Subject No 8 - PPL Meteorology
|
|
|
- Hugh Thornton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Subject No 8 - PPL Meteorology Notes: This syllabus is principally based on the meteorology as applicable to flying a single piston-engine General Aviation type aeroplane or helicopter, within New Zealand at altitudes at or below 13,000 feet. Detailed acronyms and service provider titles (e.g. SKC, MetService) are indicative of the area of knowledge required and do not limit this syllabus to those specifically listed. Each subject has been given a subject number and each topic within that subject a topic number. These reference numbers will be used on knowledge deficiency reports and will provide valuable feed back to the examination candidate. These reference numbers are common across the subject levels and therefore may not be consecutive. Sub Topic Fundamentals of the atmosphere 8.2 The atmosphere State the composition and structure of the atmosphere Describe the presence and importance of the following in the atmosphere: (a) carbon dioxide (b) ozone (c) water vapour Explain how temperature influences the ability of air to hold water vapour. 8.4 Atmospheric Pressure Describe the source of atmospheric pressure Explain the basic principle of operation of the barometer Define pressure lapse rate State the average pressure lapse rate in the lower atmosphere Explain the effect of temperature on pressure lapse rate Define and describe: (a) isobar; (b) wind velocity; (c) anticyclone ( high ); (d) depression ( low ); (e) ridge of high pressure; (f) (g) col; trough of low pressure; (h) pressure gradient Explain the relationship between pressure gradient, isobars and wind velocity (airflow around pressure systems) State the concept of convergence and divergence and describe how the associated subsidence or ascent of air influences the type of weather commonly associated with pressure systems State the unit of pressure commonly used in meteorology List the assumed conditions on which the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) is based.
2 Explain how deviation from ISA values influences performance of aircraft and their engines Define: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) QNH; QFE; altitude; height; pressure altitude Explain why an altimeter requires a subscale adjustment Explain the importance of correct subscale setting. 8.6 Temperature and Heat Exchange Processes Explain what is meant by solar radiation Describe the elements that influence the amount of incoming solar radiation Explain what is meant by terrestrial radiation Describe the elements that influence the escape of terrestrial radiation Explain the effect of solar and terrestrial radiation on the air temperature Describe the effect of latitude on the distribution of incoming solar radiation Describe the process of: (a) conduction; (b) convection Define albedo Describe the diurnal variation of surface air temperature and explain the effect of different types of surface on this variation. 8.8 Atmospheric Moisture Define: (a) condensation; (b) evaporation; (c) deposition; (d) sublimation; (e) (f) melting; freezing; (g) latent heat Explain the function of condensation nuclei during condensation State the effect of the following on the rate of evaporation: (a) air temperature; (b) moisture content of air; (c) atmospheric pressure; (d) the wind Describe the processes that change the physical state of moisture and explain how latent heat is involved in each transformation.
3 Explain what is meant by relative humidity Explain the effect of changes in temperature and moisture content of air on relative humidity Explain what is meant by dew point Explain the effect of moisture content of air on the value of the dew point Explain the effects on aircraft and engine performance of: (a) air density (b) air moisture content Explain how temperature, relative humidity and dew point values can be used to indicate differences in water content of air Wind State the direction in which the following two forces act: (a) pressure gradient; (b) Coriolis force State the effect of wind speed on the strength of the coriolis force Explain how the inter-relation between pressure gradient and coriolis force determine the circulation around pressure systems Explain what is meant by the friction layer, and describe the elements that influence the depth of the layer Explain how the friction layer affects the surface wind velocity Define the following terms: (a) gust; (b) lull; (c) squall; (d) veering; (e) backing Describe the diurnal variation of the surface wind over the: (a) land; (b) sea Describe the changes in wind velocity when climbing out of, or descending into, the friction layer Describe how an approximate wind velocity can be determined from a 25-knot windsock when at an angle of 30, 45, 75 and 90 from the vertical Describe how an approximate wind direction can be determined from: (a) ripples on water; (b) wind lanes on water; (c) wind shadow on bodies of water State Buys Ballot s Law Explain how applying Buys Ballot s Law can: (a) determine the location of high and low pressure areas; (b) establish possible errors in altimeter reading.
4 Define wind shear Describe the effects of vertical and horizontal wind shear on aircraft operations Stability of Air Explain what is meant by: (a) stable air; (b) unstable air; (c) neutrally stable air State the two factors that determine the stability of air Describe what is meant by environment lapse rate (ELR) Explain the adiabatic process Interpret graphs of steep and shallow environment lapse rates including inversions and isothermal layers State the dry adiabatic lapse rate (DALR) Explain how the relationship between the ELR and DALR can be used to determine the stability or instability of unsaturated air State the saturated adiabatic lapse rate (SALR) Explain how the relationship between the ELR and SALR can be used to determine the stability or instability of saturated air Explain the factors involved in thermal rising of air Explain how different dew point values determine the cloud base Explain the effect of increasing surface temperature on the base of convective cloud, given a constant moisture content Describe the types of cloud that could be expected in: (a) stable saturated air; (b) unstable saturated air Describe weather conditions and degrees of visibility in: (a) stable air; (b) unstable air Describe how stable and unstable air affect flying conditions Local winds New Zealand Describe the sea breeze process, including typical: (a) timing of the occurrence; (b) average strength of the sea breeze; (c) horizontal and vertical limits; (d) associated cloud development; (e) associated turbulence Describe the land breeze process, and state: (a) typical timing of the occurrence; (b) average speed of the wind; (c) most likely season for the occurrence.
5 Describe the katabatic and anabatic wind processes, and state the: (a) typical timing of the occurrence; (b) average strength of the winds; (c) effect of moist valley air on cloud/fog formation; (d) effect of gravity on Katabatic winds; (e) effect of adiabatic cooling and warming Describe the fohn wind process Given environment temperatures, dew points and mountain heights, determine the: (a) cloud base on the windward side; (b) cloud base on the lee side; (c) temperature at stated datum level on the lee side Describe the flight conditions associated with fohn wind conditions Describe the mountain wave (standing, or lee wave) process Explain the wind and weather conditions, and associated main dangers to aircraft operations, in mountain wave conditions Describe the rotor zones process and explain the associated dangers to aircraft operations Describe the effect of local obstructions on wind flow Inversions Define: (a) inversion; (b) isothermal layer Explain the effect of inversions on: (a) the formation and development of cloud; (b) visibility; (c) turbulence; (d) the relative humidity and dew point; (e) the increased risk of carburettor icing; (f) the presence of wind shear Explain the factors involved in a: (a) radiation inversion; (b) turbulence inversion; (c) subsidence inversion; (d) frontal inversion Describe the flight conditions in the presence of inversions Cloud Describe the basic cloud formation process Explain the most common method through which cloud is formed and how air is cooled to produce cloud.
