Explanation of thermal expansion differences between climate models
|
|
|
- Darren Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Explanation of thermal expansion differences between climate models Summary More than 90% of the positive Earth s energy imbalance - mainly anthropogenic as origin (Church et al. 2013) - is stored in the ocean as heat. Ocean warming results in thermal expansion and finally converts into sea level rise. During the last century, around half of the rate of sea level rise - globally averaged - was due to thermal expansion, called thermosteric sea level. For the coming century, Earth s energy imbalance is expected to be constant or to increase, depending of human activity scenarios. Consequently, sea level rise is expected to be constant or to increase, and projection accuracy of sea level is dependent on the ability of climate models to predict ocean thermal expansion. In a recent study, two researchers from the Laboratoire d Etudes en Géophysique et Océanograohie Spatiales (LEGOS), which are members of the international team of the International Space Science Institute (ISSI) on Contemporary global and regional sea level rise ( compare the thermal expansion obtained by climate models (from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project phase 5), driven by atmospheric re-analyses, with observations over the period The ensemble mean of sea level rise due to ocean warming from climate models is close to the observations - within observation uncertainty - in terms of absolute sea level rise as well as of rate of sea level rise (see Figure 1). However, the model ensemble exhibits a large spread. The authors then aim to explain this climate model spread over the twentieth and twenty-first centuries. By deriving the Earth energy budget - under the condition of continuously increasing radiative forcing F - the authors show that the thermosteric part of sea level rise depends linearly on the time-integrated radiative forcing, which represents the total energy accumulated into the Earth system due to the current positive Earth s energy imbalance. The linear relationship between thermosteric sea level rise and time-integrated F is confirmed by climate models under transient climate change like during the 20 th century or the 21 st century (under rcp4.5 and 8.5 scenarios). The constant of proportionality μ between time-integrated F and thermosteric sea level rise expresses the transient thermosteric sea level response of the climate system. It depends on the fraction of excess of heat stored in the ocean β, the expansion efciency of heat ε, the climate feedback parameter α, and the ocean heat uptake efciency κ. The model spread in μ explains most (>70%) of the model spread of the thermosteric sea level rise over the twentieth and twenty-first centuries, while the model spread in F explains the rest (see Figure 2 & 3). Furthermore, the spread in μ comes from the spread in the climate feedback parameter and in the ocean heat uptake efciency, which both vary widely across models. Over the 21 st century simulations, F explains less variance in the spread of thermosteric sea level than over the twentieth century because the anthropogenic aerosol forcing, which is responsible for most of the spread in F over the 20 th century, becomes relatively small.
2 Remarks The thermal expansion of ocean from climate models comes from the three-dimensional CMIP5 temperature and salinity fields annually averaged and converted into global mean thermosteric sea level using the UNESCO 1980 International Equation of State (IES80) and removing marginal seas and lakes ; finally, the resulting sea level is detrended by removing the corresponding long-term drift of individual climate models. The thermal expansion of ocean from climate models (average of all models) shows a rate of around 0.45 mm yr -1 for the m layer and 0.6 mm yr -1 for the whole column, similar to observations, over the period. Only few models reproduce the observed thermal expansion of global mean sea level within observation error bars (regarding or time period, for the m depth layer or the whole column) ; Models generally overestimate thermosteric sea level rise compared to observations because their value of μ is too large. The value of β, which represents the fraction of excess heat stored into the ocean, happens to higher than 1 within some climate models, suggesting energy conservation problems in these climate models. The climate model spread of α, which represents essentially the cloud feedback, is due to an incomplete knowledge of the cloud feedback as well as different ways to model the associated processes. The climate model spread of μ, which represents the link between thermosteric sea level rise and time-integrated radiative forcing, is essentially due to climate modeling of the heat transport processes within the ocean, i.e. the ocean circulation. Interesting enough, the present results suggest that observations of thermosteric sea level changes can give a constraint on μ estimated from climate models, and thus can help in reducing the spread in μ across models as well as further improve climate projections. The linear relationship between time-integrated F and thermal expansion of sea level is found to hold only during years which are not affected by intense explosive volcanic eruptions. In a warmer climate, like at the end of the 21 st century under rcp8.5 scenario, the transient thermosteric sea level response of the climate system tends to decrease as the forcing increases. It suggests that projections of future sea level beyond based on a linear equation probably overestimate thermosteric sea level rise when the radiative forcing increases with time.
3 Main references Cazenave, A., Dieng, H., Meyssignac, B., von Shuckmann, K., Decharme, B. and E. Berthier, 2014: The rate of sea-level rise. Nat. Climate Change, Volume 4, pp Church, J. and N. White, 2011: Sea-Level Rise from the Late 19 th to the Early 21 st Century. Surveys in Geophysics, Volume 32, Issue 4-5, pp Church, J., White, N., Konikow, L., Domingues, C., Cogley, J., Rignit, E., Gregory, J., van den Broeke, M., Monaghan, A. and I. Velicogna, 2011: Revisiting the Earth s sea-level and energy budgets from 1961 to Geophys. Res. Lett., Volume 38, pp L Church, J. and Coauthors, 2013: Sea Level Change. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis, Stocker, T. et al., Cambridge University Press, Domingues, C., Church, J., White, N., Gleckler, P., Wijffels, S., Barker, P. and J. Dunn, 2008: Improved estimates of upper-ocean warming and multi-decadal sea-level rise. Nature, Volume 453, pp Levitus, S., Antonov, J., Boyer, T., Baranova, O., Garcia, H., Locarnini, R., Mishonov, A., Reagan, J., Seidov, D., Yarosch, E. and M. Zweng, 2012: World ocean heat content and thermosteric sea level change ( m), Geophys. Res. Lett., Volume 39, pp L Von Schukmann, K., Palmer, M., Trenberth, K., Cazenave, A., Chambers, D., Champollion, N., Hansen, J., Josey, S., Loeb, N., Matthieu P.P., Meyssignac, N. and Wild, M., 2016: An imperative to monitor Earth s energy imbalance. Nat. Climate Change, Volume 6, pp
4 Figures Figure 1. Thermosteric sea level (mm) and trends (mm yr -1 ) referenced in 2005 over (a, c) and (b, d) Figure 2. Thermosteric sea level rise (global mean from climate models) in 2005 relative to 1900 (mm) computed from the 3D temperature and salinity fields (first group), from the climate coefcient relationship (second group), from the climate coefcient relationship using the model ensemble mean values F (third group), and for μ (fourth group).
