The effect of primordial mass segregation on the size scale of the star clusters
|
|
|
- Joseph Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The effect of primordial mass segregation on the size scale of the star clusters Hosein Haghi In collaboration with: HoseiniRad, Zonoozi, Kuepper Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS),Zanjan IPM-Spring conference-1393
2 Outline The physics of dense stellar systems Globular clusters 2-body relaxation Numerical methods: Test simulation The size scale and erosion of Galactic GCs Tow phases of mass-loss Rh Rgc relation Tdiss-- Rgc relation The impact of PMS on the size scale and dissolution of GCs
3 Part I The physics of dense stellar systems
4 Introduction: Globular clusters (GCs) ~160 Milky Way GCs Distributed out to 100Kpc. Contain coeval stars 12Gyr Gas/dust-free systems Why GCs are important? Stellar evolution, Galaxy formation and evolution
5 Dynamic Evolutionary modeling of GCs Until the late 1970s, GCs were thought of to be relatively static stellar systems: fitted with equilibrium models like King (1966) profiles. This view has changed significantly over the last thirty years: On the observational side: Strong indications for the ongoing dynamical evolution: 1- The discovery of extratidal stars surrounding globular clusters (Grillmair et al. 1995, Odenkirchen et al. 2003)
6 Dynamic Evolutionary modelling of GCs Palomar 5
7 Dynamic Evolutionary modelling of GCs Until the late 1970s, GCs were thought of to be relatively static stellar systems: fitted with equilibrium models like King (1966) profiles. This view has changed significantly over the last thirty years: On the observational side: Strong indications for the ongoing dynamical evolution: 1- The discovery of extratidal stars surrounding globular clusters (Grillmair et al. 1995, Odenkirchen et al. 2003) 2- The differences in the stellar mass-functions of globular clusters (Piotto, Cool & King 1997, de Marchi et al. 1999).
8 Initial mass function (IMF) IMF: The initial mass distribution of stars (Salpeter 1955, Kroupa 2001, 2012) dn/dlog(m) α =1.3 α = m 8
9 Mass-function slope is a tracer of mass loss Hamren et al., 2013, ApJ
10 Dynamic Evolutionary modelling of GCs Until the late 1970s, GCs were thought of to be relatively static stellar systems: fitted with equilibrium models like King (1966) profiles. This view has changed significantly over the last thirty years: On the observational side: Strong indications for the ongoing dynamical evolution: 1- The discovery of extratidal stars surrounding globular clusters (Grillmair et al. 1995, Odenkirchen et al. 2003) 2- The differences in the stellar mass-functions of globular clusters (Piotto, Cool & King 1997, de Marchi et al. 1999). On the theoretical side: N-body simulations of star cluster evolution : 1- Progresses in simulation techniques (e.g. Mikkola & Aarseth 1993, Aarseth 1999). 2- Development of the hardware (GRAPE: Makino et al. 2003, GPUs) which allows to simulate the evolution of star clusters with increasingly larger particle numbers.
11 : Weak encounters
12 2-body Relaxation
13 GCs are collisional systems 2-body interactions of stars are important in driving the dynamical evolution Galaxies that are collisionless stars are mainly moving in the collective gravitational field
14 Possible outcomes of encounters between a binary and a single star
15
16 Particles evolve due to Stellar Evolution
17 External tidal perturbations
18
19 Approach: Classical N-body problem
20 The slow progress of N-body simulations
21
22
23 Test simulation
24 Spatial distribution Test run: N=1000 equal mass, No SE, softening parameter Praagman et al. 2009
25 Density distribution Zooming in shows that the core collapses inwards. Thus a distinct core-halo structure is established where a diffuse halo surrounds a high-density core.
26 Spatial distribution: Red dots are binaries
27 Zooming in (model 1) : No core collapse The collapsing core that was evident in the sample simulation is not so obvious in this model. One of the main differences between the sample code and nbody6 is the ability to deal with close encounters.
28 Model 4
29 Part II Size scale of GCs
30 Why study the size scale of star clusters Gap in the physical size between GCs and dwe galaxies. Ultra-compact dwarfs (UCDs) can fill the gap (Gilmore et al. 2007). A well-known size distribution of GCs can also constrain the Galaxy mass model Why is the size distribution of star clusters narrowly centered around Rh=3 parsecs? Why do only a few clusters become extended with effective radii of ten parsecs or more? (Jordi & Haghi et al 2009,AJ, Frank & Haghi et al 2012,MNRAS) There is a Rh-Rgc relation independent of GCs classification No apparent correlation between radius and (mass/luminosity, metalicity, horizontal branch-morfology in GCs, but it seems the orbital shape is important (Gieles et al. (2010), van den Bergh 2012)
31 Rh-Rgc Relation Historically there are empirical relation between the cluster size and RG (Hodge ) Original work (Spitzer & Thuan 1972): Radius of isolated star cluster remains constant Classical notion: The half-mass radius changes little over 10 * two-body relaxation time (Trh) ( Lightman & Shapiro 1978, Aarseth & Heggie 1998)
32 Rh-Rgc relation (van den Bergh 1991) Size and galactocentric distance of the MW GC population. Blue circles are used for metal-poor and red squares for metal-rich clusters. The solid black line denotes the size-distance relation
33 Mass lose of simulated clusters at different galactocentric distances Madrid, Hurley, Sippel, 2012
34 Phases of mass-loss Mass loss from Stellar Evolution + 2-body relaxation Initially increases the cluster size in short time-scale Mass loss due to tidal stripping Decreases the size scale scale. Whether or not either of the two mechanisms dominates will determine the size of the star cluster (Gieles et al. 2011).
35 Haghi et al 2014, MNRAS
36 The evolution of half-mass radius of simulated clusters at different galactocentric distances expansion driven by the internal dynamics is balanced by the presence of the tidal field an initial radius of 6 pc Madrid, Hurley, Sippel, 2012
37 New Rh-Rgc relation Madrid, Hurley, Sippel, 2012
38 Direct N-body simulation DESCRIPTION OF THE MODELS Direct N-body modeling on the GPU computers of the IASBS. Number of stars N ~ 100,000 with Plummer (1911) distribution Evolution time: 13 Gyr Stellar Evolution: SSE/BSE routines developed by Hurley et al Tidal effect: galactic potential (3-component) (Allen & Santillan 1991). We used MCLUSTER (Keupper et al 2010) using the routine described in Baumgardt, De Marchi & Kroupa (2008) to set up initially segregated clusters.
