arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 4 Jun 2018
|
|
|
- Asher May
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using vo tools to investigate Quasar Spectra (UNIQS) arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 4 Jun 218 1,4, Kasia Małek 3,5, Marzena Śniegowska 1,2, Bożena Czerny 1 1 Center for Theoretical Physics, al. Lotników 32/46, Warsaw 2 Warsaw University Observatory, al. Ujazdowskie 4, -478 Warsaw 3 National Center for Nuclear Research, ul. Hoża 69, -681 Warsaw 4 Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center, ul. Bartycka 18, -716 Warsaw 5 Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille, OAMP, Université Aix-Marseille, CNRS, 38 rue Frédéric Joliot-Curie, 13388, Marseille Cedex 13, France panda@cft.edu.pl The work initially started as a test to retrace the Quasar Main Sequence diagram [13] using TOPCAT, where they (and references therein) claimed that the parameter R FeII, which defines the Eigenvector 1 (EV1) is driven by the Eddington ratio alone. We subsequently construct a refined (error and redshift limited) sample from the original QSO catalog [12]. Based on our hypothesis - the main driver of the Quasar Main Sequence is the maximum of the accretion disk temperature (T BBB ) defined by the Big Blue Bump on the Spectral Energy Distribution. We select five extreme sources that have R FeII 4. and use the SED modelling code CIGALE to fit the multi-band photometric data obtained using Vizier photometric viewer and available in literature for these sources. Incorporating the prescription for broad emission-line species dependent virial factors, we derive the black hole masses for the entire QSO catalog and compare their distribution with the black hole masses in the original catalog. Here, we show the results of our analysis for one of the 5 extreme sources, SDSSJ We also show the detailed modeling, including the Fe II pseudo-continuum to estimate and compare the value of R FeII for this object. Revisiting narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies and their place in the Universe - NLS1 Padova 9-13 April 218 Padova Botanical Garden, Italy Speaker. c Copyright owned by the author(s) under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4. International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.).
2 A Quasar Main Sequence diagram Quasars are rapidly accreting supermassive black holes at the centres of massive galaxies. Their dependence on a broad range of parameters, many of which are highly correlated, across all wavelengths reflects the diversity in the physical conditions of the regions in the vicinity of the central core. This problem is analogous to the problem of identifying what governs the stellar main sequence on the Hertzsprung-Russel diagram [15] when the classification was based purely on spectral properties of the stellar atmospheres or plots were done in color-color diagrams. Figure 1: FWHM(Hβ) - R FeII distributions for error-corrected and z-limited sample of 4989 quasars with auxiliary axis (i) Eddington ratio; and (ii) Black Hole Mass. The filled circles are all the quasars in the sample, the open squares is the subset with R FeII 2 (157 sources) and the pluses is the subset with R FeII 4 (5 sources) The test case: SDSSJ A FWHM(Hβ) R FeII diagram for 2, SDSS quasars was presented in [13] using the QSO catalog [12], where the relative Fe II strength (R FeII = EW FeII /EW Hβ ) is considered for the FeII emission within Å [1]. To remove line widths with large errors, we limit the catalog by selecting only objects with <2% error in the FWHMs and the EWs using TOPCAT [16]. This gives us our base sample with 4989 quasars. Selecting sub-samples with R FeII 4., gives us 5 sources with the maximum R FeII = 6.56 which is almost a factor 3 more than the maximum shown in Fig.1 of [13]. Maximum of the Big Blue Bump In [1], we postulated that the true driver behind the EV1 is the maximum of the temperature in a multicolor accretion disk which is also the basic parameter determining the broad band shape of the quasar continuum emission: ( ).25 Ṁ T BBB = M 2 (1) We expect that this maximum temperature depends on the ratio of the Eddington ratio to the black hole mass (or, equivalently, on the ratio of the accretion rate to square of the black hole 1
3 1 12 log ºFº [erg s 1 cm 2 ] log º [Hz] Figure 2: (a) CIGALE [9] best model fitting for SDSSJ at z =.248. Reduced χ 2 =.86. The lower panel shows the relative residual flux; (b) The CIGALE model SED: The grey curve shows the total SED from the best fit. The red curve is the total (line+continuum) emission beyond the Lyman break ( 912 Å) removed. The black circles are the photometric data points with errorbars. The fit in the blue is the interpolation from CLOUDY [5]. mass). The dependence of the quasar main sequence on Eddington ratio and the black hole mass is clearly seen from the Fig.1. Using multi-wavelength photometric data, we produce the best fit for this source using CIGALE (Fig.2a). To construct the SED, we used Vizier photometric viewer and available literature to procure the data points. The SED is shown in Fig.2b along with a CLOUDY interpolation on the overplotted data with respective errorbars. Description of the CIGALE parameters used: sfhdelayedplusexpburst - This module implements a star formation history (SFH) described as a delayed rise of the SFR up to a maximum, first followed by an exponential decrease; then followed by an exponential starburst activity. bc3 - This module implements the [2] Single Stellar Populations. nebular - Module computing the nebular emission from the ultraviolet to the near-infrared. It includes both the nebular lines and the nubular continuum. It takes into account the escape fraction and the absorption by dust. dustatt calzleit - This module implements the [3] and [7] attenuation formulae, adding an UV-bump and a power law. dl214 - This module implements the [4] infra-red models. fritz26 - [6] AGN dust torus emission. Line dependent M BH distribution Taking the prescription from [8], we derived the black hole masses from the respective line widths (Hα, Hβ, ) incorporating the line-dependent virial factors (Fig.3,4b). Using the inferred line-widths from the [12] QSO catalog, we show the distribution of black hole masses as estimated from their respective broad emission lines, and compare them with the fiducial mass estimates from the catalog. In Fig.3, the lower panel shows the spread in the T BBB distribution and a similar comparison with the T BBB derived from the fiducial mass estimates. For all the cases, we have used the mass accretion rate (Ṁ) from the QSO catalog and the accretion efficiency, η =.83. A semi-automatic spectral fitting procedure Using the approach from [14], we show a detailed modeling of the quasar spectrum which includes the Fe II pseudo-continuum (Fig.4a). Owing to our fitting procedure that takes into account 2
