Atmospheric Coupling via Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP)
|
|
|
- Roberta Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Atmospheric Coupling via Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) Cora E. Randall University of Colorado Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences
2 Acknowledgments Scott Bailey Laura Holt Chuck Bardeen Charley Jackma n Xiaohua Fang Dan Marsh Jeff France Mike Mills Lynn Harvey Dave Siskind ACE Science Team NASA, NSF
3 Vertical Coupling Troposphere to thermosphere In the polar region Mainly in winter Outline Intro to Mechanism Historical Evidence Recent Anomalies Model Results
4 Energetic Particle Precipitation Medium & High Energy Electrons Solar Protons Adapted from Lean, 1994
5 Solar-Magnetosphere Energy Low-energy particles precipitate in thermosphere NO transported downward and/or produced locally POLAR VORTEX High-energy particles precipitate in mesosphere and stratosphere Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) Ionization & Dissociation NO x and HO x NO x and HO x Destroy Ozone
6 EPP Effects on the Stratosphere
7 EPP Indirect Effect NO produced in mesosphere or thermosphere and descends to stratosphere Routine production, but MLT NO x has lifetime of days, so stratospheric effects require efficient downward transport Polar night Strong descent in MLT Confinement in Polar Vortex NO x in stratosphere destroys ozone
8 First satellite observations of EPP Indirect Effect from LIMS in NH, EPP is the ONLY source of mesospheric NO x in the polar winter! Based on Russell et al., 1984
9 Satellite observations of EPP-NO x were sparse from 1979 to EPP Investigations mainly used solar occultation data from SAGE, HALOE, and POAM Sparse geographic coverage SAGE & POAM only measure NO 2, not NO No polar night In 2003 more data became available e.g., GOMOS, MIPAS, SCIAMACHY, ACE-FTS (Still cannot measure polar night NO in MLT)
10 POAM: SH ACE-FTS: SH Randall et al., 2007 Randall et al., 2007 MIPAS: SH Funke et al.,
11 EPP-NO x enhancements accompanied by ozone reductions
12 EPP-NO x entering the Southern Hemisphere Stratosphere MIPAS EPP-NOx in 2003 = 2.4 GM (Funke et al., 2005) Adapted from Randall et al., JGR 2007 How significant is this? Up to 10% of total SH NO y (rest from N 2 O oxidation) Up to 40% of polar NO y What determines the interannual variability?
13 Correlation of EPP NO x entering the SH stratosphere with Ap and Solar f10.7 (Apr-Aug) Adapted from Randall et al., JGR 2007 Strong correlation with Ap (and auroral & MEE power, and thermospheric NO) but not F10.7 Variability in SH stratospheric NO x from EPP controlled by variation in EPP-NO x production: Stable Dynamics!
14 EPP-NO x entering the Northern Hemisphere Stratosphere vs. Ap & F10.7 Vortex Fraction In NH, correlations with Ap index & F10.7 are poor. Both dynamical variability and EPP play critical roles in controlling the NH variability : SPE : SPE+Met : Met
15 NORTH ACE NO x SOUTH Less than average EPP! Less than average EPP! Randall et al., 2009
16 NORTH SABER & ACE Polar Temp SOUTH Elevated Arctic stratopause in 2004, 2006, & 2009 Slightly different temperature color scales; range from ~170K-270K (blue-red).
17 Ratio of observed NO x in 2004, 2006, & 2009 to average NO x in 2005, 2007, & 2008 Randall, et al., 2009 NO x enhancements coincide with elevated stratopause
18 Elevated stratopause indicative of enhanced descent in (normal) mesosphere region (adiabatic compression). Enhanced descent brings down more EPP-NO x. More efficient transport leads to large stratospheric EPP IE even when EPP itself is well below average. What is the mechanism? Begins with extraordinary sudden stratospheric warming (strong and persistent; Manney et al., 2005; 2008; 2009)
19 1. Stratospheric Warming: Equator-to-pole T gradient reverses Zonal wind reverses direction 2. Planetary waves cannot propagate upward so upper stratosphere & lower mesosphere cool 3. Causes reformation of very strong upper vortex and westerly winds 4. Gravity waves with westward phase speed preferentially propagate to the mesosphere 5. Mesospheric westerly zonal wind slows induces poleward meridional wind to balance pressure gradient & Coriolis 6. Leads to enhanced descent in the polar mesosphere Brings down more NO x Adiabatic compression results in elevated stratopause [Hauchecorne et al., 2007; Siskind et al., 2007; Sahishkumar & Sridharan, 2009; Winick et al., 2009]
20 Why did we get such impressive stratospheric warmings and recovery in 2004, 2006, & 2009? We don t know. Maybe climate change, but still speculative Although 2004, 2006, and 2009 were highly unusual, the frequency of SSW seems to be increasing (~1 per year since 1999, twice as frequent as in previous half-century) Models predict more variability with climate change, so extremes might occur more often Models inconclusive with regard to frequency & strength of SSWs
21 The EPP IE Story from Observations EPP-NO x is produced continually and can contribute up to 40% of polar stratospheric NO x budget even in years with low geomagnetic activity. Ozone is depleted by EPP-NO x by 35% or more. Contribution of EPP-NO x to the stratosphere does not correlate well with the solar (F10.7) cycle. Understanding wave mean flow interactions is required to elucidate mechanisms controlling interannual variability. Improved picture of EPP effects requires continuous nighttime observations of NO x throughout the MLT.
22 Aside #1 Does EPP affect surface air temperature? CCM MODEL EEP minus NoEEP From Annika Seppälä, FMI Rozanov et al., Model results for DJF surface air temperature differences (NH).
