This watermark does not appear in the registered version - Laser- Tissue Interaction
|
|
|
- Rodger Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 S S d Laser- Tissue Interaction
2
3
4
5 Types of radiation ionizing radiation Non - ionizing radiation
6 You may click on any of the types of radiation for more detail about its particular type of interaction with matter. The different parts of the have very different effects upon interaction electromagnetic spectrum with matter. Starting with low frequency radio waves, the human body is quite transparent. (You can listen to your portable radio inside your home since the waves pass freely through the walls of your house and even through the person beside you!) As you move upward through you absorb more and more visible light to infrared and microwaves range, all the uv from the sun is ultraviolet strongly. In the lower absorbed in a thin outer layer of your skin. As you move further up into region of the spectrum, you become transparent again, x-ray the are gone. You then absorption because most of the mechanisms for absorb only a small fraction of the radiation, but that absorption involves the more violent ionization events. Each portion of the appropriate for the quantum energies electromagnetic spectrum has excitation of certain types of physical processes. The energy levels for all physical processes at the atomic and molecular levels are quantized, and if there are no available quantized energy levels with spacings which match the quantum energy of the incident radiation, to that radiation, and it will pass transparent then the material will be through Electromagnetic spectrum annotated with physiological effects
7 Microwave Interactions photons is in the range microwave of quantum energy The to ev which is in the range of energies separating the quantum states of molecular rotation and torsion. The interaction of microwaves with matter other than metallic conductors will be to rotate molecules and produce heat as result of that molecular motion. Conductors will strongly absorb microwaves and any lower frequencies because they will cause electric currents which will heat the material. Most matter, including the human body, is largely transparent to microwaves. High intensity microwaves, as in a microwave oven where they pass back and forth through the food millions of times, will heat the material by producing molecular rotations and torsions. Since the quantum energies are a million times lower than those of they cannot produce ionization and the x-rays characteristic types of radiation damage associated with ionizing radiation
8
9 Infrared The term "infrared" refers to a broad range of frequencies, beginning at the top end of those frequencies used for communication and extending up the low frequency (red) end of the visible spectrum. The wavelength range is from about 1 millimeter down to 750 nm. The range adjacent to the visible spectrum is called the "near infrared" and the longer wavelength part is called "far infrared In interactions with matter infrared primarily acts to set molecules into vibration. Infrared spectrometers are widely used to study the vibrational spectra of molecules Frequencies: x 10 Hz Wavelengths: 1 mm nm Quantum energies: ev
10 Infrared Interactions photons is infrared of quantum energy The in the range to 1.7 ev which is in the range of energies separating the quantum states of molecular vibrations. Infrared is absorbed more strongly than microwaves, but less strongly than visible light. The result of infrared absorption is heating of the tissue since it increases molecular vibrational activity. Infrared radiation does penetrate the skin further than visible light and can thus be used for photographic imaging of subcutaneous blood vessels
11
12 Visible Light The narrow visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum corresponds to the wavelengths near the maximum of the Sun's radiation curve In interactions with matter visible light primarily acts to set elevate electrons to higher energy levels White light may be separated into its spectral colors by dispersion in a prism Frequencies: x 10 HzWavelengths: nm Quantum energies: ev
13 Visible Light Interactions The primary mechanism for the absorption of visible light photons is the elevation of electrons to higher energy levels. There are many available states, so visible light is absorbed strongly. With a strong light source, red light can be transmitted through the hand or a fold of skin, showing that the red end of the spectrum is not absorbed as strongly as the violet end
14
15 While exposure to visible light causes heating, it does not cause ionization with its risks. You may be heated by the sun through a car windshield, but you will not be sunburned - that is an effect of the higher frequency uv part of sunlight which is blocked by the glass of the windshield
16 Ultraviolet The region just below the visible in wavelength is called the near ultraviolet. It is absorbed very strongly by most solid substances, and even absorbed appreciably by air. The shorter wavelengths reach the ionization energy for many molecules, so the far ultraviolet has some of the dangers attendent to other ionizing radiation The tissue effects of ultraviolet include sunburn, but can have some therapeutic effects as well. The sun is a strong source of ultraviolet radiation, but atmospheric absorption eliminates most of the shorter wavelengths. The eyes are quite susceptible to damage from ultraviolet radiation. Welders must wear protective eye shields because of the uv content of welding arcs can inflame the eyes. Snow-blindness is another example of uv inflamation; the snow reflects uv while most other substances absorb it strongly Frequencies: 7.5 x 10 x 10 HzWavelengths: 400 nm - 10 nm Quantum energies: ev
17 Ultraviolet Interactions
18
19 The near ultraviolet is absorbed very strongly in the surface layer of the skin by electron transitions. As you go to higher energies, the ionization energies for many molecules are reached and the more dangerous photoionization processes take place. Sunburn is primarily an effect of uv, and ionization produces the risk of skin cancer The ozone layer in the upper atmosphere is important for human health because it absorbs most of the harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun before it reaches the surface. The higher frequencies in the ultraviolet are ionizing radiation and can produce harmful physiological effects ranging from sunburn to skin cancer Health concerns for UV exposure are mostly for the range nm in wavelength, the range called UVB. According to Scotto, et al, the most effective biological wavelength for producing skin burns is 297 nm. Their research indicates that the biological effects increase logarithmically within the UVB range, with 330 nm being only 0.1% as effective as 297 nm for biological effects. So it is clearly important to control exposure to UVB
20 X-Rays X-ray was the name given to the highly penetrating rays which emanated when high energy electrons struck a metal target. Within a short time of their discovery, they were being used in medical facilities to image broken bones. We now know that they are high frequency electromagnetic rays which are produced when the electrons are suddenly decelerated - these rays are called bremsstrahlung radiation or "braking radiation". X-rays are also produced when electrons make transitions between lower atomic energy levels in heavy elements. X-rays produced in this way have have definite energies just like other line spectra from atomic electrons. They are called characteristic x-rays since they have energies determined by the atomic energy levels In interactions with matter x-rays are ionizing radiation and produce physiological effects which are not observed with any exposure of non-ionizing radiation, such as the risk of mutations or cancer in tissue Frequencies: 3 x 10 Hz upward Wavelengths: 10 nm - > downward Quantum energies: 124 ev -> upward
21
22
23 Since the quantum energies of x-ray photons are much too high to be absorbed in electron transitions between states for most atoms, they can interact with an electron only by knocking it completely out of the atom. That is, all x-rays are classified as ionizing radiation This can occur by giving all of the energy to an electron (photoionization) or by giving part of the energy to the photon and the remainder to a lower energy photon Compton scattering At sufficiently high energies, the x-ray photon can create an electron positron pair
24 Laser- Tissue Interaction Generally, laser radiation affects that kind of tissue, which absorbs the radiation. The absorption of laser radiation in tissue, especially in ocular tissue, is strongly wavelength dependent. The type of interaction depends on the wavelength and on the interaction duration.
