Astro 590: next 3 classes
|
|
|
- Brianna Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Astro 590: next 3 classes Dwarf galaxies as probes of evolution Distribution Kinematics The star formation history of the universe Star formation indicators Nebular abundances Starburst populations The role of AGN AGN galaxy connections High redshift galaxies QSO s Lyman-break galaxies Extremely red objects Next Monday: 15 minute presentation of final project proposal
2 Dwarf ellipticals: des The few des in the Local Group are all found around M31 M31 - Andromeda M32 N205
3 Dwarf irregulars: dis IC1613 barred Pegasus IC10 Phoenix NGC6822 SextansA NGC3109 SextansB
4 Dwarf spheroidals: dsphs Leo I Leo II Fornax Half of dwarfs in the Local Group are dsphs Draco Ursa Minor dsphs are the most common type of galaxy Faintest ones emit less optical light than globular clusters Some retain their gas
5 The Virgo Cluster Virgo Cluster Catalog (BST85) ~2000 objects Based on morphological appearance Largely confirmed by redshift measurements Binggeli, Sandage & Tammann 1985, AJ 90, 1681
6 Structure in the Virgo Cluster Extended X-ray emission implies hot ICM Redshift distribution implies substructure including main cluster around M87, secondary one around M49, plus infalling spiral groups
7 Ram pressure sweeping Spirals in Virgo are HI deficient. Hydrodynamical simulations show effectiveness of ram pressure stripping Stripping occurs if ρ ICM V 2 > 2πG Σ gas Σ stars Ram pressure exerted by stationary gas on moving galaxy V is velocity of galaxy with respect to cluster Gravitational restoring force of stars and gas in galaxy Σ is surface density Vollmer et al. 2001
8 Harassment Supporting evidence: Intra cluster diffuse light (ICL) Intergalactic stars, ~10-40% of the cluster stellar population (Feldmeier et al., 2003) Tidal debris e.g. Plumes and arc-like structures The amount of tidal debris and ICL depends on local density, which supports the merger scenario (Combes, 2004) Rings of star formation that are more common than two-armed spirals (Oemler et al., 1997) Due to bars triggered during tidal interactions? Calcaneo-Roldan et al. (2000)
9 HI Deficiency: HI properties of 324 isolated UGC galaxies: Haynes & Giovanelli, 1984 Redone, including smaller, fainter galaxies by Solanes et al. 1996, ApJ 461, 609 (morphological type dependence) Def HI = log[ M(HI:D) pred ] - log[ M(HI:D) obs ] (positive for systems more deficient than isolated galaxies of same type)
10 HI deficiency in Virgo Dots: galaxies w/ measured HI Contours: HI deficiency Grey map: ROSAT kev Solanes et al Galaxies embedded in the hot X-ray gas are deficient in their HI relative to isolated galaxies of the same size and morphology.
11 Dwarf galaxies in Virgo BST in the VCC identified some 1000 dwarfs in Virgo 90% are de s The remainder are dis and BCDs des: the dominant population in Virgo
12 Ellipticals prefer highest density regions. Spirals are found preferentially in the field. Morphological segregation What about dwarfs? Dressler 1980
13 Morphological subclustering in Virgo Binggeli, Popescu & Tammann, AApS 1993, 98, 275
14 Distribution of galaxy types in the Virgo Cluster Dwarf Ellipticals Giant ellipticals Conselice, Gallagher & Wyse (2001) Number densities vs. distance from cluster center
15 Substructure in the Local Group Galaxies mainly clustered around the two principal galaxies MW & M31 Giant spirals dsph (+dell) dirr dirr/dsph Diagram from Eva Grebel
16 Local Group des Keck/DEIMOS observations of Local Group des NGC 205 NGC 147 NGC 185 (Choi, Guhathakurta & Johnston 2003) Surface photometry of NGC 205 consistent with early tidal disruption. M. Geha 2006 Ringberg conference
17 Hierarchical Formation Scenario Large galaxies (like the Milky Way and M31) form through merger and accretion of smaller systems Traces of discrete accretion events and interactions can be identified Bullock and Johnston
18 Why study dwarf galaxies in clusters? Chris Conselice 2006 Ringberg Conf. 1. Most numerous type of galaxy, particularly so in clusters -they are normal galaxies. The ultimate galaxy formation/evolution scenario must account for these objects. 2. In hierarchical galaxy formation, low mass systems are the first to form. Kauffmann & White (1993) Low-mass galaxies may be the oldest galaxies in the universe and we can learn how large galaxies formed through merging by studying the properties of these systems. Alternatively, they may have formed their stars most recently ( downsizing ).
19 Hubble Space Telescope Survey of the Perseus Cluster core 12 Orbits centered around the core of Perseus (Conselice (PI), Held, DeRijke)
20 Dwarf ellipticals exist in clusters and morphologically appear similar to Local Group dwarf ellipticals Discovered in 1950s by G. Reaves through a Virgo cluster imaging survey There are however 5-10 as many low-mass cluster galaxies per giant galaxy as there are in groups Low-Mass Galaxies in the Perseus Cluster
21 Perseus Cluster HST survey (Conselice, Gallagher & Wyse 03 sample) Real Dwarfs Compact dwarfs Background Spirals? Ambiguous cases
22 Cluster des deviate from the color-magnitude relation Clues for this deviation are old (e.g., Held & Mould 1994) Low L galaxies in clusters are a heterogenous population Color-Magnitude diagram for Perseus galaxies with Local Group des plotted. Both 'blue' and 'red des Conselice, Gallagher & Wyse (2003)
23 Other studies have found similar trends In the Fornax cluster (Rakos et al. 2001) and Coma cluster (Poggianti et al. 2001) Others (e.g., Adami et al. 2000) find similar results Low mass galaxies in clusters are not a homogenous population, especially at M > -15
24 Cluster des likely have a mix of stellar populations some might be metal rich Three stellar synthesis-modeled age tracts at constant metallicity (3 different ones) for different age populations. Conselice et al. (2003)
25 Cluster des appear to have properties fundamentally different from low-mass galaxies in groups Question: What part of the cluster environment produced this difference? Perhaps cluster des do not form by the standard supernova feedback mechanism (Dekel & Silk 1986). Some Possibilities (all with interesting implications) 1. Delayed formation des are not old 2. Containment by the intracluster medium 3. Removal of mass from accreted galaxies 4. Very massive dark halos
26 Conselice 2006 (Ringberg conference) I. Cluster dwarf elliptical galaxies have properties that are fundamentally different from low-mass galaxies in groups, including: - spatial extent - relative density compared with giants - types of stellar populations II. Some des in clusters have kinematic and stellar populations which appear fundamentally different from giant cluster galaxies suggests a different formation scenario III. Dwarf ellipticals in clusters have stellar populations with a mix of ages and metallicities at a given luminosity IV. These properties can be explained if some low-mass cluster galaxies formed both with the cluster, while others are the remnants of stripped galaxies accreted after the cluster was in place and/or delayed formation
27 des in Virgo des are widely distributed in Virgo. Do not cluster around giants Different dynamics from Es des versus de,ns At the faint end, M B ~ -12, only 10% of des are nucleated. At the bright end, M B -16, almost 100% are. A significant fraction of des in Virgo are rotation dominated. Binggeli et al. 2000, A&A, 359, 447 Conselice et al. 2001, ApJ 559, 791. Oh & lin 2000, ApJ 543, 620 van Zee et al. 2004, AJ
28 Velocity distribution of des is large, with more substructure than giant cluster galaxies Conselice et al. (2001) A sign of their formation mechanism?
