Optical polarimetry studies of white dwarfs
|
|
|
- Franklin Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, , (2018) Optical polarimetry studies of white dwarfs A.S lowikowska 1, K.Krzeszowski 2, M.Żejmo 2, D.Blinov 3,4,5 and P.Reig 3,4 1 Toruń Centre for Astronomy, Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń, ul. Gagarina 11, Toruń, Poland, ( aga@umk.pl) 2 Janusz Gil Institute of Astronomy, University of Zielona Góra, Szafrana 2, Zielona Góra, Poland 3 Foundation for Research and Technology, Heraklion, Crete, Greece 4 University of Crete, Physics Department, Heraklion, Crete, Greece 5 Astronomical Institute, St. Petersburg State University, Universitetsky pr. 28, Petrodvoretz, St. Petersburg, Russia Received: December 13, 2017; Accepted: December 20, 2017 Abstract. We present results of the optical linear polarimetric survey of 101 white dwarfs (WDs) performed in R band with the RoboPol polarimeter. Our study shows that highly linear polarized white dwarfs are very rare. Moreover, we found that the median polarization degree of isolated DA WDs and DB WDs are similar, but lower than the median polarization of isolated DC WDs. The DB WDs in binaries seem to be more polarized than binaries containing DA+dM or double degenerated systems (DDSs) with DA component. We also present the measurements of the optical linear polarization of both components in two common proper motion binary systems (CPMBs): WD and the Sirius-like system (SLS) WD Because the vast majority of WDs have very low polarization degree on the level of less than 0.5%, they can be used as faint linear polarization standards. Key words: white dwarfs techniques: polarimetric 1. Introduction Recently, optical polarimetry studies of astrophysical sources are booming. More and more dedicated polarimeters are built, thus more polarimetric observations are performed. The RoboPol polarimeter dedicated to monitoring the polarization of blazars (Blinov et al., 2016) is a good example. At the same time, polarization observations performed with different telescope classes, from the small to the big, urgently require fainter polarization standards of both types polarized and zero-polarized. The polarized standards are required to establish the intrinsic depolarization caused by the instrument and zero-point of its position angle (PA), while the zero-polarized standards are necessary to determine the instrumental polarization (e.g. the RINGO3 polarimeter at the Liverpool Telescope, see S lowikowska et al., 2016).
2 246 A.S lowikowska, K.Krzeszowski, M.Żejmo, D.Blinov and P.Reig There are more than 23,000 WDs known up to date. For many of them, the spectral type is known. Most WD atmospheres are hydrogen-rich (DA), and almost all others are helium-rich (DB). However, a significant fraction of WDs also contain traces of heavier elements in their atmospheres, and these are labelled with Z for metals or Q for carbon, for example, DZ or DQ. There are also WDs for which the spectrum does not show any strong lines, but their atmospheres are still helium-rich. Such WDs are classified as DC-type WDs. In 2014 we started a long-term project to measure the linear optical polarization of selected WDs (for the description of the selected sample see Sec. 2 of Żejmo et al., 2017). We aim to perform a statistical analysis of the linear polarization properties of a WD sample and provide observers with a new list of faint linear polarimetric standard sources. In Żejmo et al. (2017) we presented the results of analysis of the optical linear polarization degree of 74 WDs of DA and DC spectral types, both isolated and in binary systems. Their SDSS r magnitudes range from 13 to 17. Almost all measured WDs show low polarization degree (PD < 1%). Only two of them, WD and WD , have PD higher than 1%. Żejmo et al. (2017) claim that the DC-type white dwarfs on average have higher PD (with the median PD of 0.78%) than DA type WDs (withthemedianpdof0.36%),butthereisnodifferencebetweenpdofisolated DA type WDs (0.36%) and PD of DA+dM binary systems (0.33%). Because most of WDs from our sample have low PD and they are well distributed over the sky in the right ascension range from 13 h to 24 h and declination from 11 up to 78, they can be treated as a good set of faint linear polarimetric standard stars. With our sample 1 we increased the low linear polarization standard list (e.g. Fossati et al., 2007) substantially. WDs were, and still are, commonly used as zero-polarization standard stars. Apart from our list, there are eleven well known zero-polarized WDs in the literature. Two of them, namely G 191-B2B (PD=0.09%) and GD 319 (PD=0.045%), were proposed by Turnshek et al. (1990) as the Hubble Space Telescope polarimetric standards. Long-term monitoring of G 191-B2B is presented by S lowikowska et al. (2016). Another nine were proposed by Fossati et al. (2007) as main zero-polarization standards for the FORS1 instrument on the Very Large Telescope. Their goal was to find a group of faint polarized and zero-polarized standards appropriate for telescopes with big mirrors. Their sample consists of 30 stars of different spectral types in the magnitude range from 6 to 14. However, WDs given by Fossati et al. (2007) are in the magnitude range from 11 to 13, with only one exception of 14 mag. Therefore, our list is complementary to Fossati et al. (2007) in respect of the brightness. Seventy WDs extended the existing polarimetric standard lists by a factor of 7. A larger group of zero-polarization standards facilitates the selection of standards at a convenient time of the night and position on the sky. 1
3 Optical polarimetry studies of white dwarfs 247 Additionally, we found that for low extinction values (E(B V) < 0.04), the best model that describes the dependence of PD on E(B V) is given by the equation PD max,ism [%] = 0.65 E(B V) This differs from the Fosalba et al. (2002) equation PD max,ism [%] = 3.5 E(B V) 0.8 that was derived from the fit in the E(B V) range from 0.1 to Observations and data analysis Our observations were performed at the Skinakas Observatory located in Crete (Greece) in 2014 and We used the RoboPol 2 linear polarimeter, equipped with two Wollaston prisms and two half-wave plates. It allows to measure the Stokes I, Q, U parameters simultaneously for all stellar objects within field of view and the scale of px 1 (King et al., 2014). The measurements were performed with an aperture defined as 2.5 FWHM, where FWHM is an average full width at half maximum of stellar images, which has a median valueof2.1 (4.0pixels).AllobservationswiththeRoboPolwereperformedwith the R Johnson-Cousins filter. The exposure time was adjusted according to the brightness of each target, as estimated during short pointing exposures. The data were analysed with the standard RoboPol pipeline (King et al., 2014), whose output gives the normalised Stokes parameters q = Q/I and u = U/I 3. To account for the instrumental polarization, we measured the polarization degree of 14 zero-polarized standards. The data corrected for instrumental polarization were later used to obtain the PD according to Eq. 1, while the corresponding error (σ PD ) is calculated from Eq. 5 in King et al. (2014). For low polarization signal-to-noise ratio (PD / σ PD < 3) distribution of the PD is not normal (Gaussian) and the PD values must always be positive so their uncertainties are not symmetric. This introduces a bias into any estimate. To deal with this problem we applied the debias method described by Vaillancourt (2006). Details are given in Sec. 4 of Żejmo et al. (2017). 3. Results The most intriguing object from our sample is WD It shows the highest measured linear polarization in our total sample of 101 WDs measured in 2014and2016andisanisolatedDBWDwithPDof2.66%(PD c =2.56%).This value of the PD does not depend on the chosen aperture. A close examination of its neighbourhood stars indicates that the WD polarization is intrinsic. The other two WDs with reasonably high PD are WD and WD with PD values of 1.14% and 1.25%, respectively, and both are in binary systems. WD is a DB WD with a dwarf M4 companion (Silvestri et al., Hereafter we follow the IAU convention, where the position angle is measured from the North direction increasing counter-clockwise.
