New Results on the Galactic Warp from a Stellar Population Synthesis Model
|
|
|
- Franklin Malone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 New Results on the Galactic Warp from a Stellar Population Synthesis Model A.C. Robin 1, C. Reylé 1, D.J. Marshall 2, M. Schultheis 1 (1) Institut UTINAM, Observatoire de Besançon, France (2) Université Laval, Québec, Canada Abstract : The Besancon Galaxy model is used to interpret 2MASS star counts in external regions of the Galaxy. We adjust a warp model and describe the global shape of this large scale structure. It is found that the stellar warp is asymmetric and less pronounced that the HI warp. The result is also compared with the warp as seen in the dust by Marshall et al (26) and discussed with regards to other warp studies.
2 Objective : Constrain warp origin Method : Study warp structure from stellar populations by comparing 2MASS star counts with population synthesis model simulations. Compare the stellar warp with HI and dust warps. Model simulations : Besançon galaxy model (Robin et al, 23) Use Marshall et al (26) 3D extinction map References Dame, T. M., Hartmann, Dap & Thaddeus, P. 21, ApJ, 547, 792 Drimmel, R., & Spergel, D. N. 21, ApJ, 556, 181 Levine, E. S., Blitz, L., & Heiles, C. 26, ApJ, 643, 881 Lopez-Corredoira, M. et al, 22, A&A 394, 883 Marshall, D.J., Robin, A.C., Reylé, C., Schultheis, M., Picaud, S. 26, A&A 453, 635 Marshall, D.J. 26, PhD Thesis, Université de Franche-Comté Reylé, C., Marshall, D.J., Robin, A.C., Schultheis, M., 28, in prep. Robin, A.C., Reylé, C., Derrière, S., & Picaud S. 23, A&A, 49, 523. Erratum 24, A&A, 416, 157 Skrutskie, M. F., et al. 26, AJ, 131, 1163
3 3D extinction map daks / dr [ mag kpc-1 ] y [ kpc ] x [ kpc ] 1 3D map : Extinction distribution in the plane of the Galaxy as seen!om the North Galactic Pole. The Sun is at the origin, the G.C. is marked by an X. Comparison of the projected 3D extinction map with the velocity integrated CO emission!om Dame et al. (21) Warp in the dust Extinction distribution at 8 kpc!om the sun (Marsha% et al, 26)
4 Comparison 2Mass / Standard Model Comparison between 2MASS (Skrutskie et al, 26) star counts per square degree at K<12 and model predictions. X 2 difference between 2MASS and extinction adjusted model : significant differences exist in the external bulge and in the warp (Besançon model 23)
5 Stellar warp fitting Warp parameters : symmetrical S shape, slope γ, scale length h R, Disc Cutoff R c : zwarp = γ (R Rwarp ) cos(θ θwarp ) θwarp= 9 ±1 γ =.18, h R =253 pc, R c =14 kpc γ =.9, h R =22 pc, R c =14 kpc Rwarp 8 kpc Mass N obs 6 latitude Nstars/ Nstars/1 3 Model N mod latitude (N obs -N mod )/N obs longitude longitude at positive longitudes The S warp fits the data at positive longitudes with a slope of.9 a scale length of 2.2 kpc
6 at negative longitudes γ =.18, h R =253 pc, R c =14 kpc γ =.9, h R =22 pc, R c =14 kpc latitude longitude Nstars/1 3 (Nobs-Nmod)/Nobs latitude longitude Nstars/1 3 (Nobs-Nmod)/Nobs The S warp does not fit at negative longitudes with the best fit values from positive longitudes Non axisymmetric warp in HI : Levine et al (26) Warp model fitted to HI data 3 Fourier modes m=, 1, 2
7 Test Levine warp : Positive side Negative side Levine warp : with m=1 starts at 8.5 kpc, and m=2 at 12. kpc : not a good fit at negative side! The m=2 mode does not solve Other possibilities: a cutoff at a shorter distance at negative longitudes, or a stronger flare => the disc would have an e%ipsoidal shape Warp amplitude as a fct of azimuth - For symmetric S warp - For Levine 3 Fourier modes at R=12 kpc at R=16 kpc at R=22 kpc But the ste%ar disc cuts at about 15 kpc (may be less)
8 Comparison Stars/dust/HI Slope (pc per kpc) Height (pc) at R=14 kpc Rs (kpc) Stars.9x(R-Rs) at l> 5 at l> 8.5 at l> Dust.12x(R-Rs) HI E-3x(R- Rs)-3.1E-6*(R-Rs)** (m=1) 15 (m=, m=2) Conclusions The stellar warp is found asymmetric, as is the warp in dust and gas components All models agree that the node angle direction close to sun-center (<1 ), S model fits at positive longitudes, slope smaller than in Drimmel & Spergel (21) and Lopez-Corredoira et al (22) The warp slope seems to be less steep for the stars than for the HI gas (and maybe the dust as well) The Fourier mode m=2 appears in gas and probably stars and dust, but seen at negative longitudes only Possible shifts in the position of the beginning of the warp (m=1 mode : ~8 kpc for stars, 1 kpc for the gas, m=2 mode : >15 kpc in gas, <14 kpc for stars) Different components react differently to the forces at the origin of the warp
Data sets and population synthesis
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 77, 1136 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della Data sets and population synthesis A.C. Robin CNRS-UMR6091 Observatoire de Besançon, BP1615, F-25010 Besançon cedex, France e-mail: robin@obs-besancon.fr
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 77, 1136 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della Data sets and population synthesis A.C. Robin CNRS-UMR6091 Observatoire de Besançon, BP1615, F-25010 Besançon cedex, France e-mail: robin@obs-besancon.fr
The Besançon Galaxy Model development
 The Besançon Galaxy Model development Annie C. Robin and collaborators Institut UTINAM, OSU THETA, Université Bourgogne-Franche-Comté, Besançon, France Outline Population synthesis principles New scheme
The Besançon Galaxy Model development Annie C. Robin and collaborators Institut UTINAM, OSU THETA, Université Bourgogne-Franche-Comté, Besançon, France Outline Population synthesis principles New scheme
THE GALACTIC BULGE AS SEEN BY GAIA
 143 THE GALACTIC BULGE AS SEEN BY GAIA C. Reylé 1, A.C. Robin 1, M. Schultheis 1, S. Picaud 2 1 Observatoire de Besançon, CNRS UMR 6091, BP 1615, 25010 Besançon cedex, France 2 IAG/USP Departamento de
143 THE GALACTIC BULGE AS SEEN BY GAIA C. Reylé 1, A.C. Robin 1, M. Schultheis 1, S. Picaud 2 1 Observatoire de Besançon, CNRS UMR 6091, BP 1615, 25010 Besançon cedex, France 2 IAG/USP Departamento de