23 Is there empirical evidence that EPP-NO x affects climate? Adapted from Rozanov et al., 2005 Seppälä et al., JGR 2009: Analysis of ERA-40 temperatures yields statistically significant surface air temperature differences between years with high and low EPP. Can rule out correlation with solar flux, QBO, ENSO, SAM Possible correlation with NAM or random variations in SST
24 Aside #2 What about EPP effects on clouds/aerosols? POAM III aerosol surface area increased significantly (>2σ) after January 2005 SEPs. Dynamical cause ruled out. No other such increase in 8-year record. No information from POAM at lower altitudes Mirinova et al., in preparation
25 Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model A 3D coupled chemistry climate model 0 to ~145 km Comprehensive chemistry incl. heterogeneous rx Interactive Chemistry or Specified Meteorology km vertical resolution in stratosphere 1.9º x 2.5º or 4 x 5º horizontal resolution Ref: Garcia et al., 2007
26 WACCM Parameterization of Precipitation Effects Aurora Input = Kp Distribution = Auroral Oval Roble and Ridley, 1987 Medium Energy Electrons (30 kev 2.5 MeV) Input = MEPED activity level (or hemispheric power) Distribution = Statistical patterns [Codrescu et al., JGR, 1997) Fang et al., 2008
27 WACCM Runs (free-running coupled climate-chemistry model): Seasonally varying (but annually invariant) SSTs Constant F10.7 = greenhouse gas and halogen concentrations Daily (repetitive) forcing with 3 cases of EPP: Case 1: ~Zero particle precipitation, Kp=2/3 (Ap=3) 80 years (after spin-up) = 80-member ensemble Case 2: Moderate auroral electrons, Kp=4 (Ap=27) 50 years (after spin-up) = 50-member ensemble Case 3: Moderate auroral electrons plus >30 kev electrons (level 1; occurs 40% of the time) 50 years (after spin-up) = 50-member ensemble
28 WACCM simulation similar to MIPAS ~15 ppbv 70-90º S Latitude Case 3 (realistic simulation of 2003 geomagnetic activity) ~35 ppbv But WACCM underestimates EPP-NO x by about a factor of 2. MIPAS Funke et al., 2005
29 Change in NO x due to EPP: Annual Averages Aurora Effect Case 2 minus Case 1 MEE Effect Case 3 minus Case 2 Latitude Latitude Regions without cross-hatching significant at 95% level
30 Change in NO x and O 3 due to EPP Annual Averages: Aurora + MEE (Case 3 minus Case 1) NO x Ozone HO x NO x Latitude Latitude Regions without cross-hatching significant at 95% level
31 Auroral Effect Time Series (Case 2 minus Case 1)
32 Monthly average ozone depletion of up to 15% at high southern latitudes, km Geopotential Height (km) ΔO 3 (%) ΔO 3 Corresponds to catalytic NO x destruction
33 Sep Oct NO 2 (ppbv) Approximate Altitude (km) Randall et al., 1998 Ozone (ppmv) POAM Data WACCM
34 Up to 2 K monthly average temperature changes due to Aurora + MEE. Are these changes consistent with ozone? O 3 Is heating due to less radiative cooling by O3 in polar night upper stratosphere? Geopotential Height (km) ΔT (K)
35 Altitude (km) Latitude Are temperature effects valid? Still trying to understand statistical significance: Statistically significant differences found between two sets of 80- member ensembles, both with same forcing.
36 Summary of WACCM Model Results Free-running WACCM-EEP compares well qualitatively to observations for typical (i.e., low) EEP conditions Clear descent of EPP-NO x Corresponding ozone depletion Descending NO x underestimated by factor of ~2 even for standard meteorological conditions Concerns about T statistics in polar stratosphere Specified SSTs, so cannot probe tropospheric effects Never see elevated stratopause as in 2004, 2006, 2009
37 Pressure (hpa) Pressure (hpa) Figures courtesy of Dan Marsh, NCAR MLS SD-WACCM SD-WACCM vs. MLS Temperatures, 2006 If WACCM is nudged to Met assimilation (e.g., GEOS-5) temperature & winds in stratosphere, elevated stratopause is captured. Still must modify SD-WACCM for MEE.
38 Conclusions & Outstanding Questions EPP DE (Jackman talk) and IE significantly affect polar stratospheric NO y and Ozone. Temperature effects not yet quantified. WACCM underestimates EEP effects for baseline conditions. Free-running model does not simulate unusual meteorology of 2004, 2006, 2009.
39 Some Questions What is NO x really doing in the polar night? What are the detailed dynamical mechanisms that link EPP to atmospheric change? Does EPP affect surface level temperatures? Are coupling mechanisms from the surface to the MLT changing (more favorable for enhanced EPP- NO x descent)? Is there feedback between EPP and the coupling?
40 Thanks very much!
WACCM Studies at CU-Boulder
 WACCM Studies at CU-Boulder V.L. Harvey, C.E. Randall, O.B. Toon, E. Peck, S. Benze, M. Brakebusch, L. Holt, D. Wheeler, J. France, E. Wolf, Y. Zhu, X. Fang, C. Jackman, M. Mills, D. Marsh Most Topics
WACCM Studies at CU-Boulder V.L. Harvey, C.E. Randall, O.B. Toon, E. Peck, S. Benze, M. Brakebusch, L. Holt, D. Wheeler, J. France, E. Wolf, Y. Zhu, X. Fang, C. Jackman, M. Mills, D. Marsh Most Topics
An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) on the Mesosphere and Stratosphere
 An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) on the Mesosphere and Stratosphere Charles Jackman & Dean Pesnell NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD International Workshop
An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) on the Mesosphere and Stratosphere Charles Jackman & Dean Pesnell NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD International Workshop
EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations. Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland
 EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland A. Seppälä, HEPPA-SOLARIS Workshop, Boulder, Oct 0 So far... Energetic
EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland A. Seppälä, HEPPA-SOLARIS Workshop, Boulder, Oct 0 So far... Energetic
Coupling of the polar stratosphere and mesosphere during stratospheric sudden warmings - Relevance for solar-terrestrial coupling -
 Coupling of the polar stratosphere and mesosphere during stratospheric sudden warmings - Relevance for solar-terrestrial coupling - Yvan J. Orsolini NILU - Norwegian Institute for Air Research and Birkeland
