Moving from Global to Regional Projections of Climate Change
|
|
|
- Lucinda Poppy Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Moving from Global to Regional Projections of Climate Change Mat Collins College of Engineering, Mathematics and Physical Sciences, University of Exeter, UK Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Joint Met Office Chair in Climate Change
2 Long Term Climate Change: Projections, Commitments and Irreversibility Mat Collins, Reto Knutti, Julie Arblaster, Jean-Louis Dufresne, Thierry Fichefet, Pierre Friedlingstein, Xuejie Gao, Bill Gutowski, Tim Johns, Gerhard Krinner, Mxolisi Shongwe, Claudia Tebaldi, Andrew Weaver, Michael Wehner Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude
3 Global Mean Surface Air Temperature Change Anomalies w.r.t average
4 Global Temperature Assessment The transient climate response is likely in the range of 1.0 C to 2.5 C (high confidence) and extremely unlikely greater than 3 C The CMIP5 models coincide with this range The RCPs are dominated by greenhouse gas forcing by the end of the century Associate the 5-95% range of model simulations (+/ standard deviations) with the likely range (66-100%) Only valid for likely (66-100%) Only valid for global mean temperature in long-term
5 Global Mean Surface Air Temperature Change likely = % probability 5-95% ~ likely Assessing uncertainty and robustness in projections is much more that just counting CMIP models
6 Changes Conditional on Global Mean Temperature Rise High northern latitudes expected to warm most Land warms more than ocean surface More hot and fewer cold extremes Global mean precipitation increases but regional patterns of change not uniform Contrast between wet and dry regions and seasons to increase (with regional exceptions) Tropical atmospheric circulations expected to weaken, subtropics creep polewards Arctic summer sea-ice to melt back ice free conditions likely by mid century under RCP8.5 Permafrost and snow cover to retreat Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) to weaken but not collapse N. Hemisphere storm track changes low confidence
7 Cryosphere Solid lines subset of models Shading min/max Dotted all CMIP5 models Requires the use of physical understanding in quantifying changes
8 How large is the projected change compared with internal variability? RCP8.5 Stippling: changes are large compared with internal variability variability, (greater than and two >90% of standard models deviations agree of sign internal of change variability), and at least 90% of models agree on sign of change Hatching: changes are small compared with internal variability (less than one standard deviation of internal variability
9 Surface Air Temperature Change: CMIP5 Mean
10 Surface Air Temperature Change: CMIP5 Std. Dev
11 For Regional Surface Air Temperature Changes: Mean pattern of change and its uncertainty is largely driven by thermodynamic processes; global mean, land-sea contrast, polar amplification We could build a quantitative theory of thermodynamic changes T(x,y,t) = T g (t)[p(x,y)l(o,l)] + R(x,y,t) Dynamical component Dynamical SAT changes seem much smaller although of crucial importance in the tropics (e.g. Xie et al., 2010)
12 Changes Tropical Precip + Atmospheric Circulation ω=p/q P=ωq P ωq
13 Tropical Precipitation Changes: Chadwick et al., 2013 circulation changes moisture availability circulation weakening RH changes
14 For Regional Precipitation Changes: Global mean changes are sub-clausius-clapeyron, constrained by tropospheric energy balance and lead to a weaker tropical circulation Regionally the reduced circulation is largely balanced by moisture availability leaving other factors as important drivers of regional change; SST changes, land-sea contrast, land-surface feedbacks, Dynamics clearly important here long time-scale coupling? In mid-latitudes, precipitation increase is largely due to increased moisture availability with relatively unchanged storminess. Confidence in storminess projections is low
15 Chapter 14: Climate Phenomena and their Relevance for Future Regional Climate Change El Niño-Southern Oscillation very likely remains as the dominant mode of interannual variability in the future and due to increased moisture availability, the associated precipitation variability on regional scales likely intensifies.. natural modulations of the variance and spatial pattern of El Niño-Southern Oscillation are so large in models that confidence in any specific projected change in its variability in the 21st century remains low.