29 The case of VCC 128 Debattista etal ApJL 651, L000 (rapid release) WFPC2 images => double nucleus? Separated by ~32 pc Components have same magnitude and color
30 The case of VCC 128 Debattista et al. Comparison of the galaxy (left) and the nucleus (right) with best-fitting SED (black line). Below: corresponding mean properties off the best-fit stellar populations. For the nucleus, the mass shown is for the two components combined. Best fit foreground star would be a G8V at 25 kpc but with V= /-190 km/s
31 The case of VCC 128 Debattista et al. Analysis of the nuclear spectrum assuming it is stellar. Open star = VCC 128 Open circle = NGC4486b (Kormendy & Gebhardt 2001) Others: Tremaine et al 2002
32 Internal Dynamics of NGC 205 CFHT12K mosaic images (Demers et al. 2003) Keck/ DEIMOS slitmasks chosen to lie along tidal extensions. Spectroscopic targets chosen to be likely RGB stars in NGC 205.
33 NGC 205 Inner rotation = 15 km s -1 velocity (km/s) radius (arcmin) Geha, Guhathakurta, Rich & Cooper (2006)
34 Local Group rotation curves NGC 205 Geha et al. (2006) velocity (km/s) NGC 147 Geha et al. in prep vrot = 17 km/s NGC 185 Bender et al (1991) radius (arcmin)
35 Rotation of des in Virgo Unlike des in the Local Group, some des in Virgo are rotationdominated. Long slit stellar absorption line spectroscopy from Palomar 5m Rotation curve Velocity dispersion van Zee et al 2004
36 de s as stripped di s? Rotationdominated des appear to avoid the cluster center Non-rotating des are found in the core van Zee et al 2004
37 Do dwarfs in clusters form after giants? Their globular clusters may tell us Keck spectroscopic study of globular clusters surrounding the de VCC 1386 in the Virgo cluster Numbered objects are the GCs with spectroscopy VCC 1386 in the Virgo Cluster Conselice 2006, ApJ, 639, 120
38 Color vs. Hβ diagram Similar comparison with (V-I) colors shows that ages are > 5 Gyr for these globular clusters
39 Can find des which are HI emitters - usually in outer parts Arecibo observations of des in Virgo, with HI emitters as solid circles Upper limits ~ 5*10^5 M(solar) in HI Conselice, O Neil, Gallagher & Wyse 2003 Most emitters are in the outer part of the Virgo cluster - evidence of infall and future stripping of material? or gas for a future generation of star formation?
40 The optical luminosity function LF: Number density of galaxies per unit L φ(l)dl ~ L α e L/L* dl φ(m)dm ~ (α+1)M exp( (M*-M) ) dl Press-Schechter (1974) formalism plus CDM fluctuation spectrum predicts faint end slope α = -1.8 The LF has been well-determined down to M R ~ -16 in a wide variety of environments, ranging from rich clusters to the field. The faint end (down to M R ~ -10) has been explored only in a few local regions. Low L galaxies can only be seen nearby Hard to measure redshifts for very faint, LSB objects Small number statistics render local LFs uncertain What do we know about dwarf galaxies in the Local Group and the Local Supercluster?
41 VCC Luminosity Function The LF is different among the different morphological classes The overall LF has a faint end slope of α = -1.3 But still large uncertainties Virgo is special place Small numbers at faint end VCC: Virgo Cluster Catalog Sandage, Binggeli & Tammann 1985AJ 90, 1759
42 Hunting for more dwarfs in Virgo CCD survey of 14 deg -2 part of INT WFC survey New technique for identifying dwarfs in Virgo Faint end slope of LF: /- 0.2 inner /- 0.2 outer Steeper value for the faint end slope in the outer region than the Inner core. Sabatini et al Ap Sp Sci 28, 97 Still small numbers of the faintest galaxies
43 The faint end slope of the LF Over the years, studies of the LF in Virgo have produced widely varying results for the faint end slope α of the optical LF Sandage, Binggeli & Tamman Phillips et al Trentham & Tully Sabatini et al CDM + Press-Schechter predicts α = -1.8
44 Dwarf galaxies in the Local Group des/dsphs found around giant galaxies dis found at larger distances; some isolated Where/what are the compact high velocity clouds (HVCs)? Here, we lump des and dsphs into the de class. desspan a wide range in surface brightness Right: simulation of LG des if located at 10 Mpc Katy Flint s homepage
45 Dwarfs are hard to find Green: lines of constant exponential scale length Blue: lines of constant isophotal size for an exponential profile with limiting μ of 26.7 R mag arcsec -2 Katy Flint s homepagehttp://
46 Ursa Major
47 Virgo vs Ursa Major Ursa Major Spiral-rich cluster D ~ 18.6 Mpc Fewer dwarfs than predicted ½ of dwarfs are blue irregulars α = -1.1 for 17 < M R < -11 Trentham & Tully 2002 MNRAS 335, 712 Trentham et al 2001 MNRAS 325, 385
48 Leo I: An interesting region Quite nearby D=10Mpc Leo I is dominated by early types Velocity dispersion is very small ~112 km/s Leo I contains the Leo ring of HI
49 Missing dwarfs in Leo I? Intermediate luminosity dwarfs missing!? 2' Flint et al. 2003, Ap Sp Sci 285, 191 Katy Flint s page:
50 Leo I LF by TT02 Faint end slope is very flat d/g = 1.6 +/- 0.9 Small number statistics! Trentham & Tully 2002 MNRAS 335, 712
51 Fraction of dwarfs that are des The fraction of the dwarf population that are des is much higher in Virgo than in Leo. Virgo f(de) ~ 83% Leo 40% Trentham & Tully 2002 MNRAS 335, 712