4 logm [Msun] logm / [Msun] e4 2e4 5e4 1e5 2e5 5e5 2e4 3e4 4e4 5e4 1e5 2e5 Teff [K] Teff / K Figure 3: (top panel left): broad emission line-dependent M BH distribution compared with the fiducial M BH estimates from [12] QSO catalog for all available line widths in the catalog. (top panel right): similiar distribution for the our error-corrected sample of 4989 quasars. (bottom panel left, right): The derived T BBB distribution for the entire catalog and for our sample. the Balmer continuum, starlight contamination and several FeII templates, the value of R FeII thus estimated, is This value quoted in the [12] QSO catalog is Sources with strong Fe II emission are very difficult to model reliably, particularly the determination of the stellar content and the [OIII] line intensity is difficult due to strong Fe II contamination. These issues require careful analysis making a fully-automatic procedure relatively unreliable. Discussions We are currently working to automate this procedure to incorporate the CIGALE SED modeling, the CLOUDY interpolation and the semi-automatic spectral fitting. This will allow to put finer constraints on the estimates of T BBB and simultaneously provide a more reliable value to their R FeII. One of our immediate goals is to see the distribution of these derived values of R FeII against those in the catalog. With availability of newer and more reliable data (especially in the radio to study the distribution of RL/RQ in the context of these extreme objects, and X-rays - to model the optical-uv bump more accurately) the modeled SED structure will be refined. We will also test the line-dependent mass distribution replacing FWHM with a relatively better line-width parameter - the line dispersion, σ line [11]. We would like to test our CLOUDY generated SED that considers emission from a constant density single cloud (Panda et al. in prep) to these SEDs. Acknowledgements This conference has been organized with the support of the Department of Physics and Astronomy Galileo Galilei, the University of Padova, the National Institute of Astrophysics INAF, 3
5 7 6 9:5 et:al 211 Panda et:al (RFeII ) Panda et:al (RFeII 2) Panda et:al (RFeII 4) 5 9: Flux (erg/s/cm 2 /Å) 4 3 log M H BH [M ] 8:5 2 8: Rest frame wavelength (Å) 7: log M BH [M ] Figure 4: (a) The expanded region of the Hβ line of the source (pink line). Fit components: total flux (black line), starlight (blue line), power law (green dashed line), total line contribution (red line), and lower magenta line shows shape of the Fe II template d11-5-m2-2-5-mod broadened with a Gaussian of 7 km s 1 ; (b) Comparing M BH distribution: M BH estimates from the [8] prescription against the fiducial M BH from [12] QSO catalog. The linear fits in black (QSO catalog: m(slope)=.49, r=.85) and blue (our sample: m=.54, r=.91) the Padova Planetarium, and the RadioNet consortium. RadioNet has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 22 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support by Polish grant Nr. 215/17/B/ST9/3436/. References [1] Boroson, T.A.; Green, R.F. (1992), ApJS, 8, 19 [2] Bruzual, G.; Charlot, S. (23), MNRAS, 344, 4 [3] Calzetti, D. (26), HST proposal 118 [4] Dale, D.A.; Helou, G.; Magdis, G.E.; Armus, L.; Díaz-Santos, T.; Shi, Y. (214), ApJ, 784, 1 [5] Ferland, G. J.; Porter, R. L.; van Hoof, P. A. M.; Williams, R. J. R.; Abel, N. P.; Lykins, M. L. et al. (213). The 213 Release of Cloudy. RMxAA 49, [6] Fritz, J.; Franceschini, A.; tziminaoglou, E. (26), MNRAS, 366, 3 [7] Leitherer, C.; Calzetti, D.; Martins, L.P. (22), ApJ, 574, 1 [8] Mejía-Restrepo, J. E.; Lira, P.; Netzer, H.; Trakhtenbrot, B.; Capellupo, D. M. (217), Nat. Astr., 2, 63 [9] Noll, S.; Burgarella, D.; Giovannoli, E.; Buat, V.; Marcillac, D.; Muñoz-Mateos, J. C. (29), A&A, 57, 3 [1] Panda, S.; Czerny, B.; Wildy, C. (217), FrASS, 4, 33 [11] Rafiee, A.; ll, P. B. (211), MNRAS, 415, 2932 [12], Y.; Richards, G.T.; Strauss, M.A.; ll, P.B.; Schneider, D.P.; Snedden, S.; Bizyaev, D.; Brewington, H.; Malanushenko, V.; Malanushenko, E.; Oravetz, D.; Pan, K.; Simmons, A. (211), ApJS, 194, 45 [13], Y. and Ho, L. C. (214), Nature 513, [14] Śniegowska, M.; Czerny, B.; You, B.; Panda, S.; Wang, J.-M.; Hryniewicz, K.; Wildy, C. (218), (accepted in A&A) [15] Sulentic J. W., Zwitter, T., Marziani, P., and Dultzin-cyan, D. (2), ApJl 536, L5-L9 [16] Taylor M.B. (25), ASP, 29 (TOPCAT) 4
The physical driver of the optical Eigenvector 1 in Quasar Main Sequence. arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 27 Oct 2017
![The physical driver of the optical Eigenvector 1 in Quasar Main Sequence. arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 27 Oct 2017 The physical driver of the optical Eigenvector 1 in Quasar Main Sequence. arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 27 Oct 2017](/thumbs/92/109085114.jpg) arxiv:171.118v1 [astro-ph.he] 27 Oct 217 The physical driver of the optical Eigenvector 1 in Quasar Main Sequence Swayamtrupta Panda 1,2,, Bożena Czerny 1,2 and Conor Wildy 1 1 Center for Theoretical Physics,
arxiv:171.118v1 [astro-ph.he] 27 Oct 217 The physical driver of the optical Eigenvector 1 in Quasar Main Sequence Swayamtrupta Panda 1,2,, Bożena Czerny 1,2 and Conor Wildy 1 1 Center for Theoretical Physics,
The overall uncertainty of single-epoch virial black hole mass estimates and its implication to the M BH -σ relation
 The overall uncertainty of single-epoch virial black hole mass estimates and its implication to the M BH -σ relation and Daeseong Park Seoul National University E-mail: woo@astro.snu.ac.kr, pds2001@astro.snu.ac.kr
The overall uncertainty of single-epoch virial black hole mass estimates and its implication to the M BH -σ relation and Daeseong Park Seoul National University E-mail: woo@astro.snu.ac.kr, pds2001@astro.snu.ac.kr
The Narrow-Line Region of Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 Galaxies
 The Narrow-Line Region of Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 Galaxies National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 20A Datun Road, Beijing 100012, China E-mail: dwxu@nao.cas.cn S. Komossa Technische
The Narrow-Line Region of Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 Galaxies National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 20A Datun Road, Beijing 100012, China E-mail: dwxu@nao.cas.cn S. Komossa Technische
Measuring star formation in galaxies and its evolution. Andrew Hopkins Australian Astronomical Observatory
 Measuring star formation in galaxies and its evolution Andrew Hopkins Australian Astronomical Observatory Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of
Measuring star formation in galaxies and its evolution Andrew Hopkins Australian Astronomical Observatory Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of
A Unified Model for AGN. Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006
 A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
Astrophysical Quantities
 Astr 8300 Resources Web page: http://www.astro.gsu.edu/~crenshaw/astr8300.html Electronic papers: http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abstract_service.html (ApJ, AJ, MNRAS, A&A, PASP, ARAA, etc.) General astronomy-type
Astr 8300 Resources Web page: http://www.astro.gsu.edu/~crenshaw/astr8300.html Electronic papers: http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abstract_service.html (ApJ, AJ, MNRAS, A&A, PASP, ARAA, etc.) General astronomy-type
How to measure star formation rates in galaxies?
