Exploration of Genetic Diversity for Qualitative Traits among the Extant Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Varieties and Parental Lines
|
|
|
- Hubert Derick Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp Journal homepage: Original Research Article Exploration of Genetic Diversity for Qualitative Traits among the Extant Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Varieties and Parental Lines K. Rathinavel* Central Institute for Cotton Research, Regional Station, Coimbatore , T.N., India *Corresponding author K e y w o r d s Qualitative traits, Principal component analysis, Dendrogram, Eigenvalue. Article Info Accepted: 21 June 2017 Available Online: 10 August 2017 Introduction A B S T R A C T A study was conducted to characterize and evaluate the extant varieties and parental lines of upland cotton using qualitative morphological traits for DUS testing of cotton. These data were subjected to various genetic principles. The results indicated that out of 26 traits, only 17 traits were included for Principal Component analysis (PCA) because of expression of variability. Traits like stem hairiness, flower petal colour and density of seed fuzz expressed much variation (four states) compared to other traits. Nine traits viz., hypocotyl pigmentation, leaf gossypol glands, leaf nectaries, leaf petiole pigmentation, stem pigmentation, male sterility, boll bearing habit, boll prominence of tip and boll opening showed no variability. The PCA revealed that the first seven PCs having eigen values >1 and contributed for 76.67% of the total variation. The variance explained by PC1 was mostly due to traits related to colour such as boll colour, petal colour, petal spot, anther filament colour, pollen colour, boll surface and leaf shape, whereas PC II mostly related to stem hairiness, leaf hairiness, leaf shape and bract type. Two-dimensional scatter plot was drawn supported with grouping patterns of cluster analysis. The cluster analysis classified 101 extant varieties into five divergent groups. The cluster II comprising of largest (57) genotypes followed by cluster I (36). The Shannon Weaver diversity index (H ) was used for estimating the frequency distribution of diversity index. The traits viz., hypocotyl pigmentation, leaf gossypol glands, leaf nectarines, leaf petiole pigmentation, stem pigmentation, flower male sterility, boll bearing habit, boll prominence of tip and boll opening were higher (4.62) when compared to other traits. Cotton is the leading non-food agricultural and industrial fibre crop grown in more than 80 countries (Dutt et al., 2004; Shakeel et al., 2011). Cotton is the world s most important natural textile fibre and an important source of feed, foodstuff, and oil, with approximate world consumption put at 27 million metric tons per year (Chen et al., 2007). However, yield and quality of this allimportant crop have declined over the last decade due to huge general erosion in genetic 2407 diversity of cotton varieties (Meredith, 2000). Worldwide cotton breeders and producers have expressed concern over the narrow genetic basis of cultivated cotton germplasm that has caused a decline in yield and quality. Globally cotton breeding programmes are working with a narrow germplasm pool thus resulting in genetic bottleneck through historic domestication events and selection (Iqbal et al., 1997). Characterization of germplasm plays a vital role in crop improvement. Characterization, evaluation of
2 germplasm and quantification of genetic diversity of genotypes is indispensable for a pragmatic use of plant genetic resources and also for determining evolutionary relationships (Zada et al., 2013). The present study was envisaged to characterize extant varieties of cotton genotypes collected across the Indian subcontinent for qualitative traits using correlation analysis, principal component analysis, cluster analysis and diversity analysis. Knowledge of the associations among genotypes would help to identify a set of genotypes that have maximal diversity for the analysis of the effects of genetic background. Hierarchical cluster analysis has been suggested for classifying entries of germplasm collections based on degree of similarity and dissimilarity (Van Hintum 1995). Among these biometrical procedures, the main edge of principal component analysis (PCA) is that each genotype can be assigned to only one group and it also reflects the significance of the largest contributor to the total variability at each axis of differentiation (Sharma 1998) Genetic variation for morphological traits among the extant cotton varieties has been estimated using principal component analysis, which has led to the recognition of phenotypic variability (Sarvannan et al., 2006; Esmail et al., 2008; Li et al., 2008). The objective of the present study was to evaluate the genetic diversity among cotton genotypes specifically to select the best genotypes by using PCA and cluster analysis that can be exploited in future cotton breeding programme was emanated from the data generated for characterisation and documentation of extant cotton varieties, a mandatory of Distinctiveness, Uniformity and Stability testing under The Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers Rights Act, 2001 of India which encourages stimulation and development of new plant varieties Materials and Methods The investigation was carried out at Central Institute of Cotton Research, Regional Station, Coimbatore during The experimental material consisted of 101 extant cotton varieties and parental lines of hybrids, collected from diversified agro ecological cotton growing zones of India. Sowing of seeds of each variety was taken up in randomised block design with three replications. Each variety was sown in 10 rows adopting spacing of 90 cm x 60 cm. Recommended agronomic, cultural and plant protection practices for tetraploid cotton was adopted till the harvest of crop. Qualitative characters were taken under consideration for evaluating the substantial variation and relationship among extant cotton genotypes. The ten plants were randomly selected and the observations recorded for 26 qualitative traits. The scores for hypocotyl pigmentation (HP) was given as 1- Absent, 9- Present; for leaf colour (LC) the rating given was 1- Light green, 2-Green, 3- Light red and 4-Dark red; Leaf Hairiness (LH) was scored as 5- Medium, 9- Dense; Similarly Leaf Appearance (LA) 1-Cup, 2- Flat; Leaf Gossypol Glands (LGG) as 1- Absent, 9- Present; Leaf Nectaries (LN) 1- Absent, 9- Present; Leaf petiole pigmentation (LPP) 1- Absent, 9- Present; Leaf shape (LS) 1- Palmate, 2- Semi-digitate, 3-Digitate, 4- Lanceolate; Plant stem hairiness (SH) 1- smooth, 3- sparse, 5- medium, 7-dense; plant stem pigmentation (SP) 1-Absent, 2-Present; Bract type (BT): 3- Normal, 5-Frego; Flower petal colour (FPC): 1-Cream, 2-Yellow, 3- Deep yellow, 4-purple; Flower petal spot (FPS): 1-Absent, 9-Present; Flower stigma(fs): 3-Embedded, 5-Exerted; Flower anther filament colouration (FAFC): 1- Absent, 9- Present; Flower pollen colour (FPoC): 1-White, 2- Cream, 3-Yellow, 4- Deep yellow, 5- Purple; Flower male sterility (FMS): 1-Absent, 9-Present; Boll bearing
3 habit (BBH): 1- Solitary, 9- Cluster; Boll Colour (BC): 3-Green, 5-Red; Boll shape (BSh): 3-Round, 5-Ovate, 7-Elliptic; Boll Surface (BS): 1-Smooth, 9-Pitted; Boll Prominence of tip (BPT): 1- Blunt, 9-Pointed; Boll opening (BO): 3- Semi-open, 5- Open; Seed fuzz (SF): 1-Naked, 3-Sparse, 5- Medium, 7-Dense; Seed fuzz colour (SFC): 1- White, 2-Grey, 3-Green, 4-Brown; Fibre colour (FC): 1-White, 2-Cream, 3-Green, 4- Brown; were used for this study. Scores were allocated for each trait as per the National test guide lines of Protection of plant varieties and Farmer s Right s Authority of India (plantauthority.gov.in/) Pearson correlation coefficient was worked out for the above 26 qualitative traits and correlation matrix was prepared for comparing different traits using XLSTAT version software. The standardized values of 26 qualitative traits were used to perform Principal Component Analysis (PCA) using PAST 3 (Hammer et al., 2001) to find out the relative importance of different traits and to capture the existing genetic variation. A screen plot was drawn from the Eigen values associated with a component or factor in descending order versus the number of the component or factor. Screen plot usually used for visual assessment of components or factor which explain much of the variability in the data. Shannon Weaver diversity index (H ) (Shannon and Weaver 1949) was arrived and used as a measure of phenotypic diversity of each trait. A low H index indicates extreme unbalance frequency classes for an individual traits and lack of genetic diversity. Out of 26 traits, 9 traits have not expressed for genetic variability among the extant genotypes and the remaining 17 corresponding Principal component factors were subjected to cluster analysis based on Euclidean distances and wards minimum variance using Agglomerative hierarchical clustering method through XLSTAT A hierarchical cluster analysis for pooled data was performed using scores of dissimilarity matrix as per Ward Results and Discussion Evaluation of genotypes based on qualitative traits The observations on 26 qualitative traits were recorded for all the 101 genotypes and analysed as per scores presented in table 1. The genotypes have expressed for green leaf colour (98) followed by light red (2) and one genotype dark red colour (BN red). For leaf hairiness, the highest number of genotypes is of medium (93) class followed by sparse (6) and dense (2). Majority of the genotypes were observed with flat nature of leaf (78) and rest of them is cup type (23). Three classes of leaf shape namely palmate, semi digitate and digitate were observed. Maximum numbers of genotypes (97) were observed with palmate leaf shape, while two genotypes namely 70E and GSAV 1056 are semi digitate (semi-okra) and another two genotypes viz., MDH 89 and SRT-GMS 1 were digitate (Okra). Stem hairiness recorded was medium in 73 genotypes followed by dense (16), sparse (5) and one with smooth type (GSB 39). All the genotypes were observed with normal bract type (100) except MDH 89 with frego bract. Cream petal colour was predominant (68) followed by yellow (29), purple (3) and one genotype with deep yellow petal colour (GSB 39). Flower petal spot was absent in 98 genotypes and were present in AK 32, GSAV 1056 and GSB 39. The embedded position of stigma was recorded in most of the genotypes (68) and in the remaining 33 genotypes it was exerted. Absence of anther filament colouration was observed in all the genotypes except GSAV Maximum number of genotypes had cream pollen colour (77) followed by yellow (21) and deep yellow (3). 2409