4 248 A.S lowikowska, K.Krzeszowski, M.Żejmo, D.Blinov and P.Reig 2005) and WD is of DA type with a dg0 companion (Farihi et al., 2005). Below we discuss binary and multiple systems observed within our 2016 sample. WD (GR 516, LP ): its companion is a subdwarf M5 (Silvestri et al., 2005) and is not a common proper motion binary. WD (PG , LP ): we were able to measure its companion (dwarf M4) separated by 87 (Oswalt et al., 1988). It has PD = 0.34% ± 0.33%, while PA = ± This compares with WD PD = 1.14% ± 0.15% and PA = 2. 3 ± The maximum PD caused by the ISM is 0.42%. WD : it is a multiple system resolved only in the HST images and consists of a DB WD and two dwarfs of M2 types (Farihi et al., 2010). It cannot be resolved with RoboPol because the separation between components is less than Therefore, the measured PD is the net PD (0.44% ± 0.28%) of all three. The same is for PA, ± The position angle of secondary stars is ± WD : this is a SLS with a dwarf G0 companion separated by 63 (Farihi et al., 2005). It can be resolved by RoboPol, but was unfortunately covered by the mask even in the pointing exposures. Holberg et al. (2013) give the position angle of the companion, where the orientation is measured from the WD to the companion, being (that corresponds to ) and it is aligned with the proper motion PA of found by Farihi et al. (2005). WD : it is the second SLS in our sample. We were able to measure the polarization of its K2 star (Holberg et al., 2013) separated by (Oswalt et al., 1988) and obtained PD = 0.29% ± 0.05% and PA = ± The WD in this system has PD = 0.42% ± 0.28% and PA = ± The contribution from the ISM is estimated to be less than 0.44%. Holberg et al. (2013) give PA = of the companion measured from the WD. For two CPMBs, WD and WD , we were able to measure the PD of their companions. In both cases the measured PD of the companions (dwarf M4 in case of WD and K2 in case of WD ) is smaller than the expected maximum PD ISM. Such measurements give an independent check on the contribution of the PD from the ISM, assuming that no intrinsic PD is expected from the companions M4 and K2 type dwarfs. We used the combined dataset from 2014 and 2016 to check the correlation between the interstellar polarization and the extinction. We found that for the E(B V) range from 0.0 to the maximum PD caused by the ISM is given by the relation PD max,ism (%) = 0.65 E(B V) We concluded that for three WDs with the highest PD their measured linear polarization is intrinsic. The spatial distribution of our joined sample is in good agreement with the Berdyugin et al. (2014) measurements. There are regions in the Galaxy that show a higher PD, however, most of WDs from our sample are not located in these regions. Our statistical analysis shows that the isolated DB type WDs, similarly to isolated DA type WDs, have lower median PD values in comparison to isolated DC type WDs (0.3%, 0.36% and 0.66%, respectively). On the other
5 Optical polarimetry studies of white dwarfs 249 hand, the DB WDs in binary systems have much higher PD than the PD of all other binary systems in our sample (i.e. binary DA+dM and DDSs). However, the DB binaries sample size is small, therefore our result is not conclusive. Acknowledgements. This work has been supported by Polish National Science CentregrantsDEC-2011/03/D/ST9/00656(AS,KK,MŻ)andUMO-2014/13/B/ST9/ (AS). DB acknowledges support from the St. Petersburg Univ. research grant RoboPol is a collaboration involving the University of Crete, the Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas, the California Institute of Technology, the Max-Planck Institute for Radioastronomy, the Nicolaus Copernicus University, and the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics. This work was partially supported by the RoboPol project, which is co-funded by the European Social Fund (ESF) and Greek National Resources, and by the European Comission Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) through grants PCIG10-GA JetPop and PIRSES-GA EuroCal. Data analysis and figures were partly prepared using R (R Core Team, 2013). References Berdyugin, A., Piirola, V., & Teerikorpi, P. 2014, Astron. Astrophys., 561, A24 Blinov, D., Pavlidou, V., Papadakis, I., et al. 2016, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 462, 1775 Farihi, J., Becklin, E. E., & Zuckerman, B. 2005, Astrophys. J., Suppl., 161, 394 Farihi, J., Hoard, D. W., & Wachter, S. 2010, Astrophys. J., Suppl., 190, 275 Fosalba, P., Lazarian, A., Prunet, S., & Tauber, J. A. 2002, Astrophys. J., 564, 762 Fossati, L., Bagnulo, S., Mason, E., & Landi Degl Innocenti, E. 2007, in ASP Conf. Ser., Vol. 364, The Future of Photometric, Spectrophotometric and Polarimetric Standardization, ed. C. Sterken, 503 Holberg, J. B., Oswalt, T. D., Sion, E. M., Barstow, M. A., & Burleigh, M. R. 2013, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 435, 2077 King, O. G., Blinov, D., Ramaprakash, A. N., Myserlis, I., & et al., A. 2014, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 442, 1706 Oswalt, T. D., Hintzen, P. M., & Luyten, W. J. 1988, Astrophys. J., Suppl., 66, 391 R Core Team. 2013, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria Silvestri, N. M., Hawley, S. L., & Oswalt, T. D. 2005, Astron. J., 129, 2428 S lowikowska, A., Krzeszowski, K., Żejmo, M., Reig, P., & Steele, I. 2016, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 458, 759 Turnshek, D. A., Bohlin, R. C., Williamson, II, R. L., et al. 1990, Astron. J., 99, 1243 Vaillancourt, J. E. 2006, Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac., 118, 1340 Żejmo, M., S lowikowska, A., Krzeszowski, K., Reig, P., & Blinov, D. 2017, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 464, 1294
RoboPol: optical polarimetry in Crete. P. Reig (Foundation for Research & Technology-Hellas) on behalf of the RoboPol collaboration
 RoboPol: optical polarimetry in Crete P. Reig (Foundation for Research & Technology-Hellas) on behalf of the RoboPol collaboration Outline Skinakas Observatory Robopol the instrument pipeline analysis
RoboPol: optical polarimetry in Crete P. Reig (Foundation for Research & Technology-Hellas) on behalf of the RoboPol collaboration Outline Skinakas Observatory Robopol the instrument pipeline analysis
The RoboPol project: Rotations of polarization plane in optical emission of blazars
 The RoboPol project: Rotations of polarization plane in optical emission of blazars Dmitry Blinov for the RoboPol collaboration Univ. of Crete, Heraklion, Greece http://robopol.org Kikuchi et al., 1988,
The RoboPol project: Rotations of polarization plane in optical emission of blazars Dmitry Blinov for the RoboPol collaboration Univ. of Crete, Heraklion, Greece http://robopol.org Kikuchi et al., 1988,
Standard Stars for Linear Polarization Observed with FORS1
 THE FUTURE OF PHOTOMETRIC, SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC AND POLARIMETRIC STANDARDIZATION ASP Conference Series, Vol. 364, 27 C. Sterken Standard Stars for Linear Polarization Observed with FORS1 L. Fossati, 1,2
THE FUTURE OF PHOTOMETRIC, SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC AND POLARIMETRIC STANDARDIZATION ASP Conference Series, Vol. 364, 27 C. Sterken Standard Stars for Linear Polarization Observed with FORS1 L. Fossati, 1,2
The RoboPol pipeline and control system
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stu176 The RoboPol pipeline and control system O. G. King, 1 D. Blinov, 2,3 A. N. Ramaprakash, 4 I. Myserlis, 5 E. Angelakis, 5 M. Baloković, 1 R. Feiler, 6 L. Fuhrmann, 5 T. Hovatta,
doi:10.1093/mnras/stu176 The RoboPol pipeline and control system O. G. King, 1 D. Blinov, 2,3 A. N. Ramaprakash, 4 I. Myserlis, 5 E. Angelakis, 5 M. Baloković, 1 R. Feiler, 6 L. Fuhrmann, 5 T. Hovatta,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Sep 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Sep 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Sep 2014](/thumbs/78/78226330.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2012) Printed 15 July 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The high optical polarization in the Be/X-ray binary EXO 2030+375 arxiv:1409.8411v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Sep 2014 P.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2012) Printed 15 July 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The high optical polarization in the Be/X-ray binary EXO 2030+375 arxiv:1409.8411v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Sep 2014 P.