Coupling of the polar stratosphere and mesosphere during stratospheric sudden warmings - Relevance for solar-terrestrial coupling - Yvan J. Orsolini NILU - Norwegian Institute for Air Research and Birkeland
Chemistry-Climate Models: What we have and what we need
 Chemistry-Climate Models: What we have and what we need Dan Marsh National Center for Atmospheric Research NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Outline Overview of processes in our current
Chemistry-Climate Models: What we have and what we need Dan Marsh National Center for Atmospheric Research NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Outline Overview of processes in our current
An Overview of the Impact. on the Stratosphere and Mesosphere
 An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation it ti on the Stratosphere and Mesosphere Charles Jackman NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD Aspen GCI Workshop 2010 Colorado June
An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation it ti on the Stratosphere and Mesosphere Charles Jackman NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD Aspen GCI Workshop 2010 Colorado June
Modeling polar ozone loss at the University of Colorado
 Modeling polar ozone loss at the University of Colorado CESM workshop Breckenridge, 06/21/2012 Matthias Brakebusch, Cora E. Randall, Douglas E. Kinnison, Simone Tilmes, Michelle L. Santee, Gloria L. Manney
Modeling polar ozone loss at the University of Colorado CESM workshop Breckenridge, 06/21/2012 Matthias Brakebusch, Cora E. Randall, Douglas E. Kinnison, Simone Tilmes, Michelle L. Santee, Gloria L. Manney
Atmospheric effects of energetic particle precipitation in the Arctic winter revisited
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016663, 2012 Atmospheric effects of energetic particle precipitation in the Arctic winter 1978 1979 revisited L. A. Holt, 1,2 C. E. Randall,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016663, 2012 Atmospheric effects of energetic particle precipitation in the Arctic winter 1978 1979 revisited L. A. Holt, 1,2 C. E. Randall,
Dynamical coupling between the middle atmosphere and lower thermosphere
 Dynamical coupling between the middle atmosphere and lower thermosphere Anne Smith, Dan Marsh, Nick Pedatella NCAR* Tomoko Matsuo CIRES/NOAA NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Model runs
Dynamical coupling between the middle atmosphere and lower thermosphere Anne Smith, Dan Marsh, Nick Pedatella NCAR* Tomoko Matsuo CIRES/NOAA NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Model runs
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure
 Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
Shape and Chemical Diagnostics of the Polar Vortices in WACCM
 Shape and Chemical Diagnostics of the Polar Vortices in WACCM V. Lynn Harvey, Cora Randall, Jeff France, Laura Holt, Katelynn Greer Richard Collins Dan Marsh, Doug Kinnison Laboratory for Atmospheric and
Shape and Chemical Diagnostics of the Polar Vortices in WACCM V. Lynn Harvey, Cora Randall, Jeff France, Laura Holt, Katelynn Greer Richard Collins Dan Marsh, Doug Kinnison Laboratory for Atmospheric and
Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM
 Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM Yvan J. Orsolini 1,V. Limpasuvan 2, J. Richter 3, O. K. Kvissel 4, F. Stordal 4,D. Marsh 3 1 Norwegian Institute
Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM Yvan J. Orsolini 1,V. Limpasuvan 2, J. Richter 3, O. K. Kvissel 4, F. Stordal 4,D. Marsh 3 1 Norwegian Institute
WACCM: The High-Top Model
 WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
ENERGETIC PARTICLE PRECIPITATION IN THE MESOSPHERE-LOWER THERMOSPHERE IN WACCM
 ENERGETIC PARTICLE PRECIPITATION IN THE MESOSPHERE-LOWER THERMOSPHERE IN WACCM Yvan J. ORSOLINI NILU - Norwegian Institute for Air Research, Birkeland Centre for Space Science, University of Bergen, Norway
ENERGETIC PARTICLE PRECIPITATION IN THE MESOSPHERE-LOWER THERMOSPHERE IN WACCM Yvan J. ORSOLINI NILU - Norwegian Institute for Air Research, Birkeland Centre for Space Science, University of Bergen, Norway
WACCM Studies at CU/LASP. V. Lynn Harvey, Cora Randall, Josh Pe6t, Doug Kinnison, and Dan Marsh
 WACCM Studies at CU/LASP V. Lynn Harvey, Cora Randall, Josh Pe6t, Doug Kinnison, and Dan Marsh Outline Introduc9on of the Direct vs. Indirect effect of EPP Randall et al. (2015) Ongoing Challenges in Simula9ng
WACCM Studies at CU/LASP V. Lynn Harvey, Cora Randall, Josh Pe6t, Doug Kinnison, and Dan Marsh Outline Introduc9on of the Direct vs. Indirect effect of EPP Randall et al. (2015) Ongoing Challenges in Simula9ng
WACCM: The High-Top Model
 WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
Energetic particle effects on the atmosphere and climate
 Energetic particle effects on the atmosphere and climate E. Rozanov Physikalisch-Meteorologisches Observatorium Davos and World Radiation Center (PMOD/WRC), Davos, Switzerland Institute for Atmospheric
Energetic particle effects on the atmosphere and climate E. Rozanov Physikalisch-Meteorologisches Observatorium Davos and World Radiation Center (PMOD/WRC), Davos, Switzerland Institute for Atmospheric
Stratospheric planetary wave reflection and its influence on the troposphere
 Stratospheric planetary wave reflection and its influence on the troposphere N. Harnik, Tel Aviv University J. Perlwitz, CIRES U. Colorado/NOAA ESRL T. A. Shaw, Columbia University, NY, NY, USA The following
Stratospheric planetary wave reflection and its influence on the troposphere N. Harnik, Tel Aviv University J. Perlwitz, CIRES U. Colorado/NOAA ESRL T. A. Shaw, Columbia University, NY, NY, USA The following
WACCM simulations of the mean circulation linking the mesosphere and thermosphere. Anne Smith, Rolando Garcia, Dan Marsh NCAR/ACD
 WACCM simulations of the mean circulation linking the mesosphere and thermosphere Anne Smith, Rolando Garcia, Dan Marsh NCAR/ACD trace species transport in the middle atmosphere wave driven mean circulation
WACCM simulations of the mean circulation linking the mesosphere and thermosphere Anne Smith, Rolando Garcia, Dan Marsh NCAR/ACD trace species transport in the middle atmosphere wave driven mean circulation
CESM2 (WACCM6): Stratospheric Evaluation