4 Boll colour namely green and red were observed of this green coloured bolls were found high 99 genotypes and red colour bolls appeared in BN red and GSAV Ovate boll shape (93) was observed in higher number of genotypes than round (6) and elliptic (2). Among the smooth and pitted boll surface, smooth was found in 98 genotypes and pitted recorded in GSB 39, SRT-GMS1 and GSAV The density of seed fuzz observed in maximum genotypes was medium (64) followed by dense (27), sparse (8). The genotypes BN red and GSB 39 did not bear seed fuzz and were naked. Grey seed fuzz colour (89) was found predominant followed by white (12). The fiber colour observed was cream in 94 genotypes when compared to white in the rest (7). Among the 26 qualitative traits studied, the traits like stem hairiness, flower petal colour and seed fuzz showed higher amount of variation (four groups), while other traits showed only two or three category. The traits like hypocotyl pigmentation, leaf gossypol glands, leaf nectaries, leaf petiole pigmentation, plant stem pigmentation, male sterility, boll bearing, prominence of boll tip, boll opening habit showed no variation. Kumar et al., (2013) distinguished the genotypes based on flower petal colour in cluster bean. Flower petal colour aids removal of off-type plants, contaminants there by maintenance of genetic purity of seed production plots. It was reported in cotton, that hybrids were successfully recognized and distinguished by morphological markers such as flower colour, spot position and their colours in petal, fibre colour, seed linter, leaf colour and their shapes (Hosseini 2014). Therefore, above qualitative traits will be very much useful for identifying true hybrids in hybridization programme. Correlation Correlation matrix was calculated from the standardized data of only 17 qualitative traits, since other nine characters such as hypocotyl pigmentation, leaf gossypol glands, leaf nectaries, leaf petiole pigmentation, plant stem pigmentation, male sterility, boll bearing habit, boll prominence of tip and boll opening were excluded due to lack of variability. Correlation coefficient (Pearson 1901), among the 17 qualitative traits brought out the significant positive correlation of leaf colour with boll colour, pollen colour and flower petal colour; however, negatively correlated with density of seed fuzz. The trait leaf hairiness has positive significance with stem hairiness, boll shape and density of seed fuzz. The highly positive significant correlation was observed between the traits leaf appearance with seed fuzz colour; leaf shape with stem hairiness, bract type, flower petal colour, flower anther filament colouration, flower pollen colour, boll colour and boll surface. The stem hairiness has positive association with density of seed fuzz. The flower petal colour was positively correlated with flower petal spot, anther filament colour, pollen colour and boll surface whereas negatively correlated with fibre colour. Flower petal spot exhibited a positive correlation with position of stigma, anther filament colour, pollen colour, boll colour, boll shape and boll surface. This was negatively correlated with seed fuzz colour. The positive association of position of stigma with boll colour; anther filament colour with boll colour and boll surface; pollen colour with boll colour, boll shape and boll surface; boll colour with boll surface; boll shape with boll surface were observed. Fibre colour showed negative correlation with leaf shape, pollen colour, petal colour, anther filament colour and boll surface (Table 2). 2410
5 Principal Component Analysis (PCA) The maintenance and exploitation of genetic resources could be made possible by partitioning the total variance into its components. It also provides a chance for utilization of appropriate genetic resource in crop improvement for a particular plant trait (Sneath and Sokal 1973; Pecetti et al., 1996). The Principal Component Analysis divides the total variance into different factors which is considered as a powerful tool to obtain parental lines for a successful breeding programme (Akter et al., 2009). To discern patterns of variation, PCA was performed on all variables simultaneously. In this study, seven significant principal components (PCs) extracted had Eigen value >1 and this seven values accounted for a cumulative variation of 76.67%. However, the remaining ten components contributed only 23.33% towards the total diversity for this set of cotton genotypes. Among the seven PCs which has Eigen value >1, the first principal component (PC I) explained the most variability accounted for 23.87%, followed by 11.85%, %, 8.42 %, 8.21%, 7.05% 6.52%, the remaining components respectively in the ascending order for total variation (Table 3). Table.1 Table of frequency distribution of qualitative characteristics for tetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L) Sl. No. Descriptors Scores states Number of Frequency genotypes (%) 1 Hypocotyl: Pigmentation 1 Absent Present Light green Leaf: Colour 2 Green Light red Dark red Sparse Leaf: Hairiness 5 Medium Dense Leaf: Appearance 1 Cup Flat Leaf: Gossypol glands 1 Absent Present Leaf: Nectaries 1 Absent Present Leaf: Petiole 1 Absent - - pigmentation 9 Present Palmate (Normal) Leaf: Shape 2 Semi-digitate (Semi- Okra) Digitate (Okra) Lanceolate (Super Okra) Smooth Plant: Stem hairiness 3 Sparse Medium Dense
6 10 Plant: Stem pigmentation 1 Absent Present Bract: Type 3 Normal Frego Cream Flower: Petal colour 2 Yellow Deep Yellow Purple Flower: Petal spot 1 Absent Present Flower: Stigma 3 Embedded Exerted Flower: Anther Filament 1 Absent colouration 9 Present White Cream Flower: Pollen colour 3 Yellow Deep Yellow Purple Flower: Male Sterility 1 Absent Present Boll: Bearing habit 1 Solitary Cluster Boll: Colour 3 Green Red Round Boll: Shape (longitudinal 5 Ovate section) 7 Elliptic Boll: Surface 1 Smooth Pitted Boll: Prominence of tip 1 Blunt Pointed Boll: Opening 3 Semi-open Open Naked Seed: Fuzz 3 Sparse Medium Dense White Seed: Fuzz colour 2 Grey Green Brown White Fibre: Colour 2 Cream Green Brown
7 Table.2 Correlation among qualitative traits in Gossypium hirsutum L. cotton genotypes LC LH LA LS SH BT FPC FPS FS FAFC FPOC BC BSH BS SF SFC FC LC LH LA LS SH BT FPC FPS FS FAFC FPOC BC BSH BS SF SFC FC Values in bold are significant at 5%, LC Leaf Colour; LH Leaf Hairiness; LA Leaf Appearance; LS Leaf shape; SH Stem hairiness; BT bract type; FPC Flower petal colour; FPS Flower petal spot; FS Flower stigma; FAFC Flower Anther Filament Colouration; FPOC Flower Pollen colour; BC Boll Colour; BS Boll Shape; BS Boll Surface; SF Seed Fuzz; SFC Seed Fuzz Colour; FC Fibre Colour 2413
8 Table.3 Principal Components with Eigen values >1.0 for various traits in Gossypium hirsutum L. cotton genotypes Characters Principal Components PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 PC6 PC7 Boll shape Boll Colour Flower Petal Colour Flower Petal Spot Flower Anther Filament Colour Flower Pollen Colour Fibre Colour Stem Hairiness Leaf Hairiness Leaf Shape Leaf Appearance Leaf Colour Seed Fuzz Bract Type Seed Fuzz Colour Flower Stigma Boll Shape Eigen values Variability (%) Cumulative (%)
9 Table.4 Grouping of Gossypium hirsutum L. cotton genotypes based on qualitative traits Clusters No. of genotypes Genotypes I E, AB 6, AC738, ACP 71, AH 107, AK 32, AKH 07 R, Bikaneri Nerma, Ca/H- 128, Ca/ H- 129, Ca/ MH -133, MDH 89, CPD 423, CSH -19, DHY 286 1, DS 28 F, M 12, MCU 13, T 7, VC 21, VC 22, VC 31, J 34, Khandwa 3, F 1378, G cot. 10, G cot. 16, G cot. 100, PIL 43, RHC 006, KH 11, PG 5, PG 6, K 35, L 604, LRA 5166 II 57 AK 23 B, CPD 420, CPD 428, CSH -8, G COT 18, GUJARAT 67, H 1098, H 1117, H 1157, HLS 329, BN Red, LRA 5166 (SB), M 2, MCU 3, MCU 4, MCU 7, MCU 8, NCH 11, NH 452, PH 325, PH 93, PUSA 8-6, REBA B 50, RHC 003, RS -2013, RS- 810, RS-875, RST -9, Suman, TCH 1218, H 1220, VC 32, Vikas, Vikram, H 974, HHM -1, F 286, LH 1134, F 320, LH 372, J 205, LSS, LH 886, Badnawar 1, GSHV 112, HS 6, AKH 081, Deviraj, F 1054, F 1861, F 505, F 846, LH 1556, PIL 8, LH 900, Surat Dwarf, Khandwa 2 III 5 K 34007, Kanchana, PRS 74, SH 2379, L 389 IV 2 GSB 39, SRT GMS1, V 1 GSAV 1056 Table.5 Mean values of clusters for various qualitative traits in Gossypium hirsutum L. tetraploid cotton Variable Cluster I Cluster II Cluster III Cluster IV Cluster V HP LC LH LA LGG LN LPP LS SH SP BT FPC FPS FS FAFC FPC FMS BBH BC BS BS BPT BO SF SFC FC Table.6 Shannon-Weaver Diversity Indices (H ) of different traits Characters HP LC LH LA LGG LN LPP LS SH SP BT H Characters FPC FPS FS FAFC FPC FMS BBH BC BS BS BPT H Characters BO SF SFC FC Average S.d H
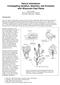
10 Component 2 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(8): Fig.1 Scatter plot based on PC1 and PC2 of qualitative characters 4 FS FPS SH SF 28 FC 27 LC LGG LN LPP SP FMS BBH HP BPT BO BT 1 3 BC FAFC SFC FPC LS BS FPC LA BS -2 LH Component 1 Fig.2 Two dimensional ordinations of 101 germplasm lines of upland cotton 2416