6 Explain what is meant by buoyancy of air Differentiate between cloud droplets and rain/shower drops State the approximate altitude limits (in NZ latitudes) of: (a) high cloud; (b) middle cloud; (c) low cloud Describe the following types of cloud and include a description of likely icing, turbulence and precipitation: (a) cirrostratus; (b) cirrocumulus; (c) cirrus; (d) altostratus; (e) altocumulus; (f) stratocumulus; (g) stratus; (h) cumulus; (i) cumulonimbus/towering cumulus; (j) nimbostratus Describe the terms used for describing the characteristics of cloud Describe the following methods whereby air is lifted, and include the effect of stability/instability on the type of cloud formed: (a) orographic lifting; (b) mechanical lifting; (c) convective lifting; (d) slow widespread ascent; (e) frontal lifting Explain the processes that contribute to cloud dispersal Precipitation Define: (a) precipitation; (b) virga Explain how cloud drops can grow through: (a) the presence of ice crystals (Bergeron process); (b) coalescence Describe the following types of precipitation: (a) rain; (b) drizzle; (c) snow; (d) sleet; (e) hail.
7 Describe the characteristics of the following types of precipitation: (a) continuous; (b) intermittent; (c) showers Describe the rate of precipitation: (a) light; (b) moderate; (c) heavy Visibility Define meteorological visibility Explain what is meant by transparency of air Explain how illumination from the sun or moon have an effect on visibility Differentiate between visibility distance and visibility range Describe the characteristics and the effect on visibility distance, of the following: (a) precipitation; (b) fog or mist; (c) haze; (d) smoke; (e) sea spray; (f) snow; (g) whiteout Explain the factors involved in slant range Fog Define fog Describe the principles of formation, required meteorological conditions, factors affecting extent of, and dispersal of: (a) radiation fog; (b) advection fog; (c) valley fog; (d) sea fog; (e) steaming fog; (f) frontal fog Describe the operational problems associated with fog Fronts and Depressions Define air mass List the different types of air masses Define source region and state the typical areas where New Zealand s source regions are found Describe what is meant by: (a) cold advection;
8 (b) warm advection Explain the typical weather conditions in New Zealand when affected by cold and warm advection Describe how divergence aloft affects the atmospheric pressure near sea level Describe the characteristics of the: (a) mid-latitude depression; (b) orographic depression; (c) thermal (heat type) depression State the symbols, and colour codes, used to describe the following fronts on weather charts: (a) cold front; (b) warm front; (c) occluded front; (d) stationary front Describe the cross section of the typical cold front including cloud, temperature and freezing level changes, precipitation, and typical width State the events before, at, and after, an idealised cold front in terms of: (a) pressure; (b) temperature; (c) wind velocity; (d) cloud; (e) precipitation; (f) visibility Describe a cross section of the typical warm front including cloud, temperature and freezing level changes, precipitation, and typical width State the events before, at, and after, an idealised warm front in terms of: (a) pressure; (b) temperature; (c) wind velocity; (d) cloud; (e) precipitation; (f) visibility Describe a cross section of the following occlusions and explain how each type develops: (a) cold occlusion; (b) warm occlusion Describe the potential dangers to VFR flight through fronts Describe the techniques, and precautions that can be taken to manage the risks of VFR flight through fronts Thunderstorms Explain the conditions to be met for the development of thunderstorms.
9 Describe the three stages of thunderstorm development Explain the development, and describe the characteristics of: (a) orographic thunderstorms; (b) heat type thunderstorms; (c) frontal thunderstorms Describe the hazards associated with thunderstorms and explain why light aircraft should avoid them Explain the origin and development of tornadoes and state the main hazards Icing Explain what is meant by supercooled water, and describe the influence of latent heat on the formation of ice Explain the process of freezing and melting With regard to airframe icing, explain the processes involved in the formation of: (a) clear ice; (b) rime ice; (c) hoar frost; (d) freezing rain State the types of cloud, and cloud drop size, that are conducive to the formation of each type of ice State the altitudes relative to the freezing level where rime ice or clear ice can be expected in cloud Give examples of conditions that could cause: (a) freezing rain; (b) hoar frost State the hazards for light aircraft from: (a) snow; (b) sleet; (c) hail Explain the influence of the following on the rate of ice accretion: (a) water content of cloud; (b) aircraft characteristics, components and airspeed State the dangers of icing to aircraft in flight and on the ground Explain the methods that can be used to manage the risks of aircraft icing Explain the environmental factors involved in carburettor icing, including; (a) moisture content; (b) temperature; (c) temperature gradient (inversions) State the temperature range in which carburettor ice typically can form Explain how the accretion rate of carburettor ice is influenced by the throttle setting Explain the conditions that can cause carburettor icing while on the ground.
10 8.32 Turbulence Describe the cause(s), factors involved, dangers, and techniques commonly used to avoid or minimise: (a) thermal (convective) turbulence; (b) mechanical turbulence small scale and large scale; (c) wind shear turbulence; (d) wake turbulence. New Zealand Meteorology 8.36 New Zealand Meteorology Describe how the following items govern the NZ climate: (a) latitude; (b) oceanic surroundings; (c) topography In general terms, describe cloudiness, gustiness, visibility and turbulence at various locations within New Zealand during typical: (a) northwest wind regimes; (b) northeast wind regimes; (c) southwest wind regimes; (d) southeast wind regimes With regard to VFR flight in a light aircraft over the Southern Alps, for typical weather scenarios, describe the meteorological considerations during flight planning and enroute including: (a) cloud base; (b) turbulence; (c) adverse and favourable winds; (d) visibility; (e) selection of tracks; (f) anticipated in-flight conditions; (g) the time frame of any weather change. Meteorological Services to Aviation 8.44 Domestic Meteorological Services for Aviation With reference to cloud amount, explain the meaning of: (a) SKC; (b) NSC; (c) FEW; (d) SCT; (e) BKN; (f) OVC; (g) CAVOK Describe how cloud and cloud base are reported.
