Spinning Dust and the 3mm Excess
|
|
|
- Meagan Hutchinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spinning Dust and the 3mm Excess 8th October 2010
2 Spinning dust 1996: COBE DMR-DIRBE (Kogut et al.) observe correlated microwave and 100 µm emission. 1997: Saskatoon 30 & 40 GHz observations; OVRO 14.5 & 32 GHz observations (Leitch et al.) I Hα (R) = 0.36EM(cm 6 pc)t(10 4 K) 0.9
3 Spinning dust 1996: COBE DMR-DIRBE (Kogut et al.) observe correlated microwave and 100 µm emission. 1997: Saskatoon 30 & 40 GHz observations; OVRO 14.5 & 32 GHz observations (Leitch et al.) I Hα (R) = 0.36EM(cm 6 pc)t(10 4 K) 0.9
4 Spinning dust 1996: COBE DMR-DIRBE (Kogut et al.) observe correlated microwave and 100 µm emission. 1997: Saskatoon 30 & 40 GHz observations; OVRO 14.5 & 32 GHz observations (Leitch et al.) I Hα (R) T 1.2
5 Spinning dust 1996: COBE DMR-DIRBE (Kogut et al.) observe correlated microwave and 100 µm emission. 1997: Saskatoon 30 & 40 GHz observations; OVRO 14.5 & 32 GHz observations (Leitch et al.) I Hα (R) T 1.2 T 10 6 K
6 Spinning dust 1998: Drain & Lazarian spinning dust model 1994: Ferrara & Dettmar - didn t consider damping 1957: Erickson - dust grains in radio sources P = 2 ω 4 µ 2 sin(θ) 2 3 c 3
7 Open diamonds: COBE (Kogut et al. 1996) Filled diamonds: Saskatoon (de Oliveira-Costa et al. 1997) Filled Squares: OVRO (Leitch et al. 1997) DL98
8 Size distribution: MRN Distribution dn da = n HA MRN [ a 3.5 +Ba 1 exp 1 2 [ ln(a/a0 ) sigma ] 2 ] DL98 MRN distribution is known to underestimate the population of small grains 12 µm and 25 µm IRAS emission as well as MIR emission features suggest a substantial population of small grains
9 Size distribution: MRN Distribution dn da = n HA MRN [ a 3.5 +Ba 1 exp 1 2 [ ln(a/a0 ) sigma ] 2 ] DL98 MRN distribution is known to underestimate the population of small grains 12 µm and 25 µm IRAS emission as well as MIR emission features suggest a substantial population of small grains
10 HII regions, dark clouds and PDRs... Green Bank (Finkbeiner et al. 2002) looked at 10 dust clouds and found two positive results: LPH96 and L1622 Scaife et al. 2007; Dickinson et al Casassus et al. 2006
11 NGC 6946
12 NGC 6946
13 NGC 6946
14 LDN 1111 Ultra-compact HII? EM > pc cm 6 M 100 M M = 0.3 M (Visser et al. 2001)
15 LDN 1111 Ultra-compact HII? EM > pc cm 6 M 100 M M = 0.3 M (Visser et al. 2001)
16 LDN 1111 Ultra-compact HII? EM > pc cm 6 M 100 M M = 0.3 M (Visser et al. 2001)
17 LDN 1111 Ultra-compact HII? EM > pc cm 6 M 100 M v = 21.4 km s 1 (Heiles et al. 1996)
18 Lynds Clouds No correlation with: Mass Protostellar activity Position And not a sample bias.
19 LDN 675 No correlation with: Mass Protostellar activity Position And not a sample bias.
20 L1221-IRS and the AMI-LA P* sample VeLLO: L int 0.1 L Is thermal emission from protostars contributing significantly?
21 LDN 1246 No correlation with: Mass Protostellar activity Position And not a sample bias.
22 LDN 1246 No correlation with: Mass Protostellar activity Position And not a sample bias.
23 The HII region contradiction RCW175: 8.6σ excess at 31 GHz. (Dickinson et al. 2008) Southern hemisphere: 6 HII regions Frequency coverage: GHz Slight excess observed in all regions Most significant excess 3.3 σ. Dickinson et al. 2007
24 The HII region contradiction Northern hemisphere: 16 HII regions Frequency coverage: GHz Correlation with IRAS 100 µm (r=0.88) but stronger correlation with NVSS 1.4 GHz (r=0.99) No excess above 1 σ Opposite effect - steepening of the spectrum Scaife et al. 2008
25 HCHII contamination Galactic observations with CMB instruments have large PSFs Objects which appear to be approx. point-like can contain contributions from a number of different sources Contamination by dense plasma is difficult to identify without priors (Todorovíc et al. 2010)
26 Contamination The optically thick spectra of HCHII regions can be confused with the low frequency side of a spinning dust spectrum. Excesses at cm-wave frequencies can be caused by a variety of protostellar emission mechanisms.
27 The 3mm excess Is the 3 mm excess seen in the spectra of UC/HCHII regions dues to spinning dust...? We need to rule out the thermal dust tail - Herschel? Could it be similar to the emission postulated in the SMC?