11 Fig.3 Dendrogram based on Ward s linkage method of qualitative characters 2417
12 The traits like boll surface, boll colour, petal colour, petal spot, anther filament colour, pollen colour and leaf shape showed considerably positive factor loadings on PC I while leaf hairiness and leaf appearance showed negative loadings. The 2 nd PC was related to diversity among cotton genotypes due to plant stem hairiness, leaf hairiness, seed fuzz, bract type and leaf shape with their positive loadings. The PC III was explained by variation due to leaf shape, leaf appearance, seed fuzz colour, and bract type with their positive loadings whereas negative loadings exhibited by leaf colour. The PC IV was elucidated diversity for leaf colour and bract type with positive loadings. The PC V exhibited variation due to bract type and flower stigma. The PC VI was related to diversity due to seed fuzz colour, flower stigma and fibre colour. The PC VII was related to diversity for boll shape and leaf appearance. Unlike quantitative traits, qualitative traits are widely preferred for morphological characterization of the germplasm, because they are relatively less influenced by the environment. They form discrete phenotypic classes and therefore highly useful tool for classifying genotypes that are predominantly assessed visually, even by novice evaluators. Thus, in large numbers of crops DUS (distinctiveness, uniformity and stability) descriptors for plant varieties are defined using qualitative traits. However, their numbers are often limited and the spectrum of variability are relatively low (Kruskal 1978). On the other hand Ghafoor et al., (2001) showed multivariate analyses would be the valid system to deal with germplasm evaluation. Grouping genotypes based on PCA biplot A scatter plot (Fig. 1) was drawn using PC1 and PC2 factor scores (Table 4). A clear pattern of grouping of genotypes was observed in the factor plane. Convex of the hull occupied by the genotypes namely L389, PRS 74, Kanchana, BN Red, Bikanari Nerma, DHY 286-1, AK 32 and SRT-GMS1 and also showed the highest point of diversity among the genotypes. These diverse genotypes can be easily distinguishable among the rest and may be used as distinct parents for further breeding programmes, especially hybridization. The genotypes AC 738 and GSAV -39 held in proximity with each other which may fall in same group. The genotype GSAV 1056 separately placed in a single point indicated its distinctness. The other genotypes are congregated in a single position in the pane. In the PC biplot, variables and genotypes are super imposed as vectors. The relative length of the vector represents the proportion of variability existed in each variable. The varieties which were far away from the origin showed more diversity with less similarity over other varieties. The distance of each variable with respect to PC-1 and PC-2 showed the contribution of these variables towards the variation of genotypes studied. High amount of variation observed for stem hairiness, leaf hairiness, bract type, leaf shape, anther filament colour, pollen colour, petal colour, boll shape, boll colour and petal spot. The traits fibre colour and leaf appearance is not in desirable direction. The remaining traits exhibited least variability (Fig. 2). The variability among the traits studied exhibited divergently across the genotypes which can be utilized effectively. Cluster analysis The factors corresponding to 17 PCs were subjected to cluster analysis based on Agglomerative hierarchical clustering performed on the Euclidean distance matrix 2418
13 utilizing the Ward s linkage method and the resultant dendrogram is presented in figure 3. The dendrogram showed five distinct clusters. The cluster II is the largest, comprising 57 genotypes followed by cluster I, which accommodate 36 genotypes. Rest of the genotypes are occupied by clusters III, IV and V each containing five, two and one genotype respectively. The cluster V is a solitary occupying the genotype GSAV 1056 (Table 4). Therefore, this genotype can be directly used as a morphological marker. May et al., (1995) reported that cluster analysis identified groups of cotton cultivars those were more closely related. The cluster I is contributed maximum by leaf hairiness (LH) and bract type (BT). Similarly, the cluster II comprised of genotypes having the highest value and reasonable values of leaf colour (LC). None of the traits contributed towards cluster III as has been exhibited. The genotypes in cluster IV showed higher values of boll surface (BS), boll shape (BSh) and petal colour. The cluster V is characterised maximum by boll surface (BS), anther filament colour (FAFC), petal spot (FPS), stem hairiness (SH), boll colour (BC), position of stigma (FS) (Table 5). Higher level of dissimilarity was found between the pairs of genotype namely Kanchana and GSAV 1056 (15.75); F 1378 and GSAV 1056 (14.697); G.cot.18 and GSAV 1056 (14.697); F 1378 and GSB 39 (14.49); G.cot. 18 and GSB 39(13.93); Kanchana and GSB 39 (13.34); F 1378 and Kanchana (5.66); G.cot.18 and Kanchana (4.899); F 1378 and G.cot.18 (2.83). However, the remaining pairs of genotype were found to possess zero dissimilarity indices. It is clearly evident that genotypes Kanchana, F 1378 and G.cot.18 were quite different from GSAV 1056 and GSB 39. The divergent genotypes can be used for hybridisation programme. It was reported that cluster analysis had the singular efficacy and ability to identify accessions with the highest level of similarity using dendrogram (Aliyu et al., 2000). Pillay and Myers (1999) and Abdukarimov et al., (2003) have observed low genetic diversity in cotton while employing cluster analysis. Shannon Weaver diversity index (H ) The H of 26 qualitative traits was used for estimating the frequency distribution of diversity index (Table 6). The H of the traits hypocotyl pigmentation, gossypol glands, leaf nectarines, petiole pigmentation, stem pigmentation, male sterility, boll bearing habit, boll prominence of tip and boll opening were higher (4.62). An average index (H ) of 4.58 was observed for 26 qualitative traits. In conclusion, the PC analysis, cluster analysis and correlation coefficient in the present set of experimental data facilitated classification of genotypes. The principal component analysis, which reduces the number of traits, is in accordance with the results of cluster analysis and correlation analysis of the characteristics. The genotype GSAV 1056 having semi digitate leaf shape, presence of petal spot, anther filament colour, red coloured boll and pitted boll surface form a solitary cluster. Therefore, this genotype can be used for future breeding programme. These distinct morphological traits can be useful for maintaining the varietal purity and aid to identify the presence off-types. In the era of Intellectual Property Rights, and Plant Breeder s Right s, qualitative morphological traits can be used as DUS (Distinctiveness, Uniformity and Stability) characters for Plant Variety Protection. In conclusion, these study clearly emphasis the use of morphological markers in characterization and utilization of plant genetic resources of cotton. 2419
14 References Abdukarimov AS, Djataev S, Abdukarimov I (2003) Cotton Research in Uzbekistan: Elite Varieties and Future Cotton Breeding. Proceedings of World Cotton Research Conference, Cape Town, 27 September 2004, Akter A, Hasan MJ, Paul AK, Mutlib MM, Hossain MK (2009) Selection of parent for improvement of restorer line in rice (Oryzasativa L.). SAARC Journal of Agriculture 7: Aliyu BN, Fawal Q, Kohel RJ (2000) Inheritance of Pubescence in Crosses between V. unguiculata and V. rhomboidea. Nigerian Journal of Genetics, 15, Chen ZJ, Scheffler B E, Dennis E, Triplett B, Zhang T, Chen X, Stelly DM, Rabinowicz PD, Town C, Arioli T, Brubaker C, Cantrell R, Lacape JM, Ulloa M, Chee P, Gingle AR, Haigler C H, Percy R, Saha S, Wilkins T, Wright RJ, Deynze AV, Zhu Y, Yu S, Guo W, Abdurakhmonov I, Katageri I, Rahman M, Zafar Y, Yu JZ, Kohel RJ, Wendel J, Paterson AH (2007) Towards sequencing cotton (Gossypium) genomes. Plant Physiol. 145: Dutt Y, Wang XD, Zhu YG, Li YY (2004) Breeding for high yield and fibre quality in coloured cotton. Plant Breed. 123: Esmail RM, Zhang JF, Abdel-Hamid AM (2008) Genetic diversity in elite cotton germplasm lines using field performance and RAPD markers. World Journal of Agriculture Science 4: Ghafoor A, Sharif A, Ahmad Z, Zahid MA, Rabbani MA (2001) Genetic Diversity in Black Gram (Vigna mungo L.). Field Crops Research, 69: Hammer O, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electr. 4: 1 9 Hosseini G (2014) Estimation of genetic parameters for quantitative and qualitative traits in cotton cultivars (Gossypium hirsutum L. and Gossypium barbadense L.) and new scaling test of additive dominance model. Journal of Plant Molecular Breeding, 2(1): Iqbal MJ, Aziz N, Saeed NA, Zafar Y (1997) Genetic diversity evaluation of some elite cotton varieties by RAPD analysis. Theore. Appl. Genet. 94: Kruskal, JB (1978) Factor analysis and principal component analysis: bilinear methods. In: Kruskal WH, Tannur JM (eds) International encyclopedia of statistics. The Free Press, New York, pp Kumar S, Joshi UN, Singh V, Singh JV, Saini ML (2013) Characterization of released and elite genotypes of guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L.) Taub.) From India proves unrelated to geographical origin. Genet Resour Crop Evol. doi: /s Li Z, Wang X, Yan Z, Guiyin Z, Wu L, Jina C, MA Z (2008) Assessment of genetic diversity in glandless cotton germplasm resources by using agronomic traits and molecular markers. Frontiers of Agriculture in China 2: May OL, Bowman DT and Ca lhoun DS (1995). Genetic diversity of US upland cotton cultivars released between 1980 and Crop Sci., 35: Meredith WR Jr. (2000) Cotton yield progress- why has it reached a plateau. Better Crops 84:6-9. Pearson K (1901) On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Philos Mag A. 6: Plantauthority.gov.in 2420