11 Describe the principle of operation, and operational effectiveness of the automated visibility sensor With respect to NZ FIR VFR operations, interpret, understand and assess information of all the descriptions contained in: (a) area forecast (ARFOR); (b) meteorological reports (METAR/SPECI/ METAR AUTO); (c) trend forecasts (TREND); (d) aerodrome forecasts (TAF); (e) SIGMET; (f) Automatic terminal information service (ATIS); (g) Aerodrome and weather information broadcasts (AWIB); (h) Basic weather reports (BWR); (i) Pilot reports; (j) Radar and Satellite imagery Interpret and assess weather information made available by: Internet, newspapers television, and radio Describe the limitations of non-aviation specific weather information.
Subject No 20 - CPL Meteorology
 Subject No 20 - CPL Meteorology Notes: This syllabus is principally based on the regional meteorology as applicable to flying a twin engine aircraft IFR, within the South Pacific region at or below FL
Subject No 20 - CPL Meteorology Notes: This syllabus is principally based on the regional meteorology as applicable to flying a twin engine aircraft IFR, within the South Pacific region at or below FL
Advisory Circular AC61-5 Revision 21
 Subject No 20 Meteorology Each subject has been given a subject number and each topic within that subject a topic number. These reference numbers will be used on knowledge deficiency reports and will provide
Subject No 20 Meteorology Each subject has been given a subject number and each topic within that subject a topic number. These reference numbers will be used on knowledge deficiency reports and will provide
Explain in plain language the coded or pictorial information contained in:
 Subject No. 20 CPL METEOROLOGY Notes: This syllabus is principally based on the regional meteorology as applicable to flying a twin engine aircraft IFR, within the South Pacific region at or below FL 250.
Subject No. 20 CPL METEOROLOGY Notes: This syllabus is principally based on the regional meteorology as applicable to flying a twin engine aircraft IFR, within the South Pacific region at or below FL 250.
Syllabus details and associated Learning Objectives (A) and EIR METEOROLOGY
 Syllabus details associated Learning Objectives 050 00 00 00 METEOROLOGY 050 01 00 00 THE ATMOSPHERE 050 01 02 00 Air temperature 050 01 02 04 Lapse rates LO Describe qualitatively quantitatively the temperature
Syllabus details associated Learning Objectives 050 00 00 00 METEOROLOGY 050 01 00 00 THE ATMOSPHERE 050 01 02 00 Air temperature 050 01 02 04 Lapse rates LO Describe qualitatively quantitatively the temperature
AIRLINE TRANSPORT PILOTS LICENSE ( METEOROLOGY)
 050 01 00 00 THE ATMOSPHERE 050 01 01 00 Composition, Extent, Vertical Division 050 01 01 01 Describe the vertical division of the atmosphere, based on the temperature variations with height: 050 01 02
050 01 00 00 THE ATMOSPHERE 050 01 01 00 Composition, Extent, Vertical Division 050 01 01 01 Describe the vertical division of the atmosphere, based on the temperature variations with height: 050 01 02
Flight Dispatcher Aviation Meteorology Required Knowledge
 Flight Dispatcher Aviation Meteorology Required Knowledge 3.1 THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE 1 Properties 2 Vertical Structure 3 ICAO Standard Atmosphere 3.2 ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE 1 Pressure Measurements 2 Station
Flight Dispatcher Aviation Meteorology Required Knowledge 3.1 THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE 1 Properties 2 Vertical Structure 3 ICAO Standard Atmosphere 3.2 ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE 1 Pressure Measurements 2 Station
NATS 1750 Lecture. Wednesday 28 th November Pearson Education, Inc.
 NATS 1750 Lecture Wednesday 28 th November 2012 Processes that lift air Orographic lifting Elevated terrains act as barriers Result can be a rainshadow desert Frontal wedging Cool air acts as a barrier
NATS 1750 Lecture Wednesday 28 th November 2012 Processes that lift air Orographic lifting Elevated terrains act as barriers Result can be a rainshadow desert Frontal wedging Cool air acts as a barrier
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17
 Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
METEOROLOGY. 1 The average height of the tropopause at 50 N is about A 14 km B 16 km C 11 km D 8 km
 1 The average height of the tropopause at 50 N is about A 14 km B 16 km C 11 km D 8 km 2 In the lower part of the stratosphere the temperature A is almost constant B decreases with altitude C increases
1 The average height of the tropopause at 50 N is about A 14 km B 16 km C 11 km D 8 km 2 In the lower part of the stratosphere the temperature A is almost constant B decreases with altitude C increases
LAPL(A)/PPL(A) question bank FCL.215, FCL.120 Rev METEOROLOGY 050
 METEOROLOGY 050 1 Below the tropopause, the ICAO Standard Atmosphere (ISA) assumes? A mean sea level pressure of 1013.25 hpa together with a mean sea level temperature of 15 C, decreasing by 1.98 C per
METEOROLOGY 050 1 Below the tropopause, the ICAO Standard Atmosphere (ISA) assumes? A mean sea level pressure of 1013.25 hpa together with a mean sea level temperature of 15 C, decreasing by 1.98 C per
EARTH SCIENCE. Prentice Hall Water in the Atmosphere Water in the Atmosphere Water in the Atmosphere.
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Water s Changes of State 1. Precipitation is any form of water that falls from a cloud. a. Examples: Snow, rain, hail, sleet 3 States of matter of water: 1.
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Water s Changes of State 1. Precipitation is any form of water that falls from a cloud. a. Examples: Snow, rain, hail, sleet 3 States of matter of water: 1.
Answers to Clicker Questions
 Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 17 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
2. A mountain breeze (katabatic wind) blows : DOWN THE SLOPE DURING THE NIGHT
 MODEL E-EXAM (ATPL) NO.3 1. Among the ten groups of clouds, the following two are mentioned specifically in MET-reports and forecasts intended for aviation: CUMULONIMBUS AND TOWERING CUMULUS 2. A mountain
MODEL E-EXAM (ATPL) NO.3 1. Among the ten groups of clouds, the following two are mentioned specifically in MET-reports and forecasts intended for aviation: CUMULONIMBUS AND TOWERING CUMULUS 2. A mountain
9/22/14. Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation. The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th.
 Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University! A cloud is a visible
Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University! A cloud is a visible
24.2 Cloud Formation 2/3/2014. Orographic Lifting. Processes That Lift Air Frontal Wedging. Convergence and Localized Convective Lifting
 2/3/2014 Orographic Lifting Processes That Lift Air Frontal Wedging A front is the boundary between two adjoining air masses having contrasting characteristics. Convergence and Localized Convective Lifting
2/3/2014 Orographic Lifting Processes That Lift Air Frontal Wedging A front is the boundary between two adjoining air masses having contrasting characteristics. Convergence and Localized Convective Lifting
LAPL/PPL question bank FCL.215, FCL.120 Rev METEOROLOGY 050
 LAPL/PPL question bank FCL.215, FCL.120 Rev. 1.7 11.10.2018 METEOROLOGY 050 1 Below the tropopause, the ICAO Standard Atmosphere (ISA) assumes? A mean sea level pressure of 1225g/m³ together with a mean
LAPL/PPL question bank FCL.215, FCL.120 Rev. 1.7 11.10.2018 METEOROLOGY 050 1 Below the tropopause, the ICAO Standard Atmosphere (ISA) assumes? A mean sea level pressure of 1225g/m³ together with a mean
5.04 Clouds and Fog. References: FTGU pages , 147. Meteorology
 5.04 Clouds and Fog References: FTGU pages 124-126, 147 Meteorology 5.04 Clouds and Fog MTPs: Cloud Classification Types and Recognition Associated Precipitation Fog Formation and Types Cloud Classification
5.04 Clouds and Fog References: FTGU pages 124-126, 147 Meteorology 5.04 Clouds and Fog MTPs: Cloud Classification Types and Recognition Associated Precipitation Fog Formation and Types Cloud Classification
WEATHER THEORY. Weather Theory Page 100 Aviation Seminars. Measurement Of Temperature, Pressure And Moisture. Stability (Cont)
 Weather Theory Page 100 WEATHER THEORY Measurement Of Temperature, Pressure And Moisture The primary cause of all changes in the earth s weather is variation of solar energy received by the Earth s regions..
Weather Theory Page 100 WEATHER THEORY Measurement Of Temperature, Pressure And Moisture The primary cause of all changes in the earth s weather is variation of solar energy received by the Earth s regions..
Chapter 6. Cloud Development and Forms
 Cloud Formation Chapter 6 Cloud Development and Forms Condensation (i.e. clouds,fog) results from: Diabatic cooling (important for fog) Adiabatic cooling (important for clouds) Clouds form due to adiabatic
Cloud Formation Chapter 6 Cloud Development and Forms Condensation (i.e. clouds,fog) results from: Diabatic cooling (important for fog) Adiabatic cooling (important for clouds) Clouds form due to adiabatic
Meteorology Clouds and Fog. Cloud Classification MTPs: Height. Shape. and. Clouds are classified by:
 Meteorology 5.04 Clouds and Fog References: FTGU pages 124-126, 147 5.04 Clouds and Fog MTPs: Cloud Classification Associated Precipitation Clouds are classified by: Cloud Classification Height Shape and
Meteorology 5.04 Clouds and Fog References: FTGU pages 124-126, 147 5.04 Clouds and Fog MTPs: Cloud Classification Associated Precipitation Clouds are classified by: Cloud Classification Height Shape and
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Unit 4 Lesson 2 Clouds and Cloud Formation. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Head in the Clouds What are clouds? A cloud is a collection of small water droplets or ice crystals that are suspended in the air. Clouds are visible because water droplets and ice crystals reflect light.
Head in the Clouds What are clouds? A cloud is a collection of small water droplets or ice crystals that are suspended in the air. Clouds are visible because water droplets and ice crystals reflect light.
Chapter 5 Forms of Condensation and Precipitation
 Chapter 5 Forms of Condensation and Precipitation Cloud Formation visible aggregate of water droplets, ice crystals, or both adiabatic cooling Classifying and Naming of clouds Processes responsible for
Chapter 5 Forms of Condensation and Precipitation Cloud Formation visible aggregate of water droplets, ice crystals, or both adiabatic cooling Classifying and Naming of clouds Processes responsible for
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1
 Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
Lecture 07 February 10, 2010 Water in the Atmosphere: Part 1 About Water on the Earth: The Hydrological Cycle Review 3-states of water, phase change and Latent Heat Indices of Water Vapor Content in the
ESS55: EARTH S ATMOSPHERE / Homework #6 / (due 5/24/2018)
 ESS55: EARTH S ATMOSPHERE / Homework #6 / (due 5/24/2018) Name Student ID: 1) 21) 41) 2) 22) 42) 3) 23) 43) 4) 24) 44) 5) 25) 45) 6) 26) 46) 7) 27) 47) 8) 28) 48) 9) 29) 49) 10) 30) 50) 11) 31) 51) 12)
ESS55: EARTH S ATMOSPHERE / Homework #6 / (due 5/24/2018) Name Student ID: 1) 21) 41) 2) 22) 42) 3) 23) 43) 4) 24) 44) 5) 25) 45) 6) 26) 46) 7) 27) 47) 8) 28) 48) 9) 29) 49) 10) 30) 50) 11) 31) 51) 12)
Miami-Dade Community College Met 1010 Introduction to Weather
 Miami-Dade Community College Met 1010 Introduction to Weather Course Description: An introduction to the fundamentals of weather and their impact on human activities. Topics include temperature, humidity,
Miami-Dade Community College Met 1010 Introduction to Weather Course Description: An introduction to the fundamentals of weather and their impact on human activities. Topics include temperature, humidity,
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts. Lecture 12 AOS 101
 Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
ISSUED BY KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA - DOWNLOADED FROM
 CHAPTER -11 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE This chapter deals with Humidity, types of humidity, relative humidity, absolute humidity, specific humidity, dew point, condensation, saturated air, types of precipitation
CHAPTER -11 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE This chapter deals with Humidity, types of humidity, relative humidity, absolute humidity, specific humidity, dew point, condensation, saturated air, types of precipitation
Thursday, June 5, Chapter 5: Condensation & Precipitation
 Thursday, June 5, 2014 Chapter 5: Condensation & Precipitation Chapter 5: Condensation and Precipitation Formation of Condensation Saturated Air Condensation Nuclei Results of Condensation Clouds Fog Dew
Thursday, June 5, 2014 Chapter 5: Condensation & Precipitation Chapter 5: Condensation and Precipitation Formation of Condensation Saturated Air Condensation Nuclei Results of Condensation Clouds Fog Dew
Mr. P s Science Test!