 CESM2 (WACCM6): Stratospheric Evaluation D. Kinnison, M. Mills, R. Garcia, D. Marsh, A. Gettelman, F. Vitt, S. Glanville, C. Bardeen, S. Tilmes, A. Smith, J-F. Lamarque, L. Emmons, A. Conley, J. Richter,
CESM2 (WACCM6): Stratospheric Evaluation D. Kinnison, M. Mills, R. Garcia, D. Marsh, A. Gettelman, F. Vitt, S. Glanville, C. Bardeen, S. Tilmes, A. Smith, J-F. Lamarque, L. Emmons, A. Conley, J. Richter,
SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole
 SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole R. Neely III, K. Smith2, D. Marsh,L. Polvani2 NCAR, 2Columbia Thanks to: Mike Mills, Francis Vitt and Sean Santos Motivation To design a stratosphere-resolving
SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole R. Neely III, K. Smith2, D. Marsh,L. Polvani2 NCAR, 2Columbia Thanks to: Mike Mills, Francis Vitt and Sean Santos Motivation To design a stratosphere-resolving
On recent interannual variability of the Arctic winter mesosphere: Implications for tracer descent
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09806, doi:10.1029/2007gl029293, 2007 On recent interannual variability of the Arctic winter mesosphere: Implications for tracer descent
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09806, doi:10.1029/2007gl029293, 2007 On recent interannual variability of the Arctic winter mesosphere: Implications for tracer descent
Analysis and hindcast experiments of the 2009 sudden stratosphere warming in WACCMX+DART
 Analysis and hindcast experiments of the 2009 sudden stratosphere warming in WACCMX+DART Nick Pedatella 1,2, Hanli Liu 1, Daniel Marsh 1,3, Jeffrey Anderson 4, and Kevin Raeder 4 1 High Altitude Observatory,
Analysis and hindcast experiments of the 2009 sudden stratosphere warming in WACCMX+DART Nick Pedatella 1,2, Hanli Liu 1, Daniel Marsh 1,3, Jeffrey Anderson 4, and Kevin Raeder 4 1 High Altitude Observatory,
Satellite measurements of nitric monoxide (NO) in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere
 Satellite measurements of nitric monoxide (NO) in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere S. Bender 1, M. Sinnhuber 1, T. von Clarmann 1, G. Stiller 1, B. Funke 2, M. López-Puertas 2, K. Pérot 3, J. Urban
Satellite measurements of nitric monoxide (NO) in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere S. Bender 1, M. Sinnhuber 1, T. von Clarmann 1, G. Stiller 1, B. Funke 2, M. López-Puertas 2, K. Pérot 3, J. Urban
Microwave Limb Sounder Observations of Polar Middle Atmosphere: Decadal and Inter-annual Variability
 Microwave Limb Sounder Observations of Polar Middle Atmosphere: Decadal and Inter-annual Variability Jae N. Lee 1, Dong L. Wu 2, Alexander ozone Ruzmaikin 1, Gloria J. Manney 1, and Sultan Hameed 4 1.
Microwave Limb Sounder Observations of Polar Middle Atmosphere: Decadal and Inter-annual Variability Jae N. Lee 1, Dong L. Wu 2, Alexander ozone Ruzmaikin 1, Gloria J. Manney 1, and Sultan Hameed 4 1.
2005 Bachelor of Arts, St. Cloud State University, summa cum laude. Mathematics
 Laura Holt Curriculum Vitæ Education 2005 Bachelor of Arts, St. Cloud State University, summa cum laude. Mathematics 2005 Bachelor of Science, St. Cloud State University, summa cum laude. Physics 2013
Laura Holt Curriculum Vitæ Education 2005 Bachelor of Arts, St. Cloud State University, summa cum laude. Mathematics 2005 Bachelor of Science, St. Cloud State University, summa cum laude. Physics 2013
Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~
 2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
Dynamical. regions during sudden stratospheric warming event (Case study of 2009 and 2013 event)
 Dynamical Coupling between high and low latitude regions during sudden stratospheric warming event (Case study of 2009 and 2013 event) Vinay Kumar 1,S. K. Dhaka 1,R. K. Choudhary 2,Shu-Peng Ho 3,M. Takahashi
Dynamical Coupling between high and low latitude regions during sudden stratospheric warming event (Case study of 2009 and 2013 event) Vinay Kumar 1,S. K. Dhaka 1,R. K. Choudhary 2,Shu-Peng Ho 3,M. Takahashi
Model simulations of stratospheric ozone loss caused by enhanced mesospheric NO x during Arctic Winter 2003/2004
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 5279 5293, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Model simulations of stratospheric
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 5279 5293, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Model simulations of stratospheric
Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of
 Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Future changes in Elevated Stratopause Events
 Future changes in Elevated Stratopause Events Janice Scheffler 1, Ulrike Langematz 1, Yvan J. Orsolini 2, Blanca Ayarzagüena 1 1 Institut für Meteorologie, Freie Universität Berlin 2 Norwegian Institute
Future changes in Elevated Stratopause Events Janice Scheffler 1, Ulrike Langematz 1, Yvan J. Orsolini 2, Blanca Ayarzagüena 1 1 Institut für Meteorologie, Freie Universität Berlin 2 Norwegian Institute
The Arctic polar troposphere, stratosphere and mesosphere during IPY
 The Arctic polar troposphere, stratosphere and mesosphere during IPY V. Lynn Harvey, R. Collins, D. Atkinson, B. Thurairajah, D. Wheeler km 70 60 stratopause 50 40 30 20 10 tropopause Outline Motivation:
The Arctic polar troposphere, stratosphere and mesosphere during IPY V. Lynn Harvey, R. Collins, D. Atkinson, B. Thurairajah, D. Wheeler km 70 60 stratopause 50 40 30 20 10 tropopause Outline Motivation:
Whole Atmosphere Simulation of Anthropogenic Climate Change
 Whole Atmosphere Simulation of Anthropogenic Climate Change Stan Solomon, Hanli Liu, Dan Marsh, Joe McInerney, Liying Qian, and Francis Vitt High Altitude Observatory National Center for Atmospheric Research
Whole Atmosphere Simulation of Anthropogenic Climate Change Stan Solomon, Hanli Liu, Dan Marsh, Joe McInerney, Liying Qian, and Francis Vitt High Altitude Observatory National Center for Atmospheric Research
The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode
 The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode Peter Watson 1, Lesley Gray 1,2 1. Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Oxford University 2. National
The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode Peter Watson 1, Lesley Gray 1,2 1. Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Oxford University 2. National