15 Pecetti L, Annicchiario P, Damania AB (1996) Geographic variation in tetraploid wheat (Triticum turgidum spp. Turgidumconvar. Durum) landraces from two provinces in Ethiopia. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 43: Pillay M, Myers GO (1999) Genetic Diversity in Cotton Assessed by Variation in Ribosomal RNA Genes and AFLP Markers. Crop Science, 39: x Saravanan S, Arutchendhil P, Raveendran TS, Koodalimgam K (2006) Assessment of genetic divergence among introgressed culture of Gossypium hirsutum L. through RAPD analysis. J. Applied Sci., Res., 2: Shakeel A, Farooq J, Ali MA, Riaz M, Faooq A, Saeed A, Saleem MF (2011) Inheritance pattern of earliness in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Aust. J. Crop Sci. 5: Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949). The mathematical theory of communication. Univ. of Illinois Press, Urbana. Sharma JR (1998) Statistical and Biometrical Techniques in Plant Breeding. New Age International (P) Limited Publishers, New Delhi Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical Taxonomy: The Principles and practice of numerical classification. Free-Man WF and Co, San Francisco, USA. Van Hintum TJL (1995) Hierarchical approaches to the analysis of genetic diversity in crop plants. In: Hodgkin, T., Brown, A.H.D., Van Hintum T.J.L., Morales, E.A.V. (Eds.) Core collection of plant genetic resources. John Wiley and Sons, pp Ward JH (1963) Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 58: Zada M, Zakir N, Rabbani MA, Shinwari ZA (2013) Assessment of genetic variation in Ethiopian mustard (Brassica carinata A. Braun) germplasm using multivariate techniques. Pak J Bot 45(S1): How to cite this article: Rathinavel, K Exploration of Genetic Diversity for Qualitative Traits among the Extant Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Varieties and Parental Lines. Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci. 6(8): doi:
Morphological characterization of elite genotypes of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)
 J. Cotton Res. Dev. 30 (1) 36-40 (January, 2016) Morphological characterization of elite genotypes of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) POOJA RAI,O. SANGWAN, S.S. SIWACH, R.S. SANGWAN, S.R. PUNDIR
J. Cotton Res. Dev. 30 (1) 36-40 (January, 2016) Morphological characterization of elite genotypes of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) POOJA RAI,O. SANGWAN, S.S. SIWACH, R.S. SANGWAN, S.R. PUNDIR
Study of Genetic Diversity in Some Newly Developed Rice Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 10 (2017) pp. 2693-2698 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.610.317
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 10 (2017) pp. 2693-2698 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.610.317
Evaluation of Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott.) Germplasm Using Multivariate Analysis
 150 Journal of Root Crops, 2011, Vol. 37 No. 2, pp. 150-154 Indian Society for Root Crops ISSN 0378-2409 Evaluation of Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott.) Germplasm Using Multivariate Analysis Central
150 Journal of Root Crops, 2011, Vol. 37 No. 2, pp. 150-154 Indian Society for Root Crops ISSN 0378-2409 Evaluation of Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott.) Germplasm Using Multivariate Analysis Central
Gene Action and Combining Ability in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Involving Indica and Tropical Japonica Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 8-16 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.002
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 8-16 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.002
Genetic Divergence Studies for the Quantitative Traits of Paddy under Coastal Saline Ecosystem
 J. Indian Soc. Coastal Agric. Res. 34(): 50-54 (016) Genetic Divergence Studies for the Quantitative Traits of Paddy under Coastal Saline Ecosystem T. ANURADHA* Agricultural Research Station, Machilipatnam
J. Indian Soc. Coastal Agric. Res. 34(): 50-54 (016) Genetic Divergence Studies for the Quantitative Traits of Paddy under Coastal Saline Ecosystem T. ANURADHA* Agricultural Research Station, Machilipatnam
Evaluation and classification of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) genotypes using principal component analysis
 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 6 (1): 167-174, January 2015 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 6 (1) Jan., 2015 167 Abstract Evaluation and classification of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) genotypes using
Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 6 (1): 167-174, January 2015 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 6 (1) Jan., 2015 167 Abstract Evaluation and classification of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) genotypes using
Komala, N. T*, Gurumurthy, R and Surendra, P
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Morphological Characterization of Advanced Lines of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Derived from Swarna x Ranbir Basmati at Seedling Stage Komala, N. T*, Gurumurthy, R and
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Morphological Characterization of Advanced Lines of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Derived from Swarna x Ranbir Basmati at Seedling Stage Komala, N. T*, Gurumurthy, R and
Morphological and Agronomical Characterization of Common Wheat Landraces (Triticum aestivum L.) Collected from Different Regions of India
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 11 (November-2015) pp. 14-23 www.ijcrar.com Morphological and Agronomical Characterization of Common Wheat Landraces (Triticum aestivum L.) Collected from Different Regions
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 11 (November-2015) pp. 14-23 www.ijcrar.com Morphological and Agronomical Characterization of Common Wheat Landraces (Triticum aestivum L.) Collected from Different Regions
Correlation and Path Coefficient Analysis in Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)
 Available online at www.ijpab.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (3): 70-80 (2015) Research Article Correlation and Path Coefficient Analysis
Available online at www.ijpab.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (3): 70-80 (2015) Research Article Correlation and Path Coefficient Analysis
Genetic Analysis for Heterotic Traits in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Using Six Parameters Model
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.029
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.029
Breeding strategy for improvement of flower and seed yields in safflower
 Breeding strategy for improvement of flower and seed yields in safflower Vrijendra Singh, N. M. Kolekar and N. Nimbkar Nimbkar Agricultural Research Institute, Lonand Road, Phaltan 415523, Maharashtra,
Breeding strategy for improvement of flower and seed yields in safflower Vrijendra Singh, N. M. Kolekar and N. Nimbkar Nimbkar Agricultural Research Institute, Lonand Road, Phaltan 415523, Maharashtra,
GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.)
 Plant Archives Vol. 14 No. 2, 2014 pp. 887-891 ISSN 0972-5210 GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.) B. Senthamizh Selvi*, J. Rajangam and R. Muthuselvi Horticultural Research Station, Tamil Nadu
Plant Archives Vol. 14 No. 2, 2014 pp. 887-891 ISSN 0972-5210 GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.) B. Senthamizh Selvi*, J. Rajangam and R. Muthuselvi Horticultural Research Station, Tamil Nadu
Genetic Variability, Coefficient of Variance, Heritability and Genetic Advance of Some Gossypium hirsutum L. Accessions
 Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2015 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Genetic Variability, Coefficient of Variance, Heritability and
Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2015 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Genetic Variability, Coefficient of Variance, Heritability and
Genetic Diversity by Multivariate Analysis Using R Software
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Shah et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (3): 181-190 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.6596 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (3):
Available online at www.ijpab.com Shah et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (3): 181-190 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.6596 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (3):
Variability Studies in Foxtail Millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv]
![Variability Studies in Foxtail Millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv] Variability Studies in Foxtail Millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv]](/thumbs/94/119241936.jpg) International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 955-960 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.115
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 955-960 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.115
CHARACTER ASSOCIATION AND PATH ANALYSIS IN GARLIC (Allium sativum L) FOR YIELD AND ITS ATTRIBUTES
 SAARC J. Agri., 11(1): 45-52 (2013) CHARACTER ASSOCIATION AND PATH ANALYSIS IN GARLIC (Allium sativum L) FOR YIELD AND ITS ATTRIBUTES S. R. Singh, N. A. Ahmed, S. Lal, Asima Amin 1, Mudasir Amin 5 S. A.
SAARC J. Agri., 11(1): 45-52 (2013) CHARACTER ASSOCIATION AND PATH ANALYSIS IN GARLIC (Allium sativum L) FOR YIELD AND ITS ATTRIBUTES S. R. Singh, N. A. Ahmed, S. Lal, Asima Amin 1, Mudasir Amin 5 S. A.