This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail.
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. King, O. G.; Blinov, D.; Ramaprakash,
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. King, O. G.; Blinov, D.; Ramaprakash,
Short-period cataclysmic variables at Observatorio Astronomico Nacional IA UNAM.
 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 43, 294 299, (214) Short-period cataclysmic variables at Observatorio Astronomico Nacional IA UNAM. S. Zharikov Observatorio Astronomico Nacional, Instituto de Astronomia,
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 43, 294 299, (214) Short-period cataclysmic variables at Observatorio Astronomico Nacional IA UNAM. S. Zharikov Observatorio Astronomico Nacional, Instituto de Astronomia,
The properties and origin of magnetic fields in white dwarfs
 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 228 235, (2018) The properties and origin of magnetic fields in white dwarfs A. Kawka Astronomical Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences 251 65 Ondřejov, The
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 228 235, (2018) The properties and origin of magnetic fields in white dwarfs A. Kawka Astronomical Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences 251 65 Ondřejov, The
HT Cas - eclipsing dwarf nova during its superoutburst in 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Dec 2013
![HT Cas - eclipsing dwarf nova during its superoutburst in 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Dec 2013 HT Cas - eclipsing dwarf nova during its superoutburst in 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Dec 2013](/thumbs/72/67094721.jpg) Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso, 1 5, () HT Cas - eclipsing dwarf nova during its superoutburst in 21 arxiv:1312.5211v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Dec 213 K.Bąkowska 1,2, A. Olech 1, A. Rutkowski 3, R.Koff
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso, 1 5, () HT Cas - eclipsing dwarf nova during its superoutburst in 21 arxiv:1312.5211v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Dec 213 K.Bąkowska 1,2, A. Olech 1, A. Rutkowski 3, R.Koff
Calibrating brown dwarf ages using white dwarfs in wide binaries
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 84, 1027 c SAIt 2013 Memorie della Calibrating brown dwarf ages using white dwarfs in wide binaries S. Catalán Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Gibbet Hill Road, Coventry
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 84, 1027 c SAIt 2013 Memorie della Calibrating brown dwarf ages using white dwarfs in wide binaries S. Catalán Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Gibbet Hill Road, Coventry
The Optical Microvariability and Spectral Changes of the BL Lacertae Object S
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (2011) 32, 97 103 c Indian Academy of Sciences The Optical Microvariability and Spectral Changes of the BL Lacertae Object S5 0716+714 H. Poon 1,, J.H.Fan 2 & J.N.Fu 1 1 Astronomy Department,
J. Astrophys. Astr. (2011) 32, 97 103 c Indian Academy of Sciences The Optical Microvariability and Spectral Changes of the BL Lacertae Object S5 0716+714 H. Poon 1,, J.H.Fan 2 & J.N.Fu 1 1 Astronomy Department,
Polarization due to rotational distortion in the bright star Regulus
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters DOI: 10.1038/s41550-017-0238-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Polarization due to rotational distortion in the bright star Regulus Daniel V. Cotton
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters DOI: 10.1038/s41550-017-0238-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Polarization due to rotational distortion in the bright star Regulus Daniel V. Cotton
STUDIES OF SELECTED VOIDS. SURFACE PHOTOMETRY OF FAINT GALAXIES IN THE DIRECTION OF IN HERCULES VOID
 STUDIES OF SELECTED VOIDS. SURFACE PHOTOMETRY OF FAINT GALAXIES IN THE DIRECTION OF 1600+18 IN HERCULES VOID G.Petrov [1], A.Y.Kniazev [2], and J.W. Fried [2] 1 Institute of Astronomy, Bulgarian Academy
STUDIES OF SELECTED VOIDS. SURFACE PHOTOMETRY OF FAINT GALAXIES IN THE DIRECTION OF 1600+18 IN HERCULES VOID G.Petrov [1], A.Y.Kniazev [2], and J.W. Fried [2] 1 Institute of Astronomy, Bulgarian Academy
1 Introduction. 2 Observations. HD , an Eccentric Ellipsoidal System
 Peremennye Zvezdy (Variable Stars) 33, No. 7, 2013 Received 24 August; accepted 30 August. HD 305629, an Eccentric Ellipsoidal System S. A. Otero 1,2, G. Di Scala 3,4 1 Buenos Aires, Argentina 2 American
Peremennye Zvezdy (Variable Stars) 33, No. 7, 2013 Received 24 August; accepted 30 August. HD 305629, an Eccentric Ellipsoidal System S. A. Otero 1,2, G. Di Scala 3,4 1 Buenos Aires, Argentina 2 American
Accurate Mass Determination of the Old White Dwarf G through Astrometric Microlensing
 Hubble Space Telescope Cycle 19 GO Proposal 871 Accurate Mass Determination of the Old White Dwarf G105-30 through Astrometric Microlensing Principal Investigator: Dr. Kailash C. Sahu Institution: Space
Hubble Space Telescope Cycle 19 GO Proposal 871 Accurate Mass Determination of the Old White Dwarf G105-30 through Astrometric Microlensing Principal Investigator: Dr. Kailash C. Sahu Institution: Space
TECHNICAL REPORT. Doc #: Date: Rev: JWST-STScI , SM-12 August 31, Authors: Karl Gordon, Ralph Bohlin. Phone:
 When there is a discrepancy between the information in this technical report and information in JDox, assume JDox is correct. TECHNICAL REPORT Title: Title: JWST Absolute Flux Calibration II: Expanded
When there is a discrepancy between the information in this technical report and information in JDox, assume JDox is correct. TECHNICAL REPORT Title: Title: JWST Absolute Flux Calibration II: Expanded
BV RI photometric sequences for nine selected dark globules
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 126, 73-80 (1997) NOVEMBER II 1997, PAGE73 BV RI photometric sequences for nine selected dark globules J.F. Lahulla 1, A. Aguirre
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 126, 73-80 (1997) NOVEMBER II 1997, PAGE73 BV RI photometric sequences for nine selected dark globules J.F. Lahulla 1, A. Aguirre
Kilo-Gauss Magnetic Fields in Three DA White Dwarfs
 14 th European Workshop on White Dwarfs ASP Conference Series, Vol. 334, 2005 D. Koester, S. Moehler Kilo-Gauss Magnetic Fields in Three DA White Dwarfs R. Aznar Cuadrado, 1 S. Jordan, 2 R. Napiwotzki,
14 th European Workshop on White Dwarfs ASP Conference Series, Vol. 334, 2005 D. Koester, S. Moehler Kilo-Gauss Magnetic Fields in Three DA White Dwarfs R. Aznar Cuadrado, 1 S. Jordan, 2 R. Napiwotzki,
BV R photometry of comparison stars in selected blazar fields
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JUNE I 1998, PAGE 305 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 130, 305 310 (1998) BV R photometry of comparison stars in selected blazar fields I. Photometric sequences
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JUNE I 1998, PAGE 305 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 130, 305 310 (1998) BV R photometry of comparison stars in selected blazar fields I. Photometric sequences
linear polarization: the electric field is oriented in a single direction circular polarization: the electric field vector rotates
