Gemini Integration Time Calculators
|
|
|
- Stuart Shaw
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gemini Integration Time Calculators Phil Puxley SPE-C-G0076 Version 1.1; June 1998 Version History: 1.0 June 1998; first draft. 1.1 June 1998; following comments from Ted von Hippel and Joe Jensen. 1. Introduction We describe the requirements and use of the Gemini instrument Integration Time Calculators (ITCs). The generic requirements are contained in the main sections of this document with specific instances for each instrument to be added, as they are developed, in the appendices. The basic models followed are those employed by the STScI/HST and ESO/VLT integration time calculators but extended for spectroscopic applications. Examples of existing calculators can be found at the following URLs: HST - STIS (imaging): STIS (spectroscopy): WFPC2: NICMOS: html SIRTF - various instruments NOAO - IRAF task CCDtime ESO NTT - SUSI camera 2. Use of the Gemini Integration Time Calculators The ITCs will be used by potential applicants, visiting and staff astronomers to estimate (a) the integration time require to obtain a particular signal-to-noise ratio and/or (b) the signal-to-noise ratio reached in a specified integration time. The calculators will therefore support proposal and observation preparation. They will be used both on-site and from remote sites, ideally via a web interface, and will be maintained by Gemini staff. In general it is to be expected that the data resulting from the ITC will be entered manually in (Phase I) proposals for telescope time SPE-C-G
2 (although future integration with the Gemini developed Phase I tool, and perhaps the Phase II Observing Tool, might be desirable). The calculators should provide as realistic a model of the performance of the instrument as possible. The onus for this is on the external and Gemini instrument scientists to provide accurate input data (backgrounds, instrument throughput etc.) and calculation algorithms. The calculation should take less than a few seconds to execute, by use of look-up tables if necessary. Thus detailed numerical simulations are not required or desired. 3. Generic User Input The user interface must allow specification of the instrument configuration, source properties and other parameters via selection from a restricted set of options. Radio buttons, menu lists and numerical value text boxes are commonly used in existing calculators and are preferred. The instrument configuration options will be specific to that instrument. See the appendices for details. The user-selectable source properties and other parameters are more generic (i.e. they are reusable by the ITCs for most if not all instruments) and include: (a) Calculation mode: calculate S/N obtained in a specified time ("S/N mode") or the integration time required to achieve a requested S/N ("IntTime mode"). (b) Image profile: this is the spatial brightness distribution of the source. Initially it should be selectable from a simplified menu list, but ultimately must include an option for the profile to be generated by, or extracted from, the Image Quality Estimator (IQE). The menu list should include: (i) Nominal point source. (The properties of this point source, e.g. image size or encircled energy, would be specified in the web help pages). (ii) Extended source of user specified angular extent and central surface brightness with either (a) uniform surface brightness, (b) exponential surface brightness profile with specified scale length or (c) R 1/4 surface brightness profile with specified effective radius. (iii) Gaussian profile with user-specified FWHM (effectively a very simplified IQE). (c) Source spectrum: this specifies the intrinsic spectrum of the source i.e. the flux density as a function of wavelength. The options must include: (i) Black body, at a user-specified temperature. - (ii) Power law: f( ), with user-specified power law index. (iii) Stellar template spectra or atmosphere models, comprising a list of spectra covering a range of spectral types and, if necessary, luminosity classes. (iv) Non-stellar models, including: Emission line objects (planetary nebula and HII region). Galaxies - normal (elliptical or spiral), at user specified redshift Galaxies - active (Seyfert 1, Seyfert 2, or QSO)., at user specified redshift SPE-C-G
3 The source spectra should be scalable by a user-specified normalization factor in several possible units: Magnitude in one of a number of recognized filter wavebands (e.g. UBVRIJHKLMNQ). Flux density at a specific wavelength (in nm or um) in either of the flux density units (i.e. per wavelength interval or per frequency interval). either as the spatially integrated emission or as surface brightness (see 3b)ii)). [The former corresponds to the direct magnitude or flux density, the latter to these same properties per square arcsec of sky]. (v) A single (synthetic) emission line specified in terms of the integrated emission line flux (units of W/m**2), line width (units of km/s or micron), and continuum flux density (units of W/m**2/um or W/m**2/Hz or Jy or mag). (vi) User-supplied spectrum, entered as a file name with the file content being ASCII columns of wavelength and signal. (d) Data processing extraction algorithm: user choice of quick or optimum. (These modes are tbd). Although the sky background information can be thought of as generic, it pertains to specific instruments and will be described in the Appendices where relevant. 4. Generic User Output (a) Imaging The ITC for imaging instruments (including the imaging mode of combined imager/spectrometers) should generate and display the exposure time to obtain a requested S/N or the S/N reached in a specific integration time. (The choice of which is a user selection). In addition, regardless of the calculation mode, the limiting magnitude for a nominal point source (see 3(b)(i)) should be displayed as an indication of the depth to which the data extends. For S/N mode and extended object profiles (see 3(b)(ii) and 3(b)(iii)), the S/N as a function of profile radius and, on the same radial scale, the brightness profile, should be calculated and displayed for a one-dimensional slice through the profile. [Ultimately we might wish to consider generating synthetic images of brightness and S/N analogous to the requirements for spectroscopic data in 4(b)]. Various additional values that are calculated as part of the processing should also be displayed. These include: Number of pixels (N) used for calculation (after binning if appropriate). Detector read noise (after non-destructive readout or binning, if appropriate) [electrons/pixel] Peak pixel value (source + background) [electrons] Background (sky + instrument) brightness [electrons/pixel] Total source signal integrated over N pixels [electrons] Total background (sky + instrument) integrated over N pixels [electrons] SPE-C-G
