INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES
|
|
|
- Josephine Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 5(6): November-December 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES Pharmaceutical Sciences Review Article!!! Received: ; Revised: ; Accepted: HPLC-NMR HYPHENATED TECHNIQUE-REVIEW K. D. Khatavkar*, D. J. Joshi, A. S. Patil Vansantidevi Patil Institute of Pharmacy, Kodoli, Tal. Panhala, Dist. Kolhapur, (M S), India Keywords: HPLC-NMR, GC-MS, GC-IR For Correspondence: K. D. Khatavkar Vansantidevi Patil Institute of Pharmacy, Kodoli, Tal. Panhala, Dist. Kolhapur, (M S), India ABSTRACT The hyphenated technique is developed from the coupling of a separation technique and an on-line spectroscopic detection technology. The remarkable improvements in hyphenated analytical methods over the last two decades have significantly broadened their applications in the analysis of biomaterials, especially natural products. In this reviewed article, recent advances in the applications of various hyphenated techniques, e.g., HPLC-NMR, GCMS, LC-MS, GC-IR etc. also including the different instrumentation required for this technique. In the context of pre-isolation analyses of crude extracts or fraction from various natural sources, isolation and on-line detection of natural products,. HPLC-NMR hyphenation offers numerous advantages compared to direct HPLC-NMR methods. Multiple trapping leads to a dramatic increase of analyte amounts available for NMR, enabling acquisition of high-quality 2D NMR data within a short time. Other new developments, including combination of solenoidal coil capillary flow-probes with microflow HPLC, are also discussed. 90 Full Text Available On
2 1] DEFINATION A Hyphenated technique is combination or coupling of two different analytical techniques with the help of proper interface. Mainly chromatographic techniques are combined with spectroscopic techniques. The term hyphenated techniques ranges from the combination of separation-separation, separation-identification &identification identification techniques. The hyphenation of these techniques leads to better analysis of the components. Hyphenated techniques show specificity and sensitivity. 1.2] Chromatography - Produces pure or nearly pure fractions of chemical components in a Mixture 1.3] Spectroscopy Produces selective information for identification using standards or library spectra. The coupling of a separation technique and an on-line spectroscopic detection technology will lead to hyphenated technique. A couple of decades ago, Hirschfield introduced the term hyphenation to refer to the on-line combination of a separation technique and one or more spectroscopic detection techniques.this technique, developed from a marriage of a separation technique and a spectroscopic detection technique, is nowadays known as hyphenated technique. In recent years, hyphenated techniques have received ever-increasing attention as the principal means to solve complex analytical problems. The power of combining separation technologies with spectroscopic techniques has been demonstrated over the years for both quantitative and qualitative analysis of unknown compounds in complex natural product extracts or fractions. To obtain structural information leading to the identification of the compounds present in a crude sample, liquid chromatography (LC), usually a highperformance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), or capillary electrophoresis (CE) is linked to spectroscopic detection techniques, e.g., Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR), photodiode array (PDA) UV vis absorbance or fluorescence emission, mass spectroscopy (MS), and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), resulting in the introduction of various modern hyphenated techniques, e.g., CE-MS, GC-MS, LC-MS, and LC-NMR. HPLC is the most widely used analytical separation technique for the qualitative and quantitative determination of compounds in natural product extracts. The physical connection of HPLC and MS or NMR has increased the capability of solving structural problems of complex natural products. Because of the greater sensitivity, LC-MS has been more extensively used than LC-NMR. The hyphenation does not always have to be between two techniques; the coupling of separation and detection techniques can involve more than one separation or detection techniques, e.g., LC-PDA-MS, LC-MS-MS, LC-NMR-MS, 91 Full Text Available On
3 LCPDA-NMR-MS, and the like. Where trace analysis is vital, and the analytic enrichment is essential, on-line coupling with solid-phase extraction (SPE), solid-phase micro extraction or large volume injection (LVI) can be incorporated to build in a more powerful integrated system, e.g., SPE-LC-MS or LVI-GC-MS. The two key elements in natural product research are the isolation and purification of compounds present in crude extracts or fractions obtained from various natural sources, and the unambiguous identification of the isolated compounds. Thus, the on-line characterization of secondary metabolites in crude natural product extracts or fractions demands high degree of sophistication, and richness of structural information, sensitivity, and selectivity. The development of various hyphenated techniques has provided the natural product researchers with extremely powerful new tools that can provide excellent separation efficiency as well as acquisition of on-line complementary spectroscopic data on an LC or GC peak of interest within a complex mixture. The main focus of this chapter is to provide an overview of basic operational principles of various modern hyphenated techniques and to present several literature examples of applications of these techniques. Detailed information on the principle, history, instrumentation, and methodology is available in li 2]WHY IT IS USED? Highly selective Highly sensitive Use in many Applications purifications Polymerization studies Natural products Pharmaceuticals FIG:-1 Schematic presentation of Hyphenation of chromatographic and spectrometric techniques. 92 Full Text Available On
4 2.1] Advantages of hyphenated techniques 1. Fast and accurate analysis 2. Higher degree of automation 3. Higher sample throughput 4. Better reproducibility 5. Reduction of contamination due to its closed system 6. Separation and quantification achieved at same time. 2.2] List of Hyphenated Techniques 1. GC-MS 2. LC-MS 3. LC-NMR 4. EC-MS 5. CE-MS 6. GC-IR 7. LC-MS-MS 8. GC-MS-MS 9. GC-GC-MS 10. GC-NMR 11. GC-AES 3] GC-MS GC is able to separate the volatile and semi volatile compounds but it unable to identify them whereas MS can identify the compound by giving its structural information at molecular level but it unable to separate them. Therefor the combination of these two techniques is took place shortly after the development of GC. GC-MS was the first technique to be hyphenated and this technique can confirm the organic volatile semi volatile compounds and residual solvents with great resolution. For the analysis of the compound by GC-MS the compound should possess the property such as volatility and thermal stability.these two techniques highly compatible with each other, the sample is in the vapour phase in both the techniques. But there is incompatibility between two techniques is GC is operate at high pressure (760 torr) and in this the Carrier gas is present whereas in case of mass spectroscopy it operates at a vaccum10 6 to l0 5torr. 93 Full Text Available On