EXTENT OF HETEROTIC EFFECTS FOR SEED YIELD AND COMPONENT CHARACTERS IN CASTOR (RICINUS COMMUNIS L.) UNDER SEMI RABI CONDITION
 Indian J. Agric. Res.., 47 (4) : 368-372, 2013 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com / indianjournals.com EXTENT OF HETEROTIC EFFECTS FOR SEED YIELD AND COMPONENT CHARACTERS IN
Indian J. Agric. Res.., 47 (4) : 368-372, 2013 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com / indianjournals.com EXTENT OF HETEROTIC EFFECTS FOR SEED YIELD AND COMPONENT CHARACTERS IN
Study of Genetic Variability and Heritability in Sugarcane (Saccharum spp. Complex)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 3112-3117 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.384
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 3112-3117 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.384
Correlation and Path Analysis Study in Dolichos Bean (Lablab purpureus L.)
 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(9): 22282235 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 23197706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 22282235 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(9): 22282235 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 23197706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 22282235 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com
Studies on Fertility Restoration Using Newly Derived Restorers in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)
 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.ci (218) 7(1): 2131-2135 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied ciences IN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 1 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.ci (218) 7(1): 2131-2135 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied ciences IN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 1 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original
Morphological Markers Related to Sex Expression in Papaya (Carica papaya L.)
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Soni et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 526-531 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5132 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4):
Available online at www.ijpab.com Soni et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 526-531 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5132 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4):
Character Association and Path Coefficient Analysis in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1966-1972 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.233
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1966-1972 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.233
Correlation, path and cluster analysis in hyacinth bean (Lablab purpureus L. Sweet)
 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Correlation, path and cluster analysis in hyacinth bean (Lablab purpureus L. Sweet) Singh, ramod K. 1*, Rai, N. 1, Lal, Hira 1, Bhardwaj, D.R.
Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Correlation, path and cluster analysis in hyacinth bean (Lablab purpureus L. Sweet) Singh, ramod K. 1*, Rai, N. 1, Lal, Hira 1, Bhardwaj, D.R.
Combining Ability Estimates for Yield and Fibre Quality Traits in Line X Tester Crosses of Upland Cotton, (Gossypium hirsutum)
 Combining Ability Estimates for Yield and Fibre Quality Traits in Line X Tester Crosses of Upland Cotton, (Gossypium hirsutum) Kaliyaperumal Ashokkumar Department of Plant Molecular Biology and Biotechnology
Combining Ability Estimates for Yield and Fibre Quality Traits in Line X Tester Crosses of Upland Cotton, (Gossypium hirsutum) Kaliyaperumal Ashokkumar Department of Plant Molecular Biology and Biotechnology
Assessment of Variability of Aromatic Rice Using Agro-Morphological Characterization
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 1835-1846 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.219
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 1835-1846 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.219
Prediction and Validation of Three Cross Hybrids in Maize (Zea mays L.)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.183
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.183
MULTIVARIATE ANALYSIS IN ONION (Allium cepa L.)
 ISSN 0258-7122 Bangladesh J. Agril. Res. 37(4): 573-582, December 2012 MULTIVARIATE ANALYSIS IN ONION (Allium cepa L.) M. H. RASHID 1, A. K. M. A. ISLAM 2, M. A. K. MIAN 3 T. HOSSAIN 4 AND M. E. KABIR
ISSN 0258-7122 Bangladesh J. Agril. Res. 37(4): 573-582, December 2012 MULTIVARIATE ANALYSIS IN ONION (Allium cepa L.) M. H. RASHID 1, A. K. M. A. ISLAM 2, M. A. K. MIAN 3 T. HOSSAIN 4 AND M. E. KABIR
ABSTRACT: 54 BREEDING OF HYBRID SOYBEAN ZAYOUDOU NO.1
 ABSTRACT: 54 BREEDING OF HYBRID SOYBEAN ZAYOUDOU NO.1 ZHANG L, DAI O, HUANG Z, LI J, ZHANG L, HU C, YANG J 1.Crop Research Institute of Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2.Key Laboratory of Crop
ABSTRACT: 54 BREEDING OF HYBRID SOYBEAN ZAYOUDOU NO.1 ZHANG L, DAI O, HUANG Z, LI J, ZHANG L, HU C, YANG J 1.Crop Research Institute of Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2.Key Laboratory of Crop
Variability, Heritability and Genetic Advance Analysis in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 2687-2691 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.321
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 2687-2691 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.321
Genetic studies of earliness in Gossypium hirsutum L.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Shakeel et al., IJAVMS, Vol. 6, Issue 3, 2012: 189-207 doi: 10.5455/ijavms.147 Genetic studies of earliness in Gossypium hirsutum L. Amir Shakeel 1, Jehanzeb Farooq 3 *Ameer Bibi 1, Shaham
RESEARCH ARTICLE Shakeel et al., IJAVMS, Vol. 6, Issue 3, 2012: 189-207 doi: 10.5455/ijavms.147 Genetic studies of earliness in Gossypium hirsutum L. Amir Shakeel 1, Jehanzeb Farooq 3 *Ameer Bibi 1, Shaham
Study of Genetic Divergence in Pea (Pisum sativum L.) based on Agro-Morphic Traits
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 3816-3821 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.448
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 3816-3821 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.448
Keywords: CGMS, combining ability, fertility restoration, heterosis, pigeonpea. Introduction
 Sri Lanka Journal of Food and Agriculture (2015) Byregowda et al. 1(2): 1-8 ISSN 2424-6913 Research Paper Identification of fertility restorers, stable combiners and heterotic combinations across environments
Sri Lanka Journal of Food and Agriculture (2015) Byregowda et al. 1(2): 1-8 ISSN 2424-6913 Research Paper Identification of fertility restorers, stable combiners and heterotic combinations across environments
COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN BIDI TOBACCO (NicotianatabacumL.)
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 1373 1380 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 1373 1380 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN
Assessment of genetic variability for quantitative and qualitative traits in Rice Germplasm Accessions (Oryza sativa L.).
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6 Special issue [] 27: 76-83 27 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-88 Journal
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6 Special issue [] 27: 76-83 27 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-88 Journal
Genetic variability, Heritability and Genetic Advance for Yield, Yield Related Components of Brinjal [Solanum melongena (L.
 Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5404 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (5): 872-878 (2017) Research Article Genetic variability, Heritability and Genetic
Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5404 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (5): 872-878 (2017) Research Article Genetic variability, Heritability and Genetic
Studies on genetic divergence on cucumber (Cucumber sativum L.)
 RESEARCH PAPER Asian Journal of Bio Science, Volume 7 Issue 2 October, 2012 169-173 Received : 14.06.2012; Revised : 15.07.2012; Accepted : 20.07.2012 Studies on genetic divergence on cucumber (Cucumber
RESEARCH PAPER Asian Journal of Bio Science, Volume 7 Issue 2 October, 2012 169-173 Received : 14.06.2012; Revised : 15.07.2012; Accepted : 20.07.2012 Studies on genetic divergence on cucumber (Cucumber
Characterization of ICRISAT-bred restorer parents of pearl millet
 Characterization of ICRISAT-bred restorer parents of pearl millet SK Gupta 1 *, Ranjana Bhattacharjee 1,2, KN Rai 1 and M Suresh Kumar 1 1. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics
Characterization of ICRISAT-bred restorer parents of pearl millet SK Gupta 1 *, Ranjana Bhattacharjee 1,2, KN Rai 1 and M Suresh Kumar 1 1. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics
Estimates of Variability for Growth and Yield Attributes in Taro (Colocasia esculenta var. Antiquorum (L.) Schott)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1282-1286 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.155
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1282-1286 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.155
DUS CHARACTERIZATION OF LINSEED (LINUM USITATISSIMUM L.) GERMPLASM
 Plant Archives Vol. 16 No. 1, 2016 pp. 297-302 ISSN 0972-5210 DUS CHARACTERIZATION OF LINSEED (LINUM USITATISSIMUM L.) GERMPLASM Namrata Dhirhi*, Rajshree Shukla, Nandan Mehta, P. K. Singh 1 and S. D.
Plant Archives Vol. 16 No. 1, 2016 pp. 297-302 ISSN 0972-5210 DUS CHARACTERIZATION OF LINSEED (LINUM USITATISSIMUM L.) GERMPLASM Namrata Dhirhi*, Rajshree Shukla, Nandan Mehta, P. K. Singh 1 and S. D.