4 In order to assess the relative noise contributions, the supplementary values generally should be displayed both for one exposure and for the entire integration (i.e. summed over all exposures). (b) Spectroscopy The ITC for spectroscopic instruments will be similar to those for the imagers, the principal difference being that they should generate and display the results graphically, as synthetic spectra. Many (all?) existing calculators approximate their calculations to an average spectroscopic element which can be inaccurate (by orders of magnitude) for the highly wavelength-dependent background of the far-red and near- and mid-ir. The graphical output will depend on the calculation mode. In S/N mode the display should contain spectra (i.e. parameter as a function of wavelength) for all of the following parameters: i. Input source model ii. Source as modified by the instrument and atmosphere response iii. Background (sky + instrument) emission iv. S/N ratio In IntTime mode the display should contain items (i - iii) above and: v. Integration time required Associated numerical information, such as the number of pixels used in the calculation, should also be displayed. SPE-C-G
5 Appendices The appendices contain instrument-specific information pertaining to the Instrument Time Calculators including details of the user inputs. The user-specified required sky background (e.g. sky continuum or OH brightness) and/or transparency (e.g. thin cirrus attenuation) should be specified in the same terms that appear in the Phase I and Observing Tool e.g. as a frequency of occurrence percentile. Examples of information that must be included in the calculation are instrument throughput, linearity, saturation, and range A-to-D converter. One use of the latter would be for the ITC to warn users if an individual exposure time would put their object in the non-linear regime of the detector or saturate the A/D (which is often less than the full well of the device). Appendix A: Acquisition Camera Appendix B: tbd Appendix C: tbd Appendix D: tbd Appendix E: tbd SPE-C-G
6 Appendix A: Acquisition Camera The Acquisition Camera (AcqCam) resides within the acquisition and guidance (A & G) unit and is thus more or less a permanent fixture on the telescope. Its principal function in its imaging role is to take images of the sky for target acquisition purposes. It will be used extensively during the commissioning phase for acquisition (pointing) and image quality measurements and, whilst it is not designed (or specified) to take scientific data, it may be also used at first light and perhaps occasionally during operations as a science imager. The AcqCam is fed the telescope beam by a pick off mirror in the lowest module of the A & G unit. The AcqCam can be reconfigured remotely to fulfil its alternative role as the High Resolution Wavefront Sensor (HRWFS). The AcqCam ITC will be the first to be developed and thus serves as a prototype for the other instrument ITCs. Properties specific to the instrument that will be set by the user are: (1) Filter: Choice from (list of filters tbd). (2) CCD configuration: (binning, number of exposures, exposure time, read-out mode (fast/slow?); need info on CCD controller capabilities) (3) Sky background (e.g. choice of days from new moon?) Static data that is required for the calculation includes [specific information is required on all of these]: (1) Telescope throughput as a function of wavelength (essentially, coating curves for each mirror in the optical train: primary, secondary, AcqCam pick-off). This is generic and will be required by other ITCs. (May need to choose silver or aluminium coating as a user option). (2) Instrument throughput (total throughput as a function of wavelength for the fixed optical train). (3) Filter transmission data i.e. table of transmission vs wavelength for each filter (this is not strictly necessary if the sky background and throughputs are specified for each filter rather than as continuous functions that need to be integrated over). (4) Sky background for each filter as a function of lunar phase. SPE-C-G
E-ELT Spectroscopic ETC: Detailed Description
 E-ELT Spectroscopic ETC: Detailed Description Jochen Liske Based on a document originally written by Pascal Ballester, Andrés Jordán, Markus Kissler- Patig & Jakob Vinther. 1. Preliminaries As of Jan 2008
E-ELT Spectroscopic ETC: Detailed Description Jochen Liske Based on a document originally written by Pascal Ballester, Andrés Jordán, Markus Kissler- Patig & Jakob Vinther. 1. Preliminaries As of Jan 2008
The Effective Spectral Resolution of the WFC and HRC Grism
 The Effective Spectral Resolution of the WFC and HRC Grism A. Pasquali, N. Pirzkal, J.R. Walsh, R.N. Hook, W. Freudling, R. Albrecht, R.A.E. Fosbury March 7, 2001 ABSTRACT We present SLIM simulations of
The Effective Spectral Resolution of the WFC and HRC Grism A. Pasquali, N. Pirzkal, J.R. Walsh, R.N. Hook, W. Freudling, R. Albrecht, R.A.E. Fosbury March 7, 2001 ABSTRACT We present SLIM simulations of
AS750 Observational Astronomy
 Lecture 9 0) Poisson! (quantum limitation) 1) Diffraction limit 2) Detection (aperture) limit a)simple case b)more realistic case 3) Atmosphere 2) Aperture limit (More realistic case) Aperture has m pixels
Lecture 9 0) Poisson! (quantum limitation) 1) Diffraction limit 2) Detection (aperture) limit a)simple case b)more realistic case 3) Atmosphere 2) Aperture limit (More realistic case) Aperture has m pixels
Optimal resolutions for optical and NIR spectroscopy S. Villanueva Jr.* a, D.L. DePoy a, J. L. Marshall a
 Optimal resolutions for optical and NIR spectroscopy S. Villanueva Jr.* a, D.L. DePoy a, J. L. Marshall a a Department of Physics and Astronomy, Texas A&M University, 4242 TAMU, College Station, TX, USA
Optimal resolutions for optical and NIR spectroscopy S. Villanueva Jr.* a, D.L. DePoy a, J. L. Marshall a a Department of Physics and Astronomy, Texas A&M University, 4242 TAMU, College Station, TX, USA
Performance of the NICMOS ETC Against Archived Data
 Performance of the NICMOS ETC Against Archived Data M. Sosey June 19, 2001 ABSTRACT A robust test of the newest version of the NICMOS Exposure Time Calculator (ETC) was conducted in order to assess its
Performance of the NICMOS ETC Against Archived Data M. Sosey June 19, 2001 ABSTRACT A robust test of the newest version of the NICMOS Exposure Time Calculator (ETC) was conducted in order to assess its
NAOYUKI TAMURA Subaru Instrument Astronomer Subaru Telescope, NAOJ
 FMOS status tt report Science workshop 2011.02.2802 28-03.0202 NAOYUKI TAMURA Subaru Instrument Astronomer Subaru Telescope, NAOJ * Overview * Recent history & current status t * Schedule & future plan
FMOS status tt report Science workshop 2011.02.2802 28-03.0202 NAOYUKI TAMURA Subaru Instrument Astronomer Subaru Telescope, NAOJ * Overview * Recent history & current status t * Schedule & future plan
Calibration of ACS Prism Slitless Spectroscopy Modes
 The 2005 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2005 A. M. Koekemoer, P. Goudfrooij, and L. L. Dressel, eds. Calibration of ACS Prism Slitless Spectroscopy Modes S. S. Larsen, M. Kümmel
The 2005 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2005 A. M. Koekemoer, P. Goudfrooij, and L. L. Dressel, eds. Calibration of ACS Prism Slitless Spectroscopy Modes S. S. Larsen, M. Kümmel
Ivan Valtchanov Herschel Science Centre European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) ESA. ESAC,20-21 Sep 2007 Ivan Valtchanov, Herschel Science Centre
 SPIRE Observing Strategies Ivan Valtchanov Herschel Science Centre European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) ESA Outline SPIRE quick overview Observing with SPIRE Astronomical Observation Templates (AOT)