 WEATHER- 2017 Mr. P s Science Test! # Name Date 1. Draw and label a weather station model. (10 pts) 2. The is the layer of the atmosphere with our weather. 3. Meteorologists classify clouds in about different
WEATHER- 2017 Mr. P s Science Test! # Name Date 1. Draw and label a weather station model. (10 pts) 2. The is the layer of the atmosphere with our weather. 3. Meteorologists classify clouds in about different
ESCI 241 Meteorology Lesson 9 Clouds and Fog
 References and Reading: MT Chapter 7 FORMATION OF CLOUDS ESCI 241 Meteorology Lesson 9 Clouds and Fog When air becomes saturated with water vapor, any excess water vapor condenses to form clouds The air
References and Reading: MT Chapter 7 FORMATION OF CLOUDS ESCI 241 Meteorology Lesson 9 Clouds and Fog When air becomes saturated with water vapor, any excess water vapor condenses to form clouds The air
Atmospheric Moisture. Relative humidity Clouds Rain/Snow. Relates to atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, exosphere, geosphere
 Atmospheric Moisture Relative humidity Clouds Rain/Snow Relates to atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, exosphere, geosphere Atmospheric moisture Water in the atmosphere Requires - vapor pressure- the amount
Atmospheric Moisture Relative humidity Clouds Rain/Snow Relates to atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, exosphere, geosphere Atmospheric moisture Water in the atmosphere Requires - vapor pressure- the amount
Precipitation AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Cloud Development: Orographic Lifting
 Precipitation AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Precipitation formation Rain Ice Lecture 14 Oct 11 2018 1 Cloud Development: Orographic Lifting
Precipitation AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Precipitation formation Rain Ice Lecture 14 Oct 11 2018 1 Cloud Development: Orographic Lifting
NATS 101, Section 13, Fall 2010 Midterm Examination #2 October 22, 2010
 EXAM NUMBER NATS 101, Section 13, Fall 2010 Midterm Examination #2 October 22, 2010 Name: KEY SID: Instructions: Write your name and student ID on ALL pages of the exam. In the multiple-choice/fill in
EXAM NUMBER NATS 101, Section 13, Fall 2010 Midterm Examination #2 October 22, 2010 Name: KEY SID: Instructions: Write your name and student ID on ALL pages of the exam. In the multiple-choice/fill in
Meteorology for Bronze
 Meteorology for Bronze By Sid Smith and Alison Mulder 1 Alison Mulder Meteorology Part 1 The Atmosphere Air Temperature and Pressure Convectional Stability and Instability Types of Pressure Distribution
Meteorology for Bronze By Sid Smith and Alison Mulder 1 Alison Mulder Meteorology Part 1 The Atmosphere Air Temperature and Pressure Convectional Stability and Instability Types of Pressure Distribution
Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation. Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
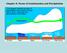 Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation Water vapor's role in the Earth's weather is major. Its the product of evaporation. It is lifted up, condenses and forms clouds. It is also a greenhouse
Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation Water vapor's role in the Earth's weather is major. Its the product of evaporation. It is lifted up, condenses and forms clouds. It is also a greenhouse
WEATHER THEORY. Stability. In general:
 Weather Theory 69 Temperature, Pressure And Moisture WEATHER THEORY Pressure Systems (Cont) Every physical process of weather is a result of a heat exchange. The standard sea level temperature is 15 degrees
Weather Theory 69 Temperature, Pressure And Moisture WEATHER THEORY Pressure Systems (Cont) Every physical process of weather is a result of a heat exchange. The standard sea level temperature is 15 degrees
Mechanical Turbulence Wind forms eddies as it blows around hanger, stands of trees or other obstructions
 Turbulence Low-level Turbulence below 15,000 feet consists of Mechanical Turbulence Convective Turbulence Frontal Turbulence Wake Turbulence Mechanical Turbulence Wind forms eddies as it blows around hanger,
Turbulence Low-level Turbulence below 15,000 feet consists of Mechanical Turbulence Convective Turbulence Frontal Turbulence Wake Turbulence Mechanical Turbulence Wind forms eddies as it blows around hanger,
The atmosphere s water
 The atmosphere s water Atmospheric Moisture and Precipitation Properties of Water The Hydrosphere and the Hydrologic Cycle Humidity The Adiabatic Process Clouds Precipitation Air Quality Main points for
The atmosphere s water Atmospheric Moisture and Precipitation Properties of Water The Hydrosphere and the Hydrologic Cycle Humidity The Adiabatic Process Clouds Precipitation Air Quality Main points for
Condensation: Dew, Fog, & Clouds. Chapter 5
 Condensation: Dew, Fog, & Clouds Chapter 5 The Formation of Dew & Frost Dew forms on objects near the ground surface when they cool below the dew point temperature. More likely on clear nights due to increased
Condensation: Dew, Fog, & Clouds Chapter 5 The Formation of Dew & Frost Dew forms on objects near the ground surface when they cool below the dew point temperature. More likely on clear nights due to increased
777 GROUNDSCHOOL Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms
 777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH
 INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH WEATHER PATTERNS Extratropical cyclones (low pressure core) and anticyclones (high pressure core) Cold fronts and warm fronts Jet stream
INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH WEATHER PATTERNS Extratropical cyclones (low pressure core) and anticyclones (high pressure core) Cold fronts and warm fronts Jet stream
Forecasting Local Weather
 Forecasting Local Weather Sea/Land Breeze Temperature Dew Fog Frost Snow Thunderstorms Tropical Cyclones Temperatures: Radiation Balance Typical Diurnal Variation of Temperature Min soon after dawn Temp
Forecasting Local Weather Sea/Land Breeze Temperature Dew Fog Frost Snow Thunderstorms Tropical Cyclones Temperatures: Radiation Balance Typical Diurnal Variation of Temperature Min soon after dawn Temp
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERIC MOISTURE Atmospheric Moisture The Nature of Water The Hydrologic Cycle Evaporation Measures of Humidity Condensation The Buoyancy of Air Precipitation
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERIC MOISTURE Atmospheric Moisture The Nature of Water The Hydrologic Cycle Evaporation Measures of Humidity Condensation The Buoyancy of Air Precipitation
Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition
 Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition Air is a combination of many gases, each with its own unique characteristics. About 99 percent of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen and oxygen, with the
Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition Air is a combination of many gases, each with its own unique characteristics. About 99 percent of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen and oxygen, with the
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 CHAPTER Y ou have already learnt that the air contains water vapour. It varies from zero to four per cent by volume of the atmosphere and plays an important role in the weather phenomena. Water is present
CHAPTER Y ou have already learnt that the air contains water vapour. It varies from zero to four per cent by volume of the atmosphere and plays an important role in the weather phenomena. Water is present
according to and water. High atmospheric pressure - Cold dry air is other air so it remains close to the earth, giving weather.
 EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Composition of the atmosphere - Earth's atmosphere consists of nitrogen ( %), oxygen ( %), small amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, argon, krypton, ozone, neon and other gases such
EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Composition of the atmosphere - Earth's atmosphere consists of nitrogen ( %), oxygen ( %), small amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, argon, krypton, ozone, neon and other gases such
The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume.
 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume. A. Oxygen B. Water Vapor C. Carbon Dioxide D. Nitrogen An isobar is a line of constant. A.
The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume. A. Oxygen B. Water Vapor C. Carbon Dioxide D. Nitrogen An isobar is a line of constant. A.
METEOROLOGY CLASS #1 LT LAZARUK AND WO2 LUCAS LAMOUREUX
 METEOROLOGY CLASS #1 LT LAZARUK AND WO2 LUCAS LAMOUREUX CLASS #1 OVERVIEW WHAT WILL YOU BE LEARNING AN INTRODUCTION THE ATMOSPHERE CLOUDS STABILITY TEMPERATURE & HUMIDITY INTRODUCTION PART 1 INTRODUCTION
METEOROLOGY CLASS #1 LT LAZARUK AND WO2 LUCAS LAMOUREUX CLASS #1 OVERVIEW WHAT WILL YOU BE LEARNING AN INTRODUCTION THE ATMOSPHERE CLOUDS STABILITY TEMPERATURE & HUMIDITY INTRODUCTION PART 1 INTRODUCTION
Chapter The transition from water vapor to liquid water is called. a. condensation b. evaporation c. sublimation d.
 Chapter-6 Multiple Choice Questions 1. The transition from water vapor to liquid water is called. a. condensation b. evaporation c. sublimation d. deposition 2. The movement of water among the great global
Chapter-6 Multiple Choice Questions 1. The transition from water vapor to liquid water is called. a. condensation b. evaporation c. sublimation d. deposition 2. The movement of water among the great global
Weather Notes. Chapter 16, 17, & 18
 Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Atmospheric Moisture and Precipitation
 Atmospheric Water Atmospheric Moisture and Precipitation Properties of Water The Hydrosphere and the Hydrologic Cycle Humidity The Adiabatic Processes Clouds Precipitation Air Quality Main topics for today
Atmospheric Water Atmospheric Moisture and Precipitation Properties of Water The Hydrosphere and the Hydrologic Cycle Humidity The Adiabatic Processes Clouds Precipitation Air Quality Main topics for today
Ch22&23 Test. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch22&23 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The two most abundant compounds in the atmosphere are carbon dioxide and a. particulates.
Ch22&23 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The two most abundant compounds in the atmosphere are carbon dioxide and a. particulates.
Climate & Earth System Science. Introduction to Meteorology & Climate. Chapter 04 Lecture 07. Peter Lynch VIS WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE MAPH 10050
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
CLOUDS, PRECIPITATION, AND WEATHER RADAR
 CHAPTER 7 CLOUDS, PRECIPITATION, AND WEATHER RADAR MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The activation temperature of most ice-forming nuclei is 0 C. a. above b. about c. well below 2. Hygroscopic nuclei water
CHAPTER 7 CLOUDS, PRECIPITATION, AND WEATHER RADAR MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The activation temperature of most ice-forming nuclei is 0 C. a. above b. about c. well below 2. Hygroscopic nuclei water
Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17. Weather and Climate
 Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17 Weather and Climate Prediction Old way Groundhog Color of the sky Modern way satellites instruments computers Goal Weather Factors Studied by meteorologists Several factors
Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17 Weather and Climate Prediction Old way Groundhog Color of the sky Modern way satellites instruments computers Goal Weather Factors Studied by meteorologists Several factors
Air Masses and Fronts II
 Air Masses and Fronts II Brief review An air mass is a large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are fairly similar in any horizontal direction Source regions for air masses tend to
Air Masses and Fronts II Brief review An air mass is a large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are fairly similar in any horizontal direction Source regions for air masses tend to
Meteorology Question bank
 Meteorology Question bank 1. Select an area in which advection fog occurs frequently and describe fully why the area you have selected is favorable to its formation. 2. Fog is comparatively rare in tropical
Meteorology Question bank 1. Select an area in which advection fog occurs frequently and describe fully why the area you have selected is favorable to its formation. 2. Fog is comparatively rare in tropical
Week: Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: EVEN Period: Week: 28 30 Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2 O 3 E *Vocabulary *Water in the Atmosphere and Clouds Notes *Cloud Drawings
clementaged.weebly.com Name: EVEN Period: Week: 28 30 Dates: 3/2 3/20 Unit: Climate Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2 O 3 E *Vocabulary *Water in the Atmosphere and Clouds Notes *Cloud Drawings
CHAPTER THREE Mechanics of Frontal Systems
 Mechanics of Frontal Systems 300. INTRODUCTION The purpose of this chapter is to introduce the student to various frontal systems, including their formation, flight conditions, and associated weather patterns,
Mechanics of Frontal Systems 300. INTRODUCTION The purpose of this chapter is to introduce the student to various frontal systems, including their formation, flight conditions, and associated weather patterns,
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #1 Page 1 of 7
 1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
Most types of clouds are found in the troposphere, and almost all weather occurs within this
 Meteorology Most types of clouds are found in the troposphere, and almost all weather occurs within this layer. Air pressure and the density of the air also decrease with altitude. That's why the cabins
Meteorology Most types of clouds are found in the troposphere, and almost all weather occurs within this layer. Air pressure and the density of the air also decrease with altitude. That's why the cabins
Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns. Meteorology
 Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns Meteorology Weather is what conditions of the atmosphere are over a short period of time. Climate is how the atmosphere "behaves" over long periods
Weather, Air Masses, Fronts and Global Wind Patterns Meteorology Weather is what conditions of the atmosphere are over a short period of time. Climate is how the atmosphere "behaves" over long periods
Preamble to Chapter 05. Hydrologic Cycle Intro. Ocean and Freshwater Distribution. Chapter 5: Atmospheric Water and Weather
 Chapter 5: Atmospheric Water and Weather Preamble to Chapter 05 Hydrologic Cycle Intro Quantity Equilibrium: Water at a relative balance over the last 2 billion years Diagram of the hydrologic cycle Ocean
Chapter 5: Atmospheric Water and Weather Preamble to Chapter 05 Hydrologic Cycle Intro Quantity Equilibrium: Water at a relative balance over the last 2 billion years Diagram of the hydrologic cycle Ocean
Chapter 5: Atmospheric Water and Weather. Preamble to Chapter 05
 Chapter 5: Atmospheric Water and Weather Preamble to Chapter 05 Hydrologic Cycle Intro Quantity Equilibrium: Water at a relative balance over the last 2 billion years Diagram of the hydrologic cycle Ocean
Chapter 5: Atmospheric Water and Weather Preamble to Chapter 05 Hydrologic Cycle Intro Quantity Equilibrium: Water at a relative balance over the last 2 billion years Diagram of the hydrologic cycle Ocean
Clouds. What they tell us about the weather
 Clouds What they tell us about the weather Spring funnel cloud over Willard, Utah 2003 Cloud coverage 581-586 How to show Cloud Coverage On a weather map meteorologists use circles shaded differently to
