Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Breckenridge, Colorado, 2016
|
|
|
- Arron Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COUPLING OPERATIONAL SNOWCOVER SIMULATIONS WITH AVALANCHE DYNAMICS CALCU- LATIONS TO ASSESS AVALANCHE DANGER IN HIGH ALTITUDE MINING OPERATIONS Vera Valero, César 1 *, Wever, Nander 2 and Bartelt, Perry 1 1 SLF Institute for snow and avalanche research WSL, Davos 2 EPFL, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Laussanne ABSTRACT: The Codelco Andina copper mine is operating in high alpine terrain where avalanches pose a threat to the operations and the infrastructure. A dedicated avalanche warning service is responsible for opening and closing the heavily used access road. To support their decision making process, a system is developed in which numerical snowpack modelling is coupled to avalanche dynamics simulations to assess avalanche risks. The primary system output is an assessment of snow cover stability as well as avalanche size and runout. Based on measurements from automatic weather stations, the temporal evolution of the snowpack is simulated using the SNOWPACK model. This model is run within the spatially explicit Alpine3D tool, taking into account the radiation budget in complex terrain. The SNOWPACK model provides snowpack stability estimates and, based on the weak layer depth, potential fracture depths and snowpack properties of the slab. For example, for wet snow avalanches, which is the major threat in the mine, the simulations indicate if water is accumulating at layer boundaries inside the snowpack. The model accumulation depth defines the potential fracture height. This information is displayed on maps, but is also directly used to provide the initial conditions for the avalanche dynamics model RAMMS for predetermined avalanche paths. The properties of the entrained snow, which we show is also an important factor to determine avalanche runout, are also provided by the Alpine3D simulations. The system in which real-time snow cover simulations are combined with avalanche dynamics simulations is a novel approach to provide avalanche forecasters with a new source of objective information to aid the avalanche risk assessment KEYWORDS: numeric modeling, avalanche dynamics, snowcover modeling, risk assessing 1. INTRODUCTION Mining activities are often located in high mountain terrain where snow avalanches can disrupt operations by blocking important transportation routes and access roads. Mine operations can be severely affected by the road closures. Since severe financial losses result because of road closures, the mine aims to minimize closure times with a tolerable risk. Often the opening-closing decisions are taken based on unreliable, scarce, and haphazard pieces of information. In this work we use avalanche dynamics simulations on selected avalanche paths in order to assess avalanche risk. The novelty in this approach is that the avalanche dynamic model (RAMMS, see Christen, 2010 and Vera, 2015) is driven by modeled snowcover conditions and not by calibrated input parameters chosen by an avalanche expert. Initial and boundary conditions, such as release heights and entrainment layers, are calculated from snowcover simulations. The goal is to test the application of a model chain which can assess the current avalanche run out distance and inundation area in a local region using current meteorological data. During the last five winter seasons, the WSL Snow and Avalanche Research Institute SLF together with the Codelco Andina copper mine (Chile) have developed an avalanche risk assessment tool that consists of a chain of modelling systems that include automatic weather stations, the snowcover models SNOWPACK and Alpine3D and avalanche dynamics model RAMMS. The model chain uses the measured meteorological data from a network of automatic weather stations. The current snow and meterological data is used to force point snowcover simulations with SNOWPACK (See Bartelt 2002, and Lehning, 2002) run within the spatially explicit Alpine3D, (Lehning, 2006). Once the snowcover conditions are modeled, the model chain writes the initial and boundary conditions for the avalanche dynamics model on 20 selected avalanche paths which typically endanger the road operation. * Corresponding author address: Vera Valero, Cesar 1 SLF Institute for snow and avalanche research WSL, Davos, cesar.vera@slf.ch 159
2 Fig.1. Example of a liquid water content calculation performed with Alpine3D projected on a 3D image from the valley. White areas indicate dry snow, colors indicate wet snow, where the color shows the maximum liquid water content somewhere in the snowpack. The outputs of the model chain can be divided into two results: (a) the snowcover modeling provides the winter operation team with a detailed information regarding snowcover stratigraphy, snow density, snow temperature and liquid water content along the entire valley. This information is very valuable in itself to assess the avalanche situation along the road (see Fig.1) The second result (b) the model chains delivers a set of avalanche simulations with the runouts and inundation areas expected in each selected avalanche path given the current snow conditions (see Fig.2). The Codelco Andina mine operates a network of automatic weather stations situated at the valley bottom at 2770 m.a.s.l., east facing at 3550 m.a.s.l., west facing at 3720 m.a.s.l and south facing at 4200 m.a.s.l. The stations deliver air temperature, atmospheric pressure, relative humidity, incoming and reflected shortwave radiation, snow height, snow surface temperature and wind measurements. The meteorological and snow information is used to drive the snowcover models SNOWPACK (See Bartelt 2002 and Lehning, 2002) distributed spatially through Alpine3D (see Lehning, 2006), see Fig.1. SNOWPACK results have been tested along the valley road by direct comparisons with traditional snow pits during the last five winter seasons, see Vera (2016). Once the snowcover conditions along the road are known the input conditions for the avalanche dynamics model RAMMS (See Christen, 2010) are written. The initial and boundary conditions for RAMMS extended simulations include fracture depth, average snow density, temperature and liquid water content in both the avalanche release and entrainment zones (see Vera, 2015 and Vera, 2016). Fig.2 3D Image of the dynamic hazard map obtained in one calculation step from the model chain. 2. MODEL CHAIN, INITIAL AND BOUNDARY CONDITIONS Fig 3. The model chain: automatic weather stations provide input into the snowcover models which in turn define the initial and boundary conditions of the avalanche dynamics simulations. The task is not trivial and requires both first hand knowledge of the local terrain and hands-on experience with the avalanche model RAMMS extended. 160
3 Historically the Cajon del rio Blanco Valley has two main avalanche cycles: dry avalanche activity during snow storms and wet avalanche cycle during the warm periods after new snow. This pattern can occur several times in a single winter season. In case of dry snow the system uses the new snow along the avalanche path for both the fracture and erosion depths in the avalanche dynamics calculations. This criteria is based on 40 year experience of the operations team. The steepness of the avalanche paths (together with the complete absence of human activity on the slopes) makes spontaneous avalanches the most frequent case for dry snow avalanches. In the case of wet snow avalanche we use the depth of the maximum water ponding at layer interfaces as described in Wever, 2016 and Vera, The snowcover simulations indicate that water accumulates at microstructural layer transitions inside the snowpack (see Fig.1). The depth at which this occurs is used to define the potential fracture depth. This method has been used for the last four winters providing satisfactory results for both avalanche occurrence prediction and avalanche size estimation (see Wever, 2016). These two criteria provide us the fracture depth and the erosion depth along the avalanche path for both dry and wet cases. The slab properties are defined by the average snow density, temperature and water content which extends from the maximum water accumulation point up to the snow cover surface. Average densities and temperature are used in the case of dry snow. These are obtained from the Alpine3D simulations at the point where the slab releases. The second input necessary to perform the avalanche dynamics simulations is the release area. The typical avalanche path in the Cajón del rio Blanco valley are steep gullies with define starting areas, which make this task tractable. For every avalanche path three different release areas are defined. Those releases are chosen from the experience and mine records from the last 40 years for each avalanche path. The final scenario chosen for each case is defined using three classes small, medium and big. The definition of each class is defined by historical records and experience. Finally, to perform an extended RAMMS simulation, several flow parameters must be defined. These parameters depend on the avalanche path steepness, roughness and torsion. However, once enough experience for each avalanche path is accumulated, these parameters are known and do not vary with different snow conditions (see Vera 2016). 