16 Extreme El Niños Cai, Borlce, Lengaigne, van Rensch, Collins, Vecchi, Timmermann, Santoso, McPhaden, Wu, England, Guilyardi, Jin. Increasing frequency of extreme El Niño events due to greenhouse warming. Nature Climate Change, 2014
17 Changing El Niño Teleconnections Chung, Power, Arblaster, Rashid, Roff, Climate Dynamics, 2014 CMIP5 Atmosphere model simulations Power, Delange, Chung, Kociuba, Keay, Nature 2013
18 Global Warming Pause or Hiatus Chapter 9, Box 9.2
19 Warming hiatus periods in CMIP5 control experiments Hiatus periods in picontrol experiments identified by generation of pseudo ensembles Realization of internal variability from picontrol + Estimate of forced response from scenario ensemble mean = Pseudo ensemble member Pseudo ensemble hiatus selection criteria: Period since 2001 with trend in global surface temperature 0.00 C/yr Equivalent picontrol hiatus selection criteria: 10 year period with trend in global surface temperature C/yr Methods 1/2 Chris Roberts, Matt Palmer, MO
20 CMIP5 historical + RCP4.5 pseudo ensembles Results 2/12 Chris Roberts, Matt Palmer, MO
21 Spatial trends in surface temperature during hiatus decades Results 5/12 Model hiatus decades shifted by C/yr for comparison with observations
22 Trade Winds Strengthening England, McGregor, Spence, Meehl, Timmermann, Cai, Sen Gupta, McPhaden, Purich, Santoso, Nature Climate Change, See also Kosaka and Xie, 2013
23 Summary Large-scale thermodynamic response of temperature relatively well understood in terms of global + land/sea + polar amplification. Could build a quantitative theory Global precipitation change understood in terms of energy balance and offset between weakening circulation and increase humidity Regional precipitation in the tropics more determined by circulation changes and coupled(?) to dynamical SST changes in tropics (RH contribution over tropical land) Robust mid-latitude thermodynamic precipitation response but low confidence in dynamical features Challenge is to combine information from imperfect models with our (sometimes quite good) understanding of physical processes
24 Further Information Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude
Transformational Climate Science. The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report
 Transformational Climate Science The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report www.exeter.ac.uk/climate2014 Working Group I The challenge of climate change #climate2014
Transformational Climate Science The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report www.exeter.ac.uk/climate2014 Working Group I The challenge of climate change #climate2014
Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods and obtained
 Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods 1999 2013 and 1979 1998 obtained from ERA-interim. Vectors are horizontal wind at 850
Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods 1999 2013 and 1979 1998 obtained from ERA-interim. Vectors are horizontal wind at 850
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis
 Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
Projections of future climate change
 Projections of future climate change Matthew Collins 1,2 and Catherine A. Senior 2 1 Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading 2 Met Office Hadley Centre,
Projections of future climate change Matthew Collins 1,2 and Catherine A. Senior 2 1 Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading 2 Met Office Hadley Centre,
CORDEX in the IPCC WGI perspective
 CORDEX in the IPCC WGI perspective Are regional patterns of chance robust? Jens H. Christensen, Fredrik Boberg, Philippe Lucas-Picher* and Ole B. Christensen Kanikicharla Krishna Kumar** Danish Meteorological
CORDEX in the IPCC WGI perspective Are regional patterns of chance robust? Jens H. Christensen, Fredrik Boberg, Philippe Lucas-Picher* and Ole B. Christensen Kanikicharla Krishna Kumar** Danish Meteorological
IPCC Chapter 12: Long- term climate change: projections, commitments and irreversibility
 GEF4400 The Earth System Autumn 2015 23.11.2015 IPCC Chapter 12: Long- term climate change: projections, commitments and irreversibility Introduction and Background (from Chapter 10 and 11) Climate Model
GEF4400 The Earth System Autumn 2015 23.11.2015 IPCC Chapter 12: Long- term climate change: projections, commitments and irreversibility Introduction and Background (from Chapter 10 and 11) Climate Model
Climate modeling: 1) Why? 2) How? 3) What?
 Climate modeling: 1) Why? 2) How? 3) What? Matthew Widlansky mwidlans@hawaii.edu 1) Why model the climate? Hawaii Fiji Sachs and Myhrvold: A Shifting Band of Rain 1 Evidence of Past Climate Change? Mean
Climate modeling: 1) Why? 2) How? 3) What? Matthew Widlansky mwidlans@hawaii.edu 1) Why model the climate? Hawaii Fiji Sachs and Myhrvold: A Shifting Band of Rain 1 Evidence of Past Climate Change? Mean
Doing science with multi-model ensembles
 Doing science with multi-model ensembles Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Biological and Energy Research Regional and Global Climate Modeling Program Why use a multi-model ensemble
Doing science with multi-model ensembles Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Biological and Energy Research Regional and Global Climate Modeling Program Why use a multi-model ensemble
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake
 Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Impacts of modes of climate variability, monsoons, ENSO, annular modes
 Impacts of modes of climate variability, monsoons, ENSO, annular modes Iracema Fonseca de Albuquerque Cavalcanti National Institute for Space Research INPE Modes of variability- preferred patterns of variability.
Impacts of modes of climate variability, monsoons, ENSO, annular modes Iracema Fonseca de Albuquerque Cavalcanti National Institute for Space Research INPE Modes of variability- preferred patterns of variability.
Challenges for Climate Science in the Arctic. Ralf Döscher Rossby Centre, SMHI, Sweden
 Challenges for Climate Science in the Arctic Ralf Döscher Rossby Centre, SMHI, Sweden The Arctic is changing 1) Why is Arctic sea ice disappearing so rapidly? 2) What are the local and remote consequences?
Challenges for Climate Science in the Arctic Ralf Döscher Rossby Centre, SMHI, Sweden The Arctic is changing 1) Why is Arctic sea ice disappearing so rapidly? 2) What are the local and remote consequences?