28 The Small Magellanic Cloud (Bot et al. 2010)
29 The Small Magellanic Cloud (Bot et al. 2010)
30 The Small Magellanic Cloud Model=Diffuse + dense PDR + moderately dense PDR PAH mass fraction consistent with MIR spectra Peak at ν 160 GHz 1 grain size : smaller grains higher emission frequencies 2 density : denser medium higher frequencies 3 ISRF : at G 0 > 10 higher ISRF higher frequencies
31 m dishes
32 m dishes
33 Conclusions Spinning dust emission has been detected in a number of distinct astronomical objects At present it is unclear what differentiates those objects which do exhibit the emission and those which do not The 3 mm excess seen in UC/HCHII regions could be due to spinning dust emission Correctly identifying the excess, given alternatives, requires well matched data at many frequencies
Dust emission. D.Maino. Radio Astronomy II. Physics Dept., University of Milano. D.Maino Dust emission 1/24
 Dust emission D.Maino Physics Dept., University of Milano Radio Astronomy II D.Maino Dust emission 1/24 New insight on Dust Emission Before WMAP and Planck with only COBE-DMR, dust is well described by
Dust emission D.Maino Physics Dept., University of Milano Radio Astronomy II D.Maino Dust emission 1/24 New insight on Dust Emission Before WMAP and Planck with only COBE-DMR, dust is well described by
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 22 Feb 1999
 Anomalous Microwave Emission arxiv:astro-ph/9902307v1 22 Feb 1999 A. Kogut Laboratory for Astronomy and Solar Physics, Code 685, Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771 Abstract. Improved knowledge
Anomalous Microwave Emission arxiv:astro-ph/9902307v1 22 Feb 1999 A. Kogut Laboratory for Astronomy and Solar Physics, Code 685, Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771 Abstract. Improved knowledge
WMAP Excess Interpreted as WIMP Annihilation
 WMAP Excess Interpreted as WIMP Annihilation idm2004, Edinburgh September 9, 2004 Douglas Finkbeiner Princeton University Outline " " " WMAP ISM emission (expected) The Galactic synchrotron Haze (unexpected)
WMAP Excess Interpreted as WIMP Annihilation idm2004, Edinburgh September 9, 2004 Douglas Finkbeiner Princeton University Outline " " " WMAP ISM emission (expected) The Galactic synchrotron Haze (unexpected)
Polarised foregrounds (synchrotron, dust and AME) and their effect on the detection of primordial CMB B-modes
 Polarised foregrounds (synchrotron, dust and AME) and their effect on the detection of primordial CMB B-modes Ricardo T. Génova Santos Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias Cosmology School in the Canary
Polarised foregrounds (synchrotron, dust and AME) and their effect on the detection of primordial CMB B-modes Ricardo T. Génova Santos Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias Cosmology School in the Canary
Correlation of the South Pole 94 data with 100 µm and 408 MHz maps
 A&A 368, 760 765 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010061 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics Correlation of the South Pole 94 data with 100 µm and 408 MHz maps J.-Ch. Hamilton 1 and K. M. Ganga 1,2 1 Physique
A&A 368, 760 765 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20010061 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics Correlation of the South Pole 94 data with 100 µm and 408 MHz maps J.-Ch. Hamilton 1 and K. M. Ganga 1,2 1 Physique
Review Article Anomalous Microwave Emission from Star Forming Regions
 Advances in Astronomy Volume 2013, Article ID 390287, 25 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/390287 Review Article Anomalous Microwave Emission from Star Forming Regions Anna M. M. Scaife Physics & Astronomy,
Advances in Astronomy Volume 2013, Article ID 390287, 25 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/390287 Review Article Anomalous Microwave Emission from Star Forming Regions Anna M. M. Scaife Physics & Astronomy,
Dust in dwarf galaxies: The case of NGC 4214
 Dust in dwarf galaxies: The case of NGC 4214 Ute Lisenfeld Israel Hermelo Monica Relaño Richard Tuffs Cristina Popescu Joerg Fischera Brent Grove Image from HST WFC3 (Image: NASA/ESA/Hubble Heritage) Dust
Dust in dwarf galaxies: The case of NGC 4214 Ute Lisenfeld Israel Hermelo Monica Relaño Richard Tuffs Cristina Popescu Joerg Fischera Brent Grove Image from HST WFC3 (Image: NASA/ESA/Hubble Heritage) Dust
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Aug 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Aug 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Aug 2009](/thumbs/75/71806432.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 17 (2005) Printed 12 August 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) AMI observations of Lynds Dark Nebulae: further evidence for anomalous cm-wave emission arxiv:0908.1655v1 [astro-ph.ga]
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 17 (2005) Printed 12 August 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) AMI observations of Lynds Dark Nebulae: further evidence for anomalous cm-wave emission arxiv:0908.1655v1 [astro-ph.ga]
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Sep 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Sep 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Sep 2009](/thumbs/88/117253265.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 0, 1 14 () Printed 25 October 18 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) VSA Observations of the Anomalous Microwave Emission in the Perseus Region arxiv:0909.4682v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Sep 29
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 0, 1 14 () Printed 25 October 18 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) VSA Observations of the Anomalous Microwave Emission in the Perseus Region arxiv:0909.4682v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Sep 29
Dust Polarization. J.Ph. Bernard Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planetologie (IRAP) Toulouse
 Dust Polarization J.Ph. Bernard Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planetologie (IRAP) Toulouse 1 Layout - Dust polarization (Extinction) - Dust polarization (Emission) - Dust polarization observational
Dust Polarization J.Ph. Bernard Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planetologie (IRAP) Toulouse 1 Layout - Dust polarization (Extinction) - Dust polarization (Emission) - Dust polarization observational
Quantum Suppression of Alignment in Spinning Nanoparticles
 Quantum Suppression of Alignment in Spinning Nanoparticles B. T. Draine Princeton University Brandon S. Hensley Jet Propulsion Laboratory Davis-Greenstein Alignment by Magnetic Dissipation Suppression
Quantum Suppression of Alignment in Spinning Nanoparticles B. T. Draine Princeton University Brandon S. Hensley Jet Propulsion Laboratory Davis-Greenstein Alignment by Magnetic Dissipation Suppression
Diffuse AME emission in Perseus
 Diffuse AME emission in Perseus A strange beast Bob Watson, JBCA Summary Tenerife experiment first hint COSMOSOMAS Leading to Perseus SED Less filtered data (1 harmonic removal) Component separation VSA
Diffuse AME emission in Perseus A strange beast Bob Watson, JBCA Summary Tenerife experiment first hint COSMOSOMAS Leading to Perseus SED Less filtered data (1 harmonic removal) Component separation VSA
New radio observations of anomalous microwave emission in the HII region RCW175
 New radio observations of anomalous microwave emission in the HII region RCW175 E.S. Battistelli 1, E. Carretti 2, A. Cruciani 1, P. de Bernardis 1, R. Genova-Santos 3, S. Masi 1, arxiv:1501.02196v1 [astro-ph.sr]