5 Figure 3. Thermosteric sea level rise (global mean from climate models) in 2099 relative to 2006 (mm) under the RCP8.5 IPCC scenario computed from the 3D temperature and salinity fields (first group), from the climate coefcient relationship (second group), from the climate coefcient relationship using the model ensemble mean values F (third group), and for μ (fourth group).
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/content/363/6423/128/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for How fast are the oceans warming? Lijing Cheng*, John Abraham, Zeke Hausfather, Kevin E. Trenberth *Corresponding author. Email:
www.sciencemag.org/content/363/6423/128/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for How fast are the oceans warming? Lijing Cheng*, John Abraham, Zeke Hausfather, Kevin E. Trenberth *Corresponding author. Email:
Projection of global and regional sea level change for the 21st century
 Projection of global and regional sea level change for the 21st century Jonathan Gregory 1,2 1 NCAS-Climate, University of Reading 2 Met Office Hadley Centre, Exeter Global mean sea level rise observed
Projection of global and regional sea level change for the 21st century Jonathan Gregory 1,2 1 NCAS-Climate, University of Reading 2 Met Office Hadley Centre, Exeter Global mean sea level rise observed
Prolog. Processes Causing Regional Sea Level Change
 Prolog Regional Variability: Causes for contemporary Regional Sea Level Changes Detlef fstammer Center für Erdsystemforschung und Nachhaltigkeit (CEN) Universität Hamburg Sea level is one of the climate
Prolog Regional Variability: Causes for contemporary Regional Sea Level Changes Detlef fstammer Center für Erdsystemforschung und Nachhaltigkeit (CEN) Universität Hamburg Sea level is one of the climate
An Assessment of IPCC 20th Century Climate Simulations Using the 15-year Sea Level Record from Altimetry Eric Leuliette, Steve Nerem, and Thomas Jakub
 An Assessment of IPCC 20th Century Climate Simulations Using the 15-year Sea Level Record from Altimetry Eric Leuliette, Steve Nerem, and Thomas Jakub Colorado Center for Astrodynamics Research and Department
An Assessment of IPCC 20th Century Climate Simulations Using the 15-year Sea Level Record from Altimetry Eric Leuliette, Steve Nerem, and Thomas Jakub Colorado Center for Astrodynamics Research and Department
Centre for Australian Weather and Climate Research A partnership between CSIRO and the Australian Bureau of Meteorology
 Improved Ocean Warming Estimates: Implications for Climate Models and Sea-Level Rise Catia Domingues 1 John Church 1,2 Neil White 1,2 Peter Gleckler 3 Susan Wijffels 1 Paul Barker 1 Jeff Dunn 1 1 Centre
Improved Ocean Warming Estimates: Implications for Climate Models and Sea-Level Rise Catia Domingues 1 John Church 1,2 Neil White 1,2 Peter Gleckler 3 Susan Wijffels 1 Paul Barker 1 Jeff Dunn 1 1 Centre
Deep ocean heat uptake as a major source of spread in transient climate change simulations
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L22701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040845, 2009 Deep ocean heat uptake as a major source of spread in transient climate change simulations J. Boé,
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L22701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040845, 2009 Deep ocean heat uptake as a major source of spread in transient climate change simulations J. Boé,
Sea level change recent past, present, future
 Sea level change recent past, present, future Anny Cazenave LEGOS-CNES Toulouse, France CCI_Colocation meeting, ESA/ESRIN Global mean sea level rise during the 20 th century (red : tide gauges; blue :
Sea level change recent past, present, future Anny Cazenave LEGOS-CNES Toulouse, France CCI_Colocation meeting, ESA/ESRIN Global mean sea level rise during the 20 th century (red : tide gauges; blue :
Climate models without preindustrial volcanic forcing underestimate historical ocean thermal expansion
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 16 164, doi:1.12/grl.5339, 213 Climate models without preindustrial volcanic forcing underestimate historical ocean thermal expansion J. M. Gregory, 1,2 D. Bi, 3 M.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 16 164, doi:1.12/grl.5339, 213 Climate models without preindustrial volcanic forcing underestimate historical ocean thermal expansion J. M. Gregory, 1,2 D. Bi, 3 M.
Why the hiatus in global mean surface temperature trends in the last decade?