 Chapter 8 Polarimetry 8.1 Description of polarized radiation The polarization of electromagnetic radiation is described by the orientation of the wave s electric field vector. There are two different cases
Chapter 8 Polarimetry 8.1 Description of polarized radiation The polarization of electromagnetic radiation is described by the orientation of the wave s electric field vector. There are two different cases
Photometry of the Dwarf Nova SDSS J in Outburst
 Wils and Krajci, JAAVSO Volume 38, 2010 33 Photometry of the Dwarf Nova SDSS J094002.56+274942.0 in Outburst Tom Krajci Astrokolkhoz Observatory, P.O. Box 1351, Cloudcroft, New Mexico 88317; tom_krajci@tularosa.net
Wils and Krajci, JAAVSO Volume 38, 2010 33 Photometry of the Dwarf Nova SDSS J094002.56+274942.0 in Outburst Tom Krajci Astrokolkhoz Observatory, P.O. Box 1351, Cloudcroft, New Mexico 88317; tom_krajci@tularosa.net
An atlas of images of Planetary Nebulae
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS APRIL I 1999, PAGE 145 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 136, 145 171 (1999) An atlas of images of Planetary Nebulae S.K. Górny 1,H.E.Schwarz 2, R.L.M. Corradi 3,
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS APRIL I 1999, PAGE 145 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 136, 145 171 (1999) An atlas of images of Planetary Nebulae S.K. Górny 1,H.E.Schwarz 2, R.L.M. Corradi 3,
Observed Properties of Stars ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Observed Properties of Stars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Extrinsic Properties Location Motion kinematics Extrinsic Properties Location Use spherical coordinate system centered on Solar System Two angles (θ,φ) Right
Observed Properties of Stars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Extrinsic Properties Location Motion kinematics Extrinsic Properties Location Use spherical coordinate system centered on Solar System Two angles (θ,φ) Right
RoboPol: optical polarization-plane rotations and flaring activity in blazars
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw158 RoboPol: optical polarization-plane rotations and flaring activity in blazars D. Blinov, 1,2,3 V. Pavlidou, 1,2 I. E. Papadakis, 1,2 T. Hovatta, 4 T. J. Pearson, 5 I. Liodakis,
doi:10.1093/mnras/stw158 RoboPol: optical polarization-plane rotations and flaring activity in blazars D. Blinov, 1,2,3 V. Pavlidou, 1,2 I. E. Papadakis, 1,2 T. Hovatta, 4 T. J. Pearson, 5 I. Liodakis,
The RoboPol optical polarization survey of gamma-ray-loud blazars
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stu904 The RoboPol optical polarization survey of gamma-ray-loud blazars V. Pavlidou, 1,2 E. Angelakis, 3 I. Myserlis, 3 D. Blinov, 2,4 O. G. King, 5 I. Papadakis, 1,2 K. Tassis, 1,2
doi:10.1093/mnras/stu904 The RoboPol optical polarization survey of gamma-ray-loud blazars V. Pavlidou, 1,2 E. Angelakis, 3 I. Myserlis, 3 D. Blinov, 2,4 O. G. King, 5 I. Papadakis, 1,2 K. Tassis, 1,2
CCD Double-Star Measurements at Altimira Observatory in 2007
 Page 27 CCD Double-Star Measurements at Altimira Observatory in 2007 Robert K. Buchheim Altimira Observatory (G76) 18 Altimira Coto de Caza, CA 92679 Email: RBuchheim@earthlink.net Abstract: CCD measurements
Page 27 CCD Double-Star Measurements at Altimira Observatory in 2007 Robert K. Buchheim Altimira Observatory (G76) 18 Altimira Coto de Caza, CA 92679 Email: RBuchheim@earthlink.net Abstract: CCD measurements
CCD astrometry and instrumental V photometry of visual double stars,
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS MAY I 1999, PAGE 525 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 136, 525 529 (1999) CCD astrometry and instrumental V photometry of visual double stars, V. Differential measurements
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS MAY I 1999, PAGE 525 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 136, 525 529 (1999) CCD astrometry and instrumental V photometry of visual double stars, V. Differential measurements
The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range
 Instrument Science Report CAL/SCS-010 The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range L. Colina, R. Bohlin, D. Calzetti, C. Skinner, S. Casertano October 3, 1996 ABSTRACT A proposal
Instrument Science Report CAL/SCS-010 The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range L. Colina, R. Bohlin, D. Calzetti, C. Skinner, S. Casertano October 3, 1996 ABSTRACT A proposal
Delaware Asteroseismic Research Center. Asteroseismology with the Whole Earth Telescope (and More!)
 Delaware Asteroseismic Research Center Asteroseismology with the Whole Earth Telescope (and More!) Asteroseismology Study of interior stellar structure as revealed by global oscillations. Important- -
Delaware Asteroseismic Research Center Asteroseismology with the Whole Earth Telescope (and More!) Asteroseismology Study of interior stellar structure as revealed by global oscillations. Important- -
1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO?
 Astronomy 418/518 final practice exam 1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO? b. Describe the visibility vs. baseline for a two element,
Astronomy 418/518 final practice exam 1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO? b. Describe the visibility vs. baseline for a two element,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 13 May 2004
 MID INFRARED OBSERVATIONS OF VAN MAANEN 2: NO SUBSTELLAR COMPANION J. Farihi and E. E. Becklin arxiv:astro-ph/0405245v1 13 May 2004 Department of Physics & Astronomy, 8371 Math Sciences Building, University
MID INFRARED OBSERVATIONS OF VAN MAANEN 2: NO SUBSTELLAR COMPANION J. Farihi and E. E. Becklin arxiv:astro-ph/0405245v1 13 May 2004 Department of Physics & Astronomy, 8371 Math Sciences Building, University
Circular polarization in comets: calibration of measurements
 Circular polarization in comets: calibration of measurements Vera Rosenbush, Nikolai Kiselev Main Astronomical Observatory of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, rosevera@mao.kiev.ua Kyiv 1 Outline
Circular polarization in comets: calibration of measurements Vera Rosenbush, Nikolai Kiselev Main Astronomical Observatory of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, rosevera@mao.kiev.ua Kyiv 1 Outline
DETERMINATION OF STELLAR ROTATION WITH GAIA AND EFFECTS OF SPECTRAL MISMATCH. A. Gomboc 1,2, D. Katz 3
 537 DETERMINATION OF STELLAR ROTATION WITH GAIA AND EFFECTS OF SPECTRAL MISMATCH A. Gomboc,2, D. Katz 3 University in Ljubljana, Jadranska 9, 00 Ljubljana, Slovenia 2 ARI, Liverpool John Moores University,
537 DETERMINATION OF STELLAR ROTATION WITH GAIA AND EFFECTS OF SPECTRAL MISMATCH A. Gomboc,2, D. Katz 3 University in Ljubljana, Jadranska 9, 00 Ljubljana, Slovenia 2 ARI, Liverpool John Moores University,
Analysis of the rich optical iron-line spectrum of the x-ray variable I Zw 1 AGN 1H
 Analysis of the rich optical iron-line spectrum of the x-ray variable I Zw 1 AGN 1H0707 495 H Winkler, B Paul Department of Physics, University of Johannesburg, PO Box 524, 2006 Auckland Park, Johannesburg,
Analysis of the rich optical iron-line spectrum of the x-ray variable I Zw 1 AGN 1H0707 495 H Winkler, B Paul Department of Physics, University of Johannesburg, PO Box 524, 2006 Auckland Park, Johannesburg,