5 3.1] Instrumentation and Working Vaporized analyte when carried through the GC column with the help of heated carrier gas the separation occurs in column only. Carrier can also be called as the mobile phase e.g. helium. Distinguishable interactions of analyte between mobile phase and stationary phase lead to separation of the compounds. The separation of the analyte is also depend on the column's dimensions (length, diameter, film thickness), type of carrier gas, column temperature (gradient) and the properties of the stationary phase. The sample travel through the length of column the difference in the boiling point and other chemical properties lead to separation of the components of the mixture. The components will be having differences in elution time and retention time due to their different adsorption or difference in the partition between mobile phase and the stationary phase resp. Then the separated components of the mixture will enter into the MS through an interphase. This is followed by ionization, mass analysis and detection of mass-to charge ratios of ions generated from each analyte by the mass spectrometer. An interface like effusion separator, jet/orifice separator & membrane separator can be used to connect GC with MS The process of ionisation not only ionise the molecule but also break the molecule into the fragments and detect these fragments with the help of electron impact ionisation and chemical ionisation The molecular ion of analyte form a finger print spectrum which is different from other analytes. GC-MS is important tool in analytical chemistry because these techniques accurately separate, identify and provide information about structure and composition from very less sample. The advantage of this technique is sometimes two different analyte will have same mass spectrum but the retention time of both the analytes is different so such type of analytes can be separated or analyses with the help of GC-MS. Two widely used Ionization techniques in GCMS are the electron impact ionization (EI) and the alternative chemical ionization (CI) in either positive or negative modes. Fig 2: Schematic presentation of GC-MS 94 Full Text Available On
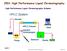
6 3.2] Application GC-MS 1. Quantitation of pollutants in drinking and waste water using official U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) methods. 2. Quantitation of drug in metabolites and urine is done for pharmacological and forensic use. 3. Identification of unknown organic compounds in hazardous waste dumps and reaction products by synthetic organic chemistry. 4. Used for drug analysis, pesticide and herbicide detection. 4] HPLC- NMR HPLC-NMR is the hyphenated technique in which HPLC is combined with the NMR. This technique is widely used for the analysis of complex mixtures which contain unknown impurities, natural products and synthetic polymers. In LC-NMR LC does the separation and NMR does the identification of the separated components. Fig:3 Schematic presentation of HPLC-NMR 4.1] Instrumentation and working HPLC-NMR is the sensitive method because the sensitivity of the NMR can be increased by use of highly magnetic field magnets and highly sensitive probes, and maturation of peripheral technologies, such as solvent elimination Technology and automatic measurement 95 Full Text Available On
7 software suitable for multicomponent analysis. Stronger the external magnetic field is, the higher the sensitivity is. The improvement in sensitivity has made for a large red uction in measurement time. The compounds showing complex spectra can also be easily analyzed with the help of increase in magnetic field which will improve the signal resolution. 4.2] Application OF HPLC-NMR 1. Identification of drug degradation products. 2. Low level impurities can be isolated and identified. 3. This technique is used for tracking pesticides, herbicides & organic pollutant for environmental monitoring. 5] GC-IR GC-IR technique is hyphenation of gas chromatography and Infrared spectroscopy. This technique is very sensitive, very expensive, sample recovery is also possible because IR is non-destructive technique in this technique the GC does the separation part where as IR perform the function of identification. Gas chromatography separate s components of The analyte. These components will travel through the column. These two techniques are linked through glass column or vacuum tubes. Interface used in this technique is internally gold coated small glass pipe connected to column by narrow tubing.light pipe is heated in order to rid condensation and maximize path length for enhanced sensitivity. Effluent from GC is directly forwarded into the heated pipe of IR at atmospheric pressure. Infrared red spectroscopy identifies thecompound by identifying the functional groups. 5.1] Application GC-IR 1. Pharmaceutical, Industrial 2. DNA Analysis of blood samples, other fluid. 6] APPLICATION OF HYPHENATED TECHNIQUES IN NATURAL PRODUCT ANALYSIS 6.1] Isolation and analysis of natural products Crude natural product extracts, which represent extremely complex mixtures of numerous compounds, can be analyzed successfully by using appropriate hyphenated techniques. Among the various hyphenated techniques, LC-PDA and LC-MS are the two most extensively used for natural product analysis. LC-NMR, as well as different multiple hyphenated techniques like LC-PDA-NMR-MS have also become popular most recently. LC- MS, if the ionization technique is chosen appropriately, can be an extremely powerful and informative tool for screening crude plant extracts. The currently available various types of 96 Full Text Available On
8 LC-MS systems allow the analysis of small nonpolar compounds to large polar constituents like oligosaccharides, proteins, and tannins present in natural product extracts. 6.2] Alkaloids Alkaloids are a large group of nitrogen-containing secondary metabolites of plant, microbial, or animal origin. Various hyphenated techniques have been used in the analysis of several types of alkaloids to date. With the development and wider availability of bench-top systems, GC-MS has become the method of choice for the analysis of various pyrolizidine and quinolizidine types of alkaloids. Quinolizidine alkaloids, the main class of alkaloids found in the family Leguminosae, have been analyzed by GC-MS recently.most of these alkaloids are sufficiently volatile and thermostable under GC conditions to permit analysis without chemical modification. However, some hydroxylatedpyrolizidine alkaloids need to be analyzed as their trimethylsilyl derivatives. Ephedrine-type alkaloids, in dietary supplements containing the Chinese herb ma huang, were analyzed by GC-MS and GC-FTIR. 6.3] Coumarins The coumarins are the largest class of 1-benzopyran derivatives that are found mainly in higher plants. HPLC-PDA can be used successfully in the analysis of various phenolic compounds, including coumarins, because of the presence of significant amounts of chromophores in these molecules. The HPLC-PDA determination of coumarins, where absorption spectra are registered with a PDA detector, provides useful information about the identity of the molecule including oxidation pattern. The retention time together with the UV spectrum of individual peaks can be considered characteristic, and can easily be used to detect known coumarins in a crude extract. The coupling of MS to LC-PDA provides further structural information that is helpful for on-line identification of individual coumarins in any crude extract. Various coumarins together with other oxygen heterocyclic compounds, e.g., psoralens and polymethoxylated flavones, present in the nonvolatile residue of the citrus essential oils of mandarin, sweet orange, bitter orange, bergamot, and grapefruit, were analyzed by atmospheric pressure ionization (API) LC-MS system equipped with an APCI probe in positive ion mode.[27] Recording MS spectra at different voltages provided information on molecular weight as well as fragment ions, and this allowed the identification of the main components in the extracts. In this study, cold-pressed citrus oils were analyzed by a Shimadzu LC system coupled with UV and MS detector with an APCI interface. The LC separation was carried out on a C18 Pinnacle column ( mm, 5 mm), eluted isocratically or using a gradient at a flow rate of 1 ml/min with the solvent mixture: solvent 97 Full Text Available On
