The Indic MathematicaL Tradition
|
|
|
- Tyrone Elliott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Indic MathematicaL Tradition Monthly Planner 2007,2008 With Panchangam Data Compliments Of Indic Studies Foundation Designed By Kosla Vepa
2
3 The Indic Mathematical tradition Aryabhata I (the elder) आयर भट Born 2765 BCE (based on modern research) conventional dating ( CE) astronomer mathematician of the ancient world
4 Ancient Vedic Astronomy First mentioned in the Vedas The Vedas can be dated to the 5th or 6 th millennium BCE using techniques now considered as a part of a discipline known as Archaeo Astronomy One of the observations that the ancients made was the day and the location of the Sun when it makes its way past the Celestial equator to the northern half of the Celestial sphere. This is known as the Vernal equinox. When this occurs the number of hours of daylight equals 12 or half the modern calendar day The Astronomy and the Astrology of India is based upon sidereal calculations. Sidereal astronomy uses the distant stars as the frame of reference and the sidereal period is the time that it takes t the object to make one full orbit around the Sun, relative to the stars. This is a more accurate computation of the true orbital period of any planetary body.
5 January 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday 1 New Year's Day 2 3 Purnima Makar Sankranti,, Uttarayana Punyakalam Martin Luther King, Jr. Amavasya Vasant Panchami Republic Day of India Dec 2006 Feb
6 The Indic Mathematical tradition The Armillary or Celestial sphere (Gola) depicts the way the ancients saw the universe,as they gazed at the sky. Armillary spheres have concentric rings to indicate planetary orbits, the zodiac band of constellations, and terrestrial and celestial measurement circles such as the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn and the equator. Sometimes they are mounted with an Orrery inside. Sometimes they are mounted as garden sundials. A Ptolemaic armillary sphere has an earth globe at the center, surrounded by celestial circle and zodiac armillary rings, demonstrating the geocentric theory of the universe developed by Ptolemy and others in ancient Greece and Rome. The latest view is that Ptolemy was certainly not the first or the only oneto develop a calculation algorithm based on a geocentric model. The Indics were already there, no pun intended, as were probably the Chinese
7 February 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Jan 2007 M ar 2007 W S M T T F S Purnima Groundhog Day Lincoln's Birthday Valentine's Day Maha Shivaratri Amavasya Yugabda 5109 President's Day Washington's Birthday
8 The Indic Mathematical tradition The Celestial sphere Known also as the Armillary sphere or Gola in Sanskrit) Showing the ecliptic and its inclination to the celestial equator and is the inclination of the earths axis to the axis perpendicular to the plane of the ecliptic About 23.5 degrees
9 March 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Feb Apr Parti al Lunar Eclipse Holi Purnima Daylight Saving Time Begins St. Patri ck's Day Solar Eclipse Chaitra, Ugadi,Hindi, Telugu New year Vernal Equinox Ramayana week Sri Ram Navami
10 The Indic Mathematical tradition The structure of Vedic Literature (continued) EachVeda consists of Samhitas, Brahmanas, Aranyakas - speculation in the solitude of wilderness eventually taking shape as the Upanishads, To these were appended what were later called the Vedangas comprising of Shiksha (phonetics) Sandhi rules Chandas (meter) Nirukta (etymology) Vyakarana (grammar) Jyotisha (astronomy and calendric functions) KalpaSutras(Ritual procedures and the associated mathematics) Note the emphasis on brevity throughout, sandhi to make the content more compact, phonetics for mnemonic purposes. Panini s Ashtadhyayi is a tour de force as the worlds oldest Grammar text and Nirukta for associativity in remembering the meaning of words
11 April 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday April Fool's Day Purnima Mahavira Jayanti Tamil New Year, Baisakhi, Vishu Partial Lunar Eclipse Ramanuja Jayanti Sankara Jayanti Narasimha Jayanti Mar May
12 The Indic Mathematical tradition Proposed chronology of the Vedics A work in progress Event Individual Date Birth Veda Vyaasa ~3300 BCE Birth Apastambha 3200 BCE Birth Baudhayana 3200 BCE Era Kaliyuga 3102 BCE Birth Aryabhata 2765 BCE Lifespan Gautama Buddha BCE Coronation Chandragupta Maurya 1554 BCE Coronation Asoka Maurya 1472 BCE Coronation Kanishka BCE Era Andhra Satavahana 833 BCE -327 BCE Coronation Chandragupta of Gupta dynasty 327 BCE Pancha Siddhanta VarahaMihira 123 BCE Reign Vikramaditya 102 BCE to 78 BCE Birth Brahmagupta 30 BCE Writings Bhaskara II Siddhanta Siromani 486 BCE
13 May 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Apr Purnima 1 Buddha Purnima 2 Annamacharya Jayanti Hanuman Jayanti Mother's Day Amavasya,Jyeshta first of 2, adhik maas Armed Forces Day Memorial Day Poornima 31 Jun
14 The Indic Mathematical tradition Precession of the equinoxes At the end of a tropical year from one vernal equinox to the next with respect to the fixed stars, the earth appears to fall short by seconds of longitude. That means it takes approximately years for the precession to complete 360 degrees or 1 revolution of the vernal equinox as it traverses a different Nakshatra every 955 years. Voila, here we have a year clock and by noting the Nakshatra in which the vernal equinox occurred we can tell when the event occurred. By dividing each Nakshatra into 4 padas we can refine the unit of time to 240 years. This is a fairly reliable method of dating events such as the composition of the Rg or the date of the Mahabharata war Precession of the equinoxes and the pole star
15 June 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday 1 2 May 2007 Jul Flag Day Adhik Maas last day Amavasya,Jyeshta shukla Father's Day Summer Solsti ce Purnima
16 The Indic Mathematical tradition Precession of the Equinoxes
17 July 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Independence Day Amavasya, Asadha shukla Dakshinayana Punyakala Guru(Vyaasa) Purnima Jun 2007 Aug
18 The Indic Mathematical tradition Deciphering the age of an event Observations about the Nakshatra in which the Vernal Equinox occurs tell us the era in which the observations took place (Archaeo-Astronomy) This is only one of the possible astronomical markers Look to manuscripts written by Astronomers and Mathematicians, since they have a penchant for precision in their observations and remarks We are at the beginning of discovery of our forgotten past
19 August 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Jul 2007 Sep Amavasya,Sravan shukla Independence Day Varalakshmi Vratam Purnima Raksha Bandhan
20 The Indic Mathematical tradition Dating of the Vedas Hermann Jacobi John Playfair In 1790, the Scottish mathematician John Playfair demonstrated that the starting-date of the astronomical observations recorded in the tables still in use among Hindu astrologers (of which three copies had reached Europe between 1687 and 1787) had to be 4300 BC.3 Playfair s argumentation, Remarks on the astronomy of the Brahmins, Edinburg 1790, is reproduced in Dharampal: Indian Science and Technology in the Eighteenth Century, Academy of Gandhian Studies, Hyderabad 1983 (Impex India, Delhi 1971), p