New radio observations of anomalous microwave emission in the HII region RCW175 E.S. Battistelli 1, E. Carretti 2, A. Cruciani 1, P. de Bernardis 1, R. Genova-Santos 3, S. Masi 1, arxiv:1501.02196v1 [astro-ph.sr]
Payne-Scott workshop on Hyper Compact HII regions Sydney, September 8, 2010
 Payne-Scott workshop on Hyper Compact HII regions Sydney, September 8, 2010 Aim Review the characteristics of regions of ionized gas within young massive star forming regions. Will focus the discussion
Payne-Scott workshop on Hyper Compact HII regions Sydney, September 8, 2010 Aim Review the characteristics of regions of ionized gas within young massive star forming regions. Will focus the discussion
364 DE OLIVEIRA-COSTA ET AL. Vol. 567
 THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 567:363È369, 2002 March 1 ( 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A NEW SPIN ON GALACTIC DUST ANGE LICA DE OLIVEIRA-COSTA,1 MAX TEGMARK,1
THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 567:363È369, 2002 March 1 ( 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A NEW SPIN ON GALACTIC DUST ANGE LICA DE OLIVEIRA-COSTA,1 MAX TEGMARK,1
CMB Foreground and separation methods. Astro 448 Yuxi Zhao 12/5/2018
 CMB Foreground and separation methods Astro 448 Yuxi Zhao 12/5/2018 Outline CMB foreground overview Thermal Dust AME (spin dust, spinning nanodiamonds? ) Synchrotron Free-free CO Zodiacal light, CIB Component
CMB Foreground and separation methods Astro 448 Yuxi Zhao 12/5/2018 Outline CMB foreground overview Thermal Dust AME (spin dust, spinning nanodiamonds? ) Synchrotron Free-free CO Zodiacal light, CIB Component
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Jan 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Jan 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Jan 2015](/thumbs/95/126256180.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc.,???? (xxxx) Printed January 215 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:151.1v1 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Jan 215 Observations of Free-Free and Anomalous Microwave Emission from LDN 2 with the
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc.,???? (xxxx) Printed January 215 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:151.1v1 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Jan 215 Observations of Free-Free and Anomalous Microwave Emission from LDN 2 with the
Observations of free free and anomalous microwave emission from LDN 1622 with the 100 m Green Bank Telescope
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1863 Observations of free free and anomalous microwave emission from LDN 1622 with the 100 m Green Bank Telescope S. E. Harper, 1 C. Dickinson 1 and K. Cleary 2 1 Jodrell Bank Centre
doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1863 Observations of free free and anomalous microwave emission from LDN 1622 with the 100 m Green Bank Telescope S. E. Harper, 1 C. Dickinson 1 and K. Cleary 2 1 Jodrell Bank Centre
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 10 Feb 2003
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 () Printed 5 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Reappraising foreground contamination in the COBE-DMR data arxiv:astro-ph/0302181v1 10 Feb 2003 A. J. Banday, 1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 () Printed 5 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Reappraising foreground contamination in the COBE-DMR data arxiv:astro-ph/0302181v1 10 Feb 2003 A. J. Banday, 1
A characterization of the diffuse Galactic emissions at large angular scales using the Tenerife data
 A characterization of the diffuse Galactic emissions at large angular scales using the Tenerife data J. F. Macías-Pérez 1,2, R.D. Davies 2, R. Watson 2, C.M. Gutierrez 3, R. Rebolo 3 1 arxiv:1301.2800v1
A characterization of the diffuse Galactic emissions at large angular scales using the Tenerife data J. F. Macías-Pérez 1,2, R.D. Davies 2, R. Watson 2, C.M. Gutierrez 3, R. Rebolo 3 1 arxiv:1301.2800v1
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 7 Apr 2006
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 () Printed 5 February 2018 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) A determination of the Spectra of Galactic components observed by WMAP arxiv:astro-ph/0511384v2 7 Apr 2006 R.D.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 () Printed 5 February 2018 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) A determination of the Spectra of Galactic components observed by WMAP arxiv:astro-ph/0511384v2 7 Apr 2006 R.D.
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Sep 2011
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Sep 2011 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Sep 2011](/thumbs/71/66235923.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. spinning variations c ESO 2013 December 21, 2013 Modelling the spinning dust emission from dense interstellar clouds N. Ysard 1, M. Juvela 1, and L. Verstraete 2
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. spinning variations c ESO 2013 December 21, 2013 Modelling the spinning dust emission from dense interstellar clouds N. Ysard 1, M. Juvela 1, and L. Verstraete 2
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33
 Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 21 Nov 2006
 Evidence for Inverted Spectrum 20 GHz Emission in the Galactic Plane arxiv:astro-ph/0611655 v1 21 Nov 2006 S. P. Boughn and J. C. Pober Department of Astronomy, Haverford College, Haverford, PA 19041;
Evidence for Inverted Spectrum 20 GHz Emission in the Galactic Plane arxiv:astro-ph/0611655 v1 21 Nov 2006 S. P. Boughn and J. C. Pober Department of Astronomy, Haverford College, Haverford, PA 19041;
Dark gas contribution to diffuse gamma-ray emission
 Dark gas contribution to diffuse gamma-ray emission Masaki Mori ICRR CANGAROO group internal seminar, November 7, 2005 Adrian Cho S. Hunter, GLAST meeting, Oct.2004 The Galactic Diffuse Gamma-ray Emission...
Dark gas contribution to diffuse gamma-ray emission Masaki Mori ICRR CANGAROO group internal seminar, November 7, 2005 Adrian Cho S. Hunter, GLAST meeting, Oct.2004 The Galactic Diffuse Gamma-ray Emission...
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 30 May 1997
 An Anomalous Component of Galactic Emission E.M. Leitch, A.C.S. Readhead, T.J. Pearson, S.T. Myers 1 California Institute of Technology, 105-4 Pasadena CA 9115 arxiv:astro-ph/970541v1 30 May 1997 ABSTRACT
An Anomalous Component of Galactic Emission E.M. Leitch, A.C.S. Readhead, T.J. Pearson, S.T. Myers 1 California Institute of Technology, 105-4 Pasadena CA 9115 arxiv:astro-ph/970541v1 30 May 1997 ABSTRACT
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Jul 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Jul 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Jul 2015](/thumbs/93/112452920.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 13 (2012) Printed 10 July 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1507.08280v1 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Jul 2015 Observations of Galactic star-forming regions with the Cosmic Background
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 13 (2012) Printed 10 July 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1507.08280v1 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Jul 2015 Observations of Galactic star-forming regions with the Cosmic Background
Galactic Dust Properties. Déborah Paradis CNES Post-doc IRAP, Toulouse
 Galactic Dust Properties Déborah Paradis CNES Post-doc IRAP, Toulouse BG emissivity λ I ν (λ) = Q abs (λ 0 ) λ 0 β emissivity = τ/n H β : spectral index B ν ( T eq,λ)n H Conventionally admitted : β = 2