25 Wavelength Considerations An overview of effects in the different wavelength ranges is shown in figure 3. In the wavelength range of about 400 nm to 1400 nm the laser beam is transmitted to the retina onto which it is focussed to a very small spot of the order of µm. Consequently the irradiance on the retina is much larger than the irradiance on the cornea (up to a factor ) and therefore a comparatively small laser power is sufficient in this wavelength range (the "retinal hazard region") to damage the retina. It should be noted that the retinal hazard region comprises both the visible wavelengths (about 400 nm to 700 nm) and the near infrared region (700 nm to 1400 nm) where radiation is not visible but it is still focussed onto the retina (see figure 3).
26 The wavelength range of 400 nm to 700 nm is defined as "visible" in the field of laser safety. However, it should be noted that there is no sharp dividing line between visible and non-visible: the sensitivity of the eye in respect of the visual stimulus is highest in the green, i.e. around 550 nm, and falls off towards red on one side and blue on the other. Radiation of 810 nm can also be seen when the intensity is correspondingly high. Cynical colleagues argue that with sufficient intensity, also 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser radiation can be seen, "but not for very long".
27 Figure 3: The part of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum which is of interest in laser safety. Ultraviolet, mid- and far-infrared radiation is absorbed by the cornea and lens of the eye, while radiation in the wavelength range of 400 nm to 1400 nm is focussed onto the retina, which results in very high irradiance levels on the retina even for small laser powers. Exposure of the skin with sufficiently high exposure levels results in skin injury. The ultraviolet and infrared region is further subdivided into wavelength regions which are relevant in terms of photobiological interactions:
28 Wavelength Considerations An overview of effects in the different wavelength ranges is shown in figure below
29
30
31 The shorthand notation for wavelength ranges in the UV and IR are closely related to the absorption depth of radiation in tissue, which is described by the absorption coefficient. A natural exponential absorption law, the Beer Lambert law, applies and therefore the inverse of the absorption coefficient is a representative value for the depth at which the irradiance has fallen to 1/e of the value at the surface. Hence a large absorption coefficient corresponds to a small penetration depth. The absorption coefficient for water and tissue as function of wavelength is shown in figure 4.
32 Figure 4: Absorption coefficient as function of wavelength for water and tissue. It can be seen that the tissue absorption is governed by the water content of the tissue for infrared wavelengths and the absorption characteristics of hemoglobin and other organic molecules in the visible and in the UV. Blood for instance has a strong absorption in the blue and green part of the spectrum, and penetration depths into the skin are greatest for the red and near IR wavelengths.
33
34 Figure 5. The type of interaction of laser radiation with tissue will be determined by the interaction duration on the one hand and the irradiance on the other. For instance, photochemical interaction mechanisms are dominant for low irradiance, long term exposure, while nonlinear effects only occur for short pulse, high irradiance exposure.
35
36
37
38
RADIATION and the EM Spectrum
 RADIATION and the EM Spectrum Radioactivity is the of high-energy particles and/or of energy from a substance as a result of of its atoms. There are several types of radiation. Radiation from the sun is
RADIATION and the EM Spectrum Radioactivity is the of high-energy particles and/or of energy from a substance as a result of of its atoms. There are several types of radiation. Radiation from the sun is
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 7 NATURE OF LIGHT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM When white light passes through a prism, it spreads out into a rainbow of colours, with red at one end and
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 7 NATURE OF LIGHT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM When white light passes through a prism, it spreads out into a rainbow of colours, with red at one end and
National 3 Waves and Radiation
 What is a wave? National 3 Waves and Radiation 1. Wave Properties The basic definition Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We
What is a wave? National 3 Waves and Radiation 1. Wave Properties The basic definition Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We
Sunlight is a combination of light-waves of various frequencies. Some
 96 The Electromagnetic Spectrum r e a d i n g Sunlight is a combination of light-waves of various frequencies. Some of the frequencies can be seen and some cannot be seen by the human eye. The reading
96 The Electromagnetic Spectrum r e a d i n g Sunlight is a combination of light-waves of various frequencies. Some of the frequencies can be seen and some cannot be seen by the human eye. The reading
Shell Atomic Model and Energy Levels
 Shell Atomic Model and Energy Levels (higher energy, deeper excitation) - Radio waves: Not absorbed and pass through tissue un-attenuated - Microwaves : Energies of Photos enough to cause molecular rotation
Shell Atomic Model and Energy Levels (higher energy, deeper excitation) - Radio waves: Not absorbed and pass through tissue un-attenuated - Microwaves : Energies of Photos enough to cause molecular rotation
LIGHT WAVES AND PARTICLES
 LIGHT WAVES AND PARTICLES THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM The light we see is only a tiny part of a much larger set of transverse waves. Like all waves, these carry energy without moving matter Although they
LIGHT WAVES AND PARTICLES THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM The light we see is only a tiny part of a much larger set of transverse waves. Like all waves, these carry energy without moving matter Although they
Frequency: the number of complete waves that pass a point in a given time. It has the symbol f. 1) SI Units: Hertz (Hz) Wavelength: The length from
 Frequency: the number of complete waves that pass a point in a given time. It has the symbol f. 1) SI Units: Hertz (Hz) Wavelength: The length from the one crest of a wave to the next. I. Electromagnetic
Frequency: the number of complete waves that pass a point in a given time. It has the symbol f. 1) SI Units: Hertz (Hz) Wavelength: The length from the one crest of a wave to the next. I. Electromagnetic
Ba (Z = 56) W (Z = 74) preferred target Mo (Z = 42) Pb (Z = 82) Pd (Z = 64)
 Produced by accelerating electrons with high voltage and allowing them to collide with metal target (anode), e.g, Tungsten. Three Events (Two types of x-ray) a) Heat X-Ray Tube b) bremsstrahlung (braking
Produced by accelerating electrons with high voltage and allowing them to collide with metal target (anode), e.g, Tungsten. Three Events (Two types of x-ray) a) Heat X-Ray Tube b) bremsstrahlung (braking
Name Class Date. What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic spectrum? How can electromagnetic waves be used?