Nighttime secondary ozone layer during major stratospheric sudden warmings in specified-dynamics WACCM
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 8346 8358, doi:10.1002/jgrd.50651, 2013 Nighttime secondary ozone layer during major stratospheric sudden warmings in specified-dynamics WACCM Olga
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 8346 8358, doi:10.1002/jgrd.50651, 2013 Nighttime secondary ozone layer during major stratospheric sudden warmings in specified-dynamics WACCM Olga
The role of stratospheric processes in large-scale teleconnections
 The role of stratospheric processes in large-scale teleconnections Judith Perlwitz NOAA/Earth System Research Laboratory and CIRES/University of Colorado Outline Introduction Comparison of features of
The role of stratospheric processes in large-scale teleconnections Judith Perlwitz NOAA/Earth System Research Laboratory and CIRES/University of Colorado Outline Introduction Comparison of features of
Tidal Coupling in the Earth s Atmosphere. Maura Hagan NCAR High Altitude Observatory
 Tidal Coupling in the Earth s Atmosphere Maura Hagan NCAR High Altitude Observatory OUTLINE Motivation - Observations Tidal Nomenclature/Characteristics/Sources Results from the Global-Scale Wave Model
Tidal Coupling in the Earth s Atmosphere Maura Hagan NCAR High Altitude Observatory OUTLINE Motivation - Observations Tidal Nomenclature/Characteristics/Sources Results from the Global-Scale Wave Model
The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate
 The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate James Keeble, Peter Braesicke, Howard Roscoe and John Pyle James.keeble@atm.ch.cam.ac.uk
The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate James Keeble, Peter Braesicke, Howard Roscoe and John Pyle James.keeble@atm.ch.cam.ac.uk
Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier
 Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel (GEOMAR), Germany SPARC Brewer-Dobson Circulation Workshop, Grindelwald, June 2012 no
Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel (GEOMAR), Germany SPARC Brewer-Dobson Circulation Workshop, Grindelwald, June 2012 no
Overview and quality of global observations of middle atmospheric water vapour by the Odin satellite
 Overview and quality of global observations of middle atmospheric water vapour by the Odin satellite J. Urban*, D.P. Murtagh*, M. Ekström,, P. Eriksson*, C. Sanchez*, A. Jones,* S. Lossow **, Y. Kasai
Overview and quality of global observations of middle atmospheric water vapour by the Odin satellite J. Urban*, D.P. Murtagh*, M. Ekström,, P. Eriksson*, C. Sanchez*, A. Jones,* S. Lossow **, Y. Kasai
CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations
 CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations Dan Marsh, Mike Mills, Natalia Calvo, Marika Holland, Cécile Hannay WAWG meeting, Boulder, February 2011 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science
CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations Dan Marsh, Mike Mills, Natalia Calvo, Marika Holland, Cécile Hannay WAWG meeting, Boulder, February 2011 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science
Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) and Its Thermosphere/Ionosphere Extension (WACCM-X)
 Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) and Its Thermosphere/Ionosphere Extension (WACCM-X) WAWG Co-Chairs: Han-Li Liu, NCAR/HAO Lorenzo Polvani, Columbia University Scientific Objectives of WACCM
Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) and Its Thermosphere/Ionosphere Extension (WACCM-X) WAWG Co-Chairs: Han-Li Liu, NCAR/HAO Lorenzo Polvani, Columbia University Scientific Objectives of WACCM
Modulation of the Semiannual Oscillation Induced by Sudden Stratospheric Warming Events
 ISWA2016@ Tokyo, Japan 14/Oct/2016 1 Modulation of the Semiannual Oscillation Induced by Sudden Stratospheric Warming Events Toshihiko Hirooka¹, *Tsuyoshi Ohata¹, Nawo Eguchi² 1 DEPS, Kyushu Univ., Fukuoka,
ISWA2016@ Tokyo, Japan 14/Oct/2016 1 Modulation of the Semiannual Oscillation Induced by Sudden Stratospheric Warming Events Toshihiko Hirooka¹, *Tsuyoshi Ohata¹, Nawo Eguchi² 1 DEPS, Kyushu Univ., Fukuoka,
The 11 year solar cycle signal in transient simulations from the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016393, 2012 The 11 year solar cycle signal in transient simulations from the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model G. Chiodo, 1 N. Calvo,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016393, 2012 The 11 year solar cycle signal in transient simulations from the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model G. Chiodo, 1 N. Calvo,
The Earth s thermosphere and coupling to the Sun:
 The Earth s thermosphere and coupling to the Sun: Does the stratosphere and troposphere care? Alan D Aylward, George Millward, Ingo Muller-Wodarg and Matthew Harris Atmospheric Physics Laboratory, Dept
The Earth s thermosphere and coupling to the Sun: Does the stratosphere and troposphere care? Alan D Aylward, George Millward, Ingo Muller-Wodarg and Matthew Harris Atmospheric Physics Laboratory, Dept
CHAPTER 5. Low latitude temperature change in the stratosphere and mesosphere. relation to Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW)
 CHAPTER 5 Low latitude temperature change in the stratosphere and mesosphere relation to Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) 5.1 Introduction To understand middle atmosphere dynamics, the basic thermal
CHAPTER 5 Low latitude temperature change in the stratosphere and mesosphere relation to Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) 5.1 Introduction To understand middle atmosphere dynamics, the basic thermal
11-year solar cycle Mechanisms and Modelling in the Stratosphere and Troposphere
 11-year solar cycle Mechanisms and Modelling in the Stratosphere and Troposphere Lesley Gray University of Reading U.K. 1. Overview of Gray et al. 2010, Solar Influence on Climate, Rev. Geophys. (in press).
11-year solar cycle Mechanisms and Modelling in the Stratosphere and Troposphere Lesley Gray University of Reading U.K. 1. Overview of Gray et al. 2010, Solar Influence on Climate, Rev. Geophys. (in press).