9 A (THF:ACN:MeOH: water¼15:5:22:58) and solvent B (100% ACN). As coumarins are UV-absorbing compounds, they could be detected at 315 nm. The MS acquisition conditions were as follows: probe high voltage, 4 kv; APCI temperature, 400 C; nebulizing gas (N2) flow rate, 2.5 L/min; curved desolvation line (CDL) voltage, 25.5 V; CDL temperature, 230 C; deflector voltage, 25 and 60 V; and acquisition mode SCAN, m/z. 6.4] Carotenoids This group of natural products includes the hydrocarbons (carotenes) and their oxygenated derivatives (xanthophylls). LC-TLS has been applied successfully for the determination of carotenoids in four marine phytoplankton species, and a good degree of separation of diadinoxanthin, diatoxanthin, and other carotenoids has been achieved by isocratic HPLC elution with a greater sensitivity and selectivity than UV detection. This technique has allowed the monitoring of the interconversion of diadinoxanthin to diatoxanthin, and changes of other carotenoids under different light conditions LC-TLS has also been found to be an ultrasensitive method for determination of b-carotene in fish oil-based supplementary drugs. 7] CONCLUSION The technique developed from the coupling of a separation technique and an on-line spectroscopic detection technology is known as hyphenated technique. The remarkable improvements in hyphenated analytical methods over the last two decades have significantly broadened their applications in the analysis of biomaterials, especially natural products. In this article, recent advances in the applications of various hyphenated techniques, e.g., GC- MS, LC-MS, LC-FTIR, LC-NMR, CE-MS, etc. in the context of preisolation analyses of crude extracts or fraction from various natural sources, isolation and on-line detection of natural products, chemotaxonomic studies, chemical fingerprinting, quality control of herbal products, dereplication of natural products, and metabolomic studies are discussed with appropriate examples. Particular emphasis is given on the hyphenated techniques that involve LC as the separation tool. 8] REFERENCES 1. Guo X, Lankmayr E, Hyphenated Techniques ingas Chromatography, Institute of AnalyticalChemistry and Food Chemistry, Graz Universityof Technology, Austria, Londhe SV, Mulgund SV, Chitre TS, Mallade PS,Barival JB, Jain KS. Hyphenated techniques in analytical world, Indian J Pharm educ Res dec 2008; 42(4). 3. Duncan WP, kirk O, Encyclopedia of chemical technology, California,johnwiley& sons vol Vogel M, Karst U. Electrochemistry mass spectrometry: an emerging hyphenated technique for bioanalysis Springer- Verlag. Anal BioanalChem 2012; 403: Wilson ID, Brinkman UA. Hyphenation and hypernation: the practice and prospects of multiple hyphenation. J Chromatogr A. 2003;1000: [PubMed] 6. Wolfender JL, Ndjoko K, Hostettmann K. LC/NMR in natural products chemistry. Curr Org Chem.1998;2: Joshi RR, Gupta KR and Patil SS: Hyphenated Technique- A Boon to Analytical World. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 3(11); Full Text Available On
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis
 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis Hansen, Steen ISBN-13: 9780470661222 Table of Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1 1.2 The
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis Hansen, Steen ISBN-13: 9780470661222 Table of Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1 1.2 The
LC-MS Based Metabolomics
 LC-MS Based Metabolomics Analysing the METABOLOME 1. Metabolite Extraction 2. Metabolite detection (with or without separation) 3. Data analysis Metabolite Detection GC-MS: Naturally volatile or made volatile
LC-MS Based Metabolomics Analysing the METABOLOME 1. Metabolite Extraction 2. Metabolite detection (with or without separation) 3. Data analysis Metabolite Detection GC-MS: Naturally volatile or made volatile
Introduction. Chapter 1. Learning Objectives
 Chapter 1 Introduction Learning Objectives To understand the need to interface liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. To understand the requirements of an interface between liquid chromatography
Chapter 1 Introduction Learning Objectives To understand the need to interface liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. To understand the requirements of an interface between liquid chromatography
Tips & Tricks GPC/SEC: Quantify and Get More Than Molar Mass Averages
 Tips & Tricks GPC/SEC: Quantify and Get More Than Molar Mass Averages Daniela Held, PSS Polymer Standards Service GmbH, Mainz, Germany Gel permeation chromatography/size-exclusion chromatography (GPC/SEC)
Tips & Tricks GPC/SEC: Quantify and Get More Than Molar Mass Averages Daniela Held, PSS Polymer Standards Service GmbH, Mainz, Germany Gel permeation chromatography/size-exclusion chromatography (GPC/SEC)
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37 Most analytes separated by HPLC are thermally stable and non-volatile (liquids) (unlike in GC) so not ionized easily by EI or CI techniques. MS must be at
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37 Most analytes separated by HPLC are thermally stable and non-volatile (liquids) (unlike in GC) so not ionized easily by EI or CI techniques. MS must be at
3) In CE separation is based on what two properties of the solutes? (3 pts)
 Final Exam Chem 311 Fall 2002 December 16 Name 1) (3 pts) In GC separation is based on the following two properties of the solutes a) polarity and size b) vapor pressure and molecular weight c) vapor pressure
Final Exam Chem 311 Fall 2002 December 16 Name 1) (3 pts) In GC separation is based on the following two properties of the solutes a) polarity and size b) vapor pressure and molecular weight c) vapor pressure
TANDEM MASS SPECTROSCOPY
 TANDEM MASS SPECTROSCOPY 1 MASS SPECTROMETER TYPES OF MASS SPECTROMETER PRINCIPLE TANDEM MASS SPECTROMETER INSTRUMENTATION QUADRAPOLE MASS ANALYZER TRIPLE QUADRAPOLE MASS ANALYZER TIME OF FLIGHT MASS ANALYSER
TANDEM MASS SPECTROSCOPY 1 MASS SPECTROMETER TYPES OF MASS SPECTROMETER PRINCIPLE TANDEM MASS SPECTROMETER INSTRUMENTATION QUADRAPOLE MASS ANALYZER TRIPLE QUADRAPOLE MASS ANALYZER TIME OF FLIGHT MASS ANALYSER
LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY-MASS SPECTROMETRY (LC/MS) Presented by: Dr. T. Nageswara Rao M.Pharm PhD KTPC
 LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY-MASS SPECTROMETRY (LC/MS) Presented by: Dr. T. Nageswara Rao M.Pharm PhD KTPC INTRODUCTION Principle: LC/MS is a technique that combines physical separation capabilities of liquid
LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY-MASS SPECTROMETRY (LC/MS) Presented by: Dr. T. Nageswara Rao M.Pharm PhD KTPC INTRODUCTION Principle: LC/MS is a technique that combines physical separation capabilities of liquid
CHROMATOGRAPHY. The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments.
 CHROMATOGRAPHY The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments. THEORY OF CHROMATOGRAPHY: Separation of two sample components in
CHROMATOGRAPHY The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments. THEORY OF CHROMATOGRAPHY: Separation of two sample components in
Chromatography. Gas Chromatography
 Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
CHMC 16 Instrumental Analysis (Syllabus)
 CHMC 16 Instrumental Analysis (Syllabus) Course Description CHMC16 is a laboratory course designed to compliment CHMC11 (Principles of Analytical Instrumentation). This course will provide a practical
CHMC 16 Instrumental Analysis (Syllabus) Course Description CHMC16 is a laboratory course designed to compliment CHMC11 (Principles of Analytical Instrumentation). This course will provide a practical
Luminescence transitions. Fluorescence spectroscopy
 Luminescence transitions Fluorescence spectroscopy Advantages: High sensitivity (single molecule detection!) Measuring increment in signal against a dark (zero) background Emission is proportional to excitation
Luminescence transitions Fluorescence spectroscopy Advantages: High sensitivity (single molecule detection!) Measuring increment in signal against a dark (zero) background Emission is proportional to excitation
CHAPTER 6 GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
 CHAPTER 6 GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Expected Outcomes Explain the principles of gas chromatography Able to state the function of each components of GC instrumentation Able to state the applications of GC 6.1
CHAPTER 6 GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Expected Outcomes Explain the principles of gas chromatography Able to state the function of each components of GC instrumentation Able to state the applications of GC 6.1
Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section: 5 Gas Chromatography (GC) Prof. Tarek A. Fayed
 Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section: 5 Gas Chromatography (GC) Prof. Tarek A. Fayed Gas Chromatography (GC) In gas chromatography, the sample is vaporized and injected onto the head of a chromatographic
Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section: 5 Gas Chromatography (GC) Prof. Tarek A. Fayed Gas Chromatography (GC) In gas chromatography, the sample is vaporized and injected onto the head of a chromatographic