 Why the hiatus in global mean surface temperature trends in the last decade? G. Bala Divecha Center for Climate Change Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore (Email: gbala@caos.iisc.ernet.in) On 27 September
Why the hiatus in global mean surface temperature trends in the last decade? G. Bala Divecha Center for Climate Change Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore (Email: gbala@caos.iisc.ernet.in) On 27 September
Assessment of the Earth s Energy and Sea Level Changes
 Assessment of the Earth s Energy and Sea Level Changes John A. Church1, Ma0hew D. Palmer2 and Susan Wijffels1 1CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Hobart, Australia 2Met Office Hadley Centre, Exeter, United Kingdom
Assessment of the Earth s Energy and Sea Level Changes John A. Church1, Ma0hew D. Palmer2 and Susan Wijffels1 1CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Hobart, Australia 2Met Office Hadley Centre, Exeter, United Kingdom
Krakatoa lives: The effect of volcanic eruptions on ocean heat content and thermal expansion
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L17702, doi:10.1029/2006gl026771, 2006 Krakatoa lives: The effect of volcanic eruptions on ocean heat content and thermal expansion P. J. Gleckler, 1 K. AchutaRao,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L17702, doi:10.1029/2006gl026771, 2006 Krakatoa lives: The effect of volcanic eruptions on ocean heat content and thermal expansion P. J. Gleckler, 1 K. AchutaRao,
Aspects of a climate observing system: energy and water. Kevin E Trenberth NCAR
 Aspects of a climate observing system: energy and water Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Tracking Earth s Global Energy Where has global warming from increased GHGs gone? Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Where did the heat
Aspects of a climate observing system: energy and water Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Tracking Earth s Global Energy Where has global warming from increased GHGs gone? Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Where did the heat
Ecole d Eté Altimétrie spatiale. Sea level variations at climatic time scales: observations & causes. Benoit Meyssignac
 Ecole d Eté 2014 Altimétrie spatiale Sea level variations at climatic time scales: observations & causes Benoit Meyssignac 1 Ecole d Eté 2014, Saint-Pierre d Oléron, 1-5 septembre 2014 Echelles climatiques
Ecole d Eté 2014 Altimétrie spatiale Sea level variations at climatic time scales: observations & causes Benoit Meyssignac 1 Ecole d Eté 2014, Saint-Pierre d Oléron, 1-5 septembre 2014 Echelles climatiques
Global warming and solar anomaly
 Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol 42, December 2013, pp 391-396 Global warming and solar anomaly D K Chakrabarty 1,$,* & S K Peshin 2,# 1 Centre for Environment Survey, Vidya Nagar Society, Ahmedabad
Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol 42, December 2013, pp 391-396 Global warming and solar anomaly D K Chakrabarty 1,$,* & S K Peshin 2,# 1 Centre for Environment Survey, Vidya Nagar Society, Ahmedabad
Anthropogenic forcing dominates global mean sea-level rise since 1970
 Anthropogenic forcing dominates global mean sea-level rise since 1970 Aimée B. A. Slangen 1,2 *, John A. Church 1, Cecile Agosta 3, Xavier Fettweis 3, Ben Marzeion 4 and Kristin Richter 5 1 CSIRO Oceans
Anthropogenic forcing dominates global mean sea-level rise since 1970 Aimée B. A. Slangen 1,2 *, John A. Church 1, Cecile Agosta 3, Xavier Fettweis 3, Ben Marzeion 4 and Kristin Richter 5 1 CSIRO Oceans
Understanding and projecting sea level change: improvements and uncertainties
 Understanding and projecting sea level change: improvements and uncertainties Jonathan Gregory On behalf of all the lead authors of Chapter 13, Sea level change John Church, Peter Clark, Anny Cazenave,
Understanding and projecting sea level change: improvements and uncertainties Jonathan Gregory On behalf of all the lead authors of Chapter 13, Sea level change John Church, Peter Clark, Anny Cazenave,
Climate Modeling and Downscaling
 Climate Modeling and Downscaling Types of climate-change experiments: a preview 1) What-if sensitivity experiments increase the optically active gases and aerosols according to an assumed scenario, and
Climate Modeling and Downscaling Types of climate-change experiments: a preview 1) What-if sensitivity experiments increase the optically active gases and aerosols according to an assumed scenario, and
ON THE PRESENT HALTING
 ON THE PRESENT HALTING OF GLOBAL WARMING by Syun-Ichi Akasofu SPPI REPRINT SERIES July 22, 2013 Climate 2013, 1 5 Climate 2013, 1, 4-11; doi:10.3390/cli1010004 Article OPEN ACCESS climate ISSN 2225-1154
ON THE PRESENT HALTING OF GLOBAL WARMING by Syun-Ichi Akasofu SPPI REPRINT SERIES July 22, 2013 Climate 2013, 1 5 Climate 2013, 1, 4-11; doi:10.3390/cli1010004 Article OPEN ACCESS climate ISSN 2225-1154
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake
 Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections. Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542
 Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542 Climate Scenarios Used for Attribution Studies of Climate Variability and
Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542 Climate Scenarios Used for Attribution Studies of Climate Variability and
Control of land-ocean temperature contrast by ocean heat uptake
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L3704, doi:0.029/2007gl029755, 2007 Control of land-ocean temperature contrast by ocean heat uptake F. Hugo Lambert and John C. H. Chiang
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L3704, doi:0.029/2007gl029755, 2007 Control of land-ocean temperature contrast by ocean heat uptake F. Hugo Lambert and John C. H. Chiang
PROCESSES CONTRIBUTING TO THE GLOBAL SEA LEVEL CHANGE
 Second Split Workshop in Atmospheric Physics and Oceanography PROCESSES CONTRIBUTING TO THE GLOBAL SEA LEVEL CHANGE Student: Maristella Berta Mentor: Prof. Stjepan Marcelja Split, 24 May 2010 INTRODUCTION
Second Split Workshop in Atmospheric Physics and Oceanography PROCESSES CONTRIBUTING TO THE GLOBAL SEA LEVEL CHANGE Student: Maristella Berta Mentor: Prof. Stjepan Marcelja Split, 24 May 2010 INTRODUCTION
Anthropogenic forcing fingerprint on the tropical Pacific sea level trend pattern from the CMIP5 simulations of the XXI st century
 Anthropogenic forcing fingerprint on the tropical Pacific sea level trend pattern from the CMIP5 simulations of the XXI st century Benoît t Meyssignac 1, David Salas y Melia Anny Cazenave 1 1 LEGOS, CNRM/Météo
Anthropogenic forcing fingerprint on the tropical Pacific sea level trend pattern from the CMIP5 simulations of the XXI st century Benoît t Meyssignac 1, David Salas y Melia Anny Cazenave 1 1 LEGOS, CNRM/Météo
1.Decadal prediction ( ) 2. Longer term (to 2100 and beyond)
 Coordinated climate change experiments (formulated by WGCM and AIMES) to be run for assessment in IPCC AR5 Two classes of models to address two time frames and two sets of science questions: 1.Decadal
Coordinated climate change experiments (formulated by WGCM and AIMES) to be run for assessment in IPCC AR5 Two classes of models to address two time frames and two sets of science questions: 1.Decadal
Consequences for Climate Feedback Interpretations
 CO 2 Forcing Induces Semi-direct Effects with Consequences for Climate Feedback Interpretations Timothy Andrews and Piers M. Forster School of Earth and Environment, University of Leeds, Leeds, LS2 9JT,