Role of the QBO in modulating the influence of the 11 year solar cycle on the atmosphere using constant forcings
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd013020, 2010 Role of the QBO in modulating the influence of the 11 year solar cycle on the atmosphere using constant forcings Katja Matthes,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd013020, 2010 Role of the QBO in modulating the influence of the 11 year solar cycle on the atmosphere using constant forcings Katja Matthes,
Direct effects of particle precipitation and ion chemistry in the middle atmosphere
 Direct effects of particle precipitation and ion chemistry in the middle atmosphere P. T. Verronen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Earth Observation Helsinki, Finland Contents of presentation 1. Middle
Direct effects of particle precipitation and ion chemistry in the middle atmosphere P. T. Verronen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Earth Observation Helsinki, Finland Contents of presentation 1. Middle
Change in Occurrence Frequency of Stratospheric Sudden Warmings. with ENSO-like SST Forcing as Simulated WACCM
 Change in Occurrence Frequency of Stratospheric Sudden Warmings with ENSO-like SST Forcing as Simulated WACCM Masakazu Taguchi* and Dennis L. Hartmann Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of
Change in Occurrence Frequency of Stratospheric Sudden Warmings with ENSO-like SST Forcing as Simulated WACCM Masakazu Taguchi* and Dennis L. Hartmann Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of
Responses of mesosphere and lower thermosphere temperatures to gravity wave forcing during stratospheric sudden warming
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042351, 2010 Responses of mesosphere and lower thermosphere temperatures to gravity wave forcing during stratospheric
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042351, 2010 Responses of mesosphere and lower thermosphere temperatures to gravity wave forcing during stratospheric
Sensitivity of Regional and Global Climate to Solar Forcing
 Sun-Climate Focused Science Team Sensitivity of Regional and Global Climate to Solar Forcing Summary of Accomplishments Year 2 July, 2006 - July, 2007 Submitted 9 August 2007 Sun-Climate Focused Science
Sun-Climate Focused Science Team Sensitivity of Regional and Global Climate to Solar Forcing Summary of Accomplishments Year 2 July, 2006 - July, 2007 Submitted 9 August 2007 Sun-Climate Focused Science
The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate
 The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate Mark P. Baldwin Northwest Research Associates, USA SORCE, 27 October 2004 Overview Climatology of the
The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate Mark P. Baldwin Northwest Research Associates, USA SORCE, 27 October 2004 Overview Climatology of the
Variability and trends in stratospheric water vapor
 Variability and trends in stratospheric water vapor Bill Randel Atmospheric Chemistry Division NCAR, Boulder, CO Photo: Liz Moyer Climatology - Seasonal cycle (by far the largest variability) - summer
Variability and trends in stratospheric water vapor Bill Randel Atmospheric Chemistry Division NCAR, Boulder, CO Photo: Liz Moyer Climatology - Seasonal cycle (by far the largest variability) - summer
Stratospheric Predictability and the Arctic Polar-night Jet Oscillation
 Stratospheric Predictability and the Arctic Polar-night Jet Oscillation Peter Hitchcock1, Ted Shepherd2 University of Toronto Now at Cambridge 2Now at Reading 1 Gloria Manney JPL, NMT, Now at NWRA NAM
Stratospheric Predictability and the Arctic Polar-night Jet Oscillation Peter Hitchcock1, Ted Shepherd2 University of Toronto Now at Cambridge 2Now at Reading 1 Gloria Manney JPL, NMT, Now at NWRA NAM
A Simulation of the Separate Climate Effects of Middle-Atmospheric and Tropospheric CO 2 Doubling
 2352 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 A Simulation of the Separate Climate Effects of Middle-Atmospheric and Tropospheric CO 2 Doubling M. SIGMOND Department of Applied Physics, Eindhoven University of Technology
2352 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 A Simulation of the Separate Climate Effects of Middle-Atmospheric and Tropospheric CO 2 Doubling M. SIGMOND Department of Applied Physics, Eindhoven University of Technology
2014 Utah NASA Space Grant Consortium Symposium 1
 2014 Utah NASA Space Grant Consortium Symposium 1 Rayleigh Scatter Lidar Observations of the Midlatitude Mesosphere's Response to Sudden Stratospheric Warmings Leda Sox 1, Vincent B. Wickwar 1, Chad Fish
2014 Utah NASA Space Grant Consortium Symposium 1 Rayleigh Scatter Lidar Observations of the Midlatitude Mesosphere's Response to Sudden Stratospheric Warmings Leda Sox 1, Vincent B. Wickwar 1, Chad Fish
AGU Chapman Conference on The Role of the Stratosphere in Climate and Climate Change in Santorini, Greece, on 28th September, 2007
 AGU Chapman Conference on The Role of the Stratosphere in Climate and Climate Change in Santorini, Greece, on 28th September, 2007 Parameter Sweep Experiments on the Remote Influences of the Equatorial
AGU Chapman Conference on The Role of the Stratosphere in Climate and Climate Change in Santorini, Greece, on 28th September, 2007 Parameter Sweep Experiments on the Remote Influences of the Equatorial
Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040419, 2009 Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040419, 2009 Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
Observed effects of solar proton events and sudden stratospheric warmings on odd nitrogen and ozone in the polar middle atmosphere
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 6837 6848, doi:1.12/jgrd.486, 13 Observed effects of solar proton events and sudden stratospheric warmings on odd nitrogen and ozone in the polar
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 6837 6848, doi:1.12/jgrd.486, 13 Observed effects of solar proton events and sudden stratospheric warmings on odd nitrogen and ozone in the polar
WACCM X Updates. CESM Workshop, June, 2017, Boulder, Colorado
 WACCM X Updates Han Li Liu and WACCM X Team NCAR/HAO: Ben Foster, Jing Liu, Gang Lu, Astrid Maute, Joe McInerney, Nick Pedatella, Liying Qian, Art Richmond, Stan Solomon, Wenbin Wang NCAR/ACOM: Chuck Bardeen,
WACCM X Updates Han Li Liu and WACCM X Team NCAR/HAO: Ben Foster, Jing Liu, Gang Lu, Astrid Maute, Joe McInerney, Nick Pedatella, Liying Qian, Art Richmond, Stan Solomon, Wenbin Wang NCAR/ACOM: Chuck Bardeen,
Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial oscillation
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012542, 2010 Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012542, 2010 Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial
Chihoko Yamashita 1,2, Han-Li Liu 1
 1 1 Gravity Waves and the High-Resolution Modeling (Using ECMWF-T799) Chihoko Yamashita 1,2, Han-Li Liu 1 1. NCAR/HAO 2. University of Colorado at Boulder AWMG/WAWG Workshop 2012-02-01 Motivations Gravity
1 1 Gravity Waves and the High-Resolution Modeling (Using ECMWF-T799) Chihoko Yamashita 1,2, Han-Li Liu 1 1. NCAR/HAO 2. University of Colorado at Boulder AWMG/WAWG Workshop 2012-02-01 Motivations Gravity
Predictability of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in sub-seasonal forecast models
 Predictability of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in sub-seasonal forecast models Alexey Karpechko Finnish Meteorological Institute with contributions from A. Charlton-Perez, N. Tyrrell, M. Balmaseda, F.
Predictability of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in sub-seasonal forecast models Alexey Karpechko Finnish Meteorological Institute with contributions from A. Charlton-Perez, N. Tyrrell, M. Balmaseda, F.