Galactic Dust Properties Déborah Paradis CNES Post-doc IRAP, Toulouse BG emissivity λ I ν (λ) = Q abs (λ 0 ) λ 0 β emissivity = τ/n H β : spectral index B ν ( T eq,λ)n H Conventionally admitted : β = 2
8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust
 8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust James Graham UC, Berkeley 1 Reading Tielens, Interstellar Medium, Ch. 5 Mathis, J. S. 1990, AARA, 28, 37 Draine, B. T., 2003, AARA, 41, 241 2 Nature
8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust James Graham UC, Berkeley 1 Reading Tielens, Interstellar Medium, Ch. 5 Mathis, J. S. 1990, AARA, 28, 37 Draine, B. T., 2003, AARA, 41, 241 2 Nature
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Sep 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Sep 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Sep 2011](/thumbs/86/93838593.jpg) Submitted to the Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/10/09 EVIDENCE FOR ANOMALOUS DUST-CORRELATED EMISSION AT 8 GHZ Michelle Lu 1, Joanna Dunkley 2, and Lyman Page
Submitted to the Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/10/09 EVIDENCE FOR ANOMALOUS DUST-CORRELATED EMISSION AT 8 GHZ Michelle Lu 1, Joanna Dunkley 2, and Lyman Page
ASTR2050 Spring Please turn in your homework now! In this class we will discuss the Interstellar Medium:
 ASTR2050 Spring 2005 Lecture 10am 29 March 2005 Please turn in your homework now! In this class we will discuss the Interstellar Medium: Introduction: Dust and Gas Extinction and Reddening Physics of Dust
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 Lecture 10am 29 March 2005 Please turn in your homework now! In this class we will discuss the Interstellar Medium: Introduction: Dust and Gas Extinction and Reddening Physics of Dust
Dust: Grain Populations, Extinction Curves, and Emission Spectra Monday, January 31, 2011
 Dust: Grain Populations, Extinction Curves, and Emission Spectra Monday, January 31, 2011 CONTENTS: 1. Introduction 2. The Extinction Curve and Abundance Constraints A. Formalities B. Features 3. Infrared
Dust: Grain Populations, Extinction Curves, and Emission Spectra Monday, January 31, 2011 CONTENTS: 1. Introduction 2. The Extinction Curve and Abundance Constraints A. Formalities B. Features 3. Infrared
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS. A conspicuous increase of Galactic contamination over CMBR anisotropies at large angular scales
 Astron. Astrophys. 346, 369 382 1999) A conspicuous increase of Galactic contamination over CMBR anisotropies at large angular scales ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Martín López-Corredoira Instituto de Astrofísica
Astron. Astrophys. 346, 369 382 1999) A conspicuous increase of Galactic contamination over CMBR anisotropies at large angular scales ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Martín López-Corredoira Instituto de Astrofísica
SOFIA observations of far-infrared hydroxyl emission toward classical ultracompact HII/OH maser regions
 SOFIA observations of far-infrared hydroxyl emission toward classical ultracompact HII/OH maser regions T. Csengeri, K. Menten, M. A. Requena-Torres, F. Wyrowski, R. Güsten, H. Wiesemeyer, H.-W. Hübers,
SOFIA observations of far-infrared hydroxyl emission toward classical ultracompact HII/OH maser regions T. Csengeri, K. Menten, M. A. Requena-Torres, F. Wyrowski, R. Güsten, H. Wiesemeyer, H.-W. Hübers,
Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5)
 Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5) Flow of story 4.1 4.2 4.3 Acquiring Spectroscopic or Photometric Redshifts Infrared SED Fitting for DSFGs Estimating L IR, T dust and M dust from an
Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5) Flow of story 4.1 4.2 4.3 Acquiring Spectroscopic or Photometric Redshifts Infrared SED Fitting for DSFGs Estimating L IR, T dust and M dust from an
Three-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP 1 ) Observations: Temperature Analysis
 Draft: December 19, 2006 Three-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP 1 ) Observations: Temperature Analysis G. Hinshaw 2, M. R. Nolta 3, C. L. Bennett 4, R. Bean 5, O. Doré 3,11, M. R. Greason
Draft: December 19, 2006 Three-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP 1 ) Observations: Temperature Analysis G. Hinshaw 2, M. R. Nolta 3, C. L. Bennett 4, R. Bean 5, O. Doré 3,11, M. R. Greason
High latitude Galactic dust emission in the BOOMERanG maps
 High latitude Galactic dust emission in the BOOMERanG maps S. Masi 1, P.A.R. Ade 2,J.J Bock 3,4, A. Boscaleri 5, B.P. Crill 3, P. de Bernardis 1, M. Giacometti 1, E. Hivon 3, V.V. Hristov 3, A.E. Lange
High latitude Galactic dust emission in the BOOMERanG maps S. Masi 1, P.A.R. Ade 2,J.J Bock 3,4, A. Boscaleri 5, B.P. Crill 3, P. de Bernardis 1, M. Giacometti 1, E. Hivon 3, V.V. Hristov 3, A.E. Lange
Electric Dipole Radiation from Spinning Dust Grains
 Submitted to The Astrophysical Journal Electric Dipole Radiation from Spinning Dust Grains B.T. Draine & A. Lazarian Princeton University Observatory, Peyton Hall, Princeton, NJ 08544 ABSTRACT We discuss
Submitted to The Astrophysical Journal Electric Dipole Radiation from Spinning Dust Grains B.T. Draine & A. Lazarian Princeton University Observatory, Peyton Hall, Princeton, NJ 08544 ABSTRACT We discuss
Ionized Hydrogen (HII)
 Ionized Hydrogen (HII) While ionized hydrogen (protons, electrons) forms the majority of the ionized phase of the ISM, it also contains ionized forms of other elements: e.g., OII, OIII, CIV, MgII. Highest
Ionized Hydrogen (HII) While ionized hydrogen (protons, electrons) forms the majority of the ionized phase of the ISM, it also contains ionized forms of other elements: e.g., OII, OIII, CIV, MgII. Highest
RAMPS: The Radio Ammonia Mid-Plane Survey. James Jackson Institute for Astrophysical Research Boston University
 RAMPS: The Radio Ammonia Mid-Plane Survey James Jackson Institute for Astrophysical Research Boston University High Frequency Workshop, Green Bank, 21 September 2015 Collaborators (partial list) Taylor
RAMPS: The Radio Ammonia Mid-Plane Survey James Jackson Institute for Astrophysical Research Boston University High Frequency Workshop, Green Bank, 21 September 2015 Collaborators (partial list) Taylor
GMC as a site of high-mass star formation
 ALMA Image: N159W GMC as a site of high-mass star formation From galaxy evolution to individual star formation kpc 1-100pc GMCs: 10 4-10 6 Mo n(h 2 ) ~ 1000cm -3 Clumps, Cores 10 2-10 3 Mo n(h 2 ) ~ >10
ALMA Image: N159W GMC as a site of high-mass star formation From galaxy evolution to individual star formation kpc 1-100pc GMCs: 10 4-10 6 Mo n(h 2 ) ~ 1000cm -3 Clumps, Cores 10 2-10 3 Mo n(h 2 ) ~ >10
Polarized Foregrounds and the CMB Al Kogut/GSFC
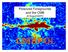 Polarized Foregrounds and the CMB Al Kogut/GSFC The Problem In A Nutshell Galactic foregrounds are 2 orders of magnitude brighter than primordial B-mode polarization from 30 to 200 GHz Polarized vs Unpolarized
Polarized Foregrounds and the CMB Al Kogut/GSFC The Problem In A Nutshell Galactic foregrounds are 2 orders of magnitude brighter than primordial B-mode polarization from 30 to 200 GHz Polarized vs Unpolarized
THE INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM: XI The Warm Ionized Medium. Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune
 THE INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM: XI The Warm Ionized Medium Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune OUTLINE Background. The warm ionized medium: Probes of conditions. Pulsar dispersion measures.