52 Far fewer dwarfs than predicted by CDM simulations Mean logarithmic slope for (-10 < M R < - 18) is 1.2. Hint of difference in slope Clear difference in dwarf-to-giant ratio (fewer dwarfs per giant in Ursa Major) TT02 LF for 6 groups Trentham & Tully 2002 MNRAS 335, 712
53 Comparison of 6 nearby groups Trentham & Tully (2002 MNRAS 335, 712) used the Suprime-Cam mosaic camera on the Subaru 8m telescope to image 6 nearby groups including Virgo to identify low surface brightness galaxies as faint as R ~ 22. Property N1407 Coma I Leo I N1023 UMa Virgo Dist (Mpc) E-Sab/Sb-Irr Vel disp (km/s) Area surveyed (Mpc -2 ) No. dw/mpc Dwarfs/giants 5.1± ± ± ± ± ±0. 8 Faint end slope α
54 Average LF of groups Average LF for the 6 groups normalized by N d as derived for each group Line has a slope / Trentham & Tully 2002 MNRAS 335, 712
55 Optical LF: Summary Low mass, faint, low surface brightness galaxies are hard to find. Both structurally and kinematically, des bear closer resemblance to dis than they do to normal Es. des and dis do not occupy the same volumes. Environment affect the morphological mix of the low mass population as well as its local number density Most studies of the optical LF suggest that environment plays a role in determining the faint end slope The discrepancies in counts of the faintest galaxies in different samples arise at least in part from the inherent difficulty in obtaining a reliable census of the faintest populations. We really don t know much about dwarf galaxies
56 Substructure in the Local Group Galaxies mainly clustered around the two principal galaxies MW & M31 Giant spirals dsph (+dell) dirr dirr/dsph Diagram from Eva Grebel
57 Stellar Streams around M31 Ibata et al McConnachie et al. 2004
58 Anatomy of M31 s Halo Giant Stream Progenitor: M32? NGC 205? PNe? Northern Spur? Northern Spur Eastern Shelf Andromeda NE (a.k.a. NE Blob Stream? G1 Clump Giant (Southern) Stream
59 M31 RGB Stars by Color (SDSS) And NE And V And IX 20 kpc Spatial Density of Probable M31 RGB Stars by Color (2 x 2 )
60 Andromeda IX Properties And IX: the lowest surface brightness (µ V,0 ~ 26.8 mag arcsec -2 ), lowest luminosity (M V = -8.3) galaxy found up to that point Low metallicity ([Fe/H] <~ - 2) σ v ~ 6 km s -1 (± 3) INT V,i 800s Zucker et al. 2004, Chapman et al. 2005
61 Andromeda IX Properties INT V,i 800s Subaru g r i Zucker et al. 2004, Chapman et al. 2005
62 Still Fainter -- Ursa Major M V = -7 (?) σ v : > 6.5 km s -1 Willman et al. 2005, Kleyna et al. 2005
63 More M31 Satellites? Andromeda V Andromeda X Andromeda IX
64 Andromeda X: Observations And X NOT And IX Subaru NGC 2419 SDSS
65 Andromeda X Properties µ V,0 ~ 26.7 mag arcsec -2 M V = -8.1 [Fe/H] <~ -2 σ v : TBD g, g - r i, g - i Zucker et al. 2006, Guhathakurta et al. 2006
66 LGS 3 Miller et al 2001, ApJ 562, 713 Stellar population dominated by old, metal poor stars but. Handful of young blue stars + HI gas Transition object between dsph and di?
67
68
Astro 6590: Dwarf galaxies
 Astro 6590: Dwarf galaxies Overview of dwarf galaxies Distinctive features of dwarfs Dwarfs vs giants Dwarfs vs globular clusters Dwarfs: challenges to CDM Missing satellite problem: how many dwarfs? The
Astro 6590: Dwarf galaxies Overview of dwarf galaxies Distinctive features of dwarfs Dwarfs vs giants Dwarfs vs globular clusters Dwarfs: challenges to CDM Missing satellite problem: how many dwarfs? The
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies
 II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
1924: Hubble classification scheme 1925: Hubble measures Cepheids (Period-Luminosity) in Andromeda case closed
 Galaxies 1920 - Curtis-Shapley debate on nature of spiral nebulae - distribution in the sky: zone of avoidance Curtis: extinction Shapley:? - apparent brightness of stars(?) observed in some nebulae Shapley:
Galaxies 1920 - Curtis-Shapley debate on nature of spiral nebulae - distribution in the sky: zone of avoidance Curtis: extinction Shapley:? - apparent brightness of stars(?) observed in some nebulae Shapley:
This week at Astro 3303
 This week at Astro 3303 HW #8-10 deal with your final project! (HW#8 is posted already) The project counts 20% of the grade and is expected to be a significant piece of work. HW#8 for next Wed: prepare
This week at Astro 3303 HW #8-10 deal with your final project! (HW#8 is posted already) The project counts 20% of the grade and is expected to be a significant piece of work. HW#8 for next Wed: prepare
Extreme Galaxies: Part I
 M87, giant elliptical in the Virgo Cluster Extreme Galaxies: Part I Looking at the extremes in galaxy properties may tell us much about the systematics of galaxy formation and evolution and can provide
M87, giant elliptical in the Virgo Cluster Extreme Galaxies: Part I Looking at the extremes in galaxy properties may tell us much about the systematics of galaxy formation and evolution and can provide
Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy
 Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories (Lick, Keck, TMT) University of California at Santa Cruz M31 s extended stellar
Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories (Lick, Keck, TMT) University of California at Santa Cruz M31 s extended stellar
HW#6 is due; please pass it in. HW#7 is posted; it requires you to write out answers clearly and completely explaining your logic.