 CHAPTER 16 12 SECTION Sound and Light The Nature of Light KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic
CHAPTER 16 12 SECTION Sound and Light The Nature of Light KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic
Light is an important form of energy for all of us
 What is Light? Light is an important form of energy for all of us it allows us to see plants rely on light for photosynthesis many chemical reactions produce light life on Earth would not exist without
What is Light? Light is an important form of energy for all of us it allows us to see plants rely on light for photosynthesis many chemical reactions produce light life on Earth would not exist without
1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory.
 Lecture 5. Radiation and energy. Objectives: 1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory: atom, subatomic particles, atomic number, mass number, atomic mass, isotopes, simplified atomic diagrams,
Lecture 5. Radiation and energy. Objectives: 1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory: atom, subatomic particles, atomic number, mass number, atomic mass, isotopes, simplified atomic diagrams,
Chapter 26: Properties of Light
 Lecture Outline Chapter 26: Properties of Light This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent Materials Opaque Materials Seeing Light The Eye Electromagnetic
Lecture Outline Chapter 26: Properties of Light This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent Materials Opaque Materials Seeing Light The Eye Electromagnetic
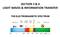
Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer
 Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer Temperature Dice Results Visible light, infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, γ-rays, microwaves, and radio are all forms of electromagnetic
Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer Temperature Dice Results Visible light, infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, γ-rays, microwaves, and radio are all forms of electromagnetic
3. The very long ones are called waves, and the very short ones are called waves.
 NASA Mission: Science Introduction to the Electromagnetic Spectrum Web Quest Directions: Load the following website which will discuss the electromagnetic spectrum in detail. http://missionscience.nasa.gov/ems/01_intro.html
NASA Mission: Science Introduction to the Electromagnetic Spectrum Web Quest Directions: Load the following website which will discuss the electromagnetic spectrum in detail. http://missionscience.nasa.gov/ems/01_intro.html
3mm Ultraviolet LED. 5mm Ultraviolet LED. Electro-Optical Chip Absolute Max. Ratings Viewing LED Part No. Peak Wave Lens Vf Iv Angle
 discrete leds T-1 (3mm), T-13/4 (5mm) UV LEDs Highly Efficient InGaN Materials Produce the Industry s Greatest Radiant Flux at 12mW Ideally Suited to Currency Validation, Medical, Test and Measurement
discrete leds T-1 (3mm), T-13/4 (5mm) UV LEDs Highly Efficient InGaN Materials Produce the Industry s Greatest Radiant Flux at 12mW Ideally Suited to Currency Validation, Medical, Test and Measurement
Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light
 Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light Key Terms: Microscope, telescope, amplitude, crest, energy, force, frequency, hertz, medium, transverse wave, trough, wave, wavelength, reflection,
Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light Key Terms: Microscope, telescope, amplitude, crest, energy, force, frequency, hertz, medium, transverse wave, trough, wave, wavelength, reflection,
Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES. Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision
 Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision Close the Gap Contemporary record of the Topics / Learning outcomes that I
Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision Close the Gap Contemporary record of the Topics / Learning outcomes that I
Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13
 Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
progressive electromagnetic wave
 LECTURE 11 Ch17 A progressive electromagnetic wave is a self-supporting, energy-carrying disturbance that travels free of its source. The light from the Sun travels through space (no medium) for only 8.3
LECTURE 11 Ch17 A progressive electromagnetic wave is a self-supporting, energy-carrying disturbance that travels free of its source. The light from the Sun travels through space (no medium) for only 8.3
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 The Electromagnetic Spectrum 1 of 19 Boardworks Ltd 2016 The Electromagnetic Spectrum 2 of 19 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Detecting waves beyond the visible spectrum 3 of 19 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Invisible light
The Electromagnetic Spectrum 1 of 19 Boardworks Ltd 2016 The Electromagnetic Spectrum 2 of 19 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Detecting waves beyond the visible spectrum 3 of 19 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Invisible light
Topic 8: Beyond Light
 Topic 8: Beyond Light The Sun is the most abundant source of direct natural light on the Earth. There are other forms of energy, invisible, that are also supplied by this source. The tiny band of visible
Topic 8: Beyond Light The Sun is the most abundant source of direct natural light on the Earth. There are other forms of energy, invisible, that are also supplied by this source. The tiny band of visible
Photochemical principles
 Chapter 1 Photochemical principles Dr. Suzan A. Khayyat 1 Photochemistry Photochemistry is concerned with the absorption, excitation and emission of photons by atoms, atomic ions, molecules, molecular
Chapter 1 Photochemical principles Dr. Suzan A. Khayyat 1 Photochemistry Photochemistry is concerned with the absorption, excitation and emission of photons by atoms, atomic ions, molecules, molecular
Classical and Planck picture. Planck s constant. Question. Quantum explanation for the Wein Effect.