3. RESULTS The outputs from the model chain are twofold: (a) the snowcover information obtained from the Alpine3D simulations in the whole valley (See Fig. 1). These simulations calculate the snow stratigraphy, snow temperature, density and snow water content in the study area. This information itself is valuable since the operation crew obtains an accurate description of the current snowcover situation for the whole valley. This information is used mainly by the winter operation team to estimate the probability of avalanche occurrence (b) Secondly, the model chain automatically initiates 20 avalanche simulations in the selected avalanche paths (see Fig. 2). The calculations can be visualized in 3D images via Google Earth or in a regular 2D projection plotting maximum flow height or avalanche height. These results (a) and (b) combine to create a socalled dynamic avalanche hazard map. The model chain recalculates every time a new meteorological measurement is available. In the following section we show two different real case studies where the model performed accurately with two different snow conditions: (a) Wet snow after a long dry warm period Figs. 4 and 5 and (b) dry snow after a storm Figs 7, 8 and Comparison real case avalanches with output simulations: wet case avalanche MO The first case study occurred on the 15 th of October 2013 on the avalanche path denoted MO-4. The MO-4 releases on a steep bowl at 3700 m.a.s.l. and is channelized into a steep gully (see Fig.4). The MO-4 avalanche released as a wet snow avalanche after a warm period without precipitation and any avalanche activity in the previous 32 days. The Alpine3D simulation calculated water percolating deep in the snowcover, see Fig.6. The calculation shows the high water ponding occurred particularly on the 15 th of October exactly when the avalanche released. This result was used to calculate the average slab properties in the input values for the RAMMS simulation (as done in Vera, 2016). The simulation matches the observed run out distance, inundation area and 161
4 the avalanche deposits patterns. The model chain was likewise able to reproduce the main features observed from the real avalanche, see Figs. 4 and 5 reached size 3-4 in the Canadian avalanche size scale. The winter operation team could operate a drone along a section of the road obtaining an accurate estimation of the run out distances and area covered by the avalanche deposits in this part of the road after the storm. Between the km 21 and km 25 of the road the drone recorded four avalanche events (see Fig.7). Three of them were simulated during the storm as part of the model output. The run out distances and area covered by deposits measured with the drone matched obtained with the ones obtained with the model chain see Figs. 7, 8 and 9. Fig.4. Avalanche path MO-4 released as wet avalanche after 32 days of stable weather and no avalanche activity damaging mining machinery 3.2 Comparison real case avalanches with output simulations: dry case storm The second case study concerns the two days snow storm occurred between the 7 th and the 8 th of August During these two days, more than 2 meters of new snow fell accompanied by north westerly winds. Those storms are typical in the central Andes where this pattern can occur several times per winter season. In this case, 16 avalanches were recorded hitting the road. All of them Fig. 5 Avalanche runout calculation performed by the model for the MO-4 avalanche path. Inset depicts the calculated deposition field of the avalanche. Note the location of the avalanche arm is well represented 162
5 Fig.6. Snow height (black solid line) and depth of maximum liquid water content, colored by the volumetric liquid water content at this depth (%) in the release area of the MO-4 avalanche, as calculated by Alpine3D. The avalanche occurred on October DISCUSSION The results obtained after two years of operational use are encouraging. We stress, however, that a pre-operational testing and calibration phase is required. This phase is ideally performed using data from representative winters. The mine is presently using the system as a reliable source of information which is directly tied into operational decision making process. The first two layers of the system, automatic weather stations and numerical snowpack modelling, are used to gather information about the current avalanche risk situation. The runout calculations also provide the decision makers with qualitative information concerning the extremity of avalanche runout. However, several research gaps remain and speciall situations can occur where the system must be improved and tested. The operation in the Cajon del rio blanco valley has an special topography and terrain characteristics that constrain the snowcover evolution and avalanche flow regime. Firstly the model chain has been tested in a valley where: The avalanche paths are mostly confined gullies with clearly defined release areas and runouts. The system is used at a local scale with uniform meteorological conditions. Warming periods with well-known wind patterns between storms are also similar. Accurate digital elevation model (DEM) and meteorological measurements are available for the entire valley. Fig.7 Comparison of the output delivered by the model chain and an aerial photography performed by a drone one day after the storm. Close up from the avalanches in Figures 8 and 9. Fig.8. Avalanche runout photography and avalanche simulation calculated for that day with the system. Fig.9. Avalanche runout photography and avalanche simulation calculated for that day with the system 163
6 No human triggering. In the entire mine working area, recreational activities are strictly forbidden and no work is performed outside the mining zones. The system was additionally tested and calibrated using four years of both meteorological and event experience. Mine records, however, document 40 years of road operation. With this information it is possible to calibrate the avalanche dynamics model which depends on the snow conditions and the avalanche paths (see Vera, 2016). The tool is used on a regular basis by the winter operation crew and is now one piece of the daily information used to make decisions on how the industrial road is to be operated. 5. CONCLUSIONS A chain of automatic weather stations coupled with numerical models has been used in an operational mode to assess the current avalanche danger in a specific, local environment. The model chain was able to provide accurate run out distance calculations and area covered by deposits using the modelled current snow conditions. The system has demonstrated that with certain prerequisites it is possible to assess the current avalanche risk in a local region. However, research gaps remain, such as the automatic specification of release areas and selection of erosion depths. The initial results are encouraging, but will always require calibration and experience of local experts. Schweizer, J.; Bellaire, S.; Fierz, C; Lehning, M & Pielmeier, C. Evaluating and improving the stability predictions of the snow cover model SNOWPACK. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol., 2006, 46, Vera Valero, C.; Jones, Y. B. W. & Bartelt, P. Release Temperature, Snowcover Entrainment and the Thermal Flow Regime of Snow Avalanches Journal of Glaciology, 2015, 61(225), Vera Valero, C.; Wever, N.; Bühler, Y.; Stoffel, L.; Margreth, S. & Bartelt, P. Modelling wet snow avalanche runout to assess road safety at a high-altitude mine in the central Andes Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Discussions, 2016, 2016, 1-41 Wever, N.; Fierz, C.; Mitterer, C.; Hirashima, H. & Lehning, M. Solving Richards Equation for snow improves snowpack meltwater runoff estimations in detailed multi-layer snowpack model Cryosphere, 2014, 8, Wever, N.; Vera Valero, C. & Fierz, C. Assessing wet snow avalanche activity using detailed physics based snowpack simulations Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43, REFERENCES Bartelt, P. & Lehning, M. A physical SNOWPACK model for the Swiss avalanche warning Part I: Numerical model Cold Reg. Sci. Technol., 2002, 35, Christen, M.; Kowalski, J. & Bartelt, P. RAMMS: Numerical simulation of dense snow avalanches in three-dimensional terrain. X, doi: /j.coldregions Cold Reg. Sci. Technol., 2010, 63, 1-14 Lehning, M.; Bartelt, P.; Brown, B. & Fierz, C. A physical SNOWPACK model for the Swiss avalanche warning Part III: Meteorological forcing, thin layer formation and evaluation Cold Reg. Sci. Technol., 2002b, 35, Lehning, M.; Völksch, I.; Gustafsson, D.; Nguyen, T. A.; Stähli, M. & Zappa, M. ALPINE3D: a detailed model of mountain surface processes and its application to snow hydrology Hydrol. Proc., John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2006, 20,
