Upcoming class schedule
|
|
|
- Maria Stevens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March then back to normal as of Tuesday 3rd April th
2 GALAXIES 626 Lecture 16: The effects of environment
3 The colour magnitude diagram Red sequence Note the bimodality of galaxy colours blue sequence Sloan DSS data
4 The colour magnitude diagram Dependence on environment
5 Fraction of red galaxies depends strongly on density.. Density dependence present at all luminosities. Bright and faint galaxies show trend with density
6 Moving galaxies from the blue to the red peak What are the implications for the galaxy transformation mechanism? Blue & red peaks are correlated with density, But Density evolves. Galaxies must move from one to the other How long do they take? If they take too long, then the gap between the peaks will be filled in...
7 Timescales for Galaxy Transformation How rapid must the blue red transition be? Two gaussian model Red Peak always fits the data well there is no room for an intermediate population. colour evolves rapidly if timescale for star formation to stop is short Blue Peak if transformations occur uniformly in time: need τ<0.5 Gyr
8 Summary There are distinct populations of red ( early ) and blue ( late ) galaxies The mean colors and spread of the two populations depends only weakly on environment But the relative abundance of the populations is a strong function of environment. Blue galaxies move quickly into the red population as their environment changes Why?
9 Evolution with redshift How does the dependence on environment change with redshift?
10 Galaxy clusters: z=0 z=0.39 z=0.83 Local galaxy clusters are dominated by passively evolving galaxies with high formation redshifts How does the evolution compare with the general field? Nature or nurture: clusters are built from groups. How do groups evolve?
11 Butcher Oemler Effect Concentrated clusters at high redshift may have Blue fraction more blue galaxies than concentrated clusters at low redshift But blue fraction depends strongly on luminosity and radius so care needs to be taken to evaluate blue fraction at same luminosity limit, and within same (appropriate) radius.
12 Cluster SFR evolution Butcher Oemler effect also seen in the general field Is the effect stronger in clusters? Field 2dF Clusters Redshift 1 Nakata et al. (2005) Based on sparsely sampled [OII] Postman, Lubin & Oke 2001 spectroscopy van Dokkum et al Suggests fraction of star Fisher et al forming galaxies evolves Czoske et al relatively weakly in clusters
13 Red galaxy fraction Red galaxy fraction Evolution of the red peak High density All galaxies MV < 20 Low density Redshift
14 Tying star formation to structure growth Groups Clusters
15 Low redshift groups Relation between star formation rate and local density Field Field
16 Groups There are fewer spiral galaxies in groups than in the field, at the same redshift. No evidence for more disturbance/irregularities in group galaxies Spiral fraction Field Spiral fraction E/S0 fraction Morphologies: Field Groups Groups Vel. Dispersion (km/s)
17 The connection between star Field formation rate, morphology Groups and environment Distributions are corrected for differences in luminosity function between group and field S0 Elliptical Early spiral Late spiral Like clusters, groups contain passive spirals: disk morphology but low star formation rates
18 Evolution in groups Fraction of non SF galaxies Use [OII] equivalent width to find fraction of galaxies without significant star formation most galaxies in groups at z~0.4 have significant star formation in contrast with local groups
19 Fraction of non SF galaxies Groups Fraction of non SF galaxies Field Group SFR evolution Fraction of non SF galaxies increases with decreasing redshift for both groups and field Insensitive to aperture effects
20 Summary More star formation in groups at z=0.5 than at z=0 On average, groups at 0<z<0.5 have less star formation and fewer spiral galaxies than the field. Passive spiral galaxies are a key component of groups at z=
21 Environmental Mechanisms Why should galaxy properties depend on the environment? Collisions / harassment "Strangulation" Ram pressure (actual effects) Different history...
22 Ram Pressure Stripping Mostly important in clusters where the surrounding gas density is high...
23 Ram Pressure Stripping ICM Clusters are not empty in fact, most baryons are in a diffuse form, the intra cluster medium As a galaxy travels through the ICM, it feels a force, the ram pressure aaaaaa 2 ρh v 2 πgσ R Σ g R The gas disk will be to radius R if: Gravitational Force due to ICM restoring force
24 Ram pressure Stripping - ICM simulations
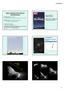
25 Galaxy NGC 4388 Expels Huge Gas Cloud NGC 4388 is a member of the the Virgo Cluster. It is classified as an active galaxy. One hypothesis holds that the gas was stripped away as NGC 4388 made its way through the intergalactic medium of the Virgo Cluster.
26 Galaxy interactions Gravitational interaction can produce major shifts in the gas and stars of the galaxy Major mergers produce massive star forming events but more minor repeated events can gradually remove the gas from a galaxy
27 Galaxy Collisions, Tides and Harassment Tidal truncation Slow encounter Depends on gradient of potential Big impact on the dark halo, but not significant for stellar component Impulsive heating Fast encounter Importance increases as relative velocity decreases Harassment The cumulative effect of repeated encounters
28 Galactic mergers Most dramatic examples: major mergers between galaxies of comparable mass. Large morphological changes as a consequence of the interaction. Observationally and theoretically, find that major mergers are uncommon - perhaps ~1 such merger in the lifetime of the Universe for a large galaxy in the field.