SPIRE Observing Strategies Ivan Valtchanov Herschel Science Centre European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) ESA Outline SPIRE quick overview Observing with SPIRE Astronomical Observation Templates (AOT)
Southern African Large Telescope. Prime Focus Imaging Spectrograph. Instrument Acceptance Testing Plan
 Southern African Large Telescope Prime Focus Imaging Spectrograph Instrument Acceptance Testing Plan Eric B. Burgh University of Wisconsin Document Number: SALT-3160AP0003 Revision 1.0 18 February 2003
Southern African Large Telescope Prime Focus Imaging Spectrograph Instrument Acceptance Testing Plan Eric B. Burgh University of Wisconsin Document Number: SALT-3160AP0003 Revision 1.0 18 February 2003
EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION
 ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 12 1 EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION An essential part of planning any observation is to estimate the total exposure time needed to satisfy your scientific goal. General considerations
ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 12 1 EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION An essential part of planning any observation is to estimate the total exposure time needed to satisfy your scientific goal. General considerations
NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation
 NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation Ron Probst NEWFIRM Instrument Scientist September 2008 NEWFIRM is a 1-2.4 micron IR camera for the NOAO 4-m telescopes. It has a flexible complement of broad
NEWFIRM Quick Guide for Proposal Preparation Ron Probst NEWFIRM Instrument Scientist September 2008 NEWFIRM is a 1-2.4 micron IR camera for the NOAO 4-m telescopes. It has a flexible complement of broad
IRS Spectroscopy of z~2 Galaxies
 IRS Spectroscopy of z~2 Galaxies Houck et al., ApJ, 2005 Weedman et al., ApJ, 2005 Lutz et al., ApJ, 2005 Astronomy 671 Jason Marshall Opening the IR Wavelength Regime for Discovery One of the primary
IRS Spectroscopy of z~2 Galaxies Houck et al., ApJ, 2005 Weedman et al., ApJ, 2005 Lutz et al., ApJ, 2005 Astronomy 671 Jason Marshall Opening the IR Wavelength Regime for Discovery One of the primary
FMOS. A Wide-field Multi-Object Infra-red Spectrograph for the Subaru Telescope. David Bonfield, Gavin Dalton
 FMOS A Wide-field Multi-Object Infra-red Spectrograph for the Subaru Telescope David Bonfield, Gavin Dalton David Bonfield Oxford University Wide Field NIR Spectroscopy WFCAM, VISTA are about to deliver
FMOS A Wide-field Multi-Object Infra-red Spectrograph for the Subaru Telescope David Bonfield, Gavin Dalton David Bonfield Oxford University Wide Field NIR Spectroscopy WFCAM, VISTA are about to deliver
1 Lecture, 2 September 1999
 1 Lecture, 2 September 1999 1.1 Observational astronomy Virtually all of our knowledge of astronomical objects was gained by observation of their light. We know how to make many kinds of detailed measurements
1 Lecture, 2 September 1999 1.1 Observational astronomy Virtually all of our knowledge of astronomical objects was gained by observation of their light. We know how to make many kinds of detailed measurements
Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System
 Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System Nathaniel Rodriguez August 26, 2009 Abstract Our research this summer focused on determining if sufficient precision could be gained from
Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System Nathaniel Rodriguez August 26, 2009 Abstract Our research this summer focused on determining if sufficient precision could be gained from
The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range
 Instrument Science Report CAL/SCS-010 The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range L. Colina, R. Bohlin, D. Calzetti, C. Skinner, S. Casertano October 3, 1996 ABSTRACT A proposal
Instrument Science Report CAL/SCS-010 The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range L. Colina, R. Bohlin, D. Calzetti, C. Skinner, S. Casertano October 3, 1996 ABSTRACT A proposal
ROSAT Roentgen Satellite. Chandra X-ray Observatory
 ROSAT Roentgen Satellite Joint facility: US, Germany, UK Operated 1990 1999 All-sky survey + pointed observations Chandra X-ray Observatory US Mission Operating 1999 present Pointed observations How do
ROSAT Roentgen Satellite Joint facility: US, Germany, UK Operated 1990 1999 All-sky survey + pointed observations Chandra X-ray Observatory US Mission Operating 1999 present Pointed observations How do
Observing with the Infrared Spectrograph
 Observing with the Infrared Spectrograph C. Grillmair, L. Armus GO Workshop 21-22 November 2002 Outline 1) Meet the IRS IST 2) Basic IRS capabilities 3) Observing and readout modes 4) Data products and
Observing with the Infrared Spectrograph C. Grillmair, L. Armus GO Workshop 21-22 November 2002 Outline 1) Meet the IRS IST 2) Basic IRS capabilities 3) Observing and readout modes 4) Data products and
GEMINI 8-M Telescopes Project
 GEMINI 8-M Telescopes Project RPT-I-G0057 Principles Behind the Gemini Instrumentation Program M. Mountain, F. Gillett, D. Robertson, D. Simons GEMINI PROJECT OFFICE 950 N. Cherry Ave. Tucson, Arizona
GEMINI 8-M Telescopes Project RPT-I-G0057 Principles Behind the Gemini Instrumentation Program M. Mountain, F. Gillett, D. Robertson, D. Simons GEMINI PROJECT OFFICE 950 N. Cherry Ave. Tucson, Arizona
Early-Science call for observing time with SAM-FP
 Early-Science call for observing time with SAM-FP 1. General description SOAR is opening a call for proposals for early-science with SAM-FP in 2016B, for 4 nights (September 29 October 2, 2016). SAM-FP
Early-Science call for observing time with SAM-FP 1. General description SOAR is opening a call for proposals for early-science with SAM-FP in 2016B, for 4 nights (September 29 October 2, 2016). SAM-FP
Exoplanets Direct imaging. Direct method of exoplanet detection. Direct imaging: observational challenges
 Black body flux (in units 10-26 W m -2 Hz -1 ) of some Solar System bodies as seen from 10 pc. A putative hot Jupiter is also shown. The planets have two peaks in their spectra. The short-wavelength peak
Black body flux (in units 10-26 W m -2 Hz -1 ) of some Solar System bodies as seen from 10 pc. A putative hot Jupiter is also shown. The planets have two peaks in their spectra. The short-wavelength peak
Deep fields around bright stars ( Galaxies around Stars )
 Deep fields around bright stars ( Galaxies around Stars ) Scientific context: the morphological evolution of faint field galaxies Near-IR observations ground-based observations with AO: PUEO/CFHT deep
Deep fields around bright stars ( Galaxies around Stars ) Scientific context: the morphological evolution of faint field galaxies Near-IR observations ground-based observations with AO: PUEO/CFHT deep
Astronomical Techniques I
 Astronomical Techniques I Lecture 8 Yogesh Wadadekar Jan-Feb 2015 IUCAA-NCRA Grad School 1 / 28 Assignment 1 will be posted on the website by tonight or tomorrow morning. Kaustubh Vaghmare (kaustubh@iucaa.ernet.in)
Astronomical Techniques I Lecture 8 Yogesh Wadadekar Jan-Feb 2015 IUCAA-NCRA Grad School 1 / 28 Assignment 1 will be posted on the website by tonight or tomorrow morning. Kaustubh Vaghmare (kaustubh@iucaa.ernet.in)