 Oct 21, 2015 Basic properties of groups and clusters of galaxies Number density, structure X-ray emission from hot ICM Estimating cluster masses Cluster scaling relations Impact of environment on galaxies
Oct 21, 2015 Basic properties of groups and clusters of galaxies Number density, structure X-ray emission from hot ICM Estimating cluster masses Cluster scaling relations Impact of environment on galaxies
Galaxies -- Introduction. Classification -- Feb 13, 2014
 Galaxies -- Introduction Classification -- Feb 13, 2014 Why Begin with Classification? The Hubble system forms the basic vocabulary of the subject. The sequence of galaxy types reflects an underlying physical
Galaxies -- Introduction Classification -- Feb 13, 2014 Why Begin with Classification? The Hubble system forms the basic vocabulary of the subject. The sequence of galaxy types reflects an underlying physical
Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Hubble Sequence. Environment! Globular Clusters in Milky Way. kpc
 Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds
 The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
This week at Astro 3303
 This week at Astro 3303 HW #8-10 deal with your final project! (HW#8 is posted already) The project counts 20% of the grade and is expected to be a significant piece of work. HW#8 for next Wed: prepare
This week at Astro 3303 HW #8-10 deal with your final project! (HW#8 is posted already) The project counts 20% of the grade and is expected to be a significant piece of work. HW#8 for next Wed: prepare
Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd. Longair, chapter 3 + literature. Monday 18th Feb
 Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd. Longair, chapter 3 + literature Monday 18th Feb 1 The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram magnitude colour LOW MASS STARS LIVE A VERY VERY LONG TIME! 2 The
Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd. Longair, chapter 3 + literature Monday 18th Feb 1 The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram magnitude colour LOW MASS STARS LIVE A VERY VERY LONG TIME! 2 The
The effects of the environment on the evolution of late-type galaxies
 The effects of the environment on the evolution of late-type galaxies Alessandro BOSELLI Samuel BOISSIER, Luca CORTESE, Giuseppe GAVAZZI, Elisa TOLOBA Boselli et al 2006, ApJ, 651, 811 Boselli et al 2008,
The effects of the environment on the evolution of late-type galaxies Alessandro BOSELLI Samuel BOISSIER, Luca CORTESE, Giuseppe GAVAZZI, Elisa TOLOBA Boselli et al 2006, ApJ, 651, 811 Boselli et al 2008,
Myung Gyoon Lee ( 李明均 )
 Myung Gyoon Lee ( 李明均 ) With Observational Cosmology Team Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Nov 1-4, 2011, The 3 rd Subaru Conference/The 1 st NAOJ Symposium, Galactic
Myung Gyoon Lee ( 李明均 ) With Observational Cosmology Team Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Nov 1-4, 2011, The 3 rd Subaru Conference/The 1 st NAOJ Symposium, Galactic
1. Overview. Theory lags behind and there are many unsolved problems, including the nature of dark matter and dark energy.
 PC2491: Galaxies 1. Overview The aim of this course is to understand the observed properties of galaxies in the hierarchical structure formation model. This is a particular exciting time to study galaxies
PC2491: Galaxies 1. Overview The aim of this course is to understand the observed properties of galaxies in the hierarchical structure formation model. This is a particular exciting time to study galaxies
Large-Scale Structure
 Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
Dwarf Galaxies - ideal Laboratories to study astrophysical Processes
 Dwarf Galaxies - ideal Laboratories to study astrophysical Processes Gerhard Hensler University of Vienna Lecture 1 Lecture "Dwarf Galaxies",, Thursday 11:30 am Content/Presenter 7.3. Organization 14.3.
Dwarf Galaxies - ideal Laboratories to study astrophysical Processes Gerhard Hensler University of Vienna Lecture 1 Lecture "Dwarf Galaxies",, Thursday 11:30 am Content/Presenter 7.3. Organization 14.3.
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
The Combined effects of ram pressure stripping, and tidal influences on Virgo cluster dwarf galaxies, using N body/ SPH simulation
 The Combined effects of ram pressure stripping, and tidal influences on Virgo cluster dwarf galaxies, using N body/ SPH simulation Author: Rory Smith, Cardiff University Collaborators: Jonathon Davies,
The Combined effects of ram pressure stripping, and tidal influences on Virgo cluster dwarf galaxies, using N body/ SPH simulation Author: Rory Smith, Cardiff University Collaborators: Jonathon Davies,
Upcoming class schedule
 Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN)
 Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN) Thomas M. Brown (tbrown@stsci.edu) and Marc Postman (postman@stsci.edu) Space Telescope Science Institute Daniela Calzetti (calzetti@astro.umass.edu)
Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN) Thomas M. Brown (tbrown@stsci.edu) and Marc Postman (postman@stsci.edu) Space Telescope Science Institute Daniela Calzetti (calzetti@astro.umass.edu)
Galaxies Guiding Questions
 Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
Dwarf Elliptical Galaxies Nelson Caldwell. Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin
 eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/2615 Dwarf Elliptical Galaxies Nelson Caldwell From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of Physics
eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/2615 Dwarf Elliptical Galaxies Nelson Caldwell From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of Physics
Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology:
 Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology: Looking more deeply at the Hubble Sequence Galaxy Morphology How do you quantify the properties of galaxies? and how do you put them in groups which allow you to study physically
Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology: Looking more deeply at the Hubble Sequence Galaxy Morphology How do you quantify the properties of galaxies? and how do you put them in groups which allow you to study physically
Myung Gyoon LEE Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea
 Myung Gyoon LEE Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Cosmology and Structure Formation (The 4 th KIAS workshop), Nov 4-6, 2010, KIAS, Korea 1 M.G. Lee, Sungsoon Lim (SNU)
Myung Gyoon LEE Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Cosmology and Structure Formation (The 4 th KIAS workshop), Nov 4-6, 2010, KIAS, Korea 1 M.G. Lee, Sungsoon Lim (SNU)
Chapter 25: Galaxy Clusters and the Structure of the Universe
 Chapter 25: Galaxy Clusters and the Structure of the Universe Distribution of galaxies Evolution of galaxies Study of distant galaxies Distance derived from redshift Hubble s constant age of the Universe:
Chapter 25: Galaxy Clusters and the Structure of the Universe Distribution of galaxies Evolution of galaxies Study of distant galaxies Distance derived from redshift Hubble s constant age of the Universe:
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
Galaxy classification
 Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Stellar Populations in the Local Group
 Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 26 Jul 2005
 A High Resolution HI Study of Selected Virgo Galaxies - Preliminary Results on Gas Morphology & Extra-Planar Gas arxiv:astro-ph/0507592v1 26 Jul 2005 Aeree Chung and J. H. van Gorkom Department of Astronomy,
A High Resolution HI Study of Selected Virgo Galaxies - Preliminary Results on Gas Morphology & Extra-Planar Gas arxiv:astro-ph/0507592v1 26 Jul 2005 Aeree Chung and J. H. van Gorkom Department of Astronomy,
Astronomy 330 Lecture Dec 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 26 10 Dec 2010 Outline Clusters Evolution of cluster populations The state of HI sensitivity Large Scale Structure Cluster Evolution Why might we expect it? What does density determine?