Nearby star candidates in the Torino observatory parallax program ABSTRACT. X corrected = X observed 8.1 (V I) Z x (1)
 A&A 464, 787 791 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20066408 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics Nearby star candidates in the Torino observatory parallax program R. L. Smart 1,M.G.Lattanzi 1, H. Jahreiß 2,
A&A 464, 787 791 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20066408 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics Nearby star candidates in the Torino observatory parallax program R. L. Smart 1,M.G.Lattanzi 1, H. Jahreiß 2,
Verification of COS/FUV Bright Object Aperture (BOA) Operations at Lifetime Position 3
 Instrument Science Report COS 2015-05(v1) Verification of COS/FUV Bright Object Aperture (BOA) Operations at Lifetime Position 3 Andrew Fox 1, John Debes 1, & Julia Roman-Duval 1 1 Space Telescope Science
Instrument Science Report COS 2015-05(v1) Verification of COS/FUV Bright Object Aperture (BOA) Operations at Lifetime Position 3 Andrew Fox 1, John Debes 1, & Julia Roman-Duval 1 1 Space Telescope Science
CCD astrometry and UBV photometry of visual binaries
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JUNE I 1998, PAGE 299 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 130, 299 304 (1998) CCD astrometry and UBV photometry of visual binaries II. Visual double stars with mainly
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JUNE I 1998, PAGE 299 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 130, 299 304 (1998) CCD astrometry and UBV photometry of visual binaries II. Visual double stars with mainly
Microvariability of Red Giant Stars
 Part 2A: Mowlavi and Jorissen, JAAVSO Volume 35, 2006 91 Microvariability of Red Giant Stars N. Mowlavi Observatoire de Genève, CH-1290 Versoix, Switzerland A. Jorissen Chercheur Qualifiè F.N.R.S., Institut
Part 2A: Mowlavi and Jorissen, JAAVSO Volume 35, 2006 91 Microvariability of Red Giant Stars N. Mowlavi Observatoire de Genève, CH-1290 Versoix, Switzerland A. Jorissen Chercheur Qualifiè F.N.R.S., Institut
Polarization of Light
 Polarization of Light A light beam which has all of the wave oscillations in a single plane of space is said to have total plane polarization. Light with an equal amount of oscillations in all directions
Polarization of Light A light beam which has all of the wave oscillations in a single plane of space is said to have total plane polarization. Light with an equal amount of oscillations in all directions
Setting UBVRI Photometric Zero-Points Using Sloan Digital Sky Survey ugriz Magnitudes
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Martin Gaskell Publications Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 10-1-2007 Setting UBVRI Photometric Zero-Points Using
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Martin Gaskell Publications Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 10-1-2007 Setting UBVRI Photometric Zero-Points Using
Investigating the Efficiency of the Beijing Faint Object Spectrograph and Camera (BFOSC) of the Xinglong 2.16-m Reflector
 Research in Astron. Astrophys. Vol. (xx) No., http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Investigating the Efficiency of the Beijing Faint Object
Research in Astron. Astrophys. Vol. (xx) No., http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Investigating the Efficiency of the Beijing Faint Object
Gaia and white dwarf - brown dwarf binaries
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 85, 731 c SAIt 2014 Memorie della Gaia and white dwarf - brown dwarf binaries S. L. Casewell Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, University Road, Leicester,
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 85, 731 c SAIt 2014 Memorie della Gaia and white dwarf - brown dwarf binaries S. L. Casewell Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, University Road, Leicester,
The Cosmological Distance Ladder. It's not perfect, but it works!
 The Cosmological Distance Ladder It's not perfect, but it works! First, we must know how big the Earth is. Next, we must determine the scale of the solar system. Copernicus (1543) correctly determined
The Cosmological Distance Ladder It's not perfect, but it works! First, we must know how big the Earth is. Next, we must determine the scale of the solar system. Copernicus (1543) correctly determined
Hubble Science Briefing: 25 Years of Seeing Stars with the Hubble Space Telescope. March 5, 2015 Dr. Rachel Osten Dr. Alex Fullerton Dr.
 Hubble Science Briefing: 25 Years of Seeing Stars with the Hubble Space Telescope March 5, 2015 Dr. Rachel Osten Dr. Alex Fullerton Dr. Jay Anderson Hubble s Insight into the Lives of Stars Comes From:
Hubble Science Briefing: 25 Years of Seeing Stars with the Hubble Space Telescope March 5, 2015 Dr. Rachel Osten Dr. Alex Fullerton Dr. Jay Anderson Hubble s Insight into the Lives of Stars Comes From:
NARROW-BAND PHOTOMETRY AND THE STELLAR POPULATIONS IN ELLIPTICAL GALAXIES*
 NARROW-BAND PHOTOMETRY AND THE STELLAR POPULATIONS IN ELLIPTICAL GALAXIES* KARL D. RAKOS Institute for Astronomy, University of Vienna, Austria TOBIAS J. KREIDL Lowell Observatory, Flagstaff, Arizona,
NARROW-BAND PHOTOMETRY AND THE STELLAR POPULATIONS IN ELLIPTICAL GALAXIES* KARL D. RAKOS Institute for Astronomy, University of Vienna, Austria TOBIAS J. KREIDL Lowell Observatory, Flagstaff, Arizona,
Atacama Submillimeter Telescope. ISM Polarimetry. C. Darren Dowell (JPL/Caltech) 2003 October 11
 Atacama Submillimeter Telescope ISM Polarimetry C. Darren Dowell (JPL/Caltech) 2003 October 11 Outline Sensitivity Extended Sources: Magnetic fields confront other forces in the Galaxy. Large-scale magnetic
Atacama Submillimeter Telescope ISM Polarimetry C. Darren Dowell (JPL/Caltech) 2003 October 11 Outline Sensitivity Extended Sources: Magnetic fields confront other forces in the Galaxy. Large-scale magnetic
SKINAKAS OBSERVATORY. Astronomy Projects for University Students PROJECT SUPERNOVA REMNANTS
 PROJECT 10 SUPERNOVA REMNANTS Objective: The purpose of this exercise is also twofold. The first one is to gain further experience with the analysis of narrow band images (as in the case of planetary nebulae)
PROJECT 10 SUPERNOVA REMNANTS Objective: The purpose of this exercise is also twofold. The first one is to gain further experience with the analysis of narrow band images (as in the case of planetary nebulae)
Zelenchukskaya region, Karachai-Cherkesia, Russia H.FALCKE, R.OSTERBART, M.SCH OLLER AND G.WEIGELT
 SPECKLE MASKING IMAGING OF THE SPECTROSCOPIC BINARIES GLIESE 150.2 AND 41 DRACONIS I.BALEGA AND Y.BALEGA Special Astrophysical Observatory Zelenchukskaya region, Karachai-Cherkesia, 357147 Russia AND H.FALCKE,
SPECKLE MASKING IMAGING OF THE SPECTROSCOPIC BINARIES GLIESE 150.2 AND 41 DRACONIS I.BALEGA AND Y.BALEGA Special Astrophysical Observatory Zelenchukskaya region, Karachai-Cherkesia, 357147 Russia AND H.FALCKE,
Two Transiting Exoplanet Candidates in Cygnus from the MASTER Project
 Peremennye Zvezdy (Variable Stars) 33, No. 2, 2013 Received 13 February; accepted 22 February. Two Transiting Exoplanet Candidates in Cygnus from the MASTER Project A. Y. Burdanov 1, A. A. Popov 1, V.
Peremennye Zvezdy (Variable Stars) 33, No. 2, 2013 Received 13 February; accepted 22 February. Two Transiting Exoplanet Candidates in Cygnus from the MASTER Project A. Y. Burdanov 1, A. A. Popov 1, V.