CO 2 Forcing Induces Semi-direct Effects with Consequences for Climate Feedback Interpretations Timothy Andrews and Piers M. Forster School of Earth and Environment, University of Leeds, Leeds, LS2 9JT,
Rising Sea Level Observations and Causes. Anny Cazenave LEGOS-CNES, Toulouse, France
 Rising Sea Level Observations and Causes Anny Cazenave LEGOS-CNES, Toulouse, France AAAS Annual Meeting, Chicago, Feb.2009 Sea Level budget: Comparison between observed sea level and sum of climate contributions
Rising Sea Level Observations and Causes Anny Cazenave LEGOS-CNES, Toulouse, France AAAS Annual Meeting, Chicago, Feb.2009 Sea Level budget: Comparison between observed sea level and sum of climate contributions
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis
 Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
PMIP3/CMIP5 Last Millennium Model Simulation Effort
 PMIP3/CMIP5 Last Millennium Model Simulation Effort Bette Otto-Bliesner and Steven Phipps National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado University of New South Wales, Sydney Outline Background
PMIP3/CMIP5 Last Millennium Model Simulation Effort Bette Otto-Bliesner and Steven Phipps National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado University of New South Wales, Sydney Outline Background
Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing (Received 30 July 2012; revised 23 October 2012)
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 30, NO. 3, 2013, 841 854 Steric Sea Level Change in Twentieth Century Historical Climate Simulation and IPCC-RCP8.5 Scenario Projection: A Comparison of Two Versions
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 30, NO. 3, 2013, 841 854 Steric Sea Level Change in Twentieth Century Historical Climate Simulation and IPCC-RCP8.5 Scenario Projection: A Comparison of Two Versions
Revisiting the Earth s sea level and energy budgets from 1961 to 2008
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl048794, 2011 Revisiting the Earth s sea level and energy budgets from 1961 to 2008 John A. Church, 1 Neil J. White, 1 Leonard F. Konikow, 2 Catia
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl048794, 2011 Revisiting the Earth s sea level and energy budgets from 1961 to 2008 John A. Church, 1 Neil J. White, 1 Leonard F. Konikow, 2 Catia
The effect of spatial averaging and glacier melt on detecting a forced signal in regional sea level
 Environmental Research Letters LETTER OPEN ACCESS The effect of spatial averaging and glacier melt on detecting a forced signal in regional sea level To cite this article: Kristin Richter et al 2017 Environ.
Environmental Research Letters LETTER OPEN ACCESS The effect of spatial averaging and glacier melt on detecting a forced signal in regional sea level To cite this article: Kristin Richter et al 2017 Environ.
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future. Basic Concepts
 Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
Advancing decadal-scale climate prediction in the North Atlantic Sector Noel Keenlyside
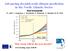 Advancing decadal-scale climate prediction in the North Atlantic Sector Noel Keenlyside M. Latif, J. Jungclaus, L. Kornblueh, E. Roeckner, V. Semenov & W. Park IPCC, 2007 How warm will be the next decade?
Advancing decadal-scale climate prediction in the North Atlantic Sector Noel Keenlyside M. Latif, J. Jungclaus, L. Kornblueh, E. Roeckner, V. Semenov & W. Park IPCC, 2007 How warm will be the next decade?
Correction notice. Nature Climate Change 2, (2012)
 Correction notice Nature Climate Change 2, 524 549 (2012) Human-induced global ocean warming on multidecadal timescales P. J. Gleckler, B. D. Santer, C. M. Domingues, D.W. Pierce, T. P. Barnett, J. A.
Correction notice Nature Climate Change 2, 524 549 (2012) Human-induced global ocean warming on multidecadal timescales P. J. Gleckler, B. D. Santer, C. M. Domingues, D.W. Pierce, T. P. Barnett, J. A.
LETTERS. Influence of the Thermohaline Circulation on Projected Sea Level Rise
 VOLUME 13 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 15 JUNE 2000 LETTERS Influence of the Thermohaline Circulation on Projected Sea Level Rise RETO KNUTTI AND THOMAS F. STOCKER Climate and Environmental Physics, Physics Institute,
VOLUME 13 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 15 JUNE 2000 LETTERS Influence of the Thermohaline Circulation on Projected Sea Level Rise RETO KNUTTI AND THOMAS F. STOCKER Climate and Environmental Physics, Physics Institute,
The importance of including variability in climate
 D. M. H. Sexton and G. R. Harris SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The importance of including variability in climate change projections used for adaptation Modification to time scaling to allow for short-term
D. M. H. Sexton and G. R. Harris SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The importance of including variability in climate change projections used for adaptation Modification to time scaling to allow for short-term
Evidence for external forcing on 20th-century climate from combined ocean-atmosphere warming patterns
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053262, 2012 Evidence for external forcing on 20th-century climate from combined ocean-atmosphere warming patterns Jan Sedláček 1 and Reto Knutti
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053262, 2012 Evidence for external forcing on 20th-century climate from combined ocean-atmosphere warming patterns Jan Sedláček 1 and Reto Knutti
Which Climate Model is Best?
 Which Climate Model is Best? Ben Santer Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550 Adapting for an Uncertain Climate: Preparing
Which Climate Model is Best? Ben Santer Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550 Adapting for an Uncertain Climate: Preparing
Photo courtesy National Geographic
 Welcome to the Polar Climate WG! Quick update: 1. CSL proposal (~85% allocation awarded, 16 month POP starts October 1) 2. All NCAR CMIP5 data on ESG within next month 3. Observational needs/uses living
Welcome to the Polar Climate WG! Quick update: 1. CSL proposal (~85% allocation awarded, 16 month POP starts October 1) 2. All NCAR CMIP5 data on ESG within next month 3. Observational needs/uses living
J. Fasullo, R.S. Nerem, and B. Hamlington NCAR / University of Colorado. Fasullo: Is Detection of Accelerated Sea Level Rise Imminent?
 Is the Detection of Accelerated Sea Level Rise Imminent? J. Fasullo, R.S. Nerem, and B. Hamlington NCAR / University of Colorado Fasullo: Is Detection of Accelerated Sea Level Rise Imminent? Climate Variability
Is the Detection of Accelerated Sea Level Rise Imminent? J. Fasullo, R.S. Nerem, and B. Hamlington NCAR / University of Colorado Fasullo: Is Detection of Accelerated Sea Level Rise Imminent? Climate Variability
Tropical Pacific modula;ons of global climate
 Tropical Pacific modula;ons of global climate Shang- Ping Xie 1 & Yu Kosaka 2 1 Scripps Inst of Oceanogr, UCSD; 2 Univ of Tokyo Develop seasonal and spa
Tropical Pacific modula;ons of global climate Shang- Ping Xie 1 & Yu Kosaka 2 1 Scripps Inst of Oceanogr, UCSD; 2 Univ of Tokyo Develop seasonal and spa
Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
The recent pause in global warming (1): What do observations of the climate system tell us? July 2013
 The recent pause in global warming (1): What do observations of the climate system tell us? July 2013 Paper1_Observing_changes_in_the_climate system_final - 1 Crown copyright 2008 Contents Executive summary...