Astronomy 330 Lecture 26 10 Dec 2010 Outline Clusters Evolution of cluster populations The state of HI sensitivity Large Scale Structure Cluster Evolution Why might we expect it? What does density determine?
What is an ultra-faint Galaxy?
 What is an ultra-faint Galaxy? UCSB KITP Feb 16 2012 Beth Willman (Haverford College) Large Magellanic Cloud, M V = -18 ~ 1/10 Milky Way luminosity image credit: Yuri Beletsky (ESO) and APOD NGC 205, M
What is an ultra-faint Galaxy? UCSB KITP Feb 16 2012 Beth Willman (Haverford College) Large Magellanic Cloud, M V = -18 ~ 1/10 Milky Way luminosity image credit: Yuri Beletsky (ESO) and APOD NGC 205, M
Survey of Astrophysics A110
 Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
 http://www.eso.org/sci/activities/santiago/personnel/visitors.html Morphological transformation in galaxy clusters > interpreted as the result of galaxy harassment (Moore et al. 1996). Harassment = 1
http://www.eso.org/sci/activities/santiago/personnel/visitors.html Morphological transformation in galaxy clusters > interpreted as the result of galaxy harassment (Moore et al. 1996). Harassment = 1
Chap.6 Formation and evolution of Local Group galaxies
 Chap.6 Formation and evolution of Local Group galaxies Properties of LG galaxies Formation history of LG galaxies Models to solve missing satellites problem Formation of Andromeda galaxy Future prospects
Chap.6 Formation and evolution of Local Group galaxies Properties of LG galaxies Formation history of LG galaxies Models to solve missing satellites problem Formation of Andromeda galaxy Future prospects
Hubble s Law. Tully-Fisher relation. The redshift. λ λ0. Are there other ways to estimate distances? Yes.
 Distances to galaxies Cepheids used by Hubble, 1924 to show that spiral nebulae like M31 were further from the Sun than any part of the Milky Way, therefore galaxies in their own right. Review of Cepheids
Distances to galaxies Cepheids used by Hubble, 1924 to show that spiral nebulae like M31 were further from the Sun than any part of the Milky Way, therefore galaxies in their own right. Review of Cepheids
2 Galaxy morphology and classification
 2 Galaxy morphology and classification Galaxy classification is an important first step towards a physical understanding of the nature of these objects. For a detailed description of classification systems
2 Galaxy morphology and classification Galaxy classification is an important first step towards a physical understanding of the nature of these objects. For a detailed description of classification systems
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 4 Mar 2004
 Recycling intergalactic and interstellar matter IAU Symposium Series, Vol. 217, 2004 Pierre-Alain Duc, Jonathan Braine and Elias Brinks, eds. Spiral Galaxy - ICM Interactions in the Virgo Cluster Jeffrey
Recycling intergalactic and interstellar matter IAU Symposium Series, Vol. 217, 2004 Pierre-Alain Duc, Jonathan Braine and Elias Brinks, eds. Spiral Galaxy - ICM Interactions in the Virgo Cluster Jeffrey
Using Globular Clusters to. Study Elliptical Galaxies. The View Isn t Bad... Omega Centauri. Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office M13
 Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
The M31 Dwarf Galaxy Population
 The M31 Dwarf Galaxy Population Marla Geha (Yale) Google Sky IRAS map Raja Guhathakurta (UCSC) Jason Kalirai (STScI) Steve Majewski (UVa) Roeland van der Marel (STScI) Racheal Beaton (UVa) Kirsten Howley
The M31 Dwarf Galaxy Population Marla Geha (Yale) Google Sky IRAS map Raja Guhathakurta (UCSC) Jason Kalirai (STScI) Steve Majewski (UVa) Roeland van der Marel (STScI) Racheal Beaton (UVa) Kirsten Howley
IV. Interacting Galaxies
 IV. Interacting Galaxies Examples of galaxies in interaction: Pairs of galaxies (NGC 4038/39) M 51 type (satellites) Arp 220 type Compact galaxy groups 2 1 B.A. Vorontsov-Velyaminov: Atlas and Catalog
IV. Interacting Galaxies Examples of galaxies in interaction: Pairs of galaxies (NGC 4038/39) M 51 type (satellites) Arp 220 type Compact galaxy groups 2 1 B.A. Vorontsov-Velyaminov: Atlas and Catalog
Galaxy clusters. Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems April 6, 2018
 Galaxy clusters László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 April 6, 2018 Satellite galaxies Large galaxies are surrounded by orbiting dwarfs approx. 14-16 satellites
Galaxy clusters László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 April 6, 2018 Satellite galaxies Large galaxies are surrounded by orbiting dwarfs approx. 14-16 satellites
Clusters and Groups of Galaxies
 Clusters and Groups of Galaxies Groups and clusters The Local Group Clusters: spatial distribution and dynamics Clusters: other components Clusters versus groups Morphology versus density Groups and Clusters
Clusters and Groups of Galaxies Groups and clusters The Local Group Clusters: spatial distribution and dynamics Clusters: other components Clusters versus groups Morphology versus density Groups and Clusters
Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically faint ellipticals. Part 3. After Chandra?
