Contents of this file
|
|
|
- Lee McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Future changes in tropical cyclone activity in high-resolution large-ensemble simulations Kohei Yoshida 1, Masato Sugi 1, Ryo Mizuta 1, Hiroyuki Murakami 2,1, Masayoshi Ishii 1 1 Meteorological Research Institute, Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan 2 Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton, NJ , USA Contents of this file Text S1 Figures S1 to S4 Table S1 Introduction This support information contains additional text, figures, and table to supplement main contents. Text S1 describes detailed experimental design of the d4pdf data set. See Mizuta et al. [201] for complete description of the experimental design. Figure S1 shows the six patterns of SST warming from past to future simulations, together with the multi-model mean pattern and model spread. The tropical mean SST warming ranges from +2. to +3.0 K (Figures S1a and c-f). In the multi-model mean, warming in the Northern Hemisphere is larger than in the Southern Hemisphere, and large warming occurs in the equatorial eastern Pacific and Atlantic (Figure S1a). The 1
2 spread among the six patterns is large in the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, and smaller in the NIO (Figure S1b). Each SST warming pattern has its warming peak in a different region of the tropics. The CCSM4-warming has its peak in the equatorial western Pacific (a La Niña or flat pattern), in which the spatial variance of SST increases in the tropics because of the enhanced longitudinal SST gradient. MRI-CGCM3-warming has its peak in the equatorial central Pacific, and the others have their peaks in the equatorial eastern Pacific (shaped like El Niño), in which the spatial variance generally reduces in the future climate. Therefore, these SST warming patterns have distinctive structures and can include better estimates of the uncertainty compared with previous studies [Murakami et al., 2012; Mizuta et al., 2014]. Figure S2 shows relative probabilities of annual TC genesis frequency in each ocean basin. TC genesis frequency in the past climate simulations generally reproduces the observations, but underestimates in ENP and NAT. As shown in Figure 1, allmember simulations have smooth probability distributions, while the probability distributions of a single-member simulation and the observations are not smooth. The mean future reduction rate of TC genesis frequency is significantly large especially in WNP, SIO, and SPA, but quite small in ENP (see also Figure 4). In each ocean basin, the rate of future change relative to the interannual variability is smaller than for the global ocean. The interannual variations of the number of regional TCs have complement relationships in individual oceans, and the interannual variations of global TC genesis frequency consequently shrinks. In individual ocean basins, especially in NIO, ENP, and NAT, the nonparametric probability distributions tend not to match with the estimated normal distributions, comparing with that in the global ocean. Figure S3 shows future changes in vertical velocity at 500 hpa and vertical wind shear of horizontal wind between 50 and 200 hpa. Both of the vertical wind and vertical shear of horizontal wind have similar distributions to those shown in Murakami et al. 2
3 [2012a; 2012b]. Future changes in atmospheric circulations such as vertical shear of horizontal wind and vertical wind tend to correspond to CAT45 TC occurrence changes consistent with previous studies. In areas from Hawaii to south of Japan, there appears both increasing vertical velocity and weakening vertical shear of horizontal wind. Figure S4 and Table S1 show future changes in the four major metrics of TC activity together with uncertainty ranges for each SST warming pattern. We can see large uncertainty ranges in the changes in the metrics in individual ocean basins. The changes in the TC activity metrics in individual ocean basins significantly depend on the prescribed SST warming patterns, especially in ENP and NAT. The TC genesis frequency increases with the MIROC5 SST pattern (+15% to +40% in ENP; +25% to +52% in NAT), but decreases for CCSM4 ( 45% to 2% in ENP; 5% to 37% in NAT). The number of CAT45 drastically increases with the MIROC5 SST (+13 to +307% in ENP; +175% to +275% in NAT), but decreases or slightly increases for CCSM4 ( 2% to +% in ENP; 3% to 17% in NAT). The lifetime maximum intensity of surface wind and mean precipitation rate have similar tendency, but the spread of the changes originated by uncertainty of SST warming pattern is smaller. The difference in changes in TC metrics is associated with changes in the SST contrast between the western Pacific and Atlantic in the tropics. While SST warming is relatively high in the tropics of ENP and NAT and low in western and central Pacific in MIROC5, it is high in the WNP and low in ENP and NAT in CCSM4 (Figure S4c and S4f). Additionally, in SPA and WNP, SST warming difference between MIROC5 and MRI-CGCM3 clearly affect the difference in changes in TC activity metrics (Figure S4f and S4h). Relative magnitude of SST warming among individual ocean basins differs in each SST warming pattern, and the difference in SST warming pattern induces the uncertainty of changes in 3
4 TC activity metrics through the relationship between regional SST warming and changes in TC metrics as discussed in Knutson et al. [2015]. 4
5 Text S1. We use the large ensemble simulation data set for current and future climates, d4pdf, which is produced by MRI-AGCM3.2H. The model is based on a numerical weather prediction model of the Japan Meteorological Agency, and is configured for research use [Mizuta et al., 2012]. The horizontal resolution is TL31 (equivalent to a 0-km horizontal grid), there are 4 vertical layers, and the model top is set at 0.01 hpa. MRI-AGCM3.2H is able to reproduce realistic TC activity apart from its intensity [Murakami et al., 2012b]. The current climate simulations were integrated for 0 years from 151 to 20 with observed SSTs and sea ice concentration from COBE-SST2 [Hirahara et al., 2014] and observed global warming gas concentrations. The current climate simulations were constituted by 0 ensemble members based on initial value perturbations of the atmosphere and short-term monthly SST perturbations. The magnitude of the monthly SST perturbations is 30% of observed interannual SST variations, which is typical SST analysis errors for recent decades. The future climate simulations were performed for 0 years with a constant warming condition roughly corresponding to the level of year 200 in the Representative Concentration Pathway.5 (RCP.5) scenario adopted in CMIP5. Because of the large variety in future SST projections, we chose six SST warming patterns projected by six coupled models: CCSM4, GFDL-CM3, HadGEM2-AO, MIROC5, MPI-ESM-MR, and MRI-CGCM3 (see Figure S1). Each SST warming pattern of the RCP.5 scenario was the difference between SST climatologies of and for each month, and then the climatological difference was scaled by a multiplier, so that MRI-AGCM3.2H reproduces 4 K surface air warming from the preindustrial level. Here, the future monthly SSTs were constructed from adding the SST warming patterns to detrended monthly COBE-SST2 from 151 to 20. The future climate simulations were constituted by 0 ensemble members based on the six future 5
6 SST patterns, initial value perturbations of the atmosphere, and short-term monthly SST perturbations. For each of six SST warming patterns, 15 ensemble experiments were performed with the perturbations of both initial values of the atmosphere and SST mentioned above. See Mizuta et al. [201] for complete description of the experimental design. Note that the future SSTs used in the present study do not have long-term warming trends for the 0-year integration period.