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 EVALUATING THE POTENTIAL OF USING SNOWPACK AND ALPINE3D SIMULATIONS IN THREE CANADIAN MOUNTAIN CLIMATES Côté K., Madore, J-B. and Langlois, A. Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada ABSTRACT:
EVALUATING THE POTENTIAL OF USING SNOWPACK AND ALPINE3D SIMULATIONS IN THREE CANADIAN MOUNTAIN CLIMATES Côté K., Madore, J-B. and Langlois, A. Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada ABSTRACT:
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Breckenridge, Colorado, 2016
 COMBINING SNOWPACK MODELS AND OBSERVATIONS FOR BETTER AVALANCHE DANGER ASSESSMENTS Fabiano Monti 1,2 *, Christoph Mitterer 1, Walter Steinkogler 1, Mathias Bavay 3, Andrea Pozzi 2 2 1 ALPsolut, Livigno,
COMBINING SNOWPACK MODELS AND OBSERVATIONS FOR BETTER AVALANCHE DANGER ASSESSMENTS Fabiano Monti 1,2 *, Christoph Mitterer 1, Walter Steinkogler 1, Mathias Bavay 3, Andrea Pozzi 2 2 1 ALPsolut, Livigno,
An operational supporting tool for assessing wet-snow avalanche danger
 An operational supporting tool for assessing wet-snow avalanche danger Christoph Mitterer*, Frank Techel, Charles Fierz and Jürg Schweizer WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland
An operational supporting tool for assessing wet-snow avalanche danger Christoph Mitterer*, Frank Techel, Charles Fierz and Jürg Schweizer WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland
International Snow Science Workshop Grenoble Chamonix Mont-Blanc
 Towards a basic avalanche characterization based on the generated seismic signal Alec van Herwijnen, Lisa Dreier, Perry Bartelt WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT:
Towards a basic avalanche characterization based on the generated seismic signal Alec van Herwijnen, Lisa Dreier, Perry Bartelt WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT:
SLOPE SCALE AVALANCHE FORECASTING IN THE ARCTIC (SVALBARD)
 SLOPE SCALE AVALANCHE FORECASTING IN THE ARCTIC (SVALBARD) Alexander Prokop 1,2 *, Holt Hancock 2, Martin Praz 3, and Elisabeth Jahn 1 1 Snow Scan Research, Engineering, Education GmbH, Vienna, Austria
SLOPE SCALE AVALANCHE FORECASTING IN THE ARCTIC (SVALBARD) Alexander Prokop 1,2 *, Holt Hancock 2, Martin Praz 3, and Elisabeth Jahn 1 1 Snow Scan Research, Engineering, Education GmbH, Vienna, Austria
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF THE RAMMS AVALANCHE DYNAMICS MODEL IN A CANADIAN TRANSITIONAL SNOW CLIMATE
 SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF THE RAMMS AVALANCHE DYNAMICS MODEL IN A CANADIAN TRANSITIONAL SNOW CLIMATE Ryan Buhler 1 *, Chris Argue 1, Bruce Jamieson 2, and Alan Jones 1 1 Dynamic Avalanche Consulting Ltd.,
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF THE RAMMS AVALANCHE DYNAMICS MODEL IN A CANADIAN TRANSITIONAL SNOW CLIMATE Ryan Buhler 1 *, Chris Argue 1, Bruce Jamieson 2, and Alan Jones 1 1 Dynamic Avalanche Consulting Ltd.,
PREDICTING SNOW COVER STABILITY WITH THE SNOW COVER MODEL SNOWPACK
 PREDICTING SNOW COVER STABILITY WITH THE SNOW COVER MODEL SNOWPACK Sascha Bellaire*, Jürg Schweizer, Charles Fierz, Michael Lehning and Christine Pielmeier WSL, Swiss Federal Institute for Snow and Avalanche
PREDICTING SNOW COVER STABILITY WITH THE SNOW COVER MODEL SNOWPACK Sascha Bellaire*, Jürg Schweizer, Charles Fierz, Michael Lehning and Christine Pielmeier WSL, Swiss Federal Institute for Snow and Avalanche
Snow Disaster Forecasting System on Roads. Suyoshi, Maeyama, Nagaoka, Japan
 SIRWEC 26 25 th -27 th Snow Disaster Forecasting System on Roads K. Nishimura 1, H. Hirashima 1, K. Kosugi 1, T. Kobayashi 1, T. Sato 1, A. Sato 1 and M. Lehning 2 1 Nagaoka Institute of Snow and Ice Studies,
SIRWEC 26 25 th -27 th Snow Disaster Forecasting System on Roads K. Nishimura 1, H. Hirashima 1, K. Kosugi 1, T. Kobayashi 1, T. Sato 1, A. Sato 1 and M. Lehning 2 1 Nagaoka Institute of Snow and Ice Studies,
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Breckenridge, Colorado, 2016
 CHARACTERISTICS OF AVALANCHE RELEASE AND AN APPROACH OF AVALANCHE FORECAST- ING SYSTEM USING SNOWPACK MODEL IN THE TIANSHAN MOUNTAINS, CHINA Osamu ABE 1*, Lanhai LI 2, Lei BAI 2, Jiansheng HAO 2, Hiroyuki
CHARACTERISTICS OF AVALANCHE RELEASE AND AN APPROACH OF AVALANCHE FORECAST- ING SYSTEM USING SNOWPACK MODEL IN THE TIANSHAN MOUNTAINS, CHINA Osamu ABE 1*, Lanhai LI 2, Lei BAI 2, Jiansheng HAO 2, Hiroyuki
Exercise: guided tour
 Exercise: guided tour Yves Bühler & Lukas Stoffel Seminar in snow, slush- and debris flows RAMMS Demonstration, September 3 rd 2013, Longyearbyen, Norway Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape
Exercise: guided tour Yves Bühler & Lukas Stoffel Seminar in snow, slush- and debris flows RAMMS Demonstration, September 3 rd 2013, Longyearbyen, Norway Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape
Development of Snow Avalanche Forecasting System in Japan
 Disaster Mitigation of Debris Flows, Slope Failures and Landslides 267 Development of Snow Avalanche Forecasting System in Japan Kouichi Nishimura, 1) Hiroyuki Hirashima, 1) Satoru Yamaguchi, 1) Kenji
Disaster Mitigation of Debris Flows, Slope Failures and Landslides 267 Development of Snow Avalanche Forecasting System in Japan Kouichi Nishimura, 1) Hiroyuki Hirashima, 1) Satoru Yamaguchi, 1) Kenji
Use of the models Safran-Crocus-Mepra in operational avalanche forecasting
 Use of the models Safran-Crocus-Mepra in operational avalanche forecasting Coléou C *, Giraud G, Danielou Y, Dumas J-L, Gendre C, Pougatch E CEN, Météo France, Grenoble, France. ABSTRACT: Avalanche forecast
Use of the models Safran-Crocus-Mepra in operational avalanche forecasting Coléou C *, Giraud G, Danielou Y, Dumas J-L, Gendre C, Pougatch E CEN, Météo France, Grenoble, France. ABSTRACT: Avalanche forecast
On modelling the formation and survival of surface hoar in complex terrain
 On modelling the formation and survival of surface hoar in complex terrain Nora Helbig* and Alec van Herwijnen WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Surface hoar
On modelling the formation and survival of surface hoar in complex terrain Nora Helbig* and Alec van Herwijnen WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Surface hoar
 Canton du Valais, Service des forêts et du paysage (SFP), section des dangers naturels Kanton Graubünden, Amt für Wald Graubünden, Naturgefahren Regione Valle d Aosta, Dipartimento Difesa del Suolo e Risorse
Canton du Valais, Service des forêts et du paysage (SFP), section des dangers naturels Kanton Graubünden, Amt für Wald Graubünden, Naturgefahren Regione Valle d Aosta, Dipartimento Difesa del Suolo e Risorse
COMPARSION of POWDER SNOW AVALANCHE SIMULATION MODELS (RAMMS and SamosAT) BASED on REFERENCE EVENTS in SWITZERLAND
 COMPARSION of POWDER SNOW AVALANCHE SIMULATION MODELS (RAMMS and SamosAT) BASED on REFERENCE EVENTS in SWITZERLAND Korbinian Schmidtner 1,, Perry Bartelt 2, Jan-Thomas Fischer 3, Rudolf Sailer 1, Matthias
COMPARSION of POWDER SNOW AVALANCHE SIMULATION MODELS (RAMMS and SamosAT) BASED on REFERENCE EVENTS in SWITZERLAND Korbinian Schmidtner 1,, Perry Bartelt 2, Jan-Thomas Fischer 3, Rudolf Sailer 1, Matthias
Modelling Wet Snow Avalanche Flow with a Temperature Dependent Coulomb Friction Function
 Modelling Wet Snow Avalanche Flow with a Temperature Dependent Coulomb Friction Function César Vera and Perry Bartelt WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research, SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: We
Modelling Wet Snow Avalanche Flow with a Temperature Dependent Coulomb Friction Function César Vera and Perry Bartelt WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research, SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: We
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 IMPROVEMENT OF SNOW GRAIN SIMULATIONS FROM THE MULTI-LAYERED THERMODYNAMIC SNOW MODEL SNOWPACK: IMPLICATIONS TO AVALANCHE RISK ASSESSMENT Jean-Benoit Madore, Kevin Coté and Alexandre Langlois Université
IMPROVEMENT OF SNOW GRAIN SIMULATIONS FROM THE MULTI-LAYERED THERMODYNAMIC SNOW MODEL SNOWPACK: IMPLICATIONS TO AVALANCHE RISK ASSESSMENT Jean-Benoit Madore, Kevin Coté and Alexandre Langlois Université
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Innsbruck, Austria, 2018
 Analysis of one avalanche zone in the Eastern Pyrenees (Val d Aran) using historical analysis, snow-climate data and mixed flowing/powder avalanche modelling. Sergi Riba Porras 1, 2 *, Carles García-Sellés