Investigating the Efficiency of the Beijing Faint Object Spectrograph and Camera (BFOSC) of the Xinglong 2.16-m Reflector
 Research in Astron. Astrophys. Vol. (xx) No., http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Investigating the Efficiency of the Beijing Faint Object
Research in Astron. Astrophys. Vol. (xx) No., http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Investigating the Efficiency of the Beijing Faint Object
Commissioning of the Hanle Autoguider
 Commissioning of the Hanle Autoguider Copenhagen University Observatory Edited November 10, 2005 Figure 1: First light image for the Hanle autoguider, obtained on September 17, 2005. A 5 second exposure
Commissioning of the Hanle Autoguider Copenhagen University Observatory Edited November 10, 2005 Figure 1: First light image for the Hanle autoguider, obtained on September 17, 2005. A 5 second exposure
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability. Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida
 Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
NICMOS Status and Plans
 1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. NICMOS Status and Plans Rodger I. Thompson Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. NICMOS Status and Plans Rodger I. Thompson Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
AAG TPoint Mapper (Version 1.40)
 AAG TPoint Mapper (Version 1.40) AAG_TPointMapper works together with Maxim DL, Pinpoint, TheSky6 and TPoint to automate the process of building a TPoint model for a GOTO telescope connected to TheSky6.
AAG TPoint Mapper (Version 1.40) AAG_TPointMapper works together with Maxim DL, Pinpoint, TheSky6 and TPoint to automate the process of building a TPoint model for a GOTO telescope connected to TheSky6.
Analysis of the rich optical iron-line spectrum of the x-ray variable I Zw 1 AGN 1H
 Analysis of the rich optical iron-line spectrum of the x-ray variable I Zw 1 AGN 1H0707 495 H Winkler, B Paul Department of Physics, University of Johannesburg, PO Box 524, 2006 Auckland Park, Johannesburg,
Analysis of the rich optical iron-line spectrum of the x-ray variable I Zw 1 AGN 1H0707 495 H Winkler, B Paul Department of Physics, University of Johannesburg, PO Box 524, 2006 Auckland Park, Johannesburg,
Automated Classification of HETDEX Spectra. Ted von Hippel (U Texas, Siena, ERAU)
 Automated Classification of HETDEX Spectra Ted von Hippel (U Texas, Siena, ERAU) Penn State HETDEX Meeting May 19-20, 2011 Outline HETDEX with stable instrumentation and lots of data ideally suited to
Automated Classification of HETDEX Spectra Ted von Hippel (U Texas, Siena, ERAU) Penn State HETDEX Meeting May 19-20, 2011 Outline HETDEX with stable instrumentation and lots of data ideally suited to
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY. Observational Astronomy (2011) 1
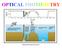 OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc
 Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Note on OSIRIS Wavelength Calibrations D. Le Mignant, Oct. 5, 2007
 Note on OSIRIS Wavelength Calibrations D. Le Mignant, Oct. 5, 2007 1. Observations and data reduction In this short note, we report on some on-going analysis of OSIRIS data in an effort to document our
Note on OSIRIS Wavelength Calibrations D. Le Mignant, Oct. 5, 2007 1. Observations and data reduction In this short note, we report on some on-going analysis of OSIRIS data in an effort to document our
Astronomical frequency comb for calibration of low and medium resolution spectrographs
 Astronomical frequency comb for calibration of low and medium resolution spectrographs innofspec at AIP has several years expertise in astronomical instrumentation. innofspec succesfully developed a new
Astronomical frequency comb for calibration of low and medium resolution spectrographs innofspec at AIP has several years expertise in astronomical instrumentation. innofspec succesfully developed a new
Infrared Astronomy. Generally ~ 1μm (10,000 Å) few hundred μm
 Infrared Astronomy Generally ~ 1μm (10,000 Å) few hundred μm Atmospheric transmission: grey regions are observable from the ground. Two regimes for IR astronomy Ground- based near/mid- IR astronomy through
Infrared Astronomy Generally ~ 1μm (10,000 Å) few hundred μm Atmospheric transmission: grey regions are observable from the ground. Two regimes for IR astronomy Ground- based near/mid- IR astronomy through
Introduction to the Sloan Survey
 Introduction to the Sloan Survey Title Rita Sinha IUCAA SDSS The SDSS uses a dedicated, 2.5-meter telescope on Apache Point, NM, equipped with two powerful special-purpose instruments. The 120-megapixel
Introduction to the Sloan Survey Title Rita Sinha IUCAA SDSS The SDSS uses a dedicated, 2.5-meter telescope on Apache Point, NM, equipped with two powerful special-purpose instruments. The 120-megapixel
SMTN-002: Calculating LSST limiting magnitudes and SNR
 SMTN-002: Calculating LSST limiting magnitudes and SNR Release Lynne Jones 2017-12-05 Contents 1 Source Counts 3 2 Instrumental Zeropoints 5 3 Sky Counts 7 4 Instrumental Noise 9 5 Source footprint (n
SMTN-002: Calculating LSST limiting magnitudes and SNR Release Lynne Jones 2017-12-05 Contents 1 Source Counts 3 2 Instrumental Zeropoints 5 3 Sky Counts 7 4 Instrumental Noise 9 5 Source footprint (n
Imaging with Micado at the E-ELT. WORKSHOP: Imaging at the E-ELT
 Imaging with Micado at the E-ELT Renato Falomo INAF Observatory of Padova, Italy WORKSHOP: Imaging at the E-ELT 29 May 2009, Garching Resolved stellar population in Virgo (high SB) Detailed View of high
Imaging with Micado at the E-ELT Renato Falomo INAF Observatory of Padova, Italy WORKSHOP: Imaging at the E-ELT 29 May 2009, Garching Resolved stellar population in Virgo (high SB) Detailed View of high
SkyMapper and the Southern Sky Survey
 and the Southern Sky Survey, Brian Schmidt and Mike Bessell Slide 1 What is? 1.35m telescope with a 5.7 sq. degree field of view To reside at Siding Spring Observatory, NSW To conduct the Southern Sky
and the Southern Sky Survey, Brian Schmidt and Mike Bessell Slide 1 What is? 1.35m telescope with a 5.7 sq. degree field of view To reside at Siding Spring Observatory, NSW To conduct the Southern Sky
Improving the Absolute Astrometry of HST Data with GSC-II
 The 2005 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2005 A. M. Koekemoer, P. Goudfrooij, and L. L. Dressel, eds. Improving the Absolute Astrometry of HST Data with GSC-II A. M. Koekemoer,
The 2005 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2005 A. M. Koekemoer, P. Goudfrooij, and L. L. Dressel, eds. Improving the Absolute Astrometry of HST Data with GSC-II A. M. Koekemoer,
9. Evolution with redshift - z > 1.5. Selection in the rest-frame UV
 11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-1 11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-2 9. Evolution with redshift - z > 1.5 Selection in
11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-1 11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-2 9. Evolution with redshift - z > 1.5 Selection in
Goals of the meeting. Catch up with JWST news and developments: ERS and GO call for proposals are coming!!