The recent pause in global warming (1): What do observations of the climate system tell us? July 2013 Paper1_Observing_changes_in_the_climate system_final - 1 Crown copyright 2008 Contents Executive summary...
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1854 Anthropogenic aerosol forcing of Atlantic tropical storms N. J. Dunstone 1, D. S. Smith 1, B. B. B. Booth 1, L. Hermanson 1, R. Eade 1 Supplementary information
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1854 Anthropogenic aerosol forcing of Atlantic tropical storms N. J. Dunstone 1, D. S. Smith 1, B. B. B. Booth 1, L. Hermanson 1, R. Eade 1 Supplementary information
Ocean Model Uncertainty
 Ocean Model Uncertainty Chris Brierley University of Reading, UK Alan Thorpe Natural Environment Research Council, UK Mat Collins Hadley Centre, Met. Office, UK Malcolm MacVean European Centre for Medium-range
Ocean Model Uncertainty Chris Brierley University of Reading, UK Alan Thorpe Natural Environment Research Council, UK Mat Collins Hadley Centre, Met. Office, UK Malcolm MacVean European Centre for Medium-range
Sea level rise and impacts projections under a future scenario with large greenhouse gas emission reductions
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047678, 2011 Sea level rise and impacts projections under a future scenario with large greenhouse gas emission reductions A. K. Pardaens, 1 J.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047678, 2011 Sea level rise and impacts projections under a future scenario with large greenhouse gas emission reductions A. K. Pardaens, 1 J.
The flow of Energy through the Earth s Climate System: Land and Ocean Exchanges
 The flow of Energy through the Earth s Climate System: Land and Ocean Exchanges Kevin E Trenberth and John T. Fasullo NCAR, Boulder, CO, USA Correspondence: Contact trenbert@ucar.edu INTRODUCTION Weather
The flow of Energy through the Earth s Climate System: Land and Ocean Exchanges Kevin E Trenberth and John T. Fasullo NCAR, Boulder, CO, USA Correspondence: Contact trenbert@ucar.edu INTRODUCTION Weather
Ocean heat content and Earth s energy imbalance: insights from climate models
 Ocean heat content and Earth s energy imbalance: insights from climate models Matt Palmer 1, Chris Roberts 1, Doug McNeall 1, Freya Garry 2, Roberto Fernandez-Bilbao 3, Jonathan Gregory 1,3 1 Met Office
Ocean heat content and Earth s energy imbalance: insights from climate models Matt Palmer 1, Chris Roberts 1, Doug McNeall 1, Freya Garry 2, Roberto Fernandez-Bilbao 3, Jonathan Gregory 1,3 1 Met Office
The response of the ocean thermal skin layer to air-sea surface heat fluxes
 The response of the ocean thermal skin layer to air-sea surface heat fluxes Elizabeth W. Wong Meteorology and Physical Oceanography Program Rosenstiel of Marine and Atmospheric Science University of Miami
The response of the ocean thermal skin layer to air-sea surface heat fluxes Elizabeth W. Wong Meteorology and Physical Oceanography Program Rosenstiel of Marine and Atmospheric Science University of Miami
Externally forced and internal variability in multi-decadal climate evolution
 Externally forced and internal variability in multi-decadal climate evolution During the last 150 years, the increasing atmospheric concentration of anthropogenic greenhouse gases has been the main driver
Externally forced and internal variability in multi-decadal climate evolution During the last 150 years, the increasing atmospheric concentration of anthropogenic greenhouse gases has been the main driver
2010 Tied as warmest year 1.34 o F (0.8 o C) total warming
 2010 Tied as warmest year 1.34 o F (0.8 o C) total warming 2010, tied for warmest year Chip Fletcher, University of Hawaii at Manoa School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, Global Surface Temperature
2010 Tied as warmest year 1.34 o F (0.8 o C) total warming 2010, tied for warmest year Chip Fletcher, University of Hawaii at Manoa School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, Global Surface Temperature
Northern European Sea Level Rise. Aslak Grinsted Centre for Ice and Climate Niels Bohr Institute University of Copenhagen
 Northern European Sea Level Rise Aslak Grinsted Centre for Ice and Climate Niels Bohr Institute University of Copenhagen Global Sea Level Rise The world is warming and this causes sea level to rise because:
Northern European Sea Level Rise Aslak Grinsted Centre for Ice and Climate Niels Bohr Institute University of Copenhagen Global Sea Level Rise The world is warming and this causes sea level to rise because:
Doing science with multi-model ensembles
 Doing science with multi-model ensembles Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Biological and Energy Research Regional and Global Climate Modeling Program Why use a multi-model ensemble
Doing science with multi-model ensembles Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Biological and Energy Research Regional and Global Climate Modeling Program Why use a multi-model ensemble
The Roles of Anthropogenic Aerosols in Future Projections of Extreme Summer Precipitation over the Asian Monsoon Region
 The Roles of Anthropogenic Aerosols in Future Projections of Extreme Summer Precipitation over the Asian Monsoon Region Alcide Zhao, David Stevenson and Massimo Bollasina Global Change, School of GeoSciences,
The Roles of Anthropogenic Aerosols in Future Projections of Extreme Summer Precipitation over the Asian Monsoon Region Alcide Zhao, David Stevenson and Massimo Bollasina Global Change, School of GeoSciences,
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales. John Houghton. C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth
 Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Changing Width of Tropical Belt WG Update. Qiang Fu Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington
 Changing Width of Tropical Belt WG Update Qiang Fu Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington v Motivation v Implication v WG Plan v Motivation Tropical width Tropical boundaries are defined