Course goals: Course goals: Lecture 1 A brief introduction to chromatography. AM Quality parameters and optimization in Chromatography
 Emqal module: M0925 - Quality parameters and optimization in is a separation technique used for quantification of mixtures of analytes Svein.mjos@kj.uib.no Exercises and lectures can be found at www.chrombox.org/emq
Emqal module: M0925 - Quality parameters and optimization in is a separation technique used for quantification of mixtures of analytes Svein.mjos@kj.uib.no Exercises and lectures can be found at www.chrombox.org/emq
A Rapid Approach to the Confirmation of Drug Metabolites in Preclinical and Clinical Bioanalysis Studies
 A Rapid Approach to the Confirmation of Drug Metabolites in Preclinical and Clinical Bioanalysis Studies APPLICATION BENEFITS Regulatory guidelines and recommendations place a greater emphasis on the detection
A Rapid Approach to the Confirmation of Drug Metabolites in Preclinical and Clinical Bioanalysis Studies APPLICATION BENEFITS Regulatory guidelines and recommendations place a greater emphasis on the detection
Gas Chromatography. Chromatography Laboratory Course. Dr. Christian Jungnickel Chromatography Course GC September 2005
 Gas Chromatography Chromatography Laboratory Course The laboratory course experiments General Aim: Gain general experience using a GC Constant Injection technique Temperature variations Qualitative and
Gas Chromatography Chromatography Laboratory Course The laboratory course experiments General Aim: Gain general experience using a GC Constant Injection technique Temperature variations Qualitative and
Introduction to Mass Spectrometry (MS)
 Introduction to Mass Spectrometry (MS) MS Mass Spectrometry (MS) This is a very powerful analytical tool that can provide information on both molecular mass and molecular structure. Molecules come in all
Introduction to Mass Spectrometry (MS) MS Mass Spectrometry (MS) This is a very powerful analytical tool that can provide information on both molecular mass and molecular structure. Molecules come in all
CHROMATOGRAPHY AND MASS SPECTROMETER
 22 CHROMATOGRAPHY AND MASS SPECTROMETER 22.1 INTRODUCTION We know that the biochemistry or biological chemistry deals with the study of molecules present in organisms. These molecules are called as biomolecules
22 CHROMATOGRAPHY AND MASS SPECTROMETER 22.1 INTRODUCTION We know that the biochemistry or biological chemistry deals with the study of molecules present in organisms. These molecules are called as biomolecules
Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry
 Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyze, identify, purify, and/or quantify
Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyze, identify, purify, and/or quantify
High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
 High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a form of column chromatography that pumps a sample mixture or analyte in a solvent (known as the
High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a form of column chromatography that pumps a sample mixture or analyte in a solvent (known as the
Chapter 31 Gas Chromatography. Carrier Gas System
 Chapter 31 Gas Chromatography GAS-LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY In gas chromatography, the components of a vaporized sample are fractionated as a consequence of being partitioned between a mobile gaseous phase
Chapter 31 Gas Chromatography GAS-LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY In gas chromatography, the components of a vaporized sample are fractionated as a consequence of being partitioned between a mobile gaseous phase
Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC)
 Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC) Mohammed N. Sabir January 2017 10-Jan-17 1 GC is a chromatographic technique utilizes gas as the mobile phase which is usually an inert gas (Hydrogen, Helium, Nitrogen
Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC) Mohammed N. Sabir January 2017 10-Jan-17 1 GC is a chromatographic technique utilizes gas as the mobile phase which is usually an inert gas (Hydrogen, Helium, Nitrogen
Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep HPLC and Flash Chromatography. Tips and Techniques to Optimize ELSD and MS based Purification
 Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep HPLC and Flash Chromatography Tips and Techniques to Optimize ELSD and MS based Purification Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep
Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep HPLC and Flash Chromatography Tips and Techniques to Optimize ELSD and MS based Purification Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep
Open Column Chromatography, GC, TLC, and HPLC
 Open Column Chromatography, GC, TLC, and HPLC Murphy, B. (2017). Introduction to Chromatography: Lecture 1. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. USES OF CHROMATOGRAPHY
Open Column Chromatography, GC, TLC, and HPLC Murphy, B. (2017). Introduction to Chromatography: Lecture 1. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. USES OF CHROMATOGRAPHY
Chapter content. Reference
 Chapter 7 HPLC Instrumental Analysis Rezaul Karim Environmental Science and Technology Jessore University of Science and Technology Chapter content Liquid Chromatography (LC); Scope; Principles Instrumentation;
Chapter 7 HPLC Instrumental Analysis Rezaul Karim Environmental Science and Technology Jessore University of Science and Technology Chapter content Liquid Chromatography (LC); Scope; Principles Instrumentation;
OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION. Michael O Leary, Jennifer Gough, Tanya Tollifson Waters Corporation, Milford, MA USA
 Use of High Speed/High Resolution Size-Based Chromatographic Separation of Surfactants and Oligomeric Materials with Single Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry Michael O Leary, Jennifer Gough, Tanya Tollifson
Use of High Speed/High Resolution Size-Based Chromatographic Separation of Surfactants and Oligomeric Materials with Single Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry Michael O Leary, Jennifer Gough, Tanya Tollifson
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6501 Analytical Instruments Regulation 2013 Academic
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6501 Analytical Instruments Regulation 2013 Academic
Disadvantage: Destructive Technique once analyzed by GC, the sample is lost
 Gas Chromatography Like other methods of chromatography, a partitioning of molecules must occur between the stationary phase and the mobile phases in order to achieve separation. This is the same equilibrium
Gas Chromatography Like other methods of chromatography, a partitioning of molecules must occur between the stationary phase and the mobile phases in order to achieve separation. This is the same equilibrium
1) In what pressure range are mass spectrometers normally operated?
 Exercises Ionization 1) In what pressure range are mass spectrometers normally operated? Mass spectrometers are usually operated in the high vacuum regime to ensure mean free paths significantly longer
Exercises Ionization 1) In what pressure range are mass spectrometers normally operated? Mass spectrometers are usually operated in the high vacuum regime to ensure mean free paths significantly longer
Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography. Principles Instrumentation Detectors Columns and Stationary Phases Applications
 Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography Principles Instrumentation Detectors Columns and Stationary Phases Applications GC-MS Schematic Interface less critical for capillary columns Several types of Mass Specs
Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography Principles Instrumentation Detectors Columns and Stationary Phases Applications GC-MS Schematic Interface less critical for capillary columns Several types of Mass Specs
Spectroscopy and Chromatography
 Spectroscopy and Chromatography Introduction Visible light is one very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The different properties of the various types of radiation depend upon their wavelength.
Spectroscopy and Chromatography Introduction Visible light is one very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The different properties of the various types of radiation depend upon their wavelength.