 Welcome Goals of the meeting Catch up with JWST news and developments: ERS and GO call for proposals are coming!! What is JWST capable of (focus on H 2 spectroscopy)? What do we need to do (models, lab)
Welcome Goals of the meeting Catch up with JWST news and developments: ERS and GO call for proposals are coming!! What is JWST capable of (focus on H 2 spectroscopy)? What do we need to do (models, lab)
The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe
 Lecture 15 The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe Intensity weighted second moments Optimal filtering Weak gravitational lensing Shear components Shear detection Inverse problem:
Lecture 15 The shapes of faint galaxies: A window unto mass in the universe Intensity weighted second moments Optimal filtering Weak gravitational lensing Shear components Shear detection Inverse problem:
APPLICATION NOTE. Filter Set Prescription Alan Holmes
 APPLICATION NOTE Filter Set Prescription Alan Holmes August 1st, 22 SBIG has a color filter set prescription specifically designed to achieve correctly balanced color images for galaxies and nebulae. Our
APPLICATION NOTE Filter Set Prescription Alan Holmes August 1st, 22 SBIG has a color filter set prescription specifically designed to achieve correctly balanced color images for galaxies and nebulae. Our
Scattered Light from the Earth Limb Measured with the STIS CCD
 Instrument Science Report STIS 98 21 Scattered Light from the Earth Limb Measured with the STIS CCD Dick Shaw, Merle Reinhart, and Jennifer Wilson 17 June 1998 ABSTRACT We describe a recent program to
Instrument Science Report STIS 98 21 Scattered Light from the Earth Limb Measured with the STIS CCD Dick Shaw, Merle Reinhart, and Jennifer Wilson 17 June 1998 ABSTRACT We describe a recent program to
GEMINI 8-M Telescopes Project
 GEMINI 8-M Telescopes Project RPT-PS-G0065 The Gemini Instrumentation Program F. C. Gillett, D. A. Simons March 25, 1996 GEMINI PROJECT OFFICE 950 N. Cherry Ave. Tucson, Arizona 85719 Phone: (520) 318-8545
GEMINI 8-M Telescopes Project RPT-PS-G0065 The Gemini Instrumentation Program F. C. Gillett, D. A. Simons March 25, 1996 GEMINI PROJECT OFFICE 950 N. Cherry Ave. Tucson, Arizona 85719 Phone: (520) 318-8545
Southern African Large Telescope. Prime Focus Imaging Spectrograph. Etalon and Filter Trade Study. Ted Williams Rutgers University
 Southern African Large Telescope Prime Focus Imaging Spectrograph Etalon and Filter Trade Study Ted Williams Rutgers University Revision 1.0 18 Sept 2001 DRAFT PFIS Fabry-Perot Imaging Spectroscopy Two
Southern African Large Telescope Prime Focus Imaging Spectrograph Etalon and Filter Trade Study Ted Williams Rutgers University Revision 1.0 18 Sept 2001 DRAFT PFIS Fabry-Perot Imaging Spectroscopy Two
1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO?