Impact of the uncertainties of the ISM when studying the IMF at intermediate masses
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 86, 562 c SAIt 2015 Memorie della Impact of the uncertainties of the ISM when studying the IMF at intermediate masses R. Mor 1, A.C. Robin 2, B. Lemasle 3, and F. Figueras 1 1 Dept. d
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 86, 562 c SAIt 2015 Memorie della Impact of the uncertainties of the ISM when studying the IMF at intermediate masses R. Mor 1, A.C. Robin 2, B. Lemasle 3, and F. Figueras 1 1 Dept. d
Estimation of Galactic model parameters in high latitudes with 2MASS ABSTRACT
 A&A 464, 565 571 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20066475 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics Estimation of Galactic model parameters in high latitudes with 2MASS A. Cabrera-Lavers 1,2, S. Bilir 3,S.Ak 3,E.Yaz
A&A 464, 565 571 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20066475 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics Estimation of Galactic model parameters in high latitudes with 2MASS A. Cabrera-Lavers 1,2, S. Bilir 3,S.Ak 3,E.Yaz
Thom et al. (2008), ApJ
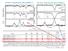 Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2017
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2017 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2017](/thumbs/77/75855038.jpg) Astronomy& Astrophysics manuscript no. EBAmoresetal_Twocolumns_Rf_LE ESO 2017 February 2, 2017 Evolution over time of the Milky Way s disc shape E. B. Amôres 1,2, A. C. Robin 2, and C. Reylé 2 1 UEFS,
Astronomy& Astrophysics manuscript no. EBAmoresetal_Twocolumns_Rf_LE ESO 2017 February 2, 2017 Evolution over time of the Milky Way s disc shape E. B. Amôres 1,2, A. C. Robin 2, and C. Reylé 2 1 UEFS,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Dec 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Dec 2018](/thumbs/92/108989521.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper dr2 warp ESO 2018 December 20, 2018 Gaia kinematics reveal a complex lopsided and twisted Galactic disc warp M. Romero-Gómez 1, C. Mateu 2, 3, L. Aguilar 4,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper dr2 warp ESO 2018 December 20, 2018 Gaia kinematics reveal a complex lopsided and twisted Galactic disc warp M. Romero-Gómez 1, C. Mateu 2, 3, L. Aguilar 4,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 27 Apr 2005
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 2MASSbul February 2, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later A boxy bulge in the Milky Way. Inversion of the stellar statistics equation with 2MASS data M. López-Corredoira
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 2MASSbul February 2, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later A boxy bulge in the Milky Way. Inversion of the stellar statistics equation with 2MASS data M. López-Corredoira
Gaia: a new vision of our Galaxy and our neighbours
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 85, 560 c SAIt 2014 Memorie della Gaia: a new vision of our Galaxy and our neighbours Annie C. Robin 1, C. Reylé 1, X. Luri 2, and the Gaia DPAC 1 Institut Utinam, CNRS-UMR6213, OSU THETA,
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 85, 560 c SAIt 2014 Memorie della Gaia: a new vision of our Galaxy and our neighbours Annie C. Robin 1, C. Reylé 1, X. Luri 2, and the Gaia DPAC 1 Institut Utinam, CNRS-UMR6213, OSU THETA,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 22 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 22 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 22 Jan 2019](/thumbs/88/115504452.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. main c ESO 2019 January 24, 2019 Letter to the Editor Gaia DR2 reveals a star formation burst in the disc 2-3 Gyr ago R. Mor 1, A.C. Robin 2, F. Figueras 1, S. Roca-Fabrega
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. main c ESO 2019 January 24, 2019 Letter to the Editor Gaia DR2 reveals a star formation burst in the disc 2-3 Gyr ago R. Mor 1, A.C. Robin 2, F. Figueras 1, S. Roca-Fabrega
The Milky Way spiral arm pattern
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 00, 199 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della The Milky Way spiral arm pattern 3D distribution of molecular gas P. Englmaier 1, M. Pohl 2, and N. Bissantz 3 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 00, 199 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della The Milky Way spiral arm pattern 3D distribution of molecular gas P. Englmaier 1, M. Pohl 2, and N. Bissantz 3 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität
Structure and Mass Distribution of the Milky Way Bulge and Disk
 Galaxy Disks and Disk Galaxies ASP Conference Series, Vol. 3 10 8, 2000 J.G. Funes, S.J., and E.M. Corsini, eds. Structure and Mass Distribution of the Milky Way Bulge and Disk Ortwin Gerhard Astronomisches
Galaxy Disks and Disk Galaxies ASP Conference Series, Vol. 3 10 8, 2000 J.G. Funes, S.J., and E.M. Corsini, eds. Structure and Mass Distribution of the Milky Way Bulge and Disk Ortwin Gerhard Astronomisches
arxiv:astro-ph/ v3 19 Sep 2006
 The Long Bar in the Milky Way. Corroboration of an old hypothesis M. López-Corredoira 1, A. Cabrera-Lavers 1,2, T. J. Mahoney 1, P. L. Hammersley 1,2, F. Garzón 1,3, C. González-Fernández 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0606201v3
The Long Bar in the Milky Way. Corroboration of an old hypothesis M. López-Corredoira 1, A. Cabrera-Lavers 1,2, T. J. Mahoney 1, P. L. Hammersley 1,2, F. Garzón 1,3, C. González-Fernández 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0606201v3
Three-Dimensional Reddening Map for Stars from 2MASS Photometry: The Method and the First Results
 arxiv:1607.00484v1 [astro-ph.sr] 2 Jul 2016 Three-Dimensional Reddening Map for Stars from 2MASS Photometry: The Method and the First Results G. A. Gontcharov September 9, 2018 Pulkovo Astronomical Observatory,