 6.1 Quantum Physics. Particle Nature of Light Particle nature of Light Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric Effect Properties of photons Ionizing radiation Radiation damage x-rays Compton effect X-ray diffraction
6.1 Quantum Physics. Particle Nature of Light Particle nature of Light Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric Effect Properties of photons Ionizing radiation Radiation damage x-rays Compton effect X-ray diffraction
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR)
 Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) It is kind of energy with wave character ( exactly as sea waves ) that can be characterized by : Wavelength ( ) : The distance between two identical points on the wave.
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) It is kind of energy with wave character ( exactly as sea waves ) that can be characterized by : Wavelength ( ) : The distance between two identical points on the wave.
Planetary Science: Investigations 9-10 I-Check Quiz STUDY GUIDE- ANSWER KEY Name HR Date
 1. How are different types of radiation arranged along the electromagnetic spectrum? A. By how fast they travel incorrect answer B. By their sources incorrect answer C. By the amount of energy they carry
1. How are different types of radiation arranged along the electromagnetic spectrum? A. By how fast they travel incorrect answer B. By their sources incorrect answer C. By the amount of energy they carry
Electromagnetic Waves
 ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION AND THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Electromagnetic Waves A wave is characterized by: Wavelength (λ - lambda) is the
ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION AND THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Electromagnetic Waves A wave is characterized by: Wavelength (λ - lambda) is the
Radiometry. Energy & Power
 Radiometry Radiometry is the measurement of optical radiation, corresponding to wavelengths between 0.01 and 1000 μm, and includes the regions commonly called the ultraviolet, the visible and the infrared.
Radiometry Radiometry is the measurement of optical radiation, corresponding to wavelengths between 0.01 and 1000 μm, and includes the regions commonly called the ultraviolet, the visible and the infrared.
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introduction Photogrammetry: Definition & applications What are we trying to do? Data acquisition systems 3-D viewing of 2-D imagery Automation (matching problem) Necessary tools: Image formation
Chapter 1: Introduction Photogrammetry: Definition & applications What are we trying to do? Data acquisition systems 3-D viewing of 2-D imagery Automation (matching problem) Necessary tools: Image formation
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER
 SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
Lecture 1 Bioradiation
 1 1 Radiation definition: Radiation, when broadly defined, includes the entire spectrum of electromagnetic waves : radiowaves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, and x-rays and particles.
1 1 Radiation definition: Radiation, when broadly defined, includes the entire spectrum of electromagnetic waves : radiowaves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, and x-rays and particles.
Production of X-rays. Radiation Safety Training for Analytical X-Ray Devices Module 9
 Module 9 This module presents information on what X-rays are and how they are produced. Introduction Module 9, Page 2 X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation. Other types of electromagnetic radiation
Module 9 This module presents information on what X-rays are and how they are produced. Introduction Module 9, Page 2 X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation. Other types of electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic Waves. Electromagnetic Spectrum. Electromagnetic Spectrum. Electromagnetic Waves. CH 27-Physics (B) Fall, 2010
 Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Spectrum CH 27-Physics (B) Fall, 2010 Electric and magnetic fields always exist When ever one is. the other is The fields can exist in a... They are at. o to each
Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Spectrum CH 27-Physics (B) Fall, 2010 Electric and magnetic fields always exist When ever one is. the other is The fields can exist in a... They are at. o to each
Which type of electromagnetic wave has a wavelength longer than that of yellow light? A. Infrared radiation C. X-rays B. Gamma Rays D.
 Which type of electromagnetic wave has a wavelength longer than that of yellow light? A. Infrared radiation C. X-rays B. Gamma Rays D. UV Rays Science Starter! 10.14-15.13! THE UNIVERSE AND ELECTROMAGNETIC
Which type of electromagnetic wave has a wavelength longer than that of yellow light? A. Infrared radiation C. X-rays B. Gamma Rays D. UV Rays Science Starter! 10.14-15.13! THE UNIVERSE AND ELECTROMAGNETIC
Absorption spectrometry summary
 Absorption spectrometry summary Rehearsal: Properties of light (electromagnetic radiation), dual nature light matter interactions (reflection, transmission, absorption, scattering) Absorption phenomena,
Absorption spectrometry summary Rehearsal: Properties of light (electromagnetic radiation), dual nature light matter interactions (reflection, transmission, absorption, scattering) Absorption phenomena,
The Nature of Light. We have a dual model
 Light and Atoms Properties of Light We can come to understand the composition of distant bodies by analyzing the light they emit This analysis can tell us about the composition as well as the temperature
Light and Atoms Properties of Light We can come to understand the composition of distant bodies by analyzing the light they emit This analysis can tell us about the composition as well as the temperature
Planetary Science: Investigations 9-10 I-Check Quiz STUDY GUIDE Name HR Date
 1. How are different types of radiation arranged along the electromagnetic spectrum? A. By how fast they travel incorrect answer B. By their sources incorrect answer C. By the amount of energy they carry
1. How are different types of radiation arranged along the electromagnetic spectrum? A. By how fast they travel incorrect answer B. By their sources incorrect answer C. By the amount of energy they carry
Light is an electromagnetic wave (EM)
 What is light? Light is a form of energy. Light travels in a straight line Light speed is 3.0 x 10 8 m/s Light is carried by photons Light can travel through a vacuum Light is a transverse wave Light is
What is light? Light is a form of energy. Light travels in a straight line Light speed is 3.0 x 10 8 m/s Light is carried by photons Light can travel through a vacuum Light is a transverse wave Light is
Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects: Session 1
 Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects: Session 1 Reading assignment: LLE Radiological Controls Manual (LLEINST 6610): Part 1 UR Radiation Safety Training Manual and Resource Book: Parts
Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects: Session 1 Reading assignment: LLE Radiological Controls Manual (LLEINST 6610): Part 1 UR Radiation Safety Training Manual and Resource Book: Parts
EP118 Optics. Content TOPIC 1 LIGHT. Department of Engineering Physics University of Gaziantep
 EP11 Optics TOPIC 1 LIGHT Department of Engineering Physics University of Gaziantep July 2011 Sayfa 1 Content 1. History of Light 2. Wave Nature of Light 3. Quantum Theory of Light 4. Elecromagnetic Wave
EP11 Optics TOPIC 1 LIGHT Department of Engineering Physics University of Gaziantep July 2011 Sayfa 1 Content 1. History of Light 2. Wave Nature of Light 3. Quantum Theory of Light 4. Elecromagnetic Wave
Name Date Class _. Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light.
 Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light. In this section, you will learn that light has both wave and particle characteristics. You will also see that visible light is just part of a wide
Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light. In this section, you will learn that light has both wave and particle characteristics. You will also see that visible light is just part of a wide
Chapter 30 X Rays GOALS. When you have mastered the material in this chapter, you will be able to:
 Chapter 30 X Rays GOALS When you have mastered the material in this chapter, you will be able to: Definitions Define each of the following terms, and use it in an operational definition: hard and soft
Chapter 30 X Rays GOALS When you have mastered the material in this chapter, you will be able to: Definitions Define each of the following terms, and use it in an operational definition: hard and soft
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR)
 Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) It is kind of energy with wave character ( exactly as sea waves ) that can be characterized by : Wavelength ( ) : The distance between two identical points on the wave.
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) It is kind of energy with wave character ( exactly as sea waves ) that can be characterized by : Wavelength ( ) : The distance between two identical points on the wave.
Lecture 3: Light absorbance
 Lecture 3: Light absorbance Perturbation Response 1 Light in Chemistry Light Response 0-3 Absorbance spectrum of benzene 2 Absorption Visible Light in Chemistry S 2 S 1 Fluorescence http://www.microscopyu.com
Lecture 3: Light absorbance Perturbation Response 1 Light in Chemistry Light Response 0-3 Absorbance spectrum of benzene 2 Absorption Visible Light in Chemistry S 2 S 1 Fluorescence http://www.microscopyu.com
((Radiation )) أيهمدغيم. Ionizing RadiationNon-ionizing radiation. This is the last sheet for Dr. Madi s lectures & its number is ((22)).
 ((Radiation )) This is the last sheet for Dr. Madi s lectures & its number is ((22)). This sheet contains (Slides and recording).. So I did my best to let you not refer to slides. First of all, there is
((Radiation )) This is the last sheet for Dr. Madi s lectures & its number is ((22)). This sheet contains (Slides and recording).. So I did my best to let you not refer to slides. First of all, there is
Spectrophotometry. Introduction
 Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
Solution 3: A glass prism deviates the violet light most and the red light least.
 EXERCISE- 6 (A) Question 1: Name three factors on which the deviation produces by a prism depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you. Solution 1: The deviation produced by the prism
EXERCISE- 6 (A) Question 1: Name three factors on which the deviation produces by a prism depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you. Solution 1: The deviation produced by the prism
Atoms and Radiation electromagnetic radiation Radiation electromagnetic
 Atoms and Radiation The information about astronomical objects (planets, stars, galaxies) can be obtained by studying the electromagnetic radiation emitted by those objects. Astronomers use the laws of
Atoms and Radiation The information about astronomical objects (planets, stars, galaxies) can be obtained by studying the electromagnetic radiation emitted by those objects. Astronomers use the laws of
Report No.: EASZF Page 2 of 14
 Report No.: EASZF01050007 age 2 of 14 Test item particulars... : Tested lamp... : continuous wave lamps pulsed lamps Tested lamp system... : Lamp classification group... : exempt risk 1 risk 2 risk 3 Lamp
Report No.: EASZF01050007 age 2 of 14 Test item particulars... : Tested lamp... : continuous wave lamps pulsed lamps Tested lamp system... : Lamp classification group... : exempt risk 1 risk 2 risk 3 Lamp
Light The EM Spectrum
 Light The EM Spectrum 1 Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation Region Wavelength (Angstroms) Wavelength (centimeters) Frequency (Hz) Energy (ev) Radio > 10 9 > 10 < 3 x 10 9 < 10-5 Microwave 10 9-10 6 10-0.01
Light The EM Spectrum 1 Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation Region Wavelength (Angstroms) Wavelength (centimeters) Frequency (Hz) Energy (ev) Radio > 10 9 > 10 < 3 x 10 9 < 10-5 Microwave 10 9-10 6 10-0.01
Radiation Safety Training Session 1: Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects
 Radiation Safety Training Session 1: Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects Reading Assignment: LLE Radiological Controls Manual (LLEINST 6610) Part 1 UR Radiation Safety Training Manual
Radiation Safety Training Session 1: Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects Reading Assignment: LLE Radiological Controls Manual (LLEINST 6610) Part 1 UR Radiation Safety Training Manual
Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4. Properties of Light
 Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4 Properties of Light There are many types of light sources... Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion The Nature of Light Pythagoras A Greek
Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4 Properties of Light There are many types of light sources... Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion The Nature of Light Pythagoras A Greek
Chapter 17, Electromagnetic Waves Physical Science, McDougal-Littell, 2008
 SECTION 1 (PP. 553-558): ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES HAVE UNIQUE TRAITS. Georgia Standards: S8P4a Identify the characteristics of electromagnetic and mechanical waves; S8P4d Describe how the behavior of waves
SECTION 1 (PP. 553-558): ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES HAVE UNIQUE TRAITS. Georgia Standards: S8P4a Identify the characteristics of electromagnetic and mechanical waves; S8P4d Describe how the behavior of waves
Wave - Particle Duality of Light
 Properties of Light Objectives Explain wave-particle duality State the speed of light Describe electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum Explain how light interacts with transparent and opaque
Properties of Light Objectives Explain wave-particle duality State the speed of light Describe electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum Explain how light interacts with transparent and opaque
Light. Mike Maloney Physics, SHS