7 Figure S1. Annual mean prescribed sea surface temperatures (SST; contours) and their future changes (color). Contour intervals are 1 C. (a) multi-model mean SST warming pattern from the six CMIP5 models, (b) standard deviation of SST warming among the six models, (c h) SST warmings of the six models. The values at the top of each panel indicate tropical-mean (30 S 30 N) SST (M) and spatial standard deviation of SST in the deep-tropics ( S N) (S). 7
8 Figure S2. Same as Figure 1 but for the two hemispheres and each ocean basin.
9 Figure S3. Future changes in climatologies of (top) vertical velocity at 500 hpa [mm/s] and (bottom) vertical shear of horizontal wind between 200 and 50 hpa [m/s]. Contours indicate the values in all-member ensemble mean of current climate simulations, and color shadings indicate difference between values in all-member ensemble mean of the future and current climate simulations. The average from July to October is used in Northern Hemisphere and that from January to April is used in Southern Hemisphere.
10 Figure S4. Same as Figure 4 but including uncertainty range for each SST warming pattern. See Table S1 for further details.
11 SST Global NH SH NIO WNP ENP NAT SIO SPA CMIP5 models (n=0 min/max) -33 (-43,-27) -2 (-3,-17) -41 (-0,-23) -20 (-4,3) -42 (-7,-23) -4 (-45,40) -23 (-5,52) -44 (-4,-25) -40 (-7,-13) Genesis frequency CCSM4 GFDL-CM3 HadGEM2-AO MIROC5 MPI-ESM-MR MRI-CGCM3-33 (-35,-30) -31 (-34,-2) -32 (-35,-2) -41 (-43,-3) -31 (-34,-2) -32 (-35,-27) -34 (-3,-31) -2 (-30,-23) -22 (-2,-17) -33 (-3,-31) -2 (-32,-2) -2 (-34,-23) -2 (-34,-23) -40 (-45,-3) -52 (-57,-4) -55 (-0, -50) -34 (-40,-2) -3 (-44,-33) - (-17, 2) -1 (-2,-3) - (-1, 3) -3 (-4,-31) -31 (-3, -22) -14 (-32, -1) -37 (-44,-33) -37 (-43,-32) -31 (-3,-23) -74 (-7,-71) -43 (-47,-3) -30 (-34,-24) -33 (-45,-2) -14 (-21,-2) 5 (-14, 21) 2 (15,40) 15 (3,24) -27 (-35,-1) -4 (-5,-37) - (-25,) -42 (-4,-3) 41 (25,52) -45 (-57,-37) -37 (-47,-27) -32 (-41, -25) -41 (-4, -34) -5 (-4, -53) -44 (-52, -3) -3 (-4,-32) -4 (-57, -43) -2 (-35,-1) -42 (-53,-33) -43 (-50,-2) -74 (-7,-70) -2 (-41,-23) -24 (-37,-13) CMIP5 models (n=0 min/max) -13 (-33,) -7 (-3,13) -2 (-,11) -1 (-1,75) -2 (-1,13) (-2,307) 20 (-3,275) -23 (-2,31) -37 (-7,37) Number of CAT45 TC CCSM4 GFDL-CM3 HadGEM2-AO MIROC5 MPI-ESM-MR MRI-CGCM3-1 (-2,-) - (-17,-2) -12 (-20,-5) -23 (-33,-14) -13 (-22,-5) -2 (-,) -23 (-3,-17) -4 (-14,) 2 (-,12) - (-23,-1) - (-20,3) 3 (-,13) -7 (-24,11) -25 (-37,-13) -4 (-5,-37) -55 (-, -37) -21 (-37, -) -12 (-3,0) 4 (-32, 41) -24 (-1, 7) 15 (-4,5) -14 (-3, 1) -11 (-32, 13) 25 (-,75) -22 (-35,-) -20 (-33,-) -13 (-21,3) -7 (-1,-7) -30 (-40,-20) 2 (-,13) -32 (-2,) 72 (40,5) (44,13) 223 (13,307) 14 (5,) (-32,40) -44 (-3,-17) 40 (0,114) -23 (-1,1) 21 (175,275) -44 (-, 35) -22 (-4,2) 7 (-,31) -15 (-37,1) -4 (-2,-34) -37 (-4,-1) -17 (-32,-1) -27 (-55,-11) -32 (-5,-1) -43 (-,-) -4 (-4,-3) - (-7,-72) -27 (-50,4) 15 (-,37) CMIP5 models (n=0 min/max) (4,13) (4,13) (-4,13) (2,22) (-5,15) 15 (1,27) (-,25) (-1,1) 0 (-1,17) Lifetime max surface wind CCSM4 GFDL-CM3 HadGEM2-AO MIROC5 MPI-ESM-MR MRI-CGCM3 7 (4,) (,11) (,) (7,12) (7,12) 12 (,13) 7 (4,) (,11) (7,11) (7,13) (7,12) 12 (,13) 7 (5,) (2,) 2 (-3,) 1 (-4,) (5,11) (,13) (3,12) 4 (0,) 11 (3,17) 13 (,22) (2,14) 12 (4, ) (5, 11) (,12) (,11) -1 (-5,5) (5,11) 13 (11,15) 7 (1,13) 17 (13,22) 15 (,20) 22 (1,27) 1 (15,22) 13 (,1) 3 (-3,) 12 (,20) (-2,1) 21 (1,25) 1 (-,1) (0,14) 12 (,1) (5,1) (-1,) (0,13) 11 (,15) (2,15) -1 (-4,5) -1 (-7,7) -1 (-,3) -14 (-1,-4) 4 (1,11) (4,17) CMIP5 models (n=0 min/max) 2 (,45) 2 (3,4) 2 (5,47) 30 (12,53) 32 (7,4) 47 (1,7) 24 (-23,7) 3 (15,2) 13 (-2,44) Lifetime max precipitation rate CCSM4 GFDL-CM3 HadGEM2-AO MIROC5 MPI-ESM-MR MRI-CGCM3 30 (24,3) 32 (27,35) 2 (23,33) 13 (,1) 27 (23,33) 40 (37,45) 27 (1,35) 33 (2,37) 30 (27,37) 11 (3,14) 2 (20,31) 42 (3,4) 3 (2,44) 2 (21,35) 21 (11,32) 1 (5,34) 30 (21,40) 37 (24,47) 23 (12, 35) 24 (13, 32) 2 (12, 44) 3 (24, 53) 32 (17, 40) 35 (25,52) 2 (20,3) 3 (33,42) 30 (24,37) 1 (7,3) 31 (22,3) 44 (3,4) 15 (1,2) 55 (43,75) 5 (43,) 2 (4,7) 54 (42,7) 3 (2, 0) (-23,2) 3 (2,7) (-,35) 51 (3, 5) 13 (-17,45) 2 (11,41) 4 (40, 2) 42 (2,5) 32 (1, 47) 30 (15, 4) 41 (34, 54) 42 (25, 5) 1 (7,2) 11 (-5,2) (-,22) -12 (-2,) 1 (7,24) 33 (1, 44) Table S1. Future percent changes of the TC metrics to the climatological mean in the current climate simulations for the global ocean, the two hemispheres and individual ocean basins. TC metrics consist of TC genesis frequency, the number of TCs for CAT45 ( 5 m/s maximum surface wind speed), lifetime maximum intensity (LMI) of surface wind, and LMI of precipitation rate averaged within 200 km of the TC center. Shown are percent changes of the ensemble mean, minimum, and maximum values 11
12 among all ensemble members. Values of n indicate the number of the ensemble members. Bold letters indicate that the change is statistically significant. 12
Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2277 Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades Masato Mori 1*, Masahiro Watanabe 1, Hideo Shiogama 2, Jun Inoue 3,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2277 Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades Masato Mori 1*, Masahiro Watanabe 1, Hideo Shiogama 2, Jun Inoue 3,
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific
 Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
Winter Forecast for GPC Tokyo. Shotaro TANAKA Tokyo Climate Center (TCC) Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
 Winter Forecast for 2013 2014 GPC Tokyo Shotaro TANAKA Tokyo Climate Center (TCC) Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) NEACOF 5, October 29 November 1, 2013 1 Outline 1. Numerical prediction 2. Interannual
Winter Forecast for 2013 2014 GPC Tokyo Shotaro TANAKA Tokyo Climate Center (TCC) Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) NEACOF 5, October 29 November 1, 2013 1 Outline 1. Numerical prediction 2. Interannual
Increasing frequency of extremely severe cyclonic storms over the Arabian Sea
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-017-0008-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Increasing frequency of extremely severe cyclonic storms over the Arabian
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-017-0008-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Increasing frequency of extremely severe cyclonic storms over the Arabian
Influence of Model Biases on Projected Future Changes in Tropical Cyclone Frequency of Occurrence*
 1MARCH 2014 M U R A K A M I E T A L. 2159 Influence of Model Biases on Projected Future Changes in Tropical Cyclone Frequency of Occurrence* HIROYUKI MURAKAMI Department of Meteorology and International