THE INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM: XI The Warm Ionized Medium Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune OUTLINE Background. The warm ionized medium: Probes of conditions. Pulsar dispersion measures.
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines!
 Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Lecture 2: Molecular Clouds: Galactic Context and Observational Tracers. Corona Australis molecular cloud: Andrew Oreshko
 Lecture 2: Molecular Clouds: Galactic Context and Observational Tracers Corona Australis molecular cloud: Andrew Oreshko Classification of Young Stellar Objects (YSOs) Spectral Index Hartmann: Accretion
Lecture 2: Molecular Clouds: Galactic Context and Observational Tracers Corona Australis molecular cloud: Andrew Oreshko Classification of Young Stellar Objects (YSOs) Spectral Index Hartmann: Accretion
Star Formation. Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase
 Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Star Formation. Spitzer Key Contributions to Date
 Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
The Interstellar Medium
 http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/~pvdwerf/teaching/ The Interstellar Medium Lecturer: Dr. Paul van der Werf Fall 2014 Oortgebouw 565, ext 5883 pvdwerf@strw.leidenuniv.nl Assistant: Kirstin Doney Huygenslaboratorium
http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/~pvdwerf/teaching/ The Interstellar Medium Lecturer: Dr. Paul van der Werf Fall 2014 Oortgebouw 565, ext 5883 pvdwerf@strw.leidenuniv.nl Assistant: Kirstin Doney Huygenslaboratorium
Galactic Observations of Terahertz C+ (GOT C+): CII Detection of Hidden H2 in the ISM
 Galactic Observations of Terahertz C+ (GOT C+): CII Detection of Hidden H2 in the ISM Bill Langer GOT C+ Team: P. Goldsmith, D. Li, J. Pineda, T. Velusamy, & H. Yorke Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California
Galactic Observations of Terahertz C+ (GOT C+): CII Detection of Hidden H2 in the ISM Bill Langer GOT C+ Team: P. Goldsmith, D. Li, J. Pineda, T. Velusamy, & H. Yorke Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California
Deuterium Fractionation in Massive Star Forming Clumps in Infrared Dark Clouds
 Deuterium Fractionation in Massive Star Forming Clumps in Infrared Dark Clouds Sheng-Yuan Liu (ASIAA) in collaboration with Vivien H.-R. Chen (NTHU) Y.-N. Su (ASIAA) Qizhou Zhang (CfA) Massive Star Formation
Deuterium Fractionation in Massive Star Forming Clumps in Infrared Dark Clouds Sheng-Yuan Liu (ASIAA) in collaboration with Vivien H.-R. Chen (NTHU) Y.-N. Su (ASIAA) Qizhou Zhang (CfA) Massive Star Formation
6: Observing Warm Phases: Dispersion ( n e dl ) & Emission ( n
 6: Observing Warm Phases: Dispersion ( n e dl ) & Emission ( n 2 e dl ) Measure James R. Graham University of California Berkeley NGC 891 NGC 891 AY 216 2 Techniques & Components The Warm Ionized Medium
6: Observing Warm Phases: Dispersion ( n e dl ) & Emission ( n 2 e dl ) Measure James R. Graham University of California Berkeley NGC 891 NGC 891 AY 216 2 Techniques & Components The Warm Ionized Medium
Anatomy of the S255-S257 complex - Triggered high-mass star formation
 Proceedings Title IAU Symposium Proceedings IAU Symposium No. IAUS237, 2006 A.C. Editor, B.D. Editor & C.E. Editor, eds. c 2006 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Anatomy of
Proceedings Title IAU Symposium Proceedings IAU Symposium No. IAUS237, 2006 A.C. Editor, B.D. Editor & C.E. Editor, eds. c 2006 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Anatomy of
The High-Energy Interstellar Medium
 The High-Energy Interstellar Medium Andy Strong MPE Garching on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics Lorentz Centre Workshop March 14-18
The High-Energy Interstellar Medium Andy Strong MPE Garching on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics Lorentz Centre Workshop March 14-18
SOFIA/GREAT observations of LMC-N 11: Does [C ii] trace regions with a large H 2 fraction?
![SOFIA/GREAT observations of LMC-N 11: Does [C ii] trace regions with a large H 2 fraction? SOFIA/GREAT observations of LMC-N 11: Does [C ii] trace regions with a large H 2 fraction?](/thumbs/75/72182908.jpg) SOFIA/GREAT observations of LMC-N 11: Does [C ii] trace regions with a large H 2 fraction? Vianney Lebouteiller Laboratoire AIM - CEA, Saclay, France Main collaborators: F. Galliano, S. Madden, M. Chevance,
SOFIA/GREAT observations of LMC-N 11: Does [C ii] trace regions with a large H 2 fraction? Vianney Lebouteiller Laboratoire AIM - CEA, Saclay, France Main collaborators: F. Galliano, S. Madden, M. Chevance,
Magnetic Fields over all Scales
 Magnetic Fields over all Scales Patrick Koch (ASIAA) 1 pc with: Hsuan-Gu Chou, Paul Ho, Ya-Wen Tang, Hsi-Wei Yen 30 mpc (CSO / Hertz @ 350µm, ~20 ) (JCMT / SCUPOL @850µm, ~10 ) (SMA@ 345 GHz: ~ 3 to 0.7
Magnetic Fields over all Scales Patrick Koch (ASIAA) 1 pc with: Hsuan-Gu Chou, Paul Ho, Ya-Wen Tang, Hsi-Wei Yen 30 mpc (CSO / Hertz @ 350µm, ~20 ) (JCMT / SCUPOL @850µm, ~10 ) (SMA@ 345 GHz: ~ 3 to 0.7
A MULTI-WAVELENGTH INVESTIGATION OF RCW175: AN HII REGION HARBORING SPINNING DUST EMISSION
 Draft version May 22, 2012 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 A MULTI-WAVELENGTH INVESTIGATION OF RCW175: AN HII REGION HARBORING SPINNING DUST EMISSION C. T. Tibbs 1, R. Paladini
Draft version May 22, 2012 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 A MULTI-WAVELENGTH INVESTIGATION OF RCW175: AN HII REGION HARBORING SPINNING DUST EMISSION C. T. Tibbs 1, R. Paladini
Planck and Virtual Observatories: Far Infra-red / Sub-mm Specificities
 JF Sygnet (Planck HFI DPCM) Planck and Virtual Observatories: Far Infra-red / Sub-mm Specificities Planck Mission, Planck Data and its Specificities (4) Data Treatment and its Specificities (4) Planck
JF Sygnet (Planck HFI DPCM) Planck and Virtual Observatories: Far Infra-red / Sub-mm Specificities Planck Mission, Planck Data and its Specificities (4) Data Treatment and its Specificities (4) Planck
Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era. François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale
 Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Motivation Dust emission Dust models Dust life cycle Planck early results Dust polarisation Outline Dust
Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Motivation Dust emission Dust models Dust life cycle Planck early results Dust polarisation Outline Dust
THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS ASTROPHYSICS VERSUS. Greg Dobler. Harvard/CfA July 14 th, TeV09
 THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Greg Dobler Harvard/CfA July 14 th, 2009 - TeV09 THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Doug Finkbeiner (CfA) Dan Hooper (FNAL) Gabrijela
THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Greg Dobler Harvard/CfA July 14 th, 2009 - TeV09 THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Doug Finkbeiner (CfA) Dan Hooper (FNAL) Gabrijela
Molecular line survey observations toward nearby galaxies with IRAM 30 m
 Molecular line survey observations toward nearby galaxies with IRAM 30 m Yuri Nishimura IoA/The University of Tokyo, NAOJ IRAM 30 m: 32 GHz in only two tunings FTS 200 khz resolution: simultaneously observing
Molecular line survey observations toward nearby galaxies with IRAM 30 m Yuri Nishimura IoA/The University of Tokyo, NAOJ IRAM 30 m: 32 GHz in only two tunings FTS 200 khz resolution: simultaneously observing
Constraining the CNM with LOFAR.
