodynamic state functions expressed in differential form We have seen that the internal energy is conserved and depends on mechanical (dw)
Chemistry Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations NC State University Thermodynamic state functions expressed in differential form We have seen that the internal energy is conserved and depends on mechanical (dw)
As you enter... (Write down the learning objective, the question and your answer.) What do you think it means for a reaction to occur spontaneously?
 Monday, March 23rd Learning objective 5.13: The student is able to predict whether or not a physical or chemical process is thermodynamically favored by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively)
Monday, March 23rd Learning objective 5.13: The student is able to predict whether or not a physical or chemical process is thermodynamically favored by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively)
Chemical Physics. Themodynamics Chemical Equilibria Ideal Gas Van der Waals Gas Phase Changes Ising Models Statistical Mechanics etc...
 Chemical Physics Themodynamics Chemical Equilibria Ideal Gas Van der Waals Gas Phase Changes Ising Models Statistical Mechanics etc... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/images/project/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclearweaponarchive.org/usa/tests/ukgrable2.jpg
Chemical Physics Themodynamics Chemical Equilibria Ideal Gas Van der Waals Gas Phase Changes Ising Models Statistical Mechanics etc... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/images/project/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclearweaponarchive.org/usa/tests/ukgrable2.jpg
Thermodynamically Favored Reactions
 Thermodynamically Favored Reactions Will go on its own- may need a little push activation energy Speed of the reaction doesn t matter 18.1 Rates of Reaction The heat given off by the corrosion reaction
Thermodynamically Favored Reactions Will go on its own- may need a little push activation energy Speed of the reaction doesn t matter 18.1 Rates of Reaction The heat given off by the corrosion reaction
Lecture Phase transformations. Fys2160,
 Lecture 12 01.10.2018 Phase transformations Fys2160, 2018 1 A phase transformation Discontinuous change in the properties of substance when the environent is changed infinitesimaly. Change between phases
Lecture 12 01.10.2018 Phase transformations Fys2160, 2018 1 A phase transformation Discontinuous change in the properties of substance when the environent is changed infinitesimaly. Change between phases
Gases and Kinetic Theory
 Gases and Kinetic Theory Chemistry 35 Fall 2000 Gases One of the four states of matter Simplest to understand both physically and chemically Gas Properties Low density Fluid Can be defined by their: 1.
Gases and Kinetic Theory Chemistry 35 Fall 2000 Gases One of the four states of matter Simplest to understand both physically and chemically Gas Properties Low density Fluid Can be defined by their: 1.
THE CORPUSCULAR NATURE OF MATTER AND ITS PHYSICAL STATES
 THE CORPUSCULAR NATURE OF MATTER AND ITS PHYSICAL STATES In this unit we are going to study the matter from a microscopic point of view using the kinetic theory. We will understand the properties of the
THE CORPUSCULAR NATURE OF MATTER AND ITS PHYSICAL STATES In this unit we are going to study the matter from a microscopic point of view using the kinetic theory. We will understand the properties of the
CHM Solids, Liquids, and Phase Changes (r15) Charles Taylor 1/9
 CHM 111 - Solids, Liquids, and Phase Changes (r15) - 2015 Charles Taylor 1/9 Introduction In CHM 110, we used kinetic theory to explain the behavior of gases. Now, we will discuss solids and liquids. While
CHM 111 - Solids, Liquids, and Phase Changes (r15) - 2015 Charles Taylor 1/9 Introduction In CHM 110, we used kinetic theory to explain the behavior of gases. Now, we will discuss solids and liquids. While
HEAT HISTORY. D. Whitehall
 1 HEAT HISTORY 18 th Century In the 18 th century it was assumed that there was an invisible substance called caloric. When objects got it was assumed that they gained caloric, therefore hot objects should
1 HEAT HISTORY 18 th Century In the 18 th century it was assumed that there was an invisible substance called caloric. When objects got it was assumed that they gained caloric, therefore hot objects should
Concepts of Thermodynamics
 Thermodynamics Industrial Revolution 1700-1800 Science of Thermodynamics Concepts of Thermodynamics Heavy Duty Work Horses Heat Engine Chapter 1 Relationship of Heat and Temperature to Energy and Work
Thermodynamics Industrial Revolution 1700-1800 Science of Thermodynamics Concepts of Thermodynamics Heavy Duty Work Horses Heat Engine Chapter 1 Relationship of Heat and Temperature to Energy and Work
Rate of Heating and Cooling
 Rate of Heating and Cooling 35 T [ o C] Example: Heating and cooling of Water E 30 Cooling S 25 Heating exponential decay 20 0 100 200 300 400 t [sec] Newton s Law of Cooling T S > T E : System S cools
Rate of Heating and Cooling 35 T [ o C] Example: Heating and cooling of Water E 30 Cooling S 25 Heating exponential decay 20 0 100 200 300 400 t [sec] Newton s Law of Cooling T S > T E : System S cools
CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry
 CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter 5 Alkene: Introduction Thermodynamics and Kinetics Midterm 2... Grades will be posted on Tuesday, Feb. 27 th.
CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter 5 Alkene: Introduction Thermodynamics and Kinetics Midterm 2... Grades will be posted on Tuesday, Feb. 27 th.
Lecture 2-3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability
 Lecture 2-3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions Van der Waals Interactions
Lecture 2-3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions Van der Waals Interactions
UNIVERSITY OF MACAU DEPARTMENT OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ENGINEERING CHEM101 - Chemistry Syllabus 1 st Semester 2010/2011 Part A Course Outline
 UNIVERSITY OF MACAU DEPARTMENT OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ENGINEERING CHEM101 - Chemistry Syllabus 1 st Semester 2010/2011 Part A Course Outline Compulsory course in Electromechanical Engineering Course description:
UNIVERSITY OF MACAU DEPARTMENT OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ENGINEERING CHEM101 - Chemistry Syllabus 1 st Semester 2010/2011 Part A Course Outline Compulsory course in Electromechanical Engineering Course description:
ALE 24. Colligative Properties (Part 2)
 Name Chem 162, Section: Group Number: ALE 24. Colligative Properties (Part 2) (Reference: 13.6 Silberberg 5 th edition) Why is calcium chloride spread on highways in the North during the Winter? The Model:
Name Chem 162, Section: Group Number: ALE 24. Colligative Properties (Part 2) (Reference: 13.6 Silberberg 5 th edition) Why is calcium chloride spread on highways in the North during the Winter? The Model:
CHEMISTRY 104 Summer Course Information
 Course Director: Tom Hummel 3016 Chem Annex 333-9111 tjhummel@illinois.edu Required Materials: Course Information A. Chemistry 104 Lecture/Quiz Chemistry by Zumdahl, Zumdahl, and Decoste 10th ed. Partial
Course Director: Tom Hummel 3016 Chem Annex 333-9111 tjhummel@illinois.edu Required Materials: Course Information A. Chemistry 104 Lecture/Quiz Chemistry by Zumdahl, Zumdahl, and Decoste 10th ed. Partial
CONTENTS 1. In this course we will cover more foundational topics such as: These topics may be taught as an independent study sometime next year.
 CONTENTS 1 0.1 Introduction 0.1.1 Prerequisites Knowledge of di erential equations is required. Some knowledge of probabilities, linear algebra, classical and quantum mechanics is a plus. 0.1.2 Units We
CONTENTS 1 0.1 Introduction 0.1.1 Prerequisites Knowledge of di erential equations is required. Some knowledge of probabilities, linear algebra, classical and quantum mechanics is a plus. 0.1.2 Units We
Physics 360 Review 3
 Physics 360 Review 3 The test will be similar to the second test in that calculators will not be allowed and that the Unit #2 material will be divided into three different parts. There will be one problem
Physics 360 Review 3 The test will be similar to the second test in that calculators will not be allowed and that the Unit #2 material will be divided into three different parts. There will be one problem
Physics 18, Introductory Physics I for Biological Sciences Spring 2010
 Physics 18 page 1/6 Physics 18, Introductory Physics I for Biological Sciences Spring 2010 - Course Description - Instructor: Dr. Derrick Kiley Office: AOB 176; Office Phone 209 228-3076 E-mail Address:
Physics 18 page 1/6 Physics 18, Introductory Physics I for Biological Sciences Spring 2010 - Course Description - Instructor: Dr. Derrick Kiley Office: AOB 176; Office Phone 209 228-3076 E-mail Address:
Chapter 5. On-line resource
 Chapter 5 The water-air heterogeneous system On-line resource on-line analytical system that portrays the thermodynamic properties of water vapor and many other gases http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/fluid/
Chapter 5 The water-air heterogeneous system On-line resource on-line analytical system that portrays the thermodynamic properties of water vapor and many other gases http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/fluid/
Physics 160 Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics: Lecture 2. Dr. Rengachary Parthasarathy Jan 28, 2013
 Physics 160 Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics: Lecture 2 Dr. Rengachary Parthasarathy Jan 28, 2013 Chapter 1: Energy in Thermal Physics Due Date Section 1.1 1.1 2/3 Section 1.2: 1.12, 1.14, 1.16,
Physics 160 Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics: Lecture 2 Dr. Rengachary Parthasarathy Jan 28, 2013 Chapter 1: Energy in Thermal Physics Due Date Section 1.1 1.1 2/3 Section 1.2: 1.12, 1.14, 1.16,
Obj: Observe and describe states of matter.