Analysis of one avalanche zone in the Eastern Pyrenees (Val d Aran) using historical analysis, snow-climate data and mixed flowing/powder avalanche modelling. Sergi Riba Porras 1, 2 *, Carles García-Sellés
Canton du Valais, Service des forêts et du paysage (SFP), section des dangers naturels Kanton Graubünden, Amt für Wald Graubünden, Naturgefahren
 Canton du Valais, Service des forêts et du paysage (SFP), section des dangers naturels Kanton Graubünden, Amt für Wald Graubünden, Naturgefahren Regione Valle d Aosta, Dipartimento Difesa del Suolo e Risorse
Canton du Valais, Service des forêts et du paysage (SFP), section des dangers naturels Kanton Graubünden, Amt für Wald Graubünden, Naturgefahren Regione Valle d Aosta, Dipartimento Difesa del Suolo e Risorse
Regional stability evaluation with modelled snow cover data
 Regional stability evaluation with modelled snow cover data Michael Schirmer *, Jürg Schweizer, Michael Lehning WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Stability
Regional stability evaluation with modelled snow cover data Michael Schirmer *, Jürg Schweizer, Michael Lehning WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Stability
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 EFFECTS OF THE THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SNOW ENTRAINMENT IN AVALANCHE RUN-OUT AT BIRD HILL, SOUTH-CENTRAL ALASKA Katreen Wikstroem Jones 1 *, David Hamre 2 and Perry Bartelt 3 1 Alaska Pacific University,
EFFECTS OF THE THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SNOW ENTRAINMENT IN AVALANCHE RUN-OUT AT BIRD HILL, SOUTH-CENTRAL ALASKA Katreen Wikstroem Jones 1 *, David Hamre 2 and Perry Bartelt 3 1 Alaska Pacific University,
Proceedings, 2012 International Snow Science Workshop, Anchorage, Alaska
 REAL TIME SNOW SLOPE STABILITY MODELING OF DIRECT ACTION AVALANCHES Scott Havens 1 *, H.P. Marshall 1, Chris Covington 2, Bill Nicholson 3, Howard Conway 4 1 Center for Geophysical Investigation of the
REAL TIME SNOW SLOPE STABILITY MODELING OF DIRECT ACTION AVALANCHES Scott Havens 1 *, H.P. Marshall 1, Chris Covington 2, Bill Nicholson 3, Howard Conway 4 1 Center for Geophysical Investigation of the
Rapid Mass Movement Simulation RAMMS
 R Rapid Mass Movement Simulation RAMMS Yves Bühler, Marc Christen, Perry Bartelt, SLF Christoph Graf & Brian McArdell, WSL WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF Switzerland: long tradition
R Rapid Mass Movement Simulation RAMMS Yves Bühler, Marc Christen, Perry Bartelt, SLF Christoph Graf & Brian McArdell, WSL WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF Switzerland: long tradition
Toward better decision tools for the management of frequent avalanches
 Toward better decision tools for the management of frequent avalanches Segor, V. 1 *, Pitet, L. 1, Bovet E. 2, Dellavedova P. 2, Sovilla B. 3, Steinkogler W. 3, Veitinger J. 3, Maggioni M. 4, Chiambretti
Toward better decision tools for the management of frequent avalanches Segor, V. 1 *, Pitet, L. 1, Bovet E. 2, Dellavedova P. 2, Sovilla B. 3, Steinkogler W. 3, Veitinger J. 3, Maggioni M. 4, Chiambretti
Fact Sheet on Snow Hydrology Products in GIN. SWE Maps
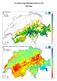 Fact Sheet on Snow Hydrology Products in GIN SWE Maps Description The snow water equivalent maps (SWE maps) present an estimation of the distribution of snow water resources in Switzerland. The maps have
Fact Sheet on Snow Hydrology Products in GIN SWE Maps Description The snow water equivalent maps (SWE maps) present an estimation of the distribution of snow water resources in Switzerland. The maps have
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 DERIVING SNOW STABILITY INFORMATION FROM SIMULATED SNOW COVER STRATIGRAPHY Fabiano Monti 1,2, Jürg Schweizer 1 and Johan Gaume 1 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland
DERIVING SNOW STABILITY INFORMATION FROM SIMULATED SNOW COVER STRATIGRAPHY Fabiano Monti 1,2, Jürg Schweizer 1 and Johan Gaume 1 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland
A MULTI-LAYER SNOW COVER MODEL FOR NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION AND CLIMATE MODELS
 A MULTI-LAYER SNOW COVER MODEL FOR NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION AND CLIMATE MODELS Sascha Bellaire 1 and Michael Lehning 1,2 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland 2 Labaratory
A MULTI-LAYER SNOW COVER MODEL FOR NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION AND CLIMATE MODELS Sascha Bellaire 1 and Michael Lehning 1,2 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland 2 Labaratory
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Breckenridge, Colorado, 2016
 COMPARISON OF MEASURED AND MODELED SNOW COVER LIQUID WATER CONTENT TO IM- PROVE LOCAL WET-SNOW AVALANCHE PREDICTION Christoph Mitterer 1*, Achim Heilig 2,3, Lino Schmid 3, Alec van Herwijnen 3, Olaf Eisen
COMPARISON OF MEASURED AND MODELED SNOW COVER LIQUID WATER CONTENT TO IM- PROVE LOCAL WET-SNOW AVALANCHE PREDICTION Christoph Mitterer 1*, Achim Heilig 2,3, Lino Schmid 3, Alec van Herwijnen 3, Olaf Eisen
Understanding snow transport processes shaping the mountain snow-cover
 Understanding snow transport processes shaping the mountain snow-cover Rebecca Mott, Michael Schirmer, Thomas Grünewald, Michael Lehning, * WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland
Understanding snow transport processes shaping the mountain snow-cover Rebecca Mott, Michael Schirmer, Thomas Grünewald, Michael Lehning, * WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland
GIS Techniques for Avalanche Path Mapping and Snow Science Observations. By Douglas D. Scott AVALANCHE MAPPING/IDEA INTEGRATION
 GIS Techniques for Avalanche Path Mapping and Snow Science Observations GIS Techniques for Avalanche Path Mapping and Snow Science Observations. By Douglas D. Scott AVALANCHE MAPPING/IDEA INTEGRATION For
GIS Techniques for Avalanche Path Mapping and Snow Science Observations GIS Techniques for Avalanche Path Mapping and Snow Science Observations. By Douglas D. Scott AVALANCHE MAPPING/IDEA INTEGRATION For
Novel Snotel Data Uses: Detecting Change in Snowpack Development Controls, and Remote Basin Snow Depth Modeling
 Novel Snotel Data Uses: Detecting Change in Snowpack Development Controls, and Remote Basin Snow Depth Modeling OVERVIEW Mark Losleben and Tyler Erickson INSTAAR, University of Colorado Mountain Research
Novel Snotel Data Uses: Detecting Change in Snowpack Development Controls, and Remote Basin Snow Depth Modeling OVERVIEW Mark Losleben and Tyler Erickson INSTAAR, University of Colorado Mountain Research
Slushflows. Christian Jaedicke Galina Ragulina Peter Gauer
 Slushflows Christian Jaedicke Galina Ragulina Peter Gauer Thoughts about future methods for slushflow warning Christian Jaedicke What is a slushflow? rapid mass movements of watersaturated snow In other
Slushflows Christian Jaedicke Galina Ragulina Peter Gauer Thoughts about future methods for slushflow warning Christian Jaedicke What is a slushflow? rapid mass movements of watersaturated snow In other
Micrometeorological processes driving snow ablation in an Alpine catchment
 The Cryosphere Discuss.,, 29 2196, 11 www.the-cryosphere-discuss.net//29/11/ doi:.194/tcd--29-11 Author(s) 11. CC Attribution 3.0 License. This discussion paper is/has been under review for the journal
The Cryosphere Discuss.,, 29 2196, 11 www.the-cryosphere-discuss.net//29/11/ doi:.194/tcd--29-11 Author(s) 11. CC Attribution 3.0 License. This discussion paper is/has been under review for the journal
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Breckenridge, Colorado, 2016
 CRITICAL LENGTH FOR THE ONSET OF CRACK PROPAGATION IN SNOW: RECONCILING SHEAR AND COLLAPSE Johan Gaume 1,2 *, Alec van Herwijnen 1, Guillaume Chambon 3, Nander Wever 1,2 and Jürg Schweizer 1 1 WSL Institute
CRITICAL LENGTH FOR THE ONSET OF CRACK PROPAGATION IN SNOW: RECONCILING SHEAR AND COLLAPSE Johan Gaume 1,2 *, Alec van Herwijnen 1, Guillaume Chambon 3, Nander Wever 1,2 and Jürg Schweizer 1 1 WSL Institute
MONITORING SNOWPACK TEMPERATURE GRADIENT USING AUTOMATIC SNOW DEPTH SENSOR
 MONITORING SNOWPACK TEMPERATURE GRADIENT USING AUTOMATIC SNOW DEPTH SENSOR Örn Ingólfsson* POLS Engineering, IS-400 Ísafjörður, ICELAND Harpa Grímsdóttir, Magni Hreinn Jónsson Icelandic Meteorological
MONITORING SNOWPACK TEMPERATURE GRADIENT USING AUTOMATIC SNOW DEPTH SENSOR Örn Ingólfsson* POLS Engineering, IS-400 Ísafjörður, ICELAND Harpa Grímsdóttir, Magni Hreinn Jónsson Icelandic Meteorological
Proceedings, 2012 International Snow Science Workshop, Anchorage, Alaska
 BACK-CALCULATION OF SMALL AVALANCHES WITH THE 2D AVALANCHE DYNAMICS MODEL RAMMS: FOUR EVENTS ARTIFICIALLY TRIGGERED AT THE SEEHORE TEST SITE IN AOSTA VALLEY (NW ITALY). M. Maggioni 1 *, M. Freppaz 1, M.