arxiv:1607.00484v1 [astro-ph.sr] 2 Jul 2016 Three-Dimensional Reddening Map for Stars from 2MASS Photometry: The Method and the First Results G. A. Gontcharov September 9, 2018 Pulkovo Astronomical Observatory,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 20 Oct 2004
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 27 September 2005 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Why the Canis Major overdensity is not due to the Warp: analysis of its radial profile and velocities
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 27 September 2005 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Why the Canis Major overdensity is not due to the Warp: analysis of its radial profile and velocities
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 4 Jan 2002
 1 arxiv:astro-ph/02053v1 4 Jan 2002 Abstract. An automated search for star clusters close to the Galactic plane ( b < 5 o ) was carried out on the Point Source Catalogue of the DENIS survey. 44% of the
1 arxiv:astro-ph/02053v1 4 Jan 2002 Abstract. An automated search for star clusters close to the Galactic plane ( b < 5 o ) was carried out on the Point Source Catalogue of the DENIS survey. 44% of the
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 26 May 2004
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Gd202 March 20, 2018 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) arxiv:astro-ph/0405526v1 26 May 2004 Probing the Canis Major stellar over-density as due to the Galactic
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Gd202 March 20, 2018 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) arxiv:astro-ph/0405526v1 26 May 2004 Probing the Canis Major stellar over-density as due to the Galactic
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2011](/thumbs/89/98822124.jpg) The Edge of the Milky Way Stellar Disk Revealed Using Clump Giant Stars as Distance Indicators arxiv:1105.3151v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2011 D. Minniti 1,2,3, R. K. Saito 1, J. Alonso-García 1, P. W. Lucas
The Edge of the Milky Way Stellar Disk Revealed Using Clump Giant Stars as Distance Indicators arxiv:1105.3151v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2011 D. Minniti 1,2,3, R. K. Saito 1, J. Alonso-García 1, P. W. Lucas
Three-Dimensional Distribution of the ISM in the Milky Way Galaxy: I. The H I Disk
 PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 55, 191 202, 2003 February 25 c 2003. Astronomical Society of Japan. Three-Dimensional Distribution of the ISM in the Milky Way Galaxy: I. The H I Disk Hiroyuki NAKANISHI
PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 55, 191 202, 2003 February 25 c 2003. Astronomical Society of Japan. Three-Dimensional Distribution of the ISM in the Milky Way Galaxy: I. The H I Disk Hiroyuki NAKANISHI
Testing the COBE/IRAS All-Sky Reddening Map Using the Galactic Globular Clusters
 Testing the COBE/IRAS All-Sky Reddening Map Using the Galactic Globular Clusters K. Z. Stanek 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., MS20, Cambridge, MA 02138 e-mail: kstanek@cfa.harvard.edu
Testing the COBE/IRAS All-Sky Reddening Map Using the Galactic Globular Clusters K. Z. Stanek 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., MS20, Cambridge, MA 02138 e-mail: kstanek@cfa.harvard.edu
Galactic structure and evolution
 and evolution Stellar populations concept Bulge and central regions Thin Disc Thick disc Halo and spheroid Kinematics and dynamics Slide 1 Galaxy content Stars (different stellar populations) Gas (neutral,
and evolution Stellar populations concept Bulge and central regions Thin Disc Thick disc Halo and spheroid Kinematics and dynamics Slide 1 Galaxy content Stars (different stellar populations) Gas (neutral,
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars
 Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars ( 東京大学 ) Noriyuki Matsunaga (The University of Tokyo) The first C-rich Miras found in the bulge All the AGB stars confirmed in the bulge were O-rich. C-rich
Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars ( 東京大学 ) Noriyuki Matsunaga (The University of Tokyo) The first C-rich Miras found in the bulge All the AGB stars confirmed in the bulge were O-rich. C-rich
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Feb 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Feb 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Feb 2017](/thumbs/75/72439277.jpg) Draft version March 1, 2017 Typeset using L A TEX preprint style in AASTeX61 MOLECULAR CLOUDS IN THE EXTREME OUTER GALAXY BETWEEN L = 34.75 TO 45.25 arxiv:1702.08633v1 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Feb 2017 Yan Sun,
Draft version March 1, 2017 Typeset using L A TEX preprint style in AASTeX61 MOLECULAR CLOUDS IN THE EXTREME OUTER GALAXY BETWEEN L = 34.75 TO 45.25 arxiv:1702.08633v1 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Feb 2017 Yan Sun,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 21 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 21 Oct 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 21 Oct 2015](/thumbs/94/121809053.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 17 (2002) Printed 22 October 2015 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Besançon Galactic model analysis of MOA-II microlensing: evidence for a mass deficit in the inner bulge arxiv:1510.06347v1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 17 (2002) Printed 22 October 2015 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Besançon Galactic model analysis of MOA-II microlensing: evidence for a mass deficit in the inner bulge arxiv:1510.06347v1
Gardner, E., Debattista, Victor P, Robin, A. C., Vasquez, S. and Zoccali, M.
 Article N body simulation insights into the X shaped bulge of the Milky Way: kinematics and distance to the Galactic Centre Gardner, E., Debattista, Victor P, Robin, A. C., Vasquez, S. and Zoccali, M.
Article N body simulation insights into the X shaped bulge of the Milky Way: kinematics and distance to the Galactic Centre Gardner, E., Debattista, Victor P, Robin, A. C., Vasquez, S. and Zoccali, M.