Genetic Variability and Heritability Estimation in Water Spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk.) Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 3018-3024 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.370
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 3018-3024 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.370
Genetic Divergence for Yield and other Quantitative Traits in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.146
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.146
Lentils biodiversity: the characterization of two local landraces
 Nimis P. L., Vignes Lebbe R. (eds.) Tools for Identifying Biodiversity: Progress and Problems pp. 327-331. ISBN 978-88-8303-295-0. EUT, 2010. Lentils biodiversity: the characterization of two local landraces
Nimis P. L., Vignes Lebbe R. (eds.) Tools for Identifying Biodiversity: Progress and Problems pp. 327-331. ISBN 978-88-8303-295-0. EUT, 2010. Lentils biodiversity: the characterization of two local landraces
Genetic Divergence of Advanced Mutant Breeding Lines, In Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) Assessed Through D 2 Statistics
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 3133-3139 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.387
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 3133-3139 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.387
American Journal of Plant Biology. Performance of Brinjal (Solanum melongena) Genotypes through Genetic Variability Analysis
 Nishi NSB et al. American Journal of Plant Biology 2017, 3:22-30 Page 1 of 9 Research Article American Journal of Plant Biology http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajplantbio/ Performance of Brinjal (Solanum
Nishi NSB et al. American Journal of Plant Biology 2017, 3:22-30 Page 1 of 9 Research Article American Journal of Plant Biology http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajplantbio/ Performance of Brinjal (Solanum
Estimation of Heterosis, Heterobeltiosis and Economic Heterosis in Dual Purpose Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]
![Estimation of Heterosis, Heterobeltiosis and Economic Heterosis in Dual Purpose Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] Estimation of Heterosis, Heterobeltiosis and Economic Heterosis in Dual Purpose Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]](/thumbs/85/92593885.jpg) International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 990-1014 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.109
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 990-1014 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.109
Correlation and path coefficient analysis for seed cotton yield and its components in American cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)
 Agric. Sci. Digest, 35 (1) 2015: 13-18 Print ISSN:0253-150X / Online ISSN:0976-0547 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com Correlation and path coefficient analysis for seed cotton
Agric. Sci. Digest, 35 (1) 2015: 13-18 Print ISSN:0253-150X / Online ISSN:0976-0547 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com Correlation and path coefficient analysis for seed cotton
Phenotypic Diversity of Sri Lankan Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Germplasm Based on Morphological Descriptors
 Tropical Agricultural Research Vol. 18 Phenotypic Diversity of Sri Lankan Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Germplasm Based on Morphological Descriptors J.H.N. Piyasundara, M.T.K. Gunasekare 1, T.U.S. Peiris
Tropical Agricultural Research Vol. 18 Phenotypic Diversity of Sri Lankan Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Germplasm Based on Morphological Descriptors J.H.N. Piyasundara, M.T.K. Gunasekare 1, T.U.S. Peiris
Genetic Variability and Correlation Studies for Yield, Yield contributing and Quality Traits in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Singh and Kumar Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (6): 686-690 (017) ISSN: 30 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1878/30-7051.5793 ISSN: 30 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (6):
Available online at www.ijpab.com Singh and Kumar Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (6): 686-690 (017) ISSN: 30 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1878/30-7051.5793 ISSN: 30 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (6):
Research Notes: G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology
 Volume 1 Article 6 4-1-1974 Research Notes: G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G.
Volume 1 Article 6 4-1-1974 Research Notes: G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G.
Development of male-sterile lines in sorghum
 Development of male-sterile lines in sorghum A Ashok Kumar, Belum VS Reddy, P Sanjana Reddy and B Ramaiah International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru 502 324, Andhra Pradesh,
Development of male-sterile lines in sorghum A Ashok Kumar, Belum VS Reddy, P Sanjana Reddy and B Ramaiah International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru 502 324, Andhra Pradesh,
HETEROSIS AND COMBINING ABILITY IN HYBRID RICE (Oryza sativa L.)
 HETEROSIS AND COMBINING ABILITY IN HYBRID RICE (Oryza sativa L.) B. S. Thorat 1, R. L. Kunkerkar 2, B. L. Thaware, M. M. Burondkar 4 and S. G. Bhave 5 1 M.Sc. (Agri.) Scholar, Dept. of Agril. Botany, 2
HETEROSIS AND COMBINING ABILITY IN HYBRID RICE (Oryza sativa L.) B. S. Thorat 1, R. L. Kunkerkar 2, B. L. Thaware, M. M. Burondkar 4 and S. G. Bhave 5 1 M.Sc. (Agri.) Scholar, Dept. of Agril. Botany, 2
Germplasm. Introduction to Plant Breeding. Germplasm 2/12/2013. Master Gardener Training. Start with a seed
 Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
Introduction to Plant Breeding. Master Gardener Training
 Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
ESTIMATION OF GENETIC DIVERSITY IN LENTIL GERMPLASM
 AGRIVITA VOLUME 33 No. 2 JUNE-2011 ISSN : 0126-0537 103 ESTIMATION OF GENETIC DIVERSITY IN LENTIL GERMPLASM A.K.M.M Alam 1*), R. Podder 1) and A. Sarker 2) 1) Pulses Research Centre, Bangladesh Agricultural
AGRIVITA VOLUME 33 No. 2 JUNE-2011 ISSN : 0126-0537 103 ESTIMATION OF GENETIC DIVERSITY IN LENTIL GERMPLASM A.K.M.M Alam 1*), R. Podder 1) and A. Sarker 2) 1) Pulses Research Centre, Bangladesh Agricultural
Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars
 J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (2010) Vol. 12: 223-231 Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars M. Rahimi 1, B. Rabiei 1*, H. Samizadeh 1, and A. Kafi Ghasemi 1 ABSTRACT Quantitative valuations
J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (2010) Vol. 12: 223-231 Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars M. Rahimi 1, B. Rabiei 1*, H. Samizadeh 1, and A. Kafi Ghasemi 1 ABSTRACT Quantitative valuations
III Conduct of tests:
 Barnyard millet (Echinocloa frumentaceae (Roxb.) Link) I Subject: These test guidelines apply to all the varieties, hybrids and parental lines of Barnyard millet (Echinocloa frumentaceae (Roxb.) Link)
Barnyard millet (Echinocloa frumentaceae (Roxb.) Link) I Subject: These test guidelines apply to all the varieties, hybrids and parental lines of Barnyard millet (Echinocloa frumentaceae (Roxb.) Link)
STUDY ON GENETIC DIVERSITY OF POINTED GOURD USING MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERS. Abstract
 ISSN 0258-7122 Bangladesh J. Agril. Res. 33(3) : 607-616, December 2008 STUDY ON GENETIC DIVERSITY OF POINTED GOURD USING MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERS A.S.M.R. KHAN 1, M.G. RABBANI 2, M.A. SIDDIQUE 3 AND M.I.
ISSN 0258-7122 Bangladesh J. Agril. Res. 33(3) : 607-616, December 2008 STUDY ON GENETIC DIVERSITY OF POINTED GOURD USING MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERS A.S.M.R. KHAN 1, M.G. RABBANI 2, M.A. SIDDIQUE 3 AND M.I.
Kodo millet (Paspalum scorbiculatum L.)
 Kodo millet (Paspalum scorbiculatum L.) I Subject: These test guidelines apply to all the varieties, hybrids and parental lines of Kodo millet (Paspalum scorbiculatum L.) II Material required: 1. The Protection
Kodo millet (Paspalum scorbiculatum L.) I Subject: These test guidelines apply to all the varieties, hybrids and parental lines of Kodo millet (Paspalum scorbiculatum L.) II Material required: 1. The Protection
How to connect to CGIAR wheat (CIMMYT and ICARDA) CRP??- Public wheat breeding for developing world
 Wheat breeding only exploits 10% of the diversity available The public sector can t breed elite varieties-how to connect to private sector breeders?? How to connect to CGIAR wheat (CIMMYT and ICARDA) CRP??-
Wheat breeding only exploits 10% of the diversity available The public sector can t breed elite varieties-how to connect to private sector breeders?? How to connect to CGIAR wheat (CIMMYT and ICARDA) CRP??-
Working Group on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants November 2011
 Working Group on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants November 2011 Highly discriminating descriptors in this descriptor list are marked with an asterisk [ ]. Characterization should preferably be done during
Working Group on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants November 2011 Highly discriminating descriptors in this descriptor list are marked with an asterisk [ ]. Characterization should preferably be done during
Linkage between genes for leaf colour, plant pubescence, number of leaflets and plant height in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.)
 Euphytica (2005) 145: 41 48 DOI: 10.1007/s10681-005-0103-z C Springer 2005 Linkage between genes for leaf colour, plant pubescence, number of leaflets and plant height in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.)
Euphytica (2005) 145: 41 48 DOI: 10.1007/s10681-005-0103-z C Springer 2005 Linkage between genes for leaf colour, plant pubescence, number of leaflets and plant height in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.)