Was the Amazon Drought of 2005 Human-Caused? Peter Cox Met Office Chair in Climate System Dynamics. Outline
 Was the Amazon Drought of 2005 Human-Caused? Peter Cox Met Office Chair in Climate System Dynamics With thanks to : Phil Harris, Chris Huntingford, Chris Jones, Richard Betts, Matthew Collins, Jose Marengo,
Was the Amazon Drought of 2005 Human-Caused? Peter Cox Met Office Chair in Climate System Dynamics With thanks to : Phil Harris, Chris Huntingford, Chris Jones, Richard Betts, Matthew Collins, Jose Marengo,
Chapter outline. Reference 12/13/2016
 Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
 IPCC WG1 FAQ What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change The IPCC is a scientific intergovernmental body set up by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and by the United Nations
IPCC WG1 FAQ What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change The IPCC is a scientific intergovernmental body set up by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and by the United Nations
The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles. Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild
 The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild WCRP OSP, Denver, 27th October 2011 1 Motivation How will precipitation
The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild WCRP OSP, Denver, 27th October 2011 1 Motivation How will precipitation
Impact of global warming on ENSO clearer now than ever before
 Impact of global warming on ENSO clearer now than ever before Scott Power, François Delage, Christine Chung ENSO in a warmer climate Guayaquil, Ecuador October 2018 Outline Projected changes in El Niño-driven
Impact of global warming on ENSO clearer now than ever before Scott Power, François Delage, Christine Chung ENSO in a warmer climate Guayaquil, Ecuador October 2018 Outline Projected changes in El Niño-driven
How might extratropical storms change in the future? Len Shaffrey National Centre for Atmospheric Science University of Reading
 How might extratropical storms change in the future? Len Shaffrey National Centre for Atmospheric Science University of Reading Extratropical storms Extratropical storms Strong winds, extreme waves, storm
How might extratropical storms change in the future? Len Shaffrey National Centre for Atmospheric Science University of Reading Extratropical storms Extratropical storms Strong winds, extreme waves, storm
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes
 High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
Global warming and Extremes of Weather. Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Global warming and Extremes of Weather Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate change Can we
Global warming and Extremes of Weather Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate change Can we
El Niño / Southern Oscillation
 El Niño / Southern Oscillation Student Packet 2 Use contents of this packet as you feel appropriate. You are free to copy and use any of the material in this lesson plan. Packet Contents Introduction on
El Niño / Southern Oscillation Student Packet 2 Use contents of this packet as you feel appropriate. You are free to copy and use any of the material in this lesson plan. Packet Contents Introduction on
How can we explain possible human contribution to weather events?
 WMO-IPCC Tokyo workshop for weather presenters, November 11, 2015 How can we explain possible human contribution to weather events? Masahiro Watanabe Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute University
WMO-IPCC Tokyo workshop for weather presenters, November 11, 2015 How can we explain possible human contribution to weather events? Masahiro Watanabe Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute University
Possible Roles of Atlantic Circulations on the Weakening Indian Monsoon Rainfall ENSO Relationship
 2376 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE Possible Roles of Atlantic Circulations on the Weakening Indian Monsoon Rainfall ENSO Relationship C.-P. CHANG, PATRICK HARR, AND JIANHUA JU Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate
2376 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE Possible Roles of Atlantic Circulations on the Weakening Indian Monsoon Rainfall ENSO Relationship C.-P. CHANG, PATRICK HARR, AND JIANHUA JU Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate
Seasonal to decadal climate prediction: filling the gap between weather forecasts and climate projections
 Seasonal to decadal climate prediction: filling the gap between weather forecasts and climate projections Doug Smith Walter Orr Roberts memorial lecture, 9 th June 2015 Contents Motivation Practical issues
Seasonal to decadal climate prediction: filling the gap between weather forecasts and climate projections Doug Smith Walter Orr Roberts memorial lecture, 9 th June 2015 Contents Motivation Practical issues
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
Climate Change Scenarios in Southern California. Robert J. Allen University of California, Riverside Department of Earth Sciences
 Climate Change Scenarios in Southern California Robert J. Allen University of California, Riverside Department of Earth Sciences Overview Climatology of Southern California Temperature and precipitation
Climate Change Scenarios in Southern California Robert J. Allen University of California, Riverside Department of Earth Sciences Overview Climatology of Southern California Temperature and precipitation
TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS
 Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Chapter 12: Long-term Climate Change: Projections, Commitments and Irreversibility
 0 0 0 0 0 Chapter : Long-term Climate Change: Projections, Commitments and Irreversibility Coordinating Lead Authors: Matthew Collins (UK), Reto Knutti (Switzerland) Lead Authors: Julie Arblaster (Australia),
0 0 0 0 0 Chapter : Long-term Climate Change: Projections, Commitments and Irreversibility Coordinating Lead Authors: Matthew Collins (UK), Reto Knutti (Switzerland) Lead Authors: Julie Arblaster (Australia),
Ben Harvey, Len Shaffrey, Tim Woollings. SRM Annual meeting, 2 nd November 2011
 Ben Harvey, Len Shaffrey, Tim Woollings SRM Annual meeting, 2 nd November 2011 Position within TEMPEST WP4 Integration and pull-through Lead Shaffrey WP1 Assessing Storms Lead Hodges Giuseppe Zappa WP2
Ben Harvey, Len Shaffrey, Tim Woollings SRM Annual meeting, 2 nd November 2011 Position within TEMPEST WP4 Integration and pull-through Lead Shaffrey WP1 Assessing Storms Lead Hodges Giuseppe Zappa WP2
What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate
 What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA POS/PSMI Joint Breakout Session 2017 US CLIVAR Summit Baltimore, August 9,
What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA POS/PSMI Joint Breakout Session 2017 US CLIVAR Summit Baltimore, August 9,
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall?
 Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
3. Climate Change. 3.1 Observations 3.2 Theory of Climate Change 3.3 Climate Change Prediction 3.4 The IPCC Process
 3. Climate Change 3.1 Observations 3.2 Theory of Climate Change 3.3 Climate Change Prediction 3.4 The IPCC Process 3.1 Observations Need to consider: Instrumental climate record of the last century or
3. Climate Change 3.1 Observations 3.2 Theory of Climate Change 3.3 Climate Change Prediction 3.4 The IPCC Process 3.1 Observations Need to consider: Instrumental climate record of the last century or
CMIP3/CMIP5 differences: Scenario (SRESA1B vs RCP4.5) Ensemble mean Tas responses: CMIP3 = 2.8 K CMIP5 = 1.9 K CMIP5 higher average resolution
 CMIP3/CMIP5 differences: Scenario (SRESA1B vs RCP4.5) Ensemble mean Tas responses: CMIP3 = 2.8 K CMIP5 = 1.9 K CMIP5 higher average resolution Several `high-top models in CMIP5 Key question What are
CMIP3/CMIP5 differences: Scenario (SRESA1B vs RCP4.5) Ensemble mean Tas responses: CMIP3 = 2.8 K CMIP5 = 1.9 K CMIP5 higher average resolution Several `high-top models in CMIP5 Key question What are
Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview
 Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Auckland, New Zealand INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON REDUCING VULNERABILITY
Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Auckland, New Zealand INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON REDUCING VULNERABILITY
Lecture 28: Observed Climate Variability and Change
 Lecture 28: Observed Climate Variability and Change 1. Introduction This chapter focuses on 6 questions - Has the climate warmed? Has the climate become wetter? Are the atmosphere/ocean circulations changing?
Lecture 28: Observed Climate Variability and Change 1. Introduction This chapter focuses on 6 questions - Has the climate warmed? Has the climate become wetter? Are the atmosphere/ocean circulations changing?
the 2 past three decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
1.Decadal prediction ( ) 2. Longer term (to 2100 and beyond)
 Coordinated climate change experiments (formulated by WGCM and AIMES) to be run for assessment in IPCC AR5 Two classes of models to address two time frames and two sets of science questions: 1.Decadal
Coordinated climate change experiments (formulated by WGCM and AIMES) to be run for assessment in IPCC AR5 Two classes of models to address two time frames and two sets of science questions: 1.Decadal
Potential Impact of climate change and variability on the Intra-Americas Sea (IAS)
 Potential Impact of climate change and variability on the Intra-Americas Sea (IAS) Sang-Ki Lee 1, Yanyun Liu 1 and Barbara Muhling 2 1 CIMAS-University of Miami and AOML-NOAA 2 Princeton University and
Potential Impact of climate change and variability on the Intra-Americas Sea (IAS) Sang-Ki Lee 1, Yanyun Liu 1 and Barbara Muhling 2 1 CIMAS-University of Miami and AOML-NOAA 2 Princeton University and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Cat Response
 2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
An ENSO-Neutral Winter
 An ENSO-Neutral Winter This issue of the Blue Water Outlook newsletter is devoted towards my thoughts on the long range outlook for winter. You will see that I take a comprehensive approach to this outlook
An ENSO-Neutral Winter This issue of the Blue Water Outlook newsletter is devoted towards my thoughts on the long range outlook for winter. You will see that I take a comprehensive approach to this outlook
Update on Climate Science. Professor Richard Betts, Met Office
 Update on Climate Science Professor Richard Betts, Met Office The science of climate change Crown copyright Met Office Prof Richard Betts Head of Climate Impacts Research Crown copyright Met Office Observing
Update on Climate Science Professor Richard Betts, Met Office The science of climate change Crown copyright Met Office Prof Richard Betts Head of Climate Impacts Research Crown copyright Met Office Observing
Relative importance of the tropics, internal variability, and Arctic amplification on midlatitude climate and weather
 Relative importance of the tropics, internal variability, and Arctic amplification on midlatitude climate and weather Arun Kumar Climate Prediction Center College Park, Maryland, USA Workshop on Arctic
Relative importance of the tropics, internal variability, and Arctic amplification on midlatitude climate and weather Arun Kumar Climate Prediction Center College Park, Maryland, USA Workshop on Arctic
Importance of clouds and aerosols in assessing climate change
 Importance of clouds and aerosols in assessing climate change Olivier Boucher, Dave Randall Chapter 7 lead authors Chapter 8 coordinating lead authors Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Climate-relevant aerosol
Importance of clouds and aerosols in assessing climate change Olivier Boucher, Dave Randall Chapter 7 lead authors Chapter 8 coordinating lead authors Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Climate-relevant aerosol
Haiyan Teng. Curriculum Vita
 Haiyan Teng Curriculum Vita Climate Change Research Section (CCR) Climate and Global Dynamics Division (CGD) National Center for Atmospheric Research 1850 Table Mesa Dr, Boulder, CO 80305 Tel: (303)497-1728
Haiyan Teng Curriculum Vita Climate Change Research Section (CCR) Climate and Global Dynamics Division (CGD) National Center for Atmospheric Research 1850 Table Mesa Dr, Boulder, CO 80305 Tel: (303)497-1728
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Event Response
 PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
Which Climate Model is Best?