 How to measure star formation rates in galaxies? Véronique Buat 1 1. Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS, LAM (Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille) UMR7326, 13388, Marseille, France Our knowledge of cosmic
How to measure star formation rates in galaxies? Véronique Buat 1 1. Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS, LAM (Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille) UMR7326, 13388, Marseille, France Our knowledge of cosmic
Star Formation Indicators
 Star Formation Indicators Calzetti 2007 astro-ph/0707.0467 Brinchmann et al. 2004 MNRAS 351, 1151 SFR indicators in general! SFR indicators are defined from the X ray to the radio! All probe the MASSIVE
Star Formation Indicators Calzetti 2007 astro-ph/0707.0467 Brinchmann et al. 2004 MNRAS 351, 1151 SFR indicators in general! SFR indicators are defined from the X ray to the radio! All probe the MASSIVE
Properties of Narrow line Seyfert 1 galaxies
 Properties of Narrow line Seyfert 1 galaxies Suvendu Rakshit 1, C. S. Stalin 1, Hum Chand 2 and Xue-Guang Zhang 3 1 Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Block II, Koramangala, Bangalore-560034, India arxiv:1706.00797v1
Properties of Narrow line Seyfert 1 galaxies Suvendu Rakshit 1, C. S. Stalin 1, Hum Chand 2 and Xue-Guang Zhang 3 1 Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Block II, Koramangala, Bangalore-560034, India arxiv:1706.00797v1
AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects
 AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects 1 Evidence for Photoionization - continuum and Hβ luminosity
AGN Physics of the Ionized Gas Physical conditions in the NLR Physical conditions in the BLR LINERs Emission-Line Diagnostics High-Energy Effects 1 Evidence for Photoionization - continuum and Hβ luminosity
Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics. Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars
 Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars Emission Mechanisms Synchrotron Radiation Starburst Galaxies Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies BL Lac Galaxies
Astr 2320 Thurs. April 27, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 21: Active Galaxies and Quasars Emission Mechanisms Synchrotron Radiation Starburst Galaxies Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies BL Lac Galaxies
ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: optical spectroscopy. From AGN classification to Black Hole mass estimation
 ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: optical spectroscopy From AGN classification to Black Hole mass estimation Second Lecture Reverberation Mapping experiments & virial BH masses estimations Estimating AGN black hole
ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: optical spectroscopy From AGN classification to Black Hole mass estimation Second Lecture Reverberation Mapping experiments & virial BH masses estimations Estimating AGN black hole
Introduction to AGN. General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo
 Introduction to AGN General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo 1 AGN What are they? Active galactic nucleus compact object in the gravitational center of a galaxy that shows evidence
Introduction to AGN General Characteristics History Components of AGN The AGN Zoo 1 AGN What are they? Active galactic nucleus compact object in the gravitational center of a galaxy that shows evidence
TEMA 6. Continuum Emission
 TEMA 6. Continuum Emission AGN Dr. Juan Pablo Torres-Papaqui Departamento de Astronomía Universidad de Guanajuato DA-UG (México) papaqui@astro.ugto.mx División de Ciencias Naturales y Exactas, Campus Guanajuato,
TEMA 6. Continuum Emission AGN Dr. Juan Pablo Torres-Papaqui Departamento de Astronomía Universidad de Guanajuato DA-UG (México) papaqui@astro.ugto.mx División de Ciencias Naturales y Exactas, Campus Guanajuato,
Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin. Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar
 Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar Quasars Quasar = Quasi-stellar (radio) source Optical: faint, blue, star-like objects Radio: point radio sources, faint blue star-like optical
Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar Quasars Quasar = Quasi-stellar (radio) source Optical: faint, blue, star-like objects Radio: point radio sources, faint blue star-like optical
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 22 Jan 2002
 Average Quasar Spectra in the Context of Eigenvector 1 1 J. W. Sulentic 2, P. Marziani 3, R. Zamanov 3, R. Bachev 2,3, M. Calvani 3, D. Dultzin-Hacyan 4 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0201362v1 22 Jan 2002 Recent
Average Quasar Spectra in the Context of Eigenvector 1 1 J. W. Sulentic 2, P. Marziani 3, R. Zamanov 3, R. Bachev 2,3, M. Calvani 3, D. Dultzin-Hacyan 4 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0201362v1 22 Jan 2002 Recent
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 16 Apr 2004
 AGN Physics with the Sloan Digital Sky Survey ASP Conference Series, Vol. 311, 2004 G.T. Richards and P.B. Hall, eds. Quasars and Narrow-Line Seyfert 1s: Trends and Selection Effects arxiv:astro-ph/0404334v1
AGN Physics with the Sloan Digital Sky Survey ASP Conference Series, Vol. 311, 2004 G.T. Richards and P.B. Hall, eds. Quasars and Narrow-Line Seyfert 1s: Trends and Selection Effects arxiv:astro-ph/0404334v1
Probing the Origin of Supermassive Black Hole Seeds with Nearby Dwarf Galaxies. Amy Reines Einstein Fellow NRAO Charlottesville
 Probing the Origin of Supermassive Black Hole Seeds with Nearby Dwarf Galaxies Amy Reines Einstein Fellow NRAO Charlottesville Motivation: The origin of supermassive BH seeds Motivation: The origin of
Probing the Origin of Supermassive Black Hole Seeds with Nearby Dwarf Galaxies Amy Reines Einstein Fellow NRAO Charlottesville Motivation: The origin of supermassive BH seeds Motivation: The origin of
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Nov 2017](/thumbs/77/75789300.jpg) arxiv:1711.08926v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Nov 2017 The relationship between Mg II broad emission and quasar inclination angle Conor Wildy 1,, and Bozena Czerny 1 1 Center for Theoretical Physics, Polish Academy
arxiv:1711.08926v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Nov 2017 The relationship between Mg II broad emission and quasar inclination angle Conor Wildy 1,, and Bozena Czerny 1 1 Center for Theoretical Physics, Polish Academy
The optical Fe II emission lines in Active Galactic Nuclei
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 15, 176 c SAIt 21 Memorie della Supplementi The optical Fe II emission lines in Active Galactic Nuclei Jelena Kovačević 1, Luka Č. Popović 1, and Milan S. Dimitrijević 1,2 1 Astronomical
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 15, 176 c SAIt 21 Memorie della Supplementi The optical Fe II emission lines in Active Galactic Nuclei Jelena Kovačević 1, Luka Č. Popović 1, and Milan S. Dimitrijević 1,2 1 Astronomical
The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey
 The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey Elisabeta Lusso Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna-INAF/OABO A. Comastri, C. Vignali, G. Zamorani, M. Brusa, E. Treister, R. Gilli, M.
The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey Elisabeta Lusso Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna-INAF/OABO A. Comastri, C. Vignali, G. Zamorani, M. Brusa, E. Treister, R. Gilli, M.
Active Galactic Nuclei
 Active Galactic Nuclei Optical spectra, distance, line width Varieties of AGN and unified scheme Variability and lifetime Black hole mass and growth Geometry: disk, BLR, NLR Reverberation mapping Jets
Active Galactic Nuclei Optical spectra, distance, line width Varieties of AGN and unified scheme Variability and lifetime Black hole mass and growth Geometry: disk, BLR, NLR Reverberation mapping Jets
- AGN feedback in action?
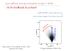 Gas outflows and star formation in type 2 AGNs - AGN feedback in action? Jong-Hak Woo (Seoul National Univ.) & Hyun-Jin Bae, Donghoon Son, Marios Karouzos Muse view of OIII outflows in NGC 7582 (Juneau+16
Gas outflows and star formation in type 2 AGNs - AGN feedback in action? Jong-Hak Woo (Seoul National Univ.) & Hyun-Jin Bae, Donghoon Son, Marios Karouzos Muse view of OIII outflows in NGC 7582 (Juneau+16
Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not?
 Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not? Y.Sophia Dai ( 戴昱 ) National Astronomical Observatories of China (NAOC) daysophia@gmail.com Close Correlations between SMBH and hosts M SMBH
Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not? Y.Sophia Dai ( 戴昱 ) National Astronomical Observatories of China (NAOC) daysophia@gmail.com Close Correlations between SMBH and hosts M SMBH
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2018](/thumbs/93/113435957.jpg) arxiv:1803866v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2018 Reverberation Mapping of High-z, High-luminosity Quasars Paulina Lira 1, Ismael Botti 2, Shai Kaspi 3 and Hagai Netzer 3,4 1, Departamento de Astronomía, Universidad
arxiv:1803866v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2018 Reverberation Mapping of High-z, High-luminosity Quasars Paulina Lira 1, Ismael Botti 2, Shai Kaspi 3 and Hagai Netzer 3,4 1, Departamento de Astronomía, Universidad
Hubble Space Telescope ultraviolet spectroscopy of blazars: emission lines properties and black hole masses. E. Pian, R. Falomo, A.
 Hubble Space Telescope ultraviolet spectroscopy of blazars: emission lines properties and black hole masses E. Pian, R. Falomo, A. Treves 1 Outline Extra Background Introduction Sample Selection Data Analysis
Hubble Space Telescope ultraviolet spectroscopy of blazars: emission lines properties and black hole masses E. Pian, R. Falomo, A. Treves 1 Outline Extra Background Introduction Sample Selection Data Analysis
Interpreting Galaxies across Cosmic Time with Binary Population Synthesis Models
 Interpreting Galaxies across Cosmic Time with Binary Population Synthesis Models Elizabeth Stanway Warwick (UK) with J J Eldridge (Auckland, NZ) and others Putting Warwick on the Map WARWICK! London @WarwickAstro
Interpreting Galaxies across Cosmic Time with Binary Population Synthesis Models Elizabeth Stanway Warwick (UK) with J J Eldridge (Auckland, NZ) and others Putting Warwick on the Map WARWICK! London @WarwickAstro
NEW CONSTRAINTS ON THE BLACK HOLE SPIN IN RADIO LOUD QUASARS
 NEW CONSTRAINTS ON THE BLACK HOLE SPIN IN RADIO LOUD QUASARS Andreas Schulze (NAOJ, EACOA Fellow)) Chris Done, Youjun Lu, Fupeng Zhang, Yoshiyuki Inoue East Asian Young Astronomers Meeting, EAYAM 2017
NEW CONSTRAINTS ON THE BLACK HOLE SPIN IN RADIO LOUD QUASARS Andreas Schulze (NAOJ, EACOA Fellow)) Chris Done, Youjun Lu, Fupeng Zhang, Yoshiyuki Inoue East Asian Young Astronomers Meeting, EAYAM 2017
The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction
 The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction Outline Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): > Why are they special? > The power source > Sources of Continuum Emission > Emission & absorption lines
The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction Outline Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): > Why are they special? > The power source > Sources of Continuum Emission > Emission & absorption lines
Luminous Quasars and AGN Surveys with ELTs
 Luminous Quasars and AGN Surveys with ELTs Roberto J. Assef Núcleo de Astronomía Universidad Diego Portales This Talk Will focus on two topics: 1. The most luminous (obscured) quasars 2. AGN surveys Big
Luminous Quasars and AGN Surveys with ELTs Roberto J. Assef Núcleo de Astronomía Universidad Diego Portales This Talk Will focus on two topics: 1. The most luminous (obscured) quasars 2. AGN surveys Big
High-redshift galaxies
 High-redshift galaxies Houjun Mo May 4, 2004 Galaxies can now be observed to z 6 Normal galaxies with 0.2 < z < 1 The Lyman-break population at z 3 The sub-mm sources at z 3 Between 1 2, spectroscopy desert,
High-redshift galaxies Houjun Mo May 4, 2004 Galaxies can now be observed to z 6 Normal galaxies with 0.2 < z < 1 The Lyman-break population at z 3 The sub-mm sources at z 3 Between 1 2, spectroscopy desert,
Active Galactic Nuclei OIII
 Active Galactic Nuclei In 1908, Edward Fath (1880-1959) observed NGC 1068 with his spectroscope, which displayed odd (and very strong) emission lines. In 1926 Hubble recorded emission lines of this and
Active Galactic Nuclei In 1908, Edward Fath (1880-1959) observed NGC 1068 with his spectroscope, which displayed odd (and very strong) emission lines. In 1926 Hubble recorded emission lines of this and
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 19 Aug 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 19 Aug 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 19 Aug 2009](/thumbs/83/88062827.jpg) The line parameters and ratios as the physical probe of the line emitting regions in AGN D. Ilić a, J. Kovačević b, L. Č. Popović b a Department of Astronomy, Faculty of Mathematics, University of Belgrade,
The line parameters and ratios as the physical probe of the line emitting regions in AGN D. Ilić a, J. Kovačević b, L. Č. Popović b a Department of Astronomy, Faculty of Mathematics, University of Belgrade,
Rajib Ganguly (University of Michigan-Flint)
 Rajib Ganguly (University of Michigan-Flint) A major theme in most recent simulations of galaxy evolution is AGN feedback, quantified by the kinetic luminosity, or power. In this ongoing work, we wish
Rajib Ganguly (University of Michigan-Flint) A major theme in most recent simulations of galaxy evolution is AGN feedback, quantified by the kinetic luminosity, or power. In this ongoing work, we wish
High Redshift Universe
 High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Dec 2001
 Spectral properties of the Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 Quasar PG1211+143 arxiv:astro-ph/0112387v1 17 Dec 2001 A. Janiuk 1, B. Czerny 1, G.M. Madejski 2 1) N. Copernicus Astronomical Centre, Bartycka 18, 00-716,
Spectral properties of the Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 Quasar PG1211+143 arxiv:astro-ph/0112387v1 17 Dec 2001 A. Janiuk 1, B. Czerny 1, G.M. Madejski 2 1) N. Copernicus Astronomical Centre, Bartycka 18, 00-716,
X-ray data analysis. Andrea Marinucci. Università degli Studi Roma Tre
 X-ray data analysis Andrea Marinucci Università degli Studi Roma Tre marinucci@fis.uniroma3.it Goal of these lectures X-ray data analysis why? what? how? Why? Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Physics in a
X-ray data analysis Andrea Marinucci Università degli Studi Roma Tre marinucci@fis.uniroma3.it Goal of these lectures X-ray data analysis why? what? how? Why? Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Physics in a
Active Galaxies & Emission Line Diagnostics
 Active Galaxies & Emission Line Diagnostics Review of Properties Discussed: 1) Powered by accretion unto a supermassive nuclear black hole 2) They are the possible precursors to luminous massive galaxies
Active Galaxies & Emission Line Diagnostics Review of Properties Discussed: 1) Powered by accretion unto a supermassive nuclear black hole 2) They are the possible precursors to luminous massive galaxies
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 23 Dec 2005
 3D spectroscopy as a tool for investigation of the BLR of lensed QSOs Luka Č. Popović Astronomical Observatory, Volgina 7, 11160 Belgrade, Serbia lpopovic@aob.bg.ac.yu arxiv:astro-ph/0512594v1 23 Dec 2005
3D spectroscopy as a tool for investigation of the BLR of lensed QSOs Luka Č. Popović Astronomical Observatory, Volgina 7, 11160 Belgrade, Serbia lpopovic@aob.bg.ac.yu arxiv:astro-ph/0512594v1 23 Dec 2005
Structure and Kinematics of the central BLR in AGN
 Structure and Kinematics of the central BLR in AGN Wolfram Kollatschny, Göttingen Divcibare, 2011 University Observatory Institute for Astrophysics Broad Line Region Size? radius: - 10-4...10-1 pc - 1...