Clouds What they tell us about the weather Spring funnel cloud over Willard, Utah 2003 Cloud coverage 581-586 How to show Cloud Coverage On a weather map meteorologists use circles shaded differently to
Unit: Weather Study Guide
 Name: Period: Unit: Weather Study Guide Define each vocabulary word on a separate piece of paper or index card. Weather Climate Temperature Wind chill Heat index Sky conditions UV index Visibility Wind
Name: Period: Unit: Weather Study Guide Define each vocabulary word on a separate piece of paper or index card. Weather Climate Temperature Wind chill Heat index Sky conditions UV index Visibility Wind
Meteorology. Types of Turbulence
 Meteorology 5.06 Turbulence, Visibility, and Fronts References: Air Command Weather Manual Chapters 7, 8, 10 and 11 FTGU pages 133, 138, 140-145, 147, 155 and 156 Aviation Weather Student Guide http://www.tpub.com/content/aviation2/p-303/index.htm
Meteorology 5.06 Turbulence, Visibility, and Fronts References: Air Command Weather Manual Chapters 7, 8, 10 and 11 FTGU pages 133, 138, 140-145, 147, 155 and 156 Aviation Weather Student Guide http://www.tpub.com/content/aviation2/p-303/index.htm
Why Is the Mountain Peak Cold? Lecture 7: Air cools when it rises. Vertical Thermal Structure. Three Things Need To Be Explained
 Lecture 7: Air cools when it rises Air expands as it rises Air cools as it expands Air pressure Lapse rates Why Is the Mountain Peak Cold? Sunlight heats the atmosphere from below Convection occurs and
Lecture 7: Air cools when it rises Air expands as it rises Air cools as it expands Air pressure Lapse rates Why Is the Mountain Peak Cold? Sunlight heats the atmosphere from below Convection occurs and
Meteorology Today. 1 Aug st Lt Libby Haynes Capt Kim Mevers
 Meteorology 1950 - Today 1 Aug 2018 1 st Lt Libby Haynes Capt Kim Mevers What is meteorology? Is it important to you? Meteorology is the science of the atmosphere embracing both weather and climate. It
Meteorology 1950 - Today 1 Aug 2018 1 st Lt Libby Haynes Capt Kim Mevers What is meteorology? Is it important to you? Meteorology is the science of the atmosphere embracing both weather and climate. It
Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time. It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the
 Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
Clouds, Precipitation
 ES 106 Clouds, Precipitation I. Condensation and cloud formation A. Condensation nuclei necessary for clouds to form 1. dust, pollen, salt, smoke 2. at sub-freezing temperature, form by deposition of water
ES 106 Clouds, Precipitation I. Condensation and cloud formation A. Condensation nuclei necessary for clouds to form 1. dust, pollen, salt, smoke 2. at sub-freezing temperature, form by deposition of water
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms
 Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2007 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2007 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
78% : component of atmosphere! 21% : 1% : Changes depending on origin of air: - originated over - originated over Ozone = O 3 Definition:
 Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
Unit 6 Part 1 Meteorology Name: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere SWBAT: Describe the composition of the atmosphere. Diagram/describe the layers of the earth s atmosphere. Weather Climate Atmospheric
9 Condensation. Learning Goals. After studying this chapter, students should be able to:
 9 Condensation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. explain the microphysical processes that operate in clouds to influence the formation and growth of cloud droplets
9 Condensation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. explain the microphysical processes that operate in clouds to influence the formation and growth of cloud droplets
Energy Forms Potential (PE) and kinetic (KE) (internal and external) Temperature and Temperature Scales March 29 Specific heat Latent heat March 30
 Review Sheet ATM S 101 Spring 2006 Disclaimer: THIS REVIEW SHEET IS INTENDED ONLY AS A STUDY GUIDE. ANY MATERIAL COVERED IN CLASS AND IN THE ASSIGNED READING IS LIKELY TO BE ON THE EXAM. Chapter 1: Earth
Review Sheet ATM S 101 Spring 2006 Disclaimer: THIS REVIEW SHEET IS INTENDED ONLY AS A STUDY GUIDE. ANY MATERIAL COVERED IN CLASS AND IN THE ASSIGNED READING IS LIKELY TO BE ON THE EXAM. Chapter 1: Earth
AIR MASSES. Large bodies of air. SOURCE REGIONS areas where air masses originate
 Large bodies of air AIR MASSES SOURCE REGIONS areas where air masses originate Uniform in composition Light surface winds Dominated by high surface pressure The longer the air mass remains over a region,
Large bodies of air AIR MASSES SOURCE REGIONS areas where air masses originate Uniform in composition Light surface winds Dominated by high surface pressure The longer the air mass remains over a region,
Final Weather Unit Study Guide
 Name: Atmospheric Composition and Layers Altitude Atmosphere Composition Troposphere Air Pressure Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere Ionosphere Sample Questions: Final Weather Unit Study Guide
Name: Atmospheric Composition and Layers Altitude Atmosphere Composition Troposphere Air Pressure Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere Ionosphere Sample Questions: Final Weather Unit Study Guide
SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER
 SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER Basic Meteorological Terminology Adiabatic - Referring to a process without the addition or removal of heat. A temperature change may come about as a result of a change in the
SEVERE AND UNUSUAL WEATHER Basic Meteorological Terminology Adiabatic - Referring to a process without the addition or removal of heat. A temperature change may come about as a result of a change in the
CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS
 Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey How are clouds made? Clouds form when air is cooled to its dewpoint
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey How are clouds made? Clouds form when air is cooled to its dewpoint
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation: Clouds and Precipitation. Dr. Michael J Passow
 Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation: Clouds and Precipitation Dr. Michael J Passow What Processes Lift Air? Clouds require three things: water vapor, a condensation nucleus, and cooling Cooling usually
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation: Clouds and Precipitation Dr. Michael J Passow What Processes Lift Air? Clouds require three things: water vapor, a condensation nucleus, and cooling Cooling usually
Geology 1347 Meteorology
 Geology 1347 Meteorology Exam 2 Review 1. The scattering of light by small particles in the atmosphere causes many familiar effects such as white clouds, blue skies, hazy skies, crepuscular rays, and colorful
Geology 1347 Meteorology Exam 2 Review 1. The scattering of light by small particles in the atmosphere causes many familiar effects such as white clouds, blue skies, hazy skies, crepuscular rays, and colorful
Water in the Atmosphere Understanding Weather and Climate
 Water in the Atmosphere Understanding Weather and Climate Climate 2 1 Cloud Development and Forms Understanding Weather and Climate Climate 2 2 Learning Objectives 1. The various atmospheric lifting mechanisms
Water in the Atmosphere Understanding Weather and Climate Climate 2 1 Cloud Development and Forms Understanding Weather and Climate Climate 2 2 Learning Objectives 1. The various atmospheric lifting mechanisms
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection
 Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND Diagnosis of thunderstorm hazards using imagery Contents Satellite imagery Visible, infrared, water vapour Basic cloud identification Identifying
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND Diagnosis of thunderstorm hazards using imagery Contents Satellite imagery Visible, infrared, water vapour Basic cloud identification Identifying
Evaporation - Water evaporates (changes from a liquid to a gas) into water vapor due to heat from the Sun.