 Which Climate Model is Best? Ben Santer Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550 Adapting for an Uncertain Climate: Preparing
Which Climate Model is Best? Ben Santer Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550 Adapting for an Uncertain Climate: Preparing
Climate changes in Finland, but how? Jouni Räisänen Department of Physics, University of Helsinki
 Climate changes in Finland, but how? Jouni Räisänen Department of Physics, University of Helsinki 19.9.2012 Outline Some basic questions and answers about climate change How are projections of climate
Climate changes in Finland, but how? Jouni Räisänen Department of Physics, University of Helsinki 19.9.2012 Outline Some basic questions and answers about climate change How are projections of climate
GPC Exeter forecast for winter Crown copyright Met Office
 GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
Mozambique. General Climate. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016
 Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016 Date: Dec 17, 2015 1. Advisory Most models are showing the continuation of a strong El-Niño episode towards the latesummer season with the expectation to start
Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016 Date: Dec 17, 2015 1. Advisory Most models are showing the continuation of a strong El-Niño episode towards the latesummer season with the expectation to start
Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic
 Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic John E. Walsh Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois 105 S. Gregory Avenue Urbana, IL 61801 phone: (217) 333-7521 fax: (217)
Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic John E. Walsh Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois 105 S. Gregory Avenue Urbana, IL 61801 phone: (217) 333-7521 fax: (217)
An Analysis of the Evolution of Physical Processes Producing Daily Widespread Precipitation Extremes in Alaska using six CMIP5 GCMs
 Meteorology Senior Theses Undergraduate Theses and Capstone Projects 12-2016 An Analysis of the Evolution of Physical Processes Producing Daily Widespread Precipitation Extremes in Alaska using six CMIP5
Meteorology Senior Theses Undergraduate Theses and Capstone Projects 12-2016 An Analysis of the Evolution of Physical Processes Producing Daily Widespread Precipitation Extremes in Alaska using six CMIP5
Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical
 1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
(1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability,
 (1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability, (2) It s Long-term Loss and Implications for Ocean Conditions Marika Holland, NCAR With contributions from: David Bailey, Alex Jahn, Jennifer Kay, Laura Landrum, Steve
(1) Arctic Sea Ice Predictability, (2) It s Long-term Loss and Implications for Ocean Conditions Marika Holland, NCAR With contributions from: David Bailey, Alex Jahn, Jennifer Kay, Laura Landrum, Steve
METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC TELECONNECTIONS: FROM CAUSAL ATTRIBUTION TO STORYLINES OF CIRCULATION CHANGE
 METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC TELECONNECTIONS: FROM CAUSAL ATTRIBUTION TO STORYLINES OF CIRCULATION CHANGE Ted Shepherd Grantham Chair of Climate Science Stratosphere-troposphere coupling: stratospheric polar
METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC TELECONNECTIONS: FROM CAUSAL ATTRIBUTION TO STORYLINES OF CIRCULATION CHANGE Ted Shepherd Grantham Chair of Climate Science Stratosphere-troposphere coupling: stratospheric polar
The scientific basis for climate change projections: History, Status, Unsolved problems
 The scientific basis for climate change projections: History, Status, Unsolved problems Isaac Held, Princeton, Feb 2008 Katrina-like storm spontaneously generated in atmospheric model Regions projected
The scientific basis for climate change projections: History, Status, Unsolved problems Isaac Held, Princeton, Feb 2008 Katrina-like storm spontaneously generated in atmospheric model Regions projected
Ocean heat content and Earth s energy imbalance: insights from climate models
 Ocean heat content and Earth s energy imbalance: insights from climate models Matt Palmer 1, Chris Roberts 1, Doug McNeall 1, Freya Garry 2, Roberto Fernandez-Bilbao 3, Jonathan Gregory 1,3 1 Met Office
Ocean heat content and Earth s energy imbalance: insights from climate models Matt Palmer 1, Chris Roberts 1, Doug McNeall 1, Freya Garry 2, Roberto Fernandez-Bilbao 3, Jonathan Gregory 1,3 1 Met Office
Chair Professor in Physical Oceanography, Ocean University of China
 Academician WU Lixin Chair Professor in Physical Oceanography, Ocean University of China Contact Information Phone: +86-532-82032852 Fax: +86-532-82032471 E-Mail: lxwu@ouc.edu.cn Address: Key Laboratory
Academician WU Lixin Chair Professor in Physical Oceanography, Ocean University of China Contact Information Phone: +86-532-82032852 Fax: +86-532-82032471 E-Mail: lxwu@ouc.edu.cn Address: Key Laboratory