Gas Chromatography. A schematic diagram of a gas chromatograph
 Gas Chromatography In gas liquid chromatography (GLC) partition of solutes occurs between a mobile gas phase (the "carrier gas") and a stationary liquid phase present in the column. The gas-phase concentration
Gas Chromatography In gas liquid chromatography (GLC) partition of solutes occurs between a mobile gas phase (the "carrier gas") and a stationary liquid phase present in the column. The gas-phase concentration
for the Novice Mass Spectrometry (^>, John Greaves and John Roboz yc**' CRC Press J Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York
 Mass Spectrometry for the Novice John Greaves and John Roboz (^>, yc**' CRC Press J Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informa business
Mass Spectrometry for the Novice John Greaves and John Roboz (^>, yc**' CRC Press J Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informa business
The Use of the ACQUITY QDa Detector for a Selective, Sensitive, and Robust Quantitative Method for a Potential Genotoxic Impurity
 The Use of the ACQUITY QDa Detector for a Selective, Sensitive, and Robust Quantitative Method for a Potential Genotoxic Impurity Janet Hammond Waters Corporation, Wilmslow, UK APPLICATION BENEFITS High
The Use of the ACQUITY QDa Detector for a Selective, Sensitive, and Robust Quantitative Method for a Potential Genotoxic Impurity Janet Hammond Waters Corporation, Wilmslow, UK APPLICATION BENEFITS High
Technical know-how in thermal analysis measurement
 Technical articles Technical know-how in thermal analysis measurement Evolved gas analysis by thermogravimetry-differential thermal analysis-mass spectrometry (TG-DTA-MS) technique Kazuko Motomura* and
Technical articles Technical know-how in thermal analysis measurement Evolved gas analysis by thermogravimetry-differential thermal analysis-mass spectrometry (TG-DTA-MS) technique Kazuko Motomura* and
Gas Chromatography (GC)
 Gas Chromatography (GC) Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11541 Saudi Arabia Office: AA53
Gas Chromatography (GC) Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11541 Saudi Arabia Office: AA53
Chromatography and other Separation Methods
 Chromatography and other Separation Methods Probably the most powerful class of modern analytical methods for analyzing mixture of components---and even for detecting a single component in a complex mixture!
Chromatography and other Separation Methods Probably the most powerful class of modern analytical methods for analyzing mixture of components---and even for detecting a single component in a complex mixture!
Multi-residue analysis of pesticides by GC-HRMS
 An Executive Summary Multi-residue analysis of pesticides by GC-HRMS Dr. Hans Mol is senior scientist at RIKILT- Wageningen UR Introduction Regulatory authorities throughout the world set and enforce strict
An Executive Summary Multi-residue analysis of pesticides by GC-HRMS Dr. Hans Mol is senior scientist at RIKILT- Wageningen UR Introduction Regulatory authorities throughout the world set and enforce strict
The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD)
 The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD) Basically all compounds which are less volatile than the mobile phase can be detected. Detection is based on a Universal property of
The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD) Basically all compounds which are less volatile than the mobile phase can be detected. Detection is based on a Universal property of
Use of High Speed/High Resolution Size-Based Chromatographic Separation of Polymeric Mixtures with Offline Infrared Detection
 Use of High Speed/High Resolution Size-Based Chromatographic Separation of Polymeric Mixtures with Michael O Leary 1, Jennifer Gough 1, Damian Morrison 1, Alain Creissen 2 1 Waters Corporation, Milford,
Use of High Speed/High Resolution Size-Based Chromatographic Separation of Polymeric Mixtures with Michael O Leary 1, Jennifer Gough 1, Damian Morrison 1, Alain Creissen 2 1 Waters Corporation, Milford,
Choosing the metabolomics platform
 GBS 748 Choosing the metabolomics platform Stephen Barnes, PhD 4 7117; sbarnes@uab.edu So, I have my samples what s next? You ve collected your samples and you may have extracted them Protein precipitation
GBS 748 Choosing the metabolomics platform Stephen Barnes, PhD 4 7117; sbarnes@uab.edu So, I have my samples what s next? You ve collected your samples and you may have extracted them Protein precipitation
Mass Spectrometry in MCAL
 Mass Spectrometry in MCAL Two systems: GC-MS, LC-MS GC seperates small, volatile, non-polar material MS is detection devise (Agilent 320-MS TQ Mass Spectrometer) Full scan monitoring SIM single ion monitoring
Mass Spectrometry in MCAL Two systems: GC-MS, LC-MS GC seperates small, volatile, non-polar material MS is detection devise (Agilent 320-MS TQ Mass Spectrometer) Full scan monitoring SIM single ion monitoring
Ch.28 HPLC. Basic types of Liquid Chromatography Partition (LLC) Adsorption (LSC) Ion Exchange (IC) Size Exclusion (SEC or Gel Chromatography)
 Ch.28 HPLC 28.1 Basic types of Liquid Chromatography Partition (LLC) Adsorption (LSC) Ion Exchange (IC) Size Exclusion (SEC or Gel Chromatography) High Performance (Pressure) LC Glass column st.steel (high
Ch.28 HPLC 28.1 Basic types of Liquid Chromatography Partition (LLC) Adsorption (LSC) Ion Exchange (IC) Size Exclusion (SEC or Gel Chromatography) High Performance (Pressure) LC Glass column st.steel (high
Chromatography. writing in color
 Chromatography writing in color Outlines of Lecture Chromatographic analysis» Principles and theory.» Definition.» Mechanism.» Types of chromatography.» Uses of Chromatography. In 1906 Mikhail Tswett used
Chromatography writing in color Outlines of Lecture Chromatographic analysis» Principles and theory.» Definition.» Mechanism.» Types of chromatography.» Uses of Chromatography. In 1906 Mikhail Tswett used
Research Equipment in the UCA Chemistry Department
 Research Equipment in the UCA Chemistry Department Varian 220 Atomic Absorption Spectrometer Atomic Absorption spectroscopy is used to measure the amount of a metal ion present in a solution. It is particularly
Research Equipment in the UCA Chemistry Department Varian 220 Atomic Absorption Spectrometer Atomic Absorption spectroscopy is used to measure the amount of a metal ion present in a solution. It is particularly
CH 2252 Instrumental Methods of Analysis Unit V Gas Chromatography. M. Subramanian
 CH 2252 Instrumental Methods of Analysis Unit V Gas Chromatography M. Subramanian Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam 603
CH 2252 Instrumental Methods of Analysis Unit V Gas Chromatography M. Subramanian Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam 603
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR-603203 EI 2302 ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS QUESTION BANK UNIT I COLORIMETRY AND SPECTROPHOTOMETRY Part A 1. State Lambert
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR-603203 EI 2302 ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS QUESTION BANK UNIT I COLORIMETRY AND SPECTROPHOTOMETRY Part A 1. State Lambert
HPLC. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Harris Chapter 25
 High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Harris Chapter 25 12/1/2005 Chem 253 - Chapter 25 1 HPLC Separation of nonvolatile or thermally unstable compounds. If the analyte/sample can be found to be
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Harris Chapter 25 12/1/2005 Chem 253 - Chapter 25 1 HPLC Separation of nonvolatile or thermally unstable compounds. If the analyte/sample can be found to be
Routine MS Detection for USP Chromatographic Methods
 Daniel S. Root, Thomas E. Wheat, and Patricia McConville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS This approach enables mass spectral analysis of peaks directly from unmodified USP HPLC
Daniel S. Root, Thomas E. Wheat, and Patricia McConville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS This approach enables mass spectral analysis of peaks directly from unmodified USP HPLC
https://www.chemicool.com/definition/chromatography.html
 CHROMATOGRAPHY 1 Chromatography - a physical method of mixture separation in which the components to be separated are distributed between two phases, one of which is stationary (stationary phase) while
CHROMATOGRAPHY 1 Chromatography - a physical method of mixture separation in which the components to be separated are distributed between two phases, one of which is stationary (stationary phase) while
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 27. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 27 Gas Chromatography Introduction GC covers all chromatographic methods in which the mobile phase is gas. It may involve either a solid stationary phase (GSC)
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 27 Gas Chromatography Introduction GC covers all chromatographic methods in which the mobile phase is gas. It may involve either a solid stationary phase (GSC)
SEAMLESS INTEGRATION OF MASS DETECTION INTO THE UV CHROMATOGRAPHIC WORKFLOW
 SEAMLESS INTEGRATION OF MASS DETECTION INTO THE UV CHROMATOGRAPHIC WORKFLOW Paula Hong, John Van Antwerp, and Patricia McConville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA Historically UV detection has been
SEAMLESS INTEGRATION OF MASS DETECTION INTO THE UV CHROMATOGRAPHIC WORKFLOW Paula Hong, John Van Antwerp, and Patricia McConville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA Historically UV detection has been
Liquid Chromatography
 Liquid Chromatography 1. Introduction and Column Packing Material 2. Retention Mechanisms in Liquid Chromatography 3. Method Development 4. Column Preparation 5. General Instrumental aspects 6. Detectors
Liquid Chromatography 1. Introduction and Column Packing Material 2. Retention Mechanisms in Liquid Chromatography 3. Method Development 4. Column Preparation 5. General Instrumental aspects 6. Detectors
Gas Chromatography. Vaporization of sample Gas-solid Physical absorption Gas-liquid Liquid immobilized on inert solid
 Gas Chromatography Vaporization of sample Gas-solid Physical absorption Gas-liquid Liquid immobilized on inert solid Principles Instrumentation Applications 18-1 Retention Volumes Volumes rather than times
Gas Chromatography Vaporization of sample Gas-solid Physical absorption Gas-liquid Liquid immobilized on inert solid Principles Instrumentation Applications 18-1 Retention Volumes Volumes rather than times
Chromatography- Separation of mixtures CHEM 212. What is solvent extraction and what is it commonly used for?