39 How Primordial Mass Segregation can affect on the size scale of GCs? Setting up INITIALLY MASS SEGREGATED equilibrium star cluster
40 Mass Segregation t = 0 The prediction of energy equipartition is confirmed in globular cluster 47 Tucanae: The average squared speed of Blue stars was 72 (km/s)^2, which is half the value found for the red stars, 144 (km/s)^2. (Meylan 2007)
41 Primordial Mass Segregation A number of observational studies have found evidence of mass segregation in clusters with ages shorter than the time needed to produce the observed segregation by two-body relaxation (de Grijs 2010) Observed segregation in young clusters would be primordial and imprinted by the star-formation process. Direct N-body modeling: we found that only models with a flattened IMF and primordial segregation are able to fit the observed slope of the mass function of diffused distant GCs, e.g., Pal 4 and Pal 14 (Zonoozi et al 2011, 2014,MNRAS). 41
42 Size evolution of a diffused halo cluster: with and without PMS Zonoozi, Haghi et al. 2011, MNRAS
43 Non-segregated vs. Segregated models Haghi et al., 2014, submitted MNRAS
44 Non-segregated vs. Segregated models
45 Non-segregated vs. Segregated models
46 Rh-Rgc relation for PMS clusters Haghi et al., 2014, submitted MNRAS
47 Dissolution of GCs
48 Vesperini 2009 Baumgardt 2003
49 Conclusion Primordial mass - segregation are able to fit the observed slope of the mass function of diffused distant GCs, e.g., Pal 4 and Pal 14 (Zonoozi et al 2011, 2014, MNRAS). Further exploring the initial values used for the set-up of the simulations is needed. Especially assuming the PMS. (Haghi, Hosieni Rad, Zonoozi, Kuepper, 2014, Submitted to MNRAS) We proposed a new explanation for very diffused halo GCs without invoking a merger events with dwarf galaxies to grow extended star clusters in the Milky Way at large galactocentric distances. Highly eccentric orbit approach (Kuepper, Zonoozi, Haghi,et al, 2014, Submitted to MNRAS) Dissolution rate of GCs is faster for PMS clusters
Direct N-body simulations of distant halo globular clusters
 Direct N-body simulations of distant halo globular clusters Hosein Haghi Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS) Zanjan, IRAN in collaboration with Akram Hasani Zonoozi (IASBS), Holger
Direct N-body simulations of distant halo globular clusters Hosein Haghi Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS) Zanjan, IRAN in collaboration with Akram Hasani Zonoozi (IASBS), Holger
Massive star clusters
 Massive star clusters as a host of compact binaries Michiko Fujii ( 藤井通子 ) The University of Tokyo Outline Massive star clusters and compact binaries Dynamical evolution of star clusters Distribution of
Massive star clusters as a host of compact binaries Michiko Fujii ( 藤井通子 ) The University of Tokyo Outline Massive star clusters and compact binaries Dynamical evolution of star clusters Distribution of
Direct N-body simulations of globular clusters III. Palomar 4 on an eccentric orbit
 Advance Access publication 2017 January 19 doi:10.1093/mnras/stx130 Direct N-body simulations of globular clusters III. Palomar 4 on an eccentric orbit Akram Hasani Zonoozi, 1 Hosein Haghi, 1 Pavel Kroupa,
Advance Access publication 2017 January 19 doi:10.1093/mnras/stx130 Direct N-body simulations of globular clusters III. Palomar 4 on an eccentric orbit Akram Hasani Zonoozi, 1 Hosein Haghi, 1 Pavel Kroupa,
MOdelling DEnse STellar systems. A personal survey
 MOdelling DEnse STellar systems A personal survey Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh, UK d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Outline 0. Introduction 1. Tools of the trade 2. Tidal effects 3. Dynamics of binaries 0.
MOdelling DEnse STellar systems A personal survey Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh, UK d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Outline 0. Introduction 1. Tools of the trade 2. Tidal effects 3. Dynamics of binaries 0.
Monte Carlo Modelling of Globular Clusters
 Monte Carlo Modelling of Globular Clusters Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Collaboration with Mirek Giersz (Warsaw) The globular cluster M4 Distance from sun Mass Core radius
Monte Carlo Modelling of Globular Clusters Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Collaboration with Mirek Giersz (Warsaw) The globular cluster M4 Distance from sun Mass Core radius
ABSTRACT 1 INTRODUCTION
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 11 (2015) Printed 24 September 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Back to the Future: Estimating Initial Globular Cluster Masses from their Present Day Stellar Mass Functions
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 11 (2015) Printed 24 September 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Back to the Future: Estimating Initial Globular Cluster Masses from their Present Day Stellar Mass Functions
Modelling individual globular clusters An Update
 Modelling individual globular clusters An Update Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Outline 1. Introduction: two kinds of model two kinds of star cluster 2. Monte Carlo models M4
Modelling individual globular clusters An Update Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Outline 1. Introduction: two kinds of model two kinds of star cluster 2. Monte Carlo models M4
Possible smoking-gun evidence for initial mass segregation in re-virialized post-gas expulsion globular clusters
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stv2207 Possible smoking-gun evidence for initial mass segregation in re-virialized post-gas expulsion globular clusters Hosein Haghi, 1 Akram Hasani Zonoozi, 1 Pavel Kroupa, 2 Sambaran
doi:10.1093/mnras/stv2207 Possible smoking-gun evidence for initial mass segregation in re-virialized post-gas expulsion globular clusters Hosein Haghi, 1 Akram Hasani Zonoozi, 1 Pavel Kroupa, 2 Sambaran
Evolution of Star Clusters on Eccentric Orbits
 Evolution of Star Clusters on Eccentric Orbits Maxwell Xu CAI (NAOC/KIAA) Collaborators: Mark Gieles, Douglas Heggie, Anna Lisa Varri Cai et al. (2016), MNRAS, 455, 596 7th KCK meeting, NAOC, Dec 15, 2015
Evolution of Star Clusters on Eccentric Orbits Maxwell Xu CAI (NAOC/KIAA) Collaborators: Mark Gieles, Douglas Heggie, Anna Lisa Varri Cai et al. (2016), MNRAS, 455, 596 7th KCK meeting, NAOC, Dec 15, 2015
The physical origin of stellar envelopes around globular clusters
 The physical origin of stellar envelopes around globular clusters Phil Breen University of Edinburgh in collaboration with A. L. Varri, J. Peñarrubia and D. C. Heggie Current observational evidence Example:
The physical origin of stellar envelopes around globular clusters Phil Breen University of Edinburgh in collaboration with A. L. Varri, J. Peñarrubia and D. C. Heggie Current observational evidence Example:
The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds
 The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
Coalescing Binary Black Holes Originating from Globular Clusters
 Coalescing Binary Black Holes Originating from Globular Clusters Abbas Askar (askar@camk.edu.pl) Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center, Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw, Poland Abbas Askar Globular