 Constraining the CNM with LOFAR. JBRO, R. van Weeren, F. Salgado, L. Morabito, C. Toribio, X. Tielens, H. Rottgering, A. Asgekar & G. White + assistance: J. McKean, R. Fallows, J. Hessels (1) Interstellar
Constraining the CNM with LOFAR. JBRO, R. van Weeren, F. Salgado, L. Morabito, C. Toribio, X. Tielens, H. Rottgering, A. Asgekar & G. White + assistance: J. McKean, R. Fallows, J. Hessels (1) Interstellar
Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System
 Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System ES2a. The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ES2b. Galaxies are made of billions
Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System ES2a. The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ES2b. Galaxies are made of billions
Exploring ISM dust with IRSIS. Emmanuel DARTOIS IAS-CNRS
 Exploring ISM dust with IRSIS Emmanuel DARTOIS IAS-CNRS IRSIS meeting 05-12-2007 Overview Intestellar ice mantles Hydrocarbons in the galaxy and outside Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Interstellar
Exploring ISM dust with IRSIS Emmanuel DARTOIS IAS-CNRS IRSIS meeting 05-12-2007 Overview Intestellar ice mantles Hydrocarbons in the galaxy and outside Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Interstellar
High Energy Astrophysics
 High Energy Astrophysics Introduction Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk January 2012 Today s introduction - The sky at different
High Energy Astrophysics Introduction Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk January 2012 Today s introduction - The sky at different
IR Instrumentation & AGN: Revealing Inner Secrets. Chris Packham University of Florida 7 th October, 2011
 IR Instrumentation & AGN: Revealing Inner Secrets Chris Packham University of Florida 7 th October, 2011 Presentation Outline T λ" i m e! Instrumentation past, present, and near future INGRID MMT-POL T-ReCS,
IR Instrumentation & AGN: Revealing Inner Secrets Chris Packham University of Florida 7 th October, 2011 Presentation Outline T λ" i m e! Instrumentation past, present, and near future INGRID MMT-POL T-ReCS,
Interstellar Dust and Extinction
 University of Oxford, Astrophysics November 12, 2007 Outline Extinction Spectral Features Emission Scattering Polarization Grain Models & Evolution Conclusions What and Why? Dust covers a range of compound
University of Oxford, Astrophysics November 12, 2007 Outline Extinction Spectral Features Emission Scattering Polarization Grain Models & Evolution Conclusions What and Why? Dust covers a range of compound
Chapter 10 The Interstellar Medium
 Chapter 10 The Interstellar Medium Guidepost You have begun your study of the sun and other stars, but now it is time to study the thin gas and dust that drifts through space between the stars. This chapter
Chapter 10 The Interstellar Medium Guidepost You have begun your study of the sun and other stars, but now it is time to study the thin gas and dust that drifts through space between the stars. This chapter
Dust. The four letter word in astrophysics. Interstellar Emission
 Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Interstellar Emission Why Dust Dust attenuates and scatters UV/optical/NIR Amount of attenuation and spectral shape depends on dust properties (grain size/type)
Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Interstellar Emission Why Dust Dust attenuates and scatters UV/optical/NIR Amount of attenuation and spectral shape depends on dust properties (grain size/type)
[13CII] observations to constrain fractionation chemistry and + column densities of C
![[13CII] observations to constrain fractionation chemistry and + column densities of C [13CII] observations to constrain fractionation chemistry and + column densities of C](/thumbs/93/113866505.jpg) [13CII] observations to constrain fractionation chemistry and + column densities of C V. Ossenkopf, M. Röllig, C. Joblin, U. Graf, A. Fuente, D. Lis, J. Stutzki, P. Pilleri, F. van der Tak, E. Bergin C+
[13CII] observations to constrain fractionation chemistry and + column densities of C V. Ossenkopf, M. Röllig, C. Joblin, U. Graf, A. Fuente, D. Lis, J. Stutzki, P. Pilleri, F. van der Tak, E. Bergin C+
Astrochemistry from a Sub-pc Scale to a kpc Scale. Satoshi Yamamoto Department of Physics and RESCUE The University of Tokyo
 Astrochemistry from a Sub-pc Scale to a kpc Scale Satoshi Yamamoto Department of Physics and RESCUE The University of Tokyo Contents Physical and Chemical Processes in Disk Formation around Solar-type
Astrochemistry from a Sub-pc Scale to a kpc Scale Satoshi Yamamoto Department of Physics and RESCUE The University of Tokyo Contents Physical and Chemical Processes in Disk Formation around Solar-type
First scientific results from QUIJOTE. constraints on radio foregrounds
 First scientific results from QUIJOTE constraints on radio foregrounds Flavien Vansyngel, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias @ CMB Foregrounds, UCSD, 2017/11/29 The QUIJOTE experiment Tenerife experiment
First scientific results from QUIJOTE constraints on radio foregrounds Flavien Vansyngel, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias @ CMB Foregrounds, UCSD, 2017/11/29 The QUIJOTE experiment Tenerife experiment
R. D. Gehrz a E. E. Becklin b, and Göran Sandell b
 Infrared Spectroscopic Studies with the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) a E. E. Becklin b, and Göran Sandell b a University of Minnesota b Universities Space Research Association
Infrared Spectroscopic Studies with the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) a E. E. Becklin b, and Göran Sandell b a University of Minnesota b Universities Space Research Association