Structure and Kinematics of the central BLR in AGN Wolfram Kollatschny, Göttingen Divcibare, 2011 University Observatory Institute for Astrophysics Broad Line Region Size? radius: - 10-4...10-1 pc - 1...
Introduction and Motivation
 1 Introduction and Motivation This last two days at this conference, we ve focused on two large questions regarding the role that AGNs play in galaxy evolution: My research focuses on exploring these questions
1 Introduction and Motivation This last two days at this conference, we ve focused on two large questions regarding the role that AGNs play in galaxy evolution: My research focuses on exploring these questions
Demographics of radio galaxies nearby and at z~0.55. Are radio galaxies signposts to black-hole mergers?
 Elaine M. Sadler Black holes in massive galaxies Demographics of radio galaxies nearby and at z~0.55 Are radio galaxies signposts to black-hole mergers? Work done with Russell Cannon, Scott Croom, Helen
Elaine M. Sadler Black holes in massive galaxies Demographics of radio galaxies nearby and at z~0.55 Are radio galaxies signposts to black-hole mergers? Work done with Russell Cannon, Scott Croom, Helen
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Dec 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Dec 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Dec 2013](/thumbs/92/110517281.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2012) Printed 22 September 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The behavior of quasar C iv emission-line properties with orientation Jessie C. Runnoe 1, M. S. Brotherton
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2012) Printed 22 September 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The behavior of quasar C iv emission-line properties with orientation Jessie C. Runnoe 1, M. S. Brotherton
CHARACTERIZATION OF AGN VARIABILITY IN THE OPTICAL AND NEAR INFRARED REGIMES
 Paulina Lira - Konrad Tristram - Patricia Arévalo - Julián Mejía-Restrepo - Luis Ho - Regis Cartier - Paolo Coppi - Minjin Kim - + CHARACTERIZATION OF AGN VARIABILITY IN THE OPTICAL AND NEAR INFRARED REGIMES
Paulina Lira - Konrad Tristram - Patricia Arévalo - Julián Mejía-Restrepo - Luis Ho - Regis Cartier - Paolo Coppi - Minjin Kim - + CHARACTERIZATION OF AGN VARIABILITY IN THE OPTICAL AND NEAR INFRARED REGIMES
Optical polarization from AGN
 Optical polarization from AGN Damien Hutsemékers (University of Liège, Belgium) Polarization & AGN II, 11-12 May 2015, Strasbourg, France 1 Outline Polarization properties of radio-quiet AGN including
Optical polarization from AGN Damien Hutsemékers (University of Liège, Belgium) Polarization & AGN II, 11-12 May 2015, Strasbourg, France 1 Outline Polarization properties of radio-quiet AGN including
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability. Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida
 Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
The Broad Line Region geometry: AGN with single peaked line proles
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 15, 171 c SAIt 2010 Memorie della Supplementi The Broad Line Region geometry: AGN with single peaked line proles E. Bon 1 and N. Gavrilović 1,2 1 Astronomical Observatory, Volgina7,
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 15, 171 c SAIt 2010 Memorie della Supplementi The Broad Line Region geometry: AGN with single peaked line proles E. Bon 1 and N. Gavrilović 1,2 1 Astronomical Observatory, Volgina7,
Gamma-ray variability of radio-loud narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies
 Gamma-ray variability of radio-loud narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies Università di Milano - Bicocca, Dip. di Fisica G. Occhialini, Piazza della Scienza 3, I-20126 Milano, Italy E-mail: giorgio.calderone@mib.infn.it
Gamma-ray variability of radio-loud narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies Università di Milano - Bicocca, Dip. di Fisica G. Occhialini, Piazza della Scienza 3, I-20126 Milano, Italy E-mail: giorgio.calderone@mib.infn.it
Galaxies with Active Nuclei. Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes
 Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 22 Mar 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 22 Mar 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 22 Mar 2018](/thumbs/94/118707883.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Varisco c ESO 2018 March 26, 2018 AGN mass estimates in large spectroscopic surveys: the effect of host galaxy light. Ludovica Varisco 1, Tullia Sbarrato 1, Giorgio
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Varisco c ESO 2018 March 26, 2018 AGN mass estimates in large spectroscopic surveys: the effect of host galaxy light. Ludovica Varisco 1, Tullia Sbarrato 1, Giorgio
Super Massive Black Hole Mass Determination and. Categorization of Narrow Absorption Line Quasars Outflows
 1 H. James Super Massive Black Hole Mass Determination and Categorization of Narrow Absorption Line Quasars Outflows By Hodari-Sadiki James April 30 th 2012 Abstract We looked at high luminosity quasars
1 H. James Super Massive Black Hole Mass Determination and Categorization of Narrow Absorption Line Quasars Outflows By Hodari-Sadiki James April 30 th 2012 Abstract We looked at high luminosity quasars
Active Galactic Nuclei - Zoology
 Active Galactic Nuclei - Zoology Normal galaxy Radio galaxy Seyfert galaxy Quasar Blazar Example Milky Way M87, Cygnus A NGC 4151 3C273 BL Lac, 3C279 Galaxy Type spiral elliptical, lenticular spiral irregular
Active Galactic Nuclei - Zoology Normal galaxy Radio galaxy Seyfert galaxy Quasar Blazar Example Milky Way M87, Cygnus A NGC 4151 3C273 BL Lac, 3C279 Galaxy Type spiral elliptical, lenticular spiral irregular
PoS(LCDU 2013)010. The extinction law at high redshift. Simona Gallerani Scuola Normale Superiore
 Scuola Normale Superiore E-mail: simona.gallerani@sns.it We analyze the optical-near infrared spectra of 33 quasars with redshifts 3.9 < z < 6.4 with the aim of investigating the properties of dust extinction
Scuola Normale Superiore E-mail: simona.gallerani@sns.it We analyze the optical-near infrared spectra of 33 quasars with redshifts 3.9 < z < 6.4 with the aim of investigating the properties of dust extinction
A zoo of transient sources. (c)2017 van Putten 1
 A zoo of transient sources (c)2017 van Putten 1 First transient @ first light UDFj-39546284, z~10.3 Bouwens, R.J., et al., Nature, 469, 504 Cuchiara, A. et al., 2011, ApJ, 736, 7 z=9.4: GRB 090429B, z~9.4
A zoo of transient sources (c)2017 van Putten 1 First transient @ first light UDFj-39546284, z~10.3 Bouwens, R.J., et al., Nature, 469, 504 Cuchiara, A. et al., 2011, ApJ, 736, 7 z=9.4: GRB 090429B, z~9.4
2. Active Galaxies. 2.1 Taxonomy 2.2 The mass of the central engine 2.3 Models of AGNs 2.4 Quasars as cosmological probes.