Coalescing Binary Black Holes Originating from Globular Clusters Abbas Askar (askar@camk.edu.pl) Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center, Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw, Poland Abbas Askar Globular
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Oct 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Oct 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Oct 2009](/thumbs/74/69946465.jpg) **FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, c **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** The Mass-to-Light Ratios of Galactic Globular Clusters arxiv:0910.4773v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Oct 2009
**FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, c **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** The Mass-to-Light Ratios of Galactic Globular Clusters arxiv:0910.4773v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Oct 2009
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 15 Jul 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 15 Jul 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 15 Jul 2015](/thumbs/91/106224981.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 36 (2014) Printed 3 October 2018 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) The initial conditions of observed star clusters - I. Method description and validation arxiv:1507.04372v1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 36 (2014) Printed 3 October 2018 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) The initial conditions of observed star clusters - I. Method description and validation arxiv:1507.04372v1
Stellar Black Hole Binary Mergers in Open ClusterS
 Stellar Black Hole Binary Mergers in Open ClusterS SARA RASTELLO Collaborators: P. Amaro-Seoane, M. Arca-Sedda, R. Capuzzo Dolcetta, G. Fragione, I.Tosta e Melo Modest 18, Santorini, greece 27/06/2018
Stellar Black Hole Binary Mergers in Open ClusterS SARA RASTELLO Collaborators: P. Amaro-Seoane, M. Arca-Sedda, R. Capuzzo Dolcetta, G. Fragione, I.Tosta e Melo Modest 18, Santorini, greece 27/06/2018
Stellar-mass black holes in a globular cluster. Douglas Heggie. University of Edinburgh, UK
 Stellar-mass black holes in a globular cluster Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh, UK d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk How many stellar-mass black holes do you expect to find? Example: M4 Assume: initial conditions
Stellar-mass black holes in a globular cluster Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh, UK d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk How many stellar-mass black holes do you expect to find? Example: M4 Assume: initial conditions
Direct N-body simulations of globular clusters I. Palomar 14
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 411, 1989 2001 (2011) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17831.x Direct N-body simulations of globular clusters I. Palomar 14 Akram Hasani Zonoozi, 1,2 Andreas H. W. Küpper, 2,3 Holger
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 411, 1989 2001 (2011) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17831.x Direct N-body simulations of globular clusters I. Palomar 14 Akram Hasani Zonoozi, 1,2 Andreas H. W. Küpper, 2,3 Holger
Can black holes be formed in dynamic interactions in star clusters?
 Can black holes be formed in dynamic interactions in star clusters? Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center, Polish Academy of Sciences Warsaw, Poland mig@camk.edu.pl MODEST 14 Workshop Bad Honnef, Germany
Can black holes be formed in dynamic interactions in star clusters? Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center, Polish Academy of Sciences Warsaw, Poland mig@camk.edu.pl MODEST 14 Workshop Bad Honnef, Germany
Kinetic Theory. Motivation - Relaxation Processes Violent Relaxation Thermodynamics of self-gravitating system
 Kinetic Theory Motivation - Relaxation Processes Violent Relaxation Thermodynamics of self-gravitating system negative heat capacity the gravothermal catastrophe The Fokker-Planck approximation Master
Kinetic Theory Motivation - Relaxation Processes Violent Relaxation Thermodynamics of self-gravitating system negative heat capacity the gravothermal catastrophe The Fokker-Planck approximation Master
The Worst-Case Scenario. The Final Parsec Problem. and. Milos Milosavljevic. California Institute of Technology. Collaborator: David Merritt
 The Final Parsec Problem and The Worst-Case Scenario Milos Milosavljevic California Institute of Technology Collaborator: David Merritt NSF AST 00-71099 NASA NAG5-6037, NAG5-9046 Sherman Fairchild Foundation
The Final Parsec Problem and The Worst-Case Scenario Milos Milosavljevic California Institute of Technology Collaborator: David Merritt NSF AST 00-71099 NASA NAG5-6037, NAG5-9046 Sherman Fairchild Foundation
Stellar-mass black holes in a globular cluster
 Stellar-mass black holes in a globular cluster Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh, UK d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Motivation Discovery of two stellar-mass BH in the Galactic globular cluster M22 (Strader+
Stellar-mass black holes in a globular cluster Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh, UK d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Motivation Discovery of two stellar-mass BH in the Galactic globular cluster M22 (Strader+
On the mass radius relation of hot stellar systems
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 408, L16 L20 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2010.00919.x On the mass radius relation of hot stellar systems Mark Gieles, 1,2,3 Holger Baumgardt, 4,5 Douglas C. Heggie 2 and Henny
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 408, L16 L20 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2010.00919.x On the mass radius relation of hot stellar systems Mark Gieles, 1,2,3 Holger Baumgardt, 4,5 Douglas C. Heggie 2 and Henny
Evolution of second generation stars in stellar disks of globular and nuclear clusters: ω Centauri as a test case
 Evolution of second generation stars in stellar disks of globular and nuclear clusters: ω Centauri as a test case Alessandra Mastrobuono-Battisti & Hagai Perets Outline Dense stellar clusters: Nuclear
Evolution of second generation stars in stellar disks of globular and nuclear clusters: ω Centauri as a test case Alessandra Mastrobuono-Battisti & Hagai Perets Outline Dense stellar clusters: Nuclear
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/147354
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/147354
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Sep 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Sep 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Sep 2016](/thumbs/73/68802853.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 9 (2015) Printed 30 September 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) On the Link Between Energy Equipartition and Radial Variation in the Stellar Mass Function of Star Clusters
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 9 (2015) Printed 30 September 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) On the Link Between Energy Equipartition and Radial Variation in the Stellar Mass Function of Star Clusters