21 September 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Aug 2007 Oct 2007 W S M T T F S Labor Day Krishna Janmashtami Amavasya, Bhadrapada shukla Ganesh Chaturthi Autumnal equinox Purnima 30
22 The Indic Mathematical tradition The difference between the sidereal day and the solar day from Wikipedia. For the same reason the sidereal year is longer than the solar or tropical year by about 20 minutes. We will come back to this when we discuss the precession of the equinoxes
23 October 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Columbus Day (Observed) Amavasya,Aswina shukla Navratri begins Saraswati Puja Madhva Jayanti Vijaya Dashami Purnima Karva chaturthi (Karva chauth) Halloween Sep Nov
24 Western Asterism name Indian Nakshatras (Sidereal Zodiac) Sector in deg,min deg,min 1. Beta Arietis Aswini Arietis Bharani Eta Tauri Karthika Alpha Tauri Rohini Lamda Orionis Mrigasira Alpha Orionis Aridra Beta Geminorum Punarvasu Delta Cancri Pushya Alpha Cancri Aslesha Alpha Leonis Magha The Indic Nakshatra System attributed to Gargeya in the Atharva Veda 11. Delta Leonis Pubba Beta Leonis Uttara Delta Corvi Hasta Alpha Virginis Chitra Alpha Bootis Chothi Beta Librae Vishakam Delta Scorpi Anuradha Alpha Scorpi Jyeshta Lamda Scorpi Moola Delta Sagittari Poorvashad Delta Sagittari Uthrashad Alpha Aquilae Sravana Alpha Delphini Dhanishta Lamda Aquar Satabhisha Alpha Pegasi Poorvabhadra Alpha Andromeda Uttrarabhadra Zeta Piscium Revathi
25 November 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Oct 2007 Dec Daylight Savings Time Ends Election Day Naraka Chaturdasi Deepavali Amavasya,Kartika shukla Vikram New Year 2064 Veterans Day Thanksgiving Purnima
26 The Indic Mathematical tradition Dating of the Mahabharata The following key dates are found to be consistent with the sky inscriptions observed by Veda Vyasa: Krishna's departure on Revati Sept. 26, 3067 BCE Krishna's arrival in Hastinapura on Bharani Sept. 28, 3067 BCE Solar eclipse on Jyeshtha amavasya Oct. 14, 3067 BCE Krittika full moon (lunar eclipse) September 29, 3067 BCE War starts on November 22, 3067 BCE (Saturn in Rohini, Jupiter in Revati) Winter solstice, January 13, 3066 BCE Bhishma's expiry, January 17, 3066 BCE Magha shukla ashtami A fierce comet at Pushya October 3067 BCE Balarama sets off on pilgrimage on Sarasvati on Pushya day Nov. 1, 3067 BCE Balarama returns from pilgrimage on Sravana day Dec. 12, 3067 BCE On the day Ghatotkaca was killed moon rose at 2 a.m., Dec. 8, 3067 BCE
27 December 2007 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Nov 2007 Jan 2008 W S M T T F S Amavasya,Margas shukla Gita jayanti Vaikunta Winter solstice Purnima Christmas New Year's Eve
28 The Indic Mathematical tradition Month Months according to Indian Panchang Suns Longitude Deg min Duration days Gregorian 2007/ Vaisakha Apr Jyestha(adhika) Asadha Sravana Bhadrapada Asvina Kartika Margasirsa Pausa Magha May 17,16 June 15 July 13 Aug. 18 Sept. 12 Oct. 10 Nov. 10 Dec. 24 Jan. 19 Synchronization and Leap Months The fundamental problem with the Indian panchang as with all lunisolar calendars is the synchronizaton (or a lack thereof) between the solar and lunar periodicities and just as we add a leap day every four years to the Gregorian calendar m we have to add a leap month or adhika maas every 2.5 years. There are 2 synchronization cycles known as the Metonic Cycle and the Saros. According to the Metonic cycle (Meton. was a Greek of 430 BCE), every 2.5 years an extra lunar month, will have to be added to keep up to 365 days. In 19 years,7 lunar months are aided to make it more accurate, i.e. 19 x = 235 lunar months. Since a lunar month is about days which gives a total of 235 x = days. However Yajnavalkya was the first to demonstrate a 95 year (19*5)synchronization cycle in the Satapatha Brahmana. Yajnavalkya was another one of those who could be termed a Man for all seasons,a multi faceted personality, a species of Homo sapien that appeared to populate the pages of ancient Indian History in much profusion 11. Phalguna Feb Caitra Mar. 19
29 January 2008 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Dec New Year's Day Amavasya, Pausa shukla Makar Sankranti Martin Luther King, Jr. Purnima Feb
30 The Indic Mathematical tradition In the 5th Mandala of Rig Veda, the 40th sukta and 5th Rik, Rishi Atri describes a total solar eclipse. Rig Veda- HYMN XL. 5. Indra. Surya. Atri. O Surya, when the Asura's descendant Svarbhanu, pierced thee through and through with darkness, All creatures looked like one who is bewildered, who knoweth not the place where he is standing. Vedic astrology refers to moon s ascending node or descending node at time of potential solar eclipse as Rahu or Swarbhanu, a demon. The passage certainly describes a total solar eclipse, magically imposed by Rahu, and people and animals being scared of the solar eclipse event.the same material is expanded in Kaushitiki or Sankhyayana Brahmana Dr.S.Balakrishna
31 February 2008 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday 1 2 Jan 2008 Mar 2008 W S M T T F S Groundhog Day Amavasya, Magha shukla Vasant panchami Lincoln's Birthday Valentine's Day President's Day Purnima Washington's Birthday
32 The Indic Mathematical tradition Definitions (see figure) Ecliptic - the great circle on the celestial sphere that lies in the plane of the earth's orbit (called the plane of the ecliptic). Because of the earth's yearly revolution around the sun, the sun appears to move in an annual journey through the heavens with the ecliptic as its path. Celestial sphere or armillary imaginary sphere enveloping the earth appears to turn as the earth rotates Celestial equator equinox (ē kwĭnŏks), क त त त त (Kranthivruth) either of two points on the celestial sphere where the ecliptic and the celestial equator intersect. Periodicity of the saptarishi or Great Bear constellation or the Ursa Major equatorial coordinate system Line of Declination Line of right ascension
33 March 2008 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Feb 2008 Apr 2008 W S M T T F S Amavasya,Phalgu shukla Vernal Equinox Holi St. Patrick's Day Easter Sunday
34 The Indic Mathematical tradition Some more definitions Sidereal Day An apparent sidereal day - the time it takes for the Earth to turn 360 degrees in its rotation; more precisely, is the time it takes a typical star to make two successive upper meridian transits. This is slightly shorter than a solar day. There are sidereal days in a tropical year, but solar days, resulting in a sidereal day of 86, seconds (or: 23 hours, 56 minutes, seconds). The reason there is one more sidereal day than "normal" days in a year is that the Earth's orbit around the Sun offsets one sidereal day, giving observers on Earth 365 1/4 days, even though the planet itself rotated 366 1/4 times (the Earth rotates in the same direction around its axis as it does around the Sun: seen from the northern sky, counter-clockwise). Midnight, in sidereal time, is when the First Point of Aries crosses the upper meridian. A mean sidereal day is reckoned, not from the actual transit, but from the transit of the mean vernal equinox (see: mean sun).