 Chromatography- Separation of mixtures CHEM 212 What is solvent extraction and what is it commonly used for? How does solvent extraction work? Write the partitioning coefficient for the following reaction:
Chromatography- Separation of mixtures CHEM 212 What is solvent extraction and what is it commonly used for? How does solvent extraction work? Write the partitioning coefficient for the following reaction:
Gas Chromatography. Presented By Mr. Venkateswarlu Mpharm KTPC
 Gas Chromatography Gas Chromatography Presented By Mr. Venkateswarlu Mpharm KTPC What is Gas Chromatography? It is also known as Gas-Liquid Chromatography (GLC) GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Separation of gaseous
Gas Chromatography Gas Chromatography Presented By Mr. Venkateswarlu Mpharm KTPC What is Gas Chromatography? It is also known as Gas-Liquid Chromatography (GLC) GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Separation of gaseous
PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY. Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC
 PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC CHROMATOGRAPHY Laboratory technique for the Separation of mixtures Chroma -"color" and graphein
PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC CHROMATOGRAPHY Laboratory technique for the Separation of mixtures Chroma -"color" and graphein
The Theory of HPLC. Quantitative and Qualitative HPLC
 The Theory of HPLC Quantitative and Qualitative HPLC i Wherever you see this symbol, it is important to access the on-line course as there is interactive material that cannot be fully shown in this reference
The Theory of HPLC Quantitative and Qualitative HPLC i Wherever you see this symbol, it is important to access the on-line course as there is interactive material that cannot be fully shown in this reference
CHEM 429 / 529 Chemical Separation Techniques
 CHEM 429 / 529 Chemical Separation Techniques Robert E. Synovec, Professor Department of Chemistry University of Washington Lecture 1 Course Introduction Goal Chromatography and Related Techniques Obtain
CHEM 429 / 529 Chemical Separation Techniques Robert E. Synovec, Professor Department of Chemistry University of Washington Lecture 1 Course Introduction Goal Chromatography and Related Techniques Obtain
Gas Chromatography (Chapter 2 and 3 in The essence of chromatography)
 Gas Chromatography 1. Introduction. Stationary phases 3. Retention in Gas-Liquid Chromatography 4. Capillary gas-chromatography 5. Sample preparation and injection 6. Detectors (Chapter and 3 in The essence
Gas Chromatography 1. Introduction. Stationary phases 3. Retention in Gas-Liquid Chromatography 4. Capillary gas-chromatography 5. Sample preparation and injection 6. Detectors (Chapter and 3 in The essence
LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY: FUNDAMENTALS AND INSTRUMENTATION
 .. LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY: FUNDAMENTALS AND INSTRUMENTATION SALVATORE FANALI PAUL R. HADDAD CouN F. PooLE PETER SCHOENMAKERS DAVID LLOYD ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS
.. LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY: FUNDAMENTALS AND INSTRUMENTATION SALVATORE FANALI PAUL R. HADDAD CouN F. PooLE PETER SCHOENMAKERS DAVID LLOYD ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS
Scientific Instrumentation in Research
 «± µ π ªï Ë Ûapple Ë Ù µ..-.. ÚıÙ Scientific Instrumentation in Research»æ «ß»å µπå* ± µ π µ å ± µ π The introduction of modern scientific instrumentation has had a dramatic effect on research and development
«± µ π ªï Ë Ûapple Ë Ù µ..-.. ÚıÙ Scientific Instrumentation in Research»æ «ß»å µπå* ± µ π µ å ± µ π The introduction of modern scientific instrumentation has had a dramatic effect on research and development
2501 High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 2501 High Performance Liquid Chromatography High Performance Liquid Chromatography Scheme Chp25:: 1 High Performance Liquid Chromatography Components of HPLC High Performance Liquid Chromatography Scheme
2501 High Performance Liquid Chromatography High Performance Liquid Chromatography Scheme Chp25:: 1 High Performance Liquid Chromatography Components of HPLC High Performance Liquid Chromatography Scheme
Analytical techniques: Environmental samples. Lecture 2 Universidade do Algarve
 Analytical techniques: Environmental samples Lecture 2 Universidade do Algarve Terms, definitions & applications Difference between technique and method: Analytical technique: Fundamental scientific application
Analytical techniques: Environmental samples Lecture 2 Universidade do Algarve Terms, definitions & applications Difference between technique and method: Analytical technique: Fundamental scientific application
OER implementation at UNS. Prof. Dr Ivana Ivančev-Tumbas University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Sciences
 OER implementation at UNS Prof. Dr Ivana Ivančev-Tumbas University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Sciences Overview 1. Planned development of OER 2. What do we need from EU partners? 3. Draft OER example Overview
OER implementation at UNS Prof. Dr Ivana Ivančev-Tumbas University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Sciences Overview 1. Planned development of OER 2. What do we need from EU partners? 3. Draft OER example Overview
2401 Gas (liquid) Chromatography
 2401 Gas (liquid) Chromatography Chromatography Scheme Gas chromatography - specifically gas-liquid chromatography - involves a sample being vaporized and injected onto the head of the chromatographic
2401 Gas (liquid) Chromatography Chromatography Scheme Gas chromatography - specifically gas-liquid chromatography - involves a sample being vaporized and injected onto the head of the chromatographic
Chemical Analysis Problem
 Chemical Analysis Problem Hair analysis is frequently used for the long-term monitoring of drug and alcohol users. You are working at a forensics laboratory and have been given the task of developing a
Chemical Analysis Problem Hair analysis is frequently used for the long-term monitoring of drug and alcohol users. You are working at a forensics laboratory and have been given the task of developing a
Gas Chromatography. Introduction
 Gas Chromatography Introduction 1.) Gas Chromatography Mobile phase (carrier gas) is a gas - Usually N 2, He, Ar and maybe H 2 - Mobile phase in liquid chromatography is a liquid Requires analyte to be
Gas Chromatography Introduction 1.) Gas Chromatography Mobile phase (carrier gas) is a gas - Usually N 2, He, Ar and maybe H 2 - Mobile phase in liquid chromatography is a liquid Requires analyte to be
FACULTY OF PHARMACY. M. Pharmacy I Semester (Suppl.) Examination, November 2015 (Common To All) Subject: Pharmaceutical Analytical Techniques
 M. Pharmacy I Semester (Suppl.) Examination, November 2015 (Common To All) Subject: Pharmaceutical Analytical Techniques Code No. 6001 / S Note: Answer any Five questions. All questions carry equal marks.