Inverting the dynamical evolution problem of globular clusters: clues to their origin
 Inverting the dynamical evolution problem of globular clusters: clues to their origin Mark Gieles Poul Alexander (Cambridge), Douglas Heggie (Edinburgh) Alice Zocchi, Miklos Peuten, Vincent Hénault-Brunet
Inverting the dynamical evolution problem of globular clusters: clues to their origin Mark Gieles Poul Alexander (Cambridge), Douglas Heggie (Edinburgh) Alice Zocchi, Miklos Peuten, Vincent Hénault-Brunet
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11686 Database: In the present study we used a photometric database collected over the last 20 years for 21 Galactic globular clusters (GCs). In each cluster the central regions have
doi:10.1038/nature11686 Database: In the present study we used a photometric database collected over the last 20 years for 21 Galactic globular clusters (GCs). In each cluster the central regions have
Multiple populations in GCs: constraints on formation scenarios from kinematics & dynamics
 Multiple populations in GCs: constraints on formation scenarios from kinematics & dynamics Vincent Hénault-Brunet Mark Gieles Oscar Agertz Justin Read Alice Zocchi IAU 316: Formation, evolution, and survival
Multiple populations in GCs: constraints on formation scenarios from kinematics & dynamics Vincent Hénault-Brunet Mark Gieles Oscar Agertz Justin Read Alice Zocchi IAU 316: Formation, evolution, and survival
Dynamical Models of the Globular Clusters M4 and NGC 6397
 Dynamical Models of the Globular Clusters M4 and NGC 6397 Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk in collaboration with Mirek Giersz CAMK, Warsaw, Poland Outline Introduction: M4 and
Dynamical Models of the Globular Clusters M4 and NGC 6397 Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk in collaboration with Mirek Giersz CAMK, Warsaw, Poland Outline Introduction: M4 and
The dynamics of neutron star and black hole binaries in young star clusters
 Michela Mapelli INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova The dynamics of neutron star and black hole binaries in young star clusters Collaborators: Mario Spera, Brunetto, Marica Branchesi, Alessandro Trani,
Michela Mapelli INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova The dynamics of neutron star and black hole binaries in young star clusters Collaborators: Mario Spera, Brunetto, Marica Branchesi, Alessandro Trani,
INTERMEDIATE-MASS BLACK HOLE INDUCED QUENCHING OF MASS SEGREGATION IN STAR CLUSTERS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 686:303Y309, 2008 October 10 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. INTERMEDIATE-MASS BLACK HOLE INDUCED QUENCHING OF MASS SEGREGATION
The Astrophysical Journal, 686:303Y309, 2008 October 10 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. INTERMEDIATE-MASS BLACK HOLE INDUCED QUENCHING OF MASS SEGREGATION
Dynamics of Stars and Black Holes in Dense Stellar Systems:
 Michela Mapelli INAF - Padova Dynamics of Stars and Black Holes in Dense Stellar Systems: Lecture IV: Dynamical processes induced by mass spectrum 0. EFFECTS OF MASS SPECTRUM 1. MASS SEGREGATION 2. EQUIPARTITION
Michela Mapelli INAF - Padova Dynamics of Stars and Black Holes in Dense Stellar Systems: Lecture IV: Dynamical processes induced by mass spectrum 0. EFFECTS OF MASS SPECTRUM 1. MASS SEGREGATION 2. EQUIPARTITION
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 May 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 May 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 May 2008](/thumbs/88/114934752.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 1 May 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Dynamical Evolution of the Mass Function and Radial Profile of the Galactic Globular Cluster System arxiv:0805.0058v1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 1 May 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Dynamical Evolution of the Mass Function and Radial Profile of the Galactic Globular Cluster System arxiv:0805.0058v1
On MOND and dark matter in ultra compact dwarf galaxies
 On MOND and dark matter in ultra compact dwarf galaxies Jörg Dabringhausen Argelander-Institut für Astronomie, University of Bonn Pavel Kroupa Michael Hilker, Michael Fellhauer, Steffen Mieske, Michael
On MOND and dark matter in ultra compact dwarf galaxies Jörg Dabringhausen Argelander-Institut für Astronomie, University of Bonn Pavel Kroupa Michael Hilker, Michael Fellhauer, Steffen Mieske, Michael
simulations - 1 J A Sellwood
 simulations - 1 J A Sellwood Collisionless stellar systems Manifest a number of complicated collective phenomena spiral arms, bar instabilities, collapses, mergers, etc. too complicated to be calculated
simulations - 1 J A Sellwood Collisionless stellar systems Manifest a number of complicated collective phenomena spiral arms, bar instabilities, collapses, mergers, etc. too complicated to be calculated
2 Ivanova, Fregeau, & Rasio
 2 Ivanova, Fregeau, & Rasio Figure 1. Orbital period vs companion mass for all observed binary MSPs in the galactic field (open circles), in 47 Tuc (solid squares) and in other globular clusters (solid
2 Ivanova, Fregeau, & Rasio Figure 1. Orbital period vs companion mass for all observed binary MSPs in the galactic field (open circles), in 47 Tuc (solid squares) and in other globular clusters (solid
Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters
 Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) Globular clusters in the Galaxy median distance from the center is 5 kpc Resolved star cluster highest
Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) Globular clusters in the Galaxy median distance from the center is 5 kpc Resolved star cluster highest
Evolution of SMBH-SMBH and SMBH-IMBH Binaries: Effect of Large Mass Ratio
 Evolution of SMBH-SMBH and SMBH-IMBH Binaries: Effect of Large Mass Ratio Jun Makino Center for Computational Astrophysics and Division Theoretical Astronomy National Astronomical Observatory of Japan
Evolution of SMBH-SMBH and SMBH-IMBH Binaries: Effect of Large Mass Ratio Jun Makino Center for Computational Astrophysics and Division Theoretical Astronomy National Astronomical Observatory of Japan
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Jun 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Jun 2017](/thumbs/90/103253735.jpg) Preprint 5 November 2017 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3.0 Mass Evaporation Rate of Globular Clusters in a Strong Tidal Field arxiv:1706.06635v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Jun 2017 Juan P. Madrid, 1,2 Nathan
Preprint 5 November 2017 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3.0 Mass Evaporation Rate of Globular Clusters in a Strong Tidal Field arxiv:1706.06635v1 [astro-ph.ga] 20 Jun 2017 Juan P. Madrid, 1,2 Nathan
Disruption time scales of star clusters in different galaxies
 A&A 429, 173 179 (2005) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20041476 c ESO 2004 Astronomy & Astrophysics Disruption time scales of star clusters in different galaxies H. J. G. L. M. Lamers 1, M. Gieles 1, and S. F.