 Astronomy 418/518 final practice exam 1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO? b. Describe the visibility vs. baseline for a two element,
Astronomy 418/518 final practice exam 1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO? b. Describe the visibility vs. baseline for a two element,
Flux Units and Line Lists
 APPENDIX 2 Flux Units and Line Lists In This Appendix... Infrared Flux Units / 255 Formulae / 258 Look-up Tables / 259 Examples / 266 Infrared Line Lists / 266 In this chapter we provide a variety of background
APPENDIX 2 Flux Units and Line Lists In This Appendix... Infrared Flux Units / 255 Formulae / 258 Look-up Tables / 259 Examples / 266 Infrared Line Lists / 266 In this chapter we provide a variety of background
Searching for Other Worlds
 Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Report on the new EFOSC2 VPH grisms
 Report on the new EFOSC2 VPH grisms Ivo Saviane Lorenzo Monaco v 1.0 March 01, 2008 1 Introduction In January 2008 the ULTRASPEC project delivered two volume-phased holographic grisms (VPHG) to be used
Report on the new EFOSC2 VPH grisms Ivo Saviane Lorenzo Monaco v 1.0 March 01, 2008 1 Introduction In January 2008 the ULTRASPEC project delivered two volume-phased holographic grisms (VPHG) to be used
Updated flux calibration and fringe modelling for the ACS/WFC G800L grism
 Updated flux calibration and fringe modelling for the ACS/WFC G800L grism H. Kuntschner, M. Kümmel, J. R. Walsh January 25, 2008 ABSTRACT A revised flux calibration is presented for the G800L grism with
Updated flux calibration and fringe modelling for the ACS/WFC G800L grism H. Kuntschner, M. Kümmel, J. R. Walsh January 25, 2008 ABSTRACT A revised flux calibration is presented for the G800L grism with
Astronomy 203 practice final examination
 Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Astronomical Experiments for the Chang E-2 Project
 Astronomical Experiments for the Chang E-2 Project Maohai Huang 1, Xiaojun Jiang 1, and Yihua Yan 1 1 National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 20A Datun Road,Chaoyang District,
Astronomical Experiments for the Chang E-2 Project Maohai Huang 1, Xiaojun Jiang 1, and Yihua Yan 1 1 National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 20A Datun Road,Chaoyang District,
Ultra Luminous Infared Galaxies. Yanling Wu Feb 22 nd,2005
 Ultra Luminous Infared Galaxies Yanling Wu Feb 22 nd,2005 The Biggest and the brightest Biggest and the best & best and the brightest Definition: LIRG: L8-1000umL
Ultra Luminous Infared Galaxies Yanling Wu Feb 22 nd,2005 The Biggest and the brightest Biggest and the best & best and the brightest Definition: LIRG: L8-1000umL
The in-orbit wavelength calibration of the WFC G800L grism
 The in-orbit wavelength calibration of the WFC G800L grism A. Pasquali, N. Pirzkal, J.R. Walsh March 5, 2003 ABSTRACT We present the G800L grism spectra of the Wolf-Rayet stars WR45 and WR96 acquired with
The in-orbit wavelength calibration of the WFC G800L grism A. Pasquali, N. Pirzkal, J.R. Walsh March 5, 2003 ABSTRACT We present the G800L grism spectra of the Wolf-Rayet stars WR45 and WR96 acquired with
Optical/IR Observational Astronomy Spectroscopy. David Buckley, SALT
 David Buckley, SALT 1 Background is really just monochromatic photometry History 1637 Descartes explained the origin of the rainbow. 1666 Newton s classic experiments on the nature of colour. 1752 Melvil
David Buckley, SALT 1 Background is really just monochromatic photometry History 1637 Descartes explained the origin of the rainbow. 1666 Newton s classic experiments on the nature of colour. 1752 Melvil
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery. Agenda. How does your eye form an image? Refraction. Example: Refraction at Sunset
 Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery Agenda Announce: Read S2 for Thursday Ch. 6 Telescopes 6.1 Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? Our goals for learning How
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery Agenda Announce: Read S2 for Thursday Ch. 6 Telescopes 6.1 Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? Our goals for learning How
FPA#64 and new substrate removed FPAs for WFC3-IR: a trade-off study
 Instrument Science Report WFC3 2005-019 ` and new substrate removed FPAs for WFC3-IR: a trade-off study Massimo Robberto (ESA/STSI) Abstract Recent tests indicate that the flight detectors selected for
Instrument Science Report WFC3 2005-019 ` and new substrate removed FPAs for WFC3-IR: a trade-off study Massimo Robberto (ESA/STSI) Abstract Recent tests indicate that the flight detectors selected for
Speckles and adaptive optics
 Chapter 9 Speckles and adaptive optics A better understanding of the atmospheric seeing and the properties of speckles is important for finding techniques to reduce the disturbing effects or to correct
Chapter 9 Speckles and adaptive optics A better understanding of the atmospheric seeing and the properties of speckles is important for finding techniques to reduce the disturbing effects or to correct
A very versatile, large A-omega, fibre-fed spectrograph design. Ian Parry IoA, Cambridge
 A very versatile, large A-omega, fibre-fed spectrograph design Ian Parry IoA, Cambridge 1 But first a quick diversion to support Alvio s case NIR multi-object spectroscopy with fibres works! CIRPASS was
A very versatile, large A-omega, fibre-fed spectrograph design Ian Parry IoA, Cambridge 1 But first a quick diversion to support Alvio s case NIR multi-object spectroscopy with fibres works! CIRPASS was
Telescopes. Optical Telescope Design. Reflecting Telescope
 Telescopes The science of astronomy was revolutionized after the invention of the telescope in the early 17th century Telescopes and detectors have been constantly improved over time in order to look at
Telescopes The science of astronomy was revolutionized after the invention of the telescope in the early 17th century Telescopes and detectors have been constantly improved over time in order to look at
Galactic Structure Mapping through 21cm Hyperfine Transition Line
 Galactic Structure Mapping through 21cm Hyperfine Transition Line Henry Shackleton MIT Department of Physics (Dated: May 14, 2017) Using a Small Radio Telescope (SRT), we measure electromagnetic radiation
Galactic Structure Mapping through 21cm Hyperfine Transition Line Henry Shackleton MIT Department of Physics (Dated: May 14, 2017) Using a Small Radio Telescope (SRT), we measure electromagnetic radiation
ACS CCDs UV and narrowband filters red leak check
 Instrument Science Report ACS 2007-03 ACS CCDs UV and narrowband filters red leak check Marco Chiaberge and Marco Sirianni May 01, 2007 ABSTRACT We present results of the observations of the star 15 Mon,
Instrument Science Report ACS 2007-03 ACS CCDs UV and narrowband filters red leak check Marco Chiaberge and Marco Sirianni May 01, 2007 ABSTRACT We present results of the observations of the star 15 Mon,
The VLT dealing with the Atmosphere, a Night Operation point of view
 The VLT dealing with the Atmosphere, a Night Operation point of view Julio Navarrete European Organization for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere Alonso de Cordova 3107, Vitacura, Santiago-Chile
The VLT dealing with the Atmosphere, a Night Operation point of view Julio Navarrete European Organization for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere Alonso de Cordova 3107, Vitacura, Santiago-Chile
Astronomy IRAF Tutorial for Exercise II Quick-look Photometry with Imexamine
 Astronomy 480 - IRAF Tutorial for Exercise II Quick-look Photometry with Imexamine Learning Objectives Files Used Define apparent and absolute magnitude. Explain how the magnitude scale is defined. Summarize
Astronomy 480 - IRAF Tutorial for Exercise II Quick-look Photometry with Imexamine Learning Objectives Files Used Define apparent and absolute magnitude. Explain how the magnitude scale is defined. Summarize
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES
 THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
Homework #7: Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, October points Profs. Rieke
 Homework #7: Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, October 31 30 points Profs. Rieke You are going to work with some famous astronomical data in this homework. The image data
Homework #7: Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, October 31 30 points Profs. Rieke You are going to work with some famous astronomical data in this homework. The image data
Introduction of near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy. Ken-ichi Tadaki (NAOJ)
 Introduction of near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy Ken-ichi Tadaki (NAOJ) Near-infrared in astronomy absorption by terrestrial atmosphere - wavelength range of 1-5 um - observable windows are limited (J,
Introduction of near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy Ken-ichi Tadaki (NAOJ) Near-infrared in astronomy absorption by terrestrial atmosphere - wavelength range of 1-5 um - observable windows are limited (J,
These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course.