Atlas and Catalog of Dark Clouds Based on the 2 Micron All Sky Survey. II. Correction of the Background Using the Besançon Galaxy Model
 PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 65, 31, 2013 April 25 c 2013. Astronomical Society of Japan. Atlas and Catalog of Dark Clouds Based on the 2 Micron All Sky Survey. II. Correction of the Background Using
PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 65, 31, 2013 April 25 c 2013. Astronomical Society of Japan. Atlas and Catalog of Dark Clouds Based on the 2 Micron All Sky Survey. II. Correction of the Background Using
(a) B-V 6 V. (b) B-V
 721 TOWARDS AN IMPROVED MODEL OF THE GALAXY Johan Holmberg 1, Chris Flynn 2, Lennart Lindegren 1 1 Lund Observatory, Box 43, SE-22100 Lund, Sweden 2 Tuorla Observatory, Vaisalantie 20, FI-21500 Piikkio,
721 TOWARDS AN IMPROVED MODEL OF THE GALAXY Johan Holmberg 1, Chris Flynn 2, Lennart Lindegren 1 1 Lund Observatory, Box 43, SE-22100 Lund, Sweden 2 Tuorla Observatory, Vaisalantie 20, FI-21500 Piikkio,
Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (2000) 21, 53-59 Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk D. Κ. Ojha, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Dr. Homi Bhabha Road, Mumbai 400 005, India Received 1999 September 14; accepted
J. Astrophys. Astr. (2000) 21, 53-59 Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk D. Κ. Ojha, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Dr. Homi Bhabha Road, Mumbai 400 005, India Received 1999 September 14; accepted
Multi-wavelength study of the Milky Way Galaxy
 29 th ASI Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 3, pp 79 83 Edited by Pushpa Khare & C. H. Ishwara-Chandra Multi-wavelength study of the Milky Way Galaxy Shashikiran Ganesh Physical Research Laboratory,
29 th ASI Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 3, pp 79 83 Edited by Pushpa Khare & C. H. Ishwara-Chandra Multi-wavelength study of the Milky Way Galaxy Shashikiran Ganesh Physical Research Laboratory,
Outer structure of the Galactic warp and flare: explaining the Canis Major over-density
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa4081-05 c ESO 2006 March 14, 2006 Outer structure of the Galactic warp and flare: explaining the Canis Major over-density Y. Momany 1,2, S. Zaggia 3,G.Gilmore
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. aa4081-05 c ESO 2006 March 14, 2006 Outer structure of the Galactic warp and flare: explaining the Canis Major over-density Y. Momany 1,2, S. Zaggia 3,G.Gilmore
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Three-dimensional interstellar dust reddening maps of the Galactic plane
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 13 (2016) Printed 6 December 2018 (MN L A TEX style file v2.2) Three-dimensional interstellar dust reddening maps of the Galactic plane and the Pan-STARRS 1 Survey (PS1;
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 13 (2016) Printed 6 December 2018 (MN L A TEX style file v2.2) Three-dimensional interstellar dust reddening maps of the Galactic plane and the Pan-STARRS 1 Survey (PS1;
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Jan 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Jan 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Jan 2010](/thumbs/91/106791467.jpg) The present-day star formation rate of the Milky-Way determined from Spitzer detected young stellar objects Thomas P. Robitaille 1,2 and Barbara A. Whitney 3 arxiv:1001.3672v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Jan 2010
The present-day star formation rate of the Milky-Way determined from Spitzer detected young stellar objects Thomas P. Robitaille 1,2 and Barbara A. Whitney 3 arxiv:1001.3672v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Jan 2010
Lecture 29. Our Galaxy: "Milky Way"
 Lecture 29 The Milky Way Galaxy Disk, Bulge, Halo Rotation Curve Galactic Center Apr 3, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 29 1 Our Galaxy: "Milky Way" Milky, diffuse band of light around sky known to ancients. Galileo
Lecture 29 The Milky Way Galaxy Disk, Bulge, Halo Rotation Curve Galactic Center Apr 3, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 29 1 Our Galaxy: "Milky Way" Milky, diffuse band of light around sky known to ancients. Galileo
Lecture 2: Molecular Clouds: Galactic Context and Observational Tracers. Corona Australis molecular cloud: Andrew Oreshko
 Lecture 2: Molecular Clouds: Galactic Context and Observational Tracers Corona Australis molecular cloud: Andrew Oreshko Classification of Young Stellar Objects (YSOs) Spectral Index Hartmann: Accretion
Lecture 2: Molecular Clouds: Galactic Context and Observational Tracers Corona Australis molecular cloud: Andrew Oreshko Classification of Young Stellar Objects (YSOs) Spectral Index Hartmann: Accretion
Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure
 Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure The Celestial Sphere http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/pog14 We use equatorial coordinates to determine the positions of stars in the sky. A stars declination (like
Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure The Celestial Sphere http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/pog14 We use equatorial coordinates to determine the positions of stars in the sky. A stars declination (like
Is the exponential distribution a good approximation of dusty galactic disks?
 Astron. Astrophys. 33, 117 123 (2000) Is the exponential distribution a good approximation of dusty galactic disks? ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS A. Misiriotis 1,2,4, N.D. Kylafis 1,2, J. Papamastorakis 1,2,
Astron. Astrophys. 33, 117 123 (2000) Is the exponential distribution a good approximation of dusty galactic disks? ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS A. Misiriotis 1,2,4, N.D. Kylafis 1,2, J. Papamastorakis 1,2,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 Jul 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 Jul 2012](/thumbs/85/92902470.jpg) Draft version August 16, 218 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 arxiv:127.3797v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 Jul 212 THE APACHE POINT OBSERVATORY GALACTIC EVOLUTION EXPERIMENT: FIRST DETECTION
Draft version August 16, 218 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 arxiv:127.3797v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 Jul 212 THE APACHE POINT OBSERVATORY GALACTIC EVOLUTION EXPERIMENT: FIRST DETECTION
3D Tomography of the Local Interstellar Medium
 3D Tomography of the Local Interstellar Medium supervised by Isabelle GRENIER DDays IRFU phds presentations days - 2 July 2015 1 Introduction Nom - Prénom : REMY Quentin Cursus : Licence physique fondamentale,
3D Tomography of the Local Interstellar Medium supervised by Isabelle GRENIER DDays IRFU phds presentations days - 2 July 2015 1 Introduction Nom - Prénom : REMY Quentin Cursus : Licence physique fondamentale,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 18 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 18 Dec 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 18 Dec 2008](/thumbs/91/105557870.jpg) Mem. S.A.It. Vol., 1 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Ì Å Ð Ý Ï Ý ËÔ Ö Ð ÖÑ È ØØ ÖÒ ØÖ ÙØ ÓÒ Ó ÅÓÐ ÙÐ Ö arxiv:0812.3491v1 [astro-ph] 18 Dec 2008 P. Englmaier 1, M. Pohl 2, and N. Bissantz 3 1 Institut für Theoretische
Mem. S.A.It. Vol., 1 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Ì Å Ð Ý Ï Ý ËÔ Ö Ð ÖÑ È ØØ ÖÒ ØÖ ÙØ ÓÒ Ó ÅÓÐ ÙÐ Ö arxiv:0812.3491v1 [astro-ph] 18 Dec 2008 P. Englmaier 1, M. Pohl 2, and N. Bissantz 3 1 Institut für Theoretische
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation. Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan)
 Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
STELLAR PARAMETERS OF M DWARFS FROM LOW AND HIGH-RESOLUTION SPECTRA TOGETHER WITH NEW MODEL ATMOSPHERES