M. Pharmacy I Semester (Suppl.) Examination, November 2015 (Common To All) Subject: Pharmaceutical Analytical Techniques Code No. 6001 / S Note: Answer any Five questions. All questions carry equal marks.
Physical Separations and Chromatography
 Lab #5A & B: Physical Separations and Chromatography Individual Objectives: At the end of these experiments you should be able to: Ø Distinguish between Rf and tr; chromatograph and chromatogram; adsorption
Lab #5A & B: Physical Separations and Chromatography Individual Objectives: At the end of these experiments you should be able to: Ø Distinguish between Rf and tr; chromatograph and chromatogram; adsorption
HYPHENATED TECHNOLOGY GUIDE
 HYPHENATED TECHNOLOGY GUIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS TG-IR...3 Hiden Analytical MS Systems for TG-MS...4 TG-MS...5 TG-GC/MS...6 TG-IR-GC/MS...8 HYPHENATED TECHNOLOGY GUIDE Coupling, or hyphenating, two instruments
HYPHENATED TECHNOLOGY GUIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS TG-IR...3 Hiden Analytical MS Systems for TG-MS...4 TG-MS...5 TG-GC/MS...6 TG-IR-GC/MS...8 HYPHENATED TECHNOLOGY GUIDE Coupling, or hyphenating, two instruments
Chem 230, Fall, 2014 Homework Set # 3 Short Answer SOLUTIONS
 Chem 230, Fall, 2014 Homework Set # 3 Short Answer SOLUTIONS 1. List two advantages of temperature programming in GC. a) Allows separation of solutes with widely varying retention factors in a reasonable
Chem 230, Fall, 2014 Homework Set # 3 Short Answer SOLUTIONS 1. List two advantages of temperature programming in GC. a) Allows separation of solutes with widely varying retention factors in a reasonable
Finnigan LCQ Advantage MAX
 www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment Finnigan LCQ Advantage MAX The Finnigan LCQ Advantage MAX ion trap mass spectrometer
www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment Finnigan LCQ Advantage MAX The Finnigan LCQ Advantage MAX ion trap mass spectrometer
Analytical Instrumentation
 Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrophotometry Environmental, food safety, toxicology, and forensic gas chromatography applications are more demanding than ever. Our portfolio of GC, GC- MS, GC-MS/MS and
Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrophotometry Environmental, food safety, toxicology, and forensic gas chromatography applications are more demanding than ever. Our portfolio of GC, GC- MS, GC-MS/MS and
HANDBOOK OF DRUG ANALYSIS
 HANDBOOK OF DRUG ANALYSIS APPLICATIONS IN FORENSIC AND CLINICAL LABORATORIES Ray H. Liu Daniel E. Gadzala American Chemical Society Washington, DC Contents Dedication Foreword Preface About the Authors
HANDBOOK OF DRUG ANALYSIS APPLICATIONS IN FORENSIC AND CLINICAL LABORATORIES Ray H. Liu Daniel E. Gadzala American Chemical Society Washington, DC Contents Dedication Foreword Preface About the Authors
Introduction to LC-MS
 Wednesday April 5, 2017 10am Introduction to LC-MS Amy Patton, MS Laboratory Manager, Pinpoint Testing, LLC Little Rock, AR DESCRIPTION: Amy Patton, laboratory manager for Pinpoint Testing, will begin
Wednesday April 5, 2017 10am Introduction to LC-MS Amy Patton, MS Laboratory Manager, Pinpoint Testing, LLC Little Rock, AR DESCRIPTION: Amy Patton, laboratory manager for Pinpoint Testing, will begin
Chapter 23 Introduction to Analytical Separations
 Chapter 23 Introduction to Analytical Separations Homework Due Monday April 24 Problems 23-1, 23-2, 23-7, 23-15, 23-27, 23-29, 23-32 Analytical Separations: Universal approach to analyzing complex mixtures
Chapter 23 Introduction to Analytical Separations Homework Due Monday April 24 Problems 23-1, 23-2, 23-7, 23-15, 23-27, 23-29, 23-32 Analytical Separations: Universal approach to analyzing complex mixtures
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
Selecting Detectors for Compounds with No Optical Absorbance
 C146-E114 Selecting Detectors for Compounds with No Optical Absorbance Technical Report vol.15 1. Features of Absorbance Detectors In HPLC, the detector is selected in accordance with the analyte. Many
C146-E114 Selecting Detectors for Compounds with No Optical Absorbance Technical Report vol.15 1. Features of Absorbance Detectors In HPLC, the detector is selected in accordance with the analyte. Many
Lab 3 Guide: Gas Chromatography (GC) (Sept 8-14)
 Lab 3 Guide: Gas Chromatography (GC) (Sept 8-14) How GC works The Basic Idea Gas chromatography (GC) is mainly used for the qualitative analysis of samples: it answers the question What chemicals are present
Lab 3 Guide: Gas Chromatography (GC) (Sept 8-14) How GC works The Basic Idea Gas chromatography (GC) is mainly used for the qualitative analysis of samples: it answers the question What chemicals are present
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
 Mass Spectrometry (MS) Alternative names: Mass spectrometric (selective) detector (MSD) Spectrometry - methods based on interaction of matter and radiation Mass spectrometry - method based on formation
Mass Spectrometry (MS) Alternative names: Mass spectrometric (selective) detector (MSD) Spectrometry - methods based on interaction of matter and radiation Mass spectrometry - method based on formation
HYPHENATED TECHNOLOGY GUIDE
 HYPHENATED TECHNOLOGY GUIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS TG-IR...3 Hiden Analytical MS Systems for TG-MS...4 TG-MS...5 TG-GC/MS...6 TG-IR-GC/MS...8 HYPHENATED TECHNOLOGY GUIDE Coupling, or hyphenating, two instruments
HYPHENATED TECHNOLOGY GUIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS TG-IR...3 Hiden Analytical MS Systems for TG-MS...4 TG-MS...5 TG-GC/MS...6 TG-IR-GC/MS...8 HYPHENATED TECHNOLOGY GUIDE Coupling, or hyphenating, two instruments
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
 Q1 Chromatography is an important analytical technique in chemistry. There is a number of techniques under the general heading of chromatography. (a) Paper and gas chromatography rely on partition to separate
Q1 Chromatography is an important analytical technique in chemistry. There is a number of techniques under the general heading of chromatography. (a) Paper and gas chromatography rely on partition to separate
Introduction to GC/MS
 Why Mass Spectrometry? Introduction to GC/MS A powerful analytical technique used to: 1.Identify unknown compounds 2. Quantify known materials down to trace levels 3. Elucidate the structure of molecules
Why Mass Spectrometry? Introduction to GC/MS A powerful analytical technique used to: 1.Identify unknown compounds 2. Quantify known materials down to trace levels 3. Elucidate the structure of molecules
Selective Formation of Benzo[c]cinnoline by Photocatalytic Reduction of 2,2 Dinitrobiphenyl with TiO 2 and UV light irradiation