35 April 2008 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday April Fool's Day Amavasya,Chaitra shukla, Chandrama na uga di Daylight Saving Time Begins Hindi Telugu New Year (Cha itra) Ram Navmi Hanuman jayanti Mar May
36 The Indic Mathematical tradition Comparison of The Àryabhatiya of Àryabhata and Astronomic values. Astronomy Constants AD Aryabhatiya 1604 BC Rotations per solar orbit Days per solar orbit Days per lunar orbit Rotations per lunar orbit
37 May 2008 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Apr 2008 Jun 2008 W S M T T F S Amavasya,Vaisak shukla Mother's Day Armed Forces Day Buddha jayanti Memorial Day (Observed)
38 The Indic Mathematical tradition ASTRONOMIC AUTHORITY Àryabhata (from Clarke and Kay) Surya Siddanta Years in Cycle 4,320,000 4,320,000 Rotations of the earth 1,582,237,500 1,582,237,828 Days 1,577,917,500 1,577,917,828 Lunar Orbits 57,753,336 57,753,336 Kay notes 57,753,339 lunar orbits rather than 57,753,336 per Clarke. Synodic Months 53,433,336 53,433,336 Mercury 17,937,920 17,937,060 Venus 7,022,388 7,022,376 Mars 2,296,824 2,296,832 Jupiter 364, ,220 Saturn 146, ,568
39 June 2008 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Amavasya,Jyeshta shukla Flag Day Father's Day Purnima Summer Solsti ce May 2008 Jul
40 The Indic Mathematical tradition Dating of the Vedas Koenrad Elst In a rather shoddy way, Friedrich Max Müller launched the hypothesis that the Rg-Veda had to be dated to about 1200 BC, and even though he later retracted it, that arbitrary guess has become the orthodoxy. A precursor to the habitual circular reasioning adopted by current day European indologists Maurice Winternitz remained skeptical of his own assumptions - We cannot explain the development of the whole of this great literature if we assume as late a date as round about 1200 BC or 1500 BC as its starting-point. 1 Hermann Jacobi John Playfair see next slide B G Tilak Orion Cosco Publications, reprint 1984, original 1895 S Balakrishna Vedic Astronomy articles
41 July 2008 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Jun Amavasya,Asadha shukla Independence Day Guru Purnima (Veda Vyaasa) Aug
42 The Indic Mathematical tradition English calendar weekdays Indian calendar weekdays Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Raviwar Somwar Mangalwar Budhwar Guruwar Shukrawar Shaniwar (Chandrawar) Chaitra Vaishakh Jeshta Ashadh Shrawan(Sawan) Bhadrapad(Bhado) Ashwin Kartik Margshirsh Paush Magha Falgoon (Fagan)
43 August 2008 Monthly Planner Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday 1 Jul Sep Done Priority Description Due Date Amavasya, Sravana Shukla Purnima, Raksha Bandhan Krishna Janmashtami Amavasya, Bhadrapada shukla 31
44 The Indic Mathematical tradition Zodiac sign Sanskrit Name Sector begin Sector end Aries Mesha Taurus Vrishabha Gemini Mithuna Cancer Karka Leo Simha Virgo Kanya Libra Tula Scorpio Vrishchika Sagittarius Dhanus Capricorn Makara Aquarius Kumbha Pisces Meena
45 September 2008 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Labor Day Purnima Autumn begins Amavasya,Aswina shukla 30 Aug Oct
46 The Indic Mathematical a region of the sky, within official borders set in 1928 by the IAU. Often recognizable by a pattern or grouping of stars. Some patterns, like the Winter Triangle, span several constellations. tradition A Constellation is
47 October 2008 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Sep 2008 Nov Vijaya dasami Columbus Day (Observed) Purnima Karva chaturthi Daylight Savings Time Ends Naraka Chaturdasi, Deepavali Amavasya,Kartika Shukla Vikram New Year 2065 Halloween
48 The Indic Mathematical tradition Asterisms (Sapta Rishi as an example) The big dipper Actually part of Ursa Major The Big Bear Or Big Raccoon? Bharateeya Jyotishya shaastra states that each Nakshatra name corresponds to a group of stars called star mansions or Asterisms. Image fom:
49 November 2008 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Oct 2008 Dec 2008 W S M T T F S Election Day Veterans Day Purnima Amavasya,Margas shukla Thanksgiving 30
50 The Indic Mathematical tradition Precession of the equinoxes and the pole star
51 December 2008 Monthly Planner Done Priority Description Due Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday , Gita Jayanti Purnima Winter solstice Christmas Amavasya,Pausa shukla New Year's Eve Nov Jan
52 The Indic Mathematical tradition I dedicate this research to the Goddess Sarasvati And the river that bears her name And the Brahmi civilization that flourished on the banks of the river for over 3000 years giving rise to the first phonetic and syllabic script Om Sarveshaam Swastir Bhavatu Sarveshaam Saantir Bhavatu Sarveshaam Poornam Bhavatu SarveshamMangalamBhavatu
Astrological Calendar. for Central Time
 2014 for Central Time January 2014 Capricorn Compliments of: Clayten Tylor Esoteric Astrologer (604)331-0251 Jan 15, 2014 Full Moon 10:53:09 PM CST Jan 1, 2014 New Moon 05:15:21 AM CST January 2014 Sun
2014 for Central Time January 2014 Capricorn Compliments of: Clayten Tylor Esoteric Astrologer (604)331-0251 Jan 15, 2014 Full Moon 10:53:09 PM CST Jan 1, 2014 New Moon 05:15:21 AM CST January 2014 Sun
ASTROLOGY CALENDAR 2018
 ASTROLOGY CALENDAR 2018 www.sarahsastrology.com Email: sarahsastrology@googlemail.com Twitter @sarahsastro Google+ sarahsastrology Facebook www.facebook.com/sarahsastrology Linkedin Sarah Cochrane Pinterest
ASTROLOGY CALENDAR 2018 www.sarahsastrology.com Email: sarahsastrology@googlemail.com Twitter @sarahsastro Google+ sarahsastrology Facebook www.facebook.com/sarahsastrology Linkedin Sarah Cochrane Pinterest
JANUARY Single Ad Business Card Size: 3.5 x 2. Single Ad Business Card Size: 3.5 x 2. Double Ad Ad Size: 3.5 x 4.125
 JANUARY 2019 Sunday MONday TUESday WEDNESday THURSday FRIday SATURday 1 2 3 4 5 New Year s Day New Moon 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 First Quarter 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Martin Luther King, Jr.
JANUARY 2019 Sunday MONday TUESday WEDNESday THURSday FRIday SATURday 1 2 3 4 5 New Year s Day New Moon 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 First Quarter 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Martin Luther King, Jr.
Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018
 1 Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018 2 What is your year in school? A. New freshman B. Returning freshman C. Sophomore D. Junior E. Senior F. I ve been here, like, forever 3 What is your major?
1 Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018 2 What is your year in school? A. New freshman B. Returning freshman C. Sophomore D. Junior E. Senior F. I ve been here, like, forever 3 What is your major?