 2. Active Galaxies 2.1 Taxonomy 2.2 The mass of the central engine 2.3 Models of AGNs 2.4 Quasars as cosmological probes Read JL chapter 3 Active galaxies: interface with JL All of JL chapter 3 is examinable,
2. Active Galaxies 2.1 Taxonomy 2.2 The mass of the central engine 2.3 Models of AGNs 2.4 Quasars as cosmological probes Read JL chapter 3 Active galaxies: interface with JL All of JL chapter 3 is examinable,
Feeding the Beast. Chris Impey (University of Arizona)
 Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
Empirical Evidence for AGN Feedback
 Empirical Evidence for AGN Feedback Christy Tremonti MPIA (Heidelberg) / U. Wisconsin-Madison Aleks Diamond-Stanic (U. Arizona), John Moustakas (NYU) Much observational and theoretical evidence supports
Empirical Evidence for AGN Feedback Christy Tremonti MPIA (Heidelberg) / U. Wisconsin-Madison Aleks Diamond-Stanic (U. Arizona), John Moustakas (NYU) Much observational and theoretical evidence supports
Analysis of the rich optical iron-line spectrum of the x-ray variable I Zw 1 AGN 1H
 Analysis of the rich optical iron-line spectrum of the x-ray variable I Zw 1 AGN 1H0707 495 H Winkler, B Paul Department of Physics, University of Johannesburg, PO Box 524, 2006 Auckland Park, Johannesburg,
Analysis of the rich optical iron-line spectrum of the x-ray variable I Zw 1 AGN 1H0707 495 H Winkler, B Paul Department of Physics, University of Johannesburg, PO Box 524, 2006 Auckland Park, Johannesburg,
Chapter 10: Unresolved Stellar Populations
 Chapter 10: Unresolved Stellar Populations We now consider the case when individual stars are not resolved. So we need to use photometric and spectroscopic observations of integrated magnitudes, colors
Chapter 10: Unresolved Stellar Populations We now consider the case when individual stars are not resolved. So we need to use photometric and spectroscopic observations of integrated magnitudes, colors
Accretion Disks. 1. Accretion Efficiency. 2. Eddington Luminosity. 3. Bondi-Hoyle Accretion. 4. Temperature profile and spectrum of accretion disk
 Accretion Disks Accretion Disks 1. Accretion Efficiency 2. Eddington Luminosity 3. Bondi-Hoyle Accretion 4. Temperature profile and spectrum of accretion disk 5. Spectra of AGN 5.1 Continuum 5.2 Line Emission
Accretion Disks Accretion Disks 1. Accretion Efficiency 2. Eddington Luminosity 3. Bondi-Hoyle Accretion 4. Temperature profile and spectrum of accretion disk 5. Spectra of AGN 5.1 Continuum 5.2 Line Emission
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 5 Nov 2003
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. February 2, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Star formation rates of distant luminous infrared galaxies derived from Hα and IR luminosities H. Flores 1,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. February 2, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Star formation rates of distant luminous infrared galaxies derived from Hα and IR luminosities H. Flores 1,
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics
 Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Extinction curves in AGN
 Extinction curves in AGN Dust plume rising to 1,500 m elevation in San Joaquin Valley, Calif., s.e. of Bakersfield, December 1977. (Wilshire et al., 1996; photo by Sam Chase) B. Czerny Copernicus Astronomical
Extinction curves in AGN Dust plume rising to 1,500 m elevation in San Joaquin Valley, Calif., s.e. of Bakersfield, December 1977. (Wilshire et al., 1996; photo by Sam Chase) B. Czerny Copernicus Astronomical
Tracing quasar narrow-line regions across redshift: a library of high-s/n optical spectra
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stv126 Tracing quasar narrow-line regions across redshift: a library of high-s/n optical spectra A. Tammour, 1 S. C. Gallagher 1 and Gordon Richards 2 1 University of Western, 1151 Richmond
doi:10.1093/mnras/stv126 Tracing quasar narrow-line regions across redshift: a library of high-s/n optical spectra A. Tammour, 1 S. C. Gallagher 1 and Gordon Richards 2 1 University of Western, 1151 Richmond
Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei
 Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei A black hole is a region of spacetime from which gravity prevents anything, including light, from escaping. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently
Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei A black hole is a region of spacetime from which gravity prevents anything, including light, from escaping. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently
Science with the Intermediate Layer
 Science with the Intermediate Layer 20 deg 2 to depth of grizy=28.6,28.1,27.7,27.1,26.6 10 7 Mpc 3 at z 2 Jenny E. Greene (Princeton/Carnegie, Hubble Fellow) Watching Galaxies Assemble Thomas et al. 2005
Science with the Intermediate Layer 20 deg 2 to depth of grizy=28.6,28.1,27.7,27.1,26.6 10 7 Mpc 3 at z 2 Jenny E. Greene (Princeton/Carnegie, Hubble Fellow) Watching Galaxies Assemble Thomas et al. 2005
Thus Far. Intro / Some Definitions Hubble Classification Components of Galaxies. Specific Galaxy Types Star Formation Clusters of Galaxies
 Thus Far Intro / Some Definitions Hubble Classification Components of Galaxies Stars Gas Dust Black Holes Dark Matter Specific Galaxy Types Star Formation Clusters of Galaxies Components of Galaxies:
Thus Far Intro / Some Definitions Hubble Classification Components of Galaxies Stars Gas Dust Black Holes Dark Matter Specific Galaxy Types Star Formation Clusters of Galaxies Components of Galaxies:
Chien-Ting Chen! Dartmouth College
 AGN vs SF 2014 Durham University Obscuration and Star formation in Luminous Quasars Chien-Ting Chen! Dartmouth College In collaboration with: Ryan C. Hickox, Stacey Alberts, David M. Alexander, Roberto
AGN vs SF 2014 Durham University Obscuration and Star formation in Luminous Quasars Chien-Ting Chen! Dartmouth College In collaboration with: Ryan C. Hickox, Stacey Alberts, David M. Alexander, Roberto
Frequency of Seyfert Type Transitions in a Sample of 102 Local Active Galactic Nuclei
 Frequency of Seyfert Type Transitions in a Sample of 102 Local Active Galactic Nuclei Jordan Runco A Thesis presented for the degree of Physics Department of Physics California Polytechnic State University
Frequency of Seyfert Type Transitions in a Sample of 102 Local Active Galactic Nuclei Jordan Runco A Thesis presented for the degree of Physics Department of Physics California Polytechnic State University
Vivienne Wild. Timing the starburst AGN connection
 Vivienne Wild Timing the starburst AGN connection There are many theories successful in explaining the observed correlations between black holes and their host galaxies. In turn, these theories play a
Vivienne Wild Timing the starburst AGN connection There are many theories successful in explaining the observed correlations between black holes and their host galaxies. In turn, these theories play a
Active Galactic Nuclei
 Active Galactic Nuclei How were they discovered? How common are they? How do we know they are giant black holes? What are their distinctive properties? Active Galactic Nuclei for most galaxies the luminosity
Active Galactic Nuclei How were they discovered? How common are they? How do we know they are giant black holes? What are their distinctive properties? Active Galactic Nuclei for most galaxies the luminosity