![Selective Formation of Benzo[c]cinnoline by Photocatalytic Reduction of 2,2 Dinitrobiphenyl with TiO 2 and UV light irradiation Selective Formation of Benzo[c]cinnoline by Photocatalytic Reduction of 2,2 Dinitrobiphenyl with TiO 2 and UV light irradiation](/thumbs/90/104361197.jpg) Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Content: Selective Formation of Benzo[c]cinnoline by Photocatalytic Reduction of
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Content: Selective Formation of Benzo[c]cinnoline by Photocatalytic Reduction of
Gas Chromatography. 1. Experiment Category: 2. Experiment Name: 3. Date and Issue number: 4. Instructor Name: 5. Institution: Ain Shams University
 Project Title: e-laboratories for Gas chromatography 1. Experiment Category: Chemistry >> chromatography 2. Experiment Name: Gas Chromatography 3. Date and Issue number: 4. Instructor Name: 5. Institution:
Project Title: e-laboratories for Gas chromatography 1. Experiment Category: Chemistry >> chromatography 2. Experiment Name: Gas Chromatography 3. Date and Issue number: 4. Instructor Name: 5. Institution:
What type of samples are common? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses. Number of samples? Aims. Sources of error. Sample preparation
 What type of samples are common? Sample preparation 1 2 Number of samples? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses 3 4 Sources of error Aims Sample has to be representative Sample has to
What type of samples are common? Sample preparation 1 2 Number of samples? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses 3 4 Sources of error Aims Sample has to be representative Sample has to
Skoog/Holler/Crouch Chapter 26 Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 6th ed. CHAPTER 26
 Skoog/Holler/Crouch Chapter 26 Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 6th ed. Instructor s Manual CHAPTE 26 26-1. (a) Elution is a process in which species are washed through a chromatographic column by
Skoog/Holler/Crouch Chapter 26 Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 6th ed. Instructor s Manual CHAPTE 26 26-1. (a) Elution is a process in which species are washed through a chromatographic column by
GUIDELINES ON THE USE OF MASS SPECTROMETRY (MS) FOR IDENTIFICATION, CONFIRMATION AND QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF RESIDUES CAC/GL
 CAC/GL 56-2005 Page 1 of 6 GUIDELINES ON THE USE OF MASS SPECTROMETRY (MS) FOR IDENTIFICATION, CONFIRMATION AND QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF RESIDUES CONFIRMATORY TESTS CAC/GL 56-2005 When analyses are
CAC/GL 56-2005 Page 1 of 6 GUIDELINES ON THE USE OF MASS SPECTROMETRY (MS) FOR IDENTIFICATION, CONFIRMATION AND QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF RESIDUES CONFIRMATORY TESTS CAC/GL 56-2005 When analyses are
Analytical Chemistry
 Analytical Chemistry Chromatographic Separations KAM021 2016 Dr. A. Jesorka, 6112, aldo@chalmers.se Introduction to Chromatographic Separations Theory of Separations -Chromatography Terms Summary: Chromatography
Analytical Chemistry Chromatographic Separations KAM021 2016 Dr. A. Jesorka, 6112, aldo@chalmers.se Introduction to Chromatographic Separations Theory of Separations -Chromatography Terms Summary: Chromatography
METHOD 3600B CLEANUP
 METHOD 3600B CLEANUP 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 3600 provides general guidance on selection of cleanup methods that are appropriate for the target analytes of interest. Cleanup methods are applied
METHOD 3600B CLEANUP 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 3600 provides general guidance on selection of cleanup methods that are appropriate for the target analytes of interest. Cleanup methods are applied
 HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY (GC)
 GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY (GC) Pre-Lab Questions Questions are to be answered before the beginning of the laboratory. The answers are due at the beginning of each experiment (the questions are for credit and
GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY (GC) Pre-Lab Questions Questions are to be answered before the beginning of the laboratory. The answers are due at the beginning of each experiment (the questions are for credit and
Quality control analytical methods- Switch from HPLC to UPLC
 Quality control analytical methods- Switch from HPLC to UPLC Dr. Y. Padmavathi M.pharm,Ph.D. Outline of Talk Analytical techniques in QC Introduction to HPLC UPLC - Principles - Advantages of UPLC - Considerations
Quality control analytical methods- Switch from HPLC to UPLC Dr. Y. Padmavathi M.pharm,Ph.D. Outline of Talk Analytical techniques in QC Introduction to HPLC UPLC - Principles - Advantages of UPLC - Considerations
Introduction to Gas Chromatography
 Introduction to Gas Chromatography 31-1 Objectives To know what is chromatography To understand the mechanism of compound separation To know the basic of gas chromatography system 31-2 Chromatography Definition
Introduction to Gas Chromatography 31-1 Objectives To know what is chromatography To understand the mechanism of compound separation To know the basic of gas chromatography system 31-2 Chromatography Definition
Translational Biomarker Core
 Translational Biomarker Core Instrumentation Thermo Scientific TSQ Quantum Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometers. There are two TSQ Quantum Ultra AM instruments available in the TBC. The TSQ Quantum Ultra
Translational Biomarker Core Instrumentation Thermo Scientific TSQ Quantum Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometers. There are two TSQ Quantum Ultra AM instruments available in the TBC. The TSQ Quantum Ultra
MODERN HPLC FOR PRACTICING SCIENTISTS
 MODERN HPLC FOR PRACTICING SCIENTISTS Michael W. Dong Synomics Pharmaceutical Services, LLC Wareham, Massachusetts WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Preface xv 1 Introduction 1
MODERN HPLC FOR PRACTICING SCIENTISTS Michael W. Dong Synomics Pharmaceutical Services, LLC Wareham, Massachusetts WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Preface xv 1 Introduction 1
IDENTIFICATION AND QUANTITATION OF HARD-TO-RESOLVE INDIVIDUAL COMPONENTS IN MIXTURES WITHOUT CHROMATOGRAPHY, CHEMOMETRICS, AND REFERENCE STANDARDS
 WHITE PAPER IDENTIFICATION AND QUANTITATION OF HARD-TO-RESOLVE INDIVIDUAL COMPONENTS IN MIXTURES WITHOUT CHROMATOGRAPHY, CHEMOMETRICS, AND REFERENCE STANDARDS Aleksandr V. Mikhonin, Matthew T. Muckle,
WHITE PAPER IDENTIFICATION AND QUANTITATION OF HARD-TO-RESOLVE INDIVIDUAL COMPONENTS IN MIXTURES WITHOUT CHROMATOGRAPHY, CHEMOMETRICS, AND REFERENCE STANDARDS Aleksandr V. Mikhonin, Matthew T. Muckle,
M M e M M H M M H. Ion Sources
 Ion Sources Overview of Various Ion Sources After introducing samples into a mass spectrometer, the next important step is the conversion of neutral molecules or compounds to gas phase ions. The ions could
Ion Sources Overview of Various Ion Sources After introducing samples into a mass spectrometer, the next important step is the conversion of neutral molecules or compounds to gas phase ions. The ions could