BACK-CALCULATION OF SMALL AVALANCHES WITH THE 2D AVALANCHE DYNAMICS MODEL RAMMS: FOUR EVENTS ARTIFICIALLY TRIGGERED AT THE SEEHORE TEST SITE IN AOSTA VALLEY (NW ITALY). M. Maggioni 1 *, M. Freppaz 1, M.
HyMet Company. Streamflow and Energy Generation Forecasting Model Columbia River Basin
 HyMet Company Streamflow and Energy Generation Forecasting Model Columbia River Basin HyMet Inc. Courthouse Square 19001 Vashon Hwy SW Suite 201 Vashon Island, WA 98070 Phone: 206-463-1610 Columbia River
HyMet Company Streamflow and Energy Generation Forecasting Model Columbia River Basin HyMet Inc. Courthouse Square 19001 Vashon Hwy SW Suite 201 Vashon Island, WA 98070 Phone: 206-463-1610 Columbia River
Automatic classification of manual snow profiles by snow structure
 Automatic classification of manual snow profiles by snow structure Frank Techel* and Christine Pielmeier WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, 7260 Davos Dorf, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Manual
Automatic classification of manual snow profiles by snow structure Frank Techel* and Christine Pielmeier WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, 7260 Davos Dorf, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Manual
2010 International Snow Science Workshop
 mavalanche SMART AVALANCHE FORECASTING WITH SMARTPHONES Christoph Suter *, Stephan Harvey and Lukas Dürr WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: The common information
mavalanche SMART AVALANCHE FORECASTING WITH SMARTPHONES Christoph Suter *, Stephan Harvey and Lukas Dürr WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: The common information
Comparison of a snowpack on a slope and flat land by focusing on the effect of water infiltration
 Comparison of a snowpack on a slope and flat land by focusing on the effect of water infiltration Shinji Ikeda 1*, Takafumi Katsushima 2, Yasuhiko Ito 1, Hiroki Matsushita 3, Yukari Takeuchi 4, Kazuya
Comparison of a snowpack on a slope and flat land by focusing on the effect of water infiltration Shinji Ikeda 1*, Takafumi Katsushima 2, Yasuhiko Ito 1, Hiroki Matsushita 3, Yukari Takeuchi 4, Kazuya
Proceedings, 2012 International Snow Science Workshop, Anchorage, Alaska
 ANALYZING THE ATMOSPHERE-SNOW ENERGY BALANCE FOR WET-SNOW AVALANCHE PREDICTION Christoph Mitterer* and Jürg Schweizer WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Melt
ANALYZING THE ATMOSPHERE-SNOW ENERGY BALANCE FOR WET-SNOW AVALANCHE PREDICTION Christoph Mitterer* and Jürg Schweizer WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Melt
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Innsbruck, Austria, 2018
 RELEASE OF AVALANCHES ON PERSISTENT WEAK LAYERS IN RELATION TO LOADING EVENTS IN COLORADO, USA Jason Konigsberg 1, Spencer Logan 1, and Ethan Greene 1 1 Colorado Avalanche Information Center, Boulder,
RELEASE OF AVALANCHES ON PERSISTENT WEAK LAYERS IN RELATION TO LOADING EVENTS IN COLORADO, USA Jason Konigsberg 1, Spencer Logan 1, and Ethan Greene 1 1 Colorado Avalanche Information Center, Boulder,
Better Decisions for Your Business Drive your company forward with ultra-precise weather forecasts
 Better Decisions for Your Business Drive your company forward with ultra-precise weather forecasts Problem: Inaccurate Forecasts, Especially over Mountainous Regions Which weather data are you using? What
Better Decisions for Your Business Drive your company forward with ultra-precise weather forecasts Problem: Inaccurate Forecasts, Especially over Mountainous Regions Which weather data are you using? What
1 INTRODUCTION. 1.1 Context
 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Context During the last 30 years ski run construction has been one of the major human activities affecting the Alpine environment. The impact of skiing on environmental factors and processes,
1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Context During the last 30 years ski run construction has been one of the major human activities affecting the Alpine environment. The impact of skiing on environmental factors and processes,
Swiss Avalanche-Dynamics Procedures for Dense Flow Avalanches
 Swiss Avalanche-Dynamics Procedures for Dense Flow Avalanches H. Gubler 1 Swiss Avalanche-Dynamics Procedures for Dense Flow Avalanches H.Gubler AlpuG Richtstattweg2 CH-7270 Davos Platz, Switzerland Introduction
Swiss Avalanche-Dynamics Procedures for Dense Flow Avalanches H. Gubler 1 Swiss Avalanche-Dynamics Procedures for Dense Flow Avalanches H.Gubler AlpuG Richtstattweg2 CH-7270 Davos Platz, Switzerland Introduction
Abstract. 1 Introduction. 2 Experimental Setup. 2.1 Data Set
 ERAD - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Comparison of the seasonal small-scale spatial variability in alpine snowfall and snow accumulation D. E. Scipión,, R. Mott,
ERAD - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Comparison of the seasonal small-scale spatial variability in alpine snowfall and snow accumulation D. E. Scipión,, R. Mott,
2010 International Snow Science Workshop
 A HIGH RESOLUTION APPROACH TO DEFINING SPATIAL SNOW HEIGHT DISTRIBUTION IN AVALANCHE RELEASE ZONES FOR DYNAMIC AVALANCHE MODELING Alexander Prokop* and Christina Delaney Institute of Mountain Risk Engineering,
A HIGH RESOLUTION APPROACH TO DEFINING SPATIAL SNOW HEIGHT DISTRIBUTION IN AVALANCHE RELEASE ZONES FOR DYNAMIC AVALANCHE MODELING Alexander Prokop* and Christina Delaney Institute of Mountain Risk Engineering,
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 SIMULATION OF THE ALPINE SNOWPACK USING METEOROLOGICAL FIELDS FROM A NON- HYDROSTATIC WEATHER FORECAST MODEL V. Vionnet 1, I. Etchevers 1, L. Auger 2, A. Colomb 3, L. Pfitzner 3, M. Lafaysse 1 and S. Morin
SIMULATION OF THE ALPINE SNOWPACK USING METEOROLOGICAL FIELDS FROM A NON- HYDROSTATIC WEATHER FORECAST MODEL V. Vionnet 1, I. Etchevers 1, L. Auger 2, A. Colomb 3, L. Pfitzner 3, M. Lafaysse 1 and S. Morin
Rapid Mass Movements System RAMMS
 Rapid Mass Movements System RAMMS Yves Bühler, Marc Christen, Perry Bartelt, Christoph Graf, Werner Gerber, Brian McArdell Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape Research WSL WSL Institute
Rapid Mass Movements System RAMMS Yves Bühler, Marc Christen, Perry Bartelt, Christoph Graf, Werner Gerber, Brian McArdell Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape Research WSL WSL Institute
Impact on Agriculture
 Weather Variability and the Impact on Agriculture InfoAg 2017 Copyright 2017, awhere. All Rights Reserved The Problem: The Earth s Atmosphere is a Heat Engine In transition 1 C warming of atmosphere Triples
Weather Variability and the Impact on Agriculture InfoAg 2017 Copyright 2017, awhere. All Rights Reserved The Problem: The Earth s Atmosphere is a Heat Engine In transition 1 C warming of atmosphere Triples
LINKING SNOW COVER PROPERTIES AND AVALANCHE DYNAMICS
 LINKING SNOW COVER PROPERTIES AND AVALANCHE DYNAMICS Walter Steinkogler 1,2, Betty Sovilla 1 and Michael Lehning 1,2 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos Dorf, Switzerland 2 CRYOS,
LINKING SNOW COVER PROPERTIES AND AVALANCHE DYNAMICS Walter Steinkogler 1,2, Betty Sovilla 1 and Michael Lehning 1,2 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos Dorf, Switzerland 2 CRYOS,
DOWNLOAD PDF SCENERY OF SWITZERLAND, AND THE CAUSES TO WHICH IT IS DUE.