 Light Mike Maloney Physics, SHS 1 Light What is LIGHT? WHERE DOES IT COME FROM? 2003 Mike Maloney 2 What is Light? Light is a wave, or rather acts like a wave. How do we know since we cannot see it? We
Light Mike Maloney Physics, SHS 1 Light What is LIGHT? WHERE DOES IT COME FROM? 2003 Mike Maloney 2 What is Light? Light is a wave, or rather acts like a wave. How do we know since we cannot see it? We
The Light of Your Life. We can see the universe because atoms emit photons
 The Light of Your Life We can see the universe because atoms emit photons Astronomy is an observational science Our messengers are Light (electromagnetic waves) Gravitational waves Cosmic rays (particles)
The Light of Your Life We can see the universe because atoms emit photons Astronomy is an observational science Our messengers are Light (electromagnetic waves) Gravitational waves Cosmic rays (particles)
Atmosphere CHANGE IS IN THE AIR
 Activity 8 UVs and Frisbees Atmosphere CHANGE IS IN THE AIR Forces of Change» Atmosphere» Activity 8» Page 1 UVs and Frisbees Overview This experiment will help students understand that ultraviolet radiation
Activity 8 UVs and Frisbees Atmosphere CHANGE IS IN THE AIR Forces of Change» Atmosphere» Activity 8» Page 1 UVs and Frisbees Overview This experiment will help students understand that ultraviolet radiation
Exposure Controls for physical Agents
 Exposure Controls for physical Agents Nature of physical agents Physical agents usually involve the transfer of energy from a source to a human receptor The energy can be in various forms: Mechanical:
Exposure Controls for physical Agents Nature of physical agents Physical agents usually involve the transfer of energy from a source to a human receptor The energy can be in various forms: Mechanical:
9/16/08 Tuesday. Chapter 3. Properties of Light. Light the Astronomer s Tool. and sometimes it can be described as a particle!
 9/16/08 Tuesday Announce: Observations? Milky Way Center movie Moon s Surface Gravity movie Questions on Gravity from Ch. 2 Ch. 3 Newton Movie Chapter 3 Light and Atoms Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
9/16/08 Tuesday Announce: Observations? Milky Way Center movie Moon s Surface Gravity movie Questions on Gravity from Ch. 2 Ch. 3 Newton Movie Chapter 3 Light and Atoms Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Because light behaves like a wave, we can describe it in one of two ways by its wavelength or by its frequency.
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Electromagnetic waves
 Lecture 21 Electromagnetic waves Atomic Physics Atomic Spectra Lasers Applications Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Waves composed of electric and magnetic fields can be created by an oscillating
Lecture 21 Electromagnetic waves Atomic Physics Atomic Spectra Lasers Applications Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Waves composed of electric and magnetic fields can be created by an oscillating
Electromagnetic Radiation
 Electromagnetic Radiation aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves). Sometimes it behaves like billiard balls (particles).
Electromagnetic Radiation aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves). Sometimes it behaves like billiard balls (particles).
Chapter 25. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 25 Electromagnetic Waves EXAM # 3 Nov. 20-21 Chapter 23 Chapter 25 Powerpoint Nov. 4 Problems from previous exams Physics in Perspective (pg. 836 837) Units of Chapter 25 The Production of Electromagnetic
Chapter 25 Electromagnetic Waves EXAM # 3 Nov. 20-21 Chapter 23 Chapter 25 Powerpoint Nov. 4 Problems from previous exams Physics in Perspective (pg. 836 837) Units of Chapter 25 The Production of Electromagnetic
Quantum and Atomic Physics - Multiple Choice
 PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. The Cathode Ray Tube experiment is associated with: (A) J. J. Thomson (B) J. S. Townsend (C) M. Plank (D) A. H. Compton 2. The electron charge was measured the first time in: (A)
PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. The Cathode Ray Tube experiment is associated with: (A) J. J. Thomson (B) J. S. Townsend (C) M. Plank (D) A. H. Compton 2. The electron charge was measured the first time in: (A)
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5. What is light? What is a wave? Radiation carries information
 Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Science 30 Unit C Review Outline GCCHS. Negatively charged Positively charged Coulomb Conductor Electric potential difference
 Science 30 Unit C Review Outline GCCHS Negatively charged Positively charged Coulomb Conductor Electric potential difference volt voltage Insulator Test body Gravitational field Field lines Solar wind
Science 30 Unit C Review Outline GCCHS Negatively charged Positively charged Coulomb Conductor Electric potential difference volt voltage Insulator Test body Gravitational field Field lines Solar wind
Fluorescence. Incandescence. Electric. Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence. Combustion
 Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion Pythagoras A Greek philosopher Believed light was beams of tiny particles The eyes could detect these particles and see
Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion Pythagoras A Greek philosopher Believed light was beams of tiny particles The eyes could detect these particles and see
HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy
 Astronomy 10 HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Use a calculator whenever necessary. For full credit, always show your work and explain how you got your answer in full, complete sentences on a separate
Astronomy 10 HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Use a calculator whenever necessary. For full credit, always show your work and explain how you got your answer in full, complete sentences on a separate
Electromagnetic Waves
 4/15/12 Chapter 26: Properties of Light Field Induction Ok, so a changing magnetic field causes a current (Faraday s law) Why do we have currents in the first place? electric fields of the charges Changing
4/15/12 Chapter 26: Properties of Light Field Induction Ok, so a changing magnetic field causes a current (Faraday s law) Why do we have currents in the first place? electric fields of the charges Changing
Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation
 Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment
 Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment Main Topics Air Pollution Control Analytical Methods Ergonomics Gas and Vapour Sampling General Practice Heat and Cold Stress
Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment Main Topics Air Pollution Control Analytical Methods Ergonomics Gas and Vapour Sampling General Practice Heat and Cold Stress
Chapter 34. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves Waves If we wish to talk about electromagnetism or light we must first understand wave motion. If you drop a rock into the water small ripples are seen on the surface of
Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves Waves If we wish to talk about electromagnetism or light we must first understand wave motion. If you drop a rock into the water small ripples are seen on the surface of
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM All waves travel the SAME speed (the speed of light) 300,000 km/sec (186,000 miles/sec) in a vacuum
 ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM All waves travel the SAME speed (the speed of light) 300,000 km/sec (186,000 miles/sec) in a vacuum 10 4 Hz 10 6 Hz 10 8 Hz 10 12 Hz 10 14 Hz 10 16 Hz 10 18 Hz 1 million 1 trillion
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM All waves travel the SAME speed (the speed of light) 300,000 km/sec (186,000 miles/sec) in a vacuum 10 4 Hz 10 6 Hz 10 8 Hz 10 12 Hz 10 14 Hz 10 16 Hz 10 18 Hz 1 million 1 trillion
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Laser & Opto-Electronic Eng. Dept rd YEAR. The Electromagnetic Waves
 Spectroscopy Interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter yields that energy is absorbed or emitted by matter in discrete quantities (quanta). Measurement of the frequency or (wave length) of the
Spectroscopy Interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter yields that energy is absorbed or emitted by matter in discrete quantities (quanta). Measurement of the frequency or (wave length) of the
L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer
![L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer](/thumbs/78/76842080.jpg) L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat transfer convection conduction emitters of seeing behind closed doors Greenhouse effect Heat Capacity How to boil water Heat flow HEAT the energy that flows from one system
L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat transfer convection conduction emitters of seeing behind closed doors Greenhouse effect Heat Capacity How to boil water Heat flow HEAT the energy that flows from one system
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 The Electromagnetic Spectrum A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted of tiny particles Newton Used this particle model to explain reflection and refraction Huygens 1678 Explained
The Electromagnetic Spectrum A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted of tiny particles Newton Used this particle model to explain reflection and refraction Huygens 1678 Explained
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM Radiation: It is defined as the process by which energy is emitted from a source and propagated through the surrounding
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM Radiation: It is defined as the process by which energy is emitted from a source and propagated through the surrounding
The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU
 The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU 1 Agilent is committed to the educational community and is willing to provide access to company-owned material. This slide
The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU 1 Agilent is committed to the educational community and is willing to provide access to company-owned material. This slide
GLOSSARY OF BASIC RADIATION PROTECTION TERMINOLOGY
 GLOSSARY OF BASIC RADIATION PROTECTION TERMINOLOGY ABSORBED DOSE: The amount of energy absorbed, as a result of radiation passing through a material, per unit mass of material. Measured in rads (1 rad
GLOSSARY OF BASIC RADIATION PROTECTION TERMINOLOGY ABSORBED DOSE: The amount of energy absorbed, as a result of radiation passing through a material, per unit mass of material. Measured in rads (1 rad
Properties of Waves. Before You Read. What are the features of a wave?
 Properties of Waves Textbook pages 134 143 Before You Read Section 4.1 Summary In this section, you will find out about waves, such as water waves, sound waves, and radio waves. On the lines below, list
Properties of Waves Textbook pages 134 143 Before You Read Section 4.1 Summary In this section, you will find out about waves, such as water waves, sound waves, and radio waves. On the lines below, list
Chapter 17 Practice Questions KEY
 Chapter 17 Practice Questions KEY 1. Long wavelength Medium wavelength Short wavelength 1. Long wavelength Radio, Microwave Medium wavelength Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet Short wavelength X ray, gamma
Chapter 17 Practice Questions KEY 1. Long wavelength Medium wavelength Short wavelength 1. Long wavelength Radio, Microwave Medium wavelength Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet Short wavelength X ray, gamma
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam 16-02-2015
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam 16-02-2015
Chapter 11 FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMAL RADIATION
 Chapter Chapter Fundamentals of Thermal Radiation FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMAL RADIATION Electromagnetic and Thermal Radiation -C Electromagnetic waves are caused by accelerated charges or changing electric
Chapter Chapter Fundamentals of Thermal Radiation FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMAL RADIATION Electromagnetic and Thermal Radiation -C Electromagnetic waves are caused by accelerated charges or changing electric
Chapter 26. Properties of Light
 Chapter 26 Properties of Light James Clerk Maxwell discovered that light is composed of a. electromagnetic waves. b. ultrasonic waves. c. infrasonic waves. d. electron vibrations. James Clerk Maxwell discovered
Chapter 26 Properties of Light James Clerk Maxwell discovered that light is composed of a. electromagnetic waves. b. ultrasonic waves. c. infrasonic waves. d. electron vibrations. James Clerk Maxwell discovered
INTRODUCTION Radiation differs from conduction and convection in that it does not require the presence of a material medium to take place.