1MARCH 2014 M U R A K A M I E T A L. 2159 Influence of Model Biases on Projected Future Changes in Tropical Cyclone Frequency of Occurrence* HIROYUKI MURAKAMI Department of Meteorology and International
Future Change of Storm Surge Risk under Global Warming Based on Mega-Ensemble Global Climate Projections (d4pdf) Tomoya Shimura1 and Nobuhito Mori 2
 Future Change of Storm Surge Risk under Global Warming Based on Mega-Ensemble Global Climate Projections (d4pdf) Tomoya Shimura1 and Nobuhito Mori 2 Abstract Long-term assessment of storm surge risk based
Future Change of Storm Surge Risk under Global Warming Based on Mega-Ensemble Global Climate Projections (d4pdf) Tomoya Shimura1 and Nobuhito Mori 2 Abstract Long-term assessment of storm surge risk based
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia
 Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia I. Introduction To assess the impact of large-scale environmental conditions on tropical cyclone
Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia I. Introduction To assess the impact of large-scale environmental conditions on tropical cyclone
Decreasing trend of tropical cyclone frequency in 228-year high-resolution AGCM simulations
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053360, 2012 Decreasing trend of tropical cyclone frequency in 228-year high-resolution AGCM simulations Masato Sugi 1,2 and Jun Yoshimura 2 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053360, 2012 Decreasing trend of tropical cyclone frequency in 228-year high-resolution AGCM simulations Masato Sugi 1,2 and Jun Yoshimura 2 Received
Tropical Cyclones in a regional climate change projections with RegCM4 over Central America CORDEX domain
 Tropical Cyclones in a regional climate change projections with RegCM4 over Central America CORDEX domain Gulilat Tefera Diro diro@sca.uqam.ca Centre ESCER, University of Quebec at Montreal (UQAM), Montreal,
Tropical Cyclones in a regional climate change projections with RegCM4 over Central America CORDEX domain Gulilat Tefera Diro diro@sca.uqam.ca Centre ESCER, University of Quebec at Montreal (UQAM), Montreal,
the 2 past three decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes
 High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods and obtained
 Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods 1999 2013 and 1979 1998 obtained from ERA-interim. Vectors are horizontal wind at 850
Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods 1999 2013 and 1979 1998 obtained from ERA-interim. Vectors are horizontal wind at 850
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS FOR:
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS FOR: Simulated reduction in Atlantic hurricane frequency under 21 st century warming conditions Thomas R. Knutson, Joseph J. Sirutis, Stephen T. Garner, Gabriel A. Vecchi, and Isaac
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS FOR: Simulated reduction in Atlantic hurricane frequency under 21 st century warming conditions Thomas R. Knutson, Joseph J. Sirutis, Stephen T. Garner, Gabriel A. Vecchi, and Isaac
Projected future increase of tropical cyclones near Hawaii. Hiroyuki Murakami, Bin Wang, Tim Li, and Akio Kitoh University of Hawaii at Manoa, IPRC
 Projected future increase of tropical cyclones near Hawaii Hiroyuki Murakami, Bin Wang, Tim Li, and Akio Kitoh University of Hawaii at Manoa, IPRC Review of effect of global warming on TC activity Knutson
Projected future increase of tropical cyclones near Hawaii Hiroyuki Murakami, Bin Wang, Tim Li, and Akio Kitoh University of Hawaii at Manoa, IPRC Review of effect of global warming on TC activity Knutson
Recent Walker circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.18/NCLIMATE2 Recent Walker circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming Shayne McGregor, Axel Timmermann, Malte F. Stuecker, Matthew H. England,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.18/NCLIMATE2 Recent Walker circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming Shayne McGregor, Axel Timmermann, Malte F. Stuecker, Matthew H. England,
Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1530 Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. Annual tropical Atlantic SST anomalies (top
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1530 Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. Annual tropical Atlantic SST anomalies (top
Development of Super High Resolution Global and Regional Climate Models
 Development of Super High Resolution Global and Regional Climate Models Project Representative Akira Noda Meteorological Research Institute Authors Akira Noda 1, Shoji Kusunoki 1 and Masanori Yoshizaki
Development of Super High Resolution Global and Regional Climate Models Project Representative Akira Noda Meteorological Research Institute Authors Akira Noda 1, Shoji Kusunoki 1 and Masanori Yoshizaki
Supplement of Insignificant effect of climate change on winter haze pollution in Beijing
 Supplement of Atmos. Chem. Phys., 18, 17489 17496, 2018 https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-17489-2018-supplement Author(s) 2018. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
Supplement of Atmos. Chem. Phys., 18, 17489 17496, 2018 https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-17489-2018-supplement Author(s) 2018. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2988 Hemispheric climate shifts driven by anthropogenic aerosol-cloud interactions Eui-Seok Chung and Brian
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2988 Hemispheric climate shifts driven by anthropogenic aerosol-cloud interactions Eui-Seok Chung and Brian
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Effect of remote sea surface temperature change on tropical cyclone potential intensity Gabriel A. Vecchi Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory NOAA Brian J. Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric
Effect of remote sea surface temperature change on tropical cyclone potential intensity Gabriel A. Vecchi Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory NOAA Brian J. Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Cat Response
 2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
More extreme precipitation in the world s dry and wet regions
 More extreme precipitation in the world s dry and wet regions Markus G. Donat, Andrew L. Lowry, Lisa V. Alexander, Paul A. O Gorman, Nicola Maher Supplementary Table S1: CMIP5 simulations used in this
More extreme precipitation in the world s dry and wet regions Markus G. Donat, Andrew L. Lowry, Lisa V. Alexander, Paul A. O Gorman, Nicola Maher Supplementary Table S1: CMIP5 simulations used in this
Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation S. Pfahl 1 *,P.A.O Gorman 2 and E. M. Fischer 1 Changes in extreme
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation S. Pfahl 1 *,P.A.O Gorman 2 and E. M. Fischer 1 Changes in extreme
Future changes in tropical cyclone activity projected by multi-physics and multi-sst ensemble experiments using the 60-kmmesh
 Future changes in tropical cyclone activity projected by multi-physics and multi-sst ensemble experiments using the 60-kmmesh MRI-AGCM Hiroyuki Murakami, Ryo Mizuta & Eiki Shindo Climate Dynamics Observational,
Future changes in tropical cyclone activity projected by multi-physics and multi-sst ensemble experiments using the 60-kmmesh MRI-AGCM Hiroyuki Murakami, Ryo Mizuta & Eiki Shindo Climate Dynamics Observational,
Reconciling the Observed and Modeled Southern Hemisphere Circulation Response to Volcanic Eruptions Supplemental Material
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1002/, 1 2 3 Reconciling the Observed and Modeled Southern Hemisphere Circulation Response to Volcanic Eruptions Supplemental Material Marie C. McGraw
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1002/, 1 2 3 Reconciling the Observed and Modeled Southern Hemisphere Circulation Response to Volcanic Eruptions Supplemental Material Marie C. McGraw
Characteristics of Storm Tracks in JMA s Seasonal Forecast Model
 Characteristics of Storm Tracks in JMA s Seasonal Forecast Model Akihiko Shimpo 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological Agency, Japan Correspondence: ashimpo@naps.kishou.go.jp INTRODUCTION
Characteristics of Storm Tracks in JMA s Seasonal Forecast Model Akihiko Shimpo 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological Agency, Japan Correspondence: ashimpo@naps.kishou.go.jp INTRODUCTION
4.3.2 Configuration. 4.3 Ensemble Prediction System Introduction
 4.3 Ensemble Prediction System 4.3.1 Introduction JMA launched its operational ensemble prediction systems (EPSs) for one-month forecasting, one-week forecasting, and seasonal forecasting in March of 1996,
4.3 Ensemble Prediction System 4.3.1 Introduction JMA launched its operational ensemble prediction systems (EPSs) for one-month forecasting, one-week forecasting, and seasonal forecasting in March of 1996,
The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models
 1 2 3 The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Seon Tae Kim and Jin-Yi Yu * Department of Earth System
1 2 3 The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Seon Tae Kim and Jin-Yi Yu * Department of Earth System
Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change: Historical Trends and Future Projections
 Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change: Historical Trends and Future Projections Thomas R. Knutson Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory / NOAA, Princeton, NJ U.S.A. IOGP/JCOMM/WCRP Workshop September 25-27,
Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change: Historical Trends and Future Projections Thomas R. Knutson Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory / NOAA, Princeton, NJ U.S.A. IOGP/JCOMM/WCRP Workshop September 25-27,
Geophysical Research Letters. Supporting Information for
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 3 Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Identifying sensitive ranges in global warming precipitation change
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 3 Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Identifying sensitive ranges in global warming precipitation change
Development of a Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean-Land General Circulation Model (GCM) at the Frontier Research Center for Global Change
 Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Development of a Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean-Land General Circulation Model (GCM) at the Frontier Research Center for Global Change Project Representative Tatsushi
Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Development of a Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean-Land General Circulation Model (GCM) at the Frontier Research Center for Global Change Project Representative Tatsushi
1. Introduction. 2. Verification of the 2010 forecasts. Research Brief 2011/ February 2011
 Research Brief 2011/01 Verification of Forecasts of Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific and Number of Tropical Cyclones Making Landfall in South China and the Korea and Japan region
Research Brief 2011/01 Verification of Forecasts of Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific and Number of Tropical Cyclones Making Landfall in South China and the Korea and Japan region
AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast
 AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season : August 12, 2018 by Dale C. S. Destin (follow @anumetservice) Director (Ag), Antigua and Barbuda Meteorological Service (ABMS) The *AnuMS (Antigua Met Service) is
AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season : August 12, 2018 by Dale C. S. Destin (follow @anumetservice) Director (Ag), Antigua and Barbuda Meteorological Service (ABMS) The *AnuMS (Antigua Met Service) is
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11784 Methods The ECHO-G model and simulations The ECHO-G model 29 consists of the 19-level ECHAM4 atmospheric model and 20-level HOPE-G ocean circulation model.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11784 Methods The ECHO-G model and simulations The ECHO-G model 29 consists of the 19-level ECHAM4 atmospheric model and 20-level HOPE-G ocean circulation model.
Supporting Information for Relation of the double-itcz bias to the atmospheric energy budget in climate models
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for Relation of the double-itcz bias to the atmospheric energy budget in climate models Ori Adam 1, Tapio Schneider 1,2, Florent Brient 1, and Tobias
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for Relation of the double-itcz bias to the atmospheric energy budget in climate models Ori Adam 1, Tapio Schneider 1,2, Florent Brient 1, and Tobias
EFFECTS OF TROPICAL CYCLONES ON OCEAN HEAT TRANSPORT AS SIMULATED BY A HIGH RESOLUTION COUPLED GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL
 ISTITUTO NAZIONALE di GEOFISICA e VULCANOLOGIA EFFECTS OF TROPICAL CYCLONES ON OCEAN HEAT TRANSPORT AS SIMULATED BY A HIGH RESOLUTION COUPLED GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL E. Scoccimarro 1 S. Gualdi 12, A.
ISTITUTO NAZIONALE di GEOFISICA e VULCANOLOGIA EFFECTS OF TROPICAL CYCLONES ON OCEAN HEAT TRANSPORT AS SIMULATED BY A HIGH RESOLUTION COUPLED GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL E. Scoccimarro 1 S. Gualdi 12, A.