 Chapter 1 : The Scenery of Switzerland (Sir John Lubbock - ) (ID) ebay The scenery of Switzerland and the causes to which it is due / Related Titles Series: Collection of British authors ; vol. These diseases
Chapter 1 : The Scenery of Switzerland (Sir John Lubbock - ) (ID) ebay The scenery of Switzerland and the causes to which it is due / Related Titles Series: Collection of British authors ; vol. These diseases
GEOGRAPHIC VARIATION IN SNOW TEMPERATURE GRADIENTS IN A MOUNTAIN SNOWPACK ABSTRACT
 GEOGRAPHIC VARIATION IN SNOW TEMPERATURE GRADIENTS IN A MOUNTAIN SNOWPACK J. S. Deems 1, K. W. Birkeland 1, K. J. Hansen 1 ABSTRACT The objective of this study was to investigate the relative importance
GEOGRAPHIC VARIATION IN SNOW TEMPERATURE GRADIENTS IN A MOUNTAIN SNOWPACK J. S. Deems 1, K. W. Birkeland 1, K. J. Hansen 1 ABSTRACT The objective of this study was to investigate the relative importance
>200 LWP+IWP (g m 2 )
 Frequency (%) 1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 CMIP5 RCM OBS SATELLITE RACMO2.3 CCSM4 CESM1_CAM4 CESM1_CAM5 CMCC CNRM CanESM2 GFDL_CM2.1 GFDL_CM3 GISS HadGEM2 IPSL_CM5A IPSL_CM5B MPI ESM NorESM1 bcc csm1 inmcm4 CMIP5
Frequency (%) 1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 CMIP5 RCM OBS SATELLITE RACMO2.3 CCSM4 CESM1_CAM4 CESM1_CAM5 CMCC CNRM CanESM2 GFDL_CM2.1 GFDL_CM3 GISS HadGEM2 IPSL_CM5A IPSL_CM5B MPI ESM NorESM1 bcc csm1 inmcm4 CMIP5
AVALANCHE FORECASTER EXCHANGE PROGRAM U.S. SWITZERLAND
 AVALANCHE FORECASTER EXCHANGE PROGRAM U.S. SWITZERLAND Matt Hill* Mount Shasta Avalanche Center, USDA Forest Service, Mt. Shasta City, CA, U.S.A. Thomas Wiesinger Swiss Federal Institute for Snow and Avalanche
AVALANCHE FORECASTER EXCHANGE PROGRAM U.S. SWITZERLAND Matt Hill* Mount Shasta Avalanche Center, USDA Forest Service, Mt. Shasta City, CA, U.S.A. Thomas Wiesinger Swiss Federal Institute for Snow and Avalanche
GLACIOLOGY LAB SNOW Introduction Equipment
 GLACIOLOGY LAB SNOW Introduction The objective of this lab is to achieve a working knowledge of the snowpack. This includes descriptions and genetic analysis of features that can be observed on the surface
GLACIOLOGY LAB SNOW Introduction The objective of this lab is to achieve a working knowledge of the snowpack. This includes descriptions and genetic analysis of features that can be observed on the surface
HELICOPTER-BASED MICROWAVE RADAR MEASUREMENTS IN ALPINE TERRAIN
 HELICOPTER-BASED MICROWAVE RADAR MEASUREMENTS IN ALPINE TERRAIN Hans-Peter Marshall, 1,2, * Karl Birkeland, 3,4 Kelly Elder, 5 Theo Meiners 6 1 Center for Geophysical Investigation of the Shallow Subsurface,
HELICOPTER-BASED MICROWAVE RADAR MEASUREMENTS IN ALPINE TERRAIN Hans-Peter Marshall, 1,2, * Karl Birkeland, 3,4 Kelly Elder, 5 Theo Meiners 6 1 Center for Geophysical Investigation of the Shallow Subsurface,
Proceedings, 2012 International Snow Science Workshop, Anchorage, Alaska
 POSITIONING OF AVALANCHE PROTECTION MEASURES USING SNOW DEPTH MAPPING VIA TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING Alexander Prokop* and Christina M. Delaney² Institute of Mountain Risk Engineering, Department of Civil
POSITIONING OF AVALANCHE PROTECTION MEASURES USING SNOW DEPTH MAPPING VIA TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING Alexander Prokop* and Christina M. Delaney² Institute of Mountain Risk Engineering, Department of Civil
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Breckenridge, Colorado, 2016 OBSERVER INDEPENDENT MEASURES OF SNOW INSTABILITY
 OBSERVER INDEPENDENT MEASURES OF SNOW INSTABILITY Benjamin Reuter*, Alec van Herwijnen, Jürg Schweizer WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Observer independent
OBSERVER INDEPENDENT MEASURES OF SNOW INSTABILITY Benjamin Reuter*, Alec van Herwijnen, Jürg Schweizer WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Observer independent
FORECASTING FOR A HELICOPTER SKIING OPERATION IN THE UNITED STATES. High Mountain Heli-Skiing P.O. Box 2221 Jackson Hole, WY ABSTRACT
 AVALANCHE FORECASTING FOR A HELICOPTER SKIING OPERATION IN THE UNITED STATES Jim Woodrnencey 1 and Jon Shick 2 High Mountain Heli-Skiing P.O. Box 2221 Jackson Hole, WY 83001 ABSTRACT Helicopter skiing
AVALANCHE FORECASTING FOR A HELICOPTER SKIING OPERATION IN THE UNITED STATES Jim Woodrnencey 1 and Jon Shick 2 High Mountain Heli-Skiing P.O. Box 2221 Jackson Hole, WY 83001 ABSTRACT Helicopter skiing
The Montague Doppler Radar, An Overview
 ISSUE PAPER SERIES The Montague Doppler Radar, An Overview June 2018 NEW YORK STATE TUG HILL COMMISSION DULLES STATE OFFICE BUILDING 317 WASHINGTON STREET WATERTOWN, NY 13601 (315) 785-2380 WWW.TUGHILL.ORG
ISSUE PAPER SERIES The Montague Doppler Radar, An Overview June 2018 NEW YORK STATE TUG HILL COMMISSION DULLES STATE OFFICE BUILDING 317 WASHINGTON STREET WATERTOWN, NY 13601 (315) 785-2380 WWW.TUGHILL.ORG
FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic areas for Risk mitigation in the Alpine space
 Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Banff, 2014
 RELATING AVALANCHES TO LARGE-SCALE OCEAN ATMOSPHERIC OSCILLATIONS Scott Thumlert 1, Sascha Bellaire 2, Bruce Jamieson 1 1 Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Calgary, AB, Canada 2 Institute of Meteorology
RELATING AVALANCHES TO LARGE-SCALE OCEAN ATMOSPHERIC OSCILLATIONS Scott Thumlert 1, Sascha Bellaire 2, Bruce Jamieson 1 1 Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Calgary, AB, Canada 2 Institute of Meteorology
The Documentation of Extreme Hydrometeorlogical Events: Two Case Studies in Utah, Water Year 2005
 The Documentation of Extreme Hydrometeorlogical Events: Two Case Studies in Utah, Water Year 2005 Tim Bardsley1*, Mark Losleben2, Randy Julander1 1. USDA, NRCS, Snow Survey Program, Salt Lake City, Utah.
The Documentation of Extreme Hydrometeorlogical Events: Two Case Studies in Utah, Water Year 2005 Tim Bardsley1*, Mark Losleben2, Randy Julander1 1. USDA, NRCS, Snow Survey Program, Salt Lake City, Utah.