Bursty stellar populations and AGN in bulges
 Bursty stellar populations and AGN in bulges Vivienne Wild (MPA Garching, MAGPOP) Guinevere Kauffmann, Tim Heckman Mergers and BH growth: Theory/Simulations Di Matteo, Springel, Hernquist, Nature 2005
Bursty stellar populations and AGN in bulges Vivienne Wild (MPA Garching, MAGPOP) Guinevere Kauffmann, Tim Heckman Mergers and BH growth: Theory/Simulations Di Matteo, Springel, Hernquist, Nature 2005
The BAT AGN Survey - Progress Report J. Tueller, C. Markwardt, L. Winter and R. Mushotzky Goddard Space Flight Center
 The BAT AGN Survey - Progress Report J. Tueller, C. Markwardt, L. Winter and R. Mushotzky Goddard Space Flight Center The Swift BAT (Burst and Transient Telescope) has been observing the whole sky in the
The BAT AGN Survey - Progress Report J. Tueller, C. Markwardt, L. Winter and R. Mushotzky Goddard Space Flight Center The Swift BAT (Burst and Transient Telescope) has been observing the whole sky in the
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 23 Jul 2004
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. draft2-aa September 1, 218 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Black hole growth by accretion Smita Mathur and Dirk Grupe arxiv:astro-ph/47512v1 23 Jul 24 Astronomy
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. draft2-aa September 1, 218 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Black hole growth by accretion Smita Mathur and Dirk Grupe arxiv:astro-ph/47512v1 23 Jul 24 Astronomy
Hot dust, warm dust and star formation in NLS1s
 Tel Aviv University E-mail: rivay@wise.tau.ac.il Hagai Netzer Tel Aviv University We present the results of a detailed investigation of the near- to far-infrared continuum emission of a large sample of
Tel Aviv University E-mail: rivay@wise.tau.ac.il Hagai Netzer Tel Aviv University We present the results of a detailed investigation of the near- to far-infrared continuum emission of a large sample of
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 20 Oct 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 20 Oct 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 20 Oct 2008](/thumbs/73/68920988.jpg) Systematic Uncertainties in Black Hole Masses Determined from Single Epoch Spectra Kelly D. Denney 1, Bradley M. Peterson 1, Matthias Dietrich 1, Marianne Vestergaard 2, and Misty C. Bentz 1,3 arxiv:0810.3234v1
Systematic Uncertainties in Black Hole Masses Determined from Single Epoch Spectra Kelly D. Denney 1, Bradley M. Peterson 1, Matthias Dietrich 1, Marianne Vestergaard 2, and Misty C. Bentz 1,3 arxiv:0810.3234v1
In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes
 In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes Stellar velocity fields MW Distant galaxies Gas motions gas disks around nearby black holes
In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes Stellar velocity fields MW Distant galaxies Gas motions gas disks around nearby black holes
Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5)
 Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5) Flow of story 4.1.1 4.1.2 4.1.3 Millimetric Spectroscopic Redshifts Millimetric Photometric Redshifts Redshift Distributions of 24 μm selected DSFG
Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5) Flow of story 4.1.1 4.1.2 4.1.3 Millimetric Spectroscopic Redshifts Millimetric Photometric Redshifts Redshift Distributions of 24 μm selected DSFG
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Aug 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Aug 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Aug 2007](/thumbs/93/112202180.jpg) THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL,???:??????, 0????????? Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 1/1/0 BLACK-HOLE MASS AND GROWTH RATE AT HIGH REDSHIFT HAGAI NETZER, 1 PAULINA LIRA, BENNY TRAKHTENBROT,
THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL,???:??????, 0????????? Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 1/1/0 BLACK-HOLE MASS AND GROWTH RATE AT HIGH REDSHIFT HAGAI NETZER, 1 PAULINA LIRA, BENNY TRAKHTENBROT,
A Search for High Redshift Type II Quasars from the SDSS BOSS Survey
 A Search for High Redshift Type II Quasars from the SDSS BOSS Survey Rachael M. Alexandroff Princeton University Department of Astrophysical Sciences Peyton Hall, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA rmalexan@princeton.edu
A Search for High Redshift Type II Quasars from the SDSS BOSS Survey Rachael M. Alexandroff Princeton University Department of Astrophysical Sciences Peyton Hall, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA rmalexan@princeton.edu
Deep Keck Spectroscopy of High-Redshift Quiescent Galaxies
 Sirio Belli Max-Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics Deep Keck Spectroscopy of High-Redshift Quiescent Galaxies with Andrew Newman and Richard Ellis Introduction Schawinski et al. 2014 red sequence
Sirio Belli Max-Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics Deep Keck Spectroscopy of High-Redshift Quiescent Galaxies with Andrew Newman and Richard Ellis Introduction Schawinski et al. 2014 red sequence
Quasars and Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)
 Quasars and Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Astronomy Summer School in Mongolia National University of Mongolia, Ulaanbaatar July 21-26, 2008 Kaz Sekiguchi Hubble Classification M94-Sa M81-Sb M101-Sc M87-E0
Quasars and Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Astronomy Summer School in Mongolia National University of Mongolia, Ulaanbaatar July 21-26, 2008 Kaz Sekiguchi Hubble Classification M94-Sa M81-Sb M101-Sc M87-E0
Foundations of Astrophysics
 Foundations of Astrophysics Barbara Ryden The Ohio State University Bradley M. Peterson The Ohio State University Preface xi 1 Early Astronomy 1 1.1 The Celestial Sphere 1 1.2 Coordinate Systems on a Sphere
Foundations of Astrophysics Barbara Ryden The Ohio State University Bradley M. Peterson The Ohio State University Preface xi 1 Early Astronomy 1 1.1 The Celestial Sphere 1 1.2 Coordinate Systems on a Sphere
Science in the Virtual Observatory
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 80, 352 c SAIt 2009 Memorie della Science in the Virtual Observatory M.G. Allen Observatoire de Strasbourg UMR 7550 11 Rue de l Universite, F-67000 Strasbourg, France e-mail: allen@astro.u-strasbg.fr
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 80, 352 c SAIt 2009 Memorie della Science in the Virtual Observatory M.G. Allen Observatoire de Strasbourg UMR 7550 11 Rue de l Universite, F-67000 Strasbourg, France e-mail: allen@astro.u-strasbg.fr
NuSTAR observation of the Arches cluster: X-ray spectrum extraction from a 2D image
 NuSTAR observation of the Arches cluster: X-ray spectrum extraction from a 2D image Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia E-mail: krivonos@iki.rssi.ru The NuSTAR mission performed a long (200
NuSTAR observation of the Arches cluster: X-ray spectrum extraction from a 2D image Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia E-mail: krivonos@iki.rssi.ru The NuSTAR mission performed a long (200
Active Galaxies & Quasars