Astronomy 291. Professor Bradley M. Peterson
 Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
Discovering the Universe
 Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events have defined the cycles of human life They have inspired great religion stories The scientific revolution
Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events have defined the cycles of human life They have inspired great religion stories The scientific revolution
Astronomy = Timekeeping
 Astronomy = Timekeeping Day, month, year Important for seasons - hunter gatherer Annual migrations Seasons important for farmers Heliacal rising of Sirius Important for navigation Longitude & GPS Important
Astronomy = Timekeeping Day, month, year Important for seasons - hunter gatherer Annual migrations Seasons important for farmers Heliacal rising of Sirius Important for navigation Longitude & GPS Important
Physics Lab #4: Learning Starry Night, Part 3
 Physics 10293 Lab #4: Learning Starry Night, Part 3 Introduction In this lab, we will continue using Starry Night to explore some of the most important concepts we will cover in lecture. Continue with
Physics 10293 Lab #4: Learning Starry Night, Part 3 Introduction In this lab, we will continue using Starry Night to explore some of the most important concepts we will cover in lecture. Continue with
Discovering the Universe
 Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events define the rhythms of human life and have inspired myths and religion stories Attempts to explain astronomical
Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events define the rhythms of human life and have inspired myths and religion stories Attempts to explain astronomical
Discovering the Universe
 Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events day and night, seasons -- have defined the rhythms of human life They have inspired great myths and
Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events day and night, seasons -- have defined the rhythms of human life They have inspired great myths and
Discovering the Universe
 Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events day and night, seasons -- have defined the rhythms of human life They have inspired great myths and
Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events day and night, seasons -- have defined the rhythms of human life They have inspired great myths and
PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates
 PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates Astronomical Clocks Earth s Rotation on its Axis Time between two successive meridian transits of the sun 1 solar day (our adopted clock time) 24 hours (86,400
PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates Astronomical Clocks Earth s Rotation on its Axis Time between two successive meridian transits of the sun 1 solar day (our adopted clock time) 24 hours (86,400
2. Knowing the Heavens
 2. Knowing the Heavens Ancient naked-eye astronomy Eighty-eight constellations The sky s ever-changing appearance The celestial sphere Celestial coordinates Seasons: Earth s axial tilt Precession of Earth
2. Knowing the Heavens Ancient naked-eye astronomy Eighty-eight constellations The sky s ever-changing appearance The celestial sphere Celestial coordinates Seasons: Earth s axial tilt Precession of Earth
Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
10/17/2012. Observing the Sky. Lecture 8. Chapter 2 Opener
 Observing the Sky Lecture 8 Chapter 2 Opener 1 Figure 2.1 Figure 2.2 2 Figure 2.6 Figure 2.4 Annotated 3 The Celestial Sphere The celestial sphere is the vast hollow sphere on which the stars appear fixed.
Observing the Sky Lecture 8 Chapter 2 Opener 1 Figure 2.1 Figure 2.2 2 Figure 2.6 Figure 2.4 Annotated 3 The Celestial Sphere The celestial sphere is the vast hollow sphere on which the stars appear fixed.
Notes on Moon Calendar 1/21/2015
 Notes on Moon Calendar 1/21/2015 I used Sun and Moon data from http://aa.usno.navy.mil/data/docs/rs_oneyear.php. I chose "District of Columbia" for location, partly because that's what came up on the screen.
Notes on Moon Calendar 1/21/2015 I used Sun and Moon data from http://aa.usno.navy.mil/data/docs/rs_oneyear.php. I chose "District of Columbia" for location, partly because that's what came up on the screen.
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky. The sky is divided into 88 unequal areas that we call constellations.
 Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time
 James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time Place & Time Read sections 15.5 and 15.6, but ignore the math. Concentrate on those sections that help explain the slides.
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time Place & Time Read sections 15.5 and 15.6, but ignore the math. Concentrate on those sections that help explain the slides.
Knowing the Heavens. Chapter Two. Guiding Questions. Naked-eye (unaided-eye) astronomy had an important place in ancient civilizations
 Knowing the Heavens Chapter Two Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same
Knowing the Heavens Chapter Two Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon. Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017
 Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
Introduction to the sky
 Introduction to the sky On a clear, moonless night, far from city lights, the night sky is magnificent. Roughly 2000 stars are visible to the unaided eye. If you know where to look, you can see Mercury,
Introduction to the sky On a clear, moonless night, far from city lights, the night sky is magnificent. Roughly 2000 stars are visible to the unaided eye. If you know where to look, you can see Mercury,
2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope )
 How do we locate stars in the heavens? 2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope ) What stars are visible from a given location? Where is the sun in the sky at any given time? Where are
How do we locate stars in the heavens? 2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope ) What stars are visible from a given location? Where is the sun in the sky at any given time? Where are
2. Modern: A constellation is a region in the sky. Every object in the sky, whether we can see it or not, is part of a constellation.
 6/14 10. Star Cluster size about 10 14 to 10 17 m importance: where stars are born composed of stars. 11. Galaxy size about 10 21 m importance: provide a stable environment for stars. Composed of stars.
6/14 10. Star Cluster size about 10 14 to 10 17 m importance: where stars are born composed of stars. 11. Galaxy size about 10 21 m importance: provide a stable environment for stars. Composed of stars.
Today in Space News: Earth s oldest rock found on the Moon.
 Today in Space News: Earth s oldest rock found on the Moon https://www.lpi.usra.edu/features/012419/oldest-rock/ Study Points Predict the approximate time of day/night you should look for first quarter
Today in Space News: Earth s oldest rock found on the Moon https://www.lpi.usra.edu/features/012419/oldest-rock/ Study Points Predict the approximate time of day/night you should look for first quarter
Biodynamic Planting Planner and Calendar India
 Biodynamic Planting Planner and Calendar India - 2016 This Calendar is released by the Biodynamic Community In India on Peter Proctor's birthday (August 28th) as a small token of gratitude for Peter's
Biodynamic Planting Planner and Calendar India - 2016 This Calendar is released by the Biodynamic Community In India on Peter Proctor's birthday (August 28th) as a small token of gratitude for Peter's
Discovering the Night Sky
 Discovering the Night Sky Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Discovering the Night Sky Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Discovering the Night Sky
 Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
November 17-19,2006,Los 19,2006,Los Angeles, CA
 Who was the Jeddi Knight who (re)defined( Zero Narrated by Kosla Vepa 4 th annual Human Empowerment Conference, November 17-19,2006,Los 19,2006,Los Angeles, CA 11/20/2006 Kosla Vepa 2 Objective Chronology
Who was the Jeddi Knight who (re)defined( Zero Narrated by Kosla Vepa 4 th annual Human Empowerment Conference, November 17-19,2006,Los 19,2006,Los Angeles, CA 11/20/2006 Kosla Vepa 2 Objective Chronology
January SUNDAY. State Representative Joseph A. Petrarca. Compliments of
 January 0 Irvis Office Building P.O. Box Harrisburg, PA 0- () - Fax: () 0- Longfellow St. Vandergrift, PA 0 () - Fax: () -000 N. Chestnut St. Derry, PA () - Fax: () - 0 Jefferson St. Latrobe, PA 0 () -0
January 0 Irvis Office Building P.O. Box Harrisburg, PA 0- () - Fax: () 0- Longfellow St. Vandergrift, PA 0 () - Fax: () -000 N. Chestnut St. Derry, PA () - Fax: () - 0 Jefferson St. Latrobe, PA 0 () -0
Numerical Model for the Orbit of the Earth
 Universal Journal of Geoscience 5(2): 33-39, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujg.2017.050203 http://www.hrpub.org Numerical Model for the Orbit of the Earth S. Karna 1,*, A. K. Mallik 2 1 Physics Department, Tri-Chandra
Universal Journal of Geoscience 5(2): 33-39, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujg.2017.050203 http://www.hrpub.org Numerical Model for the Orbit of the Earth S. Karna 1,*, A. K. Mallik 2 1 Physics Department, Tri-Chandra
Homework Assignment #9: Apparent Motions of the Heavens Due to Actual Motions of Earth
 Name Homework Assignment #9: Apparent Motions of the Heavens Due to Actual Motions of Earth 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico
Name Homework Assignment #9: Apparent Motions of the Heavens Due to Actual Motions of Earth 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico
NAKSHATRAS BY GURMEET SINGH
 NAKSHATRAS BY GURMEET SINGH #: Sign: From: Nakshatra: Star (Star) 1 Aries 00 00 00 00 46 40 Aswini Ketu Ketu 2 Aries 00 46 40 03 00 00 Aswini Ketu Venus 3 Aries 03 00 00 03 40 00 Aswini Ketu Sun 4 Aries
NAKSHATRAS BY GURMEET SINGH #: Sign: From: Nakshatra: Star (Star) 1 Aries 00 00 00 00 46 40 Aswini Ketu Ketu 2 Aries 00 46 40 03 00 00 Aswini Ketu Venus 3 Aries 03 00 00 03 40 00 Aswini Ketu Sun 4 Aries
Planetary Conjunctions and Occultation records in Stone Inscriptions in India
 Planetary Conjunctions and Occultation records in Stone Inscriptions in India Shylaja B S and Geetha K G Jawaharlal Nehru Planetarium Sri T Chowdaiah Road, High Grounds, Bengaluru, 560001 India 1. Introduction
Planetary Conjunctions and Occultation records in Stone Inscriptions in India Shylaja B S and Geetha K G Jawaharlal Nehru Planetarium Sri T Chowdaiah Road, High Grounds, Bengaluru, 560001 India 1. Introduction
2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope )
 2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope ) http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html How do we locate stars in the heavens? What stars are visible from a given location? Where is the sun
2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope ) http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html How do we locate stars in the heavens? What stars are visible from a given location? Where is the sun
Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson
 Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson From our perspective on earth The earth appears flat. We can see half the celestial sphere at any time. The earth s axis is always perpendicular to the equator.
Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson From our perspective on earth The earth appears flat. We can see half the celestial sphere at any time. The earth s axis is always perpendicular to the equator.
Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21
 Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21 Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical arguments to explain natural phenomena Also used some observa:onal data (looking at the night sky) Ancient
Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21 Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical arguments to explain natural phenomena Also used some observa:onal data (looking at the night sky) Ancient
Astronomy 100 Section 2 MWF Greg Hall
 Astronomy 100 Section 2 MWF 1200-1300 100 Greg Hall Leslie Looney Phone: 217-244-3615 Email: lwl @ uiuc. edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: MTF 10:30-11:30 a.m. or by appointment Class Web Page
Astronomy 100 Section 2 MWF 1200-1300 100 Greg Hall Leslie Looney Phone: 217-244-3615 Email: lwl @ uiuc. edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: MTF 10:30-11:30 a.m. or by appointment Class Web Page
Today. Announcements: How much do we know? Mystics, Astrology, etc.
 Announcements: Today Exam#3 Extra Credit is due by Wednesday April 25 at 8:00 am Final extra Credit Project Intelligent Design will be due April 25 at 8:00 am How much do we know? Mystics, Astrology, etc.
Announcements: Today Exam#3 Extra Credit is due by Wednesday April 25 at 8:00 am Final extra Credit Project Intelligent Design will be due April 25 at 8:00 am How much do we know? Mystics, Astrology, etc.
Winning Spring Break Story The winning spring break story was #4. This was about the girl who could not turn back time. Today Announcements:
 Today Announcements: Exam#3 Extra Credit is due by Wednesday April 25 at 8:00 am Final extra Credit Project Intelligent Design will be due April 25 at 8:00 am How much do we know? Mystics, Astrology, etc.
Today Announcements: Exam#3 Extra Credit is due by Wednesday April 25 at 8:00 am Final extra Credit Project Intelligent Design will be due April 25 at 8:00 am How much do we know? Mystics, Astrology, etc.
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
Today. Announcements: How much can we know? Mystics, Astrology, etc.
 Announcements: Today The last homework assignment, #11, is due by Wednesday April 16 at 8:00 am Final extra Credit Project What was interesting will be due Wednesday April 23 at 8:00 am Exam #3 is next
Announcements: Today The last homework assignment, #11, is due by Wednesday April 16 at 8:00 am Final extra Credit Project What was interesting will be due Wednesday April 23 at 8:00 am Exam #3 is next
Chapter S1 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter S1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. S1.1 Astronomical
Chapter S1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. S1.1 Astronomical
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy AST0111-3 (Astronomía) Semester 2014B Prof. Thomas H. Puzia Theme Our Sky 1. Celestial Sphere 2. Diurnal Movement 3. Annual Movement 4. Lunar Movement 5. The Seasons 6. Eclipses
Introduction to Astronomy AST0111-3 (Astronomía) Semester 2014B Prof. Thomas H. Puzia Theme Our Sky 1. Celestial Sphere 2. Diurnal Movement 3. Annual Movement 4. Lunar Movement 5. The Seasons 6. Eclipses
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation. How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?
 Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
Knowing the Heavens. Goals: Constellations in the Sky
 Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Astronomy. The Seasons
 Astronomy The Seasons The seasons are caused by the inclination of the Earth s axis: when a hemisphere is tipped toward the Sun, the Sun is more directly above it. At the Summer Solstice the tilt is most
Astronomy The Seasons The seasons are caused by the inclination of the Earth s axis: when a hemisphere is tipped toward the Sun, the Sun is more directly above it. At the Summer Solstice the tilt is most
Knowing the Heavens. Goals: Constellations in the Sky
 Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
6/17. Universe from Smallest to Largest:
 6/17 Universe from Smallest to Largest: 1. Quarks and Leptons fundamental building blocks of the universe size about 0 (?) importance: quarks combine together to form neutrons and protons. One of the leptons
6/17 Universe from Smallest to Largest: 1. Quarks and Leptons fundamental building blocks of the universe size about 0 (?) importance: quarks combine together to form neutrons and protons. One of the leptons
The celestial sphere, the coordinates system, seasons, phases of the moon and eclipses. Chapters 2 and S1
 The celestial sphere, the coordinates system, seasons, phases of the moon and eclipses Chapters 2 and S1 The celestial sphere and the coordinates system Chapter S1 How to find our way in the sky? Let s
The celestial sphere, the coordinates system, seasons, phases of the moon and eclipses Chapters 2 and S1 The celestial sphere and the coordinates system Chapter S1 How to find our way in the sky? Let s
Time Concepts Series. Calendars
 Time Concepts Series Calendars REM 526 Co v e r Designer: Cover Illustrator: Mike Muncy Joanne Powell A Teaching Resource From 2010, 1998 Copyright by Remedia Publications, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Printed
Time Concepts Series Calendars REM 526 Co v e r Designer: Cover Illustrator: Mike Muncy Joanne Powell A Teaching Resource From 2010, 1998 Copyright by Remedia Publications, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Printed
Mathematical Astronomy Morsels Combined Table of Contents
 Mathematical Astronomy Morsels Combined Table of Contents This is a combined table of contents for all four volumes of Mathematical Astronomy Morsels by Jean Meeus. It is organized by section, then by
Mathematical Astronomy Morsels Combined Table of Contents This is a combined table of contents for all four volumes of Mathematical Astronomy Morsels by Jean Meeus. It is organized by section, then by
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, May 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY. Test 1: Spring 2018 Number of pages: 10 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of students: 598
 ASTR 1P01 Test 1, May 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Spring 2018 Number of pages: 10 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of students: 598 Examination date: 12 May 2018 Time limit: 50 min Time of
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, May 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Spring 2018 Number of pages: 10 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 1 Number of students: 598 Examination date: 12 May 2018 Time limit: 50 min Time of
MATERIALS TO SUPPORT KINESTHETIC ASTRONOMY LESSONS
 MATERIALS TO SUPPORT KINESTHETIC ASTRONOMY LESSONS Dear Educator, The materials here support the Kinesthetic Astronomy lesson that can be downloaded from the Space Science Institute web site [click on
MATERIALS TO SUPPORT KINESTHETIC ASTRONOMY LESSONS Dear Educator, The materials here support the Kinesthetic Astronomy lesson that can be downloaded from the Space Science Institute web site [click on
Yr1 Lesson 1. The Great Circles of Astrology, the Angles, Precession,
 Yr1 Lesson 1 The Great Circles of Astrology, the Angles, Precession, Cosmic Intelligence Agency 2015 Astro Lesson 1! Signs, Symbols, Glyphs and Charts! The Celestial Sphere Great Circles of Astrology -
Yr1 Lesson 1 The Great Circles of Astrology, the Angles, Precession, Cosmic Intelligence Agency 2015 Astro Lesson 1! Signs, Symbols, Glyphs and Charts! The Celestial Sphere Great Circles of Astrology -
PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy
 PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy Dr Roger Wesson Research interests: deaths of stars. Planetary nebulae, novae and supernovae. Astronomy: some maths You can see that distances in astronomy are huge.
PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy Dr Roger Wesson Research interests: deaths of stars. Planetary nebulae, novae and supernovae. Astronomy: some maths You can see that distances in astronomy are huge.
Smalltalk 10/2/15. Dates. Brian Heinold
 Smalltalk 10/2/15 Dates Brian Heinold Leap years Leap years are every four years, right? Leap years Leap years are every four years, right? 2016, 2020, 2024, 2028,...,... Leap years Leap years are every
Smalltalk 10/2/15 Dates Brian Heinold Leap years Leap years are every four years, right? Leap years Leap years are every four years, right? 2016, 2020, 2024, 2028,...,... Leap years Leap years are every
ANNOUNCEMENTS Lingering MIDTERM EXAMS can be picked up AT THE END OF THIS LECTURE FROM BOBBY WALLACE
 ANNOUNCEMENTS Lingering MIDTERM EXAMS can be picked up AT THE END OF THIS LECTURE FROM BOBBY WALLACE HOMEWORK #6 DUE TODAY. HOMEWORK #7 AVAILABLE AFTER CLASS AND DUE NEXT THURSDAY. DECISIONS ON MIDTERM/FINAL/RESEARCH
ANNOUNCEMENTS Lingering MIDTERM EXAMS can be picked up AT THE END OF THIS LECTURE FROM BOBBY WALLACE HOMEWORK #6 DUE TODAY. HOMEWORK #7 AVAILABLE AFTER CLASS AND DUE NEXT THURSDAY. DECISIONS ON MIDTERM/FINAL/RESEARCH
Sky, Celestial Sphere and Constellations
 Sky, Celestial Sphere and Constellations Last lecture Galaxies are the main building blocks of the universe. Consists of few billions to hundreds of billions of stars, gas clouds (nebulae), star clusters,
Sky, Celestial Sphere and Constellations Last lecture Galaxies are the main building blocks of the universe. Consists of few billions to hundreds of billions of stars, gas clouds (nebulae), star clusters,
b. So at 12:00 p.m., are the shadows pointing in the direction you predicted? If they are not, you must explain this observation.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 2: Timekeeping and astronomy The following exercise illustrates some basic ideas about time, and how our position in the solar system uniquely configures the measurement
Astronomy 122 Section 1 TR Outline. The Earth is Rotating. Question Digital Computer Laboratory
 Astronomy 122 Section 1 TR 1300-1350 Outline 1320 Digital Computer Laboratory Leslie Looney Phone: 244-3615 Email: lwlw@wuiucw. wedu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: T 10:30-11:30 a.m. or by appointment
Astronomy 122 Section 1 TR 1300-1350 Outline 1320 Digital Computer Laboratory Leslie Looney Phone: 244-3615 Email: lwlw@wuiucw. wedu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: T 10:30-11:30 a.m. or by appointment
DAILY QUESTIONS 28 TH JUNE 18 REASONING - CALENDAR
 DAILY QUESTIONS 28 TH JUNE 18 REASONING - CALENDAR LEAP AND NON-LEAP YEAR *A non-leap year has 365 days whereas a leap year has 366 days. (as February has 29 days). *Every year which is divisible by 4
DAILY QUESTIONS 28 TH JUNE 18 REASONING - CALENDAR LEAP AND NON-LEAP YEAR *A non-leap year has 365 days whereas a leap year has 366 days. (as February has 29 days). *Every year which is divisible by 4
Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017
 Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017 Finish Ch. 2: Eclipses & Planetary Motion Seasons Angular Size formula Eclipses Planetary Motion Reading: For Today: Finish Chapter 2 For Monday: Start Chapter 3 Homework on
Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017 Finish Ch. 2: Eclipses & Planetary Motion Seasons Angular Size formula Eclipses Planetary Motion Reading: For Today: Finish Chapter 2 For Monday: Start Chapter 3 Homework on
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section II
 ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section II Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section II Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Origins of Modern Astronomy Earth Science, 13e Chapter 21 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Origins of Modern Astronomy Earth Science, 13e Chapter 21 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical
Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin. 43 North 89 West. September Daylight
 Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin 43 North 89 West 7 32 September 21 2005 Daylight Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin September 21,2005 7:32 43 North 89 West Names & Planetary Character Luminaries Symbols
Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin 43 North 89 West 7 32 September 21 2005 Daylight Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin September 21,2005 7:32 43 North 89 West Names & Planetary Character Luminaries Symbols
Cosmic Rhythms & Planting Calendar. Working with Rhythms is a major area where BD improves on other streams of organic practices
 Cosmic Rhythms & Planting Calendar Working with Rhythms is a major area where BD improves on other streams of organic practices Introduction Conscious incorporation of rhythms into our agricultural activities
Cosmic Rhythms & Planting Calendar Working with Rhythms is a major area where BD improves on other streams of organic practices Introduction Conscious incorporation of rhythms into our agricultural activities
29Ò 59' 41' 15Ò 17' Ñ 00Ò 53' 12 14Ò. Jan 15, 2010 New Moon Eclipse. Washington, DC 02:11:53 AM EST 49' 52' 32' 01' 05Ò D 34' 01' 23' 50' 02' 20Ò 23Ò
 January Capricorn ' Â 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Â Â Æ Ó Æ Â Ô Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Ä Ã Ã Ã Å 0 Â Â Â Â ST 0 0:: Ò' ' ' ' 0' 0 0::0 Ò ' 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0:0:0 0::00 0:: 0:0: 0:0: 0:0: 0:: ' ' ' 0' Ò ' ' ' Ò Ò 0' ' 0' Ò Ò ' '
January Capricorn ' Â 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Â Â Æ Ó Æ Â Ô Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Ä Ã Ã Ã Å 0 Â Â Â Â ST 0 0:: Ò' ' ' ' 0' 0 0::0 Ò ' 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0:0:0 0::00 0:: 0:0: 0:0: 0:0: 0:: ' ' ' 0' Ò ' ' ' Ò Ò 0' ' 0' Ò Ò ' '
2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope )
 2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope ) http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html How do we locate stars in the heavens? What stars are visible from a given location? Where is the sun
2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope ) http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html How do we locate stars in the heavens? What stars are visible from a given location? Where is the sun
Astronomy is the oldest science! Eclipses. In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Bad Omens? Comets
 Astronomy is the oldest science! In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Eclipses Bad Omens? Comets 1 The Ancient Greeks The Scientific Method Our ideas must always be consistent with our observations!
Astronomy is the oldest science! In ancient times the sky was not well understood! Eclipses Bad Omens? Comets 1 The Ancient Greeks The Scientific Method Our ideas must always be consistent with our observations!
Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018
 Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018 1 What causes the seasons? Perihelion: closest to Sun around January 4 th Northern Summer Southern Winter 147 million km 152 million km Aphelion (farthest to Sun) around July
Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018 1 What causes the seasons? Perihelion: closest to Sun around January 4 th Northern Summer Southern Winter 147 million km 152 million km Aphelion (farthest to Sun) around July
Cartesian Coordinates Need two dimensional system 2 number lines perpendicular to each other X-axis is horizontal Y-axis is vertical Position relative
 General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
Astrological Predictions How to use them Prof Dr. Praja Rao
 Astrological Predictions How to use them Prof Dr. Praja Rao I.Introduction Astrology or some modification of its version like numerology, palmistry or Tarot card reading was existing in one form or other
Astrological Predictions How to use them Prof Dr. Praja Rao I.Introduction Astrology or some modification of its version like numerology, palmistry or Tarot card reading was existing in one form or other
2015 Calendar. for Riga Latvia based on Riga Latvia Longitude, Latitude (Cannot be applicable to other parts of world)
 2015 Calendar for Riga Latvia based on Riga Latvia Longitude, Latitude (Cannot be applicable to other parts of world) Pushya Dhanus - Makara January 2015 Magha Margazhi Thai Sun:09:02-15:54 Moon:15:54
2015 Calendar for Riga Latvia based on Riga Latvia Longitude, Latitude (Cannot be applicable to other parts of world) Pushya Dhanus - Makara January 2015 Magha Margazhi Thai Sun:09:02-15:54 Moon:15:54
Lucky days for aries -gambling
 Lucky days for aries - gambling The Borg System is 100 % Lucky days for aries -gambling Happy Valentine Day 2018 Sms Greetings Wishes Quotes Wallpaper Images Welcome To Happy Valentine Day Wala World for
Lucky days for aries - gambling The Borg System is 100 % Lucky days for aries -gambling Happy Valentine Day 2018 Sms Greetings Wishes Quotes Wallpaper Images Welcome To Happy Valentine Day Wala World for
chapter 10 questions_pictures removed.notebook September 28, 2017 Chapter 10 What We Know About the Universe Has Taken Us Thousands of Years to Learn
 1. Define Star (Pg 352) Chapter 10 What We Know About the Universe Has Taken Us Thousands of Years to Learn A celestial body of hot gases with a nuclear furnace at its core that makes its own thermal energy.
1. Define Star (Pg 352) Chapter 10 What We Know About the Universe Has Taken Us Thousands of Years to Learn A celestial body of hot gases with a nuclear furnace at its core that makes its own thermal energy.
The sky and the celestial sphere
 Chapter 1 The sky and the celestial sphere The Sun, and sometimes the Moon are, by and large, the only astronomical objects visible in the day sky. Traditionally, astronomy has been a nocturnal activity.
Chapter 1 The sky and the celestial sphere The Sun, and sometimes the Moon are, by and large, the only astronomical objects visible in the day sky. Traditionally, astronomy has been a nocturnal activity.
The Perennial Ecliptic Calendar
 The Perennial Ecliptic Calendar INTRODUCTION The Perennial Ecliptic Calendar is a system for marking time in which weeks vary between seven and eight days in length, but everything else is completely regular:
The Perennial Ecliptic Calendar INTRODUCTION The Perennial Ecliptic Calendar is a system for marking time in which weeks vary between seven and eight days in length, but everything else is completely regular:
It s Full of Stars! Outline. A Sky Full of Stars. Astronomy 210. lights), about how many stars can we see with
 Astronomy 210 Section 1 MWF 1500-1550 134 Astronomy Building Leslie Looney Phone: 244-3615 Email: lwlw@wuiucw. wedu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: MTF 10:30-11:30 a.m. or by appointment This
Astronomy 210 Section 1 MWF 1500-1550 134 Astronomy Building Leslie Looney Phone: 244-3615 Email: lwlw@wuiucw. wedu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: MTF 10:30-11:30 a.m. or by appointment This
- SPACE/TIME GUIDE ARIES. Matariki rises late evening & is visible until early morning. Matariki rises. at dusk & is visible until late LEO
 TEACHER RESOURCE STARDOME OBSERVATORY & PLANETARIUM FACTS, RESOURCES AND ACTIVITIES ON... MATARIKI SCIENCE CONTENT/ CURRICULUM LINK ASTRONOMICAL SYSTEMS - SPACE/TIME GUIDE The star cluster Matariki plays
TEACHER RESOURCE STARDOME OBSERVATORY & PLANETARIUM FACTS, RESOURCES AND ACTIVITIES ON... MATARIKI SCIENCE CONTENT/ CURRICULUM LINK ASTRONOMICAL SYSTEMS - SPACE/TIME GUIDE The star cluster Matariki plays
AST 2010 Descriptive Astronomy Study Guide Exam I
 AST 2010 Descriptive Astronomy Study Guide Exam I Wayne State University 1 Introduction and overview Identify the most significant structures in the universe: Earth, planets, Sun, solar system, stars,
AST 2010 Descriptive Astronomy Study Guide Exam I Wayne State University 1 Introduction and overview Identify the most significant structures in the universe: Earth, planets, Sun, solar system, stars,
Observing the Universe for Yourself
 Observing the Universe for Yourself Figure 6-20 Solar-System Formation What does the universe look like from Earth? With the naked eye, we can see more than 2,000 stars as well as the Milky Way. A constellation
Observing the Universe for Yourself Figure 6-20 Solar-System Formation What does the universe look like from Earth? With the naked eye, we can see more than 2,000 stars as well as the Milky Way. A constellation
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky
 Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
Lunar Eclipse Wednesday (January 31 st ) Morning. Topics for Today s Class. PHYS 1403 Stars and Galaxies
 PHYS 1403 Stars and Galaxies Lunar Eclipse Wednesday (January 31 st ) Morning Super Moon so visible with naked eye Look in the western horizon Penumbral eclipse starts at 5:00 am Totality begins at 7:00
PHYS 1403 Stars and Galaxies Lunar Eclipse Wednesday (January 31 st ) Morning Super Moon so visible with naked eye Look in the western horizon Penumbral eclipse starts at 5:00 am Totality begins at 7:00
A Warm Up Exercise. The Motion of the Sun. A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise
 A Warm Up Exercise The Motion of the Sun Which of the following is NOT true of a circumpolar star? a) It rises and sets from my latitude b) Its direction can be far North c) Its direction can be far South
A Warm Up Exercise The Motion of the Sun Which of the following is NOT true of a circumpolar star? a) It rises and sets from my latitude b) Its direction can be far North c) Its direction can be far South
Where Was Mars At Your Birth?
 Where Was Mars At Your Birth? This chart will make it easy for you to determine your Mars sign. We ve listed each of the dates that Mars enters a new sign. If you were born after June 11, 1950, when Mars
Where Was Mars At Your Birth? This chart will make it easy for you to determine your Mars sign. We ve listed each of the dates that Mars enters a new sign. If you were born after June 11, 1950, when Mars
Happy Lunar New Year!