Cartographic analysis of avalanche hazard maps A comparison of relevant cartographic factors for the visualization of the avalanche bulletin
 Cartographic analysis of avalanche hazard maps A comparison of relevant cartographic factors for the visualization of the avalanche bulletin Markus Eckerstorfer, Karel Kriz University of Vienna, Department
Cartographic analysis of avalanche hazard maps A comparison of relevant cartographic factors for the visualization of the avalanche bulletin Markus Eckerstorfer, Karel Kriz University of Vienna, Department
4.5 Comparison of weather data from the Remote Automated Weather Station network and the North American Regional Reanalysis
 4.5 Comparison of weather data from the Remote Automated Weather Station network and the North American Regional Reanalysis Beth L. Hall and Timothy. J. Brown DRI, Reno, NV ABSTRACT. The North American
4.5 Comparison of weather data from the Remote Automated Weather Station network and the North American Regional Reanalysis Beth L. Hall and Timothy. J. Brown DRI, Reno, NV ABSTRACT. The North American
Glossary Accuracy precision Alpha Angle crown face Anemometer Aspect fall line Atmospheric Pressure barometric pressure Avalanche, Snow
 Glossary Glossary Accuracy The difference between the measured value and the actual or true value. A property of a measurement method and instruments used. Also see precision. Alpha Angle The angle between
Glossary Glossary Accuracy The difference between the measured value and the actual or true value. A property of a measurement method and instruments used. Also see precision. Alpha Angle The angle between
Weather and Climate 1. Elements of the weather
 Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
OVERVIEW OF THE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF AVALANCHE ACTIVITY IN RELATION TO METEOROLOGICAL AND TOPOGRAPHIC VARIABLES IN AN EXTREME MARITIME ENVIRONMENT
 OVERVIEW OF THE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF AVALANCHE ACTIVITY IN RELATION TO METEOROLOGICAL AND TOPOGRAPHIC VARIABLES IN AN EXTREME MARITIME ENVIRONMENT Jordy Hendrikx a*, Ian Owens a, Wayne Carran b, Ann
OVERVIEW OF THE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF AVALANCHE ACTIVITY IN RELATION TO METEOROLOGICAL AND TOPOGRAPHIC VARIABLES IN AN EXTREME MARITIME ENVIRONMENT Jordy Hendrikx a*, Ian Owens a, Wayne Carran b, Ann
ESTIMATING SNOWMELT CONTRIBUTION FROM THE GANGOTRI GLACIER CATCHMENT INTO THE BHAGIRATHI RIVER, INDIA ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 ESTIMATING SNOWMELT CONTRIBUTION FROM THE GANGOTRI GLACIER CATCHMENT INTO THE BHAGIRATHI RIVER, INDIA Rodney M. Chai 1, Leigh A. Stearns 2, C. J. van der Veen 1 ABSTRACT The Bhagirathi River emerges from
ESTIMATING SNOWMELT CONTRIBUTION FROM THE GANGOTRI GLACIER CATCHMENT INTO THE BHAGIRATHI RIVER, INDIA Rodney M. Chai 1, Leigh A. Stearns 2, C. J. van der Veen 1 ABSTRACT The Bhagirathi River emerges from
Operational MRCC Tools Useful and Usable by the National Weather Service
 Operational MRCC Tools Useful and Usable by the National Weather Service Vegetation Impact Program (VIP): Frost / Freeze Project Beth Hall Accumulated Winter Season Severity Index (AWSSI) Steve Hilberg
Operational MRCC Tools Useful and Usable by the National Weather Service Vegetation Impact Program (VIP): Frost / Freeze Project Beth Hall Accumulated Winter Season Severity Index (AWSSI) Steve Hilberg
The avalanche climate of Glacier National Park, B.C., Canada during
 The avalanche climate of Glacier National Park, B.C., Canada during 1965-2011 Sascha Bellaire 1,2*, Bruce Jamieson 1, Grant Statham 3 1 Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics, University of Innsbruck,
The avalanche climate of Glacier National Park, B.C., Canada during 1965-2011 Sascha Bellaire 1,2*, Bruce Jamieson 1, Grant Statham 3 1 Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics, University of Innsbruck,
Whistler Mountain is located at about 50 0 North latitude by 123 0
 - 24 - WHISTLER MOUNTAIN AVALANCHE CONTROL PROGRAMME C. Stethem and J. Hetherington Introduction Whistler Mountain is located at about 50 0 North latitude by 123 0 longitude, in the Pacific Coast Range
- 24 - WHISTLER MOUNTAIN AVALANCHE CONTROL PROGRAMME C. Stethem and J. Hetherington Introduction Whistler Mountain is located at about 50 0 North latitude by 123 0 longitude, in the Pacific Coast Range
Proceedings, 2012 International Snow Science Workshop, Anchorage, Alaska
 TOWARDS A BETTER UNDERSTANDING OF GLIDE-SNOW AVALANCHE FORMATION Christoph Mitterer* and Jürg Schweizer WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Full-depth avalanches
TOWARDS A BETTER UNDERSTANDING OF GLIDE-SNOW AVALANCHE FORMATION Christoph Mitterer* and Jürg Schweizer WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland ABSTRACT: Full-depth avalanches
Forecasting of Optical Turbulence in Support of Realtime Optical Imaging and Communication Systems
 Forecasting of Optical Turbulence in Support of Realtime Optical Imaging and Communication Systems Randall J. Alliss and Billy Felton Northrop Grumman Corporation, 15010 Conference Center Drive, Chantilly,
Forecasting of Optical Turbulence in Support of Realtime Optical Imaging and Communication Systems Randall J. Alliss and Billy Felton Northrop Grumman Corporation, 15010 Conference Center Drive, Chantilly,
MET Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16)
 MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
Prediction of Snow Water Equivalent in the Snake River Basin
 Hobbs et al. Seasonal Forecasting 1 Jon Hobbs Steve Guimond Nate Snook Meteorology 455 Seasonal Forecasting Prediction of Snow Water Equivalent in the Snake River Basin Abstract Mountainous regions of
Hobbs et al. Seasonal Forecasting 1 Jon Hobbs Steve Guimond Nate Snook Meteorology 455 Seasonal Forecasting Prediction of Snow Water Equivalent in the Snake River Basin Abstract Mountainous regions of
Brita Horlings
 Knut Christianson Brita Horlings brita2@uw.edu https://courses.washington.edu/ess431/ Natural Occurrences of Ice: Distribution and environmental factors of seasonal snow, sea ice, glaciers and permafrost
Knut Christianson Brita Horlings brita2@uw.edu https://courses.washington.edu/ess431/ Natural Occurrences of Ice: Distribution and environmental factors of seasonal snow, sea ice, glaciers and permafrost
Statistical forecasting of regional avalanche danger using simulated snow-cover data
 Journal of Glaciology, Vol. 55, No. 193, 2009 761 Statistical forecasting of regional avalanche danger using simulated snow-cover data Michael SCHIRMER, Michael LEHNING, Jürg SCHWEIZER WSL Institute for
Journal of Glaciology, Vol. 55, No. 193, 2009 761 Statistical forecasting of regional avalanche danger using simulated snow-cover data Michael SCHIRMER, Michael LEHNING, Jürg SCHWEIZER WSL Institute for
SNOW CLIMATOLOGY OF THE EASTERN SIERRA NEVADA. Susan Burak, graduate student Hydrologic Sciences University of Nevada, Reno
 SNOW CLIMATOLOGY OF THE EASTERN SIERRA NEVADA Susan Burak, graduate student Hydrologic Sciences University of Nevada, Reno David Walker, graduate student Department of Geography/154 University of Nevada
SNOW CLIMATOLOGY OF THE EASTERN SIERRA NEVADA Susan Burak, graduate student Hydrologic Sciences University of Nevada, Reno David Walker, graduate student Department of Geography/154 University of Nevada
Pass, San Juan Mountains, Southwest Colorado
 Contributory Factors To Avalanche Occurrence On Red Mountain Pass, San Juan Mountains, Southwest Colorado Sally Thompson1 and Douglas K. McCarty2 submitted for 1994 ISSW poster session Abstract Avalanche
Contributory Factors To Avalanche Occurrence On Red Mountain Pass, San Juan Mountains, Southwest Colorado Sally Thompson1 and Douglas K. McCarty2 submitted for 1994 ISSW poster session Abstract Avalanche
Weather preceding persistent deep slab avalanches
 Weather preceding persistent deep slab avalanches Michael Conlan * and Bruce Jamieson Department of Civil Engineering, University of Calgary, Alberta, Canada ABSTRACT: Deep slab avalanches release on persistent
Weather preceding persistent deep slab avalanches Michael Conlan * and Bruce Jamieson Department of Civil Engineering, University of Calgary, Alberta, Canada ABSTRACT: Deep slab avalanches release on persistent
INCA-CE achievements and status
 INCA-CE achievements and status Franziska Strauss Yong Wang Alexander Kann Benedikt Bica Ingo Meirold-Mautner INCA Central Europe Integrated nowcasting for the Central European area This project is implemented
INCA-CE achievements and status Franziska Strauss Yong Wang Alexander Kann Benedikt Bica Ingo Meirold-Mautner INCA Central Europe Integrated nowcasting for the Central European area This project is implemented
Using MODIS imagery to validate the spatial representation of snow cover extent obtained from SWAT in a data-scarce Chilean Andean watershed
 Using MODIS imagery to validate the spatial representation of snow cover extent obtained from SWAT in a data-scarce Chilean Andean watershed Alejandra Stehr 1, Oscar Link 2, Mauricio Aguayo 1 1 Centro
Using MODIS imagery to validate the spatial representation of snow cover extent obtained from SWAT in a data-scarce Chilean Andean watershed Alejandra Stehr 1, Oscar Link 2, Mauricio Aguayo 1 1 Centro
International Snow Science Workshop, Davos 2009, Proceedings
 COMPARISON AND COMPLEMENTARITIES OF AVALANCHE PRESSURE MEASUREMENTS: PIEZO-ELECTRIC LOAD CELLS AND DEFORMATION BASED PRESSURE DECONVOLUTION Djebar BAROUDI 1, Betty SOVILLA 2, Emmanuel THIBERT 1 1 Cemagref,
COMPARISON AND COMPLEMENTARITIES OF AVALANCHE PRESSURE MEASUREMENTS: PIEZO-ELECTRIC LOAD CELLS AND DEFORMATION BASED PRESSURE DECONVOLUTION Djebar BAROUDI 1, Betty SOVILLA 2, Emmanuel THIBERT 1 1 Cemagref,
An overview of the applications for early warning and mapping of the flood events in New Brunswick
 Flood Recovery, Innovation and Reponse IV 239 An overview of the applications for early warning and mapping of the flood events in New Brunswick D. Mioc 1, E. McGillivray 2, F. Anton 1, M. Mezouaghi 2,
Flood Recovery, Innovation and Reponse IV 239 An overview of the applications for early warning and mapping of the flood events in New Brunswick D. Mioc 1, E. McGillivray 2, F. Anton 1, M. Mezouaghi 2,
AUTOMATIC MEASUREMENT OF ICING ON THE WEST OF THE CZECH REPUBLIC
 AUTOMATIC MEASUREMENT OF ICING ON THE WEST OF THE CZECH REPUBLIC J. Chum, J. Vojta, J. Hošek Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Boční II / 1401, Praha 4, Czech republic 1 INTRODUCTION We report our experience
AUTOMATIC MEASUREMENT OF ICING ON THE WEST OF THE CZECH REPUBLIC J. Chum, J. Vojta, J. Hošek Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Boční II / 1401, Praha 4, Czech republic 1 INTRODUCTION We report our experience
LAB 15. Lab 15. Air Masses and Weather Conditions: How Do the Motions and Interactions of Air Masses Result in Changes in Weather Conditions?