JMA s Seasonal Prediction of South Asian Climate for Summer 2018
 JMA s Seasonal Prediction of South Asian Climate for Summer 2018 Atsushi Minami Tokyo Climate Center (TCC) Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) Contents Outline of JMA s Seasonal Ensemble Prediction System
JMA s Seasonal Prediction of South Asian Climate for Summer 2018 Atsushi Minami Tokyo Climate Center (TCC) Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) Contents Outline of JMA s Seasonal Ensemble Prediction System
ENSO Outlook by JMA. Hiroyuki Sugimoto. El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency
 ENSO Outlook by JMA Hiroyuki Sugimoto El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Outline 1. ENSO impacts on the climate 2. Current Conditions 3. Prediction by JMA/MRI-CGCM 4. Summary
ENSO Outlook by JMA Hiroyuki Sugimoto El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Outline 1. ENSO impacts on the climate 2. Current Conditions 3. Prediction by JMA/MRI-CGCM 4. Summary
AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast
 AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast Issued: April 10, 2018 by Dale C. S. Destin (follow @anumetservice) Director (Ag), Antigua and Barbuda Meteorological Service (ABMS) The *AnuMS (Antigua Met
AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast Issued: April 10, 2018 by Dale C. S. Destin (follow @anumetservice) Director (Ag), Antigua and Barbuda Meteorological Service (ABMS) The *AnuMS (Antigua Met
Toward Seamless Weather-Climate Prediction with a Global Cloud Resolving Model
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Toward Seamless Weather-Climate Prediction with a Global Cloud Resolving Model PI: Tim Li IPRC/SOEST, University of Hawaii
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Toward Seamless Weather-Climate Prediction with a Global Cloud Resolving Model PI: Tim Li IPRC/SOEST, University of Hawaii
The Implication of Ural Blocking on the East Asian Winter Climate in CMIP5 Models
 The Implication of Ural Blocking on the East Asian Winter Climate in CMIP5 Models Hoffman H. N. Cheung, Wen Zhou (hncheung-c@my.cityu.edu.hk) City University of Hong Kong Shenzhen Institute Guy Carpenter
The Implication of Ural Blocking on the East Asian Winter Climate in CMIP5 Models Hoffman H. N. Cheung, Wen Zhou (hncheung-c@my.cityu.edu.hk) City University of Hong Kong Shenzhen Institute Guy Carpenter
Future Projections of Global Wave Climate by Multi-SST and Multi-Physics Ensemble Experiments. Tomoya Shimura
 Future Projections of Global Wave Climate by Multi-SST and Multi-Physics Ensemble Experiments Graduate School of Engineering, Nobuhito Mori, Tomohiro Yasuda and Hajime Mase Disaster Prevention Research
Future Projections of Global Wave Climate by Multi-SST and Multi-Physics Ensemble Experiments Graduate School of Engineering, Nobuhito Mori, Tomohiro Yasuda and Hajime Mase Disaster Prevention Research
1. Introduction. 3. Climatology of Genesis Potential Index. Figure 1: Genesis potential index climatology annual
 C. ENSO AND GENESIS POTENTIAL INDEX IN REANALYSIS AND AGCMS Suzana J. Camargo, Kerry A. Emanuel, and Adam H. Sobel International Research Institute for Climate and Society, Columbia Earth Institute, Palisades,
C. ENSO AND GENESIS POTENTIAL INDEX IN REANALYSIS AND AGCMS Suzana J. Camargo, Kerry A. Emanuel, and Adam H. Sobel International Research Institute for Climate and Society, Columbia Earth Institute, Palisades,
Moist static energy budget diagnostics for. monsoon research. H. Annamalai
 Moist static energy budget diagnostics for monsoon research H. Annamalai JJAS Precipitation and SST Climatology I III II Multiple regional heat sources - EIO and SPCZ still experience high precipitation
Moist static energy budget diagnostics for monsoon research H. Annamalai JJAS Precipitation and SST Climatology I III II Multiple regional heat sources - EIO and SPCZ still experience high precipitation
The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview
 The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview Jae-Kyung Schemm Gerry Bell Climate Prediction Center NOAA/ NWS/ NCEP 1 Overview outline 1. Current status for the Atlantic, Eastern Pacific and Western Pacific basins
The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview Jae-Kyung Schemm Gerry Bell Climate Prediction Center NOAA/ NWS/ NCEP 1 Overview outline 1. Current status for the Atlantic, Eastern Pacific and Western Pacific basins
Impacts of modes of climate variability, monsoons, ENSO, annular modes
 Impacts of modes of climate variability, monsoons, ENSO, annular modes Iracema Fonseca de Albuquerque Cavalcanti National Institute for Space Research INPE Modes of variability- preferred patterns of variability.
Impacts of modes of climate variability, monsoons, ENSO, annular modes Iracema Fonseca de Albuquerque Cavalcanti National Institute for Space Research INPE Modes of variability- preferred patterns of variability.
The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052006, 2012 The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models Seon Tae Kim 1 and Jin-Yi Yu 1 Received 12 April 2012; revised 14 May 2012; accepted 15 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052006, 2012 The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models Seon Tae Kim 1 and Jin-Yi Yu 1 Received 12 April 2012; revised 14 May 2012; accepted 15 May
Variations of Typhoon Activity in Asia - Global Warming and/or Natural Cycles?
 Variations of Typhoon Activity in Asia - Global Warming and/or Natural Cycles? Johnny Chan Guy Carpenter Asia-Pacific Climate Impact Centre City University of Hong Kong Tropical Cyclones Affecting the
Variations of Typhoon Activity in Asia - Global Warming and/or Natural Cycles? Johnny Chan Guy Carpenter Asia-Pacific Climate Impact Centre City University of Hong Kong Tropical Cyclones Affecting the
Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models
 WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models Jerry Tjiputra 1, K. Lindsay 2, J. Orr 3, J. Segschneider 4, I. Totterdell 5, and C. Heinze 1 1 Bjerknes Centre for Climate
WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models Jerry Tjiputra 1, K. Lindsay 2, J. Orr 3, J. Segschneider 4, I. Totterdell 5, and C. Heinze 1 1 Bjerknes Centre for Climate
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA
 FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast
 AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast Issued: May 10, 2018 by Dale C. S. Destin (follow @anumetservice) Director (Ag), Antigua and Barbuda Meteorological Service (ABMS) The *AnuMS (Antigua Met
AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast Issued: May 10, 2018 by Dale C. S. Destin (follow @anumetservice) Director (Ag), Antigua and Barbuda Meteorological Service (ABMS) The *AnuMS (Antigua Met
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. What Has Changed the Proportion of Intense Hurricanes in the Last 30 Years?