 Happy Lunar New Year! (optional) To keep track of time, humans have created calendars based on the Sun (solar) the Moon (lunar) or both! Today is a New Moon Some Asian countries start the year on the second
Happy Lunar New Year! (optional) To keep track of time, humans have created calendars based on the Sun (solar) the Moon (lunar) or both! Today is a New Moon Some Asian countries start the year on the second
Astronomy. Unit 2. The Moon
 Astronomy Unit 2 The Moon 1 Traveling on Spaceship Earth Although we imagine ourselves to be at rest, the Earth takes part in the motions outlined below. The Earth spins about its N-S axis, with a period
Astronomy Unit 2 The Moon 1 Traveling on Spaceship Earth Although we imagine ourselves to be at rest, the Earth takes part in the motions outlined below. The Earth spins about its N-S axis, with a period
Chapter 2 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Discovering the Universe for Yourself
 Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
AstronomyAstrology. A lesson on the Sun s motion through the sky
 A lesson on the Sun s motion through the sky appropriate for ages 12 and up keywords: sun, moon, zodiac, constellations, sidereal, synodic A product of Discover the Cosmos created by Pamela L. Gay CosmoQuest.org/EducatorsZone
A lesson on the Sun s motion through the sky appropriate for ages 12 and up keywords: sun, moon, zodiac, constellations, sidereal, synodic A product of Discover the Cosmos created by Pamela L. Gay CosmoQuest.org/EducatorsZone
January Capricorn. Jan 4, 2011 New Moon. Jan 19, 2011 Full Moon Washington, DC 04:22:28 PM EST 16Ò 56' 02Ò 44' 06' 12Ò 16Ò 54' 28Ò 05' 07Ò 52'
 January Capricorn Ò 0' 0' Tra-Tra 0 0 Â 0 0 0 Â Â Æ Â Â Â Â Æ Â Ã Æ Â Æ Â Â Â Â Â Ó Å 0 Â Â Â 0:0: AM EST 0' Â Â Jan, New on 0' ' ' ' 0 Æ Å Å Æ 0 0 Â Å Void 0 Å Â Â Ä Ä ' 0' 0' Ò ' January 0hrs GMT Day
January Capricorn Ò 0' 0' Tra-Tra 0 0 Â 0 0 0 Â Â Æ Â Â Â Â Æ Â Ã Æ Â Æ Â Â Â Â Â Ó Å 0 Â Â Â 0:0: AM EST 0' Â Â Jan, New on 0' ' ' ' 0 Æ Å Å Æ 0 0 Â Å Void 0 Å Â Â Ä Ä ' 0' 0' Ò ' January 0hrs GMT Day
Astrology in the casebooks
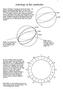 Astrology in the casebooks 1 Forman s and Napier s astrology was based on the zodiac the group of constellations through which the sun moves on its apparent course around the earth. That course is a circle
Astrology in the casebooks 1 Forman s and Napier s astrology was based on the zodiac the group of constellations through which the sun moves on its apparent course around the earth. That course is a circle
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 5 The Motion of the Earth and Moon Time, Precession, Eclipses, Tides
 Observational Astronomy - Lecture 5 The Motion of the Earth and Moon Time, Precession, Eclipses, Tides Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu March 2, 2014 1 / 29 Geosynchronous
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 5 The Motion of the Earth and Moon Time, Precession, Eclipses, Tides Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu March 2, 2014 1 / 29 Geosynchronous
Physics Lab #2:! Starry Night Introduction!
 Physics 10293 Lab #2: Starry Night Introduction Introduction In this lab, we'll learn how to use the Starry Night software to learn about the sky. Starry Night has a large number of features and options,
Physics 10293 Lab #2: Starry Night Introduction Introduction In this lab, we'll learn how to use the Starry Night software to learn about the sky. Starry Night has a large number of features and options,
Science : Introduction to Astronomy. Lecture 2 : Visual Astronomy -- Stars and Planets. Robert Fisher
 Science 3210 001 : Introduction to Astronomy Lecture 2 : Visual Astronomy -- Stars and Planets Robert Fisher Items Add/Drop Day Office Hours Vote 5 PM Tuesday 5 PM Thursday 12 Noon Friday Course Webpage
Science 3210 001 : Introduction to Astronomy Lecture 2 : Visual Astronomy -- Stars and Planets Robert Fisher Items Add/Drop Day Office Hours Vote 5 PM Tuesday 5 PM Thursday 12 Noon Friday Course Webpage
2) The number one million can be expressed in scientific notation as: (c) a) b) 10 3 c) 10 6 d)
 Astronomy Phys 181 Midterm Examination Choose the best answer from the choices provided. 1) What is the range of values that the coordinate Declination can have? (a) a) -90 to +90 degrees b) 0 to 360 degrees
Astronomy Phys 181 Midterm Examination Choose the best answer from the choices provided. 1) What is the range of values that the coordinate Declination can have? (a) a) -90 to +90 degrees b) 0 to 360 degrees
Chapter 0 2/19/2014. Lecture Outline. 0.1 The Obvious View. Charting the Heavens. 0.1 The Obvious View. 0.1 The Obvious View. Units of Chapter 0
 Lecture Outline Chapter 0 Charting the Heavens Earth is average we don t occupy any special place in the universe Universe: Totality of all space, time, matter, and energy Astronomy: Study of the universe
Lecture Outline Chapter 0 Charting the Heavens Earth is average we don t occupy any special place in the universe Universe: Totality of all space, time, matter, and energy Astronomy: Study of the universe
Astronomy = Astrometry? History of Old Astronomy ( )
 Astronomy = Astrometry? History of Old Astronomy ( ) note Astrometry means measuring the position of a celestial object in a sky. Without telescopes, this is what ancient astronomers can do for their best.
Astronomy = Astrometry? History of Old Astronomy ( ) note Astrometry means measuring the position of a celestial object in a sky. Without telescopes, this is what ancient astronomers can do for their best.
Lecture 4: DM: time and Diurnal Motion
 Dr. W. Pezzaglia Astronomy 10, Fall 2006 Page 8 Lecture 4: DM: time and Diurnal Motion Schedules: Aug 30, Wed (today) o Homework #2 due (see solutions below) o Web Site changed to: http://lpc1.clpccd.cc.ca.us/lpc/astronomy/course_websites/pezzaglia/index.html
Dr. W. Pezzaglia Astronomy 10, Fall 2006 Page 8 Lecture 4: DM: time and Diurnal Motion Schedules: Aug 30, Wed (today) o Homework #2 due (see solutions below) o Web Site changed to: http://lpc1.clpccd.cc.ca.us/lpc/astronomy/course_websites/pezzaglia/index.html
Astronomy 101 Lab Manual. Victor Andersen Community College of Aurora
 Astronomy 101 Lab Manual Victor Andersen Community College of Aurora victor.andersen@ccaurora.edu January 8, 2013 2 Contents 1 Angular Measures 5 1.1 Introduction............................ 5 1.1.1 Degrees,
Astronomy 101 Lab Manual Victor Andersen Community College of Aurora victor.andersen@ccaurora.edu January 8, 2013 2 Contents 1 Angular Measures 5 1.1 Introduction............................ 5 1.1.1 Degrees,
At Home Phases Demo. Astronomy 210. Section 1 MWF Astronomy Building. Geocentric vs. Heliocentric system. The Motion of the Planets
 Astronomy 210 Section 1 MWF 1500-1550 134 Astronomy Building This Class (Lecture 4): Early Cosmology HW #1 Due on Friday! Next Class: You missed the first planetarium show. Cosmic Revolution Music: Twilight
Astronomy 210 Section 1 MWF 1500-1550 134 Astronomy Building This Class (Lecture 4): Early Cosmology HW #1 Due on Friday! Next Class: You missed the first planetarium show. Cosmic Revolution Music: Twilight