Changing Width of Tropical Belt WG Update Qiang Fu Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington v Motivation v Implication v WG Plan v Motivation Tropical width Tropical boundaries are defined
IPCC Chapter 12: Long- term climate change: projections, commitments and irreversibility
 GEF4400 The Earth System Autumn 2015 23.11.2015 IPCC Chapter 12: Long- term climate change: projections, commitments and irreversibility Introduction and Background (from Chapter 10 and 11) Climate Model
GEF4400 The Earth System Autumn 2015 23.11.2015 IPCC Chapter 12: Long- term climate change: projections, commitments and irreversibility Introduction and Background (from Chapter 10 and 11) Climate Model
Detection and Attribution of Climate Change
 Detection and Attribution of Climate Change What is D&A? Global Mean Temperature Extreme Event Attribution Geert Jan van Oldenborgh, Sjoukje Philip (KNMI) Definitions Detection: demonstrating that climate
Detection and Attribution of Climate Change What is D&A? Global Mean Temperature Extreme Event Attribution Geert Jan van Oldenborgh, Sjoukje Philip (KNMI) Definitions Detection: demonstrating that climate
Climate changes in Finland, but how? Jouni Räisänen Department of Physics, University of Helsinki
 Climate changes in Finland, but how? Jouni Räisänen Department of Physics, University of Helsinki 19.9.2012 Outline Some basic questions and answers about climate change How are projections of climate
Climate changes in Finland, but how? Jouni Räisänen Department of Physics, University of Helsinki 19.9.2012 Outline Some basic questions and answers about climate change How are projections of climate
Global warming trend and multi-decadal climate
 Global warming trend and multi-decadal climate variability Sergey Kravtsov * and Anastasios A. Tsonis * Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to SK (kravtsov@uwm.edu) 0 Climate
Global warming trend and multi-decadal climate variability Sergey Kravtsov * and Anastasios A. Tsonis * Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to SK (kravtsov@uwm.edu) 0 Climate
The time-evolution of climatically significant salinity trends in the World Ocean
 The time-evolution of climatically significant salinity trends in the World Ocean James Reagan 1,2, Dan Seidov 2, Tim Boyer 2, Melissa Zweng 2 Contact E-mail: james.reagan@noaa.gov 1 UMD/ESSIC/CICS-MD
The time-evolution of climatically significant salinity trends in the World Ocean James Reagan 1,2, Dan Seidov 2, Tim Boyer 2, Melissa Zweng 2 Contact E-mail: james.reagan@noaa.gov 1 UMD/ESSIC/CICS-MD
GEOL/ENVS 3520 Spring 2009 Hour Exam #2
 GEOL/ENVS 3520 Spring 2009 Hour Exam #2 Enter your name, the date, your ID number, and a made-up 4-digit code (for later recall and identification of your test results) on the separate test sheet. Carefully
GEOL/ENVS 3520 Spring 2009 Hour Exam #2 Enter your name, the date, your ID number, and a made-up 4-digit code (for later recall and identification of your test results) on the separate test sheet. Carefully
Projections of 21st century Arctic sea ice loss. Alexandra Jahn University of Colorado Boulder
 Projections of 21st century Arctic sea ice loss Alexandra Jahn University of Colorado Boulder Outline Sea ice projections/ensembles 101 How is Arctic sea ice projected to change in the 21 st century? State
Projections of 21st century Arctic sea ice loss Alexandra Jahn University of Colorado Boulder Outline Sea ice projections/ensembles 101 How is Arctic sea ice projected to change in the 21 st century? State
Changes in Marine Extremes. Professor Mikis Tsimplis. The LRET Research Collegium Southampton, 11 July 2 September 2011
 Changes in Marine Extremes by Professor Mikis Tsimplis The LRET Research Collegium Southampton, 11 July 2 September 2011 1 Changes in marine extremes Mikis Tsimplis, School of Law and National Oceanography
Changes in Marine Extremes by Professor Mikis Tsimplis The LRET Research Collegium Southampton, 11 July 2 September 2011 1 Changes in marine extremes Mikis Tsimplis, School of Law and National Oceanography
Earth s Energy Imbalance
 Earth s Energy Imbalance Kevin E. Trenberth 1, John T. Fasullo 1 and Magdalena A. Balmaseda 2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research 3, Boulder, CO 80307 2. European Centre for Medium Range Weather
Earth s Energy Imbalance Kevin E. Trenberth 1, John T. Fasullo 1 and Magdalena A. Balmaseda 2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research 3, Boulder, CO 80307 2. European Centre for Medium Range Weather
CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations
 CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations Dan Marsh, Mike Mills, Natalia Calvo, Marika Holland, Cécile Hannay WAWG meeting, Boulder, February 2011 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science
CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations Dan Marsh, Mike Mills, Natalia Calvo, Marika Holland, Cécile Hannay WAWG meeting, Boulder, February 2011 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science
Long-term Behaviors of Two Versions of FGOALS2 in Preindustrial Control Simulations with Implications for 20th Century Simulations
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 30, NO. 3, 2013, 577 592 Long-term Behaviors of Two Versions of FGOALS2 in Preindustrial Control Simulations with Implications for 20th Century Simulations LIN Pengfei
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 30, NO. 3, 2013, 577 592 Long-term Behaviors of Two Versions of FGOALS2 in Preindustrial Control Simulations with Implications for 20th Century Simulations LIN Pengfei
An imperative to monitor Earth s energy imbalance
 An imperative to monitor Earth s energy imbalance K. von Schuckmann 1,2*, M. D. Palmer 3, K. E. Trenberth 4, A. Cazenave 5,6, D. Chambers 7, N. Champollion 6, J. Hansen 8, S. A. Josey 9, N. Loeb 10, P.-P.
An imperative to monitor Earth s energy imbalance K. von Schuckmann 1,2*, M. D. Palmer 3, K. E. Trenberth 4, A. Cazenave 5,6, D. Chambers 7, N. Champollion 6, J. Hansen 8, S. A. Josey 9, N. Loeb 10, P.-P.