 RADIATION INTRODUCTION Radiation differs from conduction and convection in that it does not require the presence of a material medium to take place. Radiation: The energy emitted by matter in the form
RADIATION INTRODUCTION Radiation differs from conduction and convection in that it does not require the presence of a material medium to take place. Radiation: The energy emitted by matter in the form
UNIT II. Energy Transfer of Energy. Chapter 2: Energy Transfers
 UNIT II Energy Transfer of Energy Chapter 2: Energy Transfers The ability of matter to do work or make things happen is known as Energy. There are various forms of energy. Kinetic energy is the energy
UNIT II Energy Transfer of Energy Chapter 2: Energy Transfers The ability of matter to do work or make things happen is known as Energy. There are various forms of energy. Kinetic energy is the energy
Wave Properties of Light Karolina H. Czarnecka, PhD Department of Molecular Bases of Medicine
 Wave Properties of Light Karolina H. Czarnecka, PhD Department of Molecular Bases of Medicine karolina.czarnecka@umed.lodz.pl THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FORCE One of the four fundamental forces, the electromagnetic
Wave Properties of Light Karolina H. Czarnecka, PhD Department of Molecular Bases of Medicine karolina.czarnecka@umed.lodz.pl THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FORCE One of the four fundamental forces, the electromagnetic
The greenhouse effect
 16 Waves of amplitude of 1 m roll onto a beach at a rate of one every 12 s. If the wavelength of the waves is 120 m, calculate (a) the velocity of the waves (b) how much power there is per metre along
16 Waves of amplitude of 1 m roll onto a beach at a rate of one every 12 s. If the wavelength of the waves is 120 m, calculate (a) the velocity of the waves (b) how much power there is per metre along
Wavelength (λ)- Frequency (ν)- Which of the following has a higher frequency?
 Name: Unit 5- Light and Energy Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that emits wave-like behavior as it travels through space. Amplitude (a)- Wavelength (λ)- Which
Name: Unit 5- Light and Energy Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that emits wave-like behavior as it travels through space. Amplitude (a)- Wavelength (λ)- Which
ATM S 111: Global Warming Solar Radiation. Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June
 ATM S 111: Global Warming Solar Radiation Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June 22 2010 Yesterday We Asked What factors influence climate at a given place? Sunshine (and latitude) Topography/mountains Proximity
ATM S 111: Global Warming Solar Radiation Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June 22 2010 Yesterday We Asked What factors influence climate at a given place? Sunshine (and latitude) Topography/mountains Proximity
SNC2D PHYSICS 4/27/2013. LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P ) What Is Light? What Is Light?
 SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P.380-391) What Is Light? For centuries, scientists have tried to understand the nature of light and its properties. Some of these properties are
SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P.380-391) What Is Light? For centuries, scientists have tried to understand the nature of light and its properties. Some of these properties are
Review. PHYS 162 Lecture 5a 1
 Review Light as both wave properties (freq. wavelength) and particle properties (photon is a discrete light unit) Speed of light constant in ALL rest frames time and space accomodates this (Einstein) Wavelength,
Review Light as both wave properties (freq. wavelength) and particle properties (photon is a discrete light unit) Speed of light constant in ALL rest frames time and space accomodates this (Einstein) Wavelength,
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. 5.1 Light in Everyday Life. How do we experience light?
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Historical Awareness
 Historical Awareness 1895 - Wilhem Conrad Roentgen discovered X-rays and in 1901 he received the first Nobel Prize for physics. 1903 - Marie Curie and Pierre Curie, along with Henri Becquerel were awarded
Historical Awareness 1895 - Wilhem Conrad Roentgen discovered X-rays and in 1901 he received the first Nobel Prize for physics. 1903 - Marie Curie and Pierre Curie, along with Henri Becquerel were awarded
Spectrum of Radiation. Importance of Radiation Transfer. Radiation Intensity and Wavelength. Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate
 Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Radiation Intensity and Wavelength frequency Planck s constant Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption
Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Radiation Intensity and Wavelength frequency Planck s constant Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption
The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation
 The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (How we get most of our information about the cosmos) Examples of electromagnetic
The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (How we get most of our information about the cosmos) Examples of electromagnetic
Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate
 Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption and emission Cloud and radiation Radiative-convective equilibrium
Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption and emission Cloud and radiation Radiative-convective equilibrium
1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely
 CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
RADIATION SAFETY. Working Safely with Radiation
 RADIATION SAFETY Working Safely with Radiation 12 NOV 2015 Dr. Raed Felimban Department of Transfusion Medicine King Abdul-Aziz University E-mail: felimbanr@yahoo.com KING ABDULAZIZ UNIVERSITY How most
RADIATION SAFETY Working Safely with Radiation 12 NOV 2015 Dr. Raed Felimban Department of Transfusion Medicine King Abdul-Aziz University E-mail: felimbanr@yahoo.com KING ABDULAZIZ UNIVERSITY How most
PRINCIPLES OF REMOTE SENSING. Electromagnetic Energy and Spectral Signatures
 PRINCIPLES OF REMOTE SENSING Electromagnetic Energy and Spectral Signatures Remote sensing is the science and art of acquiring and analyzing information about objects or phenomena from a distance. As humans,
PRINCIPLES OF REMOTE SENSING Electromagnetic Energy and Spectral Signatures Remote sensing is the science and art of acquiring and analyzing information about objects or phenomena from a distance. As humans,
LASERS AGAIN? Phys 1020, Day 17: Questions? LASERS: Next Up: Cameras and optics Eyes to web: Final Project Info
 LASERS AGAIN? Phys 1020, Day 17: Questions? LASERS: 14.3 Next Up: Cameras and optics Eyes to web: Final Project Info 1 Group Exercise Your pennies will simulate a two state atom; tails = ground state,
LASERS AGAIN? Phys 1020, Day 17: Questions? LASERS: 14.3 Next Up: Cameras and optics Eyes to web: Final Project Info 1 Group Exercise Your pennies will simulate a two state atom; tails = ground state,