 SF2A 2012 S. Boissier, P. de Laverny, N. Nardetto, R. Samadi, D. Valls-Gabaud and H. Wozniak (eds) STELLAR PARAMETERS OF M DWARFS FROM LOW AND HIGH-RESOLUTION SPECTRA TOGETHER WITH NEW MODEL ATMOSPHERES
SF2A 2012 S. Boissier, P. de Laverny, N. Nardetto, R. Samadi, D. Valls-Gabaud and H. Wozniak (eds) STELLAR PARAMETERS OF M DWARFS FROM LOW AND HIGH-RESOLUTION SPECTRA TOGETHER WITH NEW MODEL ATMOSPHERES
On the rotation of Gould s Belt P.O. Lindblad Abstract. 2. Observational fundamentals of Gould s Belt Key words: 1. Introduction
 Astron. Astrophys. 363, 154 158 (2000) On the rotation of Gould s Belt ASTONOMY AND ASTOPHYSICS P.O. Lindblad Stockholm Observatory, 133 36 Saltsjöbaden, Sweden (po@astro.su.se) eceived 20 June 2000 /
Astron. Astrophys. 363, 154 158 (2000) On the rotation of Gould s Belt ASTONOMY AND ASTOPHYSICS P.O. Lindblad Stockholm Observatory, 133 36 Saltsjöbaden, Sweden (po@astro.su.se) eceived 20 June 2000 /
UMa II and the Orphan Stream
 UMa II and the Orphan Stream M. Fellhauer The Cambridge Mafia Field of Streams Belokurov et al. 2006 A short The Bifurcation of the Sagittarius stream: (a typical Sagittarius like simulation) Fellhauer
UMa II and the Orphan Stream M. Fellhauer The Cambridge Mafia Field of Streams Belokurov et al. 2006 A short The Bifurcation of the Sagittarius stream: (a typical Sagittarius like simulation) Fellhauer
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 16 Sep 2009
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 16 Sep 2009 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 16 Sep 2009](/thumbs/89/99815542.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2002) Printed 30 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The Slope of the Near Infrared Extinction Law arxiv:0908.1601v2 [astro-ph.ga] 16 Sep 2009 J.J. Stead 1, M.G.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2002) Printed 30 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The Slope of the Near Infrared Extinction Law arxiv:0908.1601v2 [astro-ph.ga] 16 Sep 2009 J.J. Stead 1, M.G.
Evidence for coupling between the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy and the Milky Way warp
 Evidence for coupling between the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy and the Milky Way warp Jeremy Bailin Steward Observatory, University of Arizona 933 North Cherry Ave, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA ABSTRACT Using recent
Evidence for coupling between the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy and the Milky Way warp Jeremy Bailin Steward Observatory, University of Arizona 933 North Cherry Ave, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA ABSTRACT Using recent
Simulations of the Gaia final catalogue: expectation of the distance estimation
 Simulations of the Gaia final catalogue: expectation of the distance estimation E. Masana, Y. Isasi, R. Borrachero, X. Luri Universitat de Barcelona GAIA DPAC - CU2 Introduction Gaia DPAC (Data Processing
Simulations of the Gaia final catalogue: expectation of the distance estimation E. Masana, Y. Isasi, R. Borrachero, X. Luri Universitat de Barcelona GAIA DPAC - CU2 Introduction Gaia DPAC (Data Processing
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
 Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
Three-dimensional interstellar dust reddening maps of the Galactic plane
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 12 (2016) Printed 9 July 2018 (MN L A TEX style file v2.2) Three-dimensional interstellar dust reddening maps of the Galactic plane Based on the 2MASS data, Marshall et
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 12 (2016) Printed 9 July 2018 (MN L A TEX style file v2.2) Three-dimensional interstellar dust reddening maps of the Galactic plane Based on the 2MASS data, Marshall et
The Norma spiral arm: large-scale pitch angle
 The Norma spiral arm: large-scale pitch angle Jacques P. Vallée National Research Council of Canada, National Science Infrastructure, Herzberg Astronomy & Astrophysics, 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria,
The Norma spiral arm: large-scale pitch angle Jacques P. Vallée National Research Council of Canada, National Science Infrastructure, Herzberg Astronomy & Astrophysics, 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria,
INFORMATION ON THE MILKY WAY FROM THE 2MASS ALL SKY STAR COUNT: BIMODAL COLOR DISTRIBUTIONS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 759:94 (1pp), 212 November 1 C 212. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. doi:1.188/4-637x/759/2/94 INFORMATION ON THE MILKY WAY FROM
The Astrophysical Journal, 759:94 (1pp), 212 November 1 C 212. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. doi:1.188/4-637x/759/2/94 INFORMATION ON THE MILKY WAY FROM
The origin of the steep vertical stellar distribution in the Galactic disc
 The origin of the steep vertical stellar distribution in the Galactic disc Arunima Banerjee Department of Physics Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 India Email: arunima_banerjee@physics.iisc.ernet.in
The origin of the steep vertical stellar distribution in the Galactic disc Arunima Banerjee Department of Physics Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012 India Email: arunima_banerjee@physics.iisc.ernet.in
Time resolved X-ray spectral analysis during optical dips and accretion bursts in stars with disks of NGC2264 from Chandra/ACIS-I and CoRoT data
 X-Ray Universe - 2017 Time resolved X-ray spectral analysis during optical dips and accretion bursts in stars with disks of NGC2264 from Chandra/ACIS-I and CoRoT data Time resolved X-ray spectral analysis
X-Ray Universe - 2017 Time resolved X-ray spectral analysis during optical dips and accretion bursts in stars with disks of NGC2264 from Chandra/ACIS-I and CoRoT data Time resolved X-ray spectral analysis
CROWDED FIELDS IN THE MILKY WAY AND BEYOND. C. Babusiaux 1,2
 637 CROWDED FIELDS IN THE MILKY WAY AND BEYOND C. Babusiaux 1,2 1 Institut d Astronomie et d Astrophysique, Université Libre de Bruxelles, B-1050 Bruxelles, Belgium 2 Observatoire de Paris, GEPI / CNRS
637 CROWDED FIELDS IN THE MILKY WAY AND BEYOND C. Babusiaux 1,2 1 Institut d Astronomie et d Astrophysique, Université Libre de Bruxelles, B-1050 Bruxelles, Belgium 2 Observatoire de Paris, GEPI / CNRS
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 19 Sep 2006
 Stars and Gas in the Inner Parts of Galaxies seen in SAURON Integral Field Observations R.F. Peletier a, K. Fathi a, arxiv:astro-ph/0609551v1 19 Sep 2006 a Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, University of
Stars and Gas in the Inner Parts of Galaxies seen in SAURON Integral Field Observations R.F. Peletier a, K. Fathi a, arxiv:astro-ph/0609551v1 19 Sep 2006 a Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, University of
Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR*
 Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR* (Our galaxy is revered as Galaxy and others are merely galaxy ;-).) (SFR is less than 5 solar mass per year) MW Structure Diagram Midplane molecular layer
Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR* (Our galaxy is revered as Galaxy and others are merely galaxy ;-).) (SFR is less than 5 solar mass per year) MW Structure Diagram Midplane molecular layer
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8
 The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Apr 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Apr 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Apr 2015](/thumbs/75/71625371.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ms c ESO 2015 April 14, 2015 The incorrect rotation curve of the Milky Way Laurent Chemin 1,2, Florent Renaud 3, and Caroline Soubiran 1,2 1 Univ. Bordeaux, LAB,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ms c ESO 2015 April 14, 2015 The incorrect rotation curve of the Milky Way Laurent Chemin 1,2, Florent Renaud 3, and Caroline Soubiran 1,2 1 Univ. Bordeaux, LAB,
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7
 The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us?