 Hot gas and AGN Feedback in Nearby Groups and Galaxies Part 1. Cool cores and outbursts from supermassive black holes in clusters, groups and normal galaxies Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically
Hot gas and AGN Feedback in Nearby Groups and Galaxies Part 1. Cool cores and outbursts from supermassive black holes in clusters, groups and normal galaxies Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically
Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment
 GALAXIES 626 Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment Why classify galaxies? The Hubble system gives us our basic description of galaxies. The sequence of galaxy types may reflect an underlying physical
GALAXIES 626 Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment Why classify galaxies? The Hubble system gives us our basic description of galaxies. The sequence of galaxy types may reflect an underlying physical
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters
 Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
What HI tells us about Galaxies and Cosmology
 What HI tells us about Galaxies and Cosmology Leo P Coma P Martha Haynes June 2018 1 18.06 ALFALFA: A Census of Gas-bearing Galaxies A galaxy is a gravitationally bound object that consists of billions
What HI tells us about Galaxies and Cosmology Leo P Coma P Martha Haynes June 2018 1 18.06 ALFALFA: A Census of Gas-bearing Galaxies A galaxy is a gravitationally bound object that consists of billions
Veilleux! see MBW ! 23! 24!
 Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
Galaxy formation and evolution. Astro 850
 Galaxy formation and evolution Astro 850 Introduction What are galaxies? Systems containing many galaxies, e.g. 10 11 stars in the Milky Way. But galaxies have different properties. Properties of individual
Galaxy formation and evolution Astro 850 Introduction What are galaxies? Systems containing many galaxies, e.g. 10 11 stars in the Milky Way. But galaxies have different properties. Properties of individual
Galaxies. Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations
 Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
What HI tells us about Galaxies and Cosmology
 What HI tells us about Galaxies and Cosmology Leo P Coma P Martha Haynes UAT16 16.06.14 1 ALFALFA: A Census of Gas-bearing Galaxies A galaxy is a gravitationally bound object that consists of billions
What HI tells us about Galaxies and Cosmology Leo P Coma P Martha Haynes UAT16 16.06.14 1 ALFALFA: A Census of Gas-bearing Galaxies A galaxy is a gravitationally bound object that consists of billions
Dwarf Galaxies in the nearby Universe
 Blue Compact Dwarf Galaxies: born to be wild Polychronis Papaderos Centro de Astrofísica da Universidade do Porto & Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço Estallidos Workshop 2015 Granada May 2015
Blue Compact Dwarf Galaxies: born to be wild Polychronis Papaderos Centro de Astrofísica da Universidade do Porto & Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço Estallidos Workshop 2015 Granada May 2015
Introduction and Background:
 Introduction and Background: Often times identifying the characteristics of extreme examples of galaxy morphology and properties (e.g. Perseus A, Malin 1, NGC 1569) provides very important constraints
Introduction and Background: Often times identifying the characteristics of extreme examples of galaxy morphology and properties (e.g. Perseus A, Malin 1, NGC 1569) provides very important constraints
View of the Galaxy from within. Lecture 12: Galaxies. Comparison to an external disk galaxy. Where do we lie in our Galaxy?
 Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
Zoccali et al. 2003, A&A, 399, 931. Overview of (old) Galactic components. bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo. metallicity & age distribution
 Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies
 Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 10 May 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 10 May 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 10 May 2007](/thumbs/79/78965434.jpg) A Pair of Boötes: A New Milky Way Satellite S. M. Walsh 1, H. Jerjen 1, B. Willman 2 arxiv:0705.1378v1 [astro-ph] 10 May 2007 ABSTRACT As part of preparations for a southern sky search for faint Milky
A Pair of Boötes: A New Milky Way Satellite S. M. Walsh 1, H. Jerjen 1, B. Willman 2 arxiv:0705.1378v1 [astro-ph] 10 May 2007 ABSTRACT As part of preparations for a southern sky search for faint Milky
Clicker Question: Galaxy Classification. What type of galaxy do we live in? The Variety of Galaxy Morphologies Another barred galaxy
 Galaxies Galaxies First spiral nebula found in 1845 by the Earl of Rosse. Speculated it was beyond our Galaxy. 1920 - "Great Debate" between Shapley and Curtis on whether spiral nebulae were galaxies beyond
Galaxies Galaxies First spiral nebula found in 1845 by the Earl of Rosse. Speculated it was beyond our Galaxy. 1920 - "Great Debate" between Shapley and Curtis on whether spiral nebulae were galaxies beyond
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 10 Aug 2010
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 10 Aug 2010 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 10 Aug 2010](/thumbs/96/126790797.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 14 August 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Hubble Space Telescope survey of the Perseus Cluster -III: The effect of local environment on dwarf galaxies
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 14 August 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Hubble Space Telescope survey of the Perseus Cluster -III: The effect of local environment on dwarf galaxies
Spiral Structure. m ( Ω Ω gp ) = n κ. Closed orbits in non-inertial frames can explain the spiral pattern
 Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
A galaxy is a self-gravitating system composed of an interstellar medium, stars, and dark matter.
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is a Galaxy? It s surprisingly difficult to answer the question what is a galaxy? Many astronomers seem content to say I know one when I see one. But one possible definition
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is a Galaxy? It s surprisingly difficult to answer the question what is a galaxy? Many astronomers seem content to say I know one when I see one. But one possible definition
Morphology-Density Relation. The fraction of the population that is spiral decreases from the field to high density regions. Nature or Nurture?
 Morphology-Density Relation Spirals/Irr The fraction of the population that is spiral decreases from the field to high density regions. S0 Ellipticals Nature or Nurture? Low High [Dressler 1980] The HI
Morphology-Density Relation Spirals/Irr The fraction of the population that is spiral decreases from the field to high density regions. S0 Ellipticals Nature or Nurture? Low High [Dressler 1980] The HI
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Oct 2003
 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
**TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
The kinematics of the extreme outer halo of. M87 as revealed by Planetary Nebulae. A.Longobardi M.Arnaboldi O.Gerhard. Garching 2015, 26th Feb.