G.Witzel Physics and Astronomy Department, University of California, Los Angeles, CA , USA
 E-mail: shahzaman@ph1.uni-koeln.de A.Eckart E-mail: eckart@ph1.uni-koeln.de G.Witzel Physics and Astronomy Department, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095-1547, USA N. Sabha M. Zamaninasab
E-mail: shahzaman@ph1.uni-koeln.de A.Eckart E-mail: eckart@ph1.uni-koeln.de G.Witzel Physics and Astronomy Department, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095-1547, USA N. Sabha M. Zamaninasab
Jason Kalirai (STScI)
 Jason Kalirai (STScI) Outline An Introduction: The First Hints on How Stars Evolve. Our Current Picture of Stellar Evolution A Surprise in our Backyard: The First Discovered White Dwarf Why Search for
Jason Kalirai (STScI) Outline An Introduction: The First Hints on How Stars Evolve. Our Current Picture of Stellar Evolution A Surprise in our Backyard: The First Discovered White Dwarf Why Search for
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY. Planets around white dwarfs Matt Burleigh
 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Planets around white dwarfs Matt Burleigh Contents Original motivation DODO - results from our direct imaging survey Where do we go next? The role for E-ELT Direct imaging
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Planets around white dwarfs Matt Burleigh Contents Original motivation DODO - results from our direct imaging survey Where do we go next? The role for E-ELT Direct imaging
Wide-eld stellar photometry in Piwnice Observatory
 Wide-eld stellar photometry in Piwnice Observatory Gracjan Maciejewski Centrum Astronomii Uniwersytetu Miko laja Kopernika gm@astri.uni.torun.pl (Lecture at the Astronomical seminar in Soa on 21.03.2007.
Wide-eld stellar photometry in Piwnice Observatory Gracjan Maciejewski Centrum Astronomii Uniwersytetu Miko laja Kopernika gm@astri.uni.torun.pl (Lecture at the Astronomical seminar in Soa on 21.03.2007.
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY. Observational Astronomy (2011) 1
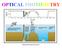 OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope
 The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
Comparison between 30 micron sources in different galaxies
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Comparison between 30 micron sources in different galaxies To cite this article: Marcin Gadkowski et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 728 062007 View
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Comparison between 30 micron sources in different galaxies To cite this article: Marcin Gadkowski et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 728 062007 View
Secondary UBV RI-CCD standard stars in the neighbourhood of Landolt standard stars,
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS OCTOBER I 2, PAGE 169 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 146, 169 177 (2) Secondary UBV RI-CCD standard stars in the neighbourhood of Landolt standard stars, D. Galadí-Enríquez
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS OCTOBER I 2, PAGE 169 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 146, 169 177 (2) Secondary UBV RI-CCD standard stars in the neighbourhood of Landolt standard stars, D. Galadí-Enríquez
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey
 The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Robert Lupton Xiaohui Fan Jim Gunn Željko Ivezić Jill Knapp Michael Strauss University of Chicago, Fermilab, Institute for Advanced Study, Japanese Participation Group, Johns
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Robert Lupton Xiaohui Fan Jim Gunn Željko Ivezić Jill Knapp Michael Strauss University of Chicago, Fermilab, Institute for Advanced Study, Japanese Participation Group, Johns
Pole searching algorithm for Wide-field all-sky image analyzing monitoring system
 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 47, 220 225, (2017) Pole searching algorithm for Wide-field all-sky image analyzing monitoring system J. Bednář, P. Skala and P. Páta Czech Technical University in
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 47, 220 225, (2017) Pole searching algorithm for Wide-field all-sky image analyzing monitoring system J. Bednář, P. Skala and P. Páta Czech Technical University in
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual
 Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual Due Oct. 21, 2011 1 Pre-Lab 1.1 Photometry and the Magnitude Scale The brightness of stars is represented by its value on the magnitude scale. The ancient Greek astronomer
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual Due Oct. 21, 2011 1 Pre-Lab 1.1 Photometry and the Magnitude Scale The brightness of stars is represented by its value on the magnitude scale. The ancient Greek astronomer
Two New Cool Variable Stars in the Field of NGC 659
 92 Two New Cool Variable Stars in the Field of NGC 659 Steven P. Souza Department of Astronomy, Williams College, Williamstown, MA, 01267; ssouza@williams.edu Received December 11, 2012; revised December
92 Two New Cool Variable Stars in the Field of NGC 659 Steven P. Souza Department of Astronomy, Williams College, Williamstown, MA, 01267; ssouza@williams.edu Received December 11, 2012; revised December
Measurement of the stellar irradiance
 Measurement of the stellar irradiance Definitions Specific Intensity : (monochromatic) per unit area normal to the direction of radiation per unit solid angle per unit wavelength unit (or frequency) per
Measurement of the stellar irradiance Definitions Specific Intensity : (monochromatic) per unit area normal to the direction of radiation per unit solid angle per unit wavelength unit (or frequency) per
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Oct 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Oct 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Oct 2012](/thumbs/93/112483577.jpg) ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 62 (2012) pp. 247 268 Photometric Maps Based on the OGLE-III Shallow Survey in the Large Magellanic Cloud arxiv:1210.4702v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Oct 2012 K. U l a c z y k 1, M. K. S z
ACTA ASTRONOMICA Vol. 62 (2012) pp. 247 268 Photometric Maps Based on the OGLE-III Shallow Survey in the Large Magellanic Cloud arxiv:1210.4702v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Oct 2012 K. U l a c z y k 1, M. K. S z
INFRARED PHOTOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WHITE DWARFS FROM THE TWO MICRON ALL SKY SURVEY AND THE SPITZER SPACE TELESCOPE
 The Astrophysical Journal, 657:1013Y1025, 2007 March 10 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A INFRARED PHOTOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WHITE DWARFS FROM THE TWO MICRON
The Astrophysical Journal, 657:1013Y1025, 2007 March 10 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A INFRARED PHOTOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WHITE DWARFS FROM THE TWO MICRON
Hα Imaging of an Interstellar Neutral Hydrogen Shell
 Hα Imaging of an Interstellar Neutral Hydrogen Shell Paul L. Vaughan Faculty Sponsor: Shauna Sallmen, Department of Physics ABSTRACT The interstellar medium (ISM) is composed of very low-density material
Hα Imaging of an Interstellar Neutral Hydrogen Shell Paul L. Vaughan Faculty Sponsor: Shauna Sallmen, Department of Physics ABSTRACT The interstellar medium (ISM) is composed of very low-density material
Pan-Planets. A Search for Transiting Planets Around Cool stars. J. Koppenhoefer, Th. Henning and the Pan-PlanetS Team
 Pan-Planets A Search for Transiting Planets Around Cool stars J. Koppenhoefer, Th. Henning and the Pan-PlanetS Team Pan-STARRS 1: 1.8m prototype telescope operated on Haleakala/Hawaii consortium of few
Pan-Planets A Search for Transiting Planets Around Cool stars J. Koppenhoefer, Th. Henning and the Pan-PlanetS Team Pan-STARRS 1: 1.8m prototype telescope operated on Haleakala/Hawaii consortium of few
Detection of Polarization Effects in Gaia Data