A&A 429, 173 179 (2005) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20041476 c ESO 2004 Astronomy & Astrophysics Disruption time scales of star clusters in different galaxies H. J. G. L. M. Lamers 1, M. Gieles 1, and S. F.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 7 Oct 2004
 Formation of ω Centauri by Tidal Stripping of a Dwarf Galaxy Makoto Ideta Astronomical Data Analysis Center, National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 2-21-1 Osawa, Mitaka, Tokyo 181-8588, Japan arxiv:astro-ph/0408431v2
Formation of ω Centauri by Tidal Stripping of a Dwarf Galaxy Makoto Ideta Astronomical Data Analysis Center, National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 2-21-1 Osawa, Mitaka, Tokyo 181-8588, Japan arxiv:astro-ph/0408431v2
Jongsuk Hong (KIAA) MODEST /06/28. Collaborators: E. Vesperini, A. Askar, M. Giersz, M. Szkudlarek & T. Bulik
 Jongsuk Hong (KIAA) MODEST-18 2018/06/28 Collaborators: E. Vesperini, A. Askar, M. Giersz, M. Szkudlarek & T. Bulik Introduction Method & models BBH mergers & Host cluster properties Merger rate estimation
Jongsuk Hong (KIAA) MODEST-18 2018/06/28 Collaborators: E. Vesperini, A. Askar, M. Giersz, M. Szkudlarek & T. Bulik Introduction Method & models BBH mergers & Host cluster properties Merger rate estimation
Forming Intermediate-Mass Black Holes in Dense Clusters Through Collisional Run-away
 Forming Intermediate-Mass Black Holes in Dense Clusters Through Collisional Run-away Marc Freitag ARI, Heidelberg freitag@ari.uni-heidelberg.de http://obswww.unige.ch/~freitag Collaboration with Atakan
Forming Intermediate-Mass Black Holes in Dense Clusters Through Collisional Run-away Marc Freitag ARI, Heidelberg freitag@ari.uni-heidelberg.de http://obswww.unige.ch/~freitag Collaboration with Atakan
Michela Mapelli. LECTURES on COLLISIONAL DYNAMICS: 1. RELEVANT TIMESCALES, FORMATION OF STAR CLUSTERS, EQUILIBRIUM MODELS
 Michela Mapelli LECTURES on COLLISIONAL DYNAMICS: 1. RELEVANT TIMESCALES, FORMATION OF STAR CLUSTERS, EQUILIBRIUM MODELS COLLISIONAL/COLLISIONLESS? Collisional systems are systems where interactions between
Michela Mapelli LECTURES on COLLISIONAL DYNAMICS: 1. RELEVANT TIMESCALES, FORMATION OF STAR CLUSTERS, EQUILIBRIUM MODELS COLLISIONAL/COLLISIONLESS? Collisional systems are systems where interactions between
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2015](/thumbs/88/114934773.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2015) Printed 4 September 2018 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) arxiv:1510.01337v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2015 Evolution of star clusters on eccentric orbits Maxwell Xu Cai
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2015) Printed 4 September 2018 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) arxiv:1510.01337v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2015 Evolution of star clusters on eccentric orbits Maxwell Xu Cai
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 16 May 2016](/thumbs/93/113265577.jpg) Draft version September 25, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 A POSSIBLE SOLUTION FOR THE M/L-[FE/H] RELATION OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS IN M31: A METALLICITY AND DENSITY DEPENDENT
Draft version September 25, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 A POSSIBLE SOLUTION FOR THE M/L-[FE/H] RELATION OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS IN M31: A METALLICITY AND DENSITY DEPENDENT
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 18 Dec 2003
 Draft version February 2, 2008 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/14/03 ON THE MAXIMUM BINARY FRACTION IN GLOBULAR CLUSTER CORES N. Ivanova, K. Belczynski 1, J.M. Fregeau 2, & F.A. Rasio
Draft version February 2, 2008 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/14/03 ON THE MAXIMUM BINARY FRACTION IN GLOBULAR CLUSTER CORES N. Ivanova, K. Belczynski 1, J.M. Fregeau 2, & F.A. Rasio
Dancing in the dark: spotting BHS & IMBH in GC
 Dancing in the dark: spotting BHS & IMBH in GC ARI-ZAH, Heidelberg University Star Clusters around the Milky Way and in the Local Group Heidelberg August 15th-17th, 2018 Unravelling stellar black hole
Dancing in the dark: spotting BHS & IMBH in GC ARI-ZAH, Heidelberg University Star Clusters around the Milky Way and in the Local Group Heidelberg August 15th-17th, 2018 Unravelling stellar black hole
Evolution of star clusters on eccentric orbits
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stv2325 Evolution of star clusters on eccentric orbits Maxwell Xu Cai ( ), 1,2 Mark Gieles, 3 Douglas C. Heggie 4 and Anna Lisa Varri 4 1 National Astronomical Observatories of China,
doi:10.1093/mnras/stv2325 Evolution of star clusters on eccentric orbits Maxwell Xu Cai ( ), 1,2 Mark Gieles, 3 Douglas C. Heggie 4 and Anna Lisa Varri 4 1 National Astronomical Observatories of China,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 27 Mar 2001
 ApJ, in press On the origin of the distribution of binary-star periods Pavel Kroupa 1 and Andreas Burkert 2 arxiv:astro-ph/0103429v1 27 Mar 2001 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik und Astrophysik Universität
ApJ, in press On the origin of the distribution of binary-star periods Pavel Kroupa 1 and Andreas Burkert 2 arxiv:astro-ph/0103429v1 27 Mar 2001 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik und Astrophysik Universität
Two paths of cluster evolution: global expansion versus core collapse
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stu1455 Two paths of cluster evolution: global expansion versus core collapse Ryan M. O Leary, Steven W. Stahler and Chung-Pei Ma Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Astrophysics
doi:10.1093/mnras/stu1455 Two paths of cluster evolution: global expansion versus core collapse Ryan M. O Leary, Steven W. Stahler and Chung-Pei Ma Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Astrophysics
White Dwarf Sequences in Dense Star Clusters
 To appear in the Astrophysical Journal White Dwarf Sequences in Dense Star Clusters Jarrod R. Hurley 1 and Michael M. Shara Department of Astrophysics, American Museum of Natural History, Central Park