 Do Now Date: March 6, 2017 Obj: Observe and describe states of matter. Copy and Solve: 1. If Dr. B has a 5.0L container at a pressure of 2 atm, how much pressure would it place on the walls of a 2.5L container?
Do Now Date: March 6, 2017 Obj: Observe and describe states of matter. Copy and Solve: 1. If Dr. B has a 5.0L container at a pressure of 2 atm, how much pressure would it place on the walls of a 2.5L container?
Lecture 24. Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Lecture 4 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory Today s Topics: Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory of Gases Phase equilibria and phase diagrams Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is an idealized model for real gases that
Lecture 4 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory Today s Topics: Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory of Gases Phase equilibria and phase diagrams Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is an idealized model for real gases that
Physics 161 Lecture 14 Kinetic Theory of Gas. October 18, 2018
 Physics 161 Lecture 14 Kinetic Theory of Gas October 18, 2018 1 Exam 1, Thursday 18 Oct The exam will start promptly at 10:00pm. You will be permitted to open your exam at 10:00pm. You will have until
Physics 161 Lecture 14 Kinetic Theory of Gas October 18, 2018 1 Exam 1, Thursday 18 Oct The exam will start promptly at 10:00pm. You will be permitted to open your exam at 10:00pm. You will have until
Lecture 11: Models of the chemical potential
 Lecture 11: 10.15.05 Models of the chemical potential Today: LAST TIME... 2 MORE ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CHEMICAL POTENTIAL AND GIBBS FREE ENERGY... 3 Chemical potentials in multicomponent systems
Lecture 11: 10.15.05 Models of the chemical potential Today: LAST TIME... 2 MORE ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CHEMICAL POTENTIAL AND GIBBS FREE ENERGY... 3 Chemical potentials in multicomponent systems
Chemistry 451. Prerequisites: CHEM 013, MATH 141, PHYS 202 or PHYS 212. Prof. Mueller/Sykes Chemistry 451 Spring 2004 Lecture 1-1
 Chemistry 451 CHEM 451 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY ( 3 credits) Introduction to chemical principles, including properties of matter and fundamentals of chemical thermodynamics. Prerequisites: CHEM 013, MATH 141,
Chemistry 451 CHEM 451 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY ( 3 credits) Introduction to chemical principles, including properties of matter and fundamentals of chemical thermodynamics. Prerequisites: CHEM 013, MATH 141,
An Introduction To Thermodynamics and Kinetics. for. Introduction To Petrography : GEOL 2335 University of Houston Spring Semester, 1996
 Introduction An Introduction To Thermodynamics and Kinetics for Introduction To Petrography : GEOL 2335 University of Houston Spring Semester, 1996 A rock sample contains calcite, quartz and wollastonite.
Introduction An Introduction To Thermodynamics and Kinetics for Introduction To Petrography : GEOL 2335 University of Houston Spring Semester, 1996 A rock sample contains calcite, quartz and wollastonite.