 Lab Handout Lab 15. Air Masses and Weather Conditions: How Do the Motions and Interactions of Air Masses Result in Changes in Weather Conditions? Introduction Meteorology is the study of the atmosphere.
Lab Handout Lab 15. Air Masses and Weather Conditions: How Do the Motions and Interactions of Air Masses Result in Changes in Weather Conditions? Introduction Meteorology is the study of the atmosphere.
Dynamic Avalanche Modeling in Natural Terrain
 Dynamic Avalanche Modeling in Natural Terrain J.T. Fischer,a,b, J. Kowalski a, S.P. Pudasaini b, S. A. Miller b a WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos Dorf, Switzerland b Department
Dynamic Avalanche Modeling in Natural Terrain J.T. Fischer,a,b, J. Kowalski a, S.P. Pudasaini b, S. A. Miller b a WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos Dorf, Switzerland b Department
Avalanche Guidelines
 improved Accessibility: Reliability and security of Alpine transport infrastructure related to mountainous hazards in a changing climate Avalanche Guidelines guide lines for snow avalanches hazard PP4
improved Accessibility: Reliability and security of Alpine transport infrastructure related to mountainous hazards in a changing climate Avalanche Guidelines guide lines for snow avalanches hazard PP4
2010 International Snow Science Workshop WET-SNOW AVALANCHE INTERACTING WITH A DEFLECTING DAM: FIELD OBSERVATIONS
 WET-SNOW AVALANCHE INTERACTING WITH A DEFLECTING DAM: FIELD OBSERVATIONS Betty Sovilla 1, Ilaria Sonatore 1,2, Stefan Margreth 1 and Marc Christen 1 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF,
WET-SNOW AVALANCHE INTERACTING WITH A DEFLECTING DAM: FIELD OBSERVATIONS Betty Sovilla 1, Ilaria Sonatore 1,2, Stefan Margreth 1 and Marc Christen 1 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF,
MeteoSwiss acceptance procedure for automatic weather stations
 MeteoSwiss acceptance procedure for automatic weather stations J. Fisler, M. Kube, E. Grueter and B. Calpini MeteoSwiss, Krähbühlstrasse 58, 8044 Zurich, Switzerland Phone:+41 44 256 9433, Email: joel.fisler@meteoswiss.ch
MeteoSwiss acceptance procedure for automatic weather stations J. Fisler, M. Kube, E. Grueter and B. Calpini MeteoSwiss, Krähbühlstrasse 58, 8044 Zurich, Switzerland Phone:+41 44 256 9433, Email: joel.fisler@meteoswiss.ch
Avalanches. Avalanche s
 Avalanches Avalanche s Avalanches were first imagined as giant snowballs which increased in size from accretion of underlying snow What are avalanches? They are flows which move under the influence of
Avalanches Avalanche s Avalanches were first imagined as giant snowballs which increased in size from accretion of underlying snow What are avalanches? They are flows which move under the influence of
GeoExtreme. Geohazards, Climate Change and Extreme Weather Events
 GeoExtreme Geohazards, Climate Change and Extreme Weather Events Overview What is GeoExtreme? Involved processes What influences slide activity? Consequences for society? Ongoing work Conclusion What is
GeoExtreme Geohazards, Climate Change and Extreme Weather Events Overview What is GeoExtreme? Involved processes What influences slide activity? Consequences for society? Ongoing work Conclusion What is
Eagle Creek Post Fire Erosion Hazard Analysis Using the WEPP Model. John Rogers & Lauren McKinney
 Eagle Creek Post Fire Erosion Hazard Analysis Using the WEPP Model John Rogers & Lauren McKinney Columbia River Gorge at Risk: Using LiDAR and GIS-based predictive modeling for regional-scale erosion susceptibility
Eagle Creek Post Fire Erosion Hazard Analysis Using the WEPP Model John Rogers & Lauren McKinney Columbia River Gorge at Risk: Using LiDAR and GIS-based predictive modeling for regional-scale erosion susceptibility
Flood Forecasting Tools for Ungauged Streams in Alberta: Status and Lessons from the Flood of 2013
 Flood Forecasting Tools for Ungauged Streams in Alberta: Status and Lessons from the Flood of 2013 John Pomeroy, Xing Fang, Kevin Shook, Tom Brown Centre for Hydrology, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon
Flood Forecasting Tools for Ungauged Streams in Alberta: Status and Lessons from the Flood of 2013 John Pomeroy, Xing Fang, Kevin Shook, Tom Brown Centre for Hydrology, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon
Winter Maintenance Report
 98.4 Official State Snowfall 150 Truck Stations 1,813 Full-time and Backup Snowfighters 840 Plow trucks - includes 47 reserve plows 30,585 Lane Miles 85% Frequency Achieving Bare Lanes 2017-18 Winter Maintenance
98.4 Official State Snowfall 150 Truck Stations 1,813 Full-time and Backup Snowfighters 840 Plow trucks - includes 47 reserve plows 30,585 Lane Miles 85% Frequency Achieving Bare Lanes 2017-18 Winter Maintenance
POTENTIAL DRY SLAB AVALANCHE TRIGGER ZONES ON WIND-AFFECTED SLOPES
 POTENTIAL DRY SLAB AVALANCHE TRIGGER ZONES ON WIND-AFFECTED SLOPES 1,2 Markus Eckerstorfer, 1,2 Wesley R. Farnsworth, 3 Karl W. Birkeland 1 Arctic Geology Department, University Centre in Svalbard, Norway
POTENTIAL DRY SLAB AVALANCHE TRIGGER ZONES ON WIND-AFFECTED SLOPES 1,2 Markus Eckerstorfer, 1,2 Wesley R. Farnsworth, 3 Karl W. Birkeland 1 Arctic Geology Department, University Centre in Svalbard, Norway
THE INVESTIGATION OF SNOWMELT PATTERNS IN AN ARCTIC UPLAND USING SAR IMAGERY
 THE INVESTIGATION OF SNOWMELT PATTERNS IN AN ARCTIC UPLAND USING SAR IMAGERY Johansson, M., Brown, I.A. and Lundén, B. Department of Physical Geography, Stockholm University, S-106 91 Stockholm, Sweden
THE INVESTIGATION OF SNOWMELT PATTERNS IN AN ARCTIC UPLAND USING SAR IMAGERY Johansson, M., Brown, I.A. and Lundén, B. Department of Physical Geography, Stockholm University, S-106 91 Stockholm, Sweden
Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Breckenridge, Colorado, 2016
 OPERATIONAL FORECASTING OF WET SNOW AVALANCHE ACTIVITY: A CASE STUDY FOR THE EASTERN EUROPEAN ALPS A. Gobiet 1 *, C. Mitterer 2,4, L. Jöbstl 1, W. Steinkogler 3,4, H. Rieder 1, M. Olefs 1, A. Studeregger
OPERATIONAL FORECASTING OF WET SNOW AVALANCHE ACTIVITY: A CASE STUDY FOR THE EASTERN EUROPEAN ALPS A. Gobiet 1 *, C. Mitterer 2,4, L. Jöbstl 1, W. Steinkogler 3,4, H. Rieder 1, M. Olefs 1, A. Studeregger