 Licensed for Personal Use Only DO NOT DISTRIBUTE These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course. Distributing them in anyway will be considered a breach
Licensed for Personal Use Only DO NOT DISTRIBUTE These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course. Distributing them in anyway will be considered a breach
Fringe Correction for STIS Near-IR Long-Slit Spectra using Contemporaneous Tungsten Flat Fields
 1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. Fringe Correction for STIS Near-IR Long-Slit Spectra using Contemporaneous Tungsten Flat Fields Paul Goudfrooij
1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. Fringe Correction for STIS Near-IR Long-Slit Spectra using Contemporaneous Tungsten Flat Fields Paul Goudfrooij
Problem Solving. radians. 180 radians Stars & Elementary Astrophysics: Introduction Press F1 for Help 41. f s. picture. equation.
 Problem Solving picture θ f = 10 m s =1 cm equation rearrange numbers with units θ factors to change units s θ = = f sinθ fθ = s / cm 10 m f 1 m 100 cm check dimensions 1 3 π 180 radians = 10 60 arcmin
Problem Solving picture θ f = 10 m s =1 cm equation rearrange numbers with units θ factors to change units s θ = = f sinθ fθ = s / cm 10 m f 1 m 100 cm check dimensions 1 3 π 180 radians = 10 60 arcmin
USING THE ISS TO ASSEMBLE A VERY LARGE TELESCOPE
 USING THE ISS TO ASSEMBLE A VERY LARGE TELESCOPE Holland C. Ford (JHU) and James H. Crocker (Lockheed Martin) Presented by Warren Moos (JHU) 4/15/2003 1 A 30-m Very Large Space Telescope (VLST) : Assumptions
USING THE ISS TO ASSEMBLE A VERY LARGE TELESCOPE Holland C. Ford (JHU) and James H. Crocker (Lockheed Martin) Presented by Warren Moos (JHU) 4/15/2003 1 A 30-m Very Large Space Telescope (VLST) : Assumptions
DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY
 AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
HETDEX Overview. Hobby Eberly Telescope Dark Energy Experiment. HETDEX is: HETDEX enables a lot of ancillary science. HETDEX Science Workshop Feb 09
 Introduction to WFU, VIRUS, & DEX Gary J. Hill, McDonald Observatory Scope What HETDEX is WFU VIRUS DEX survey parameters 1 HETDEX is: Upgrade of HET to have a new 22 arcmin wide field of view Deployment
Introduction to WFU, VIRUS, & DEX Gary J. Hill, McDonald Observatory Scope What HETDEX is WFU VIRUS DEX survey parameters 1 HETDEX is: Upgrade of HET to have a new 22 arcmin wide field of view Deployment
Grand Canyon 8-m Telescope 1929
 1 2 Grand Canyon 8-m Telescope 1929 3 A World-wide Sample of Instruments 4 Instrumentation Details Instrument name Observing Modes Start of operations Wavelength Coverage Field of View Instrument cost
1 2 Grand Canyon 8-m Telescope 1929 3 A World-wide Sample of Instruments 4 Instrumentation Details Instrument name Observing Modes Start of operations Wavelength Coverage Field of View Instrument cost
Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes
 Instrument Science Report STIS 97-14 Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes Ralph Bohlin, Space Telescope Science Institute Nicholas Collins, Hughes STX/LASP/GSFC Anne Gonnella,
Instrument Science Report STIS 97-14 Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes Ralph Bohlin, Space Telescope Science Institute Nicholas Collins, Hughes STX/LASP/GSFC Anne Gonnella,
Open Cluster Research Project
 Open Cluster Research Project I. Introduction The observational data indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium and a trace of other elements, something triggers
Open Cluster Research Project I. Introduction The observational data indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium and a trace of other elements, something triggers
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery
 Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery 6.1 Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors Our goals for learning: How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image?
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery 6.1 Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors Our goals for learning: How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image?
Mid-Infrared Ground-Based Astronomy
 Mid-Infrared Ground-Based Astronomy Patrick Roche Oxford University Topics The sky and telescopes The instruments Observing techniques Sensitivity Niches Ground-based Mid-IR Astronomy Observations of cool
Mid-Infrared Ground-Based Astronomy Patrick Roche Oxford University Topics The sky and telescopes The instruments Observing techniques Sensitivity Niches Ground-based Mid-IR Astronomy Observations of cool
Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Iowa 29:137 Astronomical Laboratory Fall 2011 Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy
 Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Iowa 29:137 Astronomical Laboratory Fall 2011 Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy 1 Introduction Throughout your astronomy education, you have read about stellar
Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Iowa 29:137 Astronomical Laboratory Fall 2011 Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy 1 Introduction Throughout your astronomy education, you have read about stellar
Imaging with SPIRIT Exposure Guide
 Imaging with SPIRIT Exposure Guide SPIRIT optical telescopes utilise extremely sensitive cameras to record the light from distant astronomical objects. Even so, exposures of several seconds up to a few
Imaging with SPIRIT Exposure Guide SPIRIT optical telescopes utilise extremely sensitive cameras to record the light from distant astronomical objects. Even so, exposures of several seconds up to a few
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33
 Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
Quantifying the Assembly History of Elliptical Galaxies
 Quantifying the Assembly History of Elliptical Galaxies Michael Pierce (University of Wyoming) A Science Use Case for GMT and TMT Origin of Elliptical Galaxies! Elliptical Galaxies Form Through Mergers!
Quantifying the Assembly History of Elliptical Galaxies Michael Pierce (University of Wyoming) A Science Use Case for GMT and TMT Origin of Elliptical Galaxies! Elliptical Galaxies Form Through Mergers!
Astronomy 114. Lecture 27: The Galaxy. Martin D. Weinberg. UMass/Astronomy Department
 Astronomy 114 Lecture 27: The Galaxy Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 27 18 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 25,26 Astronomy 114 1/23 Announcements Quiz #2: we re
Astronomy 114 Lecture 27: The Galaxy Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 27 18 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 25,26 Astronomy 114 1/23 Announcements Quiz #2: we re
2. To measure the emission lines in the hydrogen, helium and possibly other elemental spectra, and compare these to know values.