 The Milky Way From a dark site the Milky Way can be seen as a broad band across the sky What is it? telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us? that we live in a spiral
The Milky Way From a dark site the Milky Way can be seen as a broad band across the sky What is it? telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us? that we live in a spiral
Distance Measurement of Spiral Arms in the Galactic-Center Direction Using Radial-Velocity Gradients
 PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 58, 335 341, 2006 April 25 c 2006. Astronomical Society of Japan. Distance Measurement of Spiral Arms in the Galactic-Center Direction Using Radial-Velocity Gradients Yoshiaki
PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 58, 335 341, 2006 April 25 c 2006. Astronomical Society of Japan. Distance Measurement of Spiral Arms in the Galactic-Center Direction Using Radial-Velocity Gradients Yoshiaki
THE ASYMMETRIC THICK DISK: A STAR-COUNT AND KINEMATIC ANALYSIS. I. THE STAR COUNTS Jennifer E. Parker and Roberta M. Humphreys. and Jeffrey A.
 The Astronomical Journal, 126:1346 1361, 2003 September # 2003. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE ASYMMETRIC THICK DISK: A STAR-COUNT AND KINEMATIC ANALYSIS.
The Astronomical Journal, 126:1346 1361, 2003 September # 2003. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE ASYMMETRIC THICK DISK: A STAR-COUNT AND KINEMATIC ANALYSIS.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Apr 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Apr 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Apr 2008](/thumbs/89/98935004.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 12 (2008) Printed 3 April 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The incidence of mid-infrared excesses in G and K giants Mark H. Jones Department of Physics and Astronomy, The
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 12 (2008) Printed 3 April 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The incidence of mid-infrared excesses in G and K giants Mark H. Jones Department of Physics and Astronomy, The
astro-ph/ May 94
 Invited talk at 4th DAEC meeting \Unveiling Large-Scale Structure behind the Milky-Way", ed. C. Balkowski & R. Kraan-Korteweg (San Fransisco: A.S.P.), in press. How well should the DENIS Survey probe through
Invited talk at 4th DAEC meeting \Unveiling Large-Scale Structure behind the Milky-Way", ed. C. Balkowski & R. Kraan-Korteweg (San Fransisco: A.S.P.), in press. How well should the DENIS Survey probe through
Properties of the Milky Way stellar disks in the direction of the Draco dsph galaxy.
 The Galaxy Disk in Cosmological Context IAU Symposium No. 254, 2008 J. Andersen, J. Bland-Hawthorn & B. Nordström, eds. c 2008 International Astronomical Union Properties of the Milky Way stellar disks
The Galaxy Disk in Cosmological Context IAU Symposium No. 254, 2008 J. Andersen, J. Bland-Hawthorn & B. Nordström, eds. c 2008 International Astronomical Union Properties of the Milky Way stellar disks
The structure of the Milky Way s bar outside the bulge
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stv745 The structure of the Milky Way s bar outside the bulge Christopher Wegg, Ortwin Gerhard and Matthieu Portail Max-Planck-Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstrasse,
doi:10.1093/mnras/stv745 The structure of the Milky Way s bar outside the bulge Christopher Wegg, Ortwin Gerhard and Matthieu Portail Max-Planck-Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstrasse,
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
50 Years of Understanding Galactic Atomic Hydrogen with Parkes. Naomi McClure-Griffiths CSIRO Astronomy & Space Science
 50 Years of Understanding Galactic Atomic Hydrogen with Parkes Naomi McClure-Griffiths CSIRO Astronomy & Space Science Outline Parkes surveys of Galactic HI Large-scale distribution of HI in the Milky
50 Years of Understanding Galactic Atomic Hydrogen with Parkes Naomi McClure-Griffiths CSIRO Astronomy & Space Science Outline Parkes surveys of Galactic HI Large-scale distribution of HI in the Milky
dynamical constraints on the dark matter distribution in the milky way
 dynamical constraints on the dark matter distribution in the milky way Miguel Pato (Physik-Department T30d, TU Munich) Oskar Klein Centre for Cosmoparticle Physics / Wenner-Gren Fabio Iocco in collaboration
dynamical constraints on the dark matter distribution in the milky way Miguel Pato (Physik-Department T30d, TU Munich) Oskar Klein Centre for Cosmoparticle Physics / Wenner-Gren Fabio Iocco in collaboration
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 23 Apr 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 23 Apr 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 23 Apr 2007](/thumbs/81/83859213.jpg) Mon Not R Astron Soc 000, 1 6 (2007) Printed 29 May 2018 (MN LATEX style file v22) A large scale extinction map of the Galactic Anticenter from 2MASS arxiv:07042993v1 [astro-ph] 23 Apr 2007 D Froebrich
Mon Not R Astron Soc 000, 1 6 (2007) Printed 29 May 2018 (MN LATEX style file v22) A large scale extinction map of the Galactic Anticenter from 2MASS arxiv:07042993v1 [astro-ph] 23 Apr 2007 D Froebrich
The distribution of the ISM in the Milky Way. A three-dimensional large-scale model ABSTRACT
 A&A 459, 113 123 2006) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20054618 c ESO 2006 Astronomy & Astrophysics The distribution of the ISM in the Milky Way A three-dimensional large-scale model A. Misiriotis 1, E. M. Xilouris
A&A 459, 113 123 2006) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20054618 c ESO 2006 Astronomy & Astrophysics The distribution of the ISM in the Milky Way A three-dimensional large-scale model A. Misiriotis 1, E. M. Xilouris
The myth of the molecular ring
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.20515.x The myth of the molecular ring C. L. Dobbs 1,2,3 and A. Burkert 1,2 1 Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstr.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.20515.x The myth of the molecular ring C. L. Dobbs 1,2,3 and A. Burkert 1,2 1 Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstr.