29 Examples of galaxy collisions in the real universe and in a simulation (Moore et al 1995)
30 The Antennae Galaxy
31 Best place for major mergers - small groups of galaxies Galaxies in rich clusters are generally less vulnerable to mergers, despite the very high density of galaxies because the velocities are higher.
32 Galaxy Collisions, Tides and Harassment Galaxy 1 size x force Perturbation to gradient Time of velocity of star encounter in galaxy 1 m Δv =2 r b V M Perturber, galaxy 2 ΔE = GM b3 2 r 2 b V 4G M m 4 3b V Change of internal energy of galaxy 1 2 r2
33 Minor mergers between galaxies of very different masses are much more common. Example: the Magellanic clouds Bound satellites orbiting within the extended halo of the Milky Way (~50 kpc distance) Eventually will spiral in and merge Sagittarius dwarf galaxy is another satellite which is now in process of merging
34 What effect does the merger have on the disk galaxy? How fast does the spiral-in and merger occur?
35 Dynamical Friction Why does the orbit of a satellite galaxy moving within the halo of another galaxy decay? Stars in one galaxy are scattered by gravitational perturbation of passing galaxy. Stellar distribution around the intruder galaxy becomes asymmetric - higher stellar density downstream than upstream. Gravitational force from stars produces a `frictional force which slows the orbital motion.
36 How quickly will the LMC merge with the Milky Way? Simple estimate - dynamical friction time: t friction» V» V km/s dv / dt 4 pg 2 Mnm ln L ~ Solar masses Galactic density at LMC for flat rotation curve estimate 3 x 10-4 Solar masses / pc3 With these numbers, estimate orbit will decay in ~3 Gyr Close satellite galaxies will merge!
37 Strangulation - removal of the gas halo Removes surrounding gas and so stops infall and star formation
38 Strangulation - removal of the gas halo
39 Summary of Mechanisms Ram pressure Needs dense ICM and high velocities clusters Collisions / harassment Mostly in groups where slow galaxy interactions are common "Strangulation" Removal of the gas halo: no more fuel supply Similar to ram pressure stripping but much easier!
40 Mechanisms Ram pressure Density too low Needs dense ICM and high velocities clusters Collisions / harassment Groups are preferred place! "Strangulation" Removal of the gas halo: no more fuel supply Similar to ram pressure stripping but much easier! Transformation too rapid
41 Mechanisms Collisions / harassment Groups are preferred place! What next? Look at individual galaxies to see if they provide evidence to support the big picture The best mechanism to explain the observational data but most effective in galaxy groups rather than clusters
42 Summary Clear bimodality of galaxy properties More dense environments... there is less star formation A higher fraction of passive/red galaxies But... Star Forming/blue galaxies have similar properties in all environments (only the fraction changes) Passive galaxies exist in all environments Galaxy transformation is rapid! Its most likely to happen in galaxy groups rather than in clusters
43 End
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies
 Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment
 GALAXIES 626 Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment Why classify galaxies? The Hubble system gives us our basic description of galaxies. The sequence of galaxy types may reflect an underlying physical
GALAXIES 626 Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment Why classify galaxies? The Hubble system gives us our basic description of galaxies. The sequence of galaxy types may reflect an underlying physical
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
Morphological Composition of z~0.4 Groups: The site of S0 Formation?
 Morphological Composition of z~0.4 Groups: The site of S0 Formation? Dave Wilman Wilman, Oemler, Mulchaey, McGee, Balogh & Bower 2009, ApJ, 692, 298 * *Also described as a Research Highlight in Nature,
Morphological Composition of z~0.4 Groups: The site of S0 Formation? Dave Wilman Wilman, Oemler, Mulchaey, McGee, Balogh & Bower 2009, ApJ, 692, 298 * *Also described as a Research Highlight in Nature,
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy
 Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
Spiral Structure. m ( Ω Ω gp ) = n κ. Closed orbits in non-inertial frames can explain the spiral pattern
 Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
Spiral Structure In the mid-1960s Lin and Shu proposed that the spiral structure is caused by long-lived quasistatic density waves The density would be higher by about 10% to 20% Stars, dust and gas clouds
Morphological Composition of z~0.4 Groups: The site of S0 Formation?