Cosmic Microwave Background
 Cosmic Microwave Background Carlo Baccigalupi,, SISSA CMB lectures at TRR33, see the complete program at darkuniverse.uni-hd.de/view/main/winterschoollecture5 These lectures are available in pdf format
Cosmic Microwave Background Carlo Baccigalupi,, SISSA CMB lectures at TRR33, see the complete program at darkuniverse.uni-hd.de/view/main/winterschoollecture5 These lectures are available in pdf format
CARMA observations of Galactic cold cores: searching for spinning dust emission
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1760 CARMA observations of Galactic cold cores: searching for spinning dust emission C. T. Tibbs, 1,2 R. Paladini, 2 K. Cleary, 3 S. J. C. Muchovej, 3 A. M. M. Scaife, 4 M. A. Stevenson,
doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1760 CARMA observations of Galactic cold cores: searching for spinning dust emission C. T. Tibbs, 1,2 R. Paladini, 2 K. Cleary, 3 S. J. C. Muchovej, 3 A. M. M. Scaife, 4 M. A. Stevenson,
Survey of dusty AGNs based on the mid-infrared all-sky survey catalog. Shinki Oyabu (Nagoya University) & MSAGN team
 Survey of dusty AGNs based on the mid-infrared all-sky survey catalog Shinki Oyabu (Nagoya University) & MSAGN team Search for Active Galactic Nuclei Purpose 1 The MIR selection can minimize wavelength-dependent
Survey of dusty AGNs based on the mid-infrared all-sky survey catalog Shinki Oyabu (Nagoya University) & MSAGN team Search for Active Galactic Nuclei Purpose 1 The MIR selection can minimize wavelength-dependent
THE STAR FORMATION NEWSLETTER No February /5/29
 THE STAR FORMATION NEWSLETTER No.266-12 February 2015 2015/5/29 46-50 Understanding star formation in molecular clouds II. Signatures of gravitational collapse of IRDCs to Cloud-cloud collision as a trigger
THE STAR FORMATION NEWSLETTER No.266-12 February 2015 2015/5/29 46-50 Understanding star formation in molecular clouds II. Signatures of gravitational collapse of IRDCs to Cloud-cloud collision as a trigger
Searching for the dominant mode of galaxy growth! from deep extragalactic Herschel surveys! D.Elbaz (CEA Saclay)
 Searching for the dominant mode of galaxy growth! from deep extragalactic Herschel surveys! D.Elbaz (CEA Saclay) Star formation = local process (~pc scale)! How sensitive is SF to larger scales inside
Searching for the dominant mode of galaxy growth! from deep extragalactic Herschel surveys! D.Elbaz (CEA Saclay) Star formation = local process (~pc scale)! How sensitive is SF to larger scales inside
AZTEC ON ASTE: 1.1-MM CONTINUUM OBSERVATIONS TOWARD THE SMALL MAGELLANIC CLOUD
 AZTEC ON ASTE: 1.1-MM CONTINUUM OBSERVATIONS TOWARD THE SMALL MAGELLANIC CLOUD Tatsuya Takekoshi Department of Cosmosciences Graduate School of Science Hokkaido University Collaborators: Tetsuhiro Minamidani,
AZTEC ON ASTE: 1.1-MM CONTINUUM OBSERVATIONS TOWARD THE SMALL MAGELLANIC CLOUD Tatsuya Takekoshi Department of Cosmosciences Graduate School of Science Hokkaido University Collaborators: Tetsuhiro Minamidani,
igure 4 of McMullin et al McMullin et al Testi & Sargent 1998 Figure 1 of Testi & Sargent 1998:
 igure 4 of McMullin et al. 1994. Figure 1 of Testi & Sargent 1998: McMullin et al. 1994 BIMA with (only!) three elements Eight configurationsàcoverage of 2 kλ to 30 kλ Naturally wtd. Beam of 11" x 6" (for
igure 4 of McMullin et al. 1994. Figure 1 of Testi & Sargent 1998: McMullin et al. 1994 BIMA with (only!) three elements Eight configurationsàcoverage of 2 kλ to 30 kλ Naturally wtd. Beam of 11" x 6" (for
THE LAST SURVEY OF THE OLD WSRT: TOOLS AND RESULTS FOR THE FUTURE HI ABSORPTION SURVEYS
 F. Maccagni; R. Morganti; T. Oosterloo; K. Geréb; N. Maddox, J. Allison THE LAST SURVEY OF THE OLD WSRT: TOOLS AND RESULTS FOR THE FUTURE HI ABSORPTION SURVEYS A SURVEY BEFORE THE BLIND SURVEYS During
F. Maccagni; R. Morganti; T. Oosterloo; K. Geréb; N. Maddox, J. Allison THE LAST SURVEY OF THE OLD WSRT: TOOLS AND RESULTS FOR THE FUTURE HI ABSORPTION SURVEYS A SURVEY BEFORE THE BLIND SURVEYS During
Towards a free free template for CMB foregrounds
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 341, 369 384 (2003) Towards a free free template for CMB foregrounds C. Dickinson, R. D. Davies and R. J. Davis Jodrell Bank Observatory, Department of Physics & Astronomy, University
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 341, 369 384 (2003) Towards a free free template for CMB foregrounds C. Dickinson, R. D. Davies and R. J. Davis Jodrell Bank Observatory, Department of Physics & Astronomy, University
Galaxies of Many Colours: Star Formation Across Cosmic Time. z=0, t= /-0.037x10 9 years (Now)
 Galaxies of Many Colours: Star Formation Across Cosmic Time z=0, t=13.798+/-0.037x10 9 years (Now) And if you want to study the initial conditions for star formation the colour is black Dense Gas SDC335:
Galaxies of Many Colours: Star Formation Across Cosmic Time z=0, t=13.798+/-0.037x10 9 years (Now) And if you want to study the initial conditions for star formation the colour is black Dense Gas SDC335:
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 2 Mar 2005
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 5 (2005) Printed 2 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Polarized Diffuse Emission at 2.3 GHz in a High Galactic Latitude Area arxiv:astro-ph/0503043v1 2 Mar 2005 E.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 5 (2005) Printed 2 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Polarized Diffuse Emission at 2.3 GHz in a High Galactic Latitude Area arxiv:astro-ph/0503043v1 2 Mar 2005 E.