 Detection of Polarization Effects in Gaia Data Frederic Raison ADA7 14-18/05/2012 Introduction Gaia is an astrometry mission using 2 telescopes. The idea is to use Gaia as a polarimeter (low precision
Detection of Polarization Effects in Gaia Data Frederic Raison ADA7 14-18/05/2012 Introduction Gaia is an astrometry mission using 2 telescopes. The idea is to use Gaia as a polarimeter (low precision
NIGHT TIME POLARIMETRY. Stefano Bagnulo (Armagh Observatory)
 NIGHT TIME POLARIMETRY Stefano Bagnulo (Armagh Observatory) (Position) Intensity Intensity vs. time Intensity vs. wavelength Intensity vs. time AND vs. wavelength HOW MUCH? POLARIZATION BY ABSORPTION
NIGHT TIME POLARIMETRY Stefano Bagnulo (Armagh Observatory) (Position) Intensity Intensity vs. time Intensity vs. wavelength Intensity vs. time AND vs. wavelength HOW MUCH? POLARIZATION BY ABSORPTION
David Hiriart Observatorio Astronómico Nacional en la Sierra de San Pedro Mártir, B.C. Instituto de Astronomía, UNAM
 David Hiriart Observatorio Astronómico Nacional en la Sierra de San Pedro Mártir, B.C. Instituto de Astronomía, UNAM Telescopes 1 OUTLINE Scientific motivation Telescope Instrument Pipe-line data reduction
David Hiriart Observatorio Astronómico Nacional en la Sierra de San Pedro Mártir, B.C. Instituto de Astronomía, UNAM Telescopes 1 OUTLINE Scientific motivation Telescope Instrument Pipe-line data reduction
Photometric and spectroscopic observations of the 2014 eclipse of the complex binary EE Cephei
 Photometric and spectroscopic observations of the 2014 eclipse of the complex binary EE Cephei David Boyd Variable Star Section, British Astronomical Association, [davidboyd@orion.me.uk] Abstract We report
Photometric and spectroscopic observations of the 2014 eclipse of the complex binary EE Cephei David Boyd Variable Star Section, British Astronomical Association, [davidboyd@orion.me.uk] Abstract We report
Second San Juan photoelectric astrolabe catalogue
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 136, 1 5 (1999) APRIL I 1999, PAGE1 Second San Juan photoelectric astrolabe catalogue W.T. Manrique 1, Lu. Lizhi 2,R.Perdomo 3,
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 136, 1 5 (1999) APRIL I 1999, PAGE1 Second San Juan photoelectric astrolabe catalogue W.T. Manrique 1, Lu. Lizhi 2,R.Perdomo 3,
Luminosity Functions of Planetary Nebulae & Globular Clusters. By Azmain Nisak ASTR 8400
 Luminosity Functions of Planetary Nebulae & Globular Clusters By Azmain Nisak ASTR 8400 Calculating Distance! m = apparent magnitude! M = absolute magnitude! r = distance in pc GLOBULAR CLUSTERS AS DISTANCE
Luminosity Functions of Planetary Nebulae & Globular Clusters By Azmain Nisak ASTR 8400 Calculating Distance! m = apparent magnitude! M = absolute magnitude! r = distance in pc GLOBULAR CLUSTERS AS DISTANCE
WFC3/UVIS Photometric Transformations
 Instrument Science Report WFC3 2014-016 WFC3/UVIS Photometric Transformations Kailash Sahu, Susana Deustua and Elena Sabbi January 05, 2017 ABSTRACT We provide photometric transformation coefficients for
Instrument Science Report WFC3 2014-016 WFC3/UVIS Photometric Transformations Kailash Sahu, Susana Deustua and Elena Sabbi January 05, 2017 ABSTRACT We provide photometric transformation coefficients for
Fast photometry with small telescopes
 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 43, 216 227, (2014) Fast photometry with small telescopes G. Kanbach 1, A. Rau 1 and A. S lowikowska 2 1 Max-Planck-Institute for extraterrestrial Physics, Giessenbachstrasse,
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 43, 216 227, (2014) Fast photometry with small telescopes G. Kanbach 1, A. Rau 1 and A. S lowikowska 2 1 Max-Planck-Institute for extraterrestrial Physics, Giessenbachstrasse,
Light and Stars ASTR 2110 Sarazin
 Light and Stars ASTR 2110 Sarazin Doppler Effect Frequency and wavelength of light changes if source or observer move Doppler Effect v r dr radial velocity dt > 0 moving apart < 0 moving toward Doppler
Light and Stars ASTR 2110 Sarazin Doppler Effect Frequency and wavelength of light changes if source or observer move Doppler Effect v r dr radial velocity dt > 0 moving apart < 0 moving toward Doppler
White dwarfs with unresolved substellar companions and debris disks in the UKIDSS Survey
 White dwarfs with unresolved substellar companions and debris disks in the UKIDSS Survey Paul Steele 1, Matt Burleigh 1, Martin Barstow 1, Richard Jameson 1 and Paul Dobbie 2 1 Department of Physics &
White dwarfs with unresolved substellar companions and debris disks in the UKIDSS Survey Paul Steele 1, Matt Burleigh 1, Martin Barstow 1, Richard Jameson 1 and Paul Dobbie 2 1 Department of Physics &
Irradiated brown dwarfs
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 84, 1022 c SAIt 2013 Memorie della Irradiated brown dwarfs S. L. Casewell 1, M. R. Burleigh 1, K. A. Lawrie 1, P. F. L. Maxted 2, P. D. Dobbie 3, and R. Napiwotzki 4 1 Department of Physics
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 84, 1022 c SAIt 2013 Memorie della Irradiated brown dwarfs S. L. Casewell 1, M. R. Burleigh 1, K. A. Lawrie 1, P. F. L. Maxted 2, P. D. Dobbie 3, and R. Napiwotzki 4 1 Department of Physics
Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin Properties Location Distance Speed Radial velocity Proper motion Luminosity, Flux Magnitudes Magnitudes Hipparchus 1) Classified stars by brightness,
Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin Properties Location Distance Speed Radial velocity Proper motion Luminosity, Flux Magnitudes Magnitudes Hipparchus 1) Classified stars by brightness,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Dec 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Dec 2018](/thumbs/93/112143433.jpg) High-Mass X-ray binaries: illuminating the passage from massive binaries to merging compact objects Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 346, 2019 c 2019 International Astronomical Union L.M. Oskinova, ed. DOI:
High-Mass X-ray binaries: illuminating the passage from massive binaries to merging compact objects Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 346, 2019 c 2019 International Astronomical Union L.M. Oskinova, ed. DOI:
Characterization of variable stars using the ASAS and SuperWASP databases
 Characterization of variable stars using the ASAS and SuperWASP databases Derck P. Smits Dept of Mathematical Sciences, PO Box 392, UNISA, 0003, South Africa E-mail: smitsdp@unisa.ac.za Abstract. A photographic
Characterization of variable stars using the ASAS and SuperWASP databases Derck P. Smits Dept of Mathematical Sciences, PO Box 392, UNISA, 0003, South Africa E-mail: smitsdp@unisa.ac.za Abstract. A photographic
Mapping the oxygen abundance in an elliptical galaxy (NGC 5128)
 Mapping the oxygen abundance in an elliptical galaxy (NGC 5128) Jeremy R. Walsh, ESO Collaborators: George H. Jacoby, GMT Observatory, Carnegie; Reynier Peletier, Kapteyn Lab., Groningen; Nicholas A. Walton,
Mapping the oxygen abundance in an elliptical galaxy (NGC 5128) Jeremy R. Walsh, ESO Collaborators: George H. Jacoby, GMT Observatory, Carnegie; Reynier Peletier, Kapteyn Lab., Groningen; Nicholas A. Walton,
The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3
 336 The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3 Christine M. Clement Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, M5S 3H8, Canada Mike
336 The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3 Christine M. Clement Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, M5S 3H8, Canada Mike
EXTENDING THE WET TECHNIQUE TO LOWER FREQUENCIES
 Baltic Astronomy, vol.2, 468-478, 993. EXTENDING THE WET TECHNIQUE TO LOWER FREQUENCIES M. Breger and G. Handler Institute fur Astronomie, Turkenschanzstrasse 7, A-8, Vienna, Austria. Received August,
Baltic Astronomy, vol.2, 468-478, 993. EXTENDING THE WET TECHNIQUE TO LOWER FREQUENCIES M. Breger and G. Handler Institute fur Astronomie, Turkenschanzstrasse 7, A-8, Vienna, Austria. Received August,
Stellar Photometry: II. Transforming. Ast 401/Phy 580 Fall 2015