UNIT 1: CHEMISTRY FOUNDATIONS
 Advanced Placement AP Chemistry builds students' understanding of the nature and reactivity of matter. After studying chemical reactions and electrochemistry, students move on to understand how the chemical
Advanced Placement AP Chemistry builds students' understanding of the nature and reactivity of matter. After studying chemical reactions and electrochemistry, students move on to understand how the chemical
Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 Different ways to increase the internal energy of system: 2 Joule s apparatus
Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 Different ways to increase the internal energy of system: 2 Joule s apparatus
Ch 6 Gases 6 GASES. Property of gases. pressure = force/area
 6 GASES Gases are one of the three states of matter, and while this state is indispensable for chemistry's study of matter, this chapter mainly considers the relationships between volume, temperature and
6 GASES Gases are one of the three states of matter, and while this state is indispensable for chemistry's study of matter, this chapter mainly considers the relationships between volume, temperature and
Chapter 19. Chemical Thermodynamics. Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 Enthalpy A thermodynamic quantity that equal to the internal energy of a system plus the product of its volume and pressure exerted on it by its surroundings; Enthalpy is the amount of energy
Chapter 19 Enthalpy A thermodynamic quantity that equal to the internal energy of a system plus the product of its volume and pressure exerted on it by its surroundings; Enthalpy is the amount of energy
Chemistry 313 Course Syllabus / Fall 2006
 Chemistry 313 Course Syllabus / Fall 2006 Instructor: Dr. Caleb A. Arrington Course Number and Title: Chem 313 Physical Chemistry I (Thermodynamics) Meeting Place: RMSC-308 Meeting Time: M,W,&F 10:30 11:50
Chemistry 313 Course Syllabus / Fall 2006 Instructor: Dr. Caleb A. Arrington Course Number and Title: Chem 313 Physical Chemistry I (Thermodynamics) Meeting Place: RMSC-308 Meeting Time: M,W,&F 10:30 11:50
Chapter 23 Changes of Phase. Conceptual Physics Chapter 23 1
 Chapter 23 Changes of Phase Conceptual Physics Chapter 23 1 Kinetic Theory Matter exists in three common states or phases solid, liquid and gas. A fourth state plasma makes up over 90% of our universe.
Chapter 23 Changes of Phase Conceptual Physics Chapter 23 1 Kinetic Theory Matter exists in three common states or phases solid, liquid and gas. A fourth state plasma makes up over 90% of our universe.
Warm up. 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]?
![Warm up. 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]? Warm up. 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]?](/thumbs/78/77877522.jpg) Warm up 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]? 4) What is the concentration of H 2 SO 4 if 30.1 ml
Warm up 1) What is the conjugate acid of NH 3? 2) What is the conjugate base of HNO 2? 3) If the ph is 9.2, what is the [H 3 O + ], poh, and [OH - ]? 4) What is the concentration of H 2 SO 4 if 30.1 ml
CHE 371: Kinetics and Thermodynamics Fall 2008
 CHE 371: Kinetics and Thermodynamics Fall 2008 Class Meetings: Lecture: M, T, W, F 9:00 AM, Olin 103 Laboratory: T, W 1:30-5:20 PM, R 2:30-6:20 PM Instructor: Prof. Amanda Nienow, Nobel 106C, 933-7327,
CHE 371: Kinetics and Thermodynamics Fall 2008 Class Meetings: Lecture: M, T, W, F 9:00 AM, Olin 103 Laboratory: T, W 1:30-5:20 PM, R 2:30-6:20 PM Instructor: Prof. Amanda Nienow, Nobel 106C, 933-7327,
16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit. Lecture 2 (9/11/17)
 16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit By Anthony Quintano - https://www.flickr.com/photos/quintanomedia/15071865580, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=38538291
16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit By Anthony Quintano - https://www.flickr.com/photos/quintanomedia/15071865580, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=38538291
CHEM 1420: Physical Chemistry 2 Thermodynamics, Statistical Mechanics, and Kinetics
 CHEM 1420: Physical Chemistry 2 Thermodynamics, Statistical Mechanics, and Kinetics Spring 2018 Term 2184 Lecture: TTh 9:30 10:45 228 Eberly Hall Recitation: T 4:00 4:50 pm 307 Eberly Sean Garrett-Roe