HI 21-cm Study of Supernova Remnants in SKA Era
 2015. 11. 3. SKA Meeting HI 21-cm Study of Supernova Remnants in SKA Era Bon-Chul Koo (SNU, KIAS) Supernova Explosions SN explosions play a major role in the ecology and evolution of galaxies by supplying
2015. 11. 3. SKA Meeting HI 21-cm Study of Supernova Remnants in SKA Era Bon-Chul Koo (SNU, KIAS) Supernova Explosions SN explosions play a major role in the ecology and evolution of galaxies by supplying
CO Observations of the Galactic Disk Toshikazu Onishi (Nagoya University)
 CO Observations of the Galactic Disk Toshikazu Onishi (Nagoya University) Study of Molecular Observations of SNRs Samples of SNR-dense cloud interaction still poor Observations of γ-rays from CR accelerated
CO Observations of the Galactic Disk Toshikazu Onishi (Nagoya University) Study of Molecular Observations of SNRs Samples of SNR-dense cloud interaction still poor Observations of γ-rays from CR accelerated
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Sep 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Sep 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Sep 2015](/thumbs/93/113871987.jpg) draft date: October 8, 2018 Variations between Dust and Gas in the Diffuse Interstellar Medium William T. Reach arxiv:1508.07889v2 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Sep 2015 Universities Space Research Association, MS 232-11,
draft date: October 8, 2018 Variations between Dust and Gas in the Diffuse Interstellar Medium William T. Reach arxiv:1508.07889v2 [astro-ph.ga] 9 Sep 2015 Universities Space Research Association, MS 232-11,
Dust properties in the ionized gas of the Large Magellanic Cloud
 Dust properties in the ionized gas of the Large Magellanic Cloud Déborah Paradis, SSC/CESR Roberta Paladini, SSC Alberto Noriega-Crespo, SSC Guilaine Lagache, IAS Context Detection of dust emission associated
Dust properties in the ionized gas of the Large Magellanic Cloud Déborah Paradis, SSC/CESR Roberta Paladini, SSC Alberto Noriega-Crespo, SSC Guilaine Lagache, IAS Context Detection of dust emission associated
Evidence for dust emission in the Warm Ionised Medium using WHAM data
 Astron. Astrophys. 354, 247 252 (2000) Evidence for dust emission in the Warm Ionised Medium using WHAM data G. Lagache 1, L.M. Haffner 2, R.J. Reynolds 2, and S.L. Tufte 3 1 Institut d Astrophysique Spatial,
Astron. Astrophys. 354, 247 252 (2000) Evidence for dust emission in the Warm Ionised Medium using WHAM data G. Lagache 1, L.M. Haffner 2, R.J. Reynolds 2, and S.L. Tufte 3 1 Institut d Astrophysique Spatial,
Physics 224 The Interstellar Medium
 Physics 224 The Interstellar Medium Lecture #11: Dust Composition, Photoelectric Heating, Neutral Gas Outline Part I: Dust Heating & Cooling continued Part III: Dust Emission & Photoelectric Heating Part
Physics 224 The Interstellar Medium Lecture #11: Dust Composition, Photoelectric Heating, Neutral Gas Outline Part I: Dust Heating & Cooling continued Part III: Dust Emission & Photoelectric Heating Part
Interstellar gamma rays. New insights from Fermi. Andy Strong. on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration. COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010
 Interstellar gamma rays New insights from Fermi Andy Strong on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010 Session E110: ' The next generation of ground-based Cerenkov
Interstellar gamma rays New insights from Fermi Andy Strong on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010 Session E110: ' The next generation of ground-based Cerenkov
Filamentary Structures in the Galactic Plane Morphology, Physical conditions and relation with star formation
 Background: Column Density Map from Herschel Observation of Galactic Plane Hi-GAL project - field centered at (l,b) )=(224,0 ) Filamentary Structures in the Galactic Plane Morphology, Physical conditions
Background: Column Density Map from Herschel Observation of Galactic Plane Hi-GAL project - field centered at (l,b) )=(224,0 ) Filamentary Structures in the Galactic Plane Morphology, Physical conditions
Extinction curves in AGN
 Extinction curves in AGN Dust plume rising to 1,500 m elevation in San Joaquin Valley, Calif., s.e. of Bakersfield, December 1977. (Wilshire et al., 1996; photo by Sam Chase) B. Czerny Copernicus Astronomical
Extinction curves in AGN Dust plume rising to 1,500 m elevation in San Joaquin Valley, Calif., s.e. of Bakersfield, December 1977. (Wilshire et al., 1996; photo by Sam Chase) B. Czerny Copernicus Astronomical
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics
 Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5)
 Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5) Flow of story 4.1.1 4.1.2 4.1.3 Millimetric Spectroscopic Redshifts Millimetric Photometric Redshifts Redshift Distributions of 24 μm selected DSFG
Dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift (part 5) Flow of story 4.1.1 4.1.2 4.1.3 Millimetric Spectroscopic Redshifts Millimetric Photometric Redshifts Redshift Distributions of 24 μm selected DSFG
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results. Alexander Schmah
 The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
High Redshift Universe
 High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
The Extragalactic Radio Background
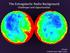 The Extragalactic Radio Background Challenges and Opportunities Al Kogut Goddard Space Flight Center Extragalactic Backgrounds Early Background Estimates T ex From Spectral Index Variations T ex = 30 80
The Extragalactic Radio Background Challenges and Opportunities Al Kogut Goddard Space Flight Center Extragalactic Backgrounds Early Background Estimates T ex From Spectral Index Variations T ex = 30 80
Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330
 The Evolving ISM in the Milky Way & Nearby Galaxies Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330 Anne Abramson 1 & Jeffrey D. P. Kenney 1 1 Astronomy Department, Yale University, P.O. Box 208101 New Haven, CT 06520-8101
The Evolving ISM in the Milky Way & Nearby Galaxies Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330 Anne Abramson 1 & Jeffrey D. P. Kenney 1 1 Astronomy Department, Yale University, P.O. Box 208101 New Haven, CT 06520-8101
Astrophysical Detection of Dark Matter
 Astrophysical Detection of Dark Matter Doug Finkbeiner, Harvard Tracy Slatyer Tongyan Lin Lauren Weiss David Rosengarten Neal Weiner, NYU Ilias Cholis Lisa Goodenough What am I doing here? Michigan undergrad:
Astrophysical Detection of Dark Matter Doug Finkbeiner, Harvard Tracy Slatyer Tongyan Lin Lauren Weiss David Rosengarten Neal Weiner, NYU Ilias Cholis Lisa Goodenough What am I doing here? Michigan undergrad:
Galactic radio loops. Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar. The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017
 Galactic radio loops Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017 Foregrounds in B-modes Adam et al., arxiv:1502.01588 1409.5738 (Planck
Galactic radio loops Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017 Foregrounds in B-modes Adam et al., arxiv:1502.01588 1409.5738 (Planck