 Stellar Photometry: II. Transforming Ast 401/Phy 580 Fall 2015 Summary We ve learned how to measure instrumental magnitudes for a star using aperture photometry or PSF-fitting: (a) Add up all of the counts
Stellar Photometry: II. Transforming Ast 401/Phy 580 Fall 2015 Summary We ve learned how to measure instrumental magnitudes for a star using aperture photometry or PSF-fitting: (a) Add up all of the counts
Rømer Science Mission Plan
 Institute of Physics and Astronomy, University of Aarhus Rømer Science Mission Plan Danish Small Satellite Programme Document No.(issue): MONS/IFA/MAN/PLN/0001(1) Date: 2001-05-29 Prepared by: Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard,
Institute of Physics and Astronomy, University of Aarhus Rømer Science Mission Plan Danish Small Satellite Programme Document No.(issue): MONS/IFA/MAN/PLN/0001(1) Date: 2001-05-29 Prepared by: Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard,
CHALLENGES RELATED TO DETECTION OF THE LATENT PERIODICITY FOR SMALL-SIZED GEO DEBRIS
 CHALLENGES RELATED TO DETECTION OF THE LATENT PERIODICITY FOR SMALL-SIZED GEO DEBRIS I. Korobtsev and M. Mishina 664033 Irkutsk, p/b 291, Institute of Solar-Terrestrial Physics SB RAS mmish@iszf.irk.ru
CHALLENGES RELATED TO DETECTION OF THE LATENT PERIODICITY FOR SMALL-SIZED GEO DEBRIS I. Korobtsev and M. Mishina 664033 Irkutsk, p/b 291, Institute of Solar-Terrestrial Physics SB RAS mmish@iszf.irk.ru
Ultra-compact binaries in the Catalina Real-time Transient Survey. The Catalina Real-time Transient Survey. A photometric study of CRTS dwarf novae
 Patrick Woudt, Brian Warner & Deanne de Budé 3rd AM CVn workshop, University of Warwick, 16-20 April 2012 The Catalina Real-time Transient Survey A photometric study of CRTS dwarf novae Phase-resolved
Patrick Woudt, Brian Warner & Deanne de Budé 3rd AM CVn workshop, University of Warwick, 16-20 April 2012 The Catalina Real-time Transient Survey A photometric study of CRTS dwarf novae Phase-resolved
FIVE FUNDED* RESEARCH POSITIONS
 OBSERVATION Sub-GROUP: 1. Masters (MSc, 1 year): Exploring extreme star-forming galaxies for SALT in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey 2. Masters (MSc,1 year): HI masses of extreme star-forming galaxies in
OBSERVATION Sub-GROUP: 1. Masters (MSc, 1 year): Exploring extreme star-forming galaxies for SALT in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey 2. Masters (MSc,1 year): HI masses of extreme star-forming galaxies in
From theory to observations
 Stellar Objects: From theory to observations 1 From theory to observations Update date: December 13, 2010 Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle,
Stellar Objects: From theory to observations 1 From theory to observations Update date: December 13, 2010 Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle,
YETI search for young transiting planets,,
 EPJ Web of Conferences 47, 34 (213) DOI: 1.151/epjconf/2134734 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 213 YETI search for young transiting planets,, Ronny Errmann 1,a, Ralph Neuhäuser 1, Guillermo
EPJ Web of Conferences 47, 34 (213) DOI: 1.151/epjconf/2134734 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 213 YETI search for young transiting planets,, Ronny Errmann 1,a, Ralph Neuhäuser 1, Guillermo
CCD Star Images: On the Determination of Moffat s PSF Shape Parameters
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (1988) 9, 17 24 CCD Star Images: On the Determination of Moffat s PSF Shape Parameters O. Bendinelli Dipartimento di Astronomia, Via Zamboni 33, I-40126 Bologna, Italy G. Parmeggiani
J. Astrophys. Astr. (1988) 9, 17 24 CCD Star Images: On the Determination of Moffat s PSF Shape Parameters O. Bendinelli Dipartimento di Astronomia, Via Zamboni 33, I-40126 Bologna, Italy G. Parmeggiani
POLICAN: A near infrared imaging Polarimeter
 POLICAN: A near infrared imaging Polarimeter Devaraj Rangaswamy dev@inaoep.mx Instituto Nacional de Astrofísica, Óptica y Electrónica (INAOE), MÉXICO Team members: Luis Carassco Abraham Luna Devaraj Rangaswamy
POLICAN: A near infrared imaging Polarimeter Devaraj Rangaswamy dev@inaoep.mx Instituto Nacional de Astrofísica, Óptica y Electrónica (INAOE), MÉXICO Team members: Luis Carassco Abraham Luna Devaraj Rangaswamy
White Dwarf Stars as Probes of Physical and Astrophysical Processes
 White Dwarf Stars as Probes of Physical and Astrophysical Processes M I K E M O N T G O M E R Y D E P A R T M E N T O F A S T R O N O M Y, M C D O N A L D O B S E R V A T O R Y A N D T H E T E X A S C
White Dwarf Stars as Probes of Physical and Astrophysical Processes M I K E M O N T G O M E R Y D E P A R T M E N T O F A S T R O N O M Y, M C D O N A L D O B S E R V A T O R Y A N D T H E T E X A S C
History of the a photometric system
 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 218 222, (2018) History of the a photometric system H.M.Maitzen 1, E.Paunzen 2 and M.Netopil 1,2 1 Institute for Astrophysics, University of Vienna, Türkenschanzstraße
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 218 222, (2018) History of the a photometric system H.M.Maitzen 1, E.Paunzen 2 and M.Netopil 1,2 1 Institute for Astrophysics, University of Vienna, Türkenschanzstraße
From theory to observations
 Stellar Objects: From theory to observations 1 From theory to observations Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle, give the prediction of the
Stellar Objects: From theory to observations 1 From theory to observations Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle, give the prediction of the
A Far-ultraviolet Fluorescent Molecular Hydrogen Emission Map of the Milky Way Galaxy
 A Far-ultraviolet Fluorescent Molecular Hydrogen Emission Map of the Milky Way Galaxy (The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 231:21 (16pp), 2017 August) November 14, 2017 Young-Soo Jo Young-Soo
A Far-ultraviolet Fluorescent Molecular Hydrogen Emission Map of the Milky Way Galaxy (The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 231:21 (16pp), 2017 August) November 14, 2017 Young-Soo Jo Young-Soo
Transit detection limits for sub-stellar and terrestrial companions to white dwarfs
 Transit detection limits for sub-stellar and terrestrial companions to white dwarfs F Faedi 1, R West 1, M R Burleigh 1, M R Goad 1 and L Hebb 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester,
Transit detection limits for sub-stellar and terrestrial companions to white dwarfs F Faedi 1, R West 1, M R Burleigh 1, M R Goad 1 and L Hebb 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester,
Eclipsing Binary Star studies: Present and future
 Eclipsing Binary Star studies: Present and future P. G. iarchos Department of Astrophysics, Astronomy and Mechanics, ational and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece Abstract The importance of Eclipsing
Eclipsing Binary Star studies: Present and future P. G. iarchos Department of Astrophysics, Astronomy and Mechanics, ational and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece Abstract The importance of Eclipsing
Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (2000) 21, 53-59 Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk D. Κ. Ojha, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Dr. Homi Bhabha Road, Mumbai 400 005, India Received 1999 September 14; accepted
J. Astrophys. Astr. (2000) 21, 53-59 Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk D. Κ. Ojha, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Dr. Homi Bhabha Road, Mumbai 400 005, India Received 1999 September 14; accepted
Hard X-ray Vela supernova observation on rocket experiment WRX-R
 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 47, 165 169, (2017) Hard X-ray Vela supernova observation on rocket experiment WRX-R V. Stehlikova 1,2, M. Urban 1, O. Nentvich 1, V. Daniel 2, L. Sieger 1 and J. Tutt
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 47, 165 169, (2017) Hard X-ray Vela supernova observation on rocket experiment WRX-R V. Stehlikova 1,2, M. Urban 1, O. Nentvich 1, V. Daniel 2, L. Sieger 1 and J. Tutt