 Erin Kathryn 2016 Weather is the conditions of Earth s atmosphere at a certain time and place. For example, sunshine, rain, hurricanes, and storms are all examples of weather. Weather is different at different
Erin Kathryn 2016 Weather is the conditions of Earth s atmosphere at a certain time and place. For example, sunshine, rain, hurricanes, and storms are all examples of weather. Weather is different at different
A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time
 WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
WEATHER & THE ATMOSPHERE A. Weather - the conditions of the variables of the atmosphere for any short period of time Meteorology - the study of weather and weather related variables - the variables: Topic
Chapter 7. Water and Atmospheric Moisture. Water on Earth Unique Properties of Water Humidity Atmospheric Stability Clouds and Fog
 Chapter 7 Water and Atmospheric Moisture Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Water kept both the terrestrial and marine ecosystems closely linked with the atmosphere. (1) Air carries water vapor and
Chapter 7 Water and Atmospheric Moisture Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Water kept both the terrestrial and marine ecosystems closely linked with the atmosphere. (1) Air carries water vapor and
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #2 Page 1 of 8
 1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather
 Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Freezing: To become hardened into ice or into a solid body Deposition: The change in state of matter
Unit 4 Review Guide: Weather Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Freezing: To become hardened into ice or into a solid body Deposition: The change in state of matter
NATURE OF THE ATMOSPHERE
 Whether preparing for a local flight or a long cross-country, flight-planning decisions based on weather can dramatically affect the safety of the flight. A solid understanding of weather theory provides
Whether preparing for a local flight or a long cross-country, flight-planning decisions based on weather can dramatically affect the safety of the flight. A solid understanding of weather theory provides
Condensation: Dew, Fog and Clouds AT350
 Condensation: Dew, Fog and Clouds AT350 T=30 C Water vapor pressure=12mb What is Td? What is the sat. water vapor T=30 C Water vapor pressure=12mb What is Td? What is the sat. water vapor ~12/42~29% POLAR
Condensation: Dew, Fog and Clouds AT350 T=30 C Water vapor pressure=12mb What is Td? What is the sat. water vapor T=30 C Water vapor pressure=12mb What is Td? What is the sat. water vapor ~12/42~29% POLAR
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY. Metr Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts. Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation.
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 356.01 Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Figure 1. Surface Chart for 1500Z 7 September 2007 1 1. Pressure
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY NAME Metr 356.01 Fall 2012 Test #1 200 pts Part I. Surface Chart Interpretation. Figure 1. Surface Chart for 1500Z 7 September 2007 1 1. Pressure
Chapter 6 Clouds. Cloud Development
 Chapter 6 Clouds Chapter overview Processes causing saturation o Cooling, moisturizing, mixing Cloud identification and classification Cloud Observations Fog Why do we care about clouds in the atmosphere?
Chapter 6 Clouds Chapter overview Processes causing saturation o Cooling, moisturizing, mixing Cloud identification and classification Cloud Observations Fog Why do we care about clouds in the atmosphere?
Water in the Atmosphere
 Water in the Atmosphere Characteristics of Water solid state at 0 o C or below (appearing as ice, snow, hail and ice crystals) liquid state between 0 o C and 100 o C (appearing as rain and cloud droplets)
Water in the Atmosphere Characteristics of Water solid state at 0 o C or below (appearing as ice, snow, hail and ice crystals) liquid state between 0 o C and 100 o C (appearing as rain and cloud droplets)
Atmosphere L AY E RS O F T H E AT MOSPHERE
 Atmosphere L AY E RS O F T H E AT MOSPHERE Why is the atmosphere divided into 5 different layers? The atmosphere is divided into five different layers because the atmosphere is not uniform, its properties
Atmosphere L AY E RS O F T H E AT MOSPHERE Why is the atmosphere divided into 5 different layers? The atmosphere is divided into five different layers because the atmosphere is not uniform, its properties
TOPICS: What are Thunderstorms? Ingredients Stages Types Lightning Downburst and Microburst
 THUNDERSTORMS TOPICS: What are Thunderstorms? Ingredients Stages Types Lightning Downburst and Microburst What are Thunderstorms? A storm produced by a cumulonimbus cloud that contains lightning and thunder
THUNDERSTORMS TOPICS: What are Thunderstorms? Ingredients Stages Types Lightning Downburst and Microburst What are Thunderstorms? A storm produced by a cumulonimbus cloud that contains lightning and thunder
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms. Spring 2018
 Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2018 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Chapter 8 cont. Clouds and Storms Spring 2018 Clouds and Storms Clouds cover ~ 50% of earth at any time. Clouds are linked to a number of condensation processes. Cloud morphology, cloud types, associated
Clouds on Mars Cloud Classification
 Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place
 Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
Weather Section 1 Weather - is the state of the atmosphere at a specific time & place Includes such conditions as air pressure, wind, temperature, and moisture in the air The Sun s heat evaporates water