To appear in the Astrophysical Journal White Dwarf Sequences in Dense Star Clusters Jarrod R. Hurley 1 and Michael M. Shara Department of Astrophysics, American Museum of Natural History, Central Park
Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters
 Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters By Riccardo Scarpa Instituto de astrofisica de Canarias Gran Telescopio Canarias The idea for this study sparked from the desire of
Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters By Riccardo Scarpa Instituto de astrofisica de Canarias Gran Telescopio Canarias The idea for this study sparked from the desire of
Super star cluster R136: puzzles outside and inside
 Super star cluster R136: puzzles outside and inside Sambaran Banerjee with Pavel Kroupa and Seungkyung Oh Argelander-Institut für Astronomie, University of Bonn @ Aarseth N-body meeting in Bonn Dec. 3-5,
Super star cluster R136: puzzles outside and inside Sambaran Banerjee with Pavel Kroupa and Seungkyung Oh Argelander-Institut für Astronomie, University of Bonn @ Aarseth N-body meeting in Bonn Dec. 3-5,
Dynamics of Stars and Black Holes in Dense Stellar Systems:
 Michela Mapelli INAF - Padova Dynamics of Stars and Black Holes in Dense Stellar Systems: Lecture I: STAR CLUSTERS AS COLLISIONAL SYSTEMS 1. Relevant timescales of dense stellar systems 2. Early evolution
Michela Mapelli INAF - Padova Dynamics of Stars and Black Holes in Dense Stellar Systems: Lecture I: STAR CLUSTERS AS COLLISIONAL SYSTEMS 1. Relevant timescales of dense stellar systems 2. Early evolution
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 1 Sep 1999
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 13 (2000) Printed 11 September 2017 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Evolution of Multi-mass Globular Clusters in Galactic Tidal Field with the Effects of Velocity Anisotropy
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 13 (2000) Printed 11 September 2017 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Evolution of Multi-mass Globular Clusters in Galactic Tidal Field with the Effects of Velocity Anisotropy
MASSIVE BLACK HOLES IN STAR CLUSTERS. II. REALISTIC CLUSTER MODELS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 613:1143 1156, 2004 October 1 # 2004. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A MASSIVE BLACK HOLES IN STAR CLUSTERS. II. REALISTIC CLUSTER
The Astrophysical Journal, 613:1143 1156, 2004 October 1 # 2004. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A MASSIVE BLACK HOLES IN STAR CLUSTERS. II. REALISTIC CLUSTER
Globular clusters and the formation of the outer Galactic halo
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 354, 713 719 (2004) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08228.x Globular clusters and the formation of the outer Galactic halo Sidney van den Bergh 1 and A. D. Mackey 2 1 Dominion Astrophysical
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 354, 713 719 (2004) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08228.x Globular clusters and the formation of the outer Galactic halo Sidney van den Bergh 1 and A. D. Mackey 2 1 Dominion Astrophysical
The Role Of Globular Clusters During Reionization
 The Role Of Globular Clusters During Reionization MKI Level 5, Room 582K Collaboration University of Queensland University of Sussex University of Stockholm Michael Drinkwater Ilian Iliev Peter Thomas
The Role Of Globular Clusters During Reionization MKI Level 5, Room 582K Collaboration University of Queensland University of Sussex University of Stockholm Michael Drinkwater Ilian Iliev Peter Thomas
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Oct 2003
 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
**TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
Is the Galactic center populated with young star clusters?
 The Evolution of Galaxies on Cosmological Timescales ASP Conference Series, Vol. 3 10 8, 1999 J. E. Beckman, and T. J. Mahoney, eds. Is the Galactic center populated with young star clusters? Simon Portegies
The Evolution of Galaxies on Cosmological Timescales ASP Conference Series, Vol. 3 10 8, 1999 J. E. Beckman, and T. J. Mahoney, eds. Is the Galactic center populated with young star clusters? Simon Portegies
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 May 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 May 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 May 2007](/thumbs/93/112236646.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2005) Printed 23 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Ratios of star cluster core and half-mass radii: a cautionary note on intermediate-mass black holes in star
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2005) Printed 23 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Ratios of star cluster core and half-mass radii: a cautionary note on intermediate-mass black holes in star
New Scenario for IMBH Formation in Globular Clusters - Recent Developm. Observational Imprints
 New Scenario for IMBH Formation in Globular Clusters - Recent Developments and Observational Imprints Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center, Polish Academy of Sciences Warsaw, Poland mig@camk.edu.pl
New Scenario for IMBH Formation in Globular Clusters - Recent Developments and Observational Imprints Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center, Polish Academy of Sciences Warsaw, Poland mig@camk.edu.pl
Steffen Mieske ESO Chile. MODEST 14 June 6, 2014
 1. Supermassive black holes in UCDs 2. How erosion of GCs has affected their specific frequencies 3. Is omega Centauri a star cluster after all? Steffen Mieske ESO Chile MODEST 14 June 6, 2014 Supermassive
1. Supermassive black holes in UCDs 2. How erosion of GCs has affected their specific frequencies 3. Is omega Centauri a star cluster after all? Steffen Mieske ESO Chile MODEST 14 June 6, 2014 Supermassive
Monte Carlo simulations of star clusters II. Tidally limited, multi mass systems with stellar evolution.