Century to multi-century sea level rise projections from CMIP5 models
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052947, 2012 Century to multi-century sea level rise projections from CMIP5 models Jianjun Yin 1 Received 28 June 2012; revised 5 August 2012;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052947, 2012 Century to multi-century sea level rise projections from CMIP5 models Jianjun Yin 1 Received 28 June 2012; revised 5 August 2012;
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
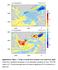 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
The Interaction between Climate Forcing and Feedbacks From the global scale to the process level
 The Interaction between Climate Forcing and Feedbacks From the global scale to the process level A. Gettelman (NCAR), L. Lin (U. Lanzhou), B. Medeiros, J. Olson (NCAR) The interaction of Forcing & Feedbacks
The Interaction between Climate Forcing and Feedbacks From the global scale to the process level A. Gettelman (NCAR), L. Lin (U. Lanzhou), B. Medeiros, J. Olson (NCAR) The interaction of Forcing & Feedbacks
Assimilation of Satellite Sea-surface Salinity Fields: Validating Ocean Analyses and Identifying Errors in Surface Buoyancy Fluxes
 Assimilation of Satellite Sea-surface Salinity Fields: Validating Ocean Analyses and Identifying Errors in Surface Buoyancy Fluxes Eric Bayler Sudhir Nadiga Avichal Mehra David Behringer NOAA/NESDIS/STAR
Assimilation of Satellite Sea-surface Salinity Fields: Validating Ocean Analyses and Identifying Errors in Surface Buoyancy Fluxes Eric Bayler Sudhir Nadiga Avichal Mehra David Behringer NOAA/NESDIS/STAR
Understanding and attributing climate variations: The role of energy. Kevin E Trenberth NCAR
 Understanding and attributing climate variations: The role of energy Kevin E Trenberth NCAR NCAR: attribution A way to organize a lot of research Makes it relevant to societal concerns Has some implications
Understanding and attributing climate variations: The role of energy Kevin E Trenberth NCAR NCAR: attribution A way to organize a lot of research Makes it relevant to societal concerns Has some implications
Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science. Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate
Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate
Tracking Earth s energy: From El Niño to global warming
 Tracking Earth s energy: From El Niño to global warming Kevin E. Trenberth and John T. Fasullo National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, USA Correspondence: Contact trenbert@ucar.edu Science
Tracking Earth s energy: From El Niño to global warming Kevin E. Trenberth and John T. Fasullo National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, USA Correspondence: Contact trenbert@ucar.edu Science
R. Hallberg, A. Adcroft, J. P. Dunne, J. P. Krasting and R. J. Stouffer NOAA/GFDL & Princeton University
 Sensitivity of 21st Century Steric Sea Level Rise to Ocean Model Formulation R. Hallberg, A. Adcroft, J. P. Dunne, J. P. Krasting and R. J. Stouffer NOAA/GFDL & Princeton University Hallberg, R., A. Adcroft,
Sensitivity of 21st Century Steric Sea Level Rise to Ocean Model Formulation R. Hallberg, A. Adcroft, J. P. Dunne, J. P. Krasting and R. J. Stouffer NOAA/GFDL & Princeton University Hallberg, R., A. Adcroft,
Forcing, feedbacks and climate sensitivity in CMIP5 coupled atmosphere-ocean climate models
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051607, 2012 Forcing, feedbacks and climate sensitivity in CMIP5 coupled atmosphere-ocean climate models Timothy Andrews, 1 Jonathan M. Gregory,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051607, 2012 Forcing, feedbacks and climate sensitivity in CMIP5 coupled atmosphere-ocean climate models Timothy Andrews, 1 Jonathan M. Gregory,
Climate Change. April 21, 2009
 Climate Change Chapter 16 April 21, 2009 Reconstructing Past Climates Techniques Glacial landscapes (fossils) CLIMAP (ocean sediment) Ice cores (layering of precipitation) p Otoliths (CaCO 3 in fish sensory
Climate Change Chapter 16 April 21, 2009 Reconstructing Past Climates Techniques Glacial landscapes (fossils) CLIMAP (ocean sediment) Ice cores (layering of precipitation) p Otoliths (CaCO 3 in fish sensory
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
Ice sheets, global warming and sea level
 Ice sheets, global warming and sea level Ralf Greve Institute of Low Temperature Science, Hokkaido University Kita-19, Nishi-8, Kita-ku, Sapporo 060-0819, Japan Fax: 81-11-706-7142, e-mail: greve@lowtem.hokudai.ac.jp
Ice sheets, global warming and sea level Ralf Greve Institute of Low Temperature Science, Hokkaido University Kita-19, Nishi-8, Kita-ku, Sapporo 060-0819, Japan Fax: 81-11-706-7142, e-mail: greve@lowtem.hokudai.ac.jp
Introduction to climate modelling: Evaluating climate models
 Introduction to climate modelling: Evaluating climate models Why? How? Professor David Karoly School of Earth Sciences, University of Melbourne Experiment design Detection and attribution of climate change
Introduction to climate modelling: Evaluating climate models Why? How? Professor David Karoly School of Earth Sciences, University of Melbourne Experiment design Detection and attribution of climate change
A Flexible Climate Model For Use In Integrated Assessments
 A Flexible Climate Model For Use In Integrated Assessments Andrei P. Sokolov and Peter H. Stone Center for Global Change Science. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Ave. Room 54-1312,
A Flexible Climate Model For Use In Integrated Assessments Andrei P. Sokolov and Peter H. Stone Center for Global Change Science. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Ave. Room 54-1312,
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA
 FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
Northern Rockies Adaptation Partnership: Climate Projections
 Northern Rockies Adaptation Partnership: Climate Projections Contents Observed and Projected Climate for the NRAP Region... 2 Observed and Projected Climate for the NRAP Central Subregion... 8 Observed
Northern Rockies Adaptation Partnership: Climate Projections Contents Observed and Projected Climate for the NRAP Region... 2 Observed and Projected Climate for the NRAP Central Subregion... 8 Observed
LETTERS. Authorized for Electronic Distribution by CSIRO, 06/08-12/08. Improved estimates of upper-ocean warming and multi-decadal sea-level rise
 Vol 453 19 June 28 doi:1.138/nature78 LETTERS Improved estimates of upper-ocean warming and multi-decadal sea-level rise Catia M. Domingues 1, John A. Church 1,2, Neil J. White 1,2, Peter J. Gleckler 3,
Vol 453 19 June 28 doi:1.138/nature78 LETTERS Improved estimates of upper-ocean warming and multi-decadal sea-level rise Catia M. Domingues 1, John A. Church 1,2, Neil J. White 1,2, Peter J. Gleckler 3,
Summary for the Greenland ice sheet
 Contribution of Greenland and Antarctica to future sea level change Catherine Ritz, Gaël Durand, Fabien Gillet-Chaulet, Olivier Gagliardini, Vincent Peyaud EDGe team, LGGE, CNRS/UJF Grenoble, France Ice
Contribution of Greenland and Antarctica to future sea level change Catherine Ritz, Gaël Durand, Fabien Gillet-Chaulet, Olivier Gagliardini, Vincent Peyaud EDGe team, LGGE, CNRS/UJF Grenoble, France Ice
Recent cooling of the upper ocean
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L18604, doi:10.1029/2006gl027033, 2006 Recent cooling of the upper ocean John M. Lyman, 1,2 Josh K. Willis, 3 and Gregory C. Johnson 1
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L18604, doi:10.1029/2006gl027033, 2006 Recent cooling of the upper ocean John M. Lyman, 1,2 Josh K. Willis, 3 and Gregory C. Johnson 1
Climate modeling: 1) Why? 2) How? 3) What?