Problem Set 4 Solutions
 Problem Set 4 Solutions AY 7b Spring 2012 Problem 1 For the very simple model of the MW where Θ() = 200 km s 1, we know that where Ω = Θ/. Since Θ const, we can rewrite this as v r (l) = (Ω Ω 0 ) sin l
Problem Set 4 Solutions AY 7b Spring 2012 Problem 1 For the very simple model of the MW where Θ() = 200 km s 1, we know that where Ω = Θ/. Since Θ const, we can rewrite this as v r (l) = (Ω Ω 0 ) sin l
The Milky Way Galaxy. Sun you are here. This is what our Galaxy would look like if we were looking at it from another galaxy.
 The Milky Way Galaxy Sun you are here. This is what our Galaxy would look like if we were looking at it from another galaxy. Examples of three Milky-Way like Galaxies 1. Roughly 100,000 light years across
The Milky Way Galaxy Sun you are here. This is what our Galaxy would look like if we were looking at it from another galaxy. Examples of three Milky-Way like Galaxies 1. Roughly 100,000 light years across
Action-based Dynamical Modeling of the Milky Way Disk with Gaia & RAVE
 IAU Symposium 330 Nice, 27. April 2017 Action-based Dynamical Modeling of the Milky Way Disk with Gaia & RAVE Wilma Trick (MPIA, Heidelberg) Hans-Walter Rix (MPIA) Jo Bovy (Uni Toronto) Open Questions
IAU Symposium 330 Nice, 27. April 2017 Action-based Dynamical Modeling of the Milky Way Disk with Gaia & RAVE Wilma Trick (MPIA, Heidelberg) Hans-Walter Rix (MPIA) Jo Bovy (Uni Toronto) Open Questions
Troy A. Porter Stanford University
 High-Energy Gamma-Rays from the Milky Way: 3D Spatial Models for the CR and Radiation Field Densities Troy A. Porter Stanford University What is GALPROP? Tool for modelling and interpreting cosmic-ray
High-Energy Gamma-Rays from the Milky Way: 3D Spatial Models for the CR and Radiation Field Densities Troy A. Porter Stanford University What is GALPROP? Tool for modelling and interpreting cosmic-ray
Astr 598: Astronomy with SDSS. Spring Quarter 2004, University of Washington, Željko Ivezić. Lecture 6: Milky Way Structure I: Thin and Thick Disks
 Astr 598: Astronomy with SDSS Spring Quarter 004, University of Washington, Željko Ivezić Lecture 6: Milky Way Structure I: Thin and Thick Disks Stellar Counts There is a lot of information about the Milky
Astr 598: Astronomy with SDSS Spring Quarter 004, University of Washington, Željko Ivezić Lecture 6: Milky Way Structure I: Thin and Thick Disks Stellar Counts There is a lot of information about the Milky
The Milky Way Galaxy. sun. Examples of three Milky-Way like Galaxies
 The Milky Way Galaxy sun This is what our Galaxy would look like if we were looking at it from another galaxy. Examples of three Milky-Way like Galaxies 1. Roughly 100,000 light years across 2. Roughly
The Milky Way Galaxy sun This is what our Galaxy would look like if we were looking at it from another galaxy. Examples of three Milky-Way like Galaxies 1. Roughly 100,000 light years across 2. Roughly
Preliminary results from the e-merlin Legacy Cyg OB2 Radio Survey
 Preliminary results from the e-merlin Legacy Cyg OB2 Radio Survey Department of Physics & Astronomy, University College London, UK. E-mail: dmf@star.ucl.ac.uk Jack Morford Department of Physics & Astronomy,
Preliminary results from the e-merlin Legacy Cyg OB2 Radio Survey Department of Physics & Astronomy, University College London, UK. E-mail: dmf@star.ucl.ac.uk Jack Morford Department of Physics & Astronomy,
The quest for the Sun s siblings: an exploratory search in the Hipparcos Catalogue
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 407, 458 464 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16921.x The quest for the Sun s siblings: an exploratory search in the Hipparcos Catalogue Anthony G. A. Brown, 1 Simon F. Portegies
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 407, 458 464 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16921.x The quest for the Sun s siblings: an exploratory search in the Hipparcos Catalogue Anthony G. A. Brown, 1 Simon F. Portegies
Lec 22 Physical Properties of Molecular Clouds
 Lec 22 Physical Properties of Molecular Clouds 1. Giant Molecular Clouds 2. Orion s Clouds 3. Correlations of Observed Properties 4. The X-Factor References Origins of Stars & Planetary Systems eds. Lada
Lec 22 Physical Properties of Molecular Clouds 1. Giant Molecular Clouds 2. Orion s Clouds 3. Correlations of Observed Properties 4. The X-Factor References Origins of Stars & Planetary Systems eds. Lada
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 23 Jul 2008
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 23 Jul 2008 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 23 Jul 2008](/thumbs/93/118039872.jpg) APJ LETTERS, ACCEPTED 7/9/8 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 A NEW SPIRAL ARM OF THE GALAXY: THE FAR 3-KPC ARM T. M. DAME AND P. THADDEUS Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics,
APJ LETTERS, ACCEPTED 7/9/8 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 A NEW SPIRAL ARM OF THE GALAXY: THE FAR 3-KPC ARM T. M. DAME AND P. THADDEUS Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics,
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau
 Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
View of the Galaxy from within. Lecture 12: Galaxies. Comparison to an external disk galaxy. Where do we lie in our Galaxy?
 Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
The incidence of mid-infrared excesses in G and K giants
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 387, 845 855 (2008) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13282.x The incidence of mid-infrared excesses in G and K giants Mark H. Jones Department of Physics and Astronomy, The Open University,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 387, 845 855 (2008) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13282.x The incidence of mid-infrared excesses in G and K giants Mark H. Jones Department of Physics and Astronomy, The Open University,
Einführung in die Astronomie II
 Einführung in die Astronomie II Teil 12 Peter Hauschildt yeti@hs.uni-hamburg.de Hamburger Sternwarte Gojenbergsweg 112 21029 Hamburg 13. September 2017 1 / 77 Overview part 12 The Galaxy Historical Overview
Einführung in die Astronomie II Teil 12 Peter Hauschildt yeti@hs.uni-hamburg.de Hamburger Sternwarte Gojenbergsweg 112 21029 Hamburg 13. September 2017 1 / 77 Overview part 12 The Galaxy Historical Overview
Sep 09, Overview of the Milky Way Structure of the Milky Way Rotation in the plane Stellar populations
 Sep 09, 2015 Overview of the Milky Way Structure of the Milky Way Rotation in the plane Stellar populations PE#4: (pick up a copy; 1 page) Kinematics of stars in the Milky Way disk Matching datasets in
Sep 09, 2015 Overview of the Milky Way Structure of the Milky Way Rotation in the plane Stellar populations PE#4: (pick up a copy; 1 page) Kinematics of stars in the Milky Way disk Matching datasets in
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Aug 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Aug 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Aug 2009](/thumbs/92/108418910.jpg) The California Molecular Cloud Charles J. Lada arxiv:0908.0646v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Aug 2009 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street Cambridge, MA 02138 clada@cfa.harvard.edu Marco Lombardi
The California Molecular Cloud Charles J. Lada arxiv:0908.0646v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Aug 2009 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street Cambridge, MA 02138 clada@cfa.harvard.edu Marco Lombardi
ESTIMATING DISTANCES FROM PARALLAXES. III. DISTANCES OF TWO MILLION STARS IN THE Gaia DR1 CATALOGUE
 Accepted to ApJ 28 September 206 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style AASTeX6 v..0 ESTIMATING DISTANCES FROM PARALLAXES. III. DISTANCES OF TWO MILLION STARS IN THE Gaia DR CATALOGUE Tri L. Astraatmadja,2
Accepted to ApJ 28 September 206 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style AASTeX6 v..0 ESTIMATING DISTANCES FROM PARALLAXES. III. DISTANCES OF TWO MILLION STARS IN THE Gaia DR CATALOGUE Tri L. Astraatmadja,2
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 28 Jul 2006
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper v10 February 2, 2018 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) The distribution of the ISM in the Milky Way A three-dimensional large-scale model A. Misiriotis
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper v10 February 2, 2018 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) The distribution of the ISM in the Milky Way A three-dimensional large-scale model A. Misiriotis
Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010 Outline Review Counts: A(m), Euclidean slope, Olbers paradox Stellar Luminosity Function: Φ(M,S) Structure of the Milky Way: disk, bulge, halo Milky Way kinematics Rotation
Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010 Outline Review Counts: A(m), Euclidean slope, Olbers paradox Stellar Luminosity Function: Φ(M,S) Structure of the Milky Way: disk, bulge, halo Milky Way kinematics Rotation
Estimates of the Enclosed Mass and its Distribution. for several Spiral Galaxies. Abstract
 Estimates of the Enclosed Mass and its Distribution for several Spiral Galaxies Geoffrey M. Williams email: gmwill@charter.net Abstract Recently, high quality rotation curves for several spiral galaxies
Estimates of the Enclosed Mass and its Distribution for several Spiral Galaxies Geoffrey M. Williams email: gmwill@charter.net Abstract Recently, high quality rotation curves for several spiral galaxies
Lecture 19 CO Observations of Molecular Clouds
 Lecture 9 CO Observations of Molecular Clouds. CO Surveys 2. Nearby molecular clouds 3. Antenna temperature and radiative transfer 4. Determining cloud conditions from CO References Tielens, Ch. 0 Myers,
Lecture 9 CO Observations of Molecular Clouds. CO Surveys 2. Nearby molecular clouds 3. Antenna temperature and radiative transfer 4. Determining cloud conditions from CO References Tielens, Ch. 0 Myers,
The Milky Way - 2 ASTR 2110 Sarazin. Center of the Milky Way
 The Milky Way - 2 ASTR 2110 Sarazin Center of the Milky Way Final Exam Tuesday, December 12, 9:00 am noon Ruffner G006 (classroom) You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any
The Milky Way - 2 ASTR 2110 Sarazin Center of the Milky Way Final Exam Tuesday, December 12, 9:00 am noon Ruffner G006 (classroom) You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 20 Nov 1996
 PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 48,?? (2018) Mass of the Galaxy Inferred from Outer Rotation Curve Mareki Honma and Yoshiaki Sofue Institute of Astronomy, University of Tokyo, 2-21-1 Osawa, Mitaka, Tokyo,
PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 48,?? (2018) Mass of the Galaxy Inferred from Outer Rotation Curve Mareki Honma and Yoshiaki Sofue Institute of Astronomy, University of Tokyo, 2-21-1 Osawa, Mitaka, Tokyo,
Cours d astrophysique III :
 Bienvenue au Cours d astrophysique III : Dynamique stellaire et galactique Semestre automne 2011 Dr. Pierre North Laboratoire d astrophysique Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Observatoire de Sauverny
Bienvenue au Cours d astrophysique III : Dynamique stellaire et galactique Semestre automne 2011 Dr. Pierre North Laboratoire d astrophysique Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Observatoire de Sauverny
A novel determination of the local dark matter density. Riccardo Catena. Institut für Theoretische Physik, Heidelberg
 A novel determination of the local dark matter density Riccardo Catena Institut für Theoretische Physik, Heidelberg 28.04.2010 R. Catena and P. Ullio, arxiv:0907.0018 [astro-ph.co]. Riccardo Catena (ITP)
A novel determination of the local dark matter density Riccardo Catena Institut für Theoretische Physik, Heidelberg 28.04.2010 R. Catena and P. Ullio, arxiv:0907.0018 [astro-ph.co]. Riccardo Catena (ITP)
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Jan 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Jan 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Jan 2012](/thumbs/89/99208115.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 7 (0000) arxiv:1201.1775v1 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Jan 2012 The myth of the molecular ring C. L. Dobbs 1,2,3 and A. Burkert 1,2 1 Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 7 (0000) arxiv:1201.1775v1 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Jan 2012 The myth of the molecular ring C. L. Dobbs 1,2,3 and A. Burkert 1,2 1 Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik,