 Morphological Composition of z~0.4 Groups: The site of S0 Formation? Dave Wilman Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, Munich Wilman, Oemler, Mulchaey, McGee, Balogh & Bower 2009, ApJ, 692,
Morphological Composition of z~0.4 Groups: The site of S0 Formation? Dave Wilman Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, Munich Wilman, Oemler, Mulchaey, McGee, Balogh & Bower 2009, ApJ, 692,
Galaxy Ecology. an Environmental Impact Assessment. Frank van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Aspen,
Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Aspen,
Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology:
 Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology: Looking more deeply at the Hubble Sequence Galaxy Morphology How do you quantify the properties of galaxies? and how do you put them in groups which allow you to study physically
Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology: Looking more deeply at the Hubble Sequence Galaxy Morphology How do you quantify the properties of galaxies? and how do you put them in groups which allow you to study physically
The Evolution of Galaxy Morphologies in Clusters
 The Evolution of Galaxy Morphologies in Clusters New Views of the Universe KICP, U. Chicago, December 2005 Marc Postman & collaborators: Frank Bartko Txitxo Benitez John Blakeslee Nick Cross Ricardo Demarco
The Evolution of Galaxy Morphologies in Clusters New Views of the Universe KICP, U. Chicago, December 2005 Marc Postman & collaborators: Frank Bartko Txitxo Benitez John Blakeslee Nick Cross Ricardo Demarco
Galaxy Systems in the Optical and Infrared. Andrea Biviano INAF/Oss.Astr.Trieste
 Galaxy Systems in the Optical and Infrared Andrea Biviano INAF/Oss.Astr.Trieste Plan of the lectures: I. Identification, global properties, and scaling relations II. Structure and dynamics III. Properties
Galaxy Systems in the Optical and Infrared Andrea Biviano INAF/Oss.Astr.Trieste Plan of the lectures: I. Identification, global properties, and scaling relations II. Structure and dynamics III. Properties
Galaxy clusters. Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems April 6, 2018
 Galaxy clusters László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 April 6, 2018 Satellite galaxies Large galaxies are surrounded by orbiting dwarfs approx. 14-16 satellites
Galaxy clusters László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 April 6, 2018 Satellite galaxies Large galaxies are surrounded by orbiting dwarfs approx. 14-16 satellites
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters
 Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
Galaxy interaction and transformation
 Galaxy interaction and transformation Houjun Mo April 13, 2004 A lot of mergers expected in hierarchical models. The main issues: The phenomena of galaxy interaction: tidal tails, mergers, starbursts When
Galaxy interaction and transformation Houjun Mo April 13, 2004 A lot of mergers expected in hierarchical models. The main issues: The phenomena of galaxy interaction: tidal tails, mergers, starbursts When
Galaxy Ecology. an Environmental Impact Assessment. Frank van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Heidelberg,
Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Heidelberg,
Chapter 19 Galaxies. Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past. halo
 Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
ASTR 200 : Lecture 25. Galaxies: internal and cluster dynamics
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 25 Galaxies: internal and cluster dynamics 1 Galaxy interactions Isolated galaxies are often spirals One can find small galaxy `groups' (like the Local group) with only a few large spiral
ASTR 200 : Lecture 25 Galaxies: internal and cluster dynamics 1 Galaxy interactions Isolated galaxies are often spirals One can find small galaxy `groups' (like the Local group) with only a few large spiral
The Combined effects of ram pressure stripping, and tidal influences on Virgo cluster dwarf galaxies, using N body/ SPH simulation
 The Combined effects of ram pressure stripping, and tidal influences on Virgo cluster dwarf galaxies, using N body/ SPH simulation Author: Rory Smith, Cardiff University Collaborators: Jonathon Davies,
The Combined effects of ram pressure stripping, and tidal influences on Virgo cluster dwarf galaxies, using N body/ SPH simulation Author: Rory Smith, Cardiff University Collaborators: Jonathon Davies,
Clusters and Groups of Galaxies
 Clusters and Groups of Galaxies Groups and clusters The Local Group Clusters: spatial distribution and dynamics Clusters: other components Clusters versus groups Morphology versus density Groups and Clusters
Clusters and Groups of Galaxies Groups and clusters The Local Group Clusters: spatial distribution and dynamics Clusters: other components Clusters versus groups Morphology versus density Groups and Clusters
The Merger History of Massive Galaxies: Observations and Theory
 The Merger History of Massive Galaxies: Observations and Theory Christopher J. Conselice (University of Nottingham) Kuala Lumpur 2009 How/when do galaxies form/evolve? Some questions a. Do galaxies evolve
The Merger History of Massive Galaxies: Observations and Theory Christopher J. Conselice (University of Nottingham) Kuala Lumpur 2009 How/when do galaxies form/evolve? Some questions a. Do galaxies evolve
The separate formation of different galaxy components
 The separate formation of different galaxy components Alfonso Aragón-Salamanca School of Physics and Astronomy University of Nottingham Overview: Galaxy properties and morphologies Main galaxy components:
The separate formation of different galaxy components Alfonso Aragón-Salamanca School of Physics and Astronomy University of Nottingham Overview: Galaxy properties and morphologies Main galaxy components:
Set 3: Galaxy Evolution
 Set 3: Galaxy Evolution Environment. Galaxies are clustered, found in groups like the local group up to large clusters of galaxies like the Coma cluster Small satellite galaxies like the LMC and SMC are
Set 3: Galaxy Evolution Environment. Galaxies are clustered, found in groups like the local group up to large clusters of galaxies like the Coma cluster Small satellite galaxies like the LMC and SMC are
HW#6 is due; please pass it in. HW#7 is posted; it requires you to write out answers clearly and completely explaining your logic.