Hurricane Risk: Importance of Climate Time Scale and Uncertainty
 Hurricane Risk: Importance of Climate Time Scale and Uncertainty FCHLPM Workshop Peter S. Dailey, Ph.D. July 23-24, 2009 2009 AIR WORLDWIDE CORPORATION 1 Agenda Importance of Understanding Climate Change,
Hurricane Risk: Importance of Climate Time Scale and Uncertainty FCHLPM Workshop Peter S. Dailey, Ph.D. July 23-24, 2009 2009 AIR WORLDWIDE CORPORATION 1 Agenda Importance of Understanding Climate Change,
The downward influence of uncertainty in the Northern Hemisphere wintertime stratospheric polar vortex response to climate change. Isla Simpson, NCAR
 The downward influence of uncertainty in the Northern Hemisphere wintertime stratospheric polar vortex response to climate change Isla Simpson, NCAR Peter Hitchcock (LMD), Richard Seager (LDEO), Yutian
The downward influence of uncertainty in the Northern Hemisphere wintertime stratospheric polar vortex response to climate change Isla Simpson, NCAR Peter Hitchcock (LMD), Richard Seager (LDEO), Yutian
Name the surface winds that blow between 0 and 30. GEO 101, February 25, 2014 Monsoon Global circulation aloft El Niño Atmospheric water
 GEO 101, February 25, 2014 Monsoon Global circulation aloft El Niño Atmospheric water Name the surface winds that blow between 0 and 30 What is the atmospheric pressure at 0? What is the atmospheric pressure
GEO 101, February 25, 2014 Monsoon Global circulation aloft El Niño Atmospheric water Name the surface winds that blow between 0 and 30 What is the atmospheric pressure at 0? What is the atmospheric pressure
Bavarian Riots, 1819
 Bavarian Riots, 1819 A Future Year Without A Summer J. Fasullo, NCAR B. Otto-Bliesner, E. Brady, S. Stevenson, R. Tomas, and E. Wahl (NOAA) Outline / Science Questions The 1815 Eruption of Mt Tambora What
Bavarian Riots, 1819 A Future Year Without A Summer J. Fasullo, NCAR B. Otto-Bliesner, E. Brady, S. Stevenson, R. Tomas, and E. Wahl (NOAA) Outline / Science Questions The 1815 Eruption of Mt Tambora What
Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean*
 JUNE 2013 W U A N D P A U L U I S 1649 Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean* YUTIAN WU AND OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant
JUNE 2013 W U A N D P A U L U I S 1649 Examination of Isentropic Circulation Response to a Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Using Statistical Transformed Eulerian Mean* YUTIAN WU AND OLIVIER PAULUIS Courant
Climate Forecast Applications Network (CFAN)
 Forecast of 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Activity April 5, 2018 Summary CFAN s inaugural April seasonal forecast for Atlantic tropical cyclone activity is based on systematic interactions among ENSO, stratospheric
Forecast of 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Activity April 5, 2018 Summary CFAN s inaugural April seasonal forecast for Atlantic tropical cyclone activity is based on systematic interactions among ENSO, stratospheric
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10
 Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
6. What has been the most effective erosive agent in the climate system? a. Water b. Ice c. Wind
 Multiple Choice. 1. Heinrich Events a. Show increased abundance of warm-water species of planktic foraminifera b. Show greater intensity since the last deglaciation c. Show increased accumulation of ice-rafted
Multiple Choice. 1. Heinrich Events a. Show increased abundance of warm-water species of planktic foraminifera b. Show greater intensity since the last deglaciation c. Show increased accumulation of ice-rafted
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NCLIMATE216 Recent intensification of wind-driven circulation in the Pacific and the ongoing warming hiatus (a) Observed wind trends 6N N 2N 2S S 6S 6E 12E 18E 12W
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NCLIMATE216 Recent intensification of wind-driven circulation in the Pacific and the ongoing warming hiatus (a) Observed wind trends 6N N 2N 2S S 6S 6E 12E 18E 12W
Significant changes to ENSO strength and impacts in the twenty-first century: Results from CMIP5
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052759, 2012 Significant changes to ENSO strength and impacts in the twenty-first century: Results from CMIP5 S. L. Stevenson 1 Received 14 June
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052759, 2012 Significant changes to ENSO strength and impacts in the twenty-first century: Results from CMIP5 S. L. Stevenson 1 Received 14 June
Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models
 WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models Jerry Tjiputra 1, K. Lindsay 2, J. Orr 3, J. Segschneider 4, I. Totterdell 5, and C. Heinze 1 1 Bjerknes Centre for Climate
WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models Jerry Tjiputra 1, K. Lindsay 2, J. Orr 3, J. Segschneider 4, I. Totterdell 5, and C. Heinze 1 1 Bjerknes Centre for Climate
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do?
 Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1854 Anthropogenic aerosol forcing of Atlantic tropical storms N. J. Dunstone 1, D. S. Smith 1, B. B. B. Booth 1, L. Hermanson 1, R. Eade 1 Supplementary information
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1854 Anthropogenic aerosol forcing of Atlantic tropical storms N. J. Dunstone 1, D. S. Smith 1, B. B. B. Booth 1, L. Hermanson 1, R. Eade 1 Supplementary information
AMOC Impacts on Climate
 AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
Tropical Pacific modula;ons of global climate
 Tropical Pacific modula;ons of global climate Shang- Ping Xie 1 & Yu Kosaka 2 1 Scripps Inst of Oceanogr, UCSD; 2 Univ of Tokyo Develop seasonal and spa
Tropical Pacific modula;ons of global climate Shang- Ping Xie 1 & Yu Kosaka 2 1 Scripps Inst of Oceanogr, UCSD; 2 Univ of Tokyo Develop seasonal and spa
Second-Order Draft Chapter 10 IPCC WG1 Fourth Assessment Report
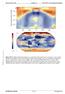 Second-Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report Figure... Multi model mean changes in a) zonal mean cloud fraction (in %), shown as a cross section though the atmosphere, and b) total cloud
Second-Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report Figure... Multi model mean changes in a) zonal mean cloud fraction (in %), shown as a cross section though the atmosphere, and b) total cloud
Dynamics of annual cycle/enso interactions
 Dynamics of annual cycle/enso interactions A. Timmermann (IPRC, UH), S. McGregor (CCRC), M. Stuecker (Met Dep., UH) F.-F. Jin (Met Dep., UH), K. Stein (Oce Dep., UH), N. Schneider (IPRC, UH), ENSO and
Dynamics of annual cycle/enso interactions A. Timmermann (IPRC, UH), S. McGregor (CCRC), M. Stuecker (Met Dep., UH) F.-F. Jin (Met Dep., UH), K. Stein (Oce Dep., UH), N. Schneider (IPRC, UH), ENSO and
ENSO amplitude changes in climate change commitment to atmospheric CO 2 doubling
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L13711, doi:10.1029/2005gl025653, 2006 ENSO amplitude changes in climate change commitment to atmospheric CO 2 doubling Sang-Wook Yeh, 1 Young-Gyu Park, 1 and Ben
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L13711, doi:10.1029/2005gl025653, 2006 ENSO amplitude changes in climate change commitment to atmospheric CO 2 doubling Sang-Wook Yeh, 1 Young-Gyu Park, 1 and Ben
Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science. Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate
Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate
Weather Outlook 2016: Cycles and Patterns Influencing Our Growing Season
 Weather Outlook 2016: Cycles and Patterns Influencing Our Growing Season Leon F. Osborne Chester Fritz Distinguished Professor of Atmospheric Sciences University of North Dakota Cycle of El Niño Events
Weather Outlook 2016: Cycles and Patterns Influencing Our Growing Season Leon F. Osborne Chester Fritz Distinguished Professor of Atmospheric Sciences University of North Dakota Cycle of El Niño Events
8.1.2 Climate Projections
 Chapter 8 Nauru 167 8.1 Climate Summary 8.1.1 Current Climate Over the past half century it is likely that there has been a warming air temperature trend at Nauru which is partly associated with warming
Chapter 8 Nauru 167 8.1 Climate Summary 8.1.1 Current Climate Over the past half century it is likely that there has been a warming air temperature trend at Nauru which is partly associated with warming
Why the hiatus in global mean surface temperature trends in the last decade?
 Why the hiatus in global mean surface temperature trends in the last decade? G. Bala Divecha Center for Climate Change Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore (Email: gbala@caos.iisc.ernet.in) On 27 September
Why the hiatus in global mean surface temperature trends in the last decade? G. Bala Divecha Center for Climate Change Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore (Email: gbala@caos.iisc.ernet.in) On 27 September
MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN
 MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN Abdul Rashid 1 Abstract: El-Nino is the dominant mod of inter- annual climate variability on a planetary scale. Its impact is associated worldwide
MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN Abdul Rashid 1 Abstract: El-Nino is the dominant mod of inter- annual climate variability on a planetary scale. Its impact is associated worldwide
Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate
 Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Does External Forcing Interfere with the AMOC's Influence on North Atlantic Sea Surface Temperature and Arctic Climate?