 4.1. Purpose 1. To record several elemental emission spectra using arc lamps filled with each element using the Ocean Optics USB650 spectrometer. 2. To measure the emission lines in the hydrogen, helium
4.1. Purpose 1. To record several elemental emission spectra using arc lamps filled with each element using the Ocean Optics USB650 spectrometer. 2. To measure the emission lines in the hydrogen, helium
Electronic Imaging in Astronomy
 Ian S, McLean Electronic Imaging in Astronomy Detectors and Instrumentation (Second Edition) j""v Published f udiisnea in association with witn fyj Springer Praxis PubUshing Publisl PR Chichester, UK Contents
Ian S, McLean Electronic Imaging in Astronomy Detectors and Instrumentation (Second Edition) j""v Published f udiisnea in association with witn fyj Springer Praxis PubUshing Publisl PR Chichester, UK Contents
Pysynphot: A Python Re Implementation of a Legacy App in Astronomy
 Pysynphot: A Python Re Implementation of a Legacy App in Astronomy Vicki Laidler 1, Perry Greenfield, Ivo Busko, Robert Jedrzejewski Science Software Branch Space Telescope Science Institute Baltimore,
Pysynphot: A Python Re Implementation of a Legacy App in Astronomy Vicki Laidler 1, Perry Greenfield, Ivo Busko, Robert Jedrzejewski Science Software Branch Space Telescope Science Institute Baltimore,
EIC Simulations. Thomas Kitching, EIC Weak Lensing & Simulation Working Groups
 EIC Simulations Thomas Kitching A. Amara, S. Bridle, O. Boulade, B. Dobke, A. Fontana, A. Grazian, A. Heavens, A. Kiessling, M. Meneghetti, S. Paulin-Henriksson, J. Rhodes, A. Refregier, A. Taylor, R.
EIC Simulations Thomas Kitching A. Amara, S. Bridle, O. Boulade, B. Dobke, A. Fontana, A. Grazian, A. Heavens, A. Kiessling, M. Meneghetti, S. Paulin-Henriksson, J. Rhodes, A. Refregier, A. Taylor, R.
AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project
 AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project I. Introduction The observational data that astronomers have gathered over many years indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium
AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project I. Introduction The observational data that astronomers have gathered over many years indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium
Life Cycle of Stars. Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ. Authors: Daniel Duggan & Sarah Roberts
 Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ Authors: Daniel Duggan & Sarah Roberts Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ Introduction Photometry is the measurement of the intensity or brightness of an astronomical
Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ Authors: Daniel Duggan & Sarah Roberts Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ Introduction Photometry is the measurement of the intensity or brightness of an astronomical
Aperture Door. Model Wrappers. Aft Bulkhead. Page 1
 Page 1 Aperture Door Model Wrappers The wrappers show the Hubble Space Telescope s exterior features and the locations of its science instruments. On Page 7 you ll find a list of the abbreviations that
Page 1 Aperture Door Model Wrappers The wrappers show the Hubble Space Telescope s exterior features and the locations of its science instruments. On Page 7 you ll find a list of the abbreviations that
MIT Invitational, Jan Astronomy C. 2. You may separate the pages, but do not forget to put your team number at the top of all answer pages.
 MIT Invitational, Jan 2019 Astronomy C Competitors: School name: Team number: INSTRUCTIONS 1. Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2. You may separate the pages, but do not forget to put
MIT Invitational, Jan 2019 Astronomy C Competitors: School name: Team number: INSTRUCTIONS 1. Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2. You may separate the pages, but do not forget to put
Chandra was launched aboard Space Shuttle Columbia on July 23, 1999!!!
 Chandra was launched aboard Space Shuttle Columbia on July 23, 1999!!! Crew Lost During Re-Entry Modern X-ray Telescopes and Detectors X-ray Telescopes X-ray Instruments Some early highlights Observations
Chandra was launched aboard Space Shuttle Columbia on July 23, 1999!!! Crew Lost During Re-Entry Modern X-ray Telescopes and Detectors X-ray Telescopes X-ray Instruments Some early highlights Observations
Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy
 Name:... Astronomy 101: Observational Astronomy Fall 2006 Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy 1 Observations 1.1 Objectives and Observation Schedule During this lab each group will target a few bright stars of
Name:... Astronomy 101: Observational Astronomy Fall 2006 Lab 4: Stellar Spectroscopy 1 Observations 1.1 Objectives and Observation Schedule During this lab each group will target a few bright stars of
A Hunt for Tidal Features in a Nearby Ultra Diffuse Galaxy
 Yale Observing Proposal Standard proposal Semester: 2018B Date: April 10, 2018 A Hunt for Tidal Features in a Nearby Ultra Diffuse Galaxy CoI: Aritra Ghosh Status: G Affil.: Yale University CoI: Dhruba
Yale Observing Proposal Standard proposal Semester: 2018B Date: April 10, 2018 A Hunt for Tidal Features in a Nearby Ultra Diffuse Galaxy CoI: Aritra Ghosh Status: G Affil.: Yale University CoI: Dhruba
Spectroscopy in Astronomy
 Spectroscopy in Astronomy History 1814 German optician Joseph von Fraunhofer sun with 600+ spectral lines; now we know more than 3000 lines 1860 German chemists Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert W. Bunsen Chemical
Spectroscopy in Astronomy History 1814 German optician Joseph von Fraunhofer sun with 600+ spectral lines; now we know more than 3000 lines 1860 German chemists Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert W. Bunsen Chemical
Gas 1: Molecular clouds
 Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
The Planetary Nebula Spectrograph
 Chapter 2 The Planetary Nebula Spectrograph The Planetary Nebula Spectrograph (PN.S) and the principles ofcounter-dispersed imaging are described in this chapter. A full description of PN.S, its motivation,
Chapter 2 The Planetary Nebula Spectrograph The Planetary Nebula Spectrograph (PN.S) and the principles ofcounter-dispersed imaging are described in this chapter. A full description of PN.S, its motivation,
Scientific Impact of the Operating Temperature for NFIRAOS on TMT
 1st AO4ELT conference, 01006 (2010) DOI:10.1051/ao4elt/201001006 Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2010 Scientific Impact of the Operating Temperature for NFIRAOS on TMT David R. Andersen
1st AO4ELT conference, 01006 (2010) DOI:10.1051/ao4elt/201001006 Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2010 Scientific Impact of the Operating Temperature for NFIRAOS on TMT David R. Andersen