CRUCIFER AND OTHER OIL OR FIBRE SPECIES. -- Cruciferae --
 CRUCIFER AND OTHER OIL OR FIBRE SPECIES -- Cruciferae -- BROWN MUSTARD (Brassica juncea L. Czernj. et Cosson) number # Vegetative - seed cotyledons: length - seed cotyledons: width - leaf: colour - leaf:
CRUCIFER AND OTHER OIL OR FIBRE SPECIES -- Cruciferae -- BROWN MUSTARD (Brassica juncea L. Czernj. et Cosson) number # Vegetative - seed cotyledons: length - seed cotyledons: width - leaf: colour - leaf:
IDENTIFICATION OF SOME HIBISCUS GERMPLASM THROUGH NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
 Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon. 13(1): 49-54, 2006 (June) IDENTIFICATION OF SOME HIBISCUS GERMPLASM THROUGH NUMERICAL ANALYSIS NAZMUL ALAM 1, MOSTAFA KAMAL PASHA AND SHAMSUDDIN AHMAD 2 Department of Botany,
Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon. 13(1): 49-54, 2006 (June) IDENTIFICATION OF SOME HIBISCUS GERMPLASM THROUGH NUMERICAL ANALYSIS NAZMUL ALAM 1, MOSTAFA KAMAL PASHA AND SHAMSUDDIN AHMAD 2 Department of Botany,
ESTIMATION OF GERMINATION POSSIBILITIES OF SOME PEAS STORAGES ACCESSIONS AND THE EVALUATION OF SOME QUALITATIVE INDICATORS ON ALBANIAN PLANT GENE BANK
 ESTIMATION OF GERMINATION POSSIBILITIES OF SOME PEAS STORAGES ACCESSIONS AND THE EVALUATION OF SOME QUALITATIVE INDICATORS ON ALBANIAN PLANT GENE BANK Conference on Biotechnological Developments 21 November
ESTIMATION OF GERMINATION POSSIBILITIES OF SOME PEAS STORAGES ACCESSIONS AND THE EVALUATION OF SOME QUALITATIVE INDICATORS ON ALBANIAN PLANT GENE BANK Conference on Biotechnological Developments 21 November
MAGNITUDE OF HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY IN SUNFLOWER OVER ENVIRONMENTS
 Pak. J. Bot., 40(1): 301-308, 2008. MAGNITUDE OF HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY IN SUNFLOWER OVER ENVIRONMENTS HAKIM KHAN 1, HIDAYAT-UR-RAHMAN 2, * HABIB AHMAD 3, HAIDAR ALI 4, INAMULLAH 3 AND MUKHTAR ALAM
Pak. J. Bot., 40(1): 301-308, 2008. MAGNITUDE OF HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY IN SUNFLOWER OVER ENVIRONMENTS HAKIM KHAN 1, HIDAYAT-UR-RAHMAN 2, * HABIB AHMAD 3, HAIDAR ALI 4, INAMULLAH 3 AND MUKHTAR ALAM
Pollen fertility Vs Spikelet fertility in F2 of a CMS based hybrids in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Aerobic condition
 Research Article Pollen fertility Vs Spikelet fertility in F of a CMS based hybrids in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Aerobic condition N.Naresh Babu,N.Shivakumar and Shailaja Hittalmani Abstract : Identification
Research Article Pollen fertility Vs Spikelet fertility in F of a CMS based hybrids in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Aerobic condition N.Naresh Babu,N.Shivakumar and Shailaja Hittalmani Abstract : Identification
TECHNICAL WORKING PARTY FOR AGRICULTURAL CROPS. Twenty-Ninth Session Uppsala, Sweden, June 27 to 30, 2000
 E TWA/29/17 ORIGINAL: English DATE: June 6, 2000 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA TECHNICAL WORKING PARTY FOR AGRICULTURAL CROPS Twenty-Ninth Session Uppsala, Sweden,
E TWA/29/17 ORIGINAL: English DATE: June 6, 2000 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA TECHNICAL WORKING PARTY FOR AGRICULTURAL CROPS Twenty-Ninth Session Uppsala, Sweden,
Genetic Diversity Study in Relation to Yield and Quality Traits in Little Millet (Panicum miliare L.)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.319
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.319
Situation of corn in Myanmar
 Situation of corn in Myanmar Phyu Phwe New Plant Variety Protection Unit Department of Agricultural Research(DAR) (2. 8.2016) Introduction Maize - second mandate cereal in Myanmar after rice Mainly utilized
Situation of corn in Myanmar Phyu Phwe New Plant Variety Protection Unit Department of Agricultural Research(DAR) (2. 8.2016) Introduction Maize - second mandate cereal in Myanmar after rice Mainly utilized
INHERITANCE OF OKRA LEAF TYPE, GOSSYPOL GLANDS AND TRICHOMES IN COTTON ABSTRACT
 Nawab et al., The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 24(2): 2014, Page: J. 526-533 Anim. Plant Sci. 24(2):2014 ISSN: 1018-7081 INHERITANCE OF OKRA LEAF TYPE, GOSSYPOL GLANDS AND TRICHOMES IN COTTON N.
Nawab et al., The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 24(2): 2014, Page: J. 526-533 Anim. Plant Sci. 24(2):2014 ISSN: 1018-7081 INHERITANCE OF OKRA LEAF TYPE, GOSSYPOL GLANDS AND TRICHOMES IN COTTON N.
Genetic Analysis of Yield and its Components of Some Egyptian Cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.) Varieties
 World Journal of Agricultural Sciences 6 (5): 65-6 00 ISSN 87-3047 IDOSI Publications 00 Genetic Analysis of Yield and its Components of Some Egyptian Cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.) Varieties 3 S.H.M.
World Journal of Agricultural Sciences 6 (5): 65-6 00 ISSN 87-3047 IDOSI Publications 00 Genetic Analysis of Yield and its Components of Some Egyptian Cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.) Varieties 3 S.H.M.
Date Received: 09/15/2013; Date Revised: 10/05/2013; Date Published Online: 10/25/2013
 ARTICLE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL Advancements in Life Sciences Date Received: 09/15/2013; Date Revised: 10/05/2013; Date Published Online: 10/25/2013 Open Access Heritability, heterosis and heterobeltiosis
ARTICLE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL Advancements in Life Sciences Date Received: 09/15/2013; Date Revised: 10/05/2013; Date Published Online: 10/25/2013 Open Access Heritability, heterosis and heterobeltiosis
IN SUNFLOWER (HELIANTHUS ANNUUS L.)
 Recent Research in Science and Technology 2009, 1(5): 202 206 ISSN: 2076-5061 www.recent-science.com GENETICS & GENOMICS USING LINE X TESTER ANALYSIS FOR EARLINESS AND PLANT HEIGHT TRAITS IN SUNFLOWER
Recent Research in Science and Technology 2009, 1(5): 202 206 ISSN: 2076-5061 www.recent-science.com GENETICS & GENOMICS USING LINE X TESTER ANALYSIS FOR EARLINESS AND PLANT HEIGHT TRAITS IN SUNFLOWER
Development of genotype independent cotton transformation protocol
 Development of genotype independent cotton transformation protocol Shyam Barampuram and Sergei Krasnyanski Department of Horticultural Science North Carolina State University What are our goals? Robust
Development of genotype independent cotton transformation protocol Shyam Barampuram and Sergei Krasnyanski Department of Horticultural Science North Carolina State University What are our goals? Robust
Estimates of Genetic variability, heritability and genetic advance of oat (Avena sativa L.) genotypes for grain and fodder yield
 Agricultural Science Research Journals Vol. 3(2), pp. 56-61, February 2013 Available online at http://www.resjournals.com/arj ISSN-L:2026-6073 2013 International Research Journals Full Length Research
Agricultural Science Research Journals Vol. 3(2), pp. 56-61, February 2013 Available online at http://www.resjournals.com/arj ISSN-L:2026-6073 2013 International Research Journals Full Length Research
Assessment of Genetic Variation in Selected Germplasm of White Jute (Corchorus capsularis L.)
 Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 39 (1): 41-53 (2016) TROPICAL AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ Assessment of Genetic Variation in Selected Germplasm of White Jute
Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 39 (1): 41-53 (2016) TROPICAL AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ Assessment of Genetic Variation in Selected Germplasm of White Jute
Genetic divergence studies for fibre yield traits in roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa l.) In terai zone of West Bengal
 Journal Crop and Weed, 11(Special Issue):90-94(015) Genetic divergence studies for fibre yield traits in roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa l.) In terai zone of West Bengal 1 N. HARI SATYANARAYANA, S. MUKHERJEE,
Journal Crop and Weed, 11(Special Issue):90-94(015) Genetic divergence studies for fibre yield traits in roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa l.) In terai zone of West Bengal 1 N. HARI SATYANARAYANA, S. MUKHERJEE,
BREEDING AND GENETICS
 The Journal of Cotton Science 6:97-103 (2002) http://journal.cotton.org, The Cotton Foundation 2002 97 BREEDING AND GENETICS Assessment of Day-Neutral Backcross Populations of Cotton Using AFLP Markers
The Journal of Cotton Science 6:97-103 (2002) http://journal.cotton.org, The Cotton Foundation 2002 97 BREEDING AND GENETICS Assessment of Day-Neutral Backcross Populations of Cotton Using AFLP Markers
Status Analysis: projecting genotype performance into long term environment discrimination space
 Status Analysis: projecting genotype performance into long term environment discrimination space Ian H. DeLacy, Vivi N. Arief, Kaye E. Basford The University of Queensland, School of Agriculture and Food
Status Analysis: projecting genotype performance into long term environment discrimination space Ian H. DeLacy, Vivi N. Arief, Kaye E. Basford The University of Queensland, School of Agriculture and Food
QUANTITATIVE INHERITANCE OF SOME PHYSIOLOGICAL TRAITS FOR SPRING WHEAT UNDER TWO DIFFERENT POPULATION DENSITIES
 Pak. J. Bot., 40(2): 581-587, 2008. QUANTITATIVE INHERITANCE OF SOME PHYSIOLOGICAL TRAITS FOR SPRING WHEAT UNDER TWO DIFFERENT POPULATION DENSITIES SYED EJAZ-UL-HASSAN * AND IHSAN KHALIQ ** * Tobacco Research
Pak. J. Bot., 40(2): 581-587, 2008. QUANTITATIVE INHERITANCE OF SOME PHYSIOLOGICAL TRAITS FOR SPRING WHEAT UNDER TWO DIFFERENT POPULATION DENSITIES SYED EJAZ-UL-HASSAN * AND IHSAN KHALIQ ** * Tobacco Research
Development of Superior Hybrids for Fibre Quality based on Heterosis and Combining Ability in Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 448-461 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.059
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 448-461 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.059
Cotton Research Institute, Nazilli-Aydın, TURKEY * Corresponding author: Received: ABSTRACT
 Turk J Field Crops 2018, 23(2), 146-150 DOI: 10.17557/tjfc.433651 THE DETERMINATION OF LEAF ANATOMY, YIELD AND QUALITY CHARACTERISTICS IN F1 AND F2 GENERATIONS OF INTERSPECIFIC COTTON HYBRIDS (Gossypium
Turk J Field Crops 2018, 23(2), 146-150 DOI: 10.17557/tjfc.433651 THE DETERMINATION OF LEAF ANATOMY, YIELD AND QUALITY CHARACTERISTICS IN F1 AND F2 GENERATIONS OF INTERSPECIFIC COTTON HYBRIDS (Gossypium
Studies on genetic diversity in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012 Vol. 8(3): 1059-1065 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012, Vol. 8(3): 1059-1065 ISSN 1686-9141 Studies on genetic
Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012 Vol. 8(3): 1059-1065 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2012, Vol. 8(3): 1059-1065 ISSN 1686-9141 Studies on genetic
GGE Biplot Analysis for Thermo Sensitive Genic Male Sterile Lines of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Multi-Environment Trials
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.021
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.021
Genetic Diversity Studies in Desmodium gangeticum (L.) DC.