 Oct 21, 2015 Basic properties of groups and clusters of galaxies Number density, structure X-ray emission from hot ICM Estimating cluster masses Cluster scaling relations Impact of environment on galaxies
Oct 21, 2015 Basic properties of groups and clusters of galaxies Number density, structure X-ray emission from hot ICM Estimating cluster masses Cluster scaling relations Impact of environment on galaxies
Galaxy classification
 Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
A100H Exploring the Universe: Evolution of Galaxies. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the Universe: Evolution of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 12, 2016 Read: Chaps 20, 21 04/12/16 slide 1 Remainder of the semester: Chaps.
A100H Exploring the Universe: Evolution of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 12, 2016 Read: Chaps 20, 21 04/12/16 slide 1 Remainder of the semester: Chaps.
The star formation history of Virgo spiral galaxies
 The star formation history of Virgo spiral galaxies Combined spectral and photometric inversion Ciro Pappalardo INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Cluster galaxies Abell 1689 Physical effects acting
The star formation history of Virgo spiral galaxies Combined spectral and photometric inversion Ciro Pappalardo INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Cluster galaxies Abell 1689 Physical effects acting
Chapter 25: Galaxy Clusters and the Structure of the Universe
 Chapter 25: Galaxy Clusters and the Structure of the Universe Distribution of galaxies Evolution of galaxies Study of distant galaxies Distance derived from redshift Hubble s constant age of the Universe:
Chapter 25: Galaxy Clusters and the Structure of the Universe Distribution of galaxies Evolution of galaxies Study of distant galaxies Distance derived from redshift Hubble s constant age of the Universe:
Veilleux! see MBW ! 23! 24!
 Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
How environment shapes galaxy evolution: the satellite galaxies' perspective
 How environment shapes galaxy evolution: the satellite galaxies' perspective Anna Pasquali Astronomisches Rechen Institut, Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg NGC 4651 Why do we care? At
How environment shapes galaxy evolution: the satellite galaxies' perspective Anna Pasquali Astronomisches Rechen Institut, Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg NGC 4651 Why do we care? At
Course evaluations. Go to the Physics and Astronomy Department website. Click on Online Course Evaluation link
 Course evaluations. Go to the Physics and Astronomy Department website. www.pa.uky.edu Click on Online Course Evaluation link Link is open now. Do it soon. The nearest stars to the Sun. Barnard s Star
Course evaluations. Go to the Physics and Astronomy Department website. www.pa.uky.edu Click on Online Course Evaluation link Link is open now. Do it soon. The nearest stars to the Sun. Barnard s Star
Role of the Environment in the Evolution of Galaxies Richard Ellis
 Role of the Environment in the Evolution of Galaxies Richard Ellis http://www.astro.caltech.edu/~rse/ay211_env.ppt Hubble s Tuning Fork (1922-1926, 1936)..describes a true order among the galaxies, not
Role of the Environment in the Evolution of Galaxies Richard Ellis http://www.astro.caltech.edu/~rse/ay211_env.ppt Hubble s Tuning Fork (1922-1926, 1936)..describes a true order among the galaxies, not
Set 3: Galaxy Evolution
 Set 3: Galaxy Evolution Environment. Galaxies are clustered, found in groups like the local group up to large clusters of galaxies like the Coma cluster Small satellite galaxies like the LMC and SMC are
Set 3: Galaxy Evolution Environment. Galaxies are clustered, found in groups like the local group up to large clusters of galaxies like the Coma cluster Small satellite galaxies like the LMC and SMC are
2. Galaxy Evolution and Environment
 Topics in Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Galaxy Evolution and Environment Laerte Sodré Jr. IAG USP Vitória, February 2019 outline What is environment Physical process Environmental effects in groups and clusters
Topics in Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Galaxy Evolution and Environment Laerte Sodré Jr. IAG USP Vitória, February 2019 outline What is environment Physical process Environmental effects in groups and clusters
Galaxies Guiding Questions
 Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
Clicker Question: Galaxy Classification. What type of galaxy do we live in? The Variety of Galaxy Morphologies Another barred galaxy
 Galaxies Galaxies First spiral nebula found in 1845 by the Earl of Rosse. Speculated it was beyond our Galaxy. 1920 - "Great Debate" between Shapley and Curtis on whether spiral nebulae were galaxies beyond
Galaxies Galaxies First spiral nebula found in 1845 by the Earl of Rosse. Speculated it was beyond our Galaxy. 1920 - "Great Debate" between Shapley and Curtis on whether spiral nebulae were galaxies beyond
Lecture 19: Galaxies. Astronomy 111
 Lecture 19: Galaxies Astronomy 111 Galaxies What is a galaxy? Large assembly of stars, gas and dust, held together by gravity Sizes: Largest: ~1 Trillion stars (or more) Smallest: ~10 Million stars Milky
Lecture 19: Galaxies Astronomy 111 Galaxies What is a galaxy? Large assembly of stars, gas and dust, held together by gravity Sizes: Largest: ~1 Trillion stars (or more) Smallest: ~10 Million stars Milky
IV. Interacting Galaxies
 IV. Interacting Galaxies Examples of galaxies in interaction: Pairs of galaxies (NGC 4038/39) M 51 type (satellites) Arp 220 type Compact galaxy groups 2 1 B.A. Vorontsov-Velyaminov: Atlas and Catalog
IV. Interacting Galaxies Examples of galaxies in interaction: Pairs of galaxies (NGC 4038/39) M 51 type (satellites) Arp 220 type Compact galaxy groups 2 1 B.A. Vorontsov-Velyaminov: Atlas and Catalog
Element abundance ratios and star formation quenching: satellite versus central galaxies
 Element abundance ratios and star formation quenching: satellite versus central galaxies Anna Gallazzi INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Co#funded)by)the)) European)Union) with: Anna Pasquali (ARI-Heidelberg)
Element abundance ratios and star formation quenching: satellite versus central galaxies Anna Gallazzi INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Co#funded)by)the)) European)Union) with: Anna Pasquali (ARI-Heidelberg)
Hubble sequence galaxy classification scheme, originally based on appearance, but correlates with other properties as well.
 Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5. The sections we are skipping are all about processes that occur in the centers of galaxies, so I d like
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5. The sections we are skipping are all about processes that occur in the centers of galaxies, so I d like
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Symbolically: E0.E7.. S0..Sa..Sb..Sc..Sd..Irr
 Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
Large-Scale Structure
 Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
A100 Exploring the Universe: Evolution of Galaxies. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100 Exploring the Universe: Evolution of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy weinberg@astro.umass.edu November 29, 2012 Read: Chaps 21, 22 11/29/12 slide 1 Exam #3: Thu 6 Dec (last class) Final
A100 Exploring the Universe: Evolution of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy weinberg@astro.umass.edu November 29, 2012 Read: Chaps 21, 22 11/29/12 slide 1 Exam #3: Thu 6 Dec (last class) Final
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies
 II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
Classification Distribution in Space Galaxy Clusters. Formation and Evolution Hubble s Law
 The American astronomer Edwin Hubble in 1924, according to appearance of galaxies categorized them into four basic types. Classification Distribution in Space Galaxy Clusters Masses Formation and Evolution
The American astronomer Edwin Hubble in 1924, according to appearance of galaxies categorized them into four basic types. Classification Distribution in Space Galaxy Clusters Masses Formation and Evolution
Two Main Techniques. I: Star-forming Galaxies
 p.1/24 The high redshift universe has been opened up to direct observation in the last few years, but most emphasis has been placed on finding the progenitors of today s massive ellipticals. p.2/24 Two
p.1/24 The high redshift universe has been opened up to direct observation in the last few years, but most emphasis has been placed on finding the progenitors of today s massive ellipticals. p.2/24 Two
Galaxies. Need a (physically) meaningful way of describing the relevant properties of a galaxy.
 Galaxies Aim to understand the characteristics of galaxies, how they have evolved in time, and how they depend on environment (location in space), size, mass, etc. Need a (physically) meaningful way of
Galaxies Aim to understand the characteristics of galaxies, how they have evolved in time, and how they depend on environment (location in space), size, mass, etc. Need a (physically) meaningful way of
Using Globular Clusters to. Study Elliptical Galaxies. The View Isn t Bad... Omega Centauri. Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office M13
 Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016
 Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Lecture11; November 1, 2016 Previously on Astro-1 Introduction to stars Measuring distances Inverse square law: luminosity vs brightness Colors and spectral types, the H-R diagram
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Lecture11; November 1, 2016 Previously on Astro-1 Introduction to stars Measuring distances Inverse square law: luminosity vs brightness Colors and spectral types, the H-R diagram
Big Galaxies Are Rare! Cepheid Distance Measurement. Clusters of Galaxies. The Nature of Galaxies
 Big Galaxies Are Rare! Potato Chip Rule: More small things than large things Big, bright spirals are easy to see, but least common Dwarf ellipticals & irregulars are most common Faint, hard to see Mostly
Big Galaxies Are Rare! Potato Chip Rule: More small things than large things Big, bright spirals are easy to see, but least common Dwarf ellipticals & irregulars are most common Faint, hard to see Mostly
Gravitational Efects and the Motion of Stars
 Gravitational Efects and the Motion of Stars On the largest scales (galaxy clusters and larger), strong evidence that the dark matter has to be non-baryonic: Abundances of light elements (hydrogen, helium
Gravitational Efects and the Motion of Stars On the largest scales (galaxy clusters and larger), strong evidence that the dark matter has to be non-baryonic: Abundances of light elements (hydrogen, helium
Bulges and Disks: How galaxy structure and star formation changes with environment. Claire Lackner Kavli IPMU, University of Tokyo February 21, 2014
 Bulges and Disks: How galaxy structure and star formation changes with environment Claire Lackner Kavli IPMU, University of Tokyo February 21, 2014 Galaxy Environment Low Density High Density Low Mass
Bulges and Disks: How galaxy structure and star formation changes with environment Claire Lackner Kavli IPMU, University of Tokyo February 21, 2014 Galaxy Environment Low Density High Density Low Mass
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
A100 Exploring the Universe: Evolution of Galaxies. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100 Exploring the Universe: Evolution of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy weinberg@astro.umass.edu November 20, 2014 Read: Chaps 20, 21 11/20/14 slide 1 3 more presentations Yes, class meets