 Climate modeling: 1) Why? 2) How? 3) What? Matthew Widlansky mwidlans@hawaii.edu 1) Why model the climate? Hawaii Fiji Sachs and Myhrvold: A Shifting Band of Rain 1 Evidence of Past Climate Change? Mean
Climate modeling: 1) Why? 2) How? 3) What? Matthew Widlansky mwidlans@hawaii.edu 1) Why model the climate? Hawaii Fiji Sachs and Myhrvold: A Shifting Band of Rain 1 Evidence of Past Climate Change? Mean
Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, EX1 3PB, UK.
 Temperature Extremes, the Past and the Future. S Brown, P Stott, and R Clark Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, EX1 3PB, UK. Tel: +44 (0)1392 886471 Fax
Temperature Extremes, the Past and the Future. S Brown, P Stott, and R Clark Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, EX1 3PB, UK. Tel: +44 (0)1392 886471 Fax
Detection and attribution of Atlantic salinity changes
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L21702, doi:10.1029/2008gl035874, 2008 Detection and attribution of Atlantic salinity changes Peter A. Stott, 1 Rowan T. Sutton, 2 and Doug M. Smith 1 Received 1
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L21702, doi:10.1029/2008gl035874, 2008 Detection and attribution of Atlantic salinity changes Peter A. Stott, 1 Rowan T. Sutton, 2 and Doug M. Smith 1 Received 1
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32. Paleoclimate
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32 Paleoclimate Natural changes in the Earth s climate also occur at much longer timescales The study of prehistoric climates and their variability is called paleoclimate.
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32 Paleoclimate Natural changes in the Earth s climate also occur at much longer timescales The study of prehistoric climates and their variability is called paleoclimate.
Chapter 14: The Changing Climate
 Chapter 14: The Changing Climate Detecting Climate Change Natural Causes of Climate Change Anthropogenic Causes of Climate Change Possible Consequences of Global Warming Climate Change? -Paleo studies
Chapter 14: The Changing Climate Detecting Climate Change Natural Causes of Climate Change Anthropogenic Causes of Climate Change Possible Consequences of Global Warming Climate Change? -Paleo studies
Contents of this file
 Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Future changes in tropical cyclone activity in high-resolution large-ensemble simulations Kohei Yoshida 1, Masato Sugi 1, Ryo Mizuta 1, Hiroyuki
Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Future changes in tropical cyclone activity in high-resolution large-ensemble simulations Kohei Yoshida 1, Masato Sugi 1, Ryo Mizuta 1, Hiroyuki
The use of marine data for attribution of climate change and constraining climate predictions
 The use of marine data for attribution of climate change and constraining climate predictions Peter Stott, Climar III, Thursday 8 May 2008 The use of marine data to: Quantify the contribution of human
The use of marine data for attribution of climate change and constraining climate predictions Peter Stott, Climar III, Thursday 8 May 2008 The use of marine data to: Quantify the contribution of human
Sea-level change: A scientific and societal challenge for the 21 st century John Church International GNSS Service Workshop, Sydney, Feb 11, 2016
 Sea-level change: A scientific and societal challenge for the 21 st century John Church International GNSS Service Workshop, Sydney, Feb 11, 2016 OCEANS AND ATMOSPHERE NATIONAL RESEARCH FLAGSHIP Our coastal
Sea-level change: A scientific and societal challenge for the 21 st century John Church International GNSS Service Workshop, Sydney, Feb 11, 2016 OCEANS AND ATMOSPHERE NATIONAL RESEARCH FLAGSHIP Our coastal
Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
How Do We Know That Human Activities Have Influenced Global Climate?
 How Do We Know That Human Activities Have Influenced Global Climate? Ben Santer Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550 Email:
How Do We Know That Human Activities Have Influenced Global Climate? Ben Santer Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550 Email:
Recent Progress in Understanding and Projecting Regional and Global Mean Sea Level Change
 Curr Clim Change Rep (2015) 1:224 246 DOI 10.1007/s40641-015-0024-4 SEA LEVEL PROJECTIONS (BP HORTON, SECTION EDITOR) Recent Progress in Understanding and Projecting Regional and Global Mean Sea Level
Curr Clim Change Rep (2015) 1:224 246 DOI 10.1007/s40641-015-0024-4 SEA LEVEL PROJECTIONS (BP HORTON, SECTION EDITOR) Recent Progress in Understanding and Projecting Regional and Global Mean Sea Level
Warming of the world ocean,
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L02604, doi:10.1029/2004gl021592, 2005 Warming of the world ocean, 1955 2003 S. Levitus, J. Antonov, and T. Boyer National Oceanographic Data Center, NOAA, Silver
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L02604, doi:10.1029/2004gl021592, 2005 Warming of the world ocean, 1955 2003 S. Levitus, J. Antonov, and T. Boyer National Oceanographic Data Center, NOAA, Silver