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 2 (2017) pp. 424-429 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.602.047
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 2 (2017) pp. 424-429 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.602.047
A Numerical Taxonomic Study of the Avocado (Persea americana Mill.) 1
 J. Amer. Soc. Hort Sci. 96(3):391-395. 1971. A Numerical Taxonomic Study of the Avocado (Persea americana Mill.) 1 A. M. Rhodes, Simon E. Malo, Carl W. Campbell 2, and S. G. Carmer 3 University of Illinois,
J. Amer. Soc. Hort Sci. 96(3):391-395. 1971. A Numerical Taxonomic Study of the Avocado (Persea americana Mill.) 1 A. M. Rhodes, Simon E. Malo, Carl W. Campbell 2, and S. G. Carmer 3 University of Illinois,
Identification of Discriminating Morphological Descriptors for Characterization of Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Germplasm in Sri Lanka
 Tropical Agricultural Research Vol. 20: 193-199 (2008) Identification of Discriminating Morphological Descriptors for Characterization of Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Germplasm in Sri Lanka J.H.N. Piyasundara,
Tropical Agricultural Research Vol. 20: 193-199 (2008) Identification of Discriminating Morphological Descriptors for Characterization of Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Germplasm in Sri Lanka J.H.N. Piyasundara,
Study of Heterosis Using Wild Abortive (WA) CMS Lines on Yield, Quality and Drought Related Traits in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 2631-2640 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.311
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 2631-2640 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.311
SABESAN Thayumanavan*, SARAVANAN Kannapiran and ANANDAN Annamalai
 ORIGINAL PAPER GENETIC DIVERGENCE ANALYSIS FOR CERTAIN YIELD AND QUALITY TRAITS IN RICE (ORYZA SATIVA L.) GROWN IN IRRIGATED SALINE LOW LAND OF ANNAMALAINAGAR, SOUTH INDIA SABESAN Thayumanavan*, SARAVANAN
ORIGINAL PAPER GENETIC DIVERGENCE ANALYSIS FOR CERTAIN YIELD AND QUALITY TRAITS IN RICE (ORYZA SATIVA L.) GROWN IN IRRIGATED SALINE LOW LAND OF ANNAMALAINAGAR, SOUTH INDIA SABESAN Thayumanavan*, SARAVANAN
Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants
 Introduction Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants Daniel Lauffer Wisconsin Fast Plants Program University of Wisconsin - Madison Since the dawn
Introduction Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants Daniel Lauffer Wisconsin Fast Plants Program University of Wisconsin - Madison Since the dawn
Genetic diversity study of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moenc) genotypes, Ethiopia
 ACTA UNIVERSITATIS SAPIENTIAE AGRICULTURE AND ENVIRONMENT, 9 (2017) 44 54 DOI: 10.1515/ausae-2017-0004 Genetic diversity study of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moenc) genotypes, Ethiopia Kassahun TESFAYE
ACTA UNIVERSITATIS SAPIENTIAE AGRICULTURE AND ENVIRONMENT, 9 (2017) 44 54 DOI: 10.1515/ausae-2017-0004 Genetic diversity study of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moenc) genotypes, Ethiopia Kassahun TESFAYE
Genetic Parameters for Yield and Yield Components in F 1 Hybrids and Parents of Bell Pepper
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 03 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.308
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 03 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.308
PLEIOTROPIC GENE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON STEM, PETIOLE AND BRACT TIP PIGMENTATION IN SUNFLOWER (Helianthus annuus L.)
 HELIA, 28, Nr. 43, p.p. 107-112, (2005) UDC 633.854.78:631.523 PLEIOTROPIC GENE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON STEM, PETIOLE AND BRACT TIP PIGMENTATION IN SUNFLOWER (Helianthus annuus L.) T.V. Deveraja * and Shanker
HELIA, 28, Nr. 43, p.p. 107-112, (2005) UDC 633.854.78:631.523 PLEIOTROPIC GENE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON STEM, PETIOLE AND BRACT TIP PIGMENTATION IN SUNFLOWER (Helianthus annuus L.) T.V. Deveraja * and Shanker
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Studies on Genetic Divergence in High Yielding Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Genotypes G. Bharathi, B. Krishna Veni*, M. Lal Ahamed and K. Jaya Lalitha Department of Genetics
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Studies on Genetic Divergence in High Yielding Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Genotypes G. Bharathi, B. Krishna Veni*, M. Lal Ahamed and K. Jaya Lalitha Department of Genetics
HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY STUDIES FOR SUPERIOR SEGREGANTS SELECTION IN CHICKPEA
 Pak. J. Bot., 39(7): 2443-2449, 2007. HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY STUDIES FOR SUPERIOR SEGREGANTS SELECTION IN CHICKPEA AHMED BAKHSH *, SHAHID RIAZ MALIK **, UMER IQBAL ** AND WAHEED ARSHAD * * PMAS Arid
Pak. J. Bot., 39(7): 2443-2449, 2007. HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY STUDIES FOR SUPERIOR SEGREGANTS SELECTION IN CHICKPEA AHMED BAKHSH *, SHAHID RIAZ MALIK **, UMER IQBAL ** AND WAHEED ARSHAD * * PMAS Arid
7.2: Natural Selection and Artificial Selection pg
 7.2: Natural Selection and Artificial Selection pg. 305-311 Key Terms: natural selection, selective pressure, fitness, artificial selection, biotechnology, and monoculture. Natural Selection is the process
7.2: Natural Selection and Artificial Selection pg. 305-311 Key Terms: natural selection, selective pressure, fitness, artificial selection, biotechnology, and monoculture. Natural Selection is the process
CHARACTERIZATION AND INHERITANCE OF COTTON LEAF PUBESCENCE
 Pak. J. Bot., 43(1): 649-658, 2011. CHARACTERIZATION AND INHERITANCE OF COTTON LEAF PUBESCENCE N. N. NAWAB 1, I. A. KHAN 1, A.A. KHAN 1 AND M. AMJAD 2 1 Department of Plant Breeding and Genetics, 2 Institute
Pak. J. Bot., 43(1): 649-658, 2011. CHARACTERIZATION AND INHERITANCE OF COTTON LEAF PUBESCENCE N. N. NAWAB 1, I. A. KHAN 1, A.A. KHAN 1 AND M. AMJAD 2 1 Department of Plant Breeding and Genetics, 2 Institute
Correlation and path coefficient analysis in tuberose
 Journal of Crop and Weed, 9(2):44-49(2013) Correlation and path coefficient analysis in tuberose VANLALRUATI, T. MANDAL AND S. PRADHAN Department of Floriculture and Landscaping, Faculty of Horticulture
Journal of Crop and Weed, 9(2):44-49(2013) Correlation and path coefficient analysis in tuberose VANLALRUATI, T. MANDAL AND S. PRADHAN Department of Floriculture and Landscaping, Faculty of Horticulture
The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein
 C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein - Dr Mohammed Ali Hussien Al- Falahe Email: dr.mohammed1953@yahoo.com Tele : 07507718671. - Was born in Baghdad Iraq 1953. - Graduated from Al-Nasar primary school in 1966.
C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein - Dr Mohammed Ali Hussien Al- Falahe Email: dr.mohammed1953@yahoo.com Tele : 07507718671. - Was born in Baghdad Iraq 1953. - Graduated from Al-Nasar primary school in 1966.