 Does External Forcing Interfere with the AMOC's Influence on North Atlantic Sea Surface Temperature and Arctic Climate? Neil Tandon and Paul Kushner Department of Physics, U of Toronto Tandon and Kushner,
Does External Forcing Interfere with the AMOC's Influence on North Atlantic Sea Surface Temperature and Arctic Climate? Neil Tandon and Paul Kushner Department of Physics, U of Toronto Tandon and Kushner,
Understanding and projecting sea level change: improvements and uncertainties
 Understanding and projecting sea level change: improvements and uncertainties Jonathan Gregory On behalf of all the lead authors of Chapter 13, Sea level change John Church, Peter Clark, Anny Cazenave,
Understanding and projecting sea level change: improvements and uncertainties Jonathan Gregory On behalf of all the lead authors of Chapter 13, Sea level change John Church, Peter Clark, Anny Cazenave,
4. Climatic changes. Past variability Future evolution
 4. Climatic changes Past variability Future evolution TROPICAL CYCLONES and CLIMATE How TCs have varied during recent and distant past? How will TC activity vary in the future? 2 CURRENT CLIMATE : how
4. Climatic changes Past variability Future evolution TROPICAL CYCLONES and CLIMATE How TCs have varied during recent and distant past? How will TC activity vary in the future? 2 CURRENT CLIMATE : how
The Climate System and Climate Models. Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado
 The Climate System and Climate Models Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado The climate system includes all components of the physical earth system that affect weather
The Climate System and Climate Models Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado The climate system includes all components of the physical earth system that affect weather
Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long
 Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long period of time Many factors influence weather & climate
Weather Atmospheric condition in one place during a limited period of time Climate Weather patterns that an area typically experiences over a long period of time Many factors influence weather & climate
WCRP Grand Challenge Workshop: Clouds, Circulation and Climate Sensitivity
 WCRP Grand Challenge Workshop: Clouds, Circulation and Climate Sensitivity Schloss Ringberg, 3700 Rottach-Egern, Germany March 24-28, 2014 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department
WCRP Grand Challenge Workshop: Clouds, Circulation and Climate Sensitivity Schloss Ringberg, 3700 Rottach-Egern, Germany March 24-28, 2014 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department
How Patterns Far Away Can Influence Our Weather. Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK
 Teleconnections How Patterns Far Away Can Influence Our Weather Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK Teleconnections Connectedness of large-scale weather patterns across the world If you poke
Teleconnections How Patterns Far Away Can Influence Our Weather Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK Teleconnections Connectedness of large-scale weather patterns across the world If you poke
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C
The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview
 The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview Jae-Kyung Schemm Gerry Bell Climate Prediction Center NOAA/ NWS/ NCEP 1 Overview outline 1. Current status for the Atlantic, Eastern Pacific and Western Pacific basins
The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview Jae-Kyung Schemm Gerry Bell Climate Prediction Center NOAA/ NWS/ NCEP 1 Overview outline 1. Current status for the Atlantic, Eastern Pacific and Western Pacific basins
Some figures courtesy of: Chris Landsea National Hurricane Center, Miami. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
 Hurricanes and Global Warming Pat Fitzpatrick Mississippi State University, GeoSystems Research Institute Some figures courtesy of: Chris Landsea National Hurricane Center, Miami Intergovernmental Panel
Hurricanes and Global Warming Pat Fitzpatrick Mississippi State University, GeoSystems Research Institute Some figures courtesy of: Chris Landsea National Hurricane Center, Miami Intergovernmental Panel
Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change: Historical Trends and Future Projections
 Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change: Historical Trends and Future Projections Thomas R. Knutson Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory / NOAA, Princeton, NJ U.S.A. IOGP/JCOMM/WCRP Workshop September 25-27,
Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change: Historical Trends and Future Projections Thomas R. Knutson Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory / NOAA, Princeton, NJ U.S.A. IOGP/JCOMM/WCRP Workshop September 25-27,
GEOL 437 Global Climate Change 5/1/18: Climate sensitivity
 GEOL 437 Global Climate Change 5/1/18: Climate sensitivity How sensitive is the climate to external radiative forcing? FAQ 12.3 Fig 1 in: Collins, M., R. Knutti, J. Arblaster, J.- L. Dufresne, T. Fichefet,
GEOL 437 Global Climate Change 5/1/18: Climate sensitivity How sensitive is the climate to external radiative forcing? FAQ 12.3 Fig 1 in: Collins, M., R. Knutti, J. Arblaster, J.- L. Dufresne, T. Fichefet,
Earth s Climate Patterns
 Earth s Climate Patterns Reading: Chapter 17, GSF 10/2/09 Also Jackson (linked on course web site) 1 What aspects of climate affect plant distributions? Climate: long-term distribution of weather in an
Earth s Climate Patterns Reading: Chapter 17, GSF 10/2/09 Also Jackson (linked on course web site) 1 What aspects of climate affect plant distributions? Climate: long-term distribution of weather in an
Presentation Overview. Southwestern Climate: Past, present and future. Global Energy Balance. What is climate?
 Southwestern Climate: Past, present and future Mike Crimmins Climate Science Extension Specialist Dept. of Soil, Water, & Env. Science & Arizona Cooperative Extension The University of Arizona Presentation
Southwestern Climate: Past, present and future Mike Crimmins Climate Science Extension Specialist Dept. of Soil, Water, & Env. Science & Arizona Cooperative Extension The University of Arizona Presentation
Can Arctic sea ice decline drive a slow-down of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)?
 Can Arctic sea ice decline drive a slow-down of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)? September 2012 NASA Alexey Fedorov Yale University with Florian Sevellec (NOC, Southampton) and Wei
Can Arctic sea ice decline drive a slow-down of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)? September 2012 NASA Alexey Fedorov Yale University with Florian Sevellec (NOC, Southampton) and Wei