CHEM 1420: Physical Chemistry 2 Thermodynamics, Statistical Mechanics, and Kinetics Spring 2018 Term 2184 Lecture: TTh 9:30 10:45 228 Eberly Hall Recitation: T 4:00 4:50 pm 307 Eberly Sean Garrett-Roe
van der Waals Isotherms near T c
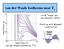 van der Waals Isotherms near T c v d W loops are not physical. Why? Patch up with Maxwell construction van der Waals Isotherms, T/T c van der Waals Isotherms near T c Look at one of the van der Waals isotherms
van der Waals Isotherms near T c v d W loops are not physical. Why? Patch up with Maxwell construction van der Waals Isotherms, T/T c van der Waals Isotherms near T c Look at one of the van der Waals isotherms
States of matter Part 1
 Physical pharmacy I 1. States of matter (2 Lectures) 2. Thermodynamics (2 Lectures) 3. Solution of non-electrolyte 4. Solution of electrolyte 5. Ionic equilibria 6. Buffered and isotonic solution Physical
Physical pharmacy I 1. States of matter (2 Lectures) 2. Thermodynamics (2 Lectures) 3. Solution of non-electrolyte 4. Solution of electrolyte 5. Ionic equilibria 6. Buffered and isotonic solution Physical
THERMODYNAMICS. The science that deals with the physical and chemical changes of matter due to work and heat flow
 THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics: (From Greek: thermos = heat and dynamic = change) The science that deals with the physical and chemical changes of matter due to work and heat flow Matter: The material of
THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics: (From Greek: thermos = heat and dynamic = change) The science that deals with the physical and chemical changes of matter due to work and heat flow Matter: The material of
Thermodynamics (Lecture Notes) Heat and Thermodynamics (7 th Edition) by Mark W. Zemansky & Richard H. Dittman
 Thermodynamics (Lecture Notes Heat and Thermodynamics (7 th Edition by Mark W. Zemansky & Richard H. Dittman 2 Chapter 1 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics 1.1 Macroscopic Point of View If
Thermodynamics (Lecture Notes Heat and Thermodynamics (7 th Edition by Mark W. Zemansky & Richard H. Dittman 2 Chapter 1 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics 1.1 Macroscopic Point of View If
Lecture 43: Equilibrium 4
 Lecture 43: Equilibrium 4 Read: BLB 15.6 15.7 HW: BLB 15:51,53,70 Sup 15:11 13 Know: LeChatelierʼs principle catalysts math refresher in BLB Appendix A Need help?? Get help!! TAs in CRC (211 Whitmore)
Lecture 43: Equilibrium 4 Read: BLB 15.6 15.7 HW: BLB 15:51,53,70 Sup 15:11 13 Know: LeChatelierʼs principle catalysts math refresher in BLB Appendix A Need help?? Get help!! TAs in CRC (211 Whitmore)
More Thermodynamics. Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes
 More Thermodynamics Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes Carnot Cycle Efficiency of Engines Entropy More Thermodynamics 1 Specific Heat of Gases
More Thermodynamics Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes Carnot Cycle Efficiency of Engines Entropy More Thermodynamics 1 Specific Heat of Gases
Unit 7 (B) Solid state Physics
 Unit 7 (B) Solid state Physics hermal Properties of solids: Zeroth law of hermodynamics: If two bodies A and B are each separated in thermal equilibrium with the third body C, then A and B are also in
Unit 7 (B) Solid state Physics hermal Properties of solids: Zeroth law of hermodynamics: If two bodies A and B are each separated in thermal equilibrium with the third body C, then A and B are also in
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases
 The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases kinetic-molecular theory of gases Originated with Ludwig Boltzman and James Clerk Maxwell in the 19th century Explains gas behavior on the basis of the motion of individual
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases kinetic-molecular theory of gases Originated with Ludwig Boltzman and James Clerk Maxwell in the 19th century Explains gas behavior on the basis of the motion of individual
Chmy 361 Elements of Physical Chemistry,
 Chmy 361 Elements of Physical Chemistry, website: http://www.chemistry.montana.edu/callis/courses/chmy361 Instructor: Pat Callis office 55 Chem/Biochem Bldg (CBB) email: pcallis@montana. edu phone: 994-5414
Chmy 361 Elements of Physical Chemistry, website: http://www.chemistry.montana.edu/callis/courses/chmy361 Instructor: Pat Callis office 55 Chem/Biochem Bldg (CBB) email: pcallis@montana. edu phone: 994-5414