 1432 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE What Has Changed the Proportion of Intense Hurricanes in the Last 30 Years? LIGUANG WU Laboratory for Atmospheres, NASA Goddard Space
1432 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE What Has Changed the Proportion of Intense Hurricanes in the Last 30 Years? LIGUANG WU Laboratory for Atmospheres, NASA Goddard Space
Tropical Cyclones - Ocean feedbacks: Effects on the Ocean Heat Transport as simulated by a High Resolution Coupled General Circulation Model
 ISTITUTO NAZIONALE di GEOFISICA e VULCANOLOGIA Tropical Cyclones - Ocean feedbacks: Effects on the Ocean Heat Transport as simulated by a High Resolution Coupled General Circulation Model E. Scoccimarro
ISTITUTO NAZIONALE di GEOFISICA e VULCANOLOGIA Tropical Cyclones - Ocean feedbacks: Effects on the Ocean Heat Transport as simulated by a High Resolution Coupled General Circulation Model E. Scoccimarro
Interpretation of Outputs from Numerical Prediction System
 Interpretation of Outputs from Numerical Prediction System Hiroshi OHNO Tokyo Climate Center (TCC)/ Climate Prediction Division of Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) Procedure of Seasonal Forecast (1) 1.
Interpretation of Outputs from Numerical Prediction System Hiroshi OHNO Tokyo Climate Center (TCC)/ Climate Prediction Division of Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) Procedure of Seasonal Forecast (1) 1.
Recent Results with the GFDL High- Resolution Coupled Modeling Systems
 Recent Results with the GFDL High- Resolution Coupled Modeling Systems Presented by Gabriel Vecchi GFDL/NOAA Princeton, NJ USA Reference: Delworth, T.L., A. Rosati, W. Anderson, A. Adcroft, V. Balaji,
Recent Results with the GFDL High- Resolution Coupled Modeling Systems Presented by Gabriel Vecchi GFDL/NOAA Princeton, NJ USA Reference: Delworth, T.L., A. Rosati, W. Anderson, A. Adcroft, V. Balaji,
Supplementary Figure 1 Current and future distribution of temperate drylands. (a b-f b-f
 Supplementary Figure 1 Current and future distribution of temperate drylands. (a) Five temperate dryland regions with their current extent for 1980-2010 (green): (b) South America; (c) North America; (d)
Supplementary Figure 1 Current and future distribution of temperate drylands. (a) Five temperate dryland regions with their current extent for 1980-2010 (green): (b) South America; (c) North America; (d)
Possible Effects of Global Warming on Tropical Cyclone Activity
 Possible Effects of Global Warming on Tropical Cyclone Activity Johnny Chan Guy Carpenter Asia-Pacific Climate Impact Centre School of Energy and Environment City University of Hong Kong Outline Background
Possible Effects of Global Warming on Tropical Cyclone Activity Johnny Chan Guy Carpenter Asia-Pacific Climate Impact Centre School of Energy and Environment City University of Hong Kong Outline Background
FLORIDA STATE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES ESTIMATING THE EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON TROPICAL CYCLONE ACTIVITY CHANA SEITZ
 FLORIDA STATE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES ESTIMATING THE EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON TROPICAL CYCLONE ACTIVITY By CHANA SEITZ A Thesis submitted to the Department of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric
FLORIDA STATE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES ESTIMATING THE EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON TROPICAL CYCLONE ACTIVITY By CHANA SEITZ A Thesis submitted to the Department of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric
4. Climatic changes. Past variability Future evolution
 4. Climatic changes Past variability Future evolution TROPICAL CYCLONES and CLIMATE How TCs have varied during recent and distant past? How will TC activity vary in the future? 2 CURRENT CLIMATE : how
4. Climatic changes Past variability Future evolution TROPICAL CYCLONES and CLIMATE How TCs have varied during recent and distant past? How will TC activity vary in the future? 2 CURRENT CLIMATE : how
Can CMIP5 models replicate long-term variability of storm characteristics in the WNP? James Bramante
 Can CMIP5 models replicate long-term variability of storm characteristics in the WNP? James Bramante The Western North Pacific Figure taken from Laing and Evans (2011). Introduction to Tropical Meteorology.
Can CMIP5 models replicate long-term variability of storm characteristics in the WNP? James Bramante The Western North Pacific Figure taken from Laing and Evans (2011). Introduction to Tropical Meteorology.
AMIP-type horizontal resolution experiments with NorESM. Øyvind Seland, Trond Iversen, Ivar Seierstad
 AMWG meeting 10th-12th February 2014 AMIP-type horizontal resolution experiments with NorESM Øyvind Seland, Trond Iversen, Ivar Seierstad Motivation: For given a computer resource, ESMs need to balance
AMWG meeting 10th-12th February 2014 AMIP-type horizontal resolution experiments with NorESM Øyvind Seland, Trond Iversen, Ivar Seierstad Motivation: For given a computer resource, ESMs need to balance
Global Warming Attenuates the. Tropical Atlantic-Pacific Teleconnection
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Supplementary Information for Global Warming Attenuates the Tropical Atlantic-Pacific Teleconnection Fan Jia 1, Lixin Wu 2*, Bolan
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Supplementary Information for Global Warming Attenuates the Tropical Atlantic-Pacific Teleconnection Fan Jia 1, Lixin Wu 2*, Bolan
Drylands face potential threat under 2 C global warming target
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3275 Drylands face potential threat under 2 C global warming target Jianping Huang 1 *, Haipeng Yu 1,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3275 Drylands face potential threat under 2 C global warming target Jianping Huang 1 *, Haipeng Yu 1,
AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast
 AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast : June 11, 2018 by Dale C. S. Destin (follow @anumetservice) Director (Ag), Antigua and Barbuda Meteorological Service (ABMS) The *AnuMS (Antigua Met Service)
AnuMS 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecast : June 11, 2018 by Dale C. S. Destin (follow @anumetservice) Director (Ag), Antigua and Barbuda Meteorological Service (ABMS) The *AnuMS (Antigua Met Service)
Supplementary Figure 1 A figure of changing surface air temperature and top-1m soil moisture: (A) Annual mean surface air temperature, and (B) top
 Supplementary Figure 1 A figure of changing surface air temperature and top-1m soil moisture: (A) Annual mean surface air temperature, and (B) top 1-m soil moisture averaged over California from CESM1.
Supplementary Figure 1 A figure of changing surface air temperature and top-1m soil moisture: (A) Annual mean surface air temperature, and (B) top 1-m soil moisture averaged over California from CESM1.