 The kinematics of the extreme outer halo of A. M.Arnaboldi O.Gerhard Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik Garching 2015, 26th Feb. Outer regions of galaxies and structure formation Formation
The kinematics of the extreme outer halo of A. M.Arnaboldi O.Gerhard Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik Garching 2015, 26th Feb. Outer regions of galaxies and structure formation Formation
Lecture 30. The Galactic Center
 Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
Star systems like our Milky Way. Galaxies
 Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
The M31 Globular Cluster System
 The M31 Globular Cluster System How alike are the GC systems of the Milky Way and M31? Jean Brodie UCO/Lick Observatory UCSC 1 GCs trace the star formation and assembly GC formation occurs early Accompanies
The M31 Globular Cluster System How alike are the GC systems of the Milky Way and M31? Jean Brodie UCO/Lick Observatory UCSC 1 GCs trace the star formation and assembly GC formation occurs early Accompanies
HST Coma Treasury Survey Structure and Evolution of Dwarf Galaxies
 HST Coma Treasury Survey Structure and Evolution of Dwarf Galaxies Habib Khosroshahi (IPM) & Ehsan Kourkchi, Sarah Eftekherzadeh, Coma Treasury Survey Team http://astronomy.swin.edu.au/coma/ A successful
HST Coma Treasury Survey Structure and Evolution of Dwarf Galaxies Habib Khosroshahi (IPM) & Ehsan Kourkchi, Sarah Eftekherzadeh, Coma Treasury Survey Team http://astronomy.swin.edu.au/coma/ A successful
Lecture 19: Galaxies. Astronomy 111
 Lecture 19: Galaxies Astronomy 111 Galaxies What is a galaxy? Large assembly of stars, gas and dust, held together by gravity Sizes: Largest: ~1 Trillion stars (or more) Smallest: ~10 Million stars Milky
Lecture 19: Galaxies Astronomy 111 Galaxies What is a galaxy? Large assembly of stars, gas and dust, held together by gravity Sizes: Largest: ~1 Trillion stars (or more) Smallest: ~10 Million stars Milky
Clusters of Galaxies Groups: Clusters poor rich Superclusters:
 Clusters of Galaxies Galaxies are not randomly strewn throughout space. Instead the majority belong to groups and clusters of galaxies. In these structures, galaxies are bound gravitationally and orbit
Clusters of Galaxies Galaxies are not randomly strewn throughout space. Instead the majority belong to groups and clusters of galaxies. In these structures, galaxies are bound gravitationally and orbit
Globular Clusters in LSB Dwarf Galaxies
 Globular Clusters in LSB Dwarf Galaxies New results from HST photometry and VLT spectroscopy Thomas H. Puzia Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics in collaboration with Margarita E. Sharina SAO, Russian Academy
Globular Clusters in LSB Dwarf Galaxies New results from HST photometry and VLT spectroscopy Thomas H. Puzia Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics in collaboration with Margarita E. Sharina SAO, Russian Academy
Quantifying the (Late) Assembly History of Galaxies. Michael Pierce (University of Wyoming)
 Quantifying the (Late) Assembly History of Galaxies Michael Pierce (University of Wyoming) What I Think We Already Know: Morphology Density Relation (Assembly Depends on Environment) (Dressler 1980) Ratio
Quantifying the (Late) Assembly History of Galaxies Michael Pierce (University of Wyoming) What I Think We Already Know: Morphology Density Relation (Assembly Depends on Environment) (Dressler 1980) Ratio
Galaxies. The majority of known galaxies fall into one of three major classes: spirals (78 %), ellipticals (18 %) and irregulars (4 %).
 Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Thus Far. Intro / Some Definitions Hubble Classification Components of Galaxies. Specific Galaxy Types Star Formation Clusters of Galaxies
 Thus Far Intro / Some Definitions Hubble Classification Components of Galaxies Stars Gas Dust Black Holes Dark Matter Specific Galaxy Types Star Formation Clusters of Galaxies Components of Galaxies:
Thus Far Intro / Some Definitions Hubble Classification Components of Galaxies Stars Gas Dust Black Holes Dark Matter Specific Galaxy Types Star Formation Clusters of Galaxies Components of Galaxies:
Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies
 Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/gfe14/index.html Longair, chapter 3 Wednesday 5th Feb Binney & Merrifield, chapter 4 1 From pretty picture to science 2 Galaxies
Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/gfe14/index.html Longair, chapter 3 Wednesday 5th Feb Binney & Merrifield, chapter 4 1 From pretty picture to science 2 Galaxies
Galaxy Systems in the Optical and Infrared. Andrea Biviano INAF/Oss.Astr.Trieste
 Galaxy Systems in the Optical and Infrared Andrea Biviano INAF/Oss.Astr.Trieste Plan of the lectures: I. Identification, global properties, and scaling relations II. Structure and dynamics III. Properties
Galaxy Systems in the Optical and Infrared Andrea Biviano INAF/Oss.Astr.Trieste Plan of the lectures: I. Identification, global properties, and scaling relations II. Structure and dynamics III. Properties
The SPLASH Survey and Hierarchical Galaxy Halo Formation Raja Guhathakurta
 The SPLASH Survey and Hierarchical Galaxy Halo Formation Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories / University of California Santa Cruz Monday, September 29, 2008 Back to the Galaxy II,
The SPLASH Survey and Hierarchical Galaxy Halo Formation Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories / University of California Santa Cruz Monday, September 29, 2008 Back to the Galaxy II,
Clusters of Galaxies Groups: Clusters poor rich Superclusters:
 Clusters of Galaxies Galaxies are not randomly strewn throughout space. Instead the majority belong to groups and clusters of galaxies. In these structures, galaxies are bound gravitationally and orbit
Clusters of Galaxies Galaxies are not randomly strewn throughout space. Instead the majority belong to groups and clusters of galaxies. In these structures, galaxies are bound gravitationally and orbit
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Symbolically: E0.E7.. S0..Sa..Sb..Sc..Sd..Irr
 Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
Astronomy 730. Evolution
 Astronomy 730 Evolution Outline } Evolution } Formation of structure } Processes on the galaxy scale } Gravitational collapse, merging, and infall } SF, feedback and chemical enrichment } Environment }
Astronomy 730 Evolution Outline } Evolution } Formation of structure } Processes on the galaxy scale } Gravitational collapse, merging, and infall } SF, feedback and chemical enrichment } Environment }
1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions
 26 1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions List of topics Hubble classification scheme see Binney & Merrifield text Galaxy surface brightness profiles (JL 2.3.1, plus additional material) Galaxy luminosity function
26 1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions List of topics Hubble classification scheme see Binney & Merrifield text Galaxy surface brightness profiles (JL 2.3.1, plus additional material) Galaxy luminosity function
DWARF GALAXIES ALSO HAVE STELLAR HALOS
 THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 467 : L13 L16, 1996 August 10 1996. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DWARF GALAXIES ALSO HAVE STELLAR HALOS DANTE MINNITI 1, 2 AND ALBERT
THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 467 : L13 L16, 1996 August 10 1996. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DWARF GALAXIES ALSO HAVE STELLAR HALOS DANTE MINNITI 1, 2 AND ALBERT
2. Galaxy Evolution and Environment
 Topics in Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Galaxy Evolution and Environment Laerte Sodré Jr. IAG USP Vitória, February 2019 outline What is environment Physical process Environmental effects in groups and clusters
Topics in Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Galaxy Evolution and Environment Laerte Sodré Jr. IAG USP Vitória, February 2019 outline What is environment Physical process Environmental effects in groups and clusters
This week at Astro Lecture 06, Sep 13, Pick up PE#6. Please turn in HW#2. HW#3 is posted
 This week at Astro 3303 Lecture 06, Sep 13, 2017 Pick up PE#6 Please turn in HW#2 HW#3 is posted Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading: Continue reading
This week at Astro 3303 Lecture 06, Sep 13, 2017 Pick up PE#6 Please turn in HW#2 HW#3 is posted Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading: Continue reading
Quantifying the Assembly History of Elliptical Galaxies
 Quantifying the Assembly History of Elliptical Galaxies Michael Pierce (University of Wyoming) A Science Use Case for GMT and TMT Origin of Elliptical Galaxies! Elliptical Galaxies Form Through Mergers!