A100 Exploring the Universe: Evolution of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy weinberg@astro.umass.edu November 20, 2014 Read: Chaps 20, 21 11/20/14 slide 1 3 more presentations Yes, class meets
Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System
 Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System ES2a. The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ES2b. Galaxies are made of billions
Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System ES2a. The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ES2b. Galaxies are made of billions
ON THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY. The Metallicity distribution of the halo in the hierarchical merging paradigm
 ON THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY The Metallicity distribution of the halo in the hierarchical merging paradigm Halo abundance patterns and stellar yields Standard chemical evolution of solar
ON THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY The Metallicity distribution of the halo in the hierarchical merging paradigm Halo abundance patterns and stellar yields Standard chemical evolution of solar
1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions
 26 1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions List of topics Hubble classification scheme see Binney & Merrifield text Galaxy surface brightness profiles (JL 2.3.1, plus additional material) Galaxy luminosity function
26 1.4 Galaxy Light Distributions List of topics Hubble classification scheme see Binney & Merrifield text Galaxy surface brightness profiles (JL 2.3.1, plus additional material) Galaxy luminosity function
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 25. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 25 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 25 Galaxies and Dark Matter Units of Chapter 25 25.1 Dark Matter in the Universe 25.2 Galaxy Collisions 25.3 Galaxy Formation
Lecture Outlines Chapter 25 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 25 Galaxies and Dark Matter Units of Chapter 25 25.1 Dark Matter in the Universe 25.2 Galaxy Collisions 25.3 Galaxy Formation
Galaxies. CESAR s Booklet
 What is a galaxy? Figure 1: A typical galaxy: our Milky Way (artist s impression). (Credit: NASA) A galaxy is a huge collection of stars and interstellar matter isolated in space and bound together by
What is a galaxy? Figure 1: A typical galaxy: our Milky Way (artist s impression). (Credit: NASA) A galaxy is a huge collection of stars and interstellar matter isolated in space and bound together by
The Different Physical Mechanisms that Drive the Star-formation Histories of Giant and Dwarf Galaxies
 The Different Physical Mechanisms that Drive the Star-formation Histories of Giant and Dwarf Galaxies Chris Haines (University of Birmingham) Adriana Gargiulo, Gianni Busarello, Francesco La Barbera, Amata
The Different Physical Mechanisms that Drive the Star-formation Histories of Giant and Dwarf Galaxies Chris Haines (University of Birmingham) Adriana Gargiulo, Gianni Busarello, Francesco La Barbera, Amata
Outline. Astronomy: The Big Picture. Galaxies are the Fundamental Ecosystems of the Universe
 Outline Homework due on Friday 11:50 am Honor credit need to have those papers soon! Exam 2 Grades are posted. THE FINAL IS DECEMBER 15 th : 7-10pm! Style Galaxies are the Fundamental Ecosystems of the
Outline Homework due on Friday 11:50 am Honor credit need to have those papers soon! Exam 2 Grades are posted. THE FINAL IS DECEMBER 15 th : 7-10pm! Style Galaxies are the Fundamental Ecosystems of the
ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney
 ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 3 January 23, 2017 The Milky Way Galaxy: Vertical Distributions of Stars & the Stellar Disk disks exist in many astrophysical systems
ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 3 January 23, 2017 The Milky Way Galaxy: Vertical Distributions of Stars & the Stellar Disk disks exist in many astrophysical systems
Astronomy 730. Evolution
 Astronomy 730 Evolution Outline } Evolution } Formation of structure } Processes on the galaxy scale } Gravitational collapse, merging, and infall } SF, feedback and chemical enrichment } Environment }
Astronomy 730 Evolution Outline } Evolution } Formation of structure } Processes on the galaxy scale } Gravitational collapse, merging, and infall } SF, feedback and chemical enrichment } Environment }
Galaxy Cluster Mergers & Star Formation
 Galaxy Cluster Mergers & Star Formation Chiara Ferrari In collaboration with: C.Benoist, J.Brinchmann, A.Cappi, A.Diaferio, L.Feretti, R.Hunstead, W.Kapferer, T.Kronberger, J.C.Mauduit, S.Maurogordato,
Galaxy Cluster Mergers & Star Formation Chiara Ferrari In collaboration with: C.Benoist, J.Brinchmann, A.Cappi, A.Diaferio, L.Feretti, R.Hunstead, W.Kapferer, T.Kronberger, J.C.Mauduit, S.Maurogordato,
Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history
 Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history Author: Ana Hočevar Advisor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Department of Physics, University of Ljubljana March 18, 2006 Abstract Galaxy formation theory which predicts canibalism