 Active Galaxies & Quasars Normal Galaxy Active Galaxy Galactic Nuclei Bright Active Galaxy NGC 5548 Galaxy Nucleus: Exact center of a galaxy and its immediate surroundings. If a spiral galaxy, it is the
Active Galaxies & Quasars Normal Galaxy Active Galaxy Galactic Nuclei Bright Active Galaxy NGC 5548 Galaxy Nucleus: Exact center of a galaxy and its immediate surroundings. If a spiral galaxy, it is the
Stellar populations of quasar host galaxies
 Knud Jahnke AIP Galaxies division Hauskolloquium 10.01.2003 Introduction/motivation Multicolour imaging On-nucleus spectroscopy What does this teach us? Outlook Overview Introduction Introduction HE 1043
Knud Jahnke AIP Galaxies division Hauskolloquium 10.01.2003 Introduction/motivation Multicolour imaging On-nucleus spectroscopy What does this teach us? Outlook Overview Introduction Introduction HE 1043
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 23 Jul 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 23 Jul 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 23 Jul 2016](/thumbs/96/127104661.jpg) Optical Spectroscopy of Four Young Radio Sources Xu-Liang Fan a,b,d, Jin-Ming Bai a,b, Chen Hu c, Jian-Guo Wang a,b arxiv:1607.06937v1 [astro-ph.he] 23 Jul 2016 a Yunnan Observatories, Chinese Academy
Optical Spectroscopy of Four Young Radio Sources Xu-Liang Fan a,b,d, Jin-Ming Bai a,b, Chen Hu c, Jian-Guo Wang a,b arxiv:1607.06937v1 [astro-ph.he] 23 Jul 2016 a Yunnan Observatories, Chinese Academy
H-alpha monitoring of OJ 287 in
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 14198 c ESO 218 November 13, 218 H-alpha monitoring of OJ 287 in 2-8 K. Nilsson 1,2, L. O. Takalo 1, H. J. Lehto 1, and A. Sillanpää 1 1 Tuorla Observatory, Department
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 14198 c ESO 218 November 13, 218 H-alpha monitoring of OJ 287 in 2-8 K. Nilsson 1,2, L. O. Takalo 1, H. J. Lehto 1, and A. Sillanpää 1 1 Tuorla Observatory, Department
Quasars as dark energy probes
 Quasars as dark energy probes Bożena Czerny Center for Theoretical Physics & Copernicus Astronomical Center, Warsaw, Poland In collaboration with J. Średzińska, M. Bilicki, M. Chodorowski, K. Hryniewicz,
Quasars as dark energy probes Bożena Czerny Center for Theoretical Physics & Copernicus Astronomical Center, Warsaw, Poland In collaboration with J. Średzińska, M. Bilicki, M. Chodorowski, K. Hryniewicz,
GALAXY EVOLUTION STUDIES AND HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING
 GALAXY EVOLUTION STUDIES AND HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING Andreas Efstathiou European University Cyprus Astrophysics and HPC group ACTIVE AREAS OF ASTRONOMY OPPORTUNITIES FOR THEORETICAL, OBSERVATIONAL AND
GALAXY EVOLUTION STUDIES AND HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING Andreas Efstathiou European University Cyprus Astrophysics and HPC group ACTIVE AREAS OF ASTRONOMY OPPORTUNITIES FOR THEORETICAL, OBSERVATIONAL AND
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 13 Apr 2006
 **FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Clusters of Galaxies at 1 < z < 2 : The Spitzer Adaptation of the Red-Sequence Cluster Survey arxiv:astro-ph/0604289
**FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Clusters of Galaxies at 1 < z < 2 : The Spitzer Adaptation of the Red-Sequence Cluster Survey arxiv:astro-ph/0604289
 ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI I. AN INTRODUCTION Sebastian F. Hoenig Lecturer & Marie Curie Fellow Outline and learning goals I. Phenomenology What are AGN? How are they identified? II. Energy output Where is
ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI I. AN INTRODUCTION Sebastian F. Hoenig Lecturer & Marie Curie Fellow Outline and learning goals I. Phenomenology What are AGN? How are they identified? II. Energy output Where is
LePhare Download Install Syntax Examples Acknowledgement Le Phare
 LePhare Download Install Syntax Examples Acknowledgement http://www.lam.fr/lephare.html Le Phare A Photometric software to measure redshifts & galaxy properties Arnouts S. & Ilbert O. Basic concept SED
LePhare Download Install Syntax Examples Acknowledgement http://www.lam.fr/lephare.html Le Phare A Photometric software to measure redshifts & galaxy properties Arnouts S. & Ilbert O. Basic concept SED
JWST Extragalactic Mock Catalog Documentation
 JWST Extragalactic Mock Catalog Documentation Version 1.1 Kevin Hainline Emma Curtis-Lake Christina Williams Jacopo Chevallard Last Update: May 23, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Mock catalog overview.....................................
JWST Extragalactic Mock Catalog Documentation Version 1.1 Kevin Hainline Emma Curtis-Lake Christina Williams Jacopo Chevallard Last Update: May 23, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Mock catalog overview.....................................
Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory November 15, 2009 Research Interests
 Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory November 15, 2009 Research Interests My recent research projects study galaxy evolution with emphasis on star formation histories, gas accretion and outflow, and galaxy
Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory November 15, 2009 Research Interests My recent research projects study galaxy evolution with emphasis on star formation histories, gas accretion and outflow, and galaxy
Survey of dusty AGNs based on the mid-infrared all-sky survey catalog. Shinki Oyabu (Nagoya University) & MSAGN team
 Survey of dusty AGNs based on the mid-infrared all-sky survey catalog Shinki Oyabu (Nagoya University) & MSAGN team Search for Active Galactic Nuclei Purpose 1 The MIR selection can minimize wavelength-dependent
Survey of dusty AGNs based on the mid-infrared all-sky survey catalog Shinki Oyabu (Nagoya University) & MSAGN team Search for Active Galactic Nuclei Purpose 1 The MIR selection can minimize wavelength-dependent
Hunting for Infrared Signatures of Supermassive Black Hole Activity in Dwarf Galaxies
 Hunting for Infrared Signatures of Supermassive Black Hole Activity in Dwarf Galaxies Kevin Hainline University of Arizona, Steward Observatory Amy Reines, NOAO Jenny Greene, Princeton University Daniel
Hunting for Infrared Signatures of Supermassive Black Hole Activity in Dwarf Galaxies Kevin Hainline University of Arizona, Steward Observatory Amy Reines, NOAO Jenny Greene, Princeton University Daniel
Low-Ionization BAL QSOs in Ultraluminous Infrared Systems
 Mass Outflow in Active Galactic Nuclei: New Perspectives ASP Conference Series, Vol. TBD, 2001 D.M. Crenshaw, S.B. Kraemer, and I.M. George Low-Ionization BAL QSOs in Ultraluminous Infrared Systems Gabriela
Mass Outflow in Active Galactic Nuclei: New Perspectives ASP Conference Series, Vol. TBD, 2001 D.M. Crenshaw, S.B. Kraemer, and I.M. George Low-Ionization BAL QSOs in Ultraluminous Infrared Systems Gabriela
The Physical Interpretation of Optical Spectra of High Redshift Galaxies
 The Physical Interpretation of Optical Spectra of High Redshift Galaxies Henry J. Pearce 1 Introduction In observational astronomy the most basic observation that can be made is how bright an astronomical
The Physical Interpretation of Optical Spectra of High Redshift Galaxies Henry J. Pearce 1 Introduction In observational astronomy the most basic observation that can be made is how bright an astronomical