An Examination of Anomalously Low Column Ozone in the Southern Hemisphere Midlatitudes During 1997
 San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Eugene C. Cordero April, 2002 An Examination of Anomalously Low Column Ozone in the Southern Hemisphere Midlatitudes During 1997 Eugene C. Cordero, San
San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Eugene C. Cordero April, 2002 An Examination of Anomalously Low Column Ozone in the Southern Hemisphere Midlatitudes During 1997 Eugene C. Cordero, San
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115, D12305, doi: /2009jd013501, 2010
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd013501, 2010 Descent from the polar mesosphere and anomalously high stratopause observed in 8 years of water vapor
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd013501, 2010 Descent from the polar mesosphere and anomalously high stratopause observed in 8 years of water vapor
Stratosphere Troposphere Coupling in a Relatively Simple AGCM: Impact of the Seasonal Cycle
 1 NOVEMBER 2006 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 5721 Stratosphere Troposphere Coupling in a Relatively Simple AGCM: Impact of the Seasonal Cycle PAUL J. KUSHNER Department of Physics, University
1 NOVEMBER 2006 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 5721 Stratosphere Troposphere Coupling in a Relatively Simple AGCM: Impact of the Seasonal Cycle PAUL J. KUSHNER Department of Physics, University
Structure of Atmosphere. (University of Washington ESS, 2015)
 Structure of Atmosphere (University of Washington ESS, 2015) Motivation and Current State of Knowledge Spatial and temporal variations in ionospheric parameters cannot be explained by solar forcing Solid
Structure of Atmosphere (University of Washington ESS, 2015) Motivation and Current State of Knowledge Spatial and temporal variations in ionospheric parameters cannot be explained by solar forcing Solid
HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE. V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva
 HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE INTRODUCTION V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva Kazan State University, Kazan, Russia When constructing empirical
HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE INTRODUCTION V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva Kazan State University, Kazan, Russia When constructing empirical
Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) ozone profile data record characteristics, quality and applications
 Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) ozone profile data record characteristics, quality and applications A presentation for the 2016 meeting of the Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (COES) Atmospheric
Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) ozone profile data record characteristics, quality and applications A presentation for the 2016 meeting of the Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (COES) Atmospheric
Assessing and understanding the role of stratospheric changes on decadal climate prediction
 MiKlip II-Status seminar, Berlin, 1-3 March 2017 Assessing and understanding the role of stratospheric changes on decadal climate prediction Martin Dameris Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, Institut
MiKlip II-Status seminar, Berlin, 1-3 March 2017 Assessing and understanding the role of stratospheric changes on decadal climate prediction Martin Dameris Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, Institut
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Special blog on winter 2016/2017 retrospective can be found here -
 March 4, 2019 Special blog on winter 2016/2017 retrospective can be found here - http://www.aer.com/winter2017 Special blog on winter 2015/2016 retrospective can be found here - http://www.aer.com/winter2016
March 4, 2019 Special blog on winter 2016/2017 retrospective can be found here - http://www.aer.com/winter2017 Special blog on winter 2015/2016 retrospective can be found here - http://www.aer.com/winter2016
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming?
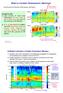 What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3136 Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades Jiankai Zhang 1, Wenshou Tian 1 *, Martyn P. Chipperfield
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3136 Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades Jiankai Zhang 1, Wenshou Tian 1 *, Martyn P. Chipperfield
A Study of Polar Mesospheric Cloud Structures and the Environment in Which These Structures Form
 A Study of Polar Mesospheric Cloud Structures and the Environment in Which These Structures Form Brentha Thurairajah Bradley Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg,
A Study of Polar Mesospheric Cloud Structures and the Environment in Which These Structures Form Brentha Thurairajah Bradley Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg,
High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
The solar cycle effect in the MLT region. Simulations with HAMMONIA
 The solar cycle effect in the MLT region Simulations with HAMMONIA Hauke Schmidt Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany Variability of solar UV irradiance as given by UARS / SOLSTICE (Maximum:
The solar cycle effect in the MLT region Simulations with HAMMONIA Hauke Schmidt Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany Variability of solar UV irradiance as given by UARS / SOLSTICE (Maximum:
Zonal-mean global teleconnection from 15 to 110 km derived from SABER and WACCM
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016750, 2012 Zonal-mean global teleconnection from 15 to 110 km derived from SABER and WACCM Bo Tan, 1 Xinzhao Chu, 1 Han-Li Liu, 2 Chihoko
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016750, 2012 Zonal-mean global teleconnection from 15 to 110 km derived from SABER and WACCM Bo Tan, 1 Xinzhao Chu, 1 Han-Li Liu, 2 Chihoko
Imperial College London
 Solar Influence on Stratosphere-Troposphere Dynamical Coupling Isla Simpson, Joanna D. Haigh, Space and Atmospheric Physics, Imperial College London Mike Blackburn, Department of Meteorology, University
Solar Influence on Stratosphere-Troposphere Dynamical Coupling Isla Simpson, Joanna D. Haigh, Space and Atmospheric Physics, Imperial College London Mike Blackburn, Department of Meteorology, University
Non-vertical propagation of gravity waves generated over the monsoon region and its effect on polar mesospheric clouds
 Non-vertical propagation of gravity waves generated over the monsoon region and its effect on polar mesospheric clouds Brentha Thurairajah 1 David Siskind 2 Scott Bailey 1 Justin Carstens 1 1 Space@VT,
Non-vertical propagation of gravity waves generated over the monsoon region and its effect on polar mesospheric clouds Brentha Thurairajah 1 David Siskind 2 Scott Bailey 1 Justin Carstens 1 1 Space@VT,
METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC TELECONNECTIONS: FROM CAUSAL ATTRIBUTION TO STORYLINES OF CIRCULATION CHANGE
 METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC TELECONNECTIONS: FROM CAUSAL ATTRIBUTION TO STORYLINES OF CIRCULATION CHANGE Ted Shepherd Grantham Chair of Climate Science Stratosphere-troposphere coupling: stratospheric polar
METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC TELECONNECTIONS: FROM CAUSAL ATTRIBUTION TO STORYLINES OF CIRCULATION CHANGE Ted Shepherd Grantham Chair of Climate Science Stratosphere-troposphere coupling: stratospheric polar
Influence of Sudden Stratosphere Warmings on the Ionosphere and Thermosphere