Quantifying the Assembly History of Elliptical Galaxies Michael Pierce (University of Wyoming) A Science Use Case for GMT and TMT Origin of Elliptical Galaxies! Elliptical Galaxies Form Through Mergers!
Summary of Last Lecture - Local Group!
 Summary of Last Lecture - Local Group Discussion of detailed properties of M31, M33 comparison to MW; differences in how they formed; MW very few 'major mergers' M31 more; not all galaxies even those close
Summary of Last Lecture - Local Group Discussion of detailed properties of M31, M33 comparison to MW; differences in how they formed; MW very few 'major mergers' M31 more; not all galaxies even those close
! # #%& () %+(%,#. / # 0 1(,& 23(4. 5( (67# :;!
 ! # #%& () %+(%,#. / # 0 1(,& 23(4. 5( (67#8.4 9299 2:;! #& (? # %&% (!) +%,! %./012.345!6+10! -0.8-1.0 7.23 1809!: 7! )+1(,!: 7! log N/O -1.2-1.4-1.6-1.8-2.0 7.6 7.8 8.0 8.2 8.4 8. 12+log
! # #%& () %+(%,#. / # 0 1(,& 23(4. 5( (67#8.4 9299 2:;! #& (? # %&% (!) +%,! %./012.345!6+10! -0.8-1.0 7.23 1809!: 7! )+1(,!: 7! log N/O -1.2-1.4-1.6-1.8-2.0 7.6 7.8 8.0 8.2 8.4 8. 12+log
The separate formation of different galaxy components
 The separate formation of different galaxy components Alfonso Aragón-Salamanca School of Physics and Astronomy University of Nottingham Overview: Galaxy properties and morphologies Main galaxy components:
The separate formation of different galaxy components Alfonso Aragón-Salamanca School of Physics and Astronomy University of Nottingham Overview: Galaxy properties and morphologies Main galaxy components:
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs
 A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
The Universe o. Galaxies. The Universe of. Galaxies. Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA
 Hello! The Universe of Galaxies The Universe o Galaxies Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA Galaxies: Stars: ~10 11 Mass: ~10 11 M Sun Contain stars, gas and dust, possibly a supermassive black hole at the centre. Much
Hello! The Universe of Galaxies The Universe o Galaxies Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA Galaxies: Stars: ~10 11 Mass: ~10 11 M Sun Contain stars, gas and dust, possibly a supermassive black hole at the centre. Much
Hubble Space Telescope survey of the Perseus Cluster I. The structure and dark matter content of cluster dwarf spheroidals
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 393, 1054 1062 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.14269.x Hubble Space Telescope survey of the Perseus Cluster I. The structure and dark matter content of cluster dwarf spheroidals
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 393, 1054 1062 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.14269.x Hubble Space Telescope survey of the Perseus Cluster I. The structure and dark matter content of cluster dwarf spheroidals
Observations of Globular Cluster Systems of Giant Galaxies
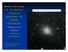 Observations of Globular Cluster Systems of Giant Galaxies Katherine Rhode Indiana University 38 x 38 R image of Virgo elliptical NGC 4472 KITP Conference January 2009 Observations of Globular Cluster
Observations of Globular Cluster Systems of Giant Galaxies Katherine Rhode Indiana University 38 x 38 R image of Virgo elliptical NGC 4472 KITP Conference January 2009 Observations of Globular Cluster
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
 Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
Globular Clusters in Massive Galaxies
 Globular Clusters in Massive Galaxies Patrick Durrell (Youngstown State University) + Pat Côté, John Blakeslee, Laura Ferrarese (Herzberg-Victoria), Eric Peng (Peking Univ) Chris Mihos (CWRU) + NGVS Team
Globular Clusters in Massive Galaxies Patrick Durrell (Youngstown State University) + Pat Côté, John Blakeslee, Laura Ferrarese (Herzberg-Victoria), Eric Peng (Peking Univ) Chris Mihos (CWRU) + NGVS Team
Astr 5465 Feb. 13, 2018 Distribution & Classification of Galaxies Distribution of Galaxies
 Astr 5465 Feb. 13, 2018 Distribution & Classification of Galaxies Distribution of Galaxies Faintest galaxies are distributed ~ uniformly over the sky except for the Galactic plane (zone of avoidance) Brighter
Astr 5465 Feb. 13, 2018 Distribution & Classification of Galaxies Distribution of Galaxies Faintest galaxies are distributed ~ uniformly over the sky except for the Galactic plane (zone of avoidance) Brighter
A Panoramic View of Globular Cluster Systems in the Virgo and Coma Clusters
 A Panoramic View of Globular Cluster Systems in the Virgo and Coma Clusters Eric Peng Peking University Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics Globular Cluster Systems z=12 GCs form early in the
A Panoramic View of Globular Cluster Systems in the Virgo and Coma Clusters Eric Peng Peking University Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics Globular Cluster Systems z=12 GCs form early in the
The Virgo cd galaxy M87 and its environment as revealed by Planetary Nebulae
 The Virgo cd galaxy M87 and its environment as A. M.Arnaboldi O.Gerhard C.J.Mihos Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik IAU XXIX GA 2015 Division J Outer regions of galaxies and structure formation
The Virgo cd galaxy M87 and its environment as A. M.Arnaboldi O.Gerhard C.J.Mihos Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik IAU XXIX GA 2015 Division J Outer regions of galaxies and structure formation
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