Significant anthropogenic-induced changes. of climate classes since 1950
 Significant anthropogenic-induced changes of climate classes since 95 (Supplementary Information) Duo Chan and Qigang Wu * School of Atmospheric Science, Nanjing University, Hankou Road #22, Nanjing, Jiangsu,
Significant anthropogenic-induced changes of climate classes since 95 (Supplementary Information) Duo Chan and Qigang Wu * School of Atmospheric Science, Nanjing University, Hankou Road #22, Nanjing, Jiangsu,
Low-level wind, moisture, and precipitation relationships near the South Pacific Convergence Zone in CMIP3/CMIP5 models
 Low-level wind, moisture, and precipitation relationships near the South Pacific Convergence Zone in CMIP3/CMIP5 models Matthew J. Niznik and Benjamin R. Lintner Rutgers University 25 April 2012 niznik@envsci.rutgers.edu
Low-level wind, moisture, and precipitation relationships near the South Pacific Convergence Zone in CMIP3/CMIP5 models Matthew J. Niznik and Benjamin R. Lintner Rutgers University 25 April 2012 niznik@envsci.rutgers.edu
Tom Knutson. Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Lab/NOAA Princeton, New Jersey. Hurricane Katrina, Aug. 2005
 1 Tom Knutson Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Lab/NOAA Princeton, New Jersey http://www.gfdl.noaa.gov/~tk Hurricane Katrina, Aug. 2005 GFDL model simulation of Atlantic hurricane activity Joe Sirutis Isaac
1 Tom Knutson Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Lab/NOAA Princeton, New Jersey http://www.gfdl.noaa.gov/~tk Hurricane Katrina, Aug. 2005 GFDL model simulation of Atlantic hurricane activity Joe Sirutis Isaac
Extratropical transition of North Atlantic tropical cyclones in variable-resolution CAM5
 Extratropical transition of North Atlantic tropical cyclones in variable-resolution CAM5 Diana Thatcher, Christiane Jablonowski University of Michigan Colin Zarzycki National Center for Atmospheric Research
Extratropical transition of North Atlantic tropical cyclones in variable-resolution CAM5 Diana Thatcher, Christiane Jablonowski University of Michigan Colin Zarzycki National Center for Atmospheric Research
CMIP5 multimodel ensemble projection of storm track change under global warming
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd018578, 2012 CMIP5 multimodel ensemble projection of storm track change under global warming Edmund K. M. Chang, 1 Yanjuan Guo, 2 and Xiaoming
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd018578, 2012 CMIP5 multimodel ensemble projection of storm track change under global warming Edmund K. M. Chang, 1 Yanjuan Guo, 2 and Xiaoming
7 December 2016 Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency
 Summary of the 2016 Asian Summer Monsoon 7 December 2016 Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency This report summarizes the characteristics of the surface climate and atmospheric/oceanographic
Summary of the 2016 Asian Summer Monsoon 7 December 2016 Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency This report summarizes the characteristics of the surface climate and atmospheric/oceanographic
Near future ( ) projection of the East Asia summer monsoon by an atmospheric global model with 20-km grid
 Near future (2015-2039) projection of the East Asia summer monsoon by an atmospheric global model with 20-km grid Shoji KUSUNOKI Meteorological Research Institute (MRI) Ryo MIZUTA, Mio MATSUEDA Advanced
Near future (2015-2039) projection of the East Asia summer monsoon by an atmospheric global model with 20-km grid Shoji KUSUNOKI Meteorological Research Institute (MRI) Ryo MIZUTA, Mio MATSUEDA Advanced
Snow occurrence changes over the central and eastern United States under future. warming scenarios
 Snow occurrence changes over the central and eastern United States under future warming scenarios Liang Ning 1,2,3* and Raymond S. Bradley 2 1 Key Laboratory of Virtual Geographic Environment of Ministry
Snow occurrence changes over the central and eastern United States under future warming scenarios Liang Ning 1,2,3* and Raymond S. Bradley 2 1 Key Laboratory of Virtual Geographic Environment of Ministry
Changes in the El Nino s spatial structure under global warming. Sang-Wook Yeh Hanyang University, Korea
 Changes in the El Nino s spatial structure under global warming Sang-Wook Yeh Hanyang University, Korea Changes in El Nino spatial structure Yeh et al. (2009) McPhaden et al. (2009) Why the spatial structure
Changes in the El Nino s spatial structure under global warming Sang-Wook Yeh Hanyang University, Korea Changes in El Nino spatial structure Yeh et al. (2009) McPhaden et al. (2009) Why the spatial structure
ENSO amplitude changes in climate change commitment to atmospheric CO 2 doubling
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L13711, doi:10.1029/2005gl025653, 2006 ENSO amplitude changes in climate change commitment to atmospheric CO 2 doubling Sang-Wook Yeh, 1 Young-Gyu Park, 1 and Ben
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L13711, doi:10.1029/2005gl025653, 2006 ENSO amplitude changes in climate change commitment to atmospheric CO 2 doubling Sang-Wook Yeh, 1 Young-Gyu Park, 1 and Ben
Outline of 4 Lectures
 Outline of 4 Lectures 1. Sept. 17, 2008: TC best track definition and datasets, global distribution of TCs; Review of history of meteorological satellites, introducing different orbits, scanning patterns,
Outline of 4 Lectures 1. Sept. 17, 2008: TC best track definition and datasets, global distribution of TCs; Review of history of meteorological satellites, introducing different orbits, scanning patterns,
S16. ASSESSING THE CONTRIBUTIONS OF EAST AFRICAN AND WEST PACIFIC WARMING TO THE 2014 BOREAL SPRING EAST AFRICAN DROUGHT
 S6. ASSESSING THE CONTRIBUTIONS OF EAST AFRICAN AND WEST PACIFIC WARMING TO THE 204 BOREAL SPRING EAST AFRICAN DROUGHT Chris Funk, Shraddhanand Shukla, Andy Hoell, and Ben Livneh This document is a supplement
S6. ASSESSING THE CONTRIBUTIONS OF EAST AFRICAN AND WEST PACIFIC WARMING TO THE 204 BOREAL SPRING EAST AFRICAN DROUGHT Chris Funk, Shraddhanand Shukla, Andy Hoell, and Ben Livneh This document is a supplement
Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction
 1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
Seasonal Outlook for Summer Season (12/05/ MJJ)
 Seasonal Outlook for Summer Season (12/05/2010 - MJJ) Ι. SEASONAL FORECASTS for MAY JUNE JULY FROM GLOBAL CIRCULATION MODELS... 2 I.1. Oceanic Forecast... 2 I.1.a Sea Surface Temperature (SST)... 2 I.1.b
Seasonal Outlook for Summer Season (12/05/2010 - MJJ) Ι. SEASONAL FORECASTS for MAY JUNE JULY FROM GLOBAL CIRCULATION MODELS... 2 I.1. Oceanic Forecast... 2 I.1.a Sea Surface Temperature (SST)... 2 I.1.b
Theoretical and Modeling Issues Related to ISO/MJO
 Theoretical and Modeling Issues Related to ISO/MJO Tim Li Department of Meteorology and IPRC University of Hawaii DYNAMO workshop, April 13-14, Boulder, Colorado 1. MJO Initiation issue: Role of air- sea
Theoretical and Modeling Issues Related to ISO/MJO Tim Li Department of Meteorology and IPRC University of Hawaii DYNAMO workshop, April 13-14, Boulder, Colorado 1. MJO Initiation issue: Role of air- sea
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Event Response
 PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
How Will Low Clouds Respond to Global Warming?