 Influence of Sudden Stratosphere Warmings on the Ionosphere and Thermosphere Nick Pedatella 1,2 1 High Altitude Observatory, National Center for Atmospheric Research 2 COSMIC Program Office, University
Influence of Sudden Stratosphere Warmings on the Ionosphere and Thermosphere Nick Pedatella 1,2 1 High Altitude Observatory, National Center for Atmospheric Research 2 COSMIC Program Office, University
Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion
 GCOE-ARS : November 18, 2010 Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion YODEN Shigeo Department of Geophysics, Kyoto University 1. Stratospheric Ozone and History of the Earth 2. Observations
GCOE-ARS : November 18, 2010 Global Warming and Climate Change Part I: Ozone Depletion YODEN Shigeo Department of Geophysics, Kyoto University 1. Stratospheric Ozone and History of the Earth 2. Observations
SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C. Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto
 SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto Mark Baldwin, Neil Butchart, Norm McFarlane, Alan O Neill, Judith Perlwitz,
SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto Mark Baldwin, Neil Butchart, Norm McFarlane, Alan O Neill, Judith Perlwitz,
CESM: A platform for atmospheric prediction from the surface to geospace
 CESM: A platform for atmospheric prediction from the surface to geospace Dan Marsh, NCAR & University of Leeds Whole Atmosphere Modelling Workshop Deimos, Tres Cantos, Spain 13-15 June, 2018 Outline NCAR
CESM: A platform for atmospheric prediction from the surface to geospace Dan Marsh, NCAR & University of Leeds Whole Atmosphere Modelling Workshop Deimos, Tres Cantos, Spain 13-15 June, 2018 Outline NCAR
Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude
 Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude weather patterns Response of the wintertime atmospheric circulation to current and projected Arctic sea ice decline Gudrun Magnusdottir and Yannick
Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude weather patterns Response of the wintertime atmospheric circulation to current and projected Arctic sea ice decline Gudrun Magnusdottir and Yannick
GPC Exeter forecast for winter Crown copyright Met Office
 GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
Empirical model of nitric oxide in the lower thermosphere
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003ja010199, 2004 Empirical model of nitric oxide in the lower thermosphere D. R. Marsh and S. C. Solomon National Center for Atmospheric Research,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003ja010199, 2004 Empirical model of nitric oxide in the lower thermosphere D. R. Marsh and S. C. Solomon National Center for Atmospheric Research,
Interannual Variations of the General Circulation and Polar Stratospheric Ozone Losses in a General Circulation Model
 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. 80, No. 4B, pp. 877--895, 2002 877 Interannual Variations of the General Circulation and Polar Stratospheric Ozone Losses in a General Circulation Model
Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. 80, No. 4B, pp. 877--895, 2002 877 Interannual Variations of the General Circulation and Polar Stratospheric Ozone Losses in a General Circulation Model
Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR
 Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR Multivariate ENSO Index + QBO shear index based on Singapore wind U50-U25 CESM Chemistry WG Meeting Boulder, CO February 10,
Comparing QBO and ENSO impacts on stratospheric transport in WACCM-SD and -FR Multivariate ENSO Index + QBO shear index based on Singapore wind U50-U25 CESM Chemistry WG Meeting Boulder, CO February 10,
ESA Ozone Climate Change Initiative: combined use of satellite ozone profile measurements
 ESA Ozone Climate Change Initiative: combined use of satellite ozone profile measurements V.F. Sofieva, E. Kyrölä, J. Tamminen, S. Tukiainen, J. Hakkarainen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Finland G.
ESA Ozone Climate Change Initiative: combined use of satellite ozone profile measurements V.F. Sofieva, E. Kyrölä, J. Tamminen, S. Tukiainen, J. Hakkarainen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Finland G.
The Scientific Value of Stratospheric Wind Measurements
 Working Group on Space-based Lidar Winds, Monterey, 2008 The Scientific Value of Stratospheric Wind Measurements Ted Shepherd Department of Physics University of Toronto The distribution of ozone (important
Working Group on Space-based Lidar Winds, Monterey, 2008 The Scientific Value of Stratospheric Wind Measurements Ted Shepherd Department of Physics University of Toronto The distribution of ozone (important
Substorm-induced energetic electron precipitation: Impact on atmospheric chemistry
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1002/, Substorm-induced energetic electron precipitation: Impact on atmospheric chemistry A. Seppälä 1, M. A. Clilverd 2, M. J. Beharrell 3, C. J Rodger
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1002/, Substorm-induced energetic electron precipitation: Impact on atmospheric chemistry A. Seppälä 1, M. A. Clilverd 2, M. J. Beharrell 3, C. J Rodger
Dynamical Impacts of Antarctic Stratospheric Ozone Depletion on the Extratropical Circulation of the Southern Hemisphere
 Dynamical Impacts of Antarctic Stratospheric Ozone Depletion on the Extratropical Circulation of the Southern Hemisphere Kevin M. Grise David W.J. Thompson Department of Atmospheric Science Colorado State
Dynamical Impacts of Antarctic Stratospheric Ozone Depletion on the Extratropical Circulation of the Southern Hemisphere Kevin M. Grise David W.J. Thompson Department of Atmospheric Science Colorado State
Large increase of NO 2 in the north polar mesosphere in January February 2004: Evidence of a dynamical origin from GOMOS/ ENVISAT and SABER/TIMED data
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L03810, doi:10.1029/2006gl027628, 2007 Large increase of NO 2 in the north polar mesosphere in January February 2004: Evidence of a dynamical origin from GOMOS/ ENVISAT
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L03810, doi:10.1029/2006gl027628, 2007 Large increase of NO 2 in the north polar mesosphere in January February 2004: Evidence of a dynamical origin from GOMOS/ ENVISAT
Thermospheric Winds. Astrid Maute. High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Science (NCAR) Boulder CO, USA
 Thermospheric Winds Astrid Maute High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Science (NCAR) Boulder CO, USA High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Research
Thermospheric Winds Astrid Maute High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Science (NCAR) Boulder CO, USA High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Research
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
WACCM-X Simulations of Climate Change in the Upper Atmosphere Stan Solomon, Hanli Liu, Dan Marsh, Joe McInerney, Liying Qian, and Francis Vitt
 WACCM-X Simulations of Climate Change in the Upper Atmosphere Stan Solomon, Hanli Liu, Dan Marsh, Joe McInerney, Liying Qian, and Francis Vitt High Altitude Observatory National Center for Atmospheric
WACCM-X Simulations of Climate Change in the Upper Atmosphere Stan Solomon, Hanli Liu, Dan Marsh, Joe McInerney, Liying Qian, and Francis Vitt High Altitude Observatory National Center for Atmospheric
Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events
 Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events Lantao Sun Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Walter A. Robinson Division of Atmospheric
Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events Lantao Sun Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Walter A. Robinson Division of Atmospheric