Galactic dynamics reveals Galactic history Author: Ana Hočevar Advisor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Department of Physics, University of Ljubljana March 18, 2006 Abstract Galaxy formation theory which predicts canibalism
Astronomy 330 Lecture Nov 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 19 12 Nov 2010 Outline Ellipticals: Formation Quenching of star-formation Mergers and heating Stellar populations Fuel consumption theorem Dominant phases with time M3 Direct approach
Astronomy 330 Lecture 19 12 Nov 2010 Outline Ellipticals: Formation Quenching of star-formation Mergers and heating Stellar populations Fuel consumption theorem Dominant phases with time M3 Direct approach
Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes
 Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes Curtis Struck Iowa State Univ. Work in collab. with B. G. Elmegreen, D. Hunter, H. Salo Lowell Workshop, Oct. 2014 Exponential profiles
Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes Curtis Struck Iowa State Univ. Work in collab. with B. G. Elmegreen, D. Hunter, H. Salo Lowell Workshop, Oct. 2014 Exponential profiles
The so-called final parsec problem
 The so-called final parsec problem most galaxies contain black holes at their centers black-hole mass is 10 6-10 10 solar masses or roughly 0.2-0.5% of the stellar mass of the host galaxy galaxies form
The so-called final parsec problem most galaxies contain black holes at their centers black-hole mass is 10 6-10 10 solar masses or roughly 0.2-0.5% of the stellar mass of the host galaxy galaxies form
Astronomy 142, Spring April 2013
 Today in Astronomy 142: associations of galaxies Groups, clusters and superclusters Galaxy cluster dynamics Dark matter in clusters of galaxies Interacting galaxies Starbursts Origin of active galaxy nuclei?
Today in Astronomy 142: associations of galaxies Groups, clusters and superclusters Galaxy cluster dynamics Dark matter in clusters of galaxies Interacting galaxies Starbursts Origin of active galaxy nuclei?
Stability of star clusters and galaxies `Passive evolution ASTR 3830: Spring 2004
 Stability of star clusters and galaxies Already mentioned different ways in which a galaxy evolves: Constituent stars evolve, with higher mass stars leaving the main sequence and producing stellar remnants.
Stability of star clusters and galaxies Already mentioned different ways in which a galaxy evolves: Constituent stars evolve, with higher mass stars leaving the main sequence and producing stellar remnants.
Other Galaxy Types. Active Galaxies. A diagram of an active galaxy, showing the primary components. Active Galaxies
 Other Galaxy Types Active Galaxies Active Galaxies Seyfert galaxies Radio galaxies Quasars Origin??? Different in appearance Produce huge amount of energy Similar mechanism a Galactic mass black hole at
Other Galaxy Types Active Galaxies Active Galaxies Seyfert galaxies Radio galaxies Quasars Origin??? Different in appearance Produce huge amount of energy Similar mechanism a Galactic mass black hole at
Galaxies. The majority of known galaxies fall into one of three major classes: spirals (78 %), ellipticals (18 %) and irregulars (4 %).
 Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Moore et al Kenney et al. 2004
 Moore et al. 1996 Kenney et al. 2004 (i) Interaction with other cluster members and/or with the cluster potential (ii) Interactions with the hot gas that permeates massive galaxy systems. The influence
Moore et al. 1996 Kenney et al. 2004 (i) Interaction with other cluster members and/or with the cluster potential (ii) Interactions with the hot gas that permeates massive galaxy systems. The influence
Lecture 30. The Galactic Center
 Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
Astronomy 330 Lecture Dec 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 26 10 Dec 2010 Outline Clusters Evolution of cluster populations The state of HI sensitivity Large Scale Structure Cluster Evolution Why might we expect it? What does density determine?
Astronomy 330 Lecture 26 10 Dec 2010 Outline Clusters Evolution of cluster populations The state of HI sensitivity Large Scale Structure Cluster Evolution Why might we expect it? What does density determine?
The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data
 Venice, October 2003 The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Emergence of the Cosmic Initial Conditions > 105 independent ~ 5 measurements
Venice, October 2003 The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Emergence of the Cosmic Initial Conditions > 105 independent ~ 5 measurements
Dark matter and galaxy formation
 Dark matter and galaxy formation Galaxy rotation The virial theorem Galaxy masses via K3 Mass-to-light ratios Rotation curves Milky Way Nearby galaxies Dark matter Baryonic or non-baryonic A problem with
Dark matter and galaxy formation Galaxy rotation The virial theorem Galaxy masses via K3 Mass-to-light ratios Rotation curves Milky Way Nearby galaxies Dark matter Baryonic or non-baryonic A problem with
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation! Star Formation Efficiency!
 Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Outline. The Rotation of the Galaxy. Astronomy: The Big Picture
 I decided to cancel class next week! No homework until you get back. Honor credit need to have those papers soon! Exam 2 Grades are posted. Nighttime observing should be posted today. Interest in grade
I decided to cancel class next week! No homework until you get back. Honor credit need to have those papers soon! Exam 2 Grades are posted. Nighttime observing should be posted today. Interest in grade
The Classification of Galaxies
 Admin. 11/9/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
Admin. 11/9/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
An analogy. "Galaxies" can be compared to "cities" What would you like to know about cities? What would you need to be able to answer these questions?
 An analogy "Galaxies" can be compared to "cities" What would you like to know about cities? how does your own city look like? how big is it? what is its population? history? how did it develop? how does
An analogy "Galaxies" can be compared to "cities" What would you like to know about cities? how does your own city look like? how big is it? what is its population? history? how did it develop? how does
View of the Galaxy from within. Lecture 12: Galaxies. Comparison to an external disk galaxy. Where do we lie in our Galaxy?
 Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
13.1 Galaxy Evolution: Introduction
 13.1 Galaxy Evolution: Introduction Galaxies Must Evolve Stars evolve: they are born from ISM, evolve, shed envelopes or explode, enriching the ISM, more stars are born Structure evolves: density fluctuations
13.1 Galaxy Evolution: Introduction Galaxies Must Evolve Stars evolve: they are born from ISM, evolve, shed envelopes or explode, enriching the ISM, more stars are born Structure evolves: density fluctuations
The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds
 The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
Our Galaxy. We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky.
 Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
BUILDING GALAXIES. Question 1: When and where did the stars form?
 BUILDING GALAXIES The unprecedented accuracy of recent observations of the power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background leaves little doubt that the universe formed in a hot big bang, later cooling
BUILDING GALAXIES The unprecedented accuracy of recent observations of the power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background leaves little doubt that the universe formed in a hot big bang, later cooling
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
LESSON 1. Solar System
 Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines!
 Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies. Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Outline PART I: The Subhalo Mass Function (van den Bosch, Tormen & Giocoli, 2005) PART II: Statistical Properties of
Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Outline PART I: The Subhalo Mass Function (van den Bosch, Tormen & Giocoli, 2005) PART II: Statistical Properties of
HI as a probe for dwarf galaxy evolution in different environments: Voids to clusters
 HI as a probe for dwarf galaxy evolution in different environments: Voids to clusters Sushma Kurapati Collaborators: Jayaram N Chengalur, NCRA, India Simon Pustilnik, SAO RAS, Russia 2017 PHISCC Workshop
HI as a probe for dwarf galaxy evolution in different environments: Voids to clusters Sushma Kurapati Collaborators: Jayaram N Chengalur, NCRA, India Simon Pustilnik, SAO RAS, Russia 2017 PHISCC Workshop
What are the best constraints on theories from galaxy dynamics?
 What are the best constraints on theories from galaxy dynamics? TDG in MOND DM MOND Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris Tuesday 29 June 2010 O.Tiret Still most baryons are unidentified 6% in galaxies
What are the best constraints on theories from galaxy dynamics? TDG in MOND DM MOND Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris Tuesday 29 June 2010 O.Tiret Still most baryons are unidentified 6% in galaxies
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th
 Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
Galaxy Formation: Overview
 Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
What is the solar system?
 Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Our Galaxy. Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust. Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye
 Our Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye We get a special view of our own galaxy because we are part of it!
Our Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye We get a special view of our own galaxy because we are part of it!
11/9/2010. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements. Sky & Telescope s Week at a Glance. iphone App available now.
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Reading Quiz #11 Wednesday Mix of questions from today s lecture & reading for Wed. on active galaxies HW#10 in ICON due Friday (11/12) by 5 pm - available
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Reading Quiz #11 Wednesday Mix of questions from today s lecture & reading for Wed. on active galaxies HW#10 in ICON due Friday (11/12) by 5 pm - available
Citation for published version (APA): Boomsma, R. (2007). The disk-halo connection in NGC 6946 and NGC 253 s.n.
 University of Groningen The disk-halo connection in NGC 6946 and NGC 253 Boomsma, Rense IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen The disk-halo connection in NGC 6946 and NGC 253 Boomsma, Rense IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
The Accretion History of the Milky Way
 The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
GALAXIES 626. The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution:
 GALAXIES 626 The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution: Chemical evolution Observation of spiral and irregular galaxies show that the fraction of heavy elements varies with the fraction of the total mass which
GALAXIES 626 The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution: Chemical evolution Observation of spiral and irregular galaxies show that the fraction of heavy elements varies with the fraction of the total mass which
Galaxy evolution in clusters from the CLASH-VLT survey
 Galaxy evolution in clusters from the CLASH-VLT survey Andrea Biviano INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste (on behalf of the CLASH-VLT team) (part of) The CLASH-VLT team M. Nonino, co-i I. Balestra
Galaxy evolution in clusters from the CLASH-VLT survey Andrea Biviano INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste (on behalf of the CLASH-VLT team) (part of) The CLASH-VLT team M. Nonino, co-i I. Balestra