 How Will Low Clouds Respond to Global Warming? By Axel Lauer & Kevin Hamilton CCSM3 UKMO HadCM3 UKMO HadGEM1 iram 2 ECHAM5/MPI OM 3 MIROC3.2(hires) 25 IPSL CM4 5 INM CM3. 4 FGOALS g1. 7 GISS ER 6 GISS
How Will Low Clouds Respond to Global Warming? By Axel Lauer & Kevin Hamilton CCSM3 UKMO HadCM3 UKMO HadGEM1 iram 2 ECHAM5/MPI OM 3 MIROC3.2(hires) 25 IPSL CM4 5 INM CM3. 4 FGOALS g1. 7 GISS ER 6 GISS
Clara Deser*, James W. Hurrell and Adam S. Phillips. Climate and Global Dynamics Division. National Center for Atmospheric Research
 1 2 Supplemental Material 3 4 5 The Role of the North Atlantic Oscillation in European Climate Projections 6 7 Clara Deser*, James W. Hurrell and Adam S. Phillips 8 9 10 11 Climate and Global Dynamics
1 2 Supplemental Material 3 4 5 The Role of the North Atlantic Oscillation in European Climate Projections 6 7 Clara Deser*, James W. Hurrell and Adam S. Phillips 8 9 10 11 Climate and Global Dynamics
Antarctic sea-ice expansion between 2000 and 2014 driven by tropical Pacific decadal climate variability
 Antarctic sea-ice expansion between 2000 and 2014 driven by tropical Pacific decadal climate variability Gerald A. Meehl 1, Julie M. Arblaster 1,2, Cecilia M. Bitz 3, Christine T.Y. Chung 4, and Haiyan
Antarctic sea-ice expansion between 2000 and 2014 driven by tropical Pacific decadal climate variability Gerald A. Meehl 1, Julie M. Arblaster 1,2, Cecilia M. Bitz 3, Christine T.Y. Chung 4, and Haiyan
The Climate System and Climate Models. Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado
 The Climate System and Climate Models Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado The climate system includes all components of the physical earth system that affect weather
The Climate System and Climate Models Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado The climate system includes all components of the physical earth system that affect weather
Evaluation of CMIP5 Simulated Clouds and TOA Radiation Budgets in the SMLs Using NASA Satellite Observations
 Evaluation of CMIP5 Simulated Clouds and TOA Radiation Budgets in the SMLs Using NASA Satellite Observations Erica K. Dolinar Xiquan Dong and Baike Xi University of North Dakota This talk is based on Dolinar
Evaluation of CMIP5 Simulated Clouds and TOA Radiation Budgets in the SMLs Using NASA Satellite Observations Erica K. Dolinar Xiquan Dong and Baike Xi University of North Dakota This talk is based on Dolinar
Climate Forecast Applications Network (CFAN)
 Forecast of 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Activity April 5, 2018 Summary CFAN s inaugural April seasonal forecast for Atlantic tropical cyclone activity is based on systematic interactions among ENSO, stratospheric
Forecast of 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Activity April 5, 2018 Summary CFAN s inaugural April seasonal forecast for Atlantic tropical cyclone activity is based on systematic interactions among ENSO, stratospheric
Research on Climate of Typhoons Affecting China
 Research on Climate of Typhoons Affecting China Xu Ming Shanghai Typhoon Institute November,25 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Typhoon disasters in China 3. Climatology and climate change of typhoon affecting
Research on Climate of Typhoons Affecting China Xu Ming Shanghai Typhoon Institute November,25 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Typhoon disasters in China 3. Climatology and climate change of typhoon affecting
Projection of Extreme Wave Climate and Modeling
 Projection of Extreme Wave Climate and Modeling Nobuhito Mori and Tomoya Shimura Kyoto University www.oceanwave.jp H.Mase, T. Yasuda, S. Nakajo (Kyoto U) A. Kitoh (MRI) H. Murakami (JAMSTEC) and others
Projection of Extreme Wave Climate and Modeling Nobuhito Mori and Tomoya Shimura Kyoto University www.oceanwave.jp H.Mase, T. Yasuda, S. Nakajo (Kyoto U) A. Kitoh (MRI) H. Murakami (JAMSTEC) and others
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
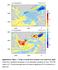 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Evidence for Weakening of Indian Summer Monsoon and SA CORDEX Results from RegCM
 Evidence for Weakening of Indian Summer Monsoon and SA CORDEX Results from RegCM S K Dash Centre for Atmospheric Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Based on a paper entitled Projected Seasonal
Evidence for Weakening of Indian Summer Monsoon and SA CORDEX Results from RegCM S K Dash Centre for Atmospheric Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Based on a paper entitled Projected Seasonal
GPC Exeter forecast for winter Crown copyright Met Office
 GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
UC Irvine Faculty Publications
 UC Irvine Faculty Publications Title A linear relationship between ENSO intensity and tropical instability wave activity in the eastern Pacific Ocean Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5w9602dn
UC Irvine Faculty Publications Title A linear relationship between ENSO intensity and tropical instability wave activity in the eastern Pacific Ocean Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5w9602dn
ENSO, AO, and climate in Japan. 15 November 2016 Yoshinori Oikawa, Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency
 ENSO, AO, and climate in Japan 15 November 2016 Yoshinori Oikawa, Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency Aims of this lecture At the end of the yesterday s lecture, Hare-run said, - In the exercise
ENSO, AO, and climate in Japan 15 November 2016 Yoshinori Oikawa, Tokyo Climate Center, Japan Meteorological Agency Aims of this lecture At the end of the yesterday s lecture, Hare-run said, - In the exercise
4C.4 TRENDS IN LARGE-SCALE CIRCULATIONS AND THERMODYNAMIC STRUCTURES IN THE TROPICS DERIVED FROM ATMOSPHERIC REANALYSES AND CLIMATE CHANGE EXPERIMENTS
 4C.4 TRENDS IN LARGE-SCALE CIRCULATIONS AND THERMODYNAMIC STRUCTURES IN THE TROPICS DERIVED FROM ATMOSPHERIC REANALYSES AND CLIMATE CHANGE EXPERIMENTS Junichi Tsutsui Central Research Institute of Electric
4C.4 TRENDS IN LARGE-SCALE CIRCULATIONS AND THERMODYNAMIC STRUCTURES IN THE TROPICS DERIVED FROM ATMOSPHERIC REANALYSES AND CLIMATE CHANGE EXPERIMENTS Junichi Tsutsui Central Research Institute of Electric
Abstract: INTRODUCTION MODEL AND EXPERIMENT
 Hydrological Research Letters 3, 49 53 (2009) Published online in J-STAGE (www.jstage.jst.go.jp/browse/hrl). DOI: 10.3178/HRL.3.49 Projection of changes in future weather extremes using super-high-resolution
Hydrological Research Letters 3, 49 53 (2009) Published online in J-STAGE (www.jstage.jst.go.jp/browse/hrl). DOI: 10.3178/HRL.3.49 Projection of changes in future weather extremes using super-high-resolution