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., (2) Monte Carlo simulations of star clusters II. Tidally limited, multi mass systems with stellar evolution. Mirek Giersz N. Copernicus Astronomical Center, Polish Academy of
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., (2) Monte Carlo simulations of star clusters II. Tidally limited, multi mass systems with stellar evolution. Mirek Giersz N. Copernicus Astronomical Center, Polish Academy of
Black Holes in Globular Clusters
 Black Holes in Globular Clusters Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Papers on black holes and globular clusters Spot the odd man out Cen M15 www.jb.man.ac.uk The pioneer phase:
Black Holes in Globular Clusters Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Papers on black holes and globular clusters Spot the odd man out Cen M15 www.jb.man.ac.uk The pioneer phase:
MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS
 MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS SIDNEY VAN DEN BERGH Dominion Astrophysical Observatory 5071 West Saanich Road Victoria, British Columbia V8X 4M6, Canada vandenbergh@dao.nrc.ca Received: 1996 July 1 ; accepted:
MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS SIDNEY VAN DEN BERGH Dominion Astrophysical Observatory 5071 West Saanich Road Victoria, British Columbia V8X 4M6, Canada vandenbergh@dao.nrc.ca Received: 1996 July 1 ; accepted:
2 Frederic A. Rasio. 2. Summary of Recent Results
 2 Frederic A. Rasio dynamical evolution of a self-gravitating spherical cluster of N point masses whose orbits in the cluster are specified by an energy E and angular momentum J, with perturbations E and
2 Frederic A. Rasio dynamical evolution of a self-gravitating spherical cluster of N point masses whose orbits in the cluster are specified by an energy E and angular momentum J, with perturbations E and
Satellites of satellites: globular cluster systems as tracers of environmental effects on Virgo early-type dwarfs
 Satellites of satellites: globular cluster systems as tracers of environmental effects on Virgo early-type dwarfs Rubén Sánchez-Janssen (ESO, Chile) J.A.L. Aguerri (IAC, Spain) (MNRAS submitted) Dynamics
Satellites of satellites: globular cluster systems as tracers of environmental effects on Virgo early-type dwarfs Rubén Sánchez-Janssen (ESO, Chile) J.A.L. Aguerri (IAC, Spain) (MNRAS submitted) Dynamics
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
 Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Dec 2013
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Dec 2013 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Dec 2013](/thumbs/92/109903381.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 6 (22) Printed 2 August 28 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) MOCCA Code for Star Cluster Simulations - II. Comparison with Simulations arxiv:2.6246v2 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Dec 23 Mirek Giersz,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 6 (22) Printed 2 August 28 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) MOCCA Code for Star Cluster Simulations - II. Comparison with Simulations arxiv:2.6246v2 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Dec 23 Mirek Giersz,
Globular Clusters in relation to the VPOS of the Milky Way
 Globular Clusters in relation to the VPOS of the Milky Way Marcel S. Pawlowski marcel.pawlowski@case.edu Collaborators: Australia: Duncan Forbes, Helmut Jerjen Austria: Gerhard Hensler, Sylvia Plöckinger
Globular Clusters in relation to the VPOS of the Milky Way Marcel S. Pawlowski marcel.pawlowski@case.edu Collaborators: Australia: Duncan Forbes, Helmut Jerjen Austria: Gerhard Hensler, Sylvia Plöckinger
Formation and evolution of compact binaries with an accreting white dwarf in globular clusters.
 Formation and evolution of compact binaries with an accreting white dwarf in globular clusters. N. Ivanova Λ and F.A. Rasio Λ Λ Department of Physics and Astronomy, 2145 Sheridan Rd, Evanston, IL 60208,
Formation and evolution of compact binaries with an accreting white dwarf in globular clusters. N. Ivanova Λ and F.A. Rasio Λ Λ Department of Physics and Astronomy, 2145 Sheridan Rd, Evanston, IL 60208,
Black Hole Subsystems in Galactic Globular Clusters: Unravelling BH Populations in GCs using MOCCA Star Cluster Simulations
 Black Hole Subsystems in Galactic Globular Clusters: Unravelling BH Populations in GCs using MOCCA Star Cluster Simulations Artist impression of a stellar mass BH detected in NGC 3201 (Giesers et al. 2018)
Black Hole Subsystems in Galactic Globular Clusters: Unravelling BH Populations in GCs using MOCCA Star Cluster Simulations Artist impression of a stellar mass BH detected in NGC 3201 (Giesers et al. 2018)
Basic N-body modelling of the evolution of globular clusters I. Time scaling
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 297, 794 806 (1998) Basic N-body modelling of the evolution of globular clusters I. Time scaling S. J. Aarseth 1 and D. C. Heggie 2 1 Institute of Astronomy, Madingley Road, Cambridge
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 297, 794 806 (1998) Basic N-body modelling of the evolution of globular clusters I. Time scaling S. J. Aarseth 1 and D. C. Heggie 2 1 Institute of Astronomy, Madingley Road, Cambridge
arxiv:astro-ph/ v3 26 Jan 2001
 Monte Carlo Simulations of Globular Cluster Evolution - II. Mass Spectra, Stellar Evolution and Lifetimes in the Galaxy. Kriten J. Joshi 1, Cody P. Nave 2, and Frederic A. Rasio 3 Department of Physics,
Monte Carlo Simulations of Globular Cluster Evolution - II. Mass Spectra, Stellar Evolution and Lifetimes in the Galaxy. Kriten J. Joshi 1, Cody P. Nave 2, and Frederic A. Rasio 3 Department of Physics,
Stars on the run: escaping from stellar clusters
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., (3) Printed January, 8 (MN LaT E X style file v.) Stars on the run: escaping from stellar clusters Guido R. I. Moyano Loyola, Jarrod R. Hurley Centre for Astrophysics and Supercomputing,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., (3) Printed January, 8 (MN LaT E X style file v.) Stars on the run: escaping from stellar clusters Guido R. I. Moyano Loyola, Jarrod R. Hurley Centre for Astrophysics and Supercomputing,
Structure of the Milky Way. Structure of the Milky Way. The Milky Way
 Key Concepts: Lecture 29: Our first steps into the Galaxy Exploration of the Galaxy: first attempts to measure its structure (Herschel, Shapley). Structure of the Milky Way Initially, star counting was
Key Concepts: Lecture 29: Our first steps into the Galaxy Exploration of the Galaxy: first attempts to measure its structure (Herschel, Shapley). Structure of the Milky Way Initially, star counting was
The initial conditions of young globular clusters in the Large Magellanic Cloud
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 286,669-680 (1997) The initial conditions of young globular clusters in the Large Magellanic Cloud Simon P. Goodwin Astronomy Centre, University of Sussex, Falmer; Brighton BN]
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 286,669-680 (1997) The initial conditions of young globular clusters in the Large Magellanic Cloud Simon P. Goodwin Astronomy Centre, University of Sussex, Falmer; Brighton BN]
Veilleux! see MBW ! 23! 24!
 Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
TEREZA JEŘÁBKOVÁ ESO GARCHING & UNIVERSITY OF BONN & CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE
 1 TEREZA JEŘÁBKOVÁ ESO GARCHING & UNIVERSITY OF BONN & CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE www: sirrah.troja.mff.cuni.cz/~tereza email: tjerabko@eso.org 17 MODEST UNDER PRAGUE S STARRY SKIES CZECH REPUBLIC 18-22
1 TEREZA JEŘÁBKOVÁ ESO GARCHING & UNIVERSITY OF BONN & CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE www: sirrah.troja.mff.cuni.cz/~tereza email: tjerabko@eso.org 17 MODEST UNDER PRAGUE S STARRY SKIES CZECH REPUBLIC 18-22
Monte Carlo simulations of star clusters ± II. Tidally limited, multimass systems with stellar evolution
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 324, 28±23 2) Monte Carlo simulations of star clusters ± II. Tidally limited, multimass systems with stellar evolution Mirek Giersz w N. Copernicus Astronomical Center, Polish
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 324, 28±23 2) Monte Carlo simulations of star clusters ± II. Tidally limited, multimass systems with stellar evolution Mirek Giersz w N. Copernicus Astronomical Center, Polish
Stellar Populations in the Local Group
 Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 15: Galaxy Interactions
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 15: Galaxy Interactions Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 Galaxy Interactions & Transformations In this lecture we discuss galaxy interactions
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 15: Galaxy Interactions Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 Galaxy Interactions & Transformations In this lecture we discuss galaxy interactions
Time /Gyrs
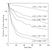 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 Time /Gyrs 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 Time /Gyrs On the destruction and over-merging of dark halos in dissipationless N-body simulations Ben Moore, Neal Katz
1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 Time /Gyrs 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 Time /Gyrs On the destruction and over-merging of dark halos in dissipationless N-body simulations Ben Moore, Neal Katz
An empirical clock to measure the dynamical age of stellar systems
 An empirical clock to measure the dynamical age of stellar systems FRANCESCO R. FERRARO Physics & Astronomy Department University of Bologna (Italy) Conception, Chile, March 4, 2015 ª 5-year project (web
An empirical clock to measure the dynamical age of stellar systems FRANCESCO R. FERRARO Physics & Astronomy Department University of Bologna (Italy) Conception, Chile, March 4, 2015 ª 5-year project (web
Black Hole Mergers at Galactic. The Final Parsec: Supermassive. Centers. Milos Milosavljevic. California Institute of Technology
 The Final Parsec: Supermassive Black Hole Mergers at Galactic Centers Milos Milosavljevic California Institute of Technology MBH Binaries Form in Galaxy Mergers Borne et al 2000 by transferring binding
The Final Parsec: Supermassive Black Hole Mergers at Galactic Centers Milos Milosavljevic California Institute of Technology MBH Binaries Form in Galaxy Mergers Borne et al 2000 by transferring binding
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli. Lecture 16
 University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year 2011-2012 Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli Lecture 16 Stellar populations Walter Baade (1893-1960) Learning outcomes The student
University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year 2011-2012 Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli Lecture 16 Stellar populations Walter Baade (1893-1960) Learning outcomes The student
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000{000 (1996) The initial conditions of young globular clusters in the LMC Simon P. Goodwin Astronomy Centre, Universi
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000{000 (1996) The initial conditions of young globular clusters in the LMC Simon P. Goodwin Astronomy Centre, University of Sussex, Falmer, Brighton BN1 9QH, UK. ABSTRACT
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000{000 (1996) The initial conditions of young globular clusters in the LMC Simon P. Goodwin Astronomy Centre, University of Sussex, Falmer, Brighton BN1 9QH, UK. ABSTRACT
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 31 Jul 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 31 Jul 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 31 Jul 2007](/thumbs/81/84026065.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (1994) Printed 1 February 8 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Origin of lower velocity dispersions of ultra-compact dwarf galaxy populations in clusters of galaxies K. Bekki
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (1994) Printed 1 February 8 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Origin of lower velocity dispersions of ultra-compact dwarf galaxy populations in clusters of galaxies K. Bekki
The structure and internal kinematics of globular clusters: tides and gravity
 The structure and internal kinematics of globular clusters: tides and gravity Antonio Sollima Antonio.sollima@oapd.inaf.it Collaborators : C. Nipoti (Univ. Bo), D. Martinez-Delgado (MPIA), M. Bellazzini
The structure and internal kinematics of globular clusters: tides and gravity Antonio Sollima Antonio.sollima@oapd.inaf.it Collaborators : C. Nipoti (Univ. Bo), D. Martinez-Delgado (MPIA), M. Bellazzini
Mass-loss rates and the mass evolution of star clusters
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 409, 305 328 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17309.x Mass-loss rates and the mass evolution of star clusters HennyJ.G.L.M.Lamers, 1 Holger Baumgar 2,3 and Mark Gieles 4,5
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 409, 305 328 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17309.x Mass-loss rates and the mass evolution of star clusters HennyJ.G.L.M.Lamers, 1 Holger Baumgar 2,3 and Mark Gieles 4,5
The evolution of binary fractions in globular clusters
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 358, 572 584 (2005) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.08804.x The evolution of binary fractions in globular clusters N. Ivanova, K. Belczynski, J. M. Fregeau and F. A. Rasio Northwestern
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 358, 572 584 (2005) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.08804.x The evolution of binary fractions in globular clusters N. Ivanova, K. Belczynski, J. M. Fregeau and F. A. Rasio Northwestern
Other stellar types. Open and globular clusters: chemical compositions
 Other stellar types Some clusters have hotter stars than we find in the solar neighbourhood -- O, B, A stars -- as well as F stars, and cooler stars (G, K, M) Hence we can establish intrinsic values (M
Other stellar types Some clusters have hotter stars than we find in the solar neighbourhood -- O, B, A stars -- as well as F stars, and cooler stars (G, K, M) Hence we can establish intrinsic values (M
Free-Floating Planets: Not So Surprising
 To appear in Astrophysical Journal: submitted August, 1, 2001 Free-Floating Planets: Not So Surprising Jarrod R. Hurley and Michael M. Shara Department of Astrophysics, American Museum of Natural History,
To appear in Astrophysical Journal: submitted August, 1, 2001 Free-Floating Planets: Not So Surprising Jarrod R. Hurley and Michael M. Shara Department of Astrophysics, American Museum of Natural History,
Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Hubble Sequence. Environment! Globular Clusters in Milky Way. kpc
 Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 25 Feb 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 25 Feb 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 25 Feb 2010](/thumbs/74/69818206.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 5 February 010 (MN LATEX style file v.) Jeans Instability of Palomar 5 s Tidal Tail arxiv:100.4870v1 [astro-ph.co] 5 Feb 010 Alice C. Quillen & Justin
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 5 February 010 (MN LATEX style file v.) Jeans Instability of Palomar 5 s Tidal Tail arxiv:100.4870v1 [astro-ph.co] 5 Feb 010 Alice C. Quillen & Justin